pub mod ml {
//! # Machine Learning
//!
//! The Machine Learning Library (MLL) is a set of classes and functions for statistical
//! classification, regression, and clustering of data.
//!
//! Most of the classification and regression algorithms are implemented as C++ classes. As the
//! algorithms have different sets of features (like an ability to handle missing measurements or
//! categorical input variables), there is a little common ground between the classes. This common
//! ground is defined by the class cv::ml::StatModel that all the other ML classes are derived from.
//!
//! See detailed overview here: [ml_intro].
use crate::{mod_prelude::*, core, sys, types};
pub mod prelude {
pub use { super::ParamGridTraitConst, super::ParamGridTrait, super::TrainDataTraitConst, super::TrainDataTrait, super::StatModelTraitConst, super::StatModelTrait, super::NormalBayesClassifierTraitConst, super::NormalBayesClassifierTrait, super::KNearestTraitConst, super::KNearestTrait, super::SVM_KernelTraitConst, super::SVM_KernelTrait, super::SVMTraitConst, super::SVMTrait, super::EMTraitConst, super::EMTrait, super::DTrees_NodeTraitConst, super::DTrees_NodeTrait, super::DTrees_SplitTraitConst, super::DTrees_SplitTrait, super::DTreesTraitConst, super::DTreesTrait, super::RTreesTraitConst, super::RTreesTrait, super::BoostTraitConst, super::BoostTrait, super::ANN_MLPTraitConst, super::ANN_MLPTrait, super::LogisticRegressionTraitConst, super::LogisticRegressionTrait, super::SVMSGDTraitConst, super::SVMSGDTrait };
}
/// The simulated annealing algorithm. See [Kirkpatrick83](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Kirkpatrick83) for details.
pub const ANN_MLP_ANNEAL: i32 = 2;
/// The back-propagation algorithm.
pub const ANN_MLP_BACKPROP: i32 = 0;
/// Gaussian function: 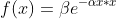
pub const ANN_MLP_GAUSSIAN: i32 = 2;
/// Identity function: 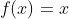
pub const ANN_MLP_IDENTITY: i32 = 0;
/// Leaky ReLU function: for x>0 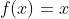 and x<=0 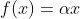
pub const ANN_MLP_LEAKYRELU: i32 = 4;
/// Do not normalize the input vectors. If this flag is not set, the training algorithm
/// normalizes each input feature independently, shifting its mean value to 0 and making the
/// standard deviation equal to 1. If the network is assumed to be updated frequently, the new
/// training data could be much different from original one. In this case, you should take care
/// of proper normalization.
pub const ANN_MLP_NO_INPUT_SCALE: i32 = 2;
/// Do not normalize the output vectors. If the flag is not set, the training algorithm
/// normalizes each output feature independently, by transforming it to the certain range
/// depending on the used activation function.
pub const ANN_MLP_NO_OUTPUT_SCALE: i32 = 4;
/// ReLU function: 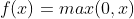
pub const ANN_MLP_RELU: i32 = 3;
/// The RPROP algorithm. See [RPROP93](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_RPROP93) for details.
pub const ANN_MLP_RPROP: i32 = 1;
/// Symmetrical sigmoid: 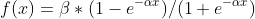
///
/// Note:
/// If you are using the default sigmoid activation function with the default parameter values
/// fparam1=0 and fparam2=0 then the function used is y = 1.7159\*tanh(2/3 \* x), so the output
/// will range from [-1.7159, 1.7159], instead of [0,1].
pub const ANN_MLP_SIGMOID_SYM: i32 = 1;
/// Update the network weights, rather than compute them from scratch. In the latter case
/// the weights are initialized using the Nguyen-Widrow algorithm.
pub const ANN_MLP_UPDATE_WEIGHTS: i32 = 1;
/// Discrete AdaBoost.
pub const Boost_DISCRETE: i32 = 0;
/// Gentle AdaBoost. It puts less weight on outlier data points and for that
/// reason is often good with regression data.
pub const Boost_GENTLE: i32 = 3;
/// LogitBoost. It can produce good regression fits.
pub const Boost_LOGIT: i32 = 2;
/// Real AdaBoost. It is a technique that utilizes confidence-rated predictions
/// and works well with categorical data.
pub const Boost_REAL: i32 = 1;
/// each training sample occupies a column of samples
pub const COL_SAMPLE: i32 = 1;
pub const DTrees_PREDICT_AUTO: i32 = 0;
pub const DTrees_PREDICT_MASK: i32 = 768;
pub const DTrees_PREDICT_MAX_VOTE: i32 = 512;
pub const DTrees_PREDICT_SUM: i32 = 256;
/// A symmetric positively defined matrix. The number of free
/// parameters in each matrix is about 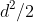. It is not recommended to use this option, unless
/// there is pretty accurate initial estimation of the parameters and/or a huge number of
/// training samples.
pub const EM_COV_MAT_DEFAULT: i32 = 1;
/// A diagonal matrix with positive diagonal elements. The number of
/// free parameters is d for each matrix. This is most commonly used option yielding good
/// estimation results.
pub const EM_COV_MAT_DIAGONAL: i32 = 1;
/// A symmetric positively defined matrix. The number of free
/// parameters in each matrix is about 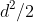. It is not recommended to use this option, unless
/// there is pretty accurate initial estimation of the parameters and/or a huge number of
/// training samples.
pub const EM_COV_MAT_GENERIC: i32 = 2;
/// A scaled identity matrix 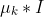. There is the only
/// parameter 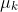 to be estimated for each matrix. The option may be used in special cases,
/// when the constraint is relevant, or as a first step in the optimization (for example in case
/// when the data is preprocessed with PCA). The results of such preliminary estimation may be
/// passed again to the optimization procedure, this time with
/// covMatType=EM::COV_MAT_DIAGONAL.
pub const EM_COV_MAT_SPHERICAL: i32 = 0;
pub const EM_DEFAULT_MAX_ITERS: i32 = 100;
pub const EM_DEFAULT_NCLUSTERS: i32 = 5;
pub const EM_START_AUTO_STEP: i32 = 0;
pub const EM_START_E_STEP: i32 = 1;
pub const EM_START_M_STEP: i32 = 2;
pub const KNearest_BRUTE_FORCE: i32 = 1;
pub const KNearest_KDTREE: i32 = 2;
pub const LogisticRegression_BATCH: i32 = 0;
/// Set MiniBatchSize to a positive integer when using this method.
pub const LogisticRegression_MINI_BATCH: i32 = 1;
/// Regularization disabled
pub const LogisticRegression_REG_DISABLE: i32 = -1;
/// %L1 norm
pub const LogisticRegression_REG_L1: i32 = 0;
/// %L2 norm
pub const LogisticRegression_REG_L2: i32 = 1;
/// each training sample is a row of samples
pub const ROW_SAMPLE: i32 = 0;
/// Average Stochastic Gradient Descent
pub const SVMSGD_ASGD: i32 = 1;
/// More accurate for the case of linearly separable sets.
pub const SVMSGD_HARD_MARGIN: i32 = 1;
/// Stochastic Gradient Descent
pub const SVMSGD_SGD: i32 = 0;
/// General case, suits to the case of non-linearly separable sets, allows outliers.
pub const SVMSGD_SOFT_MARGIN: i32 = 0;
pub const SVM_C: i32 = 0;
/// Exponential Chi2 kernel, similar to the RBF kernel:
/// 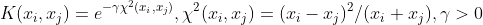.
pub const SVM_CHI2: i32 = 4;
pub const SVM_COEF: i32 = 4;
/// Returned by SVM::getKernelType in case when custom kernel has been set
pub const SVM_CUSTOM: i32 = -1;
/// C-Support Vector Classification. n-class classification (n 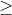 2), allows
/// imperfect separation of classes with penalty multiplier C for outliers.
pub const SVM_C_SVC: i32 = 100;
pub const SVM_DEGREE: i32 = 5;
/// -Support Vector Regression. The distance between feature vectors
/// from the training set and the fitting hyper-plane must be less than p. For outliers the
/// penalty multiplier C is used.
pub const SVM_EPS_SVR: i32 = 103;
pub const SVM_GAMMA: i32 = 1;
/// Histogram intersection kernel. A fast kernel. 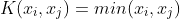.
pub const SVM_INTER: i32 = 5;
/// Linear kernel. No mapping is done, linear discrimination (or regression) is
/// done in the original feature space. It is the fastest option. 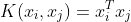.
pub const SVM_LINEAR: i32 = 0;
pub const SVM_NU: i32 = 3;
/// 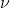-Support Vector Classification. n-class classification with possible
/// imperfect separation. Parameter 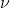 (in the range 0..1, the larger the value, the smoother
/// the decision boundary) is used instead of C.
pub const SVM_NU_SVC: i32 = 101;
/// 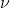-Support Vector Regression. 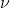 is used instead of p.
/// See [LibSVM](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_LibSVM) for details.
pub const SVM_NU_SVR: i32 = 104;
/// Distribution Estimation (One-class %SVM). All the training data are from
/// the same class, %SVM builds a boundary that separates the class from the rest of the feature
/// space.
pub const SVM_ONE_CLASS: i32 = 102;
pub const SVM_P: i32 = 2;
/// Polynomial kernel:
/// 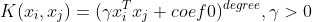.
pub const SVM_POLY: i32 = 1;
/// Radial basis function (RBF), a good choice in most cases.
/// 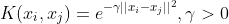.
pub const SVM_RBF: i32 = 2;
/// Sigmoid kernel: 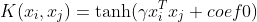.
pub const SVM_SIGMOID: i32 = 3;
pub const StatModel_COMPRESSED_INPUT: i32 = 2;
pub const StatModel_PREPROCESSED_INPUT: i32 = 4;
/// makes the method return the raw results (the sum), not the class label
pub const StatModel_RAW_OUTPUT: i32 = 1;
pub const StatModel_UPDATE_MODEL: i32 = 1;
pub const TEST_ERROR: i32 = 0;
pub const TRAIN_ERROR: i32 = 1;
/// categorical variables
pub const VAR_CATEGORICAL: i32 = 1;
/// same as VAR_ORDERED
pub const VAR_NUMERICAL: i32 = 0;
/// ordered variables
pub const VAR_ORDERED: i32 = 0;
/// possible activation functions
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum ANN_MLP_ActivationFunctions {
/// Identity function: 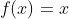
IDENTITY = 0,
/// Symmetrical sigmoid: 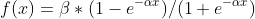
///
/// Note:
/// If you are using the default sigmoid activation function with the default parameter values
/// fparam1=0 and fparam2=0 then the function used is y = 1.7159\*tanh(2/3 \* x), so the output
/// will range from [-1.7159, 1.7159], instead of [0,1].
SIGMOID_SYM = 1,
/// Gaussian function: 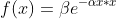
GAUSSIAN = 2,
/// ReLU function: 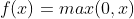
RELU = 3,
/// Leaky ReLU function: for x>0 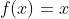 and x<=0 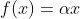
LEAKYRELU = 4,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::ANN_MLP_ActivationFunctions }
/// Train options
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum ANN_MLP_TrainFlags {
/// Update the network weights, rather than compute them from scratch. In the latter case
/// the weights are initialized using the Nguyen-Widrow algorithm.
UPDATE_WEIGHTS = 1,
/// Do not normalize the input vectors. If this flag is not set, the training algorithm
/// normalizes each input feature independently, shifting its mean value to 0 and making the
/// standard deviation equal to 1. If the network is assumed to be updated frequently, the new
/// training data could be much different from original one. In this case, you should take care
/// of proper normalization.
NO_INPUT_SCALE = 2,
/// Do not normalize the output vectors. If the flag is not set, the training algorithm
/// normalizes each output feature independently, by transforming it to the certain range
/// depending on the used activation function.
NO_OUTPUT_SCALE = 4,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::ANN_MLP_TrainFlags }
/// Available training methods
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum ANN_MLP_TrainingMethods {
/// The back-propagation algorithm.
BACKPROP = 0,
/// The RPROP algorithm. See [RPROP93](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_RPROP93) for details.
RPROP = 1,
/// The simulated annealing algorithm. See [Kirkpatrick83](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Kirkpatrick83) for details.
ANNEAL = 2,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::ANN_MLP_TrainingMethods }
/// Boosting type.
/// Gentle AdaBoost and Real AdaBoost are often the preferable choices.
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum Boost_Types {
/// Discrete AdaBoost.
DISCRETE = 0,
/// Real AdaBoost. It is a technique that utilizes confidence-rated predictions
/// and works well with categorical data.
REAL = 1,
/// LogitBoost. It can produce good regression fits.
LOGIT = 2,
/// Gentle AdaBoost. It puts less weight on outlier data points and for that
/// reason is often good with regression data.
GENTLE = 3,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::Boost_Types }
/// Predict options
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum DTrees_Flags {
PREDICT_AUTO = 0,
PREDICT_SUM = 256,
PREDICT_MAX_VOTE = 512,
PREDICT_MASK = 768,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::DTrees_Flags }
/// Type of covariation matrices
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum EM_Types {
/// A scaled identity matrix 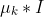. There is the only
/// parameter 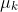 to be estimated for each matrix. The option may be used in special cases,
/// when the constraint is relevant, or as a first step in the optimization (for example in case
/// when the data is preprocessed with PCA). The results of such preliminary estimation may be
/// passed again to the optimization procedure, this time with
/// covMatType=EM::COV_MAT_DIAGONAL.
COV_MAT_SPHERICAL = 0,
/// A diagonal matrix with positive diagonal elements. The number of
/// free parameters is d for each matrix. This is most commonly used option yielding good
/// estimation results.
COV_MAT_DIAGONAL = 1,
/// A symmetric positively defined matrix. The number of free
/// parameters in each matrix is about 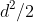. It is not recommended to use this option, unless
/// there is pretty accurate initial estimation of the parameters and/or a huge number of
/// training samples.
COV_MAT_GENERIC = 2,
// A symmetric positively defined matrix. The number of free
// parameters in each matrix is about . It is not recommended to use this option, unless
// there is pretty accurate initial estimation of the parameters and/or a huge number of
// training samples.
// Duplicate, use COV_MAT_DIAGONAL instead
// COV_MAT_DEFAULT = 1,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::EM_Types }
/// %Error types
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum ErrorTypes {
TEST_ERROR = 0,
TRAIN_ERROR = 1,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::ErrorTypes }
/// Implementations of KNearest algorithm
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum KNearest_Types {
BRUTE_FORCE = 1,
KDTREE = 2,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::KNearest_Types }
/// Training methods
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum LogisticRegression_Methods {
BATCH = 0,
/// Set MiniBatchSize to a positive integer when using this method.
MINI_BATCH = 1,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::LogisticRegression_Methods }
/// Regularization kinds
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum LogisticRegression_RegKinds {
/// Regularization disabled
REG_DISABLE = -1,
/// %L1 norm
REG_L1 = 0,
/// %L2 norm
REG_L2 = 1,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::LogisticRegression_RegKinds }
/// Margin type.
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum SVMSGD_MarginType {
/// General case, suits to the case of non-linearly separable sets, allows outliers.
SOFT_MARGIN = 0,
/// More accurate for the case of linearly separable sets.
HARD_MARGIN = 1,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::SVMSGD_MarginType }
/// SVMSGD type.
/// ASGD is often the preferable choice.
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum SVMSGD_SvmsgdType {
/// Stochastic Gradient Descent
SGD = 0,
/// Average Stochastic Gradient Descent
ASGD = 1,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::SVMSGD_SvmsgdType }
/// %SVM kernel type
///
/// A comparison of different kernels on the following 2D test case with four classes. Four
/// SVM::C_SVC SVMs have been trained (one against rest) with auto_train. Evaluation on three
/// different kernels (SVM::CHI2, SVM::INTER, SVM::RBF). The color depicts the class with max score.
/// Bright means max-score \> 0, dark means max-score \< 0.
/// 
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum SVM_KernelTypes {
/// Returned by SVM::getKernelType in case when custom kernel has been set
CUSTOM = -1,
/// Linear kernel. No mapping is done, linear discrimination (or regression) is
/// done in the original feature space. It is the fastest option. 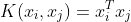.
LINEAR = 0,
/// Polynomial kernel:
/// 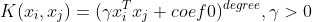.
POLY = 1,
/// Radial basis function (RBF), a good choice in most cases.
/// 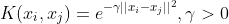.
RBF = 2,
/// Sigmoid kernel: 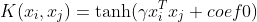.
SIGMOID = 3,
/// Exponential Chi2 kernel, similar to the RBF kernel:
/// 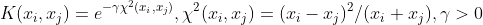.
CHI2 = 4,
/// Histogram intersection kernel. A fast kernel. 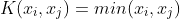.
INTER = 5,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::SVM_KernelTypes }
/// %SVM params type
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum SVM_ParamTypes {
C = 0,
GAMMA = 1,
P = 2,
NU = 3,
COEF = 4,
DEGREE = 5,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::SVM_ParamTypes }
/// %SVM type
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum SVM_Types {
/// C-Support Vector Classification. n-class classification (n  2), allows
/// imperfect separation of classes with penalty multiplier C for outliers.
C_SVC = 100,
/// 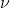-Support Vector Classification. n-class classification with possible
/// imperfect separation. Parameter 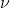 (in the range 0..1, the larger the value, the smoother
/// the decision boundary) is used instead of C.
NU_SVC = 101,
/// Distribution Estimation (One-class %SVM). All the training data are from
/// the same class, %SVM builds a boundary that separates the class from the rest of the feature
/// space.
ONE_CLASS = 102,
/// -Support Vector Regression. The distance between feature vectors
/// from the training set and the fitting hyper-plane must be less than p. For outliers the
/// penalty multiplier C is used.
EPS_SVR = 103,
/// 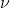-Support Vector Regression. 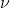 is used instead of p.
/// See [LibSVM](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_LibSVM) for details.
NU_SVR = 104,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::SVM_Types }
/// Sample types
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum SampleTypes {
/// each training sample is a row of samples
ROW_SAMPLE = 0,
/// each training sample occupies a column of samples
COL_SAMPLE = 1,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::SampleTypes }
/// Predict options
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum StatModel_Flags {
UPDATE_MODEL = 1,
// makes the method return the raw results (the sum), not the class label
// Duplicate, use UPDATE_MODEL instead
// RAW_OUTPUT = 1,
COMPRESSED_INPUT = 2,
PREPROCESSED_INPUT = 4,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::StatModel_Flags }
/// Variable types
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum VariableTypes {
/// same as VAR_ORDERED
VAR_NUMERICAL = 0,
// ordered variables
// Duplicate, use VAR_NUMERICAL instead
// VAR_ORDERED = 0,
/// categorical variables
VAR_CATEGORICAL = 1,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::VariableTypes }
pub type ANN_MLP_ANNEAL = crate::ml::ANN_MLP;
/// Creates test set
#[inline]
pub fn create_concentric_spheres_test_set(nsamples: i32, nfeatures: i32, nclasses: i32, samples: &mut impl core::ToOutputArray, responses: &mut impl core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
output_array_arg!(samples);
output_array_arg!(responses);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_createConcentricSpheresTestSet_int_int_int_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(nsamples, nfeatures, nclasses, samples.as_raw__OutputArray(), responses.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Generates _sample_ from multivariate normal distribution
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * mean: an average row vector
/// * cov: symmetric covariation matrix
/// * nsamples: returned samples count
/// * samples: returned samples array
#[inline]
pub fn rand_mv_normal(mean: &impl core::ToInputArray, cov: &impl core::ToInputArray, nsamples: i32, samples: &mut impl core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(mean);
input_array_arg!(cov);
output_array_arg!(samples);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_randMVNormal_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int_const__OutputArrayR(mean.as_raw__InputArray(), cov.as_raw__InputArray(), nsamples, samples.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ml::ANN_MLP]
pub trait ANN_MLPTraitConst: crate::ml::StatModelTraitConst {
fn as_raw_ANN_MLP(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Returns current training method
#[inline]
fn get_train_method(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getTrainMethod_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Integer vector specifying the number of neurons in each layer including the input and output layers.
/// The very first element specifies the number of elements in the input layer.
/// The last element - number of elements in the output layer.
/// ## See also
/// setLayerSizes
#[inline]
fn get_layer_sizes(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getLayerSizes_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Termination criteria of the training algorithm.
/// You can specify the maximum number of iterations (maxCount) and/or how much the error could
/// change between the iterations to make the algorithm continue (epsilon). Default value is
/// TermCriteria(TermCriteria::MAX_ITER + TermCriteria::EPS, 1000, 0.01).
/// ## See also
/// setTermCriteria
#[inline]
fn get_term_criteria(&self) -> Result<core::TermCriteria> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getTermCriteria_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// BPROP: Strength of the weight gradient term.
/// The recommended value is about 0.1. Default value is 0.1.
/// ## See also
/// setBackpropWeightScale
#[inline]
fn get_backprop_weight_scale(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getBackpropWeightScale_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// BPROP: Strength of the momentum term (the difference between weights on the 2 previous iterations).
/// This parameter provides some inertia to smooth the random fluctuations of the weights. It can
/// vary from 0 (the feature is disabled) to 1 and beyond. The value 0.1 or so is good enough.
/// Default value is 0.1.
/// ## See also
/// setBackpropMomentumScale
#[inline]
fn get_backprop_momentum_scale(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getBackpropMomentumScale_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// RPROP: Initial value 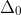 of update-values 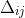.
/// Default value is 0.1.
/// ## See also
/// setRpropDW0
#[inline]
fn get_rprop_dw0(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getRpropDW0_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// RPROP: Increase factor 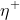.
/// It must be \>1. Default value is 1.2.
/// ## See also
/// setRpropDWPlus
#[inline]
fn get_rprop_dw_plus(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getRpropDWPlus_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// RPROP: Decrease factor 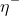.
/// It must be \<1. Default value is 0.5.
/// ## See also
/// setRpropDWMinus
#[inline]
fn get_rprop_dw_minus(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getRpropDWMinus_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// RPROP: Update-values lower limit 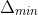.
/// It must be positive. Default value is FLT_EPSILON.
/// ## See also
/// setRpropDWMin
#[inline]
fn get_rprop_dw_min(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getRpropDWMin_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// RPROP: Update-values upper limit 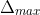.
/// It must be \>1. Default value is 50.
/// ## See also
/// setRpropDWMax
#[inline]
fn get_rprop_dw_max(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getRpropDWMax_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ANNEAL: Update initial temperature.
/// It must be \>=0. Default value is 10.
/// ## See also
/// setAnnealInitialT
#[inline]
fn get_anneal_initial_t(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getAnnealInitialT_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ANNEAL: Update final temperature.
/// It must be \>=0 and less than initialT. Default value is 0.1.
/// ## See also
/// setAnnealFinalT
#[inline]
fn get_anneal_final_t(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getAnnealFinalT_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ANNEAL: Update cooling ratio.
/// It must be \>0 and less than 1. Default value is 0.95.
/// ## See also
/// setAnnealCoolingRatio
#[inline]
fn get_anneal_cooling_ratio(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getAnnealCoolingRatio_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ANNEAL: Update iteration per step.
/// It must be \>0 . Default value is 10.
/// ## See also
/// setAnnealItePerStep
#[inline]
fn get_anneal_ite_per_step(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getAnnealItePerStep_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_weights(&self, layer_idx: i32) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getWeights_const_int(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP(), layer_idx, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::ml::ANN_MLP]
pub trait ANN_MLPTrait: crate::ml::ANN_MLPTraitConst + crate::ml::StatModelTrait {
fn as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Sets training method and common parameters.
/// ## Parameters
/// * method: Default value is ANN_MLP::RPROP. See ANN_MLP::TrainingMethods.
/// * param1: passed to setRpropDW0 for ANN_MLP::RPROP and to setBackpropWeightScale for ANN_MLP::BACKPROP and to initialT for ANN_MLP::ANNEAL.
/// * param2: passed to setRpropDWMin for ANN_MLP::RPROP and to setBackpropMomentumScale for ANN_MLP::BACKPROP and to finalT for ANN_MLP::ANNEAL.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * param1: 0
/// * param2: 0
#[inline]
fn set_train_method(&mut self, method: i32, param1: f64, param2: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setTrainMethod_int_double_double(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), method, param1, param2, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Initialize the activation function for each neuron.
/// Currently the default and the only fully supported activation function is ANN_MLP::SIGMOID_SYM.
/// ## Parameters
/// * type: The type of activation function. See ANN_MLP::ActivationFunctions.
/// * param1: The first parameter of the activation function, 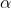. Default value is 0.
/// * param2: The second parameter of the activation function, 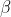. Default value is 0.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * param1: 0
/// * param2: 0
#[inline]
fn set_activation_function(&mut self, typ: i32, param1: f64, param2: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setActivationFunction_int_double_double(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), typ, param1, param2, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Integer vector specifying the number of neurons in each layer including the input and output layers.
/// The very first element specifies the number of elements in the input layer.
/// The last element - number of elements in the output layer. Default value is empty Mat.
/// ## See also
/// getLayerSizes
#[inline]
fn set_layer_sizes(&mut self, _layer_sizes: &impl core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(_layer_sizes);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setLayerSizes_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), _layer_sizes.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Termination criteria of the training algorithm.
/// You can specify the maximum number of iterations (maxCount) and/or how much the error could
/// change between the iterations to make the algorithm continue (epsilon). Default value is
/// TermCriteria(TermCriteria::MAX_ITER + TermCriteria::EPS, 1000, 0.01).
/// ## See also
/// setTermCriteria getTermCriteria
#[inline]
fn set_term_criteria(&mut self, val: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setTermCriteria_TermCriteria(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), val.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// BPROP: Strength of the weight gradient term.
/// The recommended value is about 0.1. Default value is 0.1.
/// ## See also
/// setBackpropWeightScale getBackpropWeightScale
#[inline]
fn set_backprop_weight_scale(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setBackpropWeightScale_double(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// BPROP: Strength of the momentum term (the difference between weights on the 2 previous iterations).
/// This parameter provides some inertia to smooth the random fluctuations of the weights. It can
/// vary from 0 (the feature is disabled) to 1 and beyond. The value 0.1 or so is good enough.
/// Default value is 0.1.
/// ## See also
/// setBackpropMomentumScale getBackpropMomentumScale
#[inline]
fn set_backprop_momentum_scale(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setBackpropMomentumScale_double(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// RPROP: Initial value 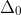 of update-values 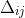.
/// Default value is 0.1.
/// ## See also
/// setRpropDW0 getRpropDW0
#[inline]
fn set_rprop_dw0(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setRpropDW0_double(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// RPROP: Increase factor 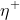.
/// It must be \>1. Default value is 1.2.
/// ## See also
/// setRpropDWPlus getRpropDWPlus
#[inline]
fn set_rprop_dw_plus(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setRpropDWPlus_double(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// RPROP: Decrease factor 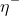.
/// It must be \<1. Default value is 0.5.
/// ## See also
/// setRpropDWMinus getRpropDWMinus
#[inline]
fn set_rprop_dw_minus(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setRpropDWMinus_double(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// RPROP: Update-values lower limit 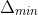.
/// It must be positive. Default value is FLT_EPSILON.
/// ## See also
/// setRpropDWMin getRpropDWMin
#[inline]
fn set_rprop_dw_min(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setRpropDWMin_double(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// RPROP: Update-values upper limit 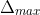.
/// It must be \>1. Default value is 50.
/// ## See also
/// setRpropDWMax getRpropDWMax
#[inline]
fn set_rprop_dw_max(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setRpropDWMax_double(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ANNEAL: Update initial temperature.
/// It must be \>=0. Default value is 10.
/// ## See also
/// setAnnealInitialT getAnnealInitialT
#[inline]
fn set_anneal_initial_t(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setAnnealInitialT_double(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ANNEAL: Update final temperature.
/// It must be \>=0 and less than initialT. Default value is 0.1.
/// ## See also
/// setAnnealFinalT getAnnealFinalT
#[inline]
fn set_anneal_final_t(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setAnnealFinalT_double(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ANNEAL: Update cooling ratio.
/// It must be \>0 and less than 1. Default value is 0.95.
/// ## See also
/// setAnnealCoolingRatio getAnnealCoolingRatio
#[inline]
fn set_anneal_cooling_ratio(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setAnnealCoolingRatio_double(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ANNEAL: Update iteration per step.
/// It must be \>0 . Default value is 10.
/// ## See also
/// setAnnealItePerStep getAnnealItePerStep
#[inline]
fn set_anneal_ite_per_step(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setAnnealItePerStep_int(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Set/initialize anneal RNG
#[inline]
fn set_anneal_energy_rng(&mut self, rng: &core::RNG) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setAnnealEnergyRNG_const_RNGR(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), rng.as_raw_RNG(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Artificial Neural Networks - Multi-Layer Perceptrons.
///
/// Unlike many other models in ML that are constructed and trained at once, in the MLP model these
/// steps are separated. First, a network with the specified topology is created using the non-default
/// constructor or the method ANN_MLP::create. All the weights are set to zeros. Then, the network is
/// trained using a set of input and output vectors. The training procedure can be repeated more than
/// once, that is, the weights can be adjusted based on the new training data.
///
/// Additional flags for StatModel::train are available: ANN_MLP::TrainFlags.
/// ## See also
/// [ml_intro_ann]
pub struct ANN_MLP {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { ANN_MLP }
impl Drop for ANN_MLP {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_ANN_MLP_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_ANN_MLP_delete(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for ANN_MLP {}
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for ANN_MLP {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for ANN_MLP {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::ml::StatModelTraitConst for ANN_MLP {
#[inline] fn as_raw_StatModel(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::StatModelTrait for ANN_MLP {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_StatModel(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::ml::ANN_MLPTraitConst for ANN_MLP {
#[inline] fn as_raw_ANN_MLP(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::ANN_MLPTrait for ANN_MLP {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl ANN_MLP {
/// Creates empty model
///
/// Use StatModel::train to train the model, Algorithm::load\<ANN_MLP\>(filename) to load the pre-trained model.
/// Note that the train method has optional flags: ANN_MLP::TrainFlags.
#[inline]
pub fn create() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::ml::ANN_MLP>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_create(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ml::ANN_MLP>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Loads and creates a serialized ANN from a file
///
/// Use ANN::save to serialize and store an ANN to disk.
/// Load the ANN from this file again, by calling this function with the path to the file.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * filepath: path to serialized ANN
#[inline]
pub fn load(filepath: &str) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::ml::ANN_MLP>> {
extern_container_arg!(filepath);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_load_const_StringR(filepath.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ml::ANN_MLP>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { ANN_MLP, core::Algorithm, cv_ANN_MLP_to_Algorithm }
/// Constant methods for [crate::ml::Boost]
pub trait BoostTraitConst: crate::ml::DTreesTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Boost(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Type of the boosting algorithm.
/// See Boost::Types. Default value is Boost::REAL.
/// ## See also
/// setBoostType
#[inline]
fn get_boost_type(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_Boost_getBoostType_const(self.as_raw_Boost(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// The number of weak classifiers.
/// Default value is 100.
/// ## See also
/// setWeakCount
#[inline]
fn get_weak_count(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_Boost_getWeakCount_const(self.as_raw_Boost(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// A threshold between 0 and 1 used to save computational time.
/// Samples with summary weight 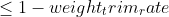 do not participate in the *next*
/// iteration of training. Set this parameter to 0 to turn off this functionality. Default value is 0.95.
/// ## See also
/// setWeightTrimRate
#[inline]
fn get_weight_trim_rate(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_Boost_getWeightTrimRate_const(self.as_raw_Boost(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::ml::Boost]
pub trait BoostTrait: crate::ml::BoostTraitConst + crate::ml::DTreesTrait {
fn as_raw_mut_Boost(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Type of the boosting algorithm.
/// See Boost::Types. Default value is Boost::REAL.
/// ## See also
/// setBoostType getBoostType
#[inline]
fn set_boost_type(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_Boost_setBoostType_int(self.as_raw_mut_Boost(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// The number of weak classifiers.
/// Default value is 100.
/// ## See also
/// setWeakCount getWeakCount
#[inline]
fn set_weak_count(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_Boost_setWeakCount_int(self.as_raw_mut_Boost(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// A threshold between 0 and 1 used to save computational time.
/// Samples with summary weight 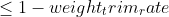 do not participate in the *next*
/// iteration of training. Set this parameter to 0 to turn off this functionality. Default value is 0.95.
/// ## See also
/// setWeightTrimRate getWeightTrimRate
#[inline]
fn set_weight_trim_rate(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_Boost_setWeightTrimRate_double(self.as_raw_mut_Boost(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Boosted tree classifier derived from DTrees
/// ## See also
/// [ml_intro_boost]
pub struct Boost {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Boost }
impl Drop for Boost {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Boost_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Boost_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Boost()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Boost {}
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for Boost {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for Boost {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::ml::DTreesTraitConst for Boost {
#[inline] fn as_raw_DTrees(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::DTreesTrait for Boost {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_DTrees(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::ml::StatModelTraitConst for Boost {
#[inline] fn as_raw_StatModel(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::StatModelTrait for Boost {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_StatModel(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::ml::BoostTraitConst for Boost {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Boost(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::BoostTrait for Boost {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Boost(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Boost {
/// Creates the empty model.
/// Use StatModel::train to train the model, Algorithm::load\<Boost\>(filename) to load the pre-trained model.
#[inline]
pub fn create() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::ml::Boost>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_Boost_create(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ml::Boost>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Loads and creates a serialized Boost from a file
///
/// Use Boost::save to serialize and store an RTree to disk.
/// Load the Boost from this file again, by calling this function with the path to the file.
/// Optionally specify the node for the file containing the classifier
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * filepath: path to serialized Boost
/// * nodeName: name of node containing the classifier
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * node_name: String()
#[inline]
pub fn load(filepath: &str, node_name: &str) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::ml::Boost>> {
extern_container_arg!(filepath);
extern_container_arg!(node_name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_Boost_load_const_StringR_const_StringR(filepath.opencv_as_extern(), node_name.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ml::Boost>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { Boost, core::Algorithm, cv_Boost_to_Algorithm }
/// Constant methods for [crate::ml::DTrees]
pub trait DTreesTraitConst: crate::ml::StatModelTraitConst {
fn as_raw_DTrees(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Cluster possible values of a categorical variable into K\<=maxCategories clusters to
/// find a suboptimal split.
/// If a discrete variable, on which the training procedure tries to make a split, takes more than
/// maxCategories values, the precise best subset estimation may take a very long time because the
/// algorithm is exponential. Instead, many decision trees engines (including our implementation)
/// try to find sub-optimal split in this case by clustering all the samples into maxCategories
/// clusters that is some categories are merged together. The clustering is applied only in n \>
/// 2-class classification problems for categorical variables with N \> max_categories possible
/// values. In case of regression and 2-class classification the optimal split can be found
/// efficiently without employing clustering, thus the parameter is not used in these cases.
/// Default value is 10.
/// ## See also
/// setMaxCategories
#[inline]
fn get_max_categories(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_getMaxCategories_const(self.as_raw_DTrees(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// The maximum possible depth of the tree.
/// That is the training algorithms attempts to split a node while its depth is less than maxDepth.
/// The root node has zero depth. The actual depth may be smaller if the other termination criteria
/// are met (see the outline of the training procedure [ml_intro_trees] "here"), and/or if the
/// tree is pruned. Default value is INT_MAX.
/// ## See also
/// setMaxDepth
#[inline]
fn get_max_depth(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_getMaxDepth_const(self.as_raw_DTrees(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// If the number of samples in a node is less than this parameter then the node will not be split.
///
/// Default value is 10.
/// ## See also
/// setMinSampleCount
#[inline]
fn get_min_sample_count(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_getMinSampleCount_const(self.as_raw_DTrees(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// If CVFolds \> 1 then algorithms prunes the built decision tree using K-fold
/// cross-validation procedure where K is equal to CVFolds.
/// Default value is 10.
/// ## See also
/// setCVFolds
#[inline]
fn get_cv_folds(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_getCVFolds_const(self.as_raw_DTrees(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// If true then surrogate splits will be built.
/// These splits allow to work with missing data and compute variable importance correctly.
/// Default value is false.
///
/// Note: currently it's not implemented.
/// ## See also
/// setUseSurrogates
#[inline]
fn get_use_surrogates(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_getUseSurrogates_const(self.as_raw_DTrees(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// If true then a pruning will be harsher.
/// This will make a tree more compact and more resistant to the training data noise but a bit less
/// accurate. Default value is true.
/// ## See also
/// setUse1SERule
#[inline]
fn get_use1_se_rule(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_getUse1SERule_const(self.as_raw_DTrees(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// If true then pruned branches are physically removed from the tree.
/// Otherwise they are retained and it is possible to get results from the original unpruned (or
/// pruned less aggressively) tree. Default value is true.
/// ## See also
/// setTruncatePrunedTree
#[inline]
fn get_truncate_pruned_tree(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_getTruncatePrunedTree_const(self.as_raw_DTrees(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Termination criteria for regression trees.
/// If all absolute differences between an estimated value in a node and values of train samples
/// in this node are less than this parameter then the node will not be split further. Default
/// value is 0.01f
/// ## See also
/// setRegressionAccuracy
#[inline]
fn get_regression_accuracy(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_getRegressionAccuracy_const(self.as_raw_DTrees(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// The array of a priori class probabilities, sorted by the class label value.
///
/// The parameter can be used to tune the decision tree preferences toward a certain class. For
/// example, if you want to detect some rare anomaly occurrence, the training base will likely
/// contain much more normal cases than anomalies, so a very good classification performance
/// will be achieved just by considering every case as normal. To avoid this, the priors can be
/// specified, where the anomaly probability is artificially increased (up to 0.5 or even
/// greater), so the weight of the misclassified anomalies becomes much bigger, and the tree is
/// adjusted properly.
///
/// You can also think about this parameter as weights of prediction categories which determine
/// relative weights that you give to misclassification. That is, if the weight of the first
/// category is 1 and the weight of the second category is 10, then each mistake in predicting
/// the second category is equivalent to making 10 mistakes in predicting the first category.
/// Default value is empty Mat.
/// ## See also
/// setPriors
#[inline]
fn get_priors(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_getPriors_const(self.as_raw_DTrees(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns indices of root nodes
#[inline]
fn get_roots(&self) -> Result<core::Vector<i32>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_getRoots_const(self.as_raw_DTrees(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Vector::<i32>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns all the nodes
///
/// all the node indices are indices in the returned vector
#[inline]
fn get_nodes(&self) -> Result<core::Vector<crate::ml::DTrees_Node>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_getNodes_const(self.as_raw_DTrees(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Vector::<crate::ml::DTrees_Node>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns all the splits
///
/// all the split indices are indices in the returned vector
#[inline]
fn get_splits(&self) -> Result<core::Vector<crate::ml::DTrees_Split>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_getSplits_const(self.as_raw_DTrees(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Vector::<crate::ml::DTrees_Split>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns all the bitsets for categorical splits
///
/// Split::subsetOfs is an offset in the returned vector
#[inline]
fn get_subsets(&self) -> Result<core::Vector<i32>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_getSubsets_const(self.as_raw_DTrees(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Vector::<i32>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::ml::DTrees]
pub trait DTreesTrait: crate::ml::DTreesTraitConst + crate::ml::StatModelTrait {
fn as_raw_mut_DTrees(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Cluster possible values of a categorical variable into K\<=maxCategories clusters to
/// find a suboptimal split.
/// If a discrete variable, on which the training procedure tries to make a split, takes more than
/// maxCategories values, the precise best subset estimation may take a very long time because the
/// algorithm is exponential. Instead, many decision trees engines (including our implementation)
/// try to find sub-optimal split in this case by clustering all the samples into maxCategories
/// clusters that is some categories are merged together. The clustering is applied only in n \>
/// 2-class classification problems for categorical variables with N \> max_categories possible
/// values. In case of regression and 2-class classification the optimal split can be found
/// efficiently without employing clustering, thus the parameter is not used in these cases.
/// Default value is 10.
/// ## See also
/// setMaxCategories getMaxCategories
#[inline]
fn set_max_categories(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_setMaxCategories_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// The maximum possible depth of the tree.
/// That is the training algorithms attempts to split a node while its depth is less than maxDepth.
/// The root node has zero depth. The actual depth may be smaller if the other termination criteria
/// are met (see the outline of the training procedure [ml_intro_trees] "here"), and/or if the
/// tree is pruned. Default value is INT_MAX.
/// ## See also
/// setMaxDepth getMaxDepth
#[inline]
fn set_max_depth(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_setMaxDepth_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// If the number of samples in a node is less than this parameter then the node will not be split.
///
/// Default value is 10.
/// ## See also
/// setMinSampleCount getMinSampleCount
#[inline]
fn set_min_sample_count(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_setMinSampleCount_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// If CVFolds \> 1 then algorithms prunes the built decision tree using K-fold
/// cross-validation procedure where K is equal to CVFolds.
/// Default value is 10.
/// ## See also
/// setCVFolds getCVFolds
#[inline]
fn set_cv_folds(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_setCVFolds_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// If true then surrogate splits will be built.
/// These splits allow to work with missing data and compute variable importance correctly.
/// Default value is false.
///
/// Note: currently it's not implemented.
/// ## See also
/// setUseSurrogates getUseSurrogates
#[inline]
fn set_use_surrogates(&mut self, val: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_setUseSurrogates_bool(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// If true then a pruning will be harsher.
/// This will make a tree more compact and more resistant to the training data noise but a bit less
/// accurate. Default value is true.
/// ## See also
/// setUse1SERule getUse1SERule
#[inline]
fn set_use1_se_rule(&mut self, val: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_setUse1SERule_bool(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// If true then pruned branches are physically removed from the tree.
/// Otherwise they are retained and it is possible to get results from the original unpruned (or
/// pruned less aggressively) tree. Default value is true.
/// ## See also
/// setTruncatePrunedTree getTruncatePrunedTree
#[inline]
fn set_truncate_pruned_tree(&mut self, val: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_setTruncatePrunedTree_bool(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Termination criteria for regression trees.
/// If all absolute differences between an estimated value in a node and values of train samples
/// in this node are less than this parameter then the node will not be split further. Default
/// value is 0.01f
/// ## See also
/// setRegressionAccuracy getRegressionAccuracy
#[inline]
fn set_regression_accuracy(&mut self, val: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_setRegressionAccuracy_float(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// The array of a priori class probabilities, sorted by the class label value.
///
/// The parameter can be used to tune the decision tree preferences toward a certain class. For
/// example, if you want to detect some rare anomaly occurrence, the training base will likely
/// contain much more normal cases than anomalies, so a very good classification performance
/// will be achieved just by considering every case as normal. To avoid this, the priors can be
/// specified, where the anomaly probability is artificially increased (up to 0.5 or even
/// greater), so the weight of the misclassified anomalies becomes much bigger, and the tree is
/// adjusted properly.
///
/// You can also think about this parameter as weights of prediction categories which determine
/// relative weights that you give to misclassification. That is, if the weight of the first
/// category is 1 and the weight of the second category is 10, then each mistake in predicting
/// the second category is equivalent to making 10 mistakes in predicting the first category.
/// Default value is empty Mat.
/// ## See also
/// setPriors getPriors
#[inline]
fn set_priors(&mut self, val: &core::Mat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_setPriors_const_MatR(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees(), val.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// The class represents a single decision tree or a collection of decision trees.
///
/// The current public interface of the class allows user to train only a single decision tree, however
/// the class is capable of storing multiple decision trees and using them for prediction (by summing
/// responses or using a voting schemes), and the derived from DTrees classes (such as RTrees and Boost)
/// use this capability to implement decision tree ensembles.
/// ## See also
/// [ml_intro_trees]
pub struct DTrees {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { DTrees }
impl Drop for DTrees {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_DTrees_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_DTrees_delete(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for DTrees {}
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for DTrees {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for DTrees {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::ml::StatModelTraitConst for DTrees {
#[inline] fn as_raw_StatModel(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::StatModelTrait for DTrees {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_StatModel(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::ml::DTreesTraitConst for DTrees {
#[inline] fn as_raw_DTrees(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::DTreesTrait for DTrees {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_DTrees(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl DTrees {
/// Creates the empty model
///
/// The static method creates empty decision tree with the specified parameters. It should be then
/// trained using train method (see StatModel::train). Alternatively, you can load the model from
/// file using Algorithm::load\<DTrees\>(filename).
#[inline]
pub fn create() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::ml::DTrees>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_create(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ml::DTrees>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Loads and creates a serialized DTrees from a file
///
/// Use DTree::save to serialize and store an DTree to disk.
/// Load the DTree from this file again, by calling this function with the path to the file.
/// Optionally specify the node for the file containing the classifier
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * filepath: path to serialized DTree
/// * nodeName: name of node containing the classifier
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * node_name: String()
#[inline]
pub fn load(filepath: &str, node_name: &str) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::ml::DTrees>> {
extern_container_arg!(filepath);
extern_container_arg!(node_name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_load_const_StringR_const_StringR(filepath.opencv_as_extern(), node_name.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ml::DTrees>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { DTrees, core::Algorithm, cv_DTrees_to_Algorithm }
/// Constant methods for [crate::ml::DTrees_Node]
pub trait DTrees_NodeTraitConst {
fn as_raw_DTrees_Node(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Value at the node: a class label in case of classification or estimated
/// function value in case of regression.
#[inline]
fn value(&self) -> f64 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_getPropValue_const(self.as_raw_DTrees_Node()) };
ret
}
/// Class index normalized to 0..class_count-1 range and assigned to the
/// node. It is used internally in classification trees and tree ensembles.
#[inline]
fn class_idx(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_getPropClassIdx_const(self.as_raw_DTrees_Node()) };
ret
}
/// Index of the parent node
#[inline]
fn parent(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_getPropParent_const(self.as_raw_DTrees_Node()) };
ret
}
/// Index of the left child node
#[inline]
fn left(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_getPropLeft_const(self.as_raw_DTrees_Node()) };
ret
}
/// Index of right child node
#[inline]
fn right(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_getPropRight_const(self.as_raw_DTrees_Node()) };
ret
}
/// Default direction where to go (-1: left or +1: right). It helps in the
/// case of missing values.
#[inline]
fn default_dir(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_getPropDefaultDir_const(self.as_raw_DTrees_Node()) };
ret
}
/// Index of the first split
#[inline]
fn split(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_getPropSplit_const(self.as_raw_DTrees_Node()) };
ret
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::ml::DTrees_Node]
pub trait DTrees_NodeTrait: crate::ml::DTrees_NodeTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_DTrees_Node(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Value at the node: a class label in case of classification or estimated
/// function value in case of regression.
#[inline]
fn set_value(&mut self, val: f64) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_setPropValue_double(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Node(), val) };
ret
}
/// Class index normalized to 0..class_count-1 range and assigned to the
/// node. It is used internally in classification trees and tree ensembles.
#[inline]
fn set_class_idx(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_setPropClassIdx_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Node(), val) };
ret
}
/// Index of the parent node
#[inline]
fn set_parent(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_setPropParent_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Node(), val) };
ret
}
/// Index of the left child node
#[inline]
fn set_left(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_setPropLeft_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Node(), val) };
ret
}
/// Index of right child node
#[inline]
fn set_right(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_setPropRight_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Node(), val) };
ret
}
/// Default direction where to go (-1: left or +1: right). It helps in the
/// case of missing values.
#[inline]
fn set_default_dir(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_setPropDefaultDir_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Node(), val) };
ret
}
/// Index of the first split
#[inline]
fn set_split(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_setPropSplit_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Node(), val) };
ret
}
}
/// The class represents a decision tree node.
pub struct DTrees_Node {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { DTrees_Node }
impl Drop for DTrees_Node {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_DTrees_Node_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_DTrees_Node_delete(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Node()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for DTrees_Node {}
impl crate::ml::DTrees_NodeTraitConst for DTrees_Node {
#[inline] fn as_raw_DTrees_Node(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::DTrees_NodeTrait for DTrees_Node {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_DTrees_Node(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl DTrees_Node {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<crate::ml::DTrees_Node> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_Node(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { crate::ml::DTrees_Node::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ml::DTrees_Split]
pub trait DTrees_SplitTraitConst {
fn as_raw_DTrees_Split(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Index of variable on which the split is created.
#[inline]
fn var_idx(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Split_getPropVarIdx_const(self.as_raw_DTrees_Split()) };
ret
}
/// If true, then the inverse split rule is used (i.e. left and right
/// branches are exchanged in the rule expressions below).
#[inline]
fn inversed(&self) -> bool {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Split_getPropInversed_const(self.as_raw_DTrees_Split()) };
ret
}
/// The split quality, a positive number. It is used to choose the best split.
#[inline]
fn quality(&self) -> f32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Split_getPropQuality_const(self.as_raw_DTrees_Split()) };
ret
}
/// Index of the next split in the list of splits for the node
#[inline]
fn next(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Split_getPropNext_const(self.as_raw_DTrees_Split()) };
ret
}
/// < The threshold value in case of split on an ordered variable.
/// The rule is:
/// ```C++
/// if var_value < c
/// then next_node <- left
/// else next_node <- right
/// ```
///
#[inline]
fn c(&self) -> f32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Split_getPropC_const(self.as_raw_DTrees_Split()) };
ret
}
/// < Offset of the bitset used by the split on a categorical variable.
/// The rule is:
/// ```C++
/// if bitset[var_value] == 1
/// then next_node <- left
/// else next_node <- right
/// ```
///
#[inline]
fn subset_ofs(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Split_getPropSubsetOfs_const(self.as_raw_DTrees_Split()) };
ret
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::ml::DTrees_Split]
pub trait DTrees_SplitTrait: crate::ml::DTrees_SplitTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_DTrees_Split(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Index of variable on which the split is created.
#[inline]
fn set_var_idx(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Split_setPropVarIdx_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Split(), val) };
ret
}
/// If true, then the inverse split rule is used (i.e. left and right
/// branches are exchanged in the rule expressions below).
#[inline]
fn set_inversed(&mut self, val: bool) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Split_setPropInversed_bool(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Split(), val) };
ret
}
/// The split quality, a positive number. It is used to choose the best split.
#[inline]
fn set_quality(&mut self, val: f32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Split_setPropQuality_float(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Split(), val) };
ret
}
/// Index of the next split in the list of splits for the node
#[inline]
fn set_next(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Split_setPropNext_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Split(), val) };
ret
}
/// < The threshold value in case of split on an ordered variable.
/// The rule is:
/// ```C++
/// if var_value < c
/// then next_node <- left
/// else next_node <- right
/// ```
///
#[inline]
fn set_c(&mut self, val: f32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Split_setPropC_float(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Split(), val) };
ret
}
/// < Offset of the bitset used by the split on a categorical variable.
/// The rule is:
/// ```C++
/// if bitset[var_value] == 1
/// then next_node <- left
/// else next_node <- right
/// ```
///
#[inline]
fn set_subset_ofs(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Split_setPropSubsetOfs_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Split(), val) };
ret
}
}
/// The class represents split in a decision tree.
pub struct DTrees_Split {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { DTrees_Split }
impl Drop for DTrees_Split {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_DTrees_Split_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_DTrees_Split_delete(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Split()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for DTrees_Split {}
impl crate::ml::DTrees_SplitTraitConst for DTrees_Split {
#[inline] fn as_raw_DTrees_Split(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::DTrees_SplitTrait for DTrees_Split {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_DTrees_Split(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl DTrees_Split {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<crate::ml::DTrees_Split> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Split_Split(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { crate::ml::DTrees_Split::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ml::EM]
pub trait EMTraitConst: crate::ml::StatModelTraitConst {
fn as_raw_EM(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// The number of mixture components in the Gaussian mixture model.
/// Default value of the parameter is EM::DEFAULT_NCLUSTERS=5. Some of %EM implementation could
/// determine the optimal number of mixtures within a specified value range, but that is not the
/// case in ML yet.
/// ## See also
/// setClustersNumber
#[inline]
fn get_clusters_number(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_getClustersNumber_const(self.as_raw_EM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Constraint on covariance matrices which defines type of matrices.
/// See EM::Types.
/// ## See also
/// setCovarianceMatrixType
#[inline]
fn get_covariance_matrix_type(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_getCovarianceMatrixType_const(self.as_raw_EM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// The termination criteria of the %EM algorithm.
/// The %EM algorithm can be terminated by the number of iterations termCrit.maxCount (number of
/// M-steps) or when relative change of likelihood logarithm is less than termCrit.epsilon. Default
/// maximum number of iterations is EM::DEFAULT_MAX_ITERS=100.
/// ## See also
/// setTermCriteria
#[inline]
fn get_term_criteria(&self) -> Result<core::TermCriteria> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_getTermCriteria_const(self.as_raw_EM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns weights of the mixtures
///
/// Returns vector with the number of elements equal to the number of mixtures.
#[inline]
fn get_weights(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_getWeights_const(self.as_raw_EM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the cluster centers (means of the Gaussian mixture)
///
/// Returns matrix with the number of rows equal to the number of mixtures and number of columns
/// equal to the space dimensionality.
#[inline]
fn get_means(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_getMeans_const(self.as_raw_EM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns covariation matrices
///
/// Returns vector of covariation matrices. Number of matrices is the number of gaussian mixtures,
/// each matrix is a square floating-point matrix NxN, where N is the space dimensionality.
#[inline]
fn get_covs(&self, covs: &mut core::Vector<core::Mat>) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_getCovs_const_vectorLMatGR(self.as_raw_EM(), covs.as_raw_mut_VectorOfMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns posterior probabilities for the provided samples
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * samples: The input samples, floating-point matrix
/// * results: The optional output  matrix of results. It contains
/// posterior probabilities for each sample from the input
/// * flags: This parameter will be ignored
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * results: noArray()
/// * flags: 0
#[inline]
fn predict(&self, samples: &impl core::ToInputArray, results: &mut impl core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<f32> {
input_array_arg!(samples);
output_array_arg!(results);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_predict_const_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(self.as_raw_EM(), samples.as_raw__InputArray(), results.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns a likelihood logarithm value and an index of the most probable mixture component
/// for the given sample.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * sample: A sample for classification. It should be a one-channel matrix of
///  or  size.
/// * probs: Optional output matrix that contains posterior probabilities of each component
/// given the sample. It has 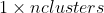 size and CV_64FC1 type.
///
/// The method returns a two-element double vector. Zero element is a likelihood logarithm value for
/// the sample. First element is an index of the most probable mixture component for the given
/// sample.
#[inline]
fn predict2(&self, sample: &impl core::ToInputArray, probs: &mut impl core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<core::Vec2d> {
input_array_arg!(sample);
output_array_arg!(probs);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_predict2_const_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_EM(), sample.as_raw__InputArray(), probs.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::ml::EM]
pub trait EMTrait: crate::ml::EMTraitConst + crate::ml::StatModelTrait {
fn as_raw_mut_EM(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// The number of mixture components in the Gaussian mixture model.
/// Default value of the parameter is EM::DEFAULT_NCLUSTERS=5. Some of %EM implementation could
/// determine the optimal number of mixtures within a specified value range, but that is not the
/// case in ML yet.
/// ## See also
/// setClustersNumber getClustersNumber
#[inline]
fn set_clusters_number(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_setClustersNumber_int(self.as_raw_mut_EM(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Constraint on covariance matrices which defines type of matrices.
/// See EM::Types.
/// ## See also
/// setCovarianceMatrixType getCovarianceMatrixType
#[inline]
fn set_covariance_matrix_type(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_setCovarianceMatrixType_int(self.as_raw_mut_EM(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// The termination criteria of the %EM algorithm.
/// The %EM algorithm can be terminated by the number of iterations termCrit.maxCount (number of
/// M-steps) or when relative change of likelihood logarithm is less than termCrit.epsilon. Default
/// maximum number of iterations is EM::DEFAULT_MAX_ITERS=100.
/// ## See also
/// setTermCriteria getTermCriteria
#[inline]
fn set_term_criteria(&mut self, val: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_setTermCriteria_const_TermCriteriaR(self.as_raw_mut_EM(), &val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Estimate the Gaussian mixture parameters from a samples set.
///
/// This variation starts with Expectation step. Initial values of the model parameters will be
/// estimated by the k-means algorithm.
///
/// Unlike many of the ML models, %EM is an unsupervised learning algorithm and it does not take
/// responses (class labels or function values) as input. Instead, it computes the *Maximum
/// Likelihood Estimate* of the Gaussian mixture parameters from an input sample set, stores all the
/// parameters inside the structure:  in probs,  in means ,  in
/// covs[k], 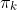 in weights , and optionally computes the output "class label" for each
/// sample:  (indices of the most
/// probable mixture component for each sample).
///
/// The trained model can be used further for prediction, just like any other classifier. The
/// trained model is similar to the NormalBayesClassifier.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * samples: Samples from which the Gaussian mixture model will be estimated. It should be a
/// one-channel matrix, each row of which is a sample. If the matrix does not have CV_64F type
/// it will be converted to the inner matrix of such type for the further computing.
/// * logLikelihoods: The optional output matrix that contains a likelihood logarithm value for
/// each sample. It has 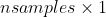 size and CV_64FC1 type.
/// * labels: The optional output "class label" for each sample:
///  (indices of the most probable
/// mixture component for each sample). It has 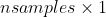 size and CV_32SC1 type.
/// * probs: The optional output matrix that contains posterior probabilities of each Gaussian
/// mixture component given the each sample. It has 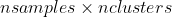 size and
/// CV_64FC1 type.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * log_likelihoods: noArray()
/// * labels: noArray()
/// * probs: noArray()
#[inline]
fn train_em(&mut self, samples: &impl core::ToInputArray, log_likelihoods: &mut impl core::ToOutputArray, labels: &mut impl core::ToOutputArray, probs: &mut impl core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(samples);
output_array_arg!(log_likelihoods);
output_array_arg!(labels);
output_array_arg!(probs);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_trainEM_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_EM(), samples.as_raw__InputArray(), log_likelihoods.as_raw__OutputArray(), labels.as_raw__OutputArray(), probs.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Estimate the Gaussian mixture parameters from a samples set.
///
/// This variation starts with Expectation step. You need to provide initial means 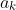 of
/// mixture components. Optionally you can pass initial weights  and covariance matrices
///  of mixture components.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * samples: Samples from which the Gaussian mixture model will be estimated. It should be a
/// one-channel matrix, each row of which is a sample. If the matrix does not have CV_64F type
/// it will be converted to the inner matrix of such type for the further computing.
/// * means0: Initial means 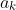 of mixture components. It is a one-channel matrix of
///  size. If the matrix does not have CV_64F type it will be
/// converted to the inner matrix of such type for the further computing.
/// * covs0: The vector of initial covariance matrices  of mixture components. Each of
/// covariance matrices is a one-channel matrix of  size. If the matrices
/// do not have CV_64F type they will be converted to the inner matrices of such type for the
/// further computing.
/// * weights0: Initial weights  of mixture components. It should be a one-channel
/// floating-point matrix with 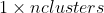 or 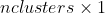 size.
/// * logLikelihoods: The optional output matrix that contains a likelihood logarithm value for
/// each sample. It has 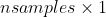 size and CV_64FC1 type.
/// * labels: The optional output "class label" for each sample:
///  (indices of the most probable
/// mixture component for each sample). It has 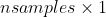 size and CV_32SC1 type.
/// * probs: The optional output matrix that contains posterior probabilities of each Gaussian
/// mixture component given the each sample. It has 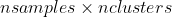 size and
/// CV_64FC1 type.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * covs0: noArray()
/// * weights0: noArray()
/// * log_likelihoods: noArray()
/// * labels: noArray()
/// * probs: noArray()
#[inline]
fn train_e(&mut self, samples: &impl core::ToInputArray, means0: &impl core::ToInputArray, covs0: &impl core::ToInputArray, weights0: &impl core::ToInputArray, log_likelihoods: &mut impl core::ToOutputArray, labels: &mut impl core::ToOutputArray, probs: &mut impl core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(samples);
input_array_arg!(means0);
input_array_arg!(covs0);
input_array_arg!(weights0);
output_array_arg!(log_likelihoods);
output_array_arg!(labels);
output_array_arg!(probs);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_trainE_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_EM(), samples.as_raw__InputArray(), means0.as_raw__InputArray(), covs0.as_raw__InputArray(), weights0.as_raw__InputArray(), log_likelihoods.as_raw__OutputArray(), labels.as_raw__OutputArray(), probs.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Estimate the Gaussian mixture parameters from a samples set.
///
/// This variation starts with Maximization step. You need to provide initial probabilities
///  to use this option.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * samples: Samples from which the Gaussian mixture model will be estimated. It should be a
/// one-channel matrix, each row of which is a sample. If the matrix does not have CV_64F type
/// it will be converted to the inner matrix of such type for the further computing.
/// * probs0: the probabilities
/// * logLikelihoods: The optional output matrix that contains a likelihood logarithm value for
/// each sample. It has 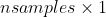 size and CV_64FC1 type.
/// * labels: The optional output "class label" for each sample:
///  (indices of the most probable
/// mixture component for each sample). It has 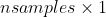 size and CV_32SC1 type.
/// * probs: The optional output matrix that contains posterior probabilities of each Gaussian
/// mixture component given the each sample. It has 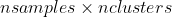 size and
/// CV_64FC1 type.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * log_likelihoods: noArray()
/// * labels: noArray()
/// * probs: noArray()
#[inline]
fn train_m(&mut self, samples: &impl core::ToInputArray, probs0: &impl core::ToInputArray, log_likelihoods: &mut impl core::ToOutputArray, labels: &mut impl core::ToOutputArray, probs: &mut impl core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(samples);
input_array_arg!(probs0);
output_array_arg!(log_likelihoods);
output_array_arg!(labels);
output_array_arg!(probs);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_trainM_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_EM(), samples.as_raw__InputArray(), probs0.as_raw__InputArray(), log_likelihoods.as_raw__OutputArray(), labels.as_raw__OutputArray(), probs.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// The class implements the Expectation Maximization algorithm.
/// ## See also
/// [ml_intro_em]
pub struct EM {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { EM }
impl Drop for EM {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_EM_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_EM_delete(self.as_raw_mut_EM()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for EM {}
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for EM {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for EM {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::ml::StatModelTraitConst for EM {
#[inline] fn as_raw_StatModel(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::StatModelTrait for EM {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_StatModel(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::ml::EMTraitConst for EM {
#[inline] fn as_raw_EM(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::EMTrait for EM {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_EM(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl EM {
/// Creates empty %EM model.
/// The model should be trained then using StatModel::train(traindata, flags) method. Alternatively, you
/// can use one of the EM::train\* methods or load it from file using Algorithm::load\<EM\>(filename).
#[inline]
pub fn create() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::ml::EM>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_create(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ml::EM>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Loads and creates a serialized EM from a file
///
/// Use EM::save to serialize and store an EM to disk.
/// Load the EM from this file again, by calling this function with the path to the file.
/// Optionally specify the node for the file containing the classifier
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * filepath: path to serialized EM
/// * nodeName: name of node containing the classifier
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * node_name: String()
#[inline]
pub fn load(filepath: &str, node_name: &str) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::ml::EM>> {
extern_container_arg!(filepath);
extern_container_arg!(node_name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_load_const_StringR_const_StringR(filepath.opencv_as_extern(), node_name.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ml::EM>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { EM, core::Algorithm, cv_EM_to_Algorithm }
/// Constant methods for [crate::ml::KNearest]
pub trait KNearestTraitConst: crate::ml::StatModelTraitConst {
fn as_raw_KNearest(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Default number of neighbors to use in predict method.
/// ## See also
/// setDefaultK
#[inline]
fn get_default_k(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_KNearest_getDefaultK_const(self.as_raw_KNearest(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Whether classification or regression model should be trained.
/// ## See also
/// setIsClassifier
#[inline]
fn get_is_classifier(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_KNearest_getIsClassifier_const(self.as_raw_KNearest(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter for KDTree implementation.
/// ## See also
/// setEmax
#[inline]
fn get_emax(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_KNearest_getEmax_const(self.as_raw_KNearest(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// %Algorithm type, one of KNearest::Types.
/// ## See also
/// setAlgorithmType
#[inline]
fn get_algorithm_type(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_KNearest_getAlgorithmType_const(self.as_raw_KNearest(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds the neighbors and predicts responses for input vectors.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * samples: Input samples stored by rows. It is a single-precision floating-point matrix of
/// `<number_of_samples> * k` size.
/// * k: Number of used nearest neighbors. Should be greater than 1.
/// * results: Vector with results of prediction (regression or classification) for each input
/// sample. It is a single-precision floating-point vector with `<number_of_samples>` elements.
/// * neighborResponses: Optional output values for corresponding neighbors. It is a single-
/// precision floating-point matrix of `<number_of_samples> * k` size.
/// * dist: Optional output distances from the input vectors to the corresponding neighbors. It
/// is a single-precision floating-point matrix of `<number_of_samples> * k` size.
///
/// For each input vector (a row of the matrix samples), the method finds the k nearest neighbors.
/// In case of regression, the predicted result is a mean value of the particular vector's neighbor
/// responses. In case of classification, the class is determined by voting.
///
/// For each input vector, the neighbors are sorted by their distances to the vector.
///
/// In case of C++ interface you can use output pointers to empty matrices and the function will
/// allocate memory itself.
///
/// If only a single input vector is passed, all output matrices are optional and the predicted
/// value is returned by the method.
///
/// The function is parallelized with the TBB library.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * neighbor_responses: noArray()
/// * dist: noArray()
#[inline]
fn find_nearest(&self, samples: &impl core::ToInputArray, k: i32, results: &mut impl core::ToOutputArray, neighbor_responses: &mut impl core::ToOutputArray, dist: &mut impl core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<f32> {
input_array_arg!(samples);
output_array_arg!(results);
output_array_arg!(neighbor_responses);
output_array_arg!(dist);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_KNearest_findNearest_const_const__InputArrayR_int_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_KNearest(), samples.as_raw__InputArray(), k, results.as_raw__OutputArray(), neighbor_responses.as_raw__OutputArray(), dist.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::ml::KNearest]
pub trait KNearestTrait: crate::ml::KNearestTraitConst + crate::ml::StatModelTrait {
fn as_raw_mut_KNearest(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Default number of neighbors to use in predict method.
/// ## See also
/// setDefaultK getDefaultK
#[inline]
fn set_default_k(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_KNearest_setDefaultK_int(self.as_raw_mut_KNearest(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Whether classification or regression model should be trained.
/// ## See also
/// setIsClassifier getIsClassifier
#[inline]
fn set_is_classifier(&mut self, val: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_KNearest_setIsClassifier_bool(self.as_raw_mut_KNearest(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter for KDTree implementation.
/// ## See also
/// setEmax getEmax
#[inline]
fn set_emax(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_KNearest_setEmax_int(self.as_raw_mut_KNearest(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// %Algorithm type, one of KNearest::Types.
/// ## See also
/// setAlgorithmType getAlgorithmType
#[inline]
fn set_algorithm_type(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_KNearest_setAlgorithmType_int(self.as_raw_mut_KNearest(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// The class implements K-Nearest Neighbors model
/// ## See also
/// [ml_intro_knn]
pub struct KNearest {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { KNearest }
impl Drop for KNearest {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_KNearest_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_KNearest_delete(self.as_raw_mut_KNearest()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for KNearest {}
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for KNearest {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for KNearest {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::ml::StatModelTraitConst for KNearest {
#[inline] fn as_raw_StatModel(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::StatModelTrait for KNearest {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_StatModel(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::ml::KNearestTraitConst for KNearest {
#[inline] fn as_raw_KNearest(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::KNearestTrait for KNearest {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_KNearest(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl KNearest {
/// Creates the empty model
///
/// The static method creates empty %KNearest classifier. It should be then trained using StatModel::train method.
#[inline]
pub fn create() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::ml::KNearest>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_KNearest_create(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ml::KNearest>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Loads and creates a serialized knearest from a file
///
/// Use KNearest::save to serialize and store an KNearest to disk.
/// Load the KNearest from this file again, by calling this function with the path to the file.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * filepath: path to serialized KNearest
#[inline]
pub fn load(filepath: &str) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::ml::KNearest>> {
extern_container_arg!(filepath);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_KNearest_load_const_StringR(filepath.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ml::KNearest>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { KNearest, core::Algorithm, cv_KNearest_to_Algorithm }
/// Constant methods for [crate::ml::LogisticRegression]
pub trait LogisticRegressionTraitConst: crate::ml::StatModelTraitConst {
fn as_raw_LogisticRegression(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Learning rate.
/// ## See also
/// setLearningRate
#[inline]
fn get_learning_rate(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_getLearningRate_const(self.as_raw_LogisticRegression(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Number of iterations.
/// ## See also
/// setIterations
#[inline]
fn get_iterations(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_getIterations_const(self.as_raw_LogisticRegression(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Kind of regularization to be applied. See LogisticRegression::RegKinds.
/// ## See also
/// setRegularization
#[inline]
fn get_regularization(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_getRegularization_const(self.as_raw_LogisticRegression(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Kind of training method used. See LogisticRegression::Methods.
/// ## See also
/// setTrainMethod
#[inline]
fn get_train_method(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_getTrainMethod_const(self.as_raw_LogisticRegression(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Specifies the number of training samples taken in each step of Mini-Batch Gradient
/// Descent. Will only be used if using LogisticRegression::MINI_BATCH training algorithm. It
/// has to take values less than the total number of training samples.
/// ## See also
/// setMiniBatchSize
#[inline]
fn get_mini_batch_size(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_getMiniBatchSize_const(self.as_raw_LogisticRegression(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Termination criteria of the algorithm.
/// ## See also
/// setTermCriteria
#[inline]
fn get_term_criteria(&self) -> Result<core::TermCriteria> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_getTermCriteria_const(self.as_raw_LogisticRegression(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Predicts responses for input samples and returns a float type.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * samples: The input data for the prediction algorithm. Matrix [m x n], where each row
/// contains variables (features) of one object being classified. Should have data type CV_32F.
/// * results: Predicted labels as a column matrix of type CV_32S.
/// * flags: Not used.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * results: noArray()
/// * flags: 0
#[inline]
fn predict(&self, samples: &impl core::ToInputArray, results: &mut impl core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<f32> {
input_array_arg!(samples);
output_array_arg!(results);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_predict_const_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(self.as_raw_LogisticRegression(), samples.as_raw__InputArray(), results.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// This function returns the trained parameters arranged across rows.
///
/// For a two class classification problem, it returns a row matrix. It returns learnt parameters of
/// the Logistic Regression as a matrix of type CV_32F.
#[inline]
fn get_learnt_thetas(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_get_learnt_thetas_const(self.as_raw_LogisticRegression(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::ml::LogisticRegression]
pub trait LogisticRegressionTrait: crate::ml::LogisticRegressionTraitConst + crate::ml::StatModelTrait {
fn as_raw_mut_LogisticRegression(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Learning rate.
/// ## See also
/// setLearningRate getLearningRate
#[inline]
fn set_learning_rate(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_setLearningRate_double(self.as_raw_mut_LogisticRegression(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Number of iterations.
/// ## See also
/// setIterations getIterations
#[inline]
fn set_iterations(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_setIterations_int(self.as_raw_mut_LogisticRegression(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Kind of regularization to be applied. See LogisticRegression::RegKinds.
/// ## See also
/// setRegularization getRegularization
#[inline]
fn set_regularization(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_setRegularization_int(self.as_raw_mut_LogisticRegression(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Kind of training method used. See LogisticRegression::Methods.
/// ## See also
/// setTrainMethod getTrainMethod
#[inline]
fn set_train_method(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_setTrainMethod_int(self.as_raw_mut_LogisticRegression(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Specifies the number of training samples taken in each step of Mini-Batch Gradient
/// Descent. Will only be used if using LogisticRegression::MINI_BATCH training algorithm. It
/// has to take values less than the total number of training samples.
/// ## See also
/// setMiniBatchSize getMiniBatchSize
#[inline]
fn set_mini_batch_size(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_setMiniBatchSize_int(self.as_raw_mut_LogisticRegression(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Termination criteria of the algorithm.
/// ## See also
/// setTermCriteria getTermCriteria
#[inline]
fn set_term_criteria(&mut self, val: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_setTermCriteria_TermCriteria(self.as_raw_mut_LogisticRegression(), val.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Implements Logistic Regression classifier.
/// ## See also
/// [ml_intro_lr]
pub struct LogisticRegression {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { LogisticRegression }
impl Drop for LogisticRegression {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_LogisticRegression_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_LogisticRegression_delete(self.as_raw_mut_LogisticRegression()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for LogisticRegression {}
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for LogisticRegression {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for LogisticRegression {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::ml::StatModelTraitConst for LogisticRegression {
#[inline] fn as_raw_StatModel(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::StatModelTrait for LogisticRegression {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_StatModel(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::ml::LogisticRegressionTraitConst for LogisticRegression {
#[inline] fn as_raw_LogisticRegression(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::LogisticRegressionTrait for LogisticRegression {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_LogisticRegression(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl LogisticRegression {
/// Creates empty model.
///
/// Creates Logistic Regression model with parameters given.
#[inline]
pub fn create() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::ml::LogisticRegression>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_create(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ml::LogisticRegression>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Loads and creates a serialized LogisticRegression from a file
///
/// Use LogisticRegression::save to serialize and store an LogisticRegression to disk.
/// Load the LogisticRegression from this file again, by calling this function with the path to the file.
/// Optionally specify the node for the file containing the classifier
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * filepath: path to serialized LogisticRegression
/// * nodeName: name of node containing the classifier
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * node_name: String()
#[inline]
pub fn load(filepath: &str, node_name: &str) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::ml::LogisticRegression>> {
extern_container_arg!(filepath);
extern_container_arg!(node_name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_load_const_StringR_const_StringR(filepath.opencv_as_extern(), node_name.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ml::LogisticRegression>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { LogisticRegression, core::Algorithm, cv_LogisticRegression_to_Algorithm }
/// Constant methods for [crate::ml::NormalBayesClassifier]
pub trait NormalBayesClassifierTraitConst: crate::ml::StatModelTraitConst {
fn as_raw_NormalBayesClassifier(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Predicts the response for sample(s).
///
/// The method estimates the most probable classes for input vectors. Input vectors (one or more)
/// are stored as rows of the matrix inputs. In case of multiple input vectors, there should be one
/// output vector outputs. The predicted class for a single input vector is returned by the method.
/// The vector outputProbs contains the output probabilities corresponding to each element of
/// result.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: 0
#[inline]
fn predict_prob(&self, inputs: &impl core::ToInputArray, outputs: &mut impl core::ToOutputArray, output_probs: &mut impl core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<f32> {
input_array_arg!(inputs);
output_array_arg!(outputs);
output_array_arg!(output_probs);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_NormalBayesClassifier_predictProb_const_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(self.as_raw_NormalBayesClassifier(), inputs.as_raw__InputArray(), outputs.as_raw__OutputArray(), output_probs.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::ml::NormalBayesClassifier]
pub trait NormalBayesClassifierTrait: crate::ml::NormalBayesClassifierTraitConst + crate::ml::StatModelTrait {
fn as_raw_mut_NormalBayesClassifier(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
/// Bayes classifier for normally distributed data.
/// ## See also
/// [ml_intro_bayes]
pub struct NormalBayesClassifier {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { NormalBayesClassifier }
impl Drop for NormalBayesClassifier {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_NormalBayesClassifier_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_NormalBayesClassifier_delete(self.as_raw_mut_NormalBayesClassifier()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for NormalBayesClassifier {}
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for NormalBayesClassifier {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for NormalBayesClassifier {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::ml::StatModelTraitConst for NormalBayesClassifier {
#[inline] fn as_raw_StatModel(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::StatModelTrait for NormalBayesClassifier {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_StatModel(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::ml::NormalBayesClassifierTraitConst for NormalBayesClassifier {
#[inline] fn as_raw_NormalBayesClassifier(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::NormalBayesClassifierTrait for NormalBayesClassifier {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_NormalBayesClassifier(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl NormalBayesClassifier {
/// Creates empty model
/// Use StatModel::train to train the model after creation.
#[inline]
pub fn create() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::ml::NormalBayesClassifier>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_NormalBayesClassifier_create(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ml::NormalBayesClassifier>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Loads and creates a serialized NormalBayesClassifier from a file
///
/// Use NormalBayesClassifier::save to serialize and store an NormalBayesClassifier to disk.
/// Load the NormalBayesClassifier from this file again, by calling this function with the path to the file.
/// Optionally specify the node for the file containing the classifier
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * filepath: path to serialized NormalBayesClassifier
/// * nodeName: name of node containing the classifier
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * node_name: String()
#[inline]
pub fn load(filepath: &str, node_name: &str) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::ml::NormalBayesClassifier>> {
extern_container_arg!(filepath);
extern_container_arg!(node_name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_NormalBayesClassifier_load_const_StringR_const_StringR(filepath.opencv_as_extern(), node_name.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ml::NormalBayesClassifier>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { NormalBayesClassifier, core::Algorithm, cv_NormalBayesClassifier_to_Algorithm }
/// Constant methods for [crate::ml::ParamGrid]
pub trait ParamGridTraitConst {
fn as_raw_ParamGrid(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Minimum value of the statmodel parameter. Default value is 0.
#[inline]
fn min_val(&self) -> f64 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ParamGrid_getPropMinVal_const(self.as_raw_ParamGrid()) };
ret
}
/// Maximum value of the statmodel parameter. Default value is 0.
#[inline]
fn max_val(&self) -> f64 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ParamGrid_getPropMaxVal_const(self.as_raw_ParamGrid()) };
ret
}
/// Logarithmic step for iterating the statmodel parameter.
///
/// The grid determines the following iteration sequence of the statmodel parameter values:
/// 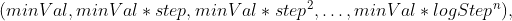
/// where  is the maximal index satisfying
/// 
/// The grid is logarithmic, so logStep must always be greater than 1. Default value is 1.
#[inline]
fn log_step(&self) -> f64 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ParamGrid_getPropLogStep_const(self.as_raw_ParamGrid()) };
ret
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::ml::ParamGrid]
pub trait ParamGridTrait: crate::ml::ParamGridTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_ParamGrid(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Minimum value of the statmodel parameter. Default value is 0.
#[inline]
fn set_min_val(&mut self, val: f64) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ParamGrid_setPropMinVal_double(self.as_raw_mut_ParamGrid(), val) };
ret
}
/// Maximum value of the statmodel parameter. Default value is 0.
#[inline]
fn set_max_val(&mut self, val: f64) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ParamGrid_setPropMaxVal_double(self.as_raw_mut_ParamGrid(), val) };
ret
}
/// Logarithmic step for iterating the statmodel parameter.
///
/// The grid determines the following iteration sequence of the statmodel parameter values:
/// 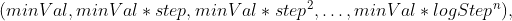
/// where  is the maximal index satisfying
/// 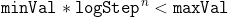
/// The grid is logarithmic, so logStep must always be greater than 1. Default value is 1.
#[inline]
fn set_log_step(&mut self, val: f64) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ParamGrid_setPropLogStep_double(self.as_raw_mut_ParamGrid(), val) };
ret
}
}
/// The structure represents the logarithmic grid range of statmodel parameters.
///
/// It is used for optimizing statmodel accuracy by varying model parameters, the accuracy estimate
/// being computed by cross-validation.
pub struct ParamGrid {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { ParamGrid }
impl Drop for ParamGrid {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_ParamGrid_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_ParamGrid_delete(self.as_raw_mut_ParamGrid()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for ParamGrid {}
impl crate::ml::ParamGridTraitConst for ParamGrid {
#[inline] fn as_raw_ParamGrid(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::ParamGridTrait for ParamGrid {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_ParamGrid(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl ParamGrid {
/// Default constructor
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<crate::ml::ParamGrid> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ParamGrid_ParamGrid(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { crate::ml::ParamGrid::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Constructor with parameters
#[inline]
pub fn for_range(_min_val: f64, _max_val: f64, _log_step: f64) -> Result<crate::ml::ParamGrid> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ParamGrid_ParamGrid_double_double_double(_min_val, _max_val, _log_step, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { crate::ml::ParamGrid::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates a ParamGrid Ptr that can be given to the %SVM::trainAuto method
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * minVal: minimum value of the parameter grid
/// * maxVal: maximum value of the parameter grid
/// * logstep: Logarithmic step for iterating the statmodel parameter
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * min_val: 0.
/// * max_val: 0.
/// * logstep: 1.
#[inline]
pub fn create(min_val: f64, max_val: f64, logstep: f64) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::ml::ParamGrid>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ParamGrid_create_double_double_double(min_val, max_val, logstep, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ml::ParamGrid>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ml::RTrees]
pub trait RTreesTraitConst: crate::ml::DTreesTraitConst {
fn as_raw_RTrees(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// If true then variable importance will be calculated and then it can be retrieved by RTrees::getVarImportance.
/// Default value is false.
/// ## See also
/// setCalculateVarImportance
#[inline]
fn get_calculate_var_importance(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_RTrees_getCalculateVarImportance_const(self.as_raw_RTrees(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// The size of the randomly selected subset of features at each tree node and that are used
/// to find the best split(s).
/// If you set it to 0 then the size will be set to the square root of the total number of
/// features. Default value is 0.
/// ## See also
/// setActiveVarCount
#[inline]
fn get_active_var_count(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_RTrees_getActiveVarCount_const(self.as_raw_RTrees(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// The termination criteria that specifies when the training algorithm stops.
/// Either when the specified number of trees is trained and added to the ensemble or when
/// sufficient accuracy (measured as OOB error) is achieved. Typically the more trees you have the
/// better the accuracy. However, the improvement in accuracy generally diminishes and asymptotes
/// pass a certain number of trees. Also to keep in mind, the number of tree increases the
/// prediction time linearly. Default value is TermCriteria(TermCriteria::MAX_ITERS +
/// TermCriteria::EPS, 50, 0.1)
/// ## See also
/// setTermCriteria
#[inline]
fn get_term_criteria(&self) -> Result<core::TermCriteria> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_RTrees_getTermCriteria_const(self.as_raw_RTrees(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the variable importance array.
/// The method returns the variable importance vector, computed at the training stage when
/// CalculateVarImportance is set to true. If this flag was set to false, the empty matrix is
/// returned.
#[inline]
fn get_var_importance(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_RTrees_getVarImportance_const(self.as_raw_RTrees(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the result of each individual tree in the forest.
/// In case the model is a regression problem, the method will return each of the trees'
/// results for each of the sample cases. If the model is a classifier, it will return
/// a Mat with samples + 1 rows, where the first row gives the class number and the
/// following rows return the votes each class had for each sample.
/// ## Parameters
/// * samples: Array containing the samples for which votes will be calculated.
/// * results: Array where the result of the calculation will be written.
/// * flags: Flags for defining the type of RTrees.
#[inline]
fn get_votes(&self, samples: &impl core::ToInputArray, results: &mut impl core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(samples);
output_array_arg!(results);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_RTrees_getVotes_const_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(self.as_raw_RTrees(), samples.as_raw__InputArray(), results.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_oob_error(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_RTrees_getOOBError_const(self.as_raw_RTrees(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::ml::RTrees]
pub trait RTreesTrait: crate::ml::DTreesTrait + crate::ml::RTreesTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_RTrees(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// If true then variable importance will be calculated and then it can be retrieved by RTrees::getVarImportance.
/// Default value is false.
/// ## See also
/// setCalculateVarImportance getCalculateVarImportance
#[inline]
fn set_calculate_var_importance(&mut self, val: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_RTrees_setCalculateVarImportance_bool(self.as_raw_mut_RTrees(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// The size of the randomly selected subset of features at each tree node and that are used
/// to find the best split(s).
/// If you set it to 0 then the size will be set to the square root of the total number of
/// features. Default value is 0.
/// ## See also
/// setActiveVarCount getActiveVarCount
#[inline]
fn set_active_var_count(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_RTrees_setActiveVarCount_int(self.as_raw_mut_RTrees(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// The termination criteria that specifies when the training algorithm stops.
/// Either when the specified number of trees is trained and added to the ensemble or when
/// sufficient accuracy (measured as OOB error) is achieved. Typically the more trees you have the
/// better the accuracy. However, the improvement in accuracy generally diminishes and asymptotes
/// pass a certain number of trees. Also to keep in mind, the number of tree increases the
/// prediction time linearly. Default value is TermCriteria(TermCriteria::MAX_ITERS +
/// TermCriteria::EPS, 50, 0.1)
/// ## See also
/// setTermCriteria getTermCriteria
#[inline]
fn set_term_criteria(&mut self, val: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_RTrees_setTermCriteria_const_TermCriteriaR(self.as_raw_mut_RTrees(), &val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// The class implements the random forest predictor.
/// ## See also
/// [ml_intro_rtrees]
pub struct RTrees {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { RTrees }
impl Drop for RTrees {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_RTrees_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_RTrees_delete(self.as_raw_mut_RTrees()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for RTrees {}
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for RTrees {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for RTrees {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::ml::DTreesTraitConst for RTrees {
#[inline] fn as_raw_DTrees(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::DTreesTrait for RTrees {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_DTrees(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::ml::StatModelTraitConst for RTrees {
#[inline] fn as_raw_StatModel(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::StatModelTrait for RTrees {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_StatModel(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::ml::RTreesTraitConst for RTrees {
#[inline] fn as_raw_RTrees(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::RTreesTrait for RTrees {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_RTrees(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl RTrees {
/// Creates the empty model.
/// Use StatModel::train to train the model, StatModel::train to create and train the model,
/// Algorithm::load to load the pre-trained model.
#[inline]
pub fn create() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::ml::RTrees>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_RTrees_create(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ml::RTrees>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Loads and creates a serialized RTree from a file
///
/// Use RTree::save to serialize and store an RTree to disk.
/// Load the RTree from this file again, by calling this function with the path to the file.
/// Optionally specify the node for the file containing the classifier
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * filepath: path to serialized RTree
/// * nodeName: name of node containing the classifier
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * node_name: String()
#[inline]
pub fn load(filepath: &str, node_name: &str) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::ml::RTrees>> {
extern_container_arg!(filepath);
extern_container_arg!(node_name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_RTrees_load_const_StringR_const_StringR(filepath.opencv_as_extern(), node_name.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ml::RTrees>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { RTrees, core::Algorithm, cv_RTrees_to_Algorithm }
/// Constant methods for [crate::ml::SVM]
pub trait SVMTraitConst: crate::ml::StatModelTraitConst {
fn as_raw_SVM(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Type of a %SVM formulation.
/// See SVM::Types. Default value is SVM::C_SVC.
/// ## See also
/// setType
#[inline]
fn get_type(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getType_const(self.as_raw_SVM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter  of a kernel function.
/// For SVM::POLY, SVM::RBF, SVM::SIGMOID or SVM::CHI2. Default value is 1.
/// ## See also
/// setGamma
#[inline]
fn get_gamma(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getGamma_const(self.as_raw_SVM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter _coef0_ of a kernel function.
/// For SVM::POLY or SVM::SIGMOID. Default value is 0.
/// ## See also
/// setCoef0
#[inline]
fn get_coef0(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getCoef0_const(self.as_raw_SVM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter _degree_ of a kernel function.
/// For SVM::POLY. Default value is 0.
/// ## See also
/// setDegree
#[inline]
fn get_degree(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getDegree_const(self.as_raw_SVM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter _C_ of a %SVM optimization problem.
/// For SVM::C_SVC, SVM::EPS_SVR or SVM::NU_SVR. Default value is 0.
/// ## See also
/// setC
#[inline]
fn get_c(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getC_const(self.as_raw_SVM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter 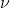 of a %SVM optimization problem.
/// For SVM::NU_SVC, SVM::ONE_CLASS or SVM::NU_SVR. Default value is 0.
/// ## See also
/// setNu
#[inline]
fn get_nu(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getNu_const(self.as_raw_SVM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter  of a %SVM optimization problem.
/// For SVM::EPS_SVR. Default value is 0.
/// ## See also
/// setP
#[inline]
fn get_p(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getP_const(self.as_raw_SVM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Optional weights in the SVM::C_SVC problem, assigned to particular classes.
/// They are multiplied by _C_ so the parameter _C_ of class _i_ becomes `classWeights(i) * C`. Thus
/// these weights affect the misclassification penalty for different classes. The larger weight,
/// the larger penalty on misclassification of data from the corresponding class. Default value is
/// empty Mat.
/// ## See also
/// setClassWeights
#[inline]
fn get_class_weights(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getClassWeights_const(self.as_raw_SVM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Termination criteria of the iterative %SVM training procedure which solves a partial
/// case of constrained quadratic optimization problem.
/// You can specify tolerance and/or the maximum number of iterations. Default value is
/// `TermCriteria( TermCriteria::MAX_ITER + TermCriteria::EPS, 1000, FLT_EPSILON )`;
/// ## See also
/// setTermCriteria
#[inline]
fn get_term_criteria(&self) -> Result<core::TermCriteria> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getTermCriteria_const(self.as_raw_SVM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Type of a %SVM kernel.
/// See SVM::KernelTypes. Default value is SVM::RBF.
#[inline]
fn get_kernel_type(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getKernelType_const(self.as_raw_SVM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Retrieves all the support vectors
///
/// The method returns all the support vectors as a floating-point matrix, where support vectors are
/// stored as matrix rows.
#[inline]
fn get_support_vectors(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getSupportVectors_const(self.as_raw_SVM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Retrieves all the uncompressed support vectors of a linear %SVM
///
/// The method returns all the uncompressed support vectors of a linear %SVM that the compressed
/// support vector, used for prediction, was derived from. They are returned in a floating-point
/// matrix, where the support vectors are stored as matrix rows.
#[inline]
fn get_uncompressed_support_vectors(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getUncompressedSupportVectors_const(self.as_raw_SVM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Retrieves the decision function
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * i: the index of the decision function. If the problem solved is regression, 1-class or
/// 2-class classification, then there will be just one decision function and the index should
/// always be 0. Otherwise, in the case of N-class classification, there will be 
/// decision functions.
/// * alpha: the optional output vector for weights, corresponding to different support vectors.
/// In the case of linear %SVM all the alpha's will be 1's.
/// * svidx: the optional output vector of indices of support vectors within the matrix of
/// support vectors (which can be retrieved by SVM::getSupportVectors). In the case of linear
/// %SVM each decision function consists of a single "compressed" support vector.
///
/// The method returns rho parameter of the decision function, a scalar subtracted from the weighted
/// sum of kernel responses.
#[inline]
fn get_decision_function(&self, i: i32, alpha: &mut impl core::ToOutputArray, svidx: &mut impl core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<f64> {
output_array_arg!(alpha);
output_array_arg!(svidx);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getDecisionFunction_const_int_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_SVM(), i, alpha.as_raw__OutputArray(), svidx.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::ml::SVM]
pub trait SVMTrait: crate::ml::SVMTraitConst + crate::ml::StatModelTrait {
fn as_raw_mut_SVM(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Type of a %SVM formulation.
/// See SVM::Types. Default value is SVM::C_SVC.
/// ## See also
/// setType getType
#[inline]
fn set_type(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_setType_int(self.as_raw_mut_SVM(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter  of a kernel function.
/// For SVM::POLY, SVM::RBF, SVM::SIGMOID or SVM::CHI2. Default value is 1.
/// ## See also
/// setGamma getGamma
#[inline]
fn set_gamma(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_setGamma_double(self.as_raw_mut_SVM(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter _coef0_ of a kernel function.
/// For SVM::POLY or SVM::SIGMOID. Default value is 0.
/// ## See also
/// setCoef0 getCoef0
#[inline]
fn set_coef0(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_setCoef0_double(self.as_raw_mut_SVM(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter _degree_ of a kernel function.
/// For SVM::POLY. Default value is 0.
/// ## See also
/// setDegree getDegree
#[inline]
fn set_degree(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_setDegree_double(self.as_raw_mut_SVM(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter _C_ of a %SVM optimization problem.
/// For SVM::C_SVC, SVM::EPS_SVR or SVM::NU_SVR. Default value is 0.
/// ## See also
/// setC getC
#[inline]
fn set_c(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_setC_double(self.as_raw_mut_SVM(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter  of a %SVM optimization problem.
/// For SVM::NU_SVC, SVM::ONE_CLASS or SVM::NU_SVR. Default value is 0.
/// ## See also
/// setNu getNu
#[inline]
fn set_nu(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_setNu_double(self.as_raw_mut_SVM(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter  of a %SVM optimization problem.
/// For SVM::EPS_SVR. Default value is 0.
/// ## See also
/// setP getP
#[inline]
fn set_p(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_setP_double(self.as_raw_mut_SVM(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Optional weights in the SVM::C_SVC problem, assigned to particular classes.
/// They are multiplied by _C_ so the parameter _C_ of class _i_ becomes `classWeights(i) * C`. Thus
/// these weights affect the misclassification penalty for different classes. The larger weight,
/// the larger penalty on misclassification of data from the corresponding class. Default value is
/// empty Mat.
/// ## See also
/// setClassWeights getClassWeights
#[inline]
fn set_class_weights(&mut self, val: &core::Mat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_setClassWeights_const_MatR(self.as_raw_mut_SVM(), val.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Termination criteria of the iterative %SVM training procedure which solves a partial
/// case of constrained quadratic optimization problem.
/// You can specify tolerance and/or the maximum number of iterations. Default value is
/// `TermCriteria( TermCriteria::MAX_ITER + TermCriteria::EPS, 1000, FLT_EPSILON )`;
/// ## See also
/// setTermCriteria getTermCriteria
#[inline]
fn set_term_criteria(&mut self, val: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_setTermCriteria_const_TermCriteriaR(self.as_raw_mut_SVM(), &val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Initialize with one of predefined kernels.
/// See SVM::KernelTypes.
#[inline]
fn set_kernel(&mut self, kernel_type: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_setKernel_int(self.as_raw_mut_SVM(), kernel_type, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Initialize with custom kernel.
/// See SVM::Kernel class for implementation details
#[inline]
fn set_custom_kernel(&mut self, _kernel: &core::Ptr<crate::ml::SVM_Kernel>) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_setCustomKernel_const_PtrLKernelGR(self.as_raw_mut_SVM(), _kernel.as_raw_PtrOfSVM_Kernel(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Trains an %SVM with optimal parameters.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * data: the training data that can be constructed using TrainData::create or
/// TrainData::loadFromCSV.
/// * kFold: Cross-validation parameter. The training set is divided into kFold subsets. One
/// subset is used to test the model, the others form the train set. So, the %SVM algorithm is
/// executed kFold times.
/// * Cgrid: grid for C
/// * gammaGrid: grid for gamma
/// * pGrid: grid for p
/// * nuGrid: grid for nu
/// * coeffGrid: grid for coeff
/// * degreeGrid: grid for degree
/// * balanced: If true and the problem is 2-class classification then the method creates more
/// balanced cross-validation subsets that is proportions between classes in subsets are close
/// to such proportion in the whole train dataset.
///
/// The method trains the %SVM model automatically by choosing the optimal parameters C, gamma, p,
/// nu, coef0, degree. Parameters are considered optimal when the cross-validation
/// estimate of the test set error is minimal.
///
/// If there is no need to optimize a parameter, the corresponding grid step should be set to any
/// value less than or equal to 1. For example, to avoid optimization in gamma, set `gammaGrid.step
/// = 0`, `gammaGrid.minVal`, `gamma_grid.maxVal` as arbitrary numbers. In this case, the value
/// `Gamma` is taken for gamma.
///
/// And, finally, if the optimization in a parameter is required but the corresponding grid is
/// unknown, you may call the function SVM::getDefaultGrid. To generate a grid, for example, for
/// gamma, call `SVM::getDefaultGrid(SVM::GAMMA)`.
///
/// This function works for the classification (SVM::C_SVC or SVM::NU_SVC) as well as for the
/// regression (SVM::EPS_SVR or SVM::NU_SVR). If it is SVM::ONE_CLASS, no optimization is made and
/// the usual %SVM with parameters specified in params is executed.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * k_fold: 10
/// * cgrid: getDefaultGrid(C)
/// * gamma_grid: getDefaultGrid(GAMMA)
/// * p_grid: getDefaultGrid(P)
/// * nu_grid: getDefaultGrid(NU)
/// * coeff_grid: getDefaultGrid(COEF)
/// * degree_grid: getDefaultGrid(DEGREE)
/// * balanced: false
#[inline]
fn train_auto(&mut self, data: &core::Ptr<crate::ml::TrainData>, k_fold: i32, mut cgrid: crate::ml::ParamGrid, mut gamma_grid: crate::ml::ParamGrid, mut p_grid: crate::ml::ParamGrid, mut nu_grid: crate::ml::ParamGrid, mut coeff_grid: crate::ml::ParamGrid, mut degree_grid: crate::ml::ParamGrid, balanced: bool) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_trainAuto_const_PtrLTrainDataGR_int_ParamGrid_ParamGrid_ParamGrid_ParamGrid_ParamGrid_ParamGrid_bool(self.as_raw_mut_SVM(), data.as_raw_PtrOfTrainData(), k_fold, cgrid.as_raw_mut_ParamGrid(), gamma_grid.as_raw_mut_ParamGrid(), p_grid.as_raw_mut_ParamGrid(), nu_grid.as_raw_mut_ParamGrid(), coeff_grid.as_raw_mut_ParamGrid(), degree_grid.as_raw_mut_ParamGrid(), balanced, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Trains an %SVM with optimal parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * samples: training samples
/// * layout: See ml::SampleTypes.
/// * responses: vector of responses associated with the training samples.
/// * kFold: Cross-validation parameter. The training set is divided into kFold subsets. One
/// subset is used to test the model, the others form the train set. So, the %SVM algorithm is
/// * Cgrid: grid for C
/// * gammaGrid: grid for gamma
/// * pGrid: grid for p
/// * nuGrid: grid for nu
/// * coeffGrid: grid for coeff
/// * degreeGrid: grid for degree
/// * balanced: If true and the problem is 2-class classification then the method creates more
/// balanced cross-validation subsets that is proportions between classes in subsets are close
/// to such proportion in the whole train dataset.
///
/// The method trains the %SVM model automatically by choosing the optimal parameters C, gamma, p,
/// nu, coef0, degree. Parameters are considered optimal when the cross-validation
/// estimate of the test set error is minimal.
///
/// This function only makes use of SVM::getDefaultGrid for parameter optimization and thus only
/// offers rudimentary parameter options.
///
/// This function works for the classification (SVM::C_SVC or SVM::NU_SVC) as well as for the
/// regression (SVM::EPS_SVR or SVM::NU_SVR). If it is SVM::ONE_CLASS, no optimization is made and
/// the usual %SVM with parameters specified in params is executed.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * k_fold: 10
/// * cgrid: SVM::getDefaultGridPtr(SVM::C)
/// * gamma_grid: SVM::getDefaultGridPtr(SVM::GAMMA)
/// * p_grid: SVM::getDefaultGridPtr(SVM::P)
/// * nu_grid: SVM::getDefaultGridPtr(SVM::NU)
/// * coeff_grid: SVM::getDefaultGridPtr(SVM::COEF)
/// * degree_grid: SVM::getDefaultGridPtr(SVM::DEGREE)
/// * balanced: false
#[inline]
fn train_auto_with_data(&mut self, samples: &impl core::ToInputArray, layout: i32, responses: &impl core::ToInputArray, k_fold: i32, mut cgrid: core::Ptr<crate::ml::ParamGrid>, mut gamma_grid: core::Ptr<crate::ml::ParamGrid>, mut p_grid: core::Ptr<crate::ml::ParamGrid>, mut nu_grid: core::Ptr<crate::ml::ParamGrid>, mut coeff_grid: core::Ptr<crate::ml::ParamGrid>, mut degree_grid: core::Ptr<crate::ml::ParamGrid>, balanced: bool) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(samples);
input_array_arg!(responses);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_trainAuto_const__InputArrayR_int_const__InputArrayR_int_PtrLParamGridG_PtrLParamGridG_PtrLParamGridG_PtrLParamGridG_PtrLParamGridG_PtrLParamGridG_bool(self.as_raw_mut_SVM(), samples.as_raw__InputArray(), layout, responses.as_raw__InputArray(), k_fold, cgrid.as_raw_mut_PtrOfParamGrid(), gamma_grid.as_raw_mut_PtrOfParamGrid(), p_grid.as_raw_mut_PtrOfParamGrid(), nu_grid.as_raw_mut_PtrOfParamGrid(), coeff_grid.as_raw_mut_PtrOfParamGrid(), degree_grid.as_raw_mut_PtrOfParamGrid(), balanced, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Support Vector Machines.
/// ## See also
/// [ml_intro_svm]
pub struct SVM {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { SVM }
impl Drop for SVM {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_SVM_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_SVM_delete(self.as_raw_mut_SVM()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for SVM {}
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for SVM {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for SVM {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::ml::StatModelTraitConst for SVM {
#[inline] fn as_raw_StatModel(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::StatModelTrait for SVM {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_StatModel(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::ml::SVMTraitConst for SVM {
#[inline] fn as_raw_SVM(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::SVMTrait for SVM {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_SVM(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl SVM {
/// Generates a grid for %SVM parameters.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * param_id: %SVM parameters IDs that must be one of the SVM::ParamTypes. The grid is
/// generated for the parameter with this ID.
///
/// The function generates a grid for the specified parameter of the %SVM algorithm. The grid may be
/// passed to the function SVM::trainAuto.
#[inline]
pub fn get_default_grid(param_id: i32) -> Result<crate::ml::ParamGrid> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getDefaultGrid_int(param_id, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { crate::ml::ParamGrid::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Generates a grid for %SVM parameters.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * param_id: %SVM parameters IDs that must be one of the SVM::ParamTypes. The grid is
/// generated for the parameter with this ID.
///
/// The function generates a grid pointer for the specified parameter of the %SVM algorithm.
/// The grid may be passed to the function SVM::trainAuto.
#[inline]
pub fn get_default_grid_ptr(param_id: i32) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::ml::ParamGrid>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getDefaultGridPtr_int(param_id, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ml::ParamGrid>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates empty model.
/// Use StatModel::train to train the model. Since %SVM has several parameters, you may want to
/// find the best parameters for your problem, it can be done with SVM::trainAuto.
#[inline]
pub fn create() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::ml::SVM>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_create(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ml::SVM>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Loads and creates a serialized svm from a file
///
/// Use SVM::save to serialize and store an SVM to disk.
/// Load the SVM from this file again, by calling this function with the path to the file.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * filepath: path to serialized svm
#[inline]
pub fn load(filepath: &str) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::ml::SVM>> {
extern_container_arg!(filepath);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_load_const_StringR(filepath.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ml::SVM>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { SVM, core::Algorithm, cv_SVM_to_Algorithm }
/// Constant methods for [crate::ml::SVM_Kernel]
pub trait SVM_KernelTraitConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_SVM_Kernel(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn get_type(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_Kernel_getType_const(self.as_raw_SVM_Kernel(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::ml::SVM_Kernel]
pub trait SVM_KernelTrait: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::ml::SVM_KernelTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_SVM_Kernel(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn calc(&mut self, vcount: i32, n: i32, vecs: &f32, another: &f32, results: &mut f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_Kernel_calc_int_int_const_floatX_const_floatX_floatX(self.as_raw_mut_SVM_Kernel(), vcount, n, vecs, another, results, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
pub struct SVM_Kernel {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { SVM_Kernel }
impl Drop for SVM_Kernel {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_SVM_Kernel_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_SVM_Kernel_delete(self.as_raw_mut_SVM_Kernel()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for SVM_Kernel {}
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for SVM_Kernel {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for SVM_Kernel {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::ml::SVM_KernelTraitConst for SVM_Kernel {
#[inline] fn as_raw_SVM_Kernel(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::SVM_KernelTrait for SVM_Kernel {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_SVM_Kernel(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl SVM_Kernel {
}
boxed_cast_base! { SVM_Kernel, core::Algorithm, cv_SVM_Kernel_to_Algorithm }
/// Constant methods for [crate::ml::SVMSGD]
pub trait SVMSGDTraitConst: crate::ml::StatModelTraitConst {
fn as_raw_SVMSGD(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// %Algorithm type, one of SVMSGD::SvmsgdType.
/// ## See also
/// setSvmsgdType
#[inline]
fn get_svmsgd_type(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_getSvmsgdType_const(self.as_raw_SVMSGD(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// %Margin type, one of SVMSGD::MarginType.
/// ## See also
/// setMarginType
#[inline]
fn get_margin_type(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_getMarginType_const(self.as_raw_SVMSGD(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter marginRegularization of a %SVMSGD optimization problem.
/// ## See also
/// setMarginRegularization
#[inline]
fn get_margin_regularization(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_getMarginRegularization_const(self.as_raw_SVMSGD(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter initialStepSize of a %SVMSGD optimization problem.
/// ## See also
/// setInitialStepSize
#[inline]
fn get_initial_step_size(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_getInitialStepSize_const(self.as_raw_SVMSGD(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter stepDecreasingPower of a %SVMSGD optimization problem.
/// ## See also
/// setStepDecreasingPower
#[inline]
fn get_step_decreasing_power(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_getStepDecreasingPower_const(self.as_raw_SVMSGD(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Termination criteria of the training algorithm.
/// You can specify the maximum number of iterations (maxCount) and/or how much the error could
/// change between the iterations to make the algorithm continue (epsilon).
/// ## See also
/// setTermCriteria
#[inline]
fn get_term_criteria(&self) -> Result<core::TermCriteria> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_getTermCriteria_const(self.as_raw_SVMSGD(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::ml::SVMSGD]
pub trait SVMSGDTrait: crate::ml::SVMSGDTraitConst + crate::ml::StatModelTrait {
fn as_raw_mut_SVMSGD(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// ## Returns
/// the weights of the trained model (decision function f(x) = weights * x + shift).
#[inline]
fn get_weights(&mut self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_getWeights(self.as_raw_mut_SVMSGD(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## Returns
/// the shift of the trained model (decision function f(x) = weights * x + shift).
#[inline]
fn get_shift(&mut self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_getShift(self.as_raw_mut_SVMSGD(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Function sets optimal parameters values for chosen SVM SGD model.
/// ## Parameters
/// * svmsgdType: is the type of SVMSGD classifier.
/// * marginType: is the type of margin constraint.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * svmsgd_type: SVMSGD::ASGD
/// * margin_type: SVMSGD::SOFT_MARGIN
#[inline]
fn set_optimal_parameters(&mut self, svmsgd_type: i32, margin_type: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_setOptimalParameters_int_int(self.as_raw_mut_SVMSGD(), svmsgd_type, margin_type, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// %Algorithm type, one of SVMSGD::SvmsgdType.
/// ## See also
/// setSvmsgdType getSvmsgdType
#[inline]
fn set_svmsgd_type(&mut self, svmsgd_type: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_setSvmsgdType_int(self.as_raw_mut_SVMSGD(), svmsgd_type, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// %Margin type, one of SVMSGD::MarginType.
/// ## See also
/// setMarginType getMarginType
#[inline]
fn set_margin_type(&mut self, margin_type: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_setMarginType_int(self.as_raw_mut_SVMSGD(), margin_type, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter marginRegularization of a %SVMSGD optimization problem.
/// ## See also
/// setMarginRegularization getMarginRegularization
#[inline]
fn set_margin_regularization(&mut self, margin_regularization: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_setMarginRegularization_float(self.as_raw_mut_SVMSGD(), margin_regularization, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter initialStepSize of a %SVMSGD optimization problem.
/// ## See also
/// setInitialStepSize getInitialStepSize
#[inline]
fn set_initial_step_size(&mut self, initial_step_size: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_setInitialStepSize_float(self.as_raw_mut_SVMSGD(), initial_step_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter stepDecreasingPower of a %SVMSGD optimization problem.
/// ## See also
/// setStepDecreasingPower getStepDecreasingPower
#[inline]
fn set_step_decreasing_power(&mut self, step_decreasing_power: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_setStepDecreasingPower_float(self.as_raw_mut_SVMSGD(), step_decreasing_power, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Termination criteria of the training algorithm.
/// You can specify the maximum number of iterations (maxCount) and/or how much the error could
/// change between the iterations to make the algorithm continue (epsilon).
/// ## See also
/// setTermCriteria getTermCriteria
#[inline]
fn set_term_criteria(&mut self, val: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_setTermCriteria_const_TermCriteriaR(self.as_raw_mut_SVMSGD(), &val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// !
/// Stochastic Gradient Descent SVM classifier
///
/// SVMSGD provides a fast and easy-to-use implementation of the SVM classifier using the Stochastic Gradient Descent approach,
/// as presented in [bottou2010large](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_bottou2010large).
///
/// The classifier has following parameters:
/// - model type,
/// - margin type,
/// - margin regularization (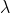),
/// - initial step size (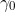),
/// - step decreasing power (),
/// - and termination criteria.
///
/// The model type may have one of the following values: \ref SGD and \ref ASGD.
///
/// - \ref SGD is the classic version of SVMSGD classifier: every next step is calculated by the formula
/// 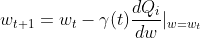
/// where
/// - 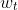 is the weights vector for decision function at step ,
/// -  is the step size of model parameters at the iteration , it is decreased on each step by the formula
/// 
/// -  is the target functional from SVM task for sample with number , this sample is chosen stochastically on each step of the algorithm.
///
/// - \ref ASGD is Average Stochastic Gradient Descent SVM Classifier. ASGD classifier averages weights vector on each step of algorithm by the formula
/// 
///
/// The recommended model type is ASGD (following [bottou2010large](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_bottou2010large)).
///
/// The margin type may have one of the following values: \ref SOFT_MARGIN or \ref HARD_MARGIN.
///
/// - You should use \ref HARD_MARGIN type, if you have linearly separable sets.
/// - You should use \ref SOFT_MARGIN type, if you have non-linearly separable sets or sets with outliers.
/// - In the general case (if you know nothing about linear separability of your sets), use SOFT_MARGIN.
///
/// The other parameters may be described as follows:
/// - Margin regularization parameter is responsible for weights decreasing at each step and for the strength of restrictions on outliers
/// (the less the parameter, the less probability that an outlier will be ignored).
/// Recommended value for SGD model is 0.0001, for ASGD model is 0.00001.
///
/// - Initial step size parameter is the initial value for the step size .
/// You will have to find the best initial step for your problem.
///
/// - Step decreasing power is the power parameter for 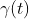 decreasing by the formula, mentioned above.
/// Recommended value for SGD model is 1, for ASGD model is 0.75.
///
/// - Termination criteria can be TermCriteria::COUNT, TermCriteria::EPS or TermCriteria::COUNT + TermCriteria::EPS.
/// You will have to find the best termination criteria for your problem.
///
/// Note that the parameters margin regularization, initial step size, and step decreasing power should be positive.
///
/// To use SVMSGD algorithm do as follows:
///
/// - first, create the SVMSGD object. The algorithm will set optimal parameters by default, but you can set your own parameters via functions setSvmsgdType(),
/// setMarginType(), setMarginRegularization(), setInitialStepSize(), and setStepDecreasingPower().
///
/// - then the SVM model can be trained using the train features and the correspondent labels by the method train().
///
/// - after that, the label of a new feature vector can be predicted using the method predict().
///
/// ```C++
/// // Create empty object
/// cv::Ptr<SVMSGD> svmsgd = SVMSGD::create();
///
/// // Train the Stochastic Gradient Descent SVM
/// svmsgd->train(trainData);
///
/// // Predict labels for the new samples
/// svmsgd->predict(samples, responses);
/// ```
///
pub struct SVMSGD {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { SVMSGD }
impl Drop for SVMSGD {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_SVMSGD_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_SVMSGD_delete(self.as_raw_mut_SVMSGD()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for SVMSGD {}
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for SVMSGD {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for SVMSGD {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::ml::StatModelTraitConst for SVMSGD {
#[inline] fn as_raw_StatModel(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::StatModelTrait for SVMSGD {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_StatModel(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::ml::SVMSGDTraitConst for SVMSGD {
#[inline] fn as_raw_SVMSGD(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::SVMSGDTrait for SVMSGD {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_SVMSGD(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl SVMSGD {
/// Creates empty model.
/// Use StatModel::train to train the model. Since %SVMSGD has several parameters, you may want to
/// find the best parameters for your problem or use setOptimalParameters() to set some default parameters.
#[inline]
pub fn create() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::ml::SVMSGD>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_create(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ml::SVMSGD>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Loads and creates a serialized SVMSGD from a file
///
/// Use SVMSGD::save to serialize and store an SVMSGD to disk.
/// Load the SVMSGD from this file again, by calling this function with the path to the file.
/// Optionally specify the node for the file containing the classifier
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * filepath: path to serialized SVMSGD
/// * nodeName: name of node containing the classifier
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * node_name: String()
#[inline]
pub fn load(filepath: &str, node_name: &str) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::ml::SVMSGD>> {
extern_container_arg!(filepath);
extern_container_arg!(node_name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_load_const_StringR_const_StringR(filepath.opencv_as_extern(), node_name.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ml::SVMSGD>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { SVMSGD, core::Algorithm, cv_SVMSGD_to_Algorithm }
/// Constant methods for [crate::ml::StatModel]
pub trait StatModelTraitConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_StatModel(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Returns the number of variables in training samples
#[inline]
fn get_var_count(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_StatModel_getVarCount_const(self.as_raw_StatModel(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn empty(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_StatModel_empty_const(self.as_raw_StatModel(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns true if the model is trained
#[inline]
fn is_trained(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_StatModel_isTrained_const(self.as_raw_StatModel(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns true if the model is classifier
#[inline]
fn is_classifier(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_StatModel_isClassifier_const(self.as_raw_StatModel(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes error on the training or test dataset
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * data: the training data
/// * test: if true, the error is computed over the test subset of the data, otherwise it's
/// computed over the training subset of the data. Please note that if you loaded a completely
/// different dataset to evaluate already trained classifier, you will probably want not to set
/// the test subset at all with TrainData::setTrainTestSplitRatio and specify test=false, so
/// that the error is computed for the whole new set. Yes, this sounds a bit confusing.
/// * resp: the optional output responses.
///
/// The method uses StatModel::predict to compute the error. For regression models the error is
/// computed as RMS, for classifiers - as a percent of missclassified samples (0%-100%).
#[inline]
fn calc_error(&self, data: &core::Ptr<crate::ml::TrainData>, test: bool, resp: &mut impl core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<f32> {
output_array_arg!(resp);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_StatModel_calcError_const_const_PtrLTrainDataGR_bool_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_StatModel(), data.as_raw_PtrOfTrainData(), test, resp.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Predicts response(s) for the provided sample(s)
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * samples: The input samples, floating-point matrix
/// * results: The optional output matrix of results.
/// * flags: The optional flags, model-dependent. See cv::ml::StatModel::Flags.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * results: noArray()
/// * flags: 0
#[inline]
fn predict(&self, samples: &impl core::ToInputArray, results: &mut impl core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<f32> {
input_array_arg!(samples);
output_array_arg!(results);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_StatModel_predict_const_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(self.as_raw_StatModel(), samples.as_raw__InputArray(), results.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::ml::StatModel]
pub trait StatModelTrait: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::ml::StatModelTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_StatModel(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Trains the statistical model
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * trainData: training data that can be loaded from file using TrainData::loadFromCSV or
/// created with TrainData::create.
/// * flags: optional flags, depending on the model. Some of the models can be updated with the
/// new training samples, not completely overwritten (such as NormalBayesClassifier or ANN_MLP).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: 0
#[inline]
fn train_with_data(&mut self, train_data: &core::Ptr<crate::ml::TrainData>, flags: i32) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_StatModel_train_const_PtrLTrainDataGR_int(self.as_raw_mut_StatModel(), train_data.as_raw_PtrOfTrainData(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Trains the statistical model
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * samples: training samples
/// * layout: See ml::SampleTypes.
/// * responses: vector of responses associated with the training samples.
#[inline]
fn train(&mut self, samples: &impl core::ToInputArray, layout: i32, responses: &impl core::ToInputArray) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(samples);
input_array_arg!(responses);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_StatModel_train_const__InputArrayR_int_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_StatModel(), samples.as_raw__InputArray(), layout, responses.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Base class for statistical models in OpenCV ML.
pub struct StatModel {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { StatModel }
impl Drop for StatModel {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_StatModel_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_StatModel_delete(self.as_raw_mut_StatModel()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for StatModel {}
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for StatModel {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for StatModel {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::ml::StatModelTraitConst for StatModel {
#[inline] fn as_raw_StatModel(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::StatModelTrait for StatModel {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_StatModel(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl StatModel {
}
boxed_cast_base! { StatModel, core::Algorithm, cv_StatModel_to_Algorithm }
/// Constant methods for [crate::ml::TrainData]
pub trait TrainDataTraitConst {
fn as_raw_TrainData(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn get_layout(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getLayout_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_n_train_samples(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getNTrainSamples_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_n_test_samples(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getNTestSamples_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_n_samples(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getNSamples_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_n_vars(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getNVars_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_n_all_vars(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getNAllVars_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_sample(&self, var_idx: &impl core::ToInputArray, sidx: i32, buf: &mut f32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(var_idx);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getSample_const_const__InputArrayR_int_floatX(self.as_raw_TrainData(), var_idx.as_raw__InputArray(), sidx, buf, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_samples(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getSamples_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_missing(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getMissing_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns matrix of train samples
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * layout: The requested layout. If it's different from the initial one, the matrix is
/// transposed. See ml::SampleTypes.
/// * compressSamples: if true, the function returns only the training samples (specified by
/// sampleIdx)
/// * compressVars: if true, the function returns the shorter training samples, containing only
/// the active variables.
///
/// In current implementation the function tries to avoid physical data copying and returns the
/// matrix stored inside TrainData (unless the transposition or compression is needed).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * layout: ROW_SAMPLE
/// * compress_samples: true
/// * compress_vars: true
#[inline]
fn get_train_samples(&self, layout: i32, compress_samples: bool, compress_vars: bool) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getTrainSamples_const_int_bool_bool(self.as_raw_TrainData(), layout, compress_samples, compress_vars, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the vector of responses
///
/// The function returns ordered or the original categorical responses. Usually it's used in
/// regression algorithms.
#[inline]
fn get_train_responses(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getTrainResponses_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the vector of normalized categorical responses
///
/// The function returns vector of responses. Each response is integer from `0` to `<number of
/// classes>-1`. The actual label value can be retrieved then from the class label vector, see
/// TrainData::getClassLabels.
#[inline]
fn get_train_norm_cat_responses(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getTrainNormCatResponses_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_test_responses(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getTestResponses_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_test_norm_cat_responses(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getTestNormCatResponses_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_responses(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getResponses_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_norm_cat_responses(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getNormCatResponses_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_sample_weights(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getSampleWeights_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_train_sample_weights(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getTrainSampleWeights_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_test_sample_weights(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getTestSampleWeights_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_var_idx(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getVarIdx_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_var_type(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getVarType_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_var_symbol_flags(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getVarSymbolFlags_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_response_type(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getResponseType_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_train_sample_idx(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getTrainSampleIdx_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_test_sample_idx(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getTestSampleIdx_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_values(&self, vi: i32, sidx: &impl core::ToInputArray, values: &mut f32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(sidx);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getValues_const_int_const__InputArrayR_floatX(self.as_raw_TrainData(), vi, sidx.as_raw__InputArray(), values, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_norm_cat_values(&self, vi: i32, sidx: &impl core::ToInputArray, values: &mut i32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(sidx);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getNormCatValues_const_int_const__InputArrayR_intX(self.as_raw_TrainData(), vi, sidx.as_raw__InputArray(), values, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_default_subst_values(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getDefaultSubstValues_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_cat_count(&self, vi: i32) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getCatCount_const_int(self.as_raw_TrainData(), vi, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the vector of class labels
///
/// The function returns vector of unique labels occurred in the responses.
#[inline]
fn get_class_labels(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getClassLabels_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_cat_ofs(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getCatOfs_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_cat_map(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getCatMap_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns matrix of test samples
#[inline]
fn get_test_samples(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getTestSamples_const(self.as_raw_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns vector of symbolic names captured in loadFromCSV()
#[inline]
fn get_names(&self, names: &mut core::Vector<String>) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getNames_const_vectorLStringGR(self.as_raw_TrainData(), names.as_raw_mut_VectorOfString(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::ml::TrainData]
pub trait TrainDataTrait: crate::ml::TrainDataTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_TrainData(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Splits the training data into the training and test parts
/// ## See also
/// TrainData::setTrainTestSplitRatio
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * shuffle: true
#[inline]
fn set_train_test_split(&mut self, count: i32, shuffle: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_setTrainTestSplit_int_bool(self.as_raw_mut_TrainData(), count, shuffle, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Splits the training data into the training and test parts
///
/// The function selects a subset of specified relative size and then returns it as the training
/// set. If the function is not called, all the data is used for training. Please, note that for
/// each of TrainData::getTrain\* there is corresponding TrainData::getTest\*, so that the test
/// subset can be retrieved and processed as well.
/// ## See also
/// TrainData::setTrainTestSplit
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * shuffle: true
#[inline]
fn set_train_test_split_ratio(&mut self, ratio: f64, shuffle: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_setTrainTestSplitRatio_double_bool(self.as_raw_mut_TrainData(), ratio, shuffle, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn shuffle_train_test(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_shuffleTrainTest(self.as_raw_mut_TrainData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Class encapsulating training data.
///
/// Please note that the class only specifies the interface of training data, but not implementation.
/// All the statistical model classes in _ml_ module accepts Ptr\<TrainData\> as parameter. In other
/// words, you can create your own class derived from TrainData and pass smart pointer to the instance
/// of this class into StatModel::train.
/// ## See also
/// [ml_intro_data]
pub struct TrainData {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { TrainData }
impl Drop for TrainData {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_TrainData_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_TrainData_delete(self.as_raw_mut_TrainData()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for TrainData {}
impl crate::ml::TrainDataTraitConst for TrainData {
#[inline] fn as_raw_TrainData(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ml::TrainDataTrait for TrainData {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_TrainData(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl TrainData {
#[inline]
pub fn missing_value() -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_missingValue(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Extract from 1D vector elements specified by passed indexes.
/// ## Parameters
/// * vec: input vector (supported types: CV_32S, CV_32F, CV_64F)
/// * idx: 1D index vector
#[inline]
pub fn get_sub_vector(vec: &core::Mat, idx: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getSubVector_const_MatR_const_MatR(vec.as_raw_Mat(), idx.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Extract from matrix rows/cols specified by passed indexes.
/// ## Parameters
/// * matrix: input matrix (supported types: CV_32S, CV_32F, CV_64F)
/// * idx: 1D index vector
/// * layout: specifies to extract rows (cv::ml::ROW_SAMPLES) or to extract columns (cv::ml::COL_SAMPLES)
#[inline]
pub fn get_sub_matrix(matrix: &core::Mat, idx: &core::Mat, layout: i32) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getSubMatrix_const_MatR_const_MatR_int(matrix.as_raw_Mat(), idx.as_raw_Mat(), layout, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Reads the dataset from a .csv file and returns the ready-to-use training data.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * filename: The input file name
/// * headerLineCount: The number of lines in the beginning to skip; besides the header, the
/// function also skips empty lines and lines staring with `#`
/// * responseStartIdx: Index of the first output variable. If -1, the function considers the
/// last variable as the response
/// * responseEndIdx: Index of the last output variable + 1. If -1, then there is single
/// response variable at responseStartIdx.
/// * varTypeSpec: The optional text string that specifies the variables' types. It has the
/// format `ord[n1-n2,n3,n4-n5,...]cat[n6,n7-n8,...]`. That is, variables from `n1 to n2`
/// (inclusive range), `n3`, `n4 to n5` ... are considered ordered and `n6`, `n7 to n8` ... are
/// considered as categorical. The range `[n1..n2] + [n3] + [n4..n5] + ... + [n6] + [n7..n8]`
/// should cover all the variables. If varTypeSpec is not specified, then algorithm uses the
/// following rules:
/// - all input variables are considered ordered by default. If some column contains has non-
/// numerical values, e.g. 'apple', 'pear', 'apple', 'apple', 'mango', the corresponding
/// variable is considered categorical.
/// - if there are several output variables, they are all considered as ordered. Error is
/// reported when non-numerical values are used.
/// - if there is a single output variable, then if its values are non-numerical or are all
/// integers, then it's considered categorical. Otherwise, it's considered ordered.
/// * delimiter: The character used to separate values in each line.
/// * missch: The character used to specify missing measurements. It should not be a digit.
/// Although it's a non-numerical value, it surely does not affect the decision of whether the
/// variable ordered or categorical.
///
/// Note: If the dataset only contains input variables and no responses, use responseStartIdx = -2
/// and responseEndIdx = 0. The output variables vector will just contain zeros.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * response_start_idx: -1
/// * response_end_idx: -1
/// * var_type_spec: String()
/// * delimiter: ','
/// * missch: '?'
#[inline]
pub fn load_from_csv(filename: &str, header_line_count: i32, response_start_idx: i32, response_end_idx: i32, var_type_spec: &str, delimiter: i8, missch: i8) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::ml::TrainData>> {
extern_container_arg!(filename);
extern_container_arg!(var_type_spec);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_loadFromCSV_const_StringR_int_int_int_const_StringR_char_char(filename.opencv_as_extern(), header_line_count, response_start_idx, response_end_idx, var_type_spec.opencv_as_extern(), delimiter, missch, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ml::TrainData>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates training data from in-memory arrays.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * samples: matrix of samples. It should have CV_32F type.
/// * layout: see ml::SampleTypes.
/// * responses: matrix of responses. If the responses are scalar, they should be stored as a
/// single row or as a single column. The matrix should have type CV_32F or CV_32S (in the
/// former case the responses are considered as ordered by default; in the latter case - as
/// categorical)
/// * varIdx: vector specifying which variables to use for training. It can be an integer vector
/// (CV_32S) containing 0-based variable indices or byte vector (CV_8U) containing a mask of
/// active variables.
/// * sampleIdx: vector specifying which samples to use for training. It can be an integer
/// vector (CV_32S) containing 0-based sample indices or byte vector (CV_8U) containing a mask
/// of training samples.
/// * sampleWeights: optional vector with weights for each sample. It should have CV_32F type.
/// * varType: optional vector of type CV_8U and size `<number_of_variables_in_samples> +
/// <number_of_variables_in_responses>`, containing types of each input and output variable. See
/// ml::VariableTypes.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * var_idx: noArray()
/// * sample_idx: noArray()
/// * sample_weights: noArray()
/// * var_type: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn create(samples: &impl core::ToInputArray, layout: i32, responses: &impl core::ToInputArray, var_idx: &impl core::ToInputArray, sample_idx: &impl core::ToInputArray, sample_weights: &impl core::ToInputArray, var_type: &impl core::ToInputArray) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::ml::TrainData>> {
input_array_arg!(samples);
input_array_arg!(responses);
input_array_arg!(var_idx);
input_array_arg!(sample_idx);
input_array_arg!(sample_weights);
input_array_arg!(var_type);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_create_const__InputArrayR_int_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(samples.as_raw__InputArray(), layout, responses.as_raw__InputArray(), var_idx.as_raw__InputArray(), sample_idx.as_raw__InputArray(), sample_weights.as_raw__InputArray(), var_type.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ml::TrainData>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
}