pub mod video {
//! # Video Analysis
//! # Motion Analysis
//! # Object Tracking
use crate::mod_prelude::*;
use crate::{core, sys, types};
pub mod prelude {
pub use super::{BackgroundSubtractorKNNTrait, BackgroundSubtractorKNNTraitConst, BackgroundSubtractorMOG2Trait, BackgroundSubtractorMOG2TraitConst, BackgroundSubtractorTrait, BackgroundSubtractorTraitConst, DISOpticalFlowTrait, DISOpticalFlowTraitConst, DenseOpticalFlowTrait, DenseOpticalFlowTraitConst, FarnebackOpticalFlowTrait, FarnebackOpticalFlowTraitConst, KalmanFilterTrait, KalmanFilterTraitConst, SparseOpticalFlowTrait, SparseOpticalFlowTraitConst, SparsePyrLKOpticalFlowTrait, SparsePyrLKOpticalFlowTraitConst, TrackerDaSiamRPNTrait, TrackerDaSiamRPNTraitConst, TrackerDaSiamRPN_ParamsTrait, TrackerDaSiamRPN_ParamsTraitConst, TrackerGOTURNTrait, TrackerGOTURNTraitConst, TrackerGOTURN_ParamsTrait, TrackerGOTURN_ParamsTraitConst, TrackerMILTrait, TrackerMILTraitConst, TrackerNanoTrait, TrackerNanoTraitConst, TrackerNano_ParamsTrait, TrackerNano_ParamsTraitConst, TrackerTrait, TrackerTraitConst, TrackerVitTrait, TrackerVitTraitConst, TrackerVit_ParamsTrait, TrackerVit_ParamsTraitConst, VariationalRefinementTrait, VariationalRefinementTraitConst};
}
pub const DISOpticalFlow_PRESET_FAST: i32 = 1;
pub const DISOpticalFlow_PRESET_MEDIUM: i32 = 2;
pub const DISOpticalFlow_PRESET_ULTRAFAST: i32 = 0;
pub const MOTION_AFFINE: i32 = 2;
pub const MOTION_EUCLIDEAN: i32 = 1;
pub const MOTION_HOMOGRAPHY: i32 = 3;
pub const MOTION_TRANSLATION: i32 = 0;
pub const OPTFLOW_FARNEBACK_GAUSSIAN: i32 = 256;
pub const OPTFLOW_LK_GET_MIN_EIGENVALS: i32 = 8;
pub const OPTFLOW_USE_INITIAL_FLOW: i32 = 4;
/// Finds an object center, size, and orientation.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * probImage: Back projection of the object histogram. See calcBackProject.
/// * window: Initial search window.
/// * criteria: Stop criteria for the underlying meanShift.
/// returns
/// (in old interfaces) Number of iterations CAMSHIFT took to converge
/// The function implements the CAMSHIFT object tracking algorithm [Bradski98](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Bradski98) . First, it finds an
/// object center using meanShift and then adjusts the window size and finds the optimal rotation. The
/// function returns the rotated rectangle structure that includes the object position, size, and
/// orientation. The next position of the search window can be obtained with RotatedRect::boundingRect()
///
/// See the OpenCV sample camshiftdemo.c that tracks colored objects.
///
///
/// Note:
/// * (Python) A sample explaining the camshift tracking algorithm can be found at
/// opencv_source_code/samples/python/camshift.py
#[inline]
pub fn cam_shift(prob_image: &impl ToInputArray, window: &mut core::Rect, criteria: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<core::RotatedRect> {
input_array_arg!(prob_image);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_CamShift_const__InputArrayR_RectR_TermCriteria(prob_image.as_raw__InputArray(), window, &criteria, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Constructs the image pyramid which can be passed to calcOpticalFlowPyrLK.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * img: 8-bit input image.
/// * pyramid: output pyramid.
/// * winSize: window size of optical flow algorithm. Must be not less than winSize argument of
/// calcOpticalFlowPyrLK. It is needed to calculate required padding for pyramid levels.
/// * maxLevel: 0-based maximal pyramid level number.
/// * withDerivatives: set to precompute gradients for the every pyramid level. If pyramid is
/// constructed without the gradients then calcOpticalFlowPyrLK will calculate them internally.
/// * pyrBorder: the border mode for pyramid layers.
/// * derivBorder: the border mode for gradients.
/// * tryReuseInputImage: put ROI of input image into the pyramid if possible. You can pass false
/// to force data copying.
/// ## Returns
/// number of levels in constructed pyramid. Can be less than maxLevel.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [build_optical_flow_pyramid] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * with_derivatives: true
/// * pyr_border: BORDER_REFLECT_101
/// * deriv_border: BORDER_CONSTANT
/// * try_reuse_input_image: true
#[inline]
pub fn build_optical_flow_pyramid_def(img: &impl ToInputArray, pyramid: &mut impl ToOutputArray, win_size: core::Size, max_level: i32) -> Result<i32> {
input_array_arg!(img);
output_array_arg!(pyramid);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_buildOpticalFlowPyramid_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_Size_int(img.as_raw__InputArray(), pyramid.as_raw__OutputArray(), &win_size, max_level, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Constructs the image pyramid which can be passed to calcOpticalFlowPyrLK.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * img: 8-bit input image.
/// * pyramid: output pyramid.
/// * winSize: window size of optical flow algorithm. Must be not less than winSize argument of
/// calcOpticalFlowPyrLK. It is needed to calculate required padding for pyramid levels.
/// * maxLevel: 0-based maximal pyramid level number.
/// * withDerivatives: set to precompute gradients for the every pyramid level. If pyramid is
/// constructed without the gradients then calcOpticalFlowPyrLK will calculate them internally.
/// * pyrBorder: the border mode for pyramid layers.
/// * derivBorder: the border mode for gradients.
/// * tryReuseInputImage: put ROI of input image into the pyramid if possible. You can pass false
/// to force data copying.
/// ## Returns
/// number of levels in constructed pyramid. Can be less than maxLevel.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * with_derivatives: true
/// * pyr_border: BORDER_REFLECT_101
/// * deriv_border: BORDER_CONSTANT
/// * try_reuse_input_image: true
#[inline]
pub fn build_optical_flow_pyramid(img: &impl ToInputArray, pyramid: &mut impl ToOutputArray, win_size: core::Size, max_level: i32, with_derivatives: bool, pyr_border: i32, deriv_border: i32, try_reuse_input_image: bool) -> Result<i32> {
input_array_arg!(img);
output_array_arg!(pyramid);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_buildOpticalFlowPyramid_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_Size_int_bool_int_int_bool(img.as_raw__InputArray(), pyramid.as_raw__OutputArray(), &win_size, max_level, with_derivatives, pyr_border, deriv_border, try_reuse_input_image, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes a dense optical flow using the Gunnar Farneback's algorithm.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * prev: first 8-bit single-channel input image.
/// * next: second input image of the same size and the same type as prev.
/// * flow: computed flow image that has the same size as prev and type CV_32FC2.
/// * pyr_scale: parameter, specifying the image scale (\<1) to build pyramids for each image;
/// pyr_scale=0.5 means a classical pyramid, where each next layer is twice smaller than the previous
/// one.
/// * levels: number of pyramid layers including the initial image; levels=1 means that no extra
/// layers are created and only the original images are used.
/// * winsize: averaging window size; larger values increase the algorithm robustness to image
/// noise and give more chances for fast motion detection, but yield more blurred motion field.
/// * iterations: number of iterations the algorithm does at each pyramid level.
/// * poly_n: size of the pixel neighborhood used to find polynomial expansion in each pixel;
/// larger values mean that the image will be approximated with smoother surfaces, yielding more
/// robust algorithm and more blurred motion field, typically poly_n =5 or 7.
/// * poly_sigma: standard deviation of the Gaussian that is used to smooth derivatives used as a
/// basis for the polynomial expansion; for poly_n=5, you can set poly_sigma=1.1, for poly_n=7, a
/// good value would be poly_sigma=1.5.
/// * flags: operation flags that can be a combination of the following:
/// * **OPTFLOW_USE_INITIAL_FLOW** uses the input flow as an initial flow approximation.
/// * **OPTFLOW_FARNEBACK_GAUSSIAN** uses the Gaussian 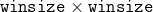
/// filter instead of a box filter of the same size for optical flow estimation; usually, this
/// option gives z more accurate flow than with a box filter, at the cost of lower speed;
/// normally, winsize for a Gaussian window should be set to a larger value to achieve the same
/// level of robustness.
///
/// The function finds an optical flow for each prev pixel using the [Farneback2003](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Farneback2003) algorithm so that
///
/// 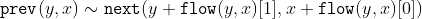
///
///
/// Note: Some examples:
///
/// * An example using the optical flow algorithm described by Gunnar Farneback can be found at
/// opencv_source_code/samples/cpp/fback.cpp
/// * (Python) An example using the optical flow algorithm described by Gunnar Farneback can be
/// found at opencv_source_code/samples/python/opt_flow.py
#[inline]
pub fn calc_optical_flow_farneback(prev: &impl ToInputArray, next: &impl ToInputArray, flow: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, pyr_scale: f64, levels: i32, winsize: i32, iterations: i32, poly_n: i32, poly_sigma: f64, flags: i32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(prev);
input_array_arg!(next);
input_output_array_arg!(flow);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_calcOpticalFlowFarneback_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_double_int_int_int_int_double_int(prev.as_raw__InputArray(), next.as_raw__InputArray(), flow.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), pyr_scale, levels, winsize, iterations, poly_n, poly_sigma, flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates an optical flow for a sparse feature set using the iterative Lucas-Kanade method with
/// pyramids.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * prevImg: first 8-bit input image or pyramid constructed by buildOpticalFlowPyramid.
/// * nextImg: second input image or pyramid of the same size and the same type as prevImg.
/// * prevPts: vector of 2D points for which the flow needs to be found; point coordinates must be
/// single-precision floating-point numbers.
/// * nextPts: output vector of 2D points (with single-precision floating-point coordinates)
/// containing the calculated new positions of input features in the second image; when
/// OPTFLOW_USE_INITIAL_FLOW flag is passed, the vector must have the same size as in the input.
/// * status: output status vector (of unsigned chars); each element of the vector is set to 1 if
/// the flow for the corresponding features has been found, otherwise, it is set to 0.
/// * err: output vector of errors; each element of the vector is set to an error for the
/// corresponding feature, type of the error measure can be set in flags parameter; if the flow wasn't
/// found then the error is not defined (use the status parameter to find such cases).
/// * winSize: size of the search window at each pyramid level.
/// * maxLevel: 0-based maximal pyramid level number; if set to 0, pyramids are not used (single
/// level), if set to 1, two levels are used, and so on; if pyramids are passed to input then
/// algorithm will use as many levels as pyramids have but no more than maxLevel.
/// * criteria: parameter, specifying the termination criteria of the iterative search algorithm
/// (after the specified maximum number of iterations criteria.maxCount or when the search window
/// moves by less than criteria.epsilon.
/// * flags: operation flags:
/// * **OPTFLOW_USE_INITIAL_FLOW** uses initial estimations, stored in nextPts; if the flag is
/// not set, then prevPts is copied to nextPts and is considered the initial estimate.
/// * **OPTFLOW_LK_GET_MIN_EIGENVALS** use minimum eigen values as an error measure (see
/// minEigThreshold description); if the flag is not set, then L1 distance between patches
/// around the original and a moved point, divided by number of pixels in a window, is used as a
/// error measure.
/// * minEigThreshold: the algorithm calculates the minimum eigen value of a 2x2 normal matrix of
/// optical flow equations (this matrix is called a spatial gradient matrix in [Bouguet00](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Bouguet00)), divided
/// by number of pixels in a window; if this value is less than minEigThreshold, then a corresponding
/// feature is filtered out and its flow is not processed, so it allows to remove bad points and get a
/// performance boost.
///
/// The function implements a sparse iterative version of the Lucas-Kanade optical flow in pyramids. See
/// [Bouguet00](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Bouguet00) . The function is parallelized with the TBB library.
///
///
/// Note: Some examples:
///
/// * An example using the Lucas-Kanade optical flow algorithm can be found at
/// opencv_source_code/samples/cpp/lkdemo.cpp
/// * (Python) An example using the Lucas-Kanade optical flow algorithm can be found at
/// opencv_source_code/samples/python/lk_track.py
/// * (Python) An example using the Lucas-Kanade tracker for homography matching can be found at
/// opencv_source_code/samples/python/lk_homography.py
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [calc_optical_flow_pyr_lk] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * win_size: Size(21,21)
/// * max_level: 3
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,30,0.01)
/// * flags: 0
/// * min_eig_threshold: 1e-4
#[inline]
pub fn calc_optical_flow_pyr_lk_def(prev_img: &impl ToInputArray, next_img: &impl ToInputArray, prev_pts: &impl ToInputArray, next_pts: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, status: &mut impl ToOutputArray, err: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(prev_img);
input_array_arg!(next_img);
input_array_arg!(prev_pts);
input_output_array_arg!(next_pts);
output_array_arg!(status);
output_array_arg!(err);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_calcOpticalFlowPyrLK_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(prev_img.as_raw__InputArray(), next_img.as_raw__InputArray(), prev_pts.as_raw__InputArray(), next_pts.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), status.as_raw__OutputArray(), err.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates an optical flow for a sparse feature set using the iterative Lucas-Kanade method with
/// pyramids.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * prevImg: first 8-bit input image or pyramid constructed by buildOpticalFlowPyramid.
/// * nextImg: second input image or pyramid of the same size and the same type as prevImg.
/// * prevPts: vector of 2D points for which the flow needs to be found; point coordinates must be
/// single-precision floating-point numbers.
/// * nextPts: output vector of 2D points (with single-precision floating-point coordinates)
/// containing the calculated new positions of input features in the second image; when
/// OPTFLOW_USE_INITIAL_FLOW flag is passed, the vector must have the same size as in the input.
/// * status: output status vector (of unsigned chars); each element of the vector is set to 1 if
/// the flow for the corresponding features has been found, otherwise, it is set to 0.
/// * err: output vector of errors; each element of the vector is set to an error for the
/// corresponding feature, type of the error measure can be set in flags parameter; if the flow wasn't
/// found then the error is not defined (use the status parameter to find such cases).
/// * winSize: size of the search window at each pyramid level.
/// * maxLevel: 0-based maximal pyramid level number; if set to 0, pyramids are not used (single
/// level), if set to 1, two levels are used, and so on; if pyramids are passed to input then
/// algorithm will use as many levels as pyramids have but no more than maxLevel.
/// * criteria: parameter, specifying the termination criteria of the iterative search algorithm
/// (after the specified maximum number of iterations criteria.maxCount or when the search window
/// moves by less than criteria.epsilon.
/// * flags: operation flags:
/// * **OPTFLOW_USE_INITIAL_FLOW** uses initial estimations, stored in nextPts; if the flag is
/// not set, then prevPts is copied to nextPts and is considered the initial estimate.
/// * **OPTFLOW_LK_GET_MIN_EIGENVALS** use minimum eigen values as an error measure (see
/// minEigThreshold description); if the flag is not set, then L1 distance between patches
/// around the original and a moved point, divided by number of pixels in a window, is used as a
/// error measure.
/// * minEigThreshold: the algorithm calculates the minimum eigen value of a 2x2 normal matrix of
/// optical flow equations (this matrix is called a spatial gradient matrix in [Bouguet00](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Bouguet00)), divided
/// by number of pixels in a window; if this value is less than minEigThreshold, then a corresponding
/// feature is filtered out and its flow is not processed, so it allows to remove bad points and get a
/// performance boost.
///
/// The function implements a sparse iterative version of the Lucas-Kanade optical flow in pyramids. See
/// [Bouguet00](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Bouguet00) . The function is parallelized with the TBB library.
///
///
/// Note: Some examples:
///
/// * An example using the Lucas-Kanade optical flow algorithm can be found at
/// opencv_source_code/samples/cpp/lkdemo.cpp
/// * (Python) An example using the Lucas-Kanade optical flow algorithm can be found at
/// opencv_source_code/samples/python/lk_track.py
/// * (Python) An example using the Lucas-Kanade tracker for homography matching can be found at
/// opencv_source_code/samples/python/lk_homography.py
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * win_size: Size(21,21)
/// * max_level: 3
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,30,0.01)
/// * flags: 0
/// * min_eig_threshold: 1e-4
#[inline]
pub fn calc_optical_flow_pyr_lk(prev_img: &impl ToInputArray, next_img: &impl ToInputArray, prev_pts: &impl ToInputArray, next_pts: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, status: &mut impl ToOutputArray, err: &mut impl ToOutputArray, win_size: core::Size, max_level: i32, criteria: core::TermCriteria, flags: i32, min_eig_threshold: f64) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(prev_img);
input_array_arg!(next_img);
input_array_arg!(prev_pts);
input_output_array_arg!(next_pts);
output_array_arg!(status);
output_array_arg!(err);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_calcOpticalFlowPyrLK_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_Size_int_TermCriteria_int_double(prev_img.as_raw__InputArray(), next_img.as_raw__InputArray(), prev_pts.as_raw__InputArray(), next_pts.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), status.as_raw__OutputArray(), err.as_raw__OutputArray(), &win_size, max_level, &criteria, flags, min_eig_threshold, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes the Enhanced Correlation Coefficient value between two images [EP08](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_EP08) .
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * templateImage: single-channel template image; CV_8U or CV_32F array.
/// * inputImage: single-channel input image to be warped to provide an image similar to
/// templateImage, same type as templateImage.
/// * inputMask: An optional mask to indicate valid values of inputImage.
/// ## See also
/// findTransformECC
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [compute_ecc] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * input_mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn compute_ecc_def(template_image: &impl ToInputArray, input_image: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<f64> {
input_array_arg!(template_image);
input_array_arg!(input_image);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_computeECC_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(template_image.as_raw__InputArray(), input_image.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes the Enhanced Correlation Coefficient value between two images [EP08](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_EP08) .
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * templateImage: single-channel template image; CV_8U or CV_32F array.
/// * inputImage: single-channel input image to be warped to provide an image similar to
/// templateImage, same type as templateImage.
/// * inputMask: An optional mask to indicate valid values of inputImage.
/// ## See also
/// findTransformECC
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * input_mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn compute_ecc(template_image: &impl ToInputArray, input_image: &impl ToInputArray, input_mask: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<f64> {
input_array_arg!(template_image);
input_array_arg!(input_image);
input_array_arg!(input_mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_computeECC_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(template_image.as_raw__InputArray(), input_image.as_raw__InputArray(), input_mask.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates KNN Background Subtractor
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * history: Length of the history.
/// * dist2Threshold: Threshold on the squared distance between the pixel and the sample to decide
/// whether a pixel is close to that sample. This parameter does not affect the background update.
/// * detectShadows: If true, the algorithm will detect shadows and mark them. It decreases the
/// speed a bit, so if you do not need this feature, set the parameter to false.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [create_background_subtractor_knn] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * history: 500
/// * dist2_threshold: 400.0
/// * detect_shadows: true
#[inline]
pub fn create_background_subtractor_knn_def() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorKNN>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createBackgroundSubtractorKNN(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorKNN>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates KNN Background Subtractor
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * history: Length of the history.
/// * dist2Threshold: Threshold on the squared distance between the pixel and the sample to decide
/// whether a pixel is close to that sample. This parameter does not affect the background update.
/// * detectShadows: If true, the algorithm will detect shadows and mark them. It decreases the
/// speed a bit, so if you do not need this feature, set the parameter to false.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * history: 500
/// * dist2_threshold: 400.0
/// * detect_shadows: true
#[inline]
pub fn create_background_subtractor_knn(history: i32, dist2_threshold: f64, detect_shadows: bool) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorKNN>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createBackgroundSubtractorKNN_int_double_bool(history, dist2_threshold, detect_shadows, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorKNN>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates MOG2 Background Subtractor
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * history: Length of the history.
/// * varThreshold: Threshold on the squared Mahalanobis distance between the pixel and the model
/// to decide whether a pixel is well described by the background model. This parameter does not
/// affect the background update.
/// * detectShadows: If true, the algorithm will detect shadows and mark them. It decreases the
/// speed a bit, so if you do not need this feature, set the parameter to false.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [create_background_subtractor_mog2] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * history: 500
/// * var_threshold: 16
/// * detect_shadows: true
#[inline]
pub fn create_background_subtractor_mog2_def() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorMOG2>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createBackgroundSubtractorMOG2(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorMOG2>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates MOG2 Background Subtractor
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * history: Length of the history.
/// * varThreshold: Threshold on the squared Mahalanobis distance between the pixel and the model
/// to decide whether a pixel is well described by the background model. This parameter does not
/// affect the background update.
/// * detectShadows: If true, the algorithm will detect shadows and mark them. It decreases the
/// speed a bit, so if you do not need this feature, set the parameter to false.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * history: 500
/// * var_threshold: 16
/// * detect_shadows: true
#[inline]
pub fn create_background_subtractor_mog2(history: i32, var_threshold: f64, detect_shadows: bool) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorMOG2>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createBackgroundSubtractorMOG2_int_double_bool(history, var_threshold, detect_shadows, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorMOG2>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes an optimal affine transformation between two 2D point sets.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: First input 2D point set stored in std::vector or Mat, or an image stored in Mat.
/// * dst: Second input 2D point set of the same size and the same type as A, or another image.
/// * fullAffine: If true, the function finds an optimal affine transformation with no additional
/// restrictions (6 degrees of freedom). Otherwise, the class of transformations to choose from is
/// limited to combinations of translation, rotation, and uniform scaling (4 degrees of freedom).
///
/// The function finds an optimal affine transform *[A|b]* (a 2 x 3 floating-point matrix) that
/// approximates best the affine transformation between:
///
/// * Two point sets
/// * Two raster images. In this case, the function first finds some features in the src image and
/// finds the corresponding features in dst image. After that, the problem is reduced to the first
/// case.
/// In case of point sets, the problem is formulated as follows: you need to find a 2x2 matrix *A* and
/// 2x1 vector *b* so that:
///
/// 
/// where src[i] and dst[i] are the i-th points in src and dst, respectively
///  can be either arbitrary (when fullAffine=true ) or have a form of
/// 
/// when fullAffine=false.
///
///
/// **Deprecated**: Use cv::estimateAffine2D, cv::estimateAffinePartial2D instead. If you are using this function
/// with images, extract points using cv::calcOpticalFlowPyrLK and then use the estimation functions.
/// ## See also
/// estimateAffine2D, estimateAffinePartial2D, getAffineTransform, getPerspectiveTransform, findHomography
#[deprecated = "Use cv::estimateAffine2D, cv::estimateAffinePartial2D instead. If you are using this function"]
#[inline]
pub fn estimate_rigid_transform(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &impl ToInputArray, full_affine: bool) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(src);
input_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_estimateRigidTransform_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_bool(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__InputArray(), full_affine, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// @overload
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [find_transform_ecc_1] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * motion_type: MOTION_AFFINE
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,50,0.001)
/// * input_mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn find_transform_ecc_1_def(template_image: &impl ToInputArray, input_image: &impl ToInputArray, warp_matrix: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray) -> Result<f64> {
input_array_arg!(template_image);
input_array_arg!(input_image);
input_output_array_arg!(warp_matrix);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findTransformECC_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR(template_image.as_raw__InputArray(), input_image.as_raw__InputArray(), warp_matrix.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds the geometric transform (warp) between two images in terms of the ECC criterion [EP08](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_EP08) .
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * templateImage: single-channel template image; CV_8U or CV_32F array.
/// * inputImage: single-channel input image which should be warped with the final warpMatrix in
/// order to provide an image similar to templateImage, same type as templateImage.
/// * warpMatrix: floating-point 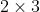 or 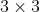 mapping matrix (warp).
/// * motionType: parameter, specifying the type of motion:
/// * **MOTION_TRANSLATION** sets a translational motion model; warpMatrix is 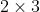 with
/// the first 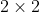 part being the unity matrix and the rest two parameters being
/// estimated.
/// * **MOTION_EUCLIDEAN** sets a Euclidean (rigid) transformation as motion model; three
/// parameters are estimated; warpMatrix is 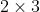.
/// * **MOTION_AFFINE** sets an affine motion model (DEFAULT); six parameters are estimated;
/// warpMatrix is 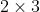.
/// * **MOTION_HOMOGRAPHY** sets a homography as a motion model; eight parameters are
/// estimated;\`warpMatrix\` is 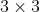.
/// * criteria: parameter, specifying the termination criteria of the ECC algorithm;
/// criteria.epsilon defines the threshold of the increment in the correlation coefficient between two
/// iterations (a negative criteria.epsilon makes criteria.maxcount the only termination criterion).
/// Default values are shown in the declaration above.
/// * inputMask: An optional mask to indicate valid values of inputImage.
/// * gaussFiltSize: An optional value indicating size of gaussian blur filter; (DEFAULT: 5)
///
/// The function estimates the optimum transformation (warpMatrix) with respect to ECC criterion
/// ([EP08](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_EP08)), that is
///
/// 
///
/// where
///
/// 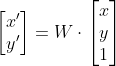
///
/// (the equation holds with homogeneous coordinates for homography). It returns the final enhanced
/// correlation coefficient, that is the correlation coefficient between the template image and the
/// final warped input image. When a 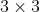 matrix is given with motionType =0, 1 or 2, the third
/// row is ignored.
///
/// Unlike findHomography and estimateRigidTransform, the function findTransformECC implements an
/// area-based alignment that builds on intensity similarities. In essence, the function updates the
/// initial transformation that roughly aligns the images. If this information is missing, the identity
/// warp (unity matrix) is used as an initialization. Note that if images undergo strong
/// displacements/rotations, an initial transformation that roughly aligns the images is necessary
/// (e.g., a simple euclidean/similarity transform that allows for the images showing the same image
/// content approximately). Use inverse warping in the second image to take an image close to the first
/// one, i.e. use the flag WARP_INVERSE_MAP with warpAffine or warpPerspective. See also the OpenCV
/// sample image_alignment.cpp that demonstrates the use of the function. Note that the function throws
/// an exception if algorithm does not converges.
/// ## See also
/// computeECC, estimateAffine2D, estimateAffinePartial2D, findHomography
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * motion_type: MOTION_AFFINE
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,50,0.001)
/// * input_mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn find_transform_ecc_1(template_image: &impl ToInputArray, input_image: &impl ToInputArray, warp_matrix: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, motion_type: i32, criteria: core::TermCriteria, input_mask: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<f64> {
input_array_arg!(template_image);
input_array_arg!(input_image);
input_output_array_arg!(warp_matrix);
input_array_arg!(input_mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findTransformECC_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_int_TermCriteria_const__InputArrayR(template_image.as_raw__InputArray(), input_image.as_raw__InputArray(), warp_matrix.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), motion_type, &criteria, input_mask.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds the geometric transform (warp) between two images in terms of the ECC criterion [EP08](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_EP08) .
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * templateImage: single-channel template image; CV_8U or CV_32F array.
/// * inputImage: single-channel input image which should be warped with the final warpMatrix in
/// order to provide an image similar to templateImage, same type as templateImage.
/// * warpMatrix: floating-point 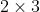 or 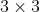 mapping matrix (warp).
/// * motionType: parameter, specifying the type of motion:
/// * **MOTION_TRANSLATION** sets a translational motion model; warpMatrix is 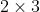 with
/// the first 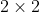 part being the unity matrix and the rest two parameters being
/// estimated.
/// * **MOTION_EUCLIDEAN** sets a Euclidean (rigid) transformation as motion model; three
/// parameters are estimated; warpMatrix is 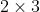.
/// * **MOTION_AFFINE** sets an affine motion model (DEFAULT); six parameters are estimated;
/// warpMatrix is 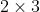.
/// * **MOTION_HOMOGRAPHY** sets a homography as a motion model; eight parameters are
/// estimated;\`warpMatrix\` is 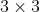.
/// * criteria: parameter, specifying the termination criteria of the ECC algorithm;
/// criteria.epsilon defines the threshold of the increment in the correlation coefficient between two
/// iterations (a negative criteria.epsilon makes criteria.maxcount the only termination criterion).
/// Default values are shown in the declaration above.
/// * inputMask: An optional mask to indicate valid values of inputImage.
/// * gaussFiltSize: An optional value indicating size of gaussian blur filter; (DEFAULT: 5)
///
/// The function estimates the optimum transformation (warpMatrix) with respect to ECC criterion
/// ([EP08](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_EP08)), that is
///
/// 
///
/// where
///
/// 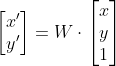
///
/// (the equation holds with homogeneous coordinates for homography). It returns the final enhanced
/// correlation coefficient, that is the correlation coefficient between the template image and the
/// final warped input image. When a 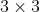 matrix is given with motionType =0, 1 or 2, the third
/// row is ignored.
///
/// Unlike findHomography and estimateRigidTransform, the function findTransformECC implements an
/// area-based alignment that builds on intensity similarities. In essence, the function updates the
/// initial transformation that roughly aligns the images. If this information is missing, the identity
/// warp (unity matrix) is used as an initialization. Note that if images undergo strong
/// displacements/rotations, an initial transformation that roughly aligns the images is necessary
/// (e.g., a simple euclidean/similarity transform that allows for the images showing the same image
/// content approximately). Use inverse warping in the second image to take an image close to the first
/// one, i.e. use the flag WARP_INVERSE_MAP with warpAffine or warpPerspective. See also the OpenCV
/// sample image_alignment.cpp that demonstrates the use of the function. Note that the function throws
/// an exception if algorithm does not converges.
/// ## See also
/// computeECC, estimateAffine2D, estimateAffinePartial2D, findHomography
#[inline]
pub fn find_transform_ecc(template_image: &impl ToInputArray, input_image: &impl ToInputArray, warp_matrix: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, motion_type: i32, criteria: core::TermCriteria, input_mask: &impl ToInputArray, gauss_filt_size: i32) -> Result<f64> {
input_array_arg!(template_image);
input_array_arg!(input_image);
input_output_array_arg!(warp_matrix);
input_array_arg!(input_mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findTransformECC_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_int_TermCriteria_const__InputArrayR_int(template_image.as_raw__InputArray(), input_image.as_raw__InputArray(), warp_matrix.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), motion_type, &criteria, input_mask.as_raw__InputArray(), gauss_filt_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds an object on a back projection image.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * probImage: Back projection of the object histogram. See calcBackProject for details.
/// * window: Initial search window.
/// * criteria: Stop criteria for the iterative search algorithm.
/// returns
/// : Number of iterations CAMSHIFT took to converge.
/// The function implements the iterative object search algorithm. It takes the input back projection of
/// an object and the initial position. The mass center in window of the back projection image is
/// computed and the search window center shifts to the mass center. The procedure is repeated until the
/// specified number of iterations criteria.maxCount is done or until the window center shifts by less
/// than criteria.epsilon. The algorithm is used inside CamShift and, unlike CamShift , the search
/// window size or orientation do not change during the search. You can simply pass the output of
/// calcBackProject to this function. But better results can be obtained if you pre-filter the back
/// projection and remove the noise. For example, you can do this by retrieving connected components
/// with findContours , throwing away contours with small area ( contourArea ), and rendering the
/// remaining contours with drawContours.
#[inline]
pub fn mean_shift(prob_image: &impl ToInputArray, window: &mut core::Rect, criteria: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<i32> {
input_array_arg!(prob_image);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_meanShift_const__InputArrayR_RectR_TermCriteria(prob_image.as_raw__InputArray(), window, &criteria, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Read a .flo file
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * path: Path to the file to be loaded
///
/// The function readOpticalFlow loads a flow field from a file and returns it as a single matrix.
/// Resulting Mat has a type CV_32FC2 - floating-point, 2-channel. First channel corresponds to the
/// flow in the horizontal direction (u), second - vertical (v).
#[inline]
pub fn read_optical_flow(path: &str) -> Result<core::Mat> {
extern_container_arg!(path);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_readOpticalFlow_const_StringR(path.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Write a .flo to disk
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * path: Path to the file to be written
/// * flow: Flow field to be stored
///
/// The function stores a flow field in a file, returns true on success, false otherwise.
/// The flow field must be a 2-channel, floating-point matrix (CV_32FC2). First channel corresponds
/// to the flow in the horizontal direction (u), second - vertical (v).
#[inline]
pub fn write_optical_flow(path: &str, flow: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<bool> {
extern_container_arg!(path);
input_array_arg!(flow);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_writeOpticalFlow_const_StringR_const__InputArrayR(path.opencv_as_extern(), flow.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Base class for background/foreground segmentation. :
///
/// The class is only used to define the common interface for the whole family of background/foreground
/// segmentation algorithms.
pub struct BackgroundSubtractor {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { BackgroundSubtractor }
impl Drop for BackgroundSubtractor {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractor_delete(self.as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractor()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for BackgroundSubtractor {}
/// Constant methods for [crate::video::BackgroundSubtractor]
pub trait BackgroundSubtractorTraitConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_BackgroundSubtractor(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Computes a background image.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * backgroundImage: The output background image.
///
///
/// Note: Sometimes the background image can be very blurry, as it contain the average background
/// statistics.
#[inline]
fn get_background_image(&self, background_image: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
output_array_arg!(background_image);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractor_getBackgroundImage_const_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_BackgroundSubtractor(), background_image.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::video::BackgroundSubtractor]
pub trait BackgroundSubtractorTrait: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractor(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Computes a foreground mask.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: Next video frame.
/// * fgmask: The output foreground mask as an 8-bit binary image.
/// * learningRate: The value between 0 and 1 that indicates how fast the background model is
/// learnt. Negative parameter value makes the algorithm to use some automatically chosen learning
/// rate. 0 means that the background model is not updated at all, 1 means that the background model
/// is completely reinitialized from the last frame.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * learning_rate: -1
#[inline]
fn apply(&mut self, image: &impl ToInputArray, fgmask: &mut impl ToOutputArray, learning_rate: f64) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(image);
output_array_arg!(fgmask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractor_apply_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double(self.as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractor(), image.as_raw__InputArray(), fgmask.as_raw__OutputArray(), learning_rate, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes a foreground mask.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: Next video frame.
/// * fgmask: The output foreground mask as an 8-bit binary image.
/// * learningRate: The value between 0 and 1 that indicates how fast the background model is
/// learnt. Negative parameter value makes the algorithm to use some automatically chosen learning
/// rate. 0 means that the background model is not updated at all, 1 means that the background model
/// is completely reinitialized from the last frame.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [BackgroundSubtractorTrait::apply] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * learning_rate: -1
#[inline]
fn apply_def(&mut self, image: &impl ToInputArray, fgmask: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(image);
output_array_arg!(fgmask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractor_apply_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractor(), image.as_raw__InputArray(), fgmask.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for BackgroundSubtractor {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("BackgroundSubtractor")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { BackgroundSubtractor, core::Algorithm, cv_BackgroundSubtractor_to_Algorithm }
boxed_cast_descendant! { BackgroundSubtractor, crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorKNN, cv_BackgroundSubtractor_to_BackgroundSubtractorKNN }
boxed_cast_descendant! { BackgroundSubtractor, crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorMOG2, cv_BackgroundSubtractor_to_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2 }
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for BackgroundSubtractor {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for BackgroundSubtractor {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { BackgroundSubtractor, core::AlgorithmTraitConst, as_raw_Algorithm, core::AlgorithmTrait, as_raw_mut_Algorithm }
impl crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorTraitConst for BackgroundSubtractor {
#[inline] fn as_raw_BackgroundSubtractor(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorTrait for BackgroundSubtractor {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractor(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { BackgroundSubtractor, crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorTraitConst, as_raw_BackgroundSubtractor, crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorTrait, as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractor }
/// K-nearest neighbours - based Background/Foreground Segmentation Algorithm.
///
/// The class implements the K-nearest neighbours background subtraction described in [Zivkovic2006](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Zivkovic2006) .
/// Very efficient if number of foreground pixels is low.
pub struct BackgroundSubtractorKNN {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { BackgroundSubtractorKNN }
impl Drop for BackgroundSubtractorKNN {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorKNN_delete(self.as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorKNN()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for BackgroundSubtractorKNN {}
/// Constant methods for [crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorKNN]
pub trait BackgroundSubtractorKNNTraitConst: crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorTraitConst {
fn as_raw_BackgroundSubtractorKNN(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Returns the number of last frames that affect the background model
#[inline]
fn get_history(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorKNN_getHistory_const(self.as_raw_BackgroundSubtractorKNN(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the number of data samples in the background model
#[inline]
fn get_n_samples(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorKNN_getNSamples_const(self.as_raw_BackgroundSubtractorKNN(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the threshold on the squared distance between the pixel and the sample
///
/// The threshold on the squared distance between the pixel and the sample to decide whether a pixel is
/// close to a data sample.
#[inline]
fn get_dist2_threshold(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorKNN_getDist2Threshold_const(self.as_raw_BackgroundSubtractorKNN(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the number of neighbours, the k in the kNN.
///
/// K is the number of samples that need to be within dist2Threshold in order to decide that that
/// pixel is matching the kNN background model.
#[inline]
fn getk_nn_samples(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorKNN_getkNNSamples_const(self.as_raw_BackgroundSubtractorKNN(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the shadow detection flag
///
/// If true, the algorithm detects shadows and marks them. See createBackgroundSubtractorKNN for
/// details.
#[inline]
fn get_detect_shadows(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorKNN_getDetectShadows_const(self.as_raw_BackgroundSubtractorKNN(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the shadow value
///
/// Shadow value is the value used to mark shadows in the foreground mask. Default value is 127. Value 0
/// in the mask always means background, 255 means foreground.
#[inline]
fn get_shadow_value(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorKNN_getShadowValue_const(self.as_raw_BackgroundSubtractorKNN(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the shadow threshold
///
/// A shadow is detected if pixel is a darker version of the background. The shadow threshold (Tau in
/// the paper) is a threshold defining how much darker the shadow can be. Tau= 0.5 means that if a pixel
/// is more than twice darker then it is not shadow. See Prati, Mikic, Trivedi and Cucchiara,
/// *Detecting Moving Shadows...*, IEEE PAMI,2003.
#[inline]
fn get_shadow_threshold(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorKNN_getShadowThreshold_const(self.as_raw_BackgroundSubtractorKNN(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorKNN]
pub trait BackgroundSubtractorKNNTrait: crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorKNNTraitConst + crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorTrait {
fn as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorKNN(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Sets the number of last frames that affect the background model
#[inline]
fn set_history(&mut self, history: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorKNN_setHistory_int(self.as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorKNN(), history, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the number of data samples in the background model.
///
/// The model needs to be reinitalized to reserve memory.
#[inline]
fn set_n_samples(&mut self, _n_n: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorKNN_setNSamples_int(self.as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorKNN(), _n_n, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the threshold on the squared distance
#[inline]
fn set_dist2_threshold(&mut self, _dist2_threshold: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorKNN_setDist2Threshold_double(self.as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorKNN(), _dist2_threshold, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the k in the kNN. How many nearest neighbours need to match.
#[inline]
fn setk_nn_samples(&mut self, _nk_nn: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorKNN_setkNNSamples_int(self.as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorKNN(), _nk_nn, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Enables or disables shadow detection
#[inline]
fn set_detect_shadows(&mut self, detect_shadows: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorKNN_setDetectShadows_bool(self.as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorKNN(), detect_shadows, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the shadow value
#[inline]
fn set_shadow_value(&mut self, value: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorKNN_setShadowValue_int(self.as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorKNN(), value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the shadow threshold
#[inline]
fn set_shadow_threshold(&mut self, threshold: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorKNN_setShadowThreshold_double(self.as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorKNN(), threshold, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for BackgroundSubtractorKNN {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("BackgroundSubtractorKNN")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { BackgroundSubtractorKNN, core::Algorithm, cv_BackgroundSubtractorKNN_to_Algorithm }
boxed_cast_base! { BackgroundSubtractorKNN, crate::video::BackgroundSubtractor, cv_BackgroundSubtractorKNN_to_BackgroundSubtractor }
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for BackgroundSubtractorKNN {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for BackgroundSubtractorKNN {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { BackgroundSubtractorKNN, core::AlgorithmTraitConst, as_raw_Algorithm, core::AlgorithmTrait, as_raw_mut_Algorithm }
impl crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorTraitConst for BackgroundSubtractorKNN {
#[inline] fn as_raw_BackgroundSubtractor(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorTrait for BackgroundSubtractorKNN {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractor(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { BackgroundSubtractorKNN, crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorTraitConst, as_raw_BackgroundSubtractor, crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorTrait, as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractor }
impl crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorKNNTraitConst for BackgroundSubtractorKNN {
#[inline] fn as_raw_BackgroundSubtractorKNN(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorKNNTrait for BackgroundSubtractorKNN {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorKNN(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { BackgroundSubtractorKNN, crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorKNNTraitConst, as_raw_BackgroundSubtractorKNN, crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorKNNTrait, as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorKNN }
/// Gaussian Mixture-based Background/Foreground Segmentation Algorithm.
///
/// The class implements the Gaussian mixture model background subtraction described in [Zivkovic2004](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Zivkovic2004)
/// and [Zivkovic2006](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Zivkovic2006) .
pub struct BackgroundSubtractorMOG2 {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { BackgroundSubtractorMOG2 }
impl Drop for BackgroundSubtractorMOG2 {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_delete(self.as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for BackgroundSubtractorMOG2 {}
/// Constant methods for [crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorMOG2]
pub trait BackgroundSubtractorMOG2TraitConst: crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorTraitConst {
fn as_raw_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Returns the number of last frames that affect the background model
#[inline]
fn get_history(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_getHistory_const(self.as_raw_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the number of gaussian components in the background model
#[inline]
fn get_n_mixtures(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_getNMixtures_const(self.as_raw_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the "background ratio" parameter of the algorithm
///
/// If a foreground pixel keeps semi-constant value for about backgroundRatio\*history frames, it's
/// considered background and added to the model as a center of a new component. It corresponds to TB
/// parameter in the paper.
#[inline]
fn get_background_ratio(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_getBackgroundRatio_const(self.as_raw_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the variance threshold for the pixel-model match
///
/// The main threshold on the squared Mahalanobis distance to decide if the sample is well described by
/// the background model or not. Related to Cthr from the paper.
#[inline]
fn get_var_threshold(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_getVarThreshold_const(self.as_raw_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the variance threshold for the pixel-model match used for new mixture component generation
///
/// Threshold for the squared Mahalanobis distance that helps decide when a sample is close to the
/// existing components (corresponds to Tg in the paper). If a pixel is not close to any component, it
/// is considered foreground or added as a new component. 3 sigma =\> Tg=3\*3=9 is default. A smaller Tg
/// value generates more components. A higher Tg value may result in a small number of components but
/// they can grow too large.
#[inline]
fn get_var_threshold_gen(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_getVarThresholdGen_const(self.as_raw_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the initial variance of each gaussian component
#[inline]
fn get_var_init(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_getVarInit_const(self.as_raw_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_var_min(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_getVarMin_const(self.as_raw_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_var_max(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_getVarMax_const(self.as_raw_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the complexity reduction threshold
///
/// This parameter defines the number of samples needed to accept to prove the component exists. CT=0.05
/// is a default value for all the samples. By setting CT=0 you get an algorithm very similar to the
/// standard Stauffer&Grimson algorithm.
#[inline]
fn get_complexity_reduction_threshold(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_getComplexityReductionThreshold_const(self.as_raw_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the shadow detection flag
///
/// If true, the algorithm detects shadows and marks them. See createBackgroundSubtractorMOG2 for
/// details.
#[inline]
fn get_detect_shadows(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_getDetectShadows_const(self.as_raw_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the shadow value
///
/// Shadow value is the value used to mark shadows in the foreground mask. Default value is 127. Value 0
/// in the mask always means background, 255 means foreground.
#[inline]
fn get_shadow_value(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_getShadowValue_const(self.as_raw_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the shadow threshold
///
/// A shadow is detected if pixel is a darker version of the background. The shadow threshold (Tau in
/// the paper) is a threshold defining how much darker the shadow can be. Tau= 0.5 means that if a pixel
/// is more than twice darker then it is not shadow. See Prati, Mikic, Trivedi and Cucchiara,
/// *Detecting Moving Shadows...*, IEEE PAMI,2003.
#[inline]
fn get_shadow_threshold(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_getShadowThreshold_const(self.as_raw_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorMOG2]
pub trait BackgroundSubtractorMOG2Trait: crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorMOG2TraitConst + crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorTrait {
fn as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Sets the number of last frames that affect the background model
#[inline]
fn set_history(&mut self, history: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_setHistory_int(self.as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(), history, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the number of gaussian components in the background model.
///
/// The model needs to be reinitalized to reserve memory.
#[inline]
fn set_n_mixtures(&mut self, nmixtures: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_setNMixtures_int(self.as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(), nmixtures, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the "background ratio" parameter of the algorithm
#[inline]
fn set_background_ratio(&mut self, ratio: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_setBackgroundRatio_double(self.as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(), ratio, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the variance threshold for the pixel-model match
#[inline]
fn set_var_threshold(&mut self, var_threshold: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_setVarThreshold_double(self.as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(), var_threshold, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the variance threshold for the pixel-model match used for new mixture component generation
#[inline]
fn set_var_threshold_gen(&mut self, var_threshold_gen: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_setVarThresholdGen_double(self.as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(), var_threshold_gen, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the initial variance of each gaussian component
#[inline]
fn set_var_init(&mut self, var_init: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_setVarInit_double(self.as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(), var_init, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_var_min(&mut self, var_min: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_setVarMin_double(self.as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(), var_min, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_var_max(&mut self, var_max: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_setVarMax_double(self.as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(), var_max, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the complexity reduction threshold
#[inline]
fn set_complexity_reduction_threshold(&mut self, ct: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_setComplexityReductionThreshold_double(self.as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(), ct, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Enables or disables shadow detection
#[inline]
fn set_detect_shadows(&mut self, detect_shadows: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_setDetectShadows_bool(self.as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(), detect_shadows, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the shadow value
#[inline]
fn set_shadow_value(&mut self, value: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_setShadowValue_int(self.as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(), value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the shadow threshold
#[inline]
fn set_shadow_threshold(&mut self, threshold: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_setShadowThreshold_double(self.as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(), threshold, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes a foreground mask.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: Next video frame. Floating point frame will be used without scaling and should be in range 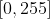.
/// * fgmask: The output foreground mask as an 8-bit binary image.
/// * learningRate: The value between 0 and 1 that indicates how fast the background model is
/// learnt. Negative parameter value makes the algorithm to use some automatically chosen learning
/// rate. 0 means that the background model is not updated at all, 1 means that the background model
/// is completely reinitialized from the last frame.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * learning_rate: -1
#[inline]
fn apply(&mut self, image: &impl ToInputArray, fgmask: &mut impl ToOutputArray, learning_rate: f64) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(image);
output_array_arg!(fgmask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_apply_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double(self.as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(), image.as_raw__InputArray(), fgmask.as_raw__OutputArray(), learning_rate, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes a foreground mask.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: Next video frame. Floating point frame will be used without scaling and should be in range 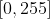.
/// * fgmask: The output foreground mask as an 8-bit binary image.
/// * learningRate: The value between 0 and 1 that indicates how fast the background model is
/// learnt. Negative parameter value makes the algorithm to use some automatically chosen learning
/// rate. 0 means that the background model is not updated at all, 1 means that the background model
/// is completely reinitialized from the last frame.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [BackgroundSubtractorMOG2Trait::apply] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * learning_rate: -1
#[inline]
fn apply_def(&mut self, image: &impl ToInputArray, fgmask: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(image);
output_array_arg!(fgmask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_apply_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(), image.as_raw__InputArray(), fgmask.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for BackgroundSubtractorMOG2 {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("BackgroundSubtractorMOG2")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { BackgroundSubtractorMOG2, core::Algorithm, cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_to_Algorithm }
boxed_cast_base! { BackgroundSubtractorMOG2, crate::video::BackgroundSubtractor, cv_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2_to_BackgroundSubtractor }
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for BackgroundSubtractorMOG2 {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for BackgroundSubtractorMOG2 {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { BackgroundSubtractorMOG2, core::AlgorithmTraitConst, as_raw_Algorithm, core::AlgorithmTrait, as_raw_mut_Algorithm }
impl crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorTraitConst for BackgroundSubtractorMOG2 {
#[inline] fn as_raw_BackgroundSubtractor(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorTrait for BackgroundSubtractorMOG2 {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractor(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { BackgroundSubtractorMOG2, crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorTraitConst, as_raw_BackgroundSubtractor, crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorTrait, as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractor }
impl crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorMOG2TraitConst for BackgroundSubtractorMOG2 {
#[inline] fn as_raw_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorMOG2Trait for BackgroundSubtractorMOG2 {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { BackgroundSubtractorMOG2, crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorMOG2TraitConst, as_raw_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2, crate::video::BackgroundSubtractorMOG2Trait, as_raw_mut_BackgroundSubtractorMOG2 }
/// DIS optical flow algorithm.
///
/// This class implements the Dense Inverse Search (DIS) optical flow algorithm. More
/// details about the algorithm can be found at [Kroeger2016](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Kroeger2016) . Includes three presets with preselected
/// parameters to provide reasonable trade-off between speed and quality. However, even the slowest preset is
/// still relatively fast, use DeepFlow if you need better quality and don't care about speed.
///
/// This implementation includes several additional features compared to the algorithm described in the paper,
/// including spatial propagation of flow vectors ([getUseSpatialPropagation]), as well as an option to
/// utilize an initial flow approximation passed to [calc] (which is, essentially, temporal propagation,
/// if the previous frame's flow field is passed).
pub struct DISOpticalFlow {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { DISOpticalFlow }
impl Drop for DISOpticalFlow {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_DISOpticalFlow_delete(self.as_raw_mut_DISOpticalFlow()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for DISOpticalFlow {}
impl DISOpticalFlow {
/// Creates an instance of DISOpticalFlow
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * preset: one of PRESET_ULTRAFAST, PRESET_FAST and PRESET_MEDIUM
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * preset: DISOpticalFlow::PRESET_FAST
#[inline]
pub fn create(preset: i32) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::video::DISOpticalFlow>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DISOpticalFlow_create_int(preset, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::video::DISOpticalFlow>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates an instance of DISOpticalFlow
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * preset: one of PRESET_ULTRAFAST, PRESET_FAST and PRESET_MEDIUM
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [DISOpticalFlow::create] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * preset: DISOpticalFlow::PRESET_FAST
#[inline]
pub fn create_def() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::video::DISOpticalFlow>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DISOpticalFlow_create(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::video::DISOpticalFlow>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::video::DISOpticalFlow]
pub trait DISOpticalFlowTraitConst: crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowTraitConst {
fn as_raw_DISOpticalFlow(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Finest level of the Gaussian pyramid on which the flow is computed (zero level
/// corresponds to the original image resolution). The final flow is obtained by bilinear upscaling.
/// ## See also
/// setFinestScale
#[inline]
fn get_finest_scale(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DISOpticalFlow_getFinestScale_const(self.as_raw_DISOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Size of an image patch for matching (in pixels). Normally, default 8x8 patches work well
/// enough in most cases.
/// ## See also
/// setPatchSize
#[inline]
fn get_patch_size(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DISOpticalFlow_getPatchSize_const(self.as_raw_DISOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Stride between neighbor patches. Must be less than patch size. Lower values correspond
/// to higher flow quality.
/// ## See also
/// setPatchStride
#[inline]
fn get_patch_stride(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DISOpticalFlow_getPatchStride_const(self.as_raw_DISOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Maximum number of gradient descent iterations in the patch inverse search stage. Higher values
/// may improve quality in some cases.
/// ## See also
/// setGradientDescentIterations
#[inline]
fn get_gradient_descent_iterations(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DISOpticalFlow_getGradientDescentIterations_const(self.as_raw_DISOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Number of fixed point iterations of variational refinement per scale. Set to zero to
/// disable variational refinement completely. Higher values will typically result in more smooth and
/// high-quality flow.
/// ## See also
/// setGradientDescentIterations
#[inline]
fn get_variational_refinement_iterations(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DISOpticalFlow_getVariationalRefinementIterations_const(self.as_raw_DISOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Weight of the smoothness term
/// ## See also
/// setVariationalRefinementAlpha
#[inline]
fn get_variational_refinement_alpha(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DISOpticalFlow_getVariationalRefinementAlpha_const(self.as_raw_DISOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Weight of the color constancy term
/// ## See also
/// setVariationalRefinementDelta
#[inline]
fn get_variational_refinement_delta(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DISOpticalFlow_getVariationalRefinementDelta_const(self.as_raw_DISOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Weight of the gradient constancy term
/// ## See also
/// setVariationalRefinementGamma
#[inline]
fn get_variational_refinement_gamma(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DISOpticalFlow_getVariationalRefinementGamma_const(self.as_raw_DISOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Norm value shift for robust penalizer
/// ## See also
/// setVariationalRefinementEpsilon
#[inline]
fn get_variational_refinement_epsilon(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DISOpticalFlow_getVariationalRefinementEpsilon_const(self.as_raw_DISOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Whether to use mean-normalization of patches when computing patch distance. It is turned on
/// by default as it typically provides a noticeable quality boost because of increased robustness to
/// illumination variations. Turn it off if you are certain that your sequence doesn't contain any changes
/// in illumination.
/// ## See also
/// setUseMeanNormalization
#[inline]
fn get_use_mean_normalization(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DISOpticalFlow_getUseMeanNormalization_const(self.as_raw_DISOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Whether to use spatial propagation of good optical flow vectors. This option is turned on by
/// default, as it tends to work better on average and can sometimes help recover from major errors
/// introduced by the coarse-to-fine scheme employed by the DIS optical flow algorithm. Turning this
/// option off can make the output flow field a bit smoother, however.
/// ## See also
/// setUseSpatialPropagation
#[inline]
fn get_use_spatial_propagation(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DISOpticalFlow_getUseSpatialPropagation_const(self.as_raw_DISOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::video::DISOpticalFlow]
pub trait DISOpticalFlowTrait: crate::video::DISOpticalFlowTraitConst + crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowTrait {
fn as_raw_mut_DISOpticalFlow(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Finest level of the Gaussian pyramid on which the flow is computed (zero level
/// corresponds to the original image resolution). The final flow is obtained by bilinear upscaling.
/// ## See also
/// setFinestScale getFinestScale
#[inline]
fn set_finest_scale(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DISOpticalFlow_setFinestScale_int(self.as_raw_mut_DISOpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Size of an image patch for matching (in pixels). Normally, default 8x8 patches work well
/// enough in most cases.
/// ## See also
/// setPatchSize getPatchSize
#[inline]
fn set_patch_size(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DISOpticalFlow_setPatchSize_int(self.as_raw_mut_DISOpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Stride between neighbor patches. Must be less than patch size. Lower values correspond
/// to higher flow quality.
/// ## See also
/// setPatchStride getPatchStride
#[inline]
fn set_patch_stride(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DISOpticalFlow_setPatchStride_int(self.as_raw_mut_DISOpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Maximum number of gradient descent iterations in the patch inverse search stage. Higher values
/// may improve quality in some cases.
/// ## See also
/// setGradientDescentIterations getGradientDescentIterations
#[inline]
fn set_gradient_descent_iterations(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DISOpticalFlow_setGradientDescentIterations_int(self.as_raw_mut_DISOpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Maximum number of gradient descent iterations in the patch inverse search stage. Higher values
/// may improve quality in some cases.
/// ## See also
/// setGradientDescentIterations getGradientDescentIterations
#[inline]
fn set_variational_refinement_iterations(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DISOpticalFlow_setVariationalRefinementIterations_int(self.as_raw_mut_DISOpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Weight of the smoothness term
/// ## See also
/// setVariationalRefinementAlpha getVariationalRefinementAlpha
#[inline]
fn set_variational_refinement_alpha(&mut self, val: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DISOpticalFlow_setVariationalRefinementAlpha_float(self.as_raw_mut_DISOpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Weight of the color constancy term
/// ## See also
/// setVariationalRefinementDelta getVariationalRefinementDelta
#[inline]
fn set_variational_refinement_delta(&mut self, val: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DISOpticalFlow_setVariationalRefinementDelta_float(self.as_raw_mut_DISOpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Weight of the gradient constancy term
/// ## See also
/// setVariationalRefinementGamma getVariationalRefinementGamma
#[inline]
fn set_variational_refinement_gamma(&mut self, val: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DISOpticalFlow_setVariationalRefinementGamma_float(self.as_raw_mut_DISOpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Norm value shift for robust penalizer
/// ## See also
/// setVariationalRefinementEpsilon getVariationalRefinementEpsilon
#[inline]
fn set_variational_refinement_epsilon(&mut self, val: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DISOpticalFlow_setVariationalRefinementEpsilon_float(self.as_raw_mut_DISOpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Whether to use mean-normalization of patches when computing patch distance. It is turned on
/// by default as it typically provides a noticeable quality boost because of increased robustness to
/// illumination variations. Turn it off if you are certain that your sequence doesn't contain any changes
/// in illumination.
/// ## See also
/// setUseMeanNormalization getUseMeanNormalization
#[inline]
fn set_use_mean_normalization(&mut self, val: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DISOpticalFlow_setUseMeanNormalization_bool(self.as_raw_mut_DISOpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Whether to use spatial propagation of good optical flow vectors. This option is turned on by
/// default, as it tends to work better on average and can sometimes help recover from major errors
/// introduced by the coarse-to-fine scheme employed by the DIS optical flow algorithm. Turning this
/// option off can make the output flow field a bit smoother, however.
/// ## See also
/// setUseSpatialPropagation getUseSpatialPropagation
#[inline]
fn set_use_spatial_propagation(&mut self, val: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DISOpticalFlow_setUseSpatialPropagation_bool(self.as_raw_mut_DISOpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for DISOpticalFlow {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("DISOpticalFlow")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { DISOpticalFlow, core::Algorithm, cv_DISOpticalFlow_to_Algorithm }
boxed_cast_base! { DISOpticalFlow, crate::video::DenseOpticalFlow, cv_DISOpticalFlow_to_DenseOpticalFlow }
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for DISOpticalFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for DISOpticalFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { DISOpticalFlow, core::AlgorithmTraitConst, as_raw_Algorithm, core::AlgorithmTrait, as_raw_mut_Algorithm }
impl crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowTraitConst for DISOpticalFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_DenseOpticalFlow(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowTrait for DISOpticalFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_DenseOpticalFlow(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { DISOpticalFlow, crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowTraitConst, as_raw_DenseOpticalFlow, crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowTrait, as_raw_mut_DenseOpticalFlow }
impl crate::video::DISOpticalFlowTraitConst for DISOpticalFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_DISOpticalFlow(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::DISOpticalFlowTrait for DISOpticalFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_DISOpticalFlow(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { DISOpticalFlow, crate::video::DISOpticalFlowTraitConst, as_raw_DISOpticalFlow, crate::video::DISOpticalFlowTrait, as_raw_mut_DISOpticalFlow }
/// Base class for dense optical flow algorithms
pub struct DenseOpticalFlow {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { DenseOpticalFlow }
impl Drop for DenseOpticalFlow {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_DenseOpticalFlow_delete(self.as_raw_mut_DenseOpticalFlow()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for DenseOpticalFlow {}
/// Constant methods for [crate::video::DenseOpticalFlow]
pub trait DenseOpticalFlowTraitConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_DenseOpticalFlow(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::video::DenseOpticalFlow]
pub trait DenseOpticalFlowTrait: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_DenseOpticalFlow(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Calculates an optical flow.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * I0: first 8-bit single-channel input image.
/// * I1: second input image of the same size and the same type as prev.
/// * flow: computed flow image that has the same size as prev and type CV_32FC2.
#[inline]
fn calc(&mut self, i0: &impl ToInputArray, i1: &impl ToInputArray, flow: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(i0);
input_array_arg!(i1);
input_output_array_arg!(flow);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DenseOpticalFlow_calc_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_DenseOpticalFlow(), i0.as_raw__InputArray(), i1.as_raw__InputArray(), flow.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Releases all inner buffers.
#[inline]
fn collect_garbage(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DenseOpticalFlow_collectGarbage(self.as_raw_mut_DenseOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for DenseOpticalFlow {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("DenseOpticalFlow")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { DenseOpticalFlow, core::Algorithm, cv_DenseOpticalFlow_to_Algorithm }
boxed_cast_descendant! { DenseOpticalFlow, crate::video::DISOpticalFlow, cv_DenseOpticalFlow_to_DISOpticalFlow }
boxed_cast_descendant! { DenseOpticalFlow, crate::video::FarnebackOpticalFlow, cv_DenseOpticalFlow_to_FarnebackOpticalFlow }
boxed_cast_descendant! { DenseOpticalFlow, crate::video::VariationalRefinement, cv_DenseOpticalFlow_to_VariationalRefinement }
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for DenseOpticalFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for DenseOpticalFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { DenseOpticalFlow, core::AlgorithmTraitConst, as_raw_Algorithm, core::AlgorithmTrait, as_raw_mut_Algorithm }
impl crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowTraitConst for DenseOpticalFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_DenseOpticalFlow(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowTrait for DenseOpticalFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_DenseOpticalFlow(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { DenseOpticalFlow, crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowTraitConst, as_raw_DenseOpticalFlow, crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowTrait, as_raw_mut_DenseOpticalFlow }
/// Class computing a dense optical flow using the Gunnar Farneback's algorithm.
pub struct FarnebackOpticalFlow {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { FarnebackOpticalFlow }
impl Drop for FarnebackOpticalFlow {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_FarnebackOpticalFlow_delete(self.as_raw_mut_FarnebackOpticalFlow()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for FarnebackOpticalFlow {}
impl FarnebackOpticalFlow {
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * num_levels: 5
/// * pyr_scale: 0.5
/// * fast_pyramids: false
/// * win_size: 13
/// * num_iters: 10
/// * poly_n: 5
/// * poly_sigma: 1.1
/// * flags: 0
#[inline]
pub fn create(num_levels: i32, pyr_scale: f64, fast_pyramids: bool, win_size: i32, num_iters: i32, poly_n: i32, poly_sigma: f64, flags: i32) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::video::FarnebackOpticalFlow>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FarnebackOpticalFlow_create_int_double_bool_int_int_int_double_int(num_levels, pyr_scale, fast_pyramids, win_size, num_iters, poly_n, poly_sigma, flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::video::FarnebackOpticalFlow>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [FarnebackOpticalFlow::create] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * num_levels: 5
/// * pyr_scale: 0.5
/// * fast_pyramids: false
/// * win_size: 13
/// * num_iters: 10
/// * poly_n: 5
/// * poly_sigma: 1.1
/// * flags: 0
#[inline]
pub fn create_def() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::video::FarnebackOpticalFlow>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FarnebackOpticalFlow_create(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::video::FarnebackOpticalFlow>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::video::FarnebackOpticalFlow]
pub trait FarnebackOpticalFlowTraitConst: crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowTraitConst {
fn as_raw_FarnebackOpticalFlow(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn get_num_levels(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FarnebackOpticalFlow_getNumLevels_const(self.as_raw_FarnebackOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_pyr_scale(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FarnebackOpticalFlow_getPyrScale_const(self.as_raw_FarnebackOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_fast_pyramids(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FarnebackOpticalFlow_getFastPyramids_const(self.as_raw_FarnebackOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_win_size(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FarnebackOpticalFlow_getWinSize_const(self.as_raw_FarnebackOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_num_iters(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FarnebackOpticalFlow_getNumIters_const(self.as_raw_FarnebackOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_poly_n(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FarnebackOpticalFlow_getPolyN_const(self.as_raw_FarnebackOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_poly_sigma(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FarnebackOpticalFlow_getPolySigma_const(self.as_raw_FarnebackOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_flags(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FarnebackOpticalFlow_getFlags_const(self.as_raw_FarnebackOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::video::FarnebackOpticalFlow]
pub trait FarnebackOpticalFlowTrait: crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowTrait + crate::video::FarnebackOpticalFlowTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_FarnebackOpticalFlow(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_num_levels(&mut self, num_levels: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FarnebackOpticalFlow_setNumLevels_int(self.as_raw_mut_FarnebackOpticalFlow(), num_levels, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_pyr_scale(&mut self, pyr_scale: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FarnebackOpticalFlow_setPyrScale_double(self.as_raw_mut_FarnebackOpticalFlow(), pyr_scale, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_fast_pyramids(&mut self, fast_pyramids: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FarnebackOpticalFlow_setFastPyramids_bool(self.as_raw_mut_FarnebackOpticalFlow(), fast_pyramids, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_win_size(&mut self, win_size: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FarnebackOpticalFlow_setWinSize_int(self.as_raw_mut_FarnebackOpticalFlow(), win_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_num_iters(&mut self, num_iters: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FarnebackOpticalFlow_setNumIters_int(self.as_raw_mut_FarnebackOpticalFlow(), num_iters, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_poly_n(&mut self, poly_n: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FarnebackOpticalFlow_setPolyN_int(self.as_raw_mut_FarnebackOpticalFlow(), poly_n, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_poly_sigma(&mut self, poly_sigma: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FarnebackOpticalFlow_setPolySigma_double(self.as_raw_mut_FarnebackOpticalFlow(), poly_sigma, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_flags(&mut self, flags: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FarnebackOpticalFlow_setFlags_int(self.as_raw_mut_FarnebackOpticalFlow(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for FarnebackOpticalFlow {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("FarnebackOpticalFlow")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { FarnebackOpticalFlow, core::Algorithm, cv_FarnebackOpticalFlow_to_Algorithm }
boxed_cast_base! { FarnebackOpticalFlow, crate::video::DenseOpticalFlow, cv_FarnebackOpticalFlow_to_DenseOpticalFlow }
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for FarnebackOpticalFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for FarnebackOpticalFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { FarnebackOpticalFlow, core::AlgorithmTraitConst, as_raw_Algorithm, core::AlgorithmTrait, as_raw_mut_Algorithm }
impl crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowTraitConst for FarnebackOpticalFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_DenseOpticalFlow(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowTrait for FarnebackOpticalFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_DenseOpticalFlow(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { FarnebackOpticalFlow, crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowTraitConst, as_raw_DenseOpticalFlow, crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowTrait, as_raw_mut_DenseOpticalFlow }
impl crate::video::FarnebackOpticalFlowTraitConst for FarnebackOpticalFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_FarnebackOpticalFlow(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::FarnebackOpticalFlowTrait for FarnebackOpticalFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_FarnebackOpticalFlow(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { FarnebackOpticalFlow, crate::video::FarnebackOpticalFlowTraitConst, as_raw_FarnebackOpticalFlow, crate::video::FarnebackOpticalFlowTrait, as_raw_mut_FarnebackOpticalFlow }
/// Kalman filter class.
///
/// The class implements a standard Kalman filter <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kalman_filter>,
/// [Welch95](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Welch95) . However, you can modify transitionMatrix, controlMatrix, and measurementMatrix to get
/// an extended Kalman filter functionality.
///
/// Note: In C API when CvKalman\* kalmanFilter structure is not needed anymore, it should be released
/// with cvReleaseKalman(&kalmanFilter)
pub struct KalmanFilter {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { KalmanFilter }
impl Drop for KalmanFilter {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_delete(self.as_raw_mut_KalmanFilter()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for KalmanFilter {}
impl KalmanFilter {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<crate::video::KalmanFilter> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_KalmanFilter(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { crate::video::KalmanFilter::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
/// ## Parameters
/// * dynamParams: Dimensionality of the state.
/// * measureParams: Dimensionality of the measurement.
/// * controlParams: Dimensionality of the control vector.
/// * type: Type of the created matrices that should be CV_32F or CV_64F.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * control_params: 0
/// * typ: CV_32F
#[inline]
pub fn new(dynam_params: i32, measure_params: i32, control_params: i32, typ: i32) -> Result<crate::video::KalmanFilter> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_KalmanFilter_int_int_int_int(dynam_params, measure_params, control_params, typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { crate::video::KalmanFilter::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// @overload
/// ## Parameters
/// * dynamParams: Dimensionality of the state.
/// * measureParams: Dimensionality of the measurement.
/// * controlParams: Dimensionality of the control vector.
/// * type: Type of the created matrices that should be CV_32F or CV_64F.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [new] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * control_params: 0
/// * typ: CV_32F
#[inline]
pub fn new_def(dynam_params: i32, measure_params: i32) -> Result<crate::video::KalmanFilter> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_KalmanFilter_int_int(dynam_params, measure_params, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { crate::video::KalmanFilter::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::video::KalmanFilter]
pub trait KalmanFilterTraitConst {
fn as_raw_KalmanFilter(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// predicted state (x'(k)): x(k)=A*x(k-1)+B*u(k)
#[inline]
fn state_pre(&self) -> core::Mat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propStatePre_const(self.as_raw_KalmanFilter()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// corrected state (x(k)): x(k)=x'(k)+K(k)*(z(k)-H*x'(k))
#[inline]
fn state_post(&self) -> core::Mat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propStatePost_const(self.as_raw_KalmanFilter()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// state transition matrix (A)
#[inline]
fn transition_matrix(&self) -> core::Mat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propTransitionMatrix_const(self.as_raw_KalmanFilter()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// control matrix (B) (not used if there is no control)
#[inline]
fn control_matrix(&self) -> core::Mat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propControlMatrix_const(self.as_raw_KalmanFilter()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// measurement matrix (H)
#[inline]
fn measurement_matrix(&self) -> core::Mat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propMeasurementMatrix_const(self.as_raw_KalmanFilter()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// process noise covariance matrix (Q)
#[inline]
fn process_noise_cov(&self) -> core::Mat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propProcessNoiseCov_const(self.as_raw_KalmanFilter()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// measurement noise covariance matrix (R)
#[inline]
fn measurement_noise_cov(&self) -> core::Mat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propMeasurementNoiseCov_const(self.as_raw_KalmanFilter()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// priori error estimate covariance matrix (P'(k)): P'(k)=A*P(k-1)*At + Q)
#[inline]
fn error_cov_pre(&self) -> core::Mat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propErrorCovPre_const(self.as_raw_KalmanFilter()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// Kalman gain matrix (K(k)): K(k)=P'(k)*Ht*inv(H*P'(k)*Ht+R)
#[inline]
fn gain(&self) -> core::Mat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propGain_const(self.as_raw_KalmanFilter()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// posteriori error estimate covariance matrix (P(k)): P(k)=(I-K(k)*H)*P'(k)
#[inline]
fn error_cov_post(&self) -> core::Mat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propErrorCovPost_const(self.as_raw_KalmanFilter()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn temp1(&self) -> core::Mat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propTemp1_const(self.as_raw_KalmanFilter()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn temp2(&self) -> core::Mat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propTemp2_const(self.as_raw_KalmanFilter()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn temp3(&self) -> core::Mat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propTemp3_const(self.as_raw_KalmanFilter()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn temp4(&self) -> core::Mat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propTemp4_const(self.as_raw_KalmanFilter()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn temp5(&self) -> core::Mat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propTemp5_const(self.as_raw_KalmanFilter()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::video::KalmanFilter]
pub trait KalmanFilterTrait: crate::video::KalmanFilterTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_KalmanFilter(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// predicted state (x'(k)): x(k)=A*x(k-1)+B*u(k)
#[inline]
fn set_state_pre(&mut self, val: core::Mat) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propStatePre_const_Mat(self.as_raw_mut_KalmanFilter(), val.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// corrected state (x(k)): x(k)=x'(k)+K(k)*(z(k)-H*x'(k))
#[inline]
fn set_state_post(&mut self, val: core::Mat) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propStatePost_const_Mat(self.as_raw_mut_KalmanFilter(), val.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// state transition matrix (A)
#[inline]
fn set_transition_matrix(&mut self, val: core::Mat) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propTransitionMatrix_const_Mat(self.as_raw_mut_KalmanFilter(), val.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// control matrix (B) (not used if there is no control)
#[inline]
fn set_control_matrix(&mut self, val: core::Mat) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propControlMatrix_const_Mat(self.as_raw_mut_KalmanFilter(), val.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// measurement matrix (H)
#[inline]
fn set_measurement_matrix(&mut self, val: core::Mat) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propMeasurementMatrix_const_Mat(self.as_raw_mut_KalmanFilter(), val.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// process noise covariance matrix (Q)
#[inline]
fn set_process_noise_cov(&mut self, val: core::Mat) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propProcessNoiseCov_const_Mat(self.as_raw_mut_KalmanFilter(), val.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// measurement noise covariance matrix (R)
#[inline]
fn set_measurement_noise_cov(&mut self, val: core::Mat) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propMeasurementNoiseCov_const_Mat(self.as_raw_mut_KalmanFilter(), val.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// priori error estimate covariance matrix (P'(k)): P'(k)=A*P(k-1)*At + Q)
#[inline]
fn set_error_cov_pre(&mut self, val: core::Mat) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propErrorCovPre_const_Mat(self.as_raw_mut_KalmanFilter(), val.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// Kalman gain matrix (K(k)): K(k)=P'(k)*Ht*inv(H*P'(k)*Ht+R)
#[inline]
fn set_gain(&mut self, val: core::Mat) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propGain_const_Mat(self.as_raw_mut_KalmanFilter(), val.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// posteriori error estimate covariance matrix (P(k)): P(k)=(I-K(k)*H)*P'(k)
#[inline]
fn set_error_cov_post(&mut self, val: core::Mat) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propErrorCovPost_const_Mat(self.as_raw_mut_KalmanFilter(), val.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_temp1(&mut self, val: core::Mat) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propTemp1_const_Mat(self.as_raw_mut_KalmanFilter(), val.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_temp2(&mut self, val: core::Mat) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propTemp2_const_Mat(self.as_raw_mut_KalmanFilter(), val.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_temp3(&mut self, val: core::Mat) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propTemp3_const_Mat(self.as_raw_mut_KalmanFilter(), val.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_temp4(&mut self, val: core::Mat) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propTemp4_const_Mat(self.as_raw_mut_KalmanFilter(), val.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_temp5(&mut self, val: core::Mat) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_propTemp5_const_Mat(self.as_raw_mut_KalmanFilter(), val.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// Re-initializes Kalman filter. The previous content is destroyed.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * dynamParams: Dimensionality of the state.
/// * measureParams: Dimensionality of the measurement.
/// * controlParams: Dimensionality of the control vector.
/// * type: Type of the created matrices that should be CV_32F or CV_64F.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * control_params: 0
/// * typ: CV_32F
#[inline]
fn init(&mut self, dynam_params: i32, measure_params: i32, control_params: i32, typ: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_init_int_int_int_int(self.as_raw_mut_KalmanFilter(), dynam_params, measure_params, control_params, typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Re-initializes Kalman filter. The previous content is destroyed.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * dynamParams: Dimensionality of the state.
/// * measureParams: Dimensionality of the measurement.
/// * controlParams: Dimensionality of the control vector.
/// * type: Type of the created matrices that should be CV_32F or CV_64F.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [KalmanFilterTrait::init] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * control_params: 0
/// * typ: CV_32F
#[inline]
fn init_def(&mut self, dynam_params: i32, measure_params: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_init_int_int(self.as_raw_mut_KalmanFilter(), dynam_params, measure_params, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes a predicted state.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * control: The optional input control
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * control: Mat()
#[inline]
fn predict(&mut self, control: &impl core::MatTraitConst) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_predict_const_MatR(self.as_raw_mut_KalmanFilter(), control.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes a predicted state.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * control: The optional input control
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [KalmanFilterTrait::predict] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * control: Mat()
#[inline]
fn predict_def(&mut self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_predict(self.as_raw_mut_KalmanFilter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Updates the predicted state from the measurement.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * measurement: The measured system parameters
#[inline]
fn correct(&mut self, measurement: &impl core::MatTraitConst) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_KalmanFilter_correct_const_MatR(self.as_raw_mut_KalmanFilter(), measurement.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for KalmanFilter {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("KalmanFilter")
.field("state_pre", &crate::video::KalmanFilterTraitConst::state_pre(self))
.field("state_post", &crate::video::KalmanFilterTraitConst::state_post(self))
.field("transition_matrix", &crate::video::KalmanFilterTraitConst::transition_matrix(self))
.field("control_matrix", &crate::video::KalmanFilterTraitConst::control_matrix(self))
.field("measurement_matrix", &crate::video::KalmanFilterTraitConst::measurement_matrix(self))
.field("process_noise_cov", &crate::video::KalmanFilterTraitConst::process_noise_cov(self))
.field("measurement_noise_cov", &crate::video::KalmanFilterTraitConst::measurement_noise_cov(self))
.field("error_cov_pre", &crate::video::KalmanFilterTraitConst::error_cov_pre(self))
.field("gain", &crate::video::KalmanFilterTraitConst::gain(self))
.field("error_cov_post", &crate::video::KalmanFilterTraitConst::error_cov_post(self))
.field("temp1", &crate::video::KalmanFilterTraitConst::temp1(self))
.field("temp2", &crate::video::KalmanFilterTraitConst::temp2(self))
.field("temp3", &crate::video::KalmanFilterTraitConst::temp3(self))
.field("temp4", &crate::video::KalmanFilterTraitConst::temp4(self))
.field("temp5", &crate::video::KalmanFilterTraitConst::temp5(self))
.finish()
}
}
impl crate::video::KalmanFilterTraitConst for KalmanFilter {
#[inline] fn as_raw_KalmanFilter(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::KalmanFilterTrait for KalmanFilter {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_KalmanFilter(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { KalmanFilter, crate::video::KalmanFilterTraitConst, as_raw_KalmanFilter, crate::video::KalmanFilterTrait, as_raw_mut_KalmanFilter }
/// Base interface for sparse optical flow algorithms.
pub struct SparseOpticalFlow {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { SparseOpticalFlow }
impl Drop for SparseOpticalFlow {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseOpticalFlow_delete(self.as_raw_mut_SparseOpticalFlow()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for SparseOpticalFlow {}
/// Constant methods for [crate::video::SparseOpticalFlow]
pub trait SparseOpticalFlowTraitConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_SparseOpticalFlow(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::video::SparseOpticalFlow]
pub trait SparseOpticalFlowTrait: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::video::SparseOpticalFlowTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_SparseOpticalFlow(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Calculates a sparse optical flow.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * prevImg: First input image.
/// * nextImg: Second input image of the same size and the same type as prevImg.
/// * prevPts: Vector of 2D points for which the flow needs to be found.
/// * nextPts: Output vector of 2D points containing the calculated new positions of input features in the second image.
/// * status: Output status vector. Each element of the vector is set to 1 if the
/// flow for the corresponding features has been found. Otherwise, it is set to 0.
/// * err: Optional output vector that contains error response for each point (inverse confidence).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * err: cv::noArray()
#[inline]
fn calc(&mut self, prev_img: &impl ToInputArray, next_img: &impl ToInputArray, prev_pts: &impl ToInputArray, next_pts: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, status: &mut impl ToOutputArray, err: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(prev_img);
input_array_arg!(next_img);
input_array_arg!(prev_pts);
input_output_array_arg!(next_pts);
output_array_arg!(status);
output_array_arg!(err);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseOpticalFlow_calc_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_SparseOpticalFlow(), prev_img.as_raw__InputArray(), next_img.as_raw__InputArray(), prev_pts.as_raw__InputArray(), next_pts.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), status.as_raw__OutputArray(), err.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates a sparse optical flow.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * prevImg: First input image.
/// * nextImg: Second input image of the same size and the same type as prevImg.
/// * prevPts: Vector of 2D points for which the flow needs to be found.
/// * nextPts: Output vector of 2D points containing the calculated new positions of input features in the second image.
/// * status: Output status vector. Each element of the vector is set to 1 if the
/// flow for the corresponding features has been found. Otherwise, it is set to 0.
/// * err: Optional output vector that contains error response for each point (inverse confidence).
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [SparseOpticalFlowTrait::calc] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * err: cv::noArray()
#[inline]
fn calc_def(&mut self, prev_img: &impl ToInputArray, next_img: &impl ToInputArray, prev_pts: &impl ToInputArray, next_pts: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, status: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(prev_img);
input_array_arg!(next_img);
input_array_arg!(prev_pts);
input_output_array_arg!(next_pts);
output_array_arg!(status);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseOpticalFlow_calc_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_SparseOpticalFlow(), prev_img.as_raw__InputArray(), next_img.as_raw__InputArray(), prev_pts.as_raw__InputArray(), next_pts.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), status.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for SparseOpticalFlow {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("SparseOpticalFlow")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { SparseOpticalFlow, core::Algorithm, cv_SparseOpticalFlow_to_Algorithm }
boxed_cast_descendant! { SparseOpticalFlow, crate::video::SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow, cv_SparseOpticalFlow_to_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow }
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for SparseOpticalFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for SparseOpticalFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { SparseOpticalFlow, core::AlgorithmTraitConst, as_raw_Algorithm, core::AlgorithmTrait, as_raw_mut_Algorithm }
impl crate::video::SparseOpticalFlowTraitConst for SparseOpticalFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_SparseOpticalFlow(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::SparseOpticalFlowTrait for SparseOpticalFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_SparseOpticalFlow(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { SparseOpticalFlow, crate::video::SparseOpticalFlowTraitConst, as_raw_SparseOpticalFlow, crate::video::SparseOpticalFlowTrait, as_raw_mut_SparseOpticalFlow }
/// Class used for calculating a sparse optical flow.
///
/// The class can calculate an optical flow for a sparse feature set using the
/// iterative Lucas-Kanade method with pyramids.
/// ## See also
/// calcOpticalFlowPyrLK
pub struct SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow }
impl Drop for SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow_delete(self.as_raw_mut_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow {}
impl SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow {
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * win_size: Size(21,21)
/// * max_level: 3
/// * crit: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,30,0.01)
/// * flags: 0
/// * min_eig_threshold: 1e-4
#[inline]
pub fn create(win_size: core::Size, max_level: i32, crit: core::TermCriteria, flags: i32, min_eig_threshold: f64) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::video::SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow_create_Size_int_TermCriteria_int_double(&win_size, max_level, &crit, flags, min_eig_threshold, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::video::SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow::create] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * win_size: Size(21,21)
/// * max_level: 3
/// * crit: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,30,0.01)
/// * flags: 0
/// * min_eig_threshold: 1e-4
#[inline]
pub fn create_def() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::video::SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow_create(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::video::SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::video::SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow]
pub trait SparsePyrLKOpticalFlowTraitConst: crate::video::SparseOpticalFlowTraitConst {
fn as_raw_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn get_win_size(&self) -> Result<core::Size> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow_getWinSize_const(self.as_raw_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_max_level(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow_getMaxLevel_const(self.as_raw_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_term_criteria(&self) -> Result<core::TermCriteria> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow_getTermCriteria_const(self.as_raw_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_flags(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow_getFlags_const(self.as_raw_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_min_eig_threshold(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow_getMinEigThreshold_const(self.as_raw_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::video::SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow]
pub trait SparsePyrLKOpticalFlowTrait: crate::video::SparseOpticalFlowTrait + crate::video::SparsePyrLKOpticalFlowTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_win_size(&mut self, win_size: core::Size) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow_setWinSize_Size(self.as_raw_mut_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow(), &win_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_max_level(&mut self, max_level: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow_setMaxLevel_int(self.as_raw_mut_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow(), max_level, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_term_criteria(&mut self, crit: &mut core::TermCriteria) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow_setTermCriteria_TermCriteriaR(self.as_raw_mut_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow(), crit, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_flags(&mut self, flags: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow_setFlags_int(self.as_raw_mut_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_min_eig_threshold(&mut self, min_eig_threshold: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow_setMinEigThreshold_double(self.as_raw_mut_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow(), min_eig_threshold, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow, core::Algorithm, cv_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow_to_Algorithm }
boxed_cast_base! { SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow, crate::video::SparseOpticalFlow, cv_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow_to_SparseOpticalFlow }
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow, core::AlgorithmTraitConst, as_raw_Algorithm, core::AlgorithmTrait, as_raw_mut_Algorithm }
impl crate::video::SparseOpticalFlowTraitConst for SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_SparseOpticalFlow(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::SparseOpticalFlowTrait for SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_SparseOpticalFlow(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow, crate::video::SparseOpticalFlowTraitConst, as_raw_SparseOpticalFlow, crate::video::SparseOpticalFlowTrait, as_raw_mut_SparseOpticalFlow }
impl crate::video::SparsePyrLKOpticalFlowTraitConst for SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::SparsePyrLKOpticalFlowTrait for SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow, crate::video::SparsePyrLKOpticalFlowTraitConst, as_raw_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow, crate::video::SparsePyrLKOpticalFlowTrait, as_raw_mut_SparsePyrLKOpticalFlow }
/// Base abstract class for the long-term tracker
pub struct Tracker {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Tracker }
impl Drop for Tracker {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_Tracker_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Tracker()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Tracker {}
/// Constant methods for [crate::video::Tracker]
pub trait TrackerTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Tracker(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::video::Tracker]
pub trait TrackerTrait: crate::video::TrackerTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Tracker(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Initialize the tracker with a known bounding box that surrounded the target
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: The initial frame
/// * boundingBox: The initial bounding box
#[inline]
fn init(&mut self, image: &impl ToInputArray, bounding_box: core::Rect) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(image);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Tracker_init_const__InputArrayR_const_RectR(self.as_raw_mut_Tracker(), image.as_raw__InputArray(), &bounding_box, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Update the tracker, find the new most likely bounding box for the target
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: The current frame
/// * boundingBox: The bounding box that represent the new target location, if true was returned, not
/// modified otherwise
///
/// ## Returns
/// True means that target was located and false means that tracker cannot locate target in
/// current frame. Note, that latter *does not* imply that tracker has failed, maybe target is indeed
/// missing from the frame (say, out of sight)
#[inline]
fn update(&mut self, image: &impl ToInputArray, bounding_box: &mut core::Rect) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(image);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Tracker_update_const__InputArrayR_RectR(self.as_raw_mut_Tracker(), image.as_raw__InputArray(), bounding_box, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for Tracker {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("Tracker")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_descendant! { Tracker, crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPN, cv_Tracker_to_TrackerDaSiamRPN }
boxed_cast_descendant! { Tracker, crate::video::TrackerGOTURN, cv_Tracker_to_TrackerGOTURN }
boxed_cast_descendant! { Tracker, crate::video::TrackerMIL, cv_Tracker_to_TrackerMIL }
boxed_cast_descendant! { Tracker, crate::video::TrackerNano, cv_Tracker_to_TrackerNano }
boxed_cast_descendant! { Tracker, crate::video::TrackerVit, cv_Tracker_to_TrackerVit }
impl crate::video::TrackerTraitConst for Tracker {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Tracker(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::TrackerTrait for Tracker {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Tracker(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { Tracker, crate::video::TrackerTraitConst, as_raw_Tracker, crate::video::TrackerTrait, as_raw_mut_Tracker }
pub struct TrackerDaSiamRPN {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { TrackerDaSiamRPN }
impl Drop for TrackerDaSiamRPN {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerDaSiamRPN_delete(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerDaSiamRPN()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for TrackerDaSiamRPN {}
impl TrackerDaSiamRPN {
/// Constructor
/// ## Parameters
/// * parameters: DaSiamRPN parameters TrackerDaSiamRPN::Params
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * parameters: TrackerDaSiamRPN::Params()
#[inline]
pub fn create(parameters: &impl crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPN_ParamsTraitConst) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPN>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerDaSiamRPN_create_const_ParamsR(parameters.as_raw_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPN>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Constructor
/// ## Parameters
/// * parameters: DaSiamRPN parameters TrackerDaSiamRPN::Params
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [TrackerDaSiamRPN::create] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * parameters: TrackerDaSiamRPN::Params()
#[inline]
pub fn create_def() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPN>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerDaSiamRPN_create(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPN>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPN]
pub trait TrackerDaSiamRPNTraitConst: crate::video::TrackerTraitConst {
fn as_raw_TrackerDaSiamRPN(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPN]
pub trait TrackerDaSiamRPNTrait: crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPNTraitConst + crate::video::TrackerTrait {
fn as_raw_mut_TrackerDaSiamRPN(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Return tracking score
#[inline]
fn get_tracking_score(&mut self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerDaSiamRPN_getTrackingScore(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerDaSiamRPN(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for TrackerDaSiamRPN {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("TrackerDaSiamRPN")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { TrackerDaSiamRPN, crate::video::Tracker, cv_TrackerDaSiamRPN_to_Tracker }
impl crate::video::TrackerTraitConst for TrackerDaSiamRPN {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Tracker(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::TrackerTrait for TrackerDaSiamRPN {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Tracker(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { TrackerDaSiamRPN, crate::video::TrackerTraitConst, as_raw_Tracker, crate::video::TrackerTrait, as_raw_mut_Tracker }
impl crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPNTraitConst for TrackerDaSiamRPN {
#[inline] fn as_raw_TrackerDaSiamRPN(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPNTrait for TrackerDaSiamRPN {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_TrackerDaSiamRPN(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { TrackerDaSiamRPN, crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPNTraitConst, as_raw_TrackerDaSiamRPN, crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPNTrait, as_raw_mut_TrackerDaSiamRPN }
pub struct TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params }
impl Drop for TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params_delete(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params {}
impl TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params_Params(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params]
pub trait TrackerDaSiamRPN_ParamsTraitConst {
fn as_raw_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn model(&self) -> String {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params_propModel_const(self.as_raw_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params()) };
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn kernel_cls1(&self) -> String {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params_propKernel_cls1_const(self.as_raw_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params()) };
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn kernel_r1(&self) -> String {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params_propKernel_r1_const(self.as_raw_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params()) };
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn backend(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params_propBackend_const(self.as_raw_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn target(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params_propTarget_const(self.as_raw_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params()) };
ret
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params]
pub trait TrackerDaSiamRPN_ParamsTrait: crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPN_ParamsTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_model(&mut self, val: &str) {
extern_container_arg!(nofail val);
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params_propModel_const_string(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params(), val.opencv_as_extern()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_kernel_cls1(&mut self, val: &str) {
extern_container_arg!(nofail val);
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params_propKernel_cls1_const_string(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params(), val.opencv_as_extern()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_kernel_r1(&mut self, val: &str) {
extern_container_arg!(nofail val);
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params_propKernel_r1_const_string(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params(), val.opencv_as_extern()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_backend(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params_propBackend_const_int(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_target(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params_propTarget_const_int(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params(), val) };
ret
}
}
impl Clone for TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params {
#[inline]
fn clone(&self) -> Self {
unsafe { Self::from_raw(sys::cv_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params_implicitClone_const(self.as_raw_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params())) }
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params")
.field("model", &crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPN_ParamsTraitConst::model(self))
.field("kernel_cls1", &crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPN_ParamsTraitConst::kernel_cls1(self))
.field("kernel_r1", &crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPN_ParamsTraitConst::kernel_r1(self))
.field("backend", &crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPN_ParamsTraitConst::backend(self))
.field("target", &crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPN_ParamsTraitConst::target(self))
.finish()
}
}
impl crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPN_ParamsTraitConst for TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params {
#[inline] fn as_raw_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPN_ParamsTrait for TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params, crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPN_ParamsTraitConst, as_raw_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params, crate::video::TrackerDaSiamRPN_ParamsTrait, as_raw_mut_TrackerDaSiamRPN_Params }
/// the GOTURN (Generic Object Tracking Using Regression Networks) tracker
///
/// GOTURN ([GOTURN](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_GOTURN)) is kind of trackers based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN). While taking all advantages of CNN trackers,
/// GOTURN is much faster due to offline training without online fine-tuning nature.
/// GOTURN tracker addresses the problem of single target tracking: given a bounding box label of an object in the first frame of the video,
/// we track that object through the rest of the video. NOTE: Current method of GOTURN does not handle occlusions; however, it is fairly
/// robust to viewpoint changes, lighting changes, and deformations.
/// Inputs of GOTURN are two RGB patches representing Target and Search patches resized to 227x227.
/// Outputs of GOTURN are predicted bounding box coordinates, relative to Search patch coordinate system, in format X1,Y1,X2,Y2.
/// Original paper is here: <http://davheld.github.io/GOTURN/GOTURN.pdf>
/// As long as original authors implementation: <https://github.com/davheld/GOTURN#train-the-tracker>
/// Implementation of training algorithm is placed in separately here due to 3d-party dependencies:
/// <https://github.com/Auron-X/GOTURN_Training_Toolkit>
/// GOTURN architecture goturn.prototxt and trained model goturn.caffemodel are accessible on opencv_extra GitHub repository.
pub struct TrackerGOTURN {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { TrackerGOTURN }
impl Drop for TrackerGOTURN {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerGOTURN_delete(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerGOTURN()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for TrackerGOTURN {}
impl TrackerGOTURN {
/// Constructor
/// ## Parameters
/// * parameters: GOTURN parameters TrackerGOTURN::Params
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * parameters: TrackerGOTURN::Params()
#[inline]
pub fn create(parameters: &impl crate::video::TrackerGOTURN_ParamsTraitConst) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::video::TrackerGOTURN>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerGOTURN_create_const_ParamsR(parameters.as_raw_TrackerGOTURN_Params(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::video::TrackerGOTURN>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Constructor
/// ## Parameters
/// * parameters: GOTURN parameters TrackerGOTURN::Params
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [TrackerGOTURN::create] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * parameters: TrackerGOTURN::Params()
#[inline]
pub fn create_def() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::video::TrackerGOTURN>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerGOTURN_create(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::video::TrackerGOTURN>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::video::TrackerGOTURN]
pub trait TrackerGOTURNTraitConst: crate::video::TrackerTraitConst {
fn as_raw_TrackerGOTURN(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::video::TrackerGOTURN]
pub trait TrackerGOTURNTrait: crate::video::TrackerGOTURNTraitConst + crate::video::TrackerTrait {
fn as_raw_mut_TrackerGOTURN(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for TrackerGOTURN {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("TrackerGOTURN")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { TrackerGOTURN, crate::video::Tracker, cv_TrackerGOTURN_to_Tracker }
impl crate::video::TrackerTraitConst for TrackerGOTURN {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Tracker(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::TrackerTrait for TrackerGOTURN {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Tracker(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { TrackerGOTURN, crate::video::TrackerTraitConst, as_raw_Tracker, crate::video::TrackerTrait, as_raw_mut_Tracker }
impl crate::video::TrackerGOTURNTraitConst for TrackerGOTURN {
#[inline] fn as_raw_TrackerGOTURN(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::TrackerGOTURNTrait for TrackerGOTURN {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_TrackerGOTURN(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { TrackerGOTURN, crate::video::TrackerGOTURNTraitConst, as_raw_TrackerGOTURN, crate::video::TrackerGOTURNTrait, as_raw_mut_TrackerGOTURN }
pub struct TrackerGOTURN_Params {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { TrackerGOTURN_Params }
impl Drop for TrackerGOTURN_Params {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerGOTURN_Params_delete(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerGOTURN_Params()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for TrackerGOTURN_Params {}
impl TrackerGOTURN_Params {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<crate::video::TrackerGOTURN_Params> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerGOTURN_Params_Params(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { crate::video::TrackerGOTURN_Params::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::video::TrackerGOTURN_Params]
pub trait TrackerGOTURN_ParamsTraitConst {
fn as_raw_TrackerGOTURN_Params(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn model_txt(&self) -> String {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerGOTURN_Params_propModelTxt_const(self.as_raw_TrackerGOTURN_Params()) };
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn model_bin(&self) -> String {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerGOTURN_Params_propModelBin_const(self.as_raw_TrackerGOTURN_Params()) };
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::video::TrackerGOTURN_Params]
pub trait TrackerGOTURN_ParamsTrait: crate::video::TrackerGOTURN_ParamsTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_TrackerGOTURN_Params(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_model_txt(&mut self, val: &str) {
extern_container_arg!(nofail val);
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerGOTURN_Params_propModelTxt_const_string(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerGOTURN_Params(), val.opencv_as_extern()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_model_bin(&mut self, val: &str) {
extern_container_arg!(nofail val);
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerGOTURN_Params_propModelBin_const_string(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerGOTURN_Params(), val.opencv_as_extern()) };
ret
}
}
impl Clone for TrackerGOTURN_Params {
#[inline]
fn clone(&self) -> Self {
unsafe { Self::from_raw(sys::cv_TrackerGOTURN_Params_implicitClone_const(self.as_raw_TrackerGOTURN_Params())) }
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for TrackerGOTURN_Params {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("TrackerGOTURN_Params")
.field("model_txt", &crate::video::TrackerGOTURN_ParamsTraitConst::model_txt(self))
.field("model_bin", &crate::video::TrackerGOTURN_ParamsTraitConst::model_bin(self))
.finish()
}
}
impl crate::video::TrackerGOTURN_ParamsTraitConst for TrackerGOTURN_Params {
#[inline] fn as_raw_TrackerGOTURN_Params(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::TrackerGOTURN_ParamsTrait for TrackerGOTURN_Params {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_TrackerGOTURN_Params(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { TrackerGOTURN_Params, crate::video::TrackerGOTURN_ParamsTraitConst, as_raw_TrackerGOTURN_Params, crate::video::TrackerGOTURN_ParamsTrait, as_raw_mut_TrackerGOTURN_Params }
/// The MIL algorithm trains a classifier in an online manner to separate the object from the
/// background.
///
/// Multiple Instance Learning avoids the drift problem for a robust tracking. The implementation is
/// based on [MIL](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_MIL) .
///
/// Original code can be found here <http://vision.ucsd.edu/~bbabenko/project_miltrack.shtml>
pub struct TrackerMIL {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { TrackerMIL }
impl Drop for TrackerMIL {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerMIL_delete(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerMIL()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for TrackerMIL {}
impl TrackerMIL {
/// Create MIL tracker instance
/// ## Parameters
/// * parameters: MIL parameters TrackerMIL::Params
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * parameters: TrackerMIL::Params()
#[inline]
pub fn create(parameters: crate::video::TrackerMIL_Params) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::video::TrackerMIL>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerMIL_create_const_ParamsR(¶meters, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::video::TrackerMIL>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Create MIL tracker instance
/// ## Parameters
/// * parameters: MIL parameters TrackerMIL::Params
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [TrackerMIL::create] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * parameters: TrackerMIL::Params()
#[inline]
pub fn create_def() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::video::TrackerMIL>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerMIL_create(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::video::TrackerMIL>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::video::TrackerMIL]
pub trait TrackerMILTraitConst: crate::video::TrackerTraitConst {
fn as_raw_TrackerMIL(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::video::TrackerMIL]
pub trait TrackerMILTrait: crate::video::TrackerMILTraitConst + crate::video::TrackerTrait {
fn as_raw_mut_TrackerMIL(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for TrackerMIL {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("TrackerMIL")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { TrackerMIL, crate::video::Tracker, cv_TrackerMIL_to_Tracker }
impl crate::video::TrackerTraitConst for TrackerMIL {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Tracker(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::TrackerTrait for TrackerMIL {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Tracker(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { TrackerMIL, crate::video::TrackerTraitConst, as_raw_Tracker, crate::video::TrackerTrait, as_raw_mut_Tracker }
impl crate::video::TrackerMILTraitConst for TrackerMIL {
#[inline] fn as_raw_TrackerMIL(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::TrackerMILTrait for TrackerMIL {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_TrackerMIL(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { TrackerMIL, crate::video::TrackerMILTraitConst, as_raw_TrackerMIL, crate::video::TrackerMILTrait, as_raw_mut_TrackerMIL }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)]
pub struct TrackerMIL_Params {
/// radius for gathering positive instances during init
pub sampler_init_in_radius: f32,
/// # negative samples to use during init
pub sampler_init_max_neg_num: i32,
/// size of search window
pub sampler_search_win_size: f32,
/// radius for gathering positive instances during tracking
pub sampler_track_in_radius: f32,
/// # positive samples to use during tracking
pub sampler_track_max_pos_num: i32,
/// # negative samples to use during tracking
pub sampler_track_max_neg_num: i32,
/// # features
pub feature_set_num_features: i32,
}
opencv_type_simple! { crate::video::TrackerMIL_Params }
impl TrackerMIL_Params {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<crate::video::TrackerMIL_Params> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerMIL_Params_Params(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// the Nano tracker is a super lightweight dnn-based general object tracking.
///
/// Nano tracker is much faster and extremely lightweight due to special model structure, the whole model size is about 1.9 MB.
/// Nano tracker needs two models: one for feature extraction (backbone) and the another for localization (neckhead).
/// Model download link: <https://github.com/HonglinChu/SiamTrackers/tree/master/NanoTrack/models/nanotrackv2>
/// Original repo is here: <https://github.com/HonglinChu/NanoTrack>
/// Author: HongLinChu, 1628464345@qq.com
pub struct TrackerNano {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { TrackerNano }
impl Drop for TrackerNano {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerNano_delete(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerNano()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for TrackerNano {}
impl TrackerNano {
/// Constructor
/// ## Parameters
/// * parameters: NanoTrack parameters TrackerNano::Params
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * parameters: TrackerNano::Params()
#[inline]
pub fn create(parameters: &impl crate::video::TrackerNano_ParamsTraitConst) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::video::TrackerNano>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerNano_create_const_ParamsR(parameters.as_raw_TrackerNano_Params(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::video::TrackerNano>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Constructor
/// ## Parameters
/// * parameters: NanoTrack parameters TrackerNano::Params
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [TrackerNano::create] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * parameters: TrackerNano::Params()
#[inline]
pub fn create_def() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::video::TrackerNano>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerNano_create(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::video::TrackerNano>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::video::TrackerNano]
pub trait TrackerNanoTraitConst: crate::video::TrackerTraitConst {
fn as_raw_TrackerNano(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::video::TrackerNano]
pub trait TrackerNanoTrait: crate::video::TrackerNanoTraitConst + crate::video::TrackerTrait {
fn as_raw_mut_TrackerNano(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Return tracking score
#[inline]
fn get_tracking_score(&mut self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerNano_getTrackingScore(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerNano(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for TrackerNano {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("TrackerNano")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { TrackerNano, crate::video::Tracker, cv_TrackerNano_to_Tracker }
impl crate::video::TrackerTraitConst for TrackerNano {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Tracker(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::TrackerTrait for TrackerNano {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Tracker(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { TrackerNano, crate::video::TrackerTraitConst, as_raw_Tracker, crate::video::TrackerTrait, as_raw_mut_Tracker }
impl crate::video::TrackerNanoTraitConst for TrackerNano {
#[inline] fn as_raw_TrackerNano(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::TrackerNanoTrait for TrackerNano {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_TrackerNano(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { TrackerNano, crate::video::TrackerNanoTraitConst, as_raw_TrackerNano, crate::video::TrackerNanoTrait, as_raw_mut_TrackerNano }
pub struct TrackerNano_Params {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { TrackerNano_Params }
impl Drop for TrackerNano_Params {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerNano_Params_delete(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerNano_Params()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for TrackerNano_Params {}
impl TrackerNano_Params {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<crate::video::TrackerNano_Params> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerNano_Params_Params(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { crate::video::TrackerNano_Params::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::video::TrackerNano_Params]
pub trait TrackerNano_ParamsTraitConst {
fn as_raw_TrackerNano_Params(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn backbone(&self) -> String {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerNano_Params_propBackbone_const(self.as_raw_TrackerNano_Params()) };
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn neckhead(&self) -> String {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerNano_Params_propNeckhead_const(self.as_raw_TrackerNano_Params()) };
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn backend(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerNano_Params_propBackend_const(self.as_raw_TrackerNano_Params()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn target(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerNano_Params_propTarget_const(self.as_raw_TrackerNano_Params()) };
ret
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::video::TrackerNano_Params]
pub trait TrackerNano_ParamsTrait: crate::video::TrackerNano_ParamsTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_TrackerNano_Params(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_backbone(&mut self, val: &str) {
extern_container_arg!(nofail val);
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerNano_Params_propBackbone_const_string(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerNano_Params(), val.opencv_as_extern()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_neckhead(&mut self, val: &str) {
extern_container_arg!(nofail val);
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerNano_Params_propNeckhead_const_string(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerNano_Params(), val.opencv_as_extern()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_backend(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerNano_Params_propBackend_const_int(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerNano_Params(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_target(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerNano_Params_propTarget_const_int(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerNano_Params(), val) };
ret
}
}
impl Clone for TrackerNano_Params {
#[inline]
fn clone(&self) -> Self {
unsafe { Self::from_raw(sys::cv_TrackerNano_Params_implicitClone_const(self.as_raw_TrackerNano_Params())) }
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for TrackerNano_Params {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("TrackerNano_Params")
.field("backbone", &crate::video::TrackerNano_ParamsTraitConst::backbone(self))
.field("neckhead", &crate::video::TrackerNano_ParamsTraitConst::neckhead(self))
.field("backend", &crate::video::TrackerNano_ParamsTraitConst::backend(self))
.field("target", &crate::video::TrackerNano_ParamsTraitConst::target(self))
.finish()
}
}
impl crate::video::TrackerNano_ParamsTraitConst for TrackerNano_Params {
#[inline] fn as_raw_TrackerNano_Params(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::TrackerNano_ParamsTrait for TrackerNano_Params {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_TrackerNano_Params(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { TrackerNano_Params, crate::video::TrackerNano_ParamsTraitConst, as_raw_TrackerNano_Params, crate::video::TrackerNano_ParamsTrait, as_raw_mut_TrackerNano_Params }
/// the VIT tracker is a super lightweight dnn-based general object tracking.
///
/// VIT tracker is much faster and extremely lightweight due to special model structure, the model file is about 767KB.
/// Model download link: <https://github.com/opencv/opencv_zoo/tree/main/models/object_tracking_vittrack>
/// Author: PengyuLiu, 1872918507@qq.com
pub struct TrackerVit {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { TrackerVit }
impl Drop for TrackerVit {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerVit_delete(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerVit()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for TrackerVit {}
impl TrackerVit {
/// Constructor
/// ## Parameters
/// * parameters: vit tracker parameters TrackerVit::Params
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * parameters: TrackerVit::Params()
#[inline]
pub fn create(parameters: &impl crate::video::TrackerVit_ParamsTraitConst) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::video::TrackerVit>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerVit_create_const_ParamsR(parameters.as_raw_TrackerVit_Params(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::video::TrackerVit>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Constructor
/// ## Parameters
/// * parameters: vit tracker parameters TrackerVit::Params
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [TrackerVit::create] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * parameters: TrackerVit::Params()
#[inline]
pub fn create_def() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::video::TrackerVit>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerVit_create(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::video::TrackerVit>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::video::TrackerVit]
pub trait TrackerVitTraitConst: crate::video::TrackerTraitConst {
fn as_raw_TrackerVit(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::video::TrackerVit]
pub trait TrackerVitTrait: crate::video::TrackerTrait + crate::video::TrackerVitTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_TrackerVit(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Return tracking score
#[inline]
fn get_tracking_score(&mut self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerVit_getTrackingScore(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerVit(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for TrackerVit {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("TrackerVit")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { TrackerVit, crate::video::Tracker, cv_TrackerVit_to_Tracker }
impl crate::video::TrackerTraitConst for TrackerVit {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Tracker(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::TrackerTrait for TrackerVit {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Tracker(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { TrackerVit, crate::video::TrackerTraitConst, as_raw_Tracker, crate::video::TrackerTrait, as_raw_mut_Tracker }
impl crate::video::TrackerVitTraitConst for TrackerVit {
#[inline] fn as_raw_TrackerVit(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::TrackerVitTrait for TrackerVit {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_TrackerVit(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { TrackerVit, crate::video::TrackerVitTraitConst, as_raw_TrackerVit, crate::video::TrackerVitTrait, as_raw_mut_TrackerVit }
pub struct TrackerVit_Params {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { TrackerVit_Params }
impl Drop for TrackerVit_Params {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerVit_Params_delete(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerVit_Params()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for TrackerVit_Params {}
impl TrackerVit_Params {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<crate::video::TrackerVit_Params> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerVit_Params_Params(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { crate::video::TrackerVit_Params::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::video::TrackerVit_Params]
pub trait TrackerVit_ParamsTraitConst {
fn as_raw_TrackerVit_Params(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn net(&self) -> String {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerVit_Params_propNet_const(self.as_raw_TrackerVit_Params()) };
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn backend(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerVit_Params_propBackend_const(self.as_raw_TrackerVit_Params()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn target(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerVit_Params_propTarget_const(self.as_raw_TrackerVit_Params()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn meanvalue(&self) -> core::Scalar {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerVit_Params_propMeanvalue_const(self.as_raw_TrackerVit_Params(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
ret
}
#[inline]
fn stdvalue(&self) -> core::Scalar {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerVit_Params_propStdvalue_const(self.as_raw_TrackerVit_Params(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
ret
}
#[inline]
fn tracking_score_threshold(&self) -> f32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerVit_Params_propTracking_score_threshold_const(self.as_raw_TrackerVit_Params()) };
ret
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::video::TrackerVit_Params]
pub trait TrackerVit_ParamsTrait: crate::video::TrackerVit_ParamsTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_TrackerVit_Params(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_net(&mut self, val: &str) {
extern_container_arg!(nofail val);
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerVit_Params_propNet_const_string(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerVit_Params(), val.opencv_as_extern()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_backend(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerVit_Params_propBackend_const_int(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerVit_Params(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_target(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerVit_Params_propTarget_const_int(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerVit_Params(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_meanvalue(&mut self, val: core::Scalar) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerVit_Params_propMeanvalue_const_Scalar(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerVit_Params(), &val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_stdvalue(&mut self, val: core::Scalar) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerVit_Params_propStdvalue_const_Scalar(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerVit_Params(), &val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_tracking_score_threshold(&mut self, val: f32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_TrackerVit_Params_propTracking_score_threshold_const_float(self.as_raw_mut_TrackerVit_Params(), val) };
ret
}
}
impl Clone for TrackerVit_Params {
#[inline]
fn clone(&self) -> Self {
unsafe { Self::from_raw(sys::cv_TrackerVit_Params_implicitClone_const(self.as_raw_TrackerVit_Params())) }
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for TrackerVit_Params {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("TrackerVit_Params")
.field("net", &crate::video::TrackerVit_ParamsTraitConst::net(self))
.field("backend", &crate::video::TrackerVit_ParamsTraitConst::backend(self))
.field("target", &crate::video::TrackerVit_ParamsTraitConst::target(self))
.field("meanvalue", &crate::video::TrackerVit_ParamsTraitConst::meanvalue(self))
.field("stdvalue", &crate::video::TrackerVit_ParamsTraitConst::stdvalue(self))
.field("tracking_score_threshold", &crate::video::TrackerVit_ParamsTraitConst::tracking_score_threshold(self))
.finish()
}
}
impl crate::video::TrackerVit_ParamsTraitConst for TrackerVit_Params {
#[inline] fn as_raw_TrackerVit_Params(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::TrackerVit_ParamsTrait for TrackerVit_Params {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_TrackerVit_Params(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { TrackerVit_Params, crate::video::TrackerVit_ParamsTraitConst, as_raw_TrackerVit_Params, crate::video::TrackerVit_ParamsTrait, as_raw_mut_TrackerVit_Params }
/// Variational optical flow refinement
///
/// This class implements variational refinement of the input flow field, i.e.
/// it uses input flow to initialize the minimization of the following functional:
/// ,
/// where  are color constancy, gradient constancy and smoothness terms
/// respectively.  is a robust penalizer to limit the
/// influence of outliers. A complete formulation and a description of the minimization
/// procedure can be found in [Brox2004](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Brox2004)
pub struct VariationalRefinement {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { VariationalRefinement }
impl Drop for VariationalRefinement {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_VariationalRefinement_delete(self.as_raw_mut_VariationalRefinement()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for VariationalRefinement {}
impl VariationalRefinement {
/// Creates an instance of VariationalRefinement
#[inline]
pub fn create() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::video::VariationalRefinement>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_VariationalRefinement_create(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::video::VariationalRefinement>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::video::VariationalRefinement]
pub trait VariationalRefinementTraitConst: crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowTraitConst {
fn as_raw_VariationalRefinement(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Number of outer (fixed-point) iterations in the minimization procedure.
/// ## See also
/// setFixedPointIterations
#[inline]
fn get_fixed_point_iterations(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_VariationalRefinement_getFixedPointIterations_const(self.as_raw_VariationalRefinement(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Number of inner successive over-relaxation (SOR) iterations
/// in the minimization procedure to solve the respective linear system.
/// ## See also
/// setSorIterations
#[inline]
fn get_sor_iterations(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_VariationalRefinement_getSorIterations_const(self.as_raw_VariationalRefinement(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Relaxation factor in SOR
/// ## See also
/// setOmega
#[inline]
fn get_omega(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_VariationalRefinement_getOmega_const(self.as_raw_VariationalRefinement(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Weight of the smoothness term
/// ## See also
/// setAlpha
#[inline]
fn get_alpha(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_VariationalRefinement_getAlpha_const(self.as_raw_VariationalRefinement(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Weight of the color constancy term
/// ## See also
/// setDelta
#[inline]
fn get_delta(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_VariationalRefinement_getDelta_const(self.as_raw_VariationalRefinement(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Weight of the gradient constancy term
/// ## See also
/// setGamma
#[inline]
fn get_gamma(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_VariationalRefinement_getGamma_const(self.as_raw_VariationalRefinement(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Norm value shift for robust penalizer
/// ## See also
/// setEpsilon
#[inline]
fn get_epsilon(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_VariationalRefinement_getEpsilon_const(self.as_raw_VariationalRefinement(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::video::VariationalRefinement]
pub trait VariationalRefinementTrait: crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowTrait + crate::video::VariationalRefinementTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_VariationalRefinement(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// [calc] function overload to handle separate horizontal (u) and vertical (v) flow components
/// (to avoid extra splits/merges)
#[inline]
fn calc_uv(&mut self, i0: &impl ToInputArray, i1: &impl ToInputArray, flow_u: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, flow_v: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(i0);
input_array_arg!(i1);
input_output_array_arg!(flow_u);
input_output_array_arg!(flow_v);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_VariationalRefinement_calcUV_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_VariationalRefinement(), i0.as_raw__InputArray(), i1.as_raw__InputArray(), flow_u.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), flow_v.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Number of outer (fixed-point) iterations in the minimization procedure.
/// ## See also
/// setFixedPointIterations getFixedPointIterations
#[inline]
fn set_fixed_point_iterations(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_VariationalRefinement_setFixedPointIterations_int(self.as_raw_mut_VariationalRefinement(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Number of inner successive over-relaxation (SOR) iterations
/// in the minimization procedure to solve the respective linear system.
/// ## See also
/// setSorIterations getSorIterations
#[inline]
fn set_sor_iterations(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_VariationalRefinement_setSorIterations_int(self.as_raw_mut_VariationalRefinement(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Relaxation factor in SOR
/// ## See also
/// setOmega getOmega
#[inline]
fn set_omega(&mut self, val: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_VariationalRefinement_setOmega_float(self.as_raw_mut_VariationalRefinement(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Weight of the smoothness term
/// ## See also
/// setAlpha getAlpha
#[inline]
fn set_alpha(&mut self, val: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_VariationalRefinement_setAlpha_float(self.as_raw_mut_VariationalRefinement(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Weight of the color constancy term
/// ## See also
/// setDelta getDelta
#[inline]
fn set_delta(&mut self, val: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_VariationalRefinement_setDelta_float(self.as_raw_mut_VariationalRefinement(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Weight of the gradient constancy term
/// ## See also
/// setGamma getGamma
#[inline]
fn set_gamma(&mut self, val: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_VariationalRefinement_setGamma_float(self.as_raw_mut_VariationalRefinement(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Norm value shift for robust penalizer
/// ## See also
/// setEpsilon getEpsilon
#[inline]
fn set_epsilon(&mut self, val: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_VariationalRefinement_setEpsilon_float(self.as_raw_mut_VariationalRefinement(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for VariationalRefinement {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("VariationalRefinement")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { VariationalRefinement, core::Algorithm, cv_VariationalRefinement_to_Algorithm }
boxed_cast_base! { VariationalRefinement, crate::video::DenseOpticalFlow, cv_VariationalRefinement_to_DenseOpticalFlow }
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for VariationalRefinement {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for VariationalRefinement {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { VariationalRefinement, core::AlgorithmTraitConst, as_raw_Algorithm, core::AlgorithmTrait, as_raw_mut_Algorithm }
impl crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowTraitConst for VariationalRefinement {
#[inline] fn as_raw_DenseOpticalFlow(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowTrait for VariationalRefinement {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_DenseOpticalFlow(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { VariationalRefinement, crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowTraitConst, as_raw_DenseOpticalFlow, crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowTrait, as_raw_mut_DenseOpticalFlow }
impl crate::video::VariationalRefinementTraitConst for VariationalRefinement {
#[inline] fn as_raw_VariationalRefinement(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::VariationalRefinementTrait for VariationalRefinement {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_VariationalRefinement(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { VariationalRefinement, crate::video::VariationalRefinementTraitConst, as_raw_VariationalRefinement, crate::video::VariationalRefinementTrait, as_raw_mut_VariationalRefinement }
}