pub mod photo {
//! # Computational Photography
//!
//! This module includes photo processing algorithms
//! # Inpainting
//! # Denoising
//! # HDR imaging
//!
//! This section describes high dynamic range imaging algorithms namely tonemapping, exposure alignment,
//! camera calibration with multiple exposures and exposure fusion.
//!
//! # Contrast Preserving Decolorization
//!
//! Useful links:
//!
//! <http://www.cse.cuhk.edu.hk/leojia/projects/color2gray/index.html>
//!
//! # Seamless Cloning
//!
//! Useful links:
//!
//! <https://www.learnopencv.com/seamless-cloning-using-opencv-python-cpp>
//!
//! # Non-Photorealistic Rendering
//!
//! Useful links:
//!
//! <http://www.inf.ufrgs.br/~eslgastal/DomainTransform>
//!
//! <https://www.learnopencv.com/non-photorealistic-rendering-using-opencv-python-c/>
use crate::mod_prelude::*;
use crate::{core, sys, types};
pub mod prelude {
pub use super::{AlignExposuresTrait, AlignExposuresTraitConst, AlignMTBTrait, AlignMTBTraitConst, CalibrateCRFTrait, CalibrateCRFTraitConst, CalibrateDebevecTrait, CalibrateDebevecTraitConst, CalibrateRobertsonTrait, CalibrateRobertsonTraitConst, MergeDebevecTrait, MergeDebevecTraitConst, MergeExposuresTrait, MergeExposuresTraitConst, MergeMertensTrait, MergeMertensTraitConst, MergeRobertsonTrait, MergeRobertsonTraitConst, TonemapDragoTrait, TonemapDragoTraitConst, TonemapMantiukTrait, TonemapMantiukTraitConst, TonemapReinhardTrait, TonemapReinhardTraitConst, TonemapTrait, TonemapTraitConst};
}
/// Use Navier-Stokes based method
pub const INPAINT_NS: i32 = 0;
/// Use the algorithm proposed by Alexandru Telea [Telea04](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Telea04)
pub const INPAINT_TELEA: i32 = 1;
pub const LDR_SIZE: i32 = 256;
/// Mixed seamless cloning.
/// This method addresses cases where simple color-based selection or alpha masking is time-consuming
/// and may result in undesirable halos. By combining structure from the source and texture from the
/// destination, mixed seamless cloning is highly effective, even with loosely defined selections.
pub const MIXED_CLONE: i32 = 2;
/// Enhanced mixed seamless cloning.
/// Similar to `MIXED_CLONE`, but with an advanced approach to ROI (Region of Interest) calculation.
/// This mode processes a larger source region by considering the entire mask area instead of only
/// the bounding rectangle of non-zero pixels.
pub const MIXED_CLONE_WIDE: i32 = 10;
/// Monochrome transfer cloning.
/// This method allows users to replace specific features of an object, such as grayscale textures
/// or patterns, with alternative features. It is particularly useful for artistic effects or
/// targeted object modifications.
pub const MONOCHROME_TRANSFER: i32 = 3;
/// Enhanced monochrome transfer cloning.
/// Similar to `MONOCHROME_TRANSFER`, but with an advanced approach to ROI (Region of Interest) calculation.
/// This mode processes a larger source region by considering the entire mask area instead of only
/// the bounding rectangle of non-zero pixels.
pub const MONOCHROME_TRANSFER_WIDE: i32 = 11;
/// Normal seamless cloning.
/// This method is ideal for inserting objects with complex outlines into a new background.
/// It preserves the original appearance and lighting of the inserted object, ensuring a natural blend.
pub const NORMAL_CLONE: i32 = 1;
/// Enhanced normal seamless cloning.
/// Similar to `NORMAL_CLONE`, but with an advanced approach to ROI (Region of Interest) calculation.
/// This mode processes a larger source region by considering the entire mask area instead of only
/// the bounding rectangle of non-zero pixels.
pub const NORMAL_CLONE_WIDE: i32 = 9;
/// Normalized Convolution Filtering
pub const NORMCONV_FILTER: i32 = 2;
/// Recursive Filtering
pub const RECURS_FILTER: i32 = 1;
/// Flags for the seamlessClone algorithm
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum SeamlessCloneFlags {
/// Normal seamless cloning.
/// This method is ideal for inserting objects with complex outlines into a new background.
/// It preserves the original appearance and lighting of the inserted object, ensuring a natural blend.
NORMAL_CLONE = 1,
/// Mixed seamless cloning.
/// This method addresses cases where simple color-based selection or alpha masking is time-consuming
/// and may result in undesirable halos. By combining structure from the source and texture from the
/// destination, mixed seamless cloning is highly effective, even with loosely defined selections.
MIXED_CLONE = 2,
/// Monochrome transfer cloning.
/// This method allows users to replace specific features of an object, such as grayscale textures
/// or patterns, with alternative features. It is particularly useful for artistic effects or
/// targeted object modifications.
MONOCHROME_TRANSFER = 3,
/// Enhanced normal seamless cloning.
/// Similar to `NORMAL_CLONE`, but with an advanced approach to ROI (Region of Interest) calculation.
/// This mode processes a larger source region by considering the entire mask area instead of only
/// the bounding rectangle of non-zero pixels.
NORMAL_CLONE_WIDE = 9,
/// Enhanced mixed seamless cloning.
/// Similar to `MIXED_CLONE`, but with an advanced approach to ROI (Region of Interest) calculation.
/// This mode processes a larger source region by considering the entire mask area instead of only
/// the bounding rectangle of non-zero pixels.
MIXED_CLONE_WIDE = 10,
/// Enhanced monochrome transfer cloning.
/// Similar to `MONOCHROME_TRANSFER`, but with an advanced approach to ROI (Region of Interest) calculation.
/// This mode processes a larger source region by considering the entire mask area instead of only
/// the bounding rectangle of non-zero pixels.
MONOCHROME_TRANSFER_WIDE = 11,
}
impl TryFrom<i32> for SeamlessCloneFlags {
type Error = crate::Error;
fn try_from(value: i32) -> Result<Self, Self::Error> {
match value {
1 => Ok(Self::NORMAL_CLONE),
2 => Ok(Self::MIXED_CLONE),
3 => Ok(Self::MONOCHROME_TRANSFER),
9 => Ok(Self::NORMAL_CLONE_WIDE),
10 => Ok(Self::MIXED_CLONE_WIDE),
11 => Ok(Self::MONOCHROME_TRANSFER_WIDE),
_ => Err(crate::Error::new(crate::core::StsBadArg, format!("Value: {value} is not valid for enum: crate::photo::SeamlessCloneFlags"))),
}
}
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::photo::SeamlessCloneFlags }
/// Given an original color image, two differently colored versions of this image can be mixed
/// seamlessly.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * mask: Input 8-bit 1 or 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src .
/// * red_mul: R-channel multiply factor.
/// * green_mul: G-channel multiply factor.
/// * blue_mul: B-channel multiply factor.
///
/// Multiplication factor is between .5 to 2.5.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [color_change] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * red_mul: 1.0f
/// * green_mul: 1.0f
/// * blue_mul: 1.0f
#[inline]
pub fn color_change_def(src: &impl ToInputArray, mask: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
input_array_arg!(mask);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_colorChange_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Given an original color image, two differently colored versions of this image can be mixed
/// seamlessly.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * mask: Input 8-bit 1 or 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src .
/// * red_mul: R-channel multiply factor.
/// * green_mul: G-channel multiply factor.
/// * blue_mul: B-channel multiply factor.
///
/// Multiplication factor is between .5 to 2.5.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * red_mul: 1.0f
/// * green_mul: 1.0f
/// * blue_mul: 1.0f
#[inline]
pub fn color_change(src: &impl ToInputArray, mask: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, red_mul: f32, green_mul: f32, blue_mul: f32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
input_array_arg!(mask);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_colorChange_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float_float_float(src.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), red_mul, green_mul, blue_mul, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates AlignMTB object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * max_bits: logarithm to the base 2 of maximal shift in each dimension. Values of 5 and 6 are
/// usually good enough (31 and 63 pixels shift respectively).
/// * exclude_range: range for exclusion bitmap that is constructed to suppress noise around the
/// median value.
/// * cut: if true cuts images, otherwise fills the new regions with zeros.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [create_align_mtb] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * max_bits: 6
/// * exclude_range: 4
/// * cut: true
#[inline]
pub fn create_align_mtb_def() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::photo::AlignMTB>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createAlignMTB(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::photo::AlignMTB>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates AlignMTB object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * max_bits: logarithm to the base 2 of maximal shift in each dimension. Values of 5 and 6 are
/// usually good enough (31 and 63 pixels shift respectively).
/// * exclude_range: range for exclusion bitmap that is constructed to suppress noise around the
/// median value.
/// * cut: if true cuts images, otherwise fills the new regions with zeros.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * max_bits: 6
/// * exclude_range: 4
/// * cut: true
#[inline]
pub fn create_align_mtb(max_bits: i32, exclude_range: i32, cut: bool) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::photo::AlignMTB>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createAlignMTB_int_int_bool(max_bits, exclude_range, cut, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::photo::AlignMTB>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates CalibrateDebevec object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * samples: number of pixel locations to use
/// * lambda: smoothness term weight. Greater values produce smoother results, but can alter the
/// response.
/// * random: if true sample pixel locations are chosen at random, otherwise they form a
/// rectangular grid.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [create_calibrate_debevec] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * samples: 70
/// * lambda: 10.0f
/// * random: false
#[inline]
pub fn create_calibrate_debevec_def() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::photo::CalibrateDebevec>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createCalibrateDebevec(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::photo::CalibrateDebevec>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates CalibrateDebevec object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * samples: number of pixel locations to use
/// * lambda: smoothness term weight. Greater values produce smoother results, but can alter the
/// response.
/// * random: if true sample pixel locations are chosen at random, otherwise they form a
/// rectangular grid.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * samples: 70
/// * lambda: 10.0f
/// * random: false
#[inline]
pub fn create_calibrate_debevec(samples: i32, lambda: f32, random: bool) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::photo::CalibrateDebevec>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createCalibrateDebevec_int_float_bool(samples, lambda, random, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::photo::CalibrateDebevec>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates CalibrateRobertson object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * max_iter: maximal number of Gauss-Seidel solver iterations.
/// * threshold: target difference between results of two successive steps of the minimization.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [create_calibrate_robertson] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * max_iter: 30
/// * threshold: 0.01f
#[inline]
pub fn create_calibrate_robertson_def() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::photo::CalibrateRobertson>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createCalibrateRobertson(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::photo::CalibrateRobertson>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates CalibrateRobertson object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * max_iter: maximal number of Gauss-Seidel solver iterations.
/// * threshold: target difference between results of two successive steps of the minimization.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * max_iter: 30
/// * threshold: 0.01f
#[inline]
pub fn create_calibrate_robertson(max_iter: i32, threshold: f32) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::photo::CalibrateRobertson>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createCalibrateRobertson_int_float(max_iter, threshold, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::photo::CalibrateRobertson>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates MergeDebevec object
#[inline]
pub fn create_merge_debevec() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::photo::MergeDebevec>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createMergeDebevec(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::photo::MergeDebevec>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates MergeMertens object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * contrast_weight: contrast measure weight. See MergeMertens.
/// * saturation_weight: saturation measure weight
/// * exposure_weight: well-exposedness measure weight
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [create_merge_mertens] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * contrast_weight: 1.0f
/// * saturation_weight: 1.0f
/// * exposure_weight: 0.0f
#[inline]
pub fn create_merge_mertens_def() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::photo::MergeMertens>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createMergeMertens(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::photo::MergeMertens>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates MergeMertens object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * contrast_weight: contrast measure weight. See MergeMertens.
/// * saturation_weight: saturation measure weight
/// * exposure_weight: well-exposedness measure weight
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * contrast_weight: 1.0f
/// * saturation_weight: 1.0f
/// * exposure_weight: 0.0f
#[inline]
pub fn create_merge_mertens(contrast_weight: f32, saturation_weight: f32, exposure_weight: f32) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::photo::MergeMertens>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createMergeMertens_float_float_float(contrast_weight, saturation_weight, exposure_weight, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::photo::MergeMertens>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates MergeRobertson object
#[inline]
pub fn create_merge_robertson() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::photo::MergeRobertson>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createMergeRobertson(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::photo::MergeRobertson>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates simple linear mapper with gamma correction
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * gamma: positive value for gamma correction. Gamma value of 1.0 implies no correction, gamma
/// equal to 2.2f is suitable for most displays.
/// Generally gamma \> 1 brightens the image and gamma \< 1 darkens it.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [create_tonemap] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * gamma: 1.0f
#[inline]
pub fn create_tonemap_def() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::photo::Tonemap>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createTonemap(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::photo::Tonemap>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates TonemapDrago object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * gamma: gamma value for gamma correction. See createTonemap
/// * saturation: positive saturation enhancement value. 1.0 preserves saturation, values greater
/// than 1 increase saturation and values less than 1 decrease it.
/// * bias: value for bias function in [0, 1] range. Values from 0.7 to 0.9 usually give best
/// results, default value is 0.85.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [create_tonemap_drago] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * gamma: 1.0f
/// * saturation: 1.0f
/// * bias: 0.85f
#[inline]
pub fn create_tonemap_drago_def() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::photo::TonemapDrago>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createTonemapDrago(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::photo::TonemapDrago>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates TonemapDrago object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * gamma: gamma value for gamma correction. See createTonemap
/// * saturation: positive saturation enhancement value. 1.0 preserves saturation, values greater
/// than 1 increase saturation and values less than 1 decrease it.
/// * bias: value for bias function in [0, 1] range. Values from 0.7 to 0.9 usually give best
/// results, default value is 0.85.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * gamma: 1.0f
/// * saturation: 1.0f
/// * bias: 0.85f
#[inline]
pub fn create_tonemap_drago(gamma: f32, saturation: f32, bias: f32) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::photo::TonemapDrago>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createTonemapDrago_float_float_float(gamma, saturation, bias, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::photo::TonemapDrago>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates TonemapMantiuk object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * gamma: gamma value for gamma correction. See createTonemap
/// * scale: contrast scale factor. HVS response is multiplied by this parameter, thus compressing
/// dynamic range. Values from 0.6 to 0.9 produce best results.
/// * saturation: saturation enhancement value. See createTonemapDrago
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [create_tonemap_mantiuk] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * gamma: 1.0f
/// * scale: 0.7f
/// * saturation: 1.0f
#[inline]
pub fn create_tonemap_mantiuk_def() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::photo::TonemapMantiuk>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createTonemapMantiuk(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::photo::TonemapMantiuk>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates TonemapMantiuk object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * gamma: gamma value for gamma correction. See createTonemap
/// * scale: contrast scale factor. HVS response is multiplied by this parameter, thus compressing
/// dynamic range. Values from 0.6 to 0.9 produce best results.
/// * saturation: saturation enhancement value. See createTonemapDrago
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * gamma: 1.0f
/// * scale: 0.7f
/// * saturation: 1.0f
#[inline]
pub fn create_tonemap_mantiuk(gamma: f32, scale: f32, saturation: f32) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::photo::TonemapMantiuk>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createTonemapMantiuk_float_float_float(gamma, scale, saturation, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::photo::TonemapMantiuk>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates TonemapReinhard object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * gamma: gamma value for gamma correction. See createTonemap
/// * intensity: result intensity in [-8, 8] range. Greater intensity produces brighter results.
/// * light_adapt: light adaptation in [0, 1] range. If 1 adaptation is based only on pixel
/// value, if 0 it's global, otherwise it's a weighted mean of this two cases.
/// * color_adapt: chromatic adaptation in [0, 1] range. If 1 channels are treated independently,
/// if 0 adaptation level is the same for each channel.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [create_tonemap_reinhard] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * gamma: 1.0f
/// * intensity: 0.0f
/// * light_adapt: 1.0f
/// * color_adapt: 0.0f
#[inline]
pub fn create_tonemap_reinhard_def() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::photo::TonemapReinhard>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createTonemapReinhard(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::photo::TonemapReinhard>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates TonemapReinhard object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * gamma: gamma value for gamma correction. See createTonemap
/// * intensity: result intensity in [-8, 8] range. Greater intensity produces brighter results.
/// * light_adapt: light adaptation in [0, 1] range. If 1 adaptation is based only on pixel
/// value, if 0 it's global, otherwise it's a weighted mean of this two cases.
/// * color_adapt: chromatic adaptation in [0, 1] range. If 1 channels are treated independently,
/// if 0 adaptation level is the same for each channel.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * gamma: 1.0f
/// * intensity: 0.0f
/// * light_adapt: 1.0f
/// * color_adapt: 0.0f
#[inline]
pub fn create_tonemap_reinhard(gamma: f32, intensity: f32, light_adapt: f32, color_adapt: f32) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::photo::TonemapReinhard>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createTonemapReinhard_float_float_float_float(gamma, intensity, light_adapt, color_adapt, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::photo::TonemapReinhard>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates simple linear mapper with gamma correction
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * gamma: positive value for gamma correction. Gamma value of 1.0 implies no correction, gamma
/// equal to 2.2f is suitable for most displays.
/// Generally gamma \> 1 brightens the image and gamma \< 1 darkens it.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * gamma: 1.0f
#[inline]
pub fn create_tonemap(gamma: f32) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::photo::Tonemap>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createTonemap_float(gamma, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::photo::Tonemap>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [fast_nl_means_denoising_colored_1] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * search_window: 21
/// * block_size: 7
/// * stream: Stream::Null()
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_colored_1_def(src: &impl core::GpuMatTraitConst, dst: &mut impl core::GpuMatTrait, h_luminance: f32, photo_render: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_fastNlMeansDenoisingColored_const_GpuMatR_GpuMatR_float_float(src.as_raw_GpuMat(), dst.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), h_luminance, photo_render, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * search_window: 21
/// * block_size: 7
/// * stream: Stream::Null()
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_colored_1(src: &impl core::GpuMatTraitConst, dst: &mut impl core::GpuMatTrait, h_luminance: f32, photo_render: f32, search_window: i32, block_size: i32, stream: &mut impl core::StreamTrait) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_fastNlMeansDenoisingColored_const_GpuMatR_GpuMatR_float_float_int_int_StreamR(src.as_raw_GpuMat(), dst.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), h_luminance, photo_render, search_window, block_size, stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Modification of fastNlMeansDenoising function for colored images
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src .
/// * h_luminance: Parameter regulating filter strength. Big h value perfectly removes noise but
/// also removes image details, smaller h value preserves details but also preserves some noise
/// * photo_render: float The same as h but for color components. For most images value equals 10 will be
/// enough to remove colored noise and do not distort colors
/// * search_window: Size in pixels of the window that is used to compute weighted average for
/// given pixel. Should be odd. Affect performance linearly: greater search_window - greater
/// denoising time. Recommended value 21 pixels
/// * block_size: Size in pixels of the template patch that is used to compute weights. Should be
/// odd. Recommended value 7 pixels
/// * stream: Stream for the asynchronous invocations.
///
/// The function converts image to CIELAB colorspace and then separately denoise L and AB components
/// with given h parameters using FastNonLocalMeansDenoising::simpleMethod function.
/// ## See also
/// fastNlMeansDenoisingColored
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [fast_nl_means_denoising_colored_cuda] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * search_window: 21
/// * block_size: 7
/// * stream: Stream::Null()
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_colored_cuda_def(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, h_luminance: f32, photo_render: f32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_fastNlMeansDenoisingColored_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float_float(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), h_luminance, photo_render, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Modification of fastNlMeansDenoising function for colored images
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src .
/// * h_luminance: Parameter regulating filter strength. Big h value perfectly removes noise but
/// also removes image details, smaller h value preserves details but also preserves some noise
/// * photo_render: float The same as h but for color components. For most images value equals 10 will be
/// enough to remove colored noise and do not distort colors
/// * search_window: Size in pixels of the window that is used to compute weighted average for
/// given pixel. Should be odd. Affect performance linearly: greater search_window - greater
/// denoising time. Recommended value 21 pixels
/// * block_size: Size in pixels of the template patch that is used to compute weights. Should be
/// odd. Recommended value 7 pixels
/// * stream: Stream for the asynchronous invocations.
///
/// The function converts image to CIELAB colorspace and then separately denoise L and AB components
/// with given h parameters using FastNonLocalMeansDenoising::simpleMethod function.
/// ## See also
/// fastNlMeansDenoisingColored
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * search_window: 21
/// * block_size: 7
/// * stream: Stream::Null()
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_colored_cuda(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, h_luminance: f32, photo_render: f32, search_window: i32, block_size: i32, stream: &mut impl core::StreamTrait) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_fastNlMeansDenoisingColored_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float_float_int_int_StreamR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), h_luminance, photo_render, search_window, block_size, stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [fast_nl_means_denoising_1] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * search_window: 21
/// * block_size: 7
/// * stream: Stream::Null()
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_1_def(src: &impl core::GpuMatTraitConst, dst: &mut impl core::GpuMatTrait, h: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_fastNlMeansDenoising_const_GpuMatR_GpuMatR_float(src.as_raw_GpuMat(), dst.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), h, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * search_window: 21
/// * block_size: 7
/// * stream: Stream::Null()
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_1(src: &impl core::GpuMatTraitConst, dst: &mut impl core::GpuMatTrait, h: f32, search_window: i32, block_size: i32, stream: &mut impl core::StreamTrait) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_fastNlMeansDenoising_const_GpuMatR_GpuMatR_float_int_int_StreamR(src.as_raw_GpuMat(), dst.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), h, search_window, block_size, stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Perform image denoising using Non-local Means Denoising algorithm
/// <http://www.ipol.im/pub/algo/bcm_non_local_means_denoising> with several computational
/// optimizations. Noise expected to be a gaussian white noise
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 1-channel, 2-channel or 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src .
/// * h: Parameter regulating filter strength. Big h value perfectly removes noise but also
/// removes image details, smaller h value preserves details but also preserves some noise
/// * search_window: Size in pixels of the window that is used to compute weighted average for
/// given pixel. Should be odd. Affect performance linearly: greater search_window - greater
/// denoising time. Recommended value 21 pixels
/// * block_size: Size in pixels of the template patch that is used to compute weights. Should be
/// odd. Recommended value 7 pixels
/// * stream: Stream for the asynchronous invocations.
///
/// This function expected to be applied to grayscale images. For colored images look at
/// FastNonLocalMeansDenoising::labMethod.
/// ## See also
/// fastNlMeansDenoising
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [fast_nl_means_denoising_cuda] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * search_window: 21
/// * block_size: 7
/// * stream: Stream::Null()
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_cuda_def(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, h: f32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_fastNlMeansDenoising_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), h, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Perform image denoising using Non-local Means Denoising algorithm
/// <http://www.ipol.im/pub/algo/bcm_non_local_means_denoising> with several computational
/// optimizations. Noise expected to be a gaussian white noise
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 1-channel, 2-channel or 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src .
/// * h: Parameter regulating filter strength. Big h value perfectly removes noise but also
/// removes image details, smaller h value preserves details but also preserves some noise
/// * search_window: Size in pixels of the window that is used to compute weighted average for
/// given pixel. Should be odd. Affect performance linearly: greater search_window - greater
/// denoising time. Recommended value 21 pixels
/// * block_size: Size in pixels of the template patch that is used to compute weights. Should be
/// odd. Recommended value 7 pixels
/// * stream: Stream for the asynchronous invocations.
///
/// This function expected to be applied to grayscale images. For colored images look at
/// FastNonLocalMeansDenoising::labMethod.
/// ## See also
/// fastNlMeansDenoising
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * search_window: 21
/// * block_size: 7
/// * stream: Stream::Null()
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_cuda(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, h: f32, search_window: i32, block_size: i32, stream: &mut impl core::StreamTrait) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_fastNlMeansDenoising_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float_int_int_StreamR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), h, search_window, block_size, stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [non_local_means_1] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * search_window: 21
/// * block_size: 7
/// * border_mode: BORDER_DEFAULT
/// * stream: Stream::Null()
#[inline]
pub fn non_local_means_1_def(src: &impl core::GpuMatTraitConst, dst: &mut impl core::GpuMatTrait, h: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_nonLocalMeans_const_GpuMatR_GpuMatR_float(src.as_raw_GpuMat(), dst.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), h, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * search_window: 21
/// * block_size: 7
/// * border_mode: BORDER_DEFAULT
/// * stream: Stream::Null()
#[inline]
pub fn non_local_means_1(src: &impl core::GpuMatTraitConst, dst: &mut impl core::GpuMatTrait, h: f32, search_window: i32, block_size: i32, border_mode: i32, stream: &mut impl core::StreamTrait) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_nonLocalMeans_const_GpuMatR_GpuMatR_float_int_int_int_StreamR(src.as_raw_GpuMat(), dst.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), h, search_window, block_size, border_mode, stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Performs pure non local means denoising without any simplification, and thus it is not fast.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Source image. Supports only CV_8UC1, CV_8UC2 and CV_8UC3.
/// * dst: Destination image.
/// * h: Filter sigma regulating filter strength for color.
/// * search_window: Size of search window.
/// * block_size: Size of block used for computing weights.
/// * borderMode: Border type. See borderInterpolate for details. BORDER_REFLECT101 ,
/// BORDER_REPLICATE , BORDER_CONSTANT , BORDER_REFLECT and BORDER_WRAP are supported for now.
/// * stream: Stream for the asynchronous version.
/// ## See also
/// fastNlMeansDenoising
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [non_local_means] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * search_window: 21
/// * block_size: 7
/// * border_mode: BORDER_DEFAULT
/// * stream: Stream::Null()
#[inline]
pub fn non_local_means_def(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, h: f32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_nonLocalMeans_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), h, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Performs pure non local means denoising without any simplification, and thus it is not fast.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Source image. Supports only CV_8UC1, CV_8UC2 and CV_8UC3.
/// * dst: Destination image.
/// * h: Filter sigma regulating filter strength for color.
/// * search_window: Size of search window.
/// * block_size: Size of block used for computing weights.
/// * borderMode: Border type. See borderInterpolate for details. BORDER_REFLECT101 ,
/// BORDER_REPLICATE , BORDER_CONSTANT , BORDER_REFLECT and BORDER_WRAP are supported for now.
/// * stream: Stream for the asynchronous version.
/// ## See also
/// fastNlMeansDenoising
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * search_window: 21
/// * block_size: 7
/// * border_mode: BORDER_DEFAULT
/// * stream: Stream::Null()
#[inline]
pub fn non_local_means(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, h: f32, search_window: i32, block_size: i32, border_mode: i32, stream: &mut impl core::StreamTrait) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_nonLocalMeans_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float_int_int_int_StreamR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), h, search_window, block_size, border_mode, stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Transforms a color image to a grayscale image. It is a basic tool in digital printing, stylized
/// black-and-white photograph rendering, and in many single channel image processing applications
/// [CL12](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_CL12) .
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * grayscale: Output 8-bit 1-channel image.
/// * color_boost: Output 8-bit 3-channel image.
///
/// This function is to be applied on color images.
#[inline]
pub fn decolor(src: &impl ToInputArray, grayscale: &mut impl ToOutputArray, color_boost: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(grayscale);
output_array_arg!(color_boost);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_decolor_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), grayscale.as_raw__OutputArray(), color_boost.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Primal-dual algorithm is an algorithm for solving special types of variational problems (that is,
/// finding a function to minimize some functional). As the image denoising, in particular, may be seen
/// as the variational problem, primal-dual algorithm then can be used to perform denoising and this is
/// exactly what is implemented.
///
/// It should be noted, that this implementation was taken from the July 2013 blog entry
/// [MA13](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_MA13) , which also contained (slightly more general) ready-to-use source code on Python.
/// Subsequently, that code was rewritten on C++ with the usage of openCV by Vadim Pisarevsky at the end
/// of July 2013 and finally it was slightly adapted by later authors.
///
/// Although the thorough discussion and justification of the algorithm involved may be found in
/// [ChambolleEtAl](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_ChambolleEtAl), it might make sense to skim over it here, following [MA13](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_MA13) . To begin
/// with, we consider the 1-byte gray-level images as the functions from the rectangular domain of
/// pixels (it may be seen as set
///  for some
/// ) into . We shall denote the noised images as  and with
/// this view, given some image 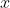 of the same size, we may measure how bad it is by the formula
///
/// 
///
///  here denotes -norm and as you see, the first addend states that we want our
/// image to be smooth (ideally, having zero gradient, thus being constant) and the second states that
/// we want our result to be close to the observations we've got. If we treat 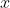 as a function, this is
/// exactly the functional what we seek to minimize and here the Primal-Dual algorithm comes into play.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * observations: This array should contain one or more noised versions of the image that is to
/// be restored.
/// * result: Here the denoised image will be stored. There is no need to do pre-allocation of
/// storage space, as it will be automatically allocated, if necessary.
/// * lambda: Corresponds to 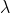 in the formulas above. As it is enlarged, the smooth
/// (blurred) images are treated more favorably than detailed (but maybe more noised) ones. Roughly
/// speaking, as it becomes smaller, the result will be more blur but more sever outliers will be
/// removed.
/// * niters: Number of iterations that the algorithm will run. Of course, as more iterations as
/// better, but it is hard to quantitatively refine this statement, so just use the default and
/// increase it if the results are poor.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [denoise_tvl1] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * lambda: 1.0
/// * niters: 30
#[inline]
pub fn denoise_tvl1_def(observations: &core::Vector<core::Mat>, result: &mut impl core::MatTrait) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_denoise_TVL1_const_vectorLMatGR_MatR(observations.as_raw_VectorOfMat(), result.as_raw_mut_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Primal-dual algorithm is an algorithm for solving special types of variational problems (that is,
/// finding a function to minimize some functional). As the image denoising, in particular, may be seen
/// as the variational problem, primal-dual algorithm then can be used to perform denoising and this is
/// exactly what is implemented.
///
/// It should be noted, that this implementation was taken from the July 2013 blog entry
/// [MA13](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_MA13) , which also contained (slightly more general) ready-to-use source code on Python.
/// Subsequently, that code was rewritten on C++ with the usage of openCV by Vadim Pisarevsky at the end
/// of July 2013 and finally it was slightly adapted by later authors.
///
/// Although the thorough discussion and justification of the algorithm involved may be found in
/// [ChambolleEtAl](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_ChambolleEtAl), it might make sense to skim over it here, following [MA13](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_MA13) . To begin
/// with, we consider the 1-byte gray-level images as the functions from the rectangular domain of
/// pixels (it may be seen as set
///  for some
/// ) into . We shall denote the noised images as  and with
/// this view, given some image 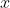 of the same size, we may measure how bad it is by the formula
///
/// 
///
///  here denotes -norm and as you see, the first addend states that we want our
/// image to be smooth (ideally, having zero gradient, thus being constant) and the second states that
/// we want our result to be close to the observations we've got. If we treat 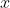 as a function, this is
/// exactly the functional what we seek to minimize and here the Primal-Dual algorithm comes into play.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * observations: This array should contain one or more noised versions of the image that is to
/// be restored.
/// * result: Here the denoised image will be stored. There is no need to do pre-allocation of
/// storage space, as it will be automatically allocated, if necessary.
/// * lambda: Corresponds to 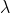 in the formulas above. As it is enlarged, the smooth
/// (blurred) images are treated more favorably than detailed (but maybe more noised) ones. Roughly
/// speaking, as it becomes smaller, the result will be more blur but more sever outliers will be
/// removed.
/// * niters: Number of iterations that the algorithm will run. Of course, as more iterations as
/// better, but it is hard to quantitatively refine this statement, so just use the default and
/// increase it if the results are poor.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * lambda: 1.0
/// * niters: 30
#[inline]
pub fn denoise_tvl1(observations: &core::Vector<core::Mat>, result: &mut impl core::MatTrait, lambda: f64, niters: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_denoise_TVL1_const_vectorLMatGR_MatR_double_int(observations.as_raw_VectorOfMat(), result.as_raw_mut_Mat(), lambda, niters, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// This filter enhances the details of a particular image.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src.
/// * sigma_s: %Range between 0 to 200.
/// * sigma_r: %Range between 0 to 1.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [detail_enhance] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * sigma_s: 10
/// * sigma_r: 0.15f
#[inline]
pub fn detail_enhance_def(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_detailEnhance_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// This filter enhances the details of a particular image.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src.
/// * sigma_s: %Range between 0 to 200.
/// * sigma_r: %Range between 0 to 1.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * sigma_s: 10
/// * sigma_r: 0.15f
#[inline]
pub fn detail_enhance(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, sigma_s: f32, sigma_r: f32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_detailEnhance_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float_float(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), sigma_s, sigma_r, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Filtering is the fundamental operation in image and video processing. Edge-preserving smoothing
/// filters are used in many different applications [EM11](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_EM11) .
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * flags: Edge preserving filters: cv::RECURS_FILTER or cv::NORMCONV_FILTER
/// * sigma_s: %Range between 0 to 200.
/// * sigma_r: %Range between 0 to 1.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [edge_preserving_filter] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * flags: 1
/// * sigma_s: 60
/// * sigma_r: 0.4f
#[inline]
pub fn edge_preserving_filter_def(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_edgePreservingFilter_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Filtering is the fundamental operation in image and video processing. Edge-preserving smoothing
/// filters are used in many different applications [EM11](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_EM11) .
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * flags: Edge preserving filters: cv::RECURS_FILTER or cv::NORMCONV_FILTER
/// * sigma_s: %Range between 0 to 200.
/// * sigma_r: %Range between 0 to 1.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: 1
/// * sigma_s: 60
/// * sigma_r: 0.4f
#[inline]
pub fn edge_preserving_filter(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, flags: i32, sigma_s: f32, sigma_r: f32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_edgePreservingFilter_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_float_float(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, sigma_s, sigma_r, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Modification of fastNlMeansDenoisingMulti function for colored images sequences
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * srcImgs: Input 8-bit 3-channel images sequence. All images should have the same type and
/// size.
/// * imgToDenoiseIndex: Target image to denoise index in srcImgs sequence
/// * temporalWindowSize: Number of surrounding images to use for target image denoising. Should
/// be odd. Images from imgToDenoiseIndex - temporalWindowSize / 2 to
/// imgToDenoiseIndex + temporalWindowSize / 2 from srcImgs will be used to denoise
/// srcImgs[imgToDenoiseIndex] image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as srcImgs images.
/// * templateWindowSize: Size in pixels of the template patch that is used to compute weights.
/// Should be odd. Recommended value 7 pixels
/// * searchWindowSize: Size in pixels of the window that is used to compute weighted average for
/// given pixel. Should be odd. Affect performance linearly: greater searchWindowsSize - greater
/// denoising time. Recommended value 21 pixels
/// * h: Parameter regulating filter strength for luminance component. Bigger h value perfectly
/// removes noise but also removes image details, smaller h value preserves details but also preserves
/// some noise.
/// * hColor: The same as h but for color components.
///
/// The function converts images to CIELAB colorspace and then separately denoise L and AB components
/// with given h parameters using fastNlMeansDenoisingMulti function.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [fast_nl_means_denoising_colored_multi] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * h: 3
/// * h_color: 3
/// * template_window_size: 7
/// * search_window_size: 21
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_colored_multi_def(src_imgs: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, img_to_denoise_index: i32, temporal_window_size: i32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src_imgs);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fastNlMeansDenoisingColoredMulti_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_int(src_imgs.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), img_to_denoise_index, temporal_window_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Modification of fastNlMeansDenoisingMulti function for colored images sequences
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * srcImgs: Input 8-bit 3-channel images sequence. All images should have the same type and
/// size.
/// * imgToDenoiseIndex: Target image to denoise index in srcImgs sequence
/// * temporalWindowSize: Number of surrounding images to use for target image denoising. Should
/// be odd. Images from imgToDenoiseIndex - temporalWindowSize / 2 to
/// imgToDenoiseIndex + temporalWindowSize / 2 from srcImgs will be used to denoise
/// srcImgs[imgToDenoiseIndex] image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as srcImgs images.
/// * templateWindowSize: Size in pixels of the template patch that is used to compute weights.
/// Should be odd. Recommended value 7 pixels
/// * searchWindowSize: Size in pixels of the window that is used to compute weighted average for
/// given pixel. Should be odd. Affect performance linearly: greater searchWindowsSize - greater
/// denoising time. Recommended value 21 pixels
/// * h: Parameter regulating filter strength for luminance component. Bigger h value perfectly
/// removes noise but also removes image details, smaller h value preserves details but also preserves
/// some noise.
/// * hColor: The same as h but for color components.
///
/// The function converts images to CIELAB colorspace and then separately denoise L and AB components
/// with given h parameters using fastNlMeansDenoisingMulti function.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * h: 3
/// * h_color: 3
/// * template_window_size: 7
/// * search_window_size: 21
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_colored_multi(src_imgs: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, img_to_denoise_index: i32, temporal_window_size: i32, h: f32, h_color: f32, template_window_size: i32, search_window_size: i32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src_imgs);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fastNlMeansDenoisingColoredMulti_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_int_float_float_int_int(src_imgs.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), img_to_denoise_index, temporal_window_size, h, h_color, template_window_size, search_window_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Modification of fastNlMeansDenoising function for colored images
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src .
/// * templateWindowSize: Size in pixels of the template patch that is used to compute weights.
/// Should be odd. Recommended value 7 pixels
/// * searchWindowSize: Size in pixels of the window that is used to compute weighted average for
/// given pixel. Should be odd. Affect performance linearly: greater searchWindowsSize - greater
/// denoising time. Recommended value 21 pixels
/// * h: Parameter regulating filter strength for luminance component. Bigger h value perfectly
/// removes noise but also removes image details, smaller h value preserves details but also preserves
/// some noise
/// * hColor: The same as h but for color components. For most images value equals 10
/// will be enough to remove colored noise and do not distort colors
///
/// The function converts image to CIELAB colorspace and then separately denoise L and AB components
/// with given h parameters using fastNlMeansDenoising function.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [fast_nl_means_denoising_colored] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * h: 3
/// * h_color: 3
/// * template_window_size: 7
/// * search_window_size: 21
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_colored_def(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fastNlMeansDenoisingColored_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Modification of fastNlMeansDenoising function for colored images
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src .
/// * templateWindowSize: Size in pixels of the template patch that is used to compute weights.
/// Should be odd. Recommended value 7 pixels
/// * searchWindowSize: Size in pixels of the window that is used to compute weighted average for
/// given pixel. Should be odd. Affect performance linearly: greater searchWindowsSize - greater
/// denoising time. Recommended value 21 pixels
/// * h: Parameter regulating filter strength for luminance component. Bigger h value perfectly
/// removes noise but also removes image details, smaller h value preserves details but also preserves
/// some noise
/// * hColor: The same as h but for color components. For most images value equals 10
/// will be enough to remove colored noise and do not distort colors
///
/// The function converts image to CIELAB colorspace and then separately denoise L and AB components
/// with given h parameters using fastNlMeansDenoising function.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * h: 3
/// * h_color: 3
/// * template_window_size: 7
/// * search_window_size: 21
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_colored(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, h: f32, h_color: f32, template_window_size: i32, search_window_size: i32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fastNlMeansDenoisingColored_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float_float_int_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), h, h_color, template_window_size, search_window_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Modification of fastNlMeansDenoising function for images sequence where consecutive images have been
/// captured in small period of time. For example video. This version of the function is for grayscale
/// images or for manual manipulation with colorspaces. See [Buades2005DenoisingIS](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Buades2005DenoisingIS) for more details
/// (open access [here](https://static.aminer.org/pdf/PDF/000/317/196/spatio_temporal_wiener_filtering_of_image_sequences_using_a_parametric.pdf)).
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * srcImgs: Input 8-bit 1-channel, 2-channel, 3-channel or
/// 4-channel images sequence. All images should have the same type and
/// size.
/// * imgToDenoiseIndex: Target image to denoise index in srcImgs sequence
/// * temporalWindowSize: Number of surrounding images to use for target image denoising. Should
/// be odd. Images from imgToDenoiseIndex - temporalWindowSize / 2 to
/// imgToDenoiseIndex + temporalWindowSize / 2 from srcImgs will be used to denoise
/// srcImgs[imgToDenoiseIndex] image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as srcImgs images.
/// * templateWindowSize: Size in pixels of the template patch that is used to compute weights.
/// Should be odd. Recommended value 7 pixels
/// * searchWindowSize: Size in pixels of the window that is used to compute weighted average for
/// given pixel. Should be odd. Affect performance linearly: greater searchWindowsSize - greater
/// denoising time. Recommended value 21 pixels
/// * h: Parameter regulating filter strength. Bigger h value
/// perfectly removes noise but also removes image details, smaller h
/// value preserves details but also preserves some noise
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [fast_nl_means_denoising_multi] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * h: 3
/// * template_window_size: 7
/// * search_window_size: 21
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_multi_def(src_imgs: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, img_to_denoise_index: i32, temporal_window_size: i32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src_imgs);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fastNlMeansDenoisingMulti_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_int(src_imgs.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), img_to_denoise_index, temporal_window_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Modification of fastNlMeansDenoising function for images sequence where consecutive images have been
/// captured in small period of time. For example video. This version of the function is for grayscale
/// images or for manual manipulation with colorspaces. See [Buades2005DenoisingIS](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Buades2005DenoisingIS) for more details
/// (open access [here](https://static.aminer.org/pdf/PDF/000/317/196/spatio_temporal_wiener_filtering_of_image_sequences_using_a_parametric.pdf)).
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * srcImgs: Input 8-bit or 16-bit (only with NORM_L1) 1-channel,
/// 2-channel, 3-channel or 4-channel images sequence. All images should
/// have the same type and size.
/// * imgToDenoiseIndex: Target image to denoise index in srcImgs sequence
/// * temporalWindowSize: Number of surrounding images to use for target image denoising. Should
/// be odd. Images from imgToDenoiseIndex - temporalWindowSize / 2 to
/// imgToDenoiseIndex + temporalWindowSize / 2 from srcImgs will be used to denoise
/// srcImgs[imgToDenoiseIndex] image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as srcImgs images.
/// * templateWindowSize: Size in pixels of the template patch that is used to compute weights.
/// Should be odd. Recommended value 7 pixels
/// * searchWindowSize: Size in pixels of the window that is used to compute weighted average for
/// given pixel. Should be odd. Affect performance linearly: greater searchWindowsSize - greater
/// denoising time. Recommended value 21 pixels
/// * h: Array of parameters regulating filter strength, either one
/// parameter applied to all channels or one per channel in dst. Big h value
/// perfectly removes noise but also removes image details, smaller h
/// value preserves details but also preserves some noise
/// * normType: Type of norm used for weight calculation. Can be either NORM_L2 or NORM_L1
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [fast_nl_means_denoising_multi_vec] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * template_window_size: 7
/// * search_window_size: 21
/// * norm_type: NORM_L2
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_multi_vec_def(src_imgs: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, img_to_denoise_index: i32, temporal_window_size: i32, h: &core::Vector<f32>) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src_imgs);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fastNlMeansDenoisingMulti_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_int_const_vectorLfloatGR(src_imgs.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), img_to_denoise_index, temporal_window_size, h.as_raw_VectorOff32(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Modification of fastNlMeansDenoising function for images sequence where consecutive images have been
/// captured in small period of time. For example video. This version of the function is for grayscale
/// images or for manual manipulation with colorspaces. See [Buades2005DenoisingIS](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Buades2005DenoisingIS) for more details
/// (open access [here](https://static.aminer.org/pdf/PDF/000/317/196/spatio_temporal_wiener_filtering_of_image_sequences_using_a_parametric.pdf)).
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * srcImgs: Input 8-bit or 16-bit (only with NORM_L1) 1-channel,
/// 2-channel, 3-channel or 4-channel images sequence. All images should
/// have the same type and size.
/// * imgToDenoiseIndex: Target image to denoise index in srcImgs sequence
/// * temporalWindowSize: Number of surrounding images to use for target image denoising. Should
/// be odd. Images from imgToDenoiseIndex - temporalWindowSize / 2 to
/// imgToDenoiseIndex + temporalWindowSize / 2 from srcImgs will be used to denoise
/// srcImgs[imgToDenoiseIndex] image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as srcImgs images.
/// * templateWindowSize: Size in pixels of the template patch that is used to compute weights.
/// Should be odd. Recommended value 7 pixels
/// * searchWindowSize: Size in pixels of the window that is used to compute weighted average for
/// given pixel. Should be odd. Affect performance linearly: greater searchWindowsSize - greater
/// denoising time. Recommended value 21 pixels
/// * h: Array of parameters regulating filter strength, either one
/// parameter applied to all channels or one per channel in dst. Big h value
/// perfectly removes noise but also removes image details, smaller h
/// value preserves details but also preserves some noise
/// * normType: Type of norm used for weight calculation. Can be either NORM_L2 or NORM_L1
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * template_window_size: 7
/// * search_window_size: 21
/// * norm_type: NORM_L2
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_multi_vec(src_imgs: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, img_to_denoise_index: i32, temporal_window_size: i32, h: &core::Vector<f32>, template_window_size: i32, search_window_size: i32, norm_type: i32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src_imgs);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fastNlMeansDenoisingMulti_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_int_const_vectorLfloatGR_int_int_int(src_imgs.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), img_to_denoise_index, temporal_window_size, h.as_raw_VectorOff32(), template_window_size, search_window_size, norm_type, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Modification of fastNlMeansDenoising function for images sequence where consecutive images have been
/// captured in small period of time. For example video. This version of the function is for grayscale
/// images or for manual manipulation with colorspaces. See [Buades2005DenoisingIS](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Buades2005DenoisingIS) for more details
/// (open access [here](https://static.aminer.org/pdf/PDF/000/317/196/spatio_temporal_wiener_filtering_of_image_sequences_using_a_parametric.pdf)).
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * srcImgs: Input 8-bit 1-channel, 2-channel, 3-channel or
/// 4-channel images sequence. All images should have the same type and
/// size.
/// * imgToDenoiseIndex: Target image to denoise index in srcImgs sequence
/// * temporalWindowSize: Number of surrounding images to use for target image denoising. Should
/// be odd. Images from imgToDenoiseIndex - temporalWindowSize / 2 to
/// imgToDenoiseIndex + temporalWindowSize / 2 from srcImgs will be used to denoise
/// srcImgs[imgToDenoiseIndex] image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as srcImgs images.
/// * templateWindowSize: Size in pixels of the template patch that is used to compute weights.
/// Should be odd. Recommended value 7 pixels
/// * searchWindowSize: Size in pixels of the window that is used to compute weighted average for
/// given pixel. Should be odd. Affect performance linearly: greater searchWindowsSize - greater
/// denoising time. Recommended value 21 pixels
/// * h: Parameter regulating filter strength. Bigger h value
/// perfectly removes noise but also removes image details, smaller h
/// value preserves details but also preserves some noise
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * h: 3
/// * template_window_size: 7
/// * search_window_size: 21
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_multi(src_imgs: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, img_to_denoise_index: i32, temporal_window_size: i32, h: f32, template_window_size: i32, search_window_size: i32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src_imgs);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fastNlMeansDenoisingMulti_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_int_float_int_int(src_imgs.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), img_to_denoise_index, temporal_window_size, h, template_window_size, search_window_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Perform image denoising using Non-local Means Denoising algorithm
/// <http://www.ipol.im/pub/algo/bcm_non_local_means_denoising/> with several computational
/// optimizations. Noise expected to be a gaussian white noise
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 1-channel, 2-channel, 3-channel or 4-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src .
/// * templateWindowSize: Size in pixels of the template patch that is used to compute weights.
/// Should be odd. Recommended value 7 pixels
/// * searchWindowSize: Size in pixels of the window that is used to compute weighted average for
/// given pixel. Should be odd. Affect performance linearly: greater searchWindowsSize - greater
/// denoising time. Recommended value 21 pixels
/// * h: Parameter regulating filter strength. Big h value perfectly removes noise but also
/// removes image details, smaller h value preserves details but also preserves some noise
///
/// This function expected to be applied to grayscale images. For colored images look at
/// fastNlMeansDenoisingColored. Advanced usage of this functions can be manual denoising of colored
/// image in different colorspaces. Such approach is used in fastNlMeansDenoisingColored by converting
/// image to CIELAB colorspace and then separately denoise L and AB components with different h
/// parameter.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [fast_nl_means_denoising] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * h: 3
/// * template_window_size: 7
/// * search_window_size: 21
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_def(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fastNlMeansDenoising_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Perform image denoising using Non-local Means Denoising algorithm
/// <http://www.ipol.im/pub/algo/bcm_non_local_means_denoising/> with several computational
/// optimizations. Noise expected to be a gaussian white noise
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit or 16-bit (only with NORM_L1) 1-channel,
/// 2-channel, 3-channel or 4-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src .
/// * templateWindowSize: Size in pixels of the template patch that is used to compute weights.
/// Should be odd. Recommended value 7 pixels
/// * searchWindowSize: Size in pixels of the window that is used to compute weighted average for
/// given pixel. Should be odd. Affect performance linearly: greater searchWindowsSize - greater
/// denoising time. Recommended value 21 pixels
/// * h: Array of parameters regulating filter strength, either one
/// parameter applied to all channels or one per channel in dst. Big h value
/// perfectly removes noise but also removes image details, smaller h
/// value preserves details but also preserves some noise
/// * normType: Type of norm used for weight calculation. Can be either NORM_L2 or NORM_L1
///
/// This function expected to be applied to grayscale images. For colored images look at
/// fastNlMeansDenoisingColored. Advanced usage of this functions can be manual denoising of colored
/// image in different colorspaces. Such approach is used in fastNlMeansDenoisingColored by converting
/// image to CIELAB colorspace and then separately denoise L and AB components with different h
/// parameter.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [fast_nl_means_denoising_vec] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * template_window_size: 7
/// * search_window_size: 21
/// * norm_type: NORM_L2
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_vec_def(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, h: &core::Vector<f32>) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fastNlMeansDenoising_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const_vectorLfloatGR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), h.as_raw_VectorOff32(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Perform image denoising using Non-local Means Denoising algorithm
/// <http://www.ipol.im/pub/algo/bcm_non_local_means_denoising/> with several computational
/// optimizations. Noise expected to be a gaussian white noise
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit or 16-bit (only with NORM_L1) 1-channel,
/// 2-channel, 3-channel or 4-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src .
/// * templateWindowSize: Size in pixels of the template patch that is used to compute weights.
/// Should be odd. Recommended value 7 pixels
/// * searchWindowSize: Size in pixels of the window that is used to compute weighted average for
/// given pixel. Should be odd. Affect performance linearly: greater searchWindowsSize - greater
/// denoising time. Recommended value 21 pixels
/// * h: Array of parameters regulating filter strength, either one
/// parameter applied to all channels or one per channel in dst. Big h value
/// perfectly removes noise but also removes image details, smaller h
/// value preserves details but also preserves some noise
/// * normType: Type of norm used for weight calculation. Can be either NORM_L2 or NORM_L1
///
/// This function expected to be applied to grayscale images. For colored images look at
/// fastNlMeansDenoisingColored. Advanced usage of this functions can be manual denoising of colored
/// image in different colorspaces. Such approach is used in fastNlMeansDenoisingColored by converting
/// image to CIELAB colorspace and then separately denoise L and AB components with different h
/// parameter.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * template_window_size: 7
/// * search_window_size: 21
/// * norm_type: NORM_L2
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_vec(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, h: &core::Vector<f32>, template_window_size: i32, search_window_size: i32, norm_type: i32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fastNlMeansDenoising_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const_vectorLfloatGR_int_int_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), h.as_raw_VectorOff32(), template_window_size, search_window_size, norm_type, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Perform image denoising using Non-local Means Denoising algorithm
/// <http://www.ipol.im/pub/algo/bcm_non_local_means_denoising/> with several computational
/// optimizations. Noise expected to be a gaussian white noise
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 1-channel, 2-channel, 3-channel or 4-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src .
/// * templateWindowSize: Size in pixels of the template patch that is used to compute weights.
/// Should be odd. Recommended value 7 pixels
/// * searchWindowSize: Size in pixels of the window that is used to compute weighted average for
/// given pixel. Should be odd. Affect performance linearly: greater searchWindowsSize - greater
/// denoising time. Recommended value 21 pixels
/// * h: Parameter regulating filter strength. Big h value perfectly removes noise but also
/// removes image details, smaller h value preserves details but also preserves some noise
///
/// This function expected to be applied to grayscale images. For colored images look at
/// fastNlMeansDenoisingColored. Advanced usage of this functions can be manual denoising of colored
/// image in different colorspaces. Such approach is used in fastNlMeansDenoisingColored by converting
/// image to CIELAB colorspace and then separately denoise L and AB components with different h
/// parameter.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * h: 3
/// * template_window_size: 7
/// * search_window_size: 21
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, h: f32, template_window_size: i32, search_window_size: i32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fastNlMeansDenoising_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float_int_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), h, template_window_size, search_window_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Applying an appropriate non-linear transformation to the gradient field inside the selection and
/// then integrating back with a Poisson solver, modifies locally the apparent illumination of an image.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * mask: Input 8-bit 1 or 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src.
/// * alpha: Value ranges between 0-2.
/// * beta: Value ranges between 0-2.
///
/// This is useful to highlight under-exposed foreground objects or to reduce specular reflections.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [illumination_change] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * alpha: 0.2f
/// * beta: 0.4f
#[inline]
pub fn illumination_change_def(src: &impl ToInputArray, mask: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
input_array_arg!(mask);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_illuminationChange_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Applying an appropriate non-linear transformation to the gradient field inside the selection and
/// then integrating back with a Poisson solver, modifies locally the apparent illumination of an image.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * mask: Input 8-bit 1 or 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src.
/// * alpha: Value ranges between 0-2.
/// * beta: Value ranges between 0-2.
///
/// This is useful to highlight under-exposed foreground objects or to reduce specular reflections.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * alpha: 0.2f
/// * beta: 0.4f
#[inline]
pub fn illumination_change(src: &impl ToInputArray, mask: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, alpha: f32, beta: f32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
input_array_arg!(mask);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_illuminationChange_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float_float(src.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), alpha, beta, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Restores the selected region in an image using the region neighborhood.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit, 16-bit unsigned or 32-bit float 1-channel or 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * inpaintMask: Inpainting mask, 8-bit 1-channel image. Non-zero pixels indicate the area that
/// needs to be inpainted.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src .
/// * inpaintRadius: Radius of a circular neighborhood of each point inpainted that is considered
/// by the algorithm.
/// * flags: Inpainting method that could be cv::INPAINT_NS or cv::INPAINT_TELEA
///
/// The function reconstructs the selected image area from the pixel near the area boundary. The
/// function may be used to remove dust and scratches from a scanned photo, or to remove undesirable
/// objects from still images or video. See <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inpainting> for more details.
///
///
/// Note:
/// * An example using the inpainting technique can be found at
/// opencv_source_code/samples/cpp/inpaint.cpp
/// * (Python) An example using the inpainting technique can be found at
/// opencv_source_code/samples/python/inpaint.py
#[inline]
pub fn inpaint(src: &impl ToInputArray, inpaint_mask: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, inpaint_radius: f64, flags: i32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
input_array_arg!(inpaint_mask);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_inpaint_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), inpaint_mask.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), inpaint_radius, flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// @example samples/cpp/tutorial_code/photo/non_photorealistic_rendering/npr_demo.cpp
/// An example using non-photorealistic line drawing functions
///
/// Pencil-like non-photorealistic line drawing
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * dst1: Output 8-bit 1-channel image.
/// * dst2: Output image with the same size and type as src.
/// * sigma_s: %Range between 0 to 200.
/// * sigma_r: %Range between 0 to 1.
/// * shade_factor: %Range between 0 to 0.1.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [pencil_sketch] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * sigma_s: 60
/// * sigma_r: 0.07f
/// * shade_factor: 0.02f
#[inline]
pub fn pencil_sketch_def(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst1: &mut impl ToOutputArray, dst2: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst1);
output_array_arg!(dst2);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_pencilSketch_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst1.as_raw__OutputArray(), dst2.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// @example samples/cpp/tutorial_code/photo/non_photorealistic_rendering/npr_demo.cpp
/// An example using non-photorealistic line drawing functions
///
/// Pencil-like non-photorealistic line drawing
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * dst1: Output 8-bit 1-channel image.
/// * dst2: Output image with the same size and type as src.
/// * sigma_s: %Range between 0 to 200.
/// * sigma_r: %Range between 0 to 1.
/// * shade_factor: %Range between 0 to 0.1.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * sigma_s: 60
/// * sigma_r: 0.07f
/// * shade_factor: 0.02f
#[inline]
pub fn pencil_sketch(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst1: &mut impl ToOutputArray, dst2: &mut impl ToOutputArray, sigma_s: f32, sigma_r: f32, shade_factor: f32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst1);
output_array_arg!(dst2);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_pencilSketch_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float_float_float(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst1.as_raw__OutputArray(), dst2.as_raw__OutputArray(), sigma_s, sigma_r, shade_factor, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// @example samples/cpp/tutorial_code/photo/seamless_cloning/cloning_demo.cpp
/// An example using seamlessClone function
///
/// Performs seamless cloning to blend a region from a source image into a destination image.
/// This function is designed for local image editing, allowing changes restricted to a region
/// (manually selected as the ROI) to be applied effortlessly and seamlessly. These changes can
/// range from slight distortions to complete replacement by novel content [PM03](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_PM03).
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: The source image (8-bit 3-channel), from which a region will be blended into the destination.
/// * dst: The destination image (8-bit 3-channel), where the src image will be blended.
/// * mask: A binary mask (8-bit, 1, 3, or 4-channel) specifying the region in the source image to blend.
/// Non-zero pixels indicate the region to be blended. If an empty Mat is provided, a mask with
/// all non-zero pixels is created internally.
/// * p: The point where the center of the src image is placed in the dst image.
/// * blend: The output image that stores the result of the seamless cloning. It has the same size and type as `dst`.
/// * flags: Flags that control the type of cloning method, can take values of `cv::SeamlessCloneFlags`.
#[inline]
pub fn seamless_clone(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &impl ToInputArray, mask: &impl ToInputArray, p: core::Point, blend: &mut impl ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
input_array_arg!(dst);
input_array_arg!(mask);
output_array_arg!(blend);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_seamlessClone_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Point_const__OutputArrayR_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), &p, blend.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Stylization aims to produce digital imagery with a wide variety of effects not focused on
/// photorealism. Edge-aware filters are ideal for stylization, as they can abstract regions of low
/// contrast while preserving, or enhancing, high-contrast features.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src.
/// * sigma_s: %Range between 0 to 200.
/// * sigma_r: %Range between 0 to 1.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [stylization] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * sigma_s: 60
/// * sigma_r: 0.45f
#[inline]
pub fn stylization_def(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_stylization_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Stylization aims to produce digital imagery with a wide variety of effects not focused on
/// photorealism. Edge-aware filters are ideal for stylization, as they can abstract regions of low
/// contrast while preserving, or enhancing, high-contrast features.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src.
/// * sigma_s: %Range between 0 to 200.
/// * sigma_r: %Range between 0 to 1.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * sigma_s: 60
/// * sigma_r: 0.45f
#[inline]
pub fn stylization(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, sigma_s: f32, sigma_r: f32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_stylization_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float_float(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), sigma_s, sigma_r, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// By retaining only the gradients at edge locations, before integrating with the Poisson solver, one
/// washes out the texture of the selected region, giving its contents a flat aspect. Here Canny Edge %Detector is used.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * mask: Input 8-bit 1 or 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src.
/// * low_threshold: %Range from 0 to 100.
/// * high_threshold: Value \> 100.
/// * kernel_size: The size of the Sobel kernel to be used.
///
///
/// Note:
/// The algorithm assumes that the color of the source image is close to that of the destination. This
/// assumption means that when the colors don't match, the source image color gets tinted toward the
/// color of the destination image.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [texture_flattening] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * low_threshold: 30
/// * high_threshold: 45
/// * kernel_size: 3
#[inline]
pub fn texture_flattening_def(src: &impl ToInputArray, mask: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
input_array_arg!(mask);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_textureFlattening_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// By retaining only the gradients at edge locations, before integrating with the Poisson solver, one
/// washes out the texture of the selected region, giving its contents a flat aspect. Here Canny Edge %Detector is used.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * mask: Input 8-bit 1 or 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src.
/// * low_threshold: %Range from 0 to 100.
/// * high_threshold: Value \> 100.
/// * kernel_size: The size of the Sobel kernel to be used.
///
///
/// Note:
/// The algorithm assumes that the color of the source image is close to that of the destination. This
/// assumption means that when the colors don't match, the source image color gets tinted toward the
/// color of the destination image.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * low_threshold: 30
/// * high_threshold: 45
/// * kernel_size: 3
#[inline]
pub fn texture_flattening(src: &impl ToInputArray, mask: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, low_threshold: f32, high_threshold: f32, kernel_size: i32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
input_array_arg!(mask);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_textureFlattening_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float_float_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), low_threshold, high_threshold, kernel_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// The base class for algorithms that align images of the same scene with different exposures
pub struct AlignExposures {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { AlignExposures }
impl Drop for AlignExposures {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_AlignExposures_delete(self.as_raw_mut_AlignExposures()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for AlignExposures {}
/// Constant methods for [crate::photo::AlignExposures]
pub trait AlignExposuresTraitConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_AlignExposures(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::photo::AlignExposures]
pub trait AlignExposuresTrait: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::photo::AlignExposuresTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_AlignExposures(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Aligns images
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: vector of input images
/// * dst: vector of aligned images
/// * times: vector of exposure time values for each image
/// * response: 256x1 matrix with inverse camera response function for each pixel value, it should
/// have the same number of channels as images.
#[inline]
fn process(&mut self, src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut core::Vector<core::Mat>, times: &impl ToInputArray, response: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
input_array_arg!(times);
input_array_arg!(response);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_AlignExposures_process_const__InputArrayR_vectorLMatGR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_AlignExposures(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw_mut_VectorOfMat(), times.as_raw__InputArray(), response.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for AlignExposures {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("AlignExposures")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { AlignExposures, core::Algorithm, cv_AlignExposures_to_Algorithm }
boxed_cast_descendant! { AlignExposures, crate::photo::AlignMTB, cv_AlignExposures_to_AlignMTB }
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for AlignExposures {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for AlignExposures {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { AlignExposures, core::AlgorithmTraitConst, as_raw_Algorithm, core::AlgorithmTrait, as_raw_mut_Algorithm }
impl crate::photo::AlignExposuresTraitConst for AlignExposures {
#[inline] fn as_raw_AlignExposures(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::photo::AlignExposuresTrait for AlignExposures {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_AlignExposures(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { AlignExposures, crate::photo::AlignExposuresTraitConst, as_raw_AlignExposures, crate::photo::AlignExposuresTrait, as_raw_mut_AlignExposures }
/// This algorithm converts images to median threshold bitmaps (1 for pixels brighter than median
/// luminance and 0 otherwise) and than aligns the resulting bitmaps using bit operations.
///
/// It is invariant to exposure, so exposure values and camera response are not necessary.
///
/// In this implementation new image regions are filled with zeros.
///
/// For more information see [GW03](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_GW03) .
pub struct AlignMTB {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { AlignMTB }
impl Drop for AlignMTB {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_AlignMTB_delete(self.as_raw_mut_AlignMTB()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for AlignMTB {}
/// Constant methods for [crate::photo::AlignMTB]
pub trait AlignMTBTraitConst: crate::photo::AlignExposuresTraitConst {
fn as_raw_AlignMTB(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn get_max_bits(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_AlignMTB_getMaxBits_const(self.as_raw_AlignMTB(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_exclude_range(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_AlignMTB_getExcludeRange_const(self.as_raw_AlignMTB(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_cut(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_AlignMTB_getCut_const(self.as_raw_AlignMTB(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::photo::AlignMTB]
pub trait AlignMTBTrait: crate::photo::AlignExposuresTrait + crate::photo::AlignMTBTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_AlignMTB(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn process_with_response(&mut self, src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut core::Vector<core::Mat>, times: &impl ToInputArray, response: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
input_array_arg!(times);
input_array_arg!(response);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_AlignMTB_process_const__InputArrayR_vectorLMatGR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_AlignMTB(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw_mut_VectorOfMat(), times.as_raw__InputArray(), response.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Short version of process, that doesn't take extra arguments.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: vector of input images
/// * dst: vector of aligned images
#[inline]
fn process(&mut self, src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut core::Vector<core::Mat>) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_AlignMTB_process_const__InputArrayR_vectorLMatGR(self.as_raw_mut_AlignMTB(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw_mut_VectorOfMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates shift between two images, i. e. how to shift the second image to correspond it with the
/// first.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * img0: first image
/// * img1: second image
#[inline]
fn calculate_shift(&mut self, img0: &impl ToInputArray, img1: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<core::Point> {
input_array_arg!(img0);
input_array_arg!(img1);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_AlignMTB_calculateShift_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_AlignMTB(), img0.as_raw__InputArray(), img1.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Helper function, that shift Mat filling new regions with zeros.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input image
/// * dst: result image
/// * shift: shift value
#[inline]
fn shift_mat(&mut self, src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, shift: core::Point) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_AlignMTB_shiftMat_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const_Point(self.as_raw_mut_AlignMTB(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), &shift, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes median threshold and exclude bitmaps of given image.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * img: input image
/// * tb: median threshold bitmap
/// * eb: exclude bitmap
#[inline]
fn compute_bitmaps(&mut self, img: &impl ToInputArray, tb: &mut impl ToOutputArray, eb: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(img);
output_array_arg!(tb);
output_array_arg!(eb);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_AlignMTB_computeBitmaps_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_AlignMTB(), img.as_raw__InputArray(), tb.as_raw__OutputArray(), eb.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_max_bits(&mut self, max_bits: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_AlignMTB_setMaxBits_int(self.as_raw_mut_AlignMTB(), max_bits, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_exclude_range(&mut self, exclude_range: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_AlignMTB_setExcludeRange_int(self.as_raw_mut_AlignMTB(), exclude_range, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_cut(&mut self, value: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_AlignMTB_setCut_bool(self.as_raw_mut_AlignMTB(), value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for AlignMTB {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("AlignMTB")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { AlignMTB, core::Algorithm, cv_AlignMTB_to_Algorithm }
boxed_cast_base! { AlignMTB, crate::photo::AlignExposures, cv_AlignMTB_to_AlignExposures }
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for AlignMTB {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for AlignMTB {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { AlignMTB, core::AlgorithmTraitConst, as_raw_Algorithm, core::AlgorithmTrait, as_raw_mut_Algorithm }
impl crate::photo::AlignExposuresTraitConst for AlignMTB {
#[inline] fn as_raw_AlignExposures(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::photo::AlignExposuresTrait for AlignMTB {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_AlignExposures(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { AlignMTB, crate::photo::AlignExposuresTraitConst, as_raw_AlignExposures, crate::photo::AlignExposuresTrait, as_raw_mut_AlignExposures }
impl crate::photo::AlignMTBTraitConst for AlignMTB {
#[inline] fn as_raw_AlignMTB(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::photo::AlignMTBTrait for AlignMTB {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_AlignMTB(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { AlignMTB, crate::photo::AlignMTBTraitConst, as_raw_AlignMTB, crate::photo::AlignMTBTrait, as_raw_mut_AlignMTB }
/// The base class for camera response calibration algorithms.
pub struct CalibrateCRF {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { CalibrateCRF }
impl Drop for CalibrateCRF {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_CalibrateCRF_delete(self.as_raw_mut_CalibrateCRF()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for CalibrateCRF {}
/// Constant methods for [crate::photo::CalibrateCRF]
pub trait CalibrateCRFTraitConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_CalibrateCRF(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::photo::CalibrateCRF]
pub trait CalibrateCRFTrait: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::photo::CalibrateCRFTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_CalibrateCRF(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Recovers inverse camera response.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: vector of input images
/// * dst: 256x1 matrix with inverse camera response function
/// * times: vector of exposure time values for each image
#[inline]
fn process(&mut self, src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, times: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
input_array_arg!(times);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_CalibrateCRF_process_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_CalibrateCRF(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), times.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for CalibrateCRF {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("CalibrateCRF")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { CalibrateCRF, core::Algorithm, cv_CalibrateCRF_to_Algorithm }
boxed_cast_descendant! { CalibrateCRF, crate::photo::CalibrateDebevec, cv_CalibrateCRF_to_CalibrateDebevec }
boxed_cast_descendant! { CalibrateCRF, crate::photo::CalibrateRobertson, cv_CalibrateCRF_to_CalibrateRobertson }
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for CalibrateCRF {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for CalibrateCRF {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { CalibrateCRF, core::AlgorithmTraitConst, as_raw_Algorithm, core::AlgorithmTrait, as_raw_mut_Algorithm }
impl crate::photo::CalibrateCRFTraitConst for CalibrateCRF {
#[inline] fn as_raw_CalibrateCRF(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::photo::CalibrateCRFTrait for CalibrateCRF {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_CalibrateCRF(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { CalibrateCRF, crate::photo::CalibrateCRFTraitConst, as_raw_CalibrateCRF, crate::photo::CalibrateCRFTrait, as_raw_mut_CalibrateCRF }
/// Inverse camera response function is extracted for each brightness value by minimizing an objective
/// function as linear system. Objective function is constructed using pixel values on the same position
/// in all images, extra term is added to make the result smoother.
///
/// For more information see [DM97](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_DM97) .
pub struct CalibrateDebevec {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { CalibrateDebevec }
impl Drop for CalibrateDebevec {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_CalibrateDebevec_delete(self.as_raw_mut_CalibrateDebevec()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for CalibrateDebevec {}
/// Constant methods for [crate::photo::CalibrateDebevec]
pub trait CalibrateDebevecTraitConst: crate::photo::CalibrateCRFTraitConst {
fn as_raw_CalibrateDebevec(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn get_lambda(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_CalibrateDebevec_getLambda_const(self.as_raw_CalibrateDebevec(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_samples(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_CalibrateDebevec_getSamples_const(self.as_raw_CalibrateDebevec(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_random(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_CalibrateDebevec_getRandom_const(self.as_raw_CalibrateDebevec(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::photo::CalibrateDebevec]
pub trait CalibrateDebevecTrait: crate::photo::CalibrateCRFTrait + crate::photo::CalibrateDebevecTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_CalibrateDebevec(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_lambda(&mut self, lambda: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_CalibrateDebevec_setLambda_float(self.as_raw_mut_CalibrateDebevec(), lambda, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_samples(&mut self, samples: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_CalibrateDebevec_setSamples_int(self.as_raw_mut_CalibrateDebevec(), samples, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_random(&mut self, random: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_CalibrateDebevec_setRandom_bool(self.as_raw_mut_CalibrateDebevec(), random, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for CalibrateDebevec {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("CalibrateDebevec")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { CalibrateDebevec, core::Algorithm, cv_CalibrateDebevec_to_Algorithm }
boxed_cast_base! { CalibrateDebevec, crate::photo::CalibrateCRF, cv_CalibrateDebevec_to_CalibrateCRF }
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for CalibrateDebevec {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for CalibrateDebevec {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { CalibrateDebevec, core::AlgorithmTraitConst, as_raw_Algorithm, core::AlgorithmTrait, as_raw_mut_Algorithm }
impl crate::photo::CalibrateCRFTraitConst for CalibrateDebevec {
#[inline] fn as_raw_CalibrateCRF(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::photo::CalibrateCRFTrait for CalibrateDebevec {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_CalibrateCRF(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { CalibrateDebevec, crate::photo::CalibrateCRFTraitConst, as_raw_CalibrateCRF, crate::photo::CalibrateCRFTrait, as_raw_mut_CalibrateCRF }
impl crate::photo::CalibrateDebevecTraitConst for CalibrateDebevec {
#[inline] fn as_raw_CalibrateDebevec(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::photo::CalibrateDebevecTrait for CalibrateDebevec {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_CalibrateDebevec(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { CalibrateDebevec, crate::photo::CalibrateDebevecTraitConst, as_raw_CalibrateDebevec, crate::photo::CalibrateDebevecTrait, as_raw_mut_CalibrateDebevec }
/// Inverse camera response function is extracted for each brightness value by minimizing an objective
/// function as linear system. This algorithm uses all image pixels.
///
/// For more information see [RB99](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_RB99) .
pub struct CalibrateRobertson {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { CalibrateRobertson }
impl Drop for CalibrateRobertson {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_CalibrateRobertson_delete(self.as_raw_mut_CalibrateRobertson()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for CalibrateRobertson {}
/// Constant methods for [crate::photo::CalibrateRobertson]
pub trait CalibrateRobertsonTraitConst: crate::photo::CalibrateCRFTraitConst {
fn as_raw_CalibrateRobertson(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn get_max_iter(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_CalibrateRobertson_getMaxIter_const(self.as_raw_CalibrateRobertson(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_threshold(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_CalibrateRobertson_getThreshold_const(self.as_raw_CalibrateRobertson(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_radiance(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_CalibrateRobertson_getRadiance_const(self.as_raw_CalibrateRobertson(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::photo::CalibrateRobertson]
pub trait CalibrateRobertsonTrait: crate::photo::CalibrateCRFTrait + crate::photo::CalibrateRobertsonTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_CalibrateRobertson(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_max_iter(&mut self, max_iter: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_CalibrateRobertson_setMaxIter_int(self.as_raw_mut_CalibrateRobertson(), max_iter, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_threshold(&mut self, threshold: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_CalibrateRobertson_setThreshold_float(self.as_raw_mut_CalibrateRobertson(), threshold, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for CalibrateRobertson {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("CalibrateRobertson")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { CalibrateRobertson, core::Algorithm, cv_CalibrateRobertson_to_Algorithm }
boxed_cast_base! { CalibrateRobertson, crate::photo::CalibrateCRF, cv_CalibrateRobertson_to_CalibrateCRF }
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for CalibrateRobertson {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for CalibrateRobertson {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { CalibrateRobertson, core::AlgorithmTraitConst, as_raw_Algorithm, core::AlgorithmTrait, as_raw_mut_Algorithm }
impl crate::photo::CalibrateCRFTraitConst for CalibrateRobertson {
#[inline] fn as_raw_CalibrateCRF(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::photo::CalibrateCRFTrait for CalibrateRobertson {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_CalibrateCRF(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { CalibrateRobertson, crate::photo::CalibrateCRFTraitConst, as_raw_CalibrateCRF, crate::photo::CalibrateCRFTrait, as_raw_mut_CalibrateCRF }
impl crate::photo::CalibrateRobertsonTraitConst for CalibrateRobertson {
#[inline] fn as_raw_CalibrateRobertson(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::photo::CalibrateRobertsonTrait for CalibrateRobertson {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_CalibrateRobertson(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { CalibrateRobertson, crate::photo::CalibrateRobertsonTraitConst, as_raw_CalibrateRobertson, crate::photo::CalibrateRobertsonTrait, as_raw_mut_CalibrateRobertson }
/// The resulting HDR image is calculated as weighted average of the exposures considering exposure
/// values and camera response.
///
/// For more information see [DM97](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_DM97) .
pub struct MergeDebevec {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { MergeDebevec }
impl Drop for MergeDebevec {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_MergeDebevec_delete(self.as_raw_mut_MergeDebevec()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for MergeDebevec {}
/// Constant methods for [crate::photo::MergeDebevec]
pub trait MergeDebevecTraitConst: crate::photo::MergeExposuresTraitConst {
fn as_raw_MergeDebevec(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::photo::MergeDebevec]
pub trait MergeDebevecTrait: crate::photo::MergeDebevecTraitConst + crate::photo::MergeExposuresTrait {
fn as_raw_mut_MergeDebevec(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn process_with_response(&mut self, src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, times: &impl ToInputArray, response: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
input_array_arg!(times);
input_array_arg!(response);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MergeDebevec_process_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_MergeDebevec(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), times.as_raw__InputArray(), response.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn process(&mut self, src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, times: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
input_array_arg!(times);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MergeDebevec_process_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_MergeDebevec(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), times.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for MergeDebevec {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("MergeDebevec")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { MergeDebevec, core::Algorithm, cv_MergeDebevec_to_Algorithm }
boxed_cast_base! { MergeDebevec, crate::photo::MergeExposures, cv_MergeDebevec_to_MergeExposures }
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for MergeDebevec {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for MergeDebevec {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { MergeDebevec, core::AlgorithmTraitConst, as_raw_Algorithm, core::AlgorithmTrait, as_raw_mut_Algorithm }
impl crate::photo::MergeExposuresTraitConst for MergeDebevec {
#[inline] fn as_raw_MergeExposures(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::photo::MergeExposuresTrait for MergeDebevec {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_MergeExposures(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { MergeDebevec, crate::photo::MergeExposuresTraitConst, as_raw_MergeExposures, crate::photo::MergeExposuresTrait, as_raw_mut_MergeExposures }
impl crate::photo::MergeDebevecTraitConst for MergeDebevec {
#[inline] fn as_raw_MergeDebevec(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::photo::MergeDebevecTrait for MergeDebevec {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_MergeDebevec(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { MergeDebevec, crate::photo::MergeDebevecTraitConst, as_raw_MergeDebevec, crate::photo::MergeDebevecTrait, as_raw_mut_MergeDebevec }
/// The base class algorithms that can merge exposure sequence to a single image.
pub struct MergeExposures {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { MergeExposures }
impl Drop for MergeExposures {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_MergeExposures_delete(self.as_raw_mut_MergeExposures()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for MergeExposures {}
/// Constant methods for [crate::photo::MergeExposures]
pub trait MergeExposuresTraitConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_MergeExposures(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::photo::MergeExposures]
pub trait MergeExposuresTrait: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::photo::MergeExposuresTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_MergeExposures(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Merges images.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: vector of input images
/// * dst: result image
/// * times: vector of exposure time values for each image
/// * response: 256x1 matrix with inverse camera response function for each pixel value, it should
/// have the same number of channels as images.
#[inline]
fn process(&mut self, src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, times: &impl ToInputArray, response: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
input_array_arg!(times);
input_array_arg!(response);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MergeExposures_process_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_MergeExposures(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), times.as_raw__InputArray(), response.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for MergeExposures {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("MergeExposures")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { MergeExposures, core::Algorithm, cv_MergeExposures_to_Algorithm }
boxed_cast_descendant! { MergeExposures, crate::photo::MergeDebevec, cv_MergeExposures_to_MergeDebevec }
boxed_cast_descendant! { MergeExposures, crate::photo::MergeMertens, cv_MergeExposures_to_MergeMertens }
boxed_cast_descendant! { MergeExposures, crate::photo::MergeRobertson, cv_MergeExposures_to_MergeRobertson }
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for MergeExposures {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for MergeExposures {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { MergeExposures, core::AlgorithmTraitConst, as_raw_Algorithm, core::AlgorithmTrait, as_raw_mut_Algorithm }
impl crate::photo::MergeExposuresTraitConst for MergeExposures {
#[inline] fn as_raw_MergeExposures(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::photo::MergeExposuresTrait for MergeExposures {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_MergeExposures(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { MergeExposures, crate::photo::MergeExposuresTraitConst, as_raw_MergeExposures, crate::photo::MergeExposuresTrait, as_raw_mut_MergeExposures }
/// Pixels are weighted using contrast, saturation and well-exposedness measures, than images are
/// combined using laplacian pyramids.
///
/// The resulting image weight is constructed as weighted average of contrast, saturation and
/// well-exposedness measures.
///
/// The resulting image doesn't require tonemapping and can be converted to 8-bit image by multiplying
/// by 255, but it's recommended to apply gamma correction and/or linear tonemapping.
///
/// For more information see [MK07](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_MK07) .
pub struct MergeMertens {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { MergeMertens }
impl Drop for MergeMertens {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_MergeMertens_delete(self.as_raw_mut_MergeMertens()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for MergeMertens {}
/// Constant methods for [crate::photo::MergeMertens]
pub trait MergeMertensTraitConst: crate::photo::MergeExposuresTraitConst {
fn as_raw_MergeMertens(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn get_contrast_weight(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MergeMertens_getContrastWeight_const(self.as_raw_MergeMertens(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_saturation_weight(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MergeMertens_getSaturationWeight_const(self.as_raw_MergeMertens(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_exposure_weight(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MergeMertens_getExposureWeight_const(self.as_raw_MergeMertens(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::photo::MergeMertens]
pub trait MergeMertensTrait: crate::photo::MergeExposuresTrait + crate::photo::MergeMertensTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_MergeMertens(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn process_with_response(&mut self, src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, times: &impl ToInputArray, response: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
input_array_arg!(times);
input_array_arg!(response);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MergeMertens_process_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_MergeMertens(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), times.as_raw__InputArray(), response.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Short version of process, that doesn't take extra arguments.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: vector of input images
/// * dst: result image
#[inline]
fn process(&mut self, src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MergeMertens_process_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_MergeMertens(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_contrast_weight(&mut self, contrast_weiht: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MergeMertens_setContrastWeight_float(self.as_raw_mut_MergeMertens(), contrast_weiht, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_saturation_weight(&mut self, saturation_weight: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MergeMertens_setSaturationWeight_float(self.as_raw_mut_MergeMertens(), saturation_weight, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_exposure_weight(&mut self, exposure_weight: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MergeMertens_setExposureWeight_float(self.as_raw_mut_MergeMertens(), exposure_weight, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for MergeMertens {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("MergeMertens")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { MergeMertens, core::Algorithm, cv_MergeMertens_to_Algorithm }
boxed_cast_base! { MergeMertens, crate::photo::MergeExposures, cv_MergeMertens_to_MergeExposures }
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for MergeMertens {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for MergeMertens {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { MergeMertens, core::AlgorithmTraitConst, as_raw_Algorithm, core::AlgorithmTrait, as_raw_mut_Algorithm }
impl crate::photo::MergeExposuresTraitConst for MergeMertens {
#[inline] fn as_raw_MergeExposures(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::photo::MergeExposuresTrait for MergeMertens {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_MergeExposures(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { MergeMertens, crate::photo::MergeExposuresTraitConst, as_raw_MergeExposures, crate::photo::MergeExposuresTrait, as_raw_mut_MergeExposures }
impl crate::photo::MergeMertensTraitConst for MergeMertens {
#[inline] fn as_raw_MergeMertens(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::photo::MergeMertensTrait for MergeMertens {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_MergeMertens(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { MergeMertens, crate::photo::MergeMertensTraitConst, as_raw_MergeMertens, crate::photo::MergeMertensTrait, as_raw_mut_MergeMertens }
/// The resulting HDR image is calculated as weighted average of the exposures considering exposure
/// values and camera response.
///
/// For more information see [RB99](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_RB99) .
pub struct MergeRobertson {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { MergeRobertson }
impl Drop for MergeRobertson {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_MergeRobertson_delete(self.as_raw_mut_MergeRobertson()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for MergeRobertson {}
/// Constant methods for [crate::photo::MergeRobertson]
pub trait MergeRobertsonTraitConst: crate::photo::MergeExposuresTraitConst {
fn as_raw_MergeRobertson(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::photo::MergeRobertson]
pub trait MergeRobertsonTrait: crate::photo::MergeExposuresTrait + crate::photo::MergeRobertsonTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_MergeRobertson(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn process_with_response(&mut self, src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, times: &impl ToInputArray, response: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
input_array_arg!(times);
input_array_arg!(response);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MergeRobertson_process_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_MergeRobertson(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), times.as_raw__InputArray(), response.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn process(&mut self, src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, times: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
input_array_arg!(times);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MergeRobertson_process_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_MergeRobertson(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), times.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for MergeRobertson {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("MergeRobertson")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { MergeRobertson, core::Algorithm, cv_MergeRobertson_to_Algorithm }
boxed_cast_base! { MergeRobertson, crate::photo::MergeExposures, cv_MergeRobertson_to_MergeExposures }
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for MergeRobertson {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for MergeRobertson {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { MergeRobertson, core::AlgorithmTraitConst, as_raw_Algorithm, core::AlgorithmTrait, as_raw_mut_Algorithm }
impl crate::photo::MergeExposuresTraitConst for MergeRobertson {
#[inline] fn as_raw_MergeExposures(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::photo::MergeExposuresTrait for MergeRobertson {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_MergeExposures(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { MergeRobertson, crate::photo::MergeExposuresTraitConst, as_raw_MergeExposures, crate::photo::MergeExposuresTrait, as_raw_mut_MergeExposures }
impl crate::photo::MergeRobertsonTraitConst for MergeRobertson {
#[inline] fn as_raw_MergeRobertson(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::photo::MergeRobertsonTrait for MergeRobertson {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_MergeRobertson(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { MergeRobertson, crate::photo::MergeRobertsonTraitConst, as_raw_MergeRobertson, crate::photo::MergeRobertsonTrait, as_raw_mut_MergeRobertson }
/// Base class for tonemapping algorithms - tools that are used to map HDR image to 8-bit range.
pub struct Tonemap {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Tonemap }
impl Drop for Tonemap {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_Tonemap_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Tonemap()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Tonemap {}
/// Constant methods for [crate::photo::Tonemap]
pub trait TonemapTraitConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Tonemap(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn get_gamma(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Tonemap_getGamma_const(self.as_raw_Tonemap(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::photo::Tonemap]
pub trait TonemapTrait: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::photo::TonemapTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Tonemap(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Tonemaps image
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: source image - CV_32FC3 Mat (float 32 bits 3 channels)
/// * dst: destination image - CV_32FC3 Mat with values in [0, 1] range
#[inline]
fn process(&mut self, src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Tonemap_process_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_Tonemap(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_gamma(&mut self, gamma: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Tonemap_setGamma_float(self.as_raw_mut_Tonemap(), gamma, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for Tonemap {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("Tonemap")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { Tonemap, core::Algorithm, cv_Tonemap_to_Algorithm }
boxed_cast_descendant! { Tonemap, crate::photo::TonemapDrago, cv_Tonemap_to_TonemapDrago }
boxed_cast_descendant! { Tonemap, crate::photo::TonemapMantiuk, cv_Tonemap_to_TonemapMantiuk }
boxed_cast_descendant! { Tonemap, crate::photo::TonemapReinhard, cv_Tonemap_to_TonemapReinhard }
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for Tonemap {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for Tonemap {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { Tonemap, core::AlgorithmTraitConst, as_raw_Algorithm, core::AlgorithmTrait, as_raw_mut_Algorithm }
impl crate::photo::TonemapTraitConst for Tonemap {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Tonemap(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::photo::TonemapTrait for Tonemap {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Tonemap(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { Tonemap, crate::photo::TonemapTraitConst, as_raw_Tonemap, crate::photo::TonemapTrait, as_raw_mut_Tonemap }
/// Adaptive logarithmic mapping is a fast global tonemapping algorithm that scales the image in
/// logarithmic domain.
///
/// Since it's a global operator the same function is applied to all the pixels, it is controlled by the
/// bias parameter.
///
/// Optional saturation enhancement is possible as described in [FL02](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_FL02) .
///
/// For more information see [DM03](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_DM03) .
pub struct TonemapDrago {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { TonemapDrago }
impl Drop for TonemapDrago {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_TonemapDrago_delete(self.as_raw_mut_TonemapDrago()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for TonemapDrago {}
/// Constant methods for [crate::photo::TonemapDrago]
pub trait TonemapDragoTraitConst: crate::photo::TonemapTraitConst {
fn as_raw_TonemapDrago(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn get_saturation(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TonemapDrago_getSaturation_const(self.as_raw_TonemapDrago(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_bias(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TonemapDrago_getBias_const(self.as_raw_TonemapDrago(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::photo::TonemapDrago]
pub trait TonemapDragoTrait: crate::photo::TonemapDragoTraitConst + crate::photo::TonemapTrait {
fn as_raw_mut_TonemapDrago(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_saturation(&mut self, saturation: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TonemapDrago_setSaturation_float(self.as_raw_mut_TonemapDrago(), saturation, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_bias(&mut self, bias: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TonemapDrago_setBias_float(self.as_raw_mut_TonemapDrago(), bias, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for TonemapDrago {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("TonemapDrago")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { TonemapDrago, core::Algorithm, cv_TonemapDrago_to_Algorithm }
boxed_cast_base! { TonemapDrago, crate::photo::Tonemap, cv_TonemapDrago_to_Tonemap }
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for TonemapDrago {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for TonemapDrago {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { TonemapDrago, core::AlgorithmTraitConst, as_raw_Algorithm, core::AlgorithmTrait, as_raw_mut_Algorithm }
impl crate::photo::TonemapTraitConst for TonemapDrago {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Tonemap(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::photo::TonemapTrait for TonemapDrago {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Tonemap(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { TonemapDrago, crate::photo::TonemapTraitConst, as_raw_Tonemap, crate::photo::TonemapTrait, as_raw_mut_Tonemap }
impl crate::photo::TonemapDragoTraitConst for TonemapDrago {
#[inline] fn as_raw_TonemapDrago(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::photo::TonemapDragoTrait for TonemapDrago {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_TonemapDrago(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { TonemapDrago, crate::photo::TonemapDragoTraitConst, as_raw_TonemapDrago, crate::photo::TonemapDragoTrait, as_raw_mut_TonemapDrago }
/// This algorithm transforms image to contrast using gradients on all levels of gaussian pyramid,
/// transforms contrast values to HVS response and scales the response. After this the image is
/// reconstructed from new contrast values.
///
/// For more information see [MM06](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_MM06) .
pub struct TonemapMantiuk {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { TonemapMantiuk }
impl Drop for TonemapMantiuk {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_TonemapMantiuk_delete(self.as_raw_mut_TonemapMantiuk()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for TonemapMantiuk {}
/// Constant methods for [crate::photo::TonemapMantiuk]
pub trait TonemapMantiukTraitConst: crate::photo::TonemapTraitConst {
fn as_raw_TonemapMantiuk(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn get_scale(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TonemapMantiuk_getScale_const(self.as_raw_TonemapMantiuk(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_saturation(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TonemapMantiuk_getSaturation_const(self.as_raw_TonemapMantiuk(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::photo::TonemapMantiuk]
pub trait TonemapMantiukTrait: crate::photo::TonemapMantiukTraitConst + crate::photo::TonemapTrait {
fn as_raw_mut_TonemapMantiuk(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_scale(&mut self, scale: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TonemapMantiuk_setScale_float(self.as_raw_mut_TonemapMantiuk(), scale, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_saturation(&mut self, saturation: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TonemapMantiuk_setSaturation_float(self.as_raw_mut_TonemapMantiuk(), saturation, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for TonemapMantiuk {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("TonemapMantiuk")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { TonemapMantiuk, core::Algorithm, cv_TonemapMantiuk_to_Algorithm }
boxed_cast_base! { TonemapMantiuk, crate::photo::Tonemap, cv_TonemapMantiuk_to_Tonemap }
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for TonemapMantiuk {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for TonemapMantiuk {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { TonemapMantiuk, core::AlgorithmTraitConst, as_raw_Algorithm, core::AlgorithmTrait, as_raw_mut_Algorithm }
impl crate::photo::TonemapTraitConst for TonemapMantiuk {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Tonemap(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::photo::TonemapTrait for TonemapMantiuk {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Tonemap(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { TonemapMantiuk, crate::photo::TonemapTraitConst, as_raw_Tonemap, crate::photo::TonemapTrait, as_raw_mut_Tonemap }
impl crate::photo::TonemapMantiukTraitConst for TonemapMantiuk {
#[inline] fn as_raw_TonemapMantiuk(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::photo::TonemapMantiukTrait for TonemapMantiuk {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_TonemapMantiuk(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { TonemapMantiuk, crate::photo::TonemapMantiukTraitConst, as_raw_TonemapMantiuk, crate::photo::TonemapMantiukTrait, as_raw_mut_TonemapMantiuk }
/// This is a global tonemapping operator that models human visual system.
///
/// Mapping function is controlled by adaptation parameter, that is computed using light adaptation and
/// color adaptation.
///
/// For more information see [RD05](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_RD05) .
pub struct TonemapReinhard {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { TonemapReinhard }
impl Drop for TonemapReinhard {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_TonemapReinhard_delete(self.as_raw_mut_TonemapReinhard()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for TonemapReinhard {}
/// Constant methods for [crate::photo::TonemapReinhard]
pub trait TonemapReinhardTraitConst: crate::photo::TonemapTraitConst {
fn as_raw_TonemapReinhard(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn get_intensity(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TonemapReinhard_getIntensity_const(self.as_raw_TonemapReinhard(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_light_adaptation(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TonemapReinhard_getLightAdaptation_const(self.as_raw_TonemapReinhard(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_color_adaptation(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TonemapReinhard_getColorAdaptation_const(self.as_raw_TonemapReinhard(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::photo::TonemapReinhard]
pub trait TonemapReinhardTrait: crate::photo::TonemapReinhardTraitConst + crate::photo::TonemapTrait {
fn as_raw_mut_TonemapReinhard(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_intensity(&mut self, intensity: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TonemapReinhard_setIntensity_float(self.as_raw_mut_TonemapReinhard(), intensity, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_light_adaptation(&mut self, light_adapt: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TonemapReinhard_setLightAdaptation_float(self.as_raw_mut_TonemapReinhard(), light_adapt, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_color_adaptation(&mut self, color_adapt: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TonemapReinhard_setColorAdaptation_float(self.as_raw_mut_TonemapReinhard(), color_adapt, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for TonemapReinhard {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("TonemapReinhard")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { TonemapReinhard, core::Algorithm, cv_TonemapReinhard_to_Algorithm }
boxed_cast_base! { TonemapReinhard, crate::photo::Tonemap, cv_TonemapReinhard_to_Tonemap }
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for TonemapReinhard {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for TonemapReinhard {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { TonemapReinhard, core::AlgorithmTraitConst, as_raw_Algorithm, core::AlgorithmTrait, as_raw_mut_Algorithm }
impl crate::photo::TonemapTraitConst for TonemapReinhard {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Tonemap(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::photo::TonemapTrait for TonemapReinhard {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Tonemap(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { TonemapReinhard, crate::photo::TonemapTraitConst, as_raw_Tonemap, crate::photo::TonemapTrait, as_raw_mut_Tonemap }
impl crate::photo::TonemapReinhardTraitConst for TonemapReinhard {
#[inline] fn as_raw_TonemapReinhard(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::photo::TonemapReinhardTrait for TonemapReinhard {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_TonemapReinhard(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { TonemapReinhard, crate::photo::TonemapReinhardTraitConst, as_raw_TonemapReinhard, crate::photo::TonemapReinhardTrait, as_raw_mut_TonemapReinhard }
}