pub mod calib3d {
//! # Camera Calibration and 3D Reconstruction
//!
//! The functions in this section use a so-called pinhole camera model. The view of a scene
//! is obtained by projecting a scene's 3D point  into the image plane using a perspective
//! transformation which forms the corresponding pixel 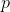. Both  and 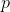 are
//! represented in homogeneous coordinates, i.e. as 3D and 2D homogeneous vector respectively. You will
//! find a brief introduction to projective geometry, homogeneous vectors and homogeneous
//! transformations at the end of this section's introduction. For more succinct notation, we often drop
//! the 'homogeneous' and say vector instead of homogeneous vector.
//!
//! The distortion-free projective transformation given by a pinhole camera model is shown below.
//!
//! 
//!
//! where  is a 3D point expressed with respect to the world coordinate system,
//! 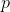 is a 2D pixel in the image plane, 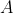 is the camera intrinsic matrix,
//!  and 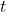 are the rotation and translation that describe the change of coordinates from
//! world to camera coordinate systems (or camera frame) and  is the projective transformation's
//! arbitrary scaling and not part of the camera model.
//!
//! The camera intrinsic matrix 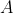 (notation used as in [Zhang2000](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Zhang2000) and also generally notated
//! as 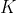) projects 3D points given in the camera coordinate system to 2D pixel coordinates, i.e.
//!
//! 
//!
//! The camera intrinsic matrix 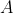 is composed of the focal lengths  and , which are
//! expressed in pixel units, and the principal point , that is usually close to the
//! image center:
//!
//! 
//!
//! and thus
//!
//! 
//!
//! The matrix of intrinsic parameters does not depend on the scene viewed. So, once estimated, it can
//! be re-used as long as the focal length is fixed (in case of a zoom lens). Thus, if an image from the
//! camera is scaled by a factor, all of these parameters need to be scaled (multiplied/divided,
//! respectively) by the same factor.
//!
//! The joint rotation-translation matrix 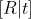 is the matrix product of a projective
//! transformation and a homogeneous transformation. The 3-by-4 projective transformation maps 3D points
//! represented in camera coordinates to 2D points in the image plane and represented in normalized
//! camera coordinates  and :
//!
//! 
//!
//! The homogeneous transformation is encoded by the extrinsic parameters  and 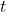 and
//! represents the change of basis from world coordinate system 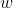 to the camera coordinate sytem
//! . Thus, given the representation of the point 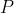 in world coordinates, , we
//! obtain 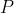's representation in the camera coordinate system, , by
//!
//! 
//!
//! This homogeneous transformation is composed out of , a 3-by-3 rotation matrix, and 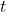, a
//! 3-by-1 translation vector:
//!
//! 
//!
//! and therefore
//!
//! 
//!
//! Combining the projective transformation and the homogeneous transformation, we obtain the projective
//! transformation that maps 3D points in world coordinates into 2D points in the image plane and in
//! normalized camera coordinates:
//!
//! 
//!
//! with  and . Putting the equations for instrincs and extrinsics together, we can write out
//!  as
//!
//! 
//!
//! If , the transformation above is equivalent to the following,
//!
//! 
//!
//! with
//!
//! 
//!
//! The following figure illustrates the pinhole camera model.
//!
//! 
//!
//! Real lenses usually have some distortion, mostly radial distortion, and slight tangential distortion.
//! So, the above model is extended as:
//!
//! 
//!
//! where
//!
//! 
//!
//! with
//!
//! 
//!
//! and
//!
//! 
//!
//! if .
//!
//! The distortion parameters are the radial coefficients , , , , , and 
//! , and  are the tangential distortion coefficients, and , , , and ,
//! are the thin prism distortion coefficients. Higher-order coefficients are not considered in OpenCV.
//!
//! The next figures show two common types of radial distortion: barrel distortion
//! ( monotonically decreasing)
//! and pincushion distortion ( monotonically increasing).
//! Radial distortion is always monotonic for real lenses,
//! and if the estimator produces a non-monotonic result,
//! this should be considered a calibration failure.
//! More generally, radial distortion must be monotonic and the distortion function must be bijective.
//! A failed estimation result may look deceptively good near the image center
//! but will work poorly in e.g. AR/SFM applications.
//! The optimization method used in OpenCV camera calibration does not include these constraints as
//! the framework does not support the required integer programming and polynomial inequalities.
//! See [issue #15992](https://github.com/opencv/opencv/issues/15992) for additional information.
//!
//! 
//! 
//!
//! In some cases, the image sensor may be tilted in order to focus an oblique plane in front of the
//! camera (Scheimpflug principle). This can be useful for particle image velocimetry (PIV) or
//! triangulation with a laser fan. The tilt causes a perspective distortion of 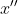 and
//! 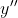. This distortion can be modeled in the following way, see e.g. [Louhichi07](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Louhichi07).
//!
//! 
//!
//! where
//!
//! 
//!
//! and the matrix  is defined by two rotations with angular parameter
//!  and , respectively,
//!
//! 
//!
//! In the functions below the coefficients are passed or returned as
//!
//! 
//!
//! vector. That is, if the vector contains four elements, it means that  . The distortion
//! coefficients do not depend on the scene viewed. Thus, they also belong to the intrinsic camera
//! parameters. And they remain the same regardless of the captured image resolution. If, for example, a
//! camera has been calibrated on images of 320 x 240 resolution, absolutely the same distortion
//! coefficients can be used for 640 x 480 images from the same camera while , ,
//! , and  need to be scaled appropriately.
//!
//! The functions below use the above model to do the following:
//!
//! * Project 3D points to the image plane given intrinsic and extrinsic parameters.
//! * Compute extrinsic parameters given intrinsic parameters, a few 3D points, and their
//! projections.
//! * Estimate intrinsic and extrinsic camera parameters from several views of a known calibration
//! pattern (every view is described by several 3D-2D point correspondences).
//! * Estimate the relative position and orientation of the stereo camera "heads" and compute the
//! *rectification* transformation that makes the camera optical axes parallel.
//!
//! <B> Homogeneous Coordinates </B><br>
//! Homogeneous Coordinates are a system of coordinates that are used in projective geometry. Their use
//! allows to represent points at infinity by finite coordinates and simplifies formulas when compared
//! to the cartesian counterparts, e.g. they have the advantage that affine transformations can be
//! expressed as linear homogeneous transformation.
//!
//! One obtains the homogeneous vector  by appending a 1 along an n-dimensional cartesian
//! vector 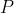 e.g. for a 3D cartesian vector the mapping  is:
//!
//! 
//!
//! For the inverse mapping , one divides all elements of the homogeneous vector
//! by its last element, e.g. for a 3D homogeneous vector one gets its 2D cartesian counterpart by:
//!
//! 
//!
//! if .
//!
//! Due to this mapping, all multiples , for , of a homogeneous point represent
//! the same point . An intuitive understanding of this property is that under a projective
//! transformation, all multiples of  are mapped to the same point. This is the physical
//! observation one does for pinhole cameras, as all points along a ray through the camera's pinhole are
//! projected to the same image point, e.g. all points along the red ray in the image of the pinhole
//! camera model above would be mapped to the same image coordinate. This property is also the source
//! for the scale ambiguity s in the equation of the pinhole camera model.
//!
//! As mentioned, by using homogeneous coordinates we can express any change of basis parameterized by
//!  and 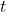 as a linear transformation, e.g. for the change of basis from coordinate system
//! 0 to coordinate system 1 becomes:
//!
//! 
//!
//!
//! Note:
//! * Many functions in this module take a camera intrinsic matrix as an input parameter. Although all
//! functions assume the same structure of this parameter, they may name it differently. The
//! parameter's description, however, will be clear in that a camera intrinsic matrix with the structure
//! shown above is required.
//! * A calibration sample for 3 cameras in a horizontal position can be found at
//! opencv_source_code/samples/cpp/3calibration.cpp
//! * A calibration sample based on a sequence of images can be found at
//! opencv_source_code/samples/cpp/calibration.cpp
//! * A calibration sample in order to do 3D reconstruction can be found at
//! opencv_source_code/samples/cpp/build3dmodel.cpp
//! * A calibration example on stereo calibration can be found at
//! opencv_source_code/samples/cpp/stereo_calib.cpp
//! * A calibration example on stereo matching can be found at
//! opencv_source_code/samples/cpp/stereo_match.cpp
//! * (Python) A camera calibration sample can be found at
//! opencv_source_code/samples/python/calibrate.py
//! # Fisheye camera model
//!
//! Definitions: Let P be a point in 3D of coordinates X in the world reference frame (stored in the
//! matrix X) The coordinate vector of P in the camera reference frame is:
//!
//! 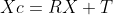
//!
//! where R is the rotation matrix corresponding to the rotation vector om: R = rodrigues(om); call x, y
//! and z the 3 coordinates of Xc:
//!
//! 
//!
//! The pinhole projection coordinates of P is [a; b] where
//!
//! 
//!
//! Fisheye distortion:
//!
//! 
//!
//! The distorted point coordinates are [x'; y'] where
//!
//! 
//!
//! Finally, conversion into pixel coordinates: The final pixel coordinates vector [u; v] where:
//!
//! 
//!
//! Summary:
//! Generic camera model [Kannala2006](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Kannala2006) with perspective projection and without distortion correction
use crate::mod_prelude::*;
use crate::{core, sys, types};
pub mod prelude {
pub use super::{LMSolverTrait, LMSolverTraitConst, LMSolver_CallbackTrait, LMSolver_CallbackTraitConst, StereoBMTrait, StereoBMTraitConst, StereoMatcherTrait, StereoMatcherTraitConst, StereoSGBMTrait, StereoSGBMTraitConst};
}
pub const CALIB_CB_ACCURACY: i32 = 32;
pub const CALIB_CB_ADAPTIVE_THRESH: i32 = 1;
pub const CALIB_CB_ASYMMETRIC_GRID: i32 = 2;
pub const CALIB_CB_CLUSTERING: i32 = 4;
pub const CALIB_CB_EXHAUSTIVE: i32 = 16;
pub const CALIB_CB_FAST_CHECK: i32 = 8;
pub const CALIB_CB_FILTER_QUADS: i32 = 4;
pub const CALIB_CB_LARGER: i32 = 64;
pub const CALIB_CB_MARKER: i32 = 128;
pub const CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE: i32 = 2;
pub const CALIB_CB_PLAIN: i32 = 256;
pub const CALIB_CB_SYMMETRIC_GRID: i32 = 1;
pub const CALIB_FIX_ASPECT_RATIO: i32 = 2;
pub const CALIB_FIX_FOCAL_LENGTH: i32 = 16;
pub const CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC: i32 = 256;
pub const CALIB_FIX_K1: i32 = 32;
pub const CALIB_FIX_K2: i32 = 64;
pub const CALIB_FIX_K3: i32 = 128;
pub const CALIB_FIX_K4: i32 = 2048;
pub const CALIB_FIX_K5: i32 = 4096;
pub const CALIB_FIX_K6: i32 = 8192;
pub const CALIB_FIX_PRINCIPAL_POINT: i32 = 4;
pub const CALIB_FIX_S1_S2_S3_S4: i32 = 65536;
pub const CALIB_FIX_TANGENT_DIST: i32 = 2097152;
pub const CALIB_FIX_TAUX_TAUY: i32 = 524288;
/// On-line Hand-Eye Calibration [Andreff99](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Andreff99)
pub const CALIB_HAND_EYE_ANDREFF: i32 = 3;
/// Hand-Eye Calibration Using Dual Quaternions [Daniilidis98](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Daniilidis98)
pub const CALIB_HAND_EYE_DANIILIDIS: i32 = 4;
/// Hand-eye Calibration [Horaud95](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Horaud95)
pub const CALIB_HAND_EYE_HORAUD: i32 = 2;
/// Robot Sensor Calibration: Solving AX = XB on the Euclidean Group [Park94](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Park94)
pub const CALIB_HAND_EYE_PARK: i32 = 1;
/// A New Technique for Fully Autonomous and Efficient 3D Robotics Hand/Eye Calibration [Tsai89](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Tsai89)
pub const CALIB_HAND_EYE_TSAI: i32 = 0;
pub const CALIB_NINTRINSIC: i32 = 18;
pub const CALIB_RATIONAL_MODEL: i32 = 16384;
/// Simultaneous robot-world and hand-eye calibration using dual-quaternions and kronecker product [Li2010SimultaneousRA](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Li2010SimultaneousRA)
pub const CALIB_ROBOT_WORLD_HAND_EYE_LI: i32 = 1;
/// Solving the robot-world/hand-eye calibration problem using the kronecker product [Shah2013SolvingTR](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Shah2013SolvingTR)
pub const CALIB_ROBOT_WORLD_HAND_EYE_SHAH: i32 = 0;
pub const CALIB_SAME_FOCAL_LENGTH: i32 = 512;
pub const CALIB_THIN_PRISM_MODEL: i32 = 32768;
pub const CALIB_TILTED_MODEL: i32 = 262144;
/// for stereoCalibrate
pub const CALIB_USE_EXTRINSIC_GUESS: i32 = 4194304;
pub const CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS: i32 = 1;
/// use LU instead of SVD decomposition for solving. much faster but potentially less precise
pub const CALIB_USE_LU: i32 = 131072;
/// use QR instead of SVD decomposition for solving. Faster but potentially less precise
pub const CALIB_USE_QR: i32 = 1048576;
pub const CALIB_ZERO_DISPARITY: i32 = 1024;
pub const CALIB_ZERO_TANGENT_DIST: i32 = 8;
pub const COV_POLISHER: i32 = 3;
pub const CirclesGridFinderParameters_ASYMMETRIC_GRID: i32 = 1;
pub const CirclesGridFinderParameters_SYMMETRIC_GRID: i32 = 0;
/// 7-point algorithm
pub const FM_7POINT: i32 = 1;
/// 8-point algorithm
pub const FM_8POINT: i32 = 2;
/// least-median algorithm. 7-point algorithm is used.
pub const FM_LMEDS: i32 = 4;
/// RANSAC algorithm. It needs at least 15 points. 7-point algorithm is used.
pub const FM_RANSAC: i32 = 8;
pub const Fisheye_CALIB_CHECK_COND: i32 = 4;
pub const Fisheye_CALIB_FIX_FOCAL_LENGTH: i32 = 2048;
pub const Fisheye_CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC: i32 = 256;
pub const Fisheye_CALIB_FIX_K1: i32 = 16;
pub const Fisheye_CALIB_FIX_K2: i32 = 32;
pub const Fisheye_CALIB_FIX_K3: i32 = 64;
pub const Fisheye_CALIB_FIX_K4: i32 = 128;
pub const Fisheye_CALIB_FIX_PRINCIPAL_POINT: i32 = 512;
pub const Fisheye_CALIB_FIX_SKEW: i32 = 8;
pub const Fisheye_CALIB_RECOMPUTE_EXTRINSIC: i32 = 2;
pub const Fisheye_CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS: i32 = 1;
pub const Fisheye_CALIB_ZERO_DISPARITY: i32 = 1024;
/// least-median of squares algorithm
pub const LMEDS: i32 = 4;
pub const LOCAL_OPTIM_GC: i32 = 3;
pub const LOCAL_OPTIM_INNER_AND_ITER_LO: i32 = 2;
pub const LOCAL_OPTIM_INNER_LO: i32 = 1;
pub const LOCAL_OPTIM_NULL: i32 = 0;
pub const LOCAL_OPTIM_SIGMA: i32 = 4;
pub const LSQ_POLISHER: i32 = 1;
pub const MAGSAC: i32 = 2;
pub const NEIGH_FLANN_KNN: i32 = 0;
pub const NEIGH_FLANN_RADIUS: i32 = 2;
pub const NEIGH_GRID: i32 = 1;
pub const NONE_POLISHER: i32 = 0;
pub const PROJ_SPHERICAL_EQRECT: i32 = 1;
pub const PROJ_SPHERICAL_ORTHO: i32 = 0;
/// RANSAC algorithm
pub const RANSAC: i32 = 8;
/// RHO algorithm
pub const RHO: i32 = 16;
pub const SAMPLING_NAPSAC: i32 = 2;
pub const SAMPLING_PROGRESSIVE_NAPSAC: i32 = 1;
pub const SAMPLING_PROSAC: i32 = 3;
pub const SAMPLING_UNIFORM: i32 = 0;
pub const SCORE_METHOD_LMEDS: i32 = 3;
pub const SCORE_METHOD_MAGSAC: i32 = 2;
pub const SCORE_METHOD_MSAC: i32 = 1;
pub const SCORE_METHOD_RANSAC: i32 = 0;
/// An Efficient Algebraic Solution to the Perspective-Three-Point Problem [Ke17](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Ke17)
pub const SOLVEPNP_AP3P: i32 = 5;
/// **Broken implementation. Using this flag will fallback to EPnP.**
///
/// A Direct Least-Squares (DLS) Method for PnP [hesch2011direct](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_hesch2011direct)
pub const SOLVEPNP_DLS: i32 = 3;
/// EPnP: Efficient Perspective-n-Point Camera Pose Estimation [lepetit2009epnp](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_lepetit2009epnp)
pub const SOLVEPNP_EPNP: i32 = 1;
/// Infinitesimal Plane-Based Pose Estimation [Collins14](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Collins14)
///
/// Object points must be coplanar.
pub const SOLVEPNP_IPPE: i32 = 6;
/// Infinitesimal Plane-Based Pose Estimation [Collins14](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Collins14)
///
/// This is a special case suitable for marker pose estimation.
///
/// 4 coplanar object points must be defined in the following order:
/// - point 0: [-squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 1: [ squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 2: [ squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 3: [-squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
pub const SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE: i32 = 7;
/// Pose refinement using non-linear Levenberg-Marquardt minimization scheme [Madsen04](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Madsen04) [Eade13](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Eade13)
///
/// Initial solution for non-planar "objectPoints" needs at least 6 points and uses the DLT algorithm.
///
/// Initial solution for planar "objectPoints" needs at least 4 points and uses pose from homography decomposition.
pub const SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE: i32 = 0;
/// Used for count
pub const SOLVEPNP_MAX_COUNT: i32 = 9;
/// Complete Solution Classification for the Perspective-Three-Point Problem [gao2003complete](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_gao2003complete)
pub const SOLVEPNP_P3P: i32 = 2;
/// SQPnP: A Consistently Fast and Globally OptimalSolution to the Perspective-n-Point Problem [Terzakis2020SQPnP](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Terzakis2020SQPnP)
pub const SOLVEPNP_SQPNP: i32 = 8;
/// **Broken implementation. Using this flag will fallback to EPnP.**
///
/// Exhaustive Linearization for Robust Camera Pose and Focal Length Estimation [penate2013exhaustive](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_penate2013exhaustive)
pub const SOLVEPNP_UPNP: i32 = 4;
pub const StereoBM_PREFILTER_NORMALIZED_RESPONSE: i32 = 0;
pub const StereoBM_PREFILTER_XSOBEL: i32 = 1;
pub const StereoMatcher_DISP_SCALE: i32 = 16;
pub const StereoMatcher_DISP_SHIFT: i32 = 4;
pub const StereoSGBM_MODE_HH: i32 = 1;
pub const StereoSGBM_MODE_HH4: i32 = 3;
pub const StereoSGBM_MODE_SGBM: i32 = 0;
pub const StereoSGBM_MODE_SGBM_3WAY: i32 = 2;
/// USAC, accurate settings
pub const USAC_ACCURATE: i32 = 36;
/// USAC algorithm, default settings
pub const USAC_DEFAULT: i32 = 32;
/// USAC, fast settings
pub const USAC_FAST: i32 = 35;
/// USAC, fundamental matrix 8 points
pub const USAC_FM_8PTS: i32 = 34;
/// USAC, runs MAGSAC++
pub const USAC_MAGSAC: i32 = 38;
/// USAC, parallel version
pub const USAC_PARALLEL: i32 = 33;
/// USAC, sorted points, runs PROSAC
pub const USAC_PROSAC: i32 = 37;
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum CirclesGridFinderParameters_GridType {
SYMMETRIC_GRID = 0,
ASYMMETRIC_GRID = 1,
}
impl TryFrom<i32> for CirclesGridFinderParameters_GridType {
type Error = crate::Error;
fn try_from(value: i32) -> Result<Self, Self::Error> {
match value {
0 => Ok(Self::SYMMETRIC_GRID),
1 => Ok(Self::ASYMMETRIC_GRID),
_ => Err(crate::Error::new(crate::core::StsBadArg, format!("Value: {value} is not valid for enum: crate::calib3d::CirclesGridFinderParameters_GridType"))),
}
}
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::calib3d::CirclesGridFinderParameters_GridType }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum HandEyeCalibrationMethod {
/// A New Technique for Fully Autonomous and Efficient 3D Robotics Hand/Eye Calibration [Tsai89](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Tsai89)
CALIB_HAND_EYE_TSAI = 0,
/// Robot Sensor Calibration: Solving AX = XB on the Euclidean Group [Park94](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Park94)
CALIB_HAND_EYE_PARK = 1,
/// Hand-eye Calibration [Horaud95](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Horaud95)
CALIB_HAND_EYE_HORAUD = 2,
/// On-line Hand-Eye Calibration [Andreff99](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Andreff99)
CALIB_HAND_EYE_ANDREFF = 3,
/// Hand-Eye Calibration Using Dual Quaternions [Daniilidis98](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Daniilidis98)
CALIB_HAND_EYE_DANIILIDIS = 4,
}
impl TryFrom<i32> for HandEyeCalibrationMethod {
type Error = crate::Error;
fn try_from(value: i32) -> Result<Self, Self::Error> {
match value {
0 => Ok(Self::CALIB_HAND_EYE_TSAI),
1 => Ok(Self::CALIB_HAND_EYE_PARK),
2 => Ok(Self::CALIB_HAND_EYE_HORAUD),
3 => Ok(Self::CALIB_HAND_EYE_ANDREFF),
4 => Ok(Self::CALIB_HAND_EYE_DANIILIDIS),
_ => Err(crate::Error::new(crate::core::StsBadArg, format!("Value: {value} is not valid for enum: crate::calib3d::HandEyeCalibrationMethod"))),
}
}
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::calib3d::HandEyeCalibrationMethod }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum LocalOptimMethod {
LOCAL_OPTIM_NULL = 0,
LOCAL_OPTIM_INNER_LO = 1,
LOCAL_OPTIM_INNER_AND_ITER_LO = 2,
LOCAL_OPTIM_GC = 3,
LOCAL_OPTIM_SIGMA = 4,
}
impl TryFrom<i32> for LocalOptimMethod {
type Error = crate::Error;
fn try_from(value: i32) -> Result<Self, Self::Error> {
match value {
0 => Ok(Self::LOCAL_OPTIM_NULL),
1 => Ok(Self::LOCAL_OPTIM_INNER_LO),
2 => Ok(Self::LOCAL_OPTIM_INNER_AND_ITER_LO),
3 => Ok(Self::LOCAL_OPTIM_GC),
4 => Ok(Self::LOCAL_OPTIM_SIGMA),
_ => Err(crate::Error::new(crate::core::StsBadArg, format!("Value: {value} is not valid for enum: crate::calib3d::LocalOptimMethod"))),
}
}
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::calib3d::LocalOptimMethod }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum NeighborSearchMethod {
NEIGH_FLANN_KNN = 0,
NEIGH_GRID = 1,
NEIGH_FLANN_RADIUS = 2,
}
impl TryFrom<i32> for NeighborSearchMethod {
type Error = crate::Error;
fn try_from(value: i32) -> Result<Self, Self::Error> {
match value {
0 => Ok(Self::NEIGH_FLANN_KNN),
1 => Ok(Self::NEIGH_GRID),
2 => Ok(Self::NEIGH_FLANN_RADIUS),
_ => Err(crate::Error::new(crate::core::StsBadArg, format!("Value: {value} is not valid for enum: crate::calib3d::NeighborSearchMethod"))),
}
}
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::calib3d::NeighborSearchMethod }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum PolishingMethod {
NONE_POLISHER = 0,
LSQ_POLISHER = 1,
MAGSAC = 2,
COV_POLISHER = 3,
}
impl TryFrom<i32> for PolishingMethod {
type Error = crate::Error;
fn try_from(value: i32) -> Result<Self, Self::Error> {
match value {
0 => Ok(Self::NONE_POLISHER),
1 => Ok(Self::LSQ_POLISHER),
2 => Ok(Self::MAGSAC),
3 => Ok(Self::COV_POLISHER),
_ => Err(crate::Error::new(crate::core::StsBadArg, format!("Value: {value} is not valid for enum: crate::calib3d::PolishingMethod"))),
}
}
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::calib3d::PolishingMethod }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum RobotWorldHandEyeCalibrationMethod {
/// Solving the robot-world/hand-eye calibration problem using the kronecker product [Shah2013SolvingTR](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Shah2013SolvingTR)
CALIB_ROBOT_WORLD_HAND_EYE_SHAH = 0,
/// Simultaneous robot-world and hand-eye calibration using dual-quaternions and kronecker product [Li2010SimultaneousRA](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Li2010SimultaneousRA)
CALIB_ROBOT_WORLD_HAND_EYE_LI = 1,
}
impl TryFrom<i32> for RobotWorldHandEyeCalibrationMethod {
type Error = crate::Error;
fn try_from(value: i32) -> Result<Self, Self::Error> {
match value {
0 => Ok(Self::CALIB_ROBOT_WORLD_HAND_EYE_SHAH),
1 => Ok(Self::CALIB_ROBOT_WORLD_HAND_EYE_LI),
_ => Err(crate::Error::new(crate::core::StsBadArg, format!("Value: {value} is not valid for enum: crate::calib3d::RobotWorldHandEyeCalibrationMethod"))),
}
}
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::calib3d::RobotWorldHandEyeCalibrationMethod }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum SamplingMethod {
SAMPLING_UNIFORM = 0,
SAMPLING_PROGRESSIVE_NAPSAC = 1,
SAMPLING_NAPSAC = 2,
SAMPLING_PROSAC = 3,
}
impl TryFrom<i32> for SamplingMethod {
type Error = crate::Error;
fn try_from(value: i32) -> Result<Self, Self::Error> {
match value {
0 => Ok(Self::SAMPLING_UNIFORM),
1 => Ok(Self::SAMPLING_PROGRESSIVE_NAPSAC),
2 => Ok(Self::SAMPLING_NAPSAC),
3 => Ok(Self::SAMPLING_PROSAC),
_ => Err(crate::Error::new(crate::core::StsBadArg, format!("Value: {value} is not valid for enum: crate::calib3d::SamplingMethod"))),
}
}
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::calib3d::SamplingMethod }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum ScoreMethod {
SCORE_METHOD_RANSAC = 0,
SCORE_METHOD_MSAC = 1,
SCORE_METHOD_MAGSAC = 2,
SCORE_METHOD_LMEDS = 3,
}
impl TryFrom<i32> for ScoreMethod {
type Error = crate::Error;
fn try_from(value: i32) -> Result<Self, Self::Error> {
match value {
0 => Ok(Self::SCORE_METHOD_RANSAC),
1 => Ok(Self::SCORE_METHOD_MSAC),
2 => Ok(Self::SCORE_METHOD_MAGSAC),
3 => Ok(Self::SCORE_METHOD_LMEDS),
_ => Err(crate::Error::new(crate::core::StsBadArg, format!("Value: {value} is not valid for enum: crate::calib3d::ScoreMethod"))),
}
}
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::calib3d::ScoreMethod }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum SolvePnPMethod {
/// Pose refinement using non-linear Levenberg-Marquardt minimization scheme [Madsen04](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Madsen04) [Eade13](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Eade13)
///
/// Initial solution for non-planar "objectPoints" needs at least 6 points and uses the DLT algorithm.
///
/// Initial solution for planar "objectPoints" needs at least 4 points and uses pose from homography decomposition.
SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE = 0,
/// EPnP: Efficient Perspective-n-Point Camera Pose Estimation [lepetit2009epnp](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_lepetit2009epnp)
SOLVEPNP_EPNP = 1,
/// Complete Solution Classification for the Perspective-Three-Point Problem [gao2003complete](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_gao2003complete)
SOLVEPNP_P3P = 2,
/// **Broken implementation. Using this flag will fallback to EPnP.**
///
/// A Direct Least-Squares (DLS) Method for PnP [hesch2011direct](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_hesch2011direct)
SOLVEPNP_DLS = 3,
/// **Broken implementation. Using this flag will fallback to EPnP.**
///
/// Exhaustive Linearization for Robust Camera Pose and Focal Length Estimation [penate2013exhaustive](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_penate2013exhaustive)
SOLVEPNP_UPNP = 4,
/// An Efficient Algebraic Solution to the Perspective-Three-Point Problem [Ke17](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Ke17)
SOLVEPNP_AP3P = 5,
/// Infinitesimal Plane-Based Pose Estimation [Collins14](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Collins14)
///
/// Object points must be coplanar.
SOLVEPNP_IPPE = 6,
/// Infinitesimal Plane-Based Pose Estimation [Collins14](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Collins14)
///
/// This is a special case suitable for marker pose estimation.
///
/// 4 coplanar object points must be defined in the following order:
/// - point 0: [-squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 1: [ squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 2: [ squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 3: [-squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE = 7,
/// SQPnP: A Consistently Fast and Globally OptimalSolution to the Perspective-n-Point Problem [Terzakis2020SQPnP](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Terzakis2020SQPnP)
SOLVEPNP_SQPNP = 8,
/// Used for count
SOLVEPNP_MAX_COUNT = 9,
}
impl TryFrom<i32> for SolvePnPMethod {
type Error = crate::Error;
fn try_from(value: i32) -> Result<Self, Self::Error> {
match value {
0 => Ok(Self::SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE),
1 => Ok(Self::SOLVEPNP_EPNP),
2 => Ok(Self::SOLVEPNP_P3P),
3 => Ok(Self::SOLVEPNP_DLS),
4 => Ok(Self::SOLVEPNP_UPNP),
5 => Ok(Self::SOLVEPNP_AP3P),
6 => Ok(Self::SOLVEPNP_IPPE),
7 => Ok(Self::SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE),
8 => Ok(Self::SOLVEPNP_SQPNP),
9 => Ok(Self::SOLVEPNP_MAX_COUNT),
_ => Err(crate::Error::new(crate::core::StsBadArg, format!("Value: {value} is not valid for enum: crate::calib3d::SolvePnPMethod"))),
}
}
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::calib3d::SolvePnPMethod }
/// cv::undistort mode
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum UndistortTypes {
PROJ_SPHERICAL_ORTHO = 0,
PROJ_SPHERICAL_EQRECT = 1,
}
impl TryFrom<i32> for UndistortTypes {
type Error = crate::Error;
fn try_from(value: i32) -> Result<Self, Self::Error> {
match value {
0 => Ok(Self::PROJ_SPHERICAL_ORTHO),
1 => Ok(Self::PROJ_SPHERICAL_EQRECT),
_ => Err(crate::Error::new(crate::core::StsBadArg, format!("Value: {value} is not valid for enum: crate::calib3d::UndistortTypes"))),
}
}
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::calib3d::UndistortTypes }
pub type CirclesGridFinderParameters2 = crate::calib3d::CirclesGridFinderParameters;
/// Computes an RQ decomposition of 3x3 matrices.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: 3x3 input matrix.
/// * mtxR: Output 3x3 upper-triangular matrix.
/// * mtxQ: Output 3x3 orthogonal matrix.
/// * Qx: Optional output 3x3 rotation matrix around x-axis.
/// * Qy: Optional output 3x3 rotation matrix around y-axis.
/// * Qz: Optional output 3x3 rotation matrix around z-axis.
///
/// The function computes a RQ decomposition using the given rotations. This function is used in
/// [decompose_projection_matrix] to decompose the left 3x3 submatrix of a projection matrix into a camera
/// and a rotation matrix.
///
/// It optionally returns three rotation matrices, one for each axis, and the three Euler angles in
/// degrees (as the return value) that could be used in OpenGL. Note, there is always more than one
/// sequence of rotations about the three principal axes that results in the same orientation of an
/// object, e.g. see [Slabaugh](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Slabaugh) . Returned three rotation matrices and corresponding three Euler angles
/// are only one of the possible solutions.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [rq_decomp3x3] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * qx: noArray()
/// * qy: noArray()
/// * qz: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn rq_decomp3x3_def(src: &impl ToInputArray, mtx_r: &mut impl ToOutputArray, mtx_q: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<core::Vec3d> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(mtx_r);
output_array_arg!(mtx_q);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RQDecomp3x3_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), mtx_r.as_raw__OutputArray(), mtx_q.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes an RQ decomposition of 3x3 matrices.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: 3x3 input matrix.
/// * mtxR: Output 3x3 upper-triangular matrix.
/// * mtxQ: Output 3x3 orthogonal matrix.
/// * Qx: Optional output 3x3 rotation matrix around x-axis.
/// * Qy: Optional output 3x3 rotation matrix around y-axis.
/// * Qz: Optional output 3x3 rotation matrix around z-axis.
///
/// The function computes a RQ decomposition using the given rotations. This function is used in
/// [decompose_projection_matrix] to decompose the left 3x3 submatrix of a projection matrix into a camera
/// and a rotation matrix.
///
/// It optionally returns three rotation matrices, one for each axis, and the three Euler angles in
/// degrees (as the return value) that could be used in OpenGL. Note, there is always more than one
/// sequence of rotations about the three principal axes that results in the same orientation of an
/// object, e.g. see [Slabaugh](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Slabaugh) . Returned three rotation matrices and corresponding three Euler angles
/// are only one of the possible solutions.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * qx: noArray()
/// * qy: noArray()
/// * qz: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn rq_decomp3x3(src: &impl ToInputArray, mtx_r: &mut impl ToOutputArray, mtx_q: &mut impl ToOutputArray, qx: &mut impl ToOutputArray, qy: &mut impl ToOutputArray, qz: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<core::Vec3d> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(mtx_r);
output_array_arg!(mtx_q);
output_array_arg!(qx);
output_array_arg!(qy);
output_array_arg!(qz);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RQDecomp3x3_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), mtx_r.as_raw__OutputArray(), mtx_q.as_raw__OutputArray(), qx.as_raw__OutputArray(), qy.as_raw__OutputArray(), qz.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Converts a rotation matrix to a rotation vector or vice versa.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input rotation vector (3x1 or 1x3) or rotation matrix (3x3).
/// * dst: Output rotation matrix (3x3) or rotation vector (3x1 or 1x3), respectively.
/// * jacobian: Optional output Jacobian matrix, 3x9 or 9x3, which is a matrix of partial
/// derivatives of the output array components with respect to the input array components.
///
/// 
///
/// Inverse transformation can be also done easily, since
///
/// 
///
/// A rotation vector is a convenient and most compact representation of a rotation matrix (since any
/// rotation matrix has just 3 degrees of freedom). The representation is used in the global 3D geometry
/// optimization procedures like [calibrateCamera], [stereoCalibrate], or [solvePnP] .
///
///
/// Note: More information about the computation of the derivative of a 3D rotation matrix with respect to its exponential coordinate
/// can be found in:
/// - A Compact Formula for the Derivative of a 3-D Rotation in Exponential Coordinates, Guillermo Gallego, Anthony J. Yezzi [Gallego2014ACF](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Gallego2014ACF)
///
///
/// Note: Useful information on SE(3) and Lie Groups can be found in:
/// - A tutorial on SE(3) transformation parameterizations and on-manifold optimization, Jose-Luis Blanco [blanco2010tutorial](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_blanco2010tutorial)
/// - Lie Groups for 2D and 3D Transformation, Ethan Eade [Eade17](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Eade17)
/// - A micro Lie theory for state estimation in robotics, Joan Solà, Jérémie Deray, Dinesh Atchuthan [Sol2018AML](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Sol2018AML)
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [rodrigues] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * jacobian: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn rodrigues_def(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Rodrigues_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Converts a rotation matrix to a rotation vector or vice versa.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input rotation vector (3x1 or 1x3) or rotation matrix (3x3).
/// * dst: Output rotation matrix (3x3) or rotation vector (3x1 or 1x3), respectively.
/// * jacobian: Optional output Jacobian matrix, 3x9 or 9x3, which is a matrix of partial
/// derivatives of the output array components with respect to the input array components.
///
/// 
///
/// Inverse transformation can be also done easily, since
///
/// 
///
/// A rotation vector is a convenient and most compact representation of a rotation matrix (since any
/// rotation matrix has just 3 degrees of freedom). The representation is used in the global 3D geometry
/// optimization procedures like [calibrateCamera], [stereoCalibrate], or [solvePnP] .
///
///
/// Note: More information about the computation of the derivative of a 3D rotation matrix with respect to its exponential coordinate
/// can be found in:
/// - A Compact Formula for the Derivative of a 3-D Rotation in Exponential Coordinates, Guillermo Gallego, Anthony J. Yezzi [Gallego2014ACF](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Gallego2014ACF)
///
///
/// Note: Useful information on SE(3) and Lie Groups can be found in:
/// - A tutorial on SE(3) transformation parameterizations and on-manifold optimization, Jose-Luis Blanco [blanco2010tutorial](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_blanco2010tutorial)
/// - Lie Groups for 2D and 3D Transformation, Ethan Eade [Eade17](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Eade17)
/// - A micro Lie theory for state estimation in robotics, Joan Solà, Jérémie Deray, Dinesh Atchuthan [Sol2018AML](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Sol2018AML)
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * jacobian: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn rodrigues(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, jacobian: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
output_array_arg!(jacobian);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Rodrigues_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), jacobian.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// @overload
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [calibrate_camera_ro] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * flags: 0
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,30,DBL_EPSILON)
#[inline]
pub fn calibrate_camera_ro_def(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, i_fixed_point: i32, camera_matrix: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, rvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, new_obj_points: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<f64> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
output_array_arg!(rvecs);
output_array_arg!(tvecs);
output_array_arg!(new_obj_points);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_calibrateCameraRO_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_int_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, i_fixed_point, camera_matrix.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), rvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), new_obj_points.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds the camera intrinsic and extrinsic parameters from several views of a calibration pattern.
///
/// This function is an extension of [calibrate_camera] with the method of releasing object which was
/// proposed in [strobl2011iccv](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_strobl2011iccv). In many common cases with inaccurate, unmeasured, roughly planar
/// targets (calibration plates), this method can dramatically improve the precision of the estimated
/// camera parameters. Both the object-releasing method and standard method are supported by this
/// function. Use the parameter **iFixedPoint** for method selection. In the internal implementation,
/// [calibrate_camera] is a wrapper for this function.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Vector of vectors of calibration pattern points in the calibration pattern
/// coordinate space. See [calibrate_camera] for details. If the method of releasing object to be used,
/// the identical calibration board must be used in each view and it must be fully visible, and all
/// objectPoints[i] must be the same and all points should be roughly close to a plane. **The calibration
/// target has to be rigid, or at least static if the camera (rather than the calibration target) is
/// shifted for grabbing images.**
/// * imagePoints: Vector of vectors of the projections of calibration pattern points. See
/// [calibrate_camera] for details.
/// * imageSize: Size of the image used only to initialize the intrinsic camera matrix.
/// * iFixedPoint: The index of the 3D object point in objectPoints[0] to be fixed. It also acts as
/// a switch for calibration method selection. If object-releasing method to be used, pass in the
/// parameter in the range of [1, objectPoints[0].size()-2], otherwise a value out of this range will
/// make standard calibration method selected. Usually the top-right corner point of the calibration
/// board grid is recommended to be fixed when object-releasing method being utilized. According to
/// \cite strobl2011iccv, two other points are also fixed. In this implementation, objectPoints[0].front
/// and objectPoints[0].back.z are used. With object-releasing method, accurate rvecs, tvecs and
/// newObjPoints are only possible if coordinates of these three fixed points are accurate enough.
/// * cameraMatrix: Output 3x3 floating-point camera matrix. See [calibrate_camera] for details.
/// * distCoeffs: Output vector of distortion coefficients. See [calibrate_camera] for details.
/// * rvecs: Output vector of rotation vectors estimated for each pattern view. See [calibrate_camera]
/// for details.
/// * tvecs: Output vector of translation vectors estimated for each pattern view.
/// * newObjPoints: The updated output vector of calibration pattern points. The coordinates might
/// be scaled based on three fixed points. The returned coordinates are accurate only if the above
/// mentioned three fixed points are accurate. If not needed, noArray() can be passed in. This parameter
/// is ignored with standard calibration method.
/// * stdDeviationsIntrinsics: Output vector of standard deviations estimated for intrinsic parameters.
/// See [calibrate_camera] for details.
/// * stdDeviationsExtrinsics: Output vector of standard deviations estimated for extrinsic parameters.
/// See [calibrate_camera] for details.
/// * stdDeviationsObjPoints: Output vector of standard deviations estimated for refined coordinates
/// of calibration pattern points. It has the same size and order as objectPoints[0] vector. This
/// parameter is ignored with standard calibration method.
/// * perViewErrors: Output vector of the RMS re-projection error estimated for each pattern view.
/// * flags: Different flags that may be zero or a combination of some predefined values. See
/// [calibrate_camera] for details. If the method of releasing object is used, the calibration time may
/// be much longer. CALIB_USE_QR or CALIB_USE_LU could be used for faster calibration with potentially
/// less precise and less stable in some rare cases.
/// * criteria: Termination criteria for the iterative optimization algorithm.
///
/// ## Returns
/// the overall RMS re-projection error.
///
/// The function estimates the intrinsic camera parameters and extrinsic parameters for each of the
/// views. The algorithm is based on [Zhang2000](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Zhang2000), [BouguetMCT](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_BouguetMCT) and [strobl2011iccv](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_strobl2011iccv). See
/// [calibrate_camera] for other detailed explanations.
/// ## See also
/// calibrateCamera, findChessboardCorners, solvePnP, initCameraMatrix2D, stereoCalibrate, undistort
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [calibrate_camera_ro_extended] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * flags: 0
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,30,DBL_EPSILON)
#[inline]
pub fn calibrate_camera_ro_extended_def(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, i_fixed_point: i32, camera_matrix: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, rvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, new_obj_points: &mut impl ToOutputArray, std_deviations_intrinsics: &mut impl ToOutputArray, std_deviations_extrinsics: &mut impl ToOutputArray, std_deviations_obj_points: &mut impl ToOutputArray, per_view_errors: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<f64> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
output_array_arg!(rvecs);
output_array_arg!(tvecs);
output_array_arg!(new_obj_points);
output_array_arg!(std_deviations_intrinsics);
output_array_arg!(std_deviations_extrinsics);
output_array_arg!(std_deviations_obj_points);
output_array_arg!(per_view_errors);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_calibrateCameraRO_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_int_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, i_fixed_point, camera_matrix.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), rvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), new_obj_points.as_raw__OutputArray(), std_deviations_intrinsics.as_raw__OutputArray(), std_deviations_extrinsics.as_raw__OutputArray(), std_deviations_obj_points.as_raw__OutputArray(), per_view_errors.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds the camera intrinsic and extrinsic parameters from several views of a calibration pattern.
///
/// This function is an extension of [calibrate_camera] with the method of releasing object which was
/// proposed in [strobl2011iccv](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_strobl2011iccv). In many common cases with inaccurate, unmeasured, roughly planar
/// targets (calibration plates), this method can dramatically improve the precision of the estimated
/// camera parameters. Both the object-releasing method and standard method are supported by this
/// function. Use the parameter **iFixedPoint** for method selection. In the internal implementation,
/// [calibrate_camera] is a wrapper for this function.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Vector of vectors of calibration pattern points in the calibration pattern
/// coordinate space. See [calibrate_camera] for details. If the method of releasing object to be used,
/// the identical calibration board must be used in each view and it must be fully visible, and all
/// objectPoints[i] must be the same and all points should be roughly close to a plane. **The calibration
/// target has to be rigid, or at least static if the camera (rather than the calibration target) is
/// shifted for grabbing images.**
/// * imagePoints: Vector of vectors of the projections of calibration pattern points. See
/// [calibrate_camera] for details.
/// * imageSize: Size of the image used only to initialize the intrinsic camera matrix.
/// * iFixedPoint: The index of the 3D object point in objectPoints[0] to be fixed. It also acts as
/// a switch for calibration method selection. If object-releasing method to be used, pass in the
/// parameter in the range of [1, objectPoints[0].size()-2], otherwise a value out of this range will
/// make standard calibration method selected. Usually the top-right corner point of the calibration
/// board grid is recommended to be fixed when object-releasing method being utilized. According to
/// \cite strobl2011iccv, two other points are also fixed. In this implementation, objectPoints[0].front
/// and objectPoints[0].back.z are used. With object-releasing method, accurate rvecs, tvecs and
/// newObjPoints are only possible if coordinates of these three fixed points are accurate enough.
/// * cameraMatrix: Output 3x3 floating-point camera matrix. See [calibrate_camera] for details.
/// * distCoeffs: Output vector of distortion coefficients. See [calibrate_camera] for details.
/// * rvecs: Output vector of rotation vectors estimated for each pattern view. See [calibrate_camera]
/// for details.
/// * tvecs: Output vector of translation vectors estimated for each pattern view.
/// * newObjPoints: The updated output vector of calibration pattern points. The coordinates might
/// be scaled based on three fixed points. The returned coordinates are accurate only if the above
/// mentioned three fixed points are accurate. If not needed, noArray() can be passed in. This parameter
/// is ignored with standard calibration method.
/// * stdDeviationsIntrinsics: Output vector of standard deviations estimated for intrinsic parameters.
/// See [calibrate_camera] for details.
/// * stdDeviationsExtrinsics: Output vector of standard deviations estimated for extrinsic parameters.
/// See [calibrate_camera] for details.
/// * stdDeviationsObjPoints: Output vector of standard deviations estimated for refined coordinates
/// of calibration pattern points. It has the same size and order as objectPoints[0] vector. This
/// parameter is ignored with standard calibration method.
/// * perViewErrors: Output vector of the RMS re-projection error estimated for each pattern view.
/// * flags: Different flags that may be zero or a combination of some predefined values. See
/// [calibrate_camera] for details. If the method of releasing object is used, the calibration time may
/// be much longer. CALIB_USE_QR or CALIB_USE_LU could be used for faster calibration with potentially
/// less precise and less stable in some rare cases.
/// * criteria: Termination criteria for the iterative optimization algorithm.
///
/// ## Returns
/// the overall RMS re-projection error.
///
/// The function estimates the intrinsic camera parameters and extrinsic parameters for each of the
/// views. The algorithm is based on [Zhang2000](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Zhang2000), [BouguetMCT](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_BouguetMCT) and [strobl2011iccv](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_strobl2011iccv). See
/// [calibrate_camera] for other detailed explanations.
/// ## See also
/// calibrateCamera, findChessboardCorners, solvePnP, initCameraMatrix2D, stereoCalibrate, undistort
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: 0
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,30,DBL_EPSILON)
#[inline]
pub fn calibrate_camera_ro_extended(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, i_fixed_point: i32, camera_matrix: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, rvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, new_obj_points: &mut impl ToOutputArray, std_deviations_intrinsics: &mut impl ToOutputArray, std_deviations_extrinsics: &mut impl ToOutputArray, std_deviations_obj_points: &mut impl ToOutputArray, per_view_errors: &mut impl ToOutputArray, flags: i32, criteria: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<f64> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
output_array_arg!(rvecs);
output_array_arg!(tvecs);
output_array_arg!(new_obj_points);
output_array_arg!(std_deviations_intrinsics);
output_array_arg!(std_deviations_extrinsics);
output_array_arg!(std_deviations_obj_points);
output_array_arg!(per_view_errors);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_calibrateCameraRO_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_int_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_TermCriteria(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, i_fixed_point, camera_matrix.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), rvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), new_obj_points.as_raw__OutputArray(), std_deviations_intrinsics.as_raw__OutputArray(), std_deviations_extrinsics.as_raw__OutputArray(), std_deviations_obj_points.as_raw__OutputArray(), per_view_errors.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, &criteria, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds the camera intrinsic and extrinsic parameters from several views of a calibration pattern.
///
/// This function is an extension of [calibrate_camera] with the method of releasing object which was
/// proposed in [strobl2011iccv](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_strobl2011iccv). In many common cases with inaccurate, unmeasured, roughly planar
/// targets (calibration plates), this method can dramatically improve the precision of the estimated
/// camera parameters. Both the object-releasing method and standard method are supported by this
/// function. Use the parameter **iFixedPoint** for method selection. In the internal implementation,
/// [calibrate_camera] is a wrapper for this function.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Vector of vectors of calibration pattern points in the calibration pattern
/// coordinate space. See [calibrate_camera] for details. If the method of releasing object to be used,
/// the identical calibration board must be used in each view and it must be fully visible, and all
/// objectPoints[i] must be the same and all points should be roughly close to a plane. **The calibration
/// target has to be rigid, or at least static if the camera (rather than the calibration target) is
/// shifted for grabbing images.**
/// * imagePoints: Vector of vectors of the projections of calibration pattern points. See
/// [calibrate_camera] for details.
/// * imageSize: Size of the image used only to initialize the intrinsic camera matrix.
/// * iFixedPoint: The index of the 3D object point in objectPoints[0] to be fixed. It also acts as
/// a switch for calibration method selection. If object-releasing method to be used, pass in the
/// parameter in the range of [1, objectPoints[0].size()-2], otherwise a value out of this range will
/// make standard calibration method selected. Usually the top-right corner point of the calibration
/// board grid is recommended to be fixed when object-releasing method being utilized. According to
/// \cite strobl2011iccv, two other points are also fixed. In this implementation, objectPoints[0].front
/// and objectPoints[0].back.z are used. With object-releasing method, accurate rvecs, tvecs and
/// newObjPoints are only possible if coordinates of these three fixed points are accurate enough.
/// * cameraMatrix: Output 3x3 floating-point camera matrix. See [calibrate_camera] for details.
/// * distCoeffs: Output vector of distortion coefficients. See [calibrate_camera] for details.
/// * rvecs: Output vector of rotation vectors estimated for each pattern view. See [calibrate_camera]
/// for details.
/// * tvecs: Output vector of translation vectors estimated for each pattern view.
/// * newObjPoints: The updated output vector of calibration pattern points. The coordinates might
/// be scaled based on three fixed points. The returned coordinates are accurate only if the above
/// mentioned three fixed points are accurate. If not needed, noArray() can be passed in. This parameter
/// is ignored with standard calibration method.
/// * stdDeviationsIntrinsics: Output vector of standard deviations estimated for intrinsic parameters.
/// See [calibrate_camera] for details.
/// * stdDeviationsExtrinsics: Output vector of standard deviations estimated for extrinsic parameters.
/// See [calibrate_camera] for details.
/// * stdDeviationsObjPoints: Output vector of standard deviations estimated for refined coordinates
/// of calibration pattern points. It has the same size and order as objectPoints[0] vector. This
/// parameter is ignored with standard calibration method.
/// * perViewErrors: Output vector of the RMS re-projection error estimated for each pattern view.
/// * flags: Different flags that may be zero or a combination of some predefined values. See
/// [calibrate_camera] for details. If the method of releasing object is used, the calibration time may
/// be much longer. CALIB_USE_QR or CALIB_USE_LU could be used for faster calibration with potentially
/// less precise and less stable in some rare cases.
/// * criteria: Termination criteria for the iterative optimization algorithm.
///
/// ## Returns
/// the overall RMS re-projection error.
///
/// The function estimates the intrinsic camera parameters and extrinsic parameters for each of the
/// views. The algorithm is based on [Zhang2000](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Zhang2000), [BouguetMCT](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_BouguetMCT) and [strobl2011iccv](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_strobl2011iccv). See
/// [calibrate_camera] for other detailed explanations.
/// ## See also
/// calibrateCamera, findChessboardCorners, solvePnP, initCameraMatrix2D, stereoCalibrate, undistort
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: 0
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,30,DBL_EPSILON)
#[inline]
pub fn calibrate_camera_ro(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, i_fixed_point: i32, camera_matrix: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, rvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, new_obj_points: &mut impl ToOutputArray, flags: i32, criteria: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<f64> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
output_array_arg!(rvecs);
output_array_arg!(tvecs);
output_array_arg!(new_obj_points);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_calibrateCameraRO_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_int_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_TermCriteria(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, i_fixed_point, camera_matrix.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), rvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), new_obj_points.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, &criteria, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// @overload
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [calibrate_camera] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * flags: 0
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,30,DBL_EPSILON)
#[inline]
pub fn calibrate_camera_def(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, camera_matrix: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, rvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<f64> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
output_array_arg!(rvecs);
output_array_arg!(tvecs);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_calibrateCamera_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, camera_matrix.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), rvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds the camera intrinsic and extrinsic parameters from several views of a calibration
/// pattern.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: In the new interface it is a vector of vectors of calibration pattern points in
/// the calibration pattern coordinate space (e.g. std::vector<std::vector<cv::Vec3f>>). The outer
/// vector contains as many elements as the number of pattern views. If the same calibration pattern
/// is shown in each view and it is fully visible, all the vectors will be the same. Although, it is
/// possible to use partially occluded patterns or even different patterns in different views. Then,
/// the vectors will be different. Although the points are 3D, they all lie in the calibration pattern's
/// XY coordinate plane (thus 0 in the Z-coordinate), if the used calibration pattern is a planar rig.
/// In the old interface all the vectors of object points from different views are concatenated
/// together.
/// * imagePoints: In the new interface it is a vector of vectors of the projections of calibration
/// pattern points (e.g. std::vector<std::vector<cv::Vec2f>>). imagePoints.size() and
/// objectPoints.size(), and imagePoints[i].size() and objectPoints[i].size() for each i, must be equal,
/// respectively. In the old interface all the vectors of object points from different views are
/// concatenated together.
/// * imageSize: Size of the image used only to initialize the camera intrinsic matrix.
/// * cameraMatrix: Input/output 3x3 floating-point camera intrinsic matrix
///  . If [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS]
/// and/or [CALIB_FIX_ASPECT_RATIO], [CALIB_FIX_PRINCIPAL_POINT] or [CALIB_FIX_FOCAL_LENGTH]
/// are specified, some or all of fx, fy, cx, cy must be initialized before calling the function.
/// * distCoeffs: Input/output vector of distortion coefficients
/// .
/// * rvecs: Output vector of rotation vectors ([Rodrigues] ) estimated for each pattern view
/// (e.g. std::vector<cv::Mat>>). That is, each i-th rotation vector together with the corresponding
/// i-th translation vector (see the next output parameter description) brings the calibration pattern
/// from the object coordinate space (in which object points are specified) to the camera coordinate
/// space. In more technical terms, the tuple of the i-th rotation and translation vector performs
/// a change of basis from object coordinate space to camera coordinate space. Due to its duality, this
/// tuple is equivalent to the position of the calibration pattern with respect to the camera coordinate
/// space.
/// * tvecs: Output vector of translation vectors estimated for each pattern view, see parameter
/// describtion above.
/// * stdDeviationsIntrinsics: Output vector of standard deviations estimated for intrinsic
/// parameters. Order of deviations values:
///  If one of parameters is not estimated, it's deviation is equals to zero.
/// * stdDeviationsExtrinsics: Output vector of standard deviations estimated for extrinsic
/// parameters. Order of deviations values:  where M is
/// the number of pattern views. 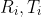 are concatenated 1x3 vectors.
/// * perViewErrors: Output vector of the RMS re-projection error estimated for each pattern view.
/// * flags: Different flags that may be zero or a combination of the following values:
/// * [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] cameraMatrix contains valid initial values of
/// fx, fy, cx, cy that are optimized further. Otherwise, (cx, cy) is initially set to the image
/// center ( imageSize is used), and focal distances are computed in a least-squares fashion.
/// Note, that if intrinsic parameters are known, there is no need to use this function just to
/// estimate extrinsic parameters. Use [solvePnP] instead.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_PRINCIPAL_POINT] The principal point is not changed during the global
/// optimization. It stays at the center or at a different location specified when
/// [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set too.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_ASPECT_RATIO] The functions consider only fy as a free parameter. The
/// ratio fx/fy stays the same as in the input cameraMatrix . When
/// [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is not set, the actual input values of fx and fy are
/// ignored, only their ratio is computed and used further.
/// * [CALIB_ZERO_TANGENT_DIST] Tangential distortion coefficients  are set
/// to zeros and stay zero.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_FOCAL_LENGTH] The focal length is not changed during the global optimization if
/// [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_K1],..., [CALIB_FIX_K6] The corresponding radial distortion
/// coefficient is not changed during the optimization. If [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is
/// set, the coefficient from the supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0.
/// * [CALIB_RATIONAL_MODEL] Coefficients k4, k5, and k6 are enabled. To provide the
/// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the
/// calibration function use the rational model and return 8 coefficients or more.
/// * [CALIB_THIN_PRISM_MODEL] Coefficients s1, s2, s3 and s4 are enabled. To provide the
/// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the
/// calibration function use the thin prism model and return 12 coefficients or more.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_S1_S2_S3_S4] The thin prism distortion coefficients are not changed during
/// the optimization. If [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set, the coefficient from the
/// supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0.
/// * [CALIB_TILTED_MODEL] Coefficients tauX and tauY are enabled. To provide the
/// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the
/// calibration function use the tilted sensor model and return 14 coefficients.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_TAUX_TAUY] The coefficients of the tilted sensor model are not changed during
/// the optimization. If [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set, the coefficient from the
/// supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0.
/// * criteria: Termination criteria for the iterative optimization algorithm.
///
/// ## Returns
/// the overall RMS re-projection error.
///
/// The function estimates the intrinsic camera parameters and extrinsic parameters for each of the
/// views. The algorithm is based on [Zhang2000](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Zhang2000) and [BouguetMCT](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_BouguetMCT) . The coordinates of 3D object
/// points and their corresponding 2D projections in each view must be specified. That may be achieved
/// by using an object with known geometry and easily detectable feature points. Such an object is
/// called a calibration rig or calibration pattern, and OpenCV has built-in support for a chessboard as
/// a calibration rig (see [findChessboardCorners]). Currently, initialization of intrinsic
/// parameters (when [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is not set) is only implemented for planar calibration
/// patterns (where Z-coordinates of the object points must be all zeros). 3D calibration rigs can also
/// be used as long as initial cameraMatrix is provided.
///
/// The algorithm performs the following steps:
///
/// * Compute the initial intrinsic parameters (the option only available for planar calibration
/// patterns) or read them from the input parameters. The distortion coefficients are all set to
/// zeros initially unless some of CALIB_FIX_K? are specified.
///
/// * Estimate the initial camera pose as if the intrinsic parameters have been already known. This is
/// done using [solvePnP] .
///
/// * Run the global Levenberg-Marquardt optimization algorithm to minimize the reprojection error,
/// that is, the total sum of squared distances between the observed feature points imagePoints and
/// the projected (using the current estimates for camera parameters and the poses) object points
/// objectPoints. See [projectPoints] for details.
///
///
/// Note:
/// If you use a non-square (i.e. non-N-by-N) grid and [findChessboardCorners] for calibration,
/// and [calibrateCamera] returns bad values (zero distortion coefficients,  and
///  very far from the image center, and/or large differences between  and
///  (ratios of 10:1 or more)), then you are probably using patternSize=cvSize(rows,cols)
/// instead of using patternSize=cvSize(cols,rows) in [findChessboardCorners].
///
///
/// Note:
/// The function may throw exceptions, if unsupported combination of parameters is provided or
/// the system is underconstrained.
/// ## See also
/// calibrateCameraRO, findChessboardCorners, solvePnP, initCameraMatrix2D, stereoCalibrate,
/// undistort
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [calibrate_camera_extended] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * flags: 0
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,30,DBL_EPSILON)
#[inline]
pub fn calibrate_camera_extended_def(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, camera_matrix: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, rvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, std_deviations_intrinsics: &mut impl ToOutputArray, std_deviations_extrinsics: &mut impl ToOutputArray, per_view_errors: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<f64> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
output_array_arg!(rvecs);
output_array_arg!(tvecs);
output_array_arg!(std_deviations_intrinsics);
output_array_arg!(std_deviations_extrinsics);
output_array_arg!(per_view_errors);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_calibrateCamera_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, camera_matrix.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), rvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), std_deviations_intrinsics.as_raw__OutputArray(), std_deviations_extrinsics.as_raw__OutputArray(), per_view_errors.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds the camera intrinsic and extrinsic parameters from several views of a calibration
/// pattern.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: In the new interface it is a vector of vectors of calibration pattern points in
/// the calibration pattern coordinate space (e.g. std::vector<std::vector<cv::Vec3f>>). The outer
/// vector contains as many elements as the number of pattern views. If the same calibration pattern
/// is shown in each view and it is fully visible, all the vectors will be the same. Although, it is
/// possible to use partially occluded patterns or even different patterns in different views. Then,
/// the vectors will be different. Although the points are 3D, they all lie in the calibration pattern's
/// XY coordinate plane (thus 0 in the Z-coordinate), if the used calibration pattern is a planar rig.
/// In the old interface all the vectors of object points from different views are concatenated
/// together.
/// * imagePoints: In the new interface it is a vector of vectors of the projections of calibration
/// pattern points (e.g. std::vector<std::vector<cv::Vec2f>>). imagePoints.size() and
/// objectPoints.size(), and imagePoints[i].size() and objectPoints[i].size() for each i, must be equal,
/// respectively. In the old interface all the vectors of object points from different views are
/// concatenated together.
/// * imageSize: Size of the image used only to initialize the camera intrinsic matrix.
/// * cameraMatrix: Input/output 3x3 floating-point camera intrinsic matrix
///  . If [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS]
/// and/or [CALIB_FIX_ASPECT_RATIO], [CALIB_FIX_PRINCIPAL_POINT] or [CALIB_FIX_FOCAL_LENGTH]
/// are specified, some or all of fx, fy, cx, cy must be initialized before calling the function.
/// * distCoeffs: Input/output vector of distortion coefficients
/// .
/// * rvecs: Output vector of rotation vectors ([Rodrigues] ) estimated for each pattern view
/// (e.g. std::vector<cv::Mat>>). That is, each i-th rotation vector together with the corresponding
/// i-th translation vector (see the next output parameter description) brings the calibration pattern
/// from the object coordinate space (in which object points are specified) to the camera coordinate
/// space. In more technical terms, the tuple of the i-th rotation and translation vector performs
/// a change of basis from object coordinate space to camera coordinate space. Due to its duality, this
/// tuple is equivalent to the position of the calibration pattern with respect to the camera coordinate
/// space.
/// * tvecs: Output vector of translation vectors estimated for each pattern view, see parameter
/// describtion above.
/// * stdDeviationsIntrinsics: Output vector of standard deviations estimated for intrinsic
/// parameters. Order of deviations values:
///  If one of parameters is not estimated, it's deviation is equals to zero.
/// * stdDeviationsExtrinsics: Output vector of standard deviations estimated for extrinsic
/// parameters. Order of deviations values:  where M is
/// the number of pattern views. 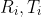 are concatenated 1x3 vectors.
/// * perViewErrors: Output vector of the RMS re-projection error estimated for each pattern view.
/// * flags: Different flags that may be zero or a combination of the following values:
/// * [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] cameraMatrix contains valid initial values of
/// fx, fy, cx, cy that are optimized further. Otherwise, (cx, cy) is initially set to the image
/// center ( imageSize is used), and focal distances are computed in a least-squares fashion.
/// Note, that if intrinsic parameters are known, there is no need to use this function just to
/// estimate extrinsic parameters. Use [solvePnP] instead.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_PRINCIPAL_POINT] The principal point is not changed during the global
/// optimization. It stays at the center or at a different location specified when
/// [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set too.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_ASPECT_RATIO] The functions consider only fy as a free parameter. The
/// ratio fx/fy stays the same as in the input cameraMatrix . When
/// [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is not set, the actual input values of fx and fy are
/// ignored, only their ratio is computed and used further.
/// * [CALIB_ZERO_TANGENT_DIST] Tangential distortion coefficients  are set
/// to zeros and stay zero.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_FOCAL_LENGTH] The focal length is not changed during the global optimization if
/// [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_K1],..., [CALIB_FIX_K6] The corresponding radial distortion
/// coefficient is not changed during the optimization. If [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is
/// set, the coefficient from the supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0.
/// * [CALIB_RATIONAL_MODEL] Coefficients k4, k5, and k6 are enabled. To provide the
/// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the
/// calibration function use the rational model and return 8 coefficients or more.
/// * [CALIB_THIN_PRISM_MODEL] Coefficients s1, s2, s3 and s4 are enabled. To provide the
/// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the
/// calibration function use the thin prism model and return 12 coefficients or more.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_S1_S2_S3_S4] The thin prism distortion coefficients are not changed during
/// the optimization. If [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set, the coefficient from the
/// supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0.
/// * [CALIB_TILTED_MODEL] Coefficients tauX and tauY are enabled. To provide the
/// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the
/// calibration function use the tilted sensor model and return 14 coefficients.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_TAUX_TAUY] The coefficients of the tilted sensor model are not changed during
/// the optimization. If [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set, the coefficient from the
/// supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0.
/// * criteria: Termination criteria for the iterative optimization algorithm.
///
/// ## Returns
/// the overall RMS re-projection error.
///
/// The function estimates the intrinsic camera parameters and extrinsic parameters for each of the
/// views. The algorithm is based on [Zhang2000](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Zhang2000) and [BouguetMCT](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_BouguetMCT) . The coordinates of 3D object
/// points and their corresponding 2D projections in each view must be specified. That may be achieved
/// by using an object with known geometry and easily detectable feature points. Such an object is
/// called a calibration rig or calibration pattern, and OpenCV has built-in support for a chessboard as
/// a calibration rig (see [findChessboardCorners]). Currently, initialization of intrinsic
/// parameters (when [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is not set) is only implemented for planar calibration
/// patterns (where Z-coordinates of the object points must be all zeros). 3D calibration rigs can also
/// be used as long as initial cameraMatrix is provided.
///
/// The algorithm performs the following steps:
///
/// * Compute the initial intrinsic parameters (the option only available for planar calibration
/// patterns) or read them from the input parameters. The distortion coefficients are all set to
/// zeros initially unless some of CALIB_FIX_K? are specified.
///
/// * Estimate the initial camera pose as if the intrinsic parameters have been already known. This is
/// done using [solvePnP] .
///
/// * Run the global Levenberg-Marquardt optimization algorithm to minimize the reprojection error,
/// that is, the total sum of squared distances between the observed feature points imagePoints and
/// the projected (using the current estimates for camera parameters and the poses) object points
/// objectPoints. See [projectPoints] for details.
///
///
/// Note:
/// If you use a non-square (i.e. non-N-by-N) grid and [findChessboardCorners] for calibration,
/// and [calibrateCamera] returns bad values (zero distortion coefficients,  and
///  very far from the image center, and/or large differences between  and
///  (ratios of 10:1 or more)), then you are probably using patternSize=cvSize(rows,cols)
/// instead of using patternSize=cvSize(cols,rows) in [findChessboardCorners].
///
///
/// Note:
/// The function may throw exceptions, if unsupported combination of parameters is provided or
/// the system is underconstrained.
/// ## See also
/// calibrateCameraRO, findChessboardCorners, solvePnP, initCameraMatrix2D, stereoCalibrate,
/// undistort
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: 0
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,30,DBL_EPSILON)
#[inline]
pub fn calibrate_camera_extended(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, camera_matrix: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, rvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, std_deviations_intrinsics: &mut impl ToOutputArray, std_deviations_extrinsics: &mut impl ToOutputArray, per_view_errors: &mut impl ToOutputArray, flags: i32, criteria: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<f64> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
output_array_arg!(rvecs);
output_array_arg!(tvecs);
output_array_arg!(std_deviations_intrinsics);
output_array_arg!(std_deviations_extrinsics);
output_array_arg!(per_view_errors);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_calibrateCamera_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_TermCriteria(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, camera_matrix.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), rvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), std_deviations_intrinsics.as_raw__OutputArray(), std_deviations_extrinsics.as_raw__OutputArray(), per_view_errors.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, &criteria, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds the camera intrinsic and extrinsic parameters from several views of a calibration
/// pattern.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: In the new interface it is a vector of vectors of calibration pattern points in
/// the calibration pattern coordinate space (e.g. std::vector<std::vector<cv::Vec3f>>). The outer
/// vector contains as many elements as the number of pattern views. If the same calibration pattern
/// is shown in each view and it is fully visible, all the vectors will be the same. Although, it is
/// possible to use partially occluded patterns or even different patterns in different views. Then,
/// the vectors will be different. Although the points are 3D, they all lie in the calibration pattern's
/// XY coordinate plane (thus 0 in the Z-coordinate), if the used calibration pattern is a planar rig.
/// In the old interface all the vectors of object points from different views are concatenated
/// together.
/// * imagePoints: In the new interface it is a vector of vectors of the projections of calibration
/// pattern points (e.g. std::vector<std::vector<cv::Vec2f>>). imagePoints.size() and
/// objectPoints.size(), and imagePoints[i].size() and objectPoints[i].size() for each i, must be equal,
/// respectively. In the old interface all the vectors of object points from different views are
/// concatenated together.
/// * imageSize: Size of the image used only to initialize the camera intrinsic matrix.
/// * cameraMatrix: Input/output 3x3 floating-point camera intrinsic matrix
///  . If [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS]
/// and/or [CALIB_FIX_ASPECT_RATIO], [CALIB_FIX_PRINCIPAL_POINT] or [CALIB_FIX_FOCAL_LENGTH]
/// are specified, some or all of fx, fy, cx, cy must be initialized before calling the function.
/// * distCoeffs: Input/output vector of distortion coefficients
/// .
/// * rvecs: Output vector of rotation vectors ([Rodrigues] ) estimated for each pattern view
/// (e.g. std::vector<cv::Mat>>). That is, each i-th rotation vector together with the corresponding
/// i-th translation vector (see the next output parameter description) brings the calibration pattern
/// from the object coordinate space (in which object points are specified) to the camera coordinate
/// space. In more technical terms, the tuple of the i-th rotation and translation vector performs
/// a change of basis from object coordinate space to camera coordinate space. Due to its duality, this
/// tuple is equivalent to the position of the calibration pattern with respect to the camera coordinate
/// space.
/// * tvecs: Output vector of translation vectors estimated for each pattern view, see parameter
/// describtion above.
/// * stdDeviationsIntrinsics: Output vector of standard deviations estimated for intrinsic
/// parameters. Order of deviations values:
///  If one of parameters is not estimated, it's deviation is equals to zero.
/// * stdDeviationsExtrinsics: Output vector of standard deviations estimated for extrinsic
/// parameters. Order of deviations values:  where M is
/// the number of pattern views. 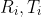 are concatenated 1x3 vectors.
/// * perViewErrors: Output vector of the RMS re-projection error estimated for each pattern view.
/// * flags: Different flags that may be zero or a combination of the following values:
/// * [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] cameraMatrix contains valid initial values of
/// fx, fy, cx, cy that are optimized further. Otherwise, (cx, cy) is initially set to the image
/// center ( imageSize is used), and focal distances are computed in a least-squares fashion.
/// Note, that if intrinsic parameters are known, there is no need to use this function just to
/// estimate extrinsic parameters. Use [solvePnP] instead.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_PRINCIPAL_POINT] The principal point is not changed during the global
/// optimization. It stays at the center or at a different location specified when
/// [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set too.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_ASPECT_RATIO] The functions consider only fy as a free parameter. The
/// ratio fx/fy stays the same as in the input cameraMatrix . When
/// [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is not set, the actual input values of fx and fy are
/// ignored, only their ratio is computed and used further.
/// * [CALIB_ZERO_TANGENT_DIST] Tangential distortion coefficients  are set
/// to zeros and stay zero.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_FOCAL_LENGTH] The focal length is not changed during the global optimization if
/// [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_K1],..., [CALIB_FIX_K6] The corresponding radial distortion
/// coefficient is not changed during the optimization. If [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is
/// set, the coefficient from the supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0.
/// * [CALIB_RATIONAL_MODEL] Coefficients k4, k5, and k6 are enabled. To provide the
/// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the
/// calibration function use the rational model and return 8 coefficients or more.
/// * [CALIB_THIN_PRISM_MODEL] Coefficients s1, s2, s3 and s4 are enabled. To provide the
/// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the
/// calibration function use the thin prism model and return 12 coefficients or more.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_S1_S2_S3_S4] The thin prism distortion coefficients are not changed during
/// the optimization. If [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set, the coefficient from the
/// supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0.
/// * [CALIB_TILTED_MODEL] Coefficients tauX and tauY are enabled. To provide the
/// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the
/// calibration function use the tilted sensor model and return 14 coefficients.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_TAUX_TAUY] The coefficients of the tilted sensor model are not changed during
/// the optimization. If [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set, the coefficient from the
/// supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0.
/// * criteria: Termination criteria for the iterative optimization algorithm.
///
/// ## Returns
/// the overall RMS re-projection error.
///
/// The function estimates the intrinsic camera parameters and extrinsic parameters for each of the
/// views. The algorithm is based on [Zhang2000](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Zhang2000) and [BouguetMCT](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_BouguetMCT) . The coordinates of 3D object
/// points and their corresponding 2D projections in each view must be specified. That may be achieved
/// by using an object with known geometry and easily detectable feature points. Such an object is
/// called a calibration rig or calibration pattern, and OpenCV has built-in support for a chessboard as
/// a calibration rig (see [findChessboardCorners]). Currently, initialization of intrinsic
/// parameters (when [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is not set) is only implemented for planar calibration
/// patterns (where Z-coordinates of the object points must be all zeros). 3D calibration rigs can also
/// be used as long as initial cameraMatrix is provided.
///
/// The algorithm performs the following steps:
///
/// * Compute the initial intrinsic parameters (the option only available for planar calibration
/// patterns) or read them from the input parameters. The distortion coefficients are all set to
/// zeros initially unless some of CALIB_FIX_K? are specified.
///
/// * Estimate the initial camera pose as if the intrinsic parameters have been already known. This is
/// done using [solvePnP] .
///
/// * Run the global Levenberg-Marquardt optimization algorithm to minimize the reprojection error,
/// that is, the total sum of squared distances between the observed feature points imagePoints and
/// the projected (using the current estimates for camera parameters and the poses) object points
/// objectPoints. See [projectPoints] for details.
///
///
/// Note:
/// If you use a non-square (i.e. non-N-by-N) grid and [findChessboardCorners] for calibration,
/// and [calibrateCamera] returns bad values (zero distortion coefficients,  and
///  very far from the image center, and/or large differences between  and
///  (ratios of 10:1 or more)), then you are probably using patternSize=cvSize(rows,cols)
/// instead of using patternSize=cvSize(cols,rows) in [findChessboardCorners].
///
///
/// Note:
/// The function may throw exceptions, if unsupported combination of parameters is provided or
/// the system is underconstrained.
/// ## See also
/// calibrateCameraRO, findChessboardCorners, solvePnP, initCameraMatrix2D, stereoCalibrate,
/// undistort
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: 0
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,30,DBL_EPSILON)
#[inline]
pub fn calibrate_camera(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, camera_matrix: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, rvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, flags: i32, criteria: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<f64> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
output_array_arg!(rvecs);
output_array_arg!(tvecs);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_calibrateCamera_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_TermCriteria(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, camera_matrix.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), rvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, &criteria, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes Hand-Eye calibration: 
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * R_gripper2base: Rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the gripper frame to the robot base frame ().
/// This is a vector (`vector<Mat>`) that contains the rotation, `(3x3)` rotation matrices or `(3x1)` rotation vectors,
/// for all the transformations from gripper frame to robot base frame.
/// * t_gripper2base: Translation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the gripper frame to the robot base frame ().
/// This is a vector (`vector<Mat>`) that contains the `(3x1)` translation vectors for all the transformations
/// from gripper frame to robot base frame.
/// * R_target2cam: Rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the target frame to the camera frame ().
/// This is a vector (`vector<Mat>`) that contains the rotation, `(3x3)` rotation matrices or `(3x1)` rotation vectors,
/// for all the transformations from calibration target frame to camera frame.
/// * t_target2cam: Rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the target frame to the camera frame ().
/// This is a vector (`vector<Mat>`) that contains the `(3x1)` translation vectors for all the transformations
/// from calibration target frame to camera frame.
/// * R_cam2gripper:[out] Estimated `(3x3)` rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the camera frame to the gripper frame ().
/// * t_cam2gripper:[out] Estimated `(3x1)` translation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the camera frame to the gripper frame ().
/// * method: One of the implemented Hand-Eye calibration method, see cv::HandEyeCalibrationMethod
///
/// The function performs the Hand-Eye calibration using various methods. One approach consists in estimating the
/// rotation then the translation (separable solutions) and the following methods are implemented:
/// - R. Tsai, R. Lenz A New Technique for Fully Autonomous and Efficient 3D Robotics Hand/EyeCalibration \cite Tsai89
/// - F. Park, B. Martin Robot Sensor Calibration: Solving AX = XB on the Euclidean Group \cite Park94
/// - R. Horaud, F. Dornaika Hand-Eye Calibration \cite Horaud95
///
/// Another approach consists in estimating simultaneously the rotation and the translation (simultaneous solutions),
/// with the following implemented methods:
/// - N. Andreff, R. Horaud, B. Espiau On-line Hand-Eye Calibration \cite Andreff99
/// - K. Daniilidis Hand-Eye Calibration Using Dual Quaternions \cite Daniilidis98
///
/// The following picture describes the Hand-Eye calibration problem where the transformation between a camera ("eye")
/// mounted on a robot gripper ("hand") has to be estimated. This configuration is called eye-in-hand.
///
/// The eye-to-hand configuration consists in a static camera observing a calibration pattern mounted on the robot
/// end-effector. The transformation from the camera to the robot base frame can then be estimated by inputting
/// the suitable transformations to the function, see below.
///
/// 
///
/// The calibration procedure is the following:
/// - a static calibration pattern is used to estimate the transformation between the target frame
/// and the camera frame
/// - the robot gripper is moved in order to acquire several poses
/// - for each pose, the homogeneous transformation between the gripper frame and the robot base frame is recorded using for
/// instance the robot kinematics
/// 
/// - for each pose, the homogeneous transformation between the calibration target frame and the camera frame is recorded using
/// for instance a pose estimation method (PnP) from 2D-3D point correspondences
/// 
///
/// The Hand-Eye calibration procedure returns the following homogeneous transformation
/// 
///
/// This problem is also known as solving the 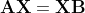 equation:
/// - for an eye-in-hand configuration
/// 
///
/// - for an eye-to-hand configuration
/// 
///
/// \note
/// Additional information can be found on this [website](http://campar.in.tum.de/Chair/HandEyeCalibration).
/// \note
/// A minimum of 2 motions with non parallel rotation axes are necessary to determine the hand-eye transformation.
/// So at least 3 different poses are required, but it is strongly recommended to use many more poses.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [calibrate_hand_eye] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * method: CALIB_HAND_EYE_TSAI
#[inline]
pub fn calibrate_hand_eye_def(r_gripper2base: &impl ToInputArray, t_gripper2base: &impl ToInputArray, r_target2cam: &impl ToInputArray, t_target2cam: &impl ToInputArray, r_cam2gripper: &mut impl ToOutputArray, t_cam2gripper: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(r_gripper2base);
input_array_arg!(t_gripper2base);
input_array_arg!(r_target2cam);
input_array_arg!(t_target2cam);
output_array_arg!(r_cam2gripper);
output_array_arg!(t_cam2gripper);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_calibrateHandEye_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(r_gripper2base.as_raw__InputArray(), t_gripper2base.as_raw__InputArray(), r_target2cam.as_raw__InputArray(), t_target2cam.as_raw__InputArray(), r_cam2gripper.as_raw__OutputArray(), t_cam2gripper.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes Hand-Eye calibration: 
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * R_gripper2base: Rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the gripper frame to the robot base frame ().
/// This is a vector (`vector<Mat>`) that contains the rotation, `(3x3)` rotation matrices or `(3x1)` rotation vectors,
/// for all the transformations from gripper frame to robot base frame.
/// * t_gripper2base: Translation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the gripper frame to the robot base frame ().
/// This is a vector (`vector<Mat>`) that contains the `(3x1)` translation vectors for all the transformations
/// from gripper frame to robot base frame.
/// * R_target2cam: Rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the target frame to the camera frame ().
/// This is a vector (`vector<Mat>`) that contains the rotation, `(3x3)` rotation matrices or `(3x1)` rotation vectors,
/// for all the transformations from calibration target frame to camera frame.
/// * t_target2cam: Rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the target frame to the camera frame ().
/// This is a vector (`vector<Mat>`) that contains the `(3x1)` translation vectors for all the transformations
/// from calibration target frame to camera frame.
/// * R_cam2gripper:[out] Estimated `(3x3)` rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the camera frame to the gripper frame ().
/// * t_cam2gripper:[out] Estimated `(3x1)` translation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the camera frame to the gripper frame ().
/// * method: One of the implemented Hand-Eye calibration method, see cv::HandEyeCalibrationMethod
///
/// The function performs the Hand-Eye calibration using various methods. One approach consists in estimating the
/// rotation then the translation (separable solutions) and the following methods are implemented:
/// - R. Tsai, R. Lenz A New Technique for Fully Autonomous and Efficient 3D Robotics Hand/EyeCalibration \cite Tsai89
/// - F. Park, B. Martin Robot Sensor Calibration: Solving AX = XB on the Euclidean Group \cite Park94
/// - R. Horaud, F. Dornaika Hand-Eye Calibration \cite Horaud95
///
/// Another approach consists in estimating simultaneously the rotation and the translation (simultaneous solutions),
/// with the following implemented methods:
/// - N. Andreff, R. Horaud, B. Espiau On-line Hand-Eye Calibration \cite Andreff99
/// - K. Daniilidis Hand-Eye Calibration Using Dual Quaternions \cite Daniilidis98
///
/// The following picture describes the Hand-Eye calibration problem where the transformation between a camera ("eye")
/// mounted on a robot gripper ("hand") has to be estimated. This configuration is called eye-in-hand.
///
/// The eye-to-hand configuration consists in a static camera observing a calibration pattern mounted on the robot
/// end-effector. The transformation from the camera to the robot base frame can then be estimated by inputting
/// the suitable transformations to the function, see below.
///
/// 
///
/// The calibration procedure is the following:
/// - a static calibration pattern is used to estimate the transformation between the target frame
/// and the camera frame
/// - the robot gripper is moved in order to acquire several poses
/// - for each pose, the homogeneous transformation between the gripper frame and the robot base frame is recorded using for
/// instance the robot kinematics
/// 
/// - for each pose, the homogeneous transformation between the calibration target frame and the camera frame is recorded using
/// for instance a pose estimation method (PnP) from 2D-3D point correspondences
/// 
///
/// The Hand-Eye calibration procedure returns the following homogeneous transformation
/// 
///
/// This problem is also known as solving the 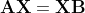 equation:
/// - for an eye-in-hand configuration
/// 
///
/// - for an eye-to-hand configuration
/// 
///
/// \note
/// Additional information can be found on this [website](http://campar.in.tum.de/Chair/HandEyeCalibration).
/// \note
/// A minimum of 2 motions with non parallel rotation axes are necessary to determine the hand-eye transformation.
/// So at least 3 different poses are required, but it is strongly recommended to use many more poses.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * method: CALIB_HAND_EYE_TSAI
#[inline]
pub fn calibrate_hand_eye(r_gripper2base: &impl ToInputArray, t_gripper2base: &impl ToInputArray, r_target2cam: &impl ToInputArray, t_target2cam: &impl ToInputArray, r_cam2gripper: &mut impl ToOutputArray, t_cam2gripper: &mut impl ToOutputArray, method: crate::calib3d::HandEyeCalibrationMethod) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(r_gripper2base);
input_array_arg!(t_gripper2base);
input_array_arg!(r_target2cam);
input_array_arg!(t_target2cam);
output_array_arg!(r_cam2gripper);
output_array_arg!(t_cam2gripper);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_calibrateHandEye_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_HandEyeCalibrationMethod(r_gripper2base.as_raw__InputArray(), t_gripper2base.as_raw__InputArray(), r_target2cam.as_raw__InputArray(), t_target2cam.as_raw__InputArray(), r_cam2gripper.as_raw__OutputArray(), t_cam2gripper.as_raw__OutputArray(), method, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes Robot-World/Hand-Eye calibration:  and 
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * R_world2cam: Rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the world frame to the camera frame ().
/// This is a vector (`vector<Mat>`) that contains the rotation, `(3x3)` rotation matrices or `(3x1)` rotation vectors,
/// for all the transformations from world frame to the camera frame.
/// * t_world2cam: Translation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the world frame to the camera frame ().
/// This is a vector (`vector<Mat>`) that contains the `(3x1)` translation vectors for all the transformations
/// from world frame to the camera frame.
/// * R_base2gripper: Rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the robot base frame to the gripper frame ().
/// This is a vector (`vector<Mat>`) that contains the rotation, `(3x3)` rotation matrices or `(3x1)` rotation vectors,
/// for all the transformations from robot base frame to the gripper frame.
/// * t_base2gripper: Rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the robot base frame to the gripper frame ().
/// This is a vector (`vector<Mat>`) that contains the `(3x1)` translation vectors for all the transformations
/// from robot base frame to the gripper frame.
/// * R_base2world:[out] Estimated `(3x3)` rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the robot base frame to the world frame ().
/// * t_base2world:[out] Estimated `(3x1)` translation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the robot base frame to the world frame ().
/// * R_gripper2cam:[out] Estimated `(3x3)` rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the gripper frame to the camera frame ().
/// * t_gripper2cam:[out] Estimated `(3x1)` translation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the gripper frame to the camera frame ().
/// * method: One of the implemented Robot-World/Hand-Eye calibration method, see cv::RobotWorldHandEyeCalibrationMethod
///
/// The function performs the Robot-World/Hand-Eye calibration using various methods. One approach consists in estimating the
/// rotation then the translation (separable solutions):
/// - M. Shah, Solving the robot-world/hand-eye calibration problem using the kronecker product \cite Shah2013SolvingTR
///
/// Another approach consists in estimating simultaneously the rotation and the translation (simultaneous solutions),
/// with the following implemented method:
/// - A. Li, L. Wang, and D. Wu, Simultaneous robot-world and hand-eye calibration using dual-quaternions and kronecker product \cite Li2010SimultaneousRA
///
/// The following picture describes the Robot-World/Hand-Eye calibration problem where the transformations between a robot and a world frame
/// and between a robot gripper ("hand") and a camera ("eye") mounted at the robot end-effector have to be estimated.
///
/// 
///
/// The calibration procedure is the following:
/// - a static calibration pattern is used to estimate the transformation between the target frame
/// and the camera frame
/// - the robot gripper is moved in order to acquire several poses
/// - for each pose, the homogeneous transformation between the gripper frame and the robot base frame is recorded using for
/// instance the robot kinematics
/// 
/// - for each pose, the homogeneous transformation between the calibration target frame (the world frame) and the camera frame is recorded using
/// for instance a pose estimation method (PnP) from 2D-3D point correspondences
/// 
///
/// The Robot-World/Hand-Eye calibration procedure returns the following homogeneous transformations
/// 
/// 
///
/// This problem is also known as solving the  equation, with:
/// - 
/// - 
/// - 
/// - 
///
/// \note
/// At least 3 measurements are required (input vectors size must be greater or equal to 3).
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [calibrate_robot_world_hand_eye] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * method: CALIB_ROBOT_WORLD_HAND_EYE_SHAH
#[inline]
pub fn calibrate_robot_world_hand_eye_def(r_world2cam: &impl ToInputArray, t_world2cam: &impl ToInputArray, r_base2gripper: &impl ToInputArray, t_base2gripper: &impl ToInputArray, r_base2world: &mut impl ToOutputArray, t_base2world: &mut impl ToOutputArray, r_gripper2cam: &mut impl ToOutputArray, t_gripper2cam: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(r_world2cam);
input_array_arg!(t_world2cam);
input_array_arg!(r_base2gripper);
input_array_arg!(t_base2gripper);
output_array_arg!(r_base2world);
output_array_arg!(t_base2world);
output_array_arg!(r_gripper2cam);
output_array_arg!(t_gripper2cam);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_calibrateRobotWorldHandEye_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(r_world2cam.as_raw__InputArray(), t_world2cam.as_raw__InputArray(), r_base2gripper.as_raw__InputArray(), t_base2gripper.as_raw__InputArray(), r_base2world.as_raw__OutputArray(), t_base2world.as_raw__OutputArray(), r_gripper2cam.as_raw__OutputArray(), t_gripper2cam.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes Robot-World/Hand-Eye calibration:  and 
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * R_world2cam: Rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the world frame to the camera frame ().
/// This is a vector (`vector<Mat>`) that contains the rotation, `(3x3)` rotation matrices or `(3x1)` rotation vectors,
/// for all the transformations from world frame to the camera frame.
/// * t_world2cam: Translation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the world frame to the camera frame ().
/// This is a vector (`vector<Mat>`) that contains the `(3x1)` translation vectors for all the transformations
/// from world frame to the camera frame.
/// * R_base2gripper: Rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the robot base frame to the gripper frame ().
/// This is a vector (`vector<Mat>`) that contains the rotation, `(3x3)` rotation matrices or `(3x1)` rotation vectors,
/// for all the transformations from robot base frame to the gripper frame.
/// * t_base2gripper: Rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the robot base frame to the gripper frame ().
/// This is a vector (`vector<Mat>`) that contains the `(3x1)` translation vectors for all the transformations
/// from robot base frame to the gripper frame.
/// * R_base2world:[out] Estimated `(3x3)` rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the robot base frame to the world frame ().
/// * t_base2world:[out] Estimated `(3x1)` translation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the robot base frame to the world frame ().
/// * R_gripper2cam:[out] Estimated `(3x3)` rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the gripper frame to the camera frame ().
/// * t_gripper2cam:[out] Estimated `(3x1)` translation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point
/// expressed in the gripper frame to the camera frame ().
/// * method: One of the implemented Robot-World/Hand-Eye calibration method, see cv::RobotWorldHandEyeCalibrationMethod
///
/// The function performs the Robot-World/Hand-Eye calibration using various methods. One approach consists in estimating the
/// rotation then the translation (separable solutions):
/// - M. Shah, Solving the robot-world/hand-eye calibration problem using the kronecker product \cite Shah2013SolvingTR
///
/// Another approach consists in estimating simultaneously the rotation and the translation (simultaneous solutions),
/// with the following implemented method:
/// - A. Li, L. Wang, and D. Wu, Simultaneous robot-world and hand-eye calibration using dual-quaternions and kronecker product \cite Li2010SimultaneousRA
///
/// The following picture describes the Robot-World/Hand-Eye calibration problem where the transformations between a robot and a world frame
/// and between a robot gripper ("hand") and a camera ("eye") mounted at the robot end-effector have to be estimated.
///
/// 
///
/// The calibration procedure is the following:
/// - a static calibration pattern is used to estimate the transformation between the target frame
/// and the camera frame
/// - the robot gripper is moved in order to acquire several poses
/// - for each pose, the homogeneous transformation between the gripper frame and the robot base frame is recorded using for
/// instance the robot kinematics
/// 
/// - for each pose, the homogeneous transformation between the calibration target frame (the world frame) and the camera frame is recorded using
/// for instance a pose estimation method (PnP) from 2D-3D point correspondences
/// 
///
/// The Robot-World/Hand-Eye calibration procedure returns the following homogeneous transformations
/// 
/// 
///
/// This problem is also known as solving the  equation, with:
/// - 
/// - 
/// - 
/// - 
///
/// \note
/// At least 3 measurements are required (input vectors size must be greater or equal to 3).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * method: CALIB_ROBOT_WORLD_HAND_EYE_SHAH
#[inline]
pub fn calibrate_robot_world_hand_eye(r_world2cam: &impl ToInputArray, t_world2cam: &impl ToInputArray, r_base2gripper: &impl ToInputArray, t_base2gripper: &impl ToInputArray, r_base2world: &mut impl ToOutputArray, t_base2world: &mut impl ToOutputArray, r_gripper2cam: &mut impl ToOutputArray, t_gripper2cam: &mut impl ToOutputArray, method: crate::calib3d::RobotWorldHandEyeCalibrationMethod) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(r_world2cam);
input_array_arg!(t_world2cam);
input_array_arg!(r_base2gripper);
input_array_arg!(t_base2gripper);
output_array_arg!(r_base2world);
output_array_arg!(t_base2world);
output_array_arg!(r_gripper2cam);
output_array_arg!(t_gripper2cam);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_calibrateRobotWorldHandEye_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_RobotWorldHandEyeCalibrationMethod(r_world2cam.as_raw__InputArray(), t_world2cam.as_raw__InputArray(), r_base2gripper.as_raw__InputArray(), t_base2gripper.as_raw__InputArray(), r_base2world.as_raw__OutputArray(), t_base2world.as_raw__OutputArray(), r_gripper2cam.as_raw__OutputArray(), t_gripper2cam.as_raw__OutputArray(), method, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes useful camera characteristics from the camera intrinsic matrix.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * cameraMatrix: Input camera intrinsic matrix that can be estimated by [calibrate_camera] or
/// [stereo_calibrate] .
/// * imageSize: Input image size in pixels.
/// * apertureWidth: Physical width in mm of the sensor.
/// * apertureHeight: Physical height in mm of the sensor.
/// * fovx: Output field of view in degrees along the horizontal sensor axis.
/// * fovy: Output field of view in degrees along the vertical sensor axis.
/// * focalLength: Focal length of the lens in mm.
/// * principalPoint: Principal point in mm.
/// * aspectRatio: 
///
/// The function computes various useful camera characteristics from the previously estimated camera
/// matrix.
///
///
/// Note:
/// Do keep in mind that the unity measure 'mm' stands for whatever unit of measure one chooses for
/// the chessboard pitch (it can thus be any value).
#[inline]
pub fn calibration_matrix_values(camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, aperture_width: f64, aperture_height: f64, fovx: &mut f64, fovy: &mut f64, focal_length: &mut f64, principal_point: &mut core::Point2d, aspect_ratio: &mut f64) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_calibrationMatrixValues_const__InputArrayR_Size_double_double_doubleR_doubleR_doubleR_Point2dR_doubleR(camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, aperture_width, aperture_height, fovx, fovy, focal_length, principal_point, aspect_ratio, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn check_chessboard(img: &impl ToInputArray, size: core::Size) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(img);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_checkChessboard_const__InputArrayR_Size(img.as_raw__InputArray(), &size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Combines two rotation-and-shift transformations.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * rvec1: First rotation vector.
/// * tvec1: First translation vector.
/// * rvec2: Second rotation vector.
/// * tvec2: Second translation vector.
/// * rvec3: Output rotation vector of the superposition.
/// * tvec3: Output translation vector of the superposition.
/// * dr3dr1: Optional output derivative of rvec3 with regard to rvec1
/// * dr3dt1: Optional output derivative of rvec3 with regard to tvec1
/// * dr3dr2: Optional output derivative of rvec3 with regard to rvec2
/// * dr3dt2: Optional output derivative of rvec3 with regard to tvec2
/// * dt3dr1: Optional output derivative of tvec3 with regard to rvec1
/// * dt3dt1: Optional output derivative of tvec3 with regard to tvec1
/// * dt3dr2: Optional output derivative of tvec3 with regard to rvec2
/// * dt3dt2: Optional output derivative of tvec3 with regard to tvec2
///
/// The functions compute:
///
/// 
///
/// where  denotes a rotation vector to a rotation matrix transformation, and
///  denotes the inverse transformation. See [rodrigues] for details.
///
/// Also, the functions can compute the derivatives of the output vectors with regards to the input
/// vectors (see [mat_mul_deriv] ). The functions are used inside [stereo_calibrate] but can also be used in
/// your own code where Levenberg-Marquardt or another gradient-based solver is used to optimize a
/// function that contains a matrix multiplication.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [compose_rt] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * dr3dr1: noArray()
/// * dr3dt1: noArray()
/// * dr3dr2: noArray()
/// * dr3dt2: noArray()
/// * dt3dr1: noArray()
/// * dt3dt1: noArray()
/// * dt3dr2: noArray()
/// * dt3dt2: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn compose_rt_def(rvec1: &impl ToInputArray, tvec1: &impl ToInputArray, rvec2: &impl ToInputArray, tvec2: &impl ToInputArray, rvec3: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvec3: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(rvec1);
input_array_arg!(tvec1);
input_array_arg!(rvec2);
input_array_arg!(tvec2);
output_array_arg!(rvec3);
output_array_arg!(tvec3);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_composeRT_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(rvec1.as_raw__InputArray(), tvec1.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec2.as_raw__InputArray(), tvec2.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec3.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvec3.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Combines two rotation-and-shift transformations.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * rvec1: First rotation vector.
/// * tvec1: First translation vector.
/// * rvec2: Second rotation vector.
/// * tvec2: Second translation vector.
/// * rvec3: Output rotation vector of the superposition.
/// * tvec3: Output translation vector of the superposition.
/// * dr3dr1: Optional output derivative of rvec3 with regard to rvec1
/// * dr3dt1: Optional output derivative of rvec3 with regard to tvec1
/// * dr3dr2: Optional output derivative of rvec3 with regard to rvec2
/// * dr3dt2: Optional output derivative of rvec3 with regard to tvec2
/// * dt3dr1: Optional output derivative of tvec3 with regard to rvec1
/// * dt3dt1: Optional output derivative of tvec3 with regard to tvec1
/// * dt3dr2: Optional output derivative of tvec3 with regard to rvec2
/// * dt3dt2: Optional output derivative of tvec3 with regard to tvec2
///
/// The functions compute:
///
/// 
///
/// where  denotes a rotation vector to a rotation matrix transformation, and
///  denotes the inverse transformation. See [rodrigues] for details.
///
/// Also, the functions can compute the derivatives of the output vectors with regards to the input
/// vectors (see [mat_mul_deriv] ). The functions are used inside [stereo_calibrate] but can also be used in
/// your own code where Levenberg-Marquardt or another gradient-based solver is used to optimize a
/// function that contains a matrix multiplication.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * dr3dr1: noArray()
/// * dr3dt1: noArray()
/// * dr3dr2: noArray()
/// * dr3dt2: noArray()
/// * dt3dr1: noArray()
/// * dt3dt1: noArray()
/// * dt3dr2: noArray()
/// * dt3dt2: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn compose_rt(rvec1: &impl ToInputArray, tvec1: &impl ToInputArray, rvec2: &impl ToInputArray, tvec2: &impl ToInputArray, rvec3: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvec3: &mut impl ToOutputArray, dr3dr1: &mut impl ToOutputArray, dr3dt1: &mut impl ToOutputArray, dr3dr2: &mut impl ToOutputArray, dr3dt2: &mut impl ToOutputArray, dt3dr1: &mut impl ToOutputArray, dt3dt1: &mut impl ToOutputArray, dt3dr2: &mut impl ToOutputArray, dt3dt2: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(rvec1);
input_array_arg!(tvec1);
input_array_arg!(rvec2);
input_array_arg!(tvec2);
output_array_arg!(rvec3);
output_array_arg!(tvec3);
output_array_arg!(dr3dr1);
output_array_arg!(dr3dt1);
output_array_arg!(dr3dr2);
output_array_arg!(dr3dt2);
output_array_arg!(dt3dr1);
output_array_arg!(dt3dt1);
output_array_arg!(dt3dr2);
output_array_arg!(dt3dt2);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_composeRT_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(rvec1.as_raw__InputArray(), tvec1.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec2.as_raw__InputArray(), tvec2.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec3.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvec3.as_raw__OutputArray(), dr3dr1.as_raw__OutputArray(), dr3dt1.as_raw__OutputArray(), dr3dr2.as_raw__OutputArray(), dr3dt2.as_raw__OutputArray(), dt3dr1.as_raw__OutputArray(), dt3dt1.as_raw__OutputArray(), dt3dr2.as_raw__OutputArray(), dt3dt2.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// For points in an image of a stereo pair, computes the corresponding epilines in the other image.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * points: Input points. 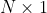 or 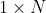 matrix of type CV_32FC2 or
/// vector\<Point2f\> .
/// * whichImage: Index of the image (1 or 2) that contains the points .
/// * F: Fundamental matrix that can be estimated using [find_fundamental_mat] or [stereo_rectify] .
/// * lines: Output vector of the epipolar lines corresponding to the points in the other image.
/// Each line 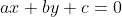 is encoded by 3 numbers 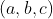 .
///
/// For every point in one of the two images of a stereo pair, the function finds the equation of the
/// corresponding epipolar line in the other image.
///
/// From the fundamental matrix definition (see [find_fundamental_mat] ), line  in the second
/// image for the point  in the first image (when whichImage=1 ) is computed as:
///
/// 
///
/// And vice versa, when whichImage=2,  is computed from  as:
///
/// 
///
/// Line coefficients are defined up to a scale. They are normalized so that  .
#[inline]
pub fn compute_correspond_epilines(points: &impl ToInputArray, which_image: i32, f: &impl ToInputArray, lines: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(points);
input_array_arg!(f);
output_array_arg!(lines);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_computeCorrespondEpilines_const__InputArrayR_int_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(points.as_raw__InputArray(), which_image, f.as_raw__InputArray(), lines.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Converts points from homogeneous to Euclidean space.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input vector of N-dimensional points.
/// * dst: Output vector of N-1-dimensional points.
///
/// The function converts points homogeneous to Euclidean space using perspective projection. That is,
/// each point (x1, x2, ... x(n-1), xn) is converted to (x1/xn, x2/xn, ..., x(n-1)/xn). When xn=0, the
/// output point coordinates will be (0,0,0,...).
#[inline]
pub fn convert_points_from_homogeneous(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_convertPointsFromHomogeneous_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Converts points to/from homogeneous coordinates.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input array or vector of 2D, 3D, or 4D points.
/// * dst: Output vector of 2D, 3D, or 4D points.
///
/// The function converts 2D or 3D points from/to homogeneous coordinates by calling either
/// [convert_points_to_homogeneous] or #convertPointsFromHomogeneous.
///
///
/// Note: The function is obsolete. Use one of the previous two functions instead.
#[inline]
pub fn convert_points_homogeneous(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_convertPointsHomogeneous_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Converts points from Euclidean to homogeneous space.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input vector of N-dimensional points.
/// * dst: Output vector of N+1-dimensional points.
///
/// The function converts points from Euclidean to homogeneous space by appending 1's to the tuple of
/// point coordinates. That is, each point (x1, x2, ..., xn) is converted to (x1, x2, ..., xn, 1).
#[inline]
pub fn convert_points_to_homogeneous(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_convertPointsToHomogeneous_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Refines coordinates of corresponding points.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * F: 3x3 fundamental matrix.
/// * points1: 1xN array containing the first set of points.
/// * points2: 1xN array containing the second set of points.
/// * newPoints1: The optimized points1.
/// * newPoints2: The optimized points2.
///
/// The function implements the Optimal Triangulation Method (see Multiple View Geometry [HartleyZ00](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_HartleyZ00) for details).
/// For each given point correspondence points1[i] \<-\> points2[i], and a fundamental matrix F, it
/// computes the corrected correspondences newPoints1[i] \<-\> newPoints2[i] that minimize the geometric
/// error  (where  is the
/// geometric distance between points  and 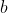 ) subject to the epipolar constraint
///  .
#[inline]
pub fn correct_matches(f: &impl ToInputArray, points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray, new_points1: &mut impl ToOutputArray, new_points2: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(f);
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
output_array_arg!(new_points1);
output_array_arg!(new_points2);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_correctMatches_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(f.as_raw__InputArray(), points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), new_points1.as_raw__OutputArray(), new_points2.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Decompose an essential matrix to possible rotations and translation.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * E: The input essential matrix.
/// * R1: One possible rotation matrix.
/// * R2: Another possible rotation matrix.
/// * t: One possible translation.
///
/// This function decomposes the essential matrix E using svd decomposition [HartleyZ00](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_HartleyZ00). In
/// general, four possible poses exist for the decomposition of E. They are ,
/// , , .
///
/// If E gives the epipolar constraint  between the image
/// points  in the first image and  in second image, then any of the tuples
/// , , ,  is a change of basis from the first
/// camera's coordinate system to the second camera's coordinate system. However, by decomposing E, one
/// can only get the direction of the translation. For this reason, the translation t is returned with
/// unit length.
#[inline]
pub fn decompose_essential_mat(e: &impl ToInputArray, r1: &mut impl ToOutputArray, r2: &mut impl ToOutputArray, t: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(e);
output_array_arg!(r1);
output_array_arg!(r2);
output_array_arg!(t);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_decomposeEssentialMat_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(e.as_raw__InputArray(), r1.as_raw__OutputArray(), r2.as_raw__OutputArray(), t.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Decompose a homography matrix to rotation(s), translation(s) and plane normal(s).
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * H: The input homography matrix between two images.
/// * K: The input camera intrinsic matrix.
/// * rotations: Array of rotation matrices.
/// * translations: Array of translation matrices.
/// * normals: Array of plane normal matrices.
///
/// This function extracts relative camera motion between two views of a planar object and returns up to
/// four mathematical solution tuples of rotation, translation, and plane normal. The decomposition of
/// the homography matrix H is described in detail in [Malis2007](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Malis2007).
///
/// If the homography H, induced by the plane, gives the constraint
///  on the source image points
/// 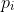 and the destination image points , then the tuple of rotations[k] and
/// translations[k] is a change of basis from the source camera's coordinate system to the destination
/// camera's coordinate system. However, by decomposing H, one can only get the translation normalized
/// by the (typically unknown) depth of the scene, i.e. its direction but with normalized length.
///
/// If point correspondences are available, at least two solutions may further be invalidated, by
/// applying positive depth constraint, i.e. all points must be in front of the camera.
#[inline]
pub fn decompose_homography_mat(h: &impl ToInputArray, k: &impl ToInputArray, rotations: &mut impl ToOutputArray, translations: &mut impl ToOutputArray, normals: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<i32> {
input_array_arg!(h);
input_array_arg!(k);
output_array_arg!(rotations);
output_array_arg!(translations);
output_array_arg!(normals);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_decomposeHomographyMat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(h.as_raw__InputArray(), k.as_raw__InputArray(), rotations.as_raw__OutputArray(), translations.as_raw__OutputArray(), normals.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Decomposes a projection matrix into a rotation matrix and a camera intrinsic matrix.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * projMatrix: 3x4 input projection matrix P.
/// * cameraMatrix: Output 3x3 camera intrinsic matrix .
/// * rotMatrix: Output 3x3 external rotation matrix R.
/// * transVect: Output 4x1 translation vector T.
/// * rotMatrixX: Optional 3x3 rotation matrix around x-axis.
/// * rotMatrixY: Optional 3x3 rotation matrix around y-axis.
/// * rotMatrixZ: Optional 3x3 rotation matrix around z-axis.
/// * eulerAngles: Optional three-element vector containing three Euler angles of rotation in
/// degrees.
///
/// The function computes a decomposition of a projection matrix into a calibration and a rotation
/// matrix and the position of a camera.
///
/// It optionally returns three rotation matrices, one for each axis, and three Euler angles that could
/// be used in OpenGL. Note, there is always more than one sequence of rotations about the three
/// principal axes that results in the same orientation of an object, e.g. see [Slabaugh](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Slabaugh) . Returned
/// three rotation matrices and corresponding three Euler angles are only one of the possible solutions.
///
/// The function is based on [rq_decomp3x3] .
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [decompose_projection_matrix] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * rot_matrix_x: noArray()
/// * rot_matrix_y: noArray()
/// * rot_matrix_z: noArray()
/// * euler_angles: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn decompose_projection_matrix_def(proj_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &mut impl ToOutputArray, rot_matrix: &mut impl ToOutputArray, trans_vect: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(proj_matrix);
output_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
output_array_arg!(rot_matrix);
output_array_arg!(trans_vect);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_decomposeProjectionMatrix_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(proj_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__OutputArray(), rot_matrix.as_raw__OutputArray(), trans_vect.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Decomposes a projection matrix into a rotation matrix and a camera intrinsic matrix.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * projMatrix: 3x4 input projection matrix P.
/// * cameraMatrix: Output 3x3 camera intrinsic matrix .
/// * rotMatrix: Output 3x3 external rotation matrix R.
/// * transVect: Output 4x1 translation vector T.
/// * rotMatrixX: Optional 3x3 rotation matrix around x-axis.
/// * rotMatrixY: Optional 3x3 rotation matrix around y-axis.
/// * rotMatrixZ: Optional 3x3 rotation matrix around z-axis.
/// * eulerAngles: Optional three-element vector containing three Euler angles of rotation in
/// degrees.
///
/// The function computes a decomposition of a projection matrix into a calibration and a rotation
/// matrix and the position of a camera.
///
/// It optionally returns three rotation matrices, one for each axis, and three Euler angles that could
/// be used in OpenGL. Note, there is always more than one sequence of rotations about the three
/// principal axes that results in the same orientation of an object, e.g. see [Slabaugh](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Slabaugh) . Returned
/// three rotation matrices and corresponding three Euler angles are only one of the possible solutions.
///
/// The function is based on [rq_decomp3x3] .
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * rot_matrix_x: noArray()
/// * rot_matrix_y: noArray()
/// * rot_matrix_z: noArray()
/// * euler_angles: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn decompose_projection_matrix(proj_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &mut impl ToOutputArray, rot_matrix: &mut impl ToOutputArray, trans_vect: &mut impl ToOutputArray, rot_matrix_x: &mut impl ToOutputArray, rot_matrix_y: &mut impl ToOutputArray, rot_matrix_z: &mut impl ToOutputArray, euler_angles: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(proj_matrix);
output_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
output_array_arg!(rot_matrix);
output_array_arg!(trans_vect);
output_array_arg!(rot_matrix_x);
output_array_arg!(rot_matrix_y);
output_array_arg!(rot_matrix_z);
output_array_arg!(euler_angles);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_decomposeProjectionMatrix_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(proj_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__OutputArray(), rot_matrix.as_raw__OutputArray(), trans_vect.as_raw__OutputArray(), rot_matrix_x.as_raw__OutputArray(), rot_matrix_y.as_raw__OutputArray(), rot_matrix_z.as_raw__OutputArray(), euler_angles.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Renders the detected chessboard corners.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: Destination image. It must be an 8-bit color image.
/// * patternSize: Number of inner corners per a chessboard row and column
/// (patternSize = cv::Size(points_per_row,points_per_column)).
/// * corners: Array of detected corners, the output of #findChessboardCorners.
/// * patternWasFound: Parameter indicating whether the complete board was found or not. The
/// return value of [find_chessboard_corners] should be passed here.
///
/// The function draws individual chessboard corners detected either as red circles if the board was not
/// found, or as colored corners connected with lines if the board was found.
#[inline]
pub fn draw_chessboard_corners(image: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, pattern_size: core::Size, corners: &impl ToInputArray, pattern_was_found: bool) -> Result<()> {
input_output_array_arg!(image);
input_array_arg!(corners);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_drawChessboardCorners_const__InputOutputArrayR_Size_const__InputArrayR_bool(image.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), &pattern_size, corners.as_raw__InputArray(), pattern_was_found, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Draw axes of the world/object coordinate system from pose estimation. see also: solvePnP
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: Input/output image. It must have 1 or 3 channels. The number of channels is not altered.
/// * cameraMatrix: Input 3x3 floating-point matrix of camera intrinsic parameters.
/// 
/// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients
/// . If the vector is empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed.
/// * rvec: Rotation vector (see [Rodrigues] ) that, together with tvec, brings points from
/// the model coordinate system to the camera coordinate system.
/// * tvec: Translation vector.
/// * length: Length of the painted axes in the same unit than tvec (usually in meters).
/// * thickness: Line thickness of the painted axes.
///
/// This function draws the axes of the world/object coordinate system w.r.t. to the camera frame.
/// OX is drawn in red, OY in green and OZ in blue.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [draw_frame_axes] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * thickness: 3
#[inline]
pub fn draw_frame_axes_def(image: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, rvec: &impl ToInputArray, tvec: &impl ToInputArray, length: f32) -> Result<()> {
input_output_array_arg!(image);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
input_array_arg!(rvec);
input_array_arg!(tvec);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_drawFrameAxes_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_float(image.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec.as_raw__InputArray(), tvec.as_raw__InputArray(), length, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Draw axes of the world/object coordinate system from pose estimation. see also: solvePnP
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: Input/output image. It must have 1 or 3 channels. The number of channels is not altered.
/// * cameraMatrix: Input 3x3 floating-point matrix of camera intrinsic parameters.
/// 
/// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients
/// . If the vector is empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed.
/// * rvec: Rotation vector (see [Rodrigues] ) that, together with tvec, brings points from
/// the model coordinate system to the camera coordinate system.
/// * tvec: Translation vector.
/// * length: Length of the painted axes in the same unit than tvec (usually in meters).
/// * thickness: Line thickness of the painted axes.
///
/// This function draws the axes of the world/object coordinate system w.r.t. to the camera frame.
/// OX is drawn in red, OY in green and OZ in blue.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * thickness: 3
#[inline]
pub fn draw_frame_axes(image: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, rvec: &impl ToInputArray, tvec: &impl ToInputArray, length: f32, thickness: i32) -> Result<()> {
input_output_array_arg!(image);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
input_array_arg!(rvec);
input_array_arg!(tvec);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_drawFrameAxes_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_float_int(image.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec.as_raw__InputArray(), tvec.as_raw__InputArray(), length, thickness, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes an optimal affine transformation between two 2D point sets.
///
/// It computes
/// 
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * from: First input 2D point set containing 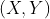.
/// * to: Second input 2D point set containing 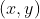.
/// * inliers: Output vector indicating which points are inliers (1-inlier, 0-outlier).
/// * method: Robust method used to compute transformation. The following methods are possible:
/// * [RANSAC] - RANSAC-based robust method
/// * [LMEDS] - Least-Median robust method
/// RANSAC is the default method.
/// * ransacReprojThreshold: Maximum reprojection error in the RANSAC algorithm to consider
/// a point as an inlier. Applies only to RANSAC.
/// * maxIters: The maximum number of robust method iterations.
/// * confidence: Confidence level, between 0 and 1, for the estimated transformation. Anything
/// between 0.95 and 0.99 is usually good enough. Values too close to 1 can slow down the estimation
/// significantly. Values lower than 0.8-0.9 can result in an incorrectly estimated transformation.
/// * refineIters: Maximum number of iterations of refining algorithm (Levenberg-Marquardt).
/// Passing 0 will disable refining, so the output matrix will be output of robust method.
///
/// ## Returns
/// Output 2D affine transformation matrix 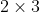 or empty matrix if transformation
/// could not be estimated. The returned matrix has the following form:
/// 
///
/// The function estimates an optimal 2D affine transformation between two 2D point sets using the
/// selected robust algorithm.
///
/// The computed transformation is then refined further (using only inliers) with the
/// Levenberg-Marquardt method to reduce the re-projection error even more.
///
///
/// Note:
/// The RANSAC method can handle practically any ratio of outliers but needs a threshold to
/// distinguish inliers from outliers. The method LMeDS does not need any threshold but it works
/// correctly only when there are more than 50% of inliers.
/// ## See also
/// estimateAffinePartial2D, getAffineTransform
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [estimate_affine_2d] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * inliers: noArray()
/// * method: RANSAC
/// * ransac_reproj_threshold: 3
/// * max_iters: 2000
/// * confidence: 0.99
/// * refine_iters: 10
#[inline]
pub fn estimate_affine_2d_def(from: &impl ToInputArray, to: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(from);
input_array_arg!(to);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_estimateAffine2D_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(from.as_raw__InputArray(), to.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn estimate_affine_2d_1(pts1: &impl ToInputArray, pts2: &impl ToInputArray, inliers: &mut impl ToOutputArray, params: crate::calib3d::UsacParams) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(pts1);
input_array_arg!(pts2);
output_array_arg!(inliers);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_estimateAffine2D_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const_UsacParamsR(pts1.as_raw__InputArray(), pts2.as_raw__InputArray(), inliers.as_raw__OutputArray(), ¶ms, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes an optimal affine transformation between two 2D point sets.
///
/// It computes
/// 
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * from: First input 2D point set containing 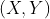.
/// * to: Second input 2D point set containing 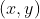.
/// * inliers: Output vector indicating which points are inliers (1-inlier, 0-outlier).
/// * method: Robust method used to compute transformation. The following methods are possible:
/// * [RANSAC] - RANSAC-based robust method
/// * [LMEDS] - Least-Median robust method
/// RANSAC is the default method.
/// * ransacReprojThreshold: Maximum reprojection error in the RANSAC algorithm to consider
/// a point as an inlier. Applies only to RANSAC.
/// * maxIters: The maximum number of robust method iterations.
/// * confidence: Confidence level, between 0 and 1, for the estimated transformation. Anything
/// between 0.95 and 0.99 is usually good enough. Values too close to 1 can slow down the estimation
/// significantly. Values lower than 0.8-0.9 can result in an incorrectly estimated transformation.
/// * refineIters: Maximum number of iterations of refining algorithm (Levenberg-Marquardt).
/// Passing 0 will disable refining, so the output matrix will be output of robust method.
///
/// ## Returns
/// Output 2D affine transformation matrix 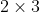 or empty matrix if transformation
/// could not be estimated. The returned matrix has the following form:
/// 
///
/// The function estimates an optimal 2D affine transformation between two 2D point sets using the
/// selected robust algorithm.
///
/// The computed transformation is then refined further (using only inliers) with the
/// Levenberg-Marquardt method to reduce the re-projection error even more.
///
///
/// Note:
/// The RANSAC method can handle practically any ratio of outliers but needs a threshold to
/// distinguish inliers from outliers. The method LMeDS does not need any threshold but it works
/// correctly only when there are more than 50% of inliers.
/// ## See also
/// estimateAffinePartial2D, getAffineTransform
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * inliers: noArray()
/// * method: RANSAC
/// * ransac_reproj_threshold: 3
/// * max_iters: 2000
/// * confidence: 0.99
/// * refine_iters: 10
#[inline]
pub fn estimate_affine_2d(from: &impl ToInputArray, to: &impl ToInputArray, inliers: &mut impl ToOutputArray, method: i32, ransac_reproj_threshold: f64, max_iters: size_t, confidence: f64, refine_iters: size_t) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(from);
input_array_arg!(to);
output_array_arg!(inliers);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_estimateAffine2D_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_double_size_t_double_size_t(from.as_raw__InputArray(), to.as_raw__InputArray(), inliers.as_raw__OutputArray(), method, ransac_reproj_threshold, max_iters, confidence, refine_iters, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes an optimal affine transformation between two 3D point sets.
///
/// It computes  minimizing 
/// where  is a 3x3 rotation matrix, 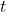 is a 3x1 translation vector and  is a
/// scalar size value. This is an implementation of the algorithm by Umeyama \cite umeyama1991least .
/// The estimated affine transform has a homogeneous scale which is a subclass of affine
/// transformations with 7 degrees of freedom. The paired point sets need to comprise at least 3
/// points each.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: First input 3D point set.
/// * dst: Second input 3D point set.
/// * scale: If null is passed, the scale parameter c will be assumed to be 1.0.
/// Else the pointed-to variable will be set to the optimal scale.
/// * force_rotation: If true, the returned rotation will never be a reflection.
/// This might be unwanted, e.g. when optimizing a transform between a right- and a
/// left-handed coordinate system.
/// ## Returns
/// 3D affine transformation matrix 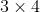 of the form
/// 
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [estimate_affine_3d_1] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * scale: nullptr
/// * force_rotation: true
#[inline]
pub fn estimate_affine_3d_1_def(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(src);
input_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_estimateAffine3D_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes an optimal affine transformation between two 3D point sets.
///
/// It computes
/// 
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: First input 3D point set containing 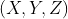.
/// * dst: Second input 3D point set containing 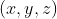.
/// * out: Output 3D affine transformation matrix 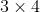 of the form
/// 
/// * inliers: Output vector indicating which points are inliers (1-inlier, 0-outlier).
/// * ransacThreshold: Maximum reprojection error in the RANSAC algorithm to consider a point as
/// an inlier.
/// * confidence: Confidence level, between 0 and 1, for the estimated transformation. Anything
/// between 0.95 and 0.99 is usually good enough. Values too close to 1 can slow down the estimation
/// significantly. Values lower than 0.8-0.9 can result in an incorrectly estimated transformation.
///
/// The function estimates an optimal 3D affine transformation between two 3D point sets using the
/// RANSAC algorithm.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [estimate_affine_3d] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * ransac_threshold: 3
/// * confidence: 0.99
#[inline]
pub fn estimate_affine_3d_def(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &impl ToInputArray, out: &mut impl ToOutputArray, inliers: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<i32> {
input_array_arg!(src);
input_array_arg!(dst);
output_array_arg!(out);
output_array_arg!(inliers);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_estimateAffine3D_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__InputArray(), out.as_raw__OutputArray(), inliers.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes an optimal affine transformation between two 3D point sets.
///
/// It computes
/// 
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: First input 3D point set containing 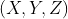.
/// * dst: Second input 3D point set containing 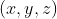.
/// * out: Output 3D affine transformation matrix 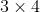 of the form
/// 
/// * inliers: Output vector indicating which points are inliers (1-inlier, 0-outlier).
/// * ransacThreshold: Maximum reprojection error in the RANSAC algorithm to consider a point as
/// an inlier.
/// * confidence: Confidence level, between 0 and 1, for the estimated transformation. Anything
/// between 0.95 and 0.99 is usually good enough. Values too close to 1 can slow down the estimation
/// significantly. Values lower than 0.8-0.9 can result in an incorrectly estimated transformation.
///
/// The function estimates an optimal 3D affine transformation between two 3D point sets using the
/// RANSAC algorithm.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * ransac_threshold: 3
/// * confidence: 0.99
#[inline]
pub fn estimate_affine_3d(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &impl ToInputArray, out: &mut impl ToOutputArray, inliers: &mut impl ToOutputArray, ransac_threshold: f64, confidence: f64) -> Result<i32> {
input_array_arg!(src);
input_array_arg!(dst);
output_array_arg!(out);
output_array_arg!(inliers);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_estimateAffine3D_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_double(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__InputArray(), out.as_raw__OutputArray(), inliers.as_raw__OutputArray(), ransac_threshold, confidence, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes an optimal affine transformation between two 3D point sets.
///
/// It computes  minimizing 
/// where  is a 3x3 rotation matrix, 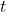 is a 3x1 translation vector and  is a
/// scalar size value. This is an implementation of the algorithm by Umeyama \cite umeyama1991least .
/// The estimated affine transform has a homogeneous scale which is a subclass of affine
/// transformations with 7 degrees of freedom. The paired point sets need to comprise at least 3
/// points each.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: First input 3D point set.
/// * dst: Second input 3D point set.
/// * scale: If null is passed, the scale parameter c will be assumed to be 1.0.
/// Else the pointed-to variable will be set to the optimal scale.
/// * force_rotation: If true, the returned rotation will never be a reflection.
/// This might be unwanted, e.g. when optimizing a transform between a right- and a
/// left-handed coordinate system.
/// ## Returns
/// 3D affine transformation matrix 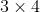 of the form
/// 
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * scale: nullptr
/// * force_rotation: true
#[inline]
pub fn estimate_affine_3d_1(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &impl ToInputArray, scale: &mut f64, force_rotation: bool) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(src);
input_array_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_estimateAffine3D_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_doubleX_bool(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__InputArray(), scale, force_rotation, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes an optimal limited affine transformation with 4 degrees of freedom between
/// two 2D point sets.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * from: First input 2D point set.
/// * to: Second input 2D point set.
/// * inliers: Output vector indicating which points are inliers.
/// * method: Robust method used to compute transformation. The following methods are possible:
/// * [RANSAC] - RANSAC-based robust method
/// * [LMEDS] - Least-Median robust method
/// RANSAC is the default method.
/// * ransacReprojThreshold: Maximum reprojection error in the RANSAC algorithm to consider
/// a point as an inlier. Applies only to RANSAC.
/// * maxIters: The maximum number of robust method iterations.
/// * confidence: Confidence level, between 0 and 1, for the estimated transformation. Anything
/// between 0.95 and 0.99 is usually good enough. Values too close to 1 can slow down the estimation
/// significantly. Values lower than 0.8-0.9 can result in an incorrectly estimated transformation.
/// * refineIters: Maximum number of iterations of refining algorithm (Levenberg-Marquardt).
/// Passing 0 will disable refining, so the output matrix will be output of robust method.
///
/// ## Returns
/// Output 2D affine transformation (4 degrees of freedom) matrix 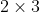 or
/// empty matrix if transformation could not be estimated.
///
/// The function estimates an optimal 2D affine transformation with 4 degrees of freedom limited to
/// combinations of translation, rotation, and uniform scaling. Uses the selected algorithm for robust
/// estimation.
///
/// The computed transformation is then refined further (using only inliers) with the
/// Levenberg-Marquardt method to reduce the re-projection error even more.
///
/// Estimated transformation matrix is:
/// 
/// Where 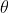 is the rotation angle,  the scaling factor and  are
/// translations in  axes respectively.
///
///
/// Note:
/// The RANSAC method can handle practically any ratio of outliers but need a threshold to
/// distinguish inliers from outliers. The method LMeDS does not need any threshold but it works
/// correctly only when there are more than 50% of inliers.
/// ## See also
/// estimateAffine2D, getAffineTransform
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [estimate_affine_partial_2d] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * inliers: noArray()
/// * method: RANSAC
/// * ransac_reproj_threshold: 3
/// * max_iters: 2000
/// * confidence: 0.99
/// * refine_iters: 10
#[inline]
pub fn estimate_affine_partial_2d_def(from: &impl ToInputArray, to: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(from);
input_array_arg!(to);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_estimateAffinePartial2D_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(from.as_raw__InputArray(), to.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes an optimal limited affine transformation with 4 degrees of freedom between
/// two 2D point sets.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * from: First input 2D point set.
/// * to: Second input 2D point set.
/// * inliers: Output vector indicating which points are inliers.
/// * method: Robust method used to compute transformation. The following methods are possible:
/// * [RANSAC] - RANSAC-based robust method
/// * [LMEDS] - Least-Median robust method
/// RANSAC is the default method.
/// * ransacReprojThreshold: Maximum reprojection error in the RANSAC algorithm to consider
/// a point as an inlier. Applies only to RANSAC.
/// * maxIters: The maximum number of robust method iterations.
/// * confidence: Confidence level, between 0 and 1, for the estimated transformation. Anything
/// between 0.95 and 0.99 is usually good enough. Values too close to 1 can slow down the estimation
/// significantly. Values lower than 0.8-0.9 can result in an incorrectly estimated transformation.
/// * refineIters: Maximum number of iterations of refining algorithm (Levenberg-Marquardt).
/// Passing 0 will disable refining, so the output matrix will be output of robust method.
///
/// ## Returns
/// Output 2D affine transformation (4 degrees of freedom) matrix 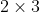 or
/// empty matrix if transformation could not be estimated.
///
/// The function estimates an optimal 2D affine transformation with 4 degrees of freedom limited to
/// combinations of translation, rotation, and uniform scaling. Uses the selected algorithm for robust
/// estimation.
///
/// The computed transformation is then refined further (using only inliers) with the
/// Levenberg-Marquardt method to reduce the re-projection error even more.
///
/// Estimated transformation matrix is:
/// 
/// Where 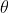 is the rotation angle,  the scaling factor and  are
/// translations in  axes respectively.
///
///
/// Note:
/// The RANSAC method can handle practically any ratio of outliers but need a threshold to
/// distinguish inliers from outliers. The method LMeDS does not need any threshold but it works
/// correctly only when there are more than 50% of inliers.
/// ## See also
/// estimateAffine2D, getAffineTransform
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * inliers: noArray()
/// * method: RANSAC
/// * ransac_reproj_threshold: 3
/// * max_iters: 2000
/// * confidence: 0.99
/// * refine_iters: 10
#[inline]
pub fn estimate_affine_partial_2d(from: &impl ToInputArray, to: &impl ToInputArray, inliers: &mut impl ToOutputArray, method: i32, ransac_reproj_threshold: f64, max_iters: size_t, confidence: f64, refine_iters: size_t) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(from);
input_array_arg!(to);
output_array_arg!(inliers);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_estimateAffinePartial2D_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_double_size_t_double_size_t(from.as_raw__InputArray(), to.as_raw__InputArray(), inliers.as_raw__OutputArray(), method, ransac_reproj_threshold, max_iters, confidence, refine_iters, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Estimates the sharpness of a detected chessboard.
///
/// Image sharpness, as well as brightness, are a critical parameter for accuracte
/// camera calibration. For accessing these parameters for filtering out
/// problematic calibraiton images, this method calculates edge profiles by traveling from
/// black to white chessboard cell centers. Based on this, the number of pixels is
/// calculated required to transit from black to white. This width of the
/// transition area is a good indication of how sharp the chessboard is imaged
/// and should be below ~3.0 pixels.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: Gray image used to find chessboard corners
/// * patternSize: Size of a found chessboard pattern
/// * corners: Corners found by [find_chessboard_corners_sb]
/// * rise_distance: Rise distance 0.8 means 10% ... 90% of the final signal strength
/// * vertical: By default edge responses for horizontal lines are calculated
/// * sharpness: Optional output array with a sharpness value for calculated edge responses (see description)
///
/// The optional sharpness array is of type CV_32FC1 and has for each calculated
/// profile one row with the following five entries:
/// * 0 = x coordinate of the underlying edge in the image
/// * 1 = y coordinate of the underlying edge in the image
/// * 2 = width of the transition area (sharpness)
/// * 3 = signal strength in the black cell (min brightness)
/// * 4 = signal strength in the white cell (max brightness)
///
/// ## Returns
/// Scalar(average sharpness, average min brightness, average max brightness,0)
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [estimate_chessboard_sharpness] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * rise_distance: 0.8F
/// * vertical: false
/// * sharpness: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn estimate_chessboard_sharpness_def(image: &impl ToInputArray, pattern_size: core::Size, corners: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<core::Scalar> {
input_array_arg!(image);
input_array_arg!(corners);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_estimateChessboardSharpness_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__InputArrayR(image.as_raw__InputArray(), &pattern_size, corners.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Estimates the sharpness of a detected chessboard.
///
/// Image sharpness, as well as brightness, are a critical parameter for accuracte
/// camera calibration. For accessing these parameters for filtering out
/// problematic calibraiton images, this method calculates edge profiles by traveling from
/// black to white chessboard cell centers. Based on this, the number of pixels is
/// calculated required to transit from black to white. This width of the
/// transition area is a good indication of how sharp the chessboard is imaged
/// and should be below ~3.0 pixels.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: Gray image used to find chessboard corners
/// * patternSize: Size of a found chessboard pattern
/// * corners: Corners found by [find_chessboard_corners_sb]
/// * rise_distance: Rise distance 0.8 means 10% ... 90% of the final signal strength
/// * vertical: By default edge responses for horizontal lines are calculated
/// * sharpness: Optional output array with a sharpness value for calculated edge responses (see description)
///
/// The optional sharpness array is of type CV_32FC1 and has for each calculated
/// profile one row with the following five entries:
/// * 0 = x coordinate of the underlying edge in the image
/// * 1 = y coordinate of the underlying edge in the image
/// * 2 = width of the transition area (sharpness)
/// * 3 = signal strength in the black cell (min brightness)
/// * 4 = signal strength in the white cell (max brightness)
///
/// ## Returns
/// Scalar(average sharpness, average min brightness, average max brightness,0)
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * rise_distance: 0.8F
/// * vertical: false
/// * sharpness: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn estimate_chessboard_sharpness(image: &impl ToInputArray, pattern_size: core::Size, corners: &impl ToInputArray, rise_distance: f32, vertical: bool, sharpness: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<core::Scalar> {
input_array_arg!(image);
input_array_arg!(corners);
output_array_arg!(sharpness);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_estimateChessboardSharpness_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__InputArrayR_float_bool_const__OutputArrayR(image.as_raw__InputArray(), &pattern_size, corners.as_raw__InputArray(), rise_distance, vertical, sharpness.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes an optimal translation between two 3D point sets.
///
/// It computes
/// 
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: First input 3D point set containing 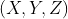.
/// * dst: Second input 3D point set containing 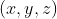.
/// * out: Output 3D translation vector 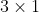 of the form
/// 
/// * inliers: Output vector indicating which points are inliers (1-inlier, 0-outlier).
/// * ransacThreshold: Maximum reprojection error in the RANSAC algorithm to consider a point as
/// an inlier.
/// * confidence: Confidence level, between 0 and 1, for the estimated transformation. Anything
/// between 0.95 and 0.99 is usually good enough. Values too close to 1 can slow down the estimation
/// significantly. Values lower than 0.8-0.9 can result in an incorrectly estimated transformation.
///
/// The function estimates an optimal 3D translation between two 3D point sets using the
/// RANSAC algorithm.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [estimate_translation_3d] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * ransac_threshold: 3
/// * confidence: 0.99
#[inline]
pub fn estimate_translation_3d_def(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &impl ToInputArray, out: &mut impl ToOutputArray, inliers: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<i32> {
input_array_arg!(src);
input_array_arg!(dst);
output_array_arg!(out);
output_array_arg!(inliers);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_estimateTranslation3D_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__InputArray(), out.as_raw__OutputArray(), inliers.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes an optimal translation between two 3D point sets.
///
/// It computes
/// 
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: First input 3D point set containing 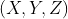.
/// * dst: Second input 3D point set containing 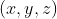.
/// * out: Output 3D translation vector 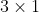 of the form
/// 
/// * inliers: Output vector indicating which points are inliers (1-inlier, 0-outlier).
/// * ransacThreshold: Maximum reprojection error in the RANSAC algorithm to consider a point as
/// an inlier.
/// * confidence: Confidence level, between 0 and 1, for the estimated transformation. Anything
/// between 0.95 and 0.99 is usually good enough. Values too close to 1 can slow down the estimation
/// significantly. Values lower than 0.8-0.9 can result in an incorrectly estimated transformation.
///
/// The function estimates an optimal 3D translation between two 3D point sets using the
/// RANSAC algorithm.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * ransac_threshold: 3
/// * confidence: 0.99
#[inline]
pub fn estimate_translation_3d(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &impl ToInputArray, out: &mut impl ToOutputArray, inliers: &mut impl ToOutputArray, ransac_threshold: f64, confidence: f64) -> Result<i32> {
input_array_arg!(src);
input_array_arg!(dst);
output_array_arg!(out);
output_array_arg!(inliers);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_estimateTranslation3D_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_double(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__InputArray(), out.as_raw__OutputArray(), inliers.as_raw__OutputArray(), ransac_threshold, confidence, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Filters homography decompositions based on additional information.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * rotations: Vector of rotation matrices.
/// * normals: Vector of plane normal matrices.
/// * beforePoints: Vector of (rectified) visible reference points before the homography is applied
/// * afterPoints: Vector of (rectified) visible reference points after the homography is applied
/// * possibleSolutions: Vector of int indices representing the viable solution set after filtering
/// * pointsMask: optional Mat/Vector of 8u type representing the mask for the inliers as given by the [find_homography] function
///
/// This function is intended to filter the output of the [decompose_homography_mat] based on additional
/// information as described in [Malis2007](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Malis2007) . The summary of the method: the [decompose_homography_mat] function
/// returns 2 unique solutions and their "opposites" for a total of 4 solutions. If we have access to the
/// sets of points visible in the camera frame before and after the homography transformation is applied,
/// we can determine which are the true potential solutions and which are the opposites by verifying which
/// homographies are consistent with all visible reference points being in front of the camera. The inputs
/// are left unchanged; the filtered solution set is returned as indices into the existing one.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [filter_homography_decomp_by_visible_refpoints] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * points_mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn filter_homography_decomp_by_visible_refpoints_def(rotations: &impl ToInputArray, normals: &impl ToInputArray, before_points: &impl ToInputArray, after_points: &impl ToInputArray, possible_solutions: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(rotations);
input_array_arg!(normals);
input_array_arg!(before_points);
input_array_arg!(after_points);
output_array_arg!(possible_solutions);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_filterHomographyDecompByVisibleRefpoints_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(rotations.as_raw__InputArray(), normals.as_raw__InputArray(), before_points.as_raw__InputArray(), after_points.as_raw__InputArray(), possible_solutions.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Filters homography decompositions based on additional information.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * rotations: Vector of rotation matrices.
/// * normals: Vector of plane normal matrices.
/// * beforePoints: Vector of (rectified) visible reference points before the homography is applied
/// * afterPoints: Vector of (rectified) visible reference points after the homography is applied
/// * possibleSolutions: Vector of int indices representing the viable solution set after filtering
/// * pointsMask: optional Mat/Vector of 8u type representing the mask for the inliers as given by the [find_homography] function
///
/// This function is intended to filter the output of the [decompose_homography_mat] based on additional
/// information as described in [Malis2007](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Malis2007) . The summary of the method: the [decompose_homography_mat] function
/// returns 2 unique solutions and their "opposites" for a total of 4 solutions. If we have access to the
/// sets of points visible in the camera frame before and after the homography transformation is applied,
/// we can determine which are the true potential solutions and which are the opposites by verifying which
/// homographies are consistent with all visible reference points being in front of the camera. The inputs
/// are left unchanged; the filtered solution set is returned as indices into the existing one.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * points_mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn filter_homography_decomp_by_visible_refpoints(rotations: &impl ToInputArray, normals: &impl ToInputArray, before_points: &impl ToInputArray, after_points: &impl ToInputArray, possible_solutions: &mut impl ToOutputArray, points_mask: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(rotations);
input_array_arg!(normals);
input_array_arg!(before_points);
input_array_arg!(after_points);
output_array_arg!(possible_solutions);
input_array_arg!(points_mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_filterHomographyDecompByVisibleRefpoints_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(rotations.as_raw__InputArray(), normals.as_raw__InputArray(), before_points.as_raw__InputArray(), after_points.as_raw__InputArray(), possible_solutions.as_raw__OutputArray(), points_mask.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Filters off small noise blobs (speckles) in the disparity map
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * img: The input 16-bit signed disparity image
/// * newVal: The disparity value used to paint-off the speckles
/// * maxSpeckleSize: The maximum speckle size to consider it a speckle. Larger blobs are not
/// affected by the algorithm
/// * maxDiff: Maximum difference between neighbor disparity pixels to put them into the same
/// blob. Note that since StereoBM, StereoSGBM and may be other algorithms return a fixed-point
/// disparity map, where disparity values are multiplied by 16, this scale factor should be taken into
/// account when specifying this parameter value.
/// * buf: The optional temporary buffer to avoid memory allocation within the function.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [filter_speckles] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * buf: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn filter_speckles_def(img: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, new_val: f64, max_speckle_size: i32, max_diff: f64) -> Result<()> {
input_output_array_arg!(img);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_filterSpeckles_const__InputOutputArrayR_double_int_double(img.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), new_val, max_speckle_size, max_diff, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Filters off small noise blobs (speckles) in the disparity map
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * img: The input 16-bit signed disparity image
/// * newVal: The disparity value used to paint-off the speckles
/// * maxSpeckleSize: The maximum speckle size to consider it a speckle. Larger blobs are not
/// affected by the algorithm
/// * maxDiff: Maximum difference between neighbor disparity pixels to put them into the same
/// blob. Note that since StereoBM, StereoSGBM and may be other algorithms return a fixed-point
/// disparity map, where disparity values are multiplied by 16, this scale factor should be taken into
/// account when specifying this parameter value.
/// * buf: The optional temporary buffer to avoid memory allocation within the function.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * buf: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn filter_speckles(img: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, new_val: f64, max_speckle_size: i32, max_diff: f64, buf: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_output_array_arg!(img);
input_output_array_arg!(buf);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_filterSpeckles_const__InputOutputArrayR_double_int_double_const__InputOutputArrayR(img.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), new_val, max_speckle_size, max_diff, buf.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// finds subpixel-accurate positions of the chessboard corners
#[inline]
pub fn find4_quad_corner_subpix(img: &impl ToInputArray, corners: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, region_size: core::Size) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(img);
input_output_array_arg!(corners);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_find4QuadCornerSubpix_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_Size(img.as_raw__InputArray(), corners.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), ®ion_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// @overload
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [find_chessboard_corners_sb] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * flags: 0
#[inline]
pub fn find_chessboard_corners_sb_def(image: &impl ToInputArray, pattern_size: core::Size, corners: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(image);
output_array_arg!(corners);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findChessboardCornersSB_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__OutputArrayR(image.as_raw__InputArray(), &pattern_size, corners.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds the positions of internal corners of the chessboard using a sector based approach.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: Source chessboard view. It must be an 8-bit grayscale or color image.
/// * patternSize: Number of inner corners per a chessboard row and column
/// ( patternSize = cv::Size(points_per_row,points_per_colum) = cv::Size(columns,rows) ).
/// * corners: Output array of detected corners.
/// * flags: Various operation flags that can be zero or a combination of the following values:
/// * [CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE] Normalize the image gamma with equalizeHist before detection.
/// * [CALIB_CB_EXHAUSTIVE] Run an exhaustive search to improve detection rate.
/// * [CALIB_CB_ACCURACY] Up sample input image to improve sub-pixel accuracy due to aliasing effects.
/// * [CALIB_CB_LARGER] The detected pattern is allowed to be larger than patternSize (see description).
/// * [CALIB_CB_MARKER] The detected pattern must have a marker (see description).
/// This should be used if an accurate camera calibration is required.
/// * meta: Optional output arrray of detected corners (CV_8UC1 and size = cv::Size(columns,rows)).
/// Each entry stands for one corner of the pattern and can have one of the following values:
/// * 0 = no meta data attached
/// * 1 = left-top corner of a black cell
/// * 2 = left-top corner of a white cell
/// * 3 = left-top corner of a black cell with a white marker dot
/// * 4 = left-top corner of a white cell with a black marker dot (pattern origin in case of markers otherwise first corner)
///
/// The function is analog to [find_chessboard_corners] but uses a localized radon
/// transformation approximated by box filters being more robust to all sort of
/// noise, faster on larger images and is able to directly return the sub-pixel
/// position of the internal chessboard corners. The Method is based on the paper
/// [duda2018](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_duda2018) "Accurate Detection and Localization of Checkerboard Corners for
/// Calibration" demonstrating that the returned sub-pixel positions are more
/// accurate than the one returned by cornerSubPix allowing a precise camera
/// calibration for demanding applications.
///
/// In the case, the flags [CALIB_CB_LARGER] or [CALIB_CB_MARKER] are given,
/// the result can be recovered from the optional meta array. Both flags are
/// helpful to use calibration patterns exceeding the field of view of the camera.
/// These oversized patterns allow more accurate calibrations as corners can be
/// utilized, which are as close as possible to the image borders. For a
/// consistent coordinate system across all images, the optional marker (see image
/// below) can be used to move the origin of the board to the location where the
/// black circle is located.
///
///
/// Note: The function requires a white boarder with roughly the same width as one
/// of the checkerboard fields around the whole board to improve the detection in
/// various environments. In addition, because of the localized radon
/// transformation it is beneficial to use round corners for the field corners
/// which are located on the outside of the board. The following figure illustrates
/// a sample checkerboard optimized for the detection. However, any other checkerboard
/// can be used as well.
///
/// Use gen_pattern.py ([tutorial_camera_calibration_pattern]) to create checkerboard.
/// 
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: 0
#[inline]
pub fn find_chessboard_corners_sb(image: &impl ToInputArray, pattern_size: core::Size, corners: &mut impl ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(image);
output_array_arg!(corners);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findChessboardCornersSB_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__OutputArrayR_int(image.as_raw__InputArray(), &pattern_size, corners.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds the positions of internal corners of the chessboard using a sector based approach.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: Source chessboard view. It must be an 8-bit grayscale or color image.
/// * patternSize: Number of inner corners per a chessboard row and column
/// ( patternSize = cv::Size(points_per_row,points_per_colum) = cv::Size(columns,rows) ).
/// * corners: Output array of detected corners.
/// * flags: Various operation flags that can be zero or a combination of the following values:
/// * [CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE] Normalize the image gamma with equalizeHist before detection.
/// * [CALIB_CB_EXHAUSTIVE] Run an exhaustive search to improve detection rate.
/// * [CALIB_CB_ACCURACY] Up sample input image to improve sub-pixel accuracy due to aliasing effects.
/// * [CALIB_CB_LARGER] The detected pattern is allowed to be larger than patternSize (see description).
/// * [CALIB_CB_MARKER] The detected pattern must have a marker (see description).
/// This should be used if an accurate camera calibration is required.
/// * meta: Optional output arrray of detected corners (CV_8UC1 and size = cv::Size(columns,rows)).
/// Each entry stands for one corner of the pattern and can have one of the following values:
/// * 0 = no meta data attached
/// * 1 = left-top corner of a black cell
/// * 2 = left-top corner of a white cell
/// * 3 = left-top corner of a black cell with a white marker dot
/// * 4 = left-top corner of a white cell with a black marker dot (pattern origin in case of markers otherwise first corner)
///
/// The function is analog to [find_chessboard_corners] but uses a localized radon
/// transformation approximated by box filters being more robust to all sort of
/// noise, faster on larger images and is able to directly return the sub-pixel
/// position of the internal chessboard corners. The Method is based on the paper
/// [duda2018](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_duda2018) "Accurate Detection and Localization of Checkerboard Corners for
/// Calibration" demonstrating that the returned sub-pixel positions are more
/// accurate than the one returned by cornerSubPix allowing a precise camera
/// calibration for demanding applications.
///
/// In the case, the flags [CALIB_CB_LARGER] or [CALIB_CB_MARKER] are given,
/// the result can be recovered from the optional meta array. Both flags are
/// helpful to use calibration patterns exceeding the field of view of the camera.
/// These oversized patterns allow more accurate calibrations as corners can be
/// utilized, which are as close as possible to the image borders. For a
/// consistent coordinate system across all images, the optional marker (see image
/// below) can be used to move the origin of the board to the location where the
/// black circle is located.
///
///
/// Note: The function requires a white boarder with roughly the same width as one
/// of the checkerboard fields around the whole board to improve the detection in
/// various environments. In addition, because of the localized radon
/// transformation it is beneficial to use round corners for the field corners
/// which are located on the outside of the board. The following figure illustrates
/// a sample checkerboard optimized for the detection. However, any other checkerboard
/// can be used as well.
///
/// Use gen_pattern.py ([tutorial_camera_calibration_pattern]) to create checkerboard.
/// 
#[inline]
pub fn find_chessboard_corners_sb_with_meta(image: &impl ToInputArray, pattern_size: core::Size, corners: &mut impl ToOutputArray, flags: i32, meta: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(image);
output_array_arg!(corners);
output_array_arg!(meta);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findChessboardCornersSB_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__OutputArrayR_int_const__OutputArrayR(image.as_raw__InputArray(), &pattern_size, corners.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, meta.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds the positions of internal corners of the chessboard.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: Source chessboard view. It must be an 8-bit grayscale or color image.
/// * patternSize: Number of inner corners per a chessboard row and column
/// ( patternSize = cv::Size(points_per_row,points_per_colum) = cv::Size(columns,rows) ).
/// * corners: Output array of detected corners.
/// * flags: Various operation flags that can be zero or a combination of the following values:
/// * [CALIB_CB_ADAPTIVE_THRESH] Use adaptive thresholding to convert the image to black
/// and white, rather than a fixed threshold level (computed from the average image brightness).
/// * [CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE] Normalize the image gamma with [equalize_hist] before
/// applying fixed or adaptive thresholding.
/// * [CALIB_CB_FILTER_QUADS] Use additional criteria (like contour area, perimeter,
/// square-like shape) to filter out false quads extracted at the contour retrieval stage.
/// * [CALIB_CB_FAST_CHECK] Run a fast check on the image that looks for chessboard corners,
/// and shortcut the call if none is found. This can drastically speed up the call in the
/// degenerate condition when no chessboard is observed.
/// * [CALIB_CB_PLAIN] All other flags are ignored. The input image is taken as is.
/// No image processing is done to improve to find the checkerboard. This has the effect of speeding up the
/// execution of the function but could lead to not recognizing the checkerboard if the image
/// is not previously binarized in the appropriate manner.
///
/// The function attempts to determine whether the input image is a view of the chessboard pattern and
/// locate the internal chessboard corners. The function returns a non-zero value if all of the corners
/// are found and they are placed in a certain order (row by row, left to right in every row).
/// Otherwise, if the function fails to find all the corners or reorder them, it returns 0. For example,
/// a regular chessboard has 8 x 8 squares and 7 x 7 internal corners, that is, points where the black
/// squares touch each other. The detected coordinates are approximate, and to determine their positions
/// more accurately, the function calls #cornerSubPix. You also may use the function [corner_sub_pix] with
/// different parameters if returned coordinates are not accurate enough.
///
/// Sample usage of detecting and drawing chessboard corners: :
/// ```C++
/// Size patternsize(8,6); //interior number of corners
/// Mat gray = ....; //source image
/// vector<Point2f> corners; //this will be filled by the detected corners
///
/// //CALIB_CB_FAST_CHECK saves a lot of time on images
/// //that do not contain any chessboard corners
/// bool patternfound = findChessboardCorners(gray, patternsize, corners,
/// CALIB_CB_ADAPTIVE_THRESH + CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE
/// + CALIB_CB_FAST_CHECK);
///
/// if(patternfound)
/// cornerSubPix(gray, corners, Size(11, 11), Size(-1, -1),
/// TermCriteria(CV_TERMCRIT_EPS + CV_TERMCRIT_ITER, 30, 0.1));
///
/// drawChessboardCorners(img, patternsize, Mat(corners), patternfound);
/// ```
///
///
/// Note: The function requires white space (like a square-thick border, the wider the better) around
/// the board to make the detection more robust in various environments. Otherwise, if there is no
/// border and the background is dark, the outer black squares cannot be segmented properly and so the
/// square grouping and ordering algorithm fails.
///
/// Use gen_pattern.py ([tutorial_camera_calibration_pattern]) to create checkerboard.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [find_chessboard_corners] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * flags: CALIB_CB_ADAPTIVE_THRESH+CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE
#[inline]
pub fn find_chessboard_corners_def(image: &impl ToInputArray, pattern_size: core::Size, corners: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(image);
output_array_arg!(corners);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findChessboardCorners_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__OutputArrayR(image.as_raw__InputArray(), &pattern_size, corners.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds the positions of internal corners of the chessboard.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: Source chessboard view. It must be an 8-bit grayscale or color image.
/// * patternSize: Number of inner corners per a chessboard row and column
/// ( patternSize = cv::Size(points_per_row,points_per_colum) = cv::Size(columns,rows) ).
/// * corners: Output array of detected corners.
/// * flags: Various operation flags that can be zero or a combination of the following values:
/// * [CALIB_CB_ADAPTIVE_THRESH] Use adaptive thresholding to convert the image to black
/// and white, rather than a fixed threshold level (computed from the average image brightness).
/// * [CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE] Normalize the image gamma with [equalize_hist] before
/// applying fixed or adaptive thresholding.
/// * [CALIB_CB_FILTER_QUADS] Use additional criteria (like contour area, perimeter,
/// square-like shape) to filter out false quads extracted at the contour retrieval stage.
/// * [CALIB_CB_FAST_CHECK] Run a fast check on the image that looks for chessboard corners,
/// and shortcut the call if none is found. This can drastically speed up the call in the
/// degenerate condition when no chessboard is observed.
/// * [CALIB_CB_PLAIN] All other flags are ignored. The input image is taken as is.
/// No image processing is done to improve to find the checkerboard. This has the effect of speeding up the
/// execution of the function but could lead to not recognizing the checkerboard if the image
/// is not previously binarized in the appropriate manner.
///
/// The function attempts to determine whether the input image is a view of the chessboard pattern and
/// locate the internal chessboard corners. The function returns a non-zero value if all of the corners
/// are found and they are placed in a certain order (row by row, left to right in every row).
/// Otherwise, if the function fails to find all the corners or reorder them, it returns 0. For example,
/// a regular chessboard has 8 x 8 squares and 7 x 7 internal corners, that is, points where the black
/// squares touch each other. The detected coordinates are approximate, and to determine their positions
/// more accurately, the function calls #cornerSubPix. You also may use the function [corner_sub_pix] with
/// different parameters if returned coordinates are not accurate enough.
///
/// Sample usage of detecting and drawing chessboard corners: :
/// ```C++
/// Size patternsize(8,6); //interior number of corners
/// Mat gray = ....; //source image
/// vector<Point2f> corners; //this will be filled by the detected corners
///
/// //CALIB_CB_FAST_CHECK saves a lot of time on images
/// //that do not contain any chessboard corners
/// bool patternfound = findChessboardCorners(gray, patternsize, corners,
/// CALIB_CB_ADAPTIVE_THRESH + CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE
/// + CALIB_CB_FAST_CHECK);
///
/// if(patternfound)
/// cornerSubPix(gray, corners, Size(11, 11), Size(-1, -1),
/// TermCriteria(CV_TERMCRIT_EPS + CV_TERMCRIT_ITER, 30, 0.1));
///
/// drawChessboardCorners(img, patternsize, Mat(corners), patternfound);
/// ```
///
///
/// Note: The function requires white space (like a square-thick border, the wider the better) around
/// the board to make the detection more robust in various environments. Otherwise, if there is no
/// border and the background is dark, the outer black squares cannot be segmented properly and so the
/// square grouping and ordering algorithm fails.
///
/// Use gen_pattern.py ([tutorial_camera_calibration_pattern]) to create checkerboard.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: CALIB_CB_ADAPTIVE_THRESH+CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE
#[inline]
pub fn find_chessboard_corners(image: &impl ToInputArray, pattern_size: core::Size, corners: &mut impl ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(image);
output_array_arg!(corners);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findChessboardCorners_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__OutputArrayR_int(image.as_raw__InputArray(), &pattern_size, corners.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// @overload
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [find_circles_grid_1] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * flags: CALIB_CB_SYMMETRIC_GRID
/// * blob_detector: SimpleBlobDetector::create()
#[inline]
pub fn find_circles_grid_1_def(image: &impl ToInputArray, pattern_size: core::Size, centers: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(image);
output_array_arg!(centers);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findCirclesGrid_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__OutputArrayR(image.as_raw__InputArray(), &pattern_size, centers.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds centers in the grid of circles.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: grid view of input circles; it must be an 8-bit grayscale or color image.
/// * patternSize: number of circles per row and column
/// ( patternSize = Size(points_per_row, points_per_colum) ).
/// * centers: output array of detected centers.
/// * flags: various operation flags that can be one of the following values:
/// * [CALIB_CB_SYMMETRIC_GRID] uses symmetric pattern of circles.
/// * [CALIB_CB_ASYMMETRIC_GRID] uses asymmetric pattern of circles.
/// * [CALIB_CB_CLUSTERING] uses a special algorithm for grid detection. It is more robust to
/// perspective distortions but much more sensitive to background clutter.
/// * blobDetector: feature detector that finds blobs like dark circles on light background.
/// If `blobDetector` is NULL then `image` represents Point2f array of candidates.
/// * parameters: struct for finding circles in a grid pattern.
///
/// The function attempts to determine whether the input image contains a grid of circles. If it is, the
/// function locates centers of the circles. The function returns a non-zero value if all of the centers
/// have been found and they have been placed in a certain order (row by row, left to right in every
/// row). Otherwise, if the function fails to find all the corners or reorder them, it returns 0.
///
/// Sample usage of detecting and drawing the centers of circles: :
/// ```C++
/// Size patternsize(7,7); //number of centers
/// Mat gray = ...; //source image
/// vector<Point2f> centers; //this will be filled by the detected centers
///
/// bool patternfound = findCirclesGrid(gray, patternsize, centers);
///
/// drawChessboardCorners(img, patternsize, Mat(centers), patternfound);
/// ```
///
///
/// Note: The function requires white space (like a square-thick border, the wider the better) around
/// the board to make the detection more robust in various environments.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: CALIB_CB_SYMMETRIC_GRID
/// * blob_detector: SimpleBlobDetector::create()
#[inline]
pub fn find_circles_grid_1(image: &impl ToInputArray, pattern_size: core::Size, centers: &mut impl ToOutputArray, flags: i32, blob_detector: Option<&core::Ptr<crate::features2d::Feature2D>>) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(image);
output_array_arg!(centers);
smart_ptr_option_arg!(ref blob_detector);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findCirclesGrid_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__OutputArrayR_int_const_PtrLFeature2DGR(image.as_raw__InputArray(), &pattern_size, centers.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, blob_detector.as_raw_PtrOfFeature2D(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds centers in the grid of circles.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: grid view of input circles; it must be an 8-bit grayscale or color image.
/// * patternSize: number of circles per row and column
/// ( patternSize = Size(points_per_row, points_per_colum) ).
/// * centers: output array of detected centers.
/// * flags: various operation flags that can be one of the following values:
/// * [CALIB_CB_SYMMETRIC_GRID] uses symmetric pattern of circles.
/// * [CALIB_CB_ASYMMETRIC_GRID] uses asymmetric pattern of circles.
/// * [CALIB_CB_CLUSTERING] uses a special algorithm for grid detection. It is more robust to
/// perspective distortions but much more sensitive to background clutter.
/// * blobDetector: feature detector that finds blobs like dark circles on light background.
/// If `blobDetector` is NULL then `image` represents Point2f array of candidates.
/// * parameters: struct for finding circles in a grid pattern.
///
/// The function attempts to determine whether the input image contains a grid of circles. If it is, the
/// function locates centers of the circles. The function returns a non-zero value if all of the centers
/// have been found and they have been placed in a certain order (row by row, left to right in every
/// row). Otherwise, if the function fails to find all the corners or reorder them, it returns 0.
///
/// Sample usage of detecting and drawing the centers of circles: :
/// ```C++
/// Size patternsize(7,7); //number of centers
/// Mat gray = ...; //source image
/// vector<Point2f> centers; //this will be filled by the detected centers
///
/// bool patternfound = findCirclesGrid(gray, patternsize, centers);
///
/// drawChessboardCorners(img, patternsize, Mat(centers), patternfound);
/// ```
///
///
/// Note: The function requires white space (like a square-thick border, the wider the better) around
/// the board to make the detection more robust in various environments.
#[inline]
pub fn find_circles_grid(image: &impl ToInputArray, pattern_size: core::Size, centers: &mut impl ToOutputArray, flags: i32, blob_detector: Option<&core::Ptr<crate::features2d::Feature2D>>, parameters: crate::calib3d::CirclesGridFinderParameters) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(image);
output_array_arg!(centers);
smart_ptr_option_arg!(ref blob_detector);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findCirclesGrid_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__OutputArrayR_int_const_PtrLFeature2DGR_const_CirclesGridFinderParametersR(image.as_raw__InputArray(), &pattern_size, centers.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, blob_detector.as_raw_PtrOfFeature2D(), ¶meters, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// @overload
/// ## Parameters
/// * points1: Array of N (N \>= 5) 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should
/// be floating-point (single or double precision).
/// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1 .
/// * focal: focal length of the camera. Note that this function assumes that points1 and points2
/// are feature points from cameras with same focal length and principal point.
/// * pp: principal point of the camera.
/// * method: Method for computing a fundamental matrix.
/// * [RANSAC] for the RANSAC algorithm.
/// * [LMEDS] for the LMedS algorithm.
/// * threshold: Parameter used for RANSAC. It is the maximum distance from a point to an epipolar
/// line in pixels, beyond which the point is considered an outlier and is not used for computing the
/// final fundamental matrix. It can be set to something like 1-3, depending on the accuracy of the
/// point localization, image resolution, and the image noise.
/// * prob: Parameter used for the RANSAC or LMedS methods only. It specifies a desirable level of
/// confidence (probability) that the estimated matrix is correct.
/// * mask: Output array of N elements, every element of which is set to 0 for outliers and to 1
/// for the other points. The array is computed only in the RANSAC and LMedS methods.
/// * maxIters: The maximum number of robust method iterations.
///
/// This function differs from the one above that it computes camera intrinsic matrix from focal length and
/// principal point:
///
/// 
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [find_essential_mat_1] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * focal: 1.0
/// * pp: Point2d(0,0)
/// * method: RANSAC
/// * prob: 0.999
/// * threshold: 1.0
/// * max_iters: 1000
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn find_essential_mat_1_def(points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findEssentialMat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates an essential matrix from the corresponding points in two images.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * points1: Array of N (N \>= 5) 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should
/// be floating-point (single or double precision).
/// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1.
/// * cameraMatrix: Camera intrinsic matrix  .
/// Note that this function assumes that points1 and points2 are feature points from cameras with the
/// same camera intrinsic matrix. If this assumption does not hold for your use case, use another
/// function overload or [undistort_points] with `P = cv::NoArray()` for both cameras to transform image
/// points to normalized image coordinates, which are valid for the identity camera intrinsic matrix.
/// When passing these coordinates, pass the identity matrix for this parameter.
/// * method: Method for computing an essential matrix.
/// * [RANSAC] for the RANSAC algorithm.
/// * [LMEDS] for the LMedS algorithm.
/// * prob: Parameter used for the RANSAC or LMedS methods only. It specifies a desirable level of
/// confidence (probability) that the estimated matrix is correct.
/// * threshold: Parameter used for RANSAC. It is the maximum distance from a point to an epipolar
/// line in pixels, beyond which the point is considered an outlier and is not used for computing the
/// final fundamental matrix. It can be set to something like 1-3, depending on the accuracy of the
/// point localization, image resolution, and the image noise.
/// * mask: Output array of N elements, every element of which is set to 0 for outliers and to 1
/// for the other points. The array is computed only in the RANSAC and LMedS methods.
/// * maxIters: The maximum number of robust method iterations.
///
/// This function estimates essential matrix based on the five-point algorithm solver in [Nister03](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Nister03) .
/// [SteweniusCFS](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_SteweniusCFS) is also a related. The epipolar geometry is described by the following equation:
///
/// 
///
/// where 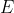 is an essential matrix,  and  are corresponding points in the first and the
/// second images, respectively. The result of this function may be passed further to
/// [decompose_essential_mat] or [recover_pose] to recover the relative pose between cameras.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [find_essential_mat] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * method: RANSAC
/// * prob: 0.999
/// * threshold: 1.0
/// * max_iters: 1000
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn find_essential_mat_def(points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findEssentialMat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates an essential matrix from the corresponding points in two images from potentially two different cameras.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * points1: Array of N (N \>= 5) 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should
/// be floating-point (single or double precision).
/// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1.
/// * cameraMatrix1: Camera matrix for the first camera 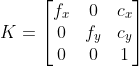 .
/// * cameraMatrix2: Camera matrix for the second camera 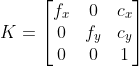 .
/// * distCoeffs1: Input vector of distortion coefficients for the first camera
/// 
/// of 4, 5, 8, 12 or 14 elements. If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed.
/// * distCoeffs2: Input vector of distortion coefficients for the second camera
/// 
/// of 4, 5, 8, 12 or 14 elements. If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed.
/// * method: Method for computing an essential matrix.
/// * [RANSAC] for the RANSAC algorithm.
/// * [LMEDS] for the LMedS algorithm.
/// * prob: Parameter used for the RANSAC or LMedS methods only. It specifies a desirable level of
/// confidence (probability) that the estimated matrix is correct.
/// * threshold: Parameter used for RANSAC. It is the maximum distance from a point to an epipolar
/// line in pixels, beyond which the point is considered an outlier and is not used for computing the
/// final fundamental matrix. It can be set to something like 1-3, depending on the accuracy of the
/// point localization, image resolution, and the image noise.
/// * mask: Output array of N elements, every element of which is set to 0 for outliers and to 1
/// for the other points. The array is computed only in the RANSAC and LMedS methods.
///
/// This function estimates essential matrix based on the five-point algorithm solver in [Nister03](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Nister03) .
/// [SteweniusCFS](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_SteweniusCFS) is also a related. The epipolar geometry is described by the following equation:
///
/// 
///
/// where 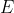 is an essential matrix,  and  are corresponding points in the first and the
/// second images, respectively. The result of this function may be passed further to
/// [decompose_essential_mat] or [recover_pose] to recover the relative pose between cameras.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [find_essential_mat_3] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * method: RANSAC
/// * prob: 0.999
/// * threshold: 1.0
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn find_essential_mat_3_def(points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix1: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs1: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix2: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs2: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix1);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs1);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix2);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs2);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findEssentialMat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix1.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs1.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix2.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs2.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn find_essential_mat_4(points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix1: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix2: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeff1: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeff2: &impl ToInputArray, mask: &mut impl ToOutputArray, params: crate::calib3d::UsacParams) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix1);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix2);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeff1);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeff2);
output_array_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findEssentialMat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const_UsacParamsR(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix1.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix2.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeff1.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeff2.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__OutputArray(), ¶ms, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates an essential matrix from the corresponding points in two images from potentially two different cameras.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * points1: Array of N (N \>= 5) 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should
/// be floating-point (single or double precision).
/// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1.
/// * cameraMatrix1: Camera matrix for the first camera 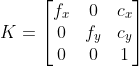 .
/// * cameraMatrix2: Camera matrix for the second camera 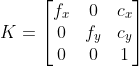 .
/// * distCoeffs1: Input vector of distortion coefficients for the first camera
/// 
/// of 4, 5, 8, 12 or 14 elements. If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed.
/// * distCoeffs2: Input vector of distortion coefficients for the second camera
/// 
/// of 4, 5, 8, 12 or 14 elements. If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed.
/// * method: Method for computing an essential matrix.
/// * [RANSAC] for the RANSAC algorithm.
/// * [LMEDS] for the LMedS algorithm.
/// * prob: Parameter used for the RANSAC or LMedS methods only. It specifies a desirable level of
/// confidence (probability) that the estimated matrix is correct.
/// * threshold: Parameter used for RANSAC. It is the maximum distance from a point to an epipolar
/// line in pixels, beyond which the point is considered an outlier and is not used for computing the
/// final fundamental matrix. It can be set to something like 1-3, depending on the accuracy of the
/// point localization, image resolution, and the image noise.
/// * mask: Output array of N elements, every element of which is set to 0 for outliers and to 1
/// for the other points. The array is computed only in the RANSAC and LMedS methods.
///
/// This function estimates essential matrix based on the five-point algorithm solver in [Nister03](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Nister03) .
/// [SteweniusCFS](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_SteweniusCFS) is also a related. The epipolar geometry is described by the following equation:
///
/// 
///
/// where  is an essential matrix,  and  are corresponding points in the first and the
/// second images, respectively. The result of this function may be passed further to
/// [decompose_essential_mat] or [recover_pose] to recover the relative pose between cameras.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * method: RANSAC
/// * prob: 0.999
/// * threshold: 1.0
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn find_essential_mat_3(points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix1: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs1: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix2: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs2: &impl ToInputArray, method: i32, prob: f64, threshold: f64, mask: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix1);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs1);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix2);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs2);
output_array_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findEssentialMat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int_double_double_const__OutputArrayR(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix1.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs1.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix2.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs2.as_raw__InputArray(), method, prob, threshold, mask.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates an essential matrix from the corresponding points in two images.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * points1: Array of N (N \>= 5) 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should
/// be floating-point (single or double precision).
/// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1.
/// * cameraMatrix: Camera intrinsic matrix  .
/// Note that this function assumes that points1 and points2 are feature points from cameras with the
/// same camera intrinsic matrix. If this assumption does not hold for your use case, use another
/// function overload or [undistort_points] with `P = cv::NoArray()` for both cameras to transform image
/// points to normalized image coordinates, which are valid for the identity camera intrinsic matrix.
/// When passing these coordinates, pass the identity matrix for this parameter.
/// * method: Method for computing an essential matrix.
/// * [RANSAC] for the RANSAC algorithm.
/// * [LMEDS] for the LMedS algorithm.
/// * prob: Parameter used for the RANSAC or LMedS methods only. It specifies a desirable level of
/// confidence (probability) that the estimated matrix is correct.
/// * threshold: Parameter used for RANSAC. It is the maximum distance from a point to an epipolar
/// line in pixels, beyond which the point is considered an outlier and is not used for computing the
/// final fundamental matrix. It can be set to something like 1-3, depending on the accuracy of the
/// point localization, image resolution, and the image noise.
/// * mask: Output array of N elements, every element of which is set to 0 for outliers and to 1
/// for the other points. The array is computed only in the RANSAC and LMedS methods.
/// * maxIters: The maximum number of robust method iterations.
///
/// This function estimates essential matrix based on the five-point algorithm solver in [Nister03](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Nister03) .
/// [SteweniusCFS](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_SteweniusCFS) is also a related. The epipolar geometry is described by the following equation:
///
/// 
///
/// where  is an essential matrix,  and  are corresponding points in the first and the
/// second images, respectively. The result of this function may be passed further to
/// [decompose_essential_mat] or [recover_pose] to recover the relative pose between cameras.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
#[inline]
pub fn find_essential_mat_matrix(points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, method: i32, prob: f64, threshold: f64, mask: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
output_array_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findEssentialMat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int_double_double_const__OutputArrayR(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), method, prob, threshold, mask.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates an essential matrix from the corresponding points in two images.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * points1: Array of N (N \>= 5) 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should
/// be floating-point (single or double precision).
/// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1.
/// * cameraMatrix: Camera intrinsic matrix  .
/// Note that this function assumes that points1 and points2 are feature points from cameras with the
/// same camera intrinsic matrix. If this assumption does not hold for your use case, use another
/// function overload or [undistort_points] with `P = cv::NoArray()` for both cameras to transform image
/// points to normalized image coordinates, which are valid for the identity camera intrinsic matrix.
/// When passing these coordinates, pass the identity matrix for this parameter.
/// * method: Method for computing an essential matrix.
/// * [RANSAC] for the RANSAC algorithm.
/// * [LMEDS] for the LMedS algorithm.
/// * prob: Parameter used for the RANSAC or LMedS methods only. It specifies a desirable level of
/// confidence (probability) that the estimated matrix is correct.
/// * threshold: Parameter used for RANSAC. It is the maximum distance from a point to an epipolar
/// line in pixels, beyond which the point is considered an outlier and is not used for computing the
/// final fundamental matrix. It can be set to something like 1-3, depending on the accuracy of the
/// point localization, image resolution, and the image noise.
/// * mask: Output array of N elements, every element of which is set to 0 for outliers and to 1
/// for the other points. The array is computed only in the RANSAC and LMedS methods.
/// * maxIters: The maximum number of robust method iterations.
///
/// This function estimates essential matrix based on the five-point algorithm solver in [Nister03](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Nister03) .
/// [SteweniusCFS](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_SteweniusCFS) is also a related. The epipolar geometry is described by the following equation:
///
/// 
///
/// where 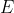 is an essential matrix,  and  are corresponding points in the first and the
/// second images, respectively. The result of this function may be passed further to
/// [decompose_essential_mat] or [recover_pose] to recover the relative pose between cameras.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * method: RANSAC
/// * prob: 0.999
/// * threshold: 1.0
/// * max_iters: 1000
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn find_essential_mat(points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, method: i32, prob: f64, threshold: f64, max_iters: i32, mask: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
output_array_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findEssentialMat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int_double_double_int_const__OutputArrayR(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), method, prob, threshold, max_iters, mask.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates an essential matrix from the corresponding points in two images.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * points1: Array of N (N \>= 5) 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should
/// be floating-point (single or double precision).
/// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1.
/// * cameraMatrix: Camera intrinsic matrix  .
/// Note that this function assumes that points1 and points2 are feature points from cameras with the
/// same camera intrinsic matrix. If this assumption does not hold for your use case, use another
/// function overload or [undistort_points] with `P = cv::NoArray()` for both cameras to transform image
/// points to normalized image coordinates, which are valid for the identity camera intrinsic matrix.
/// When passing these coordinates, pass the identity matrix for this parameter.
/// * method: Method for computing an essential matrix.
/// * [RANSAC] for the RANSAC algorithm.
/// * [LMEDS] for the LMedS algorithm.
/// * prob: Parameter used for the RANSAC or LMedS methods only. It specifies a desirable level of
/// confidence (probability) that the estimated matrix is correct.
/// * threshold: Parameter used for RANSAC. It is the maximum distance from a point to an epipolar
/// line in pixels, beyond which the point is considered an outlier and is not used for computing the
/// final fundamental matrix. It can be set to something like 1-3, depending on the accuracy of the
/// point localization, image resolution, and the image noise.
/// * mask: Output array of N elements, every element of which is set to 0 for outliers and to 1
/// for the other points. The array is computed only in the RANSAC and LMedS methods.
/// * maxIters: The maximum number of robust method iterations.
///
/// This function estimates essential matrix based on the five-point algorithm solver in [Nister03](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Nister03) .
/// [SteweniusCFS](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_SteweniusCFS) is also a related. The epipolar geometry is described by the following equation:
///
/// 
///
/// where 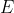 is an essential matrix,  and  are corresponding points in the first and the
/// second images, respectively. The result of this function may be passed further to
/// [decompose_essential_mat] or [recover_pose] to recover the relative pose between cameras.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
#[inline]
pub fn find_essential_mat_2(points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray, focal: f64, pp: core::Point2d, method: i32, prob: f64, threshold: f64, mask: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
output_array_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findEssentialMat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_double_Point2d_int_double_double_const__OutputArrayR(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), focal, &pp, method, prob, threshold, mask.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates an essential matrix from the corresponding points in two images.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * points1: Array of N (N \>= 5) 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should
/// be floating-point (single or double precision).
/// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1.
/// * cameraMatrix: Camera intrinsic matrix  .
/// Note that this function assumes that points1 and points2 are feature points from cameras with the
/// same camera intrinsic matrix. If this assumption does not hold for your use case, use another
/// function overload or [undistort_points] with `P = cv::NoArray()` for both cameras to transform image
/// points to normalized image coordinates, which are valid for the identity camera intrinsic matrix.
/// When passing these coordinates, pass the identity matrix for this parameter.
/// * method: Method for computing an essential matrix.
/// * [RANSAC] for the RANSAC algorithm.
/// * [LMEDS] for the LMedS algorithm.
/// * prob: Parameter used for the RANSAC or LMedS methods only. It specifies a desirable level of
/// confidence (probability) that the estimated matrix is correct.
/// * threshold: Parameter used for RANSAC. It is the maximum distance from a point to an epipolar
/// line in pixels, beyond which the point is considered an outlier and is not used for computing the
/// final fundamental matrix. It can be set to something like 1-3, depending on the accuracy of the
/// point localization, image resolution, and the image noise.
/// * mask: Output array of N elements, every element of which is set to 0 for outliers and to 1
/// for the other points. The array is computed only in the RANSAC and LMedS methods.
/// * maxIters: The maximum number of robust method iterations.
///
/// This function estimates essential matrix based on the five-point algorithm solver in [Nister03](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Nister03) .
/// [SteweniusCFS](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_SteweniusCFS) is also a related. The epipolar geometry is described by the following equation:
///
/// 
///
/// where 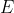 is an essential matrix,  and  are corresponding points in the first and the
/// second images, respectively. The result of this function may be passed further to
/// [decompose_essential_mat] or [recover_pose] to recover the relative pose between cameras.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * points1: Array of N (N \>= 5) 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should
/// be floating-point (single or double precision).
/// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1 .
/// * focal: focal length of the camera. Note that this function assumes that points1 and points2
/// are feature points from cameras with same focal length and principal point.
/// * pp: principal point of the camera.
/// * method: Method for computing a fundamental matrix.
/// * [RANSAC] for the RANSAC algorithm.
/// * [LMEDS] for the LMedS algorithm.
/// * threshold: Parameter used for RANSAC. It is the maximum distance from a point to an epipolar
/// line in pixels, beyond which the point is considered an outlier and is not used for computing the
/// final fundamental matrix. It can be set to something like 1-3, depending on the accuracy of the
/// point localization, image resolution, and the image noise.
/// * prob: Parameter used for the RANSAC or LMedS methods only. It specifies a desirable level of
/// confidence (probability) that the estimated matrix is correct.
/// * mask: Output array of N elements, every element of which is set to 0 for outliers and to 1
/// for the other points. The array is computed only in the RANSAC and LMedS methods.
/// * maxIters: The maximum number of robust method iterations.
///
/// This function differs from the one above that it computes camera intrinsic matrix from focal length and
/// principal point:
///
/// 
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * focal: 1.0
/// * pp: Point2d(0,0)
/// * method: RANSAC
/// * prob: 0.999
/// * threshold: 1.0
/// * max_iters: 1000
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn find_essential_mat_1(points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray, focal: f64, pp: core::Point2d, method: i32, prob: f64, threshold: f64, max_iters: i32, mask: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
output_array_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findEssentialMat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_double_Point2d_int_double_double_int_const__OutputArrayR(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), focal, &pp, method, prob, threshold, max_iters, mask.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// @overload
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [find_fundamental_mat_1] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * method: FM_RANSAC
/// * ransac_reproj_threshold: 3.
/// * confidence: 0.99
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn find_fundamental_mat_1_def(points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findFundamentalMat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// @overload
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [find_fundamental_mat_mask] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * method: FM_RANSAC
/// * ransac_reproj_threshold: 3.
/// * confidence: 0.99
#[inline]
pub fn find_fundamental_mat_mask_def(points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray, mask: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
output_array_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findFundamentalMat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn find_fundamental_mat_2(points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray, mask: &mut impl ToOutputArray, params: crate::calib3d::UsacParams) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
output_array_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findFundamentalMat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const_UsacParamsR(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__OutputArray(), ¶ms, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates a fundamental matrix from the corresponding points in two images.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * points1: Array of N points from the first image. The point coordinates should be
/// floating-point (single or double precision).
/// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1 .
/// * method: Method for computing a fundamental matrix.
/// * [FM_7POINT] for a 7-point algorithm. 
/// * [FM_8POINT] for an 8-point algorithm. 
/// * [FM_RANSAC] for the RANSAC algorithm. 
/// * [FM_LMEDS] for the LMedS algorithm. 
/// * ransacReprojThreshold: Parameter used only for RANSAC. It is the maximum distance from a point to an epipolar
/// line in pixels, beyond which the point is considered an outlier and is not used for computing the
/// final fundamental matrix. It can be set to something like 1-3, depending on the accuracy of the
/// point localization, image resolution, and the image noise.
/// * confidence: Parameter used for the RANSAC and LMedS methods only. It specifies a desirable level
/// of confidence (probability) that the estimated matrix is correct.
/// * mask:[out] optional output mask
/// * maxIters: The maximum number of robust method iterations.
///
/// The epipolar geometry is described by the following equation:
///
/// 
///
/// where 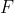 is a fundamental matrix,  and  are corresponding points in the first and the
/// second images, respectively.
///
/// The function calculates the fundamental matrix using one of four methods listed above and returns
/// the found fundamental matrix. Normally just one matrix is found. But in case of the 7-point
/// algorithm, the function may return up to 3 solutions (  matrix that stores all 3
/// matrices sequentially).
///
/// The calculated fundamental matrix may be passed further to [compute_correspond_epilines] that finds the
/// epipolar lines corresponding to the specified points. It can also be passed to
/// [stereo_rectify_uncalibrated] to compute the rectification transformation. :
/// ```C++
/// // Example. Estimation of fundamental matrix using the RANSAC algorithm
/// int point_count = 100;
/// vector<Point2f> points1(point_count);
/// vector<Point2f> points2(point_count);
///
/// // initialize the points here ...
/// for( int i = 0; i < point_count; i++ )
/// {
/// points1[i] = ...;
/// points2[i] = ...;
/// }
///
/// Mat fundamental_matrix =
/// findFundamentalMat(points1, points2, FM_RANSAC, 3, 0.99);
/// ```
///
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * method: FM_RANSAC
/// * ransac_reproj_threshold: 3.
/// * confidence: 0.99
#[inline]
pub fn find_fundamental_mat_mask(points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray, mask: &mut impl ToOutputArray, method: i32, ransac_reproj_threshold: f64, confidence: f64) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
output_array_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findFundamentalMat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_double_double(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__OutputArray(), method, ransac_reproj_threshold, confidence, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates a fundamental matrix from the corresponding points in two images.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * points1: Array of N points from the first image. The point coordinates should be
/// floating-point (single or double precision).
/// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1 .
/// * method: Method for computing a fundamental matrix.
/// * [FM_7POINT] for a 7-point algorithm. 
/// * [FM_8POINT] for an 8-point algorithm. 
/// * [FM_RANSAC] for the RANSAC algorithm. 
/// * [FM_LMEDS] for the LMedS algorithm. 
/// * ransacReprojThreshold: Parameter used only for RANSAC. It is the maximum distance from a point to an epipolar
/// line in pixels, beyond which the point is considered an outlier and is not used for computing the
/// final fundamental matrix. It can be set to something like 1-3, depending on the accuracy of the
/// point localization, image resolution, and the image noise.
/// * confidence: Parameter used for the RANSAC and LMedS methods only. It specifies a desirable level
/// of confidence (probability) that the estimated matrix is correct.
/// * mask:[out] optional output mask
/// * maxIters: The maximum number of robust method iterations.
///
/// The epipolar geometry is described by the following equation:
///
/// 
///
/// where 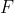 is a fundamental matrix,  and  are corresponding points in the first and the
/// second images, respectively.
///
/// The function calculates the fundamental matrix using one of four methods listed above and returns
/// the found fundamental matrix. Normally just one matrix is found. But in case of the 7-point
/// algorithm, the function may return up to 3 solutions (  matrix that stores all 3
/// matrices sequentially).
///
/// The calculated fundamental matrix may be passed further to [compute_correspond_epilines] that finds the
/// epipolar lines corresponding to the specified points. It can also be passed to
/// [stereo_rectify_uncalibrated] to compute the rectification transformation. :
/// ```C++
/// // Example. Estimation of fundamental matrix using the RANSAC algorithm
/// int point_count = 100;
/// vector<Point2f> points1(point_count);
/// vector<Point2f> points2(point_count);
///
/// // initialize the points here ...
/// for( int i = 0; i < point_count; i++ )
/// {
/// points1[i] = ...;
/// points2[i] = ...;
/// }
///
/// Mat fundamental_matrix =
/// findFundamentalMat(points1, points2, FM_RANSAC, 3, 0.99);
/// ```
///
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * method: FM_RANSAC
/// * ransac_reproj_threshold: 3.
/// * confidence: 0.99
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn find_fundamental_mat_1(points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray, method: i32, ransac_reproj_threshold: f64, confidence: f64, mask: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
output_array_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findFundamentalMat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int_double_double_const__OutputArrayR(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), method, ransac_reproj_threshold, confidence, mask.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates a fundamental matrix from the corresponding points in two images.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * points1: Array of N points from the first image. The point coordinates should be
/// floating-point (single or double precision).
/// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1 .
/// * method: Method for computing a fundamental matrix.
/// * [FM_7POINT] for a 7-point algorithm. 
/// * [FM_8POINT] for an 8-point algorithm. 
/// * [FM_RANSAC] for the RANSAC algorithm. 
/// * [FM_LMEDS] for the LMedS algorithm. 
/// * ransacReprojThreshold: Parameter used only for RANSAC. It is the maximum distance from a point to an epipolar
/// line in pixels, beyond which the point is considered an outlier and is not used for computing the
/// final fundamental matrix. It can be set to something like 1-3, depending on the accuracy of the
/// point localization, image resolution, and the image noise.
/// * confidence: Parameter used for the RANSAC and LMedS methods only. It specifies a desirable level
/// of confidence (probability) that the estimated matrix is correct.
/// * mask:[out] optional output mask
/// * maxIters: The maximum number of robust method iterations.
///
/// The epipolar geometry is described by the following equation:
///
/// 
///
/// where 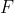 is a fundamental matrix,  and  are corresponding points in the first and the
/// second images, respectively.
///
/// The function calculates the fundamental matrix using one of four methods listed above and returns
/// the found fundamental matrix. Normally just one matrix is found. But in case of the 7-point
/// algorithm, the function may return up to 3 solutions (  matrix that stores all 3
/// matrices sequentially).
///
/// The calculated fundamental matrix may be passed further to [compute_correspond_epilines] that finds the
/// epipolar lines corresponding to the specified points. It can also be passed to
/// [stereo_rectify_uncalibrated] to compute the rectification transformation. :
/// ```C++
/// // Example. Estimation of fundamental matrix using the RANSAC algorithm
/// int point_count = 100;
/// vector<Point2f> points1(point_count);
/// vector<Point2f> points2(point_count);
///
/// // initialize the points here ...
/// for( int i = 0; i < point_count; i++ )
/// {
/// points1[i] = ...;
/// points2[i] = ...;
/// }
///
/// Mat fundamental_matrix =
/// findFundamentalMat(points1, points2, FM_RANSAC, 3, 0.99);
/// ```
///
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [find_fundamental_mat] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn find_fundamental_mat_def(points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray, method: i32, ransac_reproj_threshold: f64, confidence: f64, max_iters: i32) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findFundamentalMat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int_double_double_int(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), method, ransac_reproj_threshold, confidence, max_iters, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates a fundamental matrix from the corresponding points in two images.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * points1: Array of N points from the first image. The point coordinates should be
/// floating-point (single or double precision).
/// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1 .
/// * method: Method for computing a fundamental matrix.
/// * [FM_7POINT] for a 7-point algorithm. 
/// * [FM_8POINT] for an 8-point algorithm. 
/// * [FM_RANSAC] for the RANSAC algorithm. 
/// * [FM_LMEDS] for the LMedS algorithm. 
/// * ransacReprojThreshold: Parameter used only for RANSAC. It is the maximum distance from a point to an epipolar
/// line in pixels, beyond which the point is considered an outlier and is not used for computing the
/// final fundamental matrix. It can be set to something like 1-3, depending on the accuracy of the
/// point localization, image resolution, and the image noise.
/// * confidence: Parameter used for the RANSAC and LMedS methods only. It specifies a desirable level
/// of confidence (probability) that the estimated matrix is correct.
/// * mask:[out] optional output mask
/// * maxIters: The maximum number of robust method iterations.
///
/// The epipolar geometry is described by the following equation:
///
/// 
///
/// where 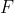 is a fundamental matrix,  and  are corresponding points in the first and the
/// second images, respectively.
///
/// The function calculates the fundamental matrix using one of four methods listed above and returns
/// the found fundamental matrix. Normally just one matrix is found. But in case of the 7-point
/// algorithm, the function may return up to 3 solutions (  matrix that stores all 3
/// matrices sequentially).
///
/// The calculated fundamental matrix may be passed further to [compute_correspond_epilines] that finds the
/// epipolar lines corresponding to the specified points. It can also be passed to
/// [stereo_rectify_uncalibrated] to compute the rectification transformation. :
/// ```C++
/// // Example. Estimation of fundamental matrix using the RANSAC algorithm
/// int point_count = 100;
/// vector<Point2f> points1(point_count);
/// vector<Point2f> points2(point_count);
///
/// // initialize the points here ...
/// for( int i = 0; i < point_count; i++ )
/// {
/// points1[i] = ...;
/// points2[i] = ...;
/// }
///
/// Mat fundamental_matrix =
/// findFundamentalMat(points1, points2, FM_RANSAC, 3, 0.99);
/// ```
///
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn find_fundamental_mat(points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray, method: i32, ransac_reproj_threshold: f64, confidence: f64, max_iters: i32, mask: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
output_array_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findFundamentalMat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int_double_double_int_const__OutputArrayR(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), method, ransac_reproj_threshold, confidence, max_iters, mask.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds a perspective transformation between two planes.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * srcPoints: Coordinates of the points in the original plane, a matrix of the type CV_32FC2
/// or vector\<Point2f\> .
/// * dstPoints: Coordinates of the points in the target plane, a matrix of the type CV_32FC2 or
/// a vector\<Point2f\> .
/// * method: Method used to compute a homography matrix. The following methods are possible:
/// * **0** - a regular method using all the points, i.e., the least squares method
/// * [RANSAC] - RANSAC-based robust method
/// * [LMEDS] - Least-Median robust method
/// * [RHO] - PROSAC-based robust method
/// * ransacReprojThreshold: Maximum allowed reprojection error to treat a point pair as an inlier
/// (used in the RANSAC and RHO methods only). That is, if
/// 
/// then the point 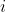 is considered as an outlier. If srcPoints and dstPoints are measured in pixels,
/// it usually makes sense to set this parameter somewhere in the range of 1 to 10.
/// * mask: Optional output mask set by a robust method ( RANSAC or LMeDS ). Note that the input
/// mask values are ignored.
/// * maxIters: The maximum number of RANSAC iterations.
/// * confidence: Confidence level, between 0 and 1.
///
/// The function finds and returns the perspective transformation 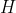 between the source and the
/// destination planes:
///
/// 
///
/// so that the back-projection error
///
/// 
///
/// is minimized. If the parameter method is set to the default value 0, the function uses all the point
/// pairs to compute an initial homography estimate with a simple least-squares scheme.
///
/// However, if not all of the point pairs ( ,  ) fit the rigid perspective
/// transformation (that is, there are some outliers), this initial estimate will be poor. In this case,
/// you can use one of the three robust methods. The methods RANSAC, LMeDS and RHO try many different
/// random subsets of the corresponding point pairs (of four pairs each, collinear pairs are discarded), estimate the homography matrix
/// using this subset and a simple least-squares algorithm, and then compute the quality/goodness of the
/// computed homography (which is the number of inliers for RANSAC or the least median re-projection error for
/// LMeDS). The best subset is then used to produce the initial estimate of the homography matrix and
/// the mask of inliers/outliers.
///
/// Regardless of the method, robust or not, the computed homography matrix is refined further (using
/// inliers only in case of a robust method) with the Levenberg-Marquardt method to reduce the
/// re-projection error even more.
///
/// The methods RANSAC and RHO can handle practically any ratio of outliers but need a threshold to
/// distinguish inliers from outliers. The method LMeDS does not need any threshold but it works
/// correctly only when there are more than 50% of inliers. Finally, if there are no outliers and the
/// noise is rather small, use the default method (method=0).
///
/// The function is used to find initial intrinsic and extrinsic matrices. Homography matrix is
/// determined up to a scale. If  is non-zero, the matrix is normalized so that .
///
/// Note: Whenever an 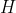 matrix cannot be estimated, an empty one will be returned.
/// ## See also
/// getAffineTransform, estimateAffine2D, estimateAffinePartial2D, getPerspectiveTransform, warpPerspective,
/// perspectiveTransform
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [find_homography_ext] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * method: 0
/// * ransac_reproj_threshold: 3
/// * mask: noArray()
/// * max_iters: 2000
/// * confidence: 0.995
#[inline]
pub fn find_homography_ext_def(src_points: &impl ToInputArray, dst_points: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(src_points);
input_array_arg!(dst_points);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findHomography_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(src_points.as_raw__InputArray(), dst_points.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// @overload
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [find_homography] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * method: 0
/// * ransac_reproj_threshold: 3
#[inline]
pub fn find_homography_def(src_points: &impl ToInputArray, dst_points: &impl ToInputArray, mask: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(src_points);
input_array_arg!(dst_points);
output_array_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findHomography_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src_points.as_raw__InputArray(), dst_points.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn find_homography_1(src_points: &impl ToInputArray, dst_points: &impl ToInputArray, mask: &mut impl ToOutputArray, params: crate::calib3d::UsacParams) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(src_points);
input_array_arg!(dst_points);
output_array_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findHomography_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const_UsacParamsR(src_points.as_raw__InputArray(), dst_points.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__OutputArray(), ¶ms, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds a perspective transformation between two planes.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * srcPoints: Coordinates of the points in the original plane, a matrix of the type CV_32FC2
/// or vector\<Point2f\> .
/// * dstPoints: Coordinates of the points in the target plane, a matrix of the type CV_32FC2 or
/// a vector\<Point2f\> .
/// * method: Method used to compute a homography matrix. The following methods are possible:
/// * **0** - a regular method using all the points, i.e., the least squares method
/// * [RANSAC] - RANSAC-based robust method
/// * [LMEDS] - Least-Median robust method
/// * [RHO] - PROSAC-based robust method
/// * ransacReprojThreshold: Maximum allowed reprojection error to treat a point pair as an inlier
/// (used in the RANSAC and RHO methods only). That is, if
/// 
/// then the point 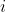 is considered as an outlier. If srcPoints and dstPoints are measured in pixels,
/// it usually makes sense to set this parameter somewhere in the range of 1 to 10.
/// * mask: Optional output mask set by a robust method ( RANSAC or LMeDS ). Note that the input
/// mask values are ignored.
/// * maxIters: The maximum number of RANSAC iterations.
/// * confidence: Confidence level, between 0 and 1.
///
/// The function finds and returns the perspective transformation 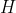 between the source and the
/// destination planes:
///
/// 
///
/// so that the back-projection error
///
/// 
///
/// is minimized. If the parameter method is set to the default value 0, the function uses all the point
/// pairs to compute an initial homography estimate with a simple least-squares scheme.
///
/// However, if not all of the point pairs ( ,  ) fit the rigid perspective
/// transformation (that is, there are some outliers), this initial estimate will be poor. In this case,
/// you can use one of the three robust methods. The methods RANSAC, LMeDS and RHO try many different
/// random subsets of the corresponding point pairs (of four pairs each, collinear pairs are discarded), estimate the homography matrix
/// using this subset and a simple least-squares algorithm, and then compute the quality/goodness of the
/// computed homography (which is the number of inliers for RANSAC or the least median re-projection error for
/// LMeDS). The best subset is then used to produce the initial estimate of the homography matrix and
/// the mask of inliers/outliers.
///
/// Regardless of the method, robust or not, the computed homography matrix is refined further (using
/// inliers only in case of a robust method) with the Levenberg-Marquardt method to reduce the
/// re-projection error even more.
///
/// The methods RANSAC and RHO can handle practically any ratio of outliers but need a threshold to
/// distinguish inliers from outliers. The method LMeDS does not need any threshold but it works
/// correctly only when there are more than 50% of inliers. Finally, if there are no outliers and the
/// noise is rather small, use the default method (method=0).
///
/// The function is used to find initial intrinsic and extrinsic matrices. Homography matrix is
/// determined up to a scale. If  is non-zero, the matrix is normalized so that .
///
/// Note: Whenever an 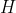 matrix cannot be estimated, an empty one will be returned.
/// ## See also
/// getAffineTransform, estimateAffine2D, estimateAffinePartial2D, getPerspectiveTransform, warpPerspective,
/// perspectiveTransform
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * method: 0
/// * ransac_reproj_threshold: 3
#[inline]
pub fn find_homography(src_points: &impl ToInputArray, dst_points: &impl ToInputArray, mask: &mut impl ToOutputArray, method: i32, ransac_reproj_threshold: f64) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(src_points);
input_array_arg!(dst_points);
output_array_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findHomography_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_double(src_points.as_raw__InputArray(), dst_points.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__OutputArray(), method, ransac_reproj_threshold, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds a perspective transformation between two planes.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * srcPoints: Coordinates of the points in the original plane, a matrix of the type CV_32FC2
/// or vector\<Point2f\> .
/// * dstPoints: Coordinates of the points in the target plane, a matrix of the type CV_32FC2 or
/// a vector\<Point2f\> .
/// * method: Method used to compute a homography matrix. The following methods are possible:
/// * **0** - a regular method using all the points, i.e., the least squares method
/// * [RANSAC] - RANSAC-based robust method
/// * [LMEDS] - Least-Median robust method
/// * [RHO] - PROSAC-based robust method
/// * ransacReprojThreshold: Maximum allowed reprojection error to treat a point pair as an inlier
/// (used in the RANSAC and RHO methods only). That is, if
/// 
/// then the point 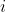 is considered as an outlier. If srcPoints and dstPoints are measured in pixels,
/// it usually makes sense to set this parameter somewhere in the range of 1 to 10.
/// * mask: Optional output mask set by a robust method ( RANSAC or LMeDS ). Note that the input
/// mask values are ignored.
/// * maxIters: The maximum number of RANSAC iterations.
/// * confidence: Confidence level, between 0 and 1.
///
/// The function finds and returns the perspective transformation 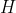 between the source and the
/// destination planes:
///
/// 
///
/// so that the back-projection error
///
/// 
///
/// is minimized. If the parameter method is set to the default value 0, the function uses all the point
/// pairs to compute an initial homography estimate with a simple least-squares scheme.
///
/// However, if not all of the point pairs ( ,  ) fit the rigid perspective
/// transformation (that is, there are some outliers), this initial estimate will be poor. In this case,
/// you can use one of the three robust methods. The methods RANSAC, LMeDS and RHO try many different
/// random subsets of the corresponding point pairs (of four pairs each, collinear pairs are discarded), estimate the homography matrix
/// using this subset and a simple least-squares algorithm, and then compute the quality/goodness of the
/// computed homography (which is the number of inliers for RANSAC or the least median re-projection error for
/// LMeDS). The best subset is then used to produce the initial estimate of the homography matrix and
/// the mask of inliers/outliers.
///
/// Regardless of the method, robust or not, the computed homography matrix is refined further (using
/// inliers only in case of a robust method) with the Levenberg-Marquardt method to reduce the
/// re-projection error even more.
///
/// The methods RANSAC and RHO can handle practically any ratio of outliers but need a threshold to
/// distinguish inliers from outliers. The method LMeDS does not need any threshold but it works
/// correctly only when there are more than 50% of inliers. Finally, if there are no outliers and the
/// noise is rather small, use the default method (method=0).
///
/// The function is used to find initial intrinsic and extrinsic matrices. Homography matrix is
/// determined up to a scale. If  is non-zero, the matrix is normalized so that .
///
/// Note: Whenever an 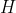 matrix cannot be estimated, an empty one will be returned.
/// ## See also
/// getAffineTransform, estimateAffine2D, estimateAffinePartial2D, getPerspectiveTransform, warpPerspective,
/// perspectiveTransform
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * method: 0
/// * ransac_reproj_threshold: 3
/// * mask: noArray()
/// * max_iters: 2000
/// * confidence: 0.995
#[inline]
pub fn find_homography_ext(src_points: &impl ToInputArray, dst_points: &impl ToInputArray, method: i32, ransac_reproj_threshold: f64, mask: &mut impl ToOutputArray, max_iters: i32, confidence: f64) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(src_points);
input_array_arg!(dst_points);
output_array_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findHomography_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int_double_const__OutputArrayR_const_int_const_double(src_points.as_raw__InputArray(), dst_points.as_raw__InputArray(), method, ransac_reproj_threshold, mask.as_raw__OutputArray(), max_iters, confidence, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Performs camera calibration
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: vector of vectors of calibration pattern points in the calibration pattern
/// coordinate space.
/// * imagePoints: vector of vectors of the projections of calibration pattern points.
/// imagePoints.size() and objectPoints.size() and imagePoints[i].size() must be equal to
/// objectPoints[i].size() for each i.
/// * image_size: Size of the image used only to initialize the camera intrinsic matrix.
/// * K: Output 3x3 floating-point camera intrinsic matrix
///  . If
/// [fisheye::CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is specified, some or all of fx, fy, cx, cy must be
/// initialized before calling the function.
/// * D: Output vector of distortion coefficients .
/// * rvecs: Output vector of rotation vectors (see [Rodrigues] ) estimated for each pattern view.
/// That is, each k-th rotation vector together with the corresponding k-th translation vector (see
/// the next output parameter description) brings the calibration pattern from the model coordinate
/// space (in which object points are specified) to the world coordinate space, that is, a real
/// position of the calibration pattern in the k-th pattern view (k=0.. *M* -1).
/// * tvecs: Output vector of translation vectors estimated for each pattern view.
/// * flags: Different flags that may be zero or a combination of the following values:
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] cameraMatrix contains valid initial values of
/// fx, fy, cx, cy that are optimized further. Otherwise, (cx, cy) is initially set to the image
/// center ( imageSize is used), and focal distances are computed in a least-squares fashion.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_RECOMPUTE_EXTRINSIC] Extrinsic will be recomputed after each iteration
/// of intrinsic optimization.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_CHECK_COND] The functions will check validity of condition number.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_FIX_SKEW] Skew coefficient (alpha) is set to zero and stay zero.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_FIX_K1],..., [fisheye::CALIB_FIX_K4] Selected distortion coefficients
/// are set to zeros and stay zero.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_FIX_PRINCIPAL_POINT] The principal point is not changed during the global
/// optimization. It stays at the center or at a different location specified when [fisheye::CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set too.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_FIX_FOCAL_LENGTH] The focal length is not changed during the global
/// optimization. It is the  or the provided ,  when [fisheye::CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set too.
/// * criteria: Termination criteria for the iterative optimization algorithm.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [calibrate] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * flags: 0
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,100,DBL_EPSILON)
#[inline]
pub fn calibrate_def(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, k: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, d: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, rvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<f64> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
input_output_array_arg!(k);
input_output_array_arg!(d);
output_array_arg!(rvecs);
output_array_arg!(tvecs);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_calibrate_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const_SizeR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, k.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), d.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), rvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Performs camera calibration
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: vector of vectors of calibration pattern points in the calibration pattern
/// coordinate space.
/// * imagePoints: vector of vectors of the projections of calibration pattern points.
/// imagePoints.size() and objectPoints.size() and imagePoints[i].size() must be equal to
/// objectPoints[i].size() for each i.
/// * image_size: Size of the image used only to initialize the camera intrinsic matrix.
/// * K: Output 3x3 floating-point camera intrinsic matrix
///  . If
/// [fisheye::CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is specified, some or all of fx, fy, cx, cy must be
/// initialized before calling the function.
/// * D: Output vector of distortion coefficients .
/// * rvecs: Output vector of rotation vectors (see [Rodrigues] ) estimated for each pattern view.
/// That is, each k-th rotation vector together with the corresponding k-th translation vector (see
/// the next output parameter description) brings the calibration pattern from the model coordinate
/// space (in which object points are specified) to the world coordinate space, that is, a real
/// position of the calibration pattern in the k-th pattern view (k=0.. *M* -1).
/// * tvecs: Output vector of translation vectors estimated for each pattern view.
/// * flags: Different flags that may be zero or a combination of the following values:
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] cameraMatrix contains valid initial values of
/// fx, fy, cx, cy that are optimized further. Otherwise, (cx, cy) is initially set to the image
/// center ( imageSize is used), and focal distances are computed in a least-squares fashion.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_RECOMPUTE_EXTRINSIC] Extrinsic will be recomputed after each iteration
/// of intrinsic optimization.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_CHECK_COND] The functions will check validity of condition number.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_FIX_SKEW] Skew coefficient (alpha) is set to zero and stay zero.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_FIX_K1],..., [fisheye::CALIB_FIX_K4] Selected distortion coefficients
/// are set to zeros and stay zero.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_FIX_PRINCIPAL_POINT] The principal point is not changed during the global
/// optimization. It stays at the center or at a different location specified when [fisheye::CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set too.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_FIX_FOCAL_LENGTH] The focal length is not changed during the global
/// optimization. It is the  or the provided ,  when [fisheye::CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set too.
/// * criteria: Termination criteria for the iterative optimization algorithm.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: 0
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,100,DBL_EPSILON)
#[inline]
pub fn calibrate(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, k: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, d: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, rvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, flags: i32, criteria: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<f64> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
input_output_array_arg!(k);
input_output_array_arg!(d);
output_array_arg!(rvecs);
output_array_arg!(tvecs);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_calibrate_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const_SizeR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_TermCriteria(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, k.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), d.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), rvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, &criteria, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Distorts 2D points using fisheye model.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * undistorted: Array of object points, 1xN/Nx1 2-channel (or vector\<Point2f\> ), where N is
/// the number of points in the view.
/// * K: Camera intrinsic matrix .
/// * D: Input vector of distortion coefficients .
/// * alpha: The skew coefficient.
/// * distorted: Output array of image points, 1xN/Nx1 2-channel, or vector\<Point2f\> .
///
/// Note that the function assumes the camera intrinsic matrix of the undistorted points to be identity.
/// This means if you want to distort image points you have to multiply them with  or
/// use another function overload.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [fisheye_distort_points] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * alpha: 0
#[inline]
pub fn fisheye_distort_points_def(undistorted: &impl ToInputArray, distorted: &mut impl ToOutputArray, k: &impl ToInputArray, d: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(undistorted);
output_array_arg!(distorted);
input_array_arg!(k);
input_array_arg!(d);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_distortPoints_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(undistorted.as_raw__InputArray(), distorted.as_raw__OutputArray(), k.as_raw__InputArray(), d.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// @overload
/// Overload of distortPoints function to handle cases when undistorted points are obtained with non-identity
/// camera matrix, e.g. output of #estimateNewCameraMatrixForUndistortRectify.
/// ## Parameters
/// * undistorted: Array of object points, 1xN/Nx1 2-channel (or vector\<Point2f\> ), where N is
/// the number of points in the view.
/// * Kundistorted: Camera intrinsic matrix used as new camera matrix for undistortion.
/// * K: Camera intrinsic matrix .
/// * D: Input vector of distortion coefficients .
/// * alpha: The skew coefficient.
/// * distorted: Output array of image points, 1xN/Nx1 2-channel, or vector\<Point2f\> .
/// ## See also
/// estimateNewCameraMatrixForUndistortRectify
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [distort_points] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * alpha: 0
#[inline]
pub fn distort_points_def(undistorted: &impl ToInputArray, distorted: &mut impl ToOutputArray, kundistorted: &impl ToInputArray, k: &impl ToInputArray, d: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(undistorted);
output_array_arg!(distorted);
input_array_arg!(kundistorted);
input_array_arg!(k);
input_array_arg!(d);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_distortPoints_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(undistorted.as_raw__InputArray(), distorted.as_raw__OutputArray(), kundistorted.as_raw__InputArray(), k.as_raw__InputArray(), d.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Distorts 2D points using fisheye model.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * undistorted: Array of object points, 1xN/Nx1 2-channel (or vector\<Point2f\> ), where N is
/// the number of points in the view.
/// * K: Camera intrinsic matrix .
/// * D: Input vector of distortion coefficients .
/// * alpha: The skew coefficient.
/// * distorted: Output array of image points, 1xN/Nx1 2-channel, or vector\<Point2f\> .
///
/// Note that the function assumes the camera intrinsic matrix of the undistorted points to be identity.
/// This means if you want to distort image points you have to multiply them with  or
/// use another function overload.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// Overload of distortPoints function to handle cases when undistorted points are obtained with non-identity
/// camera matrix, e.g. output of #estimateNewCameraMatrixForUndistortRectify.
/// * undistorted: Array of object points, 1xN/Nx1 2-channel (or vector\<Point2f\> ), where N is
/// the number of points in the view.
/// * Kundistorted: Camera intrinsic matrix used as new camera matrix for undistortion.
/// * K: Camera intrinsic matrix .
/// * D: Input vector of distortion coefficients .
/// * alpha: The skew coefficient.
/// * distorted: Output array of image points, 1xN/Nx1 2-channel, or vector\<Point2f\> .
/// ## See also
/// estimateNewCameraMatrixForUndistortRectify
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * alpha: 0
#[inline]
pub fn distort_points(undistorted: &impl ToInputArray, distorted: &mut impl ToOutputArray, kundistorted: &impl ToInputArray, k: &impl ToInputArray, d: &impl ToInputArray, alpha: f64) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(undistorted);
output_array_arg!(distorted);
input_array_arg!(kundistorted);
input_array_arg!(k);
input_array_arg!(d);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_distortPoints_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_double(undistorted.as_raw__InputArray(), distorted.as_raw__OutputArray(), kundistorted.as_raw__InputArray(), k.as_raw__InputArray(), d.as_raw__InputArray(), alpha, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Distorts 2D points using fisheye model.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * undistorted: Array of object points, 1xN/Nx1 2-channel (or vector\<Point2f\> ), where N is
/// the number of points in the view.
/// * K: Camera intrinsic matrix .
/// * D: Input vector of distortion coefficients .
/// * alpha: The skew coefficient.
/// * distorted: Output array of image points, 1xN/Nx1 2-channel, or vector\<Point2f\> .
///
/// Note that the function assumes the camera intrinsic matrix of the undistorted points to be identity.
/// This means if you want to distort image points you have to multiply them with  or
/// use another function overload.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * alpha: 0
#[inline]
pub fn fisheye_distort_points(undistorted: &impl ToInputArray, distorted: &mut impl ToOutputArray, k: &impl ToInputArray, d: &impl ToInputArray, alpha: f64) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(undistorted);
output_array_arg!(distorted);
input_array_arg!(k);
input_array_arg!(d);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_distortPoints_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_double(undistorted.as_raw__InputArray(), distorted.as_raw__OutputArray(), k.as_raw__InputArray(), d.as_raw__InputArray(), alpha, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Estimates new camera intrinsic matrix for undistortion or rectification.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * K: Camera intrinsic matrix .
/// * image_size: Size of the image
/// * D: Input vector of distortion coefficients .
/// * R: Rectification transformation in the object space: 3x3 1-channel, or vector: 3x1/1x3
/// 1-channel or 1x1 3-channel
/// * P: New camera intrinsic matrix (3x3) or new projection matrix (3x4)
/// * balance: Sets the new focal length in range between the min focal length and the max focal
/// length. Balance is in range of [0, 1].
/// * new_size: the new size
/// * fov_scale: Divisor for new focal length.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [estimate_new_camera_matrix_for_undistort_rectify] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * balance: 0.0
/// * new_size: Size()
/// * fov_scale: 1.0
#[inline]
pub fn estimate_new_camera_matrix_for_undistort_rectify_def(k: &impl ToInputArray, d: &impl ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, r: &impl ToInputArray, p: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(k);
input_array_arg!(d);
input_array_arg!(r);
output_array_arg!(p);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_estimateNewCameraMatrixForUndistortRectify_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const_SizeR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(k.as_raw__InputArray(), d.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, r.as_raw__InputArray(), p.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Estimates new camera intrinsic matrix for undistortion or rectification.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * K: Camera intrinsic matrix .
/// * image_size: Size of the image
/// * D: Input vector of distortion coefficients .
/// * R: Rectification transformation in the object space: 3x3 1-channel, or vector: 3x1/1x3
/// 1-channel or 1x1 3-channel
/// * P: New camera intrinsic matrix (3x3) or new projection matrix (3x4)
/// * balance: Sets the new focal length in range between the min focal length and the max focal
/// length. Balance is in range of [0, 1].
/// * new_size: the new size
/// * fov_scale: Divisor for new focal length.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * balance: 0.0
/// * new_size: Size()
/// * fov_scale: 1.0
#[inline]
pub fn estimate_new_camera_matrix_for_undistort_rectify(k: &impl ToInputArray, d: &impl ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, r: &impl ToInputArray, p: &mut impl ToOutputArray, balance: f64, new_size: core::Size, fov_scale: f64) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(k);
input_array_arg!(d);
input_array_arg!(r);
output_array_arg!(p);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_estimateNewCameraMatrixForUndistortRectify_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const_SizeR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_const_SizeR_double(k.as_raw__InputArray(), d.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, r.as_raw__InputArray(), p.as_raw__OutputArray(), balance, &new_size, fov_scale, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes undistortion and rectification maps for image transform by #remap. If D is empty zero
/// distortion is used, if R or P is empty identity matrixes are used.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * K: Camera intrinsic matrix .
/// * D: Input vector of distortion coefficients .
/// * R: Rectification transformation in the object space: 3x3 1-channel, or vector: 3x1/1x3
/// 1-channel or 1x1 3-channel
/// * P: New camera intrinsic matrix (3x3) or new projection matrix (3x4)
/// * size: Undistorted image size.
/// * m1type: Type of the first output map that can be CV_32FC1 or CV_16SC2 . See [convert_maps]
/// for details.
/// * map1: The first output map.
/// * map2: The second output map.
#[inline]
pub fn fisheye_init_undistort_rectify_map(k: &impl ToInputArray, d: &impl ToInputArray, r: &impl ToInputArray, p: &impl ToInputArray, size: core::Size, m1type: i32, map1: &mut impl ToOutputArray, map2: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(k);
input_array_arg!(d);
input_array_arg!(r);
input_array_arg!(p);
output_array_arg!(map1);
output_array_arg!(map2);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_initUndistortRectifyMap_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const_SizeR_int_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(k.as_raw__InputArray(), d.as_raw__InputArray(), r.as_raw__InputArray(), p.as_raw__InputArray(), &size, m1type, map1.as_raw__OutputArray(), map2.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Projects points using fisheye model
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Array of object points, 1xN/Nx1 3-channel (or vector\<Point3f\> ), where N is
/// the number of points in the view.
/// * imagePoints: Output array of image points, 2xN/Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel, or
/// vector\<Point2f\>.
/// * affine:
/// * K: Camera intrinsic matrix .
/// * D: Input vector of distortion coefficients .
/// * alpha: The skew coefficient.
/// * jacobian: Optional output 2Nx15 jacobian matrix of derivatives of image points with respect
/// to components of the focal lengths, coordinates of the principal point, distortion coefficients,
/// rotation vector, translation vector, and the skew. In the old interface different components of
/// the jacobian are returned via different output parameters.
///
/// The function computes projections of 3D points to the image plane given intrinsic and extrinsic
/// camera parameters. Optionally, the function computes Jacobians - matrices of partial derivatives of
/// image points coordinates (as functions of all the input parameters) with respect to the particular
/// parameters, intrinsic and/or extrinsic.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [fisheye_project_points] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * alpha: 0
/// * jacobian: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn fisheye_project_points_def(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &mut impl ToOutputArray, affine: core::Affine3d, k: &impl ToInputArray, d: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
output_array_arg!(image_points);
input_array_arg!(k);
input_array_arg!(d);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_projectPoints_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const_Affine3dR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__OutputArray(), &affine, k.as_raw__InputArray(), d.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Projects points using fisheye model
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Array of object points, 1xN/Nx1 3-channel (or vector\<Point3f\> ), where N is
/// the number of points in the view.
/// * imagePoints: Output array of image points, 2xN/Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel, or
/// vector\<Point2f\>.
/// * affine:
/// * K: Camera intrinsic matrix .
/// * D: Input vector of distortion coefficients .
/// * alpha: The skew coefficient.
/// * jacobian: Optional output 2Nx15 jacobian matrix of derivatives of image points with respect
/// to components of the focal lengths, coordinates of the principal point, distortion coefficients,
/// rotation vector, translation vector, and the skew. In the old interface different components of
/// the jacobian are returned via different output parameters.
///
/// The function computes projections of 3D points to the image plane given intrinsic and extrinsic
/// camera parameters. Optionally, the function computes Jacobians - matrices of partial derivatives of
/// image points coordinates (as functions of all the input parameters) with respect to the particular
/// parameters, intrinsic and/or extrinsic.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * alpha: 0
/// * jacobian: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn fisheye_project_points(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &mut impl ToOutputArray, affine: core::Affine3d, k: &impl ToInputArray, d: &impl ToInputArray, alpha: f64, jacobian: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
output_array_arg!(image_points);
input_array_arg!(k);
input_array_arg!(d);
output_array_arg!(jacobian);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_projectPoints_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const_Affine3dR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_double_const__OutputArrayR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__OutputArray(), &affine, k.as_raw__InputArray(), d.as_raw__InputArray(), alpha, jacobian.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// @overload
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [fisheye_project_points_vec] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * alpha: 0
/// * jacobian: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn fisheye_project_points_vec_def(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &mut impl ToOutputArray, rvec: &impl ToInputArray, tvec: &impl ToInputArray, k: &impl ToInputArray, d: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
output_array_arg!(image_points);
input_array_arg!(rvec);
input_array_arg!(tvec);
input_array_arg!(k);
input_array_arg!(d);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_projectPoints_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__OutputArray(), rvec.as_raw__InputArray(), tvec.as_raw__InputArray(), k.as_raw__InputArray(), d.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Projects points using fisheye model
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Array of object points, 1xN/Nx1 3-channel (or vector\<Point3f\> ), where N is
/// the number of points in the view.
/// * imagePoints: Output array of image points, 2xN/Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel, or
/// vector\<Point2f\>.
/// * affine:
/// * K: Camera intrinsic matrix .
/// * D: Input vector of distortion coefficients .
/// * alpha: The skew coefficient.
/// * jacobian: Optional output 2Nx15 jacobian matrix of derivatives of image points with respect
/// to components of the focal lengths, coordinates of the principal point, distortion coefficients,
/// rotation vector, translation vector, and the skew. In the old interface different components of
/// the jacobian are returned via different output parameters.
///
/// The function computes projections of 3D points to the image plane given intrinsic and extrinsic
/// camera parameters. Optionally, the function computes Jacobians - matrices of partial derivatives of
/// image points coordinates (as functions of all the input parameters) with respect to the particular
/// parameters, intrinsic and/or extrinsic.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * alpha: 0
/// * jacobian: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn fisheye_project_points_vec(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &mut impl ToOutputArray, rvec: &impl ToInputArray, tvec: &impl ToInputArray, k: &impl ToInputArray, d: &impl ToInputArray, alpha: f64, jacobian: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
output_array_arg!(image_points);
input_array_arg!(rvec);
input_array_arg!(tvec);
input_array_arg!(k);
input_array_arg!(d);
output_array_arg!(jacobian);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_projectPoints_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_double_const__OutputArrayR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__OutputArray(), rvec.as_raw__InputArray(), tvec.as_raw__InputArray(), k.as_raw__InputArray(), d.as_raw__InputArray(), alpha, jacobian.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds an object pose from 3D-2D point correspondences for fisheye camera moodel.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Array of object points in the object coordinate space, Nx3 1-channel or
/// 1xN/Nx1 3-channel, where N is the number of points. vector\<Point3d\> can be also passed here.
/// * imagePoints: Array of corresponding image points, Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel,
/// where N is the number of points. vector\<Point2d\> can be also passed here.
/// * cameraMatrix: Input camera intrinsic matrix  .
/// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients (4x1/1x4).
/// * rvec: Output rotation vector (see [Rodrigues] ) that, together with tvec, brings points from
/// the model coordinate system to the camera coordinate system.
/// * tvec: Output translation vector.
/// * useExtrinsicGuess: Parameter used for #SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE. If true (1), the function uses
/// the provided rvec and tvec values as initial approximations of the rotation and translation
/// vectors, respectively, and further optimizes them.
/// * flags: Method for solving a PnP problem: see [calib3d_solvePnP_flags]
/// This function returns the rotation and the translation vectors that transform a 3D point expressed in the object
/// coordinate frame to the camera coordinate frame, using different methods:
/// - P3P methods ([SOLVEPNP_P3P], [SOLVEPNP_AP3P]): need 4 input points to return a unique solution.
/// - [SOLVEPNP_IPPE] Input points must be >= 4 and object points must be coplanar.
/// - [SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE] Special case suitable for marker pose estimation.
/// Number of input points must be 4. Object points must be defined in the following order:
/// - point 0: [-squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 1: [ squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 2: [ squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 3: [-squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - for all the other flags, number of input points must be >= 4 and object points can be in any configuration.
/// * criteria: Termination criteria for internal undistortPoints call.
/// The function interally undistorts points with [undistortPoints] and call [cv::solvePnP],
/// thus the input are very similar. More information about Perspective-n-Points is described in [calib3d_solvePnP]
/// for more information.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [solve_pnp_1] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * use_extrinsic_guess: false
/// * flags: SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::MAX_ITER+TermCriteria::EPS,10,1e-8)
#[inline]
pub fn solve_pnp_1_def(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, rvec: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvec: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
output_array_arg!(rvec);
output_array_arg!(tvec);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_solvePnP_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvec.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds an object pose from 3D-2D point correspondences for fisheye camera moodel.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Array of object points in the object coordinate space, Nx3 1-channel or
/// 1xN/Nx1 3-channel, where N is the number of points. vector\<Point3d\> can be also passed here.
/// * imagePoints: Array of corresponding image points, Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel,
/// where N is the number of points. vector\<Point2d\> can be also passed here.
/// * cameraMatrix: Input camera intrinsic matrix  .
/// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients (4x1/1x4).
/// * rvec: Output rotation vector (see [Rodrigues] ) that, together with tvec, brings points from
/// the model coordinate system to the camera coordinate system.
/// * tvec: Output translation vector.
/// * useExtrinsicGuess: Parameter used for #SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE. If true (1), the function uses
/// the provided rvec and tvec values as initial approximations of the rotation and translation
/// vectors, respectively, and further optimizes them.
/// * flags: Method for solving a PnP problem: see [calib3d_solvePnP_flags]
/// This function returns the rotation and the translation vectors that transform a 3D point expressed in the object
/// coordinate frame to the camera coordinate frame, using different methods:
/// - P3P methods ([SOLVEPNP_P3P], [SOLVEPNP_AP3P]): need 4 input points to return a unique solution.
/// - [SOLVEPNP_IPPE] Input points must be >= 4 and object points must be coplanar.
/// - [SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE] Special case suitable for marker pose estimation.
/// Number of input points must be 4. Object points must be defined in the following order:
/// - point 0: [-squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 1: [ squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 2: [ squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 3: [-squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - for all the other flags, number of input points must be >= 4 and object points can be in any configuration.
/// * criteria: Termination criteria for internal undistortPoints call.
/// The function interally undistorts points with [undistortPoints] and call [cv::solvePnP],
/// thus the input are very similar. More information about Perspective-n-Points is described in [calib3d_solvePnP]
/// for more information.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * use_extrinsic_guess: false
/// * flags: SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::MAX_ITER+TermCriteria::EPS,10,1e-8)
#[inline]
pub fn solve_pnp_1(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, rvec: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvec: &mut impl ToOutputArray, use_extrinsic_guess: bool, flags: i32, criteria: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
output_array_arg!(rvec);
output_array_arg!(tvec);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_solvePnP_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_bool_int_TermCriteria(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvec.as_raw__OutputArray(), use_extrinsic_guess, flags, &criteria, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// @overload
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [fisheye_stereo_calibrate] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * flags: fisheye::CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,100,DBL_EPSILON)
#[inline]
pub fn fisheye_stereo_calibrate_def(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points1: &impl ToInputArray, image_points2: &impl ToInputArray, k1: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, d1: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, k2: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, d2: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, image_size: core::Size, r: &mut impl ToOutputArray, t: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<f64> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points1);
input_array_arg!(image_points2);
input_output_array_arg!(k1);
input_output_array_arg!(d1);
input_output_array_arg!(k2);
input_output_array_arg!(d2);
output_array_arg!(r);
output_array_arg!(t);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_stereoCalibrate_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_Size_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points1.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points2.as_raw__InputArray(), k1.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), d1.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), k2.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), d2.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), &image_size, r.as_raw__OutputArray(), t.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Performs stereo calibration
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Vector of vectors of the calibration pattern points.
/// * imagePoints1: Vector of vectors of the projections of the calibration pattern points,
/// observed by the first camera.
/// * imagePoints2: Vector of vectors of the projections of the calibration pattern points,
/// observed by the second camera.
/// * K1: Input/output first camera intrinsic matrix:
///  , 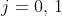 . If
/// any of [fisheye::CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] , [fisheye::CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC] are specified,
/// some or all of the matrix components must be initialized.
/// * D1: Input/output vector of distortion coefficients  of 4 elements.
/// * K2: Input/output second camera intrinsic matrix. The parameter is similar to K1 .
/// * D2: Input/output lens distortion coefficients for the second camera. The parameter is
/// similar to D1 .
/// * imageSize: Size of the image used only to initialize camera intrinsic matrix.
/// * R: Output rotation matrix between the 1st and the 2nd camera coordinate systems.
/// * T: Output translation vector between the coordinate systems of the cameras.
/// * rvecs: Output vector of rotation vectors ( [Rodrigues] ) estimated for each pattern view in the
/// coordinate system of the first camera of the stereo pair (e.g. std::vector<cv::Mat>). More in detail, each
/// i-th rotation vector together with the corresponding i-th translation vector (see the next output parameter
/// description) brings the calibration pattern from the object coordinate space (in which object points are
/// specified) to the camera coordinate space of the first camera of the stereo pair. In more technical terms,
/// the tuple of the i-th rotation and translation vector performs a change of basis from object coordinate space
/// to camera coordinate space of the first camera of the stereo pair.
/// * tvecs: Output vector of translation vectors estimated for each pattern view, see parameter description
/// of previous output parameter ( rvecs ).
/// * flags: Different flags that may be zero or a combination of the following values:
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC] Fix K1, K2? and D1, D2? so that only R, T matrices
/// are estimated.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] K1, K2 contains valid initial values of
/// fx, fy, cx, cy that are optimized further. Otherwise, (cx, cy) is initially set to the image
/// center (imageSize is used), and focal distances are computed in a least-squares fashion.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_RECOMPUTE_EXTRINSIC] Extrinsic will be recomputed after each iteration
/// of intrinsic optimization.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_CHECK_COND] The functions will check validity of condition number.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_FIX_SKEW] Skew coefficient (alpha) is set to zero and stay zero.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_FIX_K1],..., [fisheye::CALIB_FIX_K4] Selected distortion coefficients are set to zeros and stay
/// zero.
/// * criteria: Termination criteria for the iterative optimization algorithm.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [stereo_calibrate_2] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * flags: fisheye::CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,100,DBL_EPSILON)
#[inline]
pub fn stereo_calibrate_2_def(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points1: &impl ToInputArray, image_points2: &impl ToInputArray, k1: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, d1: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, k2: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, d2: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, image_size: core::Size, r: &mut impl ToOutputArray, t: &mut impl ToOutputArray, rvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<f64> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points1);
input_array_arg!(image_points2);
input_output_array_arg!(k1);
input_output_array_arg!(d1);
input_output_array_arg!(k2);
input_output_array_arg!(d2);
output_array_arg!(r);
output_array_arg!(t);
output_array_arg!(rvecs);
output_array_arg!(tvecs);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_stereoCalibrate_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_Size_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points1.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points2.as_raw__InputArray(), k1.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), d1.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), k2.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), d2.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), &image_size, r.as_raw__OutputArray(), t.as_raw__OutputArray(), rvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Performs stereo calibration
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Vector of vectors of the calibration pattern points.
/// * imagePoints1: Vector of vectors of the projections of the calibration pattern points,
/// observed by the first camera.
/// * imagePoints2: Vector of vectors of the projections of the calibration pattern points,
/// observed by the second camera.
/// * K1: Input/output first camera intrinsic matrix:
///  , 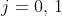 . If
/// any of [fisheye::CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] , [fisheye::CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC] are specified,
/// some or all of the matrix components must be initialized.
/// * D1: Input/output vector of distortion coefficients  of 4 elements.
/// * K2: Input/output second camera intrinsic matrix. The parameter is similar to K1 .
/// * D2: Input/output lens distortion coefficients for the second camera. The parameter is
/// similar to D1 .
/// * imageSize: Size of the image used only to initialize camera intrinsic matrix.
/// * R: Output rotation matrix between the 1st and the 2nd camera coordinate systems.
/// * T: Output translation vector between the coordinate systems of the cameras.
/// * rvecs: Output vector of rotation vectors ( [Rodrigues] ) estimated for each pattern view in the
/// coordinate system of the first camera of the stereo pair (e.g. std::vector<cv::Mat>). More in detail, each
/// i-th rotation vector together with the corresponding i-th translation vector (see the next output parameter
/// description) brings the calibration pattern from the object coordinate space (in which object points are
/// specified) to the camera coordinate space of the first camera of the stereo pair. In more technical terms,
/// the tuple of the i-th rotation and translation vector performs a change of basis from object coordinate space
/// to camera coordinate space of the first camera of the stereo pair.
/// * tvecs: Output vector of translation vectors estimated for each pattern view, see parameter description
/// of previous output parameter ( rvecs ).
/// * flags: Different flags that may be zero or a combination of the following values:
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC] Fix K1, K2? and D1, D2? so that only R, T matrices
/// are estimated.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] K1, K2 contains valid initial values of
/// fx, fy, cx, cy that are optimized further. Otherwise, (cx, cy) is initially set to the image
/// center (imageSize is used), and focal distances are computed in a least-squares fashion.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_RECOMPUTE_EXTRINSIC] Extrinsic will be recomputed after each iteration
/// of intrinsic optimization.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_CHECK_COND] The functions will check validity of condition number.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_FIX_SKEW] Skew coefficient (alpha) is set to zero and stay zero.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_FIX_K1],..., [fisheye::CALIB_FIX_K4] Selected distortion coefficients are set to zeros and stay
/// zero.
/// * criteria: Termination criteria for the iterative optimization algorithm.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: fisheye::CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,100,DBL_EPSILON)
#[inline]
pub fn stereo_calibrate_2(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points1: &impl ToInputArray, image_points2: &impl ToInputArray, k1: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, d1: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, k2: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, d2: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, image_size: core::Size, r: &mut impl ToOutputArray, t: &mut impl ToOutputArray, rvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, flags: i32, criteria: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<f64> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points1);
input_array_arg!(image_points2);
input_output_array_arg!(k1);
input_output_array_arg!(d1);
input_output_array_arg!(k2);
input_output_array_arg!(d2);
output_array_arg!(r);
output_array_arg!(t);
output_array_arg!(rvecs);
output_array_arg!(tvecs);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_stereoCalibrate_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_Size_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_TermCriteria(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points1.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points2.as_raw__InputArray(), k1.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), d1.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), k2.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), d2.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), &image_size, r.as_raw__OutputArray(), t.as_raw__OutputArray(), rvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, &criteria, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Performs stereo calibration
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Vector of vectors of the calibration pattern points.
/// * imagePoints1: Vector of vectors of the projections of the calibration pattern points,
/// observed by the first camera.
/// * imagePoints2: Vector of vectors of the projections of the calibration pattern points,
/// observed by the second camera.
/// * K1: Input/output first camera intrinsic matrix:
///  , 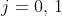 . If
/// any of [fisheye::CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] , [fisheye::CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC] are specified,
/// some or all of the matrix components must be initialized.
/// * D1: Input/output vector of distortion coefficients  of 4 elements.
/// * K2: Input/output second camera intrinsic matrix. The parameter is similar to K1 .
/// * D2: Input/output lens distortion coefficients for the second camera. The parameter is
/// similar to D1 .
/// * imageSize: Size of the image used only to initialize camera intrinsic matrix.
/// * R: Output rotation matrix between the 1st and the 2nd camera coordinate systems.
/// * T: Output translation vector between the coordinate systems of the cameras.
/// * rvecs: Output vector of rotation vectors ( [Rodrigues] ) estimated for each pattern view in the
/// coordinate system of the first camera of the stereo pair (e.g. std::vector<cv::Mat>). More in detail, each
/// i-th rotation vector together with the corresponding i-th translation vector (see the next output parameter
/// description) brings the calibration pattern from the object coordinate space (in which object points are
/// specified) to the camera coordinate space of the first camera of the stereo pair. In more technical terms,
/// the tuple of the i-th rotation and translation vector performs a change of basis from object coordinate space
/// to camera coordinate space of the first camera of the stereo pair.
/// * tvecs: Output vector of translation vectors estimated for each pattern view, see parameter description
/// of previous output parameter ( rvecs ).
/// * flags: Different flags that may be zero or a combination of the following values:
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC] Fix K1, K2? and D1, D2? so that only R, T matrices
/// are estimated.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] K1, K2 contains valid initial values of
/// fx, fy, cx, cy that are optimized further. Otherwise, (cx, cy) is initially set to the image
/// center (imageSize is used), and focal distances are computed in a least-squares fashion.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_RECOMPUTE_EXTRINSIC] Extrinsic will be recomputed after each iteration
/// of intrinsic optimization.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_CHECK_COND] The functions will check validity of condition number.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_FIX_SKEW] Skew coefficient (alpha) is set to zero and stay zero.
/// * [fisheye::CALIB_FIX_K1],..., [fisheye::CALIB_FIX_K4] Selected distortion coefficients are set to zeros and stay
/// zero.
/// * criteria: Termination criteria for the iterative optimization algorithm.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: fisheye::CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,100,DBL_EPSILON)
#[inline]
pub fn fisheye_stereo_calibrate(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points1: &impl ToInputArray, image_points2: &impl ToInputArray, k1: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, d1: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, k2: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, d2: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, image_size: core::Size, r: &mut impl ToOutputArray, t: &mut impl ToOutputArray, flags: i32, criteria: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<f64> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points1);
input_array_arg!(image_points2);
input_output_array_arg!(k1);
input_output_array_arg!(d1);
input_output_array_arg!(k2);
input_output_array_arg!(d2);
output_array_arg!(r);
output_array_arg!(t);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_stereoCalibrate_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_Size_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_TermCriteria(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points1.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points2.as_raw__InputArray(), k1.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), d1.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), k2.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), d2.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), &image_size, r.as_raw__OutputArray(), t.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, &criteria, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Stereo rectification for fisheye camera model
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * K1: First camera intrinsic matrix.
/// * D1: First camera distortion parameters.
/// * K2: Second camera intrinsic matrix.
/// * D2: Second camera distortion parameters.
/// * imageSize: Size of the image used for stereo calibration.
/// * R: Rotation matrix between the coordinate systems of the first and the second
/// cameras.
/// * tvec: Translation vector between coordinate systems of the cameras.
/// * R1: Output 3x3 rectification transform (rotation matrix) for the first camera.
/// * R2: Output 3x3 rectification transform (rotation matrix) for the second camera.
/// * P1: Output 3x4 projection matrix in the new (rectified) coordinate systems for the first
/// camera.
/// * P2: Output 3x4 projection matrix in the new (rectified) coordinate systems for the second
/// camera.
/// * Q: Output  disparity-to-depth mapping matrix (see [reproject_image_to_3d] ).
/// * flags: Operation flags that may be zero or [fisheye::CALIB_ZERO_DISPARITY] . If the flag is set,
/// the function makes the principal points of each camera have the same pixel coordinates in the
/// rectified views. And if the flag is not set, the function may still shift the images in the
/// horizontal or vertical direction (depending on the orientation of epipolar lines) to maximize the
/// useful image area.
/// * newImageSize: New image resolution after rectification. The same size should be passed to
/// [init_undistort_rectify_map] (see the stereo_calib.cpp sample in OpenCV samples directory). When (0,0)
/// is passed (default), it is set to the original imageSize . Setting it to larger value can help you
/// preserve details in the original image, especially when there is a big radial distortion.
/// * balance: Sets the new focal length in range between the min focal length and the max focal
/// length. Balance is in range of [0, 1].
/// * fov_scale: Divisor for new focal length.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [fisheye_stereo_rectify] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * new_image_size: Size()
/// * balance: 0.0
/// * fov_scale: 1.0
#[inline]
pub fn fisheye_stereo_rectify_def(k1: &impl ToInputArray, d1: &impl ToInputArray, k2: &impl ToInputArray, d2: &impl ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, r: &impl ToInputArray, tvec: &impl ToInputArray, r1: &mut impl ToOutputArray, r2: &mut impl ToOutputArray, p1: &mut impl ToOutputArray, p2: &mut impl ToOutputArray, q: &mut impl ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(k1);
input_array_arg!(d1);
input_array_arg!(k2);
input_array_arg!(d2);
input_array_arg!(r);
input_array_arg!(tvec);
output_array_arg!(r1);
output_array_arg!(r2);
output_array_arg!(p1);
output_array_arg!(p2);
output_array_arg!(q);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_stereoRectify_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const_SizeR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(k1.as_raw__InputArray(), d1.as_raw__InputArray(), k2.as_raw__InputArray(), d2.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, r.as_raw__InputArray(), tvec.as_raw__InputArray(), r1.as_raw__OutputArray(), r2.as_raw__OutputArray(), p1.as_raw__OutputArray(), p2.as_raw__OutputArray(), q.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Stereo rectification for fisheye camera model
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * K1: First camera intrinsic matrix.
/// * D1: First camera distortion parameters.
/// * K2: Second camera intrinsic matrix.
/// * D2: Second camera distortion parameters.
/// * imageSize: Size of the image used for stereo calibration.
/// * R: Rotation matrix between the coordinate systems of the first and the second
/// cameras.
/// * tvec: Translation vector between coordinate systems of the cameras.
/// * R1: Output 3x3 rectification transform (rotation matrix) for the first camera.
/// * R2: Output 3x3 rectification transform (rotation matrix) for the second camera.
/// * P1: Output 3x4 projection matrix in the new (rectified) coordinate systems for the first
/// camera.
/// * P2: Output 3x4 projection matrix in the new (rectified) coordinate systems for the second
/// camera.
/// * Q: Output 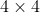 disparity-to-depth mapping matrix (see [reproject_image_to_3d] ).
/// * flags: Operation flags that may be zero or [fisheye::CALIB_ZERO_DISPARITY] . If the flag is set,
/// the function makes the principal points of each camera have the same pixel coordinates in the
/// rectified views. And if the flag is not set, the function may still shift the images in the
/// horizontal or vertical direction (depending on the orientation of epipolar lines) to maximize the
/// useful image area.
/// * newImageSize: New image resolution after rectification. The same size should be passed to
/// [init_undistort_rectify_map] (see the stereo_calib.cpp sample in OpenCV samples directory). When (0,0)
/// is passed (default), it is set to the original imageSize . Setting it to larger value can help you
/// preserve details in the original image, especially when there is a big radial distortion.
/// * balance: Sets the new focal length in range between the min focal length and the max focal
/// length. Balance is in range of [0, 1].
/// * fov_scale: Divisor for new focal length.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * new_image_size: Size()
/// * balance: 0.0
/// * fov_scale: 1.0
#[inline]
pub fn fisheye_stereo_rectify(k1: &impl ToInputArray, d1: &impl ToInputArray, k2: &impl ToInputArray, d2: &impl ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, r: &impl ToInputArray, tvec: &impl ToInputArray, r1: &mut impl ToOutputArray, r2: &mut impl ToOutputArray, p1: &mut impl ToOutputArray, p2: &mut impl ToOutputArray, q: &mut impl ToOutputArray, flags: i32, new_image_size: core::Size, balance: f64, fov_scale: f64) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(k1);
input_array_arg!(d1);
input_array_arg!(k2);
input_array_arg!(d2);
input_array_arg!(r);
input_array_arg!(tvec);
output_array_arg!(r1);
output_array_arg!(r2);
output_array_arg!(p1);
output_array_arg!(p2);
output_array_arg!(q);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_stereoRectify_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const_SizeR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_const_SizeR_double_double(k1.as_raw__InputArray(), d1.as_raw__InputArray(), k2.as_raw__InputArray(), d2.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, r.as_raw__InputArray(), tvec.as_raw__InputArray(), r1.as_raw__OutputArray(), r2.as_raw__OutputArray(), p1.as_raw__OutputArray(), p2.as_raw__OutputArray(), q.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, &new_image_size, balance, fov_scale, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Transforms an image to compensate for fisheye lens distortion.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * distorted: image with fisheye lens distortion.
/// * undistorted: Output image with compensated fisheye lens distortion.
/// * K: Camera intrinsic matrix .
/// * D: Input vector of distortion coefficients .
/// * Knew: Camera intrinsic matrix of the distorted image. By default, it is the identity matrix but you
/// may additionally scale and shift the result by using a different matrix.
/// * new_size: the new size
///
/// The function transforms an image to compensate radial and tangential lens distortion.
///
/// The function is simply a combination of #fisheye::initUndistortRectifyMap (with unity R ) and [remap]
/// (with bilinear interpolation). See the former function for details of the transformation being
/// performed.
///
/// See below the results of undistortImage.
/// * a\) result of undistort of perspective camera model (all possible coefficients (k_1, k_2, k_3,
/// k_4, k_5, k_6) of distortion were optimized under calibration)
/// * b\) result of #fisheye::undistortImage of fisheye camera model (all possible coefficients (k_1, k_2,
/// k_3, k_4) of fisheye distortion were optimized under calibration)
/// * c\) original image was captured with fisheye lens
///
/// Pictures a) and b) almost the same. But if we consider points of image located far from the center
/// of image, we can notice that on image a) these points are distorted.
///
/// 
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [fisheye_undistort_image] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * knew: cv::noArray()
/// * new_size: Size()
#[inline]
pub fn fisheye_undistort_image_def(distorted: &impl ToInputArray, undistorted: &mut impl ToOutputArray, k: &impl ToInputArray, d: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(distorted);
output_array_arg!(undistorted);
input_array_arg!(k);
input_array_arg!(d);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_undistortImage_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(distorted.as_raw__InputArray(), undistorted.as_raw__OutputArray(), k.as_raw__InputArray(), d.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Transforms an image to compensate for fisheye lens distortion.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * distorted: image with fisheye lens distortion.
/// * undistorted: Output image with compensated fisheye lens distortion.
/// * K: Camera intrinsic matrix .
/// * D: Input vector of distortion coefficients .
/// * Knew: Camera intrinsic matrix of the distorted image. By default, it is the identity matrix but you
/// may additionally scale and shift the result by using a different matrix.
/// * new_size: the new size
///
/// The function transforms an image to compensate radial and tangential lens distortion.
///
/// The function is simply a combination of #fisheye::initUndistortRectifyMap (with unity R ) and [remap]
/// (with bilinear interpolation). See the former function for details of the transformation being
/// performed.
///
/// See below the results of undistortImage.
/// * a\) result of undistort of perspective camera model (all possible coefficients (k_1, k_2, k_3,
/// k_4, k_5, k_6) of distortion were optimized under calibration)
/// * b\) result of #fisheye::undistortImage of fisheye camera model (all possible coefficients (k_1, k_2,
/// k_3, k_4) of fisheye distortion were optimized under calibration)
/// * c\) original image was captured with fisheye lens
///
/// Pictures a) and b) almost the same. But if we consider points of image located far from the center
/// of image, we can notice that on image a) these points are distorted.
///
/// 
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * knew: cv::noArray()
/// * new_size: Size()
#[inline]
pub fn fisheye_undistort_image(distorted: &impl ToInputArray, undistorted: &mut impl ToOutputArray, k: &impl ToInputArray, d: &impl ToInputArray, knew: &impl ToInputArray, new_size: core::Size) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(distorted);
output_array_arg!(undistorted);
input_array_arg!(k);
input_array_arg!(d);
input_array_arg!(knew);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_undistortImage_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const_SizeR(distorted.as_raw__InputArray(), undistorted.as_raw__OutputArray(), k.as_raw__InputArray(), d.as_raw__InputArray(), knew.as_raw__InputArray(), &new_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Undistorts 2D points using fisheye model
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * distorted: Array of object points, 1xN/Nx1 2-channel (or vector\<Point2f\> ), where N is the
/// number of points in the view.
/// * K: Camera intrinsic matrix .
/// * D: Input vector of distortion coefficients .
/// * R: Rectification transformation in the object space: 3x3 1-channel, or vector: 3x1/1x3
/// 1-channel or 1x1 3-channel
/// * P: New camera intrinsic matrix (3x3) or new projection matrix (3x4)
/// * criteria: Termination criteria
/// * undistorted: Output array of image points, 1xN/Nx1 2-channel, or vector\<Point2f\> .
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [fisheye_undistort_points] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * r: noArray()
/// * p: noArray()
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::MAX_ITER+TermCriteria::EPS,10,1e-8)
#[inline]
pub fn fisheye_undistort_points_def(distorted: &impl ToInputArray, undistorted: &mut impl ToOutputArray, k: &impl ToInputArray, d: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(distorted);
output_array_arg!(undistorted);
input_array_arg!(k);
input_array_arg!(d);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_undistortPoints_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(distorted.as_raw__InputArray(), undistorted.as_raw__OutputArray(), k.as_raw__InputArray(), d.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Undistorts 2D points using fisheye model
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * distorted: Array of object points, 1xN/Nx1 2-channel (or vector\<Point2f\> ), where N is the
/// number of points in the view.
/// * K: Camera intrinsic matrix .
/// * D: Input vector of distortion coefficients .
/// * R: Rectification transformation in the object space: 3x3 1-channel, or vector: 3x1/1x3
/// 1-channel or 1x1 3-channel
/// * P: New camera intrinsic matrix (3x3) or new projection matrix (3x4)
/// * criteria: Termination criteria
/// * undistorted: Output array of image points, 1xN/Nx1 2-channel, or vector\<Point2f\> .
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * r: noArray()
/// * p: noArray()
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::MAX_ITER+TermCriteria::EPS,10,1e-8)
#[inline]
pub fn fisheye_undistort_points(distorted: &impl ToInputArray, undistorted: &mut impl ToOutputArray, k: &impl ToInputArray, d: &impl ToInputArray, r: &impl ToInputArray, p: &impl ToInputArray, criteria: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(distorted);
output_array_arg!(undistorted);
input_array_arg!(k);
input_array_arg!(d);
input_array_arg!(r);
input_array_arg!(p);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_undistortPoints_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_TermCriteria(distorted.as_raw__InputArray(), undistorted.as_raw__OutputArray(), k.as_raw__InputArray(), d.as_raw__InputArray(), r.as_raw__InputArray(), p.as_raw__InputArray(), &criteria, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the default new camera matrix.
///
/// The function returns the camera matrix that is either an exact copy of the input cameraMatrix (when
/// centerPrinicipalPoint=false ), or the modified one (when centerPrincipalPoint=true).
///
/// In the latter case, the new camera matrix will be:
///
/// 
///
/// where  and  are 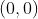 and 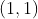 elements of cameraMatrix, respectively.
///
/// By default, the undistortion functions in OpenCV (see #initUndistortRectifyMap, #undistort) do not
/// move the principal point. However, when you work with stereo, it is important to move the principal
/// points in both views to the same y-coordinate (which is required by most of stereo correspondence
/// algorithms), and may be to the same x-coordinate too. So, you can form the new camera matrix for
/// each view where the principal points are located at the center.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * cameraMatrix: Input camera matrix.
/// * imgsize: Camera view image size in pixels.
/// * centerPrincipalPoint: Location of the principal point in the new camera matrix. The
/// parameter indicates whether this location should be at the image center or not.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [get_default_new_camera_matrix] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * imgsize: Size()
/// * center_principal_point: false
#[inline]
pub fn get_default_new_camera_matrix_def(camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_getDefaultNewCameraMatrix_const__InputArrayR(camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the default new camera matrix.
///
/// The function returns the camera matrix that is either an exact copy of the input cameraMatrix (when
/// centerPrinicipalPoint=false ), or the modified one (when centerPrincipalPoint=true).
///
/// In the latter case, the new camera matrix will be:
///
/// 
///
/// where  and  are 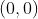 and 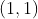 elements of cameraMatrix, respectively.
///
/// By default, the undistortion functions in OpenCV (see #initUndistortRectifyMap, #undistort) do not
/// move the principal point. However, when you work with stereo, it is important to move the principal
/// points in both views to the same y-coordinate (which is required by most of stereo correspondence
/// algorithms), and may be to the same x-coordinate too. So, you can form the new camera matrix for
/// each view where the principal points are located at the center.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * cameraMatrix: Input camera matrix.
/// * imgsize: Camera view image size in pixels.
/// * centerPrincipalPoint: Location of the principal point in the new camera matrix. The
/// parameter indicates whether this location should be at the image center or not.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * imgsize: Size()
/// * center_principal_point: false
#[inline]
pub fn get_default_new_camera_matrix(camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, imgsize: core::Size, center_principal_point: bool) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_getDefaultNewCameraMatrix_const__InputArrayR_Size_bool(camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), &imgsize, center_principal_point, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the new camera intrinsic matrix based on the free scaling parameter.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * cameraMatrix: Input camera intrinsic matrix.
/// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients
/// . If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are
/// assumed.
/// * imageSize: Original image size.
/// * alpha: Free scaling parameter between 0 (when all the pixels in the undistorted image are
/// valid) and 1 (when all the source image pixels are retained in the undistorted image). See
/// [stereo_rectify] for details.
/// * newImgSize: Image size after rectification. By default, it is set to imageSize .
/// * validPixROI: Optional output rectangle that outlines all-good-pixels region in the
/// undistorted image. See roi1, roi2 description in [stereo_rectify] .
/// * centerPrincipalPoint: Optional flag that indicates whether in the new camera intrinsic matrix the
/// principal point should be at the image center or not. By default, the principal point is chosen to
/// best fit a subset of the source image (determined by alpha) to the corrected image.
/// ## Returns
/// new_camera_matrix Output new camera intrinsic matrix.
///
/// The function computes and returns the optimal new camera intrinsic matrix based on the free scaling parameter.
/// By varying this parameter, you may retrieve only sensible pixels alpha=0 , keep all the original
/// image pixels if there is valuable information in the corners alpha=1 , or get something in between.
/// When alpha\>0 , the undistorted result is likely to have some black pixels corresponding to
/// "virtual" pixels outside of the captured distorted image. The original camera intrinsic matrix, distortion
/// coefficients, the computed new camera intrinsic matrix, and newImageSize should be passed to
/// [init_undistort_rectify_map] to produce the maps for [remap] .
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [get_optimal_new_camera_matrix] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * new_img_size: Size()
/// * valid_pix_roi: 0
/// * center_principal_point: false
#[inline]
pub fn get_optimal_new_camera_matrix_def(camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, alpha: f64) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_getOptimalNewCameraMatrix_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_double(camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, alpha, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the new camera intrinsic matrix based on the free scaling parameter.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * cameraMatrix: Input camera intrinsic matrix.
/// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients
/// . If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are
/// assumed.
/// * imageSize: Original image size.
/// * alpha: Free scaling parameter between 0 (when all the pixels in the undistorted image are
/// valid) and 1 (when all the source image pixels are retained in the undistorted image). See
/// [stereo_rectify] for details.
/// * newImgSize: Image size after rectification. By default, it is set to imageSize .
/// * validPixROI: Optional output rectangle that outlines all-good-pixels region in the
/// undistorted image. See roi1, roi2 description in [stereo_rectify] .
/// * centerPrincipalPoint: Optional flag that indicates whether in the new camera intrinsic matrix the
/// principal point should be at the image center or not. By default, the principal point is chosen to
/// best fit a subset of the source image (determined by alpha) to the corrected image.
/// ## Returns
/// new_camera_matrix Output new camera intrinsic matrix.
///
/// The function computes and returns the optimal new camera intrinsic matrix based on the free scaling parameter.
/// By varying this parameter, you may retrieve only sensible pixels alpha=0 , keep all the original
/// image pixels if there is valuable information in the corners alpha=1 , or get something in between.
/// When alpha\>0 , the undistorted result is likely to have some black pixels corresponding to
/// "virtual" pixels outside of the captured distorted image. The original camera intrinsic matrix, distortion
/// coefficients, the computed new camera intrinsic matrix, and newImageSize should be passed to
/// [init_undistort_rectify_map] to produce the maps for [remap] .
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * new_img_size: Size()
/// * valid_pix_roi: 0
/// * center_principal_point: false
#[inline]
pub fn get_optimal_new_camera_matrix(camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, alpha: f64, new_img_size: core::Size, valid_pix_roi: Option<&mut core::Rect>, center_principal_point: bool) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_getOptimalNewCameraMatrix_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_double_Size_RectX_bool(camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, alpha, &new_img_size, valid_pix_roi.map_or(::core::ptr::null_mut(), |valid_pix_roi| valid_pix_roi), center_principal_point, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// computes valid disparity ROI from the valid ROIs of the rectified images (that are returned by #stereoRectify)
#[inline]
pub fn get_valid_disparity_roi(roi1: core::Rect, roi2: core::Rect, min_disparity: i32, number_of_disparities: i32, block_size: i32) -> Result<core::Rect> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_getValidDisparityROI_Rect_Rect_int_int_int(&roi1, &roi2, min_disparity, number_of_disparities, block_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds an initial camera intrinsic matrix from 3D-2D point correspondences.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Vector of vectors of the calibration pattern points in the calibration pattern
/// coordinate space. In the old interface all the per-view vectors are concatenated. See
/// [calibrate_camera] for details.
/// * imagePoints: Vector of vectors of the projections of the calibration pattern points. In the
/// old interface all the per-view vectors are concatenated.
/// * imageSize: Image size in pixels used to initialize the principal point.
/// * aspectRatio: If it is zero or negative, both  and  are estimated independently.
/// Otherwise,  .
///
/// The function estimates and returns an initial camera intrinsic matrix for the camera calibration process.
/// Currently, the function only supports planar calibration patterns, which are patterns where each
/// object point has z-coordinate =0.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [init_camera_matrix_2d] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * aspect_ratio: 1.0
#[inline]
pub fn init_camera_matrix_2d_def(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_initCameraMatrix2D_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds an initial camera intrinsic matrix from 3D-2D point correspondences.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Vector of vectors of the calibration pattern points in the calibration pattern
/// coordinate space. In the old interface all the per-view vectors are concatenated. See
/// [calibrate_camera] for details.
/// * imagePoints: Vector of vectors of the projections of the calibration pattern points. In the
/// old interface all the per-view vectors are concatenated.
/// * imageSize: Image size in pixels used to initialize the principal point.
/// * aspectRatio: If it is zero or negative, both  and  are estimated independently.
/// Otherwise,  .
///
/// The function estimates and returns an initial camera intrinsic matrix for the camera calibration process.
/// Currently, the function only supports planar calibration patterns, which are patterns where each
/// object point has z-coordinate =0.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * aspect_ratio: 1.0
#[inline]
pub fn init_camera_matrix_2d(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, aspect_ratio: f64) -> Result<core::Mat> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_initCameraMatrix2D_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_double(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, aspect_ratio, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes the projection and inverse-rectification transformation map. In essense, this is the inverse of
/// [init_undistort_rectify_map] to accomodate stereo-rectification of projectors ('inverse-cameras') in projector-camera pairs.
///
/// The function computes the joint projection and inverse rectification transformation and represents the
/// result in the form of maps for #remap. The projected image looks like a distorted version of the original which,
/// once projected by a projector, should visually match the original. In case of a monocular camera, newCameraMatrix
/// is usually equal to cameraMatrix, or it can be computed by
/// [get_optimal_new_camera_matrix] for a better control over scaling. In case of a projector-camera pair,
/// newCameraMatrix is normally set to P1 or P2 computed by [stereo_rectify] .
///
/// The projector is oriented differently in the coordinate space, according to R. In case of projector-camera pairs,
/// this helps align the projector (in the same manner as [init_undistort_rectify_map] for the camera) to create a stereo-rectified pair. This
/// allows epipolar lines on both images to become horizontal and have the same y-coordinate (in case of a horizontally aligned projector-camera pair).
///
/// The function builds the maps for the inverse mapping algorithm that is used by #remap. That
/// is, for each pixel 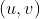 in the destination (projected and inverse-rectified) image, the function
/// computes the corresponding coordinates in the source image (that is, in the original digital image). The following process is applied:
///
/// 
/// where 
/// are the distortion coefficients vector distCoeffs.
///
/// In case of a stereo-rectified projector-camera pair, this function is called for the projector while [init_undistort_rectify_map] is called for the camera head.
/// This is done after #stereoRectify, which in turn is called after #stereoCalibrate. If the projector-camera pair
/// is not calibrated, it is still possible to compute the rectification transformations directly from
/// the fundamental matrix using #stereoRectifyUncalibrated. For the projector and camera, the function computes
/// homography H as the rectification transformation in a pixel domain, not a rotation matrix R in 3D
/// space. R can be computed from H as
/// 
/// where cameraMatrix can be chosen arbitrarily.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * cameraMatrix: Input camera matrix  .
/// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients
/// 
/// of 4, 5, 8, 12 or 14 elements. If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed.
/// * R: Optional rectification transformation in the object space (3x3 matrix). R1 or R2,
/// computed by [stereo_rectify] can be passed here. If the matrix is empty, the identity transformation
/// is assumed.
/// * newCameraMatrix: New camera matrix .
/// * size: Distorted image size.
/// * m1type: Type of the first output map. Can be CV_32FC1, CV_32FC2 or CV_16SC2, see [convert_maps]
/// * map1: The first output map for #remap.
/// * map2: The second output map for #remap.
#[inline]
pub fn init_inverse_rectification_map(camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, r: &impl ToInputArray, new_camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, size: core::Size, m1type: i32, map1: &mut impl ToOutputArray, map2: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
input_array_arg!(r);
input_array_arg!(new_camera_matrix);
output_array_arg!(map1);
output_array_arg!(map2);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_initInverseRectificationMap_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const_SizeR_int_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), r.as_raw__InputArray(), new_camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), &size, m1type, map1.as_raw__OutputArray(), map2.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes the undistortion and rectification transformation map.
///
/// The function computes the joint undistortion and rectification transformation and represents the
/// result in the form of maps for #remap. The undistorted image looks like original, as if it is
/// captured with a camera using the camera matrix =newCameraMatrix and zero distortion. In case of a
/// monocular camera, newCameraMatrix is usually equal to cameraMatrix, or it can be computed by
/// [get_optimal_new_camera_matrix] for a better control over scaling. In case of a stereo camera,
/// newCameraMatrix is normally set to P1 or P2 computed by [stereo_rectify] .
///
/// Also, this new camera is oriented differently in the coordinate space, according to R. That, for
/// example, helps to align two heads of a stereo camera so that the epipolar lines on both images
/// become horizontal and have the same y- coordinate (in case of a horizontally aligned stereo camera).
///
/// The function actually builds the maps for the inverse mapping algorithm that is used by #remap. That
/// is, for each pixel 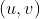 in the destination (corrected and rectified) image, the function
/// computes the corresponding coordinates in the source image (that is, in the original image from
/// camera). The following process is applied:
/// 
/// where 
/// are the distortion coefficients.
///
/// In case of a stereo camera, this function is called twice: once for each camera head, after
/// #stereoRectify, which in its turn is called after #stereoCalibrate. But if the stereo camera
/// was not calibrated, it is still possible to compute the rectification transformations directly from
/// the fundamental matrix using #stereoRectifyUncalibrated. For each camera, the function computes
/// homography H as the rectification transformation in a pixel domain, not a rotation matrix R in 3D
/// space. R can be computed from H as
/// 
/// where cameraMatrix can be chosen arbitrarily.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * cameraMatrix: Input camera matrix  .
/// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients
/// 
/// of 4, 5, 8, 12 or 14 elements. If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed.
/// * R: Optional rectification transformation in the object space (3x3 matrix). R1 or R2 ,
/// computed by [stereo_rectify] can be passed here. If the matrix is empty, the identity transformation
/// is assumed. In [init_undistort_rectify_map] R assumed to be an identity matrix.
/// * newCameraMatrix: New camera matrix .
/// * size: Undistorted image size.
/// * m1type: Type of the first output map that can be CV_32FC1, CV_32FC2 or CV_16SC2, see [convert_maps]
/// * map1: The first output map.
/// * map2: The second output map.
#[inline]
pub fn init_undistort_rectify_map(camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, r: &impl ToInputArray, new_camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, size: core::Size, m1type: i32, map1: &mut impl ToOutputArray, map2: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
input_array_arg!(r);
input_array_arg!(new_camera_matrix);
output_array_arg!(map1);
output_array_arg!(map2);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_initUndistortRectifyMap_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_int_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), r.as_raw__InputArray(), new_camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), &size, m1type, map1.as_raw__OutputArray(), map2.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// initializes maps for [remap] for wide-angle
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [init_wide_angle_proj_map] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * proj_type: PROJ_SPHERICAL_EQRECT
/// * alpha: 0
#[inline]
pub fn init_wide_angle_proj_map_def(camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, dest_image_width: i32, m1type: i32, map1: &mut impl ToOutputArray, map2: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<f32> {
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
output_array_arg!(map1);
output_array_arg!(map2);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_initWideAngleProjMap_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_int_int_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, dest_image_width, m1type, map1.as_raw__OutputArray(), map2.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// initializes maps for [remap] for wide-angle
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * proj_type: PROJ_SPHERICAL_EQRECT
/// * alpha: 0
#[inline]
pub fn init_wide_angle_proj_map(camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, dest_image_width: i32, m1type: i32, map1: &mut impl ToOutputArray, map2: &mut impl ToOutputArray, proj_type: crate::calib3d::UndistortTypes, alpha: f64) -> Result<f32> {
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
output_array_arg!(map1);
output_array_arg!(map2);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_initWideAngleProjMap_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_int_int_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_UndistortTypes_double(camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, dest_image_width, m1type, map1.as_raw__OutputArray(), map2.as_raw__OutputArray(), proj_type, alpha, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes partial derivatives of the matrix product for each multiplied matrix.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * A: First multiplied matrix.
/// * B: Second multiplied matrix.
/// * dABdA: First output derivative matrix d(A\*B)/dA of size
///  .
/// * dABdB: Second output derivative matrix d(A\*B)/dB of size
///  .
///
/// The function computes partial derivatives of the elements of the matrix product  with regard to
/// the elements of each of the two input matrices. The function is used to compute the Jacobian
/// matrices in [stereo_calibrate] but can also be used in any other similar optimization function.
#[inline]
pub fn mat_mul_deriv(a: &impl ToInputArray, b: &impl ToInputArray, d_a_bd_a: &mut impl ToOutputArray, d_a_bd_b: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(a);
input_array_arg!(b);
output_array_arg!(d_a_bd_a);
output_array_arg!(d_a_bd_b);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_matMulDeriv_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(a.as_raw__InputArray(), b.as_raw__InputArray(), d_a_bd_a.as_raw__OutputArray(), d_a_bd_b.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Projects 3D points to an image plane.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Array of object points expressed wrt. the world coordinate frame. A 3xN/Nx3
/// 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 3-channel (or vector\<Point3f\> ), where N is the number of points in the view.
/// * rvec: The rotation vector ([Rodrigues]) that, together with tvec, performs a change of
/// basis from world to camera coordinate system, see [calibrateCamera] for details.
/// * tvec: The translation vector, see parameter description above.
/// * cameraMatrix: Camera intrinsic matrix  .
/// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients
///  . If the vector is empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed.
/// * imagePoints: Output array of image points, 1xN/Nx1 2-channel, or
/// vector\<Point2f\> .
/// * jacobian: Optional output 2Nx(10+\<numDistCoeffs\>) jacobian matrix of derivatives of image
/// points with respect to components of the rotation vector, translation vector, focal lengths,
/// coordinates of the principal point and the distortion coefficients. In the old interface different
/// components of the jacobian are returned via different output parameters.
/// * aspectRatio: Optional "fixed aspect ratio" parameter. If the parameter is not 0, the
/// function assumes that the aspect ratio () is fixed and correspondingly adjusts the
/// jacobian matrix.
///
/// The function computes the 2D projections of 3D points to the image plane, given intrinsic and
/// extrinsic camera parameters. Optionally, the function computes Jacobians -matrices of partial
/// derivatives of image points coordinates (as functions of all the input parameters) with respect to
/// the particular parameters, intrinsic and/or extrinsic. The Jacobians are used during the global
/// optimization in [calibrateCamera], [solvePnP], and [stereoCalibrate]. The function itself
/// can also be used to compute a re-projection error, given the current intrinsic and extrinsic
/// parameters.
///
///
/// Note: By setting rvec = tvec = , or by setting cameraMatrix to a 3x3 identity matrix,
/// or by passing zero distortion coefficients, one can get various useful partial cases of the
/// function. This means, one can compute the distorted coordinates for a sparse set of points or apply
/// a perspective transformation (and also compute the derivatives) in the ideal zero-distortion setup.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [project_points] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * jacobian: noArray()
/// * aspect_ratio: 0
#[inline]
pub fn project_points_def(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, rvec: &impl ToInputArray, tvec: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(rvec);
input_array_arg!(tvec);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
output_array_arg!(image_points);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_projectPoints_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec.as_raw__InputArray(), tvec.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Projects 3D points to an image plane.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Array of object points expressed wrt. the world coordinate frame. A 3xN/Nx3
/// 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 3-channel (or vector\<Point3f\> ), where N is the number of points in the view.
/// * rvec: The rotation vector ([Rodrigues]) that, together with tvec, performs a change of
/// basis from world to camera coordinate system, see [calibrateCamera] for details.
/// * tvec: The translation vector, see parameter description above.
/// * cameraMatrix: Camera intrinsic matrix  .
/// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients
///  . If the vector is empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed.
/// * imagePoints: Output array of image points, 1xN/Nx1 2-channel, or
/// vector\<Point2f\> .
/// * jacobian: Optional output 2Nx(10+\<numDistCoeffs\>) jacobian matrix of derivatives of image
/// points with respect to components of the rotation vector, translation vector, focal lengths,
/// coordinates of the principal point and the distortion coefficients. In the old interface different
/// components of the jacobian are returned via different output parameters.
/// * aspectRatio: Optional "fixed aspect ratio" parameter. If the parameter is not 0, the
/// function assumes that the aspect ratio () is fixed and correspondingly adjusts the
/// jacobian matrix.
///
/// The function computes the 2D projections of 3D points to the image plane, given intrinsic and
/// extrinsic camera parameters. Optionally, the function computes Jacobians -matrices of partial
/// derivatives of image points coordinates (as functions of all the input parameters) with respect to
/// the particular parameters, intrinsic and/or extrinsic. The Jacobians are used during the global
/// optimization in [calibrateCamera], [solvePnP], and [stereoCalibrate]. The function itself
/// can also be used to compute a re-projection error, given the current intrinsic and extrinsic
/// parameters.
///
///
/// Note: By setting rvec = tvec = , or by setting cameraMatrix to a 3x3 identity matrix,
/// or by passing zero distortion coefficients, one can get various useful partial cases of the
/// function. This means, one can compute the distorted coordinates for a sparse set of points or apply
/// a perspective transformation (and also compute the derivatives) in the ideal zero-distortion setup.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * jacobian: noArray()
/// * aspect_ratio: 0
#[inline]
pub fn project_points(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, rvec: &impl ToInputArray, tvec: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &mut impl ToOutputArray, jacobian: &mut impl ToOutputArray, aspect_ratio: f64) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(rvec);
input_array_arg!(tvec);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
output_array_arg!(image_points);
output_array_arg!(jacobian);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_projectPoints_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec.as_raw__InputArray(), tvec.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__OutputArray(), jacobian.as_raw__OutputArray(), aspect_ratio, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Recovers the relative camera rotation and the translation from corresponding points in two images from two different cameras, using cheirality check. Returns the number of
/// inliers that pass the check.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * points1: Array of N 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should be
/// floating-point (single or double precision).
/// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1 .
/// * cameraMatrix1: Input/output camera matrix for the first camera, the same as in
/// [calibrateCamera]. Furthermore, for the stereo case, additional flags may be used, see below.
/// * distCoeffs1: Input/output vector of distortion coefficients, the same as in
/// [calibrateCamera].
/// * cameraMatrix2: Input/output camera matrix for the first camera, the same as in
/// [calibrateCamera]. Furthermore, for the stereo case, additional flags may be used, see below.
/// * distCoeffs2: Input/output vector of distortion coefficients, the same as in
/// [calibrateCamera].
/// * E: The output essential matrix.
/// * R: Output rotation matrix. Together with the translation vector, this matrix makes up a tuple
/// that performs a change of basis from the first camera's coordinate system to the second camera's
/// coordinate system. Note that, in general, t can not be used for this tuple, see the parameter
/// described below.
/// * t: Output translation vector. This vector is obtained by [decomposeEssentialMat] and
/// therefore is only known up to scale, i.e. t is the direction of the translation vector and has unit
/// length.
/// * method: Method for computing an essential matrix.
/// * [RANSAC] for the RANSAC algorithm.
/// * [LMEDS] for the LMedS algorithm.
/// * prob: Parameter used for the RANSAC or LMedS methods only. It specifies a desirable level of
/// confidence (probability) that the estimated matrix is correct.
/// * threshold: Parameter used for RANSAC. It is the maximum distance from a point to an epipolar
/// line in pixels, beyond which the point is considered an outlier and is not used for computing the
/// final fundamental matrix. It can be set to something like 1-3, depending on the accuracy of the
/// point localization, image resolution, and the image noise.
/// * mask: Input/output mask for inliers in points1 and points2. If it is not empty, then it marks
/// inliers in points1 and points2 for then given essential matrix E. Only these inliers will be used to
/// recover pose. In the output mask only inliers which pass the cheirality check.
///
/// This function decomposes an essential matrix using [decomposeEssentialMat] and then verifies
/// possible pose hypotheses by doing cheirality check. The cheirality check means that the
/// triangulated 3D points should have positive depth. Some details can be found in [Nister03](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Nister03).
///
/// This function can be used to process the output E and mask from [findEssentialMat]. In this
/// scenario, points1 and points2 are the same input for findEssentialMat.:
/// ```C++
/// // Example. Estimation of fundamental matrix using the RANSAC algorithm
/// int point_count = 100;
/// vector<Point2f> points1(point_count);
/// vector<Point2f> points2(point_count);
///
/// // initialize the points here ...
/// for( int i = 0; i < point_count; i++ )
/// {
/// points1[i] = ...;
/// points2[i] = ...;
/// }
///
/// // Input: camera calibration of both cameras, for example using intrinsic chessboard calibration.
/// Mat cameraMatrix1, distCoeffs1, cameraMatrix2, distCoeffs2;
///
/// // Output: Essential matrix, relative rotation and relative translation.
/// Mat E, R, t, mask;
///
/// recoverPose(points1, points2, cameraMatrix1, distCoeffs1, cameraMatrix2, distCoeffs2, E, R, t, mask);
/// ```
///
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [recover_pose_2_cameras] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * method: cv::RANSAC
/// * prob: 0.999
/// * threshold: 1.0
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn recover_pose_2_cameras_def(points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix1: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs1: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix2: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs2: &impl ToInputArray, e: &mut impl ToOutputArray, r: &mut impl ToOutputArray, t: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<i32> {
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix1);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs1);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix2);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs2);
output_array_arg!(e);
output_array_arg!(r);
output_array_arg!(t);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_recoverPose_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix1.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs1.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix2.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs2.as_raw__InputArray(), e.as_raw__OutputArray(), r.as_raw__OutputArray(), t.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Recovers the relative camera rotation and the translation from corresponding points in two images from two different cameras, using cheirality check. Returns the number of
/// inliers that pass the check.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * points1: Array of N 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should be
/// floating-point (single or double precision).
/// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1 .
/// * cameraMatrix1: Input/output camera matrix for the first camera, the same as in
/// [calibrateCamera]. Furthermore, for the stereo case, additional flags may be used, see below.
/// * distCoeffs1: Input/output vector of distortion coefficients, the same as in
/// [calibrateCamera].
/// * cameraMatrix2: Input/output camera matrix for the first camera, the same as in
/// [calibrateCamera]. Furthermore, for the stereo case, additional flags may be used, see below.
/// * distCoeffs2: Input/output vector of distortion coefficients, the same as in
/// [calibrateCamera].
/// * E: The output essential matrix.
/// * R: Output rotation matrix. Together with the translation vector, this matrix makes up a tuple
/// that performs a change of basis from the first camera's coordinate system to the second camera's
/// coordinate system. Note that, in general, t can not be used for this tuple, see the parameter
/// described below.
/// * t: Output translation vector. This vector is obtained by [decomposeEssentialMat] and
/// therefore is only known up to scale, i.e. t is the direction of the translation vector and has unit
/// length.
/// * method: Method for computing an essential matrix.
/// * [RANSAC] for the RANSAC algorithm.
/// * [LMEDS] for the LMedS algorithm.
/// * prob: Parameter used for the RANSAC or LMedS methods only. It specifies a desirable level of
/// confidence (probability) that the estimated matrix is correct.
/// * threshold: Parameter used for RANSAC. It is the maximum distance from a point to an epipolar
/// line in pixels, beyond which the point is considered an outlier and is not used for computing the
/// final fundamental matrix. It can be set to something like 1-3, depending on the accuracy of the
/// point localization, image resolution, and the image noise.
/// * mask: Input/output mask for inliers in points1 and points2. If it is not empty, then it marks
/// inliers in points1 and points2 for then given essential matrix E. Only these inliers will be used to
/// recover pose. In the output mask only inliers which pass the cheirality check.
///
/// This function decomposes an essential matrix using [decomposeEssentialMat] and then verifies
/// possible pose hypotheses by doing cheirality check. The cheirality check means that the
/// triangulated 3D points should have positive depth. Some details can be found in [Nister03](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Nister03).
///
/// This function can be used to process the output E and mask from [findEssentialMat]. In this
/// scenario, points1 and points2 are the same input for findEssentialMat.:
/// ```C++
/// // Example. Estimation of fundamental matrix using the RANSAC algorithm
/// int point_count = 100;
/// vector<Point2f> points1(point_count);
/// vector<Point2f> points2(point_count);
///
/// // initialize the points here ...
/// for( int i = 0; i < point_count; i++ )
/// {
/// points1[i] = ...;
/// points2[i] = ...;
/// }
///
/// // Input: camera calibration of both cameras, for example using intrinsic chessboard calibration.
/// Mat cameraMatrix1, distCoeffs1, cameraMatrix2, distCoeffs2;
///
/// // Output: Essential matrix, relative rotation and relative translation.
/// Mat E, R, t, mask;
///
/// recoverPose(points1, points2, cameraMatrix1, distCoeffs1, cameraMatrix2, distCoeffs2, E, R, t, mask);
/// ```
///
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * method: cv::RANSAC
/// * prob: 0.999
/// * threshold: 1.0
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn recover_pose_2_cameras(points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix1: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs1: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix2: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs2: &impl ToInputArray, e: &mut impl ToOutputArray, r: &mut impl ToOutputArray, t: &mut impl ToOutputArray, method: i32, prob: f64, threshold: f64, mask: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray) -> Result<i32> {
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix1);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs1);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix2);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs2);
output_array_arg!(e);
output_array_arg!(r);
output_array_arg!(t);
input_output_array_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_recoverPose_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_double_double_const__InputOutputArrayR(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix1.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs1.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix2.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs2.as_raw__InputArray(), e.as_raw__OutputArray(), r.as_raw__OutputArray(), t.as_raw__OutputArray(), method, prob, threshold, mask.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Recovers the relative camera rotation and the translation from an estimated essential
/// matrix and the corresponding points in two images, using chirality check. Returns the number of
/// inliers that pass the check.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * E: The input essential matrix.
/// * points1: Array of N 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should be
/// floating-point (single or double precision).
/// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1 .
/// * cameraMatrix: Camera intrinsic matrix  .
/// Note that this function assumes that points1 and points2 are feature points from cameras with the
/// same camera intrinsic matrix.
/// * R: Output rotation matrix. Together with the translation vector, this matrix makes up a tuple
/// that performs a change of basis from the first camera's coordinate system to the second camera's
/// coordinate system. Note that, in general, t can not be used for this tuple, see the parameter
/// described below.
/// * t: Output translation vector. This vector is obtained by [decomposeEssentialMat] and
/// therefore is only known up to scale, i.e. t is the direction of the translation vector and has unit
/// length.
/// * mask: Input/output mask for inliers in points1 and points2. If it is not empty, then it marks
/// inliers in points1 and points2 for the given essential matrix E. Only these inliers will be used to
/// recover pose. In the output mask only inliers which pass the chirality check.
///
/// This function decomposes an essential matrix using [decomposeEssentialMat] and then verifies
/// possible pose hypotheses by doing chirality check. The chirality check means that the
/// triangulated 3D points should have positive depth. Some details can be found in [Nister03](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Nister03).
///
/// This function can be used to process the output E and mask from [findEssentialMat]. In this
/// scenario, points1 and points2 are the same input for [find_essential_mat] :
/// ```C++
/// // Example. Estimation of fundamental matrix using the RANSAC algorithm
/// int point_count = 100;
/// vector<Point2f> points1(point_count);
/// vector<Point2f> points2(point_count);
///
/// // initialize the points here ...
/// for( int i = 0; i < point_count; i++ )
/// {
/// points1[i] = ...;
/// points2[i] = ...;
/// }
///
/// // cametra matrix with both focal lengths = 1, and principal point = (0, 0)
/// Mat cameraMatrix = Mat::eye(3, 3, CV_64F);
///
/// Mat E, R, t, mask;
///
/// E = findEssentialMat(points1, points2, cameraMatrix, RANSAC, 0.999, 1.0, mask);
/// recoverPose(E, points1, points2, cameraMatrix, R, t, mask);
/// ```
///
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [recover_pose_estimated] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn recover_pose_estimated_def(e: &impl ToInputArray, points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, r: &mut impl ToOutputArray, t: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<i32> {
input_array_arg!(e);
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
output_array_arg!(r);
output_array_arg!(t);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_recoverPose_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(e.as_raw__InputArray(), points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), r.as_raw__OutputArray(), t.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Recovers the relative camera rotation and the translation from an estimated essential
/// matrix and the corresponding points in two images, using chirality check. Returns the number of
/// inliers that pass the check.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * E: The input essential matrix.
/// * points1: Array of N 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should be
/// floating-point (single or double precision).
/// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1 .
/// * cameraMatrix: Camera intrinsic matrix  .
/// Note that this function assumes that points1 and points2 are feature points from cameras with the
/// same camera intrinsic matrix.
/// * R: Output rotation matrix. Together with the translation vector, this matrix makes up a tuple
/// that performs a change of basis from the first camera's coordinate system to the second camera's
/// coordinate system. Note that, in general, t can not be used for this tuple, see the parameter
/// described below.
/// * t: Output translation vector. This vector is obtained by [decomposeEssentialMat] and
/// therefore is only known up to scale, i.e. t is the direction of the translation vector and has unit
/// length.
/// * mask: Input/output mask for inliers in points1 and points2. If it is not empty, then it marks
/// inliers in points1 and points2 for the given essential matrix E. Only these inliers will be used to
/// recover pose. In the output mask only inliers which pass the chirality check.
///
/// This function decomposes an essential matrix using [decomposeEssentialMat] and then verifies
/// possible pose hypotheses by doing chirality check. The chirality check means that the
/// triangulated 3D points should have positive depth. Some details can be found in [Nister03](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Nister03).
///
/// This function can be used to process the output E and mask from [findEssentialMat]. In this
/// scenario, points1 and points2 are the same input for [find_essential_mat] :
/// ```C++
/// // Example. Estimation of fundamental matrix using the RANSAC algorithm
/// int point_count = 100;
/// vector<Point2f> points1(point_count);
/// vector<Point2f> points2(point_count);
///
/// // initialize the points here ...
/// for( int i = 0; i < point_count; i++ )
/// {
/// points1[i] = ...;
/// points2[i] = ...;
/// }
///
/// // cametra matrix with both focal lengths = 1, and principal point = (0, 0)
/// Mat cameraMatrix = Mat::eye(3, 3, CV_64F);
///
/// Mat E, R, t, mask;
///
/// E = findEssentialMat(points1, points2, cameraMatrix, RANSAC, 0.999, 1.0, mask);
/// recoverPose(E, points1, points2, cameraMatrix, R, t, mask);
/// ```
///
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn recover_pose_estimated(e: &impl ToInputArray, points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, r: &mut impl ToOutputArray, t: &mut impl ToOutputArray, mask: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray) -> Result<i32> {
input_array_arg!(e);
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
output_array_arg!(r);
output_array_arg!(t);
input_output_array_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_recoverPose_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR(e.as_raw__InputArray(), points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), r.as_raw__OutputArray(), t.as_raw__OutputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// @overload
/// ## Parameters
/// * E: The input essential matrix.
/// * points1: Array of N 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should be
/// floating-point (single or double precision).
/// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1.
/// * cameraMatrix: Camera intrinsic matrix  .
/// Note that this function assumes that points1 and points2 are feature points from cameras with the
/// same camera intrinsic matrix.
/// * R: Output rotation matrix. Together with the translation vector, this matrix makes up a tuple
/// that performs a change of basis from the first camera's coordinate system to the second camera's
/// coordinate system. Note that, in general, t can not be used for this tuple, see the parameter
/// description below.
/// * t: Output translation vector. This vector is obtained by [decomposeEssentialMat] and
/// therefore is only known up to scale, i.e. t is the direction of the translation vector and has unit
/// length.
/// * distanceThresh: threshold distance which is used to filter out far away points (i.e. infinite
/// points).
/// * mask: Input/output mask for inliers in points1 and points2. If it is not empty, then it marks
/// inliers in points1 and points2 for the given essential matrix E. Only these inliers will be used to
/// recover pose. In the output mask only inliers which pass the chirality check.
/// * triangulatedPoints: 3D points which were reconstructed by triangulation.
///
/// This function differs from the one above that it outputs the triangulated 3D point that are used for
/// the chirality check.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [recover_pose_triangulated] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * mask: noArray()
/// * triangulated_points: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn recover_pose_triangulated_def(e: &impl ToInputArray, points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, r: &mut impl ToOutputArray, t: &mut impl ToOutputArray, distance_thresh: f64) -> Result<i32> {
input_array_arg!(e);
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
output_array_arg!(r);
output_array_arg!(t);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_recoverPose_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double(e.as_raw__InputArray(), points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), r.as_raw__OutputArray(), t.as_raw__OutputArray(), distance_thresh, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Recovers the relative camera rotation and the translation from an estimated essential
/// matrix and the corresponding points in two images, using chirality check. Returns the number of
/// inliers that pass the check.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * E: The input essential matrix.
/// * points1: Array of N 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should be
/// floating-point (single or double precision).
/// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1 .
/// * cameraMatrix: Camera intrinsic matrix  .
/// Note that this function assumes that points1 and points2 are feature points from cameras with the
/// same camera intrinsic matrix.
/// * R: Output rotation matrix. Together with the translation vector, this matrix makes up a tuple
/// that performs a change of basis from the first camera's coordinate system to the second camera's
/// coordinate system. Note that, in general, t can not be used for this tuple, see the parameter
/// described below.
/// * t: Output translation vector. This vector is obtained by [decomposeEssentialMat] and
/// therefore is only known up to scale, i.e. t is the direction of the translation vector and has unit
/// length.
/// * mask: Input/output mask for inliers in points1 and points2. If it is not empty, then it marks
/// inliers in points1 and points2 for the given essential matrix E. Only these inliers will be used to
/// recover pose. In the output mask only inliers which pass the chirality check.
///
/// This function decomposes an essential matrix using [decomposeEssentialMat] and then verifies
/// possible pose hypotheses by doing chirality check. The chirality check means that the
/// triangulated 3D points should have positive depth. Some details can be found in [Nister03](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Nister03).
///
/// This function can be used to process the output E and mask from [findEssentialMat]. In this
/// scenario, points1 and points2 are the same input for [find_essential_mat] :
/// ```C++
/// // Example. Estimation of fundamental matrix using the RANSAC algorithm
/// int point_count = 100;
/// vector<Point2f> points1(point_count);
/// vector<Point2f> points2(point_count);
///
/// // initialize the points here ...
/// for( int i = 0; i < point_count; i++ )
/// {
/// points1[i] = ...;
/// points2[i] = ...;
/// }
///
/// // cametra matrix with both focal lengths = 1, and principal point = (0, 0)
/// Mat cameraMatrix = Mat::eye(3, 3, CV_64F);
///
/// Mat E, R, t, mask;
///
/// E = findEssentialMat(points1, points2, cameraMatrix, RANSAC, 0.999, 1.0, mask);
/// recoverPose(E, points1, points2, cameraMatrix, R, t, mask);
/// ```
///
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * E: The input essential matrix.
/// * points1: Array of N 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should be
/// floating-point (single or double precision).
/// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1.
/// * cameraMatrix: Camera intrinsic matrix  .
/// Note that this function assumes that points1 and points2 are feature points from cameras with the
/// same camera intrinsic matrix.
/// * R: Output rotation matrix. Together with the translation vector, this matrix makes up a tuple
/// that performs a change of basis from the first camera's coordinate system to the second camera's
/// coordinate system. Note that, in general, t can not be used for this tuple, see the parameter
/// description below.
/// * t: Output translation vector. This vector is obtained by [decomposeEssentialMat] and
/// therefore is only known up to scale, i.e. t is the direction of the translation vector and has unit
/// length.
/// * distanceThresh: threshold distance which is used to filter out far away points (i.e. infinite
/// points).
/// * mask: Input/output mask for inliers in points1 and points2. If it is not empty, then it marks
/// inliers in points1 and points2 for the given essential matrix E. Only these inliers will be used to
/// recover pose. In the output mask only inliers which pass the chirality check.
/// * triangulatedPoints: 3D points which were reconstructed by triangulation.
///
/// This function differs from the one above that it outputs the triangulated 3D point that are used for
/// the chirality check.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * mask: noArray()
/// * triangulated_points: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn recover_pose_triangulated(e: &impl ToInputArray, points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, r: &mut impl ToOutputArray, t: &mut impl ToOutputArray, distance_thresh: f64, mask: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, triangulated_points: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<i32> {
input_array_arg!(e);
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
output_array_arg!(r);
output_array_arg!(t);
input_output_array_arg!(mask);
output_array_arg!(triangulated_points);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_recoverPose_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(e.as_raw__InputArray(), points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), r.as_raw__OutputArray(), t.as_raw__OutputArray(), distance_thresh, mask.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), triangulated_points.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// @overload
/// ## Parameters
/// * E: The input essential matrix.
/// * points1: Array of N 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should be
/// floating-point (single or double precision).
/// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1 .
/// * R: Output rotation matrix. Together with the translation vector, this matrix makes up a tuple
/// that performs a change of basis from the first camera's coordinate system to the second camera's
/// coordinate system. Note that, in general, t can not be used for this tuple, see the parameter
/// description below.
/// * t: Output translation vector. This vector is obtained by [decomposeEssentialMat] and
/// therefore is only known up to scale, i.e. t is the direction of the translation vector and has unit
/// length.
/// * focal: Focal length of the camera. Note that this function assumes that points1 and points2
/// are feature points from cameras with same focal length and principal point.
/// * pp: principal point of the camera.
/// * mask: Input/output mask for inliers in points1 and points2. If it is not empty, then it marks
/// inliers in points1 and points2 for the given essential matrix E. Only these inliers will be used to
/// recover pose. In the output mask only inliers which pass the chirality check.
///
/// This function differs from the one above that it computes camera intrinsic matrix from focal length and
/// principal point:
///
/// 
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [recover_pose] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * focal: 1.0
/// * pp: Point2d(0,0)
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn recover_pose_def(e: &impl ToInputArray, points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray, r: &mut impl ToOutputArray, t: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<i32> {
input_array_arg!(e);
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
output_array_arg!(r);
output_array_arg!(t);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_recoverPose_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(e.as_raw__InputArray(), points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), r.as_raw__OutputArray(), t.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Recovers the relative camera rotation and the translation from an estimated essential
/// matrix and the corresponding points in two images, using chirality check. Returns the number of
/// inliers that pass the check.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * E: The input essential matrix.
/// * points1: Array of N 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should be
/// floating-point (single or double precision).
/// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1 .
/// * cameraMatrix: Camera intrinsic matrix  .
/// Note that this function assumes that points1 and points2 are feature points from cameras with the
/// same camera intrinsic matrix.
/// * R: Output rotation matrix. Together with the translation vector, this matrix makes up a tuple
/// that performs a change of basis from the first camera's coordinate system to the second camera's
/// coordinate system. Note that, in general, t can not be used for this tuple, see the parameter
/// described below.
/// * t: Output translation vector. This vector is obtained by [decomposeEssentialMat] and
/// therefore is only known up to scale, i.e. t is the direction of the translation vector and has unit
/// length.
/// * mask: Input/output mask for inliers in points1 and points2. If it is not empty, then it marks
/// inliers in points1 and points2 for the given essential matrix E. Only these inliers will be used to
/// recover pose. In the output mask only inliers which pass the chirality check.
///
/// This function decomposes an essential matrix using [decomposeEssentialMat] and then verifies
/// possible pose hypotheses by doing chirality check. The chirality check means that the
/// triangulated 3D points should have positive depth. Some details can be found in [Nister03](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Nister03).
///
/// This function can be used to process the output E and mask from [findEssentialMat]. In this
/// scenario, points1 and points2 are the same input for [find_essential_mat] :
/// ```C++
/// // Example. Estimation of fundamental matrix using the RANSAC algorithm
/// int point_count = 100;
/// vector<Point2f> points1(point_count);
/// vector<Point2f> points2(point_count);
///
/// // initialize the points here ...
/// for( int i = 0; i < point_count; i++ )
/// {
/// points1[i] = ...;
/// points2[i] = ...;
/// }
///
/// // cametra matrix with both focal lengths = 1, and principal point = (0, 0)
/// Mat cameraMatrix = Mat::eye(3, 3, CV_64F);
///
/// Mat E, R, t, mask;
///
/// E = findEssentialMat(points1, points2, cameraMatrix, RANSAC, 0.999, 1.0, mask);
/// recoverPose(E, points1, points2, cameraMatrix, R, t, mask);
/// ```
///
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * E: The input essential matrix.
/// * points1: Array of N 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should be
/// floating-point (single or double precision).
/// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1 .
/// * R: Output rotation matrix. Together with the translation vector, this matrix makes up a tuple
/// that performs a change of basis from the first camera's coordinate system to the second camera's
/// coordinate system. Note that, in general, t can not be used for this tuple, see the parameter
/// description below.
/// * t: Output translation vector. This vector is obtained by [decomposeEssentialMat] and
/// therefore is only known up to scale, i.e. t is the direction of the translation vector and has unit
/// length.
/// * focal: Focal length of the camera. Note that this function assumes that points1 and points2
/// are feature points from cameras with same focal length and principal point.
/// * pp: principal point of the camera.
/// * mask: Input/output mask for inliers in points1 and points2. If it is not empty, then it marks
/// inliers in points1 and points2 for the given essential matrix E. Only these inliers will be used to
/// recover pose. In the output mask only inliers which pass the chirality check.
///
/// This function differs from the one above that it computes camera intrinsic matrix from focal length and
/// principal point:
///
/// 
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * focal: 1.0
/// * pp: Point2d(0,0)
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn recover_pose(e: &impl ToInputArray, points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray, r: &mut impl ToOutputArray, t: &mut impl ToOutputArray, focal: f64, pp: core::Point2d, mask: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray) -> Result<i32> {
input_array_arg!(e);
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
output_array_arg!(r);
output_array_arg!(t);
input_output_array_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_recoverPose_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_Point2d_const__InputOutputArrayR(e.as_raw__InputArray(), points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), r.as_raw__OutputArray(), t.as_raw__OutputArray(), focal, &pp, mask.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// computes the rectification transformations for 3-head camera, where all the heads are on the same line.
#[inline]
pub fn rectify3_collinear(camera_matrix1: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs1: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix2: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs2: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix3: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs3: &impl ToInputArray, imgpt1: &impl ToInputArray, imgpt3: &impl ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, r12: &impl ToInputArray, t12: &impl ToInputArray, r13: &impl ToInputArray, t13: &impl ToInputArray, r1: &mut impl ToOutputArray, r2: &mut impl ToOutputArray, r3: &mut impl ToOutputArray, p1: &mut impl ToOutputArray, p2: &mut impl ToOutputArray, p3: &mut impl ToOutputArray, q: &mut impl ToOutputArray, alpha: f64, new_img_size: core::Size, roi1: &mut core::Rect, roi2: &mut core::Rect, flags: i32) -> Result<f32> {
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix1);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs1);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix2);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs2);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix3);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs3);
input_array_arg!(imgpt1);
input_array_arg!(imgpt3);
input_array_arg!(r12);
input_array_arg!(t12);
input_array_arg!(r13);
input_array_arg!(t13);
output_array_arg!(r1);
output_array_arg!(r2);
output_array_arg!(r3);
output_array_arg!(p1);
output_array_arg!(p2);
output_array_arg!(p3);
output_array_arg!(q);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_rectify3Collinear_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_Size_RectX_RectX_int(camera_matrix1.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs1.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix2.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix3.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs3.as_raw__InputArray(), imgpt1.as_raw__InputArray(), imgpt3.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, r12.as_raw__InputArray(), t12.as_raw__InputArray(), r13.as_raw__InputArray(), t13.as_raw__InputArray(), r1.as_raw__OutputArray(), r2.as_raw__OutputArray(), r3.as_raw__OutputArray(), p1.as_raw__OutputArray(), p2.as_raw__OutputArray(), p3.as_raw__OutputArray(), q.as_raw__OutputArray(), alpha, &new_img_size, roi1, roi2, flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Reprojects a disparity image to 3D space.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * disparity: Input single-channel 8-bit unsigned, 16-bit signed, 32-bit signed or 32-bit
/// floating-point disparity image. The values of 8-bit / 16-bit signed formats are assumed to have no
/// fractional bits. If the disparity is 16-bit signed format, as computed by [StereoBM] or
/// [StereoSGBM] and maybe other algorithms, it should be divided by 16 (and scaled to float) before
/// being used here.
/// * _3dImage: Output 3-channel floating-point image of the same size as disparity. Each element of
/// _3dImage(x,y) contains 3D coordinates of the point (x,y) computed from the disparity map. If one
/// uses Q obtained by [stereoRectify], then the returned points are represented in the first
/// camera's rectified coordinate system.
/// * Q:  perspective transformation matrix that can be obtained with
/// [stereoRectify].
/// * handleMissingValues: Indicates, whether the function should handle missing values (i.e.
/// points where the disparity was not computed). If handleMissingValues=true, then pixels with the
/// minimal disparity that corresponds to the outliers (see StereoMatcher::compute ) are transformed
/// to 3D points with a very large Z value (currently set to 10000).
/// * ddepth: The optional output array depth. If it is -1, the output image will have CV_32F
/// depth. ddepth can also be set to CV_16S, CV_32S or CV_32F.
///
/// The function transforms a single-channel disparity map to a 3-channel image representing a 3D
/// surface. That is, for each pixel (x,y) and the corresponding disparity d=disparity(x,y) , it
/// computes:
///
/// 
/// ## See also
/// To reproject a sparse set of points {(x,y,d),...} to 3D space, use perspectiveTransform.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [reproject_image_to_3d] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * handle_missing_values: false
/// * ddepth: -1
#[inline]
pub fn reproject_image_to_3d_def(disparity: &impl ToInputArray, _3d_image: &mut impl ToOutputArray, q: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(disparity);
output_array_arg!(_3d_image);
input_array_arg!(q);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_reprojectImageTo3D_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(disparity.as_raw__InputArray(), _3d_image.as_raw__OutputArray(), q.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Reprojects a disparity image to 3D space.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * disparity: Input single-channel 8-bit unsigned, 16-bit signed, 32-bit signed or 32-bit
/// floating-point disparity image. The values of 8-bit / 16-bit signed formats are assumed to have no
/// fractional bits. If the disparity is 16-bit signed format, as computed by [StereoBM] or
/// [StereoSGBM] and maybe other algorithms, it should be divided by 16 (and scaled to float) before
/// being used here.
/// * _3dImage: Output 3-channel floating-point image of the same size as disparity. Each element of
/// _3dImage(x,y) contains 3D coordinates of the point (x,y) computed from the disparity map. If one
/// uses Q obtained by [stereoRectify], then the returned points are represented in the first
/// camera's rectified coordinate system.
/// * Q: 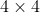 perspective transformation matrix that can be obtained with
/// [stereoRectify].
/// * handleMissingValues: Indicates, whether the function should handle missing values (i.e.
/// points where the disparity was not computed). If handleMissingValues=true, then pixels with the
/// minimal disparity that corresponds to the outliers (see StereoMatcher::compute ) are transformed
/// to 3D points with a very large Z value (currently set to 10000).
/// * ddepth: The optional output array depth. If it is -1, the output image will have CV_32F
/// depth. ddepth can also be set to CV_16S, CV_32S or CV_32F.
///
/// The function transforms a single-channel disparity map to a 3-channel image representing a 3D
/// surface. That is, for each pixel (x,y) and the corresponding disparity d=disparity(x,y) , it
/// computes:
///
/// 
/// ## See also
/// To reproject a sparse set of points {(x,y,d),...} to 3D space, use perspectiveTransform.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * handle_missing_values: false
/// * ddepth: -1
#[inline]
pub fn reproject_image_to_3d(disparity: &impl ToInputArray, _3d_image: &mut impl ToOutputArray, q: &impl ToInputArray, handle_missing_values: bool, ddepth: i32) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(disparity);
output_array_arg!(_3d_image);
input_array_arg!(q);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_reprojectImageTo3D_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_bool_int(disparity.as_raw__InputArray(), _3d_image.as_raw__OutputArray(), q.as_raw__InputArray(), handle_missing_values, ddepth, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates the Sampson Distance between two points.
///
/// The function cv::sampsonDistance calculates and returns the first order approximation of the geometric error as:
/// 
/// The fundamental matrix may be calculated using the [find_fundamental_mat] function. See [HartleyZ00](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_HartleyZ00) 11.4.3 for details.
/// ## Parameters
/// * pt1: first homogeneous 2d point
/// * pt2: second homogeneous 2d point
/// * F: fundamental matrix
/// ## Returns
/// The computed Sampson distance.
#[inline]
pub fn sampson_distance(pt1: &impl ToInputArray, pt2: &impl ToInputArray, f: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<f64> {
input_array_arg!(pt1);
input_array_arg!(pt2);
input_array_arg!(f);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_sampsonDistance_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(pt1.as_raw__InputArray(), pt2.as_raw__InputArray(), f.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds an object pose from 3 3D-2D point correspondences.
/// ## See also
/// [calib3d_solvePnP]
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Array of object points in the object coordinate space, 3x3 1-channel or
/// 1x3/3x1 3-channel. vector\<Point3f\> can be also passed here.
/// * imagePoints: Array of corresponding image points, 3x2 1-channel or 1x3/3x1 2-channel.
/// vector\<Point2f\> can be also passed here.
/// * cameraMatrix: Input camera intrinsic matrix  .
/// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients
/// . If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are
/// assumed.
/// * rvecs: Output rotation vectors (see [Rodrigues] ) that, together with tvecs, brings points from
/// the model coordinate system to the camera coordinate system. A P3P problem has up to 4 solutions.
/// * tvecs: Output translation vectors.
/// * flags: Method for solving a P3P problem:
/// * [SOLVEPNP_P3P] Method is based on the paper of X.S. Gao, X.-R. Hou, J. Tang, H.-F. Chang
/// "Complete Solution Classification for the Perspective-Three-Point Problem" ([gao2003complete](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_gao2003complete)).
/// * [SOLVEPNP_AP3P] Method is based on the paper of T. Ke and S. Roumeliotis.
/// "An Efficient Algebraic Solution to the Perspective-Three-Point Problem" ([Ke17](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Ke17)).
///
/// The function estimates the object pose given 3 object points, their corresponding image
/// projections, as well as the camera intrinsic matrix and the distortion coefficients.
///
///
/// Note:
/// The solutions are sorted by reprojection errors (lowest to highest).
#[inline]
pub fn solve_p3p(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, rvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<i32> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
output_array_arg!(rvecs);
output_array_arg!(tvecs);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_solveP3P_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), rvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds an object pose from 3D-2D point correspondences.
/// ## See also
/// [calib3d_solvePnP]
///
/// This function returns a list of all the possible solutions (a solution is a <rotation vector, translation vector>
/// couple), depending on the number of input points and the chosen method:
/// - P3P methods ([SOLVEPNP_P3P], [SOLVEPNP_AP3P]): 3 or 4 input points. Number of returned solutions can be between 0 and 4 with 3 input points.
/// - [SOLVEPNP_IPPE] Input points must be >= 4 and object points must be coplanar. Returns 2 solutions.
/// - [SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE] Special case suitable for marker pose estimation.
/// Number of input points must be 4 and 2 solutions are returned. Object points must be defined in the following order:
/// - point 0: [-squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 1: [ squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 2: [ squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 3: [-squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - for all the other flags, number of input points must be >= 4 and object points can be in any configuration.
/// Only 1 solution is returned.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Array of object points in the object coordinate space, Nx3 1-channel or
/// 1xN/Nx1 3-channel, where N is the number of points. vector\<Point3d\> can be also passed here.
/// * imagePoints: Array of corresponding image points, Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel,
/// where N is the number of points. vector\<Point2d\> can be also passed here.
/// * cameraMatrix: Input camera intrinsic matrix  .
/// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients
/// . If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are
/// assumed.
/// * rvecs: Vector of output rotation vectors (see [Rodrigues] ) that, together with tvecs, brings points from
/// the model coordinate system to the camera coordinate system.
/// * tvecs: Vector of output translation vectors.
/// * useExtrinsicGuess: Parameter used for #SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE. If true (1), the function uses
/// the provided rvec and tvec values as initial approximations of the rotation and translation
/// vectors, respectively, and further optimizes them.
/// * flags: Method for solving a PnP problem: see [calib3d_solvePnP_flags]
/// * rvec: Rotation vector used to initialize an iterative PnP refinement algorithm, when flag is [SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE]
/// and useExtrinsicGuess is set to true.
/// * tvec: Translation vector used to initialize an iterative PnP refinement algorithm, when flag is [SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE]
/// and useExtrinsicGuess is set to true.
/// * reprojectionError: Optional vector of reprojection error, that is the RMS error
/// () between the input image points
/// and the 3D object points projected with the estimated pose.
///
/// More information is described in [calib3d_solvePnP]
///
///
/// Note:
/// * An example of how to use solvePnP for planar augmented reality can be found at
/// opencv_source_code/samples/python/plane_ar.py
/// * If you are using Python:
/// - Numpy array slices won't work as input because solvePnP requires contiguous
/// arrays (enforced by the assertion using cv::Mat::checkVector() around line 55 of
/// modules/calib3d/src/solvepnp.cpp version 2.4.9)
/// - The P3P algorithm requires image points to be in an array of shape (N,1,2) due
/// to its calling of [undistort_points] (around line 75 of modules/calib3d/src/solvepnp.cpp version 2.4.9)
/// which requires 2-channel information.
/// - Thus, given some data D = np.array(...) where D.shape = (N,M), in order to use a subset of
/// it as, e.g., imagePoints, one must effectively copy it into a new array: imagePoints =
/// np.ascontiguousarray(D[:,:2]).reshape((N,1,2))
/// * The methods [SOLVEPNP_DLS] and [SOLVEPNP_UPNP] cannot be used as the current implementations are
/// unstable and sometimes give completely wrong results. If you pass one of these two
/// flags, [SOLVEPNP_EPNP] method will be used instead.
/// * The minimum number of points is 4 in the general case. In the case of [SOLVEPNP_P3P] and [SOLVEPNP_AP3P]
/// methods, it is required to use exactly 4 points (the first 3 points are used to estimate all the solutions
/// of the P3P problem, the last one is used to retain the best solution that minimizes the reprojection error).
/// * With [SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE] method and `useExtrinsicGuess=true`, the minimum number of points is 3 (3 points
/// are sufficient to compute a pose but there are up to 4 solutions). The initial solution should be close to the
/// global solution to converge.
/// * With [SOLVEPNP_IPPE] input points must be >= 4 and object points must be coplanar.
/// * With [SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE] this is a special case suitable for marker pose estimation.
/// Number of input points must be 4. Object points must be defined in the following order:
/// - point 0: [-squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 1: [ squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 2: [ squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 3: [-squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [solve_pnp_generic] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * use_extrinsic_guess: false
/// * flags: SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE
/// * rvec: noArray()
/// * tvec: noArray()
/// * reprojection_error: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn solve_pnp_generic_def(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, rvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<i32> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
output_array_arg!(rvecs);
output_array_arg!(tvecs);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_solvePnPGeneric_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), rvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds an object pose from 3D-2D point correspondences.
/// ## See also
/// [calib3d_solvePnP]
///
/// This function returns a list of all the possible solutions (a solution is a <rotation vector, translation vector>
/// couple), depending on the number of input points and the chosen method:
/// - P3P methods ([SOLVEPNP_P3P], [SOLVEPNP_AP3P]): 3 or 4 input points. Number of returned solutions can be between 0 and 4 with 3 input points.
/// - [SOLVEPNP_IPPE] Input points must be >= 4 and object points must be coplanar. Returns 2 solutions.
/// - [SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE] Special case suitable for marker pose estimation.
/// Number of input points must be 4 and 2 solutions are returned. Object points must be defined in the following order:
/// - point 0: [-squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 1: [ squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 2: [ squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 3: [-squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - for all the other flags, number of input points must be >= 4 and object points can be in any configuration.
/// Only 1 solution is returned.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Array of object points in the object coordinate space, Nx3 1-channel or
/// 1xN/Nx1 3-channel, where N is the number of points. vector\<Point3d\> can be also passed here.
/// * imagePoints: Array of corresponding image points, Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel,
/// where N is the number of points. vector\<Point2d\> can be also passed here.
/// * cameraMatrix: Input camera intrinsic matrix  .
/// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients
/// . If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are
/// assumed.
/// * rvecs: Vector of output rotation vectors (see [Rodrigues] ) that, together with tvecs, brings points from
/// the model coordinate system to the camera coordinate system.
/// * tvecs: Vector of output translation vectors.
/// * useExtrinsicGuess: Parameter used for #SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE. If true (1), the function uses
/// the provided rvec and tvec values as initial approximations of the rotation and translation
/// vectors, respectively, and further optimizes them.
/// * flags: Method for solving a PnP problem: see [calib3d_solvePnP_flags]
/// * rvec: Rotation vector used to initialize an iterative PnP refinement algorithm, when flag is [SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE]
/// and useExtrinsicGuess is set to true.
/// * tvec: Translation vector used to initialize an iterative PnP refinement algorithm, when flag is [SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE]
/// and useExtrinsicGuess is set to true.
/// * reprojectionError: Optional vector of reprojection error, that is the RMS error
/// () between the input image points
/// and the 3D object points projected with the estimated pose.
///
/// More information is described in [calib3d_solvePnP]
///
///
/// Note:
/// * An example of how to use solvePnP for planar augmented reality can be found at
/// opencv_source_code/samples/python/plane_ar.py
/// * If you are using Python:
/// - Numpy array slices won't work as input because solvePnP requires contiguous
/// arrays (enforced by the assertion using cv::Mat::checkVector() around line 55 of
/// modules/calib3d/src/solvepnp.cpp version 2.4.9)
/// - The P3P algorithm requires image points to be in an array of shape (N,1,2) due
/// to its calling of [undistort_points] (around line 75 of modules/calib3d/src/solvepnp.cpp version 2.4.9)
/// which requires 2-channel information.
/// - Thus, given some data D = np.array(...) where D.shape = (N,M), in order to use a subset of
/// it as, e.g., imagePoints, one must effectively copy it into a new array: imagePoints =
/// np.ascontiguousarray(D[:,:2]).reshape((N,1,2))
/// * The methods [SOLVEPNP_DLS] and [SOLVEPNP_UPNP] cannot be used as the current implementations are
/// unstable and sometimes give completely wrong results. If you pass one of these two
/// flags, [SOLVEPNP_EPNP] method will be used instead.
/// * The minimum number of points is 4 in the general case. In the case of [SOLVEPNP_P3P] and [SOLVEPNP_AP3P]
/// methods, it is required to use exactly 4 points (the first 3 points are used to estimate all the solutions
/// of the P3P problem, the last one is used to retain the best solution that minimizes the reprojection error).
/// * With [SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE] method and `useExtrinsicGuess=true`, the minimum number of points is 3 (3 points
/// are sufficient to compute a pose but there are up to 4 solutions). The initial solution should be close to the
/// global solution to converge.
/// * With [SOLVEPNP_IPPE] input points must be >= 4 and object points must be coplanar.
/// * With [SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE] this is a special case suitable for marker pose estimation.
/// Number of input points must be 4. Object points must be defined in the following order:
/// - point 0: [-squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 1: [ squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 2: [ squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 3: [-squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * use_extrinsic_guess: false
/// * flags: SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE
/// * rvec: noArray()
/// * tvec: noArray()
/// * reprojection_error: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn solve_pnp_generic(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, rvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, use_extrinsic_guess: bool, flags: crate::calib3d::SolvePnPMethod, rvec: &impl ToInputArray, tvec: &impl ToInputArray, reprojection_error: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<i32> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
output_array_arg!(rvecs);
output_array_arg!(tvecs);
input_array_arg!(rvec);
input_array_arg!(tvec);
output_array_arg!(reprojection_error);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_solvePnPGeneric_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_bool_SolvePnPMethod_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), rvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), use_extrinsic_guess, flags, rvec.as_raw__InputArray(), tvec.as_raw__InputArray(), reprojection_error.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds an object pose from 3D-2D point correspondences using the RANSAC scheme.
/// ## See also
/// [calib3d_solvePnP]
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Array of object points in the object coordinate space, Nx3 1-channel or
/// 1xN/Nx1 3-channel, where N is the number of points. vector\<Point3d\> can be also passed here.
/// * imagePoints: Array of corresponding image points, Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel,
/// where N is the number of points. vector\<Point2d\> can be also passed here.
/// * cameraMatrix: Input camera intrinsic matrix  .
/// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients
/// . If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are
/// assumed.
/// * rvec: Output rotation vector (see [Rodrigues] ) that, together with tvec, brings points from
/// the model coordinate system to the camera coordinate system.
/// * tvec: Output translation vector.
/// * useExtrinsicGuess: Parameter used for [SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE]. If true (1), the function uses
/// the provided rvec and tvec values as initial approximations of the rotation and translation
/// vectors, respectively, and further optimizes them.
/// * iterationsCount: Number of iterations.
/// * reprojectionError: Inlier threshold value used by the RANSAC procedure. The parameter value
/// is the maximum allowed distance between the observed and computed point projections to consider it
/// an inlier.
/// * confidence: The probability that the algorithm produces a useful result.
/// * inliers: Output vector that contains indices of inliers in objectPoints and imagePoints .
/// * flags: Method for solving a PnP problem (see [solvePnP] ).
///
/// The function estimates an object pose given a set of object points, their corresponding image
/// projections, as well as the camera intrinsic matrix and the distortion coefficients. This function finds such
/// a pose that minimizes reprojection error, that is, the sum of squared distances between the observed
/// projections imagePoints and the projected (using [projectPoints] ) objectPoints. The use of RANSAC
/// makes the function resistant to outliers.
///
///
/// Note:
/// * An example of how to use solvePNPRansac for object detection can be found at
/// opencv_source_code/samples/cpp/tutorial_code/calib3d/real_time_pose_estimation/
/// * The default method used to estimate the camera pose for the Minimal Sample Sets step
/// is #SOLVEPNP_EPNP. Exceptions are:
/// - if you choose [SOLVEPNP_P3P] or #SOLVEPNP_AP3P, these methods will be used.
/// - if the number of input points is equal to 4, [SOLVEPNP_P3P] is used.
/// * The method used to estimate the camera pose using all the inliers is defined by the
/// flags parameters unless it is equal to [SOLVEPNP_P3P] or #SOLVEPNP_AP3P. In this case,
/// the method [SOLVEPNP_EPNP] will be used instead.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [solve_pnp_ransac] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * use_extrinsic_guess: false
/// * iterations_count: 100
/// * reprojection_error: 8.0
/// * confidence: 0.99
/// * inliers: noArray()
/// * flags: SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE
#[inline]
pub fn solve_pnp_ransac_def(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, rvec: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvec: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
output_array_arg!(rvec);
output_array_arg!(tvec);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_solvePnPRansac_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvec.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds an object pose from 3D-2D point correspondences using the RANSAC scheme.
/// ## See also
/// [calib3d_solvePnP]
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Array of object points in the object coordinate space, Nx3 1-channel or
/// 1xN/Nx1 3-channel, where N is the number of points. vector\<Point3d\> can be also passed here.
/// * imagePoints: Array of corresponding image points, Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel,
/// where N is the number of points. vector\<Point2d\> can be also passed here.
/// * cameraMatrix: Input camera intrinsic matrix  .
/// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients
/// . If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are
/// assumed.
/// * rvec: Output rotation vector (see [Rodrigues] ) that, together with tvec, brings points from
/// the model coordinate system to the camera coordinate system.
/// * tvec: Output translation vector.
/// * useExtrinsicGuess: Parameter used for [SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE]. If true (1), the function uses
/// the provided rvec and tvec values as initial approximations of the rotation and translation
/// vectors, respectively, and further optimizes them.
/// * iterationsCount: Number of iterations.
/// * reprojectionError: Inlier threshold value used by the RANSAC procedure. The parameter value
/// is the maximum allowed distance between the observed and computed point projections to consider it
/// an inlier.
/// * confidence: The probability that the algorithm produces a useful result.
/// * inliers: Output vector that contains indices of inliers in objectPoints and imagePoints .
/// * flags: Method for solving a PnP problem (see [solvePnP] ).
///
/// The function estimates an object pose given a set of object points, their corresponding image
/// projections, as well as the camera intrinsic matrix and the distortion coefficients. This function finds such
/// a pose that minimizes reprojection error, that is, the sum of squared distances between the observed
/// projections imagePoints and the projected (using [projectPoints] ) objectPoints. The use of RANSAC
/// makes the function resistant to outliers.
///
///
/// Note:
/// * An example of how to use solvePNPRansac for object detection can be found at
/// opencv_source_code/samples/cpp/tutorial_code/calib3d/real_time_pose_estimation/
/// * The default method used to estimate the camera pose for the Minimal Sample Sets step
/// is #SOLVEPNP_EPNP. Exceptions are:
/// - if you choose [SOLVEPNP_P3P] or #SOLVEPNP_AP3P, these methods will be used.
/// - if the number of input points is equal to 4, [SOLVEPNP_P3P] is used.
/// * The method used to estimate the camera pose using all the inliers is defined by the
/// flags parameters unless it is equal to [SOLVEPNP_P3P] or #SOLVEPNP_AP3P. In this case,
/// the method [SOLVEPNP_EPNP] will be used instead.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * use_extrinsic_guess: false
/// * iterations_count: 100
/// * reprojection_error: 8.0
/// * confidence: 0.99
/// * inliers: noArray()
/// * flags: SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE
#[inline]
pub fn solve_pnp_ransac(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, rvec: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvec: &mut impl ToOutputArray, use_extrinsic_guess: bool, iterations_count: i32, reprojection_error: f32, confidence: f64, inliers: &mut impl ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
output_array_arg!(rvec);
output_array_arg!(tvec);
output_array_arg!(inliers);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_solvePnPRansac_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_bool_int_float_double_const__OutputArrayR_int(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvec.as_raw__OutputArray(), use_extrinsic_guess, iterations_count, reprojection_error, confidence, inliers.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [solve_pnp_ransac_1] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * params: UsacParams()
#[inline]
pub fn solve_pnp_ransac_1_def(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, rvec: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvec: &mut impl ToOutputArray, inliers: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
output_array_arg!(rvec);
output_array_arg!(tvec);
output_array_arg!(inliers);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_solvePnPRansac_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvec.as_raw__OutputArray(), inliers.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * params: UsacParams()
#[inline]
pub fn solve_pnp_ransac_1(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, rvec: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvec: &mut impl ToOutputArray, inliers: &mut impl ToOutputArray, params: crate::calib3d::UsacParams) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
output_array_arg!(rvec);
output_array_arg!(tvec);
output_array_arg!(inliers);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_solvePnPRansac_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const_UsacParamsR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvec.as_raw__OutputArray(), inliers.as_raw__OutputArray(), ¶ms, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Refine a pose (the translation and the rotation that transform a 3D point expressed in the object coordinate frame
/// to the camera coordinate frame) from a 3D-2D point correspondences and starting from an initial solution.
/// ## See also
/// [calib3d_solvePnP]
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Array of object points in the object coordinate space, Nx3 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 3-channel,
/// where N is the number of points. vector\<Point3d\> can also be passed here.
/// * imagePoints: Array of corresponding image points, Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel,
/// where N is the number of points. vector\<Point2d\> can also be passed here.
/// * cameraMatrix: Input camera intrinsic matrix  .
/// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients
/// . If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are
/// assumed.
/// * rvec: Input/Output rotation vector (see [Rodrigues] ) that, together with tvec, brings points from
/// the model coordinate system to the camera coordinate system. Input values are used as an initial solution.
/// * tvec: Input/Output translation vector. Input values are used as an initial solution.
/// * criteria: Criteria when to stop the Levenberg-Marquard iterative algorithm.
///
/// The function refines the object pose given at least 3 object points, their corresponding image
/// projections, an initial solution for the rotation and translation vector,
/// as well as the camera intrinsic matrix and the distortion coefficients.
/// The function minimizes the projection error with respect to the rotation and the translation vectors, according
/// to a Levenberg-Marquardt iterative minimization [Madsen04](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Madsen04) [Eade13](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Eade13) process.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [solve_pnp_refine_lm] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::EPS+TermCriteria::COUNT,20,FLT_EPSILON)
#[inline]
pub fn solve_pnp_refine_lm_def(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, rvec: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, tvec: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
input_output_array_arg!(rvec);
input_output_array_arg!(tvec);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_solvePnPRefineLM_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), tvec.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Refine a pose (the translation and the rotation that transform a 3D point expressed in the object coordinate frame
/// to the camera coordinate frame) from a 3D-2D point correspondences and starting from an initial solution.
/// ## See also
/// [calib3d_solvePnP]
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Array of object points in the object coordinate space, Nx3 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 3-channel,
/// where N is the number of points. vector\<Point3d\> can also be passed here.
/// * imagePoints: Array of corresponding image points, Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel,
/// where N is the number of points. vector\<Point2d\> can also be passed here.
/// * cameraMatrix: Input camera intrinsic matrix  .
/// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients
/// . If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are
/// assumed.
/// * rvec: Input/Output rotation vector (see [Rodrigues] ) that, together with tvec, brings points from
/// the model coordinate system to the camera coordinate system. Input values are used as an initial solution.
/// * tvec: Input/Output translation vector. Input values are used as an initial solution.
/// * criteria: Criteria when to stop the Levenberg-Marquard iterative algorithm.
///
/// The function refines the object pose given at least 3 object points, their corresponding image
/// projections, an initial solution for the rotation and translation vector,
/// as well as the camera intrinsic matrix and the distortion coefficients.
/// The function minimizes the projection error with respect to the rotation and the translation vectors, according
/// to a Levenberg-Marquardt iterative minimization [Madsen04](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Madsen04) [Eade13](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Eade13) process.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::EPS+TermCriteria::COUNT,20,FLT_EPSILON)
#[inline]
pub fn solve_pnp_refine_lm(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, rvec: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, tvec: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, criteria: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
input_output_array_arg!(rvec);
input_output_array_arg!(tvec);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_solvePnPRefineLM_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_TermCriteria(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), tvec.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), &criteria, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Refine a pose (the translation and the rotation that transform a 3D point expressed in the object coordinate frame
/// to the camera coordinate frame) from a 3D-2D point correspondences and starting from an initial solution.
/// ## See also
/// [calib3d_solvePnP]
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Array of object points in the object coordinate space, Nx3 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 3-channel,
/// where N is the number of points. vector\<Point3d\> can also be passed here.
/// * imagePoints: Array of corresponding image points, Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel,
/// where N is the number of points. vector\<Point2d\> can also be passed here.
/// * cameraMatrix: Input camera intrinsic matrix  .
/// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients
/// . If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are
/// assumed.
/// * rvec: Input/Output rotation vector (see [Rodrigues] ) that, together with tvec, brings points from
/// the model coordinate system to the camera coordinate system. Input values are used as an initial solution.
/// * tvec: Input/Output translation vector. Input values are used as an initial solution.
/// * criteria: Criteria when to stop the Levenberg-Marquard iterative algorithm.
/// * VVSlambda: Gain for the virtual visual servoing control law, equivalent to the 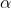
/// gain in the Damped Gauss-Newton formulation.
///
/// The function refines the object pose given at least 3 object points, their corresponding image
/// projections, an initial solution for the rotation and translation vector,
/// as well as the camera intrinsic matrix and the distortion coefficients.
/// The function minimizes the projection error with respect to the rotation and the translation vectors, using a
/// virtual visual servoing (VVS) [Chaumette06](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Chaumette06) [Marchand16](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Marchand16) scheme.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [solve_pnp_refine_vvs] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::EPS+TermCriteria::COUNT,20,FLT_EPSILON)
/// * vv_slambda: 1
#[inline]
pub fn solve_pnp_refine_vvs_def(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, rvec: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, tvec: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
input_output_array_arg!(rvec);
input_output_array_arg!(tvec);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_solvePnPRefineVVS_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), tvec.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Refine a pose (the translation and the rotation that transform a 3D point expressed in the object coordinate frame
/// to the camera coordinate frame) from a 3D-2D point correspondences and starting from an initial solution.
/// ## See also
/// [calib3d_solvePnP]
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Array of object points in the object coordinate space, Nx3 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 3-channel,
/// where N is the number of points. vector\<Point3d\> can also be passed here.
/// * imagePoints: Array of corresponding image points, Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel,
/// where N is the number of points. vector\<Point2d\> can also be passed here.
/// * cameraMatrix: Input camera intrinsic matrix  .
/// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients
/// . If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are
/// assumed.
/// * rvec: Input/Output rotation vector (see [Rodrigues] ) that, together with tvec, brings points from
/// the model coordinate system to the camera coordinate system. Input values are used as an initial solution.
/// * tvec: Input/Output translation vector. Input values are used as an initial solution.
/// * criteria: Criteria when to stop the Levenberg-Marquard iterative algorithm.
/// * VVSlambda: Gain for the virtual visual servoing control law, equivalent to the 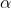
/// gain in the Damped Gauss-Newton formulation.
///
/// The function refines the object pose given at least 3 object points, their corresponding image
/// projections, an initial solution for the rotation and translation vector,
/// as well as the camera intrinsic matrix and the distortion coefficients.
/// The function minimizes the projection error with respect to the rotation and the translation vectors, using a
/// virtual visual servoing (VVS) [Chaumette06](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Chaumette06) [Marchand16](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Marchand16) scheme.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::EPS+TermCriteria::COUNT,20,FLT_EPSILON)
/// * vv_slambda: 1
#[inline]
pub fn solve_pnp_refine_vvs(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, rvec: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, tvec: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, criteria: core::TermCriteria, vv_slambda: f64) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
input_output_array_arg!(rvec);
input_output_array_arg!(tvec);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_solvePnPRefineVVS_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_TermCriteria_double(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), tvec.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), &criteria, vv_slambda, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds an object pose from 3D-2D point correspondences.
/// ## See also
/// [calib3d_solvePnP]
///
/// This function returns the rotation and the translation vectors that transform a 3D point expressed in the object
/// coordinate frame to the camera coordinate frame, using different methods:
/// - P3P methods ([SOLVEPNP_P3P], [SOLVEPNP_AP3P]): need 4 input points to return a unique solution.
/// - [SOLVEPNP_IPPE] Input points must be >= 4 and object points must be coplanar.
/// - [SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE] Special case suitable for marker pose estimation.
/// Number of input points must be 4. Object points must be defined in the following order:
/// - point 0: [-squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 1: [ squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 2: [ squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 3: [-squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - for all the other flags, number of input points must be >= 4 and object points can be in any configuration.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Array of object points in the object coordinate space, Nx3 1-channel or
/// 1xN/Nx1 3-channel, where N is the number of points. vector\<Point3d\> can be also passed here.
/// * imagePoints: Array of corresponding image points, Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel,
/// where N is the number of points. vector\<Point2d\> can be also passed here.
/// * cameraMatrix: Input camera intrinsic matrix  .
/// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients
/// . If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are
/// assumed.
/// * rvec: Output rotation vector (see [Rodrigues] ) that, together with tvec, brings points from
/// the model coordinate system to the camera coordinate system.
/// * tvec: Output translation vector.
/// * useExtrinsicGuess: Parameter used for #SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE. If true (1), the function uses
/// the provided rvec and tvec values as initial approximations of the rotation and translation
/// vectors, respectively, and further optimizes them.
/// * flags: Method for solving a PnP problem: see [calib3d_solvePnP_flags]
///
/// More information about Perspective-n-Points is described in [calib3d_solvePnP]
///
///
/// Note:
/// * An example of how to use solvePnP for planar augmented reality can be found at
/// opencv_source_code/samples/python/plane_ar.py
/// * If you are using Python:
/// - Numpy array slices won't work as input because solvePnP requires contiguous
/// arrays (enforced by the assertion using cv::Mat::checkVector() around line 55 of
/// modules/calib3d/src/solvepnp.cpp version 2.4.9)
/// - The P3P algorithm requires image points to be in an array of shape (N,1,2) due
/// to its calling of [undistort_points] (around line 75 of modules/calib3d/src/solvepnp.cpp version 2.4.9)
/// which requires 2-channel information.
/// - Thus, given some data D = np.array(...) where D.shape = (N,M), in order to use a subset of
/// it as, e.g., imagePoints, one must effectively copy it into a new array: imagePoints =
/// np.ascontiguousarray(D[:,:2]).reshape((N,1,2))
/// * The methods [SOLVEPNP_DLS] and [SOLVEPNP_UPNP] cannot be used as the current implementations are
/// unstable and sometimes give completely wrong results. If you pass one of these two
/// flags, [SOLVEPNP_EPNP] method will be used instead.
/// * The minimum number of points is 4 in the general case. In the case of [SOLVEPNP_P3P] and [SOLVEPNP_AP3P]
/// methods, it is required to use exactly 4 points (the first 3 points are used to estimate all the solutions
/// of the P3P problem, the last one is used to retain the best solution that minimizes the reprojection error).
/// * With [SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE] method and `useExtrinsicGuess=true`, the minimum number of points is 3 (3 points
/// are sufficient to compute a pose but there are up to 4 solutions). The initial solution should be close to the
/// global solution to converge.
/// * With [SOLVEPNP_IPPE] input points must be >= 4 and object points must be coplanar.
/// * With [SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE] this is a special case suitable for marker pose estimation.
/// Number of input points must be 4. Object points must be defined in the following order:
/// - point 0: [-squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 1: [ squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 2: [ squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 3: [-squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
/// * With [SOLVEPNP_SQPNP] input points must be >= 3
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [solve_pnp] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * use_extrinsic_guess: false
/// * flags: SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE
#[inline]
pub fn solve_pnp_def(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, rvec: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvec: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
output_array_arg!(rvec);
output_array_arg!(tvec);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_solvePnP_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvec.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds an object pose from 3D-2D point correspondences.
/// ## See also
/// [calib3d_solvePnP]
///
/// This function returns the rotation and the translation vectors that transform a 3D point expressed in the object
/// coordinate frame to the camera coordinate frame, using different methods:
/// - P3P methods ([SOLVEPNP_P3P], [SOLVEPNP_AP3P]): need 4 input points to return a unique solution.
/// - [SOLVEPNP_IPPE] Input points must be >= 4 and object points must be coplanar.
/// - [SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE] Special case suitable for marker pose estimation.
/// Number of input points must be 4. Object points must be defined in the following order:
/// - point 0: [-squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 1: [ squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 2: [ squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 3: [-squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - for all the other flags, number of input points must be >= 4 and object points can be in any configuration.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Array of object points in the object coordinate space, Nx3 1-channel or
/// 1xN/Nx1 3-channel, where N is the number of points. vector\<Point3d\> can be also passed here.
/// * imagePoints: Array of corresponding image points, Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel,
/// where N is the number of points. vector\<Point2d\> can be also passed here.
/// * cameraMatrix: Input camera intrinsic matrix  .
/// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients
/// . If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are
/// assumed.
/// * rvec: Output rotation vector (see [Rodrigues] ) that, together with tvec, brings points from
/// the model coordinate system to the camera coordinate system.
/// * tvec: Output translation vector.
/// * useExtrinsicGuess: Parameter used for #SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE. If true (1), the function uses
/// the provided rvec and tvec values as initial approximations of the rotation and translation
/// vectors, respectively, and further optimizes them.
/// * flags: Method for solving a PnP problem: see [calib3d_solvePnP_flags]
///
/// More information about Perspective-n-Points is described in [calib3d_solvePnP]
///
///
/// Note:
/// * An example of how to use solvePnP for planar augmented reality can be found at
/// opencv_source_code/samples/python/plane_ar.py
/// * If you are using Python:
/// - Numpy array slices won't work as input because solvePnP requires contiguous
/// arrays (enforced by the assertion using cv::Mat::checkVector() around line 55 of
/// modules/calib3d/src/solvepnp.cpp version 2.4.9)
/// - The P3P algorithm requires image points to be in an array of shape (N,1,2) due
/// to its calling of [undistort_points] (around line 75 of modules/calib3d/src/solvepnp.cpp version 2.4.9)
/// which requires 2-channel information.
/// - Thus, given some data D = np.array(...) where D.shape = (N,M), in order to use a subset of
/// it as, e.g., imagePoints, one must effectively copy it into a new array: imagePoints =
/// np.ascontiguousarray(D[:,:2]).reshape((N,1,2))
/// * The methods [SOLVEPNP_DLS] and [SOLVEPNP_UPNP] cannot be used as the current implementations are
/// unstable and sometimes give completely wrong results. If you pass one of these two
/// flags, [SOLVEPNP_EPNP] method will be used instead.
/// * The minimum number of points is 4 in the general case. In the case of [SOLVEPNP_P3P] and [SOLVEPNP_AP3P]
/// methods, it is required to use exactly 4 points (the first 3 points are used to estimate all the solutions
/// of the P3P problem, the last one is used to retain the best solution that minimizes the reprojection error).
/// * With [SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE] method and `useExtrinsicGuess=true`, the minimum number of points is 3 (3 points
/// are sufficient to compute a pose but there are up to 4 solutions). The initial solution should be close to the
/// global solution to converge.
/// * With [SOLVEPNP_IPPE] input points must be >= 4 and object points must be coplanar.
/// * With [SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE] this is a special case suitable for marker pose estimation.
/// Number of input points must be 4. Object points must be defined in the following order:
/// - point 0: [-squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 1: [ squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 2: [ squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
/// - point 3: [-squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
/// * With [SOLVEPNP_SQPNP] input points must be >= 3
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * use_extrinsic_guess: false
/// * flags: SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE
#[inline]
pub fn solve_pnp(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, rvec: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvec: &mut impl ToOutputArray, use_extrinsic_guess: bool, flags: i32) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
output_array_arg!(rvec);
output_array_arg!(tvec);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_solvePnP_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_bool_int(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvec.as_raw__OutputArray(), use_extrinsic_guess, flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// @overload
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [stereo_calibrate_1] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * flags: CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,30,1e-6)
#[inline]
pub fn stereo_calibrate_1_def(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points1: &impl ToInputArray, image_points2: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix1: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs1: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, camera_matrix2: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs2: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, image_size: core::Size, r: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, t: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, e: &mut impl ToOutputArray, f: &mut impl ToOutputArray, per_view_errors: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<f64> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points1);
input_array_arg!(image_points2);
input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix1);
input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs1);
input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix2);
input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs2);
input_output_array_arg!(r);
input_output_array_arg!(t);
output_array_arg!(e);
output_array_arg!(f);
output_array_arg!(per_view_errors);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_stereoCalibrate_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_Size_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points1.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix1.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs1.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), camera_matrix2.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs2.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), &image_size, r.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), t.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), e.as_raw__OutputArray(), f.as_raw__OutputArray(), per_view_errors.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calibrates a stereo camera set up. This function finds the intrinsic parameters
/// for each of the two cameras and the extrinsic parameters between the two cameras.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Vector of vectors of the calibration pattern points. The same structure as
/// in [calibrateCamera]. For each pattern view, both cameras need to see the same object
/// points. Therefore, objectPoints.size(), imagePoints1.size(), and imagePoints2.size() need to be
/// equal as well as objectPoints[i].size(), imagePoints1[i].size(), and imagePoints2[i].size() need to
/// be equal for each i.
/// * imagePoints1: Vector of vectors of the projections of the calibration pattern points,
/// observed by the first camera. The same structure as in [calibrateCamera].
/// * imagePoints2: Vector of vectors of the projections of the calibration pattern points,
/// observed by the second camera. The same structure as in [calibrateCamera].
/// * cameraMatrix1: Input/output camera intrinsic matrix for the first camera, the same as in
/// [calibrateCamera]. Furthermore, for the stereo case, additional flags may be used, see below.
/// * distCoeffs1: Input/output vector of distortion coefficients, the same as in
/// [calibrateCamera].
/// * cameraMatrix2: Input/output second camera intrinsic matrix for the second camera. See description for
/// cameraMatrix1.
/// * distCoeffs2: Input/output lens distortion coefficients for the second camera. See
/// description for distCoeffs1.
/// * imageSize: Size of the image used only to initialize the camera intrinsic matrices.
/// * R: Output rotation matrix. Together with the translation vector T, this matrix brings
/// points given in the first camera's coordinate system to points in the second camera's
/// coordinate system. In more technical terms, the tuple of R and T performs a change of basis
/// from the first camera's coordinate system to the second camera's coordinate system. Due to its
/// duality, this tuple is equivalent to the position of the first camera with respect to the
/// second camera coordinate system.
/// * T: Output translation vector, see description above.
/// * E: Output essential matrix.
/// * F: Output fundamental matrix.
/// * rvecs: Output vector of rotation vectors ( [Rodrigues] ) estimated for each pattern view in the
/// coordinate system of the first camera of the stereo pair (e.g. std::vector<cv::Mat>). More in detail, each
/// i-th rotation vector together with the corresponding i-th translation vector (see the next output parameter
/// description) brings the calibration pattern from the object coordinate space (in which object points are
/// specified) to the camera coordinate space of the first camera of the stereo pair. In more technical terms,
/// the tuple of the i-th rotation and translation vector performs a change of basis from object coordinate space
/// to camera coordinate space of the first camera of the stereo pair.
/// * tvecs: Output vector of translation vectors estimated for each pattern view, see parameter description
/// of previous output parameter ( rvecs ).
/// * perViewErrors: Output vector of the RMS re-projection error estimated for each pattern view.
/// * flags: Different flags that may be zero or a combination of the following values:
/// * [CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC] Fix cameraMatrix? and distCoeffs? so that only R, T, E, and F
/// matrices are estimated.
/// * [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] Optimize some or all of the intrinsic parameters
/// according to the specified flags. Initial values are provided by the user.
/// * [CALIB_USE_EXTRINSIC_GUESS] R and T contain valid initial values that are optimized further.
/// Otherwise R and T are initialized to the median value of the pattern views (each dimension separately).
/// * [CALIB_FIX_PRINCIPAL_POINT] Fix the principal points during the optimization.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_FOCAL_LENGTH] Fix  and  .
/// * [CALIB_FIX_ASPECT_RATIO] Optimize  . Fix the ratio 
/// .
/// * [CALIB_SAME_FOCAL_LENGTH] Enforce  and  .
/// * [CALIB_ZERO_TANGENT_DIST] Set tangential distortion coefficients for each camera to
/// zeros and fix there.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_K1],..., [CALIB_FIX_K6] Do not change the corresponding radial
/// distortion coefficient during the optimization. If [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set,
/// the coefficient from the supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0.
/// * [CALIB_RATIONAL_MODEL] Enable coefficients k4, k5, and k6. To provide the backward
/// compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the calibration
/// function use the rational model and return 8 coefficients. If the flag is not set, the
/// function computes and returns only 5 distortion coefficients.
/// * [CALIB_THIN_PRISM_MODEL] Coefficients s1, s2, s3 and s4 are enabled. To provide the
/// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the
/// calibration function use the thin prism model and return 12 coefficients. If the flag is not
/// set, the function computes and returns only 5 distortion coefficients.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_S1_S2_S3_S4] The thin prism distortion coefficients are not changed during
/// the optimization. If [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set, the coefficient from the
/// supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0.
/// * [CALIB_TILTED_MODEL] Coefficients tauX and tauY are enabled. To provide the
/// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the
/// calibration function use the tilted sensor model and return 14 coefficients. If the flag is not
/// set, the function computes and returns only 5 distortion coefficients.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_TAUX_TAUY] The coefficients of the tilted sensor model are not changed during
/// the optimization. If [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set, the coefficient from the
/// supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0.
/// * criteria: Termination criteria for the iterative optimization algorithm.
///
/// The function estimates the transformation between two cameras making a stereo pair. If one computes
/// the poses of an object relative to the first camera and to the second camera,
/// ( , ) and (,), respectively, for a stereo camera where the
/// relative position and orientation between the two cameras are fixed, then those poses definitely
/// relate to each other. This means, if the relative position and orientation (,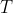) of the
/// two cameras is known, it is possible to compute (,) when (,) is
/// given. This is what the described function does. It computes (,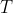) such that:
///
/// 
/// 
///
/// Therefore, one can compute the coordinate representation of a 3D point for the second camera's
/// coordinate system when given the point's coordinate representation in the first camera's coordinate
/// system:
///
/// 
///
///
/// Optionally, it computes the essential matrix E:
///
/// 
///
/// where  are components of the translation vector 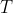 :  .
/// And the function can also compute the fundamental matrix F:
///
/// 
///
/// Besides the stereo-related information, the function can also perform a full calibration of each of
/// the two cameras. However, due to the high dimensionality of the parameter space and noise in the
/// input data, the function can diverge from the correct solution. If the intrinsic parameters can be
/// estimated with high accuracy for each of the cameras individually (for example, using
/// [calibrate_camera] ), you are recommended to do so and then pass [CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC] flag to the
/// function along with the computed intrinsic parameters. Otherwise, if all the parameters are
/// estimated at once, it makes sense to restrict some parameters, for example, pass
/// [CALIB_SAME_FOCAL_LENGTH] and [CALIB_ZERO_TANGENT_DIST] flags, which is usually a
/// reasonable assumption.
///
/// Similarly to #calibrateCamera, the function minimizes the total re-projection error for all the
/// points in all the available views from both cameras. The function returns the final value of the
/// re-projection error.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [stereo_calibrate_extended] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * flags: CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,30,1e-6)
#[inline]
pub fn stereo_calibrate_extended_def(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points1: &impl ToInputArray, image_points2: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix1: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs1: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, camera_matrix2: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs2: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, image_size: core::Size, r: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, t: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, e: &mut impl ToOutputArray, f: &mut impl ToOutputArray, rvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, per_view_errors: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<f64> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points1);
input_array_arg!(image_points2);
input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix1);
input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs1);
input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix2);
input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs2);
input_output_array_arg!(r);
input_output_array_arg!(t);
output_array_arg!(e);
output_array_arg!(f);
output_array_arg!(rvecs);
output_array_arg!(tvecs);
output_array_arg!(per_view_errors);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_stereoCalibrate_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_Size_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points1.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix1.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs1.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), camera_matrix2.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs2.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), &image_size, r.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), t.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), e.as_raw__OutputArray(), f.as_raw__OutputArray(), rvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), per_view_errors.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calibrates a stereo camera set up. This function finds the intrinsic parameters
/// for each of the two cameras and the extrinsic parameters between the two cameras.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Vector of vectors of the calibration pattern points. The same structure as
/// in [calibrateCamera]. For each pattern view, both cameras need to see the same object
/// points. Therefore, objectPoints.size(), imagePoints1.size(), and imagePoints2.size() need to be
/// equal as well as objectPoints[i].size(), imagePoints1[i].size(), and imagePoints2[i].size() need to
/// be equal for each i.
/// * imagePoints1: Vector of vectors of the projections of the calibration pattern points,
/// observed by the first camera. The same structure as in [calibrateCamera].
/// * imagePoints2: Vector of vectors of the projections of the calibration pattern points,
/// observed by the second camera. The same structure as in [calibrateCamera].
/// * cameraMatrix1: Input/output camera intrinsic matrix for the first camera, the same as in
/// [calibrateCamera]. Furthermore, for the stereo case, additional flags may be used, see below.
/// * distCoeffs1: Input/output vector of distortion coefficients, the same as in
/// [calibrateCamera].
/// * cameraMatrix2: Input/output second camera intrinsic matrix for the second camera. See description for
/// cameraMatrix1.
/// * distCoeffs2: Input/output lens distortion coefficients for the second camera. See
/// description for distCoeffs1.
/// * imageSize: Size of the image used only to initialize the camera intrinsic matrices.
/// * R: Output rotation matrix. Together with the translation vector T, this matrix brings
/// points given in the first camera's coordinate system to points in the second camera's
/// coordinate system. In more technical terms, the tuple of R and T performs a change of basis
/// from the first camera's coordinate system to the second camera's coordinate system. Due to its
/// duality, this tuple is equivalent to the position of the first camera with respect to the
/// second camera coordinate system.
/// * T: Output translation vector, see description above.
/// * E: Output essential matrix.
/// * F: Output fundamental matrix.
/// * rvecs: Output vector of rotation vectors ( [Rodrigues] ) estimated for each pattern view in the
/// coordinate system of the first camera of the stereo pair (e.g. std::vector<cv::Mat>). More in detail, each
/// i-th rotation vector together with the corresponding i-th translation vector (see the next output parameter
/// description) brings the calibration pattern from the object coordinate space (in which object points are
/// specified) to the camera coordinate space of the first camera of the stereo pair. In more technical terms,
/// the tuple of the i-th rotation and translation vector performs a change of basis from object coordinate space
/// to camera coordinate space of the first camera of the stereo pair.
/// * tvecs: Output vector of translation vectors estimated for each pattern view, see parameter description
/// of previous output parameter ( rvecs ).
/// * perViewErrors: Output vector of the RMS re-projection error estimated for each pattern view.
/// * flags: Different flags that may be zero or a combination of the following values:
/// * [CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC] Fix cameraMatrix? and distCoeffs? so that only R, T, E, and F
/// matrices are estimated.
/// * [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] Optimize some or all of the intrinsic parameters
/// according to the specified flags. Initial values are provided by the user.
/// * [CALIB_USE_EXTRINSIC_GUESS] R and T contain valid initial values that are optimized further.
/// Otherwise R and T are initialized to the median value of the pattern views (each dimension separately).
/// * [CALIB_FIX_PRINCIPAL_POINT] Fix the principal points during the optimization.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_FOCAL_LENGTH] Fix  and  .
/// * [CALIB_FIX_ASPECT_RATIO] Optimize  . Fix the ratio 
/// .
/// * [CALIB_SAME_FOCAL_LENGTH] Enforce  and  .
/// * [CALIB_ZERO_TANGENT_DIST] Set tangential distortion coefficients for each camera to
/// zeros and fix there.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_K1],..., [CALIB_FIX_K6] Do not change the corresponding radial
/// distortion coefficient during the optimization. If [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set,
/// the coefficient from the supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0.
/// * [CALIB_RATIONAL_MODEL] Enable coefficients k4, k5, and k6. To provide the backward
/// compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the calibration
/// function use the rational model and return 8 coefficients. If the flag is not set, the
/// function computes and returns only 5 distortion coefficients.
/// * [CALIB_THIN_PRISM_MODEL] Coefficients s1, s2, s3 and s4 are enabled. To provide the
/// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the
/// calibration function use the thin prism model and return 12 coefficients. If the flag is not
/// set, the function computes and returns only 5 distortion coefficients.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_S1_S2_S3_S4] The thin prism distortion coefficients are not changed during
/// the optimization. If [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set, the coefficient from the
/// supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0.
/// * [CALIB_TILTED_MODEL] Coefficients tauX and tauY are enabled. To provide the
/// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the
/// calibration function use the tilted sensor model and return 14 coefficients. If the flag is not
/// set, the function computes and returns only 5 distortion coefficients.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_TAUX_TAUY] The coefficients of the tilted sensor model are not changed during
/// the optimization. If [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set, the coefficient from the
/// supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0.
/// * criteria: Termination criteria for the iterative optimization algorithm.
///
/// The function estimates the transformation between two cameras making a stereo pair. If one computes
/// the poses of an object relative to the first camera and to the second camera,
/// ( , ) and (,), respectively, for a stereo camera where the
/// relative position and orientation between the two cameras are fixed, then those poses definitely
/// relate to each other. This means, if the relative position and orientation (,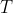) of the
/// two cameras is known, it is possible to compute (,) when (,) is
/// given. This is what the described function does. It computes (,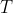) such that:
///
/// 
/// 
///
/// Therefore, one can compute the coordinate representation of a 3D point for the second camera's
/// coordinate system when given the point's coordinate representation in the first camera's coordinate
/// system:
///
/// 
///
///
/// Optionally, it computes the essential matrix E:
///
/// 
///
/// where  are components of the translation vector 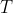 :  .
/// And the function can also compute the fundamental matrix F:
///
/// 
///
/// Besides the stereo-related information, the function can also perform a full calibration of each of
/// the two cameras. However, due to the high dimensionality of the parameter space and noise in the
/// input data, the function can diverge from the correct solution. If the intrinsic parameters can be
/// estimated with high accuracy for each of the cameras individually (for example, using
/// [calibrate_camera] ), you are recommended to do so and then pass [CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC] flag to the
/// function along with the computed intrinsic parameters. Otherwise, if all the parameters are
/// estimated at once, it makes sense to restrict some parameters, for example, pass
/// [CALIB_SAME_FOCAL_LENGTH] and [CALIB_ZERO_TANGENT_DIST] flags, which is usually a
/// reasonable assumption.
///
/// Similarly to #calibrateCamera, the function minimizes the total re-projection error for all the
/// points in all the available views from both cameras. The function returns the final value of the
/// re-projection error.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,30,1e-6)
#[inline]
pub fn stereo_calibrate_extended(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points1: &impl ToInputArray, image_points2: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix1: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs1: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, camera_matrix2: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs2: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, image_size: core::Size, r: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, t: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, e: &mut impl ToOutputArray, f: &mut impl ToOutputArray, rvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, tvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray, per_view_errors: &mut impl ToOutputArray, flags: i32, criteria: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<f64> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points1);
input_array_arg!(image_points2);
input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix1);
input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs1);
input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix2);
input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs2);
input_output_array_arg!(r);
input_output_array_arg!(t);
output_array_arg!(e);
output_array_arg!(f);
output_array_arg!(rvecs);
output_array_arg!(tvecs);
output_array_arg!(per_view_errors);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_stereoCalibrate_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_Size_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_TermCriteria(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points1.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix1.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs1.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), camera_matrix2.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs2.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), &image_size, r.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), t.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), e.as_raw__OutputArray(), f.as_raw__OutputArray(), rvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), per_view_errors.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, &criteria, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calibrates a stereo camera set up. This function finds the intrinsic parameters
/// for each of the two cameras and the extrinsic parameters between the two cameras.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Vector of vectors of the calibration pattern points. The same structure as
/// in [calibrateCamera]. For each pattern view, both cameras need to see the same object
/// points. Therefore, objectPoints.size(), imagePoints1.size(), and imagePoints2.size() need to be
/// equal as well as objectPoints[i].size(), imagePoints1[i].size(), and imagePoints2[i].size() need to
/// be equal for each i.
/// * imagePoints1: Vector of vectors of the projections of the calibration pattern points,
/// observed by the first camera. The same structure as in [calibrateCamera].
/// * imagePoints2: Vector of vectors of the projections of the calibration pattern points,
/// observed by the second camera. The same structure as in [calibrateCamera].
/// * cameraMatrix1: Input/output camera intrinsic matrix for the first camera, the same as in
/// [calibrateCamera]. Furthermore, for the stereo case, additional flags may be used, see below.
/// * distCoeffs1: Input/output vector of distortion coefficients, the same as in
/// [calibrateCamera].
/// * cameraMatrix2: Input/output second camera intrinsic matrix for the second camera. See description for
/// cameraMatrix1.
/// * distCoeffs2: Input/output lens distortion coefficients for the second camera. See
/// description for distCoeffs1.
/// * imageSize: Size of the image used only to initialize the camera intrinsic matrices.
/// * R: Output rotation matrix. Together with the translation vector T, this matrix brings
/// points given in the first camera's coordinate system to points in the second camera's
/// coordinate system. In more technical terms, the tuple of R and T performs a change of basis
/// from the first camera's coordinate system to the second camera's coordinate system. Due to its
/// duality, this tuple is equivalent to the position of the first camera with respect to the
/// second camera coordinate system.
/// * T: Output translation vector, see description above.
/// * E: Output essential matrix.
/// * F: Output fundamental matrix.
/// * rvecs: Output vector of rotation vectors ( [Rodrigues] ) estimated for each pattern view in the
/// coordinate system of the first camera of the stereo pair (e.g. std::vector<cv::Mat>). More in detail, each
/// i-th rotation vector together with the corresponding i-th translation vector (see the next output parameter
/// description) brings the calibration pattern from the object coordinate space (in which object points are
/// specified) to the camera coordinate space of the first camera of the stereo pair. In more technical terms,
/// the tuple of the i-th rotation and translation vector performs a change of basis from object coordinate space
/// to camera coordinate space of the first camera of the stereo pair.
/// * tvecs: Output vector of translation vectors estimated for each pattern view, see parameter description
/// of previous output parameter ( rvecs ).
/// * perViewErrors: Output vector of the RMS re-projection error estimated for each pattern view.
/// * flags: Different flags that may be zero or a combination of the following values:
/// * [CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC] Fix cameraMatrix? and distCoeffs? so that only R, T, E, and F
/// matrices are estimated.
/// * [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] Optimize some or all of the intrinsic parameters
/// according to the specified flags. Initial values are provided by the user.
/// * [CALIB_USE_EXTRINSIC_GUESS] R and T contain valid initial values that are optimized further.
/// Otherwise R and T are initialized to the median value of the pattern views (each dimension separately).
/// * [CALIB_FIX_PRINCIPAL_POINT] Fix the principal points during the optimization.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_FOCAL_LENGTH] Fix  and  .
/// * [CALIB_FIX_ASPECT_RATIO] Optimize  . Fix the ratio 
/// .
/// * [CALIB_SAME_FOCAL_LENGTH] Enforce  and  .
/// * [CALIB_ZERO_TANGENT_DIST] Set tangential distortion coefficients for each camera to
/// zeros and fix there.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_K1],..., [CALIB_FIX_K6] Do not change the corresponding radial
/// distortion coefficient during the optimization. If [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set,
/// the coefficient from the supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0.
/// * [CALIB_RATIONAL_MODEL] Enable coefficients k4, k5, and k6. To provide the backward
/// compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the calibration
/// function use the rational model and return 8 coefficients. If the flag is not set, the
/// function computes and returns only 5 distortion coefficients.
/// * [CALIB_THIN_PRISM_MODEL] Coefficients s1, s2, s3 and s4 are enabled. To provide the
/// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the
/// calibration function use the thin prism model and return 12 coefficients. If the flag is not
/// set, the function computes and returns only 5 distortion coefficients.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_S1_S2_S3_S4] The thin prism distortion coefficients are not changed during
/// the optimization. If [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set, the coefficient from the
/// supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0.
/// * [CALIB_TILTED_MODEL] Coefficients tauX and tauY are enabled. To provide the
/// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the
/// calibration function use the tilted sensor model and return 14 coefficients. If the flag is not
/// set, the function computes and returns only 5 distortion coefficients.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_TAUX_TAUY] The coefficients of the tilted sensor model are not changed during
/// the optimization. If [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set, the coefficient from the
/// supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0.
/// * criteria: Termination criteria for the iterative optimization algorithm.
///
/// The function estimates the transformation between two cameras making a stereo pair. If one computes
/// the poses of an object relative to the first camera and to the second camera,
/// ( , ) and (,), respectively, for a stereo camera where the
/// relative position and orientation between the two cameras are fixed, then those poses definitely
/// relate to each other. This means, if the relative position and orientation (,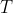) of the
/// two cameras is known, it is possible to compute (,) when (,) is
/// given. This is what the described function does. It computes (,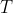) such that:
///
/// 
/// 
///
/// Therefore, one can compute the coordinate representation of a 3D point for the second camera's
/// coordinate system when given the point's coordinate representation in the first camera's coordinate
/// system:
///
/// 
///
///
/// Optionally, it computes the essential matrix E:
///
/// 
///
/// where  are components of the translation vector 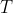 :  .
/// And the function can also compute the fundamental matrix F:
///
/// 
///
/// Besides the stereo-related information, the function can also perform a full calibration of each of
/// the two cameras. However, due to the high dimensionality of the parameter space and noise in the
/// input data, the function can diverge from the correct solution. If the intrinsic parameters can be
/// estimated with high accuracy for each of the cameras individually (for example, using
/// [calibrate_camera] ), you are recommended to do so and then pass [CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC] flag to the
/// function along with the computed intrinsic parameters. Otherwise, if all the parameters are
/// estimated at once, it makes sense to restrict some parameters, for example, pass
/// [CALIB_SAME_FOCAL_LENGTH] and [CALIB_ZERO_TANGENT_DIST] flags, which is usually a
/// reasonable assumption.
///
/// Similarly to #calibrateCamera, the function minimizes the total re-projection error for all the
/// points in all the available views from both cameras. The function returns the final value of the
/// re-projection error.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,30,1e-6)
#[inline]
pub fn stereo_calibrate_1(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points1: &impl ToInputArray, image_points2: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix1: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs1: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, camera_matrix2: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs2: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, image_size: core::Size, r: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, t: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, e: &mut impl ToOutputArray, f: &mut impl ToOutputArray, per_view_errors: &mut impl ToOutputArray, flags: i32, criteria: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<f64> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points1);
input_array_arg!(image_points2);
input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix1);
input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs1);
input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix2);
input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs2);
input_output_array_arg!(r);
input_output_array_arg!(t);
output_array_arg!(e);
output_array_arg!(f);
output_array_arg!(per_view_errors);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_stereoCalibrate_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_Size_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_TermCriteria(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points1.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix1.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs1.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), camera_matrix2.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs2.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), &image_size, r.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), t.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), e.as_raw__OutputArray(), f.as_raw__OutputArray(), per_view_errors.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, &criteria, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// @overload
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [stereo_calibrate] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * flags: CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,30,1e-6)
#[inline]
pub fn stereo_calibrate_def(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points1: &impl ToInputArray, image_points2: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix1: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs1: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, camera_matrix2: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs2: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, image_size: core::Size, r: &mut impl ToOutputArray, t: &mut impl ToOutputArray, e: &mut impl ToOutputArray, f: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<f64> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points1);
input_array_arg!(image_points2);
input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix1);
input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs1);
input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix2);
input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs2);
output_array_arg!(r);
output_array_arg!(t);
output_array_arg!(e);
output_array_arg!(f);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_stereoCalibrate_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_Size_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points1.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix1.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs1.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), camera_matrix2.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs2.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), &image_size, r.as_raw__OutputArray(), t.as_raw__OutputArray(), e.as_raw__OutputArray(), f.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calibrates a stereo camera set up. This function finds the intrinsic parameters
/// for each of the two cameras and the extrinsic parameters between the two cameras.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * objectPoints: Vector of vectors of the calibration pattern points. The same structure as
/// in [calibrateCamera]. For each pattern view, both cameras need to see the same object
/// points. Therefore, objectPoints.size(), imagePoints1.size(), and imagePoints2.size() need to be
/// equal as well as objectPoints[i].size(), imagePoints1[i].size(), and imagePoints2[i].size() need to
/// be equal for each i.
/// * imagePoints1: Vector of vectors of the projections of the calibration pattern points,
/// observed by the first camera. The same structure as in [calibrateCamera].
/// * imagePoints2: Vector of vectors of the projections of the calibration pattern points,
/// observed by the second camera. The same structure as in [calibrateCamera].
/// * cameraMatrix1: Input/output camera intrinsic matrix for the first camera, the same as in
/// [calibrateCamera]. Furthermore, for the stereo case, additional flags may be used, see below.
/// * distCoeffs1: Input/output vector of distortion coefficients, the same as in
/// [calibrateCamera].
/// * cameraMatrix2: Input/output second camera intrinsic matrix for the second camera. See description for
/// cameraMatrix1.
/// * distCoeffs2: Input/output lens distortion coefficients for the second camera. See
/// description for distCoeffs1.
/// * imageSize: Size of the image used only to initialize the camera intrinsic matrices.
/// * R: Output rotation matrix. Together with the translation vector T, this matrix brings
/// points given in the first camera's coordinate system to points in the second camera's
/// coordinate system. In more technical terms, the tuple of R and T performs a change of basis
/// from the first camera's coordinate system to the second camera's coordinate system. Due to its
/// duality, this tuple is equivalent to the position of the first camera with respect to the
/// second camera coordinate system.
/// * T: Output translation vector, see description above.
/// * E: Output essential matrix.
/// * F: Output fundamental matrix.
/// * rvecs: Output vector of rotation vectors ( [Rodrigues] ) estimated for each pattern view in the
/// coordinate system of the first camera of the stereo pair (e.g. std::vector<cv::Mat>). More in detail, each
/// i-th rotation vector together with the corresponding i-th translation vector (see the next output parameter
/// description) brings the calibration pattern from the object coordinate space (in which object points are
/// specified) to the camera coordinate space of the first camera of the stereo pair. In more technical terms,
/// the tuple of the i-th rotation and translation vector performs a change of basis from object coordinate space
/// to camera coordinate space of the first camera of the stereo pair.
/// * tvecs: Output vector of translation vectors estimated for each pattern view, see parameter description
/// of previous output parameter ( rvecs ).
/// * perViewErrors: Output vector of the RMS re-projection error estimated for each pattern view.
/// * flags: Different flags that may be zero or a combination of the following values:
/// * [CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC] Fix cameraMatrix? and distCoeffs? so that only R, T, E, and F
/// matrices are estimated.
/// * [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] Optimize some or all of the intrinsic parameters
/// according to the specified flags. Initial values are provided by the user.
/// * [CALIB_USE_EXTRINSIC_GUESS] R and T contain valid initial values that are optimized further.
/// Otherwise R and T are initialized to the median value of the pattern views (each dimension separately).
/// * [CALIB_FIX_PRINCIPAL_POINT] Fix the principal points during the optimization.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_FOCAL_LENGTH] Fix  and  .
/// * [CALIB_FIX_ASPECT_RATIO] Optimize  . Fix the ratio 
/// .
/// * [CALIB_SAME_FOCAL_LENGTH] Enforce  and  .
/// * [CALIB_ZERO_TANGENT_DIST] Set tangential distortion coefficients for each camera to
/// zeros and fix there.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_K1],..., [CALIB_FIX_K6] Do not change the corresponding radial
/// distortion coefficient during the optimization. If [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set,
/// the coefficient from the supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0.
/// * [CALIB_RATIONAL_MODEL] Enable coefficients k4, k5, and k6. To provide the backward
/// compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the calibration
/// function use the rational model and return 8 coefficients. If the flag is not set, the
/// function computes and returns only 5 distortion coefficients.
/// * [CALIB_THIN_PRISM_MODEL] Coefficients s1, s2, s3 and s4 are enabled. To provide the
/// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the
/// calibration function use the thin prism model and return 12 coefficients. If the flag is not
/// set, the function computes and returns only 5 distortion coefficients.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_S1_S2_S3_S4] The thin prism distortion coefficients are not changed during
/// the optimization. If [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set, the coefficient from the
/// supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0.
/// * [CALIB_TILTED_MODEL] Coefficients tauX and tauY are enabled. To provide the
/// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the
/// calibration function use the tilted sensor model and return 14 coefficients. If the flag is not
/// set, the function computes and returns only 5 distortion coefficients.
/// * [CALIB_FIX_TAUX_TAUY] The coefficients of the tilted sensor model are not changed during
/// the optimization. If [CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS] is set, the coefficient from the
/// supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0.
/// * criteria: Termination criteria for the iterative optimization algorithm.
///
/// The function estimates the transformation between two cameras making a stereo pair. If one computes
/// the poses of an object relative to the first camera and to the second camera,
/// ( , ) and (,), respectively, for a stereo camera where the
/// relative position and orientation between the two cameras are fixed, then those poses definitely
/// relate to each other. This means, if the relative position and orientation (,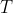) of the
/// two cameras is known, it is possible to compute (,) when (,) is
/// given. This is what the described function does. It computes (,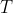) such that:
///
/// 
/// 
///
/// Therefore, one can compute the coordinate representation of a 3D point for the second camera's
/// coordinate system when given the point's coordinate representation in the first camera's coordinate
/// system:
///
/// 
///
///
/// Optionally, it computes the essential matrix E:
///
/// 
///
/// where  are components of the translation vector 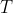 :  .
/// And the function can also compute the fundamental matrix F:
///
/// 
///
/// Besides the stereo-related information, the function can also perform a full calibration of each of
/// the two cameras. However, due to the high dimensionality of the parameter space and noise in the
/// input data, the function can diverge from the correct solution. If the intrinsic parameters can be
/// estimated with high accuracy for each of the cameras individually (for example, using
/// [calibrate_camera] ), you are recommended to do so and then pass [CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC] flag to the
/// function along with the computed intrinsic parameters. Otherwise, if all the parameters are
/// estimated at once, it makes sense to restrict some parameters, for example, pass
/// [CALIB_SAME_FOCAL_LENGTH] and [CALIB_ZERO_TANGENT_DIST] flags, which is usually a
/// reasonable assumption.
///
/// Similarly to #calibrateCamera, the function minimizes the total re-projection error for all the
/// points in all the available views from both cameras. The function returns the final value of the
/// re-projection error.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC
/// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,30,1e-6)
#[inline]
pub fn stereo_calibrate(object_points: &impl ToInputArray, image_points1: &impl ToInputArray, image_points2: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix1: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs1: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, camera_matrix2: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs2: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, image_size: core::Size, r: &mut impl ToOutputArray, t: &mut impl ToOutputArray, e: &mut impl ToOutputArray, f: &mut impl ToOutputArray, flags: i32, criteria: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<f64> {
input_array_arg!(object_points);
input_array_arg!(image_points1);
input_array_arg!(image_points2);
input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix1);
input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs1);
input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix2);
input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs2);
output_array_arg!(r);
output_array_arg!(t);
output_array_arg!(e);
output_array_arg!(f);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_stereoCalibrate_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_Size_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_TermCriteria(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points1.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix1.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs1.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), camera_matrix2.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs2.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), &image_size, r.as_raw__OutputArray(), t.as_raw__OutputArray(), e.as_raw__OutputArray(), f.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, &criteria, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes a rectification transform for an uncalibrated stereo camera.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * points1: Array of feature points in the first image.
/// * points2: The corresponding points in the second image. The same formats as in
/// [find_fundamental_mat] are supported.
/// * F: Input fundamental matrix. It can be computed from the same set of point pairs using
/// [find_fundamental_mat] .
/// * imgSize: Size of the image.
/// * H1: Output rectification homography matrix for the first image.
/// * H2: Output rectification homography matrix for the second image.
/// * threshold: Optional threshold used to filter out the outliers. If the parameter is greater
/// than zero, all the point pairs that do not comply with the epipolar geometry (that is, the points
/// for which  )
/// are rejected prior to computing the homographies. Otherwise, all the points are considered inliers.
///
/// The function computes the rectification transformations without knowing intrinsic parameters of the
/// cameras and their relative position in the space, which explains the suffix "uncalibrated". Another
/// related difference from [stereo_rectify] is that the function outputs not the rectification
/// transformations in the object (3D) space, but the planar perspective transformations encoded by the
/// homography matrices H1 and H2 . The function implements the algorithm [Hartley99](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Hartley99) .
///
///
/// Note:
/// While the algorithm does not need to know the intrinsic parameters of the cameras, it heavily
/// depends on the epipolar geometry. Therefore, if the camera lenses have a significant distortion,
/// it would be better to correct it before computing the fundamental matrix and calling this
/// function. For example, distortion coefficients can be estimated for each head of stereo camera
/// separately by using [calibrate_camera] . Then, the images can be corrected using [undistort] , or
/// just the point coordinates can be corrected with [undistort_points] .
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [stereo_rectify_uncalibrated] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * threshold: 5
#[inline]
pub fn stereo_rectify_uncalibrated_def(points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray, f: &impl ToInputArray, img_size: core::Size, h1: &mut impl ToOutputArray, h2: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
input_array_arg!(f);
output_array_arg!(h1);
output_array_arg!(h2);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_stereoRectifyUncalibrated_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), f.as_raw__InputArray(), &img_size, h1.as_raw__OutputArray(), h2.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes a rectification transform for an uncalibrated stereo camera.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * points1: Array of feature points in the first image.
/// * points2: The corresponding points in the second image. The same formats as in
/// [find_fundamental_mat] are supported.
/// * F: Input fundamental matrix. It can be computed from the same set of point pairs using
/// [find_fundamental_mat] .
/// * imgSize: Size of the image.
/// * H1: Output rectification homography matrix for the first image.
/// * H2: Output rectification homography matrix for the second image.
/// * threshold: Optional threshold used to filter out the outliers. If the parameter is greater
/// than zero, all the point pairs that do not comply with the epipolar geometry (that is, the points
/// for which  )
/// are rejected prior to computing the homographies. Otherwise, all the points are considered inliers.
///
/// The function computes the rectification transformations without knowing intrinsic parameters of the
/// cameras and their relative position in the space, which explains the suffix "uncalibrated". Another
/// related difference from [stereo_rectify] is that the function outputs not the rectification
/// transformations in the object (3D) space, but the planar perspective transformations encoded by the
/// homography matrices H1 and H2 . The function implements the algorithm [Hartley99](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Hartley99) .
///
///
/// Note:
/// While the algorithm does not need to know the intrinsic parameters of the cameras, it heavily
/// depends on the epipolar geometry. Therefore, if the camera lenses have a significant distortion,
/// it would be better to correct it before computing the fundamental matrix and calling this
/// function. For example, distortion coefficients can be estimated for each head of stereo camera
/// separately by using [calibrate_camera] . Then, the images can be corrected using [undistort] , or
/// just the point coordinates can be corrected with [undistort_points] .
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * threshold: 5
#[inline]
pub fn stereo_rectify_uncalibrated(points1: &impl ToInputArray, points2: &impl ToInputArray, f: &impl ToInputArray, img_size: core::Size, h1: &mut impl ToOutputArray, h2: &mut impl ToOutputArray, threshold: f64) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(points1);
input_array_arg!(points2);
input_array_arg!(f);
output_array_arg!(h1);
output_array_arg!(h2);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_stereoRectifyUncalibrated_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), f.as_raw__InputArray(), &img_size, h1.as_raw__OutputArray(), h2.as_raw__OutputArray(), threshold, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes rectification transforms for each head of a calibrated stereo camera.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * cameraMatrix1: First camera intrinsic matrix.
/// * distCoeffs1: First camera distortion parameters.
/// * cameraMatrix2: Second camera intrinsic matrix.
/// * distCoeffs2: Second camera distortion parameters.
/// * imageSize: Size of the image used for stereo calibration.
/// * R: Rotation matrix from the coordinate system of the first camera to the second camera,
/// see [stereoCalibrate].
/// * T: Translation vector from the coordinate system of the first camera to the second camera,
/// see [stereoCalibrate].
/// * R1: Output 3x3 rectification transform (rotation matrix) for the first camera. This matrix
/// brings points given in the unrectified first camera's coordinate system to points in the rectified
/// first camera's coordinate system. In more technical terms, it performs a change of basis from the
/// unrectified first camera's coordinate system to the rectified first camera's coordinate system.
/// * R2: Output 3x3 rectification transform (rotation matrix) for the second camera. This matrix
/// brings points given in the unrectified second camera's coordinate system to points in the rectified
/// second camera's coordinate system. In more technical terms, it performs a change of basis from the
/// unrectified second camera's coordinate system to the rectified second camera's coordinate system.
/// * P1: Output 3x4 projection matrix in the new (rectified) coordinate systems for the first
/// camera, i.e. it projects points given in the rectified first camera coordinate system into the
/// rectified first camera's image.
/// * P2: Output 3x4 projection matrix in the new (rectified) coordinate systems for the second
/// camera, i.e. it projects points given in the rectified first camera coordinate system into the
/// rectified second camera's image.
/// * Q: Output  disparity-to-depth mapping matrix (see [reprojectImageTo3D]).
/// * flags: Operation flags that may be zero or [CALIB_ZERO_DISPARITY] . If the flag is set,
/// the function makes the principal points of each camera have the same pixel coordinates in the
/// rectified views. And if the flag is not set, the function may still shift the images in the
/// horizontal or vertical direction (depending on the orientation of epipolar lines) to maximize the
/// useful image area.
/// * alpha: Free scaling parameter. If it is -1 or absent, the function performs the default
/// scaling. Otherwise, the parameter should be between 0 and 1. alpha=0 means that the rectified
/// images are zoomed and shifted so that only valid pixels are visible (no black areas after
/// rectification). alpha=1 means that the rectified image is decimated and shifted so that all the
/// pixels from the original images from the cameras are retained in the rectified images (no source
/// image pixels are lost). Any intermediate value yields an intermediate result between
/// those two extreme cases.
/// * newImageSize: New image resolution after rectification. The same size should be passed to
/// [init_undistort_rectify_map] (see the stereo_calib.cpp sample in OpenCV samples directory). When (0,0)
/// is passed (default), it is set to the original imageSize . Setting it to a larger value can help you
/// preserve details in the original image, especially when there is a big radial distortion.
/// * validPixROI1: Optional output rectangles inside the rectified images where all the pixels
/// are valid. If alpha=0 , the ROIs cover the whole images. Otherwise, they are likely to be smaller
/// (see the picture below).
/// * validPixROI2: Optional output rectangles inside the rectified images where all the pixels
/// are valid. If alpha=0 , the ROIs cover the whole images. Otherwise, they are likely to be smaller
/// (see the picture below).
///
/// The function computes the rotation matrices for each camera that (virtually) make both camera image
/// planes the same plane. Consequently, this makes all the epipolar lines parallel and thus simplifies
/// the dense stereo correspondence problem. The function takes the matrices computed by [stereo_calibrate]
/// as input. As output, it provides two rotation matrices and also two projection matrices in the new
/// coordinates. The function distinguishes the following two cases:
///
/// * **Horizontal stereo**: the first and the second camera views are shifted relative to each other
/// mainly along the x-axis (with possible small vertical shift). In the rectified images, the
/// corresponding epipolar lines in the left and right cameras are horizontal and have the same
/// y-coordinate. P1 and P2 look like:
///
/// 
///
/// 
///
/// 
///
/// where  is a horizontal shift between the cameras and  if
/// [CALIB_ZERO_DISPARITY] is set.
///
/// * **Vertical stereo**: the first and the second camera views are shifted relative to each other
/// mainly in the vertical direction (and probably a bit in the horizontal direction too). The epipolar
/// lines in the rectified images are vertical and have the same x-coordinate. P1 and P2 look like:
///
/// 
///
/// 
///
/// 
///
/// where  is a vertical shift between the cameras and  if
/// [CALIB_ZERO_DISPARITY] is set.
///
/// As you can see, the first three columns of P1 and P2 will effectively be the new "rectified" camera
/// matrices. The matrices, together with R1 and R2 , can then be passed to [init_undistort_rectify_map] to
/// initialize the rectification map for each camera.
///
/// See below the screenshot from the stereo_calib.cpp sample. Some red horizontal lines pass through
/// the corresponding image regions. This means that the images are well rectified, which is what most
/// stereo correspondence algorithms rely on. The green rectangles are roi1 and roi2 . You see that
/// their interiors are all valid pixels.
///
/// 
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [stereo_rectify] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * flags: CALIB_ZERO_DISPARITY
/// * alpha: -1
/// * new_image_size: Size()
/// * valid_pix_roi1: 0
/// * valid_pix_roi2: 0
#[inline]
pub fn stereo_rectify_def(camera_matrix1: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs1: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix2: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs2: &impl ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, r: &impl ToInputArray, t: &impl ToInputArray, r1: &mut impl ToOutputArray, r2: &mut impl ToOutputArray, p1: &mut impl ToOutputArray, p2: &mut impl ToOutputArray, q: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix1);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs1);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix2);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs2);
input_array_arg!(r);
input_array_arg!(t);
output_array_arg!(r1);
output_array_arg!(r2);
output_array_arg!(p1);
output_array_arg!(p2);
output_array_arg!(q);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_stereoRectify_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(camera_matrix1.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs1.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix2.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs2.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, r.as_raw__InputArray(), t.as_raw__InputArray(), r1.as_raw__OutputArray(), r2.as_raw__OutputArray(), p1.as_raw__OutputArray(), p2.as_raw__OutputArray(), q.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes rectification transforms for each head of a calibrated stereo camera.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * cameraMatrix1: First camera intrinsic matrix.
/// * distCoeffs1: First camera distortion parameters.
/// * cameraMatrix2: Second camera intrinsic matrix.
/// * distCoeffs2: Second camera distortion parameters.
/// * imageSize: Size of the image used for stereo calibration.
/// * R: Rotation matrix from the coordinate system of the first camera to the second camera,
/// see [stereoCalibrate].
/// * T: Translation vector from the coordinate system of the first camera to the second camera,
/// see [stereoCalibrate].
/// * R1: Output 3x3 rectification transform (rotation matrix) for the first camera. This matrix
/// brings points given in the unrectified first camera's coordinate system to points in the rectified
/// first camera's coordinate system. In more technical terms, it performs a change of basis from the
/// unrectified first camera's coordinate system to the rectified first camera's coordinate system.
/// * R2: Output 3x3 rectification transform (rotation matrix) for the second camera. This matrix
/// brings points given in the unrectified second camera's coordinate system to points in the rectified
/// second camera's coordinate system. In more technical terms, it performs a change of basis from the
/// unrectified second camera's coordinate system to the rectified second camera's coordinate system.
/// * P1: Output 3x4 projection matrix in the new (rectified) coordinate systems for the first
/// camera, i.e. it projects points given in the rectified first camera coordinate system into the
/// rectified first camera's image.
/// * P2: Output 3x4 projection matrix in the new (rectified) coordinate systems for the second
/// camera, i.e. it projects points given in the rectified first camera coordinate system into the
/// rectified second camera's image.
/// * Q: Output  disparity-to-depth mapping matrix (see [reprojectImageTo3D]).
/// * flags: Operation flags that may be zero or [CALIB_ZERO_DISPARITY] . If the flag is set,
/// the function makes the principal points of each camera have the same pixel coordinates in the
/// rectified views. And if the flag is not set, the function may still shift the images in the
/// horizontal or vertical direction (depending on the orientation of epipolar lines) to maximize the
/// useful image area.
/// * alpha: Free scaling parameter. If it is -1 or absent, the function performs the default
/// scaling. Otherwise, the parameter should be between 0 and 1. alpha=0 means that the rectified
/// images are zoomed and shifted so that only valid pixels are visible (no black areas after
/// rectification). alpha=1 means that the rectified image is decimated and shifted so that all the
/// pixels from the original images from the cameras are retained in the rectified images (no source
/// image pixels are lost). Any intermediate value yields an intermediate result between
/// those two extreme cases.
/// * newImageSize: New image resolution after rectification. The same size should be passed to
/// [init_undistort_rectify_map] (see the stereo_calib.cpp sample in OpenCV samples directory). When (0,0)
/// is passed (default), it is set to the original imageSize . Setting it to a larger value can help you
/// preserve details in the original image, especially when there is a big radial distortion.
/// * validPixROI1: Optional output rectangles inside the rectified images where all the pixels
/// are valid. If alpha=0 , the ROIs cover the whole images. Otherwise, they are likely to be smaller
/// (see the picture below).
/// * validPixROI2: Optional output rectangles inside the rectified images where all the pixels
/// are valid. If alpha=0 , the ROIs cover the whole images. Otherwise, they are likely to be smaller
/// (see the picture below).
///
/// The function computes the rotation matrices for each camera that (virtually) make both camera image
/// planes the same plane. Consequently, this makes all the epipolar lines parallel and thus simplifies
/// the dense stereo correspondence problem. The function takes the matrices computed by [stereo_calibrate]
/// as input. As output, it provides two rotation matrices and also two projection matrices in the new
/// coordinates. The function distinguishes the following two cases:
///
/// * **Horizontal stereo**: the first and the second camera views are shifted relative to each other
/// mainly along the x-axis (with possible small vertical shift). In the rectified images, the
/// corresponding epipolar lines in the left and right cameras are horizontal and have the same
/// y-coordinate. P1 and P2 look like:
///
/// 
///
/// 
///
/// 
///
/// where  is a horizontal shift between the cameras and  if
/// [CALIB_ZERO_DISPARITY] is set.
///
/// * **Vertical stereo**: the first and the second camera views are shifted relative to each other
/// mainly in the vertical direction (and probably a bit in the horizontal direction too). The epipolar
/// lines in the rectified images are vertical and have the same x-coordinate. P1 and P2 look like:
///
/// 
///
/// 
///
/// 
///
/// where  is a vertical shift between the cameras and  if
/// [CALIB_ZERO_DISPARITY] is set.
///
/// As you can see, the first three columns of P1 and P2 will effectively be the new "rectified" camera
/// matrices. The matrices, together with R1 and R2 , can then be passed to [init_undistort_rectify_map] to
/// initialize the rectification map for each camera.
///
/// See below the screenshot from the stereo_calib.cpp sample. Some red horizontal lines pass through
/// the corresponding image regions. This means that the images are well rectified, which is what most
/// stereo correspondence algorithms rely on. The green rectangles are roi1 and roi2 . You see that
/// their interiors are all valid pixels.
///
/// 
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: CALIB_ZERO_DISPARITY
/// * alpha: -1
/// * new_image_size: Size()
/// * valid_pix_roi1: 0
/// * valid_pix_roi2: 0
#[inline]
pub fn stereo_rectify(camera_matrix1: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs1: &impl ToInputArray, camera_matrix2: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs2: &impl ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, r: &impl ToInputArray, t: &impl ToInputArray, r1: &mut impl ToOutputArray, r2: &mut impl ToOutputArray, p1: &mut impl ToOutputArray, p2: &mut impl ToOutputArray, q: &mut impl ToOutputArray, flags: i32, alpha: f64, new_image_size: core::Size, valid_pix_roi1: &mut core::Rect, valid_pix_roi2: &mut core::Rect) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix1);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs1);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix2);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs2);
input_array_arg!(r);
input_array_arg!(t);
output_array_arg!(r1);
output_array_arg!(r2);
output_array_arg!(p1);
output_array_arg!(p2);
output_array_arg!(q);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_stereoRectify_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_double_Size_RectX_RectX(camera_matrix1.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs1.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix2.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs2.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, r.as_raw__InputArray(), t.as_raw__InputArray(), r1.as_raw__OutputArray(), r2.as_raw__OutputArray(), p1.as_raw__OutputArray(), p2.as_raw__OutputArray(), q.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, alpha, &new_image_size, valid_pix_roi1, valid_pix_roi2, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// This function reconstructs 3-dimensional points (in homogeneous coordinates) by using
/// their observations with a stereo camera.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * projMatr1: 3x4 projection matrix of the first camera, i.e. this matrix projects 3D points
/// given in the world's coordinate system into the first image.
/// * projMatr2: 3x4 projection matrix of the second camera, i.e. this matrix projects 3D points
/// given in the world's coordinate system into the second image.
/// * projPoints1: 2xN array of feature points in the first image. In the case of the c++ version,
/// it can be also a vector of feature points or two-channel matrix of size 1xN or Nx1.
/// * projPoints2: 2xN array of corresponding points in the second image. In the case of the c++
/// version, it can be also a vector of feature points or two-channel matrix of size 1xN or Nx1.
/// * points4D: 4xN array of reconstructed points in homogeneous coordinates. These points are
/// returned in the world's coordinate system.
///
///
/// Note:
/// Keep in mind that all input data should be of float type in order for this function to work.
///
///
/// Note:
/// If the projection matrices from [stereoRectify] are used, then the returned points are
/// represented in the first camera's rectified coordinate system.
/// ## See also
/// reprojectImageTo3D
#[inline]
pub fn triangulate_points(proj_matr1: &impl ToInputArray, proj_matr2: &impl ToInputArray, proj_points1: &impl ToInputArray, proj_points2: &impl ToInputArray, points4_d: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(proj_matr1);
input_array_arg!(proj_matr2);
input_array_arg!(proj_points1);
input_array_arg!(proj_points2);
output_array_arg!(points4_d);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_triangulatePoints_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(proj_matr1.as_raw__InputArray(), proj_matr2.as_raw__InputArray(), proj_points1.as_raw__InputArray(), proj_points2.as_raw__InputArray(), points4_d.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Compute undistorted image points position
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Observed points position, 2xN/Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel (CV_32FC2 or
/// CV_64FC2) (or vector\<Point2f\> ).
/// * dst: Output undistorted points position (1xN/Nx1 2-channel or vector\<Point2f\> ).
/// * cameraMatrix: Camera matrix  .
/// * distCoeffs: Distortion coefficients
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [undistort_image_points] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * unnamed: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::MAX_ITER+TermCriteria::EPS,5,0.01)
#[inline]
pub fn undistort_image_points_def(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_undistortImagePoints_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Compute undistorted image points position
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Observed points position, 2xN/Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel (CV_32FC2 or
/// CV_64FC2) (or vector\<Point2f\> ).
/// * dst: Output undistorted points position (1xN/Nx1 2-channel or vector\<Point2f\> ).
/// * cameraMatrix: Camera matrix  .
/// * distCoeffs: Distortion coefficients
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * unnamed: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::MAX_ITER+TermCriteria::EPS,5,0.01)
#[inline]
pub fn undistort_image_points(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, unnamed: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_undistortImagePoints_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_TermCriteria(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), &unnamed, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes the ideal point coordinates from the observed point coordinates.
///
/// The function is similar to [undistort] and [init_undistort_rectify_map] but it operates on a
/// sparse set of points instead of a raster image. Also the function performs a reverse transformation
/// to #projectPoints. In case of a 3D object, it does not reconstruct its 3D coordinates, but for a
/// planar object, it does, up to a translation vector, if the proper R is specified.
///
/// For each observed point coordinate 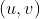 the function computes:
/// 
///
/// where *undistort* is an approximate iterative algorithm that estimates the normalized original
/// point coordinates out of the normalized distorted point coordinates ("normalized" means that the
/// coordinates do not depend on the camera matrix).
///
/// The function can be used for both a stereo camera head or a monocular camera (when R is empty).
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Observed point coordinates, 2xN/Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel (CV_32FC2 or CV_64FC2) (or
/// vector\<Point2f\> ).
/// * dst: Output ideal point coordinates (1xN/Nx1 2-channel or vector\<Point2f\> ) after undistortion and reverse perspective
/// transformation. If matrix P is identity or omitted, dst will contain normalized point coordinates.
/// * cameraMatrix: Camera matrix  .
/// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients
/// 
/// of 4, 5, 8, 12 or 14 elements. If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed.
/// * R: Rectification transformation in the object space (3x3 matrix). R1 or R2 computed by
/// [stereo_rectify] can be passed here. If the matrix is empty, the identity transformation is used.
/// * P: New camera matrix (3x3) or new projection matrix (3x4) . P1 or P2 computed by
/// [stereo_rectify] can be passed here. If the matrix is empty, the identity new camera matrix is used.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [undistort_points] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * r: noArray()
/// * p: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn undistort_points_def(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_undistortPoints_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes the ideal point coordinates from the observed point coordinates.
///
/// The function is similar to [undistort] and [init_undistort_rectify_map] but it operates on a
/// sparse set of points instead of a raster image. Also the function performs a reverse transformation
/// to #projectPoints. In case of a 3D object, it does not reconstruct its 3D coordinates, but for a
/// planar object, it does, up to a translation vector, if the proper R is specified.
///
/// For each observed point coordinate 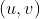 the function computes:
/// 
///
/// where *undistort* is an approximate iterative algorithm that estimates the normalized original
/// point coordinates out of the normalized distorted point coordinates ("normalized" means that the
/// coordinates do not depend on the camera matrix).
///
/// The function can be used for both a stereo camera head or a monocular camera (when R is empty).
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Observed point coordinates, 2xN/Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel (CV_32FC2 or CV_64FC2) (or
/// vector\<Point2f\> ).
/// * dst: Output ideal point coordinates (1xN/Nx1 2-channel or vector\<Point2f\> ) after undistortion and reverse perspective
/// transformation. If matrix P is identity or omitted, dst will contain normalized point coordinates.
/// * cameraMatrix: Camera matrix  .
/// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients
/// 
/// of 4, 5, 8, 12 or 14 elements. If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed.
/// * R: Rectification transformation in the object space (3x3 matrix). R1 or R2 computed by
/// [stereo_rectify] can be passed here. If the matrix is empty, the identity transformation is used.
/// * P: New camera matrix (3x3) or new projection matrix (3x4) . P1 or P2 computed by
/// [stereo_rectify] can be passed here. If the matrix is empty, the identity new camera matrix is used.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * r: noArray()
/// * p: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn undistort_points(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, r: &impl ToInputArray, p: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
input_array_arg!(r);
input_array_arg!(p);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_undistortPoints_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), r.as_raw__InputArray(), p.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes the ideal point coordinates from the observed point coordinates.
///
/// The function is similar to [undistort] and [init_undistort_rectify_map] but it operates on a
/// sparse set of points instead of a raster image. Also the function performs a reverse transformation
/// to #projectPoints. In case of a 3D object, it does not reconstruct its 3D coordinates, but for a
/// planar object, it does, up to a translation vector, if the proper R is specified.
///
/// For each observed point coordinate 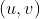 the function computes:
/// 
///
/// where *undistort* is an approximate iterative algorithm that estimates the normalized original
/// point coordinates out of the normalized distorted point coordinates ("normalized" means that the
/// coordinates do not depend on the camera matrix).
///
/// The function can be used for both a stereo camera head or a monocular camera (when R is empty).
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Observed point coordinates, 2xN/Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel (CV_32FC2 or CV_64FC2) (or
/// vector\<Point2f\> ).
/// * dst: Output ideal point coordinates (1xN/Nx1 2-channel or vector\<Point2f\> ) after undistortion and reverse perspective
/// transformation. If matrix P is identity or omitted, dst will contain normalized point coordinates.
/// * cameraMatrix: Camera matrix  .
/// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients
/// 
/// of 4, 5, 8, 12 or 14 elements. If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed.
/// * R: Rectification transformation in the object space (3x3 matrix). R1 or R2 computed by
/// [stereo_rectify] can be passed here. If the matrix is empty, the identity transformation is used.
/// * P: New camera matrix (3x3) or new projection matrix (3x4) . P1 or P2 computed by
/// [stereo_rectify] can be passed here. If the matrix is empty, the identity new camera matrix is used.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
///
/// Note: Default version of [undistort_points] does 5 iterations to compute undistorted points.
#[inline]
pub fn undistort_points_iter(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, r: &impl ToInputArray, p: &impl ToInputArray, criteria: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
input_array_arg!(r);
input_array_arg!(p);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_undistortPoints_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_TermCriteria(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), r.as_raw__InputArray(), p.as_raw__InputArray(), &criteria, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Transforms an image to compensate for lens distortion.
///
/// The function transforms an image to compensate radial and tangential lens distortion.
///
/// The function is simply a combination of [init_undistort_rectify_map] (with unity R ) and [remap]
/// (with bilinear interpolation). See the former function for details of the transformation being
/// performed.
///
/// Those pixels in the destination image, for which there is no correspondent pixels in the source
/// image, are filled with zeros (black color).
///
/// A particular subset of the source image that will be visible in the corrected image can be regulated
/// by newCameraMatrix. You can use [get_optimal_new_camera_matrix] to compute the appropriate
/// newCameraMatrix depending on your requirements.
///
/// The camera matrix and the distortion parameters can be determined using #calibrateCamera. If
/// the resolution of images is different from the resolution used at the calibration stage,  and  need to be scaled accordingly, while the distortion coefficients remain
/// the same.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input (distorted) image.
/// * dst: Output (corrected) image that has the same size and type as src .
/// * cameraMatrix: Input camera matrix 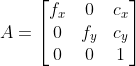 .
/// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients
/// 
/// of 4, 5, 8, 12 or 14 elements. If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed.
/// * newCameraMatrix: Camera matrix of the distorted image. By default, it is the same as
/// cameraMatrix but you may additionally scale and shift the result by using a different matrix.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [undistort] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * new_camera_matrix: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn undistort_def(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_undistort_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Transforms an image to compensate for lens distortion.
///
/// The function transforms an image to compensate radial and tangential lens distortion.
///
/// The function is simply a combination of [init_undistort_rectify_map] (with unity R ) and [remap]
/// (with bilinear interpolation). See the former function for details of the transformation being
/// performed.
///
/// Those pixels in the destination image, for which there is no correspondent pixels in the source
/// image, are filled with zeros (black color).
///
/// A particular subset of the source image that will be visible in the corrected image can be regulated
/// by newCameraMatrix. You can use [get_optimal_new_camera_matrix] to compute the appropriate
/// newCameraMatrix depending on your requirements.
///
/// The camera matrix and the distortion parameters can be determined using #calibrateCamera. If
/// the resolution of images is different from the resolution used at the calibration stage,  and  need to be scaled accordingly, while the distortion coefficients remain
/// the same.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input (distorted) image.
/// * dst: Output (corrected) image that has the same size and type as src .
/// * cameraMatrix: Input camera matrix 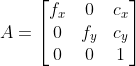 .
/// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients
/// 
/// of 4, 5, 8, 12 or 14 elements. If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed.
/// * newCameraMatrix: Camera matrix of the distorted image. By default, it is the same as
/// cameraMatrix but you may additionally scale and shift the result by using a different matrix.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * new_camera_matrix: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn undistort(src: &impl ToInputArray, dst: &mut impl ToOutputArray, camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray, new_camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(src);
output_array_arg!(dst);
input_array_arg!(camera_matrix);
input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs);
input_array_arg!(new_camera_matrix);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_undistort_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), new_camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// validates disparity using the left-right check. The matrix "cost" should be computed by the stereo correspondence algorithm
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [validate_disparity] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * disp12_max_disp: 1
#[inline]
pub fn validate_disparity_def(disparity: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, cost: &impl ToInputArray, min_disparity: i32, number_of_disparities: i32) -> Result<()> {
input_output_array_arg!(disparity);
input_array_arg!(cost);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_validateDisparity_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int_int(disparity.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), cost.as_raw__InputArray(), min_disparity, number_of_disparities, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// validates disparity using the left-right check. The matrix "cost" should be computed by the stereo correspondence algorithm
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * disp12_max_disp: 1
#[inline]
pub fn validate_disparity(disparity: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray, cost: &impl ToInputArray, min_disparity: i32, number_of_disparities: i32, disp12_max_disp: i32) -> Result<()> {
input_output_array_arg!(disparity);
input_array_arg!(cost);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_validateDisparity_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int_int_int(disparity.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), cost.as_raw__InputArray(), min_disparity, number_of_disparities, disp12_max_disp, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)]
pub struct CirclesGridFinderParameters {
pub density_neighborhood_size: core::Size2f,
pub min_density: f32,
pub kmeans_attempts: i32,
pub min_distance_to_add_keypoint: i32,
pub keypoint_scale: i32,
pub min_graph_confidence: f32,
pub vertex_gain: f32,
pub vertex_penalty: f32,
pub existing_vertex_gain: f32,
pub edge_gain: f32,
pub edge_penalty: f32,
pub convex_hull_factor: f32,
pub min_rng_edge_switch_dist: f32,
pub grid_type: crate::calib3d::CirclesGridFinderParameters_GridType,
/// Distance between two adjacent points. Used by CALIB_CB_CLUSTERING.
pub square_size: f32,
/// Max deviation from prediction. Used by CALIB_CB_CLUSTERING.
pub max_rectified_distance: f32,
}
opencv_type_simple! { crate::calib3d::CirclesGridFinderParameters }
impl CirclesGridFinderParameters {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<crate::calib3d::CirclesGridFinderParameters> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_CirclesGridFinderParameters_CirclesGridFinderParameters(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Levenberg-Marquardt solver. Starting with the specified vector of parameters it
/// optimizes the target vector criteria "err"
/// (finds local minima of each target vector component absolute value).
///
/// When needed, it calls user-provided callback.
pub struct LMSolver {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { LMSolver }
impl Drop for LMSolver {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_LMSolver_delete(self.as_raw_mut_LMSolver()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for LMSolver {}
impl LMSolver {
/// Creates Levenberg-Marquard solver
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * cb: callback
/// * maxIters: maximum number of iterations that can be further
/// modified using setMaxIters() method.
#[inline]
pub fn create(cb: &core::Ptr<crate::calib3d::LMSolver_Callback>, max_iters: i32) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::calib3d::LMSolver>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_LMSolver_create_const_PtrLCallbackGR_int(cb.as_raw_PtrOfLMSolver_Callback(), max_iters, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::calib3d::LMSolver>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn create_ext(cb: &core::Ptr<crate::calib3d::LMSolver_Callback>, max_iters: i32, eps: f64) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::calib3d::LMSolver>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_LMSolver_create_const_PtrLCallbackGR_int_double(cb.as_raw_PtrOfLMSolver_Callback(), max_iters, eps, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::calib3d::LMSolver>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::calib3d::LMSolver]
pub trait LMSolverTraitConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_LMSolver(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Runs Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm using the passed vector of parameters as the start point.
/// The final vector of parameters (whether the algorithm converged or not) is stored at the same
/// vector. The method returns the number of iterations used. If it's equal to the previously specified
/// maxIters, there is a big chance the algorithm did not converge.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * param: initial/final vector of parameters.
///
/// Note that the dimensionality of parameter space is defined by the size of param vector,
/// and the dimensionality of optimized criteria is defined by the size of err vector
/// computed by the callback.
#[inline]
fn run(&self, param: &mut impl ToInputOutputArray) -> Result<i32> {
input_output_array_arg!(param);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_LMSolver_run_const_const__InputOutputArrayR(self.as_raw_LMSolver(), param.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Retrieves the current maximum number of iterations
#[inline]
fn get_max_iters(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_LMSolver_getMaxIters_const(self.as_raw_LMSolver(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::calib3d::LMSolver]
pub trait LMSolverTrait: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::calib3d::LMSolverTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_LMSolver(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Sets the maximum number of iterations
/// ## Parameters
/// * maxIters: the number of iterations
#[inline]
fn set_max_iters(&mut self, max_iters: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_LMSolver_setMaxIters_int(self.as_raw_mut_LMSolver(), max_iters, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for LMSolver {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("LMSolver")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { LMSolver, core::Algorithm, cv_LMSolver_to_Algorithm }
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for LMSolver {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for LMSolver {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { LMSolver, core::AlgorithmTraitConst, as_raw_Algorithm, core::AlgorithmTrait, as_raw_mut_Algorithm }
impl crate::calib3d::LMSolverTraitConst for LMSolver {
#[inline] fn as_raw_LMSolver(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::calib3d::LMSolverTrait for LMSolver {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_LMSolver(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { LMSolver, crate::calib3d::LMSolverTraitConst, as_raw_LMSolver, crate::calib3d::LMSolverTrait, as_raw_mut_LMSolver }
pub struct LMSolver_Callback {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { LMSolver_Callback }
impl Drop for LMSolver_Callback {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_LMSolver_Callback_delete(self.as_raw_mut_LMSolver_Callback()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for LMSolver_Callback {}
/// Constant methods for [crate::calib3d::LMSolver_Callback]
pub trait LMSolver_CallbackTraitConst {
fn as_raw_LMSolver_Callback(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// computes error and Jacobian for the specified vector of parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * param: the current vector of parameters
/// * err: output vector of errors: err_i = actual_f_i - ideal_f_i
/// * J: output Jacobian: J_ij = d(ideal_f_i)/d(param_j)
///
/// when J=noArray(), it means that it does not need to be computed.
/// Dimensionality of error vector and param vector can be different.
/// The callback should explicitly allocate (with "create" method) each output array
/// (unless it's noArray()).
#[inline]
fn compute(&self, param: &impl ToInputArray, err: &mut impl ToOutputArray, j: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<bool> {
input_array_arg!(param);
output_array_arg!(err);
output_array_arg!(j);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_LMSolver_Callback_compute_const_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_LMSolver_Callback(), param.as_raw__InputArray(), err.as_raw__OutputArray(), j.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::calib3d::LMSolver_Callback]
pub trait LMSolver_CallbackTrait: crate::calib3d::LMSolver_CallbackTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_LMSolver_Callback(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for LMSolver_Callback {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("LMSolver_Callback")
.finish()
}
}
impl crate::calib3d::LMSolver_CallbackTraitConst for LMSolver_Callback {
#[inline] fn as_raw_LMSolver_Callback(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::calib3d::LMSolver_CallbackTrait for LMSolver_Callback {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_LMSolver_Callback(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { LMSolver_Callback, crate::calib3d::LMSolver_CallbackTraitConst, as_raw_LMSolver_Callback, crate::calib3d::LMSolver_CallbackTrait, as_raw_mut_LMSolver_Callback }
/// Class for computing stereo correspondence using the block matching algorithm, introduced and
/// contributed to OpenCV by K. Konolige.
pub struct StereoBM {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { StereoBM }
impl Drop for StereoBM {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_delete(self.as_raw_mut_StereoBM()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for StereoBM {}
impl StereoBM {
/// Creates StereoBM object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * numDisparities: the disparity search range. For each pixel algorithm will find the best
/// disparity from 0 (default minimum disparity) to numDisparities. The search range can then be
/// shifted by changing the minimum disparity.
/// * blockSize: the linear size of the blocks compared by the algorithm. The size should be odd
/// (as the block is centered at the current pixel). Larger block size implies smoother, though less
/// accurate disparity map. Smaller block size gives more detailed disparity map, but there is higher
/// chance for algorithm to find a wrong correspondence.
///
/// The function create StereoBM object. You can then call StereoBM::compute() to compute disparity for
/// a specific stereo pair.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * num_disparities: 0
/// * block_size: 21
#[inline]
pub fn create(num_disparities: i32, block_size: i32) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::calib3d::StereoBM>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_create_int_int(num_disparities, block_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::calib3d::StereoBM>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates StereoBM object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * numDisparities: the disparity search range. For each pixel algorithm will find the best
/// disparity from 0 (default minimum disparity) to numDisparities. The search range can then be
/// shifted by changing the minimum disparity.
/// * blockSize: the linear size of the blocks compared by the algorithm. The size should be odd
/// (as the block is centered at the current pixel). Larger block size implies smoother, though less
/// accurate disparity map. Smaller block size gives more detailed disparity map, but there is higher
/// chance for algorithm to find a wrong correspondence.
///
/// The function create StereoBM object. You can then call StereoBM::compute() to compute disparity for
/// a specific stereo pair.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [StereoBM::create] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * num_disparities: 0
/// * block_size: 21
#[inline]
pub fn create_def() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::calib3d::StereoBM>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_create(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::calib3d::StereoBM>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::calib3d::StereoBM]
pub trait StereoBMTraitConst: crate::calib3d::StereoMatcherTraitConst {
fn as_raw_StereoBM(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn get_pre_filter_type(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_getPreFilterType_const(self.as_raw_StereoBM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_pre_filter_size(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_getPreFilterSize_const(self.as_raw_StereoBM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_pre_filter_cap(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_getPreFilterCap_const(self.as_raw_StereoBM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_texture_threshold(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_getTextureThreshold_const(self.as_raw_StereoBM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_uniqueness_ratio(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_getUniquenessRatio_const(self.as_raw_StereoBM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_smaller_block_size(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_getSmallerBlockSize_const(self.as_raw_StereoBM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_roi1(&self) -> Result<core::Rect> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_getROI1_const(self.as_raw_StereoBM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_roi2(&self) -> Result<core::Rect> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_getROI2_const(self.as_raw_StereoBM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::calib3d::StereoBM]
pub trait StereoBMTrait: crate::calib3d::StereoBMTraitConst + crate::calib3d::StereoMatcherTrait {
fn as_raw_mut_StereoBM(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_pre_filter_type(&mut self, pre_filter_type: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_setPreFilterType_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoBM(), pre_filter_type, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_pre_filter_size(&mut self, pre_filter_size: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_setPreFilterSize_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoBM(), pre_filter_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_pre_filter_cap(&mut self, pre_filter_cap: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_setPreFilterCap_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoBM(), pre_filter_cap, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_texture_threshold(&mut self, texture_threshold: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_setTextureThreshold_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoBM(), texture_threshold, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_uniqueness_ratio(&mut self, uniqueness_ratio: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_setUniquenessRatio_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoBM(), uniqueness_ratio, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_smaller_block_size(&mut self, block_size: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_setSmallerBlockSize_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoBM(), block_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_roi1(&mut self, roi1: core::Rect) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_setROI1_Rect(self.as_raw_mut_StereoBM(), &roi1, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_roi2(&mut self, roi2: core::Rect) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_setROI2_Rect(self.as_raw_mut_StereoBM(), &roi2, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for StereoBM {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("StereoBM")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { StereoBM, core::Algorithm, cv_StereoBM_to_Algorithm }
boxed_cast_base! { StereoBM, crate::calib3d::StereoMatcher, cv_StereoBM_to_StereoMatcher }
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for StereoBM {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for StereoBM {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { StereoBM, core::AlgorithmTraitConst, as_raw_Algorithm, core::AlgorithmTrait, as_raw_mut_Algorithm }
impl crate::calib3d::StereoMatcherTraitConst for StereoBM {
#[inline] fn as_raw_StereoMatcher(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::calib3d::StereoMatcherTrait for StereoBM {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_StereoMatcher(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { StereoBM, crate::calib3d::StereoMatcherTraitConst, as_raw_StereoMatcher, crate::calib3d::StereoMatcherTrait, as_raw_mut_StereoMatcher }
impl crate::calib3d::StereoBMTraitConst for StereoBM {
#[inline] fn as_raw_StereoBM(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::calib3d::StereoBMTrait for StereoBM {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_StereoBM(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { StereoBM, crate::calib3d::StereoBMTraitConst, as_raw_StereoBM, crate::calib3d::StereoBMTrait, as_raw_mut_StereoBM }
/// The base class for stereo correspondence algorithms.
pub struct StereoMatcher {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { StereoMatcher }
impl Drop for StereoMatcher {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_delete(self.as_raw_mut_StereoMatcher()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for StereoMatcher {}
/// Constant methods for [crate::calib3d::StereoMatcher]
pub trait StereoMatcherTraitConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_StereoMatcher(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn get_min_disparity(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_getMinDisparity_const(self.as_raw_StereoMatcher(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_num_disparities(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_getNumDisparities_const(self.as_raw_StereoMatcher(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_block_size(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_getBlockSize_const(self.as_raw_StereoMatcher(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_speckle_window_size(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_getSpeckleWindowSize_const(self.as_raw_StereoMatcher(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_speckle_range(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_getSpeckleRange_const(self.as_raw_StereoMatcher(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_disp12_max_diff(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_getDisp12MaxDiff_const(self.as_raw_StereoMatcher(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::calib3d::StereoMatcher]
pub trait StereoMatcherTrait: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::calib3d::StereoMatcherTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_StereoMatcher(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Computes disparity map for the specified stereo pair
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * left: Left 8-bit single-channel image.
/// * right: Right image of the same size and the same type as the left one.
/// * disparity: Output disparity map. It has the same size as the input images. Some algorithms,
/// like StereoBM or StereoSGBM compute 16-bit fixed-point disparity map (where each disparity value
/// has 4 fractional bits), whereas other algorithms output 32-bit floating-point disparity map.
#[inline]
fn compute(&mut self, left: &impl ToInputArray, right: &impl ToInputArray, disparity: &mut impl ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
input_array_arg!(left);
input_array_arg!(right);
output_array_arg!(disparity);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_compute_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_StereoMatcher(), left.as_raw__InputArray(), right.as_raw__InputArray(), disparity.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_min_disparity(&mut self, min_disparity: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_setMinDisparity_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoMatcher(), min_disparity, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_num_disparities(&mut self, num_disparities: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_setNumDisparities_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoMatcher(), num_disparities, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_block_size(&mut self, block_size: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_setBlockSize_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoMatcher(), block_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_speckle_window_size(&mut self, speckle_window_size: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_setSpeckleWindowSize_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoMatcher(), speckle_window_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_speckle_range(&mut self, speckle_range: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_setSpeckleRange_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoMatcher(), speckle_range, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_disp12_max_diff(&mut self, disp12_max_diff: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_setDisp12MaxDiff_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoMatcher(), disp12_max_diff, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for StereoMatcher {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("StereoMatcher")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { StereoMatcher, core::Algorithm, cv_StereoMatcher_to_Algorithm }
boxed_cast_descendant! { StereoMatcher, crate::calib3d::StereoBM, cv_StereoMatcher_to_StereoBM }
boxed_cast_descendant! { StereoMatcher, crate::calib3d::StereoSGBM, cv_StereoMatcher_to_StereoSGBM }
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for StereoMatcher {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for StereoMatcher {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { StereoMatcher, core::AlgorithmTraitConst, as_raw_Algorithm, core::AlgorithmTrait, as_raw_mut_Algorithm }
impl crate::calib3d::StereoMatcherTraitConst for StereoMatcher {
#[inline] fn as_raw_StereoMatcher(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::calib3d::StereoMatcherTrait for StereoMatcher {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_StereoMatcher(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { StereoMatcher, crate::calib3d::StereoMatcherTraitConst, as_raw_StereoMatcher, crate::calib3d::StereoMatcherTrait, as_raw_mut_StereoMatcher }
/// The class implements the modified H. Hirschmuller algorithm [HH08](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_HH08) that differs from the original
/// one as follows:
///
/// * By default, the algorithm is single-pass, which means that you consider only 5 directions
/// instead of 8. Set mode=StereoSGBM::MODE_HH in createStereoSGBM to run the full variant of the
/// algorithm but beware that it may consume a lot of memory.
/// * The algorithm matches blocks, not individual pixels. Though, setting blockSize=1 reduces the
/// blocks to single pixels.
/// * Mutual information cost function is not implemented. Instead, a simpler Birchfield-Tomasi
/// sub-pixel metric from [BT98](https://docs.opencv.org/4.11.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_BT98) is used. Though, the color images are supported as well.
/// * Some pre- and post- processing steps from K. Konolige algorithm StereoBM are included, for
/// example: pre-filtering (StereoBM::PREFILTER_XSOBEL type) and post-filtering (uniqueness
/// check, quadratic interpolation and speckle filtering).
///
///
/// Note:
/// * (Python) An example illustrating the use of the StereoSGBM matching algorithm can be found
/// at opencv_source_code/samples/python/stereo_match.py
pub struct StereoSGBM {
ptr: *mut c_void,
}
opencv_type_boxed! { StereoSGBM }
impl Drop for StereoSGBM {
#[inline]
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoSGBM_delete(self.as_raw_mut_StereoSGBM()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for StereoSGBM {}
impl StereoSGBM {
/// Creates StereoSGBM object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * minDisparity: Minimum possible disparity value. Normally, it is zero but sometimes
/// rectification algorithms can shift images, so this parameter needs to be adjusted accordingly.
/// * numDisparities: Maximum disparity minus minimum disparity. The value is always greater than
/// zero. In the current implementation, this parameter must be divisible by 16.
/// * blockSize: Matched block size. It must be an odd number \>=1 . Normally, it should be
/// somewhere in the 3..11 range.
/// * P1: The first parameter controlling the disparity smoothness. See below.
/// * P2: The second parameter controlling the disparity smoothness. The larger the values are,
/// the smoother the disparity is. P1 is the penalty on the disparity change by plus or minus 1
/// between neighbor pixels. P2 is the penalty on the disparity change by more than 1 between neighbor
/// pixels. The algorithm requires P2 \> P1 . See stereo_match.cpp sample where some reasonably good
/// P1 and P2 values are shown (like 8\*number_of_image_channels\*blockSize\*blockSize and
/// 32\*number_of_image_channels\*blockSize\*blockSize , respectively).
/// * disp12MaxDiff: Maximum allowed difference (in integer pixel units) in the left-right
/// disparity check. Set it to a non-positive value to disable the check.
/// * preFilterCap: Truncation value for the prefiltered image pixels. The algorithm first
/// computes x-derivative at each pixel and clips its value by [-preFilterCap, preFilterCap] interval.
/// The result values are passed to the Birchfield-Tomasi pixel cost function.
/// * uniquenessRatio: Margin in percentage by which the best (minimum) computed cost function
/// value should "win" the second best value to consider the found match correct. Normally, a value
/// within the 5-15 range is good enough.
/// * speckleWindowSize: Maximum size of smooth disparity regions to consider their noise speckles
/// and invalidate. Set it to 0 to disable speckle filtering. Otherwise, set it somewhere in the
/// 50-200 range.
/// * speckleRange: Maximum disparity variation within each connected component. If you do speckle
/// filtering, set the parameter to a positive value, it will be implicitly multiplied by 16.
/// Normally, 1 or 2 is good enough.
/// * mode: Set it to StereoSGBM::MODE_HH to run the full-scale two-pass dynamic programming
/// algorithm. It will consume O(W\*H\*numDisparities) bytes, which is large for 640x480 stereo and
/// huge for HD-size pictures. By default, it is set to false .
///
/// The first constructor initializes StereoSGBM with all the default parameters. So, you only have to
/// set StereoSGBM::numDisparities at minimum. The second constructor enables you to set each parameter
/// to a custom value.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * min_disparity: 0
/// * num_disparities: 16
/// * block_size: 3
/// * p1: 0
/// * p2: 0
/// * disp12_max_diff: 0
/// * pre_filter_cap: 0
/// * uniqueness_ratio: 0
/// * speckle_window_size: 0
/// * speckle_range: 0
/// * mode: StereoSGBM::MODE_SGBM
#[inline]
pub fn create(min_disparity: i32, num_disparities: i32, block_size: i32, p1: i32, p2: i32, disp12_max_diff: i32, pre_filter_cap: i32, uniqueness_ratio: i32, speckle_window_size: i32, speckle_range: i32, mode: i32) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::calib3d::StereoSGBM>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoSGBM_create_int_int_int_int_int_int_int_int_int_int_int(min_disparity, num_disparities, block_size, p1, p2, disp12_max_diff, pre_filter_cap, uniqueness_ratio, speckle_window_size, speckle_range, mode, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::calib3d::StereoSGBM>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates StereoSGBM object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * minDisparity: Minimum possible disparity value. Normally, it is zero but sometimes
/// rectification algorithms can shift images, so this parameter needs to be adjusted accordingly.
/// * numDisparities: Maximum disparity minus minimum disparity. The value is always greater than
/// zero. In the current implementation, this parameter must be divisible by 16.
/// * blockSize: Matched block size. It must be an odd number \>=1 . Normally, it should be
/// somewhere in the 3..11 range.
/// * P1: The first parameter controlling the disparity smoothness. See below.
/// * P2: The second parameter controlling the disparity smoothness. The larger the values are,
/// the smoother the disparity is. P1 is the penalty on the disparity change by plus or minus 1
/// between neighbor pixels. P2 is the penalty on the disparity change by more than 1 between neighbor
/// pixels. The algorithm requires P2 \> P1 . See stereo_match.cpp sample where some reasonably good
/// P1 and P2 values are shown (like 8\*number_of_image_channels\*blockSize\*blockSize and
/// 32\*number_of_image_channels\*blockSize\*blockSize , respectively).
/// * disp12MaxDiff: Maximum allowed difference (in integer pixel units) in the left-right
/// disparity check. Set it to a non-positive value to disable the check.
/// * preFilterCap: Truncation value for the prefiltered image pixels. The algorithm first
/// computes x-derivative at each pixel and clips its value by [-preFilterCap, preFilterCap] interval.
/// The result values are passed to the Birchfield-Tomasi pixel cost function.
/// * uniquenessRatio: Margin in percentage by which the best (minimum) computed cost function
/// value should "win" the second best value to consider the found match correct. Normally, a value
/// within the 5-15 range is good enough.
/// * speckleWindowSize: Maximum size of smooth disparity regions to consider their noise speckles
/// and invalidate. Set it to 0 to disable speckle filtering. Otherwise, set it somewhere in the
/// 50-200 range.
/// * speckleRange: Maximum disparity variation within each connected component. If you do speckle
/// filtering, set the parameter to a positive value, it will be implicitly multiplied by 16.
/// Normally, 1 or 2 is good enough.
/// * mode: Set it to StereoSGBM::MODE_HH to run the full-scale two-pass dynamic programming
/// algorithm. It will consume O(W\*H\*numDisparities) bytes, which is large for 640x480 stereo and
/// huge for HD-size pictures. By default, it is set to false .
///
/// The first constructor initializes StereoSGBM with all the default parameters. So, you only have to
/// set StereoSGBM::numDisparities at minimum. The second constructor enables you to set each parameter
/// to a custom value.
///
/// ## Note
/// This alternative version of [StereoSGBM::create] function uses the following default values for its arguments:
/// * min_disparity: 0
/// * num_disparities: 16
/// * block_size: 3
/// * p1: 0
/// * p2: 0
/// * disp12_max_diff: 0
/// * pre_filter_cap: 0
/// * uniqueness_ratio: 0
/// * speckle_window_size: 0
/// * speckle_range: 0
/// * mode: StereoSGBM::MODE_SGBM
#[inline]
pub fn create_def() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::calib3d::StereoSGBM>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoSGBM_create(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::calib3d::StereoSGBM>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::calib3d::StereoSGBM]
pub trait StereoSGBMTraitConst: crate::calib3d::StereoMatcherTraitConst {
fn as_raw_StereoSGBM(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn get_pre_filter_cap(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoSGBM_getPreFilterCap_const(self.as_raw_StereoSGBM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_uniqueness_ratio(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoSGBM_getUniquenessRatio_const(self.as_raw_StereoSGBM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_p1(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoSGBM_getP1_const(self.as_raw_StereoSGBM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_p2(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoSGBM_getP2_const(self.as_raw_StereoSGBM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_mode(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoSGBM_getMode_const(self.as_raw_StereoSGBM(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::calib3d::StereoSGBM]
pub trait StereoSGBMTrait: crate::calib3d::StereoMatcherTrait + crate::calib3d::StereoSGBMTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_StereoSGBM(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_pre_filter_cap(&mut self, pre_filter_cap: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoSGBM_setPreFilterCap_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoSGBM(), pre_filter_cap, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_uniqueness_ratio(&mut self, uniqueness_ratio: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoSGBM_setUniquenessRatio_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoSGBM(), uniqueness_ratio, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_p1(&mut self, p1: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoSGBM_setP1_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoSGBM(), p1, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_p2(&mut self, p2: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoSGBM_setP2_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoSGBM(), p2, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_mode(&mut self, mode: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_StereoSGBM_setMode_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoSGBM(), mode, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl std::fmt::Debug for StereoSGBM {
#[inline]
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter) -> std::fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("StereoSGBM")
.finish()
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { StereoSGBM, core::Algorithm, cv_StereoSGBM_to_Algorithm }
boxed_cast_base! { StereoSGBM, crate::calib3d::StereoMatcher, cv_StereoSGBM_to_StereoMatcher }
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for StereoSGBM {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for StereoSGBM {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { StereoSGBM, core::AlgorithmTraitConst, as_raw_Algorithm, core::AlgorithmTrait, as_raw_mut_Algorithm }
impl crate::calib3d::StereoMatcherTraitConst for StereoSGBM {
#[inline] fn as_raw_StereoMatcher(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::calib3d::StereoMatcherTrait for StereoSGBM {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_StereoMatcher(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { StereoSGBM, crate::calib3d::StereoMatcherTraitConst, as_raw_StereoMatcher, crate::calib3d::StereoMatcherTrait, as_raw_mut_StereoMatcher }
impl crate::calib3d::StereoSGBMTraitConst for StereoSGBM {
#[inline] fn as_raw_StereoSGBM(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::calib3d::StereoSGBMTrait for StereoSGBM {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_StereoSGBM(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
boxed_ref! { StereoSGBM, crate::calib3d::StereoSGBMTraitConst, as_raw_StereoSGBM, crate::calib3d::StereoSGBMTrait, as_raw_mut_StereoSGBM }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)]
pub struct UsacParams {
pub confidence: f64,
pub is_parallel: bool,
pub lo_iterations: i32,
pub lo_method: crate::calib3d::LocalOptimMethod,
pub lo_sample_size: i32,
pub max_iterations: i32,
pub neighbors_search: crate::calib3d::NeighborSearchMethod,
pub random_generator_state: i32,
pub sampler: crate::calib3d::SamplingMethod,
pub score: crate::calib3d::ScoreMethod,
pub threshold: f64,
pub final_polisher: crate::calib3d::PolishingMethod,
pub final_polisher_iterations: i32,
}
opencv_type_simple! { crate::calib3d::UsacParams }
impl UsacParams {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<crate::calib3d::UsacParams> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UsacParams_UsacParams(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
}