#![allow(
unused_parens,
clippy::excessive_precision,
clippy::missing_safety_doc,
clippy::should_implement_trait,
clippy::too_many_arguments,
clippy::unused_unit,
clippy::let_unit_value,
clippy::derive_partial_eq_without_eq,
)]
//! # Core functionality
//! # Basic structures
//! # C structures and operations
//! # Connections with C++
//! # Operations on arrays
//! # Asynchronous API
//! # XML/YAML Persistence
//! # Clustering
//! # Utility and system functions and macros
//! # Logging facilities
//! # SSE utilities
//! # NEON utilities
//! # VSX utilities
//! # Softfloat support
//! # Utility functions for OpenCV samples
//! # OpenGL interoperability
//! # Intel IPP Asynchronous C/C++ Converters
//! # Optimization Algorithms
//! # DirectX interoperability
//! # Eigen support
//! # OpenCL support
//! # Intel VA-API/OpenCL (CL-VA) interoperability
//! # Hardware Acceleration Layer
//! # Functions
//! # Interface
//! # Universal intrinsics
//! # Private implementation helpers
//! # Low-level API for external libraries / plugins
//! # Parallel Processing
//! # Parallel backends API
use crate::{mod_prelude::*, core, sys, types};
pub mod prelude {
pub use { super::HammingTraitConst, super::HammingTrait, super::Detail_CheckContextTraitConst, super::Detail_CheckContextTrait, super::Matx_AddOpTraitConst, super::Matx_AddOpTrait, super::Matx_SubOpTraitConst, super::Matx_SubOpTrait, super::Matx_ScaleOpTraitConst, super::Matx_ScaleOpTrait, super::Matx_MulOpTraitConst, super::Matx_MulOpTrait, super::Matx_DivOpTraitConst, super::Matx_DivOpTrait, super::Matx_MatMulOpTraitConst, super::Matx_MatMulOpTrait, super::Matx_TOpTraitConst, super::Matx_TOpTrait, super::RotatedRectTraitConst, super::RotatedRectTrait, super::RangeTraitConst, super::RangeTrait, super::KeyPointTraitConst, super::KeyPointTrait, super::_InputArrayTraitConst, super::_InputArrayTrait, super::_OutputArrayTraitConst, super::_OutputArrayTrait, super::_InputOutputArrayTraitConst, super::_InputOutputArrayTrait, super::UMatDataTraitConst, super::UMatDataTrait, super::MatSizeTraitConst, super::MatSizeTrait, super::MatStepTraitConst, super::MatStepTrait, super::MatTraitConst, super::MatTrait, super::UMatTraitConst, super::UMatTrait, super::SparseMat_HdrTraitConst, super::SparseMat_HdrTrait, super::SparseMat_NodeTraitConst, super::SparseMat_NodeTrait, super::SparseMatTraitConst, super::SparseMatTrait, super::MatConstIteratorTraitConst, super::MatConstIteratorTrait, super::SparseMatConstIteratorTraitConst, super::SparseMatConstIteratorTrait, super::SparseMatIteratorTraitConst, super::SparseMatIteratorTrait, super::MatOpConst, super::MatOp, super::MatExprTraitConst, super::MatExprTrait, super::FileStorageTraitConst, super::FileStorageTrait, super::FileNodeTraitConst, super::FileNodeTrait, super::FileNodeIteratorTraitConst, super::FileNodeIteratorTrait, super::WriteStructContextTraitConst, super::WriteStructContextTrait, super::ExceptionTraitConst, super::ExceptionTrait, super::PCATraitConst, super::PCATrait, super::LDATraitConst, super::LDATrait, super::SVDTraitConst, super::SVDTrait, super::RNGTraitConst, super::RNGTrait, super::RNG_MT19937TraitConst, super::RNG_MT19937Trait, super::FormattedConst, super::Formatted, super::FormatterConst, super::Formatter, super::AlgorithmTraitConst, super::AlgorithmTrait, super::TickMeterTraitConst, super::TickMeterTrait, super::ParallelLoopBodyConst, super::ParallelLoopBody, super::CommandLineParserTraitConst, super::CommandLineParserTrait, super::TLSDataContainerConst, super::TLSDataContainer, super::NodeDataTraitConst, super::NodeDataTrait, super::MinProblemSolver_FunctionConst, super::MinProblemSolver_Function, super::MinProblemSolverConst, super::MinProblemSolver, super::DownhillSolverConst, super::DownhillSolver, super::ConjGradSolverConst, super::ConjGradSolver, super::DeviceTraitConst, super::DeviceTrait, super::Context_UserContextTraitConst, super::Context_UserContextTrait, super::ContextTraitConst, super::ContextTrait, super::PlatformTraitConst, super::PlatformTrait, super::QueueTraitConst, super::QueueTrait, super::KernelArgTraitConst, super::KernelArgTrait, super::KernelTraitConst, super::KernelTrait, super::ProgramTraitConst, super::ProgramTrait, super::ProgramSourceTraitConst, super::ProgramSourceTrait, super::PlatformInfoTraitConst, super::PlatformInfoTrait, super::Image2DTraitConst, super::Image2DTrait, super::TimerTraitConst, super::TimerTrait, super::OpenCLExecutionContextTraitConst, super::OpenCLExecutionContextTrait, super::GpuMat_AllocatorConst, super::GpuMat_Allocator, super::GpuMatTraitConst, super::GpuMatTrait, super::GpuDataTraitConst, super::GpuDataTrait, super::GpuMatNDTraitConst, super::GpuMatNDTrait, super::BufferPoolTraitConst, super::BufferPoolTrait, super::HostMemTraitConst, super::HostMemTrait, super::StreamTraitConst, super::StreamTrait, super::EventTraitConst, super::EventTrait, super::TargetArchsTraitConst, super::TargetArchsTrait, super::DeviceInfoTraitConst, super::DeviceInfoTrait, super::BufferTraitConst, super::BufferTrait, super::Texture2DTraitConst, super::Texture2DTrait, super::ArraysTraitConst, super::ArraysTrait, super::AsyncArrayTraitConst, super::AsyncArrayTrait, super::AsyncPromiseTraitConst, super::AsyncPromiseTrait, super::LogTagTraitConst, super::LogTagTrait, super::OriginalClassNameTraitConst, super::OriginalClassNameTrait };
}
pub const ACCESS_FAST: i32 = 67108864;
pub const ACCESS_MASK: i32 = 50331648;
pub const ACCESS_READ: i32 = 16777216;
pub const ACCESS_RW: i32 = 50331648;
pub const ACCESS_WRITE: i32 = 33554432;
/// `iiiiii|abcdefgh|iiiiiii` with some specified `i`
pub const BORDER_CONSTANT: i32 = 0;
/// same as BORDER_REFLECT_101
pub const BORDER_DEFAULT: i32 = 4;
/// do not look outside of ROI
pub const BORDER_ISOLATED: i32 = 16;
/// `fedcba|abcdefgh|hgfedcb`
pub const BORDER_REFLECT: i32 = 2;
/// same as BORDER_REFLECT_101
pub const BORDER_REFLECT101: i32 = 4;
/// `gfedcb|abcdefgh|gfedcba`
pub const BORDER_REFLECT_101: i32 = 4;
/// `aaaaaa|abcdefgh|hhhhhhh`
pub const BORDER_REPLICATE: i32 = 1;
/// `uvwxyz|abcdefgh|ijklmno`
pub const BORDER_TRANSPARENT: i32 = 5;
/// `cdefgh|abcdefgh|abcdefg`
pub const BORDER_WRAP: i32 = 3;
/// incorrect input align
pub const BadAlign: i32 = -21;
pub const BadAlphaChannel: i32 = -18;
/// input COI is not supported
pub const BadCOI: i32 = -24;
pub const BadCallBack: i32 = -22;
pub const BadDataPtr: i32 = -12;
/// input image depth is not supported by the function
pub const BadDepth: i32 = -17;
/// image size is invalid
pub const BadImageSize: i32 = -10;
pub const BadModelOrChSeq: i32 = -14;
pub const BadNumChannel1U: i32 = -16;
/// bad number of channels, for example, some functions accept only single channel matrices.
pub const BadNumChannels: i32 = -15;
/// offset is invalid
pub const BadOffset: i32 = -11;
/// number of dimensions is out of range
pub const BadOrder: i32 = -19;
/// incorrect input origin
pub const BadOrigin: i32 = -20;
/// incorrect input roi
pub const BadROISize: i32 = -25;
/// image step is wrong, this may happen for a non-continuous matrix.
pub const BadStep: i32 = -13;
pub const BadTileSize: i32 = -23;
/// src1 is equal to src2.
pub const CMP_EQ: i32 = 0;
/// src1 is greater than or equal to src2.
pub const CMP_GE: i32 = 2;
/// src1 is greater than src2.
pub const CMP_GT: i32 = 1;
/// src1 is less than or equal to src2.
pub const CMP_LE: i32 = 4;
/// src1 is less than src2.
pub const CMP_LT: i32 = 3;
/// src1 is unequal to src2.
pub const CMP_NE: i32 = 5;
/// If the flag is
/// specified, all the input vectors are stored as columns of the samples matrix. mean should be a
/// single-column vector in this case.
pub const COVAR_COLS: i32 = 16;
/// The output covariance matrix is calculated as:
/// 
/// covar will be a square matrix of the same size as the total number of elements in each input
/// vector. One and only one of #COVAR_SCRAMBLED and #COVAR_NORMAL must be specified.
pub const COVAR_NORMAL: i32 = 1;
/// If the flag is
/// specified, all the input vectors are stored as rows of the samples matrix. mean should be a
/// single-row vector in this case.
pub const COVAR_ROWS: i32 = 8;
/// If the flag is specified, the covariance matrix is scaled. In the
/// "normal" mode, scale is 1./nsamples . In the "scrambled" mode, scale is the reciprocal of the
/// total number of elements in each input vector. By default (if the flag is not specified), the
/// covariance matrix is not scaled ( scale=1 ).
pub const COVAR_SCALE: i32 = 4;
/// The output covariance matrix is calculated as:
/// 
/// The covariance matrix will be nsamples x nsamples. Such an unusual covariance matrix is used
/// for fast PCA of a set of very large vectors (see, for example, the EigenFaces technique for
/// face recognition). Eigenvalues of this "scrambled" matrix match the eigenvalues of the true
/// covariance matrix. The "true" eigenvectors can be easily calculated from the eigenvectors of
/// the "scrambled" covariance matrix.
pub const COVAR_SCRAMBLED: i32 = 0;
/// If the flag is specified, the function does not calculate mean from
/// the input vectors but, instead, uses the passed mean vector. This is useful if mean has been
/// pre-calculated or known in advance, or if the covariance matrix is calculated by parts. In
/// this case, mean is not a mean vector of the input sub-set of vectors but rather the mean
/// vector of the whole set.
pub const COVAR_USE_AVG: i32 = 2;
pub const CPU_AVX: i32 = 10;
pub const CPU_AVX2: i32 = 11;
/// Cascade Lake with AVX-512F/CD/BW/DQ/VL/VNNI
pub const CPU_AVX512_CLX: i32 = 261;
/// Cannon Lake with AVX-512F/CD/BW/DQ/VL/IFMA/VBMI
pub const CPU_AVX512_CNL: i32 = 260;
/// Common instructions AVX-512F/CD for all CPUs that support AVX-512
pub const CPU_AVX512_COMMON: i32 = 257;
/// Ice Lake with AVX-512F/CD/BW/DQ/VL/IFMA/VBMI/VNNI/VBMI2/BITALG/VPOPCNTDQ
pub const CPU_AVX512_ICL: i32 = 262;
/// Knights Landing with AVX-512F/CD/ER/PF
pub const CPU_AVX512_KNL: i32 = 258;
/// Knights Mill with AVX-512F/CD/ER/PF/4FMAPS/4VNNIW/VPOPCNTDQ
pub const CPU_AVX512_KNM: i32 = 259;
/// Skylake-X with AVX-512F/CD/BW/DQ/VL
pub const CPU_AVX512_SKX: i32 = 256;
pub const CPU_AVX_5124FMAPS: i32 = 27;
pub const CPU_AVX_5124VNNIW: i32 = 26;
pub const CPU_AVX_512BITALG: i32 = 24;
pub const CPU_AVX_512BW: i32 = 14;
pub const CPU_AVX_512CD: i32 = 15;
pub const CPU_AVX_512DQ: i32 = 16;
pub const CPU_AVX_512ER: i32 = 17;
pub const CPU_AVX_512F: i32 = 13;
pub const CPU_AVX_512IFMA: i32 = 18;
pub const CPU_AVX_512IFMA512: i32 = 18;
pub const CPU_AVX_512PF: i32 = 19;
pub const CPU_AVX_512VBMI: i32 = 20;
pub const CPU_AVX_512VBMI2: i32 = 22;
pub const CPU_AVX_512VL: i32 = 21;
pub const CPU_AVX_512VNNI: i32 = 23;
pub const CPU_AVX_512VPOPCNTDQ: i32 = 25;
pub const CPU_FMA3: i32 = 12;
pub const CPU_FP16: i32 = 9;
pub const CPU_LASX: i32 = 230;
pub const CPU_MAX_FEATURE: i32 = 512;
pub const CPU_MMX: i32 = 1;
pub const CPU_MSA: i32 = 150;
pub const CPU_NEON: i32 = 100;
pub const CPU_NEON_DOTPROD: i32 = 101;
pub const CPU_POPCNT: i32 = 8;
pub const CPU_RISCVV: i32 = 170;
pub const CPU_RVV: i32 = 210;
pub const CPU_SSE: i32 = 2;
pub const CPU_SSE2: i32 = 3;
pub const CPU_SSE3: i32 = 4;
pub const CPU_SSE4_1: i32 = 6;
pub const CPU_SSE4_2: i32 = 7;
pub const CPU_SSSE3: i32 = 5;
pub const CPU_VSX: i32 = 200;
pub const CPU_VSX3: i32 = 201;
pub const CV_16F: i32 = 7;
pub const CV_16FC1: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_16F,1);
pub const CV_16FC2: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_16F,2);
pub const CV_16FC3: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_16F,3);
pub const CV_16FC4: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_16F,4);
pub const CV_16S: i32 = 3;
pub const CV_16SC1: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_16S,1);
pub const CV_16SC2: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_16S,2);
pub const CV_16SC3: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_16S,3);
pub const CV_16SC4: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_16S,4);
pub const CV_16U: i32 = 2;
pub const CV_16UC1: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_16U,1);
pub const CV_16UC2: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_16U,2);
pub const CV_16UC3: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_16U,3);
pub const CV_16UC4: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_16U,4);
pub const CV_2PI: f64 = 6.283185307179586476925286766559;
pub const CV_32F: i32 = 5;
pub const CV_32FC1: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_32F,1);
pub const CV_32FC2: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_32F,2);
pub const CV_32FC3: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_32F,3);
pub const CV_32FC4: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_32F,4);
pub const CV_32S: i32 = 4;
pub const CV_32SC1: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_32S,1);
pub const CV_32SC2: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_32S,2);
pub const CV_32SC3: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_32S,3);
pub const CV_32SC4: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_32S,4);
pub const CV_64F: i32 = 6;
pub const CV_64FC1: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_64F,1);
pub const CV_64FC2: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_64F,2);
pub const CV_64FC3: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_64F,3);
pub const CV_64FC4: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_64F,4);
pub const CV_8S: i32 = 1;
pub const CV_8SC1: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_8S,1);
pub const CV_8SC2: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_8S,2);
pub const CV_8SC3: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_8S,3);
pub const CV_8SC4: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_8S,4);
pub const CV_8U: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_8UC1: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_8U,1);
pub const CV_8UC2: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_8U,2);
pub const CV_8UC3: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_8U,3);
pub const CV_8UC4: i32 = CV_MAKETYPE(CV_8U,4);
pub const CV_AVX: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_AVX2: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_AVX512_CLX: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_AVX512_CNL: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_AVX512_COMMON: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_AVX512_ICL: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_AVX512_KNL: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_AVX512_KNM: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_AVX512_SKX: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_AVX_5124FMAPS: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_AVX_5124VNNIW: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_AVX_512BITALG: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_AVX_512BW: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_AVX_512CD: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_AVX_512DQ: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_AVX_512ER: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_AVX_512F: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_AVX_512IFMA: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_AVX_512IFMA512: i32 = CV_AVX_512IFMA;
pub const CV_AVX_512PF: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_AVX_512VBMI: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_AVX_512VBMI2: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_AVX_512VL: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_AVX_512VNNI: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_AVX_512VPOPCNTDQ: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_CN_MAX: i32 = 512;
pub const CV_CN_SHIFT: i32 = 3;
pub const CV_CPU_AVX: i32 = 10;
pub const CV_CPU_AVX2: i32 = 11;
pub const CV_CPU_AVX512_CLX: i32 = 261;
pub const CV_CPU_AVX512_CNL: i32 = 260;
pub const CV_CPU_AVX512_COMMON: i32 = 257;
pub const CV_CPU_AVX512_ICL: i32 = 262;
pub const CV_CPU_AVX512_KNL: i32 = 258;
pub const CV_CPU_AVX512_KNM: i32 = 259;
pub const CV_CPU_AVX512_SKX: i32 = 256;
pub const CV_CPU_AVX_5124FMAPS: i32 = 27;
pub const CV_CPU_AVX_5124VNNIW: i32 = 26;
pub const CV_CPU_AVX_512BITALG: i32 = 24;
pub const CV_CPU_AVX_512BW: i32 = 14;
pub const CV_CPU_AVX_512CD: i32 = 15;
pub const CV_CPU_AVX_512DQ: i32 = 16;
pub const CV_CPU_AVX_512ER: i32 = 17;
pub const CV_CPU_AVX_512F: i32 = 13;
pub const CV_CPU_AVX_512IFMA: i32 = 18;
pub const CV_CPU_AVX_512IFMA512: i32 = 18;
pub const CV_CPU_AVX_512PF: i32 = 19;
pub const CV_CPU_AVX_512VBMI: i32 = 20;
pub const CV_CPU_AVX_512VBMI2: i32 = 22;
pub const CV_CPU_AVX_512VL: i32 = 21;
pub const CV_CPU_AVX_512VNNI: i32 = 23;
pub const CV_CPU_AVX_512VPOPCNTDQ: i32 = 25;
pub const CV_CPU_FMA3: i32 = 12;
pub const CV_CPU_FP16: i32 = 9;
pub const CV_CPU_LASX: i32 = 230;
pub const CV_CPU_MMX: i32 = 1;
pub const CV_CPU_MSA: i32 = 150;
pub const CV_CPU_NEON: i32 = 100;
pub const CV_CPU_NEON_DOTPROD: i32 = 101;
pub const CV_CPU_NONE: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_CPU_POPCNT: i32 = 8;
pub const CV_CPU_RISCVV: i32 = 170;
pub const CV_CPU_RVV: i32 = 210;
pub const CV_CPU_SSE: i32 = 2;
pub const CV_CPU_SSE2: i32 = 3;
pub const CV_CPU_SSE3: i32 = 4;
pub const CV_CPU_SSE4_1: i32 = 6;
pub const CV_CPU_SSE4_2: i32 = 7;
pub const CV_CPU_SSSE3: i32 = 5;
pub const CV_CPU_VSX: i32 = 200;
pub const CV_CPU_VSX3: i32 = 201;
pub const CV_CXX11: i32 = 1;
pub const CV_CXX_MOVE_SEMANTICS: i32 = 1;
pub const CV_CXX_STD_ARRAY: i32 = 1;
pub const CV_DEPTH_MAX: i32 = (1<<CV_CN_SHIFT);
pub const CV_ENABLE_UNROLLED: i32 = 1;
pub const CV_FMA3: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_FP16: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_FP16_TYPE: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_HAL_BORDER_CONSTANT: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_HAL_BORDER_ISOLATED: i32 = 16;
pub const CV_HAL_BORDER_REFLECT: i32 = 2;
pub const CV_HAL_BORDER_REFLECT_101: i32 = 4;
pub const CV_HAL_BORDER_REPLICATE: i32 = 1;
pub const CV_HAL_BORDER_TRANSPARENT: i32 = 5;
pub const CV_HAL_BORDER_WRAP: i32 = 3;
pub const CV_HAL_CMP_EQ: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_HAL_CMP_GE: i32 = 2;
pub const CV_HAL_CMP_GT: i32 = 1;
pub const CV_HAL_CMP_LE: i32 = 4;
pub const CV_HAL_CMP_LT: i32 = 3;
pub const CV_HAL_CMP_NE: i32 = 5;
pub const CV_HAL_DFT_COMPLEX_OUTPUT: i32 = 16;
pub const CV_HAL_DFT_INVERSE: i32 = 1;
pub const CV_HAL_DFT_IS_CONTINUOUS: i32 = 512;
pub const CV_HAL_DFT_IS_INPLACE: i32 = 1024;
pub const CV_HAL_DFT_REAL_OUTPUT: i32 = 32;
pub const CV_HAL_DFT_ROWS: i32 = 4;
pub const CV_HAL_DFT_SCALE: i32 = 2;
pub const CV_HAL_DFT_STAGE_COLS: i32 = 128;
pub const CV_HAL_DFT_TWO_STAGE: i32 = 64;
pub const CV_HAL_ERROR_NOT_IMPLEMENTED: i32 = 1;
pub const CV_HAL_ERROR_OK: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_HAL_ERROR_UNKNOWN: i32 = -1;
pub const CV_HAL_GEMM_1_T: i32 = 1;
pub const CV_HAL_GEMM_2_T: i32 = 2;
pub const CV_HAL_GEMM_3_T: i32 = 4;
pub const CV_HAL_SVD_FULL_UV: i32 = 8;
pub const CV_HAL_SVD_MODIFY_A: i32 = 4;
pub const CV_HAL_SVD_NO_UV: i32 = 1;
pub const CV_HAL_SVD_SHORT_UV: i32 = 2;
pub const CV_HARDWARE_MAX_FEATURE: i32 = 512;
pub const CV_IMPL_IPP: i32 = 0x04;
pub const CV_IMPL_MT: i32 = 0x10;
pub const CV_IMPL_OCL: i32 = 0x02;
pub const CV_IMPL_PLAIN: i32 = 0x01;
pub const CV_LASX: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_LOG2: f64 = 0.69314718055994530941723212145818;
pub const CV_LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG: i32 = 5;
pub const CV_LOG_LEVEL_ERROR: i32 = 2;
pub const CV_LOG_LEVEL_FATAL: i32 = 1;
pub const CV_LOG_LEVEL_INFO: i32 = 4;
pub const CV_LOG_LEVEL_SILENT: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_LOG_LEVEL_VERBOSE: i32 = 6;
pub const CV_LOG_LEVEL_WARN: i32 = 3;
pub const CV_LOG_STRIP_LEVEL: i32 = CV_LOG_LEVEL_VERBOSE;
pub const CV_MAJOR_VERSION: i32 = CV_VERSION_MAJOR;
pub const CV_MAT_CN_MASK: i32 = ((CV_CN_MAX-1)<<CV_CN_SHIFT);
pub const CV_MAT_CONT_FLAG: i32 = (1<<CV_MAT_CONT_FLAG_SHIFT);
pub const CV_MAT_CONT_FLAG_SHIFT: i32 = 14;
pub const CV_MAT_DEPTH_MASK: i32 = (CV_DEPTH_MAX-1);
pub const CV_MAT_TYPE_MASK: i32 = (CV_DEPTH_MAX*CV_CN_MAX-1);
pub const CV_MINOR_VERSION: i32 = CV_VERSION_MINOR;
pub const CV_MMX: i32 = 1;
pub const CV_MSA: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_NEON: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_PI: f64 = 3.1415926535897932384626433832795;
pub const CV_POPCNT: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_RVV: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_RVV071: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_SSE: i32 = 1;
pub const CV_SSE2: i32 = 1;
pub const CV_SSE3: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_SSE4_1: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_SSE4_2: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_SSSE3: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_STRONG_ALIGNMENT: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_SUBMAT_FLAG: i32 = (1<<CV_SUBMAT_FLAG_SHIFT);
pub const CV_SUBMAT_FLAG_SHIFT: i32 = 15;
pub const CV_SUBMINOR_VERSION: i32 = CV_VERSION_REVISION;
pub const CV_VERSION: &str = "4.7.0";
pub const CV_VERSION_MAJOR: i32 = 4;
pub const CV_VERSION_MINOR: i32 = 7;
pub const CV_VERSION_REVISION: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_VERSION_STATUS: &str = "";
pub const CV_VSX: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_VSX3: i32 = 0;
pub const CV_WASM_SIMD: i32 = 0;
pub const CV__EXCEPTION_PTR: i32 = 1;
/// performs an inverse 1D or 2D transform instead of the default forward transform.
pub const DCT_INVERSE: i32 = 1;
/// performs a forward or inverse transform of every individual row of the input
/// matrix. This flag enables you to transform multiple vectors simultaneously and can be used to
/// decrease the overhead (which is sometimes several times larger than the processing itself) to
/// perform 3D and higher-dimensional transforms and so forth.
pub const DCT_ROWS: i32 = 4;
/// Cholesky  factorization; the matrix src1 must be symmetrical and positively
/// defined
pub const DECOMP_CHOLESKY: i32 = 3;
/// eigenvalue decomposition; the matrix src1 must be symmetrical
pub const DECOMP_EIG: i32 = 2;
/// Gaussian elimination with the optimal pivot element chosen.
pub const DECOMP_LU: i32 = 0;
/// while all the previous flags are mutually exclusive, this flag can be used together with
/// any of the previous; it means that the normal equations
///  are
/// solved instead of the original system
/// 
pub const DECOMP_NORMAL: i32 = 16;
/// QR factorization; the system can be over-defined and/or the matrix src1 can be singular
pub const DECOMP_QR: i32 = 4;
/// singular value decomposition (SVD) method; the system can be over-defined and/or the matrix
/// src1 can be singular
pub const DECOMP_SVD: i32 = 1;
/// specifies that input is complex input. If this flag is set, the input must have 2 channels.
/// On the other hand, for backwards compatibility reason, if input has 2 channels, input is
/// already considered complex.
pub const DFT_COMPLEX_INPUT: i32 = 64;
/// performs a forward transformation of 1D or 2D real array; the result,
/// though being a complex array, has complex-conjugate symmetry (*CCS*, see the function
/// description below for details), and such an array can be packed into a real array of the same
/// size as input, which is the fastest option and which is what the function does by default;
/// however, you may wish to get a full complex array (for simpler spectrum analysis, and so on) -
/// pass the flag to enable the function to produce a full-size complex output array.
pub const DFT_COMPLEX_OUTPUT: i32 = 16;
/// performs an inverse 1D or 2D transform instead of the default forward
/// transform.
pub const DFT_INVERSE: i32 = 1;
/// performs an inverse transformation of a 1D or 2D complex array; the
/// result is normally a complex array of the same size, however, if the input array has
/// conjugate-complex symmetry (for example, it is a result of forward transformation with
/// DFT_COMPLEX_OUTPUT flag), the output is a real array; while the function itself does not
/// check whether the input is symmetrical or not, you can pass the flag and then the function
/// will assume the symmetry and produce the real output array (note that when the input is packed
/// into a real array and inverse transformation is executed, the function treats the input as a
/// packed complex-conjugate symmetrical array, and the output will also be a real array).
pub const DFT_REAL_OUTPUT: i32 = 32;
/// performs a forward or inverse transform of every individual row of the input
/// matrix; this flag enables you to transform multiple vectors simultaneously and can be used to
/// decrease the overhead (which is sometimes several times larger than the processing itself) to
/// perform 3D and higher-dimensional transformations and so forth.
pub const DFT_ROWS: i32 = 4;
/// scales the result: divide it by the number of array elements. Normally, it is
/// combined with DFT_INVERSE.
pub const DFT_SCALE: i32 = 2;
pub const DYNAMIC_PARALLELISM: i32 = 35;
pub const Detail_CV__LAST_TEST_OP: i32 = 7;
pub const Detail_TEST_CUSTOM: i32 = 0;
pub const Detail_TEST_EQ: i32 = 1;
pub const Detail_TEST_GE: i32 = 5;
pub const Detail_TEST_GT: i32 = 6;
pub const Detail_TEST_LE: i32 = 3;
pub const Detail_TEST_LT: i32 = 4;
pub const Detail_TEST_NE: i32 = 2;
pub const Device_EXEC_KERNEL: i32 = 1;
pub const Device_EXEC_NATIVE_KERNEL: i32 = 2;
pub const Device_FP_CORRECTLY_ROUNDED_DIVIDE_SQRT: i32 = 128;
pub const Device_FP_DENORM: i32 = 1;
pub const Device_FP_FMA: i32 = 32;
pub const Device_FP_INF_NAN: i32 = 2;
pub const Device_FP_ROUND_TO_INF: i32 = 16;
pub const Device_FP_ROUND_TO_NEAREST: i32 = 4;
pub const Device_FP_ROUND_TO_ZERO: i32 = 8;
pub const Device_FP_SOFT_FLOAT: i32 = 64;
pub const Device_LOCAL_IS_GLOBAL: i32 = 2;
pub const Device_LOCAL_IS_LOCAL: i32 = 1;
pub const Device_NO_CACHE: i32 = 0;
pub const Device_NO_LOCAL_MEM: i32 = 0;
pub const Device_READ_ONLY_CACHE: i32 = 1;
pub const Device_READ_WRITE_CACHE: i32 = 2;
pub const Device_TYPE_ACCELERATOR: i32 = 8;
pub const Device_TYPE_ALL: i32 = -1;
pub const Device_TYPE_CPU: i32 = 2;
pub const Device_TYPE_DEFAULT: i32 = 1;
pub const Device_TYPE_DGPU: i32 = 65540;
pub const Device_TYPE_GPU: i32 = 4;
pub const Device_TYPE_IGPU: i32 = 131076;
pub const Device_UNKNOWN_VENDOR: i32 = 0;
pub const Device_VENDOR_AMD: i32 = 1;
pub const Device_VENDOR_INTEL: i32 = 2;
pub const Device_VENDOR_NVIDIA: i32 = 3;
pub const ENUM_LOG_LEVEL_FORCE_INT: i32 = 2147483647;
pub const FEATURE_SET_COMPUTE_10: i32 = 10;
pub const FEATURE_SET_COMPUTE_11: i32 = 11;
pub const FEATURE_SET_COMPUTE_12: i32 = 12;
pub const FEATURE_SET_COMPUTE_13: i32 = 13;
pub const FEATURE_SET_COMPUTE_20: i32 = 20;
pub const FEATURE_SET_COMPUTE_21: i32 = 21;
pub const FEATURE_SET_COMPUTE_30: i32 = 30;
pub const FEATURE_SET_COMPUTE_32: i32 = 32;
pub const FEATURE_SET_COMPUTE_35: i32 = 35;
pub const FEATURE_SET_COMPUTE_50: i32 = 50;
pub const FLAGS_EXPAND_SAME_NAMES: i32 = 2;
pub const FLAGS_MAPPING: i32 = 1;
pub const FLAGS_NONE: i32 = 0;
/// empty structure (sequence or mapping)
pub const FileNode_EMPTY: i32 = 16;
/// synonym or REAL
pub const FileNode_FLOAT: i32 = 2;
/// compact representation of a sequence or mapping. Used only by YAML writer
pub const FileNode_FLOW: i32 = 8;
/// an integer
pub const FileNode_INT: i32 = 1;
/// mapping
pub const FileNode_MAP: i32 = 5;
/// the node has a name (i.e. it is element of a mapping).
pub const FileNode_NAMED: i32 = 32;
/// empty node
pub const FileNode_NONE: i32 = 0;
/// floating-point number
pub const FileNode_REAL: i32 = 2;
/// sequence
pub const FileNode_SEQ: i32 = 4;
/// text string in UTF-8 encoding
pub const FileNode_STR: i32 = 3;
/// synonym for STR
pub const FileNode_STRING: i32 = 3;
pub const FileNode_TYPE_MASK: i32 = 7;
/// if set, means that all the collection elements are numbers of the same type (real's or int's).
/// UNIFORM is used only when reading FileStorage; FLOW is used only when writing. So they share the same bit
pub const FileNode_UNIFORM: i32 = 8;
/// transposes src1
pub const GEMM_1_T: i32 = 1;
/// transposes src2
pub const GEMM_2_T: i32 = 2;
/// transposes src3
pub const GEMM_3_T: i32 = 4;
pub const GLOBAL_ATOMICS: i32 = 11;
/// GPU API call error
pub const GpuApiCallError: i32 = -217;
/// no CUDA support
pub const GpuNotSupported: i32 = -216;
/// image header is NULL
pub const HeaderIsNull: i32 = -9;
pub const IMPL_IPP: i32 = 1;
pub const IMPL_OPENCL: i32 = 2;
pub const IMPL_PLAIN: i32 = 0;
/// Use kmeans++ center initialization by Arthur and Vassilvitskii [Arthur2007].
pub const KMEANS_PP_CENTERS: i32 = 2;
/// Select random initial centers in each attempt.
pub const KMEANS_RANDOM_CENTERS: i32 = 0;
/// During the first (and possibly the only) attempt, use the
/// user-supplied labels instead of computing them from the initial centers. For the second and
/// further attempts, use the random or semi-random centers. Use one of KMEANS_\*_CENTERS flag
/// to specify the exact method.
pub const KMEANS_USE_INITIAL_LABELS: i32 = 1;
pub const KernelArg_CONSTANT: i32 = 8;
pub const KernelArg_LOCAL: i32 = 1;
pub const KernelArg_NO_SIZE: i32 = 256;
pub const KernelArg_PTR_ONLY: i32 = 16;
pub const KernelArg_READ_ONLY: i32 = 2;
pub const KernelArg_READ_WRITE: i32 = 6;
pub const KernelArg_WRITE_ONLY: i32 = 4;
pub const LINES: i32 = 1;
pub const LINE_LOOP: i32 = 2;
pub const LINE_STRIP: i32 = 3;
/// Debug message. Disabled in the "Release" build.
pub const LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG: i32 = 5;
/// Error message
pub const LOG_LEVEL_ERROR: i32 = 2;
/// Fatal (critical) error (unrecoverable internal error)
pub const LOG_LEVEL_FATAL: i32 = 1;
/// Info message
pub const LOG_LEVEL_INFO: i32 = 4;
/// for using in setLogVevel() call
pub const LOG_LEVEL_SILENT: i32 = 0;
/// Verbose (trace) messages. Requires verbosity level. Disabled in the "Release" build.
pub const LOG_LEVEL_VERBOSE: i32 = 6;
/// Warning message
pub const LOG_LEVEL_WARNING: i32 = 3;
pub const MaskIsTiled: i32 = -26;
pub const Mat_AUTO_STEP: usize = 0;
pub const Mat_CONTINUOUS_FLAG: i32 = 16384;
pub const Mat_DEPTH_MASK: i32 = 7;
pub const Mat_MAGIC_MASK: i32 = -65536;
pub const Mat_MAGIC_VAL: i32 = 1124007936;
pub const Mat_SUBMATRIX_FLAG: i32 = 32768;
pub const Mat_TYPE_MASK: i32 = 4095;
pub const NATIVE_DOUBLE: i32 = 13;
/// In the case of one input array, calculates the Hamming distance of the array from zero,
/// In the case of two input arrays, calculates the Hamming distance between the arrays.
pub const NORM_HAMMING: i32 = 6;
/// Similar to NORM_HAMMING, but in the calculation, each two bits of the input sequence will
/// be added and treated as a single bit to be used in the same calculation as NORM_HAMMING.
pub const NORM_HAMMING2: i32 = 7;
/// 
pub const NORM_INF: i32 = 1;
/// 
pub const NORM_L1: i32 = 2;
/// 
pub const NORM_L2: i32 = 4;
/// 
pub const NORM_L2SQR: i32 = 5;
/// flag
pub const NORM_MINMAX: i32 = 32;
/// flag
pub const NORM_RELATIVE: i32 = 8;
/// bit-mask which can be used to separate norm type from norm flags
pub const NORM_TYPE_MASK: i32 = 7;
pub const OCL_VECTOR_DEFAULT: i32 = 0;
pub const OCL_VECTOR_MAX: i32 = 1;
pub const OCL_VECTOR_OWN: i32 = 0;
pub const OPENCV_ABI_COMPATIBILITY: i32 = 400;
pub const OPENCV_USE_FASTMATH_BUILTINS: i32 = 1;
/// OpenCL API call error
pub const OpenCLApiCallError: i32 = -220;
pub const OpenCLDoubleNotSupported: i32 = -221;
/// OpenCL initialization error
pub const OpenCLInitError: i32 = -222;
pub const OpenCLNoAMDBlasFft: i32 = -223;
/// OpenGL API call error
pub const OpenGlApiCallError: i32 = -219;
/// no OpenGL support
pub const OpenGlNotSupported: i32 = -218;
pub const POINTS: i32 = 0;
pub const POLYGON: i32 = 9;
pub const Param_ALGORITHM: i32 = 6;
pub const Param_BOOLEAN: i32 = 1;
pub const Param_FLOAT: i32 = 7;
pub const Param_INT: i32 = 0;
pub const Param_MAT: i32 = 4;
pub const Param_MAT_VECTOR: i32 = 5;
pub const Param_REAL: i32 = 2;
pub const Param_SCALAR: i32 = 12;
pub const Param_STRING: i32 = 3;
pub const Param_UCHAR: i32 = 11;
pub const Param_UINT64: i32 = 9;
pub const Param_UNSIGNED_INT: i32 = 8;
pub const QUADS: i32 = 7;
pub const QUAD_STRIP: i32 = 8;
/// the output is the mean vector of all rows/columns of the matrix.
pub const REDUCE_AVG: i32 = 1;
/// the output is the maximum (column/row-wise) of all rows/columns of the matrix.
pub const REDUCE_MAX: i32 = 2;
/// the output is the minimum (column/row-wise) of all rows/columns of the matrix.
pub const REDUCE_MIN: i32 = 3;
/// the output is the sum of all rows/columns of the matrix.
pub const REDUCE_SUM: i32 = 0;
pub const RNG_NORMAL: i32 = 1;
pub const RNG_UNIFORM: i32 = 0;
/// Rotate 180 degrees clockwise
pub const ROTATE_180: i32 = 1;
/// Rotate 90 degrees clockwise
pub const ROTATE_90_CLOCKWISE: i32 = 0;
/// Rotate 270 degrees clockwise
pub const ROTATE_90_COUNTERCLOCKWISE: i32 = 2;
pub const SHARED_ATOMICS: i32 = 12;
/// there are multiple maxima for target function - the arbitrary one is returned
pub const SOLVELP_MULTI: i32 = 1;
/// there is only one maximum for target function
pub const SOLVELP_SINGLE: i32 = 0;
/// problem is unbounded (target function can achieve arbitrary high values)
pub const SOLVELP_UNBOUNDED: i32 = -2;
/// problem is unfeasible (there are no points that satisfy all the constraints imposed)
pub const SOLVELP_UNFEASIBLE: i32 = -1;
/// each matrix row is sorted in the ascending
/// order.
pub const SORT_ASCENDING: i32 = 0;
/// each matrix row is sorted in the
/// descending order; this flag and the previous one are also
/// mutually exclusive.
pub const SORT_DESCENDING: i32 = 16;
/// each matrix column is sorted
/// independently; this flag and the previous one are
/// mutually exclusive.
pub const SORT_EVERY_COLUMN: i32 = 1;
/// each matrix row is sorted independently
pub const SORT_EVERY_ROW: i32 = 0;
pub const SparseMat_HASH_BIT: i32 = -2147483648;
pub const SparseMat_HASH_SCALE: i32 = 1540483477;
pub const SparseMat_MAGIC_VAL: i32 = 1123876864;
pub const SparseMat_MAX_DIM: i32 = 32;
/// assertion failed
pub const StsAssert: i32 = -215;
/// tracing
pub const StsAutoTrace: i32 = -8;
/// pseudo error for back trace
pub const StsBackTrace: i32 = -1;
/// function arg/param is bad
pub const StsBadArg: i32 = -5;
/// flag is wrong or not supported
pub const StsBadFlag: i32 = -206;
/// unsupported function
pub const StsBadFunc: i32 = -6;
/// bad format of mask (neither 8uC1 nor 8sC1)
pub const StsBadMask: i32 = -208;
/// an allocated block has been corrupted
pub const StsBadMemBlock: i32 = -214;
/// bad CvPoint
pub const StsBadPoint: i32 = -207;
/// the input/output structure size is incorrect
pub const StsBadSize: i32 = -201;
/// division by zero
pub const StsDivByZero: i32 = -202;
/// unknown /unspecified error
pub const StsError: i32 = -2;
/// incorrect filter offset value
pub const StsFilterOffsetErr: i32 = -31;
/// incorrect filter structure content
pub const StsFilterStructContentErr: i32 = -29;
/// in-place operation is not supported
pub const StsInplaceNotSupported: i32 = -203;
/// internal error (bad state)
pub const StsInternal: i32 = -3;
/// incorrect transform kernel content
pub const StsKernelStructContentErr: i32 = -30;
/// iteration didn't converge
pub const StsNoConv: i32 = -7;
/// insufficient memory
pub const StsNoMem: i32 = -4;
/// the requested function/feature is not implemented
pub const StsNotImplemented: i32 = -213;
/// null pointer
pub const StsNullPtr: i32 = -27;
/// request can't be completed
pub const StsObjectNotFound: i32 = -204;
/// everything is ok
pub const StsOk: i32 = 0;
/// some of parameters are out of range
pub const StsOutOfRange: i32 = -211;
/// invalid syntax/structure of the parsed file
pub const StsParseError: i32 = -212;
/// formats of input/output arrays differ
pub const StsUnmatchedFormats: i32 = -205;
/// sizes of input/output structures do not match
pub const StsUnmatchedSizes: i32 = -209;
/// the data format/type is not supported by the function
pub const StsUnsupportedFormat: i32 = -210;
/// incorrect vector length
pub const StsVecLengthErr: i32 = -28;
pub const TRIANGLES: i32 = 4;
pub const TRIANGLE_FAN: i32 = 6;
pub const TRIANGLE_STRIP: i32 = 5;
pub const TYPE_FUN: i32 = 3;
pub const TYPE_GENERAL: i32 = 0;
pub const TYPE_MARKER: i32 = 1;
pub const TYPE_WRAPPER: i32 = 2;
pub const UMat_AUTO_STEP: i32 = 0;
pub const UMat_CONTINUOUS_FLAG: i32 = 16384;
pub const UMat_DEPTH_MASK: i32 = 7;
pub const UMat_MAGIC_MASK: i32 = -65536;
pub const UMat_MAGIC_VAL: i32 = 1124007936;
pub const UMat_SUBMATRIX_FLAG: i32 = 32768;
pub const UMat_TYPE_MASK: i32 = 4095;
pub const USAGE_ALLOCATE_DEVICE_MEMORY: i32 = 2;
pub const USAGE_ALLOCATE_HOST_MEMORY: i32 = 1;
pub const USAGE_ALLOCATE_SHARED_MEMORY: i32 = 4;
pub const USAGE_DEFAULT: i32 = 0;
pub const WARP_SHUFFLE_FUNCTIONS: i32 = 30;
pub const __UMAT_USAGE_FLAGS_32BIT: i32 = 2147483647;
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum AccessFlag {
ACCESS_READ = 16777216,
ACCESS_WRITE = 33554432,
ACCESS_RW = 50331648,
// Duplicate, use ACCESS_RW instead
// ACCESS_MASK = 50331648,
ACCESS_FAST = 67108864,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::AccessFlag }
/// Various border types, image boundaries are denoted with `|`
/// ## See also
/// borderInterpolate, copyMakeBorder
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum BorderTypes {
/// `iiiiii|abcdefgh|iiiiiii` with some specified `i`
BORDER_CONSTANT = 0,
/// `aaaaaa|abcdefgh|hhhhhhh`
BORDER_REPLICATE = 1,
/// `fedcba|abcdefgh|hgfedcb`
BORDER_REFLECT = 2,
/// `cdefgh|abcdefgh|abcdefg`
BORDER_WRAP = 3,
/// `gfedcb|abcdefgh|gfedcba`
BORDER_REFLECT_101 = 4,
/// `uvwxyz|abcdefgh|ijklmno`
BORDER_TRANSPARENT = 5,
// same as BORDER_REFLECT_101
// Duplicate, use BORDER_REFLECT_101 instead
// BORDER_REFLECT101 = 4,
// same as BORDER_REFLECT_101
// Duplicate, use BORDER_REFLECT101 instead
// BORDER_DEFAULT = 4,
/// do not look outside of ROI
BORDER_ISOLATED = 16,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::BorderTypes }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum Buffer_Access {
READ_ONLY = 35000,
WRITE_ONLY = 35001,
READ_WRITE = 35002,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::Buffer_Access }
/// The target defines how you intend to use the buffer object.
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum Buffer_Target {
/// The buffer will be used as a source for vertex data
ARRAY_BUFFER = 34962,
/// The buffer will be used for indices (in glDrawElements, for example)
ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER = 34963,
/// The buffer will be used for reading from OpenGL textures
PIXEL_PACK_BUFFER = 35051,
/// The buffer will be used for writing to OpenGL textures
PIXEL_UNPACK_BUFFER = 35052,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::Buffer_Target }
/// comparison types
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum CmpTypes {
/// src1 is equal to src2.
CMP_EQ = 0,
/// src1 is greater than src2.
CMP_GT = 1,
/// src1 is greater than or equal to src2.
CMP_GE = 2,
/// src1 is less than src2.
CMP_LT = 3,
/// src1 is less than or equal to src2.
CMP_LE = 4,
/// src1 is unequal to src2.
CMP_NE = 5,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::CmpTypes }
/// error codes
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum Code {
/// everything is ok
StsOk = 0,
/// pseudo error for back trace
StsBackTrace = -1,
/// unknown /unspecified error
StsError = -2,
/// internal error (bad state)
StsInternal = -3,
/// insufficient memory
StsNoMem = -4,
/// function arg/param is bad
StsBadArg = -5,
/// unsupported function
StsBadFunc = -6,
/// iteration didn't converge
StsNoConv = -7,
/// tracing
StsAutoTrace = -8,
/// image header is NULL
HeaderIsNull = -9,
/// image size is invalid
BadImageSize = -10,
/// offset is invalid
BadOffset = -11,
BadDataPtr = -12,
/// image step is wrong, this may happen for a non-continuous matrix.
BadStep = -13,
BadModelOrChSeq = -14,
/// bad number of channels, for example, some functions accept only single channel matrices.
BadNumChannels = -15,
BadNumChannel1U = -16,
/// input image depth is not supported by the function
BadDepth = -17,
BadAlphaChannel = -18,
/// number of dimensions is out of range
BadOrder = -19,
/// incorrect input origin
BadOrigin = -20,
/// incorrect input align
BadAlign = -21,
BadCallBack = -22,
BadTileSize = -23,
/// input COI is not supported
BadCOI = -24,
/// incorrect input roi
BadROISize = -25,
MaskIsTiled = -26,
/// null pointer
StsNullPtr = -27,
/// incorrect vector length
StsVecLengthErr = -28,
/// incorrect filter structure content
StsFilterStructContentErr = -29,
/// incorrect transform kernel content
StsKernelStructContentErr = -30,
/// incorrect filter offset value
StsFilterOffsetErr = -31,
/// the input/output structure size is incorrect
StsBadSize = -201,
/// division by zero
StsDivByZero = -202,
/// in-place operation is not supported
StsInplaceNotSupported = -203,
/// request can't be completed
StsObjectNotFound = -204,
/// formats of input/output arrays differ
StsUnmatchedFormats = -205,
/// flag is wrong or not supported
StsBadFlag = -206,
/// bad CvPoint
StsBadPoint = -207,
/// bad format of mask (neither 8uC1 nor 8sC1)
StsBadMask = -208,
/// sizes of input/output structures do not match
StsUnmatchedSizes = -209,
/// the data format/type is not supported by the function
StsUnsupportedFormat = -210,
/// some of parameters are out of range
StsOutOfRange = -211,
/// invalid syntax/structure of the parsed file
StsParseError = -212,
/// the requested function/feature is not implemented
StsNotImplemented = -213,
/// an allocated block has been corrupted
StsBadMemBlock = -214,
/// assertion failed
StsAssert = -215,
/// no CUDA support
GpuNotSupported = -216,
/// GPU API call error
GpuApiCallError = -217,
/// no OpenGL support
OpenGlNotSupported = -218,
/// OpenGL API call error
OpenGlApiCallError = -219,
/// OpenCL API call error
OpenCLApiCallError = -220,
OpenCLDoubleNotSupported = -221,
/// OpenCL initialization error
OpenCLInitError = -222,
OpenCLNoAMDBlasFft = -223,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::Code }
/// Covariation flags
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum CovarFlags {
/// The output covariance matrix is calculated as:
/// 
/// The covariance matrix will be nsamples x nsamples. Such an unusual covariance matrix is used
/// for fast PCA of a set of very large vectors (see, for example, the EigenFaces technique for
/// face recognition). Eigenvalues of this "scrambled" matrix match the eigenvalues of the true
/// covariance matrix. The "true" eigenvectors can be easily calculated from the eigenvectors of
/// the "scrambled" covariance matrix.
COVAR_SCRAMBLED = 0,
/// The output covariance matrix is calculated as:
/// 
/// covar will be a square matrix of the same size as the total number of elements in each input
/// vector. One and only one of #COVAR_SCRAMBLED and #COVAR_NORMAL must be specified.
COVAR_NORMAL = 1,
/// If the flag is specified, the function does not calculate mean from
/// the input vectors but, instead, uses the passed mean vector. This is useful if mean has been
/// pre-calculated or known in advance, or if the covariance matrix is calculated by parts. In
/// this case, mean is not a mean vector of the input sub-set of vectors but rather the mean
/// vector of the whole set.
COVAR_USE_AVG = 2,
/// If the flag is specified, the covariance matrix is scaled. In the
/// "normal" mode, scale is 1./nsamples . In the "scrambled" mode, scale is the reciprocal of the
/// total number of elements in each input vector. By default (if the flag is not specified), the
/// covariance matrix is not scaled ( scale=1 ).
COVAR_SCALE = 4,
/// If the flag is
/// specified, all the input vectors are stored as rows of the samples matrix. mean should be a
/// single-row vector in this case.
COVAR_ROWS = 8,
/// If the flag is
/// specified, all the input vectors are stored as columns of the samples matrix. mean should be a
/// single-column vector in this case.
COVAR_COLS = 16,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::CovarFlags }
/// Available CPU features.
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum CpuFeatures {
CPU_MMX = 1,
CPU_SSE = 2,
CPU_SSE2 = 3,
CPU_SSE3 = 4,
CPU_SSSE3 = 5,
CPU_SSE4_1 = 6,
CPU_SSE4_2 = 7,
CPU_POPCNT = 8,
CPU_FP16 = 9,
CPU_AVX = 10,
CPU_AVX2 = 11,
CPU_FMA3 = 12,
CPU_AVX_512F = 13,
CPU_AVX_512BW = 14,
CPU_AVX_512CD = 15,
CPU_AVX_512DQ = 16,
CPU_AVX_512ER = 17,
CPU_AVX_512IFMA512 = 18,
// Duplicate, use CPU_AVX_512IFMA512 instead
// CPU_AVX_512IFMA = 18,
CPU_AVX_512PF = 19,
CPU_AVX_512VBMI = 20,
CPU_AVX_512VL = 21,
CPU_AVX_512VBMI2 = 22,
CPU_AVX_512VNNI = 23,
CPU_AVX_512BITALG = 24,
CPU_AVX_512VPOPCNTDQ = 25,
CPU_AVX_5124VNNIW = 26,
CPU_AVX_5124FMAPS = 27,
CPU_NEON = 100,
CPU_NEON_DOTPROD = 101,
CPU_MSA = 150,
CPU_RISCVV = 170,
CPU_VSX = 200,
CPU_VSX3 = 201,
CPU_RVV = 210,
CPU_LASX = 230,
/// Skylake-X with AVX-512F/CD/BW/DQ/VL
CPU_AVX512_SKX = 256,
/// Common instructions AVX-512F/CD for all CPUs that support AVX-512
CPU_AVX512_COMMON = 257,
/// Knights Landing with AVX-512F/CD/ER/PF
CPU_AVX512_KNL = 258,
/// Knights Mill with AVX-512F/CD/ER/PF/4FMAPS/4VNNIW/VPOPCNTDQ
CPU_AVX512_KNM = 259,
/// Cannon Lake with AVX-512F/CD/BW/DQ/VL/IFMA/VBMI
CPU_AVX512_CNL = 260,
/// Cascade Lake with AVX-512F/CD/BW/DQ/VL/VNNI
CPU_AVX512_CLX = 261,
/// Ice Lake with AVX-512F/CD/BW/DQ/VL/IFMA/VBMI/VNNI/VBMI2/BITALG/VPOPCNTDQ
CPU_AVX512_ICL = 262,
CPU_MAX_FEATURE = 512,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::CpuFeatures }
/// matrix decomposition types
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum DecompTypes {
/// Gaussian elimination with the optimal pivot element chosen.
DECOMP_LU = 0,
/// singular value decomposition (SVD) method; the system can be over-defined and/or the matrix
/// src1 can be singular
DECOMP_SVD = 1,
/// eigenvalue decomposition; the matrix src1 must be symmetrical
DECOMP_EIG = 2,
/// Cholesky  factorization; the matrix src1 must be symmetrical and positively
/// defined
DECOMP_CHOLESKY = 3,
/// QR factorization; the system can be over-defined and/or the matrix src1 can be singular
DECOMP_QR = 4,
/// while all the previous flags are mutually exclusive, this flag can be used together with
/// any of the previous; it means that the normal equations
///  are
/// solved instead of the original system
/// 
DECOMP_NORMAL = 16,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::DecompTypes }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum Detail_TestOp {
TEST_CUSTOM = 0,
TEST_EQ = 1,
TEST_NE = 2,
TEST_LE = 3,
TEST_LT = 4,
TEST_GE = 5,
TEST_GT = 6,
CV__LAST_TEST_OP = 7,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::Detail_TestOp }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum DeviceInfo_ComputeMode {
/// < default compute mode (Multiple threads can use cudaSetDevice with this device)
ComputeModeDefault = 0,
/// < compute-exclusive-thread mode (Only one thread in one process will be able to use cudaSetDevice with this device)
ComputeModeExclusive = 1,
/// < compute-prohibited mode (No threads can use cudaSetDevice with this device)
ComputeModeProhibited = 2,
/// < compute-exclusive-process mode (Many threads in one process will be able to use cudaSetDevice with this device)
ComputeModeExclusiveProcess = 3,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::DeviceInfo_ComputeMode }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum DftFlags {
/// performs an inverse 1D or 2D transform instead of the default forward
/// transform.
DFT_INVERSE = 1,
/// scales the result: divide it by the number of array elements. Normally, it is
/// combined with DFT_INVERSE.
DFT_SCALE = 2,
/// performs a forward or inverse transform of every individual row of the input
/// matrix; this flag enables you to transform multiple vectors simultaneously and can be used to
/// decrease the overhead (which is sometimes several times larger than the processing itself) to
/// perform 3D and higher-dimensional transformations and so forth.
DFT_ROWS = 4,
/// performs a forward transformation of 1D or 2D real array; the result,
/// though being a complex array, has complex-conjugate symmetry (*CCS*, see the function
/// description below for details), and such an array can be packed into a real array of the same
/// size as input, which is the fastest option and which is what the function does by default;
/// however, you may wish to get a full complex array (for simpler spectrum analysis, and so on) -
/// pass the flag to enable the function to produce a full-size complex output array.
DFT_COMPLEX_OUTPUT = 16,
/// performs an inverse transformation of a 1D or 2D complex array; the
/// result is normally a complex array of the same size, however, if the input array has
/// conjugate-complex symmetry (for example, it is a result of forward transformation with
/// DFT_COMPLEX_OUTPUT flag), the output is a real array; while the function itself does not
/// check whether the input is symmetrical or not, you can pass the flag and then the function
/// will assume the symmetry and produce the real output array (note that when the input is packed
/// into a real array and inverse transformation is executed, the function treats the input as a
/// packed complex-conjugate symmetrical array, and the output will also be a real array).
DFT_REAL_OUTPUT = 32,
/// specifies that input is complex input. If this flag is set, the input must have 2 channels.
/// On the other hand, for backwards compatibility reason, if input has 2 channels, input is
/// already considered complex.
DFT_COMPLEX_INPUT = 64,
// performs an inverse 1D or 2D transform instead of the default forward transform.
// Duplicate, use DFT_INVERSE instead
// DCT_INVERSE = 1,
// performs a forward or inverse transform of every individual row of the input
// matrix. This flag enables you to transform multiple vectors simultaneously and can be used to
// decrease the overhead (which is sometimes several times larger than the processing itself) to
// perform 3D and higher-dimensional transforms and so forth.
// Duplicate, use DFT_ROWS instead
// DCT_ROWS = 4,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::DftFlags }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum Event_CreateFlags {
/// < Default event flag
DEFAULT = 0,
/// < Event uses blocking synchronization
BLOCKING_SYNC = 1,
/// < Event will not record timing data
DISABLE_TIMING = 2,
/// < Event is suitable for interprocess use. DisableTiming must be set
INTERPROCESS = 4,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::Event_CreateFlags }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum FLAGS {
FLAGS_NONE = 0,
FLAGS_MAPPING = 1,
FLAGS_EXPAND_SAME_NAMES = 2,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::FLAGS }
/// Enumeration providing CUDA computing features.
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum FeatureSet {
FEATURE_SET_COMPUTE_10 = 10,
FEATURE_SET_COMPUTE_11 = 11,
FEATURE_SET_COMPUTE_12 = 12,
FEATURE_SET_COMPUTE_13 = 13,
FEATURE_SET_COMPUTE_20 = 20,
FEATURE_SET_COMPUTE_21 = 21,
FEATURE_SET_COMPUTE_30 = 30,
FEATURE_SET_COMPUTE_32 = 32,
FEATURE_SET_COMPUTE_35 = 35,
FEATURE_SET_COMPUTE_50 = 50,
// Duplicate, use FEATURE_SET_COMPUTE_11 instead
// GLOBAL_ATOMICS = 11,
// Duplicate, use FEATURE_SET_COMPUTE_12 instead
// SHARED_ATOMICS = 12,
// Duplicate, use FEATURE_SET_COMPUTE_13 instead
// NATIVE_DOUBLE = 13,
// Duplicate, use FEATURE_SET_COMPUTE_30 instead
// WARP_SHUFFLE_FUNCTIONS = 30,
// Duplicate, use FEATURE_SET_COMPUTE_35 instead
// DYNAMIC_PARALLELISM = 35,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::FeatureSet }
/// file storage mode
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum FileStorage_Mode {
/// value, open the file for reading
READ = 0,
/// value, open the file for writing
WRITE = 1,
/// value, open the file for appending
APPEND = 2,
/// < flag, read data from source or write data to the internal buffer (which is
/// returned by FileStorage::release)
MEMORY = 4,
/// mask for format flags
FORMAT_MASK = 56,
// flag, auto format
// Duplicate, use READ instead
// FORMAT_AUTO = 0,
/// flag, XML format
FORMAT_XML = 8,
/// flag, YAML format
FORMAT_YAML = 16,
/// flag, JSON format
FORMAT_JSON = 24,
/// flag, write rawdata in Base64 by default. (consider using WRITE_BASE64)
BASE64 = 64,
/// flag, enable both WRITE and BASE64
WRITE_BASE64 = 65,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::FileStorage_Mode }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum FileStorage_State {
UNDEFINED = 0,
VALUE_EXPECTED = 1,
NAME_EXPECTED = 2,
INSIDE_MAP = 4,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::FileStorage_State }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum Formatter_FormatType {
FMT_DEFAULT = 0,
FMT_MATLAB = 1,
FMT_CSV = 2,
FMT_PYTHON = 3,
FMT_NUMPY = 4,
FMT_C = 5,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::Formatter_FormatType }
/// generalized matrix multiplication flags
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum GemmFlags {
/// transposes src1
GEMM_1_T = 1,
/// transposes src2
GEMM_2_T = 2,
/// transposes src3
GEMM_3_T = 4,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::GemmFlags }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum HostMem_AllocType {
PAGE_LOCKED = 1,
SHARED = 2,
WRITE_COMBINED = 4,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::HostMem_AllocType }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum IMPL {
IMPL_PLAIN = 0,
IMPL_IPP = 1,
IMPL_OPENCL = 2,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::IMPL }
/// k-Means flags
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum KmeansFlags {
/// Select random initial centers in each attempt.
KMEANS_RANDOM_CENTERS = 0,
/// Use kmeans++ center initialization by Arthur and Vassilvitskii [Arthur2007].
KMEANS_PP_CENTERS = 2,
/// During the first (and possibly the only) attempt, use the
/// user-supplied labels instead of computing them from the initial centers. For the second and
/// further attempts, use the random or semi-random centers. Use one of KMEANS_\*_CENTERS flag
/// to specify the exact method.
KMEANS_USE_INITIAL_LABELS = 1,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::KmeansFlags }
/// Supported logging levels and their semantic
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum LogLevel {
/// for using in setLogVevel() call
LOG_LEVEL_SILENT = 0,
/// Fatal (critical) error (unrecoverable internal error)
LOG_LEVEL_FATAL = 1,
/// Error message
LOG_LEVEL_ERROR = 2,
/// Warning message
LOG_LEVEL_WARNING = 3,
/// Info message
LOG_LEVEL_INFO = 4,
/// Debug message. Disabled in the "Release" build.
LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG = 5,
/// Verbose (trace) messages. Requires verbosity level. Disabled in the "Release" build.
LOG_LEVEL_VERBOSE = 6,
ENUM_LOG_LEVEL_FORCE_INT = 2147483647,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::LogLevel }
/// norm types
///
/// src1 and src2 denote input arrays.
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum NormTypes {
/// 
NORM_INF = 1,
/// 
NORM_L1 = 2,
/// 
NORM_L2 = 4,
/// 
NORM_L2SQR = 5,
/// In the case of one input array, calculates the Hamming distance of the array from zero,
/// In the case of two input arrays, calculates the Hamming distance between the arrays.
NORM_HAMMING = 6,
/// Similar to NORM_HAMMING, but in the calculation, each two bits of the input sequence will
/// be added and treated as a single bit to be used in the same calculation as NORM_HAMMING.
NORM_HAMMING2 = 7,
// bit-mask which can be used to separate norm type from norm flags
// Duplicate, use NORM_HAMMING2 instead
// NORM_TYPE_MASK = 7,
/// flag
NORM_RELATIVE = 8,
/// flag
NORM_MINMAX = 32,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::NormTypes }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum OclVectorStrategy {
OCL_VECTOR_OWN = 0,
OCL_VECTOR_MAX = 1,
// Duplicate, use OCL_VECTOR_OWN instead
// OCL_VECTOR_DEFAULT = 0,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::OclVectorStrategy }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum PCA_Flags {
/// indicates that the input samples are stored as matrix rows
DATA_AS_ROW = 0,
/// indicates that the input samples are stored as matrix columns
DATA_AS_COL = 1,
USE_AVG = 2,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::PCA_Flags }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum Param {
INT = 0,
BOOLEAN = 1,
REAL = 2,
STRING = 3,
MAT = 4,
MAT_VECTOR = 5,
ALGORITHM = 6,
FLOAT = 7,
UNSIGNED_INT = 8,
UINT64 = 9,
UCHAR = 11,
SCALAR = 12,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::Param }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum ReduceTypes {
/// the output is the sum of all rows/columns of the matrix.
REDUCE_SUM = 0,
/// the output is the mean vector of all rows/columns of the matrix.
REDUCE_AVG = 1,
/// the output is the maximum (column/row-wise) of all rows/columns of the matrix.
REDUCE_MAX = 2,
/// the output is the minimum (column/row-wise) of all rows/columns of the matrix.
REDUCE_MIN = 3,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::ReduceTypes }
/// render mode
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum RenderModes {
POINTS = 0,
LINES = 1,
LINE_LOOP = 2,
LINE_STRIP = 3,
TRIANGLES = 4,
TRIANGLE_STRIP = 5,
TRIANGLE_FAN = 6,
QUADS = 7,
QUAD_STRIP = 8,
POLYGON = 9,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::RenderModes }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum RotateFlags {
/// Rotate 90 degrees clockwise
ROTATE_90_CLOCKWISE = 0,
/// Rotate 180 degrees clockwise
ROTATE_180 = 1,
/// Rotate 270 degrees clockwise
ROTATE_90_COUNTERCLOCKWISE = 2,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::RotateFlags }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum SVD_Flags {
/// allow the algorithm to modify the decomposed matrix; it can save space and speed up
/// processing. currently ignored.
MODIFY_A = 1,
/// indicates that only a vector of singular values `w` is to be processed, while u and vt
/// will be set to empty matrices
NO_UV = 2,
/// when the matrix is not square, by default the algorithm produces u and vt matrices of
/// sufficiently large size for the further A reconstruction; if, however, FULL_UV flag is
/// specified, u and vt will be full-size square orthogonal matrices.
FULL_UV = 4,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::SVD_Flags }
/// return codes for cv::solveLP() function
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum SolveLPResult {
/// problem is unbounded (target function can achieve arbitrary high values)
SOLVELP_UNBOUNDED = -2,
/// problem is unfeasible (there are no points that satisfy all the constraints imposed)
SOLVELP_UNFEASIBLE = -1,
/// there is only one maximum for target function
SOLVELP_SINGLE = 0,
/// there are multiple maxima for target function - the arbitrary one is returned
SOLVELP_MULTI = 1,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::SolveLPResult }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum SortFlags {
/// each matrix row is sorted independently
SORT_EVERY_ROW = 0,
/// each matrix column is sorted
/// independently; this flag and the previous one are
/// mutually exclusive.
SORT_EVERY_COLUMN = 1,
// each matrix row is sorted in the ascending
// order.
// Duplicate, use SORT_EVERY_ROW instead
// SORT_ASCENDING = 0,
/// each matrix row is sorted in the
/// descending order; this flag and the previous one are also
/// mutually exclusive.
SORT_DESCENDING = 16,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::SortFlags }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum TYPE {
TYPE_GENERAL = 0,
TYPE_MARKER = 1,
TYPE_WRAPPER = 2,
TYPE_FUN = 3,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::TYPE }
/// Criteria type, can be one of: COUNT, EPS or COUNT + EPS
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum TermCriteria_Type {
/// the maximum number of iterations or elements to compute
COUNT = 1,
// ditto
// Duplicate, use COUNT instead
// MAX_ITER = 1,
/// the desired accuracy or change in parameters at which the iterative algorithm stops
EPS = 2,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::TermCriteria_Type }
/// An Image Format describes the way that the images in Textures store their data.
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum Texture2D_Format {
NONE = 0,
/// Depth
DEPTH_COMPONENT = 6402,
/// Red, Green, Blue
RGB = 6407,
/// Red, Green, Blue, Alpha
RGBA = 6408,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::Texture2D_Format }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum UMatData_MemoryFlag {
COPY_ON_MAP = 1,
HOST_COPY_OBSOLETE = 2,
DEVICE_COPY_OBSOLETE = 4,
TEMP_UMAT = 8,
TEMP_COPIED_UMAT = 24,
USER_ALLOCATED = 32,
DEVICE_MEM_MAPPED = 64,
ASYNC_CLEANUP = 128,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::UMatData_MemoryFlag }
/// Usage flags for allocator
///
/// @warning All flags except `USAGE_DEFAULT` are experimental.
///
/// @warning For the OpenCL allocator, `USAGE_ALLOCATE_SHARED_MEMORY` depends on
/// OpenCV's optional, experimental integration with OpenCL SVM. To enable this
/// integration, build OpenCV using the `WITH_OPENCL_SVM=ON` CMake option and, at
/// runtime, call `cv::ocl::Context::getDefault().setUseSVM(true);` or similar
/// code. Note that SVM is incompatible with OpenCL 1.x.
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum UMatUsageFlags {
USAGE_DEFAULT = 0,
USAGE_ALLOCATE_HOST_MEMORY = 1,
USAGE_ALLOCATE_DEVICE_MEMORY = 2,
USAGE_ALLOCATE_SHARED_MEMORY = 4,
__UMAT_USAGE_FLAGS_32BIT = 2147483647,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::UMatUsageFlags }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum _InputArray_KindFlag {
KIND_SHIFT = 16,
FIXED_TYPE = -2147483648,
FIXED_SIZE = 1073741824,
KIND_MASK = 2031616,
NONE = 0,
MAT = 65536,
MATX = 131072,
STD_VECTOR = 196608,
STD_VECTOR_VECTOR = 262144,
STD_VECTOR_MAT = 327680,
/// removed: <https://github.com/opencv/opencv/pull/17046>
EXPR = 393216,
OPENGL_BUFFER = 458752,
CUDA_HOST_MEM = 524288,
CUDA_GPU_MAT = 589824,
UMAT = 655360,
STD_VECTOR_UMAT = 720896,
STD_BOOL_VECTOR = 786432,
STD_VECTOR_CUDA_GPU_MAT = 851968,
/// removed: <https://github.com/opencv/opencv/issues/18897>
STD_ARRAY = 917504,
STD_ARRAY_MAT = 983040,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::_InputArray_KindFlag }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum _OutputArray_DepthMask {
DEPTH_MASK_8U = 1,
DEPTH_MASK_8S = 2,
DEPTH_MASK_16U = 4,
DEPTH_MASK_16S = 8,
DEPTH_MASK_32S = 16,
DEPTH_MASK_32F = 32,
DEPTH_MASK_64F = 64,
DEPTH_MASK_16F = 128,
DEPTH_MASK_ALL = 127,
DEPTH_MASK_ALL_BUT_8S = 125,
DEPTH_MASK_ALL_16F = 255,
DEPTH_MASK_FLT = 96,
}
opencv_type_enum! { core::_OutputArray_DepthMask }
pub type va_display = *mut c_void;
pub type va_surface_id = u32;
pub type Affine3d = core::Affine3<f64>;
pub type Affine3f = core::Affine3<f32>;
pub type Hamming_result_type = i32;
pub type Hamming_value_type = u8;
pub type HammingLUT = core::Hamming;
pub type InputArray<'a> = &'a core::_InputArray;
pub type InputArrayOfArrays<'a> = core::InputArray<'a>;
pub type InputOutputArray<'a> = &'a core::_InputOutputArray;
pub type InputOutputArrayOfArrays<'a> = core::InputOutputArray<'a>;
pub type Mat1b = core::Mat_<u8>;
pub type Mat1d = core::Mat_<f64>;
pub type Mat1f = core::Mat_<f32>;
pub type Mat1i = core::Mat_<i32>;
pub type Mat1s = core::Mat_<i16>;
pub type Mat1w = core::Mat_<u16>;
pub type Mat2b = core::Mat_<core::Vec2b>;
pub type Mat2d = core::Mat_<core::Vec2d>;
pub type Mat2f = core::Mat_<core::Vec2f>;
pub type Mat2i = core::Mat_<core::Vec2i>;
pub type Mat2s = core::Mat_<core::Vec2s>;
pub type Mat2w = core::Mat_<core::Vec2w>;
pub type Mat3b = core::Mat_<core::Vec3b>;
pub type Mat3d = core::Mat_<core::Vec3d>;
pub type Mat3f = core::Mat_<core::Vec3f>;
pub type Mat3i = core::Mat_<core::Vec3i>;
pub type Mat3s = core::Mat_<core::Vec3s>;
pub type Mat3w = core::Mat_<core::Vec3w>;
pub type Mat4b = core::Mat_<core::Vec4b>;
pub type Mat4d = core::Mat_<core::Vec4d>;
pub type Mat4f = core::Mat_<core::Vec4f>;
pub type Mat4i = core::Mat_<core::Vec4i>;
pub type Mat4s = core::Mat_<core::Vec4s>;
pub type Mat4w = core::Mat_<core::Vec4w>;
pub type MatConstIterator_difference_type = ptrdiff_t;
pub type MatConstIterator_pointer<'a, 'b> = &'a mut &'b u8;
pub type MatConstIterator_reference<'a> = &'a mut u8;
pub type MatConstIterator_value_type<'a> = &'a mut u8;
pub type MatND = core::Mat;
pub type Matx12d = core::Matx12<f64>;
pub type Matx12f = core::Matx12<f32>;
pub type Matx13d = core::Matx13<f64>;
pub type Matx13f = core::Matx13<f32>;
pub type Matx14d = core::Matx14<f64>;
pub type Matx14f = core::Matx14<f32>;
pub type Matx16d = core::Matx16<f64>;
pub type Matx16f = core::Matx16<f32>;
pub type Matx21d = core::Matx21<f64>;
pub type Matx21f = core::Matx21<f32>;
pub type Matx22d = core::Matx22<f64>;
pub type Matx22f = core::Matx22<f32>;
pub type Matx23d = core::Matx23<f64>;
pub type Matx23f = core::Matx23<f32>;
pub type Matx31d = core::Matx31<f64>;
pub type Matx31f = core::Matx31<f32>;
pub type Matx32d = core::Matx32<f64>;
pub type Matx32f = core::Matx32<f32>;
pub type Matx33d = core::Matx33<f64>;
pub type Matx33f = core::Matx33<f32>;
pub type Matx34d = core::Matx34<f64>;
pub type Matx34f = core::Matx34<f32>;
pub type Matx41d = core::Matx41<f64>;
pub type Matx41f = core::Matx41<f32>;
pub type Matx43d = core::Matx43<f64>;
pub type Matx43f = core::Matx43<f32>;
pub type Matx44d = core::Matx44<f64>;
pub type Matx44f = core::Matx44<f32>;
pub type Matx61d = core::Matx61<f64>;
pub type Matx61f = core::Matx61<f32>;
pub type Matx66d = core::Matx66<f64>;
pub type Matx66f = core::Matx66<f32>;
pub type OutputArray<'a> = &'a core::_OutputArray;
pub type OutputArrayOfArrays<'a> = core::OutputArray<'a>;
pub type Point = core::Point2i;
pub type Point2d = core::Point_<f64>;
pub type Point2f = core::Point_<f32>;
pub type Point2i = core::Point_<i32>;
pub type Point2l = core::Point_<i64>;
pub type Point3d = core::Point3_<f64>;
pub type Point3f = core::Point3_<f32>;
pub type Point3i = core::Point3_<i32>;
pub type Rect = core::Rect2i;
pub type Rect2d = core::Rect_<f64>;
pub type Rect2f = core::Rect_<f32>;
pub type Rect2i = core::Rect_<i32>;
pub type Scalar = core::Scalar_<f64>;
pub type Size = core::Size2i;
pub type Size2d = core::Size_<f64>;
pub type Size2f = core::Size_<f32>;
pub type Size2i = core::Size_<i32>;
pub type Size2l = core::Size_<i64>;
pub type SparseMat_const_iterator = core::SparseMatConstIterator;
pub type SparseMat_iterator = core::SparseMatIterator;
/// @name Shorter aliases for the most popular specializations of Vec<T,n>
pub type Vec2b = core::VecN<u8, 2>;
pub type Vec2d = core::VecN<f64, 2>;
pub type Vec2f = core::VecN<f32, 2>;
pub type Vec2i = core::VecN<i32, 2>;
pub type Vec2s = core::VecN<i16, 2>;
pub type Vec2w = core::VecN<u16, 2>;
pub type Vec3b = core::VecN<u8, 3>;
pub type Vec3d = core::VecN<f64, 3>;
pub type Vec3f = core::VecN<f32, 3>;
pub type Vec3i = core::VecN<i32, 3>;
pub type Vec3s = core::VecN<i16, 3>;
pub type Vec3w = core::VecN<u16, 3>;
pub type Vec4b = core::VecN<u8, 4>;
pub type Vec4d = core::VecN<f64, 4>;
pub type Vec4f = core::VecN<f32, 4>;
pub type Vec4i = core::VecN<i32, 4>;
pub type Vec4s = core::VecN<i16, 4>;
pub type Vec4w = core::VecN<u16, 4>;
pub type Vec6d = core::VecN<f64, 6>;
pub type Vec6f = core::VecN<f32, 6>;
pub type Vec6i = core::VecN<i32, 6>;
pub type Vec8i = core::VecN<i32, 8>;
pub type GpuMatND_IndexArray = core::Vector<i32>;
pub type GpuMatND_SizeArray = core::Vector<i32>;
pub type GpuMatND_StepArray = core::Vector<size_t>;
pub type Stream_StreamCallback = Option<Box<dyn FnMut(i32) -> () + Send + Sync + 'static>>;
pub type ProgramSource_hash_t = u64;
/// proxy for hal::Cholesky
#[inline]
pub fn cholesky(a: &mut f64, astep: size_t, m: i32, b: &mut f64, bstep: size_t, n: i32) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Cholesky_doubleX_size_t_int_doubleX_size_t_int(a, astep, m, b, bstep, n, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// proxy for hal::Cholesky
#[inline]
pub fn cholesky_f32(a: &mut f32, astep: size_t, m: i32, b: &mut f32, bstep: size_t, n: i32) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Cholesky_floatX_size_t_int_floatX_size_t_int(a, astep, m, b, bstep, n, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Performs a look-up table transform of an array.
///
/// The function LUT fills the output array with values from the look-up table. Indices of the entries
/// are taken from the input array. That is, the function processes each element of src as follows:
/// 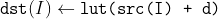
/// where
/// 
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array of 8-bit elements.
/// * lut: look-up table of 256 elements; in case of multi-channel input array, the table should
/// either have a single channel (in this case the same table is used for all channels) or the same
/// number of channels as in the input array.
/// * dst: output array of the same size and number of channels as src, and the same depth as lut.
/// ## See also
/// convertScaleAbs, Mat::convertTo
#[inline]
pub fn lut(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, lut: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(lut);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_LUT_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), lut.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// proxy for hal::LU
#[inline]
pub fn lu(a: &mut f64, astep: size_t, m: i32, b: &mut f64, bstep: size_t, n: i32) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_LU_doubleX_size_t_int_doubleX_size_t_int(a, astep, m, b, bstep, n, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// proxy for hal::LU
#[inline]
pub fn lu_f32(a: &mut f32, astep: size_t, m: i32, b: &mut f32, bstep: size_t, n: i32) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_LU_floatX_size_t_int_floatX_size_t_int(a, astep, m, b, bstep, n, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates the Mahalanobis distance between two vectors.
///
/// The function cv::Mahalanobis calculates and returns the weighted distance between two vectors:
/// 
/// The covariance matrix may be calculated using the #calcCovarMatrix function and then inverted using
/// the invert function (preferably using the #DECOMP_SVD method, as the most accurate).
/// ## Parameters
/// * v1: first 1D input vector.
/// * v2: second 1D input vector.
/// * icovar: inverse covariance matrix.
#[inline]
pub fn mahalanobis(v1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, v2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, icovar: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<f64> {
extern_container_arg!(v1);
extern_container_arg!(v2);
extern_container_arg!(icovar);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mahalanobis_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(v1.as_raw__InputArray(), v2.as_raw__InputArray(), icovar.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// wrap PCA::backProject
#[inline]
pub fn pca_back_project(data: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mean: &dyn core::ToInputArray, eigenvectors: &dyn core::ToInputArray, result: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(data);
extern_container_arg!(mean);
extern_container_arg!(eigenvectors);
extern_container_arg!(result);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_PCABackProject_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(data.as_raw__InputArray(), mean.as_raw__InputArray(), eigenvectors.as_raw__InputArray(), result.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// wrap PCA::operator() and add eigenvalues output parameter
#[inline]
pub fn pca_compute2_variance(data: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mean: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, eigenvectors: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, eigenvalues: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, retained_variance: f64) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(data);
extern_container_arg!(mean);
extern_container_arg!(eigenvectors);
extern_container_arg!(eigenvalues);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_PCACompute_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double(data.as_raw__InputArray(), mean.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), eigenvectors.as_raw__OutputArray(), eigenvalues.as_raw__OutputArray(), retained_variance, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// wrap PCA::operator() and add eigenvalues output parameter
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * max_components: 0
#[inline]
pub fn pca_compute2(data: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mean: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, eigenvectors: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, eigenvalues: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, max_components: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(data);
extern_container_arg!(mean);
extern_container_arg!(eigenvectors);
extern_container_arg!(eigenvalues);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_PCACompute_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(data.as_raw__InputArray(), mean.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), eigenvectors.as_raw__OutputArray(), eigenvalues.as_raw__OutputArray(), max_components, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// wrap PCA::operator()
#[inline]
pub fn pca_compute_variance(data: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mean: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, eigenvectors: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, retained_variance: f64) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(data);
extern_container_arg!(mean);
extern_container_arg!(eigenvectors);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_PCACompute_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double(data.as_raw__InputArray(), mean.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), eigenvectors.as_raw__OutputArray(), retained_variance, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// wrap PCA::operator()
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * max_components: 0
#[inline]
pub fn pca_compute(data: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mean: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, eigenvectors: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, max_components: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(data);
extern_container_arg!(mean);
extern_container_arg!(eigenvectors);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_PCACompute_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(data.as_raw__InputArray(), mean.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), eigenvectors.as_raw__OutputArray(), max_components, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// wrap PCA::project
#[inline]
pub fn pca_project(data: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mean: &dyn core::ToInputArray, eigenvectors: &dyn core::ToInputArray, result: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(data);
extern_container_arg!(mean);
extern_container_arg!(eigenvectors);
extern_container_arg!(result);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_PCAProject_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(data.as_raw__InputArray(), mean.as_raw__InputArray(), eigenvectors.as_raw__InputArray(), result.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes the Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) image quality metric.
///
/// This function calculates the Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) image quality metric in decibels (dB),
/// between two input arrays src1 and src2. The arrays must have the same type.
///
/// The PSNR is calculated as follows:
///
/// 
///
/// where R is the maximum integer value of depth (e.g. 255 in the case of CV_8U data)
/// and MSE is the mean squared error between the two arrays.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src1: first input array.
/// * src2: second input array of the same size as src1.
/// * R: the maximum pixel value (255 by default)
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * r: 255.
#[inline]
pub fn psnr(src1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, r: f64) -> Result<f64> {
extern_container_arg!(src1);
extern_container_arg!(src2);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_PSNR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_double(src1.as_raw__InputArray(), src2.as_raw__InputArray(), r, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// wrap SVD::backSubst
#[inline]
pub fn sv_back_subst(w: &dyn core::ToInputArray, u: &dyn core::ToInputArray, vt: &dyn core::ToInputArray, rhs: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(w);
extern_container_arg!(u);
extern_container_arg!(vt);
extern_container_arg!(rhs);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SVBackSubst_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(w.as_raw__InputArray(), u.as_raw__InputArray(), vt.as_raw__InputArray(), rhs.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// wrap SVD::compute
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: 0
#[inline]
pub fn sv_decomp(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, w: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, u: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, vt: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(w);
extern_container_arg!(u);
extern_container_arg!(vt);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SVDecomp_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), w.as_raw__OutputArray(), u.as_raw__OutputArray(), vt.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates an absolute value of each matrix element.
///
/// abs is a meta-function that is expanded to one of absdiff or convertScaleAbs forms:
/// - C = abs(A-B) is equivalent to `absdiff(A, B, C)`
/// - C = abs(A) is equivalent to `absdiff(A, Scalar::all(0), C)`
/// - C = `Mat_<Vec<uchar,n> >(abs(A*alpha + beta))` is equivalent to `convertScaleAbs(A, C, alpha,
/// beta)`
///
/// The output matrix has the same size and the same type as the input one except for the last case,
/// where C is depth=CV_8U .
/// ## Parameters
/// * m: matrix.
/// ## See also
/// [MatrixExpressions], absdiff, convertScaleAbs
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * e: matrix expression.
#[inline]
pub fn abs_matexpr(e: &core::MatExpr) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_abs_const_MatExprR(e.as_raw_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates an absolute value of each matrix element.
///
/// abs is a meta-function that is expanded to one of absdiff or convertScaleAbs forms:
/// - C = abs(A-B) is equivalent to `absdiff(A, B, C)`
/// - C = abs(A) is equivalent to `absdiff(A, Scalar::all(0), C)`
/// - C = `Mat_<Vec<uchar,n> >(abs(A*alpha + beta))` is equivalent to `convertScaleAbs(A, C, alpha,
/// beta)`
///
/// The output matrix has the same size and the same type as the input one except for the last case,
/// where C is depth=CV_8U .
/// ## Parameters
/// * m: matrix.
/// ## See also
/// [MatrixExpressions], absdiff, convertScaleAbs
#[inline]
pub fn abs(m: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_abs_const_MatR(m.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates the per-element absolute difference between two arrays or between an array and a scalar.
///
/// The function cv::absdiff calculates:
/// * Absolute difference between two arrays when they have the same
/// size and type:
/// 
/// * Absolute difference between an array and a scalar when the second
/// array is constructed from Scalar or has as many elements as the
/// number of channels in `src1`:
/// 
/// * Absolute difference between a scalar and an array when the first
/// array is constructed from Scalar or has as many elements as the
/// number of channels in `src2`:
/// 
/// where I is a multi-dimensional index of array elements. In case of
/// multi-channel arrays, each channel is processed independently.
///
/// Note: Saturation is not applied when the arrays have the depth CV_32S.
/// You may even get a negative value in the case of overflow.
/// ## Parameters
/// * src1: first input array or a scalar.
/// * src2: second input array or a scalar.
/// * dst: output array that has the same size and type as input arrays.
/// ## See also
/// cv::abs(const Mat&)
#[inline]
pub fn absdiff(src1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src1);
extern_container_arg!(src2);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_absdiff_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src1.as_raw__InputArray(), src2.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates the weighted sum of two arrays.
///
/// The function addWeighted calculates the weighted sum of two arrays as follows:
/// 
/// where I is a multi-dimensional index of array elements. In case of multi-channel arrays, each
/// channel is processed independently.
/// The function can be replaced with a matrix expression:
/// ```C++
/// dst = src1*alpha + src2*beta + gamma;
/// ```
///
///
/// Note: Saturation is not applied when the output array has the depth CV_32S. You may even get
/// result of an incorrect sign in the case of overflow.
/// ## Parameters
/// * src1: first input array.
/// * alpha: weight of the first array elements.
/// * src2: second input array of the same size and channel number as src1.
/// * beta: weight of the second array elements.
/// * gamma: scalar added to each sum.
/// * dst: output array that has the same size and number of channels as the input arrays.
/// * dtype: optional depth of the output array; when both input arrays have the same depth, dtype
/// can be set to -1, which will be equivalent to src1.depth().
/// ## See also
/// add, subtract, scaleAdd, Mat::convertTo
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * dtype: -1
#[inline]
pub fn add_weighted(src1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, alpha: f64, src2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, beta: f64, gamma: f64, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, dtype: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src1);
extern_container_arg!(src2);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_addWeighted_const__InputArrayR_double_const__InputArrayR_double_double_const__OutputArrayR_int(src1.as_raw__InputArray(), alpha, src2.as_raw__InputArray(), beta, gamma, dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), dtype, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates the per-element sum of two arrays or an array and a scalar.
///
/// The function add calculates:
/// - Sum of two arrays when both input arrays have the same size and the same number of channels:
/// 
/// - Sum of an array and a scalar when src2 is constructed from Scalar or has the same number of
/// elements as `src1.channels()`:
/// 
/// - Sum of a scalar and an array when src1 is constructed from Scalar or has the same number of
/// elements as `src2.channels()`:
/// 
/// where `I` is a multi-dimensional index of array elements. In case of multi-channel arrays, each
/// channel is processed independently.
///
/// The first function in the list above can be replaced with matrix expressions:
/// ```C++
/// dst = src1 + src2;
/// dst += src1; // equivalent to add(dst, src1, dst);
/// ```
///
/// The input arrays and the output array can all have the same or different depths. For example, you
/// can add a 16-bit unsigned array to a 8-bit signed array and store the sum as a 32-bit
/// floating-point array. Depth of the output array is determined by the dtype parameter. In the second
/// and third cases above, as well as in the first case, when src1.depth() == src2.depth(), dtype can
/// be set to the default -1. In this case, the output array will have the same depth as the input
/// array, be it src1, src2 or both.
///
/// Note: Saturation is not applied when the output array has the depth CV_32S. You may even get
/// result of an incorrect sign in the case of overflow.
/// ## Parameters
/// * src1: first input array or a scalar.
/// * src2: second input array or a scalar.
/// * dst: output array that has the same size and number of channels as the input array(s); the
/// depth is defined by dtype or src1/src2.
/// * mask: optional operation mask - 8-bit single channel array, that specifies elements of the
/// output array to be changed.
/// * dtype: optional depth of the output array (see the discussion below).
/// ## See also
/// subtract, addWeighted, scaleAdd, Mat::convertTo
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * mask: noArray()
/// * dtype: -1
#[inline]
pub fn add(src1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dtype: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src1);
extern_container_arg!(src2);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_add_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int(src1.as_raw__InputArray(), src2.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), dtype, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// naive nearest neighbor finder
///
/// see <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nearest_neighbor_search>
/// @todo document
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * norm_type: NORM_L2
/// * k: 0
/// * mask: noArray()
/// * update: 0
/// * crosscheck: false
#[inline]
pub fn batch_distance(src1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dist: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, dtype: i32, nidx: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, norm_type: i32, k: i32, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray, update: i32, crosscheck: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src1);
extern_container_arg!(src2);
extern_container_arg!(dist);
extern_container_arg!(nidx);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_batchDistance_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_const__OutputArrayR_int_int_const__InputArrayR_int_bool(src1.as_raw__InputArray(), src2.as_raw__InputArray(), dist.as_raw__OutputArray(), dtype, nidx.as_raw__OutputArray(), norm_type, k, mask.as_raw__InputArray(), update, crosscheck, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// computes bitwise conjunction of the two arrays (dst = src1 & src2)
/// Calculates the per-element bit-wise conjunction of two arrays or an
/// array and a scalar.
///
/// The function cv::bitwise_and calculates the per-element bit-wise logical conjunction for:
/// * Two arrays when src1 and src2 have the same size:
/// 
/// * An array and a scalar when src2 is constructed from Scalar or has
/// the same number of elements as `src1.channels()`:
/// 
/// * A scalar and an array when src1 is constructed from Scalar or has
/// the same number of elements as `src2.channels()`:
/// 
/// In case of floating-point arrays, their machine-specific bit
/// representations (usually IEEE754-compliant) are used for the operation.
/// In case of multi-channel arrays, each channel is processed
/// independently. In the second and third cases above, the scalar is first
/// converted to the array type.
/// ## Parameters
/// * src1: first input array or a scalar.
/// * src2: second input array or a scalar.
/// * dst: output array that has the same size and type as the input
/// arrays.
/// * mask: optional operation mask, 8-bit single channel array, that
/// specifies elements of the output array to be changed.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn bitwise_and(src1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src1);
extern_container_arg!(src2);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_bitwise_and_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(src1.as_raw__InputArray(), src2.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Inverts every bit of an array.
///
/// The function cv::bitwise_not calculates per-element bit-wise inversion of the input
/// array:
/// 
/// In case of a floating-point input array, its machine-specific bit
/// representation (usually IEEE754-compliant) is used for the operation. In
/// case of multi-channel arrays, each channel is processed independently.
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array.
/// * dst: output array that has the same size and type as the input
/// array.
/// * mask: optional operation mask, 8-bit single channel array, that
/// specifies elements of the output array to be changed.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn bitwise_not(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_bitwise_not_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates the per-element bit-wise disjunction of two arrays or an
/// array and a scalar.
///
/// The function cv::bitwise_or calculates the per-element bit-wise logical disjunction for:
/// * Two arrays when src1 and src2 have the same size:
/// 
/// * An array and a scalar when src2 is constructed from Scalar or has
/// the same number of elements as `src1.channels()`:
/// 
/// * A scalar and an array when src1 is constructed from Scalar or has
/// the same number of elements as `src2.channels()`:
/// 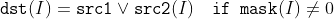
/// In case of floating-point arrays, their machine-specific bit
/// representations (usually IEEE754-compliant) are used for the operation.
/// In case of multi-channel arrays, each channel is processed
/// independently. In the second and third cases above, the scalar is first
/// converted to the array type.
/// ## Parameters
/// * src1: first input array or a scalar.
/// * src2: second input array or a scalar.
/// * dst: output array that has the same size and type as the input
/// arrays.
/// * mask: optional operation mask, 8-bit single channel array, that
/// specifies elements of the output array to be changed.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn bitwise_or(src1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src1);
extern_container_arg!(src2);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_bitwise_or_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(src1.as_raw__InputArray(), src2.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates the per-element bit-wise "exclusive or" operation on two
/// arrays or an array and a scalar.
///
/// The function cv::bitwise_xor calculates the per-element bit-wise logical "exclusive-or"
/// operation for:
/// * Two arrays when src1 and src2 have the same size:
/// 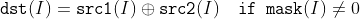
/// * An array and a scalar when src2 is constructed from Scalar or has
/// the same number of elements as `src1.channels()`:
/// 
/// * A scalar and an array when src1 is constructed from Scalar or has
/// the same number of elements as `src2.channels()`:
/// 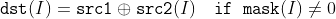
/// In case of floating-point arrays, their machine-specific bit
/// representations (usually IEEE754-compliant) are used for the operation.
/// In case of multi-channel arrays, each channel is processed
/// independently. In the 2nd and 3rd cases above, the scalar is first
/// converted to the array type.
/// ## Parameters
/// * src1: first input array or a scalar.
/// * src2: second input array or a scalar.
/// * dst: output array that has the same size and type as the input
/// arrays.
/// * mask: optional operation mask, 8-bit single channel array, that
/// specifies elements of the output array to be changed.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn bitwise_xor(src1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src1);
extern_container_arg!(src2);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_bitwise_xor_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(src1.as_raw__InputArray(), src2.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes the source location of an extrapolated pixel.
///
/// The function computes and returns the coordinate of a donor pixel corresponding to the specified
/// extrapolated pixel when using the specified extrapolation border mode. For example, if you use
/// cv::BORDER_WRAP mode in the horizontal direction, cv::BORDER_REFLECT_101 in the vertical direction and
/// want to compute value of the "virtual" pixel Point(-5, 100) in a floating-point image img , it
/// looks like:
/// ```C++
/// float val = img.at<float>(borderInterpolate(100, img.rows, cv::BORDER_REFLECT_101),
/// borderInterpolate(-5, img.cols, cv::BORDER_WRAP));
/// ```
///
/// Normally, the function is not called directly. It is used inside filtering functions and also in
/// copyMakeBorder.
/// ## Parameters
/// * p: 0-based coordinate of the extrapolated pixel along one of the axes, likely \<0 or \>= len
/// * len: Length of the array along the corresponding axis.
/// * borderType: Border type, one of the #BorderTypes, except for #BORDER_TRANSPARENT and
/// #BORDER_ISOLATED . When borderType==#BORDER_CONSTANT , the function always returns -1, regardless
/// of p and len.
/// ## See also
/// copyMakeBorder
#[inline]
pub fn border_interpolate(p: i32, len: i32, border_type: i32) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_borderInterpolate_int_int_int(p, len, border_type, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates the covariance matrix of a set of vectors.
///
/// The function cv::calcCovarMatrix calculates the covariance matrix and, optionally, the mean vector of
/// the set of input vectors.
/// ## Parameters
/// * samples: samples stored as separate matrices
/// * nsamples: number of samples
/// * covar: output covariance matrix of the type ctype and square size.
/// * mean: input or output (depending on the flags) array as the average value of the input vectors.
/// * flags: operation flags as a combination of #CovarFlags
/// * ctype: type of the matrixl; it equals 'CV_64F' by default.
/// ## See also
/// PCA, mulTransposed, Mahalanobis
/// @todo InputArrayOfArrays
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
///
/// Note: use #COVAR_ROWS or #COVAR_COLS flag
/// * samples: samples stored as rows/columns of a single matrix.
/// * covar: output covariance matrix of the type ctype and square size.
/// * mean: input or output (depending on the flags) array as the average value of the input vectors.
/// * flags: operation flags as a combination of #CovarFlags
/// * ctype: type of the matrixl; it equals 'CV_64F' by default.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * ctype: CV_64F
#[inline]
pub fn calc_covar_matrix(samples: &dyn core::ToInputArray, covar: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, mean: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, flags: i32, ctype: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(samples);
extern_container_arg!(covar);
extern_container_arg!(mean);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_calcCovarMatrix_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_int_int(samples.as_raw__InputArray(), covar.as_raw__OutputArray(), mean.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), flags, ctype, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates the magnitude and angle of 2D vectors.
///
/// The function cv::cartToPolar calculates either the magnitude, angle, or both
/// for every 2D vector (x(I),y(I)):
/// 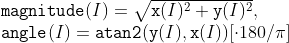
///
/// The angles are calculated with accuracy about 0.3 degrees. For the point
/// (0,0), the angle is set to 0.
/// ## Parameters
/// * x: array of x-coordinates; this must be a single-precision or
/// double-precision floating-point array.
/// * y: array of y-coordinates, that must have the same size and same type as x.
/// * magnitude: output array of magnitudes of the same size and type as x.
/// * angle: output array of angles that has the same size and type as
/// x; the angles are measured in radians (from 0 to 2\*Pi) or in degrees (0 to 360 degrees).
/// * angleInDegrees: a flag, indicating whether the angles are measured
/// in radians (which is by default), or in degrees.
/// ## See also
/// Sobel, Scharr
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * angle_in_degrees: false
#[inline]
pub fn cart_to_polar(x: &dyn core::ToInputArray, y: &dyn core::ToInputArray, magnitude: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, angle: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, angle_in_degrees: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(x);
extern_container_arg!(y);
extern_container_arg!(magnitude);
extern_container_arg!(angle);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cartToPolar_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_bool(x.as_raw__InputArray(), y.as_raw__InputArray(), magnitude.as_raw__OutputArray(), angle.as_raw__OutputArray(), angle_in_degrees, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns true if the specified feature is supported by the host hardware.
///
/// The function returns true if the host hardware supports the specified feature. When user calls
/// setUseOptimized(false), the subsequent calls to checkHardwareSupport() will return false until
/// setUseOptimized(true) is called. This way user can dynamically switch on and off the optimized code
/// in OpenCV.
/// ## Parameters
/// * feature: The feature of interest, one of cv::CpuFeatures
#[inline]
pub fn check_hardware_support(feature: i32) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_checkHardwareSupport_int(feature, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Checks every element of an input array for invalid values.
///
/// The function cv::checkRange checks that every array element is neither NaN nor infinite. When minVal \>
/// -DBL_MAX and maxVal \< DBL_MAX, the function also checks that each value is between minVal and
/// maxVal. In case of multi-channel arrays, each channel is processed independently. If some values
/// are out of range, position of the first outlier is stored in pos (when pos != NULL). Then, the
/// function either returns false (when quiet=true) or throws an exception.
/// ## Parameters
/// * a: input array.
/// * quiet: a flag, indicating whether the functions quietly return false when the array elements
/// are out of range or they throw an exception.
/// * pos: optional output parameter, when not NULL, must be a pointer to array of src.dims
/// elements.
/// * minVal: inclusive lower boundary of valid values range.
/// * maxVal: exclusive upper boundary of valid values range.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * quiet: true
/// * pos: 0
/// * min_val: -DBL_MAX
/// * max_val: DBL_MAX
#[inline]
pub fn check_range(a: &dyn core::ToInputArray, quiet: bool, pos: &mut core::Point, min_val: f64, max_val: f64) -> Result<bool> {
extern_container_arg!(a);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_checkRange_const__InputArrayR_bool_PointX_double_double(a.as_raw__InputArray(), quiet, pos, min_val, max_val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Performs the per-element comparison of two arrays or an array and scalar value.
///
/// The function compares:
/// * Elements of two arrays when src1 and src2 have the same size:
/// 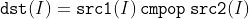
/// * Elements of src1 with a scalar src2 when src2 is constructed from
/// Scalar or has a single element:
/// 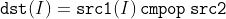
/// * src1 with elements of src2 when src1 is constructed from Scalar or
/// has a single element:
/// 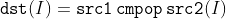
/// When the comparison result is true, the corresponding element of output
/// array is set to 255. The comparison operations can be replaced with the
/// equivalent matrix expressions:
/// ```C++
/// Mat dst1 = src1 >= src2;
/// Mat dst2 = src1 < 8;
/// ...
/// ```
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src1: first input array or a scalar; when it is an array, it must have a single channel.
/// * src2: second input array or a scalar; when it is an array, it must have a single channel.
/// * dst: output array of type ref CV_8U that has the same size and the same number of channels as
/// the input arrays.
/// * cmpop: a flag, that specifies correspondence between the arrays (cv::CmpTypes)
/// ## See also
/// checkRange, min, max, threshold
#[inline]
pub fn compare(src1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, cmpop: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src1);
extern_container_arg!(src2);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_compare_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(src1.as_raw__InputArray(), src2.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), cmpop, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Copies the lower or the upper half of a square matrix to its another half.
///
/// The function cv::completeSymm copies the lower or the upper half of a square matrix to
/// its another half. The matrix diagonal remains unchanged:
/// -  for  if
/// lowerToUpper=false
/// -  for  if
/// lowerToUpper=true
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * m: input-output floating-point square matrix.
/// * lowerToUpper: operation flag; if true, the lower half is copied to
/// the upper half. Otherwise, the upper half is copied to the lower half.
/// ## See also
/// flip, transpose
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * lower_to_upper: false
#[inline]
pub fn complete_symm(m: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, lower_to_upper: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(m);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_completeSymm_const__InputOutputArrayR_bool(m.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), lower_to_upper, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Converts an array to half precision floating number.
///
/// This function converts FP32 (single precision floating point) from/to FP16 (half precision floating point). CV_16S format is used to represent FP16 data.
/// There are two use modes (src -> dst): CV_32F -> CV_16S and CV_16S -> CV_32F. The input array has to have type of CV_32F or
/// CV_16S to represent the bit depth. If the input array is neither of them, the function will raise an error.
/// The format of half precision floating point is defined in IEEE 754-2008.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array.
/// * dst: output array.
#[inline]
pub fn convert_fp16(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_convertFp16_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Scales, calculates absolute values, and converts the result to 8-bit.
///
/// On each element of the input array, the function convertScaleAbs
/// performs three operations sequentially: scaling, taking an absolute
/// value, conversion to an unsigned 8-bit type:
/// 
/// In case of multi-channel arrays, the function processes each channel
/// independently. When the output is not 8-bit, the operation can be
/// emulated by calling the Mat::convertTo method (or by using matrix
/// expressions) and then by calculating an absolute value of the result.
/// For example:
/// ```C++
/// Mat_<float> A(30,30);
/// randu(A, Scalar(-100), Scalar(100));
/// Mat_<float> B = A*5 + 3;
/// B = abs(B);
/// // Mat_<float> B = abs(A*5+3) will also do the job,
/// // but it will allocate a temporary matrix
/// ```
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array.
/// * dst: output array.
/// * alpha: optional scale factor.
/// * beta: optional delta added to the scaled values.
/// ## See also
/// Mat::convertTo, cv::abs(const Mat&)
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * alpha: 1
/// * beta: 0
#[inline]
pub fn convert_scale_abs(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, alpha: f64, beta: f64) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_convertScaleAbs_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_double(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), alpha, beta, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Forms a border around an image.
///
/// The function copies the source image into the middle of the destination image. The areas to the
/// left, to the right, above and below the copied source image will be filled with extrapolated
/// pixels. This is not what filtering functions based on it do (they extrapolate pixels on-fly), but
/// what other more complex functions, including your own, may do to simplify image boundary handling.
///
/// The function supports the mode when src is already in the middle of dst . In this case, the
/// function does not copy src itself but simply constructs the border, for example:
///
/// ```C++
/// // let border be the same in all directions
/// int border=2;
/// // constructs a larger image to fit both the image and the border
/// Mat gray_buf(rgb.rows + border*2, rgb.cols + border*2, rgb.depth());
/// // select the middle part of it w/o copying data
/// Mat gray(gray_canvas, Rect(border, border, rgb.cols, rgb.rows));
/// // convert image from RGB to grayscale
/// cvtColor(rgb, gray, COLOR_RGB2GRAY);
/// // form a border in-place
/// copyMakeBorder(gray, gray_buf, border, border,
/// border, border, BORDER_REPLICATE);
/// // now do some custom filtering ...
/// ...
/// ```
///
///
/// Note: When the source image is a part (ROI) of a bigger image, the function will try to use the
/// pixels outside of the ROI to form a border. To disable this feature and always do extrapolation, as
/// if src was not a ROI, use borderType | #BORDER_ISOLATED.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Source image.
/// * dst: Destination image of the same type as src and the size Size(src.cols+left+right,
/// src.rows+top+bottom) .
/// * top: the top pixels
/// * bottom: the bottom pixels
/// * left: the left pixels
/// * right: Parameter specifying how many pixels in each direction from the source image rectangle
/// to extrapolate. For example, top=1, bottom=1, left=1, right=1 mean that 1 pixel-wide border needs
/// to be built.
/// * borderType: Border type. See borderInterpolate for details.
/// * value: Border value if borderType==BORDER_CONSTANT .
/// ## See also
/// borderInterpolate
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * value: Scalar()
#[inline]
pub fn copy_make_border(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, top: i32, bottom: i32, left: i32, right: i32, border_type: i32, value: core::Scalar) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_copyMakeBorder_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_int_int_int_int_const_ScalarR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), top, bottom, left, right, border_type, &value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience (python)
/// Copies the matrix to another one.
/// When the operation mask is specified, if the Mat::create call shown above reallocates the matrix, the newly allocated matrix is initialized with all zeros before copying the data.
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: source matrix.
/// * dst: Destination matrix. If it does not have a proper size or type before the operation, it is
/// reallocated.
/// * mask: Operation mask of the same size as \*this. Its non-zero elements indicate which matrix
/// elements need to be copied. The mask has to be of type CV_8U and can have 1 or multiple channels.
#[inline]
pub fn copy_to(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_copyTo_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Counts non-zero array elements.
///
/// The function returns the number of non-zero elements in src :
/// 
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: single-channel array.
/// ## See also
/// mean, meanStdDev, norm, minMaxLoc, calcCovarMatrix
#[inline]
pub fn count_non_zero(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<i32> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_countNonZero_const__InputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes the cube root of an argument.
///
/// The function cubeRoot computes . Negative arguments are handled correctly.
/// NaN and Inf are not handled. The accuracy approaches the maximum possible accuracy for
/// single-precision data.
/// ## Parameters
/// * val: A function argument.
#[inline]
pub fn cube_root(val: f32) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cubeRoot_float(val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates a continuous matrix.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * rows: Row count.
/// * cols: Column count.
/// * type: Type of the matrix.
/// * arr: Destination matrix. This parameter changes only if it has a proper type and area (
///  ).
///
/// Matrix is called continuous if its elements are stored continuously, that is, without gaps at the
/// end of each row.
#[inline]
pub fn create_continuous(rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32, arr: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(arr);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_createContinuous_int_int_int_const__OutputArrayR(rows, cols, typ, arr.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// checks whether current device supports the given feature
#[inline]
pub fn device_supports(feature_set: core::FeatureSet) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_deviceSupports_FeatureSet(feature_set, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Ensures that the size of a matrix is big enough and the matrix has a proper type.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * rows: Minimum desired number of rows.
/// * cols: Minimum desired number of columns.
/// * type: Desired matrix type.
/// * arr: Destination matrix.
///
/// The function does not reallocate memory if the matrix has proper attributes already.
#[inline]
pub fn ensure_size_is_enough(rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32, arr: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(arr);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_ensureSizeIsEnough_int_int_int_const__OutputArrayR(rows, cols, typ, arr.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the number of installed CUDA-enabled devices.
///
/// Use this function before any other CUDA functions calls. If OpenCV is compiled without CUDA support,
/// this function returns 0. If the CUDA driver is not installed, or is incompatible, this function
/// returns -1.
#[inline]
pub fn get_cuda_enabled_device_count() -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_getCudaEnabledDeviceCount(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the current device index set by cuda::setDevice or initialized by default.
#[inline]
pub fn get_device() -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_getDevice(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn print_cuda_device_info(device: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_printCudaDeviceInfo_int(device, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn print_short_cuda_device_info(device: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_printShortCudaDeviceInfo_int(device, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Page-locks the memory of matrix and maps it for the device(s).
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * m: Input matrix.
#[inline]
pub fn register_page_locked(m: &mut core::Mat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_registerPageLocked_MatR(m.as_raw_mut_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Explicitly destroys and cleans up all resources associated with the current device in the current
/// process.
///
/// Any subsequent API call to this device will reinitialize the device.
#[inline]
pub fn reset_device() -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_resetDevice(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn set_buffer_pool_config(device_id: i32, stack_size: size_t, stack_count: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_setBufferPoolConfig_int_size_t_int(device_id, stack_size, stack_count, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// BufferPool management (must be called before Stream creation)
#[inline]
pub fn set_buffer_pool_usage(on: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_setBufferPoolUsage_bool(on, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets a device and initializes it for the current thread.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * device: System index of a CUDA device starting with 0.
///
/// If the call of this function is omitted, a default device is initialized at the fist CUDA usage.
#[inline]
pub fn set_device(device: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_setDevice_int(device, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets a CUDA device and initializes it for the current thread with OpenGL interoperability.
///
/// This function should be explicitly called after OpenGL context creation and before any CUDA calls.
/// ## Parameters
/// * device: System index of a CUDA device starting with 0.
/// @ingroup core_opengl
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * device: 0
#[inline]
pub fn set_gl_device(device: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_setGlDevice_int(device, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Unmaps the memory of matrix and makes it pageable again.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * m: Input matrix.
#[inline]
pub fn unregister_page_locked(m: &mut core::Mat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_unregisterPageLocked_MatR(m.as_raw_mut_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Performs a forward or inverse discrete Cosine transform of 1D or 2D array.
///
/// The function cv::dct performs a forward or inverse discrete Cosine transform (DCT) of a 1D or 2D
/// floating-point array:
/// * Forward Cosine transform of a 1D vector of N elements:
/// 
/// where
/// 
/// and
/// ,  for *j \> 0*.
/// * Inverse Cosine transform of a 1D vector of N elements:
/// 
/// (since 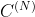 is an orthogonal matrix,  )
/// * Forward 2D Cosine transform of M x N matrix:
/// 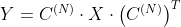
/// * Inverse 2D Cosine transform of M x N matrix:
/// 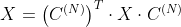
///
/// The function chooses the mode of operation by looking at the flags and size of the input array:
/// * If (flags & #DCT_INVERSE) == 0 , the function does a forward 1D or 2D transform. Otherwise, it
/// is an inverse 1D or 2D transform.
/// * If (flags & #DCT_ROWS) != 0 , the function performs a 1D transform of each row.
/// * If the array is a single column or a single row, the function performs a 1D transform.
/// * If none of the above is true, the function performs a 2D transform.
///
///
/// Note: Currently dct supports even-size arrays (2, 4, 6 ...). For data analysis and approximation, you
/// can pad the array when necessary.
/// Also, the function performance depends very much, and not monotonically, on the array size (see
/// getOptimalDFTSize ). In the current implementation DCT of a vector of size N is calculated via DFT
/// of a vector of size N/2 . Thus, the optimal DCT size N1 \>= N can be calculated as:
/// ```C++
/// size_t getOptimalDCTSize(size_t N) { return 2*getOptimalDFTSize((N+1)/2); }
/// N1 = getOptimalDCTSize(N);
/// ```
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input floating-point array.
/// * dst: output array of the same size and type as src .
/// * flags: transformation flags as a combination of cv::DftFlags (DCT_*)
/// ## See also
/// dft , getOptimalDFTSize , idct
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: 0
#[inline]
pub fn dct(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_dct_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns string of cv::Mat depth value: CV_8U -> "CV_8U" or "<invalid depth>"
#[inline]
pub fn depth_to_string(depth: i32) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_depthToString_int(depth, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn check_failed_mat_channels_1(v: i32, ctx: &core::Detail_CheckContext) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_detail_check_failed_MatChannels_const_int_const_CheckContextR(v, ctx.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn check_failed_mat_channels(v1: i32, v2: i32, ctx: &core::Detail_CheckContext) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_detail_check_failed_MatChannels_const_int_const_int_const_CheckContextR(v1, v2, ctx.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn check_failed_mat_depth_1(v: i32, ctx: &core::Detail_CheckContext) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_detail_check_failed_MatDepth_const_int_const_CheckContextR(v, ctx.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn check_failed_mat_depth(v1: i32, v2: i32, ctx: &core::Detail_CheckContext) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_detail_check_failed_MatDepth_const_int_const_int_const_CheckContextR(v1, v2, ctx.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn check_failed_mat_type_1(v: i32, ctx: &core::Detail_CheckContext) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_detail_check_failed_MatType_const_int_const_CheckContextR(v, ctx.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn check_failed_mat_type(v1: i32, v2: i32, ctx: &core::Detail_CheckContext) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_detail_check_failed_MatType_const_int_const_int_const_CheckContextR(v1, v2, ctx.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn check_failed_auto_10(v: core::Size_<i32>, ctx: &core::Detail_CheckContext) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_detail_check_failed_auto_const_Size_LintG_const_CheckContextR(v.opencv_as_extern(), ctx.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn check_failed_auto_5(v1: core::Size_<i32>, v2: core::Size_<i32>, ctx: &core::Detail_CheckContext) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_detail_check_failed_auto_const_Size_LintG_const_Size_LintG_const_CheckContextR(v1.opencv_as_extern(), v2.opencv_as_extern(), ctx.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn check_failed_auto(v1: bool, v2: bool, ctx: &core::Detail_CheckContext) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_detail_check_failed_auto_const_bool_const_bool_const_CheckContextR(v1, v2, ctx.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn check_failed_auto_9(v: f64, ctx: &core::Detail_CheckContext) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_detail_check_failed_auto_const_double_const_CheckContextR(v, ctx.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn check_failed_auto_4(v1: f64, v2: f64, ctx: &core::Detail_CheckContext) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_detail_check_failed_auto_const_double_const_double_const_CheckContextR(v1, v2, ctx.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn check_failed_auto_8(v: f32, ctx: &core::Detail_CheckContext) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_detail_check_failed_auto_const_float_const_CheckContextR(v, ctx.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn check_failed_auto_3(v1: f32, v2: f32, ctx: &core::Detail_CheckContext) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_detail_check_failed_auto_const_float_const_float_const_CheckContextR(v1, v2, ctx.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn check_failed_auto_6(v: i32, ctx: &core::Detail_CheckContext) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_detail_check_failed_auto_const_int_const_CheckContextR(v, ctx.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn check_failed_auto_1(v1: i32, v2: i32, ctx: &core::Detail_CheckContext) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_detail_check_failed_auto_const_int_const_int_const_CheckContextR(v1, v2, ctx.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn check_failed_auto_7(v: size_t, ctx: &core::Detail_CheckContext) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_detail_check_failed_auto_const_size_t_const_CheckContextR(v, ctx.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn check_failed_auto_2(v1: size_t, v2: size_t, ctx: &core::Detail_CheckContext) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_detail_check_failed_auto_const_size_t_const_size_t_const_CheckContextR(v1, v2, ctx.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn check_failed_auto_11(v1: &str, ctx: &core::Detail_CheckContext) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(v1);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_detail_check_failed_auto_const_stringR_const_CheckContextR(v1.opencv_as_extern(), ctx.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn check_failed_false(v: bool, ctx: &core::Detail_CheckContext) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_detail_check_failed_false_const_bool_const_CheckContextR(v, ctx.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn check_failed_true(v: bool, ctx: &core::Detail_CheckContext) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_detail_check_failed_true_const_bool_const_CheckContextR(v, ctx.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the determinant of a square floating-point matrix.
///
/// The function cv::determinant calculates and returns the determinant of the
/// specified matrix. For small matrices ( mtx.cols=mtx.rows\<=3 ), the
/// direct method is used. For larger matrices, the function uses LU
/// factorization with partial pivoting.
///
/// For symmetric positively-determined matrices, it is also possible to use
/// eigen decomposition to calculate the determinant.
/// ## Parameters
/// * mtx: input matrix that must have CV_32FC1 or CV_64FC1 type and
/// square size.
/// ## See also
/// trace, invert, solve, eigen, [MatrixExpressions]
#[inline]
pub fn determinant(mtx: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<f64> {
extern_container_arg!(mtx);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_determinant_const__InputArrayR(mtx.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Performs a forward or inverse Discrete Fourier transform of a 1D or 2D floating-point array.
///
/// The function cv::dft performs one of the following:
/// * Forward the Fourier transform of a 1D vector of N elements:
/// 
/// where  and 
/// * Inverse the Fourier transform of a 1D vector of N elements:
/// 
/// where 
/// * Forward the 2D Fourier transform of a M x N matrix:
/// 
/// * Inverse the 2D Fourier transform of a M x N matrix:
/// 
///
/// In case of real (single-channel) data, the output spectrum of the forward Fourier transform or input
/// spectrum of the inverse Fourier transform can be represented in a packed format called *CCS*
/// (complex-conjugate-symmetrical). It was borrowed from IPL (Intel\* Image Processing Library). Here
/// is how 2D *CCS* spectrum looks:
/// 
///
/// In case of 1D transform of a real vector, the output looks like the first row of the matrix above.
///
/// So, the function chooses an operation mode depending on the flags and size of the input array:
/// * If #DFT_ROWS is set or the input array has a single row or single column, the function
/// performs a 1D forward or inverse transform of each row of a matrix when #DFT_ROWS is set.
/// Otherwise, it performs a 2D transform.
/// * If the input array is real and #DFT_INVERSE is not set, the function performs a forward 1D or
/// 2D transform:
/// * When #DFT_COMPLEX_OUTPUT is set, the output is a complex matrix of the same size as
/// input.
/// * When #DFT_COMPLEX_OUTPUT is not set, the output is a real matrix of the same size as
/// input. In case of 2D transform, it uses the packed format as shown above. In case of a
/// single 1D transform, it looks like the first row of the matrix above. In case of
/// multiple 1D transforms (when using the #DFT_ROWS flag), each row of the output matrix
/// looks like the first row of the matrix above.
/// * If the input array is complex and either #DFT_INVERSE or #DFT_REAL_OUTPUT are not set, the
/// output is a complex array of the same size as input. The function performs a forward or
/// inverse 1D or 2D transform of the whole input array or each row of the input array
/// independently, depending on the flags DFT_INVERSE and DFT_ROWS.
/// * When #DFT_INVERSE is set and the input array is real, or it is complex but #DFT_REAL_OUTPUT
/// is set, the output is a real array of the same size as input. The function performs a 1D or 2D
/// inverse transformation of the whole input array or each individual row, depending on the flags
/// #DFT_INVERSE and #DFT_ROWS.
///
/// If #DFT_SCALE is set, the scaling is done after the transformation.
///
/// Unlike dct , the function supports arrays of arbitrary size. But only those arrays are processed
/// efficiently, whose sizes can be factorized in a product of small prime numbers (2, 3, and 5 in the
/// current implementation). Such an efficient DFT size can be calculated using the getOptimalDFTSize
/// method.
///
/// The sample below illustrates how to calculate a DFT-based convolution of two 2D real arrays:
/// ```C++
/// void convolveDFT(InputArray A, InputArray B, OutputArray C)
/// {
/// // reallocate the output array if needed
/// C.create(abs(A.rows - B.rows)+1, abs(A.cols - B.cols)+1, A.type());
/// Size dftSize;
/// // calculate the size of DFT transform
/// dftSize.width = getOptimalDFTSize(A.cols + B.cols - 1);
/// dftSize.height = getOptimalDFTSize(A.rows + B.rows - 1);
///
/// // allocate temporary buffers and initialize them with 0's
/// Mat tempA(dftSize, A.type(), Scalar::all(0));
/// Mat tempB(dftSize, B.type(), Scalar::all(0));
///
/// // copy A and B to the top-left corners of tempA and tempB, respectively
/// Mat roiA(tempA, Rect(0,0,A.cols,A.rows));
/// A.copyTo(roiA);
/// Mat roiB(tempB, Rect(0,0,B.cols,B.rows));
/// B.copyTo(roiB);
///
/// // now transform the padded A & B in-place;
/// // use "nonzeroRows" hint for faster processing
/// dft(tempA, tempA, 0, A.rows);
/// dft(tempB, tempB, 0, B.rows);
///
/// // multiply the spectrums;
/// // the function handles packed spectrum representations well
/// mulSpectrums(tempA, tempB, tempA);
///
/// // transform the product back from the frequency domain.
/// // Even though all the result rows will be non-zero,
/// // you need only the first C.rows of them, and thus you
/// // pass nonzeroRows == C.rows
/// dft(tempA, tempA, DFT_INVERSE + DFT_SCALE, C.rows);
///
/// // now copy the result back to C.
/// tempA(Rect(0, 0, C.cols, C.rows)).copyTo(C);
///
/// // all the temporary buffers will be deallocated automatically
/// }
/// ```
///
/// To optimize this sample, consider the following approaches:
/// * Since nonzeroRows != 0 is passed to the forward transform calls and since A and B are copied to
/// the top-left corners of tempA and tempB, respectively, it is not necessary to clear the whole
/// tempA and tempB. It is only necessary to clear the tempA.cols - A.cols ( tempB.cols - B.cols)
/// rightmost columns of the matrices.
/// * This DFT-based convolution does not have to be applied to the whole big arrays, especially if B
/// is significantly smaller than A or vice versa. Instead, you can calculate convolution by parts.
/// To do this, you need to split the output array C into multiple tiles. For each tile, estimate
/// which parts of A and B are required to calculate convolution in this tile. If the tiles in C are
/// too small, the speed will decrease a lot because of repeated work. In the ultimate case, when
/// each tile in C is a single pixel, the algorithm becomes equivalent to the naive convolution
/// algorithm. If the tiles are too big, the temporary arrays tempA and tempB become too big and
/// there is also a slowdown because of bad cache locality. So, there is an optimal tile size
/// somewhere in the middle.
/// * If different tiles in C can be calculated in parallel and, thus, the convolution is done by
/// parts, the loop can be threaded.
///
/// All of the above improvements have been implemented in #matchTemplate and #filter2D . Therefore, by
/// using them, you can get the performance even better than with the above theoretically optimal
/// implementation. Though, those two functions actually calculate cross-correlation, not convolution,
/// so you need to "flip" the second convolution operand B vertically and horizontally using flip .
///
/// Note:
/// * An example using the discrete fourier transform can be found at
/// opencv_source_code/samples/cpp/dft.cpp
/// * (Python) An example using the dft functionality to perform Wiener deconvolution can be found
/// at opencv_source/samples/python/deconvolution.py
/// * (Python) An example rearranging the quadrants of a Fourier image can be found at
/// opencv_source/samples/python/dft.py
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array that could be real or complex.
/// * dst: output array whose size and type depends on the flags .
/// * flags: transformation flags, representing a combination of the #DftFlags
/// * nonzeroRows: when the parameter is not zero, the function assumes that only the first
/// nonzeroRows rows of the input array (#DFT_INVERSE is not set) or only the first nonzeroRows of the
/// output array (#DFT_INVERSE is set) contain non-zeros, thus, the function can handle the rest of the
/// rows more efficiently and save some time; this technique is very useful for calculating array
/// cross-correlation or convolution using DFT.
/// ## See also
/// dct , getOptimalDFTSize , mulSpectrums, filter2D , matchTemplate , flip , cartToPolar ,
/// magnitude , phase
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: 0
/// * nonzero_rows: 0
#[inline]
pub fn dft(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32, nonzero_rows: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_dft_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, nonzero_rows, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Get OpenCV type from DirectX type
/// ## Parameters
/// * iD3DFORMAT: - enum D3DTYPE for D3D9
/// ## Returns
/// OpenCV type or -1 if there is no equivalent
#[inline]
pub fn get_type_from_d3d_format(i_d3_dformat: i32) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_directx_getTypeFromD3DFORMAT_const_int(i_d3_dformat, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Get OpenCV type from DirectX type
/// ## Parameters
/// * iDXGI_FORMAT: - enum DXGI_FORMAT for D3D10/D3D11
/// ## Returns
/// OpenCV type or -1 if there is no equivalent
#[inline]
pub fn get_type_from_dxgi_format(i_dxgi_format: i32) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_directx_getTypeFromDXGI_FORMAT_const_int(i_dxgi_format, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Performs per-element division of two arrays or a scalar by an array.
///
/// The function cv::divide divides one array by another:
/// 
/// or a scalar by an array when there is no src1 :
/// 
///
/// Different channels of multi-channel arrays are processed independently.
///
/// For integer types when src2(I) is zero, dst(I) will also be zero.
///
///
/// Note: In case of floating point data there is no special defined behavior for zero src2(I) values.
/// Regular floating-point division is used.
/// Expect correct IEEE-754 behaviour for floating-point data (with NaN, Inf result values).
///
///
/// Note: Saturation is not applied when the output array has the depth CV_32S. You may even get
/// result of an incorrect sign in the case of overflow.
/// ## Parameters
/// * src1: first input array.
/// * src2: second input array of the same size and type as src1.
/// * scale: scalar factor.
/// * dst: output array of the same size and type as src2.
/// * dtype: optional depth of the output array; if -1, dst will have depth src2.depth(), but in
/// case of an array-by-array division, you can only pass -1 when src1.depth()==src2.depth().
/// ## See also
/// multiply, add, subtract
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * scale: 1
/// * dtype: -1
#[inline]
pub fn divide2(src1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, scale: f64, dtype: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src1);
extern_container_arg!(src2);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_divide_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_int(src1.as_raw__InputArray(), src2.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), scale, dtype, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Performs per-element division of two arrays or a scalar by an array.
///
/// The function cv::divide divides one array by another:
/// 
/// or a scalar by an array when there is no src1 :
/// 
///
/// Different channels of multi-channel arrays are processed independently.
///
/// For integer types when src2(I) is zero, dst(I) will also be zero.
///
///
/// Note: In case of floating point data there is no special defined behavior for zero src2(I) values.
/// Regular floating-point division is used.
/// Expect correct IEEE-754 behaviour for floating-point data (with NaN, Inf result values).
///
///
/// Note: Saturation is not applied when the output array has the depth CV_32S. You may even get
/// result of an incorrect sign in the case of overflow.
/// ## Parameters
/// * src1: first input array.
/// * src2: second input array of the same size and type as src1.
/// * scale: scalar factor.
/// * dst: output array of the same size and type as src2.
/// * dtype: optional depth of the output array; if -1, dst will have depth src2.depth(), but in
/// case of an array-by-array division, you can only pass -1 when src1.depth()==src2.depth().
/// ## See also
/// multiply, add, subtract
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * dtype: -1
#[inline]
pub fn divide(scale: f64, src2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, dtype: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src2);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_divide_double_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(scale, src2.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), dtype, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a non-symmetric matrix (real eigenvalues only).
///
///
/// Note: Assumes real eigenvalues.
///
/// The function calculates eigenvalues and eigenvectors (optional) of the square matrix src:
/// ```C++
/// src*eigenvectors.row(i).t() = eigenvalues.at<srcType>(i)*eigenvectors.row(i).t()
/// ```
///
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input matrix (CV_32FC1 or CV_64FC1 type).
/// * eigenvalues: output vector of eigenvalues (type is the same type as src).
/// * eigenvectors: output matrix of eigenvectors (type is the same type as src). The eigenvectors are stored as subsequent matrix rows, in the same order as the corresponding eigenvalues.
/// ## See also
/// eigen
#[inline]
pub fn eigen_non_symmetric(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, eigenvalues: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, eigenvectors: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(eigenvalues);
extern_container_arg!(eigenvectors);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_eigenNonSymmetric_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), eigenvalues.as_raw__OutputArray(), eigenvectors.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a symmetric matrix.
///
/// The function cv::eigen calculates just eigenvalues, or eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the symmetric
/// matrix src:
/// ```C++
/// src*eigenvectors.row(i).t() = eigenvalues.at<srcType>(i)*eigenvectors.row(i).t()
/// ```
///
///
///
/// Note: Use cv::eigenNonSymmetric for calculation of real eigenvalues and eigenvectors of non-symmetric matrix.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input matrix that must have CV_32FC1 or CV_64FC1 type, square size and be symmetrical
/// (src ^T^ == src).
/// * eigenvalues: output vector of eigenvalues of the same type as src; the eigenvalues are stored
/// in the descending order.
/// * eigenvectors: output matrix of eigenvectors; it has the same size and type as src; the
/// eigenvectors are stored as subsequent matrix rows, in the same order as the corresponding
/// eigenvalues.
/// ## See also
/// eigenNonSymmetric, completeSymm , PCA
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * eigenvectors: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn eigen(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, eigenvalues: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, eigenvectors: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<bool> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(eigenvalues);
extern_container_arg!(eigenvectors);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_eigen_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), eigenvalues.as_raw__OutputArray(), eigenvectors.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ! Signals an error and raises the exception.
///
/// By default the function prints information about the error to stderr,
/// then it either stops if cv::setBreakOnError() had been called before or raises the exception.
/// It is possible to alternate error processing by using #redirectError().
/// ## Parameters
/// * exc: the exception raisen.
///
/// **Deprecated**: drop this version
#[deprecated = "drop this version"]
#[inline]
pub fn error_1(exc: &core::Exception) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_error_const_ExceptionR(exc.as_raw_Exception(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ! Signals an error and raises the exception.
///
/// By default the function prints information about the error to stderr,
/// then it either stops if setBreakOnError() had been called before or raises the exception.
/// It is possible to alternate error processing by using redirectError().
/// ## Parameters
/// * _code: - error code (Error::Code)
/// * _err: - error description
/// * _func: - function name. Available only when the compiler supports getting it
/// * _file: - source file name where the error has occurred
/// * _line: - line number in the source file where the error has occurred
/// ## See also
/// CV_Error, CV_Error_, CV_Assert, CV_DbgAssert
#[inline]
pub fn error(_code: i32, _err: &str, _func: &str, _file: &str, _line: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(_err);
extern_container_arg!(_func);
extern_container_arg!(_file);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_error_int_const_StringR_const_charX_const_charX_int(_code, _err.opencv_as_extern(), _func.opencv_as_extern(), _file.opencv_as_extern(), _line, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates the exponent of every array element.
///
/// The function cv::exp calculates the exponent of every element of the input
/// array:
/// 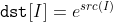
///
/// The maximum relative error is about 7e-6 for single-precision input and
/// less than 1e-10 for double-precision input. Currently, the function
/// converts denormalized values to zeros on output. Special values (NaN,
/// Inf) are not handled.
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array.
/// * dst: output array of the same size and type as src.
/// ## See also
/// log , cartToPolar , polarToCart , phase , pow , sqrt , magnitude
#[inline]
pub fn exp(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_exp_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Extracts a single channel from src (coi is 0-based index)
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array
/// * dst: output array
/// * coi: index of channel to extract
/// ## See also
/// mixChannels, split
#[inline]
pub fn extract_channel(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, coi: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_extractChannel_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), coi, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates the angle of a 2D vector in degrees.
///
/// The function fastAtan2 calculates the full-range angle of an input 2D vector. The angle is measured
/// in degrees and varies from 0 to 360 degrees. The accuracy is about 0.3 degrees.
/// ## Parameters
/// * x: x-coordinate of the vector.
/// * y: y-coordinate of the vector.
#[inline]
pub fn fast_atan2(y: f32, x: f32) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fastAtan2_float_float(y, x, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the list of locations of non-zero pixels
///
/// Given a binary matrix (likely returned from an operation such
/// as threshold(), compare(), >, ==, etc, return all of
/// the non-zero indices as a cv::Mat or std::vector<cv::Point> (x,y)
/// For example:
/// ```C++
/// cv::Mat binaryImage; // input, binary image
/// cv::Mat locations; // output, locations of non-zero pixels
/// cv::findNonZero(binaryImage, locations);
///
/// // access pixel coordinates
/// Point pnt = locations.at<Point>(i);
/// ```
///
/// or
/// ```C++
/// cv::Mat binaryImage; // input, binary image
/// vector<Point> locations; // output, locations of non-zero pixels
/// cv::findNonZero(binaryImage, locations);
///
/// // access pixel coordinates
/// Point pnt = locations[i];
/// ```
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: single-channel array
/// * idx: the output array, type of cv::Mat or std::vector<Point>, corresponding to non-zero indices in the input
#[inline]
pub fn find_non_zero(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, idx: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(idx);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_findNonZero_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), idx.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Flips a n-dimensional at given axis
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array
/// * dst: output array that has the same shape of src
/// * axis: axis that performs a flip on. 0 <= axis < src.dims.
#[inline]
pub fn flip_nd(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, axis: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_flipND_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), axis, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Flips a 2D array around vertical, horizontal, or both axes.
///
/// The function cv::flip flips the array in one of three different ways (row
/// and column indices are 0-based):
/// 
/// The example scenarios of using the function are the following:
/// * Vertical flipping of the image (flipCode == 0) to switch between
/// top-left and bottom-left image origin. This is a typical operation
/// in video processing on Microsoft Windows\* OS.
/// * Horizontal flipping of the image with the subsequent horizontal
/// shift and absolute difference calculation to check for a
/// vertical-axis symmetry (flipCode \> 0).
/// * Simultaneous horizontal and vertical flipping of the image with
/// the subsequent shift and absolute difference calculation to check
/// for a central symmetry (flipCode \< 0).
/// * Reversing the order of point arrays (flipCode \> 0 or
/// flipCode == 0).
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array.
/// * dst: output array of the same size and type as src.
/// * flipCode: a flag to specify how to flip the array; 0 means
/// flipping around the x-axis and positive value (for example, 1) means
/// flipping around y-axis. Negative value (for example, -1) means flipping
/// around both axes.
/// ## See also
/// transpose , repeat , completeSymm
#[inline]
pub fn flip(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flip_code: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_flip_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), flip_code, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Performs generalized matrix multiplication.
///
/// The function cv::gemm performs generalized matrix multiplication similar to the
/// gemm functions in BLAS level 3. For example,
/// `gemm(src1, src2, alpha, src3, beta, dst, GEMM_1_T + GEMM_3_T)`
/// corresponds to
/// 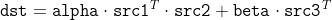
///
/// In case of complex (two-channel) data, performed a complex matrix
/// multiplication.
///
/// The function can be replaced with a matrix expression. For example, the
/// above call can be replaced with:
/// ```C++
/// dst = alpha*src1.t()*src2 + beta*src3.t();
/// ```
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src1: first multiplied input matrix that could be real(CV_32FC1,
/// CV_64FC1) or complex(CV_32FC2, CV_64FC2).
/// * src2: second multiplied input matrix of the same type as src1.
/// * alpha: weight of the matrix product.
/// * src3: third optional delta matrix added to the matrix product; it
/// should have the same type as src1 and src2.
/// * beta: weight of src3.
/// * dst: output matrix; it has the proper size and the same type as
/// input matrices.
/// * flags: operation flags (cv::GemmFlags)
/// ## See also
/// mulTransposed , transform
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: 0
#[inline]
pub fn gemm(src1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, alpha: f64, src3: &dyn core::ToInputArray, beta: f64, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src1);
extern_container_arg!(src2);
extern_container_arg!(src3);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_gemm_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_double_const__InputArrayR_double_const__OutputArrayR_int(src1.as_raw__InputArray(), src2.as_raw__InputArray(), alpha, src3.as_raw__InputArray(), beta, dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns full configuration time cmake output.
///
/// Returned value is raw cmake output including version control system revision, compiler version,
/// compiler flags, enabled modules and third party libraries, etc. Output format depends on target
/// architecture.
#[inline]
pub fn get_build_information() -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_getBuildInformation(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns list of CPU features enabled during compilation.
///
/// Returned value is a string containing space separated list of CPU features with following markers:
///
/// - no markers - baseline features
/// - prefix `*` - features enabled in dispatcher
/// - suffix `?` - features enabled but not available in HW
///
/// Example: `SSE SSE2 SSE3 *SSE4.1 *SSE4.2 *FP16 *AVX *AVX2 *AVX512-SKX?`
#[inline]
pub fn get_cpu_features_line() -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_getCPUFeaturesLine(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the number of CPU ticks.
///
/// The function returns the current number of CPU ticks on some architectures (such as x86, x64,
/// PowerPC). On other platforms the function is equivalent to getTickCount. It can also be used for
/// very accurate time measurements, as well as for RNG initialization. Note that in case of multi-CPU
/// systems a thread, from which getCPUTickCount is called, can be suspended and resumed at another CPU
/// with its own counter. So, theoretically (and practically) the subsequent calls to the function do
/// not necessary return the monotonously increasing values. Also, since a modern CPU varies the CPU
/// frequency depending on the load, the number of CPU clocks spent in some code cannot be directly
/// converted to time units. Therefore, getTickCount is generally a preferable solution for measuring
/// execution time.
#[inline]
pub fn get_cpu_tick_count() -> Result<i64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_getCPUTickCount(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn get_elem_size(typ: i32) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_getElemSize_int(typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns feature name by ID
///
/// Returns empty string if feature is not defined
#[inline]
pub fn get_hardware_feature_name(feature: i32) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_getHardwareFeatureName_int(feature, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn get_log_level_1() -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_getLogLevel(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the number of threads used by OpenCV for parallel regions.
///
/// Always returns 1 if OpenCV is built without threading support.
///
/// The exact meaning of return value depends on the threading framework used by OpenCV library:
/// - `TBB` - The number of threads, that OpenCV will try to use for parallel regions. If there is
/// any tbb::thread_scheduler_init in user code conflicting with OpenCV, then function returns
/// default number of threads used by TBB library.
/// - `OpenMP` - An upper bound on the number of threads that could be used to form a new team.
/// - `Concurrency` - The number of threads, that OpenCV will try to use for parallel regions.
/// - `GCD` - Unsupported; returns the GCD thread pool limit (512) for compatibility.
/// - `C=` - The number of threads, that OpenCV will try to use for parallel regions, if before
/// called setNumThreads with threads \> 0, otherwise returns the number of logical CPUs,
/// available for the process.
/// ## See also
/// setNumThreads, getThreadNum
#[inline]
pub fn get_num_threads() -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_getNumThreads(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the number of logical CPUs available for the process.
#[inline]
pub fn get_number_of_cpus() -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_getNumberOfCPUs(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the optimal DFT size for a given vector size.
///
/// DFT performance is not a monotonic function of a vector size. Therefore, when you calculate
/// convolution of two arrays or perform the spectral analysis of an array, it usually makes sense to
/// pad the input data with zeros to get a bit larger array that can be transformed much faster than the
/// original one. Arrays whose size is a power-of-two (2, 4, 8, 16, 32, ...) are the fastest to process.
/// Though, the arrays whose size is a product of 2's, 3's, and 5's (for example, 300 = 5\*5\*3\*2\*2)
/// are also processed quite efficiently.
///
/// The function cv::getOptimalDFTSize returns the minimum number N that is greater than or equal to vecsize
/// so that the DFT of a vector of size N can be processed efficiently. In the current implementation N
/// = 2 ^p^ \* 3 ^q^ \* 5 ^r^ for some integer p, q, r.
///
/// The function returns a negative number if vecsize is too large (very close to INT_MAX ).
///
/// While the function cannot be used directly to estimate the optimal vector size for DCT transform
/// (since the current DCT implementation supports only even-size vectors), it can be easily processed
/// as getOptimalDFTSize((vecsize+1)/2)\*2.
/// ## Parameters
/// * vecsize: vector size.
/// ## See also
/// dft , dct , idft , idct , mulSpectrums
#[inline]
pub fn get_optimal_dft_size(vecsize: i32) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_getOptimalDFTSize_int(vecsize, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the index of the currently executed thread within the current parallel region. Always
/// returns 0 if called outside of parallel region.
///
///
/// **Deprecated**: Current implementation doesn't corresponding to this documentation.
///
/// The exact meaning of the return value depends on the threading framework used by OpenCV library:
/// - `TBB` - Unsupported with current 4.1 TBB release. Maybe will be supported in future.
/// - `OpenMP` - The thread number, within the current team, of the calling thread.
/// - `Concurrency` - An ID for the virtual processor that the current context is executing on (0
/// for master thread and unique number for others, but not necessary 1,2,3,...).
/// - `GCD` - System calling thread's ID. Never returns 0 inside parallel region.
/// - `C=` - The index of the current parallel task.
/// ## See also
/// setNumThreads, getNumThreads
#[deprecated = "Current implementation doesn't corresponding to this documentation."]
#[inline]
pub fn get_thread_num() -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_getThreadNum(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the number of ticks.
///
/// The function returns the number of ticks after the certain event (for example, when the machine was
/// turned on). It can be used to initialize RNG or to measure a function execution time by reading the
/// tick count before and after the function call.
/// ## See also
/// getTickFrequency, TickMeter
#[inline]
pub fn get_tick_count() -> Result<i64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_getTickCount(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the number of ticks per second.
///
/// The function returns the number of ticks per second. That is, the following code computes the
/// execution time in seconds:
/// ```C++
/// double t = (double)getTickCount();
/// // do something ...
/// t = ((double)getTickCount() - t)/getTickFrequency();
/// ```
/// ## See also
/// getTickCount, TickMeter
#[inline]
pub fn get_tick_frequency() -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_getTickFrequency(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns major library version
#[inline]
pub fn get_version_major() -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_getVersionMajor() };
ret
}
/// Returns minor library version
#[inline]
pub fn get_version_minor() -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_getVersionMinor() };
ret
}
/// Returns revision field of the library version
#[inline]
pub fn get_version_revision() -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_getVersionRevision() };
ret
}
/// Returns library version string
///
/// For example "3.4.1-dev".
/// ## See also
/// getMajorVersion, getMinorVersion, getRevisionVersion
#[inline]
pub fn get_version_string() -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_getVersionString(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * recursive: false
#[inline]
pub fn glob(pattern: &str, result: &mut core::Vector<String>, recursive: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(mut pattern);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_glob_String_vectorLStringGR_bool(pattern.opencv_as_extern_mut(), result.as_raw_mut_VectorOfString(), recursive, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Check if use of OpenVX is possible
#[inline]
pub fn have_openvx() -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_haveOpenVX(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Applies horizontal concatenation to given matrices.
///
/// The function horizontally concatenates two or more cv::Mat matrices (with the same number of rows).
/// ```C++
/// cv::Mat matArray[] = { cv::Mat(4, 1, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(1)),
/// cv::Mat(4, 1, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(2)),
/// cv::Mat(4, 1, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(3)),};
///
/// cv::Mat out;
/// cv::hconcat( matArray, 3, out );
/// //out:
/// //[1, 2, 3;
/// // 1, 2, 3;
/// // 1, 2, 3;
/// // 1, 2, 3]
/// ```
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array or vector of matrices. all of the matrices must have the same number of rows and the same depth.
/// * nsrc: number of matrices in src.
/// * dst: output array. It has the same number of rows and depth as the src, and the sum of cols of the src.
/// ## See also
/// cv::vconcat(const Mat*, size_t, OutputArray), cv::vconcat(InputArrayOfArrays, OutputArray) and cv::vconcat(InputArray, InputArray, OutputArray)
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ```C++
/// cv::Mat_<float> A = (cv::Mat_<float>(3, 2) << 1, 4,
/// 2, 5,
/// 3, 6);
/// cv::Mat_<float> B = (cv::Mat_<float>(3, 2) << 7, 10,
/// 8, 11,
/// 9, 12);
///
/// cv::Mat C;
/// cv::hconcat(A, B, C);
/// //C:
/// //[1, 4, 7, 10;
/// // 2, 5, 8, 11;
/// // 3, 6, 9, 12]
/// ```
///
/// * src1: first input array to be considered for horizontal concatenation.
/// * src2: second input array to be considered for horizontal concatenation.
/// * dst: output array. It has the same number of rows and depth as the src1 and src2, and the sum of cols of the src1 and src2.
#[inline]
pub fn hconcat2(src1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src1);
extern_container_arg!(src2);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_hconcat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src1.as_raw__InputArray(), src2.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Applies horizontal concatenation to given matrices.
///
/// The function horizontally concatenates two or more cv::Mat matrices (with the same number of rows).
/// ```C++
/// cv::Mat matArray[] = { cv::Mat(4, 1, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(1)),
/// cv::Mat(4, 1, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(2)),
/// cv::Mat(4, 1, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(3)),};
///
/// cv::Mat out;
/// cv::hconcat( matArray, 3, out );
/// //out:
/// //[1, 2, 3;
/// // 1, 2, 3;
/// // 1, 2, 3;
/// // 1, 2, 3]
/// ```
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array or vector of matrices. all of the matrices must have the same number of rows and the same depth.
/// * nsrc: number of matrices in src.
/// * dst: output array. It has the same number of rows and depth as the src, and the sum of cols of the src.
/// ## See also
/// cv::vconcat(const Mat*, size_t, OutputArray), cv::vconcat(InputArrayOfArrays, OutputArray) and cv::vconcat(InputArray, InputArray, OutputArray)
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ```C++
/// std::vector<cv::Mat> matrices = { cv::Mat(4, 1, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(1)),
/// cv::Mat(4, 1, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(2)),
/// cv::Mat(4, 1, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(3)),};
///
/// cv::Mat out;
/// cv::hconcat( matrices, out );
/// //out:
/// //[1, 2, 3;
/// // 1, 2, 3;
/// // 1, 2, 3;
/// // 1, 2, 3]
/// ```
///
/// * src: input array or vector of matrices. all of the matrices must have the same number of rows and the same depth.
/// * dst: output array. It has the same number of rows and depth as the src, and the sum of cols of the src.
/// same depth.
#[inline]
pub fn hconcat(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_hconcat_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates the inverse Discrete Cosine Transform of a 1D or 2D array.
///
/// idct(src, dst, flags) is equivalent to dct(src, dst, flags | DCT_INVERSE).
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input floating-point single-channel array.
/// * dst: output array of the same size and type as src.
/// * flags: operation flags.
/// ## See also
/// dct, dft, idft, getOptimalDFTSize
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: 0
#[inline]
pub fn idct(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_idct_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates the inverse Discrete Fourier Transform of a 1D or 2D array.
///
/// idft(src, dst, flags) is equivalent to dft(src, dst, flags | #DFT_INVERSE) .
///
/// Note: None of dft and idft scales the result by default. So, you should pass #DFT_SCALE to one of
/// dft or idft explicitly to make these transforms mutually inverse.
/// ## See also
/// dft, dct, idct, mulSpectrums, getOptimalDFTSize
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input floating-point real or complex array.
/// * dst: output array whose size and type depend on the flags.
/// * flags: operation flags (see dft and #DftFlags).
/// * nonzeroRows: number of dst rows to process; the rest of the rows have undefined content (see
/// the convolution sample in dft description.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: 0
/// * nonzero_rows: 0
#[inline]
pub fn idft(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32, nonzero_rows: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_idft_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, nonzero_rows, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Checks if array elements lie between the elements of two other arrays.
///
/// The function checks the range as follows:
/// * For every element of a single-channel input array:
/// 
/// * For two-channel arrays:
/// 
/// * and so forth.
///
/// That is, dst (I) is set to 255 (all 1 -bits) if src (I) is within the
/// specified 1D, 2D, 3D, ... box and 0 otherwise.
///
/// When the lower and/or upper boundary parameters are scalars, the indexes
/// (I) at lowerb and upperb in the above formulas should be omitted.
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: first input array.
/// * lowerb: inclusive lower boundary array or a scalar.
/// * upperb: inclusive upper boundary array or a scalar.
/// * dst: output array of the same size as src and CV_8U type.
#[inline]
pub fn in_range(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, lowerb: &dyn core::ToInputArray, upperb: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(lowerb);
extern_container_arg!(upperb);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_inRange_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), lowerb.as_raw__InputArray(), upperb.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Inserts a single channel to dst (coi is 0-based index)
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array
/// * dst: output array
/// * coi: index of channel for insertion
/// ## See also
/// mixChannels, merge
#[inline]
pub fn insert_channel(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, coi: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_insertChannel_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), coi, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn get_flags() -> Result<core::FLAGS> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_instr_getFlags(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn reset_trace() -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_instr_resetTrace(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn set_flags(mode_flags: core::FLAGS) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_instr_setFlags_FLAGS(mode_flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn set_use_instrumentation(flag: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_instr_setUseInstrumentation_bool(flag, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn use_instrumentation() -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_instr_useInstrumentation(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds the inverse or pseudo-inverse of a matrix.
///
/// The function cv::invert inverts the matrix src and stores the result in dst
/// . When the matrix src is singular or non-square, the function calculates
/// the pseudo-inverse matrix (the dst matrix) so that norm(src\*dst - I) is
/// minimal, where I is an identity matrix.
///
/// In case of the #DECOMP_LU method, the function returns non-zero value if
/// the inverse has been successfully calculated and 0 if src is singular.
///
/// In case of the #DECOMP_SVD method, the function returns the inverse
/// condition number of src (the ratio of the smallest singular value to the
/// largest singular value) and 0 if src is singular. The SVD method
/// calculates a pseudo-inverse matrix if src is singular.
///
/// Similarly to #DECOMP_LU, the method #DECOMP_CHOLESKY works only with
/// non-singular square matrices that should also be symmetrical and
/// positively defined. In this case, the function stores the inverted
/// matrix in dst and returns non-zero. Otherwise, it returns 0.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input floating-point M x N matrix.
/// * dst: output matrix of N x M size and the same type as src.
/// * flags: inversion method (cv::DecompTypes)
/// ## See also
/// solve, SVD
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: DECOMP_LU
#[inline]
pub fn invert(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<f64> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_invert_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn get_ipp_error_location() -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ipp_getIppErrorLocation(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn get_ipp_features() -> Result<u64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ipp_getIppFeatures(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn get_ipp_status() -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ipp_getIppStatus(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn get_ipp_version() -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ipp_getIppVersion(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * funcname: NULL
/// * filename: NULL
/// * line: 0
#[inline]
pub fn set_ipp_status(status: i32, funcname: &str, filename: &str, line: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(funcname);
extern_container_arg!(filename);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ipp_setIppStatus_int_const_charX_const_charX_int(status, funcname.opencv_as_extern(), filename.opencv_as_extern(), line, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn set_use_ipp_not_exact(flag: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ipp_setUseIPP_NotExact_bool(flag, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn set_use_ipp(flag: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ipp_setUseIPP_bool(flag, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn use_ipp() -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ipp_useIPP(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn use_ipp_not_exact() -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ipp_useIPP_NotExact(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds centers of clusters and groups input samples around the clusters.
///
/// The function kmeans implements a k-means algorithm that finds the centers of cluster_count clusters
/// and groups the input samples around the clusters. As an output,  contains a
/// 0-based cluster index for the sample stored in the  row of the samples matrix.
///
///
/// Note:
/// * (Python) An example on K-means clustering can be found at
/// opencv_source_code/samples/python/kmeans.py
/// ## Parameters
/// * data: Data for clustering. An array of N-Dimensional points with float coordinates is needed.
/// Examples of this array can be:
/// * Mat points(count, 2, CV_32F);
/// * Mat points(count, 1, CV_32FC2);
/// * Mat points(1, count, CV_32FC2);
/// * std::vector\<cv::Point2f\> points(sampleCount);
/// * K: Number of clusters to split the set by.
/// * bestLabels: Input/output integer array that stores the cluster indices for every sample.
/// * criteria: The algorithm termination criteria, that is, the maximum number of iterations and/or
/// the desired accuracy. The accuracy is specified as criteria.epsilon. As soon as each of the cluster
/// centers moves by less than criteria.epsilon on some iteration, the algorithm stops.
/// * attempts: Flag to specify the number of times the algorithm is executed using different
/// initial labellings. The algorithm returns the labels that yield the best compactness (see the last
/// function parameter).
/// * flags: Flag that can take values of cv::KmeansFlags
/// * centers: Output matrix of the cluster centers, one row per each cluster center.
/// ## Returns
/// The function returns the compactness measure that is computed as
/// 
/// after every attempt. The best (minimum) value is chosen and the corresponding labels and the
/// compactness value are returned by the function. Basically, you can use only the core of the
/// function, set the number of attempts to 1, initialize labels each time using a custom algorithm,
/// pass them with the ( flags = #KMEANS_USE_INITIAL_LABELS ) flag, and then choose the best
/// (most-compact) clustering.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * centers: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn kmeans(data: &dyn core::ToInputArray, k: i32, best_labels: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, criteria: core::TermCriteria, attempts: i32, flags: i32, centers: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<f64> {
extern_container_arg!(data);
extern_container_arg!(best_labels);
extern_container_arg!(centers);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_kmeans_const__InputArrayR_int_const__InputOutputArrayR_TermCriteria_int_int_const__OutputArrayR(data.as_raw__InputArray(), k, best_labels.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), criteria.opencv_as_extern(), attempts, flags, centers.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates the natural logarithm of every array element.
///
/// The function cv::log calculates the natural logarithm of every element of the input array:
/// 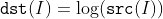
///
/// Output on zero, negative and special (NaN, Inf) values is undefined.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array.
/// * dst: output array of the same size and type as src .
/// ## See also
/// exp, cartToPolar, polarToCart, phase, pow, sqrt, magnitude
#[inline]
pub fn log(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_log_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates the magnitude of 2D vectors.
///
/// The function cv::magnitude calculates the magnitude of 2D vectors formed
/// from the corresponding elements of x and y arrays:
/// 
/// ## Parameters
/// * x: floating-point array of x-coordinates of the vectors.
/// * y: floating-point array of y-coordinates of the vectors; it must
/// have the same size as x.
/// * magnitude: output array of the same size and type as x.
/// ## See also
/// cartToPolar, polarToCart, phase, sqrt
#[inline]
pub fn magnitude(x: &dyn core::ToInputArray, y: &dyn core::ToInputArray, magnitude: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(x);
extern_container_arg!(y);
extern_container_arg!(magnitude);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_magnitude_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(x.as_raw__InputArray(), y.as_raw__InputArray(), magnitude.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn max_mat(a: &core::Mat, b: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_max_const_MatR_const_MatR(a.as_raw_Mat(), b.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates per-element maximum of two arrays or an array and a scalar.
///
/// The function cv::max calculates the per-element maximum of two arrays:
/// 
/// or array and a scalar:
/// 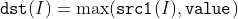
/// ## Parameters
/// * src1: first input array.
/// * src2: second input array of the same size and type as src1 .
/// * dst: output array of the same size and type as src1.
/// ## See also
/// min, compare, inRange, minMaxLoc, [MatrixExpressions]
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// needed to avoid conflicts with const _Tp& std::min(const _Tp&, const _Tp&, _Compare)
#[inline]
pub fn max_mat_to(src1: &core::Mat, src2: &core::Mat, dst: &mut core::Mat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_max_const_MatR_const_MatR_MatR(src1.as_raw_Mat(), src2.as_raw_Mat(), dst.as_raw_mut_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn max_mat_f64(a: &core::Mat, s: f64) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_max_const_MatR_double(a.as_raw_Mat(), s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates per-element maximum of two arrays or an array and a scalar.
///
/// The function cv::max calculates the per-element maximum of two arrays:
/// 
/// or array and a scalar:
/// 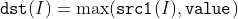
/// ## Parameters
/// * src1: first input array.
/// * src2: second input array of the same size and type as src1 .
/// * dst: output array of the same size and type as src1.
/// ## See also
/// min, compare, inRange, minMaxLoc, [MatrixExpressions]
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// needed to avoid conflicts with const _Tp& std::min(const _Tp&, const _Tp&, _Compare)
#[inline]
pub fn max_umat_to(src1: &core::UMat, src2: &core::UMat, dst: &mut core::UMat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_max_const_UMatR_const_UMatR_UMatR(src1.as_raw_UMat(), src2.as_raw_UMat(), dst.as_raw_mut_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates per-element maximum of two arrays or an array and a scalar.
///
/// The function cv::max calculates the per-element maximum of two arrays:
/// 
/// or array and a scalar:
/// 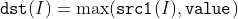
/// ## Parameters
/// * src1: first input array.
/// * src2: second input array of the same size and type as src1 .
/// * dst: output array of the same size and type as src1.
/// ## See also
/// min, compare, inRange, minMaxLoc, [MatrixExpressions]
#[inline]
pub fn max(src1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src1);
extern_container_arg!(src2);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_max_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src1.as_raw__InputArray(), src2.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn max_f64_mat(s: f64, a: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_max_double_const_MatR(s, a.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates a mean and standard deviation of array elements.
///
/// The function cv::meanStdDev calculates the mean and the standard deviation M
/// of array elements independently for each channel and returns it via the
/// output parameters:
/// 
/// When all the mask elements are 0's, the function returns
/// mean=stddev=Scalar::all(0).
///
/// Note: The calculated standard deviation is only the diagonal of the
/// complete normalized covariance matrix. If the full matrix is needed, you
/// can reshape the multi-channel array M x N to the single-channel array
/// M\*N x mtx.channels() (only possible when the matrix is continuous) and
/// then pass the matrix to calcCovarMatrix .
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array that should have from 1 to 4 channels so that the results can be stored in
/// Scalar_ 's.
/// * mean: output parameter: calculated mean value.
/// * stddev: output parameter: calculated standard deviation.
/// * mask: optional operation mask.
/// ## See also
/// countNonZero, mean, norm, minMaxLoc, calcCovarMatrix
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn mean_std_dev(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mean: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, stddev: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(mean);
extern_container_arg!(stddev);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_meanStdDev_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), mean.as_raw__OutputArray(), stddev.as_raw__OutputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates an average (mean) of array elements.
///
/// The function cv::mean calculates the mean value M of array elements,
/// independently for each channel, and return it:
/// 
/// When all the mask elements are 0's, the function returns Scalar::all(0)
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array that should have from 1 to 4 channels so that the result can be stored in
/// Scalar_ .
/// * mask: optional operation mask.
/// ## See also
/// countNonZero, meanStdDev, norm, minMaxLoc
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn mean(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<core::Scalar> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_mean_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates one multi-channel array out of several single-channel ones.
///
/// The function cv::merge merges several arrays to make a single multi-channel array. That is, each
/// element of the output array will be a concatenation of the elements of the input arrays, where
/// elements of i-th input array are treated as mv[i].channels()-element vectors.
///
/// The function cv::split does the reverse operation. If you need to shuffle channels in some other
/// advanced way, use cv::mixChannels.
///
/// The following example shows how to merge 3 single channel matrices into a single 3-channel matrix.
/// [example](https://github.com/opencv/opencv/blob/4.7.0/samples/cpp/tutorial_code/snippets/core_merge.cpp#L1)
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * mv: input array of matrices to be merged; all the matrices in mv must have the same
/// size and the same depth.
/// * count: number of input matrices when mv is a plain C array; it must be greater than zero.
/// * dst: output array of the same size and the same depth as mv[0]; The number of channels will
/// be equal to the parameter count.
/// ## See also
/// mixChannels, split, Mat::reshape
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * mv: input vector of matrices to be merged; all the matrices in mv must have the same
/// size and the same depth.
/// * dst: output array of the same size and the same depth as mv[0]; The number of channels will
/// be the total number of channels in the matrix array.
#[inline]
pub fn merge(mv: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(mv);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_merge_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(mv.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds the global minimum and maximum in an array
///
/// The function cv::minMaxIdx finds the minimum and maximum element values and their positions. The
/// extremums are searched across the whole array or, if mask is not an empty array, in the specified
/// array region. The function does not work with multi-channel arrays. If you need to find minimum or
/// maximum elements across all the channels, use Mat::reshape first to reinterpret the array as
/// single-channel. Or you may extract the particular channel using either extractImageCOI , or
/// mixChannels , or split . In case of a sparse matrix, the minimum is found among non-zero elements
/// only.
///
/// Note: When minIdx is not NULL, it must have at least 2 elements (as well as maxIdx), even if src is
/// a single-row or single-column matrix. In OpenCV (following MATLAB) each array has at least 2
/// dimensions, i.e. single-column matrix is Mx1 matrix (and therefore minIdx/maxIdx will be
/// (i1,0)/(i2,0)) and single-row matrix is 1xN matrix (and therefore minIdx/maxIdx will be
/// (0,j1)/(0,j2)).
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input single-channel array.
/// * minVal: pointer to the returned minimum value; NULL is used if not required.
/// * maxVal: pointer to the returned maximum value; NULL is used if not required.
/// * minIdx: pointer to the returned minimum location (in nD case); NULL is used if not required;
/// Otherwise, it must point to an array of src.dims elements, the coordinates of the minimum element
/// in each dimension are stored there sequentially.
/// * maxIdx: pointer to the returned maximum location (in nD case). NULL is used if not required.
/// * mask: specified array region
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * max_val: 0
/// * min_idx: 0
/// * max_idx: 0
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn min_max_idx(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, min_val: Option<&mut f64>, max_val: Option<&mut f64>, min_idx: Option<&mut i32>, max_idx: Option<&mut i32>, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_minMaxIdx_const__InputArrayR_doubleX_doubleX_intX_intX_const__InputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), min_val.map_or(::core::ptr::null_mut(), |min_val| min_val as *mut _), max_val.map_or(::core::ptr::null_mut(), |max_val| max_val as *mut _), min_idx.map_or(::core::ptr::null_mut(), |min_idx| min_idx as *mut _), max_idx.map_or(::core::ptr::null_mut(), |max_idx| max_idx as *mut _), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds the global minimum and maximum in an array.
///
/// The function cv::minMaxLoc finds the minimum and maximum element values and their positions. The
/// extremums are searched across the whole array or, if mask is not an empty array, in the specified
/// array region.
///
/// The function do not work with multi-channel arrays. If you need to find minimum or maximum
/// elements across all the channels, use Mat::reshape first to reinterpret the array as
/// single-channel. Or you may extract the particular channel using either extractImageCOI , or
/// mixChannels , or split .
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input single-channel array.
/// * minVal: pointer to the returned minimum value; NULL is used if not required.
/// * maxVal: pointer to the returned maximum value; NULL is used if not required.
/// * minLoc: pointer to the returned minimum location (in 2D case); NULL is used if not required.
/// * maxLoc: pointer to the returned maximum location (in 2D case); NULL is used if not required.
/// * mask: optional mask used to select a sub-array.
/// ## See also
/// max, min, reduceArgMin, reduceArgMax, compare, inRange, extractImageCOI, mixChannels, split, Mat::reshape
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * a: input single-channel array.
/// * minVal: pointer to the returned minimum value; NULL is used if not required.
/// * maxVal: pointer to the returned maximum value; NULL is used if not required.
/// * minIdx: pointer to the returned minimum location (in nD case); NULL is used if not required;
/// Otherwise, it must point to an array of src.dims elements, the coordinates of the minimum element
/// in each dimension are stored there sequentially.
/// * maxIdx: pointer to the returned maximum location (in nD case). NULL is used if not required.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * min_idx: 0
/// * max_idx: 0
#[inline]
pub fn min_max_loc_sparse(a: &core::SparseMat, min_val: Option<&mut f64>, max_val: Option<&mut f64>, min_idx: Option<&mut i32>, max_idx: Option<&mut i32>) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_minMaxLoc_const_SparseMatR_doubleX_doubleX_intX_intX(a.as_raw_SparseMat(), min_val.map_or(::core::ptr::null_mut(), |min_val| min_val as *mut _), max_val.map_or(::core::ptr::null_mut(), |max_val| max_val as *mut _), min_idx.map_or(::core::ptr::null_mut(), |min_idx| min_idx as *mut _), max_idx.map_or(::core::ptr::null_mut(), |max_idx| max_idx as *mut _), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds the global minimum and maximum in an array.
///
/// The function cv::minMaxLoc finds the minimum and maximum element values and their positions. The
/// extremums are searched across the whole array or, if mask is not an empty array, in the specified
/// array region.
///
/// The function do not work with multi-channel arrays. If you need to find minimum or maximum
/// elements across all the channels, use Mat::reshape first to reinterpret the array as
/// single-channel. Or you may extract the particular channel using either extractImageCOI , or
/// mixChannels , or split .
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input single-channel array.
/// * minVal: pointer to the returned minimum value; NULL is used if not required.
/// * maxVal: pointer to the returned maximum value; NULL is used if not required.
/// * minLoc: pointer to the returned minimum location (in 2D case); NULL is used if not required.
/// * maxLoc: pointer to the returned maximum location (in 2D case); NULL is used if not required.
/// * mask: optional mask used to select a sub-array.
/// ## See also
/// max, min, reduceArgMin, reduceArgMax, compare, inRange, extractImageCOI, mixChannels, split, Mat::reshape
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * max_val: 0
/// * min_loc: 0
/// * max_loc: 0
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn min_max_loc(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, min_val: Option<&mut f64>, max_val: Option<&mut f64>, min_loc: Option<&mut core::Point>, max_loc: Option<&mut core::Point>, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_minMaxLoc_const__InputArrayR_doubleX_doubleX_PointX_PointX_const__InputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), min_val.map_or(::core::ptr::null_mut(), |min_val| min_val as *mut _), max_val.map_or(::core::ptr::null_mut(), |max_val| max_val as *mut _), min_loc.map_or(::core::ptr::null_mut(), |min_loc| min_loc as *mut _), max_loc.map_or(::core::ptr::null_mut(), |max_loc| max_loc as *mut _), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn min_mat(a: &core::Mat, b: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_min_const_MatR_const_MatR(a.as_raw_Mat(), b.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates per-element minimum of two arrays or an array and a scalar.
///
/// The function cv::min calculates the per-element minimum of two arrays:
/// 
/// or array and a scalar:
/// 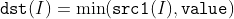
/// ## Parameters
/// * src1: first input array.
/// * src2: second input array of the same size and type as src1.
/// * dst: output array of the same size and type as src1.
/// ## See also
/// max, compare, inRange, minMaxLoc
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// needed to avoid conflicts with const _Tp& std::min(const _Tp&, const _Tp&, _Compare)
#[inline]
pub fn min_mat_to(src1: &core::Mat, src2: &core::Mat, dst: &mut core::Mat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_min_const_MatR_const_MatR_MatR(src1.as_raw_Mat(), src2.as_raw_Mat(), dst.as_raw_mut_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn min_mat_f64(a: &core::Mat, s: f64) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_min_const_MatR_double(a.as_raw_Mat(), s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates per-element minimum of two arrays or an array and a scalar.
///
/// The function cv::min calculates the per-element minimum of two arrays:
/// 
/// or array and a scalar:
/// 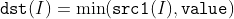
/// ## Parameters
/// * src1: first input array.
/// * src2: second input array of the same size and type as src1.
/// * dst: output array of the same size and type as src1.
/// ## See also
/// max, compare, inRange, minMaxLoc
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// needed to avoid conflicts with const _Tp& std::min(const _Tp&, const _Tp&, _Compare)
#[inline]
pub fn min_umat_to(src1: &core::UMat, src2: &core::UMat, dst: &mut core::UMat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_min_const_UMatR_const_UMatR_UMatR(src1.as_raw_UMat(), src2.as_raw_UMat(), dst.as_raw_mut_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates per-element minimum of two arrays or an array and a scalar.
///
/// The function cv::min calculates the per-element minimum of two arrays:
/// 
/// or array and a scalar:
/// 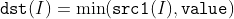
/// ## Parameters
/// * src1: first input array.
/// * src2: second input array of the same size and type as src1.
/// * dst: output array of the same size and type as src1.
/// ## See also
/// max, compare, inRange, minMaxLoc
#[inline]
pub fn min(src1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src1);
extern_container_arg!(src2);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_min_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src1.as_raw__InputArray(), src2.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn min_f64_mat(s: f64, a: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_min_double_const_MatR(s, a.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Copies specified channels from input arrays to the specified channels of
/// output arrays.
///
/// The function cv::mixChannels provides an advanced mechanism for shuffling image channels.
///
/// cv::split,cv::merge,cv::extractChannel,cv::insertChannel and some forms of cv::cvtColor are partial cases of cv::mixChannels.
///
/// In the example below, the code splits a 4-channel BGRA image into a 3-channel BGR (with B and R
/// channels swapped) and a separate alpha-channel image:
/// ```C++
/// Mat bgra( 100, 100, CV_8UC4, Scalar(255,0,0,255) );
/// Mat bgr( bgra.rows, bgra.cols, CV_8UC3 );
/// Mat alpha( bgra.rows, bgra.cols, CV_8UC1 );
///
/// // forming an array of matrices is a quite efficient operation,
/// // because the matrix data is not copied, only the headers
/// Mat out[] = { bgr, alpha };
/// // bgra[0] -> bgr[2], bgra[1] -> bgr[1],
/// // bgra[2] -> bgr[0], bgra[3] -> alpha[0]
/// int from_to[] = { 0,2, 1,1, 2,0, 3,3 };
/// mixChannels( &bgra, 1, out, 2, from_to, 4 );
/// ```
///
///
/// Note: Unlike many other new-style C++ functions in OpenCV (see the introduction section and
/// Mat::create ), cv::mixChannels requires the output arrays to be pre-allocated before calling the
/// function.
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array or vector of matrices; all of the matrices must have the same size and the
/// same depth.
/// * nsrcs: number of matrices in `src`.
/// * dst: output array or vector of matrices; all the matrices **must be allocated**; their size and
/// depth must be the same as in `src[0]`.
/// * ndsts: number of matrices in `dst`.
/// * fromTo: array of index pairs specifying which channels are copied and where; fromTo[k\*2] is
/// a 0-based index of the input channel in src, fromTo[k\*2+1] is an index of the output channel in
/// dst; the continuous channel numbering is used: the first input image channels are indexed from 0 to
/// src[0].channels()-1, the second input image channels are indexed from src[0].channels() to
/// src[0].channels() + src[1].channels()-1, and so on, the same scheme is used for the output image
/// channels; as a special case, when fromTo[k\*2] is negative, the corresponding output channel is
/// filled with zero .
/// * npairs: number of index pairs in `fromTo`.
/// ## See also
/// split, merge, extractChannel, insertChannel, cvtColor
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * src: input array or vector of matrices; all of the matrices must have the same size and the
/// same depth.
/// * dst: output array or vector of matrices; all the matrices **must be allocated**; their size and
/// depth must be the same as in src[0].
/// * fromTo: array of index pairs specifying which channels are copied and where; fromTo[k\*2] is
/// a 0-based index of the input channel in src, fromTo[k\*2+1] is an index of the output channel in
/// dst; the continuous channel numbering is used: the first input image channels are indexed from 0 to
/// src[0].channels()-1, the second input image channels are indexed from src[0].channels() to
/// src[0].channels() + src[1].channels()-1, and so on, the same scheme is used for the output image
/// channels; as a special case, when fromTo[k\*2] is negative, the corresponding output channel is
/// filled with zero .
/// * npairs: number of index pairs in fromTo.
#[inline]
pub fn mix_channels(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, from_to: &[i32]) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_mixChannels_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const_intX_size_t(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), from_to.as_ptr(), (from_to.len() / 2) as _, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Copies specified channels from input arrays to the specified channels of
/// output arrays.
///
/// The function cv::mixChannels provides an advanced mechanism for shuffling image channels.
///
/// cv::split,cv::merge,cv::extractChannel,cv::insertChannel and some forms of cv::cvtColor are partial cases of cv::mixChannels.
///
/// In the example below, the code splits a 4-channel BGRA image into a 3-channel BGR (with B and R
/// channels swapped) and a separate alpha-channel image:
/// ```C++
/// Mat bgra( 100, 100, CV_8UC4, Scalar(255,0,0,255) );
/// Mat bgr( bgra.rows, bgra.cols, CV_8UC3 );
/// Mat alpha( bgra.rows, bgra.cols, CV_8UC1 );
///
/// // forming an array of matrices is a quite efficient operation,
/// // because the matrix data is not copied, only the headers
/// Mat out[] = { bgr, alpha };
/// // bgra[0] -> bgr[2], bgra[1] -> bgr[1],
/// // bgra[2] -> bgr[0], bgra[3] -> alpha[0]
/// int from_to[] = { 0,2, 1,1, 2,0, 3,3 };
/// mixChannels( &bgra, 1, out, 2, from_to, 4 );
/// ```
///
///
/// Note: Unlike many other new-style C++ functions in OpenCV (see the introduction section and
/// Mat::create ), cv::mixChannels requires the output arrays to be pre-allocated before calling the
/// function.
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array or vector of matrices; all of the matrices must have the same size and the
/// same depth.
/// * nsrcs: number of matrices in `src`.
/// * dst: output array or vector of matrices; all the matrices **must be allocated**; their size and
/// depth must be the same as in `src[0]`.
/// * ndsts: number of matrices in `dst`.
/// * fromTo: array of index pairs specifying which channels are copied and where; fromTo[k\*2] is
/// a 0-based index of the input channel in src, fromTo[k\*2+1] is an index of the output channel in
/// dst; the continuous channel numbering is used: the first input image channels are indexed from 0 to
/// src[0].channels()-1, the second input image channels are indexed from src[0].channels() to
/// src[0].channels() + src[1].channels()-1, and so on, the same scheme is used for the output image
/// channels; as a special case, when fromTo[k\*2] is negative, the corresponding output channel is
/// filled with zero .
/// * npairs: number of index pairs in `fromTo`.
/// ## See also
/// split, merge, extractChannel, insertChannel, cvtColor
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * src: input array or vector of matrices; all of the matrices must have the same size and the
/// same depth.
/// * dst: output array or vector of matrices; all the matrices **must be allocated**; their size and
/// depth must be the same as in src[0].
/// * fromTo: array of index pairs specifying which channels are copied and where; fromTo[k\*2] is
/// a 0-based index of the input channel in src, fromTo[k\*2+1] is an index of the output channel in
/// dst; the continuous channel numbering is used: the first input image channels are indexed from 0 to
/// src[0].channels()-1, the second input image channels are indexed from src[0].channels() to
/// src[0].channels() + src[1].channels()-1, and so on, the same scheme is used for the output image
/// channels; as a special case, when fromTo[k\*2] is negative, the corresponding output channel is
/// filled with zero .
#[inline]
pub fn mix_channels_vec(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, from_to: &core::Vector<i32>) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_mixChannels_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const_vectorLintGR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), from_to.as_raw_VectorOfi32(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Performs the per-element multiplication of two Fourier spectrums.
///
/// The function cv::mulSpectrums performs the per-element multiplication of the two CCS-packed or complex
/// matrices that are results of a real or complex Fourier transform.
///
/// The function, together with dft and idft , may be used to calculate convolution (pass conjB=false )
/// or correlation (pass conjB=true ) of two arrays rapidly. When the arrays are complex, they are
/// simply multiplied (per element) with an optional conjugation of the second-array elements. When the
/// arrays are real, they are assumed to be CCS-packed (see dft for details).
/// ## Parameters
/// * a: first input array.
/// * b: second input array of the same size and type as src1 .
/// * c: output array of the same size and type as src1 .
/// * flags: operation flags; currently, the only supported flag is cv::DFT_ROWS, which indicates that
/// each row of src1 and src2 is an independent 1D Fourier spectrum. If you do not want to use this flag, then simply add a `0` as value.
/// * conjB: optional flag that conjugates the second input array before the multiplication (true)
/// or not (false).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * conj_b: false
#[inline]
pub fn mul_spectrums(a: &dyn core::ToInputArray, b: &dyn core::ToInputArray, c: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32, conj_b: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(a);
extern_container_arg!(b);
extern_container_arg!(c);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_mulSpectrums_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_bool(a.as_raw__InputArray(), b.as_raw__InputArray(), c.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, conj_b, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates the product of a matrix and its transposition.
///
/// The function cv::mulTransposed calculates the product of src and its
/// transposition:
/// 
/// if aTa=true , and
/// 
/// otherwise. The function is used to calculate the covariance matrix. With
/// zero delta, it can be used as a faster substitute for general matrix
/// product A\*B when B=A'
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input single-channel matrix. Note that unlike gemm, the
/// function can multiply not only floating-point matrices.
/// * dst: output square matrix.
/// * aTa: Flag specifying the multiplication ordering. See the
/// description below.
/// * delta: Optional delta matrix subtracted from src before the
/// multiplication. When the matrix is empty ( delta=noArray() ), it is
/// assumed to be zero, that is, nothing is subtracted. If it has the same
/// size as src , it is simply subtracted. Otherwise, it is "repeated" (see
/// repeat ) to cover the full src and then subtracted. Type of the delta
/// matrix, when it is not empty, must be the same as the type of created
/// output matrix. See the dtype parameter description below.
/// * scale: Optional scale factor for the matrix product.
/// * dtype: Optional type of the output matrix. When it is negative,
/// the output matrix will have the same type as src . Otherwise, it will be
/// type=CV_MAT_DEPTH(dtype) that should be either CV_32F or CV_64F .
/// ## See also
/// calcCovarMatrix, gemm, repeat, reduce
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * delta: noArray()
/// * scale: 1
/// * dtype: -1
#[inline]
pub fn mul_transposed(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, a_ta: bool, delta: &dyn core::ToInputArray, scale: f64, dtype: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
extern_container_arg!(delta);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_mulTransposed_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_bool_const__InputArrayR_double_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), a_ta, delta.as_raw__InputArray(), scale, dtype, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates the per-element scaled product of two arrays.
///
/// The function multiply calculates the per-element product of two arrays:
///
/// 
///
/// There is also a [MatrixExpressions] -friendly variant of the first function. See Mat::mul .
///
/// For a not-per-element matrix product, see gemm .
///
///
/// Note: Saturation is not applied when the output array has the depth
/// CV_32S. You may even get result of an incorrect sign in the case of
/// overflow.
/// ## Parameters
/// * src1: first input array.
/// * src2: second input array of the same size and the same type as src1.
/// * dst: output array of the same size and type as src1.
/// * scale: optional scale factor.
/// * dtype: optional depth of the output array
/// ## See also
/// add, subtract, divide, scaleAdd, addWeighted, accumulate, accumulateProduct, accumulateSquare,
/// Mat::convertTo
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * scale: 1
/// * dtype: -1
#[inline]
pub fn multiply(src1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, scale: f64, dtype: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src1);
extern_container_arg!(src2);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_multiply_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_int(src1.as_raw__InputArray(), src2.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), scale, dtype, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn no_array() -> core::_InputOutputArray {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_noArray() };
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputOutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// Calculates an absolute difference norm or a relative difference norm.
///
/// This version of cv::norm calculates the absolute difference norm
/// or the relative difference norm of arrays src1 and src2.
/// The type of norm to calculate is specified using #NormTypes.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src1: first input array.
/// * src2: second input array of the same size and the same type as src1.
/// * normType: type of the norm (see #NormTypes).
/// * mask: optional operation mask; it must have the same size as src1 and CV_8UC1 type.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * src: first input array.
/// * normType: type of the norm (see #NormTypes).
#[inline]
pub fn norm_sparse(src: &core::SparseMat, norm_type: i32) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_norm_const_SparseMatR_int(src.as_raw_SparseMat(), norm_type, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates an absolute difference norm or a relative difference norm.
///
/// This version of cv::norm calculates the absolute difference norm
/// or the relative difference norm of arrays src1 and src2.
/// The type of norm to calculate is specified using #NormTypes.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src1: first input array.
/// * src2: second input array of the same size and the same type as src1.
/// * normType: type of the norm (see #NormTypes).
/// * mask: optional operation mask; it must have the same size as src1 and CV_8UC1 type.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * norm_type: NORM_L2
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn norm2(src1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, norm_type: i32, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<f64> {
extern_container_arg!(src1);
extern_container_arg!(src2);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_norm_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int_const__InputArrayR(src1.as_raw__InputArray(), src2.as_raw__InputArray(), norm_type, mask.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates the absolute norm of an array.
///
/// This version of #norm calculates the absolute norm of src1. The type of norm to calculate is specified using #NormTypes.
///
/// As example for one array consider the function .
/// The  and  norm for the sample value 
/// is calculated as follows
/// \f{align*}
/// \| r(-1) \|_{L_1} &= |-1| + |2| = 3 \\
/// \| r(-1) \|_{L_2} &= \sqrt{(-1)^{2} + (2)^{2}} = \sqrt{5} \\
/// \| r(-1) \|_{L_\infty} &= \max(|-1|,|2|) = 2
/// \f}
/// and for  the calculation is
/// \f{align*}
/// \| r(0.5) \|_{L_1} &= |0.5| + |0.5| = 1 \\
/// \| r(0.5) \|_{L_2} &= \sqrt{(0.5)^{2} + (0.5)^{2}} = \sqrt{0.5} \\
/// \| r(0.5) \|_{L_\infty} &= \max(|0.5|,|0.5|) = 0.5.
/// \f}
/// The following graphic shows all values for the three norm functions  and .
/// It is notable that the  norm forms the upper and the  norm forms the lower border for the example function 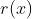.
/// 
///
/// When the mask parameter is specified and it is not empty, the norm is
///
/// If normType is not specified, #NORM_L2 is used.
/// calculated only over the region specified by the mask.
///
/// Multi-channel input arrays are treated as single-channel arrays, that is,
/// the results for all channels are combined.
///
/// Hamming norms can only be calculated with CV_8U depth arrays.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src1: first input array.
/// * normType: type of the norm (see #NormTypes).
/// * mask: optional operation mask; it must have the same size as src1 and CV_8UC1 type.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * norm_type: NORM_L2
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn norm(src1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, norm_type: i32, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<f64> {
extern_container_arg!(src1);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_norm_const__InputArrayR_int_const__InputArrayR(src1.as_raw__InputArray(), norm_type, mask.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Normalizes the norm or value range of an array.
///
/// The function cv::normalize normalizes scale and shift the input array elements so that
/// 
/// (where p=Inf, 1 or 2) when normType=NORM_INF, NORM_L1, or NORM_L2, respectively; or so that
/// 
///
/// when normType=NORM_MINMAX (for dense arrays only). The optional mask specifies a sub-array to be
/// normalized. This means that the norm or min-n-max are calculated over the sub-array, and then this
/// sub-array is modified to be normalized. If you want to only use the mask to calculate the norm or
/// min-max but modify the whole array, you can use norm and Mat::convertTo.
///
/// In case of sparse matrices, only the non-zero values are analyzed and transformed. Because of this,
/// the range transformation for sparse matrices is not allowed since it can shift the zero level.
///
/// Possible usage with some positive example data:
/// ```C++
/// vector<double> positiveData = { 2.0, 8.0, 10.0 };
/// vector<double> normalizedData_l1, normalizedData_l2, normalizedData_inf, normalizedData_minmax;
///
/// // Norm to probability (total count)
/// // sum(numbers) = 20.0
/// // 2.0 0.1 (2.0/20.0)
/// // 8.0 0.4 (8.0/20.0)
/// // 10.0 0.5 (10.0/20.0)
/// normalize(positiveData, normalizedData_l1, 1.0, 0.0, NORM_L1);
///
/// // Norm to unit vector: ||positiveData|| = 1.0
/// // 2.0 0.15
/// // 8.0 0.62
/// // 10.0 0.77
/// normalize(positiveData, normalizedData_l2, 1.0, 0.0, NORM_L2);
///
/// // Norm to max element
/// // 2.0 0.2 (2.0/10.0)
/// // 8.0 0.8 (8.0/10.0)
/// // 10.0 1.0 (10.0/10.0)
/// normalize(positiveData, normalizedData_inf, 1.0, 0.0, NORM_INF);
///
/// // Norm to range [0.0;1.0]
/// // 2.0 0.0 (shift to left border)
/// // 8.0 0.75 (6.0/8.0)
/// // 10.0 1.0 (shift to right border)
/// normalize(positiveData, normalizedData_minmax, 1.0, 0.0, NORM_MINMAX);
/// ```
///
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array.
/// * dst: output array of the same size as src .
/// * alpha: norm value to normalize to or the lower range boundary in case of the range
/// normalization.
/// * beta: upper range boundary in case of the range normalization; it is not used for the norm
/// normalization.
/// * norm_type: normalization type (see cv::NormTypes).
/// * dtype: when negative, the output array has the same type as src; otherwise, it has the same
/// number of channels as src and the depth =CV_MAT_DEPTH(dtype).
/// * mask: optional operation mask.
/// ## See also
/// norm, Mat::convertTo, SparseMat::convertTo
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * src: input array.
/// * dst: output array of the same size as src .
/// * alpha: norm value to normalize to or the lower range boundary in case of the range
/// normalization.
/// * normType: normalization type (see cv::NormTypes).
#[inline]
pub fn normalize_sparse(src: &core::SparseMat, dst: &mut core::SparseMat, alpha: f64, norm_type: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_normalize_const_SparseMatR_SparseMatR_double_int(src.as_raw_SparseMat(), dst.as_raw_mut_SparseMat(), alpha, norm_type, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Normalizes the norm or value range of an array.
///
/// The function cv::normalize normalizes scale and shift the input array elements so that
/// 
/// (where p=Inf, 1 or 2) when normType=NORM_INF, NORM_L1, or NORM_L2, respectively; or so that
/// 
///
/// when normType=NORM_MINMAX (for dense arrays only). The optional mask specifies a sub-array to be
/// normalized. This means that the norm or min-n-max are calculated over the sub-array, and then this
/// sub-array is modified to be normalized. If you want to only use the mask to calculate the norm or
/// min-max but modify the whole array, you can use norm and Mat::convertTo.
///
/// In case of sparse matrices, only the non-zero values are analyzed and transformed. Because of this,
/// the range transformation for sparse matrices is not allowed since it can shift the zero level.
///
/// Possible usage with some positive example data:
/// ```C++
/// vector<double> positiveData = { 2.0, 8.0, 10.0 };
/// vector<double> normalizedData_l1, normalizedData_l2, normalizedData_inf, normalizedData_minmax;
///
/// // Norm to probability (total count)
/// // sum(numbers) = 20.0
/// // 2.0 0.1 (2.0/20.0)
/// // 8.0 0.4 (8.0/20.0)
/// // 10.0 0.5 (10.0/20.0)
/// normalize(positiveData, normalizedData_l1, 1.0, 0.0, NORM_L1);
///
/// // Norm to unit vector: ||positiveData|| = 1.0
/// // 2.0 0.15
/// // 8.0 0.62
/// // 10.0 0.77
/// normalize(positiveData, normalizedData_l2, 1.0, 0.0, NORM_L2);
///
/// // Norm to max element
/// // 2.0 0.2 (2.0/10.0)
/// // 8.0 0.8 (8.0/10.0)
/// // 10.0 1.0 (10.0/10.0)
/// normalize(positiveData, normalizedData_inf, 1.0, 0.0, NORM_INF);
///
/// // Norm to range [0.0;1.0]
/// // 2.0 0.0 (shift to left border)
/// // 8.0 0.75 (6.0/8.0)
/// // 10.0 1.0 (shift to right border)
/// normalize(positiveData, normalizedData_minmax, 1.0, 0.0, NORM_MINMAX);
/// ```
///
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array.
/// * dst: output array of the same size as src .
/// * alpha: norm value to normalize to or the lower range boundary in case of the range
/// normalization.
/// * beta: upper range boundary in case of the range normalization; it is not used for the norm
/// normalization.
/// * norm_type: normalization type (see cv::NormTypes).
/// * dtype: when negative, the output array has the same type as src; otherwise, it has the same
/// number of channels as src and the depth =CV_MAT_DEPTH(dtype).
/// * mask: optional operation mask.
/// ## See also
/// norm, Mat::convertTo, SparseMat::convertTo
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * alpha: 1
/// * beta: 0
/// * norm_type: NORM_L2
/// * dtype: -1
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn normalize(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, alpha: f64, beta: f64, norm_type: i32, dtype: i32, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_normalize_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_double_double_int_int_const__InputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), alpha, beta, norm_type, dtype, mask.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Attaches OpenCL context to OpenCV
///
/// Note:
/// OpenCV will check if available OpenCL platform has platformName name, then assign context to
/// OpenCV and call `clRetainContext` function. The deviceID device will be used as target device and
/// new command queue will be created.
/// ## Parameters
/// * platformName: name of OpenCL platform to attach, this string is used to check if platform is available to OpenCV at runtime
/// * platformID: ID of platform attached context was created for
/// * context: OpenCL context to be attached to OpenCV
/// * deviceID: ID of device, must be created from attached context
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn attach_context(platform_name: &str, platform_id: *mut c_void, context: *mut c_void, device_id: *mut c_void) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(platform_name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_ocl_attachContext_const_StringR_voidX_voidX_voidX(platform_name.opencv_as_extern(), platform_id, context, device_id, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn build_options_add_matrix_description(build_options: &mut String, name: &str, _m: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
string_arg_output_send!(via build_options_via);
extern_container_arg!(name);
extern_container_arg!(_m);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_buildOptionsAddMatrixDescription_StringR_const_StringR_const__InputArrayR(&mut build_options_via, name.opencv_as_extern(), _m.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
string_arg_output_receive!(build_options_via => build_options);
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * src2: noArray()
/// * src3: noArray()
/// * src4: noArray()
/// * src5: noArray()
/// * src6: noArray()
/// * src7: noArray()
/// * src8: noArray()
/// * src9: noArray()
/// * strat: OCL_VECTOR_DEFAULT
#[inline]
pub fn check_optimal_vector_width(vector_widths: &i32, src1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src3: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src4: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src5: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src6: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src7: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src8: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src9: &dyn core::ToInputArray, strat: core::OclVectorStrategy) -> Result<i32> {
extern_container_arg!(src1);
extern_container_arg!(src2);
extern_container_arg!(src3);
extern_container_arg!(src4);
extern_container_arg!(src5);
extern_container_arg!(src6);
extern_container_arg!(src7);
extern_container_arg!(src8);
extern_container_arg!(src9);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_checkOptimalVectorWidth_const_intX_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_OclVectorStrategy(vector_widths, src1.as_raw__InputArray(), src2.as_raw__InputArray(), src3.as_raw__InputArray(), src4.as_raw__InputArray(), src5.as_raw__InputArray(), src6.as_raw__InputArray(), src7.as_raw__InputArray(), src8.as_raw__InputArray(), src9.as_raw__InputArray(), strat, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Convert OpenCL buffer to UMat
///
/// Note:
/// OpenCL buffer (cl_mem_buffer) should contain 2D image data, compatible with OpenCV. Memory
/// content is not copied from `clBuffer` to UMat. Instead, buffer handle assigned to UMat and
/// `clRetainMemObject` is called.
/// ## Parameters
/// * cl_mem_buffer: source clBuffer handle
/// * step: num of bytes in single row
/// * rows: number of rows
/// * cols: number of cols
/// * type: OpenCV type of image
/// * dst: destination UMat
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn convert_from_buffer(cl_mem_buffer: *mut c_void, step: size_t, rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32, dst: &mut core::UMat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_ocl_convertFromBuffer_voidX_size_t_int_int_int_UMatR(cl_mem_buffer, step, rows, cols, typ, dst.as_raw_mut_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Convert OpenCL image2d_t to UMat
///
/// Note:
/// OpenCL `image2d_t` (cl_mem_image), should be compatible with OpenCV UMat formats. Memory content
/// is copied from image to UMat with `clEnqueueCopyImageToBuffer` function.
/// ## Parameters
/// * cl_mem_image: source image2d_t handle
/// * dst: destination UMat
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn convert_from_image(cl_mem_image: *mut c_void, dst: &mut core::UMat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_ocl_convertFromImage_voidX_UMatR(cl_mem_image, dst.as_raw_mut_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn convert_type_str(sdepth: i32, ddepth: i32, cn: i32, buf: &mut String) -> Result<String> {
string_arg_output_send!(via buf_via);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_convertTypeStr_int_int_int_charX(sdepth, ddepth, cn, &mut buf_via, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
string_arg_output_receive!(buf_via => buf);
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn finish() -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_finish(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn get_opencl_error_string(error_code: i32) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_getOpenCLErrorString_int(error_code, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn get_platfoms_info(platform_info: &mut core::Vector<core::PlatformInfo>) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_getPlatfomsInfo_vectorLPlatformInfoGR(platform_info.as_raw_mut_VectorOfPlatformInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn have_amd_blas() -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_haveAmdBlas(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn have_amd_fft() -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_haveAmdFft(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn have_opencl() -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_haveOpenCL(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn have_svm() -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_haveSVM(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * ddepth: -1
/// * name: NULL
#[inline]
pub fn kernel_to_str(_kernel: &dyn core::ToInputArray, ddepth: i32, name: &str) -> Result<String> {
extern_container_arg!(_kernel);
extern_container_arg!(name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_kernelToStr_const__InputArrayR_int_const_charX(_kernel.as_raw__InputArray(), ddepth, name.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn memop_type_to_str(t: i32) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_memopTypeToStr_int(t, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * src2: noArray()
/// * src3: noArray()
/// * src4: noArray()
/// * src5: noArray()
/// * src6: noArray()
/// * src7: noArray()
/// * src8: noArray()
/// * src9: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn predict_optimal_vector_width_max(src1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src3: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src4: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src5: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src6: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src7: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src8: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src9: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<i32> {
extern_container_arg!(src1);
extern_container_arg!(src2);
extern_container_arg!(src3);
extern_container_arg!(src4);
extern_container_arg!(src5);
extern_container_arg!(src6);
extern_container_arg!(src7);
extern_container_arg!(src8);
extern_container_arg!(src9);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_predictOptimalVectorWidthMax_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(src1.as_raw__InputArray(), src2.as_raw__InputArray(), src3.as_raw__InputArray(), src4.as_raw__InputArray(), src5.as_raw__InputArray(), src6.as_raw__InputArray(), src7.as_raw__InputArray(), src8.as_raw__InputArray(), src9.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * src2: noArray()
/// * src3: noArray()
/// * src4: noArray()
/// * src5: noArray()
/// * src6: noArray()
/// * src7: noArray()
/// * src8: noArray()
/// * src9: noArray()
/// * strat: OCL_VECTOR_DEFAULT
#[inline]
pub fn predict_optimal_vector_width(src1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src3: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src4: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src5: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src6: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src7: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src8: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src9: &dyn core::ToInputArray, strat: core::OclVectorStrategy) -> Result<i32> {
extern_container_arg!(src1);
extern_container_arg!(src2);
extern_container_arg!(src3);
extern_container_arg!(src4);
extern_container_arg!(src5);
extern_container_arg!(src6);
extern_container_arg!(src7);
extern_container_arg!(src8);
extern_container_arg!(src9);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_predictOptimalVectorWidth_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_OclVectorStrategy(src1.as_raw__InputArray(), src2.as_raw__InputArray(), src3.as_raw__InputArray(), src4.as_raw__InputArray(), src5.as_raw__InputArray(), src6.as_raw__InputArray(), src7.as_raw__InputArray(), src8.as_raw__InputArray(), src9.as_raw__InputArray(), strat, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn set_use_opencl(flag: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_setUseOpenCL_bool(flag, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn type_to_str(t: i32) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_typeToStr_int(t, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn use_opencl() -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_useOpenCL(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn vecop_type_to_str(t: i32) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_vecopTypeToStr_int(t, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Converts Texture2D object to OutputArray.
/// ## Parameters
/// * texture: - source Texture2D object.
/// * dst: - destination OutputArray.
#[inline]
pub fn convert_from_gl_texture_2d(texture: &core::Texture2D, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_convertFromGLTexture2D_const_Texture2DR_const__OutputArrayR(texture.as_raw_Texture2D(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Converts InputArray to Texture2D object.
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: - source InputArray.
/// * texture: - destination Texture2D object.
#[inline]
pub fn convert_to_gl_texture_2d(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, texture: &mut core::Texture2D) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_convertToGLTexture2D_const__InputArrayR_Texture2DR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), texture.as_raw_mut_Texture2D(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Maps Buffer object to process on CL side (convert to UMat).
///
/// Function creates CL buffer from GL one, and then constructs UMat that can be used
/// to process buffer data with OpenCV functions. Note that in current implementation
/// UMat constructed this way doesn't own corresponding GL buffer object, so it is
/// the user responsibility to close down CL/GL buffers relationships by explicitly
/// calling unmapGLBuffer() function.
/// ## Parameters
/// * buffer: - source Buffer object.
/// * accessFlags: - data access flags (ACCESS_READ|ACCESS_WRITE).
/// ## Returns
/// Returns UMat object
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * access_flags: ACCESS_READ|ACCESS_WRITE
#[inline]
pub fn map_gl_buffer(buffer: &core::Buffer, access_flags: core::AccessFlag) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_mapGLBuffer_const_BufferR_AccessFlag(buffer.as_raw_Buffer(), access_flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates OpenCL context from GL.
/// ## Returns
/// Returns reference to OpenCL Context
#[inline]
pub fn initialize_context_from_gl() -> Result<core::Context> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_ocl_initializeContextFromGL(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Context::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Render OpenGL texture or primitives.
/// ## Parameters
/// * tex: Texture to draw.
/// * wndRect: Region of window, where to draw a texture (normalized coordinates).
/// * texRect: Region of texture to draw (normalized coordinates).
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * arr: Array of privitives vertices.
/// * indices: Array of vertices indices (host or device memory).
/// * mode: Render mode. One of cv::ogl::RenderModes
/// * color: Color for all vertices. Will be used if arr doesn't contain color array.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * mode: POINTS
/// * color: Scalar::all(255)
#[inline]
pub fn render_2(arr: &core::Arrays, indices: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mode: i32, color: core::Scalar) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(indices);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_render_const_ArraysR_const__InputArrayR_int_Scalar(arr.as_raw_Arrays(), indices.as_raw__InputArray(), mode, color.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Render OpenGL texture or primitives.
/// ## Parameters
/// * tex: Texture to draw.
/// * wndRect: Region of window, where to draw a texture (normalized coordinates).
/// * texRect: Region of texture to draw (normalized coordinates).
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * arr: Array of privitives vertices.
/// * mode: Render mode. One of cv::ogl::RenderModes
/// * color: Color for all vertices. Will be used if arr doesn't contain color array.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * mode: POINTS
/// * color: Scalar::all(255)
#[inline]
pub fn render_1(arr: &core::Arrays, mode: i32, color: core::Scalar) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_render_const_ArraysR_int_Scalar(arr.as_raw_Arrays(), mode, color.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Render OpenGL texture or primitives.
/// ## Parameters
/// * tex: Texture to draw.
/// * wndRect: Region of window, where to draw a texture (normalized coordinates).
/// * texRect: Region of texture to draw (normalized coordinates).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * wnd_rect: Rect_<double>(0.0,0.0,1.0,1.0)
/// * tex_rect: Rect_<double>(0.0,0.0,1.0,1.0)
#[inline]
pub fn render(tex: &core::Texture2D, wnd_rect: core::Rect_<f64>, tex_rect: core::Rect_<f64>) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_render_const_Texture2DR_Rect_LdoubleG_Rect_LdoubleG(tex.as_raw_Texture2D(), wnd_rect.opencv_as_extern(), tex_rect.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Unmaps Buffer object (releases UMat, previously mapped from Buffer).
///
/// Function must be called explicitly by the user for each UMat previously constructed
/// by the call to mapGLBuffer() function.
/// ## Parameters
/// * u: - source UMat, created by mapGLBuffer().
#[inline]
pub fn unmap_gl_buffer(u: &mut core::UMat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_unmapGLBuffer_UMatR(u.as_raw_mut_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn add_matexpr_matexpr(e1: &core::MatExpr, e2: &core::MatExpr) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorA_const_MatExprR_const_MatExprR(e1.as_raw_MatExpr(), e2.as_raw_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn add_matexpr_mat(e: &core::MatExpr, m: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorA_const_MatExprR_const_MatR(e.as_raw_MatExpr(), m.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn add_matexpr_scalar(e: &core::MatExpr, s: core::Scalar) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorA_const_MatExprR_const_ScalarR(e.as_raw_MatExpr(), &s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn add_mat_matexpr(m: &core::Mat, e: &core::MatExpr) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorA_const_MatR_const_MatExprR(m.as_raw_Mat(), e.as_raw_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// @relates cv::MatExpr
#[inline]
pub fn add_mat_mat(a: &core::Mat, b: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorA_const_MatR_const_MatR(a.as_raw_Mat(), b.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn add_mat_scalar(a: &core::Mat, s: core::Scalar) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorA_const_MatR_const_ScalarR(a.as_raw_Mat(), &s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn add_scalar_matexpr(s: core::Scalar, e: &core::MatExpr) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorA_const_ScalarR_const_MatExprR(&s, e.as_raw_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn add_scalar_mat(s: core::Scalar, a: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorA_const_ScalarR_const_MatR(&s, a.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn div_matexpr_matexpr(e1: &core::MatExpr, e2: &core::MatExpr) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorD_const_MatExprR_const_MatExprR(e1.as_raw_MatExpr(), e2.as_raw_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn div_matexpr_mat(e: &core::MatExpr, m: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorD_const_MatExprR_const_MatR(e.as_raw_MatExpr(), m.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn div_matexpr_f64(e: &core::MatExpr, s: f64) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorD_const_MatExprR_double(e.as_raw_MatExpr(), s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn div_mat_matexpr(m: &core::Mat, e: &core::MatExpr) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorD_const_MatR_const_MatExprR(m.as_raw_Mat(), e.as_raw_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn div_mat_mat(a: &core::Mat, b: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorD_const_MatR_const_MatR(a.as_raw_Mat(), b.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn div_mat_f64(a: &core::Mat, s: f64) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorD_const_MatR_double(a.as_raw_Mat(), s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn div_f64_matexpr(s: f64, e: &core::MatExpr) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorD_double_const_MatExprR(s, e.as_raw_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn div_f64_mat(s: f64, a: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorD_double_const_MatR(s, a.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// @relates cv::FileNodeIterator
#[inline]
pub fn equals_filenodeiterator_filenodeiterator(it1: &core::FileNodeIterator, it2: &core::FileNodeIterator) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorEQ_const_FileNodeIteratorR_const_FileNodeIteratorR(it1.as_raw_FileNodeIterator(), it2.as_raw_FileNodeIterator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn equals_mat_mat(a: &core::Mat, b: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorEQ_const_MatR_const_MatR(a.as_raw_Mat(), b.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn equals_mat_f64(a: &core::Mat, s: f64) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorEQ_const_MatR_double(a.as_raw_Mat(), s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn equals_f64_mat(s: f64, a: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorEQ_double_const_MatR(s, a.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn greater_than_or_equal_mat_mat(a: &core::Mat, b: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorGE_const_MatR_const_MatR(a.as_raw_Mat(), b.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn greater_than_or_equal_mat_f64(a: &core::Mat, s: f64) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorGE_const_MatR_double(a.as_raw_Mat(), s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn greater_than_or_equal_f64_mat(s: f64, a: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorGE_double_const_MatR(s, a.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn greater_than_mat_mat(a: &core::Mat, b: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorG_const_MatR_const_MatR(a.as_raw_Mat(), b.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn greater_than_mat_f64(a: &core::Mat, s: f64) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorG_const_MatR_double(a.as_raw_Mat(), s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn greater_than_f64_mat(s: f64, a: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorG_double_const_MatR(s, a.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn less_than_or_equal_mat_mat(a: &core::Mat, b: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorLE_const_MatR_const_MatR(a.as_raw_Mat(), b.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn less_than_or_equal_mat_f64(a: &core::Mat, s: f64) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorLE_const_MatR_double(a.as_raw_Mat(), s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn less_than_or_equal_f64_mat(s: f64, a: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorLE_double_const_MatR(s, a.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn less_than_mat_mat(a: &core::Mat, b: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorL_const_MatR_const_MatR(a.as_raw_Mat(), b.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn less_than_mat_f64(a: &core::Mat, s: f64) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorL_const_MatR_double(a.as_raw_Mat(), s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn less_than_f64_mat(s: f64, a: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorL_double_const_MatR(s, a.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn not_equals_filenodeiterator_filenodeiterator(it1: &core::FileNodeIterator, it2: &core::FileNodeIterator) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorNE_const_FileNodeIteratorR_const_FileNodeIteratorR(it1.as_raw_FileNodeIterator(), it2.as_raw_FileNodeIterator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn not_equals_mat_mat(a: &core::Mat, b: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorNE_const_MatR_const_MatR(a.as_raw_Mat(), b.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn not_equals_mat_f64(a: &core::Mat, s: f64) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorNE_const_MatR_double(a.as_raw_Mat(), s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn not_equals_f64_mat(s: f64, a: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorNE_double_const_MatR(s, a.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn negate(m: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorNOTB_const_MatR(m.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn or_mat_mat(a: &core::Mat, b: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorOR_const_MatR_const_MatR(a.as_raw_Mat(), b.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn or_mat_scalar(a: &core::Mat, s: core::Scalar) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorOR_const_MatR_const_ScalarR(a.as_raw_Mat(), &s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn or_scalar_mat(s: core::Scalar, a: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorOR_const_ScalarR_const_MatR(&s, a.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn and_mat_mat(a: &core::Mat, b: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorR_const_MatR_const_MatR(a.as_raw_Mat(), b.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn and_mat_scalar(a: &core::Mat, s: core::Scalar) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorR_const_MatR_const_ScalarR(a.as_raw_Mat(), &s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn and_scalar_mat(s: core::Scalar, a: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorR_const_ScalarR_const_MatR(&s, a.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn sub_matexpr(e: &core::MatExpr) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorS_const_MatExprR(e.as_raw_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn sub_matexpr_matexpr(e1: &core::MatExpr, e2: &core::MatExpr) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorS_const_MatExprR_const_MatExprR(e1.as_raw_MatExpr(), e2.as_raw_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn sub_matexpr_mat(e: &core::MatExpr, m: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorS_const_MatExprR_const_MatR(e.as_raw_MatExpr(), m.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn sub_matexpr_scalar(e: &core::MatExpr, s: core::Scalar) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorS_const_MatExprR_const_ScalarR(e.as_raw_MatExpr(), &s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn sub_mat(m: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorS_const_MatR(m.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn sub_mat_matexpr(m: &core::Mat, e: &core::MatExpr) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorS_const_MatR_const_MatExprR(m.as_raw_Mat(), e.as_raw_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn sub_mat_mat(a: &core::Mat, b: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorS_const_MatR_const_MatR(a.as_raw_Mat(), b.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn sub_mat_scalar(a: &core::Mat, s: core::Scalar) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorS_const_MatR_const_ScalarR(a.as_raw_Mat(), &s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn sub_scalar_matexpr(s: core::Scalar, e: &core::MatExpr) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorS_const_ScalarR_const_MatExprR(&s, e.as_raw_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn sub_scalar_mat(s: core::Scalar, a: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorS_const_ScalarR_const_MatR(&s, a.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn xor_mat_mat(a: &core::Mat, b: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorXOR_const_MatR_const_MatR(a.as_raw_Mat(), b.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn xor_mat_scalar(a: &core::Mat, s: core::Scalar) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorXOR_const_MatR_const_ScalarR(a.as_raw_Mat(), &s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn xor_scalar_mat(s: core::Scalar, a: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorXOR_const_ScalarR_const_MatR(&s, a.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn mul_matexpr_matexpr(e1: &core::MatExpr, e2: &core::MatExpr) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorX_const_MatExprR_const_MatExprR(e1.as_raw_MatExpr(), e2.as_raw_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn mul_matexpr_mat(e: &core::MatExpr, m: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorX_const_MatExprR_const_MatR(e.as_raw_MatExpr(), m.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn mul_matexpr_f64(e: &core::MatExpr, s: f64) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorX_const_MatExprR_double(e.as_raw_MatExpr(), s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn mul_mat_matexpr(m: &core::Mat, e: &core::MatExpr) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorX_const_MatR_const_MatExprR(m.as_raw_Mat(), e.as_raw_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn mul_mat_mat(a: &core::Mat, b: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorX_const_MatR_const_MatR(a.as_raw_Mat(), b.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn mul_mat_f64(a: &core::Mat, s: f64) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorX_const_MatR_double(a.as_raw_Mat(), s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn mul_f64_matexpr(s: f64, e: &core::MatExpr) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorX_double_const_MatExprR(s, e.as_raw_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn mul_f64_mat(s: f64, a: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_operatorX_double_const_MatR(s, a.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parallel data processor
///
/// @ingroup core_parallel
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * nstripes: -1.
#[inline]
pub fn parallel_for_(range: &core::Range, body: &dyn core::ParallelLoopBody, nstripes: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_parallel_for__const_RangeR_const_ParallelLoopBodyR_double(range.as_raw_Range(), body.as_raw_ParallelLoopBody(), nstripes, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// converts NaNs to the given number
/// ## Parameters
/// * a: input/output matrix (CV_32F type).
/// * val: value to convert the NaNs
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * val: 0
#[inline]
pub fn patch_na_ns(a: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(a);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_patchNaNs_const__InputOutputArrayR_double(a.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Performs the perspective matrix transformation of vectors.
///
/// The function cv::perspectiveTransform transforms every element of src by
/// treating it as a 2D or 3D vector, in the following way:
/// 
/// where
/// 
/// and
/// 
///
/// Here a 3D vector transformation is shown. In case of a 2D vector
/// transformation, the z component is omitted.
///
///
/// Note: The function transforms a sparse set of 2D or 3D vectors. If you
/// want to transform an image using perspective transformation, use
/// warpPerspective . If you have an inverse problem, that is, you want to
/// compute the most probable perspective transformation out of several
/// pairs of corresponding points, you can use getPerspectiveTransform or
/// findHomography .
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input two-channel or three-channel floating-point array; each
/// element is a 2D/3D vector to be transformed.
/// * dst: output array of the same size and type as src.
/// * m: 3x3 or 4x4 floating-point transformation matrix.
/// ## See also
/// transform, warpPerspective, getPerspectiveTransform, findHomography
#[inline]
pub fn perspective_transform(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, m: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
extern_container_arg!(m);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_perspectiveTransform_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), m.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates the rotation angle of 2D vectors.
///
/// The function cv::phase calculates the rotation angle of each 2D vector that
/// is formed from the corresponding elements of x and y :
/// 
///
/// The angle estimation accuracy is about 0.3 degrees. When x(I)=y(I)=0 ,
/// the corresponding angle(I) is set to 0.
/// ## Parameters
/// * x: input floating-point array of x-coordinates of 2D vectors.
/// * y: input array of y-coordinates of 2D vectors; it must have the
/// same size and the same type as x.
/// * angle: output array of vector angles; it has the same size and
/// same type as x .
/// * angleInDegrees: when true, the function calculates the angle in
/// degrees, otherwise, they are measured in radians.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * angle_in_degrees: false
#[inline]
pub fn phase(x: &dyn core::ToInputArray, y: &dyn core::ToInputArray, angle: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, angle_in_degrees: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(x);
extern_container_arg!(y);
extern_container_arg!(angle);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_phase_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_bool(x.as_raw__InputArray(), y.as_raw__InputArray(), angle.as_raw__OutputArray(), angle_in_degrees, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates x and y coordinates of 2D vectors from their magnitude and angle.
///
/// The function cv::polarToCart calculates the Cartesian coordinates of each 2D
/// vector represented by the corresponding elements of magnitude and angle:
/// 
///
/// The relative accuracy of the estimated coordinates is about 1e-6.
/// ## Parameters
/// * magnitude: input floating-point array of magnitudes of 2D vectors;
/// it can be an empty matrix (=Mat()), in this case, the function assumes
/// that all the magnitudes are =1; if it is not empty, it must have the
/// same size and type as angle.
/// * angle: input floating-point array of angles of 2D vectors.
/// * x: output array of x-coordinates of 2D vectors; it has the same
/// size and type as angle.
/// * y: output array of y-coordinates of 2D vectors; it has the same
/// size and type as angle.
/// * angleInDegrees: when true, the input angles are measured in
/// degrees, otherwise, they are measured in radians.
/// ## See also
/// cartToPolar, magnitude, phase, exp, log, pow, sqrt
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * angle_in_degrees: false
#[inline]
pub fn polar_to_cart(magnitude: &dyn core::ToInputArray, angle: &dyn core::ToInputArray, x: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, y: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, angle_in_degrees: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(magnitude);
extern_container_arg!(angle);
extern_container_arg!(x);
extern_container_arg!(y);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_polarToCart_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_bool(magnitude.as_raw__InputArray(), angle.as_raw__InputArray(), x.as_raw__OutputArray(), y.as_raw__OutputArray(), angle_in_degrees, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Raises every array element to a power.
///
/// The function cv::pow raises every element of the input array to power :
/// 
///
/// So, for a non-integer power exponent, the absolute values of input array
/// elements are used. However, it is possible to get true values for
/// negative values using some extra operations. In the example below,
/// computing the 5th root of array src shows:
/// ```C++
/// Mat mask = src < 0;
/// pow(src, 1./5, dst);
/// subtract(Scalar::all(0), dst, dst, mask);
/// ```
///
/// For some values of power, such as integer values, 0.5 and -0.5,
/// specialized faster algorithms are used.
///
/// Special values (NaN, Inf) are not handled.
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array.
/// * power: exponent of power.
/// * dst: output array of the same size and type as src.
/// ## See also
/// sqrt, exp, log, cartToPolar, polarToCart
#[inline]
pub fn pow(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, power: f64, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_pow_const__InputArrayR_double_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), power, dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Shuffles the array elements randomly.
///
/// The function cv::randShuffle shuffles the specified 1D array by randomly choosing pairs of elements and
/// swapping them. The number of such swap operations will be dst.rows\*dst.cols\*iterFactor .
/// ## Parameters
/// * dst: input/output numerical 1D array.
/// * iterFactor: scale factor that determines the number of random swap operations (see the details
/// below).
/// * rng: optional random number generator used for shuffling; if it is zero, theRNG () is used
/// instead.
/// ## See also
/// RNG, sort
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * iter_factor: 1.
/// * rng: 0
#[inline]
pub fn rand_shuffle(dst: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, iter_factor: f64, rng: &mut core::RNG) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_randShuffle_const__InputOutputArrayR_double_RNGX(dst.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), iter_factor, rng.as_raw_mut_RNG(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Fills the array with normally distributed random numbers.
///
/// The function cv::randn fills the matrix dst with normally distributed random numbers with the specified
/// mean vector and the standard deviation matrix. The generated random numbers are clipped to fit the
/// value range of the output array data type.
/// ## Parameters
/// * dst: output array of random numbers; the array must be pre-allocated and have 1 to 4 channels.
/// * mean: mean value (expectation) of the generated random numbers.
/// * stddev: standard deviation of the generated random numbers; it can be either a vector (in
/// which case a diagonal standard deviation matrix is assumed) or a square matrix.
/// ## See also
/// RNG, randu
#[inline]
pub fn randn(dst: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, mean: &dyn core::ToInputArray, stddev: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(dst);
extern_container_arg!(mean);
extern_container_arg!(stddev);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_randn_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(dst.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), mean.as_raw__InputArray(), stddev.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Generates a single uniformly-distributed random number or an array of random numbers.
///
/// Non-template variant of the function fills the matrix dst with uniformly-distributed
/// random numbers from the specified range:
/// 
/// ## Parameters
/// * dst: output array of random numbers; the array must be pre-allocated.
/// * low: inclusive lower boundary of the generated random numbers.
/// * high: exclusive upper boundary of the generated random numbers.
/// ## See also
/// RNG, randn, theRNG
#[inline]
pub fn randu(dst: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, low: &dyn core::ToInputArray, high: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(dst);
extern_container_arg!(low);
extern_container_arg!(high);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_randu_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(dst.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), low.as_raw__InputArray(), high.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn read_dmatch(node: &core::FileNode, value: &mut core::DMatch, default_value: core::DMatch) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_read_const_FileNodeR_DMatchR_const_DMatchR(node.as_raw_FileNode(), value, &default_value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn read_keypoint(node: &core::FileNode, value: &mut core::KeyPoint, default_value: &core::KeyPoint) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_read_const_FileNodeR_KeyPointR_const_KeyPointR(node.as_raw_FileNode(), value.as_raw_mut_KeyPoint(), default_value.as_raw_KeyPoint(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * default_mat: Mat()
#[inline]
pub fn read_mat(node: &core::FileNode, mat: &mut core::Mat, default_mat: &core::Mat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_read_const_FileNodeR_MatR_const_MatR(node.as_raw_FileNode(), mat.as_raw_mut_Mat(), default_mat.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * default_mat: SparseMat()
#[inline]
pub fn read_sparsemat(node: &core::FileNode, mat: &mut core::SparseMat, default_mat: &core::SparseMat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_read_const_FileNodeR_SparseMatR_const_SparseMatR(node.as_raw_FileNode(), mat.as_raw_mut_SparseMat(), default_mat.as_raw_SparseMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn read_f64(node: &core::FileNode, value: &mut f64, default_value: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_read_const_FileNodeR_doubleR_double(node.as_raw_FileNode(), value, default_value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn read_f32(node: &core::FileNode, value: &mut f32, default_value: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_read_const_FileNodeR_floatR_float(node.as_raw_FileNode(), value, default_value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// @relates cv::FileNode
#[inline]
pub fn read_i32(node: &core::FileNode, value: &mut i32, default_value: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_read_const_FileNodeR_intR_int(node.as_raw_FileNode(), value, default_value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn read_str(node: &core::FileNode, value: &mut String, default_value: &str) -> Result<()> {
string_arg_output_send!(via value_via);
extern_container_arg!(default_value);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_read_const_FileNodeR_stringR_const_stringR(node.as_raw_FileNode(), &mut value_via, default_value.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
string_arg_output_receive!(value_via => value);
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn read_dmatch_vec_legacy(node: &core::FileNode, matches: &mut core::Vector<core::DMatch>) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_read_const_FileNodeR_vectorLDMatchGR(node.as_raw_FileNode(), matches.as_raw_mut_VectorOfDMatch(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn read_keypoint_vec_legacy(node: &core::FileNode, keypoints: &mut core::Vector<core::KeyPoint>) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_read_const_FileNodeR_vectorLKeyPointGR(node.as_raw_FileNode(), keypoints.as_raw_mut_VectorOfKeyPoint(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds out if there is any intersection between two rectangles
///
/// mainly useful for language bindings
/// ## Parameters
/// * rect1: First rectangle
/// * rect2: Second rectangle
/// ## Returns
/// the area of the intersection
#[inline]
pub fn rectangle_intersection_area(a: core::Rect2d, b: core::Rect2d) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_rectangleIntersectionArea_const_Rect2dR_const_Rect2dR(&a, &b, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds indices of max elements along provided axis
///
///
/// Note:
/// - If input or output array is not continuous, this function will create an internal copy.
/// - NaN handling is left unspecified, see patchNaNs().
/// - The returned index is always in bounds of input matrix.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input single-channel array.
/// * dst: output array of type CV_32SC1 with the same dimensionality as src,
/// except for axis being reduced - it should be set to 1.
/// * lastIndex: whether to get the index of first or last occurrence of max.
/// * axis: axis to reduce along.
/// ## See also
/// reduceArgMin, minMaxLoc, min, max, compare, reduce
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * last_index: false
#[inline]
pub fn reduce_arg_max(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, axis: i32, last_index: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_reduceArgMax_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_bool(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), axis, last_index, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds indices of min elements along provided axis
///
///
/// Note:
/// - If input or output array is not continuous, this function will create an internal copy.
/// - NaN handling is left unspecified, see patchNaNs().
/// - The returned index is always in bounds of input matrix.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input single-channel array.
/// * dst: output array of type CV_32SC1 with the same dimensionality as src,
/// except for axis being reduced - it should be set to 1.
/// * lastIndex: whether to get the index of first or last occurrence of min.
/// * axis: axis to reduce along.
/// ## See also
/// reduceArgMax, minMaxLoc, min, max, compare, reduce
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * last_index: false
#[inline]
pub fn reduce_arg_min(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, axis: i32, last_index: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_reduceArgMin_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_bool(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), axis, last_index, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Reduces a matrix to a vector.
///
/// The function #reduce reduces the matrix to a vector by treating the matrix rows/columns as a set of
/// 1D vectors and performing the specified operation on the vectors until a single row/column is
/// obtained. For example, the function can be used to compute horizontal and vertical projections of a
/// raster image. In case of #REDUCE_MAX and #REDUCE_MIN , the output image should have the same type as the source one.
/// In case of #REDUCE_SUM and #REDUCE_AVG , the output may have a larger element bit-depth to preserve accuracy.
/// And multi-channel arrays are also supported in these two reduction modes.
///
/// The following code demonstrates its usage for a single channel matrix.
/// [example](https://github.com/opencv/opencv/blob/4.7.0/samples/cpp/tutorial_code/snippets/core_reduce.cpp#L1)
///
/// And the following code demonstrates its usage for a two-channel matrix.
/// [example2](https://github.com/opencv/opencv/blob/4.7.0/samples/cpp/tutorial_code/snippets/core_reduce.cpp#L1)
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input 2D matrix.
/// * dst: output vector. Its size and type is defined by dim and dtype parameters.
/// * dim: dimension index along which the matrix is reduced. 0 means that the matrix is reduced to
/// a single row. 1 means that the matrix is reduced to a single column.
/// * rtype: reduction operation that could be one of #ReduceTypes
/// * dtype: when negative, the output vector will have the same type as the input matrix,
/// otherwise, its type will be CV_MAKE_TYPE(CV_MAT_DEPTH(dtype), src.channels()).
/// ## See also
/// repeat, reduceArgMin, reduceArgMax
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * dtype: -1
#[inline]
pub fn reduce(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, dim: i32, rtype: i32, dtype: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_reduce_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_int_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), dim, rtype, dtype, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Fills the output array with repeated copies of the input array.
///
/// The function cv::repeat duplicates the input array one or more times along each of the two axes:
/// 
/// The second variant of the function is more convenient to use with [MatrixExpressions].
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array to replicate.
/// * ny: Flag to specify how many times the `src` is repeated along the
/// vertical axis.
/// * nx: Flag to specify how many times the `src` is repeated along the
/// horizontal axis.
/// * dst: output array of the same type as `src`.
/// ## See also
/// cv::reduce
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * src: input array to replicate.
/// * ny: Flag to specify how many times the `src` is repeated along the
/// vertical axis.
/// * nx: Flag to specify how many times the `src` is repeated along the
/// horizontal axis.
#[inline]
pub fn repeat(src: &core::Mat, ny: i32, nx: i32) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_repeat_const_MatR_int_int(src.as_raw_Mat(), ny, nx, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Fills the output array with repeated copies of the input array.
///
/// The function cv::repeat duplicates the input array one or more times along each of the two axes:
/// 
/// The second variant of the function is more convenient to use with [MatrixExpressions].
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array to replicate.
/// * ny: Flag to specify how many times the `src` is repeated along the
/// vertical axis.
/// * nx: Flag to specify how many times the `src` is repeated along the
/// horizontal axis.
/// * dst: output array of the same type as `src`.
/// ## See also
/// cv::reduce
#[inline]
pub fn repeat_to(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, ny: i32, nx: i32, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_repeat_const__InputArrayR_int_int_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), ny, nx, dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Rotates a 2D array in multiples of 90 degrees.
/// The function cv::rotate rotates the array in one of three different ways:
/// * Rotate by 90 degrees clockwise (rotateCode = ROTATE_90_CLOCKWISE).
/// * Rotate by 180 degrees clockwise (rotateCode = ROTATE_180).
/// * Rotate by 270 degrees clockwise (rotateCode = ROTATE_90_COUNTERCLOCKWISE).
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array.
/// * dst: output array of the same type as src. The size is the same with ROTATE_180,
/// and the rows and cols are switched for ROTATE_90_CLOCKWISE and ROTATE_90_COUNTERCLOCKWISE.
/// * rotateCode: an enum to specify how to rotate the array; see the enum #RotateFlags
/// ## See also
/// transpose , repeat , completeSymm, flip, RotateFlags
#[inline]
pub fn rotate(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, rotate_code: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_rotate_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), rotate_code, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Override search data path by adding new search location
///
/// Use this only to override default behavior
/// Passed paths are used in LIFO order.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * path: Path to used samples data
#[inline]
pub fn add_samples_data_search_path(path: &str) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(path);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_samples_addSamplesDataSearchPath_const_StringR(path.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Append samples search data sub directory
///
/// General usage is to add OpenCV modules name (`<opencv_contrib>/modules/<name>/samples/data` -> `<name>/samples/data` + `modules/<name>/samples/data`).
/// Passed subdirectories are used in LIFO order.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * subdir: samples data sub directory
#[inline]
pub fn add_samples_data_search_sub_directory(subdir: &str) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(subdir);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_samples_addSamplesDataSearchSubDirectory_const_StringR(subdir.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * silent_mode: false
#[inline]
pub fn find_file_or_keep(relative_path: &str, silent_mode: bool) -> Result<String> {
extern_container_arg!(relative_path);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_samples_findFileOrKeep_const_StringR_bool(relative_path.opencv_as_extern(), silent_mode, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Try to find requested data file
///
/// Search directories:
///
/// 1. Directories passed via `addSamplesDataSearchPath()`
/// 2. OPENCV_SAMPLES_DATA_PATH_HINT environment variable
/// 3. OPENCV_SAMPLES_DATA_PATH environment variable
/// If parameter value is not empty and nothing is found then stop searching.
/// 4. Detects build/install path based on:
/// a. current working directory (CWD)
/// b. and/or binary module location (opencv_core/opencv_world, doesn't work with static linkage)
/// 5. Scan `<source>/{,data,samples/data}` directories if build directory is detected or the current directory is in source tree.
/// 6. Scan `<install>/share/OpenCV` directory if install directory is detected.
/// ## See also
/// cv::utils::findDataFile
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * relative_path: Relative path to data file
/// * required: Specify "file not found" handling.
/// If true, function prints information message and raises cv::Exception.
/// If false, function returns empty result
/// * silentMode: Disables messages
/// ## Returns
/// Returns path (absolute or relative to the current directory) or empty string if file is not found
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * required: true
/// * silent_mode: false
#[inline]
pub fn find_file(relative_path: &str, required: bool, silent_mode: bool) -> Result<String> {
extern_container_arg!(relative_path);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_samples_findFile_const_StringR_bool_bool(relative_path.opencv_as_extern(), required, silent_mode, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates the sum of a scaled array and another array.
///
/// The function scaleAdd is one of the classical primitive linear algebra operations, known as DAXPY
/// or SAXPY in [BLAS](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Basic_Linear_Algebra_Subprograms). It calculates
/// the sum of a scaled array and another array:
/// 
/// The function can also be emulated with a matrix expression, for example:
/// ```C++
/// Mat A(3, 3, CV_64F);
/// ...
/// A.row(0) = A.row(1)*2 + A.row(2);
/// ```
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src1: first input array.
/// * alpha: scale factor for the first array.
/// * src2: second input array of the same size and type as src1.
/// * dst: output array of the same size and type as src1.
/// ## See also
/// add, addWeighted, subtract, Mat::dot, Mat::convertTo
#[inline]
pub fn scale_add(src1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, alpha: f64, src2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src1);
extern_container_arg!(src2);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_scaleAdd_const__InputArrayR_double_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src1.as_raw__InputArray(), alpha, src2.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets/resets the break-on-error mode.
///
/// When the break-on-error mode is set, the default error handler issues a hardware exception, which
/// can make debugging more convenient.
///
/// \return the previous state
#[inline]
pub fn set_break_on_error(flag: bool) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_setBreakOnError_bool(flag, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Initializes a scaled identity matrix.
///
/// The function cv::setIdentity initializes a scaled identity matrix:
/// 
///
/// The function can also be emulated using the matrix initializers and the
/// matrix expressions:
/// ```C++
/// Mat A = Mat::eye(4, 3, CV_32F)*5;
/// // A will be set to [[5, 0, 0], [0, 5, 0], [0, 0, 5], [0, 0, 0]]
/// ```
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * mtx: matrix to initialize (not necessarily square).
/// * s: value to assign to diagonal elements.
/// ## See also
/// Mat::zeros, Mat::ones, Mat::setTo, Mat::operator=
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * s: Scalar(1)
#[inline]
pub fn set_identity(mtx: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, s: core::Scalar) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(mtx);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_setIdentity_const__InputOutputArrayR_const_ScalarR(mtx.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), &s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// @cond IGNORED
#[inline]
pub fn set_log_level_1(level: i32) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_setLogLevel_int(level, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// OpenCV will try to set the number of threads for the next parallel region.
///
/// If threads == 0, OpenCV will disable threading optimizations and run all it's functions
/// sequentially. Passing threads \< 0 will reset threads number to system default. This function must
/// be called outside of parallel region.
///
/// OpenCV will try to run its functions with specified threads number, but some behaviour differs from
/// framework:
/// * `TBB` - User-defined parallel constructions will run with the same threads number, if
/// another is not specified. If later on user creates his own scheduler, OpenCV will use it.
/// * `OpenMP` - No special defined behaviour.
/// * `Concurrency` - If threads == 1, OpenCV will disable threading optimizations and run its
/// functions sequentially.
/// * `GCD` - Supports only values \<= 0.
/// * `C=` - No special defined behaviour.
/// ## Parameters
/// * nthreads: Number of threads used by OpenCV.
/// ## See also
/// getNumThreads, getThreadNum
#[inline]
pub fn set_num_threads(nthreads: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_setNumThreads_int(nthreads, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets state of default random number generator.
///
/// The function cv::setRNGSeed sets state of default random number generator to custom value.
/// ## Parameters
/// * seed: new state for default random number generator
/// ## See also
/// RNG, randu, randn
#[inline]
pub fn set_rng_seed(seed: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_setRNGSeed_int(seed, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Enable/disable use of OpenVX
#[inline]
pub fn set_use_openvx(flag: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_setUseOpenVX_bool(flag, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Enables or disables the optimized code.
///
/// The function can be used to dynamically turn on and off optimized dispatched code (code that uses SSE4.2, AVX/AVX2,
/// and other instructions on the platforms that support it). It sets a global flag that is further
/// checked by OpenCV functions. Since the flag is not checked in the inner OpenCV loops, it is only
/// safe to call the function on the very top level in your application where you can be sure that no
/// other OpenCV function is currently executed.
///
/// By default, the optimized code is enabled unless you disable it in CMake. The current status can be
/// retrieved using useOptimized.
/// ## Parameters
/// * onoff: The boolean flag specifying whether the optimized code should be used (onoff=true)
/// or not (onoff=false).
#[inline]
pub fn set_use_optimized(onoff: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_setUseOptimized_bool(onoff, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds the real roots of a cubic equation.
///
/// The function solveCubic finds the real roots of a cubic equation:
/// * if coeffs is a 4-element vector:
/// 
/// * if coeffs is a 3-element vector:
/// 
///
/// The roots are stored in the roots array.
/// ## Parameters
/// * coeffs: equation coefficients, an array of 3 or 4 elements.
/// * roots: output array of real roots that has 1 or 3 elements.
/// ## Returns
/// number of real roots. It can be 0, 1 or 2.
#[inline]
pub fn solve_cubic(coeffs: &dyn core::ToInputArray, roots: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<i32> {
extern_container_arg!(coeffs);
extern_container_arg!(roots);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_solveCubic_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), roots.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Solve given (non-integer) linear programming problem using the Simplex Algorithm (Simplex Method).
///
/// What we mean here by "linear programming problem" (or LP problem, for short) can be formulated as:
///
/// 
///
/// Where  is fixed `1`-by-`n` row-vector, 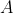 is fixed `m`-by-`n` matrix, 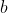 is fixed `m`-by-`1`
/// column vector and  is an arbitrary `n`-by-`1` column vector, which satisfies the constraints.
///
/// Simplex algorithm is one of many algorithms that are designed to handle this sort of problems
/// efficiently. Although it is not optimal in theoretical sense (there exist algorithms that can solve
/// any problem written as above in polynomial time, while simplex method degenerates to exponential
/// time for some special cases), it is well-studied, easy to implement and is shown to work well for
/// real-life purposes.
///
/// The particular implementation is taken almost verbatim from **Introduction to Algorithms, third
/// edition** by T. H. Cormen, C. E. Leiserson, R. L. Rivest and Clifford Stein. In particular, the
/// Bland's rule <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bland%27s_rule> is used to prevent cycling.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * Func: This row-vector corresponds to  in the LP problem formulation (see above). It should
/// contain 32- or 64-bit floating point numbers. As a convenience, column-vector may be also submitted,
/// in the latter case it is understood to correspond to .
/// * Constr: `m`-by-`n+1` matrix, whose rightmost column corresponds to  in formulation above
/// and the remaining to . It should contain 32- or 64-bit floating point numbers.
/// * z: The solution will be returned here as a column-vector - it corresponds to  in the
/// formulation above. It will contain 64-bit floating point numbers.
/// ## Returns
/// One of cv::SolveLPResult
#[inline]
pub fn solve_lp(func: &dyn core::ToInputArray, constr: &dyn core::ToInputArray, z: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<i32> {
extern_container_arg!(func);
extern_container_arg!(constr);
extern_container_arg!(z);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_solveLP_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(func.as_raw__InputArray(), constr.as_raw__InputArray(), z.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds the real or complex roots of a polynomial equation.
///
/// The function cv::solvePoly finds real and complex roots of a polynomial equation:
/// 
/// ## Parameters
/// * coeffs: array of polynomial coefficients.
/// * roots: output (complex) array of roots.
/// * maxIters: maximum number of iterations the algorithm does.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * max_iters: 300
#[inline]
pub fn solve_poly(coeffs: &dyn core::ToInputArray, roots: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, max_iters: i32) -> Result<f64> {
extern_container_arg!(coeffs);
extern_container_arg!(roots);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_solvePoly_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), roots.as_raw__OutputArray(), max_iters, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Solves one or more linear systems or least-squares problems.
///
/// The function cv::solve solves a linear system or least-squares problem (the
/// latter is possible with SVD or QR methods, or by specifying the flag
/// #DECOMP_NORMAL ):
/// 
///
/// If #DECOMP_LU or #DECOMP_CHOLESKY method is used, the function returns 1
/// if src1 (or  ) is non-singular. Otherwise,
/// it returns 0. In the latter case, dst is not valid. Other methods find a
/// pseudo-solution in case of a singular left-hand side part.
///
///
/// Note: If you want to find a unity-norm solution of an under-defined
/// singular system  , the function solve
/// will not do the work. Use SVD::solveZ instead.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src1: input matrix on the left-hand side of the system.
/// * src2: input matrix on the right-hand side of the system.
/// * dst: output solution.
/// * flags: solution (matrix inversion) method (#DecompTypes)
/// ## See also
/// invert, SVD, eigen
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: DECOMP_LU
#[inline]
pub fn solve(src1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<bool> {
extern_container_arg!(src1);
extern_container_arg!(src2);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_solve_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(src1.as_raw__InputArray(), src2.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sorts each row or each column of a matrix.
///
/// The function cv::sortIdx sorts each matrix row or each matrix column in the
/// ascending or descending order. So you should pass two operation flags to
/// get desired behaviour. Instead of reordering the elements themselves, it
/// stores the indices of sorted elements in the output array. For example:
/// ```C++
/// Mat A = Mat::eye(3,3,CV_32F), B;
/// sortIdx(A, B, SORT_EVERY_ROW + SORT_ASCENDING);
/// // B will probably contain
/// // (because of equal elements in A some permutations are possible):
/// // [[1, 2, 0], [0, 2, 1], [0, 1, 2]]
/// ```
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input single-channel array.
/// * dst: output integer array of the same size as src.
/// * flags: operation flags that could be a combination of cv::SortFlags
/// ## See also
/// sort, randShuffle
#[inline]
pub fn sort_idx(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_sortIdx_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sorts each row or each column of a matrix.
///
/// The function cv::sort sorts each matrix row or each matrix column in
/// ascending or descending order. So you should pass two operation flags to
/// get desired behaviour. If you want to sort matrix rows or columns
/// lexicographically, you can use STL std::sort generic function with the
/// proper comparison predicate.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input single-channel array.
/// * dst: output array of the same size and type as src.
/// * flags: operation flags, a combination of #SortFlags
/// ## See also
/// sortIdx, randShuffle
#[inline]
pub fn sort(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_sort_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Divides a multi-channel array into several single-channel arrays.
///
/// The function cv::split splits a multi-channel array into separate single-channel arrays:
/// 
/// If you need to extract a single channel or do some other sophisticated channel permutation, use
/// mixChannels .
///
/// The following example demonstrates how to split a 3-channel matrix into 3 single channel matrices.
/// [example](https://github.com/opencv/opencv/blob/4.7.0/samples/cpp/tutorial_code/snippets/core_split.cpp#L1)
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input multi-channel array.
/// * mvbegin: output array; the number of arrays must match src.channels(); the arrays themselves are
/// reallocated, if needed.
/// ## See also
/// merge, mixChannels, cvtColor
#[inline]
pub fn split_slice(src: &core::Mat, mvbegin: &mut core::Mat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_split_const_MatR_MatX(src.as_raw_Mat(), mvbegin.as_raw_mut_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Divides a multi-channel array into several single-channel arrays.
///
/// The function cv::split splits a multi-channel array into separate single-channel arrays:
/// 
/// If you need to extract a single channel or do some other sophisticated channel permutation, use
/// mixChannels .
///
/// The following example demonstrates how to split a 3-channel matrix into 3 single channel matrices.
/// [example](https://github.com/opencv/opencv/blob/4.7.0/samples/cpp/tutorial_code/snippets/core_split.cpp#L1)
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input multi-channel array.
/// * mvbegin: output array; the number of arrays must match src.channels(); the arrays themselves are
/// reallocated, if needed.
/// ## See also
/// merge, mixChannels, cvtColor
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * m: input multi-channel array.
/// * mv: output vector of arrays; the arrays themselves are reallocated, if needed.
#[inline]
pub fn split(m: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mv: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(m);
extern_container_arg!(mv);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_split_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(m.as_raw__InputArray(), mv.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates a square root of array elements.
///
/// The function cv::sqrt calculates a square root of each input array element.
/// In case of multi-channel arrays, each channel is processed
/// independently. The accuracy is approximately the same as of the built-in
/// std::sqrt .
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input floating-point array.
/// * dst: output array of the same size and type as src.
#[inline]
pub fn sqrt(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_sqrt_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates the per-element difference between two arrays or array and a scalar.
///
/// The function subtract calculates:
/// - Difference between two arrays, when both input arrays have the same size and the same number of
/// channels:
/// 
/// - Difference between an array and a scalar, when src2 is constructed from Scalar or has the same
/// number of elements as `src1.channels()`:
/// 
/// - Difference between a scalar and an array, when src1 is constructed from Scalar or has the same
/// number of elements as `src2.channels()`:
/// 
/// - The reverse difference between a scalar and an array in the case of `SubRS`:
/// 
/// where I is a multi-dimensional index of array elements. In case of multi-channel arrays, each
/// channel is processed independently.
///
/// The first function in the list above can be replaced with matrix expressions:
/// ```C++
/// dst = src1 - src2;
/// dst -= src1; // equivalent to subtract(dst, src1, dst);
/// ```
///
/// The input arrays and the output array can all have the same or different depths. For example, you
/// can subtract to 8-bit unsigned arrays and store the difference in a 16-bit signed array. Depth of
/// the output array is determined by dtype parameter. In the second and third cases above, as well as
/// in the first case, when src1.depth() == src2.depth(), dtype can be set to the default -1. In this
/// case the output array will have the same depth as the input array, be it src1, src2 or both.
///
/// Note: Saturation is not applied when the output array has the depth CV_32S. You may even get
/// result of an incorrect sign in the case of overflow.
/// ## Parameters
/// * src1: first input array or a scalar.
/// * src2: second input array or a scalar.
/// * dst: output array of the same size and the same number of channels as the input array.
/// * mask: optional operation mask; this is an 8-bit single channel array that specifies elements
/// of the output array to be changed.
/// * dtype: optional depth of the output array
/// ## See also
/// add, addWeighted, scaleAdd, Mat::convertTo
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * mask: noArray()
/// * dtype: -1
#[inline]
pub fn subtract(src1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dtype: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src1);
extern_container_arg!(src2);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_subtract_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int(src1.as_raw__InputArray(), src2.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), dtype, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates the sum of array elements.
///
/// The function cv::sum calculates and returns the sum of array elements,
/// independently for each channel.
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array that must have from 1 to 4 channels.
/// ## See also
/// countNonZero, mean, meanStdDev, norm, minMaxLoc, reduce
#[inline]
pub fn sum_elems(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<core::Scalar> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_sum_const__InputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Swaps two matrices
#[inline]
pub fn swap(a: &mut core::Mat, b: &mut core::Mat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_swap_MatR_MatR(a.as_raw_mut_Mat(), b.as_raw_mut_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Swaps two matrices
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
#[inline]
pub fn swap_umat(a: &mut core::UMat, b: &mut core::UMat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_swap_UMatR_UMatR(a.as_raw_mut_UMat(), b.as_raw_mut_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * suffix: 0
#[inline]
pub fn tempfile(suffix: &str) -> Result<String> {
extern_container_arg!(suffix);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_tempfile_const_charX(suffix.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the default random number generator.
///
/// The function cv::theRNG returns the default random number generator. For each thread, there is a
/// separate random number generator, so you can use the function safely in multi-thread environments.
/// If you just need to get a single random number using this generator or initialize an array, you can
/// use randu or randn instead. But if you are going to generate many random numbers inside a loop, it
/// is much faster to use this function to retrieve the generator and then use RNG::operator _Tp() .
/// ## See also
/// RNG, randu, randn
#[inline]
pub fn the_rng() -> Result<core::RNG> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_theRNG(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::RNG::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the trace of a matrix.
///
/// The function cv::trace returns the sum of the diagonal elements of the
/// matrix mtx .
/// 
/// ## Parameters
/// * mtx: input matrix.
#[inline]
pub fn trace(mtx: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<core::Scalar> {
extern_container_arg!(mtx);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_trace_const__InputArrayR(mtx.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Performs the matrix transformation of every array element.
///
/// The function cv::transform performs the matrix transformation of every
/// element of the array src and stores the results in dst :
/// 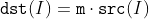
/// (when m.cols=src.channels() ), or
/// 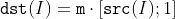
/// (when m.cols=src.channels()+1 )
///
/// Every element of the N -channel array src is interpreted as N -element
/// vector that is transformed using the M x N or M x (N+1) matrix m to
/// M-element vector - the corresponding element of the output array dst .
///
/// The function may be used for geometrical transformation of
/// N -dimensional points, arbitrary linear color space transformation (such
/// as various kinds of RGB to YUV transforms), shuffling the image
/// channels, and so forth.
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array that must have as many channels (1 to 4) as
/// m.cols or m.cols-1.
/// * dst: output array of the same size and depth as src; it has as
/// many channels as m.rows.
/// * m: transformation 2x2 or 2x3 floating-point matrix.
/// ## See also
/// perspectiveTransform, getAffineTransform, estimateAffine2D, warpAffine, warpPerspective
#[inline]
pub fn transform(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, m: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
extern_container_arg!(m);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_transform_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), m.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Transpose for n-dimensional matrices.
///
///
/// Note: Input should be continuous single-channel matrix.
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array.
/// * order: a permutation of [0,1,..,N-1] where N is the number of axes of src.
/// The i’th axis of dst will correspond to the axis numbered order[i] of the input.
/// * dst: output array of the same type as src.
#[inline]
pub fn transpose_nd(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, order: &core::Vector<i32>, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_transposeND_const__InputArrayR_const_vectorLintGR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), order.as_raw_VectorOfi32(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Transposes a matrix.
///
/// The function cv::transpose transposes the matrix src :
/// 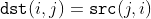
///
/// Note: No complex conjugation is done in case of a complex matrix. It
/// should be done separately if needed.
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array.
/// * dst: output array of the same type as src.
#[inline]
pub fn transpose(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_transpose_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns string of cv::Mat depth value: CV_8UC3 -> "CV_8UC3" or "<invalid type>"
#[inline]
pub fn type_to_string(typ: i32) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_typeToString_int(typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Check if use of OpenVX is enabled
#[inline]
pub fn use_openvx() -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_useOpenVX(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the status of optimized code usage.
///
/// The function returns true if the optimized code is enabled. Otherwise, it returns false.
#[inline]
pub fn use_optimized() -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_useOptimized(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn dump_bool(argument: bool) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_dumpBool_bool(argument, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn dump_c_string(argument: &str) -> Result<String> {
extern_container_arg!(argument);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_dumpCString_const_charX(argument.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn dump_double(argument: f64) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_dumpDouble_double(argument, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn dump_float(argument: f32) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_dumpFloat_float(argument, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn dump_input_array_of_arrays(argument: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<String> {
extern_container_arg!(argument);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_dumpInputArrayOfArrays_const__InputArrayR(argument.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn dump_input_array(argument: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<String> {
extern_container_arg!(argument);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_dumpInputArray_const__InputArrayR(argument.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn dump_input_output_array_of_arrays(argument: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray) -> Result<String> {
extern_container_arg!(argument);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_dumpInputOutputArrayOfArrays_const__InputOutputArrayR(argument.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn dump_input_output_array(argument: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray) -> Result<String> {
extern_container_arg!(argument);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_dumpInputOutputArray_const__InputOutputArrayR(argument.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn dump_int64(argument: i64) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_dumpInt64_int64_t(argument, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn dump_int(argument: i32) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_dumpInt_int(argument, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn dump_range(argument: &core::Range) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_dumpRange_const_RangeR(argument.as_raw_Range(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn dump_rect(argument: core::Rect) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_dumpRect_const_RectR(&argument, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn dump_rotated_rect(argument: &core::RotatedRect) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_dumpRotatedRect_const_RotatedRectR(argument.as_raw_RotatedRect(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn dump_size_t(argument: size_t) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_dumpSizeT_size_t(argument, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn dump_string(argument: &str) -> Result<String> {
extern_container_arg!(argument);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_dumpString_const_StringR(argument.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn dump_term_criteria(argument: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_dumpTermCriteria_const_TermCriteriaR(&argument, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * value: cv::Vec2i(42,24)
#[inline]
pub fn dump_vec2i(value: core::Vec2i) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_dumpVec2i_const_Vec2i(value.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn dump_vector_of_double(vec: &core::Vector<f64>) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_dumpVectorOfDouble_const_vectorLdoubleGR(vec.as_raw_VectorOff64(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn dump_vector_of_int(vec: &core::Vector<i32>) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_dumpVectorOfInt_const_vectorLintGR(vec.as_raw_VectorOfi32(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn dump_vector_of_rect(vec: &core::Vector<core::Rect>) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_dumpVectorOfRect_const_vectorLRectGR(vec.as_raw_VectorOfRect(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn get_cache_directory_for_downloads() -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_fs_getCacheDirectoryForDownloads(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn generate_vector_of_int(len: size_t, vec: &mut core::Vector<i32>) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_generateVectorOfInt_size_t_vectorLintGR(len, vec.as_raw_mut_VectorOfi32(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn generate_vector_of_mat(len: size_t, rows: i32, cols: i32, dtype: i32, vec: &mut core::Vector<core::Mat>) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_generateVectorOfMat_size_t_int_int_int_vectorLMatGR(len, rows, cols, dtype, vec.as_raw_mut_VectorOfMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn generate_vector_of_rect(len: size_t, vec: &mut core::Vector<core::Rect>) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_generateVectorOfRect_size_t_vectorLRectGR(len, vec.as_raw_mut_VectorOfRect(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn get_thread_id() -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_getThreadID(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Get global logging level
#[inline]
pub fn get_log_level() -> Result<core::LogLevel> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_logging_getLogLevel(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn get_log_tag_level(tag: &str) -> Result<core::LogLevel> {
extern_container_arg!(tag);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_logging_getLogTagLevel_const_charX(tag.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Get global log tag
#[inline]
pub fn get_global_log_tag() -> Result<core::LogTag> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_logging_internal_getGlobalLogTag(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::LogTag::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Write log message
#[inline]
pub fn write_log_message_ex(log_level: core::LogLevel, tag: &str, file: &str, line: i32, func: &str, message: &str) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(tag);
extern_container_arg!(file);
extern_container_arg!(func);
extern_container_arg!(message);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_logging_internal_writeLogMessageEx_LogLevel_const_charX_const_charX_int_const_charX_const_charX(log_level, tag.opencv_as_extern(), file.opencv_as_extern(), line, func.opencv_as_extern(), message.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Write log message
#[inline]
pub fn write_log_message(log_level: core::LogLevel, message: &str) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(message);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_logging_internal_writeLogMessage_LogLevel_const_charX(log_level, message.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn register_log_tag(plogtag: &mut core::LogTag) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_logging_registerLogTag_LogTagX(plogtag.as_raw_mut_LogTag(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Set global logging level
/// ## Returns
/// previous logging level
#[inline]
pub fn set_log_level(log_level: core::LogLevel) -> Result<core::LogLevel> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_logging_setLogLevel_LogLevel(log_level, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn set_log_tag_level(tag: &str, level: core::LogLevel) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(tag);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_logging_setLogTagLevel_const_charX_LogLevel(tag.opencv_as_extern(), level, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn test_echo_boolean_function(flag: bool) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_nested_testEchoBooleanFunction_bool(flag, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn test_async_array(argument: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<core::AsyncArray> {
extern_container_arg!(argument);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_testAsyncArray_const__InputArrayR(argument.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::AsyncArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn test_async_exception() -> Result<core::AsyncArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_testAsyncException(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::AsyncArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn test_overload_resolution_1(rect: core::Rect) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_testOverloadResolution_const_RectR(&rect, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * point: Point(42,24)
#[inline]
pub fn test_overload_resolution(value: i32, point: core::Point) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_testOverloadResolution_int_const_PointR(value, &point, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn test_overwrite_native_method(argument: i32) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_testOverwriteNativeMethod_int(argument, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn test_raise_general_exception() -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_testRaiseGeneralException(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * lambda: 2
/// * from: 3
#[inline]
pub fn test_reserved_keyword_conversion(positional_argument: i32, lambda: i32, from: i32) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_testReservedKeywordConversion_int_int_int(positional_argument, lambda, from, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn test_rotated_rect_vector(x: f32, y: f32, w: f32, h: f32, angle: f32) -> Result<core::Vector<core::RotatedRect>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_testRotatedRectVector_float_float_float_float_float(x, y, w, h, angle, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Vector::<core::RotatedRect>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn test_rotated_rect(x: f32, y: f32, w: f32, h: f32, angle: f32) -> Result<core::RotatedRect> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_testRotatedRect_float_float_float_float_float(x, y, w, h, angle, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::RotatedRect::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Converts VASurfaceID object to OutputArray.
/// ## Parameters
/// * display: - VADisplay object.
/// * surface: - source VASurfaceID object.
/// * size: - size of image represented by VASurfaceID object.
/// * dst: - destination OutputArray.
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn convert_from_va_surface(display: core::va_display, surface: core::va_surface_id, size: core::Size, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_va_intel_convertFromVASurface_VADisplay_VASurfaceID_Size_const__OutputArrayR(display, surface, size.opencv_as_extern(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Converts InputArray to VASurfaceID object.
/// ## Parameters
/// * display: - VADisplay object.
/// * src: - source InputArray.
/// * surface: - destination VASurfaceID object.
/// * size: - size of image represented by VASurfaceID object.
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn convert_to_va_surface(display: core::va_display, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, surface: core::va_surface_id, size: core::Size) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_va_intel_convertToVASurface_VADisplay_const__InputArrayR_VASurfaceID_Size(display, src.as_raw__InputArray(), surface, size.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates OpenCL context from VA.
/// ## Parameters
/// * display: - VADisplay for which CL interop should be established.
/// * tryInterop: - try to set up for interoperability, if true; set up for use slow copy if false.
/// ## Returns
/// Returns reference to OpenCL Context
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * try_interop: true
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn initialize_context_from_va(display: core::va_display, try_interop: bool) -> Result<core::Context> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_va_intel_ocl_initializeContextFromVA_VADisplay_bool(display, try_interop, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::Context::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Applies vertical concatenation to given matrices.
///
/// The function vertically concatenates two or more cv::Mat matrices (with the same number of cols).
/// ```C++
/// cv::Mat matArray[] = { cv::Mat(1, 4, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(1)),
/// cv::Mat(1, 4, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(2)),
/// cv::Mat(1, 4, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(3)),};
///
/// cv::Mat out;
/// cv::vconcat( matArray, 3, out );
/// //out:
/// //[1, 1, 1, 1;
/// // 2, 2, 2, 2;
/// // 3, 3, 3, 3]
/// ```
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array or vector of matrices. all of the matrices must have the same number of cols and the same depth.
/// * nsrc: number of matrices in src.
/// * dst: output array. It has the same number of cols and depth as the src, and the sum of rows of the src.
/// ## See also
/// cv::hconcat(const Mat*, size_t, OutputArray), cv::hconcat(InputArrayOfArrays, OutputArray) and cv::hconcat(InputArray, InputArray, OutputArray)
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ```C++
/// cv::Mat_<float> A = (cv::Mat_<float>(3, 2) << 1, 7,
/// 2, 8,
/// 3, 9);
/// cv::Mat_<float> B = (cv::Mat_<float>(3, 2) << 4, 10,
/// 5, 11,
/// 6, 12);
///
/// cv::Mat C;
/// cv::vconcat(A, B, C);
/// //C:
/// //[1, 7;
/// // 2, 8;
/// // 3, 9;
/// // 4, 10;
/// // 5, 11;
/// // 6, 12]
/// ```
///
/// * src1: first input array to be considered for vertical concatenation.
/// * src2: second input array to be considered for vertical concatenation.
/// * dst: output array. It has the same number of cols and depth as the src1 and src2, and the sum of rows of the src1 and src2.
#[inline]
pub fn vconcat2(src1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src1);
extern_container_arg!(src2);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_vconcat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src1.as_raw__InputArray(), src2.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Applies vertical concatenation to given matrices.
///
/// The function vertically concatenates two or more cv::Mat matrices (with the same number of cols).
/// ```C++
/// cv::Mat matArray[] = { cv::Mat(1, 4, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(1)),
/// cv::Mat(1, 4, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(2)),
/// cv::Mat(1, 4, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(3)),};
///
/// cv::Mat out;
/// cv::vconcat( matArray, 3, out );
/// //out:
/// //[1, 1, 1, 1;
/// // 2, 2, 2, 2;
/// // 3, 3, 3, 3]
/// ```
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array or vector of matrices. all of the matrices must have the same number of cols and the same depth.
/// * nsrc: number of matrices in src.
/// * dst: output array. It has the same number of cols and depth as the src, and the sum of rows of the src.
/// ## See also
/// cv::hconcat(const Mat*, size_t, OutputArray), cv::hconcat(InputArrayOfArrays, OutputArray) and cv::hconcat(InputArray, InputArray, OutputArray)
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ```C++
/// std::vector<cv::Mat> matrices = { cv::Mat(1, 4, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(1)),
/// cv::Mat(1, 4, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(2)),
/// cv::Mat(1, 4, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(3)),};
///
/// cv::Mat out;
/// cv::vconcat( matrices, out );
/// //out:
/// //[1, 1, 1, 1;
/// // 2, 2, 2, 2;
/// // 3, 3, 3, 3]
/// ```
///
/// * src: input array or vector of matrices. all of the matrices must have the same number of cols and the same depth
/// * dst: output array. It has the same number of cols and depth as the src, and the sum of rows of the src.
/// same depth.
#[inline]
pub fn vconcat(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_vconcat_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn write_scalar_str(fs: &mut core::FileStorage, value: &str) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(value);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_writeScalar_FileStorageR_const_StringR(fs.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), value.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn write_scalar_f64(fs: &mut core::FileStorage, value: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_writeScalar_FileStorageR_double(fs.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn write_scalar_f32(fs: &mut core::FileStorage, value: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_writeScalar_FileStorageR_float(fs.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn write_scalar_i32(fs: &mut core::FileStorage, value: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_writeScalar_FileStorageR_int(fs.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn write_mat(fs: &mut core::FileStorage, name: &str, value: &core::Mat) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_write_FileStorageR_const_StringR_const_MatR(fs.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), name.opencv_as_extern(), value.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn write_sparsemat(fs: &mut core::FileStorage, name: &str, value: &core::SparseMat) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_write_FileStorageR_const_StringR_const_SparseMatR(fs.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), name.opencv_as_extern(), value.as_raw_SparseMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn write_str(fs: &mut core::FileStorage, name: &str, value: &str) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(name);
extern_container_arg!(value);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_write_FileStorageR_const_StringR_const_StringR(fs.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), name.opencv_as_extern(), value.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn write_dmatch_vec(fs: &mut core::FileStorage, name: &str, value: &core::Vector<core::DMatch>) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_write_FileStorageR_const_StringR_const_vectorLDMatchGR(fs.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), name.opencv_as_extern(), value.as_raw_VectorOfDMatch(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn write_keypoint_vec(fs: &mut core::FileStorage, name: &str, value: &core::Vector<core::KeyPoint>) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_write_FileStorageR_const_StringR_const_vectorLKeyPointGR(fs.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), name.opencv_as_extern(), value.as_raw_VectorOfKeyPoint(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn write_f64(fs: &mut core::FileStorage, name: &str, value: f64) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_write_FileStorageR_const_StringR_double(fs.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), name.opencv_as_extern(), value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn write_f32(fs: &mut core::FileStorage, name: &str, value: f32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_write_FileStorageR_const_StringR_float(fs.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), name.opencv_as_extern(), value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// @relates cv::FileStorage
#[inline]
pub fn write_i32(fs: &mut core::FileStorage, name: &str, value: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_write_FileStorageR_const_StringR_int(fs.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), name.opencv_as_extern(), value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Algorithm]
pub trait AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Stores algorithm parameters in a file storage
#[inline]
fn write(&self, fs: &mut core::FileStorage) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Algorithm_write_const_FileStorageR(self.as_raw_Algorithm(), fs.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Stores algorithm parameters in a file storage
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
#[inline]
fn write_1(&self, fs: &mut core::FileStorage, name: &str) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Algorithm_write_const_FileStorageR_const_StringR(self.as_raw_Algorithm(), fs.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), name.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// @deprecated
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * name: String()
#[inline]
fn write_with_name(&self, fs: &core::Ptr<core::FileStorage>, name: &str) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Algorithm_write_const_const_PtrLFileStorageGR_const_StringR(self.as_raw_Algorithm(), fs.as_raw_PtrOfFileStorage(), name.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns true if the Algorithm is empty (e.g. in the very beginning or after unsuccessful read
#[inline]
fn empty(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Algorithm_empty_const(self.as_raw_Algorithm(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Saves the algorithm to a file.
/// In order to make this method work, the derived class must implement Algorithm::write(FileStorage& fs).
#[inline]
fn save(&self, filename: &str) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(filename);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Algorithm_save_const_const_StringR(self.as_raw_Algorithm(), filename.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the algorithm string identifier.
/// This string is used as top level xml/yml node tag when the object is saved to a file or string.
#[inline]
fn get_default_name(&self) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Algorithm_getDefaultName_const(self.as_raw_Algorithm(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Algorithm]
pub trait AlgorithmTrait: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Clears the algorithm state
#[inline]
fn clear(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Algorithm_clear(self.as_raw_mut_Algorithm(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Reads algorithm parameters from a file storage
#[inline]
fn read(&mut self, fn_: &core::FileNode) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Algorithm_read_const_FileNodeR(self.as_raw_mut_Algorithm(), fn_.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// This is a base class for all more or less complex algorithms in OpenCV
///
/// especially for classes of algorithms, for which there can be multiple implementations. The examples
/// are stereo correspondence (for which there are algorithms like block matching, semi-global block
/// matching, graph-cut etc.), background subtraction (which can be done using mixture-of-gaussians
/// models, codebook-based algorithm etc.), optical flow (block matching, Lucas-Kanade, Horn-Schunck
/// etc.).
///
/// Here is example of SimpleBlobDetector use in your application via Algorithm interface:
/// [Algorithm](https://github.com/opencv/opencv/blob/4.7.0/samples/cpp/tutorial_code/snippets/core_various.cpp#L1)
pub struct Algorithm {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Algorithm }
impl Drop for Algorithm {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Algorithm_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Algorithm_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Algorithm()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Algorithm {}
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for Algorithm {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for Algorithm {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Algorithm {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::Algorithm> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Algorithm_Algorithm(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Algorithm::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::AsyncArray]
pub trait AsyncArrayTraitConst {
fn as_raw_AsyncArray(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Fetch the result.
/// ## Parameters
/// * dst:[out] destination array
///
/// Waits for result until container has valid result.
/// Throws exception if exception was stored as a result.
///
/// Throws exception on invalid container state.
///
///
/// Note: Result or stored exception can be fetched only once.
#[inline]
fn get(&self, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_AsyncArray_get_const_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_AsyncArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Retrieving the result with timeout
/// ## Parameters
/// * dst:[out] destination array
/// * timeoutNs: timeout in nanoseconds, -1 for infinite wait
///
/// ## Returns
/// true if result is ready, false if the timeout has expired
///
///
/// Note: Result or stored exception can be fetched only once.
#[inline]
fn get_with_timeout(&self, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, timeout_ns: i64) -> Result<bool> {
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_AsyncArray_get_const_const__OutputArrayR_int64_t(self.as_raw_AsyncArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), timeout_ns, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_with_timeout_f64(&self, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, timeout_ns: f64) -> Result<bool> {
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_AsyncArray_get_const_const__OutputArrayR_double(self.as_raw_AsyncArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), timeout_ns, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn wait_for(&self, timeout_ns: i64) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_AsyncArray_wait_for_const_int64_t(self.as_raw_AsyncArray(), timeout_ns, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn wait_for_f64(&self, timeout_ns: f64) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_AsyncArray_wait_for_const_double(self.as_raw_AsyncArray(), timeout_ns, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn valid(&self) -> bool {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_AsyncArray_valid_const(self.as_raw_AsyncArray()) };
ret
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::AsyncArray]
pub trait AsyncArrayTrait: core::AsyncArrayTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_AsyncArray(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn release(&mut self) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_AsyncArray_release(self.as_raw_mut_AsyncArray()) };
ret
}
}
/// Returns result of asynchronous operations
///
/// Object has attached asynchronous state.
/// Assignment operator doesn't clone asynchronous state (it is shared between all instances).
///
/// Result can be fetched via get() method only once.
pub struct AsyncArray {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { AsyncArray }
impl Drop for AsyncArray {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_AsyncArray_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_AsyncArray_delete(self.as_raw_mut_AsyncArray()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for AsyncArray {}
impl core::AsyncArrayTraitConst for AsyncArray {
#[inline] fn as_raw_AsyncArray(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AsyncArrayTrait for AsyncArray {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_AsyncArray(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl AsyncArray {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> core::AsyncArray {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_AsyncArray_AsyncArray() };
let ret = unsafe { core::AsyncArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy(o: &core::AsyncArray) -> core::AsyncArray {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_AsyncArray_AsyncArray_const_AsyncArrayR(o.as_raw_AsyncArray()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::AsyncArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy_mut(mut o: core::AsyncArray) -> Result<core::AsyncArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_AsyncArray_AsyncArray_AsyncArrayRR(o.as_raw_mut_AsyncArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::AsyncArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl Default for AsyncArray {
#[inline]
/// Forwards to infallible Self::default()
fn default() -> Self {
Self::default()
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::AsyncPromise]
pub trait AsyncPromiseTraitConst {
fn as_raw_AsyncPromise(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn _get_impl(&self) -> *mut c_void {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_AsyncPromise__getImpl_const(self.as_raw_AsyncPromise()) };
ret
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::AsyncPromise]
pub trait AsyncPromiseTrait: core::AsyncPromiseTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_AsyncPromise(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn release(&mut self) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_AsyncPromise_release(self.as_raw_mut_AsyncPromise()) };
ret
}
/// Returns associated AsyncArray
///
/// Note: Can be called once
#[inline]
fn get_array_result(&mut self) -> Result<core::AsyncArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_AsyncPromise_getArrayResult(self.as_raw_mut_AsyncPromise(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::AsyncArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Stores asynchronous result.
/// ## Parameters
/// * value: result
#[inline]
fn set_value(&mut self, value: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(value);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_AsyncPromise_setValue_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_AsyncPromise(), value.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Stores exception.
/// ## Parameters
/// * exception: exception to be raised in AsyncArray
#[inline]
fn set_exception(&mut self, exception: &core::Exception) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_AsyncPromise_setException_const_ExceptionR(self.as_raw_mut_AsyncPromise(), exception.as_raw_Exception(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Provides result of asynchronous operations
pub struct AsyncPromise {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { AsyncPromise }
impl Drop for AsyncPromise {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_AsyncPromise_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_AsyncPromise_delete(self.as_raw_mut_AsyncPromise()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for AsyncPromise {}
impl core::AsyncPromiseTraitConst for AsyncPromise {
#[inline] fn as_raw_AsyncPromise(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AsyncPromiseTrait for AsyncPromise {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_AsyncPromise(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl AsyncPromise {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> core::AsyncPromise {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_AsyncPromise_AsyncPromise() };
let ret = unsafe { core::AsyncPromise::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy(o: &core::AsyncPromise) -> core::AsyncPromise {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_AsyncPromise_AsyncPromise_const_AsyncPromiseR(o.as_raw_AsyncPromise()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::AsyncPromise::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy_mut(mut o: core::AsyncPromise) -> Result<core::AsyncPromise> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_AsyncPromise_AsyncPromise_AsyncPromiseRR(o.as_raw_mut_AsyncPromise(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::AsyncPromise::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl Default for AsyncPromise {
#[inline]
/// Forwards to infallible Self::default()
fn default() -> Self {
Self::default()
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::CommandLineParser]
pub trait CommandLineParserTraitConst {
fn as_raw_CommandLineParser(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Returns application path
///
/// This method returns the path to the executable from the command line (`argv[0]`).
///
/// For example, if the application has been started with such a command:
/// ```C++
/// $ ./bin/my-executable
/// ```
///
/// this method will return `./bin`.
#[inline]
fn get_path_to_application(&self) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_CommandLineParser_getPathToApplication_const(self.as_raw_CommandLineParser(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Check if field was provided in the command line
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * name: argument name to check
#[inline]
fn has(&self, name: &str) -> Result<bool> {
extern_container_arg!(name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_CommandLineParser_has_const_const_StringR(self.as_raw_CommandLineParser(), name.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Check for parsing errors
///
/// Returns false if error occurred while accessing the parameters (bad conversion, missing arguments,
/// etc.). Call [printErrors] to print error messages list.
#[inline]
fn check(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_CommandLineParser_check_const(self.as_raw_CommandLineParser(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Print help message
///
/// This method will print standard help message containing the about message and arguments description.
/// ## See also
/// about
#[inline]
fn print_message(&self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_CommandLineParser_printMessage_const(self.as_raw_CommandLineParser(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Print list of errors occurred
/// ## See also
/// check
#[inline]
fn print_errors(&self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_CommandLineParser_printErrors_const(self.as_raw_CommandLineParser(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::CommandLineParser]
pub trait CommandLineParserTrait: core::CommandLineParserTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_CommandLineParser(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Set the about message
///
/// The about message will be shown when [printMessage] is called, right before arguments table.
#[inline]
fn about(&mut self, message: &str) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(message);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_CommandLineParser_about_const_StringR(self.as_raw_mut_CommandLineParser(), message.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Designed for command line parsing
///
/// The sample below demonstrates how to use CommandLineParser:
/// ```C++
/// CommandLineParser parser(argc, argv, keys);
/// parser.about("Application name v1.0.0");
///
/// if (parser.has("help"))
/// {
/// parser.printMessage();
/// return 0;
/// }
///
/// int N = parser.get<int>("N");
/// double fps = parser.get<double>("fps");
/// String path = parser.get<String>("path");
///
/// use_time_stamp = parser.has("timestamp");
///
/// String img1 = parser.get<String>(0);
/// String img2 = parser.get<String>(1);
///
/// int repeat = parser.get<int>(2);
///
/// if (!parser.check())
/// {
/// parser.printErrors();
/// return 0;
/// }
/// ```
///
///
/// ### Keys syntax
///
/// The keys parameter is a string containing several blocks, each one is enclosed in curly braces and
/// describes one argument. Each argument contains three parts separated by the `|` symbol:
///
/// -# argument names is a space-separated list of option synonyms (to mark argument as positional, prefix it with the `@` symbol)
/// -# default value will be used if the argument was not provided (can be empty)
/// -# help message (can be empty)
///
/// For example:
///
/// ```C++
/// const String keys =
/// "{help h usage ? | | print this message }"
/// "{@image1 | | image1 for compare }"
/// "{@image2 |<none>| image2 for compare }"
/// "{@repeat |1 | number }"
/// "{path |. | path to file }"
/// "{fps | -1.0 | fps for output video }"
/// "{N count |100 | count of objects }"
/// "{ts timestamp | | use time stamp }"
/// ;
/// }
/// ```
///
///
/// Note that there are no default values for `help` and `timestamp` so we can check their presence using the `has()` method.
/// Arguments with default values are considered to be always present. Use the `get()` method in these cases to check their
/// actual value instead.
///
/// String keys like `get<String>("@image1")` return the empty string `""` by default - even with an empty default value.
/// Use the special `<none>` default value to enforce that the returned string must not be empty. (like in `get<String>("@image2")`)
///
/// ### Usage
///
/// For the described keys:
///
/// ```C++
/// # Good call (3 positional parameters: image1, image2 and repeat; N is 200, ts is true)
/// $ ./app -N=200 1.png 2.jpg 19 -ts
///
/// # Bad call
/// $ ./app -fps=aaa
/// ERRORS:
/// Parameter "fps": can not convert: [aaa] to [double]
/// ```
///
pub struct CommandLineParser {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { CommandLineParser }
impl Drop for CommandLineParser {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_CommandLineParser_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_CommandLineParser_delete(self.as_raw_mut_CommandLineParser()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for CommandLineParser {}
impl core::CommandLineParserTraitConst for CommandLineParser {
#[inline] fn as_raw_CommandLineParser(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::CommandLineParserTrait for CommandLineParser {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_CommandLineParser(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl CommandLineParser {
/// Constructor
///
/// Initializes command line parser object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * argc: number of command line arguments (from main())
/// * argv: array of command line arguments (from main())
/// * keys: string describing acceptable command line parameters (see class description for syntax)
#[inline]
pub fn new(argc: i32, argv: &[&str], keys: &str) -> Result<core::CommandLineParser> {
string_array_arg!(argv);
extern_container_arg!(keys);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_CommandLineParser_CommandLineParser_int_const_charXX_const_StringR(argc, argv.as_ptr(), keys.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::CommandLineParser::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Copy constructor
#[inline]
pub fn copy(parser: &core::CommandLineParser) -> Result<core::CommandLineParser> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_CommandLineParser_CommandLineParser_const_CommandLineParserR(parser.as_raw_CommandLineParser(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::CommandLineParser::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::ConjGradSolver]
pub trait ConjGradSolverConst: core::MinProblemSolverConst {
fn as_raw_ConjGradSolver(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// This class is used to perform the non-linear non-constrained minimization of a function
/// with known gradient,
///
/// defined on an *n*-dimensional Euclidean space, using the **Nonlinear Conjugate Gradient method**.
/// The implementation was done based on the beautifully clear explanatory article [An Introduction to
/// the Conjugate Gradient Method Without the Agonizing
/// Pain](http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~quake-papers/painless-conjugate-gradient.pdf) by Jonathan Richard
/// Shewchuk. The method can be seen as an adaptation of a standard Conjugate Gradient method (see, for
/// example <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conjugate_gradient_method>) for numerically solving the
/// systems of linear equations.
///
/// It should be noted, that this method, although deterministic, is rather a heuristic method and
/// therefore may converge to a local minima, not necessary a global one. What is even more disastrous,
/// most of its behaviour is ruled by gradient, therefore it essentially cannot distinguish between
/// local minima and maxima. Therefore, if it starts sufficiently near to the local maximum, it may
/// converge to it. Another obvious restriction is that it should be possible to compute the gradient of
/// a function at any point, thus it is preferable to have analytic expression for gradient and
/// computational burden should be born by the user.
///
/// The latter responsibility is accomplished via the getGradient method of a
/// MinProblemSolver::Function interface (which represents function being optimized). This method takes
/// point a point in *n*-dimensional space (first argument represents the array of coordinates of that
/// point) and compute its gradient (it should be stored in the second argument as an array).
///
///
/// Note: class ConjGradSolver thus does not add any new methods to the basic MinProblemSolver interface.
///
///
/// Note: term criteria should meet following condition:
/// ```C++
/// termcrit.type == (TermCriteria::MAX_ITER + TermCriteria::EPS) && termcrit.epsilon > 0 && termcrit.maxCount > 0
/// // or
/// termcrit.type == TermCriteria::MAX_ITER) && termcrit.maxCount > 0
/// ```
///
pub trait ConjGradSolver: core::ConjGradSolverConst + core::MinProblemSolver {
fn as_raw_mut_ConjGradSolver(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
impl dyn ConjGradSolver + '_ {
/// This function returns the reference to the ready-to-use ConjGradSolver object.
///
/// All the parameters are optional, so this procedure can be called even without parameters at
/// all. In this case, the default values will be used. As default value for terminal criteria are
/// the only sensible ones, MinProblemSolver::setFunction() should be called upon the obtained
/// object, if the function was not given to create(). Otherwise, the two ways (submit it to
/// create() or miss it out and call the MinProblemSolver::setFunction()) are absolutely equivalent
/// (and will drop the same errors in the same way, should invalid input be detected).
/// ## Parameters
/// * f: Pointer to the function that will be minimized, similarly to the one you submit via
/// MinProblemSolver::setFunction.
/// * termcrit: Terminal criteria to the algorithm, similarly to the one you submit via
/// MinProblemSolver::setTermCriteria.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * f: Ptr<ConjGradSolver::Function>()
/// * termcrit: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::MAX_ITER+TermCriteria::EPS,5000,0.000001)
#[inline]
pub fn create(f: &core::Ptr<dyn core::MinProblemSolver_Function>, termcrit: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn core::ConjGradSolver>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ConjGradSolver_create_const_PtrLFunctionGR_TermCriteria(f.as_raw_PtrOfMinProblemSolver_Function(), termcrit.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn core::ConjGradSolver>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Class for matching keypoint descriptors
///
/// query descriptor index, train descriptor index, train image index, and distance between
/// descriptors.
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)]
pub struct DMatch {
/// query descriptor index
pub query_idx: i32,
/// train descriptor index
pub train_idx: i32,
/// train image index
pub img_idx: i32,
pub distance: f32,
}
opencv_type_simple! { core::DMatch }
impl DMatch {
#[inline]
pub fn less_than(self, m: core::DMatch) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DMatch_operatorL_const_const_DMatchR(self.opencv_as_extern(), &m, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ////////////////////////////// DMatch ////////////////////////////////
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::DMatch> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DMatch_DMatch(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn new(_query_idx: i32, _train_idx: i32, _distance: f32) -> Result<core::DMatch> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DMatch_DMatch_int_int_float(_query_idx, _train_idx, _distance, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn new_index(_query_idx: i32, _train_idx: i32, _img_idx: i32, _distance: f32) -> Result<core::DMatch> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DMatch_DMatch_int_int_int_float(_query_idx, _train_idx, _img_idx, _distance, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::DownhillSolver]
pub trait DownhillSolverConst: core::MinProblemSolverConst {
fn as_raw_DownhillSolver(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Returns the initial step that will be used in downhill simplex algorithm.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * step: Initial step that will be used in algorithm. Note, that although corresponding setter
/// accepts column-vectors as well as row-vectors, this method will return a row-vector.
/// ## See also
/// DownhillSolver::setInitStep
#[inline]
fn get_init_step(&self, step: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(step);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DownhillSolver_getInitStep_const_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_DownhillSolver(), step.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// This class is used to perform the non-linear non-constrained minimization of a function,
///
/// defined on an `n`-dimensional Euclidean space, using the **Nelder-Mead method**, also known as
/// **downhill simplex method**. The basic idea about the method can be obtained from
/// <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nelder-Mead_method>.
///
/// It should be noted, that this method, although deterministic, is rather a heuristic and therefore
/// may converge to a local minima, not necessary a global one. It is iterative optimization technique,
/// which at each step uses an information about the values of a function evaluated only at `n+1`
/// points, arranged as a *simplex* in `n`-dimensional space (hence the second name of the method). At
/// each step new point is chosen to evaluate function at, obtained value is compared with previous
/// ones and based on this information simplex changes it's shape , slowly moving to the local minimum.
/// Thus this method is using *only* function values to make decision, on contrary to, say, Nonlinear
/// Conjugate Gradient method (which is also implemented in optim).
///
/// Algorithm stops when the number of function evaluations done exceeds termcrit.maxCount, when the
/// function values at the vertices of simplex are within termcrit.epsilon range or simplex becomes so
/// small that it can enclosed in a box with termcrit.epsilon sides, whatever comes first, for some
/// defined by user positive integer termcrit.maxCount and positive non-integer termcrit.epsilon.
///
///
/// Note: DownhillSolver is a derivative of the abstract interface
/// cv::MinProblemSolver, which in turn is derived from the Algorithm interface and is used to
/// encapsulate the functionality, common to all non-linear optimization algorithms in the optim
/// module.
///
///
/// Note: term criteria should meet following condition:
/// ```C++
/// termcrit.type == (TermCriteria::MAX_ITER + TermCriteria::EPS) && termcrit.epsilon > 0 && termcrit.maxCount > 0
/// ```
///
pub trait DownhillSolver: core::DownhillSolverConst + core::MinProblemSolver {
fn as_raw_mut_DownhillSolver(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Sets the initial step that will be used in downhill simplex algorithm.
///
/// Step, together with initial point (given in DownhillSolver::minimize) are two `n`-dimensional
/// vectors that are used to determine the shape of initial simplex. Roughly said, initial point
/// determines the position of a simplex (it will become simplex's centroid), while step determines the
/// spread (size in each dimension) of a simplex. To be more precise, if  are
/// the initial step and initial point respectively, the vertices of a simplex will be:
///  and  for  where  denotes
/// projections of the initial step of *n*-th coordinate (the result of projection is treated to be
/// vector given by , where  form canonical basis)
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * step: Initial step that will be used in algorithm. Roughly said, it determines the spread
/// (size in each dimension) of an initial simplex.
#[inline]
fn set_init_step(&mut self, step: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(step);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DownhillSolver_setInitStep_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_DownhillSolver(), step.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl dyn DownhillSolver + '_ {
/// This function returns the reference to the ready-to-use DownhillSolver object.
///
/// All the parameters are optional, so this procedure can be called even without parameters at
/// all. In this case, the default values will be used. As default value for terminal criteria are
/// the only sensible ones, MinProblemSolver::setFunction() and DownhillSolver::setInitStep()
/// should be called upon the obtained object, if the respective parameters were not given to
/// create(). Otherwise, the two ways (give parameters to createDownhillSolver() or miss them out
/// and call the MinProblemSolver::setFunction() and DownhillSolver::setInitStep()) are absolutely
/// equivalent (and will drop the same errors in the same way, should invalid input be detected).
/// ## Parameters
/// * f: Pointer to the function that will be minimized, similarly to the one you submit via
/// MinProblemSolver::setFunction.
/// * initStep: Initial step, that will be used to construct the initial simplex, similarly to the one
/// you submit via MinProblemSolver::setInitStep.
/// * termcrit: Terminal criteria to the algorithm, similarly to the one you submit via
/// MinProblemSolver::setTermCriteria.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * f: Ptr<MinProblemSolver::Function>()
/// * init_step: Mat_<double>(1,1,0.0)
/// * termcrit: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::MAX_ITER+TermCriteria::EPS,5000,0.000001)
#[inline]
pub fn create(f: &core::Ptr<dyn core::MinProblemSolver_Function>, init_step: &dyn core::ToInputArray, termcrit: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn core::DownhillSolver>> {
extern_container_arg!(init_step);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_DownhillSolver_create_const_PtrLFunctionGR_const__InputArrayR_TermCriteria(f.as_raw_PtrOfMinProblemSolver_Function(), init_step.as_raw__InputArray(), termcrit.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn core::DownhillSolver>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Exception]
pub trait ExceptionTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Exception(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// the formatted error message
#[inline]
fn msg(&self) -> String {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Exception_getPropMsg_const(self.as_raw_Exception()) };
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// error code see also: CVStatus
#[inline]
fn code(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Exception_getPropCode_const(self.as_raw_Exception()) };
ret
}
/// error description
#[inline]
fn err(&self) -> String {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Exception_getPropErr_const(self.as_raw_Exception()) };
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// function name. Available only when the compiler supports getting it
#[inline]
fn func(&self) -> String {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Exception_getPropFunc_const(self.as_raw_Exception()) };
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// source file name where the error has occurred
#[inline]
fn file(&self) -> String {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Exception_getPropFile_const(self.as_raw_Exception()) };
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// line number in the source file where the error has occurred
#[inline]
fn line(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Exception_getPropLine_const(self.as_raw_Exception()) };
ret
}
/// !
/// \return the error description and the context as a text string.
#[inline]
fn what(&self) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Exception_what_const(self.as_raw_Exception(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Exception]
pub trait ExceptionTrait: core::ExceptionTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Exception(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// the formatted error message
#[inline]
fn set_msg(&mut self, val: &str) {
extern_container_arg!(nofail mut val);
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Exception_setPropMsg_String(self.as_raw_mut_Exception(), val.opencv_as_extern_mut()) };
ret
}
/// error code see also: CVStatus
#[inline]
fn set_code(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Exception_setPropCode_int(self.as_raw_mut_Exception(), val) };
ret
}
/// error description
#[inline]
fn set_err(&mut self, val: &str) {
extern_container_arg!(nofail mut val);
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Exception_setPropErr_String(self.as_raw_mut_Exception(), val.opencv_as_extern_mut()) };
ret
}
/// function name. Available only when the compiler supports getting it
#[inline]
fn set_func(&mut self, val: &str) {
extern_container_arg!(nofail mut val);
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Exception_setPropFunc_String(self.as_raw_mut_Exception(), val.opencv_as_extern_mut()) };
ret
}
/// source file name where the error has occurred
#[inline]
fn set_file(&mut self, val: &str) {
extern_container_arg!(nofail mut val);
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Exception_setPropFile_String(self.as_raw_mut_Exception(), val.opencv_as_extern_mut()) };
ret
}
/// line number in the source file where the error has occurred
#[inline]
fn set_line(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Exception_setPropLine_int(self.as_raw_mut_Exception(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn format_message(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Exception_formatMessage(self.as_raw_mut_Exception(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// ! Class passed to an error.
///
/// This class encapsulates all or almost all necessary
/// information about the error happened in the program. The exception is
/// usually constructed and thrown implicitly via CV_Error and CV_Error_ macros.
/// ## See also
/// error
pub struct Exception {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Exception }
impl Drop for Exception {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Exception_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Exception_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Exception()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Exception {}
impl core::ExceptionTraitConst for Exception {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Exception(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::ExceptionTrait for Exception {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Exception(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Exception {
/// !
/// Default constructor
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::Exception> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Exception_Exception(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Exception::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// !
/// Full constructor. Normally the constructor is not called explicitly.
/// Instead, the macros CV_Error(), CV_Error_() and CV_Assert() are used.
#[inline]
pub fn new(_code: i32, _err: &str, _func: &str, _file: &str, _line: i32) -> Result<core::Exception> {
extern_container_arg!(_err);
extern_container_arg!(_func);
extern_container_arg!(_file);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Exception_Exception_int_const_StringR_const_StringR_const_StringR_int(_code, _err.opencv_as_extern(), _func.opencv_as_extern(), _file.opencv_as_extern(), _line, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Exception::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::FileNode]
pub trait FileNodeTraitConst {
fn as_raw_FileNode(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn block_idx(&self) -> size_t {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_getPropBlockIdx_const(self.as_raw_FileNode()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn ofs(&self) -> size_t {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_getPropOfs_const(self.as_raw_FileNode()) };
ret
}
/// Returns element of a mapping node or a sequence node.
/// ## Parameters
/// * nodename: Name of an element in the mapping node.
/// ## Returns
/// Returns the element with the given identifier.
#[inline]
fn get(&self, nodename: &str) -> Result<core::FileNode> {
extern_container_arg!(nodename);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_operator___const_const_StringR(self.as_raw_FileNode(), nodename.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::FileNode::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns element of a mapping node or a sequence node.
/// ## Parameters
/// * nodename: Name of an element in the mapping node.
/// ## Returns
/// Returns the element with the given identifier.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * nodename: Name of an element in the mapping node.
#[inline]
fn get_node(&self, nodename: &str) -> Result<core::FileNode> {
extern_container_arg!(nodename);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_operator___const_const_charX(self.as_raw_FileNode(), nodename.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::FileNode::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns element of a mapping node or a sequence node.
/// ## Parameters
/// * nodename: Name of an element in the mapping node.
/// ## Returns
/// Returns the element with the given identifier.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * i: Index of an element in the sequence node.
#[inline]
fn at(&self, i: i32) -> Result<core::FileNode> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_operator___const_int(self.as_raw_FileNode(), i, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::FileNode::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns keys of a mapping node.
/// ## Returns
/// Keys of a mapping node.
#[inline]
fn keys(&self) -> Result<core::Vector<String>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_keys_const(self.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Vector::<String>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns type of the node.
/// ## Returns
/// Type of the node. See FileNode::Type
#[inline]
fn typ(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_type_const(self.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns true if the node is empty
#[inline]
fn empty(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_empty_const(self.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns true if the node is a "none" object
#[inline]
fn is_none(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_isNone_const(self.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns true if the node is a sequence
#[inline]
fn is_seq(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_isSeq_const(self.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns true if the node is a mapping
#[inline]
fn is_map(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_isMap_const(self.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns true if the node is an integer
#[inline]
fn is_int(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_isInt_const(self.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns true if the node is a floating-point number
#[inline]
fn is_real(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_isReal_const(self.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns true if the node is a text string
#[inline]
fn is_string(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_isString_const(self.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns true if the node has a name
#[inline]
fn is_named(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_isNamed_const(self.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns the node name or an empty string if the node is nameless
#[inline]
fn name(&self) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_name_const(self.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns the number of elements in the node, if it is a sequence or mapping, or 1 otherwise.
#[inline]
fn size(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_size_const(self.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns raw size of the FileNode in bytes
#[inline]
fn raw_size(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_rawSize_const(self.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns the node content as an integer. If the node stores floating-point number, it is rounded.
#[inline]
fn to_i32(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_operator_int_const(self.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns the node content as float
#[inline]
fn to_f32(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_operator_float_const(self.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns the node content as double
#[inline]
fn to_f64(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_operator_double_const(self.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns the node content as text string
#[inline]
fn to_string(&self) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_operator_std_string_const(self.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn ptr(&self) -> Result<*const u8> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_ptr_const(self.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns iterator pointing to the first node element
#[inline]
fn begin(&self) -> Result<core::FileNodeIterator> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_begin_const(self.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::FileNodeIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns iterator pointing to the element following the last node element
#[inline]
fn end(&self) -> Result<core::FileNodeIterator> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_end_const(self.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::FileNodeIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Reads node elements to the buffer with the specified format.
///
/// Usually it is more convenient to use operator `>>` instead of this method.
/// ## Parameters
/// * fmt: Specification of each array element. See [format_spec] "format specification"
/// * vec: Pointer to the destination array.
/// * len: Number of bytes to read (buffer size limit). If it is greater than number of
/// remaining elements then all of them will be read.
#[inline]
unsafe fn read_raw(&self, fmt: &str, vec: *mut c_void, len: size_t) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(fmt);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_FileNode_readRaw_const_const_StringR_voidX_size_t(self.as_raw_FileNode(), fmt.opencv_as_extern(), vec, len, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Simplified reading API to use with bindings.
#[inline]
fn real(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_real_const(self.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Simplified reading API to use with bindings.
#[inline]
fn string(&self) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_string_const(self.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Simplified reading API to use with bindings.
#[inline]
fn mat(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_mat_const(self.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::FileNode]
pub trait FileNodeTrait: core::FileNodeTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_FileNode(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_block_idx(&mut self, val: size_t) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_setPropBlockIdx_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_FileNode(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_ofs(&mut self, val: size_t) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_setPropOfs_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_FileNode(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn ptr_1(&mut self) -> Result<*mut u8> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_ptr(self.as_raw_mut_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Internal method used when reading FileStorage.
/// Sets the type (int, real or string) and value of the previously created node.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * len: -1
#[inline]
unsafe fn set_value(&mut self, typ: i32, value: *const c_void, len: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_FileNode_setValue_int_const_voidX_int(self.as_raw_mut_FileNode(), typ, value, len, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// File Storage Node class.
///
/// The node is used to store each and every element of the file storage opened for reading. When
/// XML/YAML file is read, it is first parsed and stored in the memory as a hierarchical collection of
/// nodes. Each node can be a "leaf" that is contain a single number or a string, or be a collection of
/// other nodes. There can be named collections (mappings) where each element has a name and it is
/// accessed by a name, and ordered collections (sequences) where elements do not have names but rather
/// accessed by index. Type of the file node can be determined using FileNode::type method.
///
/// Note that file nodes are only used for navigating file storages opened for reading. When a file
/// storage is opened for writing, no data is stored in memory after it is written.
pub struct FileNode {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { FileNode }
impl Drop for FileNode {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_FileNode_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_FileNode_delete(self.as_raw_mut_FileNode()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for FileNode {}
impl core::FileNodeTraitConst for FileNode {
#[inline] fn as_raw_FileNode(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::FileNodeTrait for FileNode {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_FileNode(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl FileNode {
/// The constructors.
///
/// These constructors are used to create a default file node, construct it from obsolete structures or
/// from the another file node.
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::FileNode> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_FileNode(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::FileNode::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// The constructors.
///
/// These constructors are used to create a default file node, construct it from obsolete structures or
/// from the another file node.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * fs: Pointer to the file storage structure.
/// * blockIdx: Index of the memory block where the file node is stored
/// * ofs: Offset in bytes from the beginning of the serialized storage
///
/// @deprecated
#[inline]
pub fn new(fs: &core::FileStorage, block_idx: size_t, ofs: size_t) -> Result<core::FileNode> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_FileNode_const_FileStorageX_size_t_size_t(fs.as_raw_FileStorage(), block_idx, ofs, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::FileNode::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// The constructors.
///
/// These constructors are used to create a default file node, construct it from obsolete structures or
/// from the another file node.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * node: File node to be used as initialization for the created file node.
#[inline]
pub fn copy(node: &core::FileNode) -> Result<core::FileNode> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_FileNode_const_FileNodeR(node.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::FileNode::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn is_map(flags: i32) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_isMap_int(flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn is_seq(flags: i32) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_isSeq_int(flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn is_collection(flags: i32) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_isCollection_int(flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn is_empty_collection(flags: i32) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_isEmptyCollection_int(flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn is_flow(flags: i32) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNode_isFlow_int(flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::FileNodeIterator]
pub trait FileNodeIteratorTraitConst {
fn as_raw_FileNodeIterator(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// returns the currently observed element
#[inline]
fn try_deref(&self) -> Result<core::FileNode> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNodeIterator_operatorX_const(self.as_raw_FileNodeIterator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::FileNode::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns the number of remaining (not read yet) elements
#[inline]
fn remaining(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNodeIterator_remaining_const(self.as_raw_FileNodeIterator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn equal_to(&self, it: &core::FileNodeIterator) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNodeIterator_equalTo_const_const_FileNodeIteratorR(self.as_raw_FileNodeIterator(), it.as_raw_FileNodeIterator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::FileNodeIterator]
pub trait FileNodeIteratorTrait: core::FileNodeIteratorTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_FileNodeIterator(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// moves iterator to the next node
#[inline]
fn incr(&mut self) -> Result<core::FileNodeIterator> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNodeIterator_operatorAA(self.as_raw_mut_FileNodeIterator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::FileNodeIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Reads node elements to the buffer with the specified format.
///
/// Usually it is more convenient to use operator `>>` instead of this method.
/// ## Parameters
/// * fmt: Specification of each array element. See [format_spec] "format specification"
/// * vec: Pointer to the destination array.
/// * len: Number of bytes to read (buffer size limit). If it is greater than number of
/// remaining elements then all of them will be read.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * len: (size_t)INT_MAX
#[inline]
unsafe fn read_raw(&mut self, fmt: &str, vec: *mut c_void, len: size_t) -> Result<core::FileNodeIterator> {
extern_container_arg!(fmt);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_FileNodeIterator_readRaw_const_StringR_voidX_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_FileNodeIterator(), fmt.opencv_as_extern(), vec, len, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::FileNodeIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// used to iterate through sequences and mappings.
///
/// A standard STL notation, with node.begin(), node.end() denoting the beginning and the end of a
/// sequence, stored in node. See the data reading sample in the beginning of the section.
pub struct FileNodeIterator {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { FileNodeIterator }
impl Drop for FileNodeIterator {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_FileNodeIterator_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_FileNodeIterator_delete(self.as_raw_mut_FileNodeIterator()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for FileNodeIterator {}
impl core::FileNodeIteratorTraitConst for FileNodeIterator {
#[inline] fn as_raw_FileNodeIterator(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::FileNodeIteratorTrait for FileNodeIterator {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_FileNodeIterator(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl FileNodeIterator {
/// The constructors.
///
/// These constructors are used to create a default iterator, set it to specific element in a file node
/// or construct it from another iterator.
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::FileNodeIterator> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNodeIterator_FileNodeIterator(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::FileNodeIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// The constructors.
///
/// These constructors are used to create a default iterator, set it to specific element in a file node
/// or construct it from another iterator.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * node: File node - the collection to iterate over;
/// it can be a scalar (equivalent to 1-element collection) or "none" (equivalent to empty collection).
/// * seekEnd: - true if iterator needs to be set after the last element of the node;
/// that is:
/// * node.begin() => FileNodeIterator(node, false)
/// * node.end() => FileNodeIterator(node, true)
#[inline]
pub fn new(node: &core::FileNode, seek_end: bool) -> Result<core::FileNodeIterator> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNodeIterator_FileNodeIterator_const_FileNodeR_bool(node.as_raw_FileNode(), seek_end, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::FileNodeIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// The constructors.
///
/// These constructors are used to create a default iterator, set it to specific element in a file node
/// or construct it from another iterator.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * it: Iterator to be used as initialization for the created iterator.
#[inline]
pub fn copy(it: &core::FileNodeIterator) -> Result<core::FileNodeIterator> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileNodeIterator_FileNodeIterator_const_FileNodeIteratorR(it.as_raw_FileNodeIterator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::FileNodeIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::FileStorage]
pub trait FileStorageTraitConst {
fn as_raw_FileStorage(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn state(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_FileStorage_getPropState_const(self.as_raw_FileStorage()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn elname(&self) -> String {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_FileStorage_getPropElname_const(self.as_raw_FileStorage()) };
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// Checks whether the file is opened.
///
/// ## Returns
/// true if the object is associated with the current file and false otherwise. It is a
/// good practice to call this method after you tried to open a file.
#[inline]
fn is_opened(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileStorage_isOpened_const(self.as_raw_FileStorage(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the first element of the top-level mapping.
/// ## Returns
/// The first element of the top-level mapping.
#[inline]
fn get_first_top_level_node(&self) -> Result<core::FileNode> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileStorage_getFirstTopLevelNode_const(self.as_raw_FileStorage(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::FileNode::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the top-level mapping
/// ## Parameters
/// * streamidx: Zero-based index of the stream. In most cases there is only one stream in the file.
/// However, YAML supports multiple streams and so there can be several.
/// ## Returns
/// The top-level mapping.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * streamidx: 0
#[inline]
fn root(&self, streamidx: i32) -> Result<core::FileNode> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileStorage_root_const_int(self.as_raw_FileStorage(), streamidx, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::FileNode::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the specified element of the top-level mapping.
/// ## Parameters
/// * nodename: Name of the file node.
/// ## Returns
/// Node with the given name.
#[inline]
fn get(&self, nodename: &str) -> Result<core::FileNode> {
extern_container_arg!(nodename);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileStorage_operator___const_const_StringR(self.as_raw_FileStorage(), nodename.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::FileNode::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the specified element of the top-level mapping.
/// ## Parameters
/// * nodename: Name of the file node.
/// ## Returns
/// Node with the given name.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
#[inline]
fn get_node(&self, nodename: &str) -> Result<core::FileNode> {
extern_container_arg!(nodename);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileStorage_operator___const_const_charX(self.as_raw_FileStorage(), nodename.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::FileNode::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the current format.
/// ## Returns
/// The current format, see FileStorage::Mode
#[inline]
fn get_format(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileStorage_getFormat_const(self.as_raw_FileStorage(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::FileStorage]
pub trait FileStorageTrait: core::FileStorageTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_FileStorage(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_state(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_FileStorage_setPropState_int(self.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_elname(&mut self, val: &str) {
extern_container_arg!(nofail mut val);
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_FileStorage_setPropElname_string(self.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), val.opencv_as_extern_mut()) };
ret
}
/// Opens a file.
///
/// See description of parameters in FileStorage::FileStorage. The method calls FileStorage::release
/// before opening the file.
/// ## Parameters
/// * filename: Name of the file to open or the text string to read the data from.
/// Extension of the file (.xml, .yml/.yaml or .json) determines its format (XML, YAML or JSON
/// respectively). Also you can append .gz to work with compressed files, for example myHugeMatrix.xml.gz. If both
/// FileStorage::WRITE and FileStorage::MEMORY flags are specified, source is used just to specify
/// the output file format (e.g. mydata.xml, .yml etc.). A file name can also contain parameters.
/// You can use this format, "*?base64" (e.g. "file.json?base64" (case sensitive)), as an alternative to
/// FileStorage::BASE64 flag.
/// * flags: Mode of operation. One of FileStorage::Mode
/// * encoding: Encoding of the file. Note that UTF-16 XML encoding is not supported currently and
/// you should use 8-bit encoding instead of it.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * encoding: String()
#[inline]
fn open(&mut self, filename: &str, flags: i32, encoding: &str) -> Result<bool> {
extern_container_arg!(filename);
extern_container_arg!(encoding);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileStorage_open_const_StringR_int_const_StringR(self.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), filename.opencv_as_extern(), flags, encoding.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Closes the file and releases all the memory buffers.
///
/// Call this method after all I/O operations with the storage are finished.
#[inline]
fn release(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileStorage_release(self.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Closes the file and releases all the memory buffers.
///
/// Call this method after all I/O operations with the storage are finished. If the storage was
/// opened for writing data and FileStorage::WRITE was specified
#[inline]
fn release_and_get_string(&mut self) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileStorage_releaseAndGetString(self.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Simplified writing API to use with bindings.
/// ## Parameters
/// * name: Name of the written object. When writing to sequences (a.k.a. "arrays"), pass an empty string.
/// * val: Value of the written object.
#[inline]
fn write_i32(&mut self, name: &str, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileStorage_write_const_StringR_int(self.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), name.opencv_as_extern(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Simplified writing API to use with bindings.
/// ## Parameters
/// * name: Name of the written object. When writing to sequences (a.k.a. "arrays"), pass an empty string.
/// * val: Value of the written object.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
#[inline]
fn write_f64(&mut self, name: &str, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileStorage_write_const_StringR_double(self.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), name.opencv_as_extern(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Simplified writing API to use with bindings.
/// ## Parameters
/// * name: Name of the written object. When writing to sequences (a.k.a. "arrays"), pass an empty string.
/// * val: Value of the written object.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
#[inline]
fn write_str(&mut self, name: &str, val: &str) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(name);
extern_container_arg!(val);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileStorage_write_const_StringR_const_StringR(self.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), name.opencv_as_extern(), val.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Simplified writing API to use with bindings.
/// ## Parameters
/// * name: Name of the written object. When writing to sequences (a.k.a. "arrays"), pass an empty string.
/// * val: Value of the written object.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
#[inline]
fn write_mat(&mut self, name: &str, val: &core::Mat) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileStorage_write_const_StringR_const_MatR(self.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), name.opencv_as_extern(), val.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Simplified writing API to use with bindings.
/// ## Parameters
/// * name: Name of the written object. When writing to sequences (a.k.a. "arrays"), pass an empty string.
/// * val: Value of the written object.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
#[inline]
fn write_str_vec(&mut self, name: &str, val: &core::Vector<String>) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileStorage_write_const_StringR_const_vectorLStringGR(self.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), name.opencv_as_extern(), val.as_raw_VectorOfString(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Writes multiple numbers.
///
/// Writes one or more numbers of the specified format to the currently written structure. Usually it is
/// more convenient to use operator `<<` instead of this method.
/// ## Parameters
/// * fmt: Specification of each array element, see [format_spec] "format specification"
/// * vec: Pointer to the written array.
/// * len: Number of the uchar elements to write.
#[inline]
unsafe fn write_raw(&mut self, fmt: &str, vec: *const c_void, len: size_t) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(fmt);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_FileStorage_writeRaw_const_StringR_const_voidX_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), fmt.opencv_as_extern(), vec, len, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Writes a comment.
///
/// The function writes a comment into file storage. The comments are skipped when the storage is read.
/// ## Parameters
/// * comment: The written comment, single-line or multi-line
/// * append: If true, the function tries to put the comment at the end of current line.
/// Else if the comment is multi-line, or if it does not fit at the end of the current
/// line, the comment starts a new line.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * append: false
#[inline]
fn write_comment(&mut self, comment: &str, append: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(comment);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileStorage_writeComment_const_StringR_bool(self.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), comment.opencv_as_extern(), append, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Starts to write a nested structure (sequence or a mapping).
/// ## Parameters
/// * name: name of the structure. When writing to sequences (a.k.a. "arrays"), pass an empty string.
/// * flags: type of the structure (FileNode::MAP or FileNode::SEQ (both with optional FileNode::FLOW)).
/// * typeName: optional name of the type you store. The effect of setting this depends on the storage format.
/// I.e. if the format has a specification for storing type information, this parameter is used.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * type_name: String()
#[inline]
fn start_write_struct(&mut self, name: &str, flags: i32, type_name: &str) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(name);
extern_container_arg!(type_name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileStorage_startWriteStruct_const_StringR_int_const_StringR(self.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), name.opencv_as_extern(), flags, type_name.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finishes writing nested structure (should pair startWriteStruct())
#[inline]
fn end_write_struct(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileStorage_endWriteStruct(self.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// XML/YAML/JSON file storage class that encapsulates all the information necessary for writing or
/// reading data to/from a file.
pub struct FileStorage {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { FileStorage }
impl Drop for FileStorage {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_FileStorage_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_FileStorage_delete(self.as_raw_mut_FileStorage()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for FileStorage {}
impl core::FileStorageTraitConst for FileStorage {
#[inline] fn as_raw_FileStorage(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::FileStorageTrait for FileStorage {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_FileStorage(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl FileStorage {
/// The constructors.
///
/// The full constructor opens the file. Alternatively you can use the default constructor and then
/// call FileStorage::open.
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::FileStorage> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileStorage_FileStorage(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::FileStorage::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// The constructors.
///
/// The full constructor opens the file. Alternatively you can use the default constructor and then
/// call FileStorage::open.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// @copydoc open()
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * encoding: String()
#[inline]
pub fn new(filename: &str, flags: i32, encoding: &str) -> Result<core::FileStorage> {
extern_container_arg!(filename);
extern_container_arg!(encoding);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileStorage_FileStorage_const_StringR_int_const_StringR(filename.opencv_as_extern(), flags, encoding.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::FileStorage::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the normalized object name for the specified name of a file.
/// ## Parameters
/// * filename: Name of a file
/// ## Returns
/// The normalized object name.
#[inline]
pub fn get_default_object_name(filename: &str) -> Result<String> {
extern_container_arg!(filename);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_FileStorage_getDefaultObjectName_const_StringR(filename.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Formatted]
pub trait FormattedConst {
fn as_raw_Formatted(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// @todo document
pub trait Formatted: core::FormattedConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Formatted(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn next(&mut self) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Formatted_next(self.as_raw_mut_Formatted(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn reset(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Formatted_reset(self.as_raw_mut_Formatted(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Formatter]
pub trait FormatterConst {
fn as_raw_Formatter(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn format(&self, mtx: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn core::Formatted>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Formatter_format_const_const_MatR(self.as_raw_Formatter(), mtx.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn core::Formatted>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// @todo document
pub trait Formatter: core::FormatterConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Formatter(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * p: 4
#[inline]
fn set16f_precision(&mut self, p: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Formatter_set16fPrecision_int(self.as_raw_mut_Formatter(), p, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * p: 8
#[inline]
fn set32f_precision(&mut self, p: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Formatter_set32fPrecision_int(self.as_raw_mut_Formatter(), p, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * p: 16
#[inline]
fn set64f_precision(&mut self, p: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Formatter_set64fPrecision_int(self.as_raw_mut_Formatter(), p, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * ml: true
#[inline]
fn set_multiline(&mut self, ml: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Formatter_setMultiline_bool(self.as_raw_mut_Formatter(), ml, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl dyn Formatter + '_ {
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * fmt: FMT_DEFAULT
#[inline]
pub fn get(fmt: core::Formatter_FormatType) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn core::Formatter>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Formatter_get_FormatType(fmt, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn core::Formatter>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Hamming]
pub trait HammingTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Hamming(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// this will count the bits in a ^ b
#[inline]
fn apply(&self, a: &u8, b: &u8, size: i32) -> Result<core::Hamming_result_type> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Hamming_operator___const_const_unsigned_charX_const_unsigned_charX_int(self.as_raw_Hamming(), a, b, size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Hamming]
pub trait HammingTrait: core::HammingTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Hamming(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
pub struct Hamming {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Hamming }
impl Drop for Hamming {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Hamming_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Hamming_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Hamming()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Hamming {}
impl core::HammingTraitConst for Hamming {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Hamming(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::HammingTrait for Hamming {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Hamming(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Hamming {
pub const normType: u32 = 6;
}
/// Constant methods for [core::KeyPoint]
pub trait KeyPointTraitConst {
fn as_raw_KeyPoint(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// coordinates of the keypoints
#[inline]
fn pt(&self) -> core::Point2f {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_KeyPoint_getPropPt_const(self.as_raw_KeyPoint(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
ret
}
/// diameter of the meaningful keypoint neighborhood
#[inline]
fn size(&self) -> f32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KeyPoint_getPropSize_const(self.as_raw_KeyPoint()) };
ret
}
/// computed orientation of the keypoint (-1 if not applicable);
/// it's in [0,360) degrees and measured relative to
/// image coordinate system, ie in clockwise.
#[inline]
fn angle(&self) -> f32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KeyPoint_getPropAngle_const(self.as_raw_KeyPoint()) };
ret
}
/// the response by which the most strong keypoints have been selected. Can be used for the further sorting or subsampling
#[inline]
fn response(&self) -> f32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KeyPoint_getPropResponse_const(self.as_raw_KeyPoint()) };
ret
}
/// octave (pyramid layer) from which the keypoint has been extracted
#[inline]
fn octave(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KeyPoint_getPropOctave_const(self.as_raw_KeyPoint()) };
ret
}
/// object class (if the keypoints need to be clustered by an object they belong to)
#[inline]
fn class_id(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KeyPoint_getPropClass_id_const(self.as_raw_KeyPoint()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn hash(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_KeyPoint_hash_const(self.as_raw_KeyPoint(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::KeyPoint]
pub trait KeyPointTrait: core::KeyPointTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_KeyPoint(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// coordinates of the keypoints
#[inline]
fn set_pt(&mut self, val: core::Point2f) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KeyPoint_setPropPt_Point2f(self.as_raw_mut_KeyPoint(), val.opencv_as_extern()) };
ret
}
/// diameter of the meaningful keypoint neighborhood
#[inline]
fn set_size(&mut self, val: f32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KeyPoint_setPropSize_float(self.as_raw_mut_KeyPoint(), val) };
ret
}
/// computed orientation of the keypoint (-1 if not applicable);
/// it's in [0,360) degrees and measured relative to
/// image coordinate system, ie in clockwise.
#[inline]
fn set_angle(&mut self, val: f32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KeyPoint_setPropAngle_float(self.as_raw_mut_KeyPoint(), val) };
ret
}
/// the response by which the most strong keypoints have been selected. Can be used for the further sorting or subsampling
#[inline]
fn set_response(&mut self, val: f32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KeyPoint_setPropResponse_float(self.as_raw_mut_KeyPoint(), val) };
ret
}
/// octave (pyramid layer) from which the keypoint has been extracted
#[inline]
fn set_octave(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KeyPoint_setPropOctave_int(self.as_raw_mut_KeyPoint(), val) };
ret
}
/// object class (if the keypoints need to be clustered by an object they belong to)
#[inline]
fn set_class_id(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_KeyPoint_setPropClass_id_int(self.as_raw_mut_KeyPoint(), val) };
ret
}
}
/// Data structure for salient point detectors.
///
/// The class instance stores a keypoint, i.e. a point feature found by one of many available keypoint
/// detectors, such as Harris corner detector, #FAST, %StarDetector, %SURF, %SIFT etc.
///
/// The keypoint is characterized by the 2D position, scale (proportional to the diameter of the
/// neighborhood that needs to be taken into account), orientation and some other parameters. The
/// keypoint neighborhood is then analyzed by another algorithm that builds a descriptor (usually
/// represented as a feature vector). The keypoints representing the same object in different images
/// can then be matched using %KDTree or another method.
pub struct KeyPoint {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { KeyPoint }
impl Drop for KeyPoint {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_KeyPoint_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_KeyPoint_delete(self.as_raw_mut_KeyPoint()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for KeyPoint {}
impl core::KeyPointTraitConst for KeyPoint {
#[inline] fn as_raw_KeyPoint(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::KeyPointTrait for KeyPoint {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_KeyPoint(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl KeyPoint {
/// the default constructor
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::KeyPoint> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_KeyPoint_KeyPoint(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::KeyPoint::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## Parameters
/// * pt: x & y coordinates of the keypoint
/// * size: keypoint diameter
/// * angle: keypoint orientation
/// * response: keypoint detector response on the keypoint (that is, strength of the keypoint)
/// * octave: pyramid octave in which the keypoint has been detected
/// * class_id: object id
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * angle: -1
/// * response: 0
/// * octave: 0
/// * class_id: -1
#[inline]
pub fn new_point(pt: core::Point2f, size: f32, angle: f32, response: f32, octave: i32, class_id: i32) -> Result<core::KeyPoint> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_KeyPoint_KeyPoint_Point2f_float_float_float_int_int(pt.opencv_as_extern(), size, angle, response, octave, class_id, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::KeyPoint::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## Parameters
/// * x: x-coordinate of the keypoint
/// * y: y-coordinate of the keypoint
/// * size: keypoint diameter
/// * angle: keypoint orientation
/// * response: keypoint detector response on the keypoint (that is, strength of the keypoint)
/// * octave: pyramid octave in which the keypoint has been detected
/// * class_id: object id
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * angle: -1
/// * response: 0
/// * octave: 0
/// * class_id: -1
#[inline]
pub fn new_coords(x: f32, y: f32, size: f32, angle: f32, response: f32, octave: i32, class_id: i32) -> Result<core::KeyPoint> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_KeyPoint_KeyPoint_float_float_float_float_float_int_int(x, y, size, angle, response, octave, class_id, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::KeyPoint::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// This method converts vector of keypoints to vector of points or the reverse, where each keypoint is
/// assigned the same size and the same orientation.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * keypoints: Keypoints obtained from any feature detection algorithm like SIFT/SURF/ORB
/// * points2f: Array of (x,y) coordinates of each keypoint
/// * keypointIndexes: Array of indexes of keypoints to be converted to points. (Acts like a mask to
/// convert only specified keypoints)
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * keypoint_indexes: std::vector<int>()
#[inline]
pub fn convert(keypoints: &core::Vector<core::KeyPoint>, points2f: &mut core::Vector<core::Point2f>, keypoint_indexes: &core::Vector<i32>) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_KeyPoint_convert_const_vectorLKeyPointGR_vectorLPoint2fGR_const_vectorLintGR(keypoints.as_raw_VectorOfKeyPoint(), points2f.as_raw_mut_VectorOfPoint2f(), keypoint_indexes.as_raw_VectorOfi32(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// This method converts vector of keypoints to vector of points or the reverse, where each keypoint is
/// assigned the same size and the same orientation.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * keypoints: Keypoints obtained from any feature detection algorithm like SIFT/SURF/ORB
/// * points2f: Array of (x,y) coordinates of each keypoint
/// * keypointIndexes: Array of indexes of keypoints to be converted to points. (Acts like a mask to
/// convert only specified keypoints)
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * points2f: Array of (x,y) coordinates of each keypoint
/// * keypoints: Keypoints obtained from any feature detection algorithm like SIFT/SURF/ORB
/// * size: keypoint diameter
/// * response: keypoint detector response on the keypoint (that is, strength of the keypoint)
/// * octave: pyramid octave in which the keypoint has been detected
/// * class_id: object id
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * size: 1
/// * response: 1
/// * octave: 0
/// * class_id: -1
#[inline]
pub fn convert_to(points2f: &core::Vector<core::Point2f>, keypoints: &mut core::Vector<core::KeyPoint>, size: f32, response: f32, octave: i32, class_id: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_KeyPoint_convert_const_vectorLPoint2fGR_vectorLKeyPointGR_float_float_int_int(points2f.as_raw_VectorOfPoint2f(), keypoints.as_raw_mut_VectorOfKeyPoint(), size, response, octave, class_id, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// This method computes overlap for pair of keypoints. Overlap is the ratio between area of keypoint
/// regions' intersection and area of keypoint regions' union (considering keypoint region as circle).
/// If they don't overlap, we get zero. If they coincide at same location with same size, we get 1.
/// ## Parameters
/// * kp1: First keypoint
/// * kp2: Second keypoint
#[inline]
pub fn overlap(kp1: &core::KeyPoint, kp2: &core::KeyPoint) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_KeyPoint_overlap_const_KeyPointR_const_KeyPointR(kp1.as_raw_KeyPoint(), kp2.as_raw_KeyPoint(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::LDA]
pub trait LDATraitConst {
fn as_raw_LDA(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Serializes this object to a given filename.
#[inline]
fn save(&self, filename: &str) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(filename);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_LDA_save_const_const_StringR(self.as_raw_LDA(), filename.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Serializes this object to a given cv::FileStorage.
#[inline]
fn save_1(&self, fs: &mut core::FileStorage) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_LDA_save_const_FileStorageR(self.as_raw_LDA(), fs.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the eigenvectors of this LDA.
#[inline]
fn eigenvectors(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_LDA_eigenvectors_const(self.as_raw_LDA(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the eigenvalues of this LDA.
#[inline]
fn eigenvalues(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_LDA_eigenvalues_const(self.as_raw_LDA(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::LDA]
pub trait LDATrait: core::LDATraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_LDA(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Deserializes this object from a given filename.
#[inline]
fn load(&mut self, filename: &str) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(filename);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_LDA_load_const_StringR(self.as_raw_mut_LDA(), filename.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Deserializes this object from a given cv::FileStorage.
#[inline]
fn load_1(&mut self, node: &core::FileStorage) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_LDA_load_const_FileStorageR(self.as_raw_mut_LDA(), node.as_raw_FileStorage(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Compute the discriminants for data in src (row aligned) and labels.
#[inline]
fn compute(&mut self, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, labels: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(labels);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_LDA_compute_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_LDA(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), labels.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Projects samples into the LDA subspace.
/// src may be one or more row aligned samples.
#[inline]
fn project(&mut self, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_LDA_project_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_LDA(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Reconstructs projections from the LDA subspace.
/// src may be one or more row aligned projections.
#[inline]
fn reconstruct(&mut self, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_LDA_reconstruct_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_LDA(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Linear Discriminant Analysis
/// @todo document this class
pub struct LDA {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { LDA }
impl Drop for LDA {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_LDA_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_LDA_delete(self.as_raw_mut_LDA()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for LDA {}
impl core::LDATraitConst for LDA {
#[inline] fn as_raw_LDA(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::LDATrait for LDA {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_LDA(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl LDA {
/// constructor
/// Initializes a LDA with num_components (default 0).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * num_components: 0
#[inline]
pub fn new(num_components: i32) -> Result<core::LDA> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_LDA_LDA_int(num_components, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::LDA::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Initializes and performs a Discriminant Analysis with Fisher's
/// Optimization Criterion on given data in src and corresponding labels
/// in labels. If 0 (or less) number of components are given, they are
/// automatically determined for given data in computation.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * num_components: 0
#[inline]
pub fn new_with_data(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, labels: &dyn core::ToInputArray, num_components: i32) -> Result<core::LDA> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(labels);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_LDA_LDA_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), labels.as_raw__InputArray(), num_components, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::LDA::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn subspace_project(w: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mean: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> {
extern_container_arg!(w);
extern_container_arg!(mean);
extern_container_arg!(src);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_LDA_subspaceProject_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(w.as_raw__InputArray(), mean.as_raw__InputArray(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn subspace_reconstruct(w: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mean: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> {
extern_container_arg!(w);
extern_container_arg!(mean);
extern_container_arg!(src);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_LDA_subspaceReconstruct_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(w.as_raw__InputArray(), mean.as_raw__InputArray(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Mat]
pub trait MatTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Mat(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// ! includes several bit-fields:
/// - the magic signature
/// - continuity flag
/// - depth
/// - number of channels
#[inline]
fn flags(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_getPropFlags_const(self.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// the matrix dimensionality, >= 2
#[inline]
fn dims(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_getPropDims_const(self.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// the number of rows and columns or (-1, -1) when the matrix has more than 2 dimensions
#[inline]
fn rows(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_getPropRows_const(self.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// the number of rows and columns or (-1, -1) when the matrix has more than 2 dimensions
#[inline]
fn cols(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_getPropCols_const(self.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// helper fields used in locateROI and adjustROI
#[inline]
fn datastart(&self) -> *const u8 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_getPropDatastart_const(self.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn dataend(&self) -> *const u8 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_getPropDataend_const(self.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn datalimit(&self) -> *const u8 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_getPropDatalimit_const(self.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn mat_size(&self) -> core::MatSize {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_getPropSize_const(self.as_raw_Mat()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::MatSize::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn mat_step(&self) -> core::MatStep {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_getPropStep_const(self.as_raw_Mat()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::MatStep::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// retrieve UMat from Mat
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * usage_flags: USAGE_DEFAULT
#[inline]
fn get_umat(&self, access_flags: core::AccessFlag, usage_flags: core::UMatUsageFlags) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_getUMat_const_AccessFlag_UMatUsageFlags(self.as_raw_Mat(), access_flags, usage_flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates a matrix header for the specified matrix row.
///
/// The method makes a new header for the specified matrix row and returns it. This is an O(1)
/// operation, regardless of the matrix size. The underlying data of the new matrix is shared with the
/// original matrix. Here is the example of one of the classical basic matrix processing operations,
/// axpy, used by LU and many other algorithms:
/// ```C++
/// inline void matrix_axpy(Mat& A, int i, int j, double alpha)
/// {
/// A.row(i) += A.row(j)*alpha;
/// }
/// ```
///
///
/// Note: In the current implementation, the following code does not work as expected:
/// ```C++
/// Mat A;
/// ...
/// A.row(i) = A.row(j); // will not work
/// ```
///
/// This happens because A.row(i) forms a temporary header that is further assigned to another header.
/// Remember that each of these operations is O(1), that is, no data is copied. Thus, the above
/// assignment is not true if you may have expected the j-th row to be copied to the i-th row. To
/// achieve that, you should either turn this simple assignment into an expression or use the
/// Mat::copyTo method:
/// ```C++
/// Mat A;
/// ...
/// // works, but looks a bit obscure.
/// A.row(i) = A.row(j) + 0;
/// // this is a bit longer, but the recommended method.
/// A.row(j).copyTo(A.row(i));
/// ```
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * y: A 0-based row index.
#[inline]
fn row(&self, y: i32) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_row_const_int(self.as_raw_Mat(), y, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates a matrix header for the specified matrix column.
///
/// The method makes a new header for the specified matrix column and returns it. This is an O(1)
/// operation, regardless of the matrix size. The underlying data of the new matrix is shared with the
/// original matrix. See also the Mat::row description.
/// ## Parameters
/// * x: A 0-based column index.
#[inline]
fn col(&self, x: i32) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_col_const_int(self.as_raw_Mat(), x, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates a matrix header for the specified row span.
///
/// The method makes a new header for the specified row span of the matrix. Similarly to Mat::row and
/// Mat::col , this is an O(1) operation.
/// ## Parameters
/// * startrow: An inclusive 0-based start index of the row span.
/// * endrow: An exclusive 0-based ending index of the row span.
#[inline]
fn row_bounds(&self, startrow: i32, endrow: i32) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_rowRange_const_int_int(self.as_raw_Mat(), startrow, endrow, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates a matrix header for the specified row span.
///
/// The method makes a new header for the specified row span of the matrix. Similarly to Mat::row and
/// Mat::col , this is an O(1) operation.
/// ## Parameters
/// * startrow: An inclusive 0-based start index of the row span.
/// * endrow: An exclusive 0-based ending index of the row span.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * r: Range structure containing both the start and the end indices.
#[inline]
fn row_range(&self, r: &core::Range) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_rowRange_const_const_RangeR(self.as_raw_Mat(), r.as_raw_Range(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates a matrix header for the specified column span.
///
/// The method makes a new header for the specified column span of the matrix. Similarly to Mat::row and
/// Mat::col , this is an O(1) operation.
/// ## Parameters
/// * startcol: An inclusive 0-based start index of the column span.
/// * endcol: An exclusive 0-based ending index of the column span.
#[inline]
fn col_bounds(&self, startcol: i32, endcol: i32) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_colRange_const_int_int(self.as_raw_Mat(), startcol, endcol, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates a matrix header for the specified column span.
///
/// The method makes a new header for the specified column span of the matrix. Similarly to Mat::row and
/// Mat::col , this is an O(1) operation.
/// ## Parameters
/// * startcol: An inclusive 0-based start index of the column span.
/// * endcol: An exclusive 0-based ending index of the column span.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * r: Range structure containing both the start and the end indices.
#[inline]
fn col_range(&self, r: &core::Range) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_colRange_const_const_RangeR(self.as_raw_Mat(), r.as_raw_Range(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Extracts a diagonal from a matrix
///
/// The method makes a new header for the specified matrix diagonal. The new matrix is represented as a
/// single-column matrix. Similarly to Mat::row and Mat::col, this is an O(1) operation.
/// ## Parameters
/// * d: index of the diagonal, with the following values:
/// - `d=0` is the main diagonal.
/// - `d<0` is a diagonal from the lower half. For example, d=-1 means the diagonal is set
/// immediately below the main one.
/// - `d>0` is a diagonal from the upper half. For example, d=1 means the diagonal is set
/// immediately above the main one.
/// For example:
/// ```C++
/// Mat m = (Mat_<int>(3,3) <<
/// 1,2,3,
/// 4,5,6,
/// 7,8,9);
/// Mat d0 = m.diag(0);
/// Mat d1 = m.diag(1);
/// Mat d_1 = m.diag(-1);
/// ```
///
/// The resulting matrices are
/// ```C++
/// d0 =
/// [1;
/// 5;
/// 9]
/// d1 =
/// [2;
/// 6]
/// d_1 =
/// [4;
/// 8]
/// ```
///
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * d: 0
#[inline]
fn diag(&self, d: i32) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_diag_const_int(self.as_raw_Mat(), d, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates a full copy of the array and the underlying data.
///
/// The method creates a full copy of the array. The original step[] is not taken into account. So, the
/// array copy is a continuous array occupying total()*elemSize() bytes.
#[inline]
#[must_use]
fn try_clone(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_clone_const(self.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Copies the matrix to another one.
///
/// The method copies the matrix data to another matrix. Before copying the data, the method invokes :
/// ```C++
/// m.create(this->size(), this->type());
/// ```
///
/// so that the destination matrix is reallocated if needed. While m.copyTo(m); works flawlessly, the
/// function does not handle the case of a partial overlap between the source and the destination
/// matrices.
///
/// When the operation mask is specified, if the Mat::create call shown above reallocates the matrix,
/// the newly allocated matrix is initialized with all zeros before copying the data.
/// ## Parameters
/// * m: Destination matrix. If it does not have a proper size or type before the operation, it is
/// reallocated.
#[inline]
fn copy_to(&self, m: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(m);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_copyTo_const_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_Mat(), m.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Copies the matrix to another one.
///
/// The method copies the matrix data to another matrix. Before copying the data, the method invokes :
/// ```C++
/// m.create(this->size(), this->type());
/// ```
///
/// so that the destination matrix is reallocated if needed. While m.copyTo(m); works flawlessly, the
/// function does not handle the case of a partial overlap between the source and the destination
/// matrices.
///
/// When the operation mask is specified, if the Mat::create call shown above reallocates the matrix,
/// the newly allocated matrix is initialized with all zeros before copying the data.
/// ## Parameters
/// * m: Destination matrix. If it does not have a proper size or type before the operation, it is
/// reallocated.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * m: Destination matrix. If it does not have a proper size or type before the operation, it is
/// reallocated.
/// * mask: Operation mask of the same size as \*this. Its non-zero elements indicate which matrix
/// elements need to be copied. The mask has to be of type CV_8U and can have 1 or multiple channels.
#[inline]
fn copy_to_masked(&self, m: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(m);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_copyTo_const_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_Mat(), m.as_raw__OutputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Converts an array to another data type with optional scaling.
///
/// The method converts source pixel values to the target data type. saturate_cast\<\> is applied at
/// the end to avoid possible overflows:
///
/// 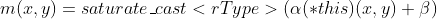
/// ## Parameters
/// * m: output matrix; if it does not have a proper size or type before the operation, it is
/// reallocated.
/// * rtype: desired output matrix type or, rather, the depth since the number of channels are the
/// same as the input has; if rtype is negative, the output matrix will have the same type as the input.
/// * alpha: optional scale factor.
/// * beta: optional delta added to the scaled values.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * alpha: 1
/// * beta: 0
#[inline]
fn convert_to(&self, m: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, rtype: i32, alpha: f64, beta: f64) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(m);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_convertTo_const_const__OutputArrayR_int_double_double(self.as_raw_Mat(), m.as_raw__OutputArray(), rtype, alpha, beta, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Provides a functional form of convertTo.
///
/// This is an internally used method called by the [MatrixExpressions] engine.
/// ## Parameters
/// * m: Destination array.
/// * type: Desired destination array depth (or -1 if it should be the same as the source type).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * typ: -1
#[inline]
fn assign_to(&self, m: &mut core::Mat, typ: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_assignTo_const_MatR_int(self.as_raw_Mat(), m.as_raw_mut_Mat(), typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Changes the shape and/or the number of channels of a 2D matrix without copying the data.
///
/// The method makes a new matrix header for \*this elements. The new matrix may have a different size
/// and/or different number of channels. Any combination is possible if:
/// * No extra elements are included into the new matrix and no elements are excluded. Consequently,
/// the product rows\*cols\*channels() must stay the same after the transformation.
/// * No data is copied. That is, this is an O(1) operation. Consequently, if you change the number of
/// rows, or the operation changes the indices of elements row in some other way, the matrix must be
/// continuous. See Mat::isContinuous .
///
/// For example, if there is a set of 3D points stored as an STL vector, and you want to represent the
/// points as a 3xN matrix, do the following:
/// ```C++
/// std::vector<Point3f> vec;
/// ...
/// Mat pointMat = Mat(vec). // convert vector to Mat, O(1) operation
/// reshape(1). // make Nx3 1-channel matrix out of Nx1 3-channel.
/// // Also, an O(1) operation
/// t(); // finally, transpose the Nx3 matrix.
/// // This involves copying all the elements
/// ```
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * cn: New number of channels. If the parameter is 0, the number of channels remains the same.
/// * rows: New number of rows. If the parameter is 0, the number of rows remains the same.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * rows: 0
#[inline]
fn reshape(&self, cn: i32, rows: i32) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_reshape_const_int_int(self.as_raw_Mat(), cn, rows, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Changes the shape and/or the number of channels of a 2D matrix without copying the data.
///
/// The method makes a new matrix header for \*this elements. The new matrix may have a different size
/// and/or different number of channels. Any combination is possible if:
/// * No extra elements are included into the new matrix and no elements are excluded. Consequently,
/// the product rows\*cols\*channels() must stay the same after the transformation.
/// * No data is copied. That is, this is an O(1) operation. Consequently, if you change the number of
/// rows, or the operation changes the indices of elements row in some other way, the matrix must be
/// continuous. See Mat::isContinuous .
///
/// For example, if there is a set of 3D points stored as an STL vector, and you want to represent the
/// points as a 3xN matrix, do the following:
/// ```C++
/// std::vector<Point3f> vec;
/// ...
/// Mat pointMat = Mat(vec). // convert vector to Mat, O(1) operation
/// reshape(1). // make Nx3 1-channel matrix out of Nx1 3-channel.
/// // Also, an O(1) operation
/// t(); // finally, transpose the Nx3 matrix.
/// // This involves copying all the elements
/// ```
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * cn: New number of channels. If the parameter is 0, the number of channels remains the same.
/// * rows: New number of rows. If the parameter is 0, the number of rows remains the same.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
#[inline]
fn reshape_nd(&self, cn: i32, newsz: &[i32]) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_reshape_const_int_int_const_intX(self.as_raw_Mat(), cn, newsz.len() as _, newsz.as_ptr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Changes the shape and/or the number of channels of a 2D matrix without copying the data.
///
/// The method makes a new matrix header for \*this elements. The new matrix may have a different size
/// and/or different number of channels. Any combination is possible if:
/// * No extra elements are included into the new matrix and no elements are excluded. Consequently,
/// the product rows\*cols\*channels() must stay the same after the transformation.
/// * No data is copied. That is, this is an O(1) operation. Consequently, if you change the number of
/// rows, or the operation changes the indices of elements row in some other way, the matrix must be
/// continuous. See Mat::isContinuous .
///
/// For example, if there is a set of 3D points stored as an STL vector, and you want to represent the
/// points as a 3xN matrix, do the following:
/// ```C++
/// std::vector<Point3f> vec;
/// ...
/// Mat pointMat = Mat(vec). // convert vector to Mat, O(1) operation
/// reshape(1). // make Nx3 1-channel matrix out of Nx1 3-channel.
/// // Also, an O(1) operation
/// t(); // finally, transpose the Nx3 matrix.
/// // This involves copying all the elements
/// ```
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * cn: New number of channels. If the parameter is 0, the number of channels remains the same.
/// * rows: New number of rows. If the parameter is 0, the number of rows remains the same.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
#[inline]
fn reshape_nd_vec(&self, cn: i32, newshape: &core::Vector<i32>) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_reshape_const_int_const_vectorLintGR(self.as_raw_Mat(), cn, newshape.as_raw_VectorOfi32(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Transposes a matrix.
///
/// The method performs matrix transposition by means of matrix expressions. It does not perform the
/// actual transposition but returns a temporary matrix transposition object that can be further used as
/// a part of more complex matrix expressions or can be assigned to a matrix:
/// ```C++
/// Mat A1 = A + Mat::eye(A.size(), A.type())*lambda;
/// Mat C = A1.t()*A1; // compute (A + lambda*I)^t * (A + lamda*I)
/// ```
///
#[inline]
fn t(&self) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_t_const(self.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Inverses a matrix.
///
/// The method performs a matrix inversion by means of matrix expressions. This means that a temporary
/// matrix inversion object is returned by the method and can be used further as a part of more complex
/// matrix expressions or can be assigned to a matrix.
/// ## Parameters
/// * method: Matrix inversion method. One of cv::DecompTypes
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * method: DECOMP_LU
#[inline]
fn inv(&self, method: i32) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_inv_const_int(self.as_raw_Mat(), method, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Performs an element-wise multiplication or division of the two matrices.
///
/// The method returns a temporary object encoding per-element array multiplication, with optional
/// scale. Note that this is not a matrix multiplication that corresponds to a simpler "\*" operator.
///
/// Example:
/// ```C++
/// Mat C = A.mul(5/B); // equivalent to divide(A, B, C, 5)
/// ```
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * m: Another array of the same type and the same size as \*this, or a matrix expression.
/// * scale: Optional scale factor.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * scale: 1
#[inline]
fn mul(&self, m: &dyn core::ToInputArray, scale: f64) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
extern_container_arg!(m);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_mul_const_const__InputArrayR_double(self.as_raw_Mat(), m.as_raw__InputArray(), scale, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes a cross-product of two 3-element vectors.
///
/// The method computes a cross-product of two 3-element vectors. The vectors must be 3-element
/// floating-point vectors of the same shape and size. The result is another 3-element vector of the
/// same shape and type as operands.
/// ## Parameters
/// * m: Another cross-product operand.
#[inline]
fn cross(&self, m: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> {
extern_container_arg!(m);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_cross_const_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_Mat(), m.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes a dot-product of two vectors.
///
/// The method computes a dot-product of two matrices. If the matrices are not single-column or
/// single-row vectors, the top-to-bottom left-to-right scan ordering is used to treat them as 1D
/// vectors. The vectors must have the same size and type. If the matrices have more than one channel,
/// the dot products from all the channels are summed together.
/// ## Parameters
/// * m: another dot-product operand.
#[inline]
fn dot(&self, m: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<f64> {
extern_container_arg!(m);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_dot_const_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_Mat(), m.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Locates the matrix header within a parent matrix.
///
/// After you extracted a submatrix from a matrix using Mat::row, Mat::col, Mat::rowRange,
/// Mat::colRange, and others, the resultant submatrix points just to the part of the original big
/// matrix. However, each submatrix contains information (represented by datastart and dataend
/// fields) that helps reconstruct the original matrix size and the position of the extracted
/// submatrix within the original matrix. The method locateROI does exactly that.
/// ## Parameters
/// * wholeSize: Output parameter that contains the size of the whole matrix containing *this*
/// as a part.
/// * ofs: Output parameter that contains an offset of *this* inside the whole matrix.
#[inline]
fn locate_roi(&self, whole_size: &mut core::Size, ofs: &mut core::Point) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_locateROI_const_SizeR_PointR(self.as_raw_Mat(), whole_size, ofs, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Extracts a rectangular submatrix.
///
/// The operators make a new header for the specified sub-array of \*this . They are the most
/// generalized forms of Mat::row, Mat::col, Mat::rowRange, and Mat::colRange . For example,
/// `A(Range(0, 10), Range::all())` is equivalent to `A.rowRange(0, 10)`. Similarly to all of the above,
/// the operators are O(1) operations, that is, no matrix data is copied.
/// ## Parameters
/// * rowRange: Start and end row of the extracted submatrix. The upper boundary is not included. To
/// select all the rows, use Range::all().
/// * colRange: Start and end column of the extracted submatrix. The upper boundary is not included.
/// To select all the columns, use Range::all().
#[inline]
fn apply(&self, mut row_range: core::Range, mut col_range: core::Range) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_operator___const_Range_Range(self.as_raw_Mat(), row_range.as_raw_mut_Range(), col_range.as_raw_mut_Range(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Extracts a rectangular submatrix.
///
/// The operators make a new header for the specified sub-array of \*this . They are the most
/// generalized forms of Mat::row, Mat::col, Mat::rowRange, and Mat::colRange . For example,
/// `A(Range(0, 10), Range::all())` is equivalent to `A.rowRange(0, 10)`. Similarly to all of the above,
/// the operators are O(1) operations, that is, no matrix data is copied.
/// ## Parameters
/// * rowRange: Start and end row of the extracted submatrix. The upper boundary is not included. To
/// select all the rows, use Range::all().
/// * colRange: Start and end column of the extracted submatrix. The upper boundary is not included.
/// To select all the columns, use Range::all().
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * roi: Extracted submatrix specified as a rectangle.
#[inline]
fn apply_1(&self, roi: core::Rect) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_operator___const_const_RectR(self.as_raw_Mat(), &roi, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Extracts a rectangular submatrix.
///
/// The operators make a new header for the specified sub-array of \*this . They are the most
/// generalized forms of Mat::row, Mat::col, Mat::rowRange, and Mat::colRange . For example,
/// `A(Range(0, 10), Range::all())` is equivalent to `A.rowRange(0, 10)`. Similarly to all of the above,
/// the operators are O(1) operations, that is, no matrix data is copied.
/// ## Parameters
/// * rowRange: Start and end row of the extracted submatrix. The upper boundary is not included. To
/// select all the rows, use Range::all().
/// * colRange: Start and end column of the extracted submatrix. The upper boundary is not included.
/// To select all the columns, use Range::all().
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * ranges: Array of selected ranges along each array dimension.
#[inline]
fn apply_2(&self, ranges: &core::Range) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_operator___const_const_RangeX(self.as_raw_Mat(), ranges.as_raw_Range(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Extracts a rectangular submatrix.
///
/// The operators make a new header for the specified sub-array of \*this . They are the most
/// generalized forms of Mat::row, Mat::col, Mat::rowRange, and Mat::colRange . For example,
/// `A(Range(0, 10), Range::all())` is equivalent to `A.rowRange(0, 10)`. Similarly to all of the above,
/// the operators are O(1) operations, that is, no matrix data is copied.
/// ## Parameters
/// * rowRange: Start and end row of the extracted submatrix. The upper boundary is not included. To
/// select all the rows, use Range::all().
/// * colRange: Start and end column of the extracted submatrix. The upper boundary is not included.
/// To select all the columns, use Range::all().
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * ranges: Array of selected ranges along each array dimension.
#[inline]
fn apply_3(&self, ranges: &core::Vector<core::Range>) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_operator___const_const_vectorLRangeGR(self.as_raw_Mat(), ranges.as_raw_VectorOfRange(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Reports whether the matrix is continuous or not.
///
/// The method returns true if the matrix elements are stored continuously without gaps at the end of
/// each row. Otherwise, it returns false. Obviously, 1x1 or 1xN matrices are always continuous.
/// Matrices created with Mat::create are always continuous. But if you extract a part of the matrix
/// using Mat::col, Mat::diag, and so on, or constructed a matrix header for externally allocated data,
/// such matrices may no longer have this property.
///
/// The continuity flag is stored as a bit in the Mat::flags field and is computed automatically when
/// you construct a matrix header. Thus, the continuity check is a very fast operation, though
/// theoretically it could be done as follows:
/// ```C++
/// // alternative implementation of Mat::isContinuous()
/// bool myCheckMatContinuity(const Mat& m)
/// {
/// //return (m.flags & Mat::CONTINUOUS_FLAG) != 0;
/// return m.rows == 1 || m.step == m.cols*m.elemSize();
/// }
/// ```
///
/// The method is used in quite a few of OpenCV functions. The point is that element-wise operations
/// (such as arithmetic and logical operations, math functions, alpha blending, color space
/// transformations, and others) do not depend on the image geometry. Thus, if all the input and output
/// arrays are continuous, the functions can process them as very long single-row vectors. The example
/// below illustrates how an alpha-blending function can be implemented:
/// ```C++
/// template<typename T>
/// void alphaBlendRGBA(const Mat& src1, const Mat& src2, Mat& dst)
/// {
/// const float alpha_scale = (float)std::numeric_limits<T>::max(),
/// inv_scale = 1.f/alpha_scale;
///
/// CV_Assert( src1.type() == src2.type() &&
/// src1.type() == CV_MAKETYPE(traits::Depth<T>::value, 4) &&
/// src1.size() == src2.size());
/// Size size = src1.size();
/// dst.create(size, src1.type());
///
/// // here is the idiom: check the arrays for continuity and,
/// // if this is the case,
/// // treat the arrays as 1D vectors
/// if( src1.isContinuous() && src2.isContinuous() && dst.isContinuous() )
/// {
/// size.width *= size.height;
/// size.height = 1;
/// }
/// size.width *= 4;
///
/// for( int i = 0; i < size.height; i++ )
/// {
/// // when the arrays are continuous,
/// // the outer loop is executed only once
/// const T* ptr1 = src1.ptr<T>(i);
/// const T* ptr2 = src2.ptr<T>(i);
/// T* dptr = dst.ptr<T>(i);
///
/// for( int j = 0; j < size.width; j += 4 )
/// {
/// float alpha = ptr1[j+3]*inv_scale, beta = ptr2[j+3]*inv_scale;
/// dptr[j] = saturate_cast<T>(ptr1[j]*alpha + ptr2[j]*beta);
/// dptr[j+1] = saturate_cast<T>(ptr1[j+1]*alpha + ptr2[j+1]*beta);
/// dptr[j+2] = saturate_cast<T>(ptr1[j+2]*alpha + ptr2[j+2]*beta);
/// dptr[j+3] = saturate_cast<T>((1 - (1-alpha)*(1-beta))*alpha_scale);
/// }
/// }
/// }
/// ```
///
/// This approach, while being very simple, can boost the performance of a simple element-operation by
/// 10-20 percents, especially if the image is rather small and the operation is quite simple.
///
/// Another OpenCV idiom in this function, a call of Mat::create for the destination array, that
/// allocates the destination array unless it already has the proper size and type. And while the newly
/// allocated arrays are always continuous, you still need to check the destination array because
/// Mat::create does not always allocate a new matrix.
#[inline]
fn is_continuous(&self) -> bool {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_isContinuous_const(self.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// returns true if the matrix is a submatrix of another matrix
#[inline]
fn is_submatrix(&self) -> bool {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_isSubmatrix_const(self.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// Returns the matrix element size in bytes.
///
/// The method returns the matrix element size in bytes. For example, if the matrix type is CV_16SC3 ,
/// the method returns 3\*sizeof(short) or 6.
#[inline]
fn elem_size(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_elemSize_const(self.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the size of each matrix element channel in bytes.
///
/// The method returns the matrix element channel size in bytes, that is, it ignores the number of
/// channels. For example, if the matrix type is CV_16SC3 , the method returns sizeof(short) or 2.
#[inline]
fn elem_size1(&self) -> size_t {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_elemSize1_const(self.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// Returns the type of a matrix element.
///
/// The method returns a matrix element type. This is an identifier compatible with the CvMat type
/// system, like CV_16SC3 or 16-bit signed 3-channel array, and so on.
#[inline]
fn typ(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_type_const(self.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// Returns the depth of a matrix element.
///
/// The method returns the identifier of the matrix element depth (the type of each individual channel).
/// For example, for a 16-bit signed element array, the method returns CV_16S . A complete list of
/// matrix types contains the following values:
/// * CV_8U - 8-bit unsigned integers ( 0..255 )
/// * CV_8S - 8-bit signed integers ( -128..127 )
/// * CV_16U - 16-bit unsigned integers ( 0..65535 )
/// * CV_16S - 16-bit signed integers ( -32768..32767 )
/// * CV_32S - 32-bit signed integers ( -2147483648..2147483647 )
/// * CV_32F - 32-bit floating-point numbers ( -FLT_MAX..FLT_MAX, INF, NAN )
/// * CV_64F - 64-bit floating-point numbers ( -DBL_MAX..DBL_MAX, INF, NAN )
#[inline]
fn depth(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_depth_const(self.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// Returns the number of matrix channels.
///
/// The method returns the number of matrix channels.
#[inline]
fn channels(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_channels_const(self.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// Returns a normalized step.
///
/// The method returns a matrix step divided by Mat::elemSize1() . It can be useful to quickly access an
/// arbitrary matrix element.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * i: 0
#[inline]
fn step1(&self, i: i32) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_step1_const_int(self.as_raw_Mat(), i, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns true if the array has no elements.
///
/// The method returns true if Mat::total() is 0 or if Mat::data is NULL. Because of pop_back() and
/// resize() methods `M.total() == 0` does not imply that `M.data == NULL`.
#[inline]
fn empty(&self) -> bool {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_empty_const(self.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// Returns the total number of array elements.
///
/// The method returns the number of array elements (a number of pixels if the array represents an
/// image).
#[inline]
fn total(&self) -> size_t {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_total_const(self.as_raw_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// Returns the total number of array elements.
///
/// The method returns the number of elements within a certain sub-array slice with startDim <= dim < endDim
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * end_dim: INT_MAX
#[inline]
fn total_slice(&self, start_dim: i32, end_dim: i32) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_total_const_int_int(self.as_raw_Mat(), start_dim, end_dim, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## Parameters
/// * elemChannels: Number of channels or number of columns the matrix should have.
/// For a 2-D matrix, when the matrix has only 1 column, then it should have
/// elemChannels channels; When the matrix has only 1 channel,
/// then it should have elemChannels columns.
/// For a 3-D matrix, it should have only one channel. Furthermore,
/// if the number of planes is not one, then the number of rows
/// within every plane has to be 1; if the number of rows within
/// every plane is not 1, then the number of planes has to be 1.
/// * depth: The depth the matrix should have. Set it to -1 when any depth is fine.
/// * requireContinuous: Set it to true to require the matrix to be continuous
/// ## Returns
/// -1 if the requirement is not satisfied.
/// Otherwise, it returns the number of elements in the matrix. Note
/// that an element may have multiple channels.
///
/// The following code demonstrates its usage for a 2-d matrix:
/// [example-2d](https://github.com/opencv/opencv/blob/4.7.0/samples/cpp/tutorial_code/snippets/core_mat_checkVector.cpp#L1)
///
/// The following code demonstrates its usage for a 3-d matrix:
/// [example-3d](https://github.com/opencv/opencv/blob/4.7.0/samples/cpp/tutorial_code/snippets/core_mat_checkVector.cpp#L1)
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * depth: -1
/// * require_continuous: true
#[inline]
fn check_vector(&self, elem_channels: i32, depth: i32, require_continuous: bool) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_checkVector_const_int_int_bool(self.as_raw_Mat(), elem_channels, depth, require_continuous, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns a pointer to the specified matrix row.
///
/// The methods return `uchar*` or typed pointer to the specified matrix row. See the sample in
/// Mat::isContinuous to know how to use these methods.
/// ## Parameters
/// * i0: A 0-based row index.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * i0: 0
#[inline]
fn ptr(&self, i0: i32) -> Result<*const u8> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_ptr_const_int(self.as_raw_Mat(), i0, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns a pointer to the specified matrix row.
///
/// The methods return `uchar*` or typed pointer to the specified matrix row. See the sample in
/// Mat::isContinuous to know how to use these methods.
/// ## Parameters
/// * i0: A 0-based row index.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * row: Index along the dimension 0
/// * col: Index along the dimension 1
#[inline]
fn ptr_2d(&self, row: i32, col: i32) -> Result<*const u8> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_ptr_const_int_int(self.as_raw_Mat(), row, col, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns a pointer to the specified matrix row.
///
/// The methods return `uchar*` or typed pointer to the specified matrix row. See the sample in
/// Mat::isContinuous to know how to use these methods.
/// ## Parameters
/// * i0: A 0-based row index.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
#[inline]
fn ptr_3d(&self, i0: i32, i1: i32, i2: i32) -> Result<*const u8> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_ptr_const_int_int_int(self.as_raw_Mat(), i0, i1, i2, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns a pointer to the specified matrix row.
///
/// The methods return `uchar*` or typed pointer to the specified matrix row. See the sample in
/// Mat::isContinuous to know how to use these methods.
/// ## Parameters
/// * i0: A 0-based row index.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
#[inline]
fn ptr_nd(&self, idx: &[i32]) -> Result<*const u8> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_ptr_const_const_intX(self.as_raw_Mat(), idx.as_ptr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns a reference to the specified array element.
///
/// The template methods return a reference to the specified array element. For the sake of higher
/// performance, the index range checks are only performed in the Debug configuration.
///
/// Note that the variants with a single index (i) can be used to access elements of single-row or
/// single-column 2-dimensional arrays. That is, if, for example, A is a 1 x N floating-point matrix and
/// B is an M x 1 integer matrix, you can simply write `A.at<float>(k+4)` and `B.at<int>(2*i+1)`
/// instead of `A.at<float>(0,k+4)` and `B.at<int>(2*i+1,0)`, respectively.
///
/// The example below initializes a Hilbert matrix:
/// ```C++
/// Mat H(100, 100, CV_64F);
/// for(int i = 0; i < H.rows; i++)
/// for(int j = 0; j < H.cols; j++)
/// H.at<double>(i,j)=1./(i+j+1);
/// ```
///
///
/// Keep in mind that the size identifier used in the at operator cannot be chosen at random. It depends
/// on the image from which you are trying to retrieve the data. The table below gives a better insight in this:
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_8U` then use `Mat.at<uchar>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_8S` then use `Mat.at<schar>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_16U` then use `Mat.at<ushort>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_16S` then use `Mat.at<short>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_32S` then use `Mat.at<int>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_32F` then use `Mat.at<float>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_64F` then use `Mat.at<double>(y,x)`.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * i0: Index along the dimension 0
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * i0: Index along the dimension 0
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * i0: 0
fn at<T: core::DataType>(&self, i0: i32) -> Result<&T> { core::mat_forward::at(self, i0) }
/// Returns a reference to the specified array element.
///
/// The template methods return a reference to the specified array element. For the sake of higher
/// performance, the index range checks are only performed in the Debug configuration.
///
/// Note that the variants with a single index (i) can be used to access elements of single-row or
/// single-column 2-dimensional arrays. That is, if, for example, A is a 1 x N floating-point matrix and
/// B is an M x 1 integer matrix, you can simply write `A.at<float>(k+4)` and `B.at<int>(2*i+1)`
/// instead of `A.at<float>(0,k+4)` and `B.at<int>(2*i+1,0)`, respectively.
///
/// The example below initializes a Hilbert matrix:
/// ```C++
/// Mat H(100, 100, CV_64F);
/// for(int i = 0; i < H.rows; i++)
/// for(int j = 0; j < H.cols; j++)
/// H.at<double>(i,j)=1./(i+j+1);
/// ```
///
///
/// Keep in mind that the size identifier used in the at operator cannot be chosen at random. It depends
/// on the image from which you are trying to retrieve the data. The table below gives a better insight in this:
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_8U` then use `Mat.at<uchar>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_8S` then use `Mat.at<schar>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_16U` then use `Mat.at<ushort>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_16S` then use `Mat.at<short>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_32S` then use `Mat.at<int>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_32F` then use `Mat.at<float>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_64F` then use `Mat.at<double>(y,x)`.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * i0: Index along the dimension 0
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * row: Index along the dimension 0
/// * col: Index along the dimension 1
fn at_2d<T: core::DataType>(&self, row: i32, col: i32) -> Result<&T> { core::mat_forward::at_2d(self, row, col) }
/// Returns a reference to the specified array element.
///
/// The template methods return a reference to the specified array element. For the sake of higher
/// performance, the index range checks are only performed in the Debug configuration.
///
/// Note that the variants with a single index (i) can be used to access elements of single-row or
/// single-column 2-dimensional arrays. That is, if, for example, A is a 1 x N floating-point matrix and
/// B is an M x 1 integer matrix, you can simply write `A.at<float>(k+4)` and `B.at<int>(2*i+1)`
/// instead of `A.at<float>(0,k+4)` and `B.at<int>(2*i+1,0)`, respectively.
///
/// The example below initializes a Hilbert matrix:
/// ```C++
/// Mat H(100, 100, CV_64F);
/// for(int i = 0; i < H.rows; i++)
/// for(int j = 0; j < H.cols; j++)
/// H.at<double>(i,j)=1./(i+j+1);
/// ```
///
///
/// Keep in mind that the size identifier used in the at operator cannot be chosen at random. It depends
/// on the image from which you are trying to retrieve the data. The table below gives a better insight in this:
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_8U` then use `Mat.at<uchar>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_8S` then use `Mat.at<schar>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_16U` then use `Mat.at<ushort>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_16S` then use `Mat.at<short>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_32S` then use `Mat.at<int>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_32F` then use `Mat.at<float>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_64F` then use `Mat.at<double>(y,x)`.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * i0: Index along the dimension 0
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * i0: Index along the dimension 0
/// * i1: Index along the dimension 1
/// * i2: Index along the dimension 2
fn at_3d<T: core::DataType>(&self, i0: i32, i1: i32, i2: i32) -> Result<&T> { core::mat_forward::at_3d(self, i0, i1, i2) }
/// Returns a reference to the specified array element.
///
/// The template methods return a reference to the specified array element. For the sake of higher
/// performance, the index range checks are only performed in the Debug configuration.
///
/// Note that the variants with a single index (i) can be used to access elements of single-row or
/// single-column 2-dimensional arrays. That is, if, for example, A is a 1 x N floating-point matrix and
/// B is an M x 1 integer matrix, you can simply write `A.at<float>(k+4)` and `B.at<int>(2*i+1)`
/// instead of `A.at<float>(0,k+4)` and `B.at<int>(2*i+1,0)`, respectively.
///
/// The example below initializes a Hilbert matrix:
/// ```C++
/// Mat H(100, 100, CV_64F);
/// for(int i = 0; i < H.rows; i++)
/// for(int j = 0; j < H.cols; j++)
/// H.at<double>(i,j)=1./(i+j+1);
/// ```
///
///
/// Keep in mind that the size identifier used in the at operator cannot be chosen at random. It depends
/// on the image from which you are trying to retrieve the data. The table below gives a better insight in this:
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_8U` then use `Mat.at<uchar>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_8S` then use `Mat.at<schar>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_16U` then use `Mat.at<ushort>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_16S` then use `Mat.at<short>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_32S` then use `Mat.at<int>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_32F` then use `Mat.at<float>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_64F` then use `Mat.at<double>(y,x)`.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * i0: Index along the dimension 0
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * idx: Array of Mat::dims indices.
fn at_nd<T: core::DataType>(&self, idx: &[i32]) -> Result<&T> { core::mat_forward::at_nd(self, idx) }
/// Returns a reference to the specified array element.
///
/// The template methods return a reference to the specified array element. For the sake of higher
/// performance, the index range checks are only performed in the Debug configuration.
///
/// Note that the variants with a single index (i) can be used to access elements of single-row or
/// single-column 2-dimensional arrays. That is, if, for example, A is a 1 x N floating-point matrix and
/// B is an M x 1 integer matrix, you can simply write `A.at<float>(k+4)` and `B.at<int>(2*i+1)`
/// instead of `A.at<float>(0,k+4)` and `B.at<int>(2*i+1,0)`, respectively.
///
/// The example below initializes a Hilbert matrix:
/// ```C++
/// Mat H(100, 100, CV_64F);
/// for(int i = 0; i < H.rows; i++)
/// for(int j = 0; j < H.cols; j++)
/// H.at<double>(i,j)=1./(i+j+1);
/// ```
///
///
/// Keep in mind that the size identifier used in the at operator cannot be chosen at random. It depends
/// on the image from which you are trying to retrieve the data. The table below gives a better insight in this:
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_8U` then use `Mat.at<uchar>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_8S` then use `Mat.at<schar>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_16U` then use `Mat.at<ushort>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_16S` then use `Mat.at<short>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_32S` then use `Mat.at<int>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_32F` then use `Mat.at<float>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_64F` then use `Mat.at<double>(y,x)`.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * i0: Index along the dimension 0
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// special versions for 2D arrays (especially convenient for referencing image pixels)
/// * pt: Element position specified as Point(j,i) .
fn at_pt<T: core::DataType>(&self, pt: core::Point) -> Result<&T> { core::mat_forward::at_pt(self, pt) }
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Mat]
pub trait MatTrait: core::MatTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Mat(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// ! includes several bit-fields:
/// - the magic signature
/// - continuity flag
/// - depth
/// - number of channels
#[inline]
fn set_flags(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_setPropFlags_int(self.as_raw_mut_Mat(), val) };
ret
}
/// the matrix dimensionality, >= 2
#[inline]
fn set_dims(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_setPropDims_int(self.as_raw_mut_Mat(), val) };
ret
}
/// the number of rows and columns or (-1, -1) when the matrix has more than 2 dimensions
#[inline]
fn set_rows(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_setPropRows_int(self.as_raw_mut_Mat(), val) };
ret
}
/// the number of rows and columns or (-1, -1) when the matrix has more than 2 dimensions
#[inline]
fn set_cols(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_setPropCols_int(self.as_raw_mut_Mat(), val) };
ret
}
/// pointer to the data
#[inline]
fn data_mut(&mut self) -> *mut u8 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_getPropData(self.as_raw_mut_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// pointer to the data
#[inline]
unsafe fn set_data(&mut self, val: *mut u8) {
let ret = { sys::cv_Mat_setPropData_unsigned_charX(self.as_raw_mut_Mat(), val) };
ret
}
/// interaction with UMat
#[inline]
fn u(&mut self) -> core::UMatData {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_getPropU(self.as_raw_mut_Mat()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::UMatData::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// interaction with UMat
#[inline]
fn set_u(&mut self, val: &mut core::UMatData) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_setPropU_UMatDataX(self.as_raw_mut_Mat(), val.as_raw_mut_UMatData()) };
ret
}
/// Sets all or some of the array elements to the specified value.
///
/// This is an advanced variant of the Mat::operator=(const Scalar& s) operator.
/// ## Parameters
/// * value: Assigned scalar converted to the actual array type.
/// * mask: Operation mask of the same size as \*this. Its non-zero elements indicate which matrix
/// elements need to be copied. The mask has to be of type CV_8U and can have 1 or multiple channels
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
fn set_to(&mut self, value: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> {
extern_container_arg!(value);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_setTo_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_Mat(), value.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Allocates new array data if needed.
///
/// This is one of the key Mat methods. Most new-style OpenCV functions and methods that produce arrays
/// call this method for each output array. The method uses the following algorithm:
///
/// -# If the current array shape and the type match the new ones, return immediately. Otherwise,
/// de-reference the previous data by calling Mat::release.
/// -# Initialize the new header.
/// -# Allocate the new data of total()\*elemSize() bytes.
/// -# Allocate the new, associated with the data, reference counter and set it to 1.
///
/// Such a scheme makes the memory management robust and efficient at the same time and helps avoid
/// extra typing for you. This means that usually there is no need to explicitly allocate output arrays.
/// That is, instead of writing:
/// ```C++
/// Mat color;
/// ...
/// Mat gray(color.rows, color.cols, color.depth());
/// cvtColor(color, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
/// ```
///
/// you can simply write:
/// ```C++
/// Mat color;
/// ...
/// Mat gray;
/// cvtColor(color, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
/// ```
///
/// because cvtColor, as well as the most of OpenCV functions, calls Mat::create() for the output array
/// internally.
/// ## Parameters
/// * rows: New number of rows.
/// * cols: New number of columns.
/// * type: New matrix type.
#[inline]
unsafe fn create_rows_cols(&mut self, rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_Mat_create_int_int_int(self.as_raw_mut_Mat(), rows, cols, typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Allocates new array data if needed.
///
/// This is one of the key Mat methods. Most new-style OpenCV functions and methods that produce arrays
/// call this method for each output array. The method uses the following algorithm:
///
/// -# If the current array shape and the type match the new ones, return immediately. Otherwise,
/// de-reference the previous data by calling Mat::release.
/// -# Initialize the new header.
/// -# Allocate the new data of total()\*elemSize() bytes.
/// -# Allocate the new, associated with the data, reference counter and set it to 1.
///
/// Such a scheme makes the memory management robust and efficient at the same time and helps avoid
/// extra typing for you. This means that usually there is no need to explicitly allocate output arrays.
/// That is, instead of writing:
/// ```C++
/// Mat color;
/// ...
/// Mat gray(color.rows, color.cols, color.depth());
/// cvtColor(color, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
/// ```
///
/// you can simply write:
/// ```C++
/// Mat color;
/// ...
/// Mat gray;
/// cvtColor(color, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
/// ```
///
/// because cvtColor, as well as the most of OpenCV functions, calls Mat::create() for the output array
/// internally.
/// ## Parameters
/// * rows: New number of rows.
/// * cols: New number of columns.
/// * type: New matrix type.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * size: Alternative new matrix size specification: Size(cols, rows)
/// * type: New matrix type.
#[inline]
unsafe fn create_size(&mut self, size: core::Size, typ: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_Mat_create_Size_int(self.as_raw_mut_Mat(), size.opencv_as_extern(), typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Allocates new array data if needed.
///
/// This is one of the key Mat methods. Most new-style OpenCV functions and methods that produce arrays
/// call this method for each output array. The method uses the following algorithm:
///
/// -# If the current array shape and the type match the new ones, return immediately. Otherwise,
/// de-reference the previous data by calling Mat::release.
/// -# Initialize the new header.
/// -# Allocate the new data of total()\*elemSize() bytes.
/// -# Allocate the new, associated with the data, reference counter and set it to 1.
///
/// Such a scheme makes the memory management robust and efficient at the same time and helps avoid
/// extra typing for you. This means that usually there is no need to explicitly allocate output arrays.
/// That is, instead of writing:
/// ```C++
/// Mat color;
/// ...
/// Mat gray(color.rows, color.cols, color.depth());
/// cvtColor(color, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
/// ```
///
/// you can simply write:
/// ```C++
/// Mat color;
/// ...
/// Mat gray;
/// cvtColor(color, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
/// ```
///
/// because cvtColor, as well as the most of OpenCV functions, calls Mat::create() for the output array
/// internally.
/// ## Parameters
/// * rows: New number of rows.
/// * cols: New number of columns.
/// * type: New matrix type.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * ndims: New array dimensionality.
/// * sizes: Array of integers specifying a new array shape.
/// * type: New matrix type.
#[inline]
unsafe fn create_nd(&mut self, sizes: &[i32], typ: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_Mat_create_int_const_intX_int(self.as_raw_mut_Mat(), sizes.len() as _, sizes.as_ptr(), typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Allocates new array data if needed.
///
/// This is one of the key Mat methods. Most new-style OpenCV functions and methods that produce arrays
/// call this method for each output array. The method uses the following algorithm:
///
/// -# If the current array shape and the type match the new ones, return immediately. Otherwise,
/// de-reference the previous data by calling Mat::release.
/// -# Initialize the new header.
/// -# Allocate the new data of total()\*elemSize() bytes.
/// -# Allocate the new, associated with the data, reference counter and set it to 1.
///
/// Such a scheme makes the memory management robust and efficient at the same time and helps avoid
/// extra typing for you. This means that usually there is no need to explicitly allocate output arrays.
/// That is, instead of writing:
/// ```C++
/// Mat color;
/// ...
/// Mat gray(color.rows, color.cols, color.depth());
/// cvtColor(color, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
/// ```
///
/// you can simply write:
/// ```C++
/// Mat color;
/// ...
/// Mat gray;
/// cvtColor(color, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
/// ```
///
/// because cvtColor, as well as the most of OpenCV functions, calls Mat::create() for the output array
/// internally.
/// ## Parameters
/// * rows: New number of rows.
/// * cols: New number of columns.
/// * type: New matrix type.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * sizes: Array of integers specifying a new array shape.
/// * type: New matrix type.
#[inline]
unsafe fn create_nd_vec(&mut self, sizes: &core::Vector<i32>, typ: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_Mat_create_const_vectorLintGR_int(self.as_raw_mut_Mat(), sizes.as_raw_VectorOfi32(), typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Increments the reference counter.
///
/// The method increments the reference counter associated with the matrix data. If the matrix header
/// points to an external data set (see Mat::Mat ), the reference counter is NULL, and the method has no
/// effect in this case. Normally, to avoid memory leaks, the method should not be called explicitly. It
/// is called implicitly by the matrix assignment operator. The reference counter increment is an atomic
/// operation on the platforms that support it. Thus, it is safe to operate on the same matrices
/// asynchronously in different threads.
#[inline]
fn addref(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_addref(self.as_raw_mut_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Decrements the reference counter and deallocates the matrix if needed.
///
/// The method decrements the reference counter associated with the matrix data. When the reference
/// counter reaches 0, the matrix data is deallocated and the data and the reference counter pointers
/// are set to NULL's. If the matrix header points to an external data set (see Mat::Mat ), the
/// reference counter is NULL, and the method has no effect in this case.
///
/// This method can be called manually to force the matrix data deallocation. But since this method is
/// automatically called in the destructor, or by any other method that changes the data pointer, it is
/// usually not needed. The reference counter decrement and check for 0 is an atomic operation on the
/// platforms that support it. Thus, it is safe to operate on the same matrices asynchronously in
/// different threads.
#[inline]
fn release(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_release(self.as_raw_mut_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// internal use function, consider to use 'release' method instead; deallocates the matrix data
#[inline]
fn deallocate(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_deallocate(self.as_raw_mut_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Reserves space for the certain number of rows.
///
/// The method reserves space for sz rows. If the matrix already has enough space to store sz rows,
/// nothing happens. If the matrix is reallocated, the first Mat::rows rows are preserved. The method
/// emulates the corresponding method of the STL vector class.
/// ## Parameters
/// * sz: Number of rows.
#[inline]
fn reserve(&mut self, sz: size_t) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_reserve_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_Mat(), sz, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Reserves space for the certain number of bytes.
///
/// The method reserves space for sz bytes. If the matrix already has enough space to store sz bytes,
/// nothing happens. If matrix has to be reallocated its previous content could be lost.
/// ## Parameters
/// * sz: Number of bytes.
#[inline]
fn reserve_buffer(&mut self, sz: size_t) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_reserveBuffer_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_Mat(), sz, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Changes the number of matrix rows.
///
/// The methods change the number of matrix rows. If the matrix is reallocated, the first
/// min(Mat::rows, sz) rows are preserved. The methods emulate the corresponding methods of the STL
/// vector class.
/// ## Parameters
/// * sz: New number of rows.
#[inline]
fn resize(&mut self, sz: size_t) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_resize_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_Mat(), sz, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Changes the number of matrix rows.
///
/// The methods change the number of matrix rows. If the matrix is reallocated, the first
/// min(Mat::rows, sz) rows are preserved. The methods emulate the corresponding methods of the STL
/// vector class.
/// ## Parameters
/// * sz: New number of rows.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * sz: New number of rows.
/// * s: Value assigned to the newly added elements.
#[inline]
fn resize_with_default(&mut self, sz: size_t, s: core::Scalar) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_resize_size_t_const_ScalarR(self.as_raw_mut_Mat(), sz, &s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Adds elements to the bottom of the matrix.
///
/// The methods add one or more elements to the bottom of the matrix. They emulate the corresponding
/// method of the STL vector class. When elem is Mat , its type and the number of columns must be the
/// same as in the container matrix.
/// ## Parameters
/// * elem: Added element(s).
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * m: Added line(s).
#[inline]
fn push_back(&mut self, m: &core::Mat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_push_back_const_MatR(self.as_raw_mut_Mat(), m.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Removes elements from the bottom of the matrix.
///
/// The method removes one or more rows from the bottom of the matrix.
/// ## Parameters
/// * nelems: Number of removed rows. If it is greater than the total number of rows, an exception
/// is thrown.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * nelems: 1
#[inline]
fn pop_back(&mut self, nelems: size_t) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_pop_back_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_Mat(), nelems, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Adjusts a submatrix size and position within the parent matrix.
///
/// The method is complimentary to Mat::locateROI . The typical use of these functions is to determine
/// the submatrix position within the parent matrix and then shift the position somehow. Typically, it
/// can be required for filtering operations when pixels outside of the ROI should be taken into
/// account. When all the method parameters are positive, the ROI needs to grow in all directions by the
/// specified amount, for example:
/// ```C++
/// A.adjustROI(2, 2, 2, 2);
/// ```
///
/// In this example, the matrix size is increased by 4 elements in each direction. The matrix is shifted
/// by 2 elements to the left and 2 elements up, which brings in all the necessary pixels for the
/// filtering with the 5x5 kernel.
///
/// adjustROI forces the adjusted ROI to be inside of the parent matrix that is boundaries of the
/// adjusted ROI are constrained by boundaries of the parent matrix. For example, if the submatrix A is
/// located in the first row of a parent matrix and you called A.adjustROI(2, 2, 2, 2) then A will not
/// be increased in the upward direction.
///
/// The function is used internally by the OpenCV filtering functions, like filter2D , morphological
/// operations, and so on.
/// ## Parameters
/// * dtop: Shift of the top submatrix boundary upwards.
/// * dbottom: Shift of the bottom submatrix boundary downwards.
/// * dleft: Shift of the left submatrix boundary to the left.
/// * dright: Shift of the right submatrix boundary to the right.
/// ## See also
/// copyMakeBorder
#[inline]
fn adjust_roi(&mut self, dtop: i32, dbottom: i32, dleft: i32, dright: i32) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_adjustROI_int_int_int_int(self.as_raw_mut_Mat(), dtop, dbottom, dleft, dright, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns a pointer to the specified matrix row.
///
/// The methods return `uchar*` or typed pointer to the specified matrix row. See the sample in
/// Mat::isContinuous to know how to use these methods.
/// ## Parameters
/// * i0: A 0-based row index.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * i0: 0
#[inline]
fn ptr_mut(&mut self, i0: i32) -> Result<*mut u8> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_ptr_int(self.as_raw_mut_Mat(), i0, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns a pointer to the specified matrix row.
///
/// The methods return `uchar*` or typed pointer to the specified matrix row. See the sample in
/// Mat::isContinuous to know how to use these methods.
/// ## Parameters
/// * i0: A 0-based row index.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * row: Index along the dimension 0
/// * col: Index along the dimension 1
#[inline]
fn ptr_2d_mut(&mut self, row: i32, col: i32) -> Result<*mut u8> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_ptr_int_int(self.as_raw_mut_Mat(), row, col, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns a pointer to the specified matrix row.
///
/// The methods return `uchar*` or typed pointer to the specified matrix row. See the sample in
/// Mat::isContinuous to know how to use these methods.
/// ## Parameters
/// * i0: A 0-based row index.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
#[inline]
fn ptr_3d_mut(&mut self, i0: i32, i1: i32, i2: i32) -> Result<*mut u8> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_ptr_int_int_int(self.as_raw_mut_Mat(), i0, i1, i2, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns a pointer to the specified matrix row.
///
/// The methods return `uchar*` or typed pointer to the specified matrix row. See the sample in
/// Mat::isContinuous to know how to use these methods.
/// ## Parameters
/// * i0: A 0-based row index.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
#[inline]
fn ptr_nd_mut(&mut self, idx: &[i32]) -> Result<*mut u8> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_ptr_const_intX(self.as_raw_mut_Mat(), idx.as_ptr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns a reference to the specified array element.
///
/// The template methods return a reference to the specified array element. For the sake of higher
/// performance, the index range checks are only performed in the Debug configuration.
///
/// Note that the variants with a single index (i) can be used to access elements of single-row or
/// single-column 2-dimensional arrays. That is, if, for example, A is a 1 x N floating-point matrix and
/// B is an M x 1 integer matrix, you can simply write `A.at<float>(k+4)` and `B.at<int>(2*i+1)`
/// instead of `A.at<float>(0,k+4)` and `B.at<int>(2*i+1,0)`, respectively.
///
/// The example below initializes a Hilbert matrix:
/// ```C++
/// Mat H(100, 100, CV_64F);
/// for(int i = 0; i < H.rows; i++)
/// for(int j = 0; j < H.cols; j++)
/// H.at<double>(i,j)=1./(i+j+1);
/// ```
///
///
/// Keep in mind that the size identifier used in the at operator cannot be chosen at random. It depends
/// on the image from which you are trying to retrieve the data. The table below gives a better insight in this:
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_8U` then use `Mat.at<uchar>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_8S` then use `Mat.at<schar>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_16U` then use `Mat.at<ushort>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_16S` then use `Mat.at<short>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_32S` then use `Mat.at<int>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_32F` then use `Mat.at<float>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_64F` then use `Mat.at<double>(y,x)`.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * i0: Index along the dimension 0
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * i0: 0
fn at_mut<T: core::DataType>(&mut self, i0: i32) -> Result<&mut T> { core::mat_forward::at_mut(self, i0) }
/// Returns a reference to the specified array element.
///
/// The template methods return a reference to the specified array element. For the sake of higher
/// performance, the index range checks are only performed in the Debug configuration.
///
/// Note that the variants with a single index (i) can be used to access elements of single-row or
/// single-column 2-dimensional arrays. That is, if, for example, A is a 1 x N floating-point matrix and
/// B is an M x 1 integer matrix, you can simply write `A.at<float>(k+4)` and `B.at<int>(2*i+1)`
/// instead of `A.at<float>(0,k+4)` and `B.at<int>(2*i+1,0)`, respectively.
///
/// The example below initializes a Hilbert matrix:
/// ```C++
/// Mat H(100, 100, CV_64F);
/// for(int i = 0; i < H.rows; i++)
/// for(int j = 0; j < H.cols; j++)
/// H.at<double>(i,j)=1./(i+j+1);
/// ```
///
///
/// Keep in mind that the size identifier used in the at operator cannot be chosen at random. It depends
/// on the image from which you are trying to retrieve the data. The table below gives a better insight in this:
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_8U` then use `Mat.at<uchar>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_8S` then use `Mat.at<schar>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_16U` then use `Mat.at<ushort>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_16S` then use `Mat.at<short>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_32S` then use `Mat.at<int>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_32F` then use `Mat.at<float>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_64F` then use `Mat.at<double>(y,x)`.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * i0: Index along the dimension 0
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * row: Index along the dimension 0
/// * col: Index along the dimension 1
fn at_2d_mut<T: core::DataType>(&mut self, row: i32, col: i32) -> Result<&mut T> { core::mat_forward::at_2d_mut(self, row, col) }
/// Returns a reference to the specified array element.
///
/// The template methods return a reference to the specified array element. For the sake of higher
/// performance, the index range checks are only performed in the Debug configuration.
///
/// Note that the variants with a single index (i) can be used to access elements of single-row or
/// single-column 2-dimensional arrays. That is, if, for example, A is a 1 x N floating-point matrix and
/// B is an M x 1 integer matrix, you can simply write `A.at<float>(k+4)` and `B.at<int>(2*i+1)`
/// instead of `A.at<float>(0,k+4)` and `B.at<int>(2*i+1,0)`, respectively.
///
/// The example below initializes a Hilbert matrix:
/// ```C++
/// Mat H(100, 100, CV_64F);
/// for(int i = 0; i < H.rows; i++)
/// for(int j = 0; j < H.cols; j++)
/// H.at<double>(i,j)=1./(i+j+1);
/// ```
///
///
/// Keep in mind that the size identifier used in the at operator cannot be chosen at random. It depends
/// on the image from which you are trying to retrieve the data. The table below gives a better insight in this:
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_8U` then use `Mat.at<uchar>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_8S` then use `Mat.at<schar>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_16U` then use `Mat.at<ushort>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_16S` then use `Mat.at<short>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_32S` then use `Mat.at<int>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_32F` then use `Mat.at<float>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_64F` then use `Mat.at<double>(y,x)`.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * i0: Index along the dimension 0
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * i0: Index along the dimension 0
/// * i1: Index along the dimension 1
/// * i2: Index along the dimension 2
fn at_3d_mut<T: core::DataType>(&mut self, i0: i32, i1: i32, i2: i32) -> Result<&mut T> { core::mat_forward::at_3d_mut(self, i0, i1, i2) }
/// Returns a reference to the specified array element.
///
/// The template methods return a reference to the specified array element. For the sake of higher
/// performance, the index range checks are only performed in the Debug configuration.
///
/// Note that the variants with a single index (i) can be used to access elements of single-row or
/// single-column 2-dimensional arrays. That is, if, for example, A is a 1 x N floating-point matrix and
/// B is an M x 1 integer matrix, you can simply write `A.at<float>(k+4)` and `B.at<int>(2*i+1)`
/// instead of `A.at<float>(0,k+4)` and `B.at<int>(2*i+1,0)`, respectively.
///
/// The example below initializes a Hilbert matrix:
/// ```C++
/// Mat H(100, 100, CV_64F);
/// for(int i = 0; i < H.rows; i++)
/// for(int j = 0; j < H.cols; j++)
/// H.at<double>(i,j)=1./(i+j+1);
/// ```
///
///
/// Keep in mind that the size identifier used in the at operator cannot be chosen at random. It depends
/// on the image from which you are trying to retrieve the data. The table below gives a better insight in this:
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_8U` then use `Mat.at<uchar>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_8S` then use `Mat.at<schar>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_16U` then use `Mat.at<ushort>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_16S` then use `Mat.at<short>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_32S` then use `Mat.at<int>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_32F` then use `Mat.at<float>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_64F` then use `Mat.at<double>(y,x)`.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * i0: Index along the dimension 0
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * idx: Array of Mat::dims indices.
fn at_nd_mut<T: core::DataType>(&mut self, idx: &[i32]) -> Result<&mut T> { core::mat_forward::at_nd_mut(self, idx) }
/// Returns a reference to the specified array element.
///
/// The template methods return a reference to the specified array element. For the sake of higher
/// performance, the index range checks are only performed in the Debug configuration.
///
/// Note that the variants with a single index (i) can be used to access elements of single-row or
/// single-column 2-dimensional arrays. That is, if, for example, A is a 1 x N floating-point matrix and
/// B is an M x 1 integer matrix, you can simply write `A.at<float>(k+4)` and `B.at<int>(2*i+1)`
/// instead of `A.at<float>(0,k+4)` and `B.at<int>(2*i+1,0)`, respectively.
///
/// The example below initializes a Hilbert matrix:
/// ```C++
/// Mat H(100, 100, CV_64F);
/// for(int i = 0; i < H.rows; i++)
/// for(int j = 0; j < H.cols; j++)
/// H.at<double>(i,j)=1./(i+j+1);
/// ```
///
///
/// Keep in mind that the size identifier used in the at operator cannot be chosen at random. It depends
/// on the image from which you are trying to retrieve the data. The table below gives a better insight in this:
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_8U` then use `Mat.at<uchar>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_8S` then use `Mat.at<schar>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_16U` then use `Mat.at<ushort>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_16S` then use `Mat.at<short>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_32S` then use `Mat.at<int>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_32F` then use `Mat.at<float>(y,x)`.
/// - If matrix is of type `CV_64F` then use `Mat.at<double>(y,x)`.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * i0: Index along the dimension 0
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// special versions for 2D arrays (especially convenient for referencing image pixels)
/// * pt: Element position specified as Point(j,i) .
fn at_pt_mut<T: core::DataType>(&mut self, pt: core::Point) -> Result<&mut T> { core::mat_forward::at_pt_mut(self, pt) }
/// internal use method: updates the continuity flag
#[inline]
fn update_continuity_flag(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_updateContinuityFlag(self.as_raw_mut_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// n-dimensional dense array class \anchor CVMat_Details
///
/// The class Mat represents an n-dimensional dense numerical single-channel or multi-channel array. It
/// can be used to store real or complex-valued vectors and matrices, grayscale or color images, voxel
/// volumes, vector fields, point clouds, tensors, histograms (though, very high-dimensional histograms
/// may be better stored in a SparseMat ). The data layout of the array `M` is defined by the array
/// `M.step[]`, so that the address of element 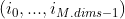, where 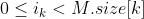, is
/// computed as:
/// 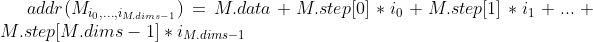
/// In case of a 2-dimensional array, the above formula is reduced to:
/// 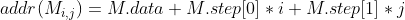
/// Note that `M.step[i] >= M.step[i+1]` (in fact, `M.step[i] >= M.step[i+1]*M.size[i+1]` ). This means
/// that 2-dimensional matrices are stored row-by-row, 3-dimensional matrices are stored plane-by-plane,
/// and so on. M.step[M.dims-1] is minimal and always equal to the element size M.elemSize() .
///
/// So, the data layout in Mat is compatible with the majority of dense array types from the standard
/// toolkits and SDKs, such as Numpy (ndarray), Win32 (independent device bitmaps), and others,
/// that is, with any array that uses *steps* (or *strides*) to compute the position of a pixel.
/// Due to this compatibility, it is possible to make a Mat header for user-allocated data and process
/// it in-place using OpenCV functions.
///
/// There are many different ways to create a Mat object. The most popular options are listed below:
///
/// - Use the create(nrows, ncols, type) method or the similar Mat(nrows, ncols, type[, fillValue])
/// constructor. A new array of the specified size and type is allocated. type has the same meaning as
/// in the cvCreateMat method. For example, CV_8UC1 means a 8-bit single-channel array, CV_32FC2
/// means a 2-channel (complex) floating-point array, and so on.
/// ```C++
/// // make a 7x7 complex matrix filled with 1+3j.
/// Mat M(7,7,CV_32FC2,Scalar(1,3));
/// // and now turn M to a 100x60 15-channel 8-bit matrix.
/// // The old content will be deallocated
/// M.create(100,60,CV_8UC(15));
/// ```
///
/// As noted in the introduction to this chapter, create() allocates only a new array when the shape
/// or type of the current array are different from the specified ones.
///
/// - Create a multi-dimensional array:
/// ```C++
/// // create a 100x100x100 8-bit array
/// int sz[] = {100, 100, 100};
/// Mat bigCube(3, sz, CV_8U, Scalar::all(0));
/// ```
///
/// It passes the number of dimensions =1 to the Mat constructor but the created array will be
/// 2-dimensional with the number of columns set to 1. So, Mat::dims is always \>= 2 (can also be 0
/// when the array is empty).
///
/// - Use a copy constructor or assignment operator where there can be an array or expression on the
/// right side (see below). As noted in the introduction, the array assignment is an O(1) operation
/// because it only copies the header and increases the reference counter. The Mat::clone() method can
/// be used to get a full (deep) copy of the array when you need it.
///
/// - Construct a header for a part of another array. It can be a single row, single column, several
/// rows, several columns, rectangular region in the array (called a *minor* in algebra) or a
/// diagonal. Such operations are also O(1) because the new header references the same data. You can
/// actually modify a part of the array using this feature, for example:
/// ```C++
/// // add the 5-th row, multiplied by 3 to the 3rd row
/// M.row(3) = M.row(3) + M.row(5)*3;
/// // now copy the 7-th column to the 1-st column
/// // M.col(1) = M.col(7); // this will not work
/// Mat M1 = M.col(1);
/// M.col(7).copyTo(M1);
/// // create a new 320x240 image
/// Mat img(Size(320,240),CV_8UC3);
/// // select a ROI
/// Mat roi(img, Rect(10,10,100,100));
/// // fill the ROI with (0,255,0) (which is green in RGB space);
/// // the original 320x240 image will be modified
/// roi = Scalar(0,255,0);
/// ```
///
/// Due to the additional datastart and dataend members, it is possible to compute a relative
/// sub-array position in the main *container* array using locateROI():
/// ```C++
/// Mat A = Mat::eye(10, 10, CV_32S);
/// // extracts A columns, 1 (inclusive) to 3 (exclusive).
/// Mat B = A(Range::all(), Range(1, 3));
/// // extracts B rows, 5 (inclusive) to 9 (exclusive).
/// // that is, C \~ A(Range(5, 9), Range(1, 3))
/// Mat C = B(Range(5, 9), Range::all());
/// Size size; Point ofs;
/// C.locateROI(size, ofs);
/// // size will be (width=10,height=10) and the ofs will be (x=1, y=5)
/// ```
///
/// As in case of whole matrices, if you need a deep copy, use the `clone()` method of the extracted
/// sub-matrices.
///
/// - Make a header for user-allocated data. It can be useful to do the following:
/// -# Process "foreign" data using OpenCV (for example, when you implement a DirectShow\* filter or
/// a processing module for gstreamer, and so on). For example:
/// ```C++
/// Mat process_video_frame(const unsigned char* pixels,
/// int width, int height, int step)
/// {
/// // wrap input buffer
/// Mat img(height, width, CV_8UC3, (unsigned char*)pixels, step);
///
/// Mat result;
/// GaussianBlur(img, result, Size(7, 7), 1.5, 1.5);
///
/// return result;
/// }
/// ```
///
/// -# Quickly initialize small matrices and/or get a super-fast element access.
/// ```C++
/// double m[3][3] = {{a, b, c}, {d, e, f}, {g, h, i}};
/// Mat M = Mat(3, 3, CV_64F, m).inv();
/// ```
///
/// .
///
/// - Use MATLAB-style array initializers, zeros(), ones(), eye(), for example:
/// ```C++
/// // create a double-precision identity matrix and add it to M.
/// M += Mat::eye(M.rows, M.cols, CV_64F);
/// ```
///
///
/// - Use a comma-separated initializer:
/// ```C++
/// // create a 3x3 double-precision identity matrix
/// Mat M = (Mat_<double>(3,3) << 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1);
/// ```
///
/// With this approach, you first call a constructor of the Mat class with the proper parameters, and
/// then you just put `<< operator` followed by comma-separated values that can be constants,
/// variables, expressions, and so on. Also, note the extra parentheses required to avoid compilation
/// errors.
///
/// Once the array is created, it is automatically managed via a reference-counting mechanism. If the
/// array header is built on top of user-allocated data, you should handle the data by yourself. The
/// array data is deallocated when no one points to it. If you want to release the data pointed by a
/// array header before the array destructor is called, use Mat::release().
///
/// The next important thing to learn about the array class is element access. This manual already
/// described how to compute an address of each array element. Normally, you are not required to use the
/// formula directly in the code. If you know the array element type (which can be retrieved using the
/// method Mat::type() ), you can access the element  of a 2-dimensional array as:
/// ```C++
/// M.at<double>(i,j) += 1.f;
/// ```
///
/// assuming that `M` is a double-precision floating-point array. There are several variants of the method
/// at for a different number of dimensions.
///
/// If you need to process a whole row of a 2D array, the most efficient way is to get the pointer to
/// the row first, and then just use the plain C operator [] :
/// ```C++
/// // compute sum of positive matrix elements
/// // (assuming that M is a double-precision matrix)
/// double sum=0;
/// for(int i = 0; i < M.rows; i++)
/// {
/// const double* Mi = M.ptr<double>(i);
/// for(int j = 0; j < M.cols; j++)
/// sum += std::max(Mi[j], 0.);
/// }
/// ```
///
/// Some operations, like the one above, do not actually depend on the array shape. They just process
/// elements of an array one by one (or elements from multiple arrays that have the same coordinates,
/// for example, array addition). Such operations are called *element-wise*. It makes sense to check
/// whether all the input/output arrays are continuous, namely, have no gaps at the end of each row. If
/// yes, process them as a long single row:
/// ```C++
/// // compute the sum of positive matrix elements, optimized variant
/// double sum=0;
/// int cols = M.cols, rows = M.rows;
/// if(M.isContinuous())
/// {
/// cols *= rows;
/// rows = 1;
/// }
/// for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
/// {
/// const double* Mi = M.ptr<double>(i);
/// for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++)
/// sum += std::max(Mi[j], 0.);
/// }
/// ```
///
/// In case of the continuous matrix, the outer loop body is executed just once. So, the overhead is
/// smaller, which is especially noticeable in case of small matrices.
///
/// Finally, there are STL-style iterators that are smart enough to skip gaps between successive rows:
/// ```C++
/// // compute sum of positive matrix elements, iterator-based variant
/// double sum=0;
/// MatConstIterator_<double> it = M.begin<double>(), it_end = M.end<double>();
/// for(; it != it_end; ++it)
/// sum += std::max(*it, 0.);
/// ```
///
/// The matrix iterators are random-access iterators, so they can be passed to any STL algorithm,
/// including std::sort().
///
///
/// Note: Matrix Expressions and arithmetic see MatExpr
pub struct Mat {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Mat }
impl Drop for Mat {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Mat_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Mat_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Mat()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Mat {}
impl core::MatTraitConst for Mat {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Mat(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::MatTrait for Mat {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Mat(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Mat {
/// These are various constructors that form a matrix. As noted in the AutomaticAllocation, often
/// the default constructor is enough, and the proper matrix will be allocated by an OpenCV function.
/// The constructed matrix can further be assigned to another matrix or matrix expression or can be
/// allocated with Mat::create . In the former case, the old content is de-referenced.
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> core::Mat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_Mat() };
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// These are various constructors that form a matrix. As noted in the AutomaticAllocation, often
/// the default constructor is enough, and the proper matrix will be allocated by an OpenCV function.
/// The constructed matrix can further be assigned to another matrix or matrix expression or can be
/// allocated with Mat::create . In the former case, the old content is de-referenced.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * rows: Number of rows in a 2D array.
/// * cols: Number of columns in a 2D array.
/// * type: Array type. Use CV_8UC1, ..., CV_64FC4 to create 1-4 channel matrices, or
/// CV_8UC(n), ..., CV_64FC(n) to create multi-channel (up to CV_CN_MAX channels) matrices.
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn new_rows_cols(rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_Mat_Mat_int_int_int(rows, cols, typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// These are various constructors that form a matrix. As noted in the AutomaticAllocation, often
/// the default constructor is enough, and the proper matrix will be allocated by an OpenCV function.
/// The constructed matrix can further be assigned to another matrix or matrix expression or can be
/// allocated with Mat::create . In the former case, the old content is de-referenced.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * size: 2D array size: Size(cols, rows) . In the Size() constructor, the number of rows and the
/// number of columns go in the reverse order.
/// * type: Array type. Use CV_8UC1, ..., CV_64FC4 to create 1-4 channel matrices, or
/// CV_8UC(n), ..., CV_64FC(n) to create multi-channel (up to CV_CN_MAX channels) matrices.
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn new_size(size: core::Size, typ: i32) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_Mat_Mat_Size_int(size.opencv_as_extern(), typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// These are various constructors that form a matrix. As noted in the AutomaticAllocation, often
/// the default constructor is enough, and the proper matrix will be allocated by an OpenCV function.
/// The constructed matrix can further be assigned to another matrix or matrix expression or can be
/// allocated with Mat::create . In the former case, the old content is de-referenced.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * rows: Number of rows in a 2D array.
/// * cols: Number of columns in a 2D array.
/// * type: Array type. Use CV_8UC1, ..., CV_64FC4 to create 1-4 channel matrices, or
/// CV_8UC(n), ..., CV_64FC(n) to create multi-channel (up to CV_CN_MAX channels) matrices.
/// * s: An optional value to initialize each matrix element with. To set all the matrix elements to
/// the particular value after the construction, use the assignment operator
/// Mat::operator=(const Scalar& value) .
#[inline]
pub fn new_rows_cols_with_default(rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32, s: core::Scalar) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_Mat_int_int_int_const_ScalarR(rows, cols, typ, &s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// These are various constructors that form a matrix. As noted in the AutomaticAllocation, often
/// the default constructor is enough, and the proper matrix will be allocated by an OpenCV function.
/// The constructed matrix can further be assigned to another matrix or matrix expression or can be
/// allocated with Mat::create . In the former case, the old content is de-referenced.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * size: 2D array size: Size(cols, rows) . In the Size() constructor, the number of rows and the
/// number of columns go in the reverse order.
/// * type: Array type. Use CV_8UC1, ..., CV_64FC4 to create 1-4 channel matrices, or
/// CV_8UC(n), ..., CV_64FC(n) to create multi-channel (up to CV_CN_MAX channels) matrices.
/// * s: An optional value to initialize each matrix element with. To set all the matrix elements to
/// the particular value after the construction, use the assignment operator
/// Mat::operator=(const Scalar& value) .
#[inline]
pub fn new_size_with_default(size: core::Size, typ: i32, s: core::Scalar) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_Mat_Size_int_const_ScalarR(size.opencv_as_extern(), typ, &s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// These are various constructors that form a matrix. As noted in the AutomaticAllocation, often
/// the default constructor is enough, and the proper matrix will be allocated by an OpenCV function.
/// The constructed matrix can further be assigned to another matrix or matrix expression or can be
/// allocated with Mat::create . In the former case, the old content is de-referenced.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * ndims: Array dimensionality.
/// * sizes: Array of integers specifying an n-dimensional array shape.
/// * type: Array type. Use CV_8UC1, ..., CV_64FC4 to create 1-4 channel matrices, or
/// CV_8UC(n), ..., CV_64FC(n) to create multi-channel (up to CV_CN_MAX channels) matrices.
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn new_nd(ndims: i32, sizes: &i32, typ: i32) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_Mat_Mat_int_const_intX_int(ndims, sizes, typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// These are various constructors that form a matrix. As noted in the AutomaticAllocation, often
/// the default constructor is enough, and the proper matrix will be allocated by an OpenCV function.
/// The constructed matrix can further be assigned to another matrix or matrix expression or can be
/// allocated with Mat::create . In the former case, the old content is de-referenced.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * sizes: Array of integers specifying an n-dimensional array shape.
/// * type: Array type. Use CV_8UC1, ..., CV_64FC4 to create 1-4 channel matrices, or
/// CV_8UC(n), ..., CV_64FC(n) to create multi-channel (up to CV_CN_MAX channels) matrices.
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn new_nd_vec(sizes: &core::Vector<i32>, typ: i32) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_Mat_Mat_const_vectorLintGR_int(sizes.as_raw_VectorOfi32(), typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// These are various constructors that form a matrix. As noted in the AutomaticAllocation, often
/// the default constructor is enough, and the proper matrix will be allocated by an OpenCV function.
/// The constructed matrix can further be assigned to another matrix or matrix expression or can be
/// allocated with Mat::create . In the former case, the old content is de-referenced.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * ndims: Array dimensionality.
/// * sizes: Array of integers specifying an n-dimensional array shape.
/// * type: Array type. Use CV_8UC1, ..., CV_64FC4 to create 1-4 channel matrices, or
/// CV_8UC(n), ..., CV_64FC(n) to create multi-channel (up to CV_CN_MAX channels) matrices.
/// * s: An optional value to initialize each matrix element with. To set all the matrix elements to
/// the particular value after the construction, use the assignment operator
/// Mat::operator=(const Scalar& value) .
#[inline]
pub fn new_nd_with_default(sizes: &[i32], typ: i32, s: core::Scalar) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_Mat_int_const_intX_int_const_ScalarR(sizes.len() as _, sizes.as_ptr(), typ, &s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// These are various constructors that form a matrix. As noted in the AutomaticAllocation, often
/// the default constructor is enough, and the proper matrix will be allocated by an OpenCV function.
/// The constructed matrix can further be assigned to another matrix or matrix expression or can be
/// allocated with Mat::create . In the former case, the old content is de-referenced.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * sizes: Array of integers specifying an n-dimensional array shape.
/// * type: Array type. Use CV_8UC1, ..., CV_64FC4 to create 1-4 channel matrices, or
/// CV_8UC(n), ..., CV_64FC(n) to create multi-channel (up to CV_CN_MAX channels) matrices.
/// * s: An optional value to initialize each matrix element with. To set all the matrix elements to
/// the particular value after the construction, use the assignment operator
/// Mat::operator=(const Scalar& value) .
#[inline]
pub fn new_nd_vec_with_default(sizes: &core::Vector<i32>, typ: i32, s: core::Scalar) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_Mat_const_vectorLintGR_int_const_ScalarR(sizes.as_raw_VectorOfi32(), typ, &s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// These are various constructors that form a matrix. As noted in the AutomaticAllocation, often
/// the default constructor is enough, and the proper matrix will be allocated by an OpenCV function.
/// The constructed matrix can further be assigned to another matrix or matrix expression or can be
/// allocated with Mat::create . In the former case, the old content is de-referenced.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * m: Array that (as a whole or partly) is assigned to the constructed matrix. No data is copied
/// by these constructors. Instead, the header pointing to m data or its sub-array is constructed and
/// associated with it. The reference counter, if any, is incremented. So, when you modify the matrix
/// formed using such a constructor, you also modify the corresponding elements of m . If you want to
/// have an independent copy of the sub-array, use Mat::clone() .
#[inline]
pub fn copy(m: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_Mat_const_MatR(m.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// These are various constructors that form a matrix. As noted in the AutomaticAllocation, often
/// the default constructor is enough, and the proper matrix will be allocated by an OpenCV function.
/// The constructed matrix can further be assigned to another matrix or matrix expression or can be
/// allocated with Mat::create . In the former case, the old content is de-referenced.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * rows: Number of rows in a 2D array.
/// * cols: Number of columns in a 2D array.
/// * type: Array type. Use CV_8UC1, ..., CV_64FC4 to create 1-4 channel matrices, or
/// CV_8UC(n), ..., CV_64FC(n) to create multi-channel (up to CV_CN_MAX channels) matrices.
/// * data: Pointer to the user data. Matrix constructors that take data and step parameters do not
/// allocate matrix data. Instead, they just initialize the matrix header that points to the specified
/// data, which means that no data is copied. This operation is very efficient and can be used to
/// process external data using OpenCV functions. The external data is not automatically deallocated, so
/// you should take care of it.
/// * step: Number of bytes each matrix row occupies. The value should include the padding bytes at
/// the end of each row, if any. If the parameter is missing (set to AUTO_STEP ), no padding is assumed
/// and the actual step is calculated as cols*elemSize(). See Mat::elemSize.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * step: AUTO_STEP
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn new_rows_cols_with_data(rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32, data: *mut c_void, step: size_t) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_Mat_Mat_int_int_int_voidX_size_t(rows, cols, typ, data, step, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// These are various constructors that form a matrix. As noted in the AutomaticAllocation, often
/// the default constructor is enough, and the proper matrix will be allocated by an OpenCV function.
/// The constructed matrix can further be assigned to another matrix or matrix expression or can be
/// allocated with Mat::create . In the former case, the old content is de-referenced.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * size: 2D array size: Size(cols, rows) . In the Size() constructor, the number of rows and the
/// number of columns go in the reverse order.
/// * type: Array type. Use CV_8UC1, ..., CV_64FC4 to create 1-4 channel matrices, or
/// CV_8UC(n), ..., CV_64FC(n) to create multi-channel (up to CV_CN_MAX channels) matrices.
/// * data: Pointer to the user data. Matrix constructors that take data and step parameters do not
/// allocate matrix data. Instead, they just initialize the matrix header that points to the specified
/// data, which means that no data is copied. This operation is very efficient and can be used to
/// process external data using OpenCV functions. The external data is not automatically deallocated, so
/// you should take care of it.
/// * step: Number of bytes each matrix row occupies. The value should include the padding bytes at
/// the end of each row, if any. If the parameter is missing (set to AUTO_STEP ), no padding is assumed
/// and the actual step is calculated as cols*elemSize(). See Mat::elemSize.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * step: AUTO_STEP
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn new_size_with_data(size: core::Size, typ: i32, data: *mut c_void, step: size_t) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_Mat_Mat_Size_int_voidX_size_t(size.opencv_as_extern(), typ, data, step, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// These are various constructors that form a matrix. As noted in the AutomaticAllocation, often
/// the default constructor is enough, and the proper matrix will be allocated by an OpenCV function.
/// The constructed matrix can further be assigned to another matrix or matrix expression or can be
/// allocated with Mat::create . In the former case, the old content is de-referenced.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * ndims: Array dimensionality.
/// * sizes: Array of integers specifying an n-dimensional array shape.
/// * type: Array type. Use CV_8UC1, ..., CV_64FC4 to create 1-4 channel matrices, or
/// CV_8UC(n), ..., CV_64FC(n) to create multi-channel (up to CV_CN_MAX channels) matrices.
/// * data: Pointer to the user data. Matrix constructors that take data and step parameters do not
/// allocate matrix data. Instead, they just initialize the matrix header that points to the specified
/// data, which means that no data is copied. This operation is very efficient and can be used to
/// process external data using OpenCV functions. The external data is not automatically deallocated, so
/// you should take care of it.
/// * steps: Array of ndims-1 steps in case of a multi-dimensional array (the last step is always
/// set to the element size). If not specified, the matrix is assumed to be continuous.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * steps: 0
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn new_nd_with_data(sizes: &[i32], typ: i32, data: *mut c_void, steps: Option<&[size_t]>) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_Mat_Mat_int_const_intX_int_voidX_const_size_tX(sizes.len() as _, sizes.as_ptr(), typ, data, steps.map_or(::core::ptr::null(), |steps| steps.as_ptr()), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// These are various constructors that form a matrix. As noted in the AutomaticAllocation, often
/// the default constructor is enough, and the proper matrix will be allocated by an OpenCV function.
/// The constructed matrix can further be assigned to another matrix or matrix expression or can be
/// allocated with Mat::create . In the former case, the old content is de-referenced.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * sizes: Array of integers specifying an n-dimensional array shape.
/// * type: Array type. Use CV_8UC1, ..., CV_64FC4 to create 1-4 channel matrices, or
/// CV_8UC(n), ..., CV_64FC(n) to create multi-channel (up to CV_CN_MAX channels) matrices.
/// * data: Pointer to the user data. Matrix constructors that take data and step parameters do not
/// allocate matrix data. Instead, they just initialize the matrix header that points to the specified
/// data, which means that no data is copied. This operation is very efficient and can be used to
/// process external data using OpenCV functions. The external data is not automatically deallocated, so
/// you should take care of it.
/// * steps: Array of ndims-1 steps in case of a multi-dimensional array (the last step is always
/// set to the element size). If not specified, the matrix is assumed to be continuous.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * steps: 0
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn new_nd_vec_with_data(sizes: &core::Vector<i32>, typ: i32, data: *mut c_void, steps: Option<&[size_t]>) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_Mat_Mat_const_vectorLintGR_int_voidX_const_size_tX(sizes.as_raw_VectorOfi32(), typ, data, steps.map_or(::core::ptr::null(), |steps| steps.as_ptr()), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// These are various constructors that form a matrix. As noted in the AutomaticAllocation, often
/// the default constructor is enough, and the proper matrix will be allocated by an OpenCV function.
/// The constructed matrix can further be assigned to another matrix or matrix expression or can be
/// allocated with Mat::create . In the former case, the old content is de-referenced.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * m: Array that (as a whole or partly) is assigned to the constructed matrix. No data is copied
/// by these constructors. Instead, the header pointing to m data or its sub-array is constructed and
/// associated with it. The reference counter, if any, is incremented. So, when you modify the matrix
/// formed using such a constructor, you also modify the corresponding elements of m . If you want to
/// have an independent copy of the sub-array, use Mat::clone() .
/// * rowRange: Range of the m rows to take. As usual, the range start is inclusive and the range
/// end is exclusive. Use Range::all() to take all the rows.
/// * colRange: Range of the m columns to take. Use Range::all() to take all the columns.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * col_range: Range::all()
#[inline]
pub fn rowscols(m: &core::Mat, row_range: &core::Range, col_range: &core::Range) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_Mat_const_MatR_const_RangeR_const_RangeR(m.as_raw_Mat(), row_range.as_raw_Range(), col_range.as_raw_Range(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// These are various constructors that form a matrix. As noted in the AutomaticAllocation, often
/// the default constructor is enough, and the proper matrix will be allocated by an OpenCV function.
/// The constructed matrix can further be assigned to another matrix or matrix expression or can be
/// allocated with Mat::create . In the former case, the old content is de-referenced.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * m: Array that (as a whole or partly) is assigned to the constructed matrix. No data is copied
/// by these constructors. Instead, the header pointing to m data or its sub-array is constructed and
/// associated with it. The reference counter, if any, is incremented. So, when you modify the matrix
/// formed using such a constructor, you also modify the corresponding elements of m . If you want to
/// have an independent copy of the sub-array, use Mat::clone() .
/// * roi: Region of interest.
#[inline]
pub fn roi(m: &core::Mat, roi: core::Rect) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_Mat_const_MatR_const_RectR(m.as_raw_Mat(), &roi, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// These are various constructors that form a matrix. As noted in the AutomaticAllocation, often
/// the default constructor is enough, and the proper matrix will be allocated by an OpenCV function.
/// The constructed matrix can further be assigned to another matrix or matrix expression or can be
/// allocated with Mat::create . In the former case, the old content is de-referenced.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * m: Array that (as a whole or partly) is assigned to the constructed matrix. No data is copied
/// by these constructors. Instead, the header pointing to m data or its sub-array is constructed and
/// associated with it. The reference counter, if any, is incremented. So, when you modify the matrix
/// formed using such a constructor, you also modify the corresponding elements of m . If you want to
/// have an independent copy of the sub-array, use Mat::clone() .
/// * ranges: Array of selected ranges of m along each dimensionality.
#[inline]
pub fn ranges(m: &core::Mat, ranges: &core::Vector<core::Range>) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_Mat_const_MatR_const_vectorLRangeGR(m.as_raw_Mat(), ranges.as_raw_VectorOfRange(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// download data from GpuMat
#[inline]
pub fn from_gpumat(m: &core::GpuMat) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_Mat_const_GpuMatR(m.as_raw_GpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// creates a diagonal matrix
///
/// The method creates a square diagonal matrix from specified main diagonal.
/// ## Parameters
/// * d: One-dimensional matrix that represents the main diagonal.
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn diag_mat(d: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_diag_const_MatR(d.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns a zero array of the specified size and type.
///
/// The method returns a Matlab-style zero array initializer. It can be used to quickly form a constant
/// array as a function parameter, part of a matrix expression, or as a matrix initializer:
/// ```C++
/// Mat A;
/// A = Mat::zeros(3, 3, CV_32F);
/// ```
///
/// In the example above, a new matrix is allocated only if A is not a 3x3 floating-point matrix.
/// Otherwise, the existing matrix A is filled with zeros.
/// ## Parameters
/// * rows: Number of rows.
/// * cols: Number of columns.
/// * type: Created matrix type.
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn zeros(rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_zeros_int_int_int(rows, cols, typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns a zero array of the specified size and type.
///
/// The method returns a Matlab-style zero array initializer. It can be used to quickly form a constant
/// array as a function parameter, part of a matrix expression, or as a matrix initializer:
/// ```C++
/// Mat A;
/// A = Mat::zeros(3, 3, CV_32F);
/// ```
///
/// In the example above, a new matrix is allocated only if A is not a 3x3 floating-point matrix.
/// Otherwise, the existing matrix A is filled with zeros.
/// ## Parameters
/// * rows: Number of rows.
/// * cols: Number of columns.
/// * type: Created matrix type.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * size: Alternative to the matrix size specification Size(cols, rows) .
/// * type: Created matrix type.
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn zeros_size(size: core::Size, typ: i32) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_zeros_Size_int(size.opencv_as_extern(), typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns a zero array of the specified size and type.
///
/// The method returns a Matlab-style zero array initializer. It can be used to quickly form a constant
/// array as a function parameter, part of a matrix expression, or as a matrix initializer:
/// ```C++
/// Mat A;
/// A = Mat::zeros(3, 3, CV_32F);
/// ```
///
/// In the example above, a new matrix is allocated only if A is not a 3x3 floating-point matrix.
/// Otherwise, the existing matrix A is filled with zeros.
/// ## Parameters
/// * rows: Number of rows.
/// * cols: Number of columns.
/// * type: Created matrix type.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * ndims: Array dimensionality.
/// * sz: Array of integers specifying the array shape.
/// * type: Created matrix type.
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn zeros_nd(sz: &[i32], typ: i32) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_zeros_int_const_intX_int(sz.len() as _, sz.as_ptr(), typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns an array of all 1's of the specified size and type.
///
/// The method returns a Matlab-style 1's array initializer, similarly to Mat::zeros. Note that using
/// this method you can initialize an array with an arbitrary value, using the following Matlab idiom:
/// ```C++
/// Mat A = Mat::ones(100, 100, CV_8U)*3; // make 100x100 matrix filled with 3.
/// ```
///
/// The above operation does not form a 100x100 matrix of 1's and then multiply it by 3. Instead, it
/// just remembers the scale factor (3 in this case) and use it when actually invoking the matrix
/// initializer.
///
/// Note: In case of multi-channels type, only the first channel will be initialized with 1's, the
/// others will be set to 0's.
/// ## Parameters
/// * rows: Number of rows.
/// * cols: Number of columns.
/// * type: Created matrix type.
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn ones(rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_ones_int_int_int(rows, cols, typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns an array of all 1's of the specified size and type.
///
/// The method returns a Matlab-style 1's array initializer, similarly to Mat::zeros. Note that using
/// this method you can initialize an array with an arbitrary value, using the following Matlab idiom:
/// ```C++
/// Mat A = Mat::ones(100, 100, CV_8U)*3; // make 100x100 matrix filled with 3.
/// ```
///
/// The above operation does not form a 100x100 matrix of 1's and then multiply it by 3. Instead, it
/// just remembers the scale factor (3 in this case) and use it when actually invoking the matrix
/// initializer.
///
/// Note: In case of multi-channels type, only the first channel will be initialized with 1's, the
/// others will be set to 0's.
/// ## Parameters
/// * rows: Number of rows.
/// * cols: Number of columns.
/// * type: Created matrix type.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * size: Alternative to the matrix size specification Size(cols, rows) .
/// * type: Created matrix type.
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn ones_size(size: core::Size, typ: i32) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_ones_Size_int(size.opencv_as_extern(), typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns an array of all 1's of the specified size and type.
///
/// The method returns a Matlab-style 1's array initializer, similarly to Mat::zeros. Note that using
/// this method you can initialize an array with an arbitrary value, using the following Matlab idiom:
/// ```C++
/// Mat A = Mat::ones(100, 100, CV_8U)*3; // make 100x100 matrix filled with 3.
/// ```
///
/// The above operation does not form a 100x100 matrix of 1's and then multiply it by 3. Instead, it
/// just remembers the scale factor (3 in this case) and use it when actually invoking the matrix
/// initializer.
///
/// Note: In case of multi-channels type, only the first channel will be initialized with 1's, the
/// others will be set to 0's.
/// ## Parameters
/// * rows: Number of rows.
/// * cols: Number of columns.
/// * type: Created matrix type.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * ndims: Array dimensionality.
/// * sz: Array of integers specifying the array shape.
/// * type: Created matrix type.
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn ones_nd(sz: &[i32], typ: i32) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_ones_int_const_intX_int(sz.len() as _, sz.as_ptr(), typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns an identity matrix of the specified size and type.
///
/// The method returns a Matlab-style identity matrix initializer, similarly to Mat::zeros. Similarly to
/// Mat::ones, you can use a scale operation to create a scaled identity matrix efficiently:
/// ```C++
/// // make a 4x4 diagonal matrix with 0.1's on the diagonal.
/// Mat A = Mat::eye(4, 4, CV_32F)*0.1;
/// ```
///
///
/// Note: In case of multi-channels type, identity matrix will be initialized only for the first channel,
/// the others will be set to 0's
/// ## Parameters
/// * rows: Number of rows.
/// * cols: Number of columns.
/// * type: Created matrix type.
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn eye(rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_eye_int_int_int(rows, cols, typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns an identity matrix of the specified size and type.
///
/// The method returns a Matlab-style identity matrix initializer, similarly to Mat::zeros. Similarly to
/// Mat::ones, you can use a scale operation to create a scaled identity matrix efficiently:
/// ```C++
/// // make a 4x4 diagonal matrix with 0.1's on the diagonal.
/// Mat A = Mat::eye(4, 4, CV_32F)*0.1;
/// ```
///
///
/// Note: In case of multi-channels type, identity matrix will be initialized only for the first channel,
/// the others will be set to 0's
/// ## Parameters
/// * rows: Number of rows.
/// * cols: Number of columns.
/// * type: Created matrix type.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * size: Alternative matrix size specification as Size(cols, rows) .
/// * type: Created matrix type.
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn eye_size(size: core::Size, typ: i32) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_eye_Size_int(size.opencv_as_extern(), typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy_mut(mut m: core::Mat) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Mat_Mat_MatRR(m.as_raw_mut_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl Clone for Mat {
#[inline]
/// Calls try_clone() and panics if that fails
fn clone(&self) -> Self {
self.try_clone().expect("Cannot clone Mat")
}
}
impl Default for Mat {
#[inline]
/// Forwards to infallible Self::default()
fn default() -> Self {
Self::default()
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::MatConstIterator]
pub trait MatConstIteratorTraitConst {
fn as_raw_MatConstIterator(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn m(&self) -> core::Mat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatConstIterator_getPropM_const(self.as_raw_MatConstIterator()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn elem_size(&self) -> size_t {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatConstIterator_getPropElemSize_const(self.as_raw_MatConstIterator()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn ptr(&self) -> *const u8 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatConstIterator_getPropPtr_const(self.as_raw_MatConstIterator()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn slice_start(&self) -> *const u8 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatConstIterator_getPropSliceStart_const(self.as_raw_MatConstIterator()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn slice_end(&self) -> *const u8 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatConstIterator_getPropSliceEnd_const(self.as_raw_MatConstIterator()) };
ret
}
/// returns the current matrix element
#[inline]
fn try_deref(&self) -> Result<*const u8> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatConstIterator_operatorX_const(self.as_raw_MatConstIterator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns the i-th matrix element, relative to the current
#[inline]
fn get(&self, i: ptrdiff_t) -> Result<*const u8> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatConstIterator_operator___const_ptrdiff_t(self.as_raw_MatConstIterator(), i, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns the current iterator position
#[inline]
fn pos(&self) -> Result<core::Point> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatConstIterator_pos_const(self.as_raw_MatConstIterator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns the current iterator position
#[inline]
fn pos_to(&self, _idx: &mut i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatConstIterator_pos_const_intX(self.as_raw_MatConstIterator(), _idx, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn lpos(&self) -> Result<ptrdiff_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatConstIterator_lpos_const(self.as_raw_MatConstIterator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::MatConstIterator]
pub trait MatConstIteratorTrait: core::MatConstIteratorTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_MatConstIterator(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_elem_size(&mut self, val: size_t) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatConstIterator_setPropElemSize_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_MatConstIterator(), val) };
ret
}
/// decrements the iterator
#[inline]
fn decr(&mut self) -> Result<core::MatConstIterator> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatConstIterator_operatorSS(self.as_raw_mut_MatConstIterator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatConstIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// increments the iterator
#[inline]
fn incr(&mut self) -> Result<core::MatConstIterator> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatConstIterator_operatorAA(self.as_raw_mut_MatConstIterator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatConstIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * relative: false
#[inline]
fn seek(&mut self, ofs: ptrdiff_t, relative: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatConstIterator_seek_ptrdiff_t_bool(self.as_raw_mut_MatConstIterator(), ofs, relative, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * relative: false
#[inline]
fn seek_idx(&mut self, _idx: &i32, relative: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatConstIterator_seek_const_intX_bool(self.as_raw_mut_MatConstIterator(), _idx, relative, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// /////////////////////////////// MatConstIterator //////////////////////////////////
pub struct MatConstIterator {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { MatConstIterator }
impl Drop for MatConstIterator {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_MatConstIterator_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_MatConstIterator_delete(self.as_raw_mut_MatConstIterator()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for MatConstIterator {}
impl core::MatConstIteratorTraitConst for MatConstIterator {
#[inline] fn as_raw_MatConstIterator(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::MatConstIteratorTrait for MatConstIterator {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_MatConstIterator(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl MatConstIterator {
/// default constructor
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::MatConstIterator> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatConstIterator_MatConstIterator(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatConstIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// constructor that sets the iterator to the beginning of the matrix
#[inline]
pub fn over(_m: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatConstIterator> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatConstIterator_MatConstIterator_const_MatX(_m.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatConstIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// constructor that sets the iterator to the specified element of the matrix
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * _col: 0
#[inline]
pub fn with_rows_cols(_m: &core::Mat, _row: i32, _col: i32) -> Result<core::MatConstIterator> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatConstIterator_MatConstIterator_const_MatX_int_int(_m.as_raw_Mat(), _row, _col, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatConstIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// constructor that sets the iterator to the specified element of the matrix
#[inline]
pub fn with_start(_m: &core::Mat, _pt: core::Point) -> Result<core::MatConstIterator> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatConstIterator_MatConstIterator_const_MatX_Point(_m.as_raw_Mat(), _pt.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatConstIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// copy constructor
#[inline]
pub fn copy(it: &core::MatConstIterator) -> Result<core::MatConstIterator> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatConstIterator_MatConstIterator_const_MatConstIteratorR(it.as_raw_MatConstIterator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatConstIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::MatExpr]
pub trait MatExprTraitConst {
fn as_raw_MatExpr(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn flags(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_getPropFlags_const(self.as_raw_MatExpr()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn a(&self) -> core::Mat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_getPropA_const(self.as_raw_MatExpr()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn b(&self) -> core::Mat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_getPropB_const(self.as_raw_MatExpr()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn c(&self) -> core::Mat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_getPropC_const(self.as_raw_MatExpr()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn alpha(&self) -> f64 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_getPropAlpha_const(self.as_raw_MatExpr()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn beta(&self) -> f64 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_getPropBeta_const(self.as_raw_MatExpr()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn s(&self) -> core::Scalar {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_getPropS_const(self.as_raw_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
ret
}
#[inline]
fn to_mat(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_operator_cv_Mat_const(self.as_raw_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn size(&self) -> Result<core::Size> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_size_const(self.as_raw_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn typ(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_type_const(self.as_raw_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn row(&self, y: i32) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_row_const_int(self.as_raw_MatExpr(), y, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn col(&self, x: i32) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_col_const_int(self.as_raw_MatExpr(), x, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * d: 0
#[inline]
fn diag(&self, d: i32) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_diag_const_int(self.as_raw_MatExpr(), d, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn apply(&self, row_range: &core::Range, col_range: &core::Range) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_operator___const_const_RangeR_const_RangeR(self.as_raw_MatExpr(), row_range.as_raw_Range(), col_range.as_raw_Range(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn apply_1(&self, roi: core::Rect) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_operator___const_const_RectR(self.as_raw_MatExpr(), &roi, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn t(&self) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_t_const(self.as_raw_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * method: DECOMP_LU
#[inline]
fn inv(&self, method: i32) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_inv_const_int(self.as_raw_MatExpr(), method, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * scale: 1
#[inline]
fn mul_matexpr(&self, e: &core::MatExpr, scale: f64) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_mul_const_const_MatExprR_double(self.as_raw_MatExpr(), e.as_raw_MatExpr(), scale, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * scale: 1
#[inline]
fn mul(&self, m: &core::Mat, scale: f64) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_mul_const_const_MatR_double(self.as_raw_MatExpr(), m.as_raw_Mat(), scale, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn cross(&self, m: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_cross_const_const_MatR(self.as_raw_MatExpr(), m.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn dot(&self, m: &core::Mat) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_dot_const_const_MatR(self.as_raw_MatExpr(), m.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::MatExpr]
pub trait MatExprTrait: core::MatExprTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_MatExpr(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_flags(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_setPropFlags_int(self.as_raw_mut_MatExpr(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_a(&mut self, mut val: core::Mat) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_setPropA_Mat(self.as_raw_mut_MatExpr(), val.as_raw_mut_Mat()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_b(&mut self, mut val: core::Mat) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_setPropB_Mat(self.as_raw_mut_MatExpr(), val.as_raw_mut_Mat()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_c(&mut self, mut val: core::Mat) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_setPropC_Mat(self.as_raw_mut_MatExpr(), val.as_raw_mut_Mat()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_alpha(&mut self, val: f64) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_setPropAlpha_double(self.as_raw_mut_MatExpr(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_beta(&mut self, val: f64) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_setPropBeta_double(self.as_raw_mut_MatExpr(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_s(&mut self, val: core::Scalar) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_setPropS_Scalar(self.as_raw_mut_MatExpr(), val.opencv_as_extern()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn swap(&mut self, b: &mut core::MatExpr) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_swap_MatExprR(self.as_raw_mut_MatExpr(), b.as_raw_mut_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Matrix expression representation
/// @anchor MatrixExpressions
/// This is a list of implemented matrix operations that can be combined in arbitrary complex
/// expressions (here A, B stand for matrices ( Mat ), s for a scalar ( Scalar ), alpha for a
/// real-valued scalar ( double )):
/// * Addition, subtraction, negation: `A+B`, `A-B`, `A+s`, `A-s`, `s+A`, `s-A`, `-A`
/// * Scaling: `A*alpha`
/// * Per-element multiplication and division: `A.mul(B)`, `A/B`, `alpha/A`
/// * Matrix multiplication: `A*B`
/// * Transposition: `A.t()` (means A<sup>T</sup>)
/// * Matrix inversion and pseudo-inversion, solving linear systems and least-squares problems:
/// `A.inv([method]) (~ A<sup>-1</sup>)`, `A.inv([method])*B (~ X: AX=B)`
/// * Comparison: `A cmpop B`, `A cmpop alpha`, `alpha cmpop A`, where *cmpop* is one of
/// `>`, `>=`, `==`, `!=`, `<=`, `<`. The result of comparison is an 8-bit single channel mask whose
/// elements are set to 255 (if the particular element or pair of elements satisfy the condition) or
/// 0.
/// * Bitwise logical operations: `A logicop B`, `A logicop s`, `s logicop A`, `~A`, where *logicop* is one of
/// `&`, `|`, `^`.
/// * Element-wise minimum and maximum: `min(A, B)`, `min(A, alpha)`, `max(A, B)`, `max(A, alpha)`
/// * Element-wise absolute value: `abs(A)`
/// * Cross-product, dot-product: `A.cross(B)`, `A.dot(B)`
/// * Any function of matrix or matrices and scalars that returns a matrix or a scalar, such as norm,
/// mean, sum, countNonZero, trace, determinant, repeat, and others.
/// * Matrix initializers ( Mat::eye(), Mat::zeros(), Mat::ones() ), matrix comma-separated
/// initializers, matrix constructors and operators that extract sub-matrices (see Mat description).
/// * Mat_<destination_type>() constructors to cast the result to the proper type.
///
/// Note: Comma-separated initializers and probably some other operations may require additional
/// explicit Mat() or Mat_<T>() constructor calls to resolve a possible ambiguity.
///
/// Here are examples of matrix expressions:
/// ```C++
/// // compute pseudo-inverse of A, equivalent to A.inv(DECOMP_SVD)
/// SVD svd(A);
/// Mat pinvA = svd.vt.t()*Mat::diag(1./svd.w)*svd.u.t();
///
/// // compute the new vector of parameters in the Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm
/// x -= (A.t()*A + lambda*Mat::eye(A.cols,A.cols,A.type())).inv(DECOMP_CHOLESKY)*(A.t()*err);
///
/// // sharpen image using "unsharp mask" algorithm
/// Mat blurred; double sigma = 1, threshold = 5, amount = 1;
/// GaussianBlur(img, blurred, Size(), sigma, sigma);
/// Mat lowContrastMask = abs(img - blurred) < threshold;
/// Mat sharpened = img*(1+amount) + blurred*(-amount);
/// img.copyTo(sharpened, lowContrastMask);
/// ```
///
pub struct MatExpr {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { MatExpr }
impl Drop for MatExpr {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_MatExpr_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_MatExpr_delete(self.as_raw_mut_MatExpr()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for MatExpr {}
impl core::MatExprTraitConst for MatExpr {
#[inline] fn as_raw_MatExpr(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::MatExprTrait for MatExpr {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_MatExpr(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl MatExpr {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_MatExpr(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_mat(m: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_MatExpr_const_MatR(m.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * _a: Mat()
/// * _b: Mat()
/// * _c: Mat()
/// * _alpha: 1
/// * _beta: 1
/// * _s: Scalar()
#[inline]
pub fn new(_op: &dyn core::MatOp, _flags: i32, _a: &core::Mat, _b: &core::Mat, _c: &core::Mat, _alpha: f64, _beta: f64, _s: core::Scalar) -> Result<core::MatExpr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatExpr_MatExpr_const_MatOpX_int_const_MatR_const_MatR_const_MatR_double_double_const_ScalarR(_op.as_raw_MatOp(), _flags, _a.as_raw_Mat(), _b.as_raw_Mat(), _c.as_raw_Mat(), _alpha, _beta, &_s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::MatExpr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::MatOp]
pub trait MatOpConst {
fn as_raw_MatOp(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn element_wise(&self, expr: &core::MatExpr) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatOp_elementWise_const_const_MatExprR(self.as_raw_MatOp(), expr.as_raw_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * typ: -1
#[inline]
fn assign(&self, expr: &core::MatExpr, m: &mut core::Mat, typ: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatOp_assign_const_const_MatExprR_MatR_int(self.as_raw_MatOp(), expr.as_raw_MatExpr(), m.as_raw_mut_Mat(), typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn roi(&self, expr: &core::MatExpr, row_range: &core::Range, col_range: &core::Range, res: &mut core::MatExpr) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatOp_roi_const_const_MatExprR_const_RangeR_const_RangeR_MatExprR(self.as_raw_MatOp(), expr.as_raw_MatExpr(), row_range.as_raw_Range(), col_range.as_raw_Range(), res.as_raw_mut_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn diag(&self, expr: &core::MatExpr, d: i32, res: &mut core::MatExpr) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatOp_diag_const_const_MatExprR_int_MatExprR(self.as_raw_MatOp(), expr.as_raw_MatExpr(), d, res.as_raw_mut_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn aug_assign_add(&self, expr: &core::MatExpr, m: &mut core::Mat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatOp_augAssignAdd_const_const_MatExprR_MatR(self.as_raw_MatOp(), expr.as_raw_MatExpr(), m.as_raw_mut_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn aug_assign_subtract(&self, expr: &core::MatExpr, m: &mut core::Mat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatOp_augAssignSubtract_const_const_MatExprR_MatR(self.as_raw_MatOp(), expr.as_raw_MatExpr(), m.as_raw_mut_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn aug_assign_multiply(&self, expr: &core::MatExpr, m: &mut core::Mat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatOp_augAssignMultiply_const_const_MatExprR_MatR(self.as_raw_MatOp(), expr.as_raw_MatExpr(), m.as_raw_mut_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn aug_assign_divide(&self, expr: &core::MatExpr, m: &mut core::Mat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatOp_augAssignDivide_const_const_MatExprR_MatR(self.as_raw_MatOp(), expr.as_raw_MatExpr(), m.as_raw_mut_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn aug_assign_and(&self, expr: &core::MatExpr, m: &mut core::Mat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatOp_augAssignAnd_const_const_MatExprR_MatR(self.as_raw_MatOp(), expr.as_raw_MatExpr(), m.as_raw_mut_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn aug_assign_or(&self, expr: &core::MatExpr, m: &mut core::Mat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatOp_augAssignOr_const_const_MatExprR_MatR(self.as_raw_MatOp(), expr.as_raw_MatExpr(), m.as_raw_mut_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn aug_assign_xor(&self, expr: &core::MatExpr, m: &mut core::Mat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatOp_augAssignXor_const_const_MatExprR_MatR(self.as_raw_MatOp(), expr.as_raw_MatExpr(), m.as_raw_mut_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn add(&self, expr1: &core::MatExpr, expr2: &core::MatExpr, res: &mut core::MatExpr) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatOp_add_const_const_MatExprR_const_MatExprR_MatExprR(self.as_raw_MatOp(), expr1.as_raw_MatExpr(), expr2.as_raw_MatExpr(), res.as_raw_mut_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn add_scalar(&self, expr1: &core::MatExpr, s: core::Scalar, res: &mut core::MatExpr) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatOp_add_const_const_MatExprR_const_ScalarR_MatExprR(self.as_raw_MatOp(), expr1.as_raw_MatExpr(), &s, res.as_raw_mut_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn subtract(&self, expr1: &core::MatExpr, expr2: &core::MatExpr, res: &mut core::MatExpr) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatOp_subtract_const_const_MatExprR_const_MatExprR_MatExprR(self.as_raw_MatOp(), expr1.as_raw_MatExpr(), expr2.as_raw_MatExpr(), res.as_raw_mut_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn subtract_scalar(&self, s: core::Scalar, expr: &core::MatExpr, res: &mut core::MatExpr) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatOp_subtract_const_const_ScalarR_const_MatExprR_MatExprR(self.as_raw_MatOp(), &s, expr.as_raw_MatExpr(), res.as_raw_mut_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * scale: 1
#[inline]
fn multiply(&self, expr1: &core::MatExpr, expr2: &core::MatExpr, res: &mut core::MatExpr, scale: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatOp_multiply_const_const_MatExprR_const_MatExprR_MatExprR_double(self.as_raw_MatOp(), expr1.as_raw_MatExpr(), expr2.as_raw_MatExpr(), res.as_raw_mut_MatExpr(), scale, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn multiply_f64(&self, expr1: &core::MatExpr, s: f64, res: &mut core::MatExpr) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatOp_multiply_const_const_MatExprR_double_MatExprR(self.as_raw_MatOp(), expr1.as_raw_MatExpr(), s, res.as_raw_mut_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * scale: 1
#[inline]
fn divide(&self, expr1: &core::MatExpr, expr2: &core::MatExpr, res: &mut core::MatExpr, scale: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatOp_divide_const_const_MatExprR_const_MatExprR_MatExprR_double(self.as_raw_MatOp(), expr1.as_raw_MatExpr(), expr2.as_raw_MatExpr(), res.as_raw_mut_MatExpr(), scale, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn divide_f64(&self, s: f64, expr: &core::MatExpr, res: &mut core::MatExpr) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatOp_divide_const_double_const_MatExprR_MatExprR(self.as_raw_MatOp(), s, expr.as_raw_MatExpr(), res.as_raw_mut_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn abs(&self, expr: &core::MatExpr, res: &mut core::MatExpr) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatOp_abs_const_const_MatExprR_MatExprR(self.as_raw_MatOp(), expr.as_raw_MatExpr(), res.as_raw_mut_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn transpose(&self, expr: &core::MatExpr, res: &mut core::MatExpr) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatOp_transpose_const_const_MatExprR_MatExprR(self.as_raw_MatOp(), expr.as_raw_MatExpr(), res.as_raw_mut_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn matmul(&self, expr1: &core::MatExpr, expr2: &core::MatExpr, res: &mut core::MatExpr) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatOp_matmul_const_const_MatExprR_const_MatExprR_MatExprR(self.as_raw_MatOp(), expr1.as_raw_MatExpr(), expr2.as_raw_MatExpr(), res.as_raw_mut_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn invert(&self, expr: &core::MatExpr, method: i32, res: &mut core::MatExpr) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatOp_invert_const_const_MatExprR_int_MatExprR(self.as_raw_MatOp(), expr.as_raw_MatExpr(), method, res.as_raw_mut_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn size(&self, expr: &core::MatExpr) -> Result<core::Size> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatOp_size_const_const_MatExprR(self.as_raw_MatOp(), expr.as_raw_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn typ(&self, expr: &core::MatExpr) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatOp_type_const_const_MatExprR(self.as_raw_MatOp(), expr.as_raw_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// ////////////////////////////// Matrix Expressions /////////////////////////////////
pub trait MatOp: core::MatOpConst {
fn as_raw_mut_MatOp(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
/// Constant methods for [core::MatSize]
pub trait MatSizeTraitConst {
fn as_raw_MatSize(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn dims(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatSize_dims_const(self.as_raw_MatSize()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn apply(&self) -> Result<core::Size> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatSize_operator___const(self.as_raw_MatSize(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get(&self, i: i32) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatSize_operator___const_int(self.as_raw_MatSize(), i, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn to_xconst_i32(&self) -> *const i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatSize_operator_const_intX_const(self.as_raw_MatSize()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn equals(&self, sz: &core::MatSize) -> bool {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatSize_operatorEQ_const_const_MatSizeR(self.as_raw_MatSize(), sz.as_raw_MatSize()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn not_equals(&self, sz: &core::MatSize) -> bool {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatSize_operatorNE_const_const_MatSizeR(self.as_raw_MatSize(), sz.as_raw_MatSize()) };
ret
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::MatSize]
pub trait MatSizeTrait: core::MatSizeTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_MatSize(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn p(&mut self) -> *mut i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatSize_getPropP(self.as_raw_mut_MatSize()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
unsafe fn set_p(&mut self, val: *mut i32) {
let ret = { sys::cv_MatSize_setPropP_intX(self.as_raw_mut_MatSize(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn get_mut(&mut self, i: i32) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatSize_operator___int(self.as_raw_mut_MatSize(), i, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
pub struct MatSize {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { MatSize }
impl Drop for MatSize {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_MatSize_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_MatSize_delete(self.as_raw_mut_MatSize()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for MatSize {}
impl core::MatSizeTraitConst for MatSize {
#[inline] fn as_raw_MatSize(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::MatSizeTrait for MatSize {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_MatSize(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl MatSize {
/// ////////////////////////// MatSize ////////////////////////////
#[inline]
pub fn new(_p: &mut i32) -> core::MatSize {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatSize_MatSize_intX(_p) };
let ret = unsafe { core::MatSize::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::MatStep]
pub trait MatStepTraitConst {
fn as_raw_MatStep(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn get(&self, i: i32) -> size_t {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatStep_operator___const_int(self.as_raw_MatStep(), i) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn to_size_t(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MatStep_operator_size_t_const(self.as_raw_MatStep(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::MatStep]
pub trait MatStepTrait: core::MatStepTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_MatStep(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn p(&mut self) -> *mut size_t {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatStep_getPropP(self.as_raw_mut_MatStep()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
unsafe fn set_p(&mut self, val: *mut size_t) {
let ret = { sys::cv_MatStep_setPropP_size_tX(self.as_raw_mut_MatStep(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn buf(&mut self) -> &mut [size_t; 2] {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatStep_getPropBuf(self.as_raw_mut_MatStep()) };
let ret = unsafe { ret.as_mut() }.expect("Function returned null pointer");
ret
}
#[inline]
fn get_mut(&mut self, i: i32) -> size_t {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatStep_operator___int(self.as_raw_mut_MatStep(), i) };
ret
}
}
pub struct MatStep {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { MatStep }
impl Drop for MatStep {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_MatStep_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_MatStep_delete(self.as_raw_mut_MatStep()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for MatStep {}
impl core::MatStepTraitConst for MatStep {
#[inline] fn as_raw_MatStep(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::MatStepTrait for MatStep {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_MatStep(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl MatStep {
/// ////////////////////////// MatStep ////////////////////////////
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> core::MatStep {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatStep_MatStep() };
let ret = unsafe { core::MatStep::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
pub fn new(s: size_t) -> core::MatStep {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_MatStep_MatStep_size_t(s) };
let ret = unsafe { core::MatStep::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
}
impl Default for MatStep {
#[inline]
/// Forwards to infallible Self::default()
fn default() -> Self {
Self::default()
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Matx_AddOp]
pub trait Matx_AddOpTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Matx_AddOp(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Matx_AddOp]
pub trait Matx_AddOpTrait: core::Matx_AddOpTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Matx_AddOp(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
/// @cond IGNORED
pub struct Matx_AddOp {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Matx_AddOp }
impl Drop for Matx_AddOp {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Matx_AddOp_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Matx_AddOp_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Matx_AddOp()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Matx_AddOp {}
impl core::Matx_AddOpTraitConst for Matx_AddOp {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Matx_AddOp(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::Matx_AddOpTrait for Matx_AddOp {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Matx_AddOp(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Matx_AddOp {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::Matx_AddOp> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Matx_AddOp_Matx_AddOp(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Matx_AddOp::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy(unnamed: &core::Matx_AddOp) -> Result<core::Matx_AddOp> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Matx_AddOp_Matx_AddOp_const_Matx_AddOpR(unnamed.as_raw_Matx_AddOp(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Matx_AddOp::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Matx_DivOp]
pub trait Matx_DivOpTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Matx_DivOp(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Matx_DivOp]
pub trait Matx_DivOpTrait: core::Matx_DivOpTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Matx_DivOp(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
pub struct Matx_DivOp {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Matx_DivOp }
impl Drop for Matx_DivOp {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Matx_DivOp_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Matx_DivOp_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Matx_DivOp()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Matx_DivOp {}
impl core::Matx_DivOpTraitConst for Matx_DivOp {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Matx_DivOp(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::Matx_DivOpTrait for Matx_DivOp {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Matx_DivOp(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Matx_DivOp {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::Matx_DivOp> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Matx_DivOp_Matx_DivOp(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Matx_DivOp::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy(unnamed: &core::Matx_DivOp) -> Result<core::Matx_DivOp> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Matx_DivOp_Matx_DivOp_const_Matx_DivOpR(unnamed.as_raw_Matx_DivOp(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Matx_DivOp::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Matx_MatMulOp]
pub trait Matx_MatMulOpTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Matx_MatMulOp(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Matx_MatMulOp]
pub trait Matx_MatMulOpTrait: core::Matx_MatMulOpTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Matx_MatMulOp(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
pub struct Matx_MatMulOp {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Matx_MatMulOp }
impl Drop for Matx_MatMulOp {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Matx_MatMulOp_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Matx_MatMulOp_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Matx_MatMulOp()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Matx_MatMulOp {}
impl core::Matx_MatMulOpTraitConst for Matx_MatMulOp {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Matx_MatMulOp(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::Matx_MatMulOpTrait for Matx_MatMulOp {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Matx_MatMulOp(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Matx_MatMulOp {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::Matx_MatMulOp> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Matx_MatMulOp_Matx_MatMulOp(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Matx_MatMulOp::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy(unnamed: &core::Matx_MatMulOp) -> Result<core::Matx_MatMulOp> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Matx_MatMulOp_Matx_MatMulOp_const_Matx_MatMulOpR(unnamed.as_raw_Matx_MatMulOp(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Matx_MatMulOp::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Matx_MulOp]
pub trait Matx_MulOpTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Matx_MulOp(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Matx_MulOp]
pub trait Matx_MulOpTrait: core::Matx_MulOpTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Matx_MulOp(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
pub struct Matx_MulOp {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Matx_MulOp }
impl Drop for Matx_MulOp {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Matx_MulOp_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Matx_MulOp_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Matx_MulOp()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Matx_MulOp {}
impl core::Matx_MulOpTraitConst for Matx_MulOp {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Matx_MulOp(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::Matx_MulOpTrait for Matx_MulOp {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Matx_MulOp(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Matx_MulOp {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::Matx_MulOp> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Matx_MulOp_Matx_MulOp(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Matx_MulOp::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy(unnamed: &core::Matx_MulOp) -> Result<core::Matx_MulOp> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Matx_MulOp_Matx_MulOp_const_Matx_MulOpR(unnamed.as_raw_Matx_MulOp(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Matx_MulOp::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Matx_ScaleOp]
pub trait Matx_ScaleOpTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Matx_ScaleOp(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Matx_ScaleOp]
pub trait Matx_ScaleOpTrait: core::Matx_ScaleOpTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Matx_ScaleOp(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
pub struct Matx_ScaleOp {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Matx_ScaleOp }
impl Drop for Matx_ScaleOp {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Matx_ScaleOp_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Matx_ScaleOp_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Matx_ScaleOp()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Matx_ScaleOp {}
impl core::Matx_ScaleOpTraitConst for Matx_ScaleOp {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Matx_ScaleOp(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::Matx_ScaleOpTrait for Matx_ScaleOp {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Matx_ScaleOp(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Matx_ScaleOp {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::Matx_ScaleOp> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Matx_ScaleOp_Matx_ScaleOp(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Matx_ScaleOp::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy(unnamed: &core::Matx_ScaleOp) -> Result<core::Matx_ScaleOp> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Matx_ScaleOp_Matx_ScaleOp_const_Matx_ScaleOpR(unnamed.as_raw_Matx_ScaleOp(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Matx_ScaleOp::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Matx_SubOp]
pub trait Matx_SubOpTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Matx_SubOp(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Matx_SubOp]
pub trait Matx_SubOpTrait: core::Matx_SubOpTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Matx_SubOp(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
pub struct Matx_SubOp {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Matx_SubOp }
impl Drop for Matx_SubOp {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Matx_SubOp_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Matx_SubOp_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Matx_SubOp()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Matx_SubOp {}
impl core::Matx_SubOpTraitConst for Matx_SubOp {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Matx_SubOp(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::Matx_SubOpTrait for Matx_SubOp {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Matx_SubOp(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Matx_SubOp {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::Matx_SubOp> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Matx_SubOp_Matx_SubOp(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Matx_SubOp::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy(unnamed: &core::Matx_SubOp) -> Result<core::Matx_SubOp> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Matx_SubOp_Matx_SubOp_const_Matx_SubOpR(unnamed.as_raw_Matx_SubOp(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Matx_SubOp::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Matx_TOp]
pub trait Matx_TOpTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Matx_TOp(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Matx_TOp]
pub trait Matx_TOpTrait: core::Matx_TOpTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Matx_TOp(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
pub struct Matx_TOp {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Matx_TOp }
impl Drop for Matx_TOp {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Matx_TOp_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Matx_TOp_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Matx_TOp()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Matx_TOp {}
impl core::Matx_TOpTraitConst for Matx_TOp {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Matx_TOp(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::Matx_TOpTrait for Matx_TOp {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Matx_TOp(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Matx_TOp {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::Matx_TOp> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Matx_TOp_Matx_TOp(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Matx_TOp::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy(unnamed: &core::Matx_TOp) -> Result<core::Matx_TOp> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Matx_TOp_Matx_TOp_const_Matx_TOpR(unnamed.as_raw_Matx_TOp(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Matx_TOp::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::MinProblemSolver]
pub trait MinProblemSolverConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_MinProblemSolver(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Getter for the optimized function.
///
/// The optimized function is represented by Function interface, which requires derivatives to
/// implement the calc(double*) and getDim() methods to evaluate the function.
///
/// ## Returns
/// Smart-pointer to an object that implements Function interface - it represents the
/// function that is being optimized. It can be empty, if no function was given so far.
#[inline]
fn get_function(&self) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn core::MinProblemSolver_Function>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MinProblemSolver_getFunction_const(self.as_raw_MinProblemSolver(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn core::MinProblemSolver_Function>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Getter for the previously set terminal criteria for this algorithm.
///
/// ## Returns
/// Deep copy of the terminal criteria used at the moment.
#[inline]
fn get_term_criteria(&self) -> Result<core::TermCriteria> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MinProblemSolver_getTermCriteria_const(self.as_raw_MinProblemSolver(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Basic interface for all solvers
pub trait MinProblemSolver: core::AlgorithmTrait + core::MinProblemSolverConst {
fn as_raw_mut_MinProblemSolver(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Setter for the optimized function.
///
/// *It should be called at least once before the call to* minimize(), as default value is not usable.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * f: The new function to optimize.
#[inline]
fn set_function(&mut self, f: &core::Ptr<dyn core::MinProblemSolver_Function>) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MinProblemSolver_setFunction_const_PtrLFunctionGR(self.as_raw_mut_MinProblemSolver(), f.as_raw_PtrOfMinProblemSolver_Function(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Set terminal criteria for solver.
///
/// This method *is not necessary* to be called before the first call to minimize(), as the default
/// value is sensible.
///
/// Algorithm stops when the number of function evaluations done exceeds termcrit.maxCount, when
/// the function values at the vertices of simplex are within termcrit.epsilon range or simplex
/// becomes so small that it can enclosed in a box with termcrit.epsilon sides, whatever comes
/// first.
/// ## Parameters
/// * termcrit: Terminal criteria to be used, represented as cv::TermCriteria structure.
#[inline]
fn set_term_criteria(&mut self, termcrit: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MinProblemSolver_setTermCriteria_const_TermCriteriaR(self.as_raw_mut_MinProblemSolver(), &termcrit, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// actually runs the algorithm and performs the minimization.
///
/// The sole input parameter determines the centroid of the starting simplex (roughly, it tells
/// where to start), all the others (terminal criteria, initial step, function to be minimized) are
/// supposed to be set via the setters before the call to this method or the default values (not
/// always sensible) will be used.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * x: The initial point, that will become a centroid of an initial simplex. After the algorithm
/// will terminate, it will be set to the point where the algorithm stops, the point of possible
/// minimum.
/// ## Returns
/// The value of a function at the point found.
#[inline]
fn minimize(&mut self, x: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray) -> Result<f64> {
extern_container_arg!(x);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MinProblemSolver_minimize_const__InputOutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_MinProblemSolver(), x.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::MinProblemSolver_Function]
pub trait MinProblemSolver_FunctionConst {
fn as_raw_MinProblemSolver_Function(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn get_dims(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MinProblemSolver_Function_getDims_const(self.as_raw_MinProblemSolver_Function(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_gradient_eps(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MinProblemSolver_Function_getGradientEps_const(self.as_raw_MinProblemSolver_Function(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn calc(&self, x: &f64) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MinProblemSolver_Function_calc_const_const_doubleX(self.as_raw_MinProblemSolver_Function(), x, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Represents function being optimized
pub trait MinProblemSolver_Function: core::MinProblemSolver_FunctionConst {
fn as_raw_mut_MinProblemSolver_Function(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn get_gradient(&mut self, x: &f64, grad: &mut f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_MinProblemSolver_Function_getGradient_const_doubleX_doubleX(self.as_raw_mut_MinProblemSolver_Function(), x, grad, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// struct returned by cv::moments
///
/// The spatial moments  are computed as:
///
/// 
///
/// The central moments  are computed as:
///
/// 
///
/// where  is the mass center:
///
/// 
///
/// The normalized central moments  are computed as:
///
/// 
///
///
/// Note:
/// , 
///  , hence the values are not
/// stored.
///
/// The moments of a contour are defined in the same way but computed using the Green's formula (see
/// <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Green_theorem>). So, due to a limited raster resolution, the moments
/// computed for a contour are slightly different from the moments computed for the same rasterized
/// contour.
///
///
/// Note:
/// Since the contour moments are computed using Green formula, you may get seemingly odd results for
/// contours with self-intersections, e.g. a zero area (m00) for butterfly-shaped contours.
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)]
pub struct Moments {
/// @name spatial moments
pub m00: f64,
/// @name spatial moments
pub m10: f64,
/// @name spatial moments
pub m01: f64,
/// @name spatial moments
pub m20: f64,
/// @name spatial moments
pub m11: f64,
/// @name spatial moments
pub m02: f64,
/// @name spatial moments
pub m30: f64,
/// @name spatial moments
pub m21: f64,
/// @name spatial moments
pub m12: f64,
/// @name spatial moments
pub m03: f64,
/// @name central moments
pub mu20: f64,
/// @name central moments
pub mu11: f64,
/// @name central moments
pub mu02: f64,
/// @name central moments
pub mu30: f64,
/// @name central moments
pub mu21: f64,
/// @name central moments
pub mu12: f64,
/// @name central moments
pub mu03: f64,
/// @name central normalized moments
pub nu20: f64,
/// @name central normalized moments
pub nu11: f64,
/// @name central normalized moments
pub nu02: f64,
/// @name central normalized moments
pub nu30: f64,
/// @name central normalized moments
pub nu21: f64,
/// @name central normalized moments
pub nu12: f64,
/// @name central normalized moments
pub nu03: f64,
}
opencv_type_simple! { core::Moments }
impl Moments {
/// the default constructor
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::Moments> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Moments_Moments(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// the full constructor
#[inline]
pub fn new(m00: f64, m10: f64, m01: f64, m20: f64, m11: f64, m02: f64, m30: f64, m21: f64, m12: f64, m03: f64) -> Result<core::Moments> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Moments_Moments_double_double_double_double_double_double_double_double_double_double(m00, m10, m01, m20, m11, m02, m30, m21, m12, m03, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::PCA]
pub trait PCATraitConst {
fn as_raw_PCA(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// eigenvectors of the covariation matrix
#[inline]
fn eigenvectors(&self) -> core::Mat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_PCA_getPropEigenvectors_const(self.as_raw_PCA()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// eigenvalues of the covariation matrix
#[inline]
fn eigenvalues(&self) -> core::Mat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_PCA_getPropEigenvalues_const(self.as_raw_PCA()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// mean value subtracted before the projection and added after the back projection
#[inline]
fn mean(&self) -> core::Mat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_PCA_getPropMean_const(self.as_raw_PCA()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// Projects vector(s) to the principal component subspace.
///
/// The methods project one or more vectors to the principal component
/// subspace, where each vector projection is represented by coefficients in
/// the principal component basis. The first form of the method returns the
/// matrix that the second form writes to the result. So the first form can
/// be used as a part of expression while the second form can be more
/// efficient in a processing loop.
/// ## Parameters
/// * vec: input vector(s); must have the same dimensionality and the
/// same layout as the input data used at %PCA phase, that is, if
/// DATA_AS_ROW are specified, then `vec.cols==data.cols`
/// (vector dimensionality) and `vec.rows` is the number of vectors to
/// project, and the same is true for the PCA::DATA_AS_COL case.
#[inline]
fn project(&self, vec: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> {
extern_container_arg!(vec);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_PCA_project_const_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_PCA(), vec.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Projects vector(s) to the principal component subspace.
///
/// The methods project one or more vectors to the principal component
/// subspace, where each vector projection is represented by coefficients in
/// the principal component basis. The first form of the method returns the
/// matrix that the second form writes to the result. So the first form can
/// be used as a part of expression while the second form can be more
/// efficient in a processing loop.
/// ## Parameters
/// * vec: input vector(s); must have the same dimensionality and the
/// same layout as the input data used at %PCA phase, that is, if
/// DATA_AS_ROW are specified, then `vec.cols==data.cols`
/// (vector dimensionality) and `vec.rows` is the number of vectors to
/// project, and the same is true for the PCA::DATA_AS_COL case.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * vec: input vector(s); must have the same dimensionality and the
/// same layout as the input data used at PCA phase, that is, if
/// DATA_AS_ROW are specified, then `vec.cols==data.cols`
/// (vector dimensionality) and `vec.rows` is the number of vectors to
/// project, and the same is true for the PCA::DATA_AS_COL case.
/// * result: output vectors; in case of PCA::DATA_AS_COL, the
/// output matrix has as many columns as the number of input vectors, this
/// means that `result.cols==vec.cols` and the number of rows match the
/// number of principal components (for example, `maxComponents` parameter
/// passed to the constructor).
#[inline]
fn project_to(&self, vec: &dyn core::ToInputArray, result: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(vec);
extern_container_arg!(result);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_PCA_project_const_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_PCA(), vec.as_raw__InputArray(), result.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Reconstructs vectors from their PC projections.
///
/// The methods are inverse operations to PCA::project. They take PC
/// coordinates of projected vectors and reconstruct the original vectors.
/// Unless all the principal components have been retained, the
/// reconstructed vectors are different from the originals. But typically,
/// the difference is small if the number of components is large enough (but
/// still much smaller than the original vector dimensionality). As a
/// result, PCA is used.
/// ## Parameters
/// * vec: coordinates of the vectors in the principal component
/// subspace, the layout and size are the same as of PCA::project output
/// vectors.
#[inline]
fn back_project(&self, vec: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> {
extern_container_arg!(vec);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_PCA_backProject_const_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_PCA(), vec.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Reconstructs vectors from their PC projections.
///
/// The methods are inverse operations to PCA::project. They take PC
/// coordinates of projected vectors and reconstruct the original vectors.
/// Unless all the principal components have been retained, the
/// reconstructed vectors are different from the originals. But typically,
/// the difference is small if the number of components is large enough (but
/// still much smaller than the original vector dimensionality). As a
/// result, PCA is used.
/// ## Parameters
/// * vec: coordinates of the vectors in the principal component
/// subspace, the layout and size are the same as of PCA::project output
/// vectors.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * vec: coordinates of the vectors in the principal component
/// subspace, the layout and size are the same as of PCA::project output
/// vectors.
/// * result: reconstructed vectors; the layout and size are the same as
/// of PCA::project input vectors.
#[inline]
fn back_project_to(&self, vec: &dyn core::ToInputArray, result: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(vec);
extern_container_arg!(result);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_PCA_backProject_const_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_PCA(), vec.as_raw__InputArray(), result.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// write PCA objects
///
/// Writes [eigenvalues] [eigenvectors] and [mean] to specified FileStorage
#[inline]
fn write(&self, fs: &mut core::FileStorage) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_PCA_write_const_FileStorageR(self.as_raw_PCA(), fs.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::PCA]
pub trait PCATrait: core::PCATraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_PCA(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// eigenvectors of the covariation matrix
#[inline]
fn set_eigenvectors(&mut self, mut val: core::Mat) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_PCA_setPropEigenvectors_Mat(self.as_raw_mut_PCA(), val.as_raw_mut_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// eigenvalues of the covariation matrix
#[inline]
fn set_eigenvalues(&mut self, mut val: core::Mat) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_PCA_setPropEigenvalues_Mat(self.as_raw_mut_PCA(), val.as_raw_mut_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// mean value subtracted before the projection and added after the back projection
#[inline]
fn set_mean(&mut self, mut val: core::Mat) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_PCA_setPropMean_Mat(self.as_raw_mut_PCA(), val.as_raw_mut_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// performs %PCA
///
/// The operator performs %PCA of the supplied dataset. It is safe to reuse
/// the same PCA structure for multiple datasets. That is, if the structure
/// has been previously used with another dataset, the existing internal
/// data is reclaimed and the new [eigenvalues], [eigenvectors] and [mean] are allocated and computed.
///
/// The computed [eigenvalues] are sorted from the largest to the smallest and
/// the corresponding [eigenvectors] are stored as eigenvectors rows.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * data: input samples stored as the matrix rows or as the matrix
/// columns.
/// * mean: optional mean value; if the matrix is empty (noArray()),
/// the mean is computed from the data.
/// * flags: operation flags; currently the parameter is only used to
/// specify the data layout. (Flags)
/// * maxComponents: maximum number of components that PCA should
/// retain; by default, all the components are retained.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * max_components: 0
#[inline]
fn apply(&mut self, data: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mean: &dyn core::ToInputArray, flags: i32, max_components: i32) -> Result<core::PCA> {
extern_container_arg!(data);
extern_container_arg!(mean);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_PCA_operator___const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int_int(self.as_raw_mut_PCA(), data.as_raw__InputArray(), mean.as_raw__InputArray(), flags, max_components, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::PCA::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// performs %PCA
///
/// The operator performs %PCA of the supplied dataset. It is safe to reuse
/// the same PCA structure for multiple datasets. That is, if the structure
/// has been previously used with another dataset, the existing internal
/// data is reclaimed and the new [eigenvalues], [eigenvectors] and [mean] are allocated and computed.
///
/// The computed [eigenvalues] are sorted from the largest to the smallest and
/// the corresponding [eigenvectors] are stored as eigenvectors rows.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * data: input samples stored as the matrix rows or as the matrix
/// columns.
/// * mean: optional mean value; if the matrix is empty (noArray()),
/// the mean is computed from the data.
/// * flags: operation flags; currently the parameter is only used to
/// specify the data layout. (Flags)
/// * maxComponents: maximum number of components that PCA should
/// retain; by default, all the components are retained.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * data: input samples stored as the matrix rows or as the matrix
/// columns.
/// * mean: optional mean value; if the matrix is empty (noArray()),
/// the mean is computed from the data.
/// * flags: operation flags; currently the parameter is only used to
/// specify the data layout. (PCA::Flags)
/// * retainedVariance: Percentage of variance that %PCA should retain.
/// Using this parameter will let the %PCA decided how many components to
/// retain but it will always keep at least 2.
#[inline]
fn apply_1(&mut self, data: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mean: &dyn core::ToInputArray, flags: i32, retained_variance: f64) -> Result<core::PCA> {
extern_container_arg!(data);
extern_container_arg!(mean);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_PCA_operator___const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int_double(self.as_raw_mut_PCA(), data.as_raw__InputArray(), mean.as_raw__InputArray(), flags, retained_variance, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::PCA::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// load PCA objects
///
/// Loads [eigenvalues] [eigenvectors] and [mean] from specified FileNode
#[inline]
fn read(&mut self, fn_: &core::FileNode) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_PCA_read_const_FileNodeR(self.as_raw_mut_PCA(), fn_.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Principal Component Analysis
///
/// The class is used to calculate a special basis for a set of vectors. The
/// basis will consist of eigenvectors of the covariance matrix calculated
/// from the input set of vectors. The class %PCA can also transform
/// vectors to/from the new coordinate space defined by the basis. Usually,
/// in this new coordinate system, each vector from the original set (and
/// any linear combination of such vectors) can be quite accurately
/// approximated by taking its first few components, corresponding to the
/// eigenvectors of the largest eigenvalues of the covariance matrix.
/// Geometrically it means that you calculate a projection of the vector to
/// a subspace formed by a few eigenvectors corresponding to the dominant
/// eigenvalues of the covariance matrix. And usually such a projection is
/// very close to the original vector. So, you can represent the original
/// vector from a high-dimensional space with a much shorter vector
/// consisting of the projected vector's coordinates in the subspace. Such a
/// transformation is also known as Karhunen-Loeve Transform, or KLT.
/// See <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Principal_component_analysis>
///
/// The sample below is the function that takes two matrices. The first
/// function stores a set of vectors (a row per vector) that is used to
/// calculate PCA. The second function stores another "test" set of vectors
/// (a row per vector). First, these vectors are compressed with PCA, then
/// reconstructed back, and then the reconstruction error norm is computed
/// and printed for each vector. :
///
/// ```C++
/// using namespace cv;
///
/// PCA compressPCA(const Mat& pcaset, int maxComponents,
/// const Mat& testset, Mat& compressed)
/// {
/// PCA pca(pcaset, // pass the data
/// Mat(), // we do not have a pre-computed mean vector,
/// // so let the PCA engine to compute it
/// PCA::DATA_AS_ROW, // indicate that the vectors
/// // are stored as matrix rows
/// // (use PCA::DATA_AS_COL if the vectors are
/// // the matrix columns)
/// maxComponents // specify, how many principal components to retain
/// );
/// // if there is no test data, just return the computed basis, ready-to-use
/// if( !testset.data )
/// return pca;
/// CV_Assert( testset.cols == pcaset.cols );
///
/// compressed.create(testset.rows, maxComponents, testset.type());
///
/// Mat reconstructed;
/// for( int i = 0; i < testset.rows; i++ )
/// {
/// Mat vec = testset.row(i), coeffs = compressed.row(i), reconstructed;
/// // compress the vector, the result will be stored
/// // in the i-th row of the output matrix
/// pca.project(vec, coeffs);
/// // and then reconstruct it
/// pca.backProject(coeffs, reconstructed);
/// // and measure the error
/// printf("%d. diff = %g\n", i, norm(vec, reconstructed, NORM_L2));
/// }
/// return pca;
/// }
/// ```
/// ## See also
/// calcCovarMatrix, mulTransposed, SVD, dft, dct
pub struct PCA {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { PCA }
impl Drop for PCA {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_PCA_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_PCA_delete(self.as_raw_mut_PCA()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for PCA {}
impl core::PCATraitConst for PCA {
#[inline] fn as_raw_PCA(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::PCATrait for PCA {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_PCA(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl PCA {
/// default constructor
///
/// The default constructor initializes an empty %PCA structure. The other
/// constructors initialize the structure and call PCA::operator()().
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::PCA> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_PCA_PCA(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::PCA::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// default constructor
///
/// The default constructor initializes an empty %PCA structure. The other
/// constructors initialize the structure and call PCA::operator()().
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * data: input samples stored as matrix rows or matrix columns.
/// * mean: optional mean value; if the matrix is empty (@c noArray()),
/// the mean is computed from the data.
/// * flags: operation flags; currently the parameter is only used to
/// specify the data layout (PCA::Flags)
/// * maxComponents: maximum number of components that %PCA should
/// retain; by default, all the components are retained.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * max_components: 0
#[inline]
pub fn new(data: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mean: &dyn core::ToInputArray, flags: i32, max_components: i32) -> Result<core::PCA> {
extern_container_arg!(data);
extern_container_arg!(mean);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_PCA_PCA_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int_int(data.as_raw__InputArray(), mean.as_raw__InputArray(), flags, max_components, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::PCA::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// default constructor
///
/// The default constructor initializes an empty %PCA structure. The other
/// constructors initialize the structure and call PCA::operator()().
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * data: input samples stored as matrix rows or matrix columns.
/// * mean: optional mean value; if the matrix is empty (noArray()),
/// the mean is computed from the data.
/// * flags: operation flags; currently the parameter is only used to
/// specify the data layout (PCA::Flags)
/// * retainedVariance: Percentage of variance that PCA should retain.
/// Using this parameter will let the PCA decided how many components to
/// retain but it will always keep at least 2.
#[inline]
pub fn new_with_variance(data: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mean: &dyn core::ToInputArray, flags: i32, retained_variance: f64) -> Result<core::PCA> {
extern_container_arg!(data);
extern_container_arg!(mean);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_PCA_PCA_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int_double(data.as_raw__InputArray(), mean.as_raw__InputArray(), flags, retained_variance, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::PCA::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::ParallelLoopBody]
pub trait ParallelLoopBodyConst {
fn as_raw_ParallelLoopBody(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn apply(&self, range: &core::Range) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ParallelLoopBody_operator___const_const_RangeR(self.as_raw_ParallelLoopBody(), range.as_raw_Range(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Base class for parallel data processors
///
/// @ingroup core_parallel
pub trait ParallelLoopBody: core::ParallelLoopBodyConst {
fn as_raw_mut_ParallelLoopBody(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
/// Constant methods for [core::RNG]
pub trait RNGTraitConst {
fn as_raw_RNG(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn state(&self) -> u64 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_getPropState_const(self.as_raw_RNG()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn equals(&self, other: &core::RNG) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_operatorEQ_const_const_RNGR(self.as_raw_RNG(), other.as_raw_RNG(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::RNG]
pub trait RNGTrait: core::RNGTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_RNG(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_state(&mut self, val: u64) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_setPropState_uint64_t(self.as_raw_mut_RNG(), val) };
ret
}
/// The method updates the state using the MWC algorithm and returns the
/// next 32-bit random number.
#[inline]
fn next(&mut self) -> Result<u32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_next(self.as_raw_mut_RNG(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Each of the methods updates the state using the MWC algorithm and
/// returns the next random number of the specified type. In case of integer
/// types, the returned number is from the available value range for the
/// specified type. In case of floating-point types, the returned value is
/// from [0,1) range.
#[inline]
fn to_u8(&mut self) -> Result<u8> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_operator_unsigned_char(self.as_raw_mut_RNG(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
#[inline]
fn to_i8(&mut self) -> Result<i8> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_operator_signed_char(self.as_raw_mut_RNG(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
#[inline]
fn to_u16(&mut self) -> Result<u16> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_operator_unsigned_short(self.as_raw_mut_RNG(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
#[inline]
fn to_i16(&mut self) -> Result<i16> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_operator_short(self.as_raw_mut_RNG(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
#[inline]
fn to_u32(&mut self) -> Result<u32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_operator_unsigned_int(self.as_raw_mut_RNG(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
#[inline]
fn to_i32(&mut self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_operator_int(self.as_raw_mut_RNG(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
#[inline]
fn to_f32(&mut self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_operator_float(self.as_raw_mut_RNG(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
#[inline]
fn to_f64(&mut self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_operator_double(self.as_raw_mut_RNG(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns a random integer sampled uniformly from [0, N).
///
/// The methods transform the state using the MWC algorithm and return the
/// next random number. The first form is equivalent to RNG::next . The
/// second form returns the random number modulo N , which means that the
/// result is in the range [0, N) .
#[inline]
fn apply(&mut self) -> Result<u32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_operator__(self.as_raw_mut_RNG(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns a random integer sampled uniformly from [0, N).
///
/// The methods transform the state using the MWC algorithm and return the
/// next random number. The first form is equivalent to RNG::next . The
/// second form returns the random number modulo N , which means that the
/// result is in the range [0, N) .
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * N: upper non-inclusive boundary of the returned random number.
#[inline]
fn apply_1(&mut self, n: u32) -> Result<u32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_operator___unsigned_int(self.as_raw_mut_RNG(), n, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns uniformly distributed integer random number from [a,b) range
///
/// The methods transform the state using the MWC algorithm and return the
/// next uniformly-distributed random number of the specified type, deduced
/// from the input parameter type, from the range [a, b) . There is a nuance
/// illustrated by the following sample:
///
/// ```C++
/// RNG rng;
///
/// // always produces 0
/// double a = rng.uniform(0, 1);
///
/// // produces double from [0, 1)
/// double a1 = rng.uniform((double)0, (double)1);
///
/// // produces float from [0, 1)
/// float b = rng.uniform(0.f, 1.f);
///
/// // produces double from [0, 1)
/// double c = rng.uniform(0., 1.);
///
/// // may cause compiler error because of ambiguity:
/// // RNG::uniform(0, (int)0.999999)? or RNG::uniform((double)0, 0.99999)?
/// double d = rng.uniform(0, 0.999999);
/// ```
///
///
/// The compiler does not take into account the type of the variable to
/// which you assign the result of RNG::uniform . The only thing that
/// matters to the compiler is the type of a and b parameters. So, if you
/// want a floating-point random number, but the range boundaries are
/// integer numbers, either put dots in the end, if they are constants, or
/// use explicit type cast operators, as in the a1 initialization above.
/// ## Parameters
/// * a: lower inclusive boundary of the returned random number.
/// * b: upper non-inclusive boundary of the returned random number.
#[inline]
fn uniform(&mut self, a: i32, b: i32) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_uniform_int_int(self.as_raw_mut_RNG(), a, b, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns uniformly distributed integer random number from [a,b) range
///
/// The methods transform the state using the MWC algorithm and return the
/// next uniformly-distributed random number of the specified type, deduced
/// from the input parameter type, from the range [a, b) . There is a nuance
/// illustrated by the following sample:
///
/// ```C++
/// RNG rng;
///
/// // always produces 0
/// double a = rng.uniform(0, 1);
///
/// // produces double from [0, 1)
/// double a1 = rng.uniform((double)0, (double)1);
///
/// // produces float from [0, 1)
/// float b = rng.uniform(0.f, 1.f);
///
/// // produces double from [0, 1)
/// double c = rng.uniform(0., 1.);
///
/// // may cause compiler error because of ambiguity:
/// // RNG::uniform(0, (int)0.999999)? or RNG::uniform((double)0, 0.99999)?
/// double d = rng.uniform(0, 0.999999);
/// ```
///
///
/// The compiler does not take into account the type of the variable to
/// which you assign the result of RNG::uniform . The only thing that
/// matters to the compiler is the type of a and b parameters. So, if you
/// want a floating-point random number, but the range boundaries are
/// integer numbers, either put dots in the end, if they are constants, or
/// use explicit type cast operators, as in the a1 initialization above.
/// ## Parameters
/// * a: lower inclusive boundary of the returned random number.
/// * b: upper non-inclusive boundary of the returned random number.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
#[inline]
fn uniform_1(&mut self, a: f32, b: f32) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_uniform_float_float(self.as_raw_mut_RNG(), a, b, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns uniformly distributed integer random number from [a,b) range
///
/// The methods transform the state using the MWC algorithm and return the
/// next uniformly-distributed random number of the specified type, deduced
/// from the input parameter type, from the range [a, b) . There is a nuance
/// illustrated by the following sample:
///
/// ```C++
/// RNG rng;
///
/// // always produces 0
/// double a = rng.uniform(0, 1);
///
/// // produces double from [0, 1)
/// double a1 = rng.uniform((double)0, (double)1);
///
/// // produces float from [0, 1)
/// float b = rng.uniform(0.f, 1.f);
///
/// // produces double from [0, 1)
/// double c = rng.uniform(0., 1.);
///
/// // may cause compiler error because of ambiguity:
/// // RNG::uniform(0, (int)0.999999)? or RNG::uniform((double)0, 0.99999)?
/// double d = rng.uniform(0, 0.999999);
/// ```
///
///
/// The compiler does not take into account the type of the variable to
/// which you assign the result of RNG::uniform . The only thing that
/// matters to the compiler is the type of a and b parameters. So, if you
/// want a floating-point random number, but the range boundaries are
/// integer numbers, either put dots in the end, if they are constants, or
/// use explicit type cast operators, as in the a1 initialization above.
/// ## Parameters
/// * a: lower inclusive boundary of the returned random number.
/// * b: upper non-inclusive boundary of the returned random number.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
#[inline]
fn uniform_2(&mut self, a: f64, b: f64) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_uniform_double_double(self.as_raw_mut_RNG(), a, b, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Fills arrays with random numbers.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * mat: 2D or N-dimensional matrix; currently matrices with more than
/// 4 channels are not supported by the methods, use Mat::reshape as a
/// possible workaround.
/// * distType: distribution type, RNG::UNIFORM or RNG::NORMAL.
/// * a: first distribution parameter; in case of the uniform
/// distribution, this is an inclusive lower boundary, in case of the normal
/// distribution, this is a mean value.
/// * b: second distribution parameter; in case of the uniform
/// distribution, this is a non-inclusive upper boundary, in case of the
/// normal distribution, this is a standard deviation (diagonal of the
/// standard deviation matrix or the full standard deviation matrix).
/// * saturateRange: pre-saturation flag; for uniform distribution only;
/// if true, the method will first convert a and b to the acceptable value
/// range (according to the mat datatype) and then will generate uniformly
/// distributed random numbers within the range [saturate(a), saturate(b)),
/// if saturateRange=false, the method will generate uniformly distributed
/// random numbers in the original range [a, b) and then will saturate them,
/// it means, for example, that
/// <tt>theRNG().fill(mat_8u, RNG::UNIFORM, -DBL_MAX, DBL_MAX)</tt> will likely
/// produce array mostly filled with 0's and 255's, since the range (0, 255)
/// is significantly smaller than [-DBL_MAX, DBL_MAX).
///
/// Each of the methods fills the matrix with the random values from the
/// specified distribution. As the new numbers are generated, the RNG state
/// is updated accordingly. In case of multiple-channel images, every
/// channel is filled independently, which means that RNG cannot generate
/// samples from the multi-dimensional Gaussian distribution with
/// non-diagonal covariance matrix directly. To do that, the method
/// generates samples from multi-dimensional standard Gaussian distribution
/// with zero mean and identity covariation matrix, and then transforms them
/// using transform to get samples from the specified Gaussian distribution.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * saturate_range: false
#[inline]
fn fill(&mut self, mat: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, dist_type: i32, a: &dyn core::ToInputArray, b: &dyn core::ToInputArray, saturate_range: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(mat);
extern_container_arg!(a);
extern_container_arg!(b);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_fill_const__InputOutputArrayR_int_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_bool(self.as_raw_mut_RNG(), mat.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_type, a.as_raw__InputArray(), b.as_raw__InputArray(), saturate_range, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the next random number sampled from the Gaussian distribution
/// ## Parameters
/// * sigma: standard deviation of the distribution.
///
/// The method transforms the state using the MWC algorithm and returns the
/// next random number from the Gaussian distribution N(0,sigma) . That is,
/// the mean value of the returned random numbers is zero and the standard
/// deviation is the specified sigma .
#[inline]
fn gaussian(&mut self, sigma: f64) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_gaussian_double(self.as_raw_mut_RNG(), sigma, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Random Number Generator
///
/// Random number generator. It encapsulates the state (currently, a 64-bit
/// integer) and has methods to return scalar random values and to fill
/// arrays with random values. Currently it supports uniform and Gaussian
/// (normal) distributions. The generator uses Multiply-With-Carry
/// algorithm, introduced by G. Marsaglia (
/// <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multiply-with-carry> ).
/// Gaussian-distribution random numbers are generated using the Ziggurat
/// algorithm ( <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ziggurat_algorithm> ),
/// introduced by G. Marsaglia and W. W. Tsang.
pub struct RNG {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { RNG }
impl Drop for RNG {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_RNG_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_RNG_delete(self.as_raw_mut_RNG()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for RNG {}
impl core::RNGTraitConst for RNG {
#[inline] fn as_raw_RNG(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::RNGTrait for RNG {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_RNG(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl RNG {
/// constructor
///
/// These are the RNG constructors. The first form sets the state to some
/// pre-defined value, equal to 2\*\*32-1 in the current implementation. The
/// second form sets the state to the specified value. If you passed state=0
/// , the constructor uses the above default value instead to avoid the
/// singular random number sequence, consisting of all zeros.
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::RNG> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_RNG(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::RNG::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// constructor
///
/// These are the RNG constructors. The first form sets the state to some
/// pre-defined value, equal to 2\*\*32-1 in the current implementation. The
/// second form sets the state to the specified value. If you passed state=0
/// , the constructor uses the above default value instead to avoid the
/// singular random number sequence, consisting of all zeros.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * state: 64-bit value used to initialize the RNG.
#[inline]
pub fn new(state: u64) -> Result<core::RNG> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_RNG_uint64_t(state, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::RNG::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::RNG_MT19937]
pub trait RNG_MT19937TraitConst {
fn as_raw_RNG_MT19937(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::RNG_MT19937]
pub trait RNG_MT19937Trait: core::RNG_MT19937TraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_RNG_MT19937(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn seed(&mut self, s: u32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_MT19937_seed_unsigned_int(self.as_raw_mut_RNG_MT19937(), s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn next(&mut self) -> Result<u32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_MT19937_next(self.as_raw_mut_RNG_MT19937(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn to_i32(&mut self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_MT19937_operator_int(self.as_raw_mut_RNG_MT19937(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn to_u32(&mut self) -> Result<u32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_MT19937_operator_unsigned_int(self.as_raw_mut_RNG_MT19937(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn to_f32(&mut self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_MT19937_operator_float(self.as_raw_mut_RNG_MT19937(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn to_f64(&mut self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_MT19937_operator_double(self.as_raw_mut_RNG_MT19937(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn apply(&mut self, n: u32) -> Result<u32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_MT19937_operator___unsigned_int(self.as_raw_mut_RNG_MT19937(), n, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn apply_1(&mut self) -> Result<u32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_MT19937_operator__(self.as_raw_mut_RNG_MT19937(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns uniformly distributed integer random number from [a,b) range
#[inline]
fn uniform(&mut self, a: i32, b: i32) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_MT19937_uniform_int_int(self.as_raw_mut_RNG_MT19937(), a, b, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns uniformly distributed floating-point random number from [a,b) range
#[inline]
fn uniform_1(&mut self, a: f32, b: f32) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_MT19937_uniform_float_float(self.as_raw_mut_RNG_MT19937(), a, b, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns uniformly distributed double-precision floating-point random number from [a,b) range
#[inline]
fn uniform_2(&mut self, a: f64, b: f64) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_MT19937_uniform_double_double(self.as_raw_mut_RNG_MT19937(), a, b, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mersenne Twister random number generator
///
/// Inspired by <http://www.math.sci.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/~m-mat/MT/MT2002/CODES/mt19937ar.c>
/// @todo document
pub struct RNG_MT19937 {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { RNG_MT19937 }
impl Drop for RNG_MT19937 {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_RNG_MT19937_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_RNG_MT19937_delete(self.as_raw_mut_RNG_MT19937()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for RNG_MT19937 {}
impl core::RNG_MT19937TraitConst for RNG_MT19937 {
#[inline] fn as_raw_RNG_MT19937(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::RNG_MT19937Trait for RNG_MT19937 {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_RNG_MT19937(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl RNG_MT19937 {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::RNG_MT19937> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_MT19937_RNG_MT19937(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::RNG_MT19937::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn new(s: u32) -> Result<core::RNG_MT19937> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RNG_MT19937_RNG_MT19937_unsigned_int(s, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::RNG_MT19937::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Range]
pub trait RangeTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Range(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn start(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Range_getPropStart_const(self.as_raw_Range()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn end(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Range_getPropEnd_const(self.as_raw_Range()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn size(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Range_size_const(self.as_raw_Range(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn empty(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Range_empty_const(self.as_raw_Range(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Range]
pub trait RangeTrait: core::RangeTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Range(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_start(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Range_setPropStart_int(self.as_raw_mut_Range(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_end(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_Range_setPropEnd_int(self.as_raw_mut_Range(), val) };
ret
}
}
/// Template class specifying a continuous subsequence (slice) of a sequence.
///
/// The class is used to specify a row or a column span in a matrix ( Mat ) and for many other purposes.
/// Range(a,b) is basically the same as a:b in Matlab or a..b in Python. As in Python, start is an
/// inclusive left boundary of the range and end is an exclusive right boundary of the range. Such a
/// half-opened interval is usually denoted as  .
///
/// The static method Range::all() returns a special variable that means "the whole sequence" or "the
/// whole range", just like " : " in Matlab or " ... " in Python. All the methods and functions in
/// OpenCV that take Range support this special Range::all() value. But, of course, in case of your own
/// custom processing, you will probably have to check and handle it explicitly:
/// ```C++
/// void my_function(..., const Range& r, ....)
/// {
/// if(r == Range::all()) {
/// // process all the data
/// }
/// else {
/// // process [r.start, r.end)
/// }
/// }
/// ```
///
pub struct Range {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Range }
impl Drop for Range {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Range_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Range_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Range()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Range {}
impl core::RangeTraitConst for Range {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Range(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::RangeTrait for Range {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Range(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Range {
/// ////////////////////////////// Range /////////////////////////////////
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::Range> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Range_Range(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Range::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn new(_start: i32, _end: i32) -> Result<core::Range> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Range_Range_int_int(_start, _end, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Range::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn all() -> Result<core::Range> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_Range_all(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Range::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::RotatedRect]
pub trait RotatedRectTraitConst {
fn as_raw_RotatedRect(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// returns the rectangle mass center
#[inline]
fn center(&self) -> core::Point2f {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RotatedRect_getPropCenter_const(self.as_raw_RotatedRect(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
ret
}
/// returns width and height of the rectangle
#[inline]
fn size(&self) -> core::Size2f {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RotatedRect_getPropSize_const(self.as_raw_RotatedRect(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
ret
}
/// returns the rotation angle. When the angle is 0, 90, 180, 270 etc., the rectangle becomes an up-right rectangle.
#[inline]
fn angle(&self) -> f32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_RotatedRect_getPropAngle_const(self.as_raw_RotatedRect()) };
ret
}
/// returns 4 vertices of the rectangle
/// ## Parameters
/// * pts: The points array for storing rectangle vertices. The order is bottomLeft, topLeft, topRight, bottomRight.
#[inline]
fn points(&self, pts: &mut [core::Point2f]) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RotatedRect_points_const_Point2fX(self.as_raw_RotatedRect(), pts.as_mut_ptr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns the minimal up-right integer rectangle containing the rotated rectangle
#[inline]
fn bounding_rect(&self) -> Result<core::Rect> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RotatedRect_boundingRect_const(self.as_raw_RotatedRect(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns the minimal (exact) floating point rectangle containing the rotated rectangle, not intended for use with images
#[inline]
fn bounding_rect2f(&self) -> Result<core::Rect_<f32>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RotatedRect_boundingRect2f_const(self.as_raw_RotatedRect(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::RotatedRect]
pub trait RotatedRectTrait: core::RotatedRectTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_RotatedRect(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// returns the rectangle mass center
#[inline]
fn set_center(&mut self, val: core::Point2f) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_RotatedRect_setPropCenter_Point2f(self.as_raw_mut_RotatedRect(), val.opencv_as_extern()) };
ret
}
/// returns width and height of the rectangle
#[inline]
fn set_size(&mut self, val: core::Size2f) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_RotatedRect_setPropSize_Size2f(self.as_raw_mut_RotatedRect(), val.opencv_as_extern()) };
ret
}
/// returns the rotation angle. When the angle is 0, 90, 180, 270 etc., the rectangle becomes an up-right rectangle.
#[inline]
fn set_angle(&mut self, val: f32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_RotatedRect_setPropAngle_float(self.as_raw_mut_RotatedRect(), val) };
ret
}
}
/// The class represents rotated (i.e. not up-right) rectangles on a plane.
///
/// Each rectangle is specified by the center point (mass center), length of each side (represented by
/// #Size2f structure) and the rotation angle in degrees.
///
/// The sample below demonstrates how to use RotatedRect:
/// [RotatedRect_demo](https://github.com/opencv/opencv/blob/4.7.0/samples/cpp/tutorial_code/snippets/core_various.cpp#L1)
/// 
/// ## See also
/// CamShift, fitEllipse, minAreaRect, CvBox2D
pub struct RotatedRect {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { RotatedRect }
impl Drop for RotatedRect {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_RotatedRect_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_RotatedRect_delete(self.as_raw_mut_RotatedRect()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for RotatedRect {}
impl core::RotatedRectTraitConst for RotatedRect {
#[inline] fn as_raw_RotatedRect(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::RotatedRectTrait for RotatedRect {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_RotatedRect(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl RotatedRect {
/// default constructor
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::RotatedRect> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RotatedRect_RotatedRect(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::RotatedRect::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// full constructor
/// ## Parameters
/// * center: The rectangle mass center.
/// * size: Width and height of the rectangle.
/// * angle: The rotation angle in a clockwise direction. When the angle is 0, 90, 180, 270 etc.,
/// the rectangle becomes an up-right rectangle.
#[inline]
pub fn new(center: core::Point2f, size: core::Size2f, angle: f32) -> Result<core::RotatedRect> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RotatedRect_RotatedRect_const_Point2fR_const_Size2fR_float(¢er, &size, angle, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::RotatedRect::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Any 3 end points of the RotatedRect. They must be given in order (either clockwise or
/// anticlockwise).
#[inline]
pub fn for_points(point1: core::Point2f, point2: core::Point2f, point3: core::Point2f) -> Result<core::RotatedRect> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_RotatedRect_RotatedRect_const_Point2fR_const_Point2fR_const_Point2fR(&point1, &point2, &point3, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::RotatedRect::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::SVD]
pub trait SVDTraitConst {
fn as_raw_SVD(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn u(&self) -> core::Mat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SVD_getPropU_const(self.as_raw_SVD()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn w(&self) -> core::Mat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SVD_getPropW_const(self.as_raw_SVD()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn vt(&self) -> core::Mat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SVD_getPropVt_const(self.as_raw_SVD()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// performs a singular value back substitution.
///
/// The method calculates a back substitution for the specified right-hand
/// side:
///
/// 
///
/// Using this technique you can either get a very accurate solution of the
/// convenient linear system, or the best (in the least-squares terms)
/// pseudo-solution of an overdetermined linear system.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * rhs: right-hand side of a linear system (u\*w\*v')\*dst = rhs to
/// be solved, where A has been previously decomposed.
///
/// * dst: found solution of the system.
///
///
/// Note: Explicit SVD with the further back substitution only makes sense
/// if you need to solve many linear systems with the same left-hand side
/// (for example, src ). If all you need is to solve a single system
/// (possibly with multiple rhs immediately available), simply call solve
/// add pass #DECOMP_SVD there. It does absolutely the same thing.
#[inline]
fn back_subst(&self, rhs: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(rhs);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SVD_backSubst_const_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_SVD(), rhs.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::SVD]
pub trait SVDTrait: core::SVDTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_SVD(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_u(&mut self, mut val: core::Mat) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SVD_setPropU_Mat(self.as_raw_mut_SVD(), val.as_raw_mut_Mat()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_w(&mut self, mut val: core::Mat) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SVD_setPropW_Mat(self.as_raw_mut_SVD(), val.as_raw_mut_Mat()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_vt(&mut self, mut val: core::Mat) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SVD_setPropVt_Mat(self.as_raw_mut_SVD(), val.as_raw_mut_Mat()) };
ret
}
/// the operator that performs SVD. The previously allocated u, w and vt are released.
///
/// The operator performs the singular value decomposition of the supplied
/// matrix. The u,`vt` , and the vector of singular values w are stored in
/// the structure. The same SVD structure can be reused many times with
/// different matrices. Each time, if needed, the previous u,`vt` , and w
/// are reclaimed and the new matrices are created, which is all handled by
/// Mat::create.
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: decomposed matrix. The depth has to be CV_32F or CV_64F.
/// * flags: operation flags (SVD::Flags)
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: 0
#[inline]
fn apply(&mut self, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<core::SVD> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SVD_operator___const__InputArrayR_int(self.as_raw_mut_SVD(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::SVD::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Singular Value Decomposition
///
/// Class for computing Singular Value Decomposition of a floating-point
/// matrix. The Singular Value Decomposition is used to solve least-square
/// problems, under-determined linear systems, invert matrices, compute
/// condition numbers, and so on.
///
/// If you want to compute a condition number of a matrix or an absolute value of
/// its determinant, you do not need `u` and `vt`. You can pass
/// flags=SVD::NO_UV|... . Another flag SVD::FULL_UV indicates that full-size u
/// and vt must be computed, which is not necessary most of the time.
/// ## See also
/// invert, solve, eigen, determinant
pub struct SVD {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { SVD }
impl Drop for SVD {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_SVD_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_SVD_delete(self.as_raw_mut_SVD()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for SVD {}
impl core::SVDTraitConst for SVD {
#[inline] fn as_raw_SVD(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::SVDTrait for SVD {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_SVD(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl SVD {
/// the default constructor
///
/// initializes an empty SVD structure
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::SVD> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SVD_SVD(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::SVD::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// the default constructor
///
/// initializes an empty SVD structure
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// initializes an empty SVD structure and then calls SVD::operator()
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: decomposed matrix. The depth has to be CV_32F or CV_64F.
/// * flags: operation flags (SVD::Flags)
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: 0
#[inline]
pub fn new(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<core::SVD> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SVD_SVD_const__InputArrayR_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::SVD::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// decomposes matrix and stores the results to user-provided matrices
///
/// The methods/functions perform SVD of matrix. Unlike SVD::SVD constructor
/// and SVD::operator(), they store the results to the user-provided
/// matrices:
///
/// ```C++
/// Mat A, w, u, vt;
/// SVD::compute(A, w, u, vt);
/// ```
///
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: decomposed matrix. The depth has to be CV_32F or CV_64F.
/// * w: calculated singular values
/// * u: calculated left singular vectors
/// * vt: transposed matrix of right singular vectors
/// * flags: operation flags - see SVD::Flags.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: 0
#[inline]
pub fn compute_ext(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, w: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, u: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, vt: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(w);
extern_container_arg!(u);
extern_container_arg!(vt);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SVD_compute_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), w.as_raw__OutputArray(), u.as_raw__OutputArray(), vt.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// decomposes matrix and stores the results to user-provided matrices
///
/// The methods/functions perform SVD of matrix. Unlike SVD::SVD constructor
/// and SVD::operator(), they store the results to the user-provided
/// matrices:
///
/// ```C++
/// Mat A, w, u, vt;
/// SVD::compute(A, w, u, vt);
/// ```
///
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: decomposed matrix. The depth has to be CV_32F or CV_64F.
/// * w: calculated singular values
/// * u: calculated left singular vectors
/// * vt: transposed matrix of right singular vectors
/// * flags: operation flags - see SVD::Flags.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// computes singular values of a matrix
/// * src: decomposed matrix. The depth has to be CV_32F or CV_64F.
/// * w: calculated singular values
/// * flags: operation flags - see SVD::Flags.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: 0
#[inline]
pub fn compute(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, w: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(w);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SVD_compute_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), w.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// performs back substitution
#[inline]
pub fn back_subst_multi(w: &dyn core::ToInputArray, u: &dyn core::ToInputArray, vt: &dyn core::ToInputArray, rhs: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(w);
extern_container_arg!(u);
extern_container_arg!(vt);
extern_container_arg!(rhs);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SVD_backSubst_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(w.as_raw__InputArray(), u.as_raw__InputArray(), vt.as_raw__InputArray(), rhs.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// solves an under-determined singular linear system
///
/// The method finds a unit-length solution x of a singular linear system
/// A\*x = 0. Depending on the rank of A, there can be no solutions, a
/// single solution or an infinite number of solutions. In general, the
/// algorithm solves the following problem:
/// 
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: left-hand-side matrix.
/// * dst: found solution.
#[inline]
pub fn solve_z(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SVD_solveZ_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::SparseMat]
pub trait SparseMatTraitConst {
fn as_raw_SparseMat(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn flags(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_getPropFlags_const(self.as_raw_SparseMat()) };
ret
}
/// creates full copy of the matrix
#[inline]
#[must_use]
fn try_clone(&self) -> Result<core::SparseMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_clone_const(self.as_raw_SparseMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::SparseMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// copies all the data to the destination matrix. All the previous content of m is erased
#[inline]
fn copy_to(&self, m: &mut core::SparseMat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_copyTo_const_SparseMatR(self.as_raw_SparseMat(), m.as_raw_mut_SparseMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// converts sparse matrix to dense matrix.
#[inline]
fn copy_to_mat(&self, m: &mut core::Mat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_copyTo_const_MatR(self.as_raw_SparseMat(), m.as_raw_mut_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// multiplies all the matrix elements by the specified scale factor alpha and converts the results to the specified data type
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * alpha: 1
#[inline]
fn convert_to(&self, m: &mut core::SparseMat, rtype: i32, alpha: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_convertTo_const_SparseMatR_int_double(self.as_raw_SparseMat(), m.as_raw_mut_SparseMat(), rtype, alpha, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// converts sparse matrix to dense n-dim matrix with optional type conversion and scaling.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * m:[out] - output matrix; if it does not have a proper size or type before the operation,
/// it is reallocated
/// * rtype: - desired output matrix type or, rather, the depth since the number of channels
/// are the same as the input has; if rtype is negative, the output matrix will have the
/// same type as the input.
/// * alpha: - optional scale factor
/// * beta: - optional delta added to the scaled values
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * alpha: 1
/// * beta: 0
#[inline]
fn convert_to_1(&self, m: &mut core::Mat, rtype: i32, alpha: f64, beta: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_convertTo_const_MatR_int_double_double(self.as_raw_SparseMat(), m.as_raw_mut_Mat(), rtype, alpha, beta, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * typ: -1
#[inline]
fn assign_to(&self, m: &mut core::SparseMat, typ: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_assignTo_const_SparseMatR_int(self.as_raw_SparseMat(), m.as_raw_mut_SparseMat(), typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns the size of each element in bytes (not including the overhead - the space occupied by SparseMat::Node elements)
#[inline]
fn elem_size(&self) -> size_t {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_elemSize_const(self.as_raw_SparseMat()) };
ret
}
/// returns elemSize()/channels()
#[inline]
fn elem_size1(&self) -> size_t {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_elemSize1_const(self.as_raw_SparseMat()) };
ret
}
/// returns type of sparse matrix elements
#[inline]
fn typ(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_type_const(self.as_raw_SparseMat()) };
ret
}
/// returns the depth of sparse matrix elements
#[inline]
fn depth(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_depth_const(self.as_raw_SparseMat()) };
ret
}
/// returns the number of channels
#[inline]
fn channels(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_channels_const(self.as_raw_SparseMat()) };
ret
}
/// returns the array of sizes, or NULL if the matrix is not allocated
#[inline]
fn size(&self) -> Result<*const i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_size_const(self.as_raw_SparseMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns the size of i-th matrix dimension (or 0)
#[inline]
fn size_1(&self, i: i32) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_size_const_int(self.as_raw_SparseMat(), i, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns the matrix dimensionality
#[inline]
fn dims(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_dims_const(self.as_raw_SparseMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns the number of non-zero elements (=the number of hash table nodes)
#[inline]
fn nzcount(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_nzcount_const(self.as_raw_SparseMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// computes the element hash value (1D case)
#[inline]
fn hash(&self, i0: i32) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_hash_const_int(self.as_raw_SparseMat(), i0, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// computes the element hash value (2D case)
#[inline]
fn hash_1(&self, i0: i32, i1: i32) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_hash_const_int_int(self.as_raw_SparseMat(), i0, i1, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// computes the element hash value (3D case)
#[inline]
fn hash_2(&self, i0: i32, i1: i32, i2: i32) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_hash_const_int_int_int(self.as_raw_SparseMat(), i0, i1, i2, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// computes the element hash value (nD case)
#[inline]
fn hash_3(&self, idx: &i32) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_hash_const_const_intX(self.as_raw_SparseMat(), idx, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns the read-only sparse matrix iterator at the matrix beginning
#[inline]
fn begin(&self) -> Result<core::SparseMatConstIterator> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_begin_const(self.as_raw_SparseMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::SparseMatConstIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns the read-only sparse matrix iterator at the matrix end
#[inline]
fn end(&self) -> Result<core::SparseMatConstIterator> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_end_const(self.as_raw_SparseMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::SparseMatConstIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn node(&self, nidx: size_t) -> Result<core::SparseMat_Node> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_node_const_size_t(self.as_raw_SparseMat(), nidx, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::SparseMat_Node::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::SparseMat]
pub trait SparseMatTrait: core::SparseMatTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_SparseMat(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_flags(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_setPropFlags_int(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn hdr(&mut self) -> core::SparseMat_Hdr {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_getPropHdr(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::SparseMat_Hdr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_hdr(&mut self, val: &mut core::SparseMat_Hdr) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_setPropHdr_HdrX(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat(), val.as_raw_mut_SparseMat_Hdr()) };
ret
}
/// reallocates sparse matrix.
///
/// If the matrix already had the proper size and type,
/// it is simply cleared with clear(), otherwise,
/// the old matrix is released (using release()) and the new one is allocated.
#[inline]
fn create(&mut self, dims: i32, _sizes: &i32, _type: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_create_int_const_intX_int(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat(), dims, _sizes, _type, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// sets all the sparse matrix elements to 0, which means clearing the hash table.
#[inline]
fn clear(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_clear(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// manually increments the reference counter to the header.
#[inline]
fn addref(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_addref(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn release(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_release(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// specialized variants for 1D, 2D, 3D cases and the generic_type one for n-D case.
/// return pointer to the matrix element.
/// - if the element is there (it's non-zero), the pointer to it is returned
/// - if it's not there and createMissing=false, NULL pointer is returned
/// - if it's not there and createMissing=true, then the new element
/// is created and initialized with 0. Pointer to it is returned
/// - if the optional hashval pointer is not NULL, the element hash value is
/// not computed, but *hashval is taken instead.
///
/// returns pointer to the specified element (1D case)
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * hashval: 0
#[inline]
fn ptr(&mut self, i0: i32, create_missing: bool, hashval: &mut size_t) -> Result<*mut u8> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_ptr_int_bool_size_tX(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat(), i0, create_missing, hashval, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns pointer to the specified element (2D case)
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * hashval: 0
#[inline]
fn ptr_1(&mut self, i0: i32, i1: i32, create_missing: bool, hashval: &mut size_t) -> Result<*mut u8> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_ptr_int_int_bool_size_tX(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat(), i0, i1, create_missing, hashval, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns pointer to the specified element (3D case)
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * hashval: 0
#[inline]
fn ptr_2(&mut self, i0: i32, i1: i32, i2: i32, create_missing: bool, hashval: &mut size_t) -> Result<*mut u8> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_ptr_int_int_int_bool_size_tX(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat(), i0, i1, i2, create_missing, hashval, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns pointer to the specified element (nD case)
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * hashval: 0
#[inline]
fn ptr_3(&mut self, idx: &i32, create_missing: bool, hashval: &mut size_t) -> Result<*mut u8> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_ptr_const_intX_bool_size_tX(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat(), idx, create_missing, hashval, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// erases the specified element (2D case)
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * hashval: 0
#[inline]
fn erase(&mut self, i0: i32, i1: i32, hashval: &mut size_t) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_erase_int_int_size_tX(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat(), i0, i1, hashval, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// erases the specified element (3D case)
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * hashval: 0
#[inline]
fn erase_1(&mut self, i0: i32, i1: i32, i2: i32, hashval: &mut size_t) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_erase_int_int_int_size_tX(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat(), i0, i1, i2, hashval, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// erases the specified element (nD case)
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * hashval: 0
#[inline]
fn erase_2(&mut self, idx: &i32, hashval: &mut size_t) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_erase_const_intX_size_tX(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat(), idx, hashval, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// return the sparse matrix iterator pointing to the first sparse matrix element
///
/// returns the sparse matrix iterator at the matrix beginning
#[inline]
fn begin_mut(&mut self) -> Result<core::SparseMatIterator> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_begin(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::SparseMatIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// return the sparse matrix iterator pointing to the element following the last sparse matrix element
///
/// returns the sparse matrix iterator at the matrix end
#[inline]
fn end_mut(&mut self) -> Result<core::SparseMatIterator> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_end(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::SparseMatIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// /////////// some internal-use methods ///////////////
#[inline]
fn node_1(&mut self, nidx: size_t) -> Result<core::SparseMat_Node> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_node_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat(), nidx, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::SparseMat_Node::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn new_node(&mut self, idx: &i32, hashval: size_t) -> Result<*mut u8> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_newNode_const_intX_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat(), idx, hashval, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn remove_node(&mut self, hidx: size_t, nidx: size_t, previdx: size_t) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_removeNode_size_t_size_t_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat(), hidx, nidx, previdx, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn resize_hash_tab(&mut self, newsize: size_t) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_resizeHashTab_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat(), newsize, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// The class SparseMat represents multi-dimensional sparse numerical arrays.
///
/// Such a sparse array can store elements of any type that Mat can store. *Sparse* means that only
/// non-zero elements are stored (though, as a result of operations on a sparse matrix, some of its
/// stored elements can actually become 0. It is up to you to detect such elements and delete them
/// using SparseMat::erase ). The non-zero elements are stored in a hash table that grows when it is
/// filled so that the search time is O(1) in average (regardless of whether element is there or not).
/// Elements can be accessed using the following methods:
/// * Query operations (SparseMat::ptr and the higher-level SparseMat::ref, SparseMat::value and
/// SparseMat::find), for example:
/// ```C++
/// const int dims = 5;
/// int size[5] = {10, 10, 10, 10, 10};
/// SparseMat sparse_mat(dims, size, CV_32F);
/// for(int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
/// {
/// int idx[dims];
/// for(int k = 0; k < dims; k++)
/// idx[k] = rand() % size[k];
/// sparse_mat.ref<float>(idx) += 1.f;
/// }
/// cout << "nnz = " << sparse_mat.nzcount() << endl;
/// ```
///
/// * Sparse matrix iterators. They are similar to MatIterator but different from NAryMatIterator.
/// That is, the iteration loop is familiar to STL users:
/// ```C++
/// // prints elements of a sparse floating-point matrix
/// // and the sum of elements.
/// SparseMatConstIterator_<float>
/// it = sparse_mat.begin<float>(),
/// it_end = sparse_mat.end<float>();
/// double s = 0;
/// int dims = sparse_mat.dims();
/// for(; it != it_end; ++it)
/// {
/// // print element indices and the element value
/// const SparseMat::Node* n = it.node();
/// printf("(");
/// for(int i = 0; i < dims; i++)
/// printf("%d%s", n->idx[i], i < dims-1 ? ", " : ")");
/// printf(": %g\n", it.value<float>());
/// s += *it;
/// }
/// printf("Element sum is %g\n", s);
/// ```
///
/// If you run this loop, you will notice that elements are not enumerated in a logical order
/// (lexicographical, and so on). They come in the same order as they are stored in the hash table
/// (semi-randomly). You may collect pointers to the nodes and sort them to get the proper ordering.
/// Note, however, that pointers to the nodes may become invalid when you add more elements to the
/// matrix. This may happen due to possible buffer reallocation.
/// * Combination of the above 2 methods when you need to process 2 or more sparse matrices
/// simultaneously. For example, this is how you can compute unnormalized cross-correlation of the 2
/// floating-point sparse matrices:
/// ```C++
/// double cross_corr(const SparseMat& a, const SparseMat& b)
/// {
/// const SparseMat *_a = &a, *_b = &b;
/// // if b contains less elements than a,
/// // it is faster to iterate through b
/// if(_a->nzcount() > _b->nzcount())
/// std::swap(_a, _b);
/// SparseMatConstIterator_<float> it = _a->begin<float>(),
/// it_end = _a->end<float>();
/// double ccorr = 0;
/// for(; it != it_end; ++it)
/// {
/// // take the next element from the first matrix
/// float avalue = *it;
/// const Node* anode = it.node();
/// // and try to find an element with the same index in the second matrix.
/// // since the hash value depends only on the element index,
/// // reuse the hash value stored in the node
/// float bvalue = _b->value<float>(anode->idx,&anode->hashval);
/// ccorr += avalue*bvalue;
/// }
/// return ccorr;
/// }
/// ```
///
pub struct SparseMat {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { SparseMat }
impl Drop for SparseMat {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_SparseMat_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_SparseMat_delete(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for SparseMat {}
impl core::SparseMatTraitConst for SparseMat {
#[inline] fn as_raw_SparseMat(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::SparseMatTrait for SparseMat {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_SparseMat(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl SparseMat {
/// Various SparseMat constructors.
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::SparseMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_SparseMat(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::SparseMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Various SparseMat constructors.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * dims: Array dimensionality.
/// * _sizes: Sparce matrix size on all dementions.
/// * _type: Sparse matrix data type.
#[inline]
pub fn new(dims: i32, _sizes: &i32, _type: i32) -> Result<core::SparseMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_SparseMat_int_const_intX_int(dims, _sizes, _type, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::SparseMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Various SparseMat constructors.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * m: Source matrix for copy constructor. If m is dense matrix (ocvMat) then it will be converted
/// to sparse representation.
#[inline]
pub fn copy(m: &core::SparseMat) -> Result<core::SparseMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_SparseMat_const_SparseMatR(m.as_raw_SparseMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::SparseMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Various SparseMat constructors.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * m: Source matrix for copy constructor. If m is dense matrix (ocvMat) then it will be converted
/// to sparse representation.
#[inline]
pub fn from_mat(m: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::SparseMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_SparseMat_const_MatR(m.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::SparseMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl Clone for SparseMat {
#[inline]
/// Calls try_clone() and panics if that fails
fn clone(&self) -> Self {
self.try_clone().expect("Cannot clone SparseMat")
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::SparseMat_Hdr]
pub trait SparseMat_HdrTraitConst {
fn as_raw_SparseMat_Hdr(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn refcount(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_Hdr_getPropRefcount_const(self.as_raw_SparseMat_Hdr()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn dims(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_Hdr_getPropDims_const(self.as_raw_SparseMat_Hdr()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn value_offset(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_Hdr_getPropValueOffset_const(self.as_raw_SparseMat_Hdr()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn node_size(&self) -> size_t {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_Hdr_getPropNodeSize_const(self.as_raw_SparseMat_Hdr()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn node_count(&self) -> size_t {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_Hdr_getPropNodeCount_const(self.as_raw_SparseMat_Hdr()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn free_list(&self) -> size_t {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_Hdr_getPropFreeList_const(self.as_raw_SparseMat_Hdr()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn pool(&self) -> core::Vector<u8> {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_Hdr_getPropPool_const(self.as_raw_SparseMat_Hdr()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Vector::<u8>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn hashtab(&self) -> core::Vector<size_t> {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_Hdr_getPropHashtab_const(self.as_raw_SparseMat_Hdr()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Vector::<size_t>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::SparseMat_Hdr]
pub trait SparseMat_HdrTrait: core::SparseMat_HdrTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_SparseMat_Hdr(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_refcount(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_Hdr_setPropRefcount_int(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat_Hdr(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_dims(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_Hdr_setPropDims_int(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat_Hdr(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_value_offset(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_Hdr_setPropValueOffset_int(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat_Hdr(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_node_size(&mut self, val: size_t) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_Hdr_setPropNodeSize_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat_Hdr(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_node_count(&mut self, val: size_t) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_Hdr_setPropNodeCount_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat_Hdr(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_free_list(&mut self, val: size_t) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_Hdr_setPropFreeList_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat_Hdr(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_pool(&mut self, mut val: core::Vector<u8>) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_Hdr_setPropPool_vectorLunsigned_charG(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat_Hdr(), val.as_raw_mut_VectorOfu8()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_hashtab(&mut self, mut val: core::Vector<size_t>) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_Hdr_setPropHashtab_vectorLsize_tG(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat_Hdr(), val.as_raw_mut_VectorOfsize_t()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn size(&mut self) -> &mut [i32; 32] {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_Hdr_getPropSize(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat_Hdr()) };
let ret = unsafe { ret.as_mut() }.expect("Function returned null pointer");
ret
}
#[inline]
fn clear(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_Hdr_clear(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat_Hdr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// the sparse matrix header
pub struct SparseMat_Hdr {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { SparseMat_Hdr }
impl Drop for SparseMat_Hdr {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_SparseMat_Hdr_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_SparseMat_Hdr_delete(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat_Hdr()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for SparseMat_Hdr {}
impl core::SparseMat_HdrTraitConst for SparseMat_Hdr {
#[inline] fn as_raw_SparseMat_Hdr(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::SparseMat_HdrTrait for SparseMat_Hdr {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_SparseMat_Hdr(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl SparseMat_Hdr {
#[inline]
pub fn new(_sizes: &[i32], _type: i32) -> Result<core::SparseMat_Hdr> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_Hdr_Hdr_int_const_intX_int(_sizes.len() as _, _sizes.as_ptr(), _type, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::SparseMat_Hdr::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::SparseMat_Node]
pub trait SparseMat_NodeTraitConst {
fn as_raw_SparseMat_Node(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// hash value
#[inline]
fn hashval(&self) -> size_t {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_Node_getPropHashval_const(self.as_raw_SparseMat_Node()) };
ret
}
/// index of the next node in the same hash table entry
#[inline]
fn next(&self) -> size_t {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_Node_getPropNext_const(self.as_raw_SparseMat_Node()) };
ret
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::SparseMat_Node]
pub trait SparseMat_NodeTrait: core::SparseMat_NodeTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_SparseMat_Node(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// hash value
#[inline]
fn set_hashval(&mut self, val: size_t) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_Node_setPropHashval_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat_Node(), val) };
ret
}
/// index of the next node in the same hash table entry
#[inline]
fn set_next(&mut self, val: size_t) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_Node_setPropNext_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat_Node(), val) };
ret
}
/// index of the matrix element
#[inline]
fn idx(&mut self) -> &mut [i32; 32] {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMat_Node_getPropIdx(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat_Node()) };
let ret = unsafe { ret.as_mut() }.expect("Function returned null pointer");
ret
}
}
/// sparse matrix node - element of a hash table
pub struct SparseMat_Node {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { SparseMat_Node }
impl Drop for SparseMat_Node {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_SparseMat_Node_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_SparseMat_Node_delete(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMat_Node()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for SparseMat_Node {}
impl core::SparseMat_NodeTraitConst for SparseMat_Node {
#[inline] fn as_raw_SparseMat_Node(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::SparseMat_NodeTrait for SparseMat_Node {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_SparseMat_Node(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl SparseMat_Node {
}
/// Constant methods for [core::SparseMatConstIterator]
pub trait SparseMatConstIteratorTraitConst {
fn as_raw_SparseMatConstIterator(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn m(&self) -> core::SparseMat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMatConstIterator_getPropM_const(self.as_raw_SparseMatConstIterator()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::SparseMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn hashidx(&self) -> size_t {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMatConstIterator_getPropHashidx_const(self.as_raw_SparseMatConstIterator()) };
ret
}
/// returns the current node of the sparse matrix. it.node->idx is the current element index
#[inline]
fn node(&self) -> Result<core::SparseMat_Node> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMatConstIterator_node_const(self.as_raw_SparseMatConstIterator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::SparseMat_Node::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::SparseMatConstIterator]
pub trait SparseMatConstIteratorTrait: core::SparseMatConstIteratorTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_SparseMatConstIterator(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_hashidx(&mut self, val: size_t) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMatConstIterator_setPropHashidx_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMatConstIterator(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn ptr(&mut self) -> *mut u8 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMatConstIterator_getPropPtr(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMatConstIterator()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
unsafe fn set_ptr(&mut self, val: *mut u8) {
let ret = { sys::cv_SparseMatConstIterator_setPropPtr_unsigned_charX(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMatConstIterator(), val) };
ret
}
/// moves iterator to the previous element
#[inline]
#[cfg(not(target_os = "windows"))]
fn decr(&mut self) -> Result<core::SparseMatConstIterator> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMatConstIterator_operatorSS(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMatConstIterator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::SparseMatConstIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// moves iterator to the next element
#[inline]
fn incr(&mut self) -> Result<core::SparseMatConstIterator> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMatConstIterator_operatorAA(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMatConstIterator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::SparseMatConstIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// moves iterator to the element after the last element
#[inline]
fn seek_end(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMatConstIterator_seekEnd(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMatConstIterator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Read-Only Sparse Matrix Iterator.
///
/// Here is how to use the iterator to compute the sum of floating-point sparse matrix elements:
///
/// \code
/// SparseMatConstIterator it = m.begin(), it_end = m.end();
/// double s = 0;
/// CV_Assert( m.type() == CV_32F );
/// for( ; it != it_end; ++it )
/// s += it.value<float>();
/// \endcode
pub struct SparseMatConstIterator {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { SparseMatConstIterator }
impl Drop for SparseMatConstIterator {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_SparseMatConstIterator_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_SparseMatConstIterator_delete(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMatConstIterator()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for SparseMatConstIterator {}
impl core::SparseMatConstIteratorTraitConst for SparseMatConstIterator {
#[inline] fn as_raw_SparseMatConstIterator(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::SparseMatConstIteratorTrait for SparseMatConstIterator {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_SparseMatConstIterator(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl SparseMatConstIterator {
/// the default constructor
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::SparseMatConstIterator> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMatConstIterator_SparseMatConstIterator(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::SparseMatConstIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// the full constructor setting the iterator to the first sparse matrix element
#[inline]
pub fn new(_m: &core::SparseMat) -> Result<core::SparseMatConstIterator> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMatConstIterator_SparseMatConstIterator_const_SparseMatX(_m.as_raw_SparseMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::SparseMatConstIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// the copy constructor
#[inline]
pub fn copy(it: &core::SparseMatConstIterator) -> Result<core::SparseMatConstIterator> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMatConstIterator_SparseMatConstIterator_const_SparseMatConstIteratorR(it.as_raw_SparseMatConstIterator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::SparseMatConstIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::SparseMatIterator]
pub trait SparseMatIteratorTraitConst: core::SparseMatConstIteratorTraitConst {
fn as_raw_SparseMatIterator(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// returns pointer to the current sparse matrix node. it.node->idx is the index of the current element (do not modify it!)
#[inline]
fn node(&self) -> Result<core::SparseMat_Node> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMatIterator_node_const(self.as_raw_SparseMatIterator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::SparseMat_Node::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::SparseMatIterator]
pub trait SparseMatIteratorTrait: core::SparseMatConstIteratorTrait + core::SparseMatIteratorTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_SparseMatIterator(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// moves iterator to the next element
#[inline]
fn incr(&mut self) -> Result<core::SparseMatIterator> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMatIterator_operatorAA(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMatIterator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::SparseMatIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Read-write Sparse Matrix Iterator
///
/// The class is similar to cv::SparseMatConstIterator,
/// but can be used for in-place modification of the matrix elements.
pub struct SparseMatIterator {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { SparseMatIterator }
impl Drop for SparseMatIterator {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_SparseMatIterator_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_SparseMatIterator_delete(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMatIterator()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for SparseMatIterator {}
impl core::SparseMatConstIteratorTraitConst for SparseMatIterator {
#[inline] fn as_raw_SparseMatConstIterator(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::SparseMatConstIteratorTrait for SparseMatIterator {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_SparseMatConstIterator(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl core::SparseMatIteratorTraitConst for SparseMatIterator {
#[inline] fn as_raw_SparseMatIterator(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::SparseMatIteratorTrait for SparseMatIterator {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_SparseMatIterator(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl SparseMatIterator {
/// the default constructor
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::SparseMatIterator> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMatIterator_SparseMatIterator(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::SparseMatIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// the full constructor setting the iterator to the first sparse matrix element
#[inline]
pub fn new(_m: &mut core::SparseMat) -> Result<core::SparseMatIterator> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMatIterator_SparseMatIterator_SparseMatX(_m.as_raw_mut_SparseMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::SparseMatIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// the copy constructor
#[inline]
pub fn copy(it: &core::SparseMatIterator) -> Result<core::SparseMatIterator> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_SparseMatIterator_SparseMatIterator_const_SparseMatIteratorR(it.as_raw_SparseMatIterator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::SparseMatIterator::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { SparseMatIterator, core::SparseMatConstIterator, cv_SparseMatIterator_to_SparseMatConstIterator }
/// Constant methods for [core::TLSDataContainer]
pub trait TLSDataContainerConst {
fn as_raw_TLSDataContainer(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// TLS container base implementation
///
/// Don't use directly.
/// ## See also
/// TLSData, TLSDataAccumulator templates
pub trait TLSDataContainer: core::TLSDataContainerConst {
fn as_raw_mut_TLSDataContainer(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn cleanup(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TLSDataContainer_cleanup(self.as_raw_mut_TLSDataContainer(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// The class defining termination criteria for iterative algorithms.
///
/// You can initialize it by default constructor and then override any parameters, or the structure may
/// be fully initialized using the advanced variant of the constructor.
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)]
pub struct TermCriteria {
/// the type of termination criteria: COUNT, EPS or COUNT + EPS
pub typ: i32,
/// the maximum number of iterations/elements
pub max_count: i32,
/// the desired accuracy
pub epsilon: f64,
}
opencv_type_simple! { core::TermCriteria }
impl TermCriteria {
#[inline]
pub fn is_valid(self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TermCriteria_isValid_const(self.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// default constructor
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::TermCriteria> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TermCriteria_TermCriteria(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## Parameters
/// * type: The type of termination criteria, one of TermCriteria::Type
/// * maxCount: The maximum number of iterations or elements to compute.
/// * epsilon: The desired accuracy or change in parameters at which the iterative algorithm stops.
#[inline]
pub fn new(typ: i32, max_count: i32, epsilon: f64) -> Result<core::TermCriteria> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TermCriteria_TermCriteria_int_int_double(typ, max_count, epsilon, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::TickMeter]
pub trait TickMeterTraitConst {
fn as_raw_TickMeter(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// returns counted ticks.
#[inline]
fn get_time_ticks(&self) -> Result<i64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TickMeter_getTimeTicks_const(self.as_raw_TickMeter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns passed time in microseconds.
#[inline]
fn get_time_micro(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TickMeter_getTimeMicro_const(self.as_raw_TickMeter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns passed time in milliseconds.
#[inline]
fn get_time_milli(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TickMeter_getTimeMilli_const(self.as_raw_TickMeter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns passed time in seconds.
#[inline]
fn get_time_sec(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TickMeter_getTimeSec_const(self.as_raw_TickMeter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns internal counter value.
#[inline]
fn get_counter(&self) -> Result<i64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TickMeter_getCounter_const(self.as_raw_TickMeter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns average FPS (frames per second) value.
#[inline]
fn get_fps(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TickMeter_getFPS_const(self.as_raw_TickMeter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns average time in seconds
#[inline]
fn get_avg_time_sec(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TickMeter_getAvgTimeSec_const(self.as_raw_TickMeter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns average time in milliseconds
#[inline]
fn get_avg_time_milli(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TickMeter_getAvgTimeMilli_const(self.as_raw_TickMeter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::TickMeter]
pub trait TickMeterTrait: core::TickMeterTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_TickMeter(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// starts counting ticks.
#[inline]
fn start(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TickMeter_start(self.as_raw_mut_TickMeter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// stops counting ticks.
#[inline]
fn stop(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TickMeter_stop(self.as_raw_mut_TickMeter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// resets internal values.
#[inline]
fn reset(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TickMeter_reset(self.as_raw_mut_TickMeter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// a Class to measure passing time.
///
/// The class computes passing time by counting the number of ticks per second. That is, the following code computes the
/// execution time in seconds:
/// [TickMeter_total](https://github.com/opencv/opencv/blob/4.7.0/samples/cpp/tutorial_code/snippets/core_various.cpp#L1)
///
/// It is also possible to compute the average time over multiple runs:
/// [TickMeter_average](https://github.com/opencv/opencv/blob/4.7.0/samples/cpp/tutorial_code/snippets/core_various.cpp#L1)
/// ## See also
/// getTickCount, getTickFrequency
pub struct TickMeter {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { TickMeter }
impl Drop for TickMeter {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_TickMeter_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_TickMeter_delete(self.as_raw_mut_TickMeter()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for TickMeter {}
impl core::TickMeterTraitConst for TickMeter {
#[inline] fn as_raw_TickMeter(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::TickMeterTrait for TickMeter {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_TickMeter(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl TickMeter {
/// the default constructor
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::TickMeter> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_TickMeter_TickMeter(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::TickMeter::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::UMat]
pub trait UMatTraitConst {
fn as_raw_UMat(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// ! includes several bit-fields:
/// - the magic signature
/// - continuity flag
/// - depth
/// - number of channels
#[inline]
fn flags(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_getPropFlags_const(self.as_raw_UMat()) };
ret
}
/// the matrix dimensionality, >= 2
#[inline]
fn dims(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_getPropDims_const(self.as_raw_UMat()) };
ret
}
/// number of rows in the matrix; -1 when the matrix has more than 2 dimensions
#[inline]
fn rows(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_getPropRows_const(self.as_raw_UMat()) };
ret
}
/// number of columns in the matrix; -1 when the matrix has more than 2 dimensions
#[inline]
fn cols(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_getPropCols_const(self.as_raw_UMat()) };
ret
}
/// usage flags for allocator; recommend do not set directly, instead set during construct/create/getUMat
#[inline]
fn usage_flags(&self) -> core::UMatUsageFlags {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_getPropUsageFlags_const(self.as_raw_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
ret
}
/// offset of the submatrix (or 0)
#[inline]
fn offset(&self) -> size_t {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_getPropOffset_const(self.as_raw_UMat()) };
ret
}
/// dimensional size of the matrix; accessible in various formats
#[inline]
fn mat_size(&self) -> core::MatSize {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_getPropSize_const(self.as_raw_UMat()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::MatSize::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// number of bytes each matrix element/row/plane/dimension occupies
#[inline]
fn mat_step(&self) -> core::MatStep {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_getPropStep_const(self.as_raw_UMat()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::MatStep::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn get_mat(&self, flags: core::AccessFlag) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_getMat_const_AccessFlag(self.as_raw_UMat(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns a new matrix header for the specified row
#[inline]
fn row(&self, y: i32) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_row_const_int(self.as_raw_UMat(), y, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns a new matrix header for the specified column
#[inline]
fn col(&self, x: i32) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_col_const_int(self.as_raw_UMat(), x, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ... for the specified row span
#[inline]
fn row_bounds(&self, startrow: i32, endrow: i32) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_rowRange_const_int_int(self.as_raw_UMat(), startrow, endrow, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn row_range(&self, r: &core::Range) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_rowRange_const_const_RangeR(self.as_raw_UMat(), r.as_raw_Range(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ... for the specified column span
#[inline]
fn col_bounds(&self, startcol: i32, endcol: i32) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_colRange_const_int_int(self.as_raw_UMat(), startcol, endcol, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn col_range(&self, r: &core::Range) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_colRange_const_const_RangeR(self.as_raw_UMat(), r.as_raw_Range(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ... for the specified diagonal
/// (d=0 - the main diagonal,
/// >0 - a diagonal from the upper half,
/// <0 - a diagonal from the lower half)
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * d: 0
#[inline]
fn diag(&self, d: i32) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_diag_const_int(self.as_raw_UMat(), d, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns deep copy of the matrix, i.e. the data is copied
#[inline]
#[must_use]
fn try_clone(&self) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_clone_const(self.as_raw_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// copies the matrix content to "m".
#[inline]
fn copy_to(&self, m: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(m);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_copyTo_const_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_UMat(), m.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// copies those matrix elements to "m" that are marked with non-zero mask elements.
#[inline]
fn copy_to_masked(&self, m: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(m);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_copyTo_const_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_UMat(), m.as_raw__OutputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// converts matrix to another datatype with optional scaling. See cvConvertScale.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * alpha: 1
/// * beta: 0
#[inline]
fn convert_to(&self, m: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, rtype: i32, alpha: f64, beta: f64) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(m);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_convertTo_const_const__OutputArrayR_int_double_double(self.as_raw_UMat(), m.as_raw__OutputArray(), rtype, alpha, beta, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * typ: -1
#[inline]
fn assign_to(&self, m: &mut core::UMat, typ: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_assignTo_const_UMatR_int(self.as_raw_UMat(), m.as_raw_mut_UMat(), typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// creates alternative matrix header for the same data, with different
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * rows: 0
#[inline]
fn reshape(&self, cn: i32, rows: i32) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_reshape_const_int_int(self.as_raw_UMat(), cn, rows, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn reshape_1(&self, cn: i32, newndims: i32, newsz: &i32) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_reshape_const_int_int_const_intX(self.as_raw_UMat(), cn, newndims, newsz, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// matrix transposition by means of matrix expressions
#[inline]
fn t(&self) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_t_const(self.as_raw_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// matrix inversion by means of matrix expressions
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * method: DECOMP_LU
#[inline]
fn inv(&self, method: i32) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_inv_const_int(self.as_raw_UMat(), method, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// per-element matrix multiplication by means of matrix expressions
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * scale: 1
#[inline]
fn mul(&self, m: &dyn core::ToInputArray, scale: f64) -> Result<core::UMat> {
extern_container_arg!(m);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_mul_const_const__InputArrayR_double(self.as_raw_UMat(), m.as_raw__InputArray(), scale, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// computes dot-product
#[inline]
fn dot(&self, m: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<f64> {
extern_container_arg!(m);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_dot_const_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_UMat(), m.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// locates matrix header within a parent matrix. See below
#[inline]
fn locate_roi(&self, whole_size: &mut core::Size, ofs: &mut core::Point) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_locateROI_const_SizeR_PointR(self.as_raw_UMat(), whole_size, ofs, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// extracts a rectangular sub-matrix
#[inline]
fn apply(&self, mut row_range: core::Range, mut col_range: core::Range) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_operator___const_Range_Range(self.as_raw_UMat(), row_range.as_raw_mut_Range(), col_range.as_raw_mut_Range(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn apply_1(&self, roi: core::Rect) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_operator___const_const_RectR(self.as_raw_UMat(), &roi, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn apply_2(&self, ranges: &core::Range) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_operator___const_const_RangeX(self.as_raw_UMat(), ranges.as_raw_Range(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn apply_3(&self, ranges: &core::Vector<core::Range>) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_operator___const_const_vectorLRangeGR(self.as_raw_UMat(), ranges.as_raw_VectorOfRange(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns true iff the matrix data is continuous
#[inline]
fn is_continuous(&self) -> bool {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_isContinuous_const(self.as_raw_UMat()) };
ret
}
/// returns true if the matrix is a submatrix of another matrix
#[inline]
fn is_submatrix(&self) -> bool {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_isSubmatrix_const(self.as_raw_UMat()) };
ret
}
/// returns element size in bytes,
#[inline]
fn elem_size(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_elemSize_const(self.as_raw_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns the size of element channel in bytes.
#[inline]
fn elem_size1(&self) -> size_t {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_elemSize1_const(self.as_raw_UMat()) };
ret
}
/// returns element type, similar to CV_MAT_TYPE(cvmat->type)
#[inline]
fn typ(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_type_const(self.as_raw_UMat()) };
ret
}
/// returns element type, similar to CV_MAT_DEPTH(cvmat->type)
#[inline]
fn depth(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_depth_const(self.as_raw_UMat()) };
ret
}
/// returns element type, similar to CV_MAT_CN(cvmat->type)
#[inline]
fn channels(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_channels_const(self.as_raw_UMat()) };
ret
}
/// returns step/elemSize1()
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * i: 0
#[inline]
fn step1(&self, i: i32) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_step1_const_int(self.as_raw_UMat(), i, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns true if matrix data is NULL
#[inline]
fn empty(&self) -> bool {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_empty_const(self.as_raw_UMat()) };
ret
}
/// returns the total number of matrix elements
#[inline]
fn total(&self) -> size_t {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_total_const(self.as_raw_UMat()) };
ret
}
/// returns N if the matrix is 1-channel (N x ptdim) or ptdim-channel (1 x N) or (N x 1); negative number otherwise
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * depth: -1
/// * require_continuous: true
#[inline]
fn check_vector(&self, elem_channels: i32, depth: i32, require_continuous: bool) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_checkVector_const_int_int_bool(self.as_raw_UMat(), elem_channels, depth, require_continuous, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ! Returns the OpenCL buffer handle on which UMat operates on.
/// The UMat instance should be kept alive during the use of the handle to prevent the buffer to be
/// returned to the OpenCV buffer pool.
#[inline]
fn handle(&self, access_flags: core::AccessFlag) -> Result<*mut c_void> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_handle_const_AccessFlag(self.as_raw_UMat(), access_flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn ndoffset(&self, ofs: &mut size_t) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_ndoffset_const_size_tX(self.as_raw_UMat(), ofs, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::UMat]
pub trait UMatTrait: core::UMatTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_UMat(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// ! includes several bit-fields:
/// - the magic signature
/// - continuity flag
/// - depth
/// - number of channels
#[inline]
fn set_flags(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_setPropFlags_int(self.as_raw_mut_UMat(), val) };
ret
}
/// the matrix dimensionality, >= 2
#[inline]
fn set_dims(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_setPropDims_int(self.as_raw_mut_UMat(), val) };
ret
}
/// number of rows in the matrix; -1 when the matrix has more than 2 dimensions
#[inline]
fn set_rows(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_setPropRows_int(self.as_raw_mut_UMat(), val) };
ret
}
/// number of columns in the matrix; -1 when the matrix has more than 2 dimensions
#[inline]
fn set_cols(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_setPropCols_int(self.as_raw_mut_UMat(), val) };
ret
}
/// usage flags for allocator; recommend do not set directly, instead set during construct/create/getUMat
#[inline]
fn set_usage_flags(&mut self, val: core::UMatUsageFlags) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_setPropUsageFlags_UMatUsageFlags(self.as_raw_mut_UMat(), val) };
ret
}
/// black-box container of UMat data
#[inline]
fn u(&mut self) -> core::UMatData {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_getPropU(self.as_raw_mut_UMat()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::UMatData::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// black-box container of UMat data
#[inline]
fn set_u(&mut self, val: &mut core::UMatData) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_setPropU_UMatDataX(self.as_raw_mut_UMat(), val.as_raw_mut_UMatData()) };
ret
}
/// offset of the submatrix (or 0)
#[inline]
fn set_offset(&mut self, val: size_t) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_setPropOffset_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_UMat(), val) };
ret
}
/// sets some of the matrix elements to s, according to the mask
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
fn set_to(&mut self, value: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<core::UMat> {
extern_container_arg!(value);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_setTo_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_UMat(), value.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// allocates new matrix data unless the matrix already has specified size and type.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * usage_flags: USAGE_DEFAULT
#[inline]
unsafe fn create_rows_cols(&mut self, rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32, usage_flags: core::UMatUsageFlags) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_UMat_create_int_int_int_UMatUsageFlags(self.as_raw_mut_UMat(), rows, cols, typ, usage_flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * usage_flags: USAGE_DEFAULT
#[inline]
unsafe fn create_size(&mut self, size: core::Size, typ: i32, usage_flags: core::UMatUsageFlags) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_UMat_create_Size_int_UMatUsageFlags(self.as_raw_mut_UMat(), size.opencv_as_extern(), typ, usage_flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * usage_flags: USAGE_DEFAULT
#[inline]
unsafe fn create_nd(&mut self, sizes: &[i32], typ: i32, usage_flags: core::UMatUsageFlags) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_UMat_create_int_const_intX_int_UMatUsageFlags(self.as_raw_mut_UMat(), sizes.len() as _, sizes.as_ptr(), typ, usage_flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * usage_flags: USAGE_DEFAULT
#[inline]
unsafe fn create_nd_vec(&mut self, sizes: &core::Vector<i32>, typ: i32, usage_flags: core::UMatUsageFlags) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_UMat_create_const_vectorLintGR_int_UMatUsageFlags(self.as_raw_mut_UMat(), sizes.as_raw_VectorOfi32(), typ, usage_flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// increases the reference counter; use with care to avoid memleaks
#[inline]
fn addref(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_addref(self.as_raw_mut_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// decreases reference counter;
#[inline]
fn release(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_release(self.as_raw_mut_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// deallocates the matrix data
#[inline]
fn deallocate(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_deallocate(self.as_raw_mut_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// moves/resizes the current matrix ROI inside the parent matrix.
#[inline]
fn adjust_roi(&mut self, dtop: i32, dbottom: i32, dleft: i32, dright: i32) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_adjustROI_int_int_int_int(self.as_raw_mut_UMat(), dtop, dbottom, dleft, dright, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// internal use method: updates the continuity flag
#[inline]
fn update_continuity_flag(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_updateContinuityFlag(self.as_raw_mut_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// @todo document
pub struct UMat {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { UMat }
impl Drop for UMat {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_UMat_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_UMat_delete(self.as_raw_mut_UMat()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for UMat {}
impl core::UMatTraitConst for UMat {
#[inline] fn as_raw_UMat(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::UMatTrait for UMat {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_UMat(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl UMat {
/// default constructor
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * usage_flags: USAGE_DEFAULT
#[inline]
pub fn new(usage_flags: core::UMatUsageFlags) -> core::UMat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_UMat_UMatUsageFlags(usage_flags) };
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// constructs 2D matrix of the specified size and type
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * usage_flags: USAGE_DEFAULT
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn new_rows_cols(rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32, usage_flags: core::UMatUsageFlags) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_UMat_UMat_int_int_int_UMatUsageFlags(rows, cols, typ, usage_flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * usage_flags: USAGE_DEFAULT
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn new_size(size: core::Size, typ: i32, usage_flags: core::UMatUsageFlags) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_UMat_UMat_Size_int_UMatUsageFlags(size.opencv_as_extern(), typ, usage_flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// constructs 2D matrix and fills it with the specified value _s.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * usage_flags: USAGE_DEFAULT
#[inline]
pub fn new_rows_cols_with_default(rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32, s: core::Scalar, usage_flags: core::UMatUsageFlags) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_UMat_int_int_int_const_ScalarR_UMatUsageFlags(rows, cols, typ, &s, usage_flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * usage_flags: USAGE_DEFAULT
#[inline]
pub fn new_size_with_default(size: core::Size, typ: i32, s: core::Scalar, usage_flags: core::UMatUsageFlags) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_UMat_Size_int_const_ScalarR_UMatUsageFlags(size.opencv_as_extern(), typ, &s, usage_flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// constructs n-dimensional matrix
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * usage_flags: USAGE_DEFAULT
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn new_nd(sizes: &[i32], typ: i32, usage_flags: core::UMatUsageFlags) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_UMat_UMat_int_const_intX_int_UMatUsageFlags(sizes.len() as _, sizes.as_ptr(), typ, usage_flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * usage_flags: USAGE_DEFAULT
#[inline]
pub fn new_nd_with_default(sizes: &[i32], typ: i32, s: core::Scalar, usage_flags: core::UMatUsageFlags) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_UMat_int_const_intX_int_const_ScalarR_UMatUsageFlags(sizes.len() as _, sizes.as_ptr(), typ, &s, usage_flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// copy constructor
#[inline]
pub fn copy(m: &core::UMat) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_UMat_const_UMatR(m.as_raw_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// creates a matrix header for a part of the bigger matrix
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * col_range: Range::all()
#[inline]
pub fn rowscols(m: &core::UMat, row_range: &core::Range, col_range: &core::Range) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_UMat_const_UMatR_const_RangeR_const_RangeR(m.as_raw_UMat(), row_range.as_raw_Range(), col_range.as_raw_Range(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn roi(m: &core::UMat, roi: core::Rect) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_UMat_const_UMatR_const_RectR(m.as_raw_UMat(), &roi, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn ranges(m: &core::UMat, ranges: &core::Vector<core::Range>) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_UMat_const_UMatR_const_vectorLRangeGR(m.as_raw_UMat(), ranges.as_raw_VectorOfRange(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// constructs a square diagonal matrix which main diagonal is vector "d"
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn diag(d: &core::UMat, usage_flags: core::UMatUsageFlags) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_diag_const_UMatR_UMatUsageFlags(d.as_raw_UMat(), usage_flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn diag_1(d: &core::UMat) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_diag_const_UMatR(d.as_raw_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Matlab-style matrix initialization
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn zeros(rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32, usage_flags: core::UMatUsageFlags) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_zeros_int_int_int_UMatUsageFlags(rows, cols, typ, usage_flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn zeros_1(size: core::Size, typ: i32, usage_flags: core::UMatUsageFlags) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_zeros_Size_int_UMatUsageFlags(size.opencv_as_extern(), typ, usage_flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn zeros_2(ndims: i32, sz: &i32, typ: i32, usage_flags: core::UMatUsageFlags) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_zeros_int_const_intX_int_UMatUsageFlags(ndims, sz, typ, usage_flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn zeros_3(rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_zeros_int_int_int(rows, cols, typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn zeros_4(size: core::Size, typ: i32) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_zeros_Size_int(size.opencv_as_extern(), typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn zeros_5(ndims: i32, sz: &i32, typ: i32) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_zeros_int_const_intX_int(ndims, sz, typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn ones(rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32, usage_flags: core::UMatUsageFlags) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_ones_int_int_int_UMatUsageFlags(rows, cols, typ, usage_flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn ones_1(size: core::Size, typ: i32, usage_flags: core::UMatUsageFlags) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_ones_Size_int_UMatUsageFlags(size.opencv_as_extern(), typ, usage_flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn ones_2(ndims: i32, sz: &i32, typ: i32, usage_flags: core::UMatUsageFlags) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_ones_int_const_intX_int_UMatUsageFlags(ndims, sz, typ, usage_flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn ones_3(rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_ones_int_int_int(rows, cols, typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn ones_4(size: core::Size, typ: i32) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_ones_Size_int(size.opencv_as_extern(), typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn ones_5(ndims: i32, sz: &i32, typ: i32) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_ones_int_const_intX_int(ndims, sz, typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn eye(rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32, usage_flags: core::UMatUsageFlags) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_eye_int_int_int_UMatUsageFlags(rows, cols, typ, usage_flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn eye_1(size: core::Size, typ: i32, usage_flags: core::UMatUsageFlags) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_eye_Size_int_UMatUsageFlags(size.opencv_as_extern(), typ, usage_flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn eye_2(rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_eye_int_int_int(rows, cols, typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
#[must_use]
pub fn eye_3(size: core::Size, typ: i32) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_eye_Size_int(size.opencv_as_extern(), typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy_mut(mut m: core::UMat) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMat_UMat_UMatRR(m.as_raw_mut_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl Clone for UMat {
#[inline]
/// Calls try_clone() and panics if that fails
fn clone(&self) -> Self {
self.try_clone().expect("Cannot clone UMat")
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::UMatData]
pub trait UMatDataTraitConst {
fn as_raw_UMatData(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn urefcount(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_getPropUrefcount_const(self.as_raw_UMatData()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn refcount(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_getPropRefcount_const(self.as_raw_UMatData()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn size(&self) -> size_t {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_getPropSize_const(self.as_raw_UMatData()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn flags(&self) -> core::UMatData_MemoryFlag {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_getPropFlags_const(self.as_raw_UMatData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
ret
}
#[inline]
fn allocator_flags_(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_getPropAllocatorFlags__const(self.as_raw_UMatData()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn mapcount(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_getPropMapcount_const(self.as_raw_UMatData()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn host_copy_obsolete(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_hostCopyObsolete_const(self.as_raw_UMatData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn device_copy_obsolete(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_deviceCopyObsolete_const(self.as_raw_UMatData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn device_mem_mapped(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_deviceMemMapped_const(self.as_raw_UMatData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn copy_on_map(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_copyOnMap_const(self.as_raw_UMatData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn temp_umat(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_tempUMat_const(self.as_raw_UMatData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn temp_copied_umat(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_tempCopiedUMat_const(self.as_raw_UMatData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::UMatData]
pub trait UMatDataTrait: core::UMatDataTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_UMatData(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_urefcount(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_setPropUrefcount_int(self.as_raw_mut_UMatData(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_refcount(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_setPropRefcount_int(self.as_raw_mut_UMatData(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn data(&mut self) -> *mut u8 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_getPropData(self.as_raw_mut_UMatData()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
unsafe fn set_data(&mut self, val: *mut u8) {
let ret = { sys::cv_UMatData_setPropData_unsigned_charX(self.as_raw_mut_UMatData(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn origdata(&mut self) -> *mut u8 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_getPropOrigdata(self.as_raw_mut_UMatData()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
unsafe fn set_origdata(&mut self, val: *mut u8) {
let ret = { sys::cv_UMatData_setPropOrigdata_unsigned_charX(self.as_raw_mut_UMatData(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_size(&mut self, val: size_t) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_setPropSize_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_UMatData(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_flags(&mut self, val: core::UMatData_MemoryFlag) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_setPropFlags_MemoryFlag(self.as_raw_mut_UMatData(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn handle(&mut self) -> *mut c_void {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_getPropHandle(self.as_raw_mut_UMatData()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
unsafe fn set_handle(&mut self, val: *mut c_void) {
let ret = { sys::cv_UMatData_setPropHandle_voidX(self.as_raw_mut_UMatData(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn userdata(&mut self) -> *mut c_void {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_getPropUserdata(self.as_raw_mut_UMatData()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
unsafe fn set_userdata(&mut self, val: *mut c_void) {
let ret = { sys::cv_UMatData_setPropUserdata_voidX(self.as_raw_mut_UMatData(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_allocator_flags_(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_setPropAllocatorFlags__int(self.as_raw_mut_UMatData(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_mapcount(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_setPropMapcount_int(self.as_raw_mut_UMatData(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn original_umat_data(&mut self) -> core::UMatData {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_getPropOriginalUMatData(self.as_raw_mut_UMatData()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::UMatData::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_original_umat_data(&mut self, val: &mut core::UMatData) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_setPropOriginalUMatData_UMatDataX(self.as_raw_mut_UMatData(), val.as_raw_mut_UMatData()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn lock(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_lock(self.as_raw_mut_UMatData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn unlock(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_unlock(self.as_raw_mut_UMatData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn mark_host_copy_obsolete(&mut self, flag: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_markHostCopyObsolete_bool(self.as_raw_mut_UMatData(), flag, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn mark_device_copy_obsolete(&mut self, flag: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_markDeviceCopyObsolete_bool(self.as_raw_mut_UMatData(), flag, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn mark_device_mem_mapped(&mut self, flag: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_UMatData_markDeviceMemMapped_bool(self.as_raw_mut_UMatData(), flag, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
pub struct UMatData {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { UMatData }
impl Drop for UMatData {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_UMatData_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_UMatData_delete(self.as_raw_mut_UMatData()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for UMatData {}
impl core::UMatDataTraitConst for UMatData {
#[inline] fn as_raw_UMatData(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::UMatDataTrait for UMatData {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_UMatData(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl UMatData {
}
/// Constant methods for [core::_InputArray]
pub trait _InputArrayTraitConst {
fn as_raw__InputArray(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * idx: -1
#[inline]
fn get_mat(&self, idx: i32) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_getMat_const_int(self.as_raw__InputArray(), idx, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * idx: -1
#[inline]
fn get_mat_(&self, idx: i32) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_getMat__const_int(self.as_raw__InputArray(), idx, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * idx: -1
#[inline]
fn get_umat(&self, idx: i32) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_getUMat_const_int(self.as_raw__InputArray(), idx, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_mat_vector(&self, mv: &mut core::Vector<core::Mat>) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_getMatVector_const_vectorLMatGR(self.as_raw__InputArray(), mv.as_raw_mut_VectorOfMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_umat_vector(&self, umv: &mut core::Vector<core::UMat>) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_getUMatVector_const_vectorLUMatGR(self.as_raw__InputArray(), umv.as_raw_mut_VectorOfUMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_gpu_mat_vector(&self, gpumv: &mut core::Vector<core::GpuMat>) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_getGpuMatVector_const_vectorLGpuMatGR(self.as_raw__InputArray(), gpumv.as_raw_mut_VectorOfGpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_gpu_mat(&self) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_getGpuMat_const(self.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_o_gl_buffer(&self) -> Result<core::Buffer> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_getOGlBuffer_const(self.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Buffer::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_flags(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_getFlags_const(self.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_obj(&self) -> Result<*mut c_void> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_getObj_const(self.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_sz(&self) -> Result<core::Size> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_getSz_const(self.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn kind(&self) -> Result<core::_InputArray_KindFlag> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_kind_const(self.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * i: -1
#[inline]
fn dims(&self, i: i32) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_dims_const_int(self.as_raw__InputArray(), i, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * i: -1
#[inline]
fn cols(&self, i: i32) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_cols_const_int(self.as_raw__InputArray(), i, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * i: -1
#[inline]
fn rows(&self, i: i32) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_rows_const_int(self.as_raw__InputArray(), i, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * i: -1
#[inline]
fn size(&self, i: i32) -> Result<core::Size> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_size_const_int(self.as_raw__InputArray(), i, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * i: -1
#[inline]
fn sizend(&self, sz: &mut i32, i: i32) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_sizend_const_intX_int(self.as_raw__InputArray(), sz, i, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn same_size(&self, arr: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<bool> {
extern_container_arg!(arr);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_sameSize_const_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw__InputArray(), arr.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * i: -1
#[inline]
fn total(&self, i: i32) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_total_const_int(self.as_raw__InputArray(), i, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * i: -1
#[inline]
fn typ(&self, i: i32) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_type_const_int(self.as_raw__InputArray(), i, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * i: -1
#[inline]
fn depth(&self, i: i32) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_depth_const_int(self.as_raw__InputArray(), i, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * i: -1
#[inline]
fn channels(&self, i: i32) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_channels_const_int(self.as_raw__InputArray(), i, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * i: -1
#[inline]
fn is_continuous(&self, i: i32) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_isContinuous_const_int(self.as_raw__InputArray(), i, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * i: -1
#[inline]
fn is_submatrix(&self, i: i32) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_isSubmatrix_const_int(self.as_raw__InputArray(), i, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn empty(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_empty_const(self.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn copy_to(&self, arr: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(arr);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_copyTo_const_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw__InputArray(), arr.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn copy_to_masked(&self, arr: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(arr);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_copyTo_const_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw__InputArray(), arr.as_raw__OutputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * i: -1
#[inline]
fn offset(&self, i: i32) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_offset_const_int(self.as_raw__InputArray(), i, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * i: -1
#[inline]
fn step(&self, i: i32) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_step_const_int(self.as_raw__InputArray(), i, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn is_mat(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_isMat_const(self.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn is_umat(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_isUMat_const(self.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn is_mat_vector(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_isMatVector_const(self.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn is_umat_vector(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_isUMatVector_const(self.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn is_matx(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_isMatx_const(self.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn is_vector(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_isVector_const(self.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn is_gpu_mat(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_isGpuMat_const(self.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn is_gpu_mat_vector(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray_isGpuMatVector_const(self.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::_InputArray]
pub trait _InputArrayTrait: core::_InputArrayTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut__InputArray(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
/// This is the proxy class for passing read-only input arrays into OpenCV functions.
///
/// It is defined as:
/// ```C++
/// typedef const _InputArray& InputArray;
/// ```
///
/// where _InputArray is a class that can be constructed from `Mat`, `Mat_<T>`, `Matx<T, m, n>`,
/// `std::vector<T>`, `std::vector<std::vector<T> >`, `std::vector<Mat>`, `std::vector<Mat_<T> >`,
/// `UMat`, `std::vector<UMat>` or `double`. It can also be constructed from a matrix expression.
///
/// Since this is mostly implementation-level class, and its interface may change in future versions, we
/// do not describe it in details. There are a few key things, though, that should be kept in mind:
///
/// * When you see in the reference manual or in OpenCV source code a function that takes
/// InputArray, it means that you can actually pass `Mat`, `Matx`, `vector<T>` etc. (see above the
/// complete list).
/// * Optional input arguments: If some of the input arrays may be empty, pass cv::noArray() (or
/// simply cv::Mat() as you probably did before).
/// * The class is designed solely for passing parameters. That is, normally you *should not*
/// declare class members, local and global variables of this type.
/// * If you want to design your own function or a class method that can operate of arrays of
/// multiple types, you can use InputArray (or OutputArray) for the respective parameters. Inside
/// a function you should use _InputArray::getMat() method to construct a matrix header for the
/// array (without copying data). _InputArray::kind() can be used to distinguish Mat from
/// `vector<>` etc., but normally it is not needed.
///
/// Here is how you can use a function that takes InputArray :
/// ```C++
/// std::vector<Point2f> vec;
/// // points or a circle
/// for( int i = 0; i < 30; i++ )
/// vec.push_back(Point2f((float)(100 + 30*cos(i*CV_PI*2/5)),
/// (float)(100 - 30*sin(i*CV_PI*2/5))));
/// cv::transform(vec, vec, cv::Matx23f(0.707, -0.707, 10, 0.707, 0.707, 20));
/// ```
///
/// That is, we form an STL vector containing points, and apply in-place affine transformation to the
/// vector using the 2x3 matrix created inline as `Matx<float, 2, 3>` instance.
///
/// Here is how such a function can be implemented (for simplicity, we implement a very specific case of
/// it, according to the assertion statement inside) :
/// ```C++
/// void myAffineTransform(InputArray _src, OutputArray _dst, InputArray _m)
/// {
/// // get Mat headers for input arrays. This is O(1) operation,
/// // unless _src and/or _m are matrix expressions.
/// Mat src = _src.getMat(), m = _m.getMat();
/// CV_Assert( src.type() == CV_32FC2 && m.type() == CV_32F && m.size() == Size(3, 2) );
///
/// // [re]create the output array so that it has the proper size and type.
/// // In case of Mat it calls Mat::create, in case of STL vector it calls vector::resize.
/// _dst.create(src.size(), src.type());
/// Mat dst = _dst.getMat();
///
/// for( int i = 0; i < src.rows; i++ )
/// for( int j = 0; j < src.cols; j++ )
/// {
/// Point2f pt = src.at<Point2f>(i, j);
/// dst.at<Point2f>(i, j) = Point2f(m.at<float>(0, 0)*pt.x +
/// m.at<float>(0, 1)*pt.y +
/// m.at<float>(0, 2),
/// m.at<float>(1, 0)*pt.x +
/// m.at<float>(1, 1)*pt.y +
/// m.at<float>(1, 2));
/// }
/// }
/// ```
///
/// There is another related type, InputArrayOfArrays, which is currently defined as a synonym for
/// InputArray:
/// ```C++
/// typedef InputArray InputArrayOfArrays;
/// ```
///
/// It denotes function arguments that are either vectors of vectors or vectors of matrices. A separate
/// synonym is needed to generate Python/Java etc. wrappers properly. At the function implementation
/// level their use is similar, but _InputArray::getMat(idx) should be used to get header for the
/// idx-th component of the outer vector and _InputArray::size().area() should be used to find the
/// number of components (vectors/matrices) of the outer vector.
///
/// In general, type support is limited to cv::Mat types. Other types are forbidden.
/// But in some cases we need to support passing of custom non-general Mat types, like arrays of cv::KeyPoint, cv::DMatch, etc.
/// This data is not intended to be interpreted as an image data, or processed somehow like regular cv::Mat.
/// To pass such custom type use rawIn() / rawOut() / rawInOut() wrappers.
/// Custom type is wrapped as Mat-compatible `CV_8UC<N>` values (N = sizeof(T), N <= CV_CN_MAX).
pub struct _InputArray {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { _InputArray }
impl Drop for _InputArray {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv__InputArray_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv__InputArray_delete(self.as_raw_mut__InputArray()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for _InputArray {}
impl core::_InputArrayTraitConst for _InputArray {
#[inline] fn as_raw__InputArray(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::_InputArrayTrait for _InputArray {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut__InputArray(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl _InputArray {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::_InputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray__InputArray(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn new(_flags: i32, _obj: *mut c_void) -> Result<core::_InputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv__InputArray__InputArray_int_voidX(_flags, _obj, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::_InputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_mat(m: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::_InputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray__InputArray_const_MatR(m.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_matexpr(expr: &core::MatExpr) -> Result<core::_InputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray__InputArray_const_MatExprR(expr.as_raw_MatExpr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_mat_vec(vec: &core::Vector<core::Mat>) -> Result<core::_InputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray__InputArray_const_vectorLMatGR(vec.as_raw_VectorOfMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_bool_vec(vec: &core::Vector<bool>) -> Result<core::_InputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray__InputArray_const_vectorLboolGR(vec.as_raw_VectorOfbool(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_f64(val: &f64) -> Result<core::_InputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray__InputArray_const_doubleR(val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_gpumat(d_mat: &core::GpuMat) -> Result<core::_InputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray__InputArray_const_GpuMatR(d_mat.as_raw_GpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_gpumat_vec(d_mat_array: &core::Vector<core::GpuMat>) -> Result<core::_InputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray__InputArray_const_vectorLGpuMatGR(d_mat_array.as_raw_VectorOfGpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn new_1(buf: &core::Buffer) -> Result<core::_InputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray__InputArray_const_BufferR(buf.as_raw_Buffer(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_hostmem(cuda_mem: &core::HostMem) -> Result<core::_InputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray__InputArray_const_HostMemR(cuda_mem.as_raw_HostMem(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_umat(um: &core::UMat) -> Result<core::_InputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray__InputArray_const_UMatR(um.as_raw_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_umat_vec(umv: &core::Vector<core::UMat>) -> Result<core::_InputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputArray__InputArray_const_vectorLUMatGR(umv.as_raw_VectorOfUMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::_InputOutputArray]
pub trait _InputOutputArrayTraitConst: core::_OutputArrayTraitConst {
fn as_raw__InputOutputArray(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::_InputOutputArray]
pub trait _InputOutputArrayTrait: core::_InputOutputArrayTraitConst + core::_OutputArrayTrait {
fn as_raw_mut__InputOutputArray(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
pub struct _InputOutputArray {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { _InputOutputArray }
impl Drop for _InputOutputArray {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv__InputOutputArray_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv__InputOutputArray_delete(self.as_raw_mut__InputOutputArray()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for _InputOutputArray {}
impl core::_InputArrayTraitConst for _InputOutputArray {
#[inline] fn as_raw__InputArray(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::_InputArrayTrait for _InputOutputArray {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut__InputArray(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl core::_OutputArrayTraitConst for _InputOutputArray {
#[inline] fn as_raw__OutputArray(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::_OutputArrayTrait for _InputOutputArray {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut__OutputArray(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl core::_InputOutputArrayTraitConst for _InputOutputArray {
#[inline] fn as_raw__InputOutputArray(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::_InputOutputArrayTrait for _InputOutputArray {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut__InputOutputArray(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl _InputOutputArray {
/// ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::_InputOutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputOutputArray__InputOutputArray(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputOutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn new(_flags: i32, _obj: *mut c_void) -> Result<core::_InputOutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv__InputOutputArray__InputOutputArray_int_voidX(_flags, _obj, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::_InputOutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_mat_mut(m: &mut core::Mat) -> Result<core::_InputOutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputOutputArray__InputOutputArray_MatR(m.as_raw_mut_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputOutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_mat_vec_mut(vec: &mut core::Vector<core::Mat>) -> Result<core::_InputOutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputOutputArray__InputOutputArray_vectorLMatGR(vec.as_raw_mut_VectorOfMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputOutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_gpumat_mut(d_mat: &mut core::GpuMat) -> Result<core::_InputOutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputOutputArray__InputOutputArray_GpuMatR(d_mat.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputOutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn new_1(buf: &mut core::Buffer) -> Result<core::_InputOutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputOutputArray__InputOutputArray_BufferR(buf.as_raw_mut_Buffer(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputOutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_hostmem_mut(cuda_mem: &mut core::HostMem) -> Result<core::_InputOutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputOutputArray__InputOutputArray_HostMemR(cuda_mem.as_raw_mut_HostMem(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputOutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_umat_mut(m: &mut core::UMat) -> Result<core::_InputOutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputOutputArray__InputOutputArray_UMatR(m.as_raw_mut_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputOutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_umat_vec_mut(vec: &mut core::Vector<core::UMat>) -> Result<core::_InputOutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputOutputArray__InputOutputArray_vectorLUMatGR(vec.as_raw_mut_VectorOfUMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputOutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_mat(m: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::_InputOutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputOutputArray__InputOutputArray_const_MatR(m.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputOutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_mat_vec(vec: &core::Vector<core::Mat>) -> Result<core::_InputOutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputOutputArray__InputOutputArray_const_vectorLMatGR(vec.as_raw_VectorOfMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputOutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_gpumat(d_mat: &core::GpuMat) -> Result<core::_InputOutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputOutputArray__InputOutputArray_const_GpuMatR(d_mat.as_raw_GpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputOutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_gpumat_vec(d_mat: &core::Vector<core::GpuMat>) -> Result<core::_InputOutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputOutputArray__InputOutputArray_const_vectorLGpuMatGR(d_mat.as_raw_VectorOfGpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputOutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn new_2(buf: &core::Buffer) -> Result<core::_InputOutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputOutputArray__InputOutputArray_const_BufferR(buf.as_raw_Buffer(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputOutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_hostmem(cuda_mem: &core::HostMem) -> Result<core::_InputOutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputOutputArray__InputOutputArray_const_HostMemR(cuda_mem.as_raw_HostMem(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputOutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_umat(m: &core::UMat) -> Result<core::_InputOutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputOutputArray__InputOutputArray_const_UMatR(m.as_raw_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputOutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_umat_vec(vec: &core::Vector<core::UMat>) -> Result<core::_InputOutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__InputOutputArray__InputOutputArray_const_vectorLUMatGR(vec.as_raw_VectorOfUMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_InputOutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { _InputOutputArray, core::_InputArray, cv__InputOutputArray_to__InputArray }
boxed_cast_base! { _InputOutputArray, core::_OutputArray, cv__InputOutputArray_to__OutputArray }
/// Constant methods for [core::_OutputArray]
pub trait _OutputArrayTraitConst: core::_InputArrayTraitConst {
fn as_raw__OutputArray(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn fixed_size(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray_fixedSize_const(self.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn fixed_type(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray_fixedType_const(self.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn needed(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray_needed_const(self.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * i: -1
#[inline]
fn get_mat_ref(&self, i: i32) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray_getMatRef_const_int(self.as_raw__OutputArray(), i, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * i: -1
#[inline]
fn get_umat_ref(&self, i: i32) -> Result<core::UMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray_getUMatRef_const_int(self.as_raw__OutputArray(), i, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_gpu_mat_ref(&self) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray_getGpuMatRef_const(self.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_gpu_mat_vec_ref(&self) -> Result<core::Vector<core::GpuMat>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray_getGpuMatVecRef_const(self.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Vector::<core::GpuMat>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_o_gl_buffer_ref(&self) -> Result<core::Buffer> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray_getOGlBufferRef_const(self.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Buffer::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_host_mem_ref(&self) -> Result<core::HostMem> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray_getHostMemRef_const(self.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::HostMem::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * i: -1
/// * allow_transposed: false
/// * fixed_depth_mask: static_cast<_OutputArray::DepthMask>(0)
#[inline]
fn create_size(&self, sz: core::Size, typ: i32, i: i32, allow_transposed: bool, fixed_depth_mask: core::_OutputArray_DepthMask) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray_create_const_Size_int_int_bool_DepthMask(self.as_raw__OutputArray(), sz.opencv_as_extern(), typ, i, allow_transposed, fixed_depth_mask, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * i: -1
/// * allow_transposed: false
/// * fixed_depth_mask: static_cast<_OutputArray::DepthMask>(0)
#[inline]
fn create(&self, rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32, i: i32, allow_transposed: bool, fixed_depth_mask: core::_OutputArray_DepthMask) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray_create_const_int_int_int_int_bool_DepthMask(self.as_raw__OutputArray(), rows, cols, typ, i, allow_transposed, fixed_depth_mask, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * i: -1
/// * allow_transposed: false
/// * fixed_depth_mask: static_cast<_OutputArray::DepthMask>(0)
#[inline]
fn create_nd(&self, size: &[i32], typ: i32, i: i32, allow_transposed: bool, fixed_depth_mask: core::_OutputArray_DepthMask) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray_create_const_int_const_intX_int_int_bool_DepthMask(self.as_raw__OutputArray(), size.len() as _, size.as_ptr(), typ, i, allow_transposed, fixed_depth_mask, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
unsafe fn create_same_size(&self, arr: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mtype: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(arr);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv__OutputArray_createSameSize_const_const__InputArrayR_int(self.as_raw__OutputArray(), arr.as_raw__InputArray(), mtype, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn release(&self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray_release_const(self.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn clear(&self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray_clear_const(self.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * mask: _InputArray()
#[inline]
fn set_to(&self, value: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(value);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray_setTo_const_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw__OutputArray(), value.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn assign(&self, u: &core::UMat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray_assign_const_const_UMatR(self.as_raw__OutputArray(), u.as_raw_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn assign_1(&self, m: &core::Mat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray_assign_const_const_MatR(self.as_raw__OutputArray(), m.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn assign_2(&self, v: &core::Vector<core::UMat>) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray_assign_const_const_vectorLUMatGR(self.as_raw__OutputArray(), v.as_raw_VectorOfUMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn assign_3(&self, v: &core::Vector<core::Mat>) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray_assign_const_const_vectorLMatGR(self.as_raw__OutputArray(), v.as_raw_VectorOfMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn move_(&self, u: &mut core::UMat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray_move_const_UMatR(self.as_raw__OutputArray(), u.as_raw_mut_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn move__1(&self, m: &mut core::Mat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray_move_const_MatR(self.as_raw__OutputArray(), m.as_raw_mut_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::_OutputArray]
pub trait _OutputArrayTrait: core::_InputArrayTrait + core::_OutputArrayTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut__OutputArray(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
/// This type is very similar to InputArray except that it is used for input/output and output function
/// parameters.
///
/// Just like with InputArray, OpenCV users should not care about OutputArray, they just pass `Mat`,
/// `vector<T>` etc. to the functions. The same limitation as for `InputArray`: *Do not explicitly
/// create OutputArray instances* applies here too.
///
/// If you want to make your function polymorphic (i.e. accept different arrays as output parameters),
/// it is also not very difficult. Take the sample above as the reference. Note that
/// _OutputArray::create() needs to be called before _OutputArray::getMat(). This way you guarantee
/// that the output array is properly allocated.
///
/// Optional output parameters. If you do not need certain output array to be computed and returned to
/// you, pass cv::noArray(), just like you would in the case of optional input array. At the
/// implementation level, use _OutputArray::needed() to check if certain output array needs to be
/// computed or not.
///
/// There are several synonyms for OutputArray that are used to assist automatic Python/Java/... wrapper
/// generators:
/// ```C++
/// typedef OutputArray OutputArrayOfArrays;
/// typedef OutputArray InputOutputArray;
/// typedef OutputArray InputOutputArrayOfArrays;
/// ```
///
pub struct _OutputArray {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { _OutputArray }
impl Drop for _OutputArray {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv__OutputArray_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv__OutputArray_delete(self.as_raw_mut__OutputArray()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for _OutputArray {}
impl core::_InputArrayTraitConst for _OutputArray {
#[inline] fn as_raw__InputArray(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::_InputArrayTrait for _OutputArray {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut__InputArray(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl core::_OutputArrayTraitConst for _OutputArray {
#[inline] fn as_raw__OutputArray(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::_OutputArrayTrait for _OutputArray {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut__OutputArray(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl _OutputArray {
/// /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::_OutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray__OutputArray(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_OutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn new(_flags: i32, _obj: *mut c_void) -> Result<core::_OutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv__OutputArray__OutputArray_int_voidX(_flags, _obj, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::_OutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_mat_mut(m: &mut core::Mat) -> Result<core::_OutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray__OutputArray_MatR(m.as_raw_mut_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_OutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_mat_vec_mut(vec: &mut core::Vector<core::Mat>) -> Result<core::_OutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray__OutputArray_vectorLMatGR(vec.as_raw_mut_VectorOfMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_OutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_gpumat_mut(d_mat: &mut core::GpuMat) -> Result<core::_OutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray__OutputArray_GpuMatR(d_mat.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_OutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_gpumat_vec_mut(d_mat: &mut core::Vector<core::GpuMat>) -> Result<core::_OutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray__OutputArray_vectorLGpuMatGR(d_mat.as_raw_mut_VectorOfGpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_OutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn new_1(buf: &mut core::Buffer) -> Result<core::_OutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray__OutputArray_BufferR(buf.as_raw_mut_Buffer(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_OutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_hostmem_mut(cuda_mem: &mut core::HostMem) -> Result<core::_OutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray__OutputArray_HostMemR(cuda_mem.as_raw_mut_HostMem(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_OutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_umat_mut(m: &mut core::UMat) -> Result<core::_OutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray__OutputArray_UMatR(m.as_raw_mut_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_OutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_umat_vec_mut(vec: &mut core::Vector<core::UMat>) -> Result<core::_OutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray__OutputArray_vectorLUMatGR(vec.as_raw_mut_VectorOfUMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_OutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_mat(m: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::_OutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray__OutputArray_const_MatR(m.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_OutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_mat_vec(vec: &core::Vector<core::Mat>) -> Result<core::_OutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray__OutputArray_const_vectorLMatGR(vec.as_raw_VectorOfMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_OutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_gpumat(d_mat: &core::GpuMat) -> Result<core::_OutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray__OutputArray_const_GpuMatR(d_mat.as_raw_GpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_OutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
#[cfg(not(target_os = "windows"))]
pub fn from_gpumat_vec(d_mat: &core::Vector<core::GpuMat>) -> Result<core::_OutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray__OutputArray_const_vectorLGpuMatGR(d_mat.as_raw_VectorOfGpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_OutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn new_2(buf: &core::Buffer) -> Result<core::_OutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray__OutputArray_const_BufferR(buf.as_raw_Buffer(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_OutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_hostmem(cuda_mem: &core::HostMem) -> Result<core::_OutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray__OutputArray_const_HostMemR(cuda_mem.as_raw_HostMem(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_OutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_umat(m: &core::UMat) -> Result<core::_OutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray__OutputArray_const_UMatR(m.as_raw_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_OutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_umat_vec(vec: &core::Vector<core::UMat>) -> Result<core::_OutputArray> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv__OutputArray__OutputArray_const_vectorLUMatGR(vec.as_raw_VectorOfUMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::_OutputArray::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { _OutputArray, core::_InputArray, cv__OutputArray_to__InputArray }
/// Constant methods for [core::BufferPool]
pub trait BufferPoolTraitConst {
fn as_raw_BufferPool(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Returns the allocator associated with the stream.
#[inline]
fn get_allocator(&self) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn core::GpuMat_Allocator>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_BufferPool_getAllocator_const(self.as_raw_BufferPool(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn core::GpuMat_Allocator>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::BufferPool]
pub trait BufferPoolTrait: core::BufferPoolTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_BufferPool(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Allocates a new GpuMat of given size and type.
#[inline]
fn get_buffer(&mut self, rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_BufferPool_getBuffer_int_int_int(self.as_raw_mut_BufferPool(), rows, cols, typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Allocates a new GpuMat of given size and type.
#[inline]
fn get_buffer_1(&mut self, size: core::Size, typ: i32) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_BufferPool_getBuffer_Size_int(self.as_raw_mut_BufferPool(), size.opencv_as_extern(), typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// BufferPool for use with CUDA streams
///
/// BufferPool utilizes Stream's allocator to create new buffers for GpuMat's. It is
/// only useful when enabled with #setBufferPoolUsage.
///
/// ```C++
/// setBufferPoolUsage(true);
/// ```
///
///
///
/// Note: #setBufferPoolUsage must be called \em before any Stream declaration.
///
/// Users may specify custom allocator for Stream and may implement their own stream based
/// functions utilizing the same underlying GPU memory management.
///
/// If custom allocator is not specified, BufferPool utilizes StackAllocator by
/// default. StackAllocator allocates a chunk of GPU device memory beforehand,
/// and when GpuMat is declared later on, it is given the pre-allocated memory.
/// This kind of strategy reduces the number of calls for memory allocating APIs
/// such as cudaMalloc or cudaMallocPitch.
///
/// Below is an example that utilizes BufferPool with StackAllocator:
///
/// ```C++
/// #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
///
/// using namespace cv;
/// using namespace cv::cuda
///
/// int main()
/// {
/// setBufferPoolUsage(true); // Tell OpenCV that we are going to utilize BufferPool
/// setBufferPoolConfig(getDevice(), 1024 * 1024 * 64, 2); // Allocate 64 MB, 2 stacks (default is 10 MB, 5 stacks)
///
/// Stream stream1, stream2; // Each stream uses 1 stack
/// BufferPool pool1(stream1), pool2(stream2);
///
/// GpuMat d_src1 = pool1.getBuffer(4096, 4096, CV_8UC1); // 16MB
/// GpuMat d_dst1 = pool1.getBuffer(4096, 4096, CV_8UC3); // 48MB, pool1 is now full
///
/// GpuMat d_src2 = pool2.getBuffer(1024, 1024, CV_8UC1); // 1MB
/// GpuMat d_dst2 = pool2.getBuffer(1024, 1024, CV_8UC3); // 3MB
///
/// cvtColor(d_src1, d_dst1, CV_GRAY2BGR, 0, stream1);
/// cvtColor(d_src2, d_dst2, CV_GRAY2BGR, 0, stream2);
/// }
/// ```
///
///
/// If we allocate another GpuMat on pool1 in the above example, it will be carried out by
/// the DefaultAllocator since the stack for pool1 is full.
///
/// ```C++
/// GpuMat d_add1 = pool1.getBuffer(1024, 1024, CV_8UC1); // Stack for pool1 is full, memory is allocated with DefaultAllocator
/// ```
///
///
/// If a third stream is declared in the above example, allocating with #getBuffer
/// within that stream will also be carried out by the DefaultAllocator because we've run out of
/// stacks.
///
/// ```C++
/// Stream stream3; // Only 2 stacks were allocated, we've run out of stacks
/// BufferPool pool3(stream3);
/// GpuMat d_src3 = pool3.getBuffer(1024, 1024, CV_8UC1); // Memory is allocated with DefaultAllocator
/// ```
///
///
/// @warning When utilizing StackAllocator, deallocation order is important.
///
/// Just like a stack, deallocation must be done in LIFO order. Below is an example of
/// erroneous usage that violates LIFO rule. If OpenCV is compiled in Debug mode, this
/// sample code will emit CV_Assert error.
///
/// ```C++
/// int main()
/// {
/// setBufferPoolUsage(true); // Tell OpenCV that we are going to utilize BufferPool
/// Stream stream; // A default size (10 MB) stack is allocated to this stream
/// BufferPool pool(stream);
///
/// GpuMat mat1 = pool.getBuffer(1024, 1024, CV_8UC1); // Allocate mat1 (1MB)
/// GpuMat mat2 = pool.getBuffer(1024, 1024, CV_8UC1); // Allocate mat2 (1MB)
///
/// mat1.release(); // erroneous usage : mat2 must be deallocated before mat1
/// }
/// ```
///
///
/// Since C++ local variables are destroyed in the reverse order of construction,
/// the code sample below satisfies the LIFO rule. Local GpuMat's are deallocated
/// and the corresponding memory is automatically returned to the pool for later usage.
///
/// ```C++
/// int main()
/// {
/// setBufferPoolUsage(true); // Tell OpenCV that we are going to utilize BufferPool
/// setBufferPoolConfig(getDevice(), 1024 * 1024 * 64, 2); // Allocate 64 MB, 2 stacks (default is 10 MB, 5 stacks)
///
/// Stream stream1, stream2; // Each stream uses 1 stack
/// BufferPool pool1(stream1), pool2(stream2);
///
/// for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
/// {
/// GpuMat d_src1 = pool1.getBuffer(4096, 4096, CV_8UC1); // 16MB
/// GpuMat d_dst1 = pool1.getBuffer(4096, 4096, CV_8UC3); // 48MB, pool1 is now full
///
/// GpuMat d_src2 = pool2.getBuffer(1024, 1024, CV_8UC1); // 1MB
/// GpuMat d_dst2 = pool2.getBuffer(1024, 1024, CV_8UC3); // 3MB
///
/// d_src1.setTo(Scalar(i), stream1);
/// d_src2.setTo(Scalar(i), stream2);
///
/// cvtColor(d_src1, d_dst1, CV_GRAY2BGR, 0, stream1);
/// cvtColor(d_src2, d_dst2, CV_GRAY2BGR, 0, stream2);
/// // The order of destruction of the local variables is:
/// // d_dst2 => d_src2 => d_dst1 => d_src1
/// // LIFO rule is satisfied, this code runs without error
/// }
/// }
/// ```
///
pub struct BufferPool {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { BufferPool }
impl Drop for BufferPool {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_BufferPool_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_BufferPool_delete(self.as_raw_mut_BufferPool()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for BufferPool {}
impl core::BufferPoolTraitConst for BufferPool {
#[inline] fn as_raw_BufferPool(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::BufferPoolTrait for BufferPool {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_BufferPool(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl BufferPool {
/// Gets the BufferPool for the given stream.
#[inline]
pub fn new(stream: &mut core::Stream) -> Result<core::BufferPool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_BufferPool_BufferPool_StreamR(stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::BufferPool::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::DeviceInfo]
pub trait DeviceInfoTraitConst {
fn as_raw_DeviceInfo(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Returns system index of the CUDA device starting with 0.
#[inline]
fn device_id(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_deviceID_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ASCII string identifying device
#[inline]
fn name(&self) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_name_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// global memory available on device in bytes
#[inline]
fn total_global_mem(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_totalGlobalMem_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// shared memory available per block in bytes
#[inline]
fn shared_mem_per_block(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_sharedMemPerBlock_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// 32-bit registers available per block
#[inline]
fn regs_per_block(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_regsPerBlock_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// warp size in threads
#[inline]
fn warp_size(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_warpSize_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// maximum pitch in bytes allowed by memory copies
#[inline]
fn mem_pitch(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_memPitch_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// maximum number of threads per block
#[inline]
fn max_threads_per_block(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_maxThreadsPerBlock_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// maximum size of each dimension of a block
#[inline]
fn max_threads_dim(&self) -> Result<core::Vec3i> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_maxThreadsDim_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// maximum size of each dimension of a grid
#[inline]
fn max_grid_size(&self) -> Result<core::Vec3i> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_maxGridSize_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// clock frequency in kilohertz
#[inline]
fn clock_rate(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_clockRate_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// constant memory available on device in bytes
#[inline]
fn total_const_mem(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_totalConstMem_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// major compute capability
#[inline]
fn major_version(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_majorVersion_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// minor compute capability
#[inline]
fn minor_version(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_minorVersion_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// alignment requirement for textures
#[inline]
fn texture_alignment(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_textureAlignment_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// pitch alignment requirement for texture references bound to pitched memory
#[inline]
fn texture_pitch_alignment(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_texturePitchAlignment_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// number of multiprocessors on device
#[inline]
fn multi_processor_count(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_multiProcessorCount_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// specified whether there is a run time limit on kernels
#[inline]
fn kernel_exec_timeout_enabled(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_kernelExecTimeoutEnabled_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// device is integrated as opposed to discrete
#[inline]
fn integrated(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_integrated_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// device can map host memory with cudaHostAlloc/cudaHostGetDevicePointer
#[inline]
fn can_map_host_memory(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_canMapHostMemory_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// compute mode
#[inline]
fn compute_mode(&self) -> Result<core::DeviceInfo_ComputeMode> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_computeMode_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// maximum 1D texture size
#[inline]
fn max_texture1_d(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_maxTexture1D_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// maximum 1D mipmapped texture size
#[inline]
fn max_texture1_d_mipmap(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_maxTexture1DMipmap_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// maximum size for 1D textures bound to linear memory
#[inline]
fn max_texture1_d_linear(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_maxTexture1DLinear_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// maximum 2D texture dimensions
#[inline]
fn max_texture_2d(&self) -> Result<core::Vec2i> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_maxTexture2D_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// maximum 2D mipmapped texture dimensions
#[inline]
fn max_texture2_d_mipmap(&self) -> Result<core::Vec2i> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_maxTexture2DMipmap_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// maximum dimensions (width, height, pitch) for 2D textures bound to pitched memory
#[inline]
fn max_texture2_d_linear(&self) -> Result<core::Vec3i> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_maxTexture2DLinear_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// maximum 2D texture dimensions if texture gather operations have to be performed
#[inline]
fn max_texture2_d_gather(&self) -> Result<core::Vec2i> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_maxTexture2DGather_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// maximum 3D texture dimensions
#[inline]
fn max_texture_3d(&self) -> Result<core::Vec3i> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_maxTexture3D_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// maximum Cubemap texture dimensions
#[inline]
fn max_texture_cubemap(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_maxTextureCubemap_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// maximum 1D layered texture dimensions
#[inline]
fn max_texture1_d_layered(&self) -> Result<core::Vec2i> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_maxTexture1DLayered_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// maximum 2D layered texture dimensions
#[inline]
fn max_texture2_d_layered(&self) -> Result<core::Vec3i> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_maxTexture2DLayered_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// maximum Cubemap layered texture dimensions
#[inline]
fn max_texture_cubemap_layered(&self) -> Result<core::Vec2i> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_maxTextureCubemapLayered_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// maximum 1D surface size
#[inline]
fn max_surface1_d(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_maxSurface1D_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// maximum 2D surface dimensions
#[inline]
fn max_surface_2d(&self) -> Result<core::Vec2i> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_maxSurface2D_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// maximum 3D surface dimensions
#[inline]
fn max_surface_3d(&self) -> Result<core::Vec3i> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_maxSurface3D_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// maximum 1D layered surface dimensions
#[inline]
fn max_surface1_d_layered(&self) -> Result<core::Vec2i> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_maxSurface1DLayered_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// maximum 2D layered surface dimensions
#[inline]
fn max_surface2_d_layered(&self) -> Result<core::Vec3i> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_maxSurface2DLayered_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// maximum Cubemap surface dimensions
#[inline]
fn max_surface_cubemap(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_maxSurfaceCubemap_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// maximum Cubemap layered surface dimensions
#[inline]
fn max_surface_cubemap_layered(&self) -> Result<core::Vec2i> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_maxSurfaceCubemapLayered_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// alignment requirements for surfaces
#[inline]
fn surface_alignment(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_surfaceAlignment_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// device can possibly execute multiple kernels concurrently
#[inline]
fn concurrent_kernels(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_concurrentKernels_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// device has ECC support enabled
#[inline]
fn ecc_enabled(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_ECCEnabled_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// PCI bus ID of the device
#[inline]
fn pci_bus_id(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_pciBusID_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// PCI device ID of the device
#[inline]
fn pci_device_id(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_pciDeviceID_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// PCI domain ID of the device
#[inline]
fn pci_domain_id(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_pciDomainID_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// true if device is a Tesla device using TCC driver, false otherwise
#[inline]
fn tcc_driver(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_tccDriver_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// number of asynchronous engines
#[inline]
fn async_engine_count(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_asyncEngineCount_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// device shares a unified address space with the host
#[inline]
fn unified_addressing(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_unifiedAddressing_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// peak memory clock frequency in kilohertz
#[inline]
fn memory_clock_rate(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_memoryClockRate_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// global memory bus width in bits
#[inline]
fn memory_bus_width(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_memoryBusWidth_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// size of L2 cache in bytes
#[inline]
fn l2_cache_size(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_l2CacheSize_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// maximum resident threads per multiprocessor
#[inline]
fn max_threads_per_multi_processor(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_maxThreadsPerMultiProcessor_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// gets free and total device memory
#[inline]
fn query_memory(&self, total_memory: &mut size_t, free_memory: &mut size_t) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_queryMemory_const_size_tR_size_tR(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), total_memory, free_memory, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn free_memory(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_freeMemory_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn total_memory(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_totalMemory_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Provides information on CUDA feature support.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * feature_set: Features to be checked. See cuda::FeatureSet.
///
/// This function returns true if the device has the specified CUDA feature. Otherwise, it returns false
#[inline]
fn supports(&self, feature_set: core::FeatureSet) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_supports_const_FeatureSet(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), feature_set, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Checks the CUDA module and device compatibility.
///
/// This function returns true if the CUDA module can be run on the specified device. Otherwise, it
/// returns false .
#[inline]
fn is_compatible(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_isCompatible_const(self.as_raw_DeviceInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::DeviceInfo]
pub trait DeviceInfoTrait: core::DeviceInfoTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_DeviceInfo(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
/// Class providing functionality for querying the specified GPU properties.
pub struct DeviceInfo {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { DeviceInfo }
impl Drop for DeviceInfo {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_DeviceInfo_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_DeviceInfo_delete(self.as_raw_mut_DeviceInfo()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for DeviceInfo {}
impl core::DeviceInfoTraitConst for DeviceInfo {
#[inline] fn as_raw_DeviceInfo(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::DeviceInfoTrait for DeviceInfo {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_DeviceInfo(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl DeviceInfo {
/// creates DeviceInfo object for the current GPU
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::DeviceInfo> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_DeviceInfo(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::DeviceInfo::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// The constructors.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * device_id: System index of the CUDA device starting with 0.
///
/// Constructs the DeviceInfo object for the specified device. If device_id parameter is missed, it
/// constructs an object for the current device.
#[inline]
pub fn new(device_id: i32) -> Result<core::DeviceInfo> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_DeviceInfo_DeviceInfo_int(device_id, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::DeviceInfo::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Event]
pub trait EventTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Event(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// queries an event's status
#[inline]
fn query_if_complete(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_Event_queryIfComplete_const(self.as_raw_Event(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Event]
pub trait EventTrait: core::EventTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Event(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// records an event
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * stream: Stream::Null()
#[inline]
fn record(&mut self, stream: &mut core::Stream) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_Event_record_StreamR(self.as_raw_mut_Event(), stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// waits for an event to complete
#[inline]
fn wait_for_completion(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_Event_waitForCompletion(self.as_raw_mut_Event(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
pub struct Event {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Event }
impl Drop for Event {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Event_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Event_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Event()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Event {}
impl core::EventTraitConst for Event {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Event(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::EventTrait for Event {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Event(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Event {
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: Event::CreateFlags::DEFAULT
#[inline]
pub fn new(flags: core::Event_CreateFlags) -> Result<core::Event> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_Event_Event_const_CreateFlags(flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Event::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// computes the elapsed time between events
#[inline]
pub fn elapsed_time(start: &core::Event, end: &core::Event) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_Event_elapsedTime_const_EventR_const_EventR(start.as_raw_Event(), end.as_raw_Event(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::GpuData]
pub trait GpuDataTraitConst {
fn as_raw_GpuData(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn size(&self) -> size_t {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuData_getPropSize_const(self.as_raw_GpuData()) };
ret
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::GpuData]
pub trait GpuDataTrait: core::GpuDataTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_GpuData(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn data(&mut self) -> *mut u8 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuData_getPropData(self.as_raw_mut_GpuData()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
unsafe fn set_data(&mut self, val: *mut u8) {
let ret = { sys::cv_cuda_GpuData_setPropData_unsigned_charX(self.as_raw_mut_GpuData(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_size(&mut self, val: size_t) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuData_setPropSize_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_GpuData(), val) };
ret
}
}
pub struct GpuData {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { GpuData }
impl Drop for GpuData {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_GpuData_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_GpuData_delete(self.as_raw_mut_GpuData()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for GpuData {}
impl core::GpuDataTraitConst for GpuData {
#[inline] fn as_raw_GpuData(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::GpuDataTrait for GpuData {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_GpuData(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl GpuData {
#[inline]
pub fn new(_size: size_t) -> Result<core::GpuData> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuData_GpuData_size_t(_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuData::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::GpuMat]
pub trait GpuMatTraitConst {
fn as_raw_GpuMat(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// ! includes several bit-fields:
/// - the magic signature
/// - continuity flag
/// - depth
/// - number of channels
#[inline]
fn flags(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_getPropFlags_const(self.as_raw_GpuMat()) };
ret
}
/// the number of rows and columns
#[inline]
fn rows(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_getPropRows_const(self.as_raw_GpuMat()) };
ret
}
/// the number of rows and columns
#[inline]
fn cols(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_getPropCols_const(self.as_raw_GpuMat()) };
ret
}
/// a distance between successive rows in bytes; includes the gap if any
#[inline]
fn step(&self) -> size_t {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_getPropStep_const(self.as_raw_GpuMat()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn dataend(&self) -> *const u8 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_getPropDataend_const(self.as_raw_GpuMat()) };
ret
}
/// Performs data download from GpuMat (Blocking call)
///
/// This function copies data from device memory to host memory. As being a blocking call, it is
/// guaranteed that the copy operation is finished when this function returns.
#[inline]
fn download(&self, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_download_const_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Performs data download from GpuMat (Non-Blocking call)
///
/// This function copies data from device memory to host memory. As being a non-blocking call, this
/// function may return even if the copy operation is not finished.
///
/// The copy operation may be overlapped with operations in other non-default streams if \p stream is
/// not the default stream and \p dst is HostMem allocated with HostMem::PAGE_LOCKED option.
#[inline]
fn download_async(&self, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, stream: &mut core::Stream) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_download_const_const__OutputArrayR_StreamR(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns deep copy of the GpuMat, i.e. the data is copied
#[inline]
fn try_clone(&self) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_clone_const(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// copies the GpuMat content to device memory (Blocking call)
#[inline]
fn copy_to(&self, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_copyTo_const_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// copies the GpuMat content to device memory (Non-Blocking call)
#[inline]
fn copy_to_1(&self, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, stream: &mut core::Stream) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_copyTo_const_const__OutputArrayR_StreamR(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// copies those GpuMat elements to "m" that are marked with non-zero mask elements (Blocking call)
#[inline]
fn copy_to_2(&self, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(dst);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_copyTo_const_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// copies those GpuMat elements to "m" that are marked with non-zero mask elements (Non-Blocking call)
#[inline]
fn copy_to_3(&self, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray, stream: &mut core::Stream) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(dst);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_copyTo_const_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_StreamR(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// converts GpuMat to another datatype (Blocking call)
#[inline]
fn convert_to(&self, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, rtype: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_convertTo_const_const__OutputArrayR_int(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), rtype, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// converts GpuMat to another datatype (Non-Blocking call)
#[inline]
fn convert_to_1(&self, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, rtype: i32, stream: &mut core::Stream) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_convertTo_const_const__OutputArrayR_int_StreamR(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), rtype, stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// converts GpuMat to another datatype with scaling (Blocking call)
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * beta: 0.0
#[inline]
fn convert_to_2(&self, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, rtype: i32, alpha: f64, beta: f64) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_convertTo_const_const__OutputArrayR_int_double_double(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), rtype, alpha, beta, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// converts GpuMat to another datatype with scaling (Non-Blocking call)
#[inline]
fn convert_to_3(&self, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, rtype: i32, alpha: f64, stream: &mut core::Stream) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_convertTo_const_const__OutputArrayR_int_double_StreamR(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), rtype, alpha, stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// converts GpuMat to another datatype with scaling (Non-Blocking call)
#[inline]
fn convert_to_4(&self, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, rtype: i32, alpha: f64, beta: f64, stream: &mut core::Stream) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_convertTo_const_const__OutputArrayR_int_double_double_StreamR(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), rtype, alpha, beta, stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * typ: -1
#[inline]
fn assign_to(&self, m: &mut core::GpuMat, typ: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_assignTo_const_GpuMatR_int(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), m.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * y: 0
#[inline]
fn ptr(&self, y: i32) -> Result<*const u8> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_ptr_const_int(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), y, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns a new GpuMat header for the specified row
#[inline]
fn row(&self, y: i32) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_row_const_int(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), y, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns a new GpuMat header for the specified column
#[inline]
fn col(&self, x: i32) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_col_const_int(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), x, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ... for the specified row span
#[inline]
fn row_range(&self, startrow: i32, endrow: i32) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_rowRange_const_int_int(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), startrow, endrow, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn row_range_1(&self, mut r: core::Range) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_rowRange_const_Range(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), r.as_raw_mut_Range(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ... for the specified column span
#[inline]
fn col_range(&self, startcol: i32, endcol: i32) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_colRange_const_int_int(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), startcol, endcol, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn col_range_1(&self, mut r: core::Range) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_colRange_const_Range(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), r.as_raw_mut_Range(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// extracts a rectangular sub-GpuMat (this is a generalized form of row, rowRange etc.)
#[inline]
fn apply(&self, mut row_range: core::Range, mut col_range: core::Range) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_operator___const_Range_Range(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), row_range.as_raw_mut_Range(), col_range.as_raw_mut_Range(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn apply_1(&self, roi: core::Rect) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_operator___const_Rect(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), roi.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// creates alternative GpuMat header for the same data, with different
/// number of channels and/or different number of rows
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * rows: 0
#[inline]
fn reshape(&self, cn: i32, rows: i32) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_reshape_const_int_int(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), cn, rows, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// locates GpuMat header within a parent GpuMat
#[inline]
fn locate_roi(&self, whole_size: &mut core::Size, ofs: &mut core::Point) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_locateROI_const_SizeR_PointR(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), whole_size, ofs, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns true iff the GpuMat data is continuous
/// (i.e. when there are no gaps between successive rows)
#[inline]
fn is_continuous(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_isContinuous_const(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns element size in bytes
#[inline]
fn elem_size(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_elemSize_const(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns the size of element channel in bytes
#[inline]
fn elem_size1(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_elemSize1_const(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns element type
#[inline]
fn typ(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_type_const(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns element type
#[inline]
fn depth(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_depth_const(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns number of channels
#[inline]
fn channels(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_channels_const(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns step/elemSize1()
#[inline]
fn step1(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_step1_const(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns GpuMat size : width == number of columns, height == number of rows
#[inline]
fn size(&self) -> Result<core::Size> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_size_const(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns true if GpuMat data is NULL
#[inline]
fn empty(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_empty_const(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn cuda_ptr(&self) -> Result<*mut c_void> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_cudaPtr_const(self.as_raw_GpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::GpuMat]
pub trait GpuMatTrait: core::GpuMatTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_GpuMat(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// ! includes several bit-fields:
/// - the magic signature
/// - continuity flag
/// - depth
/// - number of channels
#[inline]
fn set_flags(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_setPropFlags_int(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), val) };
ret
}
/// the number of rows and columns
#[inline]
fn set_rows(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_setPropRows_int(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), val) };
ret
}
/// the number of rows and columns
#[inline]
fn set_cols(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_setPropCols_int(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), val) };
ret
}
/// a distance between successive rows in bytes; includes the gap if any
#[inline]
fn set_step(&mut self, val: size_t) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_setPropStep_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), val) };
ret
}
/// pointer to the data
#[inline]
fn data(&mut self) -> *mut u8 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_getPropData(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat()) };
ret
}
/// pointer to the data
#[inline]
unsafe fn set_data(&mut self, val: *mut u8) {
let ret = { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_setPropData_unsigned_charX(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), val) };
ret
}
/// pointer to the reference counter;
/// when GpuMat points to user-allocated data, the pointer is NULL
#[inline]
fn refcount(&mut self) -> *mut i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_getPropRefcount(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat()) };
ret
}
/// pointer to the reference counter;
/// when GpuMat points to user-allocated data, the pointer is NULL
#[inline]
unsafe fn set_refcount(&mut self, val: *mut i32) {
let ret = { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_setPropRefcount_intX(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), val) };
ret
}
/// helper fields used in locateROI and adjustROI
#[inline]
fn datastart(&mut self) -> *mut u8 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_getPropDatastart(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat()) };
ret
}
/// helper fields used in locateROI and adjustROI
#[inline]
unsafe fn set_datastart(&mut self, val: *mut u8) {
let ret = { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_setPropDatastart_unsigned_charX(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), val) };
ret
}
/// allocator
#[inline]
fn allocator(&mut self) -> types::AbstractRefMut<dyn core::GpuMat_Allocator> {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_getPropAllocator(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat()) };
let ret = unsafe { types::AbstractRefMut::<dyn core::GpuMat_Allocator>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// allocator
#[inline]
unsafe fn set_allocator(&mut self, val: &mut dyn core::GpuMat_Allocator) {
let ret = { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_setPropAllocator_AllocatorX(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), val.as_raw_mut_GpuMat_Allocator()) };
ret
}
/// allocates new GpuMat data unless the GpuMat already has specified size and type
#[inline]
fn create(&mut self, rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_create_int_int_int(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), rows, cols, typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn create_1(&mut self, size: core::Size, typ: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_create_Size_int(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), size.opencv_as_extern(), typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// decreases reference counter, deallocate the data when reference counter reaches 0
#[inline]
fn release(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_release(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// swaps with other smart pointer
#[inline]
fn swap(&mut self, mat: &mut core::GpuMat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_swap_GpuMatR(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), mat.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Performs data upload to GpuMat (Blocking call)
///
/// This function copies data from host memory to device memory. As being a blocking call, it is
/// guaranteed that the copy operation is finished when this function returns.
#[inline]
fn upload(&mut self, arr: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(arr);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_upload_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), arr.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Performs data upload to GpuMat (Non-Blocking call)
///
/// This function copies data from host memory to device memory. As being a non-blocking call, this
/// function may return even if the copy operation is not finished.
///
/// The copy operation may be overlapped with operations in other non-default streams if \p stream is
/// not the default stream and \p dst is HostMem allocated with HostMem::PAGE_LOCKED option.
#[inline]
fn upload_async(&mut self, arr: &dyn core::ToInputArray, stream: &mut core::Stream) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(arr);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_upload_const__InputArrayR_StreamR(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), arr.as_raw__InputArray(), stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// sets some of the GpuMat elements to s (Blocking call)
#[inline]
fn set_to(&mut self, s: core::Scalar) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_setTo_Scalar(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), s.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// sets some of the GpuMat elements to s (Non-Blocking call)
#[inline]
fn set_to_1(&mut self, s: core::Scalar, stream: &mut core::Stream) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_setTo_Scalar_StreamR(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), s.opencv_as_extern(), stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// sets some of the GpuMat elements to s, according to the mask (Blocking call)
#[inline]
fn set_to_2(&mut self, s: core::Scalar, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
extern_container_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_setTo_Scalar_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), s.opencv_as_extern(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// sets some of the GpuMat elements to s, according to the mask (Non-Blocking call)
#[inline]
fn set_to_3(&mut self, s: core::Scalar, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray, stream: &mut core::Stream) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
extern_container_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_setTo_Scalar_const__InputArrayR_StreamR(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), s.opencv_as_extern(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns pointer to y-th row
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * y: 0
#[inline]
fn ptr_1(&mut self, y: i32) -> Result<*mut u8> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_ptr_int(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), y, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// moves/resizes the current GpuMat ROI inside the parent GpuMat
#[inline]
fn adjust_roi(&mut self, dtop: i32, dbottom: i32, dleft: i32, dright: i32) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_adjustROI_int_int_int_int(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), dtop, dbottom, dleft, dright, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// internal use method: updates the continuity flag
#[inline]
fn update_continuity_flag(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_updateContinuityFlag(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Base storage class for GPU memory with reference counting.
///
/// Its interface matches the Mat interface with the following limitations:
///
/// * no arbitrary dimensions support (only 2D)
/// * no functions that return references to their data (because references on GPU are not valid for
/// CPU)
/// * no expression templates technique support
///
/// Beware that the latter limitation may lead to overloaded matrix operators that cause memory
/// allocations. The GpuMat class is convertible to cuda::PtrStepSz and cuda::PtrStep so it can be
/// passed directly to the kernel.
///
///
/// Note: In contrast with Mat, in most cases GpuMat::isContinuous() == false . This means that rows are
/// aligned to a size depending on the hardware. Single-row GpuMat is always a continuous matrix.
///
///
/// Note: You are not recommended to leave static or global GpuMat variables allocated, that is, to rely
/// on its destructor. The destruction order of such variables and CUDA context is undefined. GPU memory
/// release function returns error if the CUDA context has been destroyed before.
///
/// Some member functions are described as a "Blocking Call" while some are described as a
/// "Non-Blocking Call". Blocking functions are synchronous to host. It is guaranteed that the GPU
/// operation is finished when the function returns. However, non-blocking functions are asynchronous to
/// host. Those functions may return even if the GPU operation is not finished.
///
/// Compared to their blocking counterpart, non-blocking functions accept Stream as an additional
/// argument. If a non-default stream is passed, the GPU operation may overlap with operations in other
/// streams.
/// ## See also
/// Mat
pub struct GpuMat {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { GpuMat }
impl Drop for GpuMat {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_GpuMat_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_GpuMat_delete(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for GpuMat {}
impl core::GpuMatTraitConst for GpuMat {
#[inline] fn as_raw_GpuMat(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::GpuMatTrait for GpuMat {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_GpuMat(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl GpuMat {
/// default allocator
#[inline]
pub fn default_allocator() -> Result<types::AbstractRefMut<'static, dyn core::GpuMat_Allocator>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_defaultAllocator(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { types::AbstractRefMut::<'static, dyn core::GpuMat_Allocator>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn set_default_allocator(allocator: &mut dyn core::GpuMat_Allocator) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_setDefaultAllocator_AllocatorX(allocator.as_raw_mut_GpuMat_Allocator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// default constructor
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * allocator: GpuMat::defaultAllocator()
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn new(allocator: &mut dyn core::GpuMat_Allocator) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_GpuMat_AllocatorX(allocator.as_raw_mut_GpuMat_Allocator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// constructs GpuMat of the specified size and type
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * allocator: GpuMat::defaultAllocator()
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn new_rows_cols(rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32, allocator: &mut dyn core::GpuMat_Allocator) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_GpuMat_int_int_int_AllocatorX(rows, cols, typ, allocator.as_raw_mut_GpuMat_Allocator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * allocator: GpuMat::defaultAllocator()
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn new_size(size: core::Size, typ: i32, allocator: &mut dyn core::GpuMat_Allocator) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_GpuMat_Size_int_AllocatorX(size.opencv_as_extern(), typ, allocator.as_raw_mut_GpuMat_Allocator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// constructs GpuMat and fills it with the specified value _s
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * allocator: GpuMat::defaultAllocator()
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn new_rows_cols_with_default(rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32, s: core::Scalar, allocator: &mut dyn core::GpuMat_Allocator) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_GpuMat_int_int_int_Scalar_AllocatorX(rows, cols, typ, s.opencv_as_extern(), allocator.as_raw_mut_GpuMat_Allocator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * allocator: GpuMat::defaultAllocator()
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn new_size_with_default(size: core::Size, typ: i32, s: core::Scalar, allocator: &mut dyn core::GpuMat_Allocator) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_GpuMat_Size_int_Scalar_AllocatorX(size.opencv_as_extern(), typ, s.opencv_as_extern(), allocator.as_raw_mut_GpuMat_Allocator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// copy constructor
#[inline]
pub fn copy(m: &core::GpuMat) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_GpuMat_const_GpuMatR(m.as_raw_GpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// constructor for GpuMat headers pointing to user-allocated data
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * step: Mat::AUTO_STEP
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn new_rows_cols_with_data(rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32, data: *mut c_void, step: size_t) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_GpuMat_int_int_int_voidX_size_t(rows, cols, typ, data, step, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * step: Mat::AUTO_STEP
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn new_size_with_data(size: core::Size, typ: i32, data: *mut c_void, step: size_t) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_GpuMat_Size_int_voidX_size_t(size.opencv_as_extern(), typ, data, step, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// creates a GpuMat header for a part of the bigger matrix
#[inline]
pub fn rowscols(m: &core::GpuMat, mut row_range: core::Range, mut col_range: core::Range) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_GpuMat_const_GpuMatR_Range_Range(m.as_raw_GpuMat(), row_range.as_raw_mut_Range(), col_range.as_raw_mut_Range(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn roi(m: &core::GpuMat, roi: core::Rect) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_GpuMat_const_GpuMatR_Rect(m.as_raw_GpuMat(), roi.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// builds GpuMat from host memory (Blocking call)
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * allocator: GpuMat::defaultAllocator()
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn from_hostmem(arr: &dyn core::ToInputArray, allocator: &mut dyn core::GpuMat_Allocator) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
extern_container_arg!(arr);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_GpuMat_const__InputArrayR_AllocatorX(arr.as_raw__InputArray(), allocator.as_raw_mut_GpuMat_Allocator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl Clone for GpuMat {
#[inline]
/// Calls try_clone() and panics if that fails
fn clone(&self) -> Self {
self.try_clone().expect("Cannot clone GpuMat")
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::GpuMat_Allocator]
pub trait GpuMat_AllocatorConst {
fn as_raw_GpuMat_Allocator(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
pub trait GpuMat_Allocator: core::GpuMat_AllocatorConst {
fn as_raw_mut_GpuMat_Allocator(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn allocate(&mut self, mat: &mut core::GpuMat, rows: i32, cols: i32, elem_size: size_t) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_Allocator_allocate_GpuMatX_int_int_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat_Allocator(), mat.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), rows, cols, elem_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn free(&mut self, mat: &mut core::GpuMat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMat_Allocator_free_GpuMatX(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMat_Allocator(), mat.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::GpuMatND]
pub trait GpuMatNDTraitConst {
fn as_raw_GpuMatND(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// ! includes several bit-fields:
/// - the magic signature
/// - continuity flag
/// - depth
/// - number of channels
#[inline]
fn flags(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_getPropFlags_const(self.as_raw_GpuMatND()) };
ret
}
/// matrix dimensionality
#[inline]
fn dims(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_getPropDims_const(self.as_raw_GpuMatND()) };
ret
}
/// shape of this array
#[inline]
fn size(&self) -> core::Vector<i32> {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_getPropSize_const(self.as_raw_GpuMatND()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Vector::<i32>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// ! step values
/// Their semantics is identical to the semantics of step for Mat.
#[inline]
fn step(&self) -> core::Vector<size_t> {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_getPropStep_const(self.as_raw_GpuMatND()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Vector::<size_t>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// Creates a full copy of the array and the underlying data.
/// The method creates a full copy of the array. It mimics the behavior of Mat::clone(), i.e.
/// the original step is not taken into account. So, the array copy is a continuous array
/// occupying total()\*elemSize() bytes.
#[inline]
fn try_clone(&self) -> Result<core::GpuMatND> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_clone_const(self.as_raw_GpuMatND(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMatND::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates a full copy of the array and the underlying data.
/// The method creates a full copy of the array. It mimics the behavior of Mat::clone(), i.e.
/// the original step is not taken into account. So, the array copy is a continuous array
/// occupying total()\*elemSize() bytes.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// This overload is non-blocking, so it may return even if the copy operation is not finished.
#[inline]
fn clone_1(&self, stream: &mut core::Stream) -> Result<core::GpuMatND> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_clone_const_StreamR(self.as_raw_GpuMatND(), stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMatND::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Extracts a sub-matrix.
/// The operator makes a new header for the specified sub-array of \*this.
/// The operator is an O(1) operation, that is, no matrix data is copied.
/// ## Parameters
/// * ranges: Array of selected ranges along each dimension.
#[inline]
fn apply(&self, ranges: &core::Vector<core::Range>) -> Result<core::GpuMatND> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_operator___const_const_vectorLRangeGR(self.as_raw_GpuMatND(), ranges.as_raw_VectorOfRange(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMatND::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates a GpuMat header for a 2D plane part of an n-dim matrix.
///
/// Note: The returned GpuMat is constructed with the constructor for user-allocated data.
/// That is, It does not perform reference counting.
///
/// Note: This function does not increment this GpuMatND's reference counter.
#[inline]
fn create_gpu_mat_header(&self, mut idx: core::GpuMatND_IndexArray, mut row_range: core::Range, mut col_range: core::Range) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_createGpuMatHeader_const_IndexArray_Range_Range(self.as_raw_GpuMatND(), idx.as_raw_mut_VectorOfi32(), row_range.as_raw_mut_Range(), col_range.as_raw_mut_Range(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates a GpuMat header for a 2D plane part of an n-dim matrix.
///
/// Note: The returned GpuMat is constructed with the constructor for user-allocated data.
/// That is, It does not perform reference counting.
///
/// Note: This function does not increment this GpuMatND's reference counter.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// Creates a GpuMat header if this GpuMatND is effectively 2D.
///
/// Note: The returned GpuMat is constructed with the constructor for user-allocated data.
/// That is, It does not perform reference counting.
///
/// Note: This function does not increment this GpuMatND's reference counter.
#[inline]
fn create_gpu_mat_header_1(&self) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_createGpuMatHeader_const(self.as_raw_GpuMatND(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Extracts a 2D plane part of an n-dim matrix.
/// It differs from createGpuMatHeader(IndexArray, Range, Range) in that it clones a part of this
/// GpuMatND to the returned GpuMat.
///
/// Note: This operator does not increment this GpuMatND's reference counter;
#[inline]
fn apply_1(&self, mut idx: core::GpuMatND_IndexArray, mut row_range: core::Range, mut col_range: core::Range) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_operator___const_IndexArray_Range_Range(self.as_raw_GpuMatND(), idx.as_raw_mut_VectorOfi32(), row_range.as_raw_mut_Range(), col_range.as_raw_mut_Range(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Extracts a 2D plane part of an n-dim matrix if this GpuMatND is effectively 2D.
/// It differs from createGpuMatHeader() in that it clones a part of this GpuMatND.
///
/// Note: This operator does not increment this GpuMatND's reference counter;
#[inline]
fn to_gpu_mat(&self) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_operator_cv_cuda_GpuMat_const(self.as_raw_GpuMatND(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn download(&self, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_download_const_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_GpuMatND(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn download_1(&self, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, stream: &mut core::Stream) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_download_const_const__OutputArrayR_StreamR(self.as_raw_GpuMatND(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns true iff the GpuMatND data is continuous
/// (i.e. when there are no gaps between successive rows)
#[inline]
fn is_continuous(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_isContinuous_const(self.as_raw_GpuMatND(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns true if the matrix is a sub-matrix of another matrix
#[inline]
fn is_submatrix(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_isSubmatrix_const(self.as_raw_GpuMatND(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns element size in bytes
#[inline]
fn elem_size(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_elemSize_const(self.as_raw_GpuMatND(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns the size of element channel in bytes
#[inline]
fn elem_size1(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_elemSize1_const(self.as_raw_GpuMatND(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns true if data is null
#[inline]
fn empty(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_empty_const(self.as_raw_GpuMatND(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns true if not empty and points to external(user-allocated) gpu memory
#[inline]
fn external(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_external_const(self.as_raw_GpuMatND(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns pointer to the first byte of the GPU memory
#[inline]
fn get_device_ptr(&self) -> Result<*mut u8> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_getDevicePtr_const(self.as_raw_GpuMatND(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns the total number of array elements
#[inline]
fn total(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_total_const(self.as_raw_GpuMatND(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns the size of underlying memory in bytes
#[inline]
fn total_mem_size(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_totalMemSize_const(self.as_raw_GpuMatND(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns element type
#[inline]
fn typ(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_type_const(self.as_raw_GpuMatND(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::GpuMatND]
pub trait GpuMatNDTrait: core::GpuMatNDTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_GpuMatND(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// ! includes several bit-fields:
/// - the magic signature
/// - continuity flag
/// - depth
/// - number of channels
#[inline]
fn set_flags(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_setPropFlags_int(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMatND(), val) };
ret
}
/// matrix dimensionality
#[inline]
fn set_dims(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_setPropDims_int(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMatND(), val) };
ret
}
/// shape of this array
#[inline]
fn set_size(&mut self, mut val: core::GpuMatND_SizeArray) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_setPropSize_SizeArray(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMatND(), val.as_raw_mut_VectorOfi32()) };
ret
}
/// ! step values
/// Their semantics is identical to the semantics of step for Mat.
#[inline]
fn set_step(&mut self, mut val: core::GpuMatND_StepArray) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_setPropStep_StepArray(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMatND(), val.as_raw_mut_VectorOfsize_t()) };
ret
}
/// Allocates GPU memory.
/// Suppose there is some GPU memory already allocated. In that case, this method may choose to reuse that
/// GPU memory under the specific condition: it must be of the same size and type, not externally allocated,
/// the GPU memory is continuous(i.e., isContinuous() is true), and is not a sub-matrix of another GpuMatND
/// (i.e., isSubmatrix() is false). In other words, this method guarantees that the GPU memory allocated by
/// this method is always continuous and is not a sub-region of another GpuMatND.
#[inline]
fn create(&mut self, mut size: core::GpuMatND_SizeArray, typ: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_create_SizeArray_int(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMatND(), size.as_raw_mut_VectorOfi32(), typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn release(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_release(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMatND(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn swap(&mut self, m: &mut core::GpuMatND) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_swap_GpuMatNDR(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMatND(), m.as_raw_mut_GpuMatND()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn upload(&mut self, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_upload_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMatND(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn upload_1(&mut self, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, stream: &mut core::Stream) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_upload_const__InputArrayR_StreamR(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMatND(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
pub struct GpuMatND {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { GpuMatND }
impl Drop for GpuMatND {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_GpuMatND_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_GpuMatND_delete(self.as_raw_mut_GpuMatND()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for GpuMatND {}
impl core::GpuMatNDTraitConst for GpuMatND {
#[inline] fn as_raw_GpuMatND(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::GpuMatNDTrait for GpuMatND {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_GpuMatND(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl GpuMatND {
/// default constructor
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::GpuMatND> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_GpuMatND(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMatND::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// default constructor
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * size: Array of integers specifying an n-dimensional array shape.
/// * type: Array type. Use CV_8UC1, ..., CV_16FC4 to create 1-4 channel matrices, or
/// CV_8UC(n), ..., CV_64FC(n) to create multi-channel (up to CV_CN_MAX channels) matrices.
#[inline]
pub fn new(mut size: core::GpuMatND_SizeArray, typ: i32) -> Result<core::GpuMatND> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_GpuMatND_SizeArray_int(size.as_raw_mut_VectorOfi32(), typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMatND::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// default constructor
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * size: Array of integers specifying an n-dimensional array shape.
/// * type: Array type. Use CV_8UC1, ..., CV_16FC4 to create 1-4 channel matrices, or
/// CV_8UC(n), ..., CV_64FC(n) to create multi-channel (up to CV_CN_MAX channels) matrices.
/// * data: Pointer to the user data. Matrix constructors that take data and step parameters do not
/// allocate matrix data. Instead, they just initialize the matrix header that points to the specified
/// data, which means that no data is copied. This operation is very efficient and can be used to
/// process external data using OpenCV functions. The external data is not automatically deallocated, so
/// you should take care of it.
/// * step: Array of _size.size()-1 steps in case of a multi-dimensional array (the last step is always
/// set to the element size). If not specified, the matrix is assumed to be continuous.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * step: StepArray()
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn new_1(mut size: core::GpuMatND_SizeArray, typ: i32, data: *mut c_void, mut step: core::GpuMatND_StepArray) -> Result<core::GpuMatND> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_GpuMatND_SizeArray_int_voidX_StepArray(size.as_raw_mut_VectorOfi32(), typ, data, step.as_raw_mut_VectorOfsize_t(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::GpuMatND::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy(unnamed: &core::GpuMatND) -> core::GpuMatND {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_GpuMatND_const_GpuMatNDR(unnamed.as_raw_GpuMatND()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMatND::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy_mut(mut unnamed: core::GpuMatND) -> core::GpuMatND {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_GpuMatND_GpuMatND_GpuMatNDRR(unnamed.as_raw_mut_GpuMatND()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMatND::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
}
impl Clone for GpuMatND {
#[inline]
/// Calls try_clone() and panics if that fails
fn clone(&self) -> Self {
self.try_clone().expect("Cannot clone GpuMatND")
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::HostMem]
pub trait HostMemTraitConst {
fn as_raw_HostMem(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn flags(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_getPropFlags_const(self.as_raw_HostMem()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn rows(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_getPropRows_const(self.as_raw_HostMem()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn cols(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_getPropCols_const(self.as_raw_HostMem()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn step(&self) -> size_t {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_getPropStep_const(self.as_raw_HostMem()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn dataend(&self) -> *const u8 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_getPropDataend_const(self.as_raw_HostMem()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn alloc_type(&self) -> core::HostMem_AllocType {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_getPropAlloc_type_const(self.as_raw_HostMem(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
ret
}
/// returns deep copy of the matrix, i.e. the data is copied
#[inline]
fn try_clone(&self) -> Result<core::HostMem> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_clone_const(self.as_raw_HostMem(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::HostMem::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// creates alternative HostMem header for the same data, with different
/// number of channels and/or different number of rows
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * rows: 0
#[inline]
fn reshape(&self, cn: i32, rows: i32) -> Result<core::HostMem> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_reshape_const_int_int(self.as_raw_HostMem(), cn, rows, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::HostMem::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns matrix header with disabled reference counting for HostMem data.
#[inline]
fn create_mat_header(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_createMatHeader_const(self.as_raw_HostMem(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Maps CPU memory to GPU address space and creates the cuda::GpuMat header without reference counting
/// for it.
///
/// This can be done only if memory was allocated with the SHARED flag and if it is supported by the
/// hardware. Laptops often share video and CPU memory, so address spaces can be mapped, which
/// eliminates an extra copy.
#[inline]
fn create_gpu_mat_header(&self) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_createGpuMatHeader_const(self.as_raw_HostMem(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn is_continuous(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_isContinuous_const(self.as_raw_HostMem(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn elem_size(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_elemSize_const(self.as_raw_HostMem(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn elem_size1(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_elemSize1_const(self.as_raw_HostMem(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn typ(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_type_const(self.as_raw_HostMem(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn depth(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_depth_const(self.as_raw_HostMem(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn channels(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_channels_const(self.as_raw_HostMem(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn step1(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_step1_const(self.as_raw_HostMem(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn size(&self) -> Result<core::Size> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_size_const(self.as_raw_HostMem(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn empty(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_empty_const(self.as_raw_HostMem(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::HostMem]
pub trait HostMemTrait: core::HostMemTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_HostMem(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_flags(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_setPropFlags_int(self.as_raw_mut_HostMem(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_rows(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_setPropRows_int(self.as_raw_mut_HostMem(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_cols(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_setPropCols_int(self.as_raw_mut_HostMem(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_step(&mut self, val: size_t) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_setPropStep_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_HostMem(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn data(&mut self) -> *mut u8 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_getPropData(self.as_raw_mut_HostMem()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
unsafe fn set_data(&mut self, val: *mut u8) {
let ret = { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_setPropData_unsigned_charX(self.as_raw_mut_HostMem(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn refcount(&mut self) -> *mut i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_getPropRefcount(self.as_raw_mut_HostMem()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
unsafe fn set_refcount(&mut self, val: *mut i32) {
let ret = { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_setPropRefcount_intX(self.as_raw_mut_HostMem(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn datastart(&mut self) -> *mut u8 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_getPropDatastart(self.as_raw_mut_HostMem()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
unsafe fn set_datastart(&mut self, val: *mut u8) {
let ret = { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_setPropDatastart_unsigned_charX(self.as_raw_mut_HostMem(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_alloc_type(&mut self, val: core::HostMem_AllocType) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_setPropAlloc_type_AllocType(self.as_raw_mut_HostMem(), val) };
ret
}
/// swaps with other smart pointer
#[inline]
fn swap(&mut self, b: &mut core::HostMem) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_swap_HostMemR(self.as_raw_mut_HostMem(), b.as_raw_mut_HostMem(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// allocates new matrix data unless the matrix already has specified size and type.
#[inline]
fn create(&mut self, rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_create_int_int_int(self.as_raw_mut_HostMem(), rows, cols, typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn create_1(&mut self, size: core::Size, typ: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_create_Size_int(self.as_raw_mut_HostMem(), size.opencv_as_extern(), typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// decrements reference counter and released memory if needed.
#[inline]
fn release(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_release(self.as_raw_mut_HostMem(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Class with reference counting wrapping special memory type allocation functions from CUDA.
///
/// Its interface is also Mat-like but with additional memory type parameters.
///
/// * **PAGE_LOCKED** sets a page locked memory type used commonly for fast and asynchronous
/// uploading/downloading data from/to GPU.
/// * **SHARED** specifies a zero copy memory allocation that enables mapping the host memory to GPU
/// address space, if supported.
/// * **WRITE_COMBINED** sets the write combined buffer that is not cached by CPU. Such buffers are
/// used to supply GPU with data when GPU only reads it. The advantage is a better CPU cache
/// utilization.
///
///
/// Note: Allocation size of such memory types is usually limited. For more details, see *CUDA 2.2
/// Pinned Memory APIs* document or *CUDA C Programming Guide*.
pub struct HostMem {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { HostMem }
impl Drop for HostMem {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_HostMem_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_HostMem_delete(self.as_raw_mut_HostMem()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for HostMem {}
impl core::HostMemTraitConst for HostMem {
#[inline] fn as_raw_HostMem(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::HostMemTrait for HostMem {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_HostMem(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl HostMem {
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * alloc_type: HostMem::AllocType::PAGE_LOCKED
#[inline]
pub fn new(alloc_type: core::HostMem_AllocType) -> Result<core::HostMem> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_HostMem_AllocType(alloc_type, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::HostMem::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy(m: &core::HostMem) -> Result<core::HostMem> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_HostMem_const_HostMemR(m.as_raw_HostMem(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::HostMem::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * alloc_type: HostMem::AllocType::PAGE_LOCKED
#[inline]
pub fn new_1(rows: i32, cols: i32, typ: i32, alloc_type: core::HostMem_AllocType) -> Result<core::HostMem> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_HostMem_int_int_int_AllocType(rows, cols, typ, alloc_type, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::HostMem::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * alloc_type: HostMem::AllocType::PAGE_LOCKED
#[inline]
pub fn new_2(size: core::Size, typ: i32, alloc_type: core::HostMem_AllocType) -> Result<core::HostMem> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_HostMem_Size_int_AllocType(size.opencv_as_extern(), typ, alloc_type, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::HostMem::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// creates from host memory with coping data
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * alloc_type: HostMem::AllocType::PAGE_LOCKED
#[inline]
pub fn new_3(arr: &dyn core::ToInputArray, alloc_type: core::HostMem_AllocType) -> Result<core::HostMem> {
extern_container_arg!(arr);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_HostMem_HostMem_const__InputArrayR_AllocType(arr.as_raw__InputArray(), alloc_type, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::HostMem::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl Clone for HostMem {
#[inline]
/// Calls try_clone() and panics if that fails
fn clone(&self) -> Self {
self.try_clone().expect("Cannot clone HostMem")
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Stream]
pub trait StreamTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Stream(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Returns true if the current stream queue is finished. Otherwise, it returns false.
#[inline]
fn query_if_complete(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_Stream_queryIfComplete_const(self.as_raw_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// return Pointer to CUDA stream
#[inline]
fn cuda_ptr(&self) -> Result<*mut c_void> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_Stream_cudaPtr_const(self.as_raw_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Stream]
pub trait StreamTrait: core::StreamTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Stream(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Blocks the current CPU thread until all operations in the stream are complete.
#[inline]
fn wait_for_completion(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_Stream_waitForCompletion(self.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Makes a compute stream wait on an event.
#[inline]
fn wait_event(&mut self, event: &core::Event) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_Stream_waitEvent_const_EventR(self.as_raw_mut_Stream(), event.as_raw_Event(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Adds a callback to be called on the host after all currently enqueued items in the stream have
/// completed.
///
///
/// Note: Callbacks must not make any CUDA API calls. Callbacks must not perform any synchronization
/// that may depend on outstanding device work or other callbacks that are not mandated to run earlier.
/// Callbacks without a mandated order (in independent streams) execute in undefined order and may be
/// serialized.
#[inline]
fn enqueue_host_callback(&mut self, callback: core::Stream_StreamCallback) -> Result<()> {
callback_arg!(callback_trampoline(status: i32, user_data: *mut c_void) -> () => user_data in callbacks => callback(status: i32) -> ());
userdata_arg!(user_data in callbacks => callback);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_Stream_enqueueHostCallback_StreamCallback_voidX(self.as_raw_mut_Stream(), callback_trampoline, user_data, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// This class encapsulates a queue of asynchronous calls.
///
///
/// Note: Currently, you may face problems if an operation is enqueued twice with different data. Some
/// functions use the constant GPU memory, and next call may update the memory before the previous one
/// has been finished. But calling different operations asynchronously is safe because each operation
/// has its own constant buffer. Memory copy/upload/download/set operations to the buffers you hold are
/// also safe.
///
///
/// Note: The Stream class is not thread-safe. Please use different Stream objects for different CPU threads.
///
/// ```C++
/// void thread1()
/// {
/// cv::cuda::Stream stream1;
/// cv::cuda::func1(..., stream1);
/// }
///
/// void thread2()
/// {
/// cv::cuda::Stream stream2;
/// cv::cuda::func2(..., stream2);
/// }
/// ```
///
///
///
/// Note: By default all CUDA routines are launched in Stream::Null() object, if the stream is not specified by user.
/// In multi-threading environment the stream objects must be passed explicitly (see previous note).
pub struct Stream {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Stream }
impl Drop for Stream {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Stream_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Stream_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Stream()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Stream {}
impl core::StreamTraitConst for Stream {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Stream(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::StreamTrait for Stream {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Stream(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Stream {
/// creates a new asynchronous stream
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::Stream> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_Stream_Stream(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Stream::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// creates a new asynchronous stream with custom allocator
#[inline]
pub fn new(allocator: &core::Ptr<dyn core::GpuMat_Allocator>) -> Result<core::Stream> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_Stream_Stream_const_PtrLAllocatorGR(allocator.as_raw_PtrOfGpuMat_Allocator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Stream::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// creates a new Stream using the cudaFlags argument to determine the behaviors of the stream
///
///
/// Note: The cudaFlags parameter is passed to the underlying api cudaStreamCreateWithFlags() and
/// supports the same parameter values.
/// ```C++
/// // creates an OpenCV cuda::Stream that manages an asynchronous, non-blocking,
/// // non-default CUDA stream
/// cv::cuda::Stream cvStream(cudaStreamNonBlocking);
/// ```
///
#[inline]
pub fn new_1(cuda_flags: size_t) -> Result<core::Stream> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_Stream_Stream_const_size_t(cuda_flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Stream::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// return Stream object for default CUDA stream
#[inline]
pub fn null() -> Result<core::Stream> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_Stream_Null(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Stream::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::TargetArchs]
pub trait TargetArchsTraitConst {
fn as_raw_TargetArchs(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::TargetArchs]
pub trait TargetArchsTrait: core::TargetArchsTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_TargetArchs(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
/// Class providing a set of static methods to check what NVIDIA\* card architecture the CUDA module was
/// built for.
///
/// According to the CUDA C Programming Guide Version 3.2: "PTX code produced for some specific compute
/// capability can always be compiled to binary code of greater or equal compute capability".
pub struct TargetArchs {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { TargetArchs }
impl Drop for TargetArchs {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_TargetArchs_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_TargetArchs_delete(self.as_raw_mut_TargetArchs()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for TargetArchs {}
impl core::TargetArchsTraitConst for TargetArchs {
#[inline] fn as_raw_TargetArchs(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::TargetArchsTrait for TargetArchs {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_TargetArchs(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl TargetArchs {
/// The following method checks whether the module was built with the support of the given feature:
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * feature_set: Features to be checked. See :ocvcuda::FeatureSet.
#[inline]
pub fn built_with(feature_set: core::FeatureSet) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_TargetArchs_builtWith_FeatureSet(feature_set, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// There is a set of methods to check whether the module contains intermediate (PTX) or binary CUDA
/// code for the given architecture(s):
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * major: Major compute capability version.
/// * minor: Minor compute capability version.
#[inline]
pub fn has(major: i32, minor: i32) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_TargetArchs_has_int_int(major, minor, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn has_ptx(major: i32, minor: i32) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_TargetArchs_hasPtx_int_int(major, minor, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn has_bin(major: i32, minor: i32) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_TargetArchs_hasBin_int_int(major, minor, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn has_equal_or_less_ptx(major: i32, minor: i32) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_TargetArchs_hasEqualOrLessPtx_int_int(major, minor, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn has_equal_or_greater(major: i32, minor: i32) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_TargetArchs_hasEqualOrGreater_int_int(major, minor, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn has_equal_or_greater_ptx(major: i32, minor: i32) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_TargetArchs_hasEqualOrGreaterPtx_int_int(major, minor, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn has_equal_or_greater_bin(major: i32, minor: i32) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_TargetArchs_hasEqualOrGreaterBin_int_int(major, minor, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Detail_CheckContext]
pub trait Detail_CheckContextTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Detail_CheckContext(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn func(&self) -> String {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_detail_CheckContext_getPropFunc_const(self.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext()) };
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn file(&self) -> String {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_detail_CheckContext_getPropFile_const(self.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext()) };
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn line(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_detail_CheckContext_getPropLine_const(self.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn test_op(&self) -> core::Detail_TestOp {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_detail_CheckContext_getPropTestOp_const(self.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
ret
}
#[inline]
fn message(&self) -> String {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_detail_CheckContext_getPropMessage_const(self.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext()) };
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn p1_str(&self) -> String {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_detail_CheckContext_getPropP1_str_const(self.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext()) };
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn p2_str(&self) -> String {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_detail_CheckContext_getPropP2_str_const(self.as_raw_Detail_CheckContext()) };
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Detail_CheckContext]
pub trait Detail_CheckContextTrait: core::Detail_CheckContextTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Detail_CheckContext(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_line(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_detail_CheckContext_setPropLine_int(self.as_raw_mut_Detail_CheckContext(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_test_op(&mut self, val: core::Detail_TestOp) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_detail_CheckContext_setPropTestOp_TestOp(self.as_raw_mut_Detail_CheckContext(), val) };
ret
}
}
pub struct Detail_CheckContext {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Detail_CheckContext }
impl Drop for Detail_CheckContext {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Detail_CheckContext_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Detail_CheckContext_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Detail_CheckContext()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Detail_CheckContext {}
impl core::Detail_CheckContextTraitConst for Detail_CheckContext {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Detail_CheckContext(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::Detail_CheckContextTrait for Detail_CheckContext {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Detail_CheckContext(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Detail_CheckContext {
}
/// Constant methods for [core::NodeData]
pub trait NodeDataTraitConst {
fn as_raw_NodeData(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn m_fun_name(&self) -> String {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_instr_NodeData_getPropM_funName_const(self.as_raw_NodeData()) };
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn m_instr_type(&self) -> core::TYPE {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_instr_NodeData_getPropM_instrType_const(self.as_raw_NodeData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
ret
}
#[inline]
fn m_impl_type(&self) -> core::IMPL {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_instr_NodeData_getPropM_implType_const(self.as_raw_NodeData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
ret
}
#[inline]
fn m_file_name(&self) -> String {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_instr_NodeData_getPropM_fileName_const(self.as_raw_NodeData()) };
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn m_line_num(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_instr_NodeData_getPropM_lineNum_const(self.as_raw_NodeData()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn m_always_expand(&self) -> bool {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_instr_NodeData_getPropM_alwaysExpand_const(self.as_raw_NodeData()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn m_fun_error(&self) -> bool {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_instr_NodeData_getPropM_funError_const(self.as_raw_NodeData()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn m_counter(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_instr_NodeData_getPropM_counter_const(self.as_raw_NodeData()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn m_ticks_total(&self) -> u64 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_instr_NodeData_getPropM_ticksTotal_const(self.as_raw_NodeData()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn m_threads(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_instr_NodeData_getPropM_threads_const(self.as_raw_NodeData()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn get_total_ms(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_instr_NodeData_getTotalMs_const(self.as_raw_NodeData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_mean_ms(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_instr_NodeData_getMeanMs_const(self.as_raw_NodeData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::NodeData]
pub trait NodeDataTrait: core::NodeDataTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_NodeData(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_m_fun_name(&mut self, val: &str) {
extern_container_arg!(nofail mut val);
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_instr_NodeData_setPropM_funName_String(self.as_raw_mut_NodeData(), val.opencv_as_extern_mut()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_m_instr_type(&mut self, val: core::TYPE) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_instr_NodeData_setPropM_instrType_TYPE(self.as_raw_mut_NodeData(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_m_impl_type(&mut self, val: core::IMPL) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_instr_NodeData_setPropM_implType_IMPL(self.as_raw_mut_NodeData(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_m_line_num(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_instr_NodeData_setPropM_lineNum_int(self.as_raw_mut_NodeData(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn m_ret_address(&mut self) -> *mut c_void {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_instr_NodeData_getPropM_retAddress(self.as_raw_mut_NodeData()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
unsafe fn set_m_ret_address(&mut self, val: *mut c_void) {
let ret = { sys::cv_instr_NodeData_setPropM_retAddress_voidX(self.as_raw_mut_NodeData(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_m_always_expand(&mut self, val: bool) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_instr_NodeData_setPropM_alwaysExpand_bool(self.as_raw_mut_NodeData(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_m_fun_error(&mut self, val: bool) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_instr_NodeData_setPropM_funError_bool(self.as_raw_mut_NodeData(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_m_counter(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_instr_NodeData_setPropM_counter_int(self.as_raw_mut_NodeData(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_m_ticks_total(&mut self, val: u64) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_instr_NodeData_setPropM_ticksTotal_uint64_t(self.as_raw_mut_NodeData(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_m_threads(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_instr_NodeData_setPropM_threads_int(self.as_raw_mut_NodeData(), val) };
ret
}
}
pub struct NodeData {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { NodeData }
impl Drop for NodeData {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_NodeData_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_NodeData_delete(self.as_raw_mut_NodeData()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for NodeData {}
impl core::NodeDataTraitConst for NodeData {
#[inline] fn as_raw_NodeData(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::NodeDataTrait for NodeData {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_NodeData(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl NodeData {
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * fun_name: 0
/// * file_name: NULL
/// * line_num: 0
/// * ret_address: NULL
/// * always_expand: false
/// * instr_type: TYPE_GENERAL
/// * impl_type: IMPL_PLAIN
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn new(fun_name: &str, file_name: &str, line_num: i32, ret_address: *mut c_void, always_expand: bool, instr_type: core::TYPE, impl_type: core::IMPL) -> Result<core::NodeData> {
extern_container_arg!(fun_name);
extern_container_arg!(file_name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_instr_NodeData_NodeData_const_charX_const_charX_int_voidX_bool_TYPE_IMPL(fun_name.opencv_as_extern(), file_name.opencv_as_extern(), line_num, ret_address, always_expand, instr_type, impl_type, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::NodeData::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy_mut(ref_: &mut core::NodeData) -> Result<core::NodeData> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_instr_NodeData_NodeData_NodeDataR(ref_.as_raw_mut_NodeData(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::NodeData::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::WriteStructContext]
pub trait WriteStructContextTraitConst {
fn as_raw_WriteStructContext(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::WriteStructContext]
pub trait WriteStructContextTrait: core::WriteStructContextTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_WriteStructContext(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
pub struct WriteStructContext {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { WriteStructContext }
impl Drop for WriteStructContext {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_WriteStructContext_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_WriteStructContext_delete(self.as_raw_mut_WriteStructContext()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for WriteStructContext {}
impl core::WriteStructContextTraitConst for WriteStructContext {
#[inline] fn as_raw_WriteStructContext(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::WriteStructContextTrait for WriteStructContext {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_WriteStructContext(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl WriteStructContext {
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * type_name: String()
#[inline]
pub fn new(_fs: &mut core::FileStorage, name: &str, flags: i32, type_name: &str) -> Result<core::WriteStructContext> {
extern_container_arg!(name);
extern_container_arg!(type_name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_internal_WriteStructContext_WriteStructContext_FileStorageR_const_StringR_int_const_StringR(_fs.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), name.opencv_as_extern(), flags, type_name.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::WriteStructContext::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Context]
pub trait ContextTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Context(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn ndevices(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Context_ndevices_const(self.as_raw_Context(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn device(&self, idx: size_t) -> Result<core::Device> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Context_device_const_size_t(self.as_raw_Context(), idx, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Device::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## Returns
/// cl_context value
#[inline]
fn ptr(&self) -> Result<*mut c_void> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Context_ptr_const(self.as_raw_Context(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Get OpenCL context property specified on context creation
/// ## Parameters
/// * propertyId: Property id (CL_CONTEXT_* as defined in cl_context_properties type)
/// ## Returns
/// Property value if property was specified on clCreateContext, or NULL if context created without the property
#[inline]
fn get_opencl_context_property(&self, property_id: i32) -> Result<*mut c_void> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Context_getOpenCLContextProperty_const_int(self.as_raw_Context(), property_id, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn use_svm(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Context_useSVM_const(self.as_raw_Context(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn empty(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Context_empty_const(self.as_raw_Context(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Context]
pub trait ContextTrait: core::ContextTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Context(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// @deprecated
#[inline]
fn create(&mut self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Context_create(self.as_raw_mut_Context(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// @deprecated
#[inline]
fn create_with_type(&mut self, dtype: i32) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Context_create_int(self.as_raw_mut_Context(), dtype, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_prog(&mut self, prog: &core::ProgramSource, buildopt: &str, errmsg: &mut String) -> Result<core::Program> {
extern_container_arg!(buildopt);
string_arg_output_send!(via errmsg_via);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Context_getProg_const_ProgramSourceR_const_StringR_StringR(self.as_raw_mut_Context(), prog.as_raw_ProgramSource(), buildopt.opencv_as_extern(), &mut errmsg_via, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Program::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
string_arg_output_receive!(errmsg_via => errmsg);
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn unload_prog(&mut self, prog: &mut core::Program) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Context_unloadProg_ProgramR(self.as_raw_mut_Context(), prog.as_raw_mut_Program(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_use_svm(&mut self, enabled: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Context_setUseSVM_bool(self.as_raw_mut_Context(), enabled, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn release(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Context_release(self.as_raw_mut_Context(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
pub struct Context {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Context }
impl Drop for Context {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Context_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Context_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Context()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Context {}
impl core::ContextTraitConst for Context {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Context(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::ContextTrait for Context {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Context(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Context {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> core::Context {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Context_Context() };
let ret = unsafe { core::Context::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
pub fn new_with_type(dtype: i32) -> Result<core::Context> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Context_Context_int(dtype, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Context::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy(c: &core::Context) -> Result<core::Context> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Context_Context_const_ContextR(c.as_raw_Context(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Context::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy_mut(mut c: core::Context) -> core::Context {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Context_Context_ContextRR(c.as_raw_mut_Context()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Context::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * initialize: true
#[inline]
pub fn get_default(initialize: bool) -> Result<core::Context> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Context_getDefault_bool(initialize, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Context::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## Parameters
/// * context: OpenCL handle (cl_context). clRetainContext() is called on success
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn from_handle(context: *mut c_void) -> Result<core::Context> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_ocl_Context_fromHandle_voidX(context, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::Context::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_device(device: &core::Device) -> Result<core::Context> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Context_fromDevice_const_DeviceR(device.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Context::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn create(configuration: &str) -> Result<core::Context> {
extern_container_arg!(configuration);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Context_create_const_stringR(configuration.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Context::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl Default for Context {
#[inline]
/// Forwards to infallible Self::default()
fn default() -> Self {
Self::default()
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Context_UserContext]
pub trait Context_UserContextTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Context_UserContext(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Context_UserContext]
pub trait Context_UserContextTrait: core::Context_UserContextTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Context_UserContext(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
pub struct Context_UserContext {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Context_UserContext }
impl Drop for Context_UserContext {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Context_UserContext_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Context_UserContext_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Context_UserContext()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Context_UserContext {}
impl core::Context_UserContextTraitConst for Context_UserContext {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Context_UserContext(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::Context_UserContextTrait for Context_UserContext {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Context_UserContext(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Context_UserContext {
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Device]
pub trait DeviceTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Device(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn name(&self) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_name_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn extensions(&self) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_extensions_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn is_extension_supported(&self, extension_name: &str) -> Result<bool> {
extern_container_arg!(extension_name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_isExtensionSupported_const_const_StringR(self.as_raw_Device(), extension_name.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn version(&self) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_version_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn vendor_name(&self) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_vendorName_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn opencl_c_version(&self) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_OpenCL_C_Version_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn opencl_version(&self) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_OpenCLVersion_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn device_version_major(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_deviceVersionMajor_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn device_version_minor(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_deviceVersionMinor_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn driver_version(&self) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_driverVersion_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn ptr(&self) -> Result<*mut c_void> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_ptr_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn typ(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_type_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn address_bits(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_addressBits_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn available(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_available_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn compiler_available(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_compilerAvailable_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn linker_available(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_linkerAvailable_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn double_fp_config(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_doubleFPConfig_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn single_fp_config(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_singleFPConfig_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn half_fp_config(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_halfFPConfig_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn endian_little(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_endianLittle_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn error_correction_support(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_errorCorrectionSupport_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn execution_capabilities(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_executionCapabilities_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn global_mem_cache_size(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_globalMemCacheSize_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn global_mem_cache_type(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_globalMemCacheType_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn global_mem_cache_line_size(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_globalMemCacheLineSize_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn global_mem_size(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_globalMemSize_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn local_mem_size(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_localMemSize_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn local_mem_type(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_localMemType_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn host_unified_memory(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_hostUnifiedMemory_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn image_support(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_imageSupport_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn image_from_buffer_support(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_imageFromBufferSupport_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn image_pitch_alignment(&self) -> Result<u32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_imagePitchAlignment_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn image_base_address_alignment(&self) -> Result<u32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_imageBaseAddressAlignment_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// deprecated, use isExtensionSupported() method (probably with "cl_khr_subgroups" value)
#[inline]
fn intel_subgroups_support(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_intelSubgroupsSupport_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn image2_d_max_width(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_image2DMaxWidth_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn image2_d_max_height(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_image2DMaxHeight_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn image3_d_max_width(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_image3DMaxWidth_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn image3_d_max_height(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_image3DMaxHeight_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn image3_d_max_depth(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_image3DMaxDepth_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn image_max_buffer_size(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_imageMaxBufferSize_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn image_max_array_size(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_imageMaxArraySize_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn vendor_id(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_vendorID_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn is_amd(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_isAMD_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn is_intel(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_isIntel_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn is_n_vidia(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_isNVidia_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn max_clock_frequency(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_maxClockFrequency_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn max_compute_units(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_maxComputeUnits_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn max_constant_args(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_maxConstantArgs_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn max_constant_buffer_size(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_maxConstantBufferSize_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn max_mem_alloc_size(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_maxMemAllocSize_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn max_parameter_size(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_maxParameterSize_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn max_read_image_args(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_maxReadImageArgs_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn max_write_image_args(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_maxWriteImageArgs_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn max_samplers(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_maxSamplers_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn max_work_group_size(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_maxWorkGroupSize_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn max_work_item_dims(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_maxWorkItemDims_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn max_work_item_sizes(&self, unnamed: &mut size_t) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_maxWorkItemSizes_const_size_tX(self.as_raw_Device(), unnamed, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn mem_base_addr_align(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_memBaseAddrAlign_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn native_vector_width_char(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_nativeVectorWidthChar_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn native_vector_width_short(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_nativeVectorWidthShort_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn native_vector_width_int(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_nativeVectorWidthInt_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn native_vector_width_long(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_nativeVectorWidthLong_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn native_vector_width_float(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_nativeVectorWidthFloat_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn native_vector_width_double(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_nativeVectorWidthDouble_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn native_vector_width_half(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_nativeVectorWidthHalf_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn preferred_vector_width_char(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_preferredVectorWidthChar_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn preferred_vector_width_short(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_preferredVectorWidthShort_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn preferred_vector_width_int(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_preferredVectorWidthInt_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn preferred_vector_width_long(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_preferredVectorWidthLong_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn preferred_vector_width_float(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_preferredVectorWidthFloat_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn preferred_vector_width_double(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_preferredVectorWidthDouble_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn preferred_vector_width_half(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_preferredVectorWidthHalf_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn printf_buffer_size(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_printfBufferSize_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn profiling_timer_resolution(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_profilingTimerResolution_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn empty(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_empty_const(self.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Device]
pub trait DeviceTrait: core::DeviceTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Device(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
unsafe fn set(&mut self, d: *mut c_void) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_ocl_Device_set_voidX(self.as_raw_mut_Device(), d, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
pub struct Device {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Device }
impl Drop for Device {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Device_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Device_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Device()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Device {}
impl core::DeviceTraitConst for Device {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Device(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::DeviceTrait for Device {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Device(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Device {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> core::Device {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_Device() };
let ret = unsafe { core::Device::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn new(d: *mut c_void) -> Result<core::Device> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_ocl_Device_Device_voidX(d, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::Device::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy(d: &core::Device) -> Result<core::Device> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_Device_const_DeviceR(d.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Device::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy_mut(mut d: core::Device) -> core::Device {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_Device_DeviceRR(d.as_raw_mut_Device()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Device::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
pub fn get_default() -> Result<core::Device> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Device_getDefault(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Device::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## Parameters
/// * d: OpenCL handle (cl_device_id). clRetainDevice() is called on success.
///
///
/// Note: Ownership of the passed device is passed to OpenCV on success.
/// The caller should additionally call `clRetainDevice` on it if it intends
/// to continue using the device.
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn from_handle(d: *mut c_void) -> Result<core::Device> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_ocl_Device_fromHandle_voidX(d, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::Device::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl Default for Device {
#[inline]
/// Forwards to infallible Self::default()
fn default() -> Self {
Self::default()
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Image2D]
pub trait Image2DTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Image2D(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn ptr(&self) -> Result<*mut c_void> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Image2D_ptr_const(self.as_raw_Image2D(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Image2D]
pub trait Image2DTrait: core::Image2DTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Image2D(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
pub struct Image2D {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Image2D }
impl Drop for Image2D {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Image2D_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Image2D_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Image2D()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Image2D {}
impl core::Image2DTraitConst for Image2D {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Image2D(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::Image2DTrait for Image2D {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Image2D(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Image2D {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> core::Image2D {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Image2D_Image2D() };
let ret = unsafe { core::Image2D::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: UMat object from which to get image properties and data
/// * norm: flag to enable the use of normalized channel data types
/// * alias: flag indicating that the image should alias the src UMat. If true, changes to the
/// image or src will be reflected in both objects.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * norm: false
/// * alias: false
#[inline]
pub fn new(src: &core::UMat, norm: bool, alias: bool) -> Result<core::Image2D> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Image2D_Image2D_const_UMatR_bool_bool(src.as_raw_UMat(), norm, alias, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Image2D::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy(i: &core::Image2D) -> Result<core::Image2D> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Image2D_Image2D_const_Image2DR(i.as_raw_Image2D(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Image2D::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy_mut(mut unnamed: core::Image2D) -> core::Image2D {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Image2D_Image2D_Image2DRR(unnamed.as_raw_mut_Image2D()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Image2D::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// Indicates if creating an aliased image should succeed.
/// Depends on the underlying platform and the dimensions of the UMat.
#[inline]
pub fn can_create_alias(u: &core::UMat) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Image2D_canCreateAlias_const_UMatR(u.as_raw_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Indicates if the image format is supported.
#[inline]
pub fn is_format_supported(depth: i32, cn: i32, norm: bool) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Image2D_isFormatSupported_int_int_bool(depth, cn, norm, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl Default for Image2D {
#[inline]
/// Forwards to infallible Self::default()
fn default() -> Self {
Self::default()
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Kernel]
pub trait KernelTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Kernel(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn empty(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Kernel_empty_const(self.as_raw_Kernel(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn work_group_size(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Kernel_workGroupSize_const(self.as_raw_Kernel(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn prefered_work_group_size_multiple(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Kernel_preferedWorkGroupSizeMultiple_const(self.as_raw_Kernel(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn compile_work_group_size(&self, wsz: &mut [size_t]) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Kernel_compileWorkGroupSize_const_size_tX(self.as_raw_Kernel(), wsz.as_mut_ptr(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn local_mem_size(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Kernel_localMemSize_const(self.as_raw_Kernel(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn ptr(&self) -> Result<*mut c_void> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Kernel_ptr_const(self.as_raw_Kernel(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Kernel]
pub trait KernelTrait: core::KernelTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Kernel(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn create(&mut self, kname: &str, prog: &core::Program) -> Result<bool> {
extern_container_arg!(kname);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Kernel_create_const_charX_const_ProgramR(self.as_raw_mut_Kernel(), kname.opencv_as_extern(), prog.as_raw_Program(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * errmsg: 0
#[inline]
fn create_ext(&mut self, kname: &str, prog: &core::ProgramSource, buildopts: &str, errmsg: &mut String) -> Result<bool> {
extern_container_arg!(kname);
extern_container_arg!(buildopts);
string_arg_output_send!(via errmsg_via);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Kernel_create_const_charX_const_ProgramSourceR_const_StringR_StringX(self.as_raw_mut_Kernel(), kname.opencv_as_extern(), prog.as_raw_ProgramSource(), buildopts.opencv_as_extern(), &mut errmsg_via, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
string_arg_output_receive!(errmsg_via => errmsg);
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
unsafe fn set(&mut self, i: i32, value: *const c_void, sz: size_t) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_ocl_Kernel_set_int_const_voidX_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_Kernel(), i, value, sz, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_1(&mut self, i: i32, image_2d: &core::Image2D) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Kernel_set_int_const_Image2DR(self.as_raw_mut_Kernel(), i, image_2d.as_raw_Image2D(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_umat(&mut self, i: i32, m: &core::UMat) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Kernel_set_int_const_UMatR(self.as_raw_mut_Kernel(), i, m.as_raw_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_kernel_arg(&mut self, i: i32, arg: &core::KernelArg) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Kernel_set_int_const_KernelArgR(self.as_raw_mut_Kernel(), i, arg.as_raw_KernelArg(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Run the OpenCL kernel (globalsize value may be adjusted)
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * dims: the work problem dimensions. It is the length of globalsize and localsize. It can be either 1, 2 or 3.
/// * globalsize: work items for each dimension. It is not the final globalsize passed to
/// OpenCL. Each dimension will be adjusted to the nearest integer divisible by the corresponding
/// value in localsize. If localsize is NULL, it will still be adjusted depending on dims. The
/// adjusted values are greater than or equal to the original values.
/// * localsize: work-group size for each dimension.
/// * sync: specify whether to wait for OpenCL computation to finish before return.
/// * q: command queue
///
///
/// Note: Use run_() if your kernel code doesn't support adjusted globalsize.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * q: Queue()
#[inline]
fn run(&mut self, dims: i32, globalsize: &mut [size_t], localsize: &mut [size_t], sync: bool, q: &core::Queue) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Kernel_run_int_size_tX_size_tX_bool_const_QueueR(self.as_raw_mut_Kernel(), dims, globalsize.as_mut_ptr(), localsize.as_mut_ptr(), sync, q.as_raw_Queue(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Run the OpenCL kernel
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * dims: the work problem dimensions. It is the length of globalsize and localsize. It can be either 1, 2 or 3.
/// * globalsize: work items for each dimension. This value is passed to OpenCL without changes.
/// * localsize: work-group size for each dimension.
/// * sync: specify whether to wait for OpenCL computation to finish before return.
/// * q: command queue
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * q: Queue()
#[inline]
fn run_(&mut self, dims: i32, globalsize: &mut [size_t], localsize: &mut [size_t], sync: bool, q: &core::Queue) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Kernel_run__int_size_tX_size_tX_bool_const_QueueR(self.as_raw_mut_Kernel(), dims, globalsize.as_mut_ptr(), localsize.as_mut_ptr(), sync, q.as_raw_Queue(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * q: Queue()
#[inline]
fn run_task(&mut self, sync: bool, q: &core::Queue) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Kernel_runTask_bool_const_QueueR(self.as_raw_mut_Kernel(), sync, q.as_raw_Queue(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Similar to synchronized run_() call with returning of kernel execution time
///
/// Separate OpenCL command queue may be used (with CL_QUEUE_PROFILING_ENABLE)
/// ## Returns
/// Execution time in nanoseconds or negative number on error
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * q: Queue()
#[inline]
fn run_profiling(&mut self, dims: i32, globalsize: &mut [size_t], localsize: &mut [size_t], q: &core::Queue) -> Result<i64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Kernel_runProfiling_int_size_tX_size_tX_const_QueueR(self.as_raw_mut_Kernel(), dims, globalsize.as_mut_ptr(), localsize.as_mut_ptr(), q.as_raw_Queue(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
pub struct Kernel {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Kernel }
impl Drop for Kernel {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Kernel_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Kernel_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Kernel()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Kernel {}
impl core::KernelTraitConst for Kernel {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Kernel(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::KernelTrait for Kernel {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Kernel(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Kernel {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> core::Kernel {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Kernel_Kernel() };
let ret = unsafe { core::Kernel::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
pub fn new(kname: &str, prog: &core::Program) -> Result<core::Kernel> {
extern_container_arg!(kname);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Kernel_Kernel_const_charX_const_ProgramR(kname.opencv_as_extern(), prog.as_raw_Program(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Kernel::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * buildopts: String()
/// * errmsg: 0
#[inline]
pub fn new_1(kname: &str, prog: &core::ProgramSource, buildopts: &str, errmsg: &mut String) -> Result<core::Kernel> {
extern_container_arg!(kname);
extern_container_arg!(buildopts);
string_arg_output_send!(via errmsg_via);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Kernel_Kernel_const_charX_const_ProgramSourceR_const_StringR_StringX(kname.opencv_as_extern(), prog.as_raw_ProgramSource(), buildopts.opencv_as_extern(), &mut errmsg_via, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Kernel::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
string_arg_output_receive!(errmsg_via => errmsg);
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy(k: &core::Kernel) -> Result<core::Kernel> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Kernel_Kernel_const_KernelR(k.as_raw_Kernel(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Kernel::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy_mut(mut k: core::Kernel) -> core::Kernel {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Kernel_Kernel_KernelRR(k.as_raw_mut_Kernel()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Kernel::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
}
impl Default for Kernel {
#[inline]
/// Forwards to infallible Self::default()
fn default() -> Self {
Self::default()
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::KernelArg]
pub trait KernelArgTraitConst {
fn as_raw_KernelArg(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn flags(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_KernelArg_getPropFlags_const(self.as_raw_KernelArg()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn obj(&self) -> *const c_void {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_KernelArg_getPropObj_const(self.as_raw_KernelArg()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn sz(&self) -> size_t {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_KernelArg_getPropSz_const(self.as_raw_KernelArg()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn wscale(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_KernelArg_getPropWscale_const(self.as_raw_KernelArg()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn iwscale(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_KernelArg_getPropIwscale_const(self.as_raw_KernelArg()) };
ret
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::KernelArg]
pub trait KernelArgTrait: core::KernelArgTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_KernelArg(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_flags(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_KernelArg_setPropFlags_int(self.as_raw_mut_KernelArg(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn m(&mut self) -> core::UMat {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_KernelArg_getPropM(self.as_raw_mut_KernelArg()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::UMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_m(&mut self, val: &mut core::UMat) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_KernelArg_setPropM_UMatX(self.as_raw_mut_KernelArg(), val.as_raw_mut_UMat()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_sz(&mut self, val: size_t) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_KernelArg_setPropSz_size_t(self.as_raw_mut_KernelArg(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_wscale(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_KernelArg_setPropWscale_int(self.as_raw_mut_KernelArg(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_iwscale(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_KernelArg_setPropIwscale_int(self.as_raw_mut_KernelArg(), val) };
ret
}
}
pub struct KernelArg {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { KernelArg }
impl Drop for KernelArg {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_KernelArg_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_KernelArg_delete(self.as_raw_mut_KernelArg()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for KernelArg {}
impl core::KernelArgTraitConst for KernelArg {
#[inline] fn as_raw_KernelArg(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::KernelArgTrait for KernelArg {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_KernelArg(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl KernelArg {
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * wscale: 1
/// * iwscale: 1
/// * _obj: 0
/// * _sz: 0
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn new(_flags: i32, _m: &mut core::UMat, wscale: i32, iwscale: i32, _obj: *const c_void, _sz: size_t) -> Result<core::KernelArg> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_ocl_KernelArg_KernelArg_int_UMatX_int_int_const_voidX_size_t(_flags, _m.as_raw_mut_UMat(), wscale, iwscale, _obj, _sz, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::KernelArg::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> core::KernelArg {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_KernelArg_KernelArg() };
let ret = unsafe { core::KernelArg::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
pub fn local(local_mem_size: size_t) -> Result<core::KernelArg> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_KernelArg_Local_size_t(local_mem_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::KernelArg::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn ptr_write_only(m: &core::UMat) -> Result<core::KernelArg> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_KernelArg_PtrWriteOnly_const_UMatR(m.as_raw_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::KernelArg::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn ptr_read_only(m: &core::UMat) -> Result<core::KernelArg> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_KernelArg_PtrReadOnly_const_UMatR(m.as_raw_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::KernelArg::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn ptr_read_write(m: &core::UMat) -> Result<core::KernelArg> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_KernelArg_PtrReadWrite_const_UMatR(m.as_raw_UMat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::KernelArg::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * wscale: 1
/// * iwscale: 1
#[inline]
pub fn read_write(m: &core::UMat, wscale: i32, iwscale: i32) -> Result<core::KernelArg> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_KernelArg_ReadWrite_const_UMatR_int_int(m.as_raw_UMat(), wscale, iwscale, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::KernelArg::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * wscale: 1
/// * iwscale: 1
#[inline]
pub fn read_write_no_size(m: &core::UMat, wscale: i32, iwscale: i32) -> Result<core::KernelArg> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_KernelArg_ReadWriteNoSize_const_UMatR_int_int(m.as_raw_UMat(), wscale, iwscale, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::KernelArg::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * wscale: 1
/// * iwscale: 1
#[inline]
pub fn read_only(m: &core::UMat, wscale: i32, iwscale: i32) -> Result<core::KernelArg> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_KernelArg_ReadOnly_const_UMatR_int_int(m.as_raw_UMat(), wscale, iwscale, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::KernelArg::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * wscale: 1
/// * iwscale: 1
#[inline]
pub fn write_only(m: &core::UMat, wscale: i32, iwscale: i32) -> Result<core::KernelArg> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_KernelArg_WriteOnly_const_UMatR_int_int(m.as_raw_UMat(), wscale, iwscale, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::KernelArg::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * wscale: 1
/// * iwscale: 1
#[inline]
pub fn read_only_no_size(m: &core::UMat, wscale: i32, iwscale: i32) -> Result<core::KernelArg> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_KernelArg_ReadOnlyNoSize_const_UMatR_int_int(m.as_raw_UMat(), wscale, iwscale, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::KernelArg::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * wscale: 1
/// * iwscale: 1
#[inline]
pub fn write_only_no_size(m: &core::UMat, wscale: i32, iwscale: i32) -> Result<core::KernelArg> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_KernelArg_WriteOnlyNoSize_const_UMatR_int_int(m.as_raw_UMat(), wscale, iwscale, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::KernelArg::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn constant(m: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::KernelArg> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_KernelArg_Constant_const_MatR(m.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::KernelArg::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl Default for KernelArg {
#[inline]
/// Forwards to infallible Self::default()
fn default() -> Self {
Self::default()
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::OpenCLExecutionContext]
pub trait OpenCLExecutionContextTraitConst {
fn as_raw_OpenCLExecutionContext(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Get associated ocl::Context
#[inline]
fn get_context(&self) -> Result<core::Context> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_OpenCLExecutionContext_getContext_const(self.as_raw_OpenCLExecutionContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Context::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Get the single default associated ocl::Device
#[inline]
fn get_device(&self) -> Result<core::Device> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_OpenCLExecutionContext_getDevice_const(self.as_raw_OpenCLExecutionContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Device::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Get the single ocl::Queue that is associated with the ocl::Context and
/// the single default ocl::Device
#[inline]
fn get_queue(&self) -> Result<core::Queue> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_OpenCLExecutionContext_getQueue_const(self.as_raw_OpenCLExecutionContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Queue::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn use_opencl(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_OpenCLExecutionContext_useOpenCL_const(self.as_raw_OpenCLExecutionContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Bind this OpenCL execution context to current thread.
///
/// Context can't be empty.
///
///
/// Note: clFinish is not called for queue of previous execution context
#[inline]
fn bind(&self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_OpenCLExecutionContext_bind_const(self.as_raw_OpenCLExecutionContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates new execution context with same OpenCV context and device
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * q: OpenCL queue
#[inline]
fn clone_with_new_queue(&self, q: &core::Queue) -> Result<core::OpenCLExecutionContext> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_OpenCLExecutionContext_cloneWithNewQueue_const_const_QueueR(self.as_raw_OpenCLExecutionContext(), q.as_raw_Queue(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::OpenCLExecutionContext::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates new execution context with same OpenCV context and device
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * q: OpenCL queue
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
#[inline]
fn clone_with_new_queue_1(&self) -> Result<core::OpenCLExecutionContext> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_OpenCLExecutionContext_cloneWithNewQueue_const(self.as_raw_OpenCLExecutionContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::OpenCLExecutionContext::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn empty(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_OpenCLExecutionContext_empty_const(self.as_raw_OpenCLExecutionContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::OpenCLExecutionContext]
pub trait OpenCLExecutionContextTrait: core::OpenCLExecutionContextTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_OpenCLExecutionContext(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_use_opencl(&mut self, flag: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_OpenCLExecutionContext_setUseOpenCL_bool(self.as_raw_mut_OpenCLExecutionContext(), flag, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn release(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_OpenCLExecutionContext_release(self.as_raw_mut_OpenCLExecutionContext(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
pub struct OpenCLExecutionContext {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { OpenCLExecutionContext }
impl Drop for OpenCLExecutionContext {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_OpenCLExecutionContext_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_OpenCLExecutionContext_delete(self.as_raw_mut_OpenCLExecutionContext()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for OpenCLExecutionContext {}
impl core::OpenCLExecutionContextTraitConst for OpenCLExecutionContext {
#[inline] fn as_raw_OpenCLExecutionContext(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::OpenCLExecutionContextTrait for OpenCLExecutionContext {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_OpenCLExecutionContext(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl OpenCLExecutionContext {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> core::OpenCLExecutionContext {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_OpenCLExecutionContext_OpenCLExecutionContext() };
let ret = unsafe { core::OpenCLExecutionContext::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy(unnamed: &core::OpenCLExecutionContext) -> core::OpenCLExecutionContext {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_OpenCLExecutionContext_OpenCLExecutionContext_const_OpenCLExecutionContextR(unnamed.as_raw_OpenCLExecutionContext()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::OpenCLExecutionContext::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy_mut(mut unnamed: core::OpenCLExecutionContext) -> core::OpenCLExecutionContext {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_OpenCLExecutionContext_OpenCLExecutionContext_OpenCLExecutionContextRR(unnamed.as_raw_mut_OpenCLExecutionContext()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::OpenCLExecutionContext::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// Get OpenCL execution context of current thread.
///
/// Initialize OpenCL execution context if it is empty
/// - create new
/// - reuse context of the main thread (threadID = 0)
#[inline]
pub fn get_current() -> Result<core::OpenCLExecutionContext> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_OpenCLExecutionContext_getCurrent(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::OpenCLExecutionContext::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Get OpenCL execution context of current thread (can be empty)
#[inline]
pub fn get_current_ref() -> Result<core::OpenCLExecutionContext> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_OpenCLExecutionContext_getCurrentRef(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::OpenCLExecutionContext::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates OpenCL execution context
/// OpenCV will check if available OpenCL platform has platformName name,
/// then assign context to OpenCV.
/// The deviceID device will be used as target device and a new command queue will be created.
///
///
/// Note: On success, ownership of one reference of the context and device is taken.
/// The caller should additionally call `clRetainContext` and/or `clRetainDevice`
/// to increase the reference count if it wishes to continue using them.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * platformName: name of OpenCL platform to attach, this string is used to check if platform is available to OpenCV at runtime
/// * platformID: ID of platform attached context was created for (cl_platform_id)
/// * context: OpenCL context to be attached to OpenCV (cl_context)
/// * deviceID: OpenCL device (cl_device_id)
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn create(platform_name: &str, platform_id: *mut c_void, context: *mut c_void, device_id: *mut c_void) -> Result<core::OpenCLExecutionContext> {
extern_container_arg!(platform_name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_ocl_OpenCLExecutionContext_create_const_stringR_voidX_voidX_voidX(platform_name.opencv_as_extern(), platform_id, context, device_id, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::OpenCLExecutionContext::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates OpenCL execution context
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * context: non-empty OpenCL context
/// * device: non-empty OpenCL device (must be a part of context)
/// * queue: non-empty OpenCL queue for provided context and device
#[inline]
pub fn create_1(context: &core::Context, device: &core::Device, queue: &core::Queue) -> Result<core::OpenCLExecutionContext> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_OpenCLExecutionContext_create_const_ContextR_const_DeviceR_const_QueueR(context.as_raw_Context(), device.as_raw_Device(), queue.as_raw_Queue(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::OpenCLExecutionContext::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates OpenCL execution context
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * context: non-empty OpenCL context
/// * device: non-empty OpenCL device (must be a part of context)
/// * queue: non-empty OpenCL queue for provided context and device
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
#[inline]
pub fn create_2(context: &core::Context, device: &core::Device) -> Result<core::OpenCLExecutionContext> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_OpenCLExecutionContext_create_const_ContextR_const_DeviceR(context.as_raw_Context(), device.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::OpenCLExecutionContext::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl Default for OpenCLExecutionContext {
#[inline]
/// Forwards to infallible Self::default()
fn default() -> Self {
Self::default()
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Platform]
pub trait PlatformTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Platform(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn ptr(&self) -> Result<*mut c_void> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Platform_ptr_const(self.as_raw_Platform(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn empty(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Platform_empty_const(self.as_raw_Platform(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Platform]
pub trait PlatformTrait: core::PlatformTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Platform(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
/// @deprecated
pub struct Platform {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Platform }
impl Drop for Platform {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Platform_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Platform_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Platform()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Platform {}
impl core::PlatformTraitConst for Platform {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Platform(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::PlatformTrait for Platform {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Platform(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Platform {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> core::Platform {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Platform_Platform() };
let ret = unsafe { core::Platform::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy(p: &core::Platform) -> Result<core::Platform> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Platform_Platform_const_PlatformR(p.as_raw_Platform(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Platform::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy_mut(mut p: core::Platform) -> core::Platform {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Platform_Platform_PlatformRR(p.as_raw_mut_Platform()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Platform::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// @deprecated
#[inline]
pub fn get_default() -> Result<core::Platform> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Platform_getDefault(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Platform::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl Default for Platform {
#[inline]
/// Forwards to infallible Self::default()
fn default() -> Self {
Self::default()
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::PlatformInfo]
pub trait PlatformInfoTraitConst {
fn as_raw_PlatformInfo(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn name(&self) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_PlatformInfo_name_const(self.as_raw_PlatformInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn vendor(&self) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_PlatformInfo_vendor_const(self.as_raw_PlatformInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// See CL_PLATFORM_VERSION
#[inline]
fn version(&self) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_PlatformInfo_version_const(self.as_raw_PlatformInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn version_major(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_PlatformInfo_versionMajor_const(self.as_raw_PlatformInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn version_minor(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_PlatformInfo_versionMinor_const(self.as_raw_PlatformInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn device_number(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_PlatformInfo_deviceNumber_const(self.as_raw_PlatformInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_device(&self, device: &mut core::Device, d: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_PlatformInfo_getDevice_const_DeviceR_int(self.as_raw_PlatformInfo(), device.as_raw_mut_Device(), d, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn empty(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_PlatformInfo_empty_const(self.as_raw_PlatformInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::PlatformInfo]
pub trait PlatformInfoTrait: core::PlatformInfoTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_PlatformInfo(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
pub struct PlatformInfo {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { PlatformInfo }
impl Drop for PlatformInfo {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_PlatformInfo_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_PlatformInfo_delete(self.as_raw_mut_PlatformInfo()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for PlatformInfo {}
impl core::PlatformInfoTraitConst for PlatformInfo {
#[inline] fn as_raw_PlatformInfo(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::PlatformInfoTrait for PlatformInfo {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_PlatformInfo(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl PlatformInfo {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> core::PlatformInfo {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_PlatformInfo_PlatformInfo() };
let ret = unsafe { core::PlatformInfo::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// ## Parameters
/// * id: pointer cl_platform_id (cl_platform_id*)
#[inline]
pub unsafe fn new(id: *mut c_void) -> Result<core::PlatformInfo> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
{ sys::cv_ocl_PlatformInfo_PlatformInfo_voidX(id, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = { core::PlatformInfo::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy(i: &core::PlatformInfo) -> Result<core::PlatformInfo> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_PlatformInfo_PlatformInfo_const_PlatformInfoR(i.as_raw_PlatformInfo(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::PlatformInfo::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy_mut(mut i: core::PlatformInfo) -> core::PlatformInfo {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_PlatformInfo_PlatformInfo_PlatformInfoRR(i.as_raw_mut_PlatformInfo()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::PlatformInfo::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
}
impl Default for PlatformInfo {
#[inline]
/// Forwards to infallible Self::default()
fn default() -> Self {
Self::default()
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Program]
pub trait ProgramTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Program(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn ptr(&self) -> Result<*mut c_void> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Program_ptr_const(self.as_raw_Program(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Query device-specific program binary.
///
/// Returns RAW OpenCL executable binary without additional attachments.
/// ## See also
/// ProgramSource::fromBinary
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * binary:[out] output buffer
#[inline]
fn get_binary(&self, binary: &mut core::Vector<i8>) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Program_getBinary_const_vectorLcharGR(self.as_raw_Program(), binary.as_raw_mut_VectorOfi8(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn empty(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Program_empty_const(self.as_raw_Program(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn write(&self, buf: &mut String) -> Result<bool> {
string_arg_output_send!(via buf_via);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Program_write_const_StringR(self.as_raw_Program(), &mut buf_via, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
string_arg_output_receive!(buf_via => buf);
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn source(&self) -> Result<core::ProgramSource> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Program_source_const(self.as_raw_Program(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::ProgramSource::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_prefix(&self) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Program_getPrefix_const(self.as_raw_Program(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Program]
pub trait ProgramTrait: core::ProgramTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Program(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn create(&mut self, src: &core::ProgramSource, buildflags: &str, errmsg: &mut String) -> Result<bool> {
extern_container_arg!(buildflags);
string_arg_output_send!(via errmsg_via);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Program_create_const_ProgramSourceR_const_StringR_StringR(self.as_raw_mut_Program(), src.as_raw_ProgramSource(), buildflags.opencv_as_extern(), &mut errmsg_via, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
string_arg_output_receive!(errmsg_via => errmsg);
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn read(&mut self, buf: &str, buildflags: &str) -> Result<bool> {
extern_container_arg!(buf);
extern_container_arg!(buildflags);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Program_read_const_StringR_const_StringR(self.as_raw_mut_Program(), buf.opencv_as_extern(), buildflags.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
pub struct Program {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Program }
impl Drop for Program {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Program_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Program_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Program()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Program {}
impl core::ProgramTraitConst for Program {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Program(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::ProgramTrait for Program {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Program(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Program {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> core::Program {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Program_Program() };
let ret = unsafe { core::Program::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
pub fn new(src: &core::ProgramSource, buildflags: &str, errmsg: &mut String) -> Result<core::Program> {
extern_container_arg!(buildflags);
string_arg_output_send!(via errmsg_via);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Program_Program_const_ProgramSourceR_const_StringR_StringR(src.as_raw_ProgramSource(), buildflags.opencv_as_extern(), &mut errmsg_via, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Program::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
string_arg_output_receive!(errmsg_via => errmsg);
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy(prog: &core::Program) -> Result<core::Program> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Program_Program_const_ProgramR(prog.as_raw_Program(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Program::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy_mut(mut prog: core::Program) -> core::Program {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Program_Program_ProgramRR(prog.as_raw_mut_Program()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Program::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
pub fn get_prefix_build_flags(buildflags: &str) -> Result<String> {
extern_container_arg!(buildflags);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Program_getPrefix_const_StringR(buildflags.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl Default for Program {
#[inline]
/// Forwards to infallible Self::default()
fn default() -> Self {
Self::default()
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::ProgramSource]
pub trait ProgramSourceTraitConst {
fn as_raw_ProgramSource(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn source(&self) -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_ProgramSource_source_const(self.as_raw_ProgramSource(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn hash(&self) -> Result<core::ProgramSource_hash_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_ProgramSource_hash_const(self.as_raw_ProgramSource(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn empty(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_ProgramSource_empty_const(self.as_raw_ProgramSource(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::ProgramSource]
pub trait ProgramSourceTrait: core::ProgramSourceTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_ProgramSource(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
pub struct ProgramSource {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { ProgramSource }
impl Drop for ProgramSource {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_ProgramSource_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_ProgramSource_delete(self.as_raw_mut_ProgramSource()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for ProgramSource {}
impl core::ProgramSourceTraitConst for ProgramSource {
#[inline] fn as_raw_ProgramSource(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::ProgramSourceTrait for ProgramSource {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_ProgramSource(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl ProgramSource {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> core::ProgramSource {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_ProgramSource_ProgramSource() };
let ret = unsafe { core::ProgramSource::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
pub fn new(module: &str, name: &str, code_str: &str, code_hash: &str) -> Result<core::ProgramSource> {
extern_container_arg!(module);
extern_container_arg!(name);
extern_container_arg!(code_str);
extern_container_arg!(code_hash);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_ProgramSource_ProgramSource_const_StringR_const_StringR_const_StringR_const_StringR(module.opencv_as_extern(), name.opencv_as_extern(), code_str.opencv_as_extern(), code_hash.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::ProgramSource::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn from_str(prog: &str) -> Result<core::ProgramSource> {
extern_container_arg!(prog);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_ProgramSource_ProgramSource_const_StringR(prog.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::ProgramSource::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy(prog: &core::ProgramSource) -> Result<core::ProgramSource> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_ProgramSource_ProgramSource_const_ProgramSourceR(prog.as_raw_ProgramSource(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::ProgramSource::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy_mut(mut prog: core::ProgramSource) -> core::ProgramSource {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_ProgramSource_ProgramSource_ProgramSourceRR(prog.as_raw_mut_ProgramSource()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::ProgramSource::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// Describe OpenCL program binary.
/// Do not call clCreateProgramWithBinary() and/or clBuildProgram().
///
/// Caller should guarantee binary buffer lifetime greater than ProgramSource object (and any of its copies).
///
/// This kind of binary is not portable between platforms in general - it is specific to OpenCL vendor / device / driver version.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * module: name of program owner module
/// * name: unique name of program (module+name is used as key for OpenCL program caching)
/// * binary: buffer address. See buffer lifetime requirement in description.
/// * size: buffer size
/// * buildOptions: additional program-related build options passed to clBuildProgram()
/// ## Returns
/// created ProgramSource object
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * build_options: cv::String()
#[inline]
pub fn from_binary(module: &str, name: &str, binary: &u8, size: size_t, build_options: &str) -> Result<core::ProgramSource> {
extern_container_arg!(module);
extern_container_arg!(name);
extern_container_arg!(build_options);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_ProgramSource_fromBinary_const_StringR_const_StringR_const_unsigned_charX_const_size_t_const_StringR(module.opencv_as_extern(), name.opencv_as_extern(), binary, size, build_options.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::ProgramSource::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Describe OpenCL program in SPIR format.
/// Do not call clCreateProgramWithBinary() and/or clBuildProgram().
///
/// Supports SPIR 1.2 by default (pass '-spir-std=X.Y' in buildOptions to override this behavior)
///
/// Caller should guarantee binary buffer lifetime greater than ProgramSource object (and any of its copies).
///
/// Programs in this format are portable between OpenCL implementations with 'khr_spir' extension:
/// <https://www.khronos.org/registry/OpenCL/sdk/2.0/docs/man/xhtml/cl_khr_spir.html>
/// (but they are not portable between different platforms: 32-bit / 64-bit)
///
/// Note: these programs can't support vendor specific extensions, like 'cl_intel_subgroups'.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * module: name of program owner module
/// * name: unique name of program (module+name is used as key for OpenCL program caching)
/// * binary: buffer address. See buffer lifetime requirement in description.
/// * size: buffer size
/// * buildOptions: additional program-related build options passed to clBuildProgram()
/// (these options are added automatically: '-x spir' and '-spir-std=1.2')
/// ## Returns
/// created ProgramSource object.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * build_options: cv::String()
#[inline]
pub fn from_spir(module: &str, name: &str, binary: &u8, size: size_t, build_options: &str) -> Result<core::ProgramSource> {
extern_container_arg!(module);
extern_container_arg!(name);
extern_container_arg!(build_options);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_ProgramSource_fromSPIR_const_StringR_const_StringR_const_unsigned_charX_const_size_t_const_StringR(module.opencv_as_extern(), name.opencv_as_extern(), binary, size, build_options.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::ProgramSource::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl Default for ProgramSource {
#[inline]
/// Forwards to infallible Self::default()
fn default() -> Self {
Self::default()
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Queue]
pub trait QueueTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Queue(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn ptr(&self) -> Result<*mut c_void> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Queue_ptr_const(self.as_raw_Queue(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns OpenCL command queue with enable profiling mode support
#[inline]
fn get_profiling_queue(&self) -> Result<core::Queue> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Queue_getProfilingQueue_const(self.as_raw_Queue(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Queue::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn empty(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Queue_empty_const(self.as_raw_Queue(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Queue]
pub trait QueueTrait: core::QueueTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Queue(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * c: Context()
/// * d: Device()
#[inline]
fn create(&mut self, c: &core::Context, d: &core::Device) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Queue_create_const_ContextR_const_DeviceR(self.as_raw_mut_Queue(), c.as_raw_Context(), d.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn finish(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Queue_finish(self.as_raw_mut_Queue(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
pub struct Queue {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Queue }
impl Drop for Queue {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Queue_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Queue_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Queue()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Queue {}
impl core::QueueTraitConst for Queue {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Queue(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::QueueTrait for Queue {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Queue(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Queue {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> core::Queue {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Queue_Queue() };
let ret = unsafe { core::Queue::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * d: Device()
#[inline]
pub fn new(c: &core::Context, d: &core::Device) -> Result<core::Queue> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Queue_Queue_const_ContextR_const_DeviceR(c.as_raw_Context(), d.as_raw_Device(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Queue::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy(q: &core::Queue) -> Result<core::Queue> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Queue_Queue_const_QueueR(q.as_raw_Queue(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Queue::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy_mut(mut q: core::Queue) -> core::Queue {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Queue_Queue_QueueRR(q.as_raw_mut_Queue()) };
let ret = unsafe { core::Queue::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
pub fn get_default() -> Result<core::Queue> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Queue_getDefault(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Queue::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl Default for Queue {
#[inline]
/// Forwards to infallible Self::default()
fn default() -> Self {
Self::default()
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Timer]
pub trait TimerTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Timer(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn duration_ns(&self) -> Result<u64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Timer_durationNS_const(self.as_raw_Timer(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Timer]
pub trait TimerTrait: core::TimerTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Timer(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn start(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Timer_start(self.as_raw_mut_Timer(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn stop(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Timer_stop(self.as_raw_mut_Timer(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
pub struct Timer {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Timer }
impl Drop for Timer {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Timer_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Timer_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Timer()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Timer {}
impl core::TimerTraitConst for Timer {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Timer(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::TimerTrait for Timer {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Timer(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Timer {
#[inline]
pub fn new(q: &core::Queue) -> Result<core::Timer> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ocl_Timer_Timer_const_QueueR(q.as_raw_Queue(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Timer::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Arrays]
pub trait ArraysTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Arrays(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Binds all vertex arrays.
#[inline]
fn bind(&self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Arrays_bind_const(self.as_raw_Arrays(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the vertex count.
#[inline]
fn size(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Arrays_size_const(self.as_raw_Arrays(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn empty(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Arrays_empty_const(self.as_raw_Arrays(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Arrays]
pub trait ArraysTrait: core::ArraysTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Arrays(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Sets an array of vertex coordinates.
/// ## Parameters
/// * vertex: array with vertex coordinates, can be both host and device memory.
#[inline]
fn set_vertex_array(&mut self, vertex: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(vertex);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Arrays_setVertexArray_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_Arrays(), vertex.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Resets vertex coordinates.
#[inline]
fn reset_vertex_array(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Arrays_resetVertexArray(self.as_raw_mut_Arrays(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets an array of vertex colors.
/// ## Parameters
/// * color: array with vertex colors, can be both host and device memory.
#[inline]
fn set_color_array(&mut self, color: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(color);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Arrays_setColorArray_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_Arrays(), color.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Resets vertex colors.
#[inline]
fn reset_color_array(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Arrays_resetColorArray(self.as_raw_mut_Arrays(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets an array of vertex normals.
/// ## Parameters
/// * normal: array with vertex normals, can be both host and device memory.
#[inline]
fn set_normal_array(&mut self, normal: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(normal);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Arrays_setNormalArray_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_Arrays(), normal.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Resets vertex normals.
#[inline]
fn reset_normal_array(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Arrays_resetNormalArray(self.as_raw_mut_Arrays(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets an array of vertex texture coordinates.
/// ## Parameters
/// * texCoord: array with vertex texture coordinates, can be both host and device memory.
#[inline]
fn set_tex_coord_array(&mut self, tex_coord: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(tex_coord);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Arrays_setTexCoordArray_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_Arrays(), tex_coord.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Resets vertex texture coordinates.
#[inline]
fn reset_tex_coord_array(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Arrays_resetTexCoordArray(self.as_raw_mut_Arrays(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Releases all inner buffers.
#[inline]
fn release(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Arrays_release(self.as_raw_mut_Arrays(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets auto release mode all inner buffers.
/// ## Parameters
/// * flag: Auto release mode.
#[inline]
fn set_auto_release(&mut self, flag: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Arrays_setAutoRelease_bool(self.as_raw_mut_Arrays(), flag, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Wrapper for OpenGL Client-Side Vertex arrays.
///
/// ogl::Arrays stores vertex data in ogl::Buffer objects.
pub struct Arrays {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Arrays }
impl Drop for Arrays {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Arrays_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Arrays_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Arrays()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Arrays {}
impl core::ArraysTraitConst for Arrays {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Arrays(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::ArraysTrait for Arrays {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Arrays(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Arrays {
/// Default constructor
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::Arrays> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Arrays_Arrays(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Arrays::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Buffer]
pub trait BufferTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Buffer(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Copies from OpenGL buffer to host/device memory or another OpenGL buffer object.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * arr: Destination array (host or device memory, can be Mat , cuda::GpuMat , std::vector or
/// ogl::Buffer ).
#[inline]
fn copy_to(&self, arr: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(arr);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_copyTo_const_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_Buffer(), arr.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Copies from OpenGL buffer to host/device memory or another OpenGL buffer object.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * arr: Destination array (host or device memory, can be Mat , cuda::GpuMat , std::vector or
/// ogl::Buffer ).
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
#[inline]
fn copy_to_1(&self, arr: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, stream: &mut core::Stream) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(arr);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_copyTo_const_const__OutputArrayR_StreamR(self.as_raw_Buffer(), arr.as_raw__OutputArray(), stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates a full copy of the buffer object and the underlying data.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * target: Buffer usage for destination buffer.
/// * autoRelease: Auto release mode for destination buffer.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * target: ARRAY_BUFFER
/// * auto_release: false
#[inline]
fn clone(&self, target: core::Buffer_Target, auto_release: bool) -> Result<core::Buffer> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_clone_const_Target_bool(self.as_raw_Buffer(), target, auto_release, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Buffer::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Binds OpenGL buffer to the specified buffer binding point.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * target: Binding point. See cv::ogl::Buffer::Target .
#[inline]
fn bind(&self, target: core::Buffer_Target) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_bind_const_Target(self.as_raw_Buffer(), target, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn rows(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_rows_const(self.as_raw_Buffer(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn cols(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_cols_const(self.as_raw_Buffer(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn size(&self) -> Result<core::Size> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_size_const(self.as_raw_Buffer(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn empty(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_empty_const(self.as_raw_Buffer(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn typ(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_type_const(self.as_raw_Buffer(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn depth(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_depth_const(self.as_raw_Buffer(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn channels(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_channels_const(self.as_raw_Buffer(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn elem_size(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_elemSize_const(self.as_raw_Buffer(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn elem_size1(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_elemSize1_const(self.as_raw_Buffer(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// get OpenGL opject id
#[inline]
fn buf_id(&self) -> Result<u32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_bufId_const(self.as_raw_Buffer(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Buffer]
pub trait BufferTrait: core::BufferTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Buffer(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Allocates memory for ogl::Buffer object.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * arows: Number of rows in a 2D array.
/// * acols: Number of columns in a 2D array.
/// * atype: Array type ( CV_8UC1, ..., CV_64FC4 ). See Mat for details.
/// * target: Buffer usage. See cv::ogl::Buffer::Target .
/// * autoRelease: Auto release mode (if true, release will be called in object's destructor).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * target: ARRAY_BUFFER
/// * auto_release: false
#[inline]
fn create(&mut self, arows: i32, acols: i32, atype: i32, target: core::Buffer_Target, auto_release: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_create_int_int_int_Target_bool(self.as_raw_mut_Buffer(), arows, acols, atype, target, auto_release, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Allocates memory for ogl::Buffer object.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * arows: Number of rows in a 2D array.
/// * acols: Number of columns in a 2D array.
/// * atype: Array type ( CV_8UC1, ..., CV_64FC4 ). See Mat for details.
/// * target: Buffer usage. See cv::ogl::Buffer::Target .
/// * autoRelease: Auto release mode (if true, release will be called in object's destructor).
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * asize: 2D array size.
/// * atype: Array type ( CV_8UC1, ..., CV_64FC4 ). See Mat for details.
/// * target: Buffer usage. See cv::ogl::Buffer::Target .
/// * autoRelease: Auto release mode (if true, release will be called in object's destructor).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * target: ARRAY_BUFFER
/// * auto_release: false
#[inline]
fn create_size(&mut self, asize: core::Size, atype: i32, target: core::Buffer_Target, auto_release: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_create_Size_int_Target_bool(self.as_raw_mut_Buffer(), asize.opencv_as_extern(), atype, target, auto_release, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Decrements the reference counter and destroys the buffer object if needed.
///
/// The function will call setAutoRelease(true) .
#[inline]
fn release(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_release(self.as_raw_mut_Buffer(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets auto release mode.
///
/// The lifetime of the OpenGL object is tied to the lifetime of the context. If OpenGL context was
/// bound to a window it could be released at any time (user can close a window). If object's destructor
/// is called after destruction of the context it will cause an error. Thus ogl::Buffer doesn't destroy
/// OpenGL object in destructor by default (all OpenGL resources will be released with OpenGL context).
/// This function can force ogl::Buffer destructor to destroy OpenGL object.
/// ## Parameters
/// * flag: Auto release mode (if true, release will be called in object's destructor).
#[inline]
fn set_auto_release(&mut self, flag: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_setAutoRelease_bool(self.as_raw_mut_Buffer(), flag, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Copies from host/device memory to OpenGL buffer.
/// ## Parameters
/// * arr: Input array (host or device memory, it can be Mat , cuda::GpuMat or std::vector ).
/// * target: Buffer usage. See cv::ogl::Buffer::Target .
/// * autoRelease: Auto release mode (if true, release will be called in object's destructor).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * target: ARRAY_BUFFER
/// * auto_release: false
#[inline]
fn copy_from(&mut self, arr: &dyn core::ToInputArray, target: core::Buffer_Target, auto_release: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(arr);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_copyFrom_const__InputArrayR_Target_bool(self.as_raw_mut_Buffer(), arr.as_raw__InputArray(), target, auto_release, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Copies from host/device memory to OpenGL buffer.
/// ## Parameters
/// * arr: Input array (host or device memory, it can be Mat , cuda::GpuMat or std::vector ).
/// * target: Buffer usage. See cv::ogl::Buffer::Target .
/// * autoRelease: Auto release mode (if true, release will be called in object's destructor).
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * target: ARRAY_BUFFER
/// * auto_release: false
#[inline]
fn copy_from_1(&mut self, arr: &dyn core::ToInputArray, stream: &mut core::Stream, target: core::Buffer_Target, auto_release: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(arr);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_copyFrom_const__InputArrayR_StreamR_Target_bool(self.as_raw_mut_Buffer(), arr.as_raw__InputArray(), stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), target, auto_release, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Maps OpenGL buffer to host memory.
///
/// mapHost maps to the client's address space the entire data store of the buffer object. The data can
/// then be directly read and/or written relative to the returned pointer, depending on the specified
/// access policy.
///
/// A mapped data store must be unmapped with ogl::Buffer::unmapHost before its buffer object is used.
///
/// This operation can lead to memory transfers between host and device.
///
/// Only one buffer object can be mapped at a time.
/// ## Parameters
/// * access: Access policy, indicating whether it will be possible to read from, write to, or both
/// read from and write to the buffer object's mapped data store. The symbolic constant must be
/// ogl::Buffer::READ_ONLY , ogl::Buffer::WRITE_ONLY or ogl::Buffer::READ_WRITE .
#[inline]
fn map_host(&mut self, access: core::Buffer_Access) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_mapHost_Access(self.as_raw_mut_Buffer(), access, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Unmaps OpenGL buffer.
#[inline]
fn unmap_host(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_unmapHost(self.as_raw_mut_Buffer(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// map to device memory (blocking)
#[inline]
fn map_device(&mut self) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_mapDevice(self.as_raw_mut_Buffer(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn unmap_device(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_unmapDevice(self.as_raw_mut_Buffer(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Maps OpenGL buffer to CUDA device memory.
///
/// This operation doesn't copy data. Several buffer objects can be mapped to CUDA memory at a time.
///
/// A mapped data store must be unmapped with ogl::Buffer::unmapDevice before its buffer object is used.
#[inline]
fn map_device_1(&mut self, stream: &mut core::Stream) -> Result<core::GpuMat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_mapDevice_StreamR(self.as_raw_mut_Buffer(), stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::GpuMat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Unmaps OpenGL buffer.
#[inline]
fn unmap_device_1(&mut self, stream: &mut core::Stream) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_unmapDevice_StreamR(self.as_raw_mut_Buffer(), stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Smart pointer for OpenGL buffer object with reference counting.
///
/// Buffer Objects are OpenGL objects that store an array of unformatted memory allocated by the OpenGL
/// context. These can be used to store vertex data, pixel data retrieved from images or the
/// framebuffer, and a variety of other things.
///
/// ogl::Buffer has interface similar with Mat interface and represents 2D array memory.
///
/// ogl::Buffer supports memory transfers between host and device and also can be mapped to CUDA memory.
pub struct Buffer {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Buffer }
impl Drop for Buffer {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Buffer_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Buffer_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Buffer()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Buffer {}
impl core::BufferTraitConst for Buffer {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Buffer(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::BufferTrait for Buffer {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Buffer(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Buffer {
/// The constructors.
///
/// Creates empty ogl::Buffer object, creates ogl::Buffer object from existed buffer ( abufId
/// parameter), allocates memory for ogl::Buffer object or copies from host/device memory.
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::Buffer> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_Buffer(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Buffer::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// The constructors.
///
/// Creates empty ogl::Buffer object, creates ogl::Buffer object from existed buffer ( abufId
/// parameter), allocates memory for ogl::Buffer object or copies from host/device memory.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * arows: Number of rows in a 2D array.
/// * acols: Number of columns in a 2D array.
/// * atype: Array type ( CV_8UC1, ..., CV_64FC4 ). See Mat for details.
/// * abufId: Buffer object name.
/// * autoRelease: Auto release mode (if true, release will be called in object's destructor).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * auto_release: false
#[inline]
pub fn new(arows: i32, acols: i32, atype: i32, abuf_id: u32, auto_release: bool) -> Result<core::Buffer> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_Buffer_int_int_int_unsigned_int_bool(arows, acols, atype, abuf_id, auto_release, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Buffer::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// The constructors.
///
/// Creates empty ogl::Buffer object, creates ogl::Buffer object from existed buffer ( abufId
/// parameter), allocates memory for ogl::Buffer object or copies from host/device memory.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * asize: 2D array size.
/// * atype: Array type ( CV_8UC1, ..., CV_64FC4 ). See Mat for details.
/// * abufId: Buffer object name.
/// * autoRelease: Auto release mode (if true, release will be called in object's destructor).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * auto_release: false
#[inline]
pub fn new_1(asize: core::Size, atype: i32, abuf_id: u32, auto_release: bool) -> Result<core::Buffer> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_Buffer_Size_int_unsigned_int_bool(asize.opencv_as_extern(), atype, abuf_id, auto_release, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Buffer::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// The constructors.
///
/// Creates empty ogl::Buffer object, creates ogl::Buffer object from existed buffer ( abufId
/// parameter), allocates memory for ogl::Buffer object or copies from host/device memory.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * arows: Number of rows in a 2D array.
/// * acols: Number of columns in a 2D array.
/// * atype: Array type ( CV_8UC1, ..., CV_64FC4 ). See Mat for details.
/// * target: Buffer usage. See cv::ogl::Buffer::Target .
/// * autoRelease: Auto release mode (if true, release will be called in object's destructor).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * target: ARRAY_BUFFER
/// * auto_release: false
#[inline]
pub fn new_2(arows: i32, acols: i32, atype: i32, target: core::Buffer_Target, auto_release: bool) -> Result<core::Buffer> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_Buffer_int_int_int_Target_bool(arows, acols, atype, target, auto_release, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Buffer::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// The constructors.
///
/// Creates empty ogl::Buffer object, creates ogl::Buffer object from existed buffer ( abufId
/// parameter), allocates memory for ogl::Buffer object or copies from host/device memory.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * asize: 2D array size.
/// * atype: Array type ( CV_8UC1, ..., CV_64FC4 ). See Mat for details.
/// * target: Buffer usage. See cv::ogl::Buffer::Target .
/// * autoRelease: Auto release mode (if true, release will be called in object's destructor).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * target: ARRAY_BUFFER
/// * auto_release: false
#[inline]
pub fn new_3(asize: core::Size, atype: i32, target: core::Buffer_Target, auto_release: bool) -> Result<core::Buffer> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_Buffer_Size_int_Target_bool(asize.opencv_as_extern(), atype, target, auto_release, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Buffer::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// The constructors.
///
/// Creates empty ogl::Buffer object, creates ogl::Buffer object from existed buffer ( abufId
/// parameter), allocates memory for ogl::Buffer object or copies from host/device memory.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * arr: Input array (host or device memory, it can be Mat , cuda::GpuMat or std::vector ).
/// * target: Buffer usage. See cv::ogl::Buffer::Target .
/// * autoRelease: Auto release mode (if true, release will be called in object's destructor).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * target: ARRAY_BUFFER
/// * auto_release: false
#[inline]
pub fn new_4(arr: &dyn core::ToInputArray, target: core::Buffer_Target, auto_release: bool) -> Result<core::Buffer> {
extern_container_arg!(arr);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_Buffer_const__InputArrayR_Target_bool(arr.as_raw__InputArray(), target, auto_release, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Buffer::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Unbind any buffers from the specified binding point.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * target: Binding point. See cv::ogl::Buffer::Target .
#[inline]
pub fn unbind(target: core::Buffer_Target) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Buffer_unbind_Target(target, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::Texture2D]
pub trait Texture2DTraitConst {
fn as_raw_Texture2D(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Copies from OpenGL texture to host/device memory or another OpenGL texture object.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * arr: Destination array (host or device memory, can be Mat , cuda::GpuMat , ogl::Buffer or
/// ogl::Texture2D ).
/// * ddepth: Destination depth.
/// * autoRelease: Auto release mode for destination buffer (if arr is OpenGL buffer or texture).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * ddepth: CV_32F
/// * auto_release: false
#[inline]
fn copy_to(&self, arr: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, ddepth: i32, auto_release: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(arr);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Texture2D_copyTo_const_const__OutputArrayR_int_bool(self.as_raw_Texture2D(), arr.as_raw__OutputArray(), ddepth, auto_release, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Binds texture to current active texture unit for GL_TEXTURE_2D target.
#[inline]
fn bind(&self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Texture2D_bind_const(self.as_raw_Texture2D(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn rows(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Texture2D_rows_const(self.as_raw_Texture2D(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn cols(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Texture2D_cols_const(self.as_raw_Texture2D(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn size(&self) -> Result<core::Size> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Texture2D_size_const(self.as_raw_Texture2D(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn empty(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Texture2D_empty_const(self.as_raw_Texture2D(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn format(&self) -> Result<core::Texture2D_Format> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Texture2D_format_const(self.as_raw_Texture2D(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// get OpenGL opject id
#[inline]
fn tex_id(&self) -> Result<u32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Texture2D_texId_const(self.as_raw_Texture2D(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::Texture2D]
pub trait Texture2DTrait: core::Texture2DTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_Texture2D(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Allocates memory for ogl::Texture2D object.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * arows: Number of rows.
/// * acols: Number of columns.
/// * aformat: Image format. See cv::ogl::Texture2D::Format .
/// * autoRelease: Auto release mode (if true, release will be called in object's destructor).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * auto_release: false
#[inline]
fn create(&mut self, arows: i32, acols: i32, aformat: core::Texture2D_Format, auto_release: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Texture2D_create_int_int_Format_bool(self.as_raw_mut_Texture2D(), arows, acols, aformat, auto_release, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Allocates memory for ogl::Texture2D object.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * arows: Number of rows.
/// * acols: Number of columns.
/// * aformat: Image format. See cv::ogl::Texture2D::Format .
/// * autoRelease: Auto release mode (if true, release will be called in object's destructor).
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// * asize: 2D array size.
/// * aformat: Image format. See cv::ogl::Texture2D::Format .
/// * autoRelease: Auto release mode (if true, release will be called in object's destructor).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * auto_release: false
#[inline]
fn create_1(&mut self, asize: core::Size, aformat: core::Texture2D_Format, auto_release: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Texture2D_create_Size_Format_bool(self.as_raw_mut_Texture2D(), asize.opencv_as_extern(), aformat, auto_release, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Decrements the reference counter and destroys the texture object if needed.
///
/// The function will call setAutoRelease(true) .
#[inline]
fn release(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Texture2D_release(self.as_raw_mut_Texture2D(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets auto release mode.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * flag: Auto release mode (if true, release will be called in object's destructor).
///
/// The lifetime of the OpenGL object is tied to the lifetime of the context. If OpenGL context was
/// bound to a window it could be released at any time (user can close a window). If object's destructor
/// is called after destruction of the context it will cause an error. Thus ogl::Texture2D doesn't
/// destroy OpenGL object in destructor by default (all OpenGL resources will be released with OpenGL
/// context). This function can force ogl::Texture2D destructor to destroy OpenGL object.
#[inline]
fn set_auto_release(&mut self, flag: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Texture2D_setAutoRelease_bool(self.as_raw_mut_Texture2D(), flag, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Copies from host/device memory to OpenGL texture.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * arr: Input array (host or device memory, it can be Mat , cuda::GpuMat or ogl::Buffer ).
/// * autoRelease: Auto release mode (if true, release will be called in object's destructor).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * auto_release: false
#[inline]
fn copy_from(&mut self, arr: &dyn core::ToInputArray, auto_release: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(arr);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Texture2D_copyFrom_const__InputArrayR_bool(self.as_raw_mut_Texture2D(), arr.as_raw__InputArray(), auto_release, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Smart pointer for OpenGL 2D texture memory with reference counting.
pub struct Texture2D {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { Texture2D }
impl Drop for Texture2D {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_Texture2D_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_Texture2D_delete(self.as_raw_mut_Texture2D()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for Texture2D {}
impl core::Texture2DTraitConst for Texture2D {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Texture2D(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::Texture2DTrait for Texture2D {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Texture2D(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl Texture2D {
/// The constructors.
///
/// Creates empty ogl::Texture2D object, allocates memory for ogl::Texture2D object or copies from
/// host/device memory.
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<core::Texture2D> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Texture2D_Texture2D(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Texture2D::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// The constructors.
///
/// Creates empty ogl::Texture2D object, allocates memory for ogl::Texture2D object or copies from
/// host/device memory.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * auto_release: false
#[inline]
pub fn new(arows: i32, acols: i32, aformat: core::Texture2D_Format, atex_id: u32, auto_release: bool) -> Result<core::Texture2D> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Texture2D_Texture2D_int_int_Format_unsigned_int_bool(arows, acols, aformat, atex_id, auto_release, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Texture2D::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// The constructors.
///
/// Creates empty ogl::Texture2D object, allocates memory for ogl::Texture2D object or copies from
/// host/device memory.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * auto_release: false
#[inline]
pub fn new_1(asize: core::Size, aformat: core::Texture2D_Format, atex_id: u32, auto_release: bool) -> Result<core::Texture2D> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Texture2D_Texture2D_Size_Format_unsigned_int_bool(asize.opencv_as_extern(), aformat, atex_id, auto_release, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Texture2D::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// The constructors.
///
/// Creates empty ogl::Texture2D object, allocates memory for ogl::Texture2D object or copies from
/// host/device memory.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * arows: Number of rows.
/// * acols: Number of columns.
/// * aformat: Image format. See cv::ogl::Texture2D::Format .
/// * autoRelease: Auto release mode (if true, release will be called in object's destructor).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * auto_release: false
#[inline]
pub fn new_2(arows: i32, acols: i32, aformat: core::Texture2D_Format, auto_release: bool) -> Result<core::Texture2D> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Texture2D_Texture2D_int_int_Format_bool(arows, acols, aformat, auto_release, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Texture2D::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// The constructors.
///
/// Creates empty ogl::Texture2D object, allocates memory for ogl::Texture2D object or copies from
/// host/device memory.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * asize: 2D array size.
/// * aformat: Image format. See cv::ogl::Texture2D::Format .
/// * autoRelease: Auto release mode (if true, release will be called in object's destructor).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * auto_release: false
#[inline]
pub fn new_3(asize: core::Size, aformat: core::Texture2D_Format, auto_release: bool) -> Result<core::Texture2D> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Texture2D_Texture2D_Size_Format_bool(asize.opencv_as_extern(), aformat, auto_release, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Texture2D::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// The constructors.
///
/// Creates empty ogl::Texture2D object, allocates memory for ogl::Texture2D object or copies from
/// host/device memory.
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * arr: Input array (host or device memory, it can be Mat , cuda::GpuMat or ogl::Buffer ).
/// * autoRelease: Auto release mode (if true, release will be called in object's destructor).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * auto_release: false
#[inline]
pub fn new_4(arr: &dyn core::ToInputArray, auto_release: bool) -> Result<core::Texture2D> {
extern_container_arg!(arr);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ogl_Texture2D_Texture2D_const__InputArrayR_bool(arr.as_raw__InputArray(), auto_release, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Texture2D::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)]
pub struct ClassWithKeywordProperties {
pub lambda: i32,
pub except: i32,
}
opencv_type_simple! { core::ClassWithKeywordProperties }
impl ClassWithKeywordProperties {
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * lambda_arg: 24
/// * except_arg: 42
#[inline]
pub fn new(lambda_arg: i32, except_arg: i32) -> Result<core::ClassWithKeywordProperties> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_ClassWithKeywordProperties_ClassWithKeywordProperties_int_int(lambda_arg, except_arg, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::LogTag]
pub trait LogTagTraitConst {
fn as_raw_LogTag(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn name(&self) -> String {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_utils_logging_LogTag_getPropName_const(self.as_raw_LogTag()) };
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn level(&self) -> core::LogLevel {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_logging_LogTag_getPropLevel_const(self.as_raw_LogTag(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
ret
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::LogTag]
pub trait LogTagTrait: core::LogTagTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_LogTag(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_level(&mut self, val: core::LogLevel) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_utils_logging_LogTag_setPropLevel_LogLevel(self.as_raw_mut_LogTag(), val) };
ret
}
}
pub struct LogTag {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { LogTag }
impl Drop for LogTag {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_LogTag_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_LogTag_delete(self.as_raw_mut_LogTag()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for LogTag {}
impl core::LogTagTraitConst for LogTag {
#[inline] fn as_raw_LogTag(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::LogTagTrait for LogTag {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_LogTag(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl LogTag {
#[inline]
pub fn new(_name: &str, _level: core::LogLevel) -> Result<core::LogTag> {
extern_container_arg!(_name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_logging_LogTag_LogTag_const_charX_LogLevel(_name.opencv_as_extern(), _level, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::LogTag::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [core::OriginalClassName]
pub trait OriginalClassNameTraitConst {
fn as_raw_OriginalClassName(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn get_int_param(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_nested_OriginalClassName_getIntParam_const(self.as_raw_OriginalClassName(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_float_param(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_nested_OriginalClassName_getFloatParam_const(self.as_raw_OriginalClassName(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [core::OriginalClassName]
pub trait OriginalClassNameTrait: core::OriginalClassNameTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_OriginalClassName(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
pub struct OriginalClassName {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { OriginalClassName }
impl Drop for OriginalClassName {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_OriginalClassName_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_OriginalClassName_delete(self.as_raw_mut_OriginalClassName()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for OriginalClassName {}
impl core::OriginalClassNameTraitConst for OriginalClassName {
#[inline] fn as_raw_OriginalClassName(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::OriginalClassNameTrait for OriginalClassName {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_OriginalClassName(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl OriginalClassName {
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * params: OriginalClassName::Params()
#[inline]
pub fn new(params: core::OriginalClassName_Params) -> Result<core::OriginalClassName> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_nested_OriginalClassName_OriginalClassName_const_ParamsR(¶ms, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::OriginalClassName::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn original_name() -> Result<String> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_nested_OriginalClassName_originalName(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { String::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * params: OriginalClassName::Params()
#[inline]
pub fn create(params: core::OriginalClassName_Params) -> Result<core::Ptr<core::OriginalClassName>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_nested_OriginalClassName_create_const_ParamsR(¶ms, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<core::OriginalClassName>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)]
pub struct OriginalClassName_Params {
pub int_value: i32,
pub float_value: f32,
}
opencv_type_simple! { core::OriginalClassName_Params }
impl OriginalClassName_Params {
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * int_param: 123
/// * float_param: 3.5f
#[inline]
pub fn new(int_param: i32, float_param: f32) -> Result<core::OriginalClassName_Params> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_utils_nested_OriginalClassName_Params_Params_int_float(int_param, float_param, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
pub use crate::manual::core::*;