#![allow(
unused_parens,
clippy::excessive_precision,
clippy::missing_safety_doc,
clippy::should_implement_trait,
clippy::too_many_arguments,
clippy::unused_unit,
clippy::let_unit_value,
clippy::derive_partial_eq_without_eq,
)]
//! # Optical Flow Algorithms
//!
//! Dense optical flow algorithms compute motion for each point:
//!
//! - cv::optflow::calcOpticalFlowSF
//! - cv::optflow::createOptFlow_DeepFlow
//!
//! Motion templates is alternative technique for detecting motion and computing its direction.
//! See samples/motempl.py.
//!
//! - cv::motempl::updateMotionHistory
//! - cv::motempl::calcMotionGradient
//! - cv::motempl::calcGlobalOrientation
//! - cv::motempl::segmentMotion
//!
//! Functions reading and writing .flo files in "Middlebury" format, see: <http://vision.middlebury.edu/flow/code/flow-code/README.txt>
//!
//! - cv::optflow::readOpticalFlow
//! - cv::optflow::writeOpticalFlow
use crate::{mod_prelude::*, core, sys, types};
pub mod prelude {
pub use { super::PCAPriorTraitConst, super::PCAPriorTrait, super::OpticalFlowPCAFlowTraitConst, super::OpticalFlowPCAFlowTrait, super::GPCPatchDescriptorTraitConst, super::GPCPatchDescriptorTrait, super::GPCPatchSampleTraitConst, super::GPCPatchSampleTrait, super::GPCTrainingSamplesTraitConst, super::GPCTrainingSamplesTrait, super::GPCTreeTraitConst, super::GPCTreeTrait, super::GPCDetailsTraitConst, super::GPCDetailsTrait, super::RLOFOpticalFlowParameterTraitConst, super::RLOFOpticalFlowParameterTrait, super::DenseRLOFOpticalFlowConst, super::DenseRLOFOpticalFlow, super::SparseRLOFOpticalFlowConst, super::SparseRLOFOpticalFlow, super::DualTVL1OpticalFlowConst, super::DualTVL1OpticalFlow };
}
/// Better quality but slow
pub const GPC_DESCRIPTOR_DCT: i32 = 0;
/// Worse quality but much faster
pub const GPC_DESCRIPTOR_WHT: i32 = 1;
/// < Edge-preserving interpolation using ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator, see [Revaud2015](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Revaud2015),Geistert2016.
pub const INTERP_EPIC: i32 = 1;
/// < Fast geodesic interpolation, see [Geistert2016](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Geistert2016)
pub const INTERP_GEO: i32 = 0;
/// < SLIC based robust interpolation using ximgproc::RICInterpolator, see [Hu2017](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Hu2017).
pub const INTERP_RIC: i32 = 2;
/// < Apply a adaptive support region obtained by cross-based segmentation
/// as described in [Senst2014](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2014)
pub const SR_CROSS: i32 = 1;
/// < Apply a constant support region
pub const SR_FIXED: i32 = 0;
/// < Apply optimized iterative refinement based bilinear equation solutions
/// as described in [Senst2013](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2013)
pub const ST_BILINEAR: i32 = 1;
/// < Apply standard iterative refinement
pub const ST_STANDART: i32 = 0;
/// Descriptor types for the Global Patch Collider.
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum GPCDescType {
/// Better quality but slow
GPC_DESCRIPTOR_DCT = 0,
/// Worse quality but much faster
GPC_DESCRIPTOR_WHT = 1,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::optflow::GPCDescType }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum InterpolationType {
/// < Fast geodesic interpolation, see [Geistert2016](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Geistert2016)
INTERP_GEO = 0,
/// < Edge-preserving interpolation using ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator, see [Revaud2015](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Revaud2015),Geistert2016.
INTERP_EPIC = 1,
/// < SLIC based robust interpolation using ximgproc::RICInterpolator, see [Hu2017](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Hu2017).
INTERP_RIC = 2,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::optflow::InterpolationType }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum SolverType {
/// < Apply standard iterative refinement
ST_STANDART = 0,
/// < Apply optimized iterative refinement based bilinear equation solutions
/// as described in [Senst2013](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2013)
ST_BILINEAR = 1,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::optflow::SolverType }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum SupportRegionType {
/// < Apply a constant support region
SR_FIXED = 0,
/// < Apply a adaptive support region obtained by cross-based segmentation
/// as described in [Senst2014](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2014)
SR_CROSS = 1,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::optflow::SupportRegionType }
/// Calculates a global motion orientation in a selected region.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * orientation: Motion gradient orientation image calculated by the function calcMotionGradient
/// * mask: Mask image. It may be a conjunction of a valid gradient mask, also calculated by
/// calcMotionGradient , and the mask of a region whose direction needs to be calculated.
/// * mhi: Motion history image calculated by updateMotionHistory .
/// * timestamp: Timestamp passed to updateMotionHistory .
/// * duration: Maximum duration of a motion track in milliseconds, passed to updateMotionHistory
///
/// The function calculates an average motion direction in the selected region and returns the angle
/// between 0 degrees and 360 degrees. The average direction is computed from the weighted orientation
/// histogram, where a recent motion has a larger weight and the motion occurred in the past has a
/// smaller weight, as recorded in mhi .
#[inline]
pub fn calc_global_orientation(orientation: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mhi: &dyn core::ToInputArray, timestamp: f64, duration: f64) -> Result<f64> {
extern_container_arg!(orientation);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
extern_container_arg!(mhi);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_motempl_calcGlobalOrientation_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_double_double(orientation.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), mhi.as_raw__InputArray(), timestamp, duration, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates a gradient orientation of a motion history image.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * mhi: Motion history single-channel floating-point image.
/// * mask: Output mask image that has the type CV_8UC1 and the same size as mhi . Its non-zero
/// elements mark pixels where the motion gradient data is correct.
/// * orientation: Output motion gradient orientation image that has the same type and the same
/// size as mhi . Each pixel of the image is a motion orientation, from 0 to 360 degrees.
/// * delta1: Minimal (or maximal) allowed difference between mhi values within a pixel
/// neighborhood.
/// * delta2: Maximal (or minimal) allowed difference between mhi values within a pixel
/// neighborhood. That is, the function finds the minimum (  ) and maximum (  ) mhi
/// values over 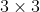 neighborhood of each pixel and marks the motion orientation at 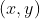
/// as valid only if
/// 
/// * apertureSize: Aperture size of the Sobel operator.
///
/// The function calculates a gradient orientation at each pixel 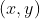 as:
///
/// 
///
/// In fact, fastAtan2 and phase are used so that the computed angle is measured in degrees and covers
/// the full range 0..360. Also, the mask is filled to indicate pixels where the computed angle is
/// valid.
///
///
/// Note:
/// * (Python) An example on how to perform a motion template technique can be found at
/// opencv_source_code/samples/python2/motempl.py
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * aperture_size: 3
#[inline]
pub fn calc_motion_gradient(mhi: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mask: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, orientation: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, delta1: f64, delta2: f64, aperture_size: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(mhi);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
extern_container_arg!(orientation);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_motempl_calcMotionGradient_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_double_int(mhi.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__OutputArray(), orientation.as_raw__OutputArray(), delta1, delta2, aperture_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Splits a motion history image into a few parts corresponding to separate independent motions (for
/// example, left hand, right hand).
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * mhi: Motion history image.
/// * segmask: Image where the found mask should be stored, single-channel, 32-bit floating-point.
/// * boundingRects: Vector containing ROIs of motion connected components.
/// * timestamp: Current time in milliseconds or other units.
/// * segThresh: Segmentation threshold that is recommended to be equal to the interval between
/// motion history "steps" or greater.
///
/// The function finds all of the motion segments and marks them in segmask with individual values
/// (1,2,...). It also computes a vector with ROIs of motion connected components. After that the motion
/// direction for every component can be calculated with calcGlobalOrientation using the extracted mask
/// of the particular component.
#[inline]
pub fn segment_motion(mhi: &dyn core::ToInputArray, segmask: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, bounding_rects: &mut core::Vector<core::Rect>, timestamp: f64, seg_thresh: f64) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(mhi);
extern_container_arg!(segmask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_motempl_segmentMotion_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_vectorLRectGR_double_double(mhi.as_raw__InputArray(), segmask.as_raw__OutputArray(), bounding_rects.as_raw_mut_VectorOfRect(), timestamp, seg_thresh, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Updates the motion history image by a moving silhouette.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * silhouette: Silhouette mask that has non-zero pixels where the motion occurs.
/// * mhi: Motion history image that is updated by the function (single-channel, 32-bit
/// floating-point).
/// * timestamp: Current time in milliseconds or other units.
/// * duration: Maximal duration of the motion track in the same units as timestamp .
///
/// The function updates the motion history image as follows:
///
/// 
///
/// That is, MHI pixels where the motion occurs are set to the current timestamp , while the pixels
/// where the motion happened last time a long time ago are cleared.
///
/// The function, together with calcMotionGradient and calcGlobalOrientation , implements a motion
/// templates technique described in [Davis97](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Davis97) and [Bradski00](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Bradski00) .
#[inline]
pub fn update_motion_history(silhouette: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mhi: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, timestamp: f64, duration: f64) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(silhouette);
extern_container_arg!(mhi);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_motempl_updateMotionHistory_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_double_double(silhouette.as_raw__InputArray(), mhi.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), timestamp, duration, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Fast dense optical flow computation based on robust local optical flow (RLOF) algorithms and sparse-to-dense interpolation scheme.
///
/// The RLOF is a fast local optical flow approach described in [Senst2012](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2012) [Senst2013](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2013) [Senst2014](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2014)
/// and [Senst2016](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2016) similar to the pyramidal iterative Lucas-Kanade method as
/// proposed by [Bouguet00](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Bouguet00). More details and experiments can be found in the following thesis [Senst2019](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2019).
/// The implementation is derived from optflow::calcOpticalFlowPyrLK().
///
/// The sparse-to-dense interpolation scheme allows for fast computation of dense optical flow using RLOF (see [Geistert2016](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Geistert2016)).
/// For this scheme the following steps are applied:
/// -# motion vector seeded at a regular sampled grid are computed. The sparsity of this grid can be configured with setGridStep
/// -# (optinally) errornous motion vectors are filter based on the forward backward confidence. The threshold can be configured
/// with setForwardBackward. The filter is only applied if the threshold >0 but than the runtime is doubled due to the estimation
/// of the backward flow.
/// -# Vector field interpolation is applied to the motion vector set to obtain a dense vector field.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * I0: first 8-bit input image. If The cross-based RLOF is used (by selecting optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter::supportRegionType
/// = SupportRegionType::SR_CROSS) image has to be a 8-bit 3 channel image.
/// * I1: second 8-bit input image. If The cross-based RLOF is used (by selecting optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter::supportRegionType
/// = SupportRegionType::SR_CROSS) image has to be a 8-bit 3 channel image.
/// * flow: computed flow image that has the same size as I0 and type CV_32FC2.
/// * rlofParam: see optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter
/// * forwardBackwardThreshold: Threshold for the forward backward confidence check.
/// For each grid point  a motion vector  is computed.
/// If the forward backward error 
/// is larger than threshold given by this function then the motion vector will not be used by the following
/// vector field interpolation.  denotes the backward flow. Note, the forward backward test
/// will only be applied if the threshold > 0. This may results into a doubled runtime for the motion estimation.
/// * gridStep: Size of the grid to spawn the motion vectors. For each grid point a motion vector is computed.
/// Some motion vectors will be removed due to the forwatd backward threshold (if set >0). The rest will be the
/// base of the vector field interpolation.
/// * interp_type: interpolation method used to compute the dense optical flow. Two interpolation algorithms are
/// supported:
/// - **INTERP_GEO** applies the fast geodesic interpolation, see [Geistert2016](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Geistert2016).
/// - **INTERP_EPIC_RESIDUAL** applies the edge-preserving interpolation, see [Revaud2015](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Revaud2015),Geistert2016.
/// * epicK: see ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator sets the respective parameter.
/// * epicSigma: see ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator sets the respective parameter.
/// * epicLambda: see ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator sets the respective parameter.
/// * ricSPSize: see ximgproc::RICInterpolator sets the respective parameter.
/// * ricSLICType: see ximgproc::RICInterpolator sets the respective parameter.
/// * use_post_proc: enables ximgproc::fastGlobalSmootherFilter() parameter.
/// * fgsLambda: sets the respective ximgproc::fastGlobalSmootherFilter() parameter.
/// * fgsSigma: sets the respective ximgproc::fastGlobalSmootherFilter() parameter.
/// * use_variational_refinement: enables VariationalRefinement
///
/// Parameters have been described in [Senst2012](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2012), [Senst2013](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2013), [Senst2014](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2014), [Senst2016](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2016).
/// For the RLOF configuration see optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter for further details.
///
/// Note: If the grid size is set to (1,1) and the forward backward threshold <= 0 that the dense optical flow field is purely
/// computed with the RLOF.
///
///
/// Note: SIMD parallelization is only available when compiling with SSE4.1.
///
/// Note: Note that in output, if no correspondences are found between \a I0 and \a I1, the \a flow is set to 0.
/// ## See also
/// optflow::DenseRLOFOpticalFlow, optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * rlof_param: Ptr<RLOFOpticalFlowParameter>()
/// * forward_backward_threshold: 0
/// * grid_step: Size(6,6)
/// * interp_type: InterpolationType::INTERP_EPIC
/// * epic_k: 128
/// * epic_sigma: 0.05f
/// * epic_lambda: 100.f
/// * ric_sp_size: 15
/// * ric_slic_type: 100
/// * use_post_proc: true
/// * fgs_lambda: 500.0f
/// * fgs_sigma: 1.5f
/// * use_variational_refinement: false
#[inline]
pub fn calc_optical_flow_dense_rlof(i0: &dyn core::ToInputArray, i1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, flow: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, mut rlof_param: core::Ptr<crate::optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter>, forward_backward_threshold: f32, grid_step: core::Size, interp_type: crate::optflow::InterpolationType, epic_k: i32, epic_sigma: f32, epic_lambda: f32, ric_sp_size: i32, ric_slic_type: i32, use_post_proc: bool, fgs_lambda: f32, fgs_sigma: f32, use_variational_refinement: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(i0);
extern_container_arg!(i1);
extern_container_arg!(flow);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_calcOpticalFlowDenseRLOF_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_PtrLRLOFOpticalFlowParameterG_float_Size_InterpolationType_int_float_float_int_int_bool_float_float_bool(i0.as_raw__InputArray(), i1.as_raw__InputArray(), flow.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), rlof_param.as_raw_mut_PtrOfRLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), forward_backward_threshold, grid_step.opencv_as_extern(), interp_type, epic_k, epic_sigma, epic_lambda, ric_sp_size, ric_slic_type, use_post_proc, fgs_lambda, fgs_sigma, use_variational_refinement, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculate an optical flow using "SimpleFlow" algorithm.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * from: First 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * to: Second 8-bit 3-channel image of the same size as prev
/// * flow: computed flow image that has the same size as prev and type CV_32FC2
/// * layers: Number of layers
/// * averaging_block_size: Size of block through which we sum up when calculate cost function
/// for pixel
/// * max_flow: maximal flow that we search at each level
/// * sigma_dist: vector smooth spatial sigma parameter
/// * sigma_color: vector smooth color sigma parameter
/// * postprocess_window: window size for postprocess cross bilateral filter
/// * sigma_dist_fix: spatial sigma for postprocess cross bilateralf filter
/// * sigma_color_fix: color sigma for postprocess cross bilateral filter
/// * occ_thr: threshold for detecting occlusions
/// * upscale_averaging_radius: window size for bilateral upscale operation
/// * upscale_sigma_dist: spatial sigma for bilateral upscale operation
/// * upscale_sigma_color: color sigma for bilateral upscale operation
/// * speed_up_thr: threshold to detect point with irregular flow - where flow should be
/// recalculated after upscale
///
/// See [Tao2012](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Tao2012) . And site of project - <http://graphics.berkeley.edu/papers/Tao-SAN-2012-05/>.
///
///
/// Note:
/// * An example using the simpleFlow algorithm can be found at samples/simpleflow_demo.cpp
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
#[inline]
pub fn calc_optical_flow_sf(from: &dyn core::ToInputArray, to: &dyn core::ToInputArray, flow: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, layers: i32, averaging_block_size: i32, max_flow: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(from);
extern_container_arg!(to);
extern_container_arg!(flow);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_calcOpticalFlowSF_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_int_int(from.as_raw__InputArray(), to.as_raw__InputArray(), flow.as_raw__OutputArray(), layers, averaging_block_size, max_flow, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculate an optical flow using "SimpleFlow" algorithm.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * from: First 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * to: Second 8-bit 3-channel image of the same size as prev
/// * flow: computed flow image that has the same size as prev and type CV_32FC2
/// * layers: Number of layers
/// * averaging_block_size: Size of block through which we sum up when calculate cost function
/// for pixel
/// * max_flow: maximal flow that we search at each level
/// * sigma_dist: vector smooth spatial sigma parameter
/// * sigma_color: vector smooth color sigma parameter
/// * postprocess_window: window size for postprocess cross bilateral filter
/// * sigma_dist_fix: spatial sigma for postprocess cross bilateralf filter
/// * sigma_color_fix: color sigma for postprocess cross bilateral filter
/// * occ_thr: threshold for detecting occlusions
/// * upscale_averaging_radius: window size for bilateral upscale operation
/// * upscale_sigma_dist: spatial sigma for bilateral upscale operation
/// * upscale_sigma_color: color sigma for bilateral upscale operation
/// * speed_up_thr: threshold to detect point with irregular flow - where flow should be
/// recalculated after upscale
///
/// See [Tao2012](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Tao2012) . And site of project - <http://graphics.berkeley.edu/papers/Tao-SAN-2012-05/>.
///
///
/// Note:
/// * An example using the simpleFlow algorithm can be found at samples/simpleflow_demo.cpp
#[inline]
pub fn calc_optical_flow_sf_1(from: &dyn core::ToInputArray, to: &dyn core::ToInputArray, flow: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, layers: i32, averaging_block_size: i32, max_flow: i32, sigma_dist: f64, sigma_color: f64, postprocess_window: i32, sigma_dist_fix: f64, sigma_color_fix: f64, occ_thr: f64, upscale_averaging_radius: i32, upscale_sigma_dist: f64, upscale_sigma_color: f64, speed_up_thr: f64) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(from);
extern_container_arg!(to);
extern_container_arg!(flow);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_calcOpticalFlowSF_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_int_int_double_double_int_double_double_double_int_double_double_double(from.as_raw__InputArray(), to.as_raw__InputArray(), flow.as_raw__OutputArray(), layers, averaging_block_size, max_flow, sigma_dist, sigma_color, postprocess_window, sigma_dist_fix, sigma_color_fix, occ_thr, upscale_averaging_radius, upscale_sigma_dist, upscale_sigma_color, speed_up_thr, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates fast optical flow for a sparse feature set using the robust local optical flow (RLOF) similar
/// to optflow::calcOpticalFlowPyrLK().
///
/// The RLOF is a fast local optical flow approach described in [Senst2012](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2012) [Senst2013](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2013) [Senst2014](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2014)
/// and [Senst2016](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2016) similar to the pyramidal iterative Lucas-Kanade method as
/// proposed by [Bouguet00](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Bouguet00). More details and experiments can be found in the following thesis [Senst2019](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2019).
/// The implementation is derived from optflow::calcOpticalFlowPyrLK().
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * prevImg: first 8-bit input image. If The cross-based RLOF is used (by selecting optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter::supportRegionType
/// = SupportRegionType::SR_CROSS) image has to be a 8-bit 3 channel image.
/// * nextImg: second 8-bit input image. If The cross-based RLOF is used (by selecting optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter::supportRegionType
/// = SupportRegionType::SR_CROSS) image has to be a 8-bit 3 channel image.
/// * prevPts: vector of 2D points for which the flow needs to be found; point coordinates must be single-precision
/// floating-point numbers.
/// * nextPts: output vector of 2D points (with single-precision floating-point coordinates) containing the calculated
/// new positions of input features in the second image; when optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter::useInitialFlow variable is true the vector must
/// have the same size as in the input and contain the initialization point correspondences.
/// * status: output status vector (of unsigned chars); each element of the vector is set to 1 if the flow for the
/// corresponding features has passed the forward backward check.
/// * err: output vector of errors; each element of the vector is set to the forward backward error for the corresponding feature.
/// * rlofParam: see optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter
/// * forwardBackwardThreshold: Threshold for the forward backward confidence check. If forewardBackwardThreshold <=0 the forward
///
///
/// Note: SIMD parallelization is only available when compiling with SSE4.1.
///
/// Parameters have been described in [Senst2012](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2012), [Senst2013](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2013), [Senst2014](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2014) and [Senst2016](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2016).
/// For the RLOF configuration see optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter for further details.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * rlof_param: Ptr<RLOFOpticalFlowParameter>()
/// * forward_backward_threshold: 0
#[inline]
pub fn calc_optical_flow_sparse_rlof(prev_img: &dyn core::ToInputArray, next_img: &dyn core::ToInputArray, prev_pts: &dyn core::ToInputArray, next_pts: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, status: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, err: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, mut rlof_param: core::Ptr<crate::optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter>, forward_backward_threshold: f32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(prev_img);
extern_container_arg!(next_img);
extern_container_arg!(prev_pts);
extern_container_arg!(next_pts);
extern_container_arg!(status);
extern_container_arg!(err);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_calcOpticalFlowSparseRLOF_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_PtrLRLOFOpticalFlowParameterG_float(prev_img.as_raw__InputArray(), next_img.as_raw__InputArray(), prev_pts.as_raw__InputArray(), next_pts.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), status.as_raw__OutputArray(), err.as_raw__OutputArray(), rlof_param.as_raw_mut_PtrOfRLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), forward_backward_threshold, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Fast dense optical flow based on PyrLK sparse matches interpolation.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * from: first 8-bit 3-channel or 1-channel image.
/// * to: second 8-bit 3-channel or 1-channel image of the same size as from
/// * flow: computed flow image that has the same size as from and CV_32FC2 type
/// * grid_step: stride used in sparse match computation. Lower values usually
/// result in higher quality but slow down the algorithm.
/// * k: number of nearest-neighbor matches considered, when fitting a locally affine
/// model. Lower values can make the algorithm noticeably faster at the cost of
/// some quality degradation.
/// * sigma: parameter defining how fast the weights decrease in the locally-weighted affine
/// fitting. Higher values can help preserve fine details, lower values can help to get rid
/// of the noise in the output flow.
/// * use_post_proc: defines whether the ximgproc::fastGlobalSmootherFilter() is used
/// for post-processing after interpolation
/// * fgs_lambda: see the respective parameter of the ximgproc::fastGlobalSmootherFilter()
/// * fgs_sigma: see the respective parameter of the ximgproc::fastGlobalSmootherFilter()
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * grid_step: 8
/// * k: 128
/// * sigma: 0.05f
/// * use_post_proc: true
/// * fgs_lambda: 500.0f
/// * fgs_sigma: 1.5f
#[inline]
pub fn calc_optical_flow_sparse_to_dense(from: &dyn core::ToInputArray, to: &dyn core::ToInputArray, flow: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, grid_step: i32, k: i32, sigma: f32, use_post_proc: bool, fgs_lambda: f32, fgs_sigma: f32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(from);
extern_container_arg!(to);
extern_container_arg!(flow);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_calcOpticalFlowSparseToDense_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_int_float_bool_float_float(from.as_raw__InputArray(), to.as_raw__InputArray(), flow.as_raw__OutputArray(), grid_step, k, sigma, use_post_proc, fgs_lambda, fgs_sigma, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// DeepFlow optical flow algorithm implementation.
///
/// The class implements the DeepFlow optical flow algorithm described in [Weinzaepfel2013](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Weinzaepfel2013) . See
/// also <http://lear.inrialpes.fr/src/deepmatching/> .
/// Parameters - class fields - that may be modified after creating a class instance:
/// * member float alpha
/// Smoothness assumption weight
/// * member float delta
/// Color constancy assumption weight
/// * member float gamma
/// Gradient constancy weight
/// * member float sigma
/// Gaussian smoothing parameter
/// * member int minSize
/// Minimal dimension of an image in the pyramid (next, smaller images in the pyramid are generated
/// until one of the dimensions reaches this size)
/// * member float downscaleFactor
/// Scaling factor in the image pyramid (must be \< 1)
/// * member int fixedPointIterations
/// How many iterations on each level of the pyramid
/// * member int sorIterations
/// Iterations of Succesive Over-Relaxation (solver)
/// * member float omega
/// Relaxation factor in SOR
#[inline]
pub fn create_opt_flow_deep_flow() -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::video::DenseOpticalFlow>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_createOptFlow_DeepFlow(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::video::DenseOpticalFlow>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Additional interface to the Dense RLOF algorithm - optflow::calcOpticalFlowDenseRLOF()
#[inline]
pub fn create_opt_flow_dense_rlof() -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::video::DenseOpticalFlow>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_createOptFlow_DenseRLOF(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::video::DenseOpticalFlow>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates instance of cv::DenseOpticalFlow
#[inline]
pub fn create_opt_flow_dual_tvl1() -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::optflow::DualTVL1OpticalFlow>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_createOptFlow_DualTVL1(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::optflow::DualTVL1OpticalFlow>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Additional interface to the Farneback's algorithm - calcOpticalFlowFarneback()
#[inline]
pub fn create_opt_flow_farneback() -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::video::DenseOpticalFlow>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_createOptFlow_Farneback(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::video::DenseOpticalFlow>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates an instance of PCAFlow
#[inline]
pub fn create_opt_flow_pca_flow() -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::video::DenseOpticalFlow>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_createOptFlow_PCAFlow(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::video::DenseOpticalFlow>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Additional interface to the SimpleFlow algorithm - calcOpticalFlowSF()
#[inline]
pub fn create_opt_flow_simple_flow() -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::video::DenseOpticalFlow>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_createOptFlow_SimpleFlow(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::video::DenseOpticalFlow>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Additional interface to the Sparse RLOF algorithm - optflow::calcOpticalFlowSparseRLOF()
#[inline]
pub fn create_opt_flow_sparse_rlof() -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::video::SparseOpticalFlow>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_createOptFlow_SparseRLOF(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::video::SparseOpticalFlow>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Additional interface to the SparseToDenseFlow algorithm - calcOpticalFlowSparseToDense()
#[inline]
pub fn create_opt_flow_sparse_to_dense() -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::video::DenseOpticalFlow>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_createOptFlow_SparseToDense(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::video::DenseOpticalFlow>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn read(fn_: &core::FileNode, node: &mut crate::optflow::GPCTree_Node, unnamed: crate::optflow::GPCTree_Node) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_read_const_FileNodeR_NodeR_Node(fn_.as_raw_FileNode(), node, unnamed.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn write(fs: &mut core::FileStorage, name: &str, node: crate::optflow::GPCTree_Node) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(name);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_write_FileStorageR_const_StringR_const_NodeR(fs.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), name.opencv_as_extern(), &node, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::optflow::DenseRLOFOpticalFlow]
pub trait DenseRLOFOpticalFlowConst: crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowConst {
fn as_raw_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Configuration of the RLOF alogrithm.
/// ## See also
/// optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter, getRLOFOpticalFlowParameter
/// optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter, setRLOFOpticalFlowParameter
#[inline]
fn get_rlof_optical_flow_parameter(&self) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_getRLOFOpticalFlowParameter_const(self.as_raw_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Threshold for the forward backward confidence check
/// For each grid point  a motion vector  is computed.
/// * If the forward backward error 
/// * is larger than threshold given by this function then the motion vector will not be used by the following
/// * vector field interpolation.  denotes the backward flow. Note, the forward backward test
/// * will only be applied if the threshold > 0. This may results into a doubled runtime for the motion estimation.
/// * getForwardBackward, setGridStep
/// ## See also
/// setForwardBackward
#[inline]
fn get_forward_backward(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_getForwardBackward_const(self.as_raw_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Size of the grid to spawn the motion vectors.
/// For each grid point a motion vector is computed. Some motion vectors will be removed due to the forwatd backward
/// * threshold (if set >0). The rest will be the base of the vector field interpolation.
/// * see also: getForwardBackward, setGridStep
#[inline]
fn get_grid_step(&self) -> Result<core::Size> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_getGridStep_const(self.as_raw_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Interpolation used to compute the dense optical flow.
/// Two interpolation algorithms are supported
/// * - **INTERP_GEO** applies the fast geodesic interpolation, see [Geistert2016](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Geistert2016).
/// * - **INTERP_EPIC_RESIDUAL** applies the edge-preserving interpolation, see [Revaud2015](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Revaud2015),Geistert2016.
/// * see also: ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator, getInterpolation
/// * see also: ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator, setInterpolation
#[inline]
fn get_interpolation(&self) -> Result<crate::optflow::InterpolationType> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_getInterpolation_const(self.as_raw_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// see ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator() K value.
/// K is a number of nearest-neighbor matches considered, when fitting a locally affine
/// * model. Usually it should be around 128. However, lower values would make the interpolation noticeably faster.
/// * see also: ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator, setEPICK
#[inline]
fn get_epick(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_getEPICK_const(self.as_raw_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// see ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator() sigma value.
/// Sigma is a parameter defining how fast the weights decrease in the locally-weighted affine
/// * fitting. Higher values can help preserve fine details, lower values can help to get rid of noise in the
/// * output flow.
/// * see also: ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator, setEPICSigma
#[inline]
fn get_epic_sigma(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_getEPICSigma_const(self.as_raw_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// see ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator() lambda value.
/// Lambda is a parameter defining the weight of the edge-aware term in geodesic distance,
/// * should be in the range of 0 to 1000.
/// * see also: ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator, setEPICSigma
#[inline]
fn get_epic_lambda(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_getEPICLambda_const(self.as_raw_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// see ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator().
/// Sets the respective fastGlobalSmootherFilter() parameter.
/// * see also: ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator, setFgsLambda
#[inline]
fn get_fgs_lambda(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_getFgsLambda_const(self.as_raw_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// see ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator().
/// Sets the respective fastGlobalSmootherFilter() parameter.
/// * see also: ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator, ximgproc::fastGlobalSmootherFilter, setFgsSigma
#[inline]
fn get_fgs_sigma(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_getFgsSigma_const(self.as_raw_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// enables ximgproc::fastGlobalSmootherFilter
///
/// * see also: getUsePostProc
/// * see also: ximgproc::fastGlobalSmootherFilter, setUsePostProc
#[inline]
fn get_use_post_proc(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_getUsePostProc_const(self.as_raw_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// enables VariationalRefinement
///
/// * see also: getUseVariationalRefinement
/// * see also: ximgproc::fastGlobalSmootherFilter, setUsePostProc
#[inline]
fn get_use_variational_refinement(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_getUseVariationalRefinement_const(self.as_raw_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter to tune the approximate size of the superpixel used for oversegmentation.
///
/// * see also: cv::ximgproc::createSuperpixelSLIC, cv::ximgproc::RICInterpolator
/// * see also: setRICSPSize
#[inline]
fn get_ricsp_size(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_getRICSPSize_const(self.as_raw_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter to choose superpixel algorithm variant to use:
/// - cv::ximgproc::SLICType SLIC segments image using a desired region_size (value: 100)
/// - cv::ximgproc::SLICType SLICO will optimize using adaptive compactness factor (value: 101)
/// - cv::ximgproc::SLICType MSLIC will optimize using manifold methods resulting in more content-sensitive superpixels (value: 102).
/// ## See also
/// cv::ximgproc::createSuperpixelSLIC, cv::ximgproc::RICInterpolator
/// * setRICSLICType
#[inline]
fn get_ricslic_type(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_getRICSLICType_const(self.as_raw_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Fast dense optical flow computation based on robust local optical flow (RLOF) algorithms and sparse-to-dense interpolation
/// scheme.
///
/// The RLOF is a fast local optical flow approach described in [Senst2012](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2012) [Senst2013](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2013) [Senst2014](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2014)
/// and [Senst2016](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2016) similar to the pyramidal iterative Lucas-Kanade method as
/// proposed by [Bouguet00](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Bouguet00). More details and experiments can be found in the following thesis [Senst2019](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2019).
/// The implementation is derived from optflow::calcOpticalFlowPyrLK().
///
/// The sparse-to-dense interpolation scheme allows for fast computation of dense optical flow using RLOF (see [Geistert2016](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Geistert2016)).
/// For this scheme the following steps are applied:
/// -# motion vector seeded at a regular sampled grid are computed. The sparsity of this grid can be configured with setGridStep
/// -# (optinally) errornous motion vectors are filter based on the forward backward confidence. The threshold can be configured
/// with setForwardBackward. The filter is only applied if the threshold >0 but than the runtime is doubled due to the estimation
/// of the backward flow.
/// -# Vector field interpolation is applied to the motion vector set to obtain a dense vector field.
///
/// For the RLOF configuration see optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter for further details.
/// Parameters have been described in [Senst2012](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2012) [Senst2013](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2013) [Senst2014](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2014) and [Senst2016](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2016).
///
///
/// Note: If the grid size is set to (1,1) and the forward backward threshold <= 0 than pixelwise dense optical flow field is
/// computed by RLOF without using interpolation.
///
///
/// Note: Note that in output, if no correspondences are found between \a I0 and \a I1, the \a flow is set to 0.
/// ## See also
/// optflow::calcOpticalFlowDenseRLOF(), optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter
pub trait DenseRLOFOpticalFlow: crate::optflow::DenseRLOFOpticalFlowConst + crate::video::DenseOpticalFlow {
fn as_raw_mut_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Configuration of the RLOF alogrithm.
/// ## See also
/// optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter, getRLOFOpticalFlowParameter
#[inline]
fn set_rlof_optical_flow_parameter(&mut self, mut val: core::Ptr<crate::optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter>) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_setRLOFOpticalFlowParameter_PtrLRLOFOpticalFlowParameterG(self.as_raw_mut_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(), val.as_raw_mut_PtrOfRLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Threshold for the forward backward confidence check
/// For each grid point  a motion vector  is computed.
/// * If the forward backward error 
/// * is larger than threshold given by this function then the motion vector will not be used by the following
/// * vector field interpolation.  denotes the backward flow. Note, the forward backward test
/// * will only be applied if the threshold > 0. This may results into a doubled runtime for the motion estimation.
/// * see also: getForwardBackward, setGridStep
#[inline]
fn set_forward_backward(&mut self, val: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_setForwardBackward_float(self.as_raw_mut_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Size of the grid to spawn the motion vectors.
/// For each grid point a motion vector is computed. Some motion vectors will be removed due to the forwatd backward
/// * threshold (if set >0). The rest will be the base of the vector field interpolation.
/// * see also: getForwardBackward, setGridStep
/// * see also: getGridStep
#[inline]
fn set_grid_step(&mut self, val: core::Size) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_setGridStep_Size(self.as_raw_mut_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(), val.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Interpolation used to compute the dense optical flow.
/// Two interpolation algorithms are supported
/// * - **INTERP_GEO** applies the fast geodesic interpolation, see [Geistert2016](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Geistert2016).
/// * - **INTERP_EPIC_RESIDUAL** applies the edge-preserving interpolation, see [Revaud2015](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Revaud2015),Geistert2016.
/// * see also: ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator, getInterpolation
#[inline]
fn set_interpolation(&mut self, val: crate::optflow::InterpolationType) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_setInterpolation_InterpolationType(self.as_raw_mut_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// see ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator() K value.
/// K is a number of nearest-neighbor matches considered, when fitting a locally affine
/// * model. Usually it should be around 128. However, lower values would make the interpolation noticeably faster.
/// * see also: ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator, setEPICK
/// * see also: ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator, getEPICK
#[inline]
fn set_epick(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_setEPICK_int(self.as_raw_mut_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// see ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator() sigma value.
/// Sigma is a parameter defining how fast the weights decrease in the locally-weighted affine
/// * fitting. Higher values can help preserve fine details, lower values can help to get rid of noise in the
/// * output flow.
/// * see also: ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator, setEPICSigma
/// * see also: ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator, getEPICSigma
#[inline]
fn set_epic_sigma(&mut self, val: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_setEPICSigma_float(self.as_raw_mut_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// see ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator() lambda value.
/// Lambda is a parameter defining the weight of the edge-aware term in geodesic distance,
/// * should be in the range of 0 to 1000.
/// * see also: ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator, setEPICSigma
/// * see also: ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator, getEPICLambda
#[inline]
fn set_epic_lambda(&mut self, val: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_setEPICLambda_float(self.as_raw_mut_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// see ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator().
/// Sets the respective fastGlobalSmootherFilter() parameter.
/// * see also: ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator, setFgsLambda
/// * see also: ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator, ximgproc::fastGlobalSmootherFilter, getFgsLambda
#[inline]
fn set_fgs_lambda(&mut self, val: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_setFgsLambda_float(self.as_raw_mut_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// see ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator().
/// Sets the respective fastGlobalSmootherFilter() parameter.
/// * see also: ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator, ximgproc::fastGlobalSmootherFilter, setFgsSigma
/// * see also: ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator, ximgproc::fastGlobalSmootherFilter, getFgsSigma
#[inline]
fn set_fgs_sigma(&mut self, val: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_setFgsSigma_float(self.as_raw_mut_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// enables ximgproc::fastGlobalSmootherFilter
///
/// * see also: getUsePostProc
#[inline]
fn set_use_post_proc(&mut self, val: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_setUsePostProc_bool(self.as_raw_mut_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// enables VariationalRefinement
///
/// * see also: getUseVariationalRefinement
#[inline]
fn set_use_variational_refinement(&mut self, val: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_setUseVariationalRefinement_bool(self.as_raw_mut_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter to tune the approximate size of the superpixel used for oversegmentation.
///
/// * see also: cv::ximgproc::createSuperpixelSLIC, cv::ximgproc::RICInterpolator
#[inline]
fn set_ricsp_size(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_setRICSPSize_int(self.as_raw_mut_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter to choose superpixel algorithm variant to use:
/// - cv::ximgproc::SLICType SLIC segments image using a desired region_size (value: 100)
/// - cv::ximgproc::SLICType SLICO will optimize using adaptive compactness factor (value: 101)
/// - cv::ximgproc::SLICType MSLIC will optimize using manifold methods resulting in more content-sensitive superpixels (value: 102).
/// ## See also
/// cv::ximgproc::createSuperpixelSLIC, cv::ximgproc::RICInterpolator
#[inline]
fn set_ricslic_type(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_setRICSLICType_int(self.as_raw_mut_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl dyn DenseRLOFOpticalFlow + '_ {
/// Creates instance of optflow::DenseRLOFOpticalFlow
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * rlofParam: see optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter
/// * forwardBackwardThreshold: see setForwardBackward
/// * gridStep: see setGridStep
/// * interp_type: see setInterpolation
/// * epicK: see setEPICK
/// * epicSigma: see setEPICSigma
/// * epicLambda: see setEPICLambda
/// * ricSPSize: see setRICSPSize
/// * ricSLICType: see setRICSLICType
/// * use_post_proc: see setUsePostProc
/// * fgsLambda: see setFgsLambda
/// * fgsSigma: see setFgsSigma
/// * use_variational_refinement: see setUseVariationalRefinement
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * rlof_param: Ptr<RLOFOpticalFlowParameter>()
/// * forward_backward_threshold: 1.f
/// * grid_step: Size(6,6)
/// * interp_type: InterpolationType::INTERP_EPIC
/// * epic_k: 128
/// * epic_sigma: 0.05f
/// * epic_lambda: 999.0f
/// * ric_sp_size: 15
/// * ric_slic_type: 100
/// * use_post_proc: true
/// * fgs_lambda: 500.0f
/// * fgs_sigma: 1.5f
/// * use_variational_refinement: false
#[inline]
pub fn create(mut rlof_param: core::Ptr<crate::optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter>, forward_backward_threshold: f32, grid_step: core::Size, interp_type: crate::optflow::InterpolationType, epic_k: i32, epic_sigma: f32, epic_lambda: f32, ric_sp_size: i32, ric_slic_type: i32, use_post_proc: bool, fgs_lambda: f32, fgs_sigma: f32, use_variational_refinement: bool) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::optflow::DenseRLOFOpticalFlow>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DenseRLOFOpticalFlow_create_PtrLRLOFOpticalFlowParameterG_float_Size_InterpolationType_int_float_float_int_int_bool_float_float_bool(rlof_param.as_raw_mut_PtrOfRLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), forward_backward_threshold, grid_step.opencv_as_extern(), interp_type, epic_k, epic_sigma, epic_lambda, ric_sp_size, ric_slic_type, use_post_proc, fgs_lambda, fgs_sigma, use_variational_refinement, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::optflow::DenseRLOFOpticalFlow>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::optflow::DualTVL1OpticalFlow]
pub trait DualTVL1OpticalFlowConst: crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowConst {
fn as_raw_DualTVL1OpticalFlow(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Time step of the numerical scheme
/// ## See also
/// setTau
#[inline]
fn get_tau(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DualTVL1OpticalFlow_getTau_const(self.as_raw_DualTVL1OpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Weight parameter for the data term, attachment parameter
/// ## See also
/// setLambda
#[inline]
fn get_lambda(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DualTVL1OpticalFlow_getLambda_const(self.as_raw_DualTVL1OpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Weight parameter for (u - v)^2, tightness parameter
/// ## See also
/// setTheta
#[inline]
fn get_theta(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DualTVL1OpticalFlow_getTheta_const(self.as_raw_DualTVL1OpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// coefficient for additional illumination variation term
/// ## See also
/// setGamma
#[inline]
fn get_gamma(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DualTVL1OpticalFlow_getGamma_const(self.as_raw_DualTVL1OpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Number of scales used to create the pyramid of images
/// ## See also
/// setScalesNumber
#[inline]
fn get_scales_number(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DualTVL1OpticalFlow_getScalesNumber_const(self.as_raw_DualTVL1OpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Number of warpings per scale
/// ## See also
/// setWarpingsNumber
#[inline]
fn get_warpings_number(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DualTVL1OpticalFlow_getWarpingsNumber_const(self.as_raw_DualTVL1OpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Stopping criterion threshold used in the numerical scheme, which is a trade-off between precision and running time
/// ## See also
/// setEpsilon
#[inline]
fn get_epsilon(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DualTVL1OpticalFlow_getEpsilon_const(self.as_raw_DualTVL1OpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Inner iterations (between outlier filtering) used in the numerical scheme
/// ## See also
/// setInnerIterations
#[inline]
fn get_inner_iterations(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DualTVL1OpticalFlow_getInnerIterations_const(self.as_raw_DualTVL1OpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Outer iterations (number of inner loops) used in the numerical scheme
/// ## See also
/// setOuterIterations
#[inline]
fn get_outer_iterations(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DualTVL1OpticalFlow_getOuterIterations_const(self.as_raw_DualTVL1OpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Use initial flow
/// ## See also
/// setUseInitialFlow
#[inline]
fn get_use_initial_flow(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DualTVL1OpticalFlow_getUseInitialFlow_const(self.as_raw_DualTVL1OpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Step between scales (<1)
/// ## See also
/// setScaleStep
#[inline]
fn get_scale_step(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DualTVL1OpticalFlow_getScaleStep_const(self.as_raw_DualTVL1OpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Median filter kernel size (1 = no filter) (3 or 5)
/// ## See also
/// setMedianFiltering
#[inline]
fn get_median_filtering(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DualTVL1OpticalFlow_getMedianFiltering_const(self.as_raw_DualTVL1OpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// "Dual TV L1" Optical Flow Algorithm.
///
/// The class implements the "Dual TV L1" optical flow algorithm described in [Zach2007](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Zach2007) and
/// [Javier2012](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Javier2012) .
/// Here are important members of the class that control the algorithm, which you can set after
/// constructing the class instance:
///
/// * member double tau
/// Time step of the numerical scheme.
///
/// * member double lambda
/// Weight parameter for the data term, attachment parameter. This is the most relevant
/// parameter, which determines the smoothness of the output. The smaller this parameter is,
/// the smoother the solutions we obtain. It depends on the range of motions of the images, so
/// its value should be adapted to each image sequence.
///
/// * member double theta
/// Weight parameter for (u - v)\^2, tightness parameter. It serves as a link between the
/// attachment and the regularization terms. In theory, it should have a small value in order
/// to maintain both parts in correspondence. The method is stable for a large range of values
/// of this parameter.
///
/// * member int nscales
/// Number of scales used to create the pyramid of images.
///
/// * member int warps
/// Number of warpings per scale. Represents the number of times that I1(x+u0) and grad(
/// I1(x+u0) ) are computed per scale. This is a parameter that assures the stability of the
/// method. It also affects the running time, so it is a compromise between speed and
/// accuracy.
///
/// * member double epsilon
/// Stopping criterion threshold used in the numerical scheme, which is a trade-off between
/// precision and running time. A small value will yield more accurate solutions at the
/// expense of a slower convergence.
///
/// * member int iterations
/// Stopping criterion iterations number used in the numerical scheme.
///
/// C. Zach, T. Pock and H. Bischof, "A Duality Based Approach for Realtime TV-L1 Optical Flow".
/// Javier Sanchez, Enric Meinhardt-Llopis and Gabriele Facciolo. "TV-L1 Optical Flow Estimation".
pub trait DualTVL1OpticalFlow: crate::optflow::DualTVL1OpticalFlowConst + crate::video::DenseOpticalFlow {
fn as_raw_mut_DualTVL1OpticalFlow(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Time step of the numerical scheme
/// ## See also
/// setTau getTau
#[inline]
fn set_tau(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DualTVL1OpticalFlow_setTau_double(self.as_raw_mut_DualTVL1OpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Weight parameter for the data term, attachment parameter
/// ## See also
/// setLambda getLambda
#[inline]
fn set_lambda(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DualTVL1OpticalFlow_setLambda_double(self.as_raw_mut_DualTVL1OpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Weight parameter for (u - v)^2, tightness parameter
/// ## See also
/// setTheta getTheta
#[inline]
fn set_theta(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DualTVL1OpticalFlow_setTheta_double(self.as_raw_mut_DualTVL1OpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// coefficient for additional illumination variation term
/// ## See also
/// setGamma getGamma
#[inline]
fn set_gamma(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DualTVL1OpticalFlow_setGamma_double(self.as_raw_mut_DualTVL1OpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Number of scales used to create the pyramid of images
/// ## See also
/// setScalesNumber getScalesNumber
#[inline]
fn set_scales_number(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DualTVL1OpticalFlow_setScalesNumber_int(self.as_raw_mut_DualTVL1OpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Number of warpings per scale
/// ## See also
/// setWarpingsNumber getWarpingsNumber
#[inline]
fn set_warpings_number(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DualTVL1OpticalFlow_setWarpingsNumber_int(self.as_raw_mut_DualTVL1OpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Stopping criterion threshold used in the numerical scheme, which is a trade-off between precision and running time
/// ## See also
/// setEpsilon getEpsilon
#[inline]
fn set_epsilon(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DualTVL1OpticalFlow_setEpsilon_double(self.as_raw_mut_DualTVL1OpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Inner iterations (between outlier filtering) used in the numerical scheme
/// ## See also
/// setInnerIterations getInnerIterations
#[inline]
fn set_inner_iterations(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DualTVL1OpticalFlow_setInnerIterations_int(self.as_raw_mut_DualTVL1OpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Outer iterations (number of inner loops) used in the numerical scheme
/// ## See also
/// setOuterIterations getOuterIterations
#[inline]
fn set_outer_iterations(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DualTVL1OpticalFlow_setOuterIterations_int(self.as_raw_mut_DualTVL1OpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Use initial flow
/// ## See also
/// setUseInitialFlow getUseInitialFlow
#[inline]
fn set_use_initial_flow(&mut self, val: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DualTVL1OpticalFlow_setUseInitialFlow_bool(self.as_raw_mut_DualTVL1OpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Step between scales (<1)
/// ## See also
/// setScaleStep getScaleStep
#[inline]
fn set_scale_step(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DualTVL1OpticalFlow_setScaleStep_double(self.as_raw_mut_DualTVL1OpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Median filter kernel size (1 = no filter) (3 or 5)
/// ## See also
/// setMedianFiltering getMedianFiltering
#[inline]
fn set_median_filtering(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DualTVL1OpticalFlow_setMedianFiltering_int(self.as_raw_mut_DualTVL1OpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl dyn DualTVL1OpticalFlow + '_ {
/// Creates instance of cv::DualTVL1OpticalFlow
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * tau: 0.25
/// * lambda: 0.15
/// * theta: 0.3
/// * nscales: 5
/// * warps: 5
/// * epsilon: 0.01
/// * innner_iterations: 30
/// * outer_iterations: 10
/// * scale_step: 0.8
/// * gamma: 0.0
/// * median_filtering: 5
/// * use_initial_flow: false
#[inline]
pub fn create(tau: f64, lambda: f64, theta: f64, nscales: i32, warps: i32, epsilon: f64, innner_iterations: i32, outer_iterations: i32, scale_step: f64, gamma: f64, median_filtering: i32, use_initial_flow: bool) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::optflow::DualTVL1OpticalFlow>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_DualTVL1OpticalFlow_create_double_double_double_int_int_double_int_int_double_double_int_bool(tau, lambda, theta, nscales, warps, epsilon, innner_iterations, outer_iterations, scale_step, gamma, median_filtering, use_initial_flow, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::optflow::DualTVL1OpticalFlow>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::optflow::GPCDetails]
pub trait GPCDetailsTraitConst {
fn as_raw_GPCDetails(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::optflow::GPCDetails]
pub trait GPCDetailsTrait: crate::optflow::GPCDetailsTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_GPCDetails(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
pub struct GPCDetails {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { GPCDetails }
impl Drop for GPCDetails {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_GPCDetails_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_GPCDetails_delete(self.as_raw_mut_GPCDetails()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for GPCDetails {}
impl crate::optflow::GPCDetailsTraitConst for GPCDetails {
#[inline] fn as_raw_GPCDetails(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::optflow::GPCDetailsTrait for GPCDetails {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_GPCDetails(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl GPCDetails {
#[inline]
pub fn drop_outliers(corr: &mut core::Vector<core::Tuple<(core::Point2i, core::Point2i)>>) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCDetails_dropOutliers_vectorLpairLcv_Point2i__cv_Point2iGGR(corr.as_raw_mut_VectorOfTupleOfPoint2i_Point2i(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn get_all_descriptors_for_image(img_ch: &core::Mat, descr: &mut core::Vector<crate::optflow::GPCPatchDescriptor>, mp: crate::optflow::GPCMatchingParams, typ: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCDetails_getAllDescriptorsForImage_const_MatX_vectorLGPCPatchDescriptorGR_const_GPCMatchingParamsR_int(img_ch.as_raw_Mat(), descr.as_raw_mut_VectorOfGPCPatchDescriptor(), &mp, typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn get_coordinates_from_index(index: size_t, sz: core::Size, x: &mut i32, y: &mut i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCDetails_getCoordinatesFromIndex_size_t_Size_intR_intR(index, sz.opencv_as_extern(), x, y, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Class encapsulating matching parameters.
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)]
pub struct GPCMatchingParams {
/// Whether to use OpenCL to speed up the matching.
pub use_opencl: bool,
}
opencv_type_simple! { crate::optflow::GPCMatchingParams }
impl GPCMatchingParams {
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * _use_opencl: false
#[inline]
pub fn new(_use_opencl: bool) -> Result<crate::optflow::GPCMatchingParams> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCMatchingParams_GPCMatchingParams_bool(_use_opencl, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn copy(params: crate::optflow::GPCMatchingParams) -> Result<crate::optflow::GPCMatchingParams> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCMatchingParams_GPCMatchingParams_const_GPCMatchingParamsR(¶ms, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::optflow::GPCPatchDescriptor]
pub trait GPCPatchDescriptorTraitConst {
fn as_raw_GPCPatchDescriptor(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn feature(&self) -> core::VecN<f64, 18> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCPatchDescriptor_getPropFeature_const(self.as_raw_GPCPatchDescriptor(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
ret
}
#[inline]
fn dot(&self, coef: core::VecN<f64, 18>) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCPatchDescriptor_dot_const_const_VecLdouble__18GR(self.as_raw_GPCPatchDescriptor(), &coef, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn is_separated(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCPatchDescriptor_isSeparated_const(self.as_raw_GPCPatchDescriptor(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::optflow::GPCPatchDescriptor]
pub trait GPCPatchDescriptorTrait: crate::optflow::GPCPatchDescriptorTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_GPCPatchDescriptor(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_feature(&mut self, val: core::VecN<f64, 18>) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCPatchDescriptor_setPropFeature_VecLdouble__18G(self.as_raw_mut_GPCPatchDescriptor(), val.opencv_as_extern()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn mark_as_separated(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCPatchDescriptor_markAsSeparated(self.as_raw_mut_GPCPatchDescriptor(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
pub struct GPCPatchDescriptor {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { GPCPatchDescriptor }
impl Drop for GPCPatchDescriptor {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_GPCPatchDescriptor_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_GPCPatchDescriptor_delete(self.as_raw_mut_GPCPatchDescriptor()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for GPCPatchDescriptor {}
impl crate::optflow::GPCPatchDescriptorTraitConst for GPCPatchDescriptor {
#[inline] fn as_raw_GPCPatchDescriptor(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::optflow::GPCPatchDescriptorTrait for GPCPatchDescriptor {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_GPCPatchDescriptor(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl GPCPatchDescriptor {
/// number of features in a patch descriptor
pub const nFeatures: u32 = 18;
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::optflow::GPCPatchSample]
pub trait GPCPatchSampleTraitConst {
fn as_raw_GPCPatchSample(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn ref_(&self) -> crate::optflow::GPCPatchDescriptor {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCPatchSample_getPropRef_const(self.as_raw_GPCPatchSample()) };
let ret = unsafe { crate::optflow::GPCPatchDescriptor::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn pos(&self) -> crate::optflow::GPCPatchDescriptor {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCPatchSample_getPropPos_const(self.as_raw_GPCPatchSample()) };
let ret = unsafe { crate::optflow::GPCPatchDescriptor::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn neg(&self) -> crate::optflow::GPCPatchDescriptor {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCPatchSample_getPropNeg_const(self.as_raw_GPCPatchSample()) };
let ret = unsafe { crate::optflow::GPCPatchDescriptor::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn get_directions(&self, refdir: &mut bool, posdir: &mut bool, negdir: &mut bool, coef: core::VecN<f64, 18>, rhs: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCPatchSample_getDirections_const_boolR_boolR_boolR_const_VecLdouble__18GR_double(self.as_raw_GPCPatchSample(), refdir, posdir, negdir, &coef, rhs, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::optflow::GPCPatchSample]
pub trait GPCPatchSampleTrait: crate::optflow::GPCPatchSampleTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_GPCPatchSample(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_ref(&mut self, mut val: crate::optflow::GPCPatchDescriptor) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCPatchSample_setPropRef_GPCPatchDescriptor(self.as_raw_mut_GPCPatchSample(), val.as_raw_mut_GPCPatchDescriptor()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_pos(&mut self, mut val: crate::optflow::GPCPatchDescriptor) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCPatchSample_setPropPos_GPCPatchDescriptor(self.as_raw_mut_GPCPatchSample(), val.as_raw_mut_GPCPatchDescriptor()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_neg(&mut self, mut val: crate::optflow::GPCPatchDescriptor) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCPatchSample_setPropNeg_GPCPatchDescriptor(self.as_raw_mut_GPCPatchSample(), val.as_raw_mut_GPCPatchDescriptor()) };
ret
}
}
pub struct GPCPatchSample {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { GPCPatchSample }
impl Drop for GPCPatchSample {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_GPCPatchSample_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_GPCPatchSample_delete(self.as_raw_mut_GPCPatchSample()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for GPCPatchSample {}
impl crate::optflow::GPCPatchSampleTraitConst for GPCPatchSample {
#[inline] fn as_raw_GPCPatchSample(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::optflow::GPCPatchSampleTrait for GPCPatchSample {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_GPCPatchSample(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl GPCPatchSample {
}
/// Class encapsulating training parameters.
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)]
pub struct GPCTrainingParams {
/// Maximum tree depth to stop partitioning.
pub max_tree_depth: u32,
/// Minimum number of samples in the node to stop partitioning.
pub min_number_of_samples: i32,
/// Type of descriptors to use.
pub descriptor_type: i32,
/// Print progress to stdout.
pub print_progress: bool,
}
opencv_type_simple! { crate::optflow::GPCTrainingParams }
impl GPCTrainingParams {
#[inline]
pub fn check(self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCTrainingParams_check_const(self.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * _max_tree_depth: 20
/// * _min_number_of_samples: 3
/// * _descriptor_type: GPC_DESCRIPTOR_DCT
/// * _print_progress: true
#[inline]
pub fn new(_max_tree_depth: u32, _min_number_of_samples: i32, _descriptor_type: crate::optflow::GPCDescType, _print_progress: bool) -> Result<crate::optflow::GPCTrainingParams> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCTrainingParams_GPCTrainingParams_unsigned_int_int_GPCDescType_bool(_max_tree_depth, _min_number_of_samples, _descriptor_type, _print_progress, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::optflow::GPCTrainingSamples]
pub trait GPCTrainingSamplesTraitConst {
fn as_raw_GPCTrainingSamples(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn size(&self) -> Result<size_t> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCTrainingSamples_size_const(self.as_raw_GPCTrainingSamples(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn typ(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCTrainingSamples_type_const(self.as_raw_GPCTrainingSamples(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::optflow::GPCTrainingSamples]
pub trait GPCTrainingSamplesTrait: crate::optflow::GPCTrainingSamplesTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_GPCTrainingSamples(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
/// Class encapsulating training samples.
pub struct GPCTrainingSamples {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { GPCTrainingSamples }
impl Drop for GPCTrainingSamples {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_GPCTrainingSamples_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_GPCTrainingSamples_delete(self.as_raw_mut_GPCTrainingSamples()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for GPCTrainingSamples {}
impl crate::optflow::GPCTrainingSamplesTraitConst for GPCTrainingSamples {
#[inline] fn as_raw_GPCTrainingSamples(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::optflow::GPCTrainingSamplesTrait for GPCTrainingSamples {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_GPCTrainingSamples(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl GPCTrainingSamples {
/// This function can be used to extract samples from a pair of images and a ground truth flow.
/// Sizes of all the provided vectors must be equal.
#[inline]
pub fn create(images_from: &core::Vector<String>, images_to: &core::Vector<String>, gt: &core::Vector<String>, descriptor_type: i32) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::optflow::GPCTrainingSamples>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCTrainingSamples_create_const_vectorLStringGR_const_vectorLStringGR_const_vectorLStringGR_int(images_from.as_raw_VectorOfString(), images_to.as_raw_VectorOfString(), gt.as_raw_VectorOfString(), descriptor_type, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::optflow::GPCTrainingSamples>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn create_1(images_from: &dyn core::ToInputArray, images_to: &dyn core::ToInputArray, gt: &dyn core::ToInputArray, descriptor_type: i32) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::optflow::GPCTrainingSamples>> {
extern_container_arg!(images_from);
extern_container_arg!(images_to);
extern_container_arg!(gt);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCTrainingSamples_create_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int(images_from.as_raw__InputArray(), images_to.as_raw__InputArray(), gt.as_raw__InputArray(), descriptor_type, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::optflow::GPCTrainingSamples>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::optflow::GPCTree]
pub trait GPCTreeTraitConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_GPCTree(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn write(&self, fs: &mut core::FileStorage) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCTree_write_const_FileStorageR(self.as_raw_GPCTree(), fs.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn find_leaf_for_patch(&self, descr: &crate::optflow::GPCPatchDescriptor) -> Result<u32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCTree_findLeafForPatch_const_const_GPCPatchDescriptorR(self.as_raw_GPCTree(), descr.as_raw_GPCPatchDescriptor(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn equals(&self, t: &crate::optflow::GPCTree) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCTree_operatorEQ_const_const_GPCTreeR(self.as_raw_GPCTree(), t.as_raw_GPCTree(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_descriptor_type(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCTree_getDescriptorType_const(self.as_raw_GPCTree(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::optflow::GPCTree]
pub trait GPCTreeTrait: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::optflow::GPCTreeTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_GPCTree(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * params: GPCTrainingParams()
#[inline]
fn train(&mut self, samples: &mut crate::optflow::GPCTrainingSamples, params: crate::optflow::GPCTrainingParams) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCTree_train_GPCTrainingSamplesR_const_GPCTrainingParams(self.as_raw_mut_GPCTree(), samples.as_raw_mut_GPCTrainingSamples(), params.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn read(&mut self, fn_: &core::FileNode) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCTree_read_const_FileNodeR(self.as_raw_mut_GPCTree(), fn_.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Class for individual tree.
pub struct GPCTree {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { GPCTree }
impl Drop for GPCTree {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_GPCTree_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_GPCTree_delete(self.as_raw_mut_GPCTree()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for GPCTree {}
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for GPCTree {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for GPCTree {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::optflow::GPCTreeTraitConst for GPCTree {
#[inline] fn as_raw_GPCTree(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::optflow::GPCTreeTrait for GPCTree {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_GPCTree(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl GPCTree {
#[inline]
pub fn create() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::optflow::GPCTree>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCTree_create(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::optflow::GPCTree>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { GPCTree, core::Algorithm, cv_GPCTree_to_Algorithm }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)]
pub struct GPCTree_Node {
/// Hyperplane coefficients
pub coef: core::VecN<f64, 18>,
/// Bias term of the hyperplane
pub rhs: f64,
pub left: u32,
pub right: u32,
}
opencv_type_simple! { crate::optflow::GPCTree_Node }
impl GPCTree_Node {
#[inline]
pub fn equals(self, n: crate::optflow::GPCTree_Node) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_GPCTree_Node_operatorEQ_const_const_NodeR(self.opencv_as_extern(), &n, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::optflow::OpticalFlowPCAFlow]
pub trait OpticalFlowPCAFlowTraitConst: crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowConst {
fn as_raw_OpticalFlowPCAFlow(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::optflow::OpticalFlowPCAFlow]
pub trait OpticalFlowPCAFlowTrait: crate::optflow::OpticalFlowPCAFlowTraitConst + crate::video::DenseOpticalFlow {
fn as_raw_mut_OpticalFlowPCAFlow(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn calc(&mut self, i0: &dyn core::ToInputArray, i1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, flow: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(i0);
extern_container_arg!(i1);
extern_container_arg!(flow);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_OpticalFlowPCAFlow_calc_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_OpticalFlowPCAFlow(), i0.as_raw__InputArray(), i1.as_raw__InputArray(), flow.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn collect_garbage(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_OpticalFlowPCAFlow_collectGarbage(self.as_raw_mut_OpticalFlowPCAFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// PCAFlow algorithm.
pub struct OpticalFlowPCAFlow {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { OpticalFlowPCAFlow }
impl Drop for OpticalFlowPCAFlow {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_OpticalFlowPCAFlow_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_OpticalFlowPCAFlow_delete(self.as_raw_mut_OpticalFlowPCAFlow()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for OpticalFlowPCAFlow {}
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for OpticalFlowPCAFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for OpticalFlowPCAFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::video::DenseOpticalFlowConst for OpticalFlowPCAFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_DenseOpticalFlow(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::video::DenseOpticalFlow for OpticalFlowPCAFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_DenseOpticalFlow(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::optflow::OpticalFlowPCAFlowTraitConst for OpticalFlowPCAFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_OpticalFlowPCAFlow(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::optflow::OpticalFlowPCAFlowTrait for OpticalFlowPCAFlow {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_OpticalFlowPCAFlow(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl OpticalFlowPCAFlow {
/// Creates an instance of PCAFlow algorithm.
/// ## Parameters
/// * _prior: Learned prior or no prior (default). see also: cv::optflow::PCAPrior
/// * _basisSize: Number of basis vectors.
/// * _sparseRate: Controls density of sparse matches.
/// * _retainedCornersFraction: Retained corners fraction.
/// * _occlusionsThreshold: Occlusion threshold.
/// * _dampingFactor: Regularization term for solving least-squares. It is not related to the prior regularization.
/// * _claheClip: Clip parameter for CLAHE.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * _prior: Ptr<constPCAPrior>()
/// * _basis_size: Size(18,14)
/// * _sparse_rate: 0.024
/// * _retained_corners_fraction: 0.2
/// * _occlusions_threshold: 0.0003
/// * _damping_factor: 0.00002
/// * _clahe_clip: 14
#[inline]
pub fn new(_prior: core::Ptr<crate::optflow::PCAPrior>, _basis_size: core::Size, _sparse_rate: f32, _retained_corners_fraction: f32, _occlusions_threshold: f32, _damping_factor: f32, _clahe_clip: f32) -> Result<crate::optflow::OpticalFlowPCAFlow> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_OpticalFlowPCAFlow_OpticalFlowPCAFlow_PtrLconst_PCAPriorG_const_Size_float_float_float_float_float(_prior.as_raw_PtrOfPCAPrior(), _basis_size.opencv_as_extern(), _sparse_rate, _retained_corners_fraction, _occlusions_threshold, _damping_factor, _clahe_clip, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { crate::optflow::OpticalFlowPCAFlow::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { OpticalFlowPCAFlow, core::Algorithm, cv_OpticalFlowPCAFlow_to_Algorithm }
/// Constant methods for [crate::optflow::PCAPrior]
pub trait PCAPriorTraitConst {
fn as_raw_PCAPrior(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn get_padding(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_PCAPrior_getPadding_const(self.as_raw_PCAPrior(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_basis_size(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_PCAPrior_getBasisSize_const(self.as_raw_PCAPrior(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn fill_constraints(&self, a1: &mut f32, a2: &mut f32, b1: &mut f32, b2: &mut f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_PCAPrior_fillConstraints_const_floatX_floatX_floatX_floatX(self.as_raw_PCAPrior(), a1, a2, b1, b2, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::optflow::PCAPrior]
pub trait PCAPriorTrait: crate::optflow::PCAPriorTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_PCAPrior(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
///
/// This class can be used for imposing a learned prior on the resulting optical flow.
/// Solution will be regularized according to this prior.
/// You need to generate appropriate prior file with "learn_prior.py" script beforehand.
pub struct PCAPrior {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { PCAPrior }
impl Drop for PCAPrior {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_PCAPrior_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_PCAPrior_delete(self.as_raw_mut_PCAPrior()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for PCAPrior {}
impl crate::optflow::PCAPriorTraitConst for PCAPrior {
#[inline] fn as_raw_PCAPrior(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::optflow::PCAPriorTrait for PCAPrior {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_PCAPrior(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl PCAPrior {
#[inline]
pub fn new(path_to_prior: &str) -> Result<crate::optflow::PCAPrior> {
extern_container_arg!(path_to_prior);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_PCAPrior_PCAPrior_const_charX(path_to_prior.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { crate::optflow::PCAPrior::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter]
pub trait RLOFOpticalFlowParameterTraitConst {
fn as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn solver_type(&self) -> crate::optflow::SolverType {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getPropSolverType_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
ret
}
#[inline]
fn support_region_type(&self) -> crate::optflow::SupportRegionType {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getPropSupportRegionType_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
ret
}
#[inline]
fn norm_sigma0(&self) -> f32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getPropNormSigma0_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn norm_sigma1(&self) -> f32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getPropNormSigma1_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn small_win_size(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getPropSmallWinSize_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn large_win_size(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getPropLargeWinSize_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn cross_segmentation_threshold(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getPropCrossSegmentationThreshold_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn max_level(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getPropMaxLevel_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn use_initial_flow(&self) -> bool {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getPropUseInitialFlow_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn use_illumination_model(&self) -> bool {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getPropUseIlluminationModel_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn use_global_motion_prior(&self) -> bool {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getPropUseGlobalMotionPrior_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn max_iteration(&self) -> i32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getPropMaxIteration_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn min_eigen_value(&self) -> f32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getPropMinEigenValue_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn global_motion_ransac_threshold(&self) -> f32 {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getPropGlobalMotionRansacThreshold_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter()) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn get_solver_type(&self) -> Result<crate::optflow::SolverType> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getSolverType_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_support_region_type(&self) -> Result<crate::optflow::SupportRegionType> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getSupportRegionType_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_norm_sigma0(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getNormSigma0_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_norm_sigma1(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getNormSigma1_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_small_win_size(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getSmallWinSize_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_large_win_size(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getLargeWinSize_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_cross_segmentation_threshold(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getCrossSegmentationThreshold_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_max_level(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getMaxLevel_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_use_initial_flow(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getUseInitialFlow_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_use_illumination_model(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getUseIlluminationModel_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_use_global_motion_prior(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getUseGlobalMotionPrior_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_max_iteration(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getMaxIteration_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_min_eigen_value(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getMinEigenValue_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_global_motion_ransac_threshold(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_getGlobalMotionRansacThreshold_const(self.as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter]
pub trait RLOFOpticalFlowParameterTrait: crate::optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameterTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_solver_type(&mut self, val: crate::optflow::SolverType) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setPropSolverType_SolverType(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_support_region_type(&mut self, val: crate::optflow::SupportRegionType) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setPropSupportRegionType_SupportRegionType(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_norm_sigma0(&mut self, val: f32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setPropNormSigma0_float(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_norm_sigma1(&mut self, val: f32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setPropNormSigma1_float(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_small_win_size(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setPropSmallWinSize_int(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_large_win_size(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setPropLargeWinSize_int(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_cross_segmentation_threshold(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setPropCrossSegmentationThreshold_int(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_max_level(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setPropMaxLevel_int(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_use_initial_flow(&mut self, val: bool) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setPropUseInitialFlow_bool(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_use_illumination_model(&mut self, val: bool) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setPropUseIlluminationModel_bool(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_use_global_motion_prior(&mut self, val: bool) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setPropUseGlobalMotionPrior_bool(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_max_iteration(&mut self, val: i32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setPropMaxIteration_int(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_min_eigen_value(&mut self, val: f32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setPropMinEigenValue_float(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val) };
ret
}
#[inline]
fn set_global_motion_ransac_threshold(&mut self, val: f32) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setPropGlobalMotionRansacThreshold_float(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val) };
ret
}
/// Enable M-estimator or disable and use least-square estimator.
/// Enables M-estimator by setting sigma parameters to (3.2, 7.0). Disabling M-estimator can reduce
/// * runtime, while enabling can improve the accuracy.
/// ## Parameters
/// * val: If true M-estimator is used. If false least-square estimator is used.
/// * see also: setNormSigma0, setNormSigma1
#[inline]
fn set_use_m_estimator(&mut self, val: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setUseMEstimator_bool(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_solver_type_1(&mut self, val: crate::optflow::SolverType) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setSolverType_SolverType(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_support_region_type_1(&mut self, val: crate::optflow::SupportRegionType) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setSupportRegionType_SupportRegionType(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_norm_sigma0_1(&mut self, val: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setNormSigma0_float(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_norm_sigma1_1(&mut self, val: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setNormSigma1_float(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_small_win_size_1(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setSmallWinSize_int(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_large_win_size_1(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setLargeWinSize_int(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_cross_segmentation_threshold_1(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setCrossSegmentationThreshold_int(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_max_level_1(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setMaxLevel_int(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_use_initial_flow_1(&mut self, val: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setUseInitialFlow_bool(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_use_illumination_model_1(&mut self, val: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setUseIlluminationModel_bool(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_use_global_motion_prior_1(&mut self, val: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setUseGlobalMotionPrior_bool(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_max_iteration_1(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setMaxIteration_int(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_min_eigen_value_1(&mut self, val: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setMinEigenValue_float(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_global_motion_ransac_threshold_1(&mut self, val: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_setGlobalMotionRansacThreshold_float(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// This is used store and set up the parameters of the robust local optical flow (RLOF) algoritm.
///
/// The RLOF is a fast local optical flow approach described in [Senst2012](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2012) [Senst2013](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2013) [Senst2014](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2014)
/// and [Senst2016](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2016) similar to the pyramidal iterative Lucas-Kanade method as
/// proposed by [Bouguet00](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Bouguet00). More details and experiments can be found in the following thesis [Senst2019](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2019).
/// The implementation is derived from optflow::calcOpticalFlowPyrLK().
/// This RLOF implementation can be seen as an improved pyramidal iterative Lucas-Kanade and includes
/// a set of improving modules. The main improvements in respect to the pyramidal iterative Lucas-Kanade
/// are:
/// - A more robust redecending M-estimator framework (see [Senst2012](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2012)) to improve the accuracy at
/// motion boundaries and appearing and disappearing pixels.
/// - an adaptive support region strategies to improve the accuracy at motion boundaries to reduce the
/// corona effect, i.e oversmoothing of the PLK at motion/object boundaries. The cross-based segementation
/// strategy (SR_CROSS) proposed in [Senst2014](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2014) uses a simple segmenation approach to obtain the optimal
/// shape of the support region.
/// - To deal with illumination changes (outdoor sequences and shadow) the intensity constancy assumption
/// based optical flow equation has been adopt with the Gennert and Negahdaripour illumination model
/// (see [Senst2016](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2016)). This model can be switched on/off with the useIlluminationModel variable.
/// - By using a global motion prior initialization (see [Senst2016](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2016)) of the iterative refinement
/// the accuracy could be significantly improved for large displacements. This initialization can be
/// switched on and of with useGlobalMotionPrior variable.
///
/// The RLOF can be computed with the SparseOpticalFlow class or function interface to track a set of features
/// or with the DenseOpticalFlow class or function interface to compute dense optical flow.
/// ## See also
/// optflow::DenseRLOFOpticalFlow, optflow::calcOpticalFlowDenseRLOF(), optflow::SparseRLOFOpticalFlow, optflow::calcOpticalFlowSparseRLOF()
pub struct RLOFOpticalFlowParameter {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { RLOFOpticalFlowParameter }
impl Drop for RLOFOpticalFlowParameter {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_delete(self.as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for RLOFOpticalFlowParameter {}
impl crate::optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameterTraitConst for RLOFOpticalFlowParameter {
#[inline] fn as_raw_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameterTrait for RLOFOpticalFlowParameter {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl RLOFOpticalFlowParameter {
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<crate::optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { crate::optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates instance of optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter
#[inline]
pub fn create() -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_RLOFOpticalFlowParameter_create(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::optflow::SparseRLOFOpticalFlow]
pub trait SparseRLOFOpticalFlowConst: crate::video::SparseOpticalFlowConst {
fn as_raw_SparseRLOFOpticalFlow(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// @copydoc DenseRLOFOpticalFlow::setRLOFOpticalFlowParameter
/// ## See also
/// setRLOFOpticalFlowParameter
#[inline]
fn get_rlof_optical_flow_parameter(&self) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_SparseRLOFOpticalFlow_getRLOFOpticalFlowParameter_const(self.as_raw_SparseRLOFOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Threshold for the forward backward confidence check
/// For each feature point a motion vector  is computed.
/// * If the forward backward error 
/// * is larger than threshold given by this function then the status will not be used by the following
/// * vector field interpolation.  denotes the backward flow. Note, the forward backward test
/// * will only be applied if the threshold > 0. This may results into a doubled runtime for the motion estimation.
/// * see also: setForwardBackward
/// * see also: setForwardBackward
#[inline]
fn get_forward_backward(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_SparseRLOFOpticalFlow_getForwardBackward_const(self.as_raw_SparseRLOFOpticalFlow(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Class used for calculation sparse optical flow and feature tracking with robust local optical flow (RLOF) algorithms.
///
/// The RLOF is a fast local optical flow approach described in [Senst2012](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2012) [Senst2013](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2013) [Senst2014](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2014)
/// and [Senst2016](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2016) similar to the pyramidal iterative Lucas-Kanade method as
/// proposed by [Bouguet00](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Bouguet00). More details and experiments can be found in the following thesis [Senst2019](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2019).
/// The implementation is derived from optflow::calcOpticalFlowPyrLK().
///
/// For the RLOF configuration see optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter for further details.
/// Parameters have been described in [Senst2012](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2012), [Senst2013](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2013), [Senst2014](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2014) and [Senst2016](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Senst2016).
///
///
/// Note: SIMD parallelization is only available when compiling with SSE4.1.
/// ## See also
/// optflow::calcOpticalFlowSparseRLOF(), optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter
pub trait SparseRLOFOpticalFlow: crate::optflow::SparseRLOFOpticalFlowConst + crate::video::SparseOpticalFlow {
fn as_raw_mut_SparseRLOFOpticalFlow(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// @copydoc DenseRLOFOpticalFlow::setRLOFOpticalFlowParameter
#[inline]
fn set_rlof_optical_flow_parameter(&mut self, mut val: core::Ptr<crate::optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter>) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_SparseRLOFOpticalFlow_setRLOFOpticalFlowParameter_PtrLRLOFOpticalFlowParameterG(self.as_raw_mut_SparseRLOFOpticalFlow(), val.as_raw_mut_PtrOfRLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Threshold for the forward backward confidence check
/// For each feature point a motion vector  is computed.
/// * If the forward backward error 
/// * is larger than threshold given by this function then the status will not be used by the following
/// * vector field interpolation.  denotes the backward flow. Note, the forward backward test
/// * will only be applied if the threshold > 0. This may results into a doubled runtime for the motion estimation.
/// * see also: setForwardBackward
#[inline]
fn set_forward_backward(&mut self, val: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_SparseRLOFOpticalFlow_setForwardBackward_float(self.as_raw_mut_SparseRLOFOpticalFlow(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl dyn SparseRLOFOpticalFlow + '_ {
/// Creates instance of SparseRLOFOpticalFlow
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * rlofParam: see setRLOFOpticalFlowParameter
/// * forwardBackwardThreshold: see setForwardBackward
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * rlof_param: Ptr<RLOFOpticalFlowParameter>()
/// * forward_backward_threshold: 1.f
#[inline]
pub fn create(mut rlof_param: core::Ptr<crate::optflow::RLOFOpticalFlowParameter>, forward_backward_threshold: f32) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::optflow::SparseRLOFOpticalFlow>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_optflow_SparseRLOFOpticalFlow_create_PtrLRLOFOpticalFlowParameterG_float(rlof_param.as_raw_mut_PtrOfRLOFOpticalFlowParameter(), forward_backward_threshold, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::optflow::SparseRLOFOpticalFlow>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}