Expand description
§range-set-blaze
Integer sets as fast, sorted, integer ranges with full set operations
The integers can be any size (u8 to u128) and may be signed (i8 to i128). The set operations include union, intersection, difference, symmetric difference, and complement.
The crate’s main struct is RangeSetBlaze, a set of integers. See the documentation for details.
Unlike the standard
BTreeSetandHashSet,RangeSetBlazedoes not store every integer in the set. Rather, it stores sorted & disjoint ranges of integers in a cache-efficientBTreeMap. It differs from other interval libraries – that we know of – by offering full set operations and by being optimized for sets of clumpy integers.We can construct a
RangeSetBlazefrom unsorted & redundant integers (or ranges). When the inputs are clumpy, construction will be linear in the number of inputs and set operations will be sped up quadratically.
The crate’s main trait is SortedDisjoint. It is implemented by iterators of sorted & disjoint ranges of integers. See the SortedDisjoint documentation for details.
With any
SortedDisjointiterator we can perform set operations in one pass through the ranges and with minimal (constant) memory. It enforces the “sorted & disjoint” constraint at compile time. This trait is inspired by theSortedIteratortrait from the sorted_iter crate.SortedDisjointdiffers from its inspiration by specializing on disjoint integer ranges.
The crate supports no_std, WASM, and embedded projects. Use the command:
cargo add range-set-blaze --features "alloc" --no-default-features§Benchmarks
See the benchmarks for performance comparisons with other range-related crates.
Generally, for many tasks involving clumpy integers and ranges, RangeSetBlaze is much faster than alternatives.
The benchmarks are in the benches directory. To run them, use cargo bench.
§Articles
-
Nine Rules for Creating Fast, Safe, and Compatible Data Structures in Rust: Lessons from RangeSetBlaze in Towards Data Science. It provides a high-level overview of the crate and its design.
-
Nine Rules for Running Rust on the Web and on Embedded: Practical Lessons from Porting range-set-blaze to no_std and WASM in Towards Data Science. It covers porting to “no_std”.
-
Check AI-Generated Code Perfectly and Automatically My Experience Applying Kani’s Formal Verification to ChatGPT-Suggested Rust Code. Shows how to prove overflow safety.
-
Nine Rules to Formally Validate Rust Algorithms with Dafny in Towards Data Science. It shows how to formally validate one of the crate’s algorithms.
-
Nine Rules for SIMD Acceleration of your Rust Code: General Lessons from Boosting Data Ingestion in the range-set-blaze Crate by 7x in Towards Data Science
-
Also see: CHANGELOG
§Examples
Example 1
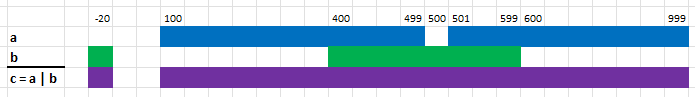
Here we take the union (operator “|”) of two RangeSetBlaze’s:
use range_set_blaze::RangeSetBlaze;
// a is the set of integers from 100 to 499 (inclusive) and 501 to 1000 (inclusive)
let a = RangeSetBlaze::from_iter([100..=499, 501..=999]);
// b is the set of integers -20 and the range 400 to 599 (inclusive)
let b = RangeSetBlaze::from_iter([-20..=-20, 400..=599]);
// c is the union of a and b, namely -20 and 100 to 999 (inclusive)
let c = a | b;
assert_eq!(c, RangeSetBlaze::from_iter([-20..=-20, 100..=999]));Example 2
In biology, suppose we want to find the intron regions of a gene but we are given only the transcription region and the exon regions.
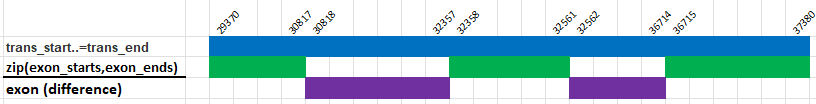
We create a RangeSetBlaze for the transcription region and a RangeSetBlaze for all the exon regions.
Then we take the difference between the transcription region and exon regions to find the intron regions.
use range_set_blaze::RangeSetBlaze;
let line = "chr15 29370 37380 29370,32358,36715 30817,32561,37380";
// split the line on white space
let mut iter = line.split_whitespace();
let chr = iter.next().unwrap();
// Parse the start and end of the transcription region into a RangeSetBlaze
let trans_start: i32 = iter.next().unwrap().parse().unwrap();
let trans_end: i32 = iter.next().unwrap().parse().unwrap();
let trans = RangeSetBlaze::from_iter([trans_start..=trans_end]);
assert_eq!(trans, RangeSetBlaze::from_iter([29370..=37380]));
// Parse the start and end of the exons into a RangeSetBlaze
let exon_starts = iter.next().unwrap().split(',').map(|s| s.parse::<i32>());
let exon_ends = iter.next().unwrap().split(',').map(|s| s.parse::<i32>());
let exon_ranges = exon_starts
.zip(exon_ends)
.map(|(s, e)| s.unwrap()..=e.unwrap());
let exons = RangeSetBlaze::from_iter(exon_ranges);
assert_eq!(
exons,
RangeSetBlaze::from_iter([29370..=30817, 32358..=32561, 36715..=37380])
);
// Use 'set difference' to find the introns
let intron = trans - exons;
assert_eq!(intron, RangeSetBlaze::from_iter([30818..=32357, 32562..=36714]));
for range in intron.ranges() {
let (start, end) = range.into_inner();
println!("{chr}\t{start}\t{end}");
}Modules§
- prelude
- This prelude module provides a convenient way to import the most commonly used types, traits, and functions.
Macros§
- intersection_
dyn - Intersects one or more
SortedDisjointiterators, creating a newSortedDisjointiterator. The input iterators need not to be of the same type. - union_
dyn - Unions one or more
SortedDisjointiterators, creating a newSortedDisjointiterator. The input iterators need not to be of the same type.
Structs§
- Assume
Sorted Starts - Gives any iterator of ranges the
SortedStartstrait without any checking. - Check
Sorted Disjoint - Gives the
SortedDisjointtrait to any iterator of ranges. The iterator will panic if/when it finds that the ranges are not actually sorted and disjoint. - DynSorted
Disjoint - Gives
SortedDisjointiterators a uniform type. Used by theunion_dynandintersection_dynmacros to give all their input iterators the same type. - Into
Iter - A (double-ended) iterator over the integer elements of a
RangeSetBlaze. - Into
Ranges Iter - An iterator that moves out the ranges in the
RangeSetBlaze, i.e., the integers as sorted & disjoint ranges. - Iter
- A (double-ended) iterator over the integer elements of a
RangeSetBlaze. - KMerge
- Works with
UnionIterto turn twoSortedDisjointiterators into aSortedDisjointiterator of their union, i.e., all the integers in any input iterator, as sorted & disjoint ranges. - Merge
- Works with
UnionIterto turn any number ofSortedDisjointiterators into aSortedDisjointiterator of their union, i.e., all the integers in any input iterator, as sorted & disjoint ranges. - NotIter
- Turns a
SortedDisjointiterator into aSortedDisjointiterator of its complement, i.e., all the integers not in the original iterator, as sorted & disjoint ranges. - Range
SetBlaze - A set of integers stored as sorted & disjoint ranges.
- Ranges
Iter - An iterator that visits the ranges in the
RangeSetBlaze, i.e., the integers as sorted & disjoint ranges. - Rogs
Iter Deprecated - Experimental: An iterator over
Rogs (ranges or gaps) in aRangeSetBlaze. - Union
Iter - Turns any number of
SortedStartsiterators into aSortedDisjointiterator of their union, i.e., all the integers in any input iterator, as sorted & disjoint ranges. UsesMergeorKMerge.
Enums§
- Rog
Deprecated - Experimental: Represents an range or gap in a
RangeSetBlaze.
Traits§
- Integer
- The element trait of the
RangeSetBlazeandSortedDisjoint, specificallyu8tou128(includingusize) andi8toi128(includingisize). - Multiway
Range SetBlaze - The trait used to provide methods on multiple
RangeSetBlaze’s, specificallyunionandintersection. - Multiway
Range SetBlaze Ref - The trait used to provide methods on multiple
RangeSetBlazereferences, specificallyunionandintersection. - Multiway
Sorted Disjoint - The trait used to define methods on multiple
SortedDisjointiterators, specificallyunionandintersection. - Sorted
Disjoint - The trait used to mark iterators that provide ranges that are sorted by start and disjoint. Set operations on iterators that implement this trait can be performed in linear time.
- Sorted
Starts - A trait used to mark iterators that provide ranges sorted by start, but not necessarily by end, and may overlap.


