Expand description
§range-set-blaze
Integer sets as fast, sorted integer ranges; Maps with integer-range keys; Full set operations
Supports all of Rust’s integer-like types, u8 to u128, i8 to i128, char (Unicode characters), Ipv4Addr, and Ipv6Addr.
Set operations—union, intersection, difference, symmetric difference, and complement— are available on both sets and maps.
The crate’s main structs are:
RangeSetBlaze, a set of integers. See the set documentation for details.RangeMapBlaze, a map from integers to values. See the map documentation for details.
Unlike the standard
BTreeSet/BTreeMapandHashSet/HashMap,RangeSetBlazedoes not store every integer in the set. Rather, it stores sorted & disjoint ranges of integers in a cache-efficientBTreeMap. It differs from other interval libraries – that we know of – by offering full set operations and by being optimized for sets of clumpy integers.We can construct a
RangeSetBlazeorRangeMapBlazefrom unsorted & redundant integers (or ranges). When the inputs are clumpy, construction will be linear in the number of inputs and set operations will be sped up quadratically.⚠️ Warning: All RangeMapBlaze operations (
into_iter, union, difference, symmetric difference, etc.) now give precedence to the right-hand map when ranges overlap. This change (from version 0.2.0) aligns with the behavior ofBTreeMapandHashMap.
The crate’s main traits are
SortedDisjoint, implemented by iterators of sorted & disjoint ranges of integers. See documentation for details.SortedDisjointMap, implemented by iterators of pairs, where the first item is a sorted & disjoint range of integers. The second item is a value. See documentation for details.
With any
SortedDisjointorSortedDisjointMapiterator we can perform set operations in one pass through the ranges and with minimal (constant) memory. The package enforces the “sorted & disjoint” constraint at compile time (making invalid states unrepresentable).
The crate supports no_std, WASM, and embedded (with alloc) projects. For no_std, etc., Use the command:
cargo add range-set-blaze --no-default-features§Benchmarks
See the set benchmarks and map benchmarks for performance comparisons with other range-related crates.
Generally, for many tasks involving clumpy integers and ranges, RangeSetBlaze is much faster than alternatives.
The benchmarks are in the benches directory. To run them, use cargo bench.
§Articles
-
Nine Rules for Creating Fast, Safe, and Compatible Data Structures in Rust: Lessons from RangeSetBlaze in Towards Data Science. It provides a high-level overview of the crate and its design.
-
Nine Rules for Running Rust on the Web and on Embedded: Practical Lessons from Porting range-set-blaze to no_std and WASM in Towards Data Science. It covers porting to “
no_std”. -
Check AI-Generated Code Perfectly and Automatically My Experience Applying Kani’s Formal Verification to ChatGPT-Suggested Rust Code. Shows how to prove overflow safety.
-
Nine Rules to Formally Validate Rust Algorithms with Dafny in Towards Data Science. It shows how to formally validate one of the crate’s algorithms.
-
Nine Rules for SIMD Acceleration of your Rust Code: General Lessons from Boosting Data Ingestion in the range-set-blaze Crate by 7x in Towards Data Science
-
Also see: CHANGELOG
§Examples
Example 1: Set Operations
Here we take the union (operator “|”) of two RangeSetBlaze’s:
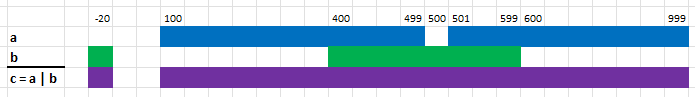
use range_set_blaze::prelude::*;
// a is the set of integers from 100 to 499 (inclusive) and 501 to 1000 (inclusive)
let a = RangeSetBlaze::from_iter([100..=499, 501..=999]);
// b is the set of integers -20 and the range 400 to 599 (inclusive)
let b = RangeSetBlaze::from_iter([-20..=-20, 400..=599]);
// c is the union of a and b, namely -20 and 100 to 999 (inclusive)
let c = a | b;
assert_eq!(c, RangeSetBlaze::from_iter([-20..=-20, 100..=999]));Example 2: Maps (and Network Addresses)
In networking, we can use RangeMapBlaze to visualize routing tables.
It efficiently merges adjacent or overlapping routes with identical next-hops, removes overlaps
(respecting priority), and provides fast lookups. While specialized prefix trees (tries) are typically
used in production routers for maximum efficiency, this example shows how RangeMapBlaze makes the information more understandable. Similar concepts apply when working with other range-mappings like font tables.
use range_set_blaze::prelude::*;
use std::net::Ipv4Addr;
// A routing table, sorted by prefix length (so, highest priority last)
let routing = [
// destination, prefix, next hop, interface
("0.0.0.0", 0, "152.10.0.0", "eth0"),
("10.0.0.0", 8, "10.3.4.2", "eth1"),
("10.0.1.12", 30, "10.1.1.0", "eth2"),
("10.0.1.8", 30, "10.1.1.0", "eth2"),
("10.0.1.7", 32, "10.1.1.0", "eth2"),
];
// Create a RangeMapBlaze from the routing table
let range_map = routing
.iter()
.map(|(dest, prefix_len, next_hop, interface)| {
let dest: Ipv4Addr = dest.parse().unwrap();
let next_hop: Ipv4Addr = next_hop.parse().unwrap();
let mask = u32::MAX.checked_shr(*prefix_len).unwrap_or(0);
let range_start = Ipv4Addr::from(u32::from(dest) & !mask);
let range_end = Ipv4Addr::from(u32::from(dest) | mask);
(range_start..=range_end, (next_hop, interface))
})
.collect::<RangeMapBlaze<_, _>>();
// Print the now disjoint, sorted ranges and their associated values
for (range, (next_hop, interface)) in range_map.range_values() {
println!("{range:?} → ({next_hop}, {interface})");
}
// Look up an address
assert_eq!(
range_map.get(Ipv4Addr::new(10, 0, 1, 6)),
Some(&(Ipv4Addr::new(10, 3, 4, 2), &"eth1"))
);Output:
0.0.0.0..=9.255.255.255 → (152.10.0.0, eth0)
10.0.0.0..=10.0.1.6 → (10.3.4.2, eth1)
10.0.1.7..=10.0.1.15 → (10.1.1.0, eth2)
10.0.1.16..=10.255.255.255 → (10.3.4.2, eth1)
11.0.0.0..=255.255.255.255 → (152.10.0.0, eth0)Example 3: Biology
In biology, suppose we want to find the intron regions of a gene but we are given only the transcription region and the exon regions.
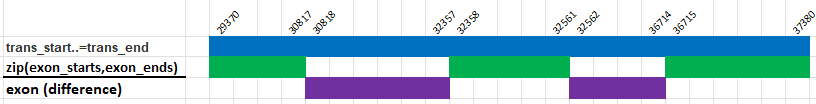
We create a RangeSetBlaze for the transcription region and a RangeSetBlaze for all the exon regions.
Then we take the difference between the transcription region and exon regions to find the intron regions.
use range_set_blaze::prelude::*;
let line = "chr15 29370 37380 29370,32358,36715 30817,32561,37380";
// split the line on white space
let mut iter = line.split_whitespace();
let chrom = iter.next().unwrap();
// Parse the start and end of the transcription region into a RangeSetBlaze
let trans_start: i32 = iter.next().unwrap().parse().unwrap();
let trans_end: i32 = iter.next().unwrap().parse().unwrap();
let trans = RangeSetBlaze::from_iter([trans_start..=trans_end]);
assert_eq!(trans, RangeSetBlaze::from_iter([29370..=37380]));
// Parse the start and end of the exons into a RangeSetBlaze
let exon_starts = iter.next().unwrap().split(',').map(|s| s.parse::<i32>());
let exon_ends = iter.next().unwrap().split(',').map(|s| s.parse::<i32>());
let exon_ranges = exon_starts
.zip(exon_ends)
.map(|(s, e)| s.unwrap()..=e.unwrap());
let exons = RangeSetBlaze::from_iter(exon_ranges);
assert_eq!(exons, RangeSetBlaze::from_iter([29370..=30817, 32358..=32561, 36715..=37380]));
// Use 'set difference' to find the introns
let intron = trans - exons;
assert_eq!(intron, RangeSetBlaze::from_iter([30818..=32357, 32562..=36714]));
for range in intron.ranges() {
let (start, end) = range.into_inner();
println!("{chrom}\t{start}\t{end}");
}§Contributing
Contributions are welcome! For development workflow, local testing, and CI information, see CONTRIBUTING.md.
Quick start for developers:
# Install just task runner
cargo install just
# Run all checks before pushing
just check-allSee just --list for all available development commands.
Modules§
- prelude
- This prelude module provides a convenient way to import the most commonly used types, traits, and functions.
Macros§
- intersection_
dyn - Intersects zero or more
SortedDisjointiterators, creating a newSortedDisjointiterator. The input iterators need not be of the same type. - intersection_
map_ dyn - Intersects zero or more
SortedDisjointMapiterators, creating a newSortedDisjointMapiterator. The input iterators need not be of the same type. - symmetric_
difference_ dyn - Computes the symmetric difference of zero or more
SortedDisjointiterators, creating a newSortedDisjointiterator. The input iterators need not be of the same type. - symmetric_
difference_ map_ dyn - Computes the symmetric difference of zero or more
SortedDisjointMapiterators, creating a newSortedDisjointMapiterator. The input iterators need not be of the same type. - union_
dyn - Unions zero or more
SortedDisjointiterators, creating a newSortedDisjointiterator. The input iterators need not be of the same type. - union_
map_ dyn - Unions zero or more
SortedDisjointMapiterators, creating a newSortedDisjointMapiterator. The input iterators need not be of the same type.
Structs§
- Assume
Priority Sorted Starts Map - Used internally by
UnionIterMapandSymDiffIterMap. - Assume
Sorted Starts - Gives any iterator of ranges the
SortedStartstrait without any checking. - Check
Sorted Disjoint - Gives the
SortedDisjointtrait to any iterator of ranges. The iterator will panic if/when it finds that the ranges are not actually sorted and disjoint. - Check
Sorted Disjoint Map - Gives the
SortedDisjointMaptrait to any iterator of range-value pairs. Will panic if the trait is not satisfied. - DynSorted
Disjoint - Gives
SortedDisjointiterators a uniform type. Used by theunion_dyn, etc. macros to give all their input iterators the same type. - DynSorted
Disjoint Map - Gives
SortedDisjointMapiterators a uniform type. Used by theunion_map_dyn, etc. macros to give all their input iterators the same type. - Intersection
Iter Map - This
structis created by theintersectionandmap_and_set_intersectionmethods onSortedDisjointMap. See the methods’ documentation for more. - Into
Iter - An iterator over the integer elements of a
RangeSetBlaze. Double-ended. - Into
Iter Map - An iterator over the integer elements of a
RangeMapBlaze. Double-ended. - Into
Keys - An iterator over the integer elements of a
RangeMapBlaze. Double-ended. - Into
Range Values Iter - This
structis created by theinto_range_valuesmethod onRangeMapBlaze. Seeinto_range_values’s documentation for more. Double-ended. - Into
Ranges Iter - This
structis created by theinto_rangesmethod onRangeSetBlaze. Seeinto_ranges’s documentation for more. Double-ended. - Into
Values - An iterator over the values of a
RangeMapBlaze. Double-ended. - Iter
- An iterator over the integer elements of a
RangeSetBlaze. Double-ended. - IterMap
- An iterator over the integer elements of a
RangeMapBlaze. Double-ended. - KMerge
- Used internally by
UnionIterandSymDiffIter. - KMerge
Map - Used internally by
UnionIterMapandSymDiffIterMap. - Keys
- An iterator over the integer elements of a
RangeMapBlaze. Double-ended. - MapInto
Ranges Iter - This
structis created by theinto_rangesmethod onRangeMapBlaze. Seeinto_ranges’s documentation for more. - MapRanges
Iter - This
structis created by therangesmethod onRangeMapBlaze. Seeranges’s documentation for more. - Merge
- Used internally by
UnionIterandSymDiffIter. - Merge
Map - Used internally by
UnionIterMapandSymDiffIterMap. - NotIter
- The output of
SortedDisjoint::complementandSortedDisjointMap::complement_with. - Range
MapBlaze - A map from integers to values stored as a map of sorted & disjoint ranges to values.
- Range
Once RangeOnceis an iterator which emits a singleRangeInclusivevalue before fusing.- Range
SetBlaze - A set of integers stored as sorted & disjoint ranges.
- Range
Values Iter - This
structis created by therange_valuesmethod onRangeMapBlaze. Seerange_values’s documentation for more. Double-ended. - Range
Values ToRanges Iter - This
structis used internally. - Ranges
Iter - This
structis created by therangesmethod onRangeSetBlaze. Seeranges’s documentation for more. Double-ended. - Rogs
Iter Deprecated - Experimental: This struct is created by the
rogs_rangemethod onRangeSetBlaze. Seerogs_rangefor more information. - SymDiff
Iter - This
structis created by thesymmetric_differencemethod onSortedDisjoint. Seesymmetric_difference’s documentation for more. - SymDiff
Iter Map - This
structis created by thesymmetric_differencemethod onSortedDisjointMap. Seesymmetric_difference’s documentation for more. - Union
Iter - This
structis created by theunionmethod onSortedStarts. Seeunion’s documentation for more. - Union
Iter Map - This
structis created by theunionmethod. Seeunion’s documentation for more. - Values
- An iterator over the values of a
RangeMapBlaze. Double-ended.
Enums§
- Rog
Deprecated - Experimental: Represents an range or gap in a
RangeSetBlaze. - UInt
Plus One - Represents values from
0tou128::MAX + 1(inclusive).
Traits§
- Integer
- Represents elements that can be used within
RangeSetBlazeand as keys inRangeMapBlaze. - Into
String - Converts the implementing type into a String by consuming it.
- Multiway
Range MapBlaze - Provides methods on zero or more
RangeMapBlaze’s, specificallyunion,intersectionandsymmetric_difference. - Multiway
Range MapBlaze Ref - Provides methods on zero or more
RangeMapBlazereferences, specificallyunion,intersectionandsymmetric_difference. - Multiway
Range SetBlaze - Provides methods on zero or more
RangeSetBlaze’s, specificallyunion,intersectionandsymmetric_difference. - Multiway
Range SetBlaze Ref - Provides methods on zero or more
RangeSetBlazereferences, specificallyunion,intersection, andsymmetric_difference. - Multiway
Sorted Disjoint - Provides methods on zero or more
SortedDisjointiterators, specificallyunion,intersection, andsymmetric_difference. - Multiway
Sorted Disjoint Map - Provides methods on zero or more
SortedDisjointMapiterators, specificallyunion,intersection, andsymmetric_difference. - Sorted
Disjoint - Marks iterators that provide ranges that are sorted by start and disjoint. Set operations on iterators that implement this trait can be performed in linear time.
- Sorted
Disjoint Map - Marks iterators that provide
(range, value)pairs that are sorted and disjoint. Set operations on iterators that implement this trait can be performed in linear time. - Sorted
Starts - Used internally. Marks iterators that provide ranges sorted by start, but that are not necessarily disjoint. The ranges are non-empty.
- Sorted
Starts Map - Used internally. Marks iterators that provide
(range, value)pairs that are sorted by the range’s start, but that are not necessarily disjoint. - Value
Ref - A trait for cloneable references to
Eq + Clonevalues, used by theSortedDisjointMaptrait.


