#[repr(C)]pub struct Vertex {
pub pos: Vec3,
pub norm: Vec3,
pub uv: Vec2,
pub col: Color32,
}Expand description
This represents a single vertex in a Mesh, all StereoKit Meshes currently use this exact layout! It’s good to fill out all values of a Vertex explicitly, as default values for the normal (0,0,0) and color (0,0,0,0) will cause your mesh to appear completely black, or even transparent in most shaders! https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Vertex.html
§Examples
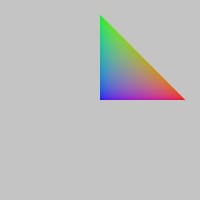
use stereokit_rust::{maths::{Vec3, Vec2, Matrix}, util::Color32, mesh::{Mesh,Vertex}, material::Material};
// Creating vertices with all fields specified
let vertices = [
Vertex::new(Vec3::ZERO,Vec3::UP,None, Some(Color32::rgb(0, 0, 255))),
Vertex::new(Vec3::X, Vec3::UP,Some(Vec2::X),Some(Color32::rgb(255, 0, 0))),
Vertex::new(Vec3::Y, Vec3::UP,Some(Vec2::Y),Some(Color32::rgb(0,255, 0))),
];
let indices = [0, 1, 2, 2, 1, 0];
let mut mesh = Mesh::new();
mesh.id("most_basic_mesh").keep_data(true).set_data(&vertices, &indices, true);
let material = Material::pbr();
filename_scr = "screenshots/basic_mesh.jpeg";
test_screenshot!( // !!!! Get a proper main loop !!!!
mesh.draw(token, &material, Matrix::IDENTITY, None, None);
);
Fields§
§pos: Vec3Position of the vertex, in model space coordinates.
norm: Vec3The normal of this vertex, or the direction the vertex is facing. Preferably normalized.
uv: Vec2The texture coordinates at this vertex.
col: Color32The color of the vertex. If you aren’t using it, set it to white.
Implementations§
Source§impl Vertex
impl Vertex
Sourcepub fn new<V: Into<Vec3>>(
position: V,
normal: V,
texture_coordinate: Option<Vec2>,
color: Option<Color32>,
) -> Self
pub fn new<V: Into<Vec3>>( position: V, normal: V, texture_coordinate: Option<Vec2>, color: Option<Color32>, ) -> Self
Create a new Vertex. https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Vertex/Vertex.html
position- Location of the vertex, this is typically meters in model space.normal- The direction the Vertex is facing. Never leave this as zero, or your lighting may turn out black! A good default value if you don’t know what to put here is (0,1,0), but a Mesh composed entirely of this value will have flat lighting.texture_coordinate- If None, set the value to Vec2::ZEROcolor- If None, set the value to Color32::WHITE
§Examples
use stereokit_rust::{maths::{Vec3, Vec2}, mesh::Vertex, util::Color32};
let vertex = Vertex::new([0.0, 0.0, 0.0], [0.0, 1.0, 0.0], None, None);
let vertex_bis = Vertex{
pos: Vec3::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0),
norm: Vec3::new(0.0, 1.0, 0.0),
uv: Vec2::ZERO,
col: Color32::WHITE};
assert_eq!(vertex, vertex_bis);
let vertex = Vertex::new([0.0, 0.0, 0.0], [0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
Some(Vec2::ZERO), Some(Color32::BLACK_TRANSPARENT) );
let vertex_default = Vertex::default();
assert_eq!(vertex, vertex_default);Trait Implementations§
impl Copy for Vertex
impl StructuralPartialEq for Vertex
Auto Trait Implementations§
impl Freeze for Vertex
impl RefUnwindSafe for Vertex
impl Send for Vertex
impl Sync for Vertex
impl Unpin for Vertex
impl UnwindSafe for Vertex
Blanket Implementations§
Source§impl<T> BorrowMut<T> for Twhere
T: ?Sized,
impl<T> BorrowMut<T> for Twhere
T: ?Sized,
Source§fn borrow_mut(&mut self) -> &mut T
fn borrow_mut(&mut self) -> &mut T
Mutably borrows from an owned value. Read more
Source§impl<T> CloneToUninit for Twhere
T: Clone,
impl<T> CloneToUninit for Twhere
T: Clone,
Source§impl<T> Downcast for Twhere
T: Any,
impl<T> Downcast for Twhere
T: Any,
Source§fn into_any(self: Box<T>) -> Box<dyn Any>
fn into_any(self: Box<T>) -> Box<dyn Any>
Convert
Box<dyn Trait> (where Trait: Downcast) to Box<dyn Any>. Box<dyn Any> can
then be further downcast into Box<ConcreteType> where ConcreteType implements Trait.Source§fn into_any_rc(self: Rc<T>) -> Rc<dyn Any>
fn into_any_rc(self: Rc<T>) -> Rc<dyn Any>
Convert
Rc<Trait> (where Trait: Downcast) to Rc<Any>. Rc<Any> can then be
further downcast into Rc<ConcreteType> where ConcreteType implements Trait.Source§fn as_any(&self) -> &(dyn Any + 'static)
fn as_any(&self) -> &(dyn Any + 'static)
Convert
&Trait (where Trait: Downcast) to &Any. This is needed since Rust cannot
generate &Any’s vtable from &Trait’s.Source§fn as_any_mut(&mut self) -> &mut (dyn Any + 'static)
fn as_any_mut(&mut self) -> &mut (dyn Any + 'static)
Convert
&mut Trait (where Trait: Downcast) to &Any. This is needed since Rust cannot
generate &mut Any’s vtable from &mut Trait’s.