#[repr(C)]pub struct Bounds {
pub center: Vec3,
pub dimensions: Vec3,
}Expand description
Bounds is an axis aligned bounding box type that can be used for storing the sizes of objects, calculating containment, intersections, and more!
While the constructor uses a center+dimensions for creating a bounds, don’t forget the static From* methods that allow you to define a Bounds from different types of data! https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds.html
§Examples
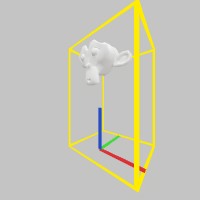
use stereokit_rust::{maths::{Vec3, Matrix, Pose}, model::Model, ui::Ui,
mesh::Mesh, material::Material, util::named_colors};
let model = Model::from_file("center.glb", None).unwrap().copy();
let cube = Mesh::cube();
let mut material_cube = Material::ui_box();
material_cube.color_tint(named_colors::GOLD)
.border_size(0.05);
let scale = 0.4;
let bounds = model.get_bounds() * scale;
let transform = Matrix::s(Vec3::ONE * scale);
let transform_cube = Matrix::t_s( bounds.center, bounds.dimensions);
let mut handle_pose =
Pose::new([0.0,-0.95,-0.65], Some([0.0, 140.0, 0.0].into()));
filename_scr = "screenshots/bounds.jpeg";
test_screenshot!( // !!!! Get a proper main loop !!!!
Ui::handle_begin( "Model Handle", &mut handle_pose,
bounds, false, None, None);
model.draw(token, transform, None, None);
cube.draw(token, &material_cube, transform_cube, None, None);
Ui::handle_end();
);
Fields§
§center: Vec3§dimensions: Vec3Implementations§
Source§impl Bounds
impl Bounds
Sourcepub fn new<V: Into<Vec3>>(center: V, dimensions: V) -> Bounds
pub fn new<V: Into<Vec3>>(center: V, dimensions: V) -> Bounds
Creates a bounding box object! https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/Bounds.html
- center - The exact center of the box.
- dimensions - The total size of the box, from one end to the other. This is the width, height, and depth of the Bounds.
§Examples
use stereokit_rust::maths::{Vec3, Bounds};
let bounds = Bounds::new([1.0, 2.0, 3.0], [4.0, 5.0, 6.0]);
assert_eq!(bounds.center, Vec3::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0));
assert_eq!(bounds.dimensions, Vec3::new(4.0, 5.0, 6.0));Sourcepub fn bounds_centered(dimensions: impl Into<Vec3>) -> Bounds
pub fn bounds_centered(dimensions: impl Into<Vec3>) -> Bounds
Creates a bounding box object centered around zero! https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/Bounds.html
- dimensions - The total size of the box, from one end to the other. This is the width, height, and depth of the Bounds.
§Examples
use stereokit_rust::maths::{Vec3, Bounds};
let bounds = Bounds::bounds_centered( [4.0, 5.0, 6.0]);
assert_eq!(bounds.center, Vec3::ZERO);
assert_eq!(bounds.dimensions, Vec3::new(4.0, 5.0, 6.0));Sourcepub fn from_corner<V: Into<Vec3>>(bottom_left_back: V, dimensions: V) -> Bounds
pub fn from_corner<V: Into<Vec3>>(bottom_left_back: V, dimensions: V) -> Bounds
Create a bounding box from a corner, plus box dimensions. https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/FromCorner.html
- bottom_left_back - The -X,-Y,-Z corner of the box.
- dimensions - The dimensions of the bounding box.
§Examples
use stereokit_rust::maths::{Vec3, Bounds};
let bounds = Bounds::from_corner( Vec3::ZERO, [1.0, 2.0, 3.0].into());
assert_eq!(bounds.center, [0.5, 1.0, 1.5].into());
assert_eq!(bounds.dimensions, Vec3::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0));Sourcepub fn from_corners<V: Into<Vec3>>(
bottom_left_back: V,
top_right_front: V,
) -> Bounds
pub fn from_corners<V: Into<Vec3>>( bottom_left_back: V, top_right_front: V, ) -> Bounds
Create a bounding box between two corner points. https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/FromCorners.html
- bottom_left_back - The -X,-Y,-Z corner of the box.
- top_right_front - The +X,+Y,+Z corner of the box.
§Examples
use stereokit_rust::maths::{Vec3, Bounds};
let bounds = Bounds::from_corners( Vec3::ZERO, Vec3::ONE);
assert_eq!(bounds.center, Vec3::ONE / 2.0);
assert_eq!(bounds.dimensions, Vec3::ONE);Sourcepub fn grown_point(&mut self, pt: impl Into<Vec3>) -> &mut Self
pub fn grown_point(&mut self, pt: impl Into<Vec3>) -> &mut Self
Grow the Bounds to encapsulate the provided point. Returns the result, and does NOT modify the current bounds. https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/Grown.html
- pt - The point to encapsulate! This should be in the same space as the bounds.
see also `bounds_grow_to_fit_pt
§Examples
use stereokit_rust::maths::{Vec3, Bounds};
let mut bounds = Bounds::from_corners( Vec3::ZERO, Vec3::ONE);
bounds.grown_point(Vec3::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0));
assert_eq!(bounds.center, Vec3{ x: 0.5, y: 1.0, z: 1.5 });
assert_eq!(bounds.dimensions, Vec3 { x: 1.0, y: 2.0, z: 3.0 });Sourcepub fn grown_box<M: Into<Matrix>>(
&mut self,
box_: impl AsRef<Bounds>,
opt_box_transform: M,
) -> &mut Self
pub fn grown_box<M: Into<Matrix>>( &mut self, box_: impl AsRef<Bounds>, opt_box_transform: M, ) -> &mut Self
Grow the Bounds to encapsulate the provided box after it has been transformed by the provided matrix transform. This will transform each corner of the box, and expand the bounds to encapsulate each point! https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/Grown.html
- box_ - the box to encapsulate! The corners of this box are transformed, and then used to grow the bounds.
- opt_box_transform - to center use Matrix::IDENTITY
see also [bounds_grow_to_fit_box] see also [bounds_grow_to_fit_pt]
§Examples
use stereokit_rust::maths::{Vec3, Matrix, Bounds};
let mut bounds = Bounds::from_corners( Vec3::ZERO, Vec3::ONE);
let bounds_plus = Bounds::from_corners( Vec3::ONE, Vec3::ONE * 2.0);
bounds.grown_box(bounds_plus, Matrix::IDENTITY);
assert_eq!(bounds.center, Vec3::ONE);
assert_eq!(bounds.dimensions, Vec3::ONE * 2.0);Sourcepub fn scale(&mut self, scale: f32) -> &mut Self
pub fn scale(&mut self, scale: f32) -> &mut Self
Scale this bounds. It will scale the center as well as the dimensions! Modifies this bounds object. https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/Scale.html
- scale - The scale to apply.
see also Bounds::scale_vec Bounds::scaled Bounds::scaled_vec and ‘/’ ‘*’ operator
§Examples
use stereokit_rust::maths::{Vec3, Matrix, Bounds};
let mut bounds = Bounds::from_corners( Vec3::ZERO, Vec3::ONE);
bounds.scale(2.0);
let bounds_plus = Bounds::from_corners( Vec3::ZERO, Vec3::ONE) * 2.0;
assert_eq!(bounds.center, bounds_plus.center);
assert_eq!(bounds.dimensions, bounds_plus.dimensions);Sourcepub fn scale_vec(&mut self, scale: impl Into<Vec3>) -> &mut Self
pub fn scale_vec(&mut self, scale: impl Into<Vec3>) -> &mut Self
Scale this bounds. It will scale the center as well as the dimensions! Modifies this bounds object. https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/Scale.html
- scale - The scale to apply.
see also Bounds::scale Bounds::scaled_vec Bounds::scaled and ‘/’ ‘*’ operator
§Examples
use stereokit_rust::maths::{Vec3, Matrix, Bounds};
let mut bounds = Bounds::from_corners( Vec3::ZERO, Vec3::ONE);
bounds.scale_vec([1.0, 2.0, 3.0]);
let bounds_plus = Bounds::from_corners( Vec3::ZERO, Vec3::ONE) * Vec3::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);
assert_eq!(bounds.center, bounds_plus.center);
assert_eq!(bounds.dimensions, bounds_plus.dimensions);Sourcepub fn contains_point(&self, pt: impl Into<Vec3>) -> bool
pub fn contains_point(&self, pt: impl Into<Vec3>) -> bool
Does the Bounds contain the given point? This includes points that are on the surface of the Bounds. https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/Contains.html
- pt - A point in the same coordinate space as the Bounds.
see also bounds_point_contains
§Examples
use stereokit_rust::maths::{Vec3, Bounds, Matrix};
// A cube of 1 meter per side at this position, aligned with x y and z axis.
let box_transform = Matrix::t([10.0, 1.0, 2.0]);
let box_bounds = Bounds::bounds_centered([1.0,1.0,1.0]);
let inv = box_transform.get_inverse();
let point1 = inv.transform_point([10.2, 1.3, 2.4]);
let point2 = inv.transform_point([10.9, 1.8, 2.1]);
let point3 = inv.transform_point([10.5, 2.01, 1.7]);
let point4 = inv.transform_point([9.5, 0.7, 1.5]);
assert!(box_bounds.contains_point(point1), "point1 should be inside");
assert!(!box_bounds.contains_point(point2), "point2 should be outside");
assert!(!box_bounds.contains_point(point3), "point3 should be outside");
assert!(box_bounds.contains_point(point4), "point4 should be inside");
assert!(box_bounds.contains_point([0.5, 0.5, 0.5]),
"inverse point should be inside");Sourcepub fn contains_line<V3: Into<Vec3>>(&self, line_pt1: V3, line_pt2: V3) -> bool
pub fn contains_line<V3: Into<Vec3>>(&self, line_pt1: V3, line_pt2: V3) -> bool
Does the Bounds contain or intersects with the given line? https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/Contains.html
- line_pt1 - The first point on the line.
- line_pt2 - The second point on the line.
see also bounds_line_contains
§Examples
use stereokit_rust::maths::{Vec3, Bounds, Matrix};
// A cube of 1 meter per side at this position, aligned with x y and z axis.
let box_transform = Matrix::t([10.0, 1.0, 2.0]);
let box_bounds = Bounds::bounds_centered([1.0,1.0,1.0]);
let inv = box_transform.get_inverse();
let point1 = inv.transform_point([10.2, 1.3, 2.4]);
let point2 = inv.transform_point([10.9, 1.8, 2.1]);
let point3 = inv.transform_point([10.5, 2.01, 1.7]);
let point4 = inv.transform_point([9.5, 0.7, 1.5]);
assert!(box_bounds.contains_line(point1, point2), "point1-point2 should be inside");
assert!(!box_bounds.contains_line(point2, point3), "point2-point3 should be outside");
assert!(box_bounds.contains_line(point3, point4), "point3-point4 should be inside");
assert!(box_bounds.contains_line(point4, point1), "point4-point1 should be inside");
assert!(box_bounds.contains_line([0.1, 0.1, 0.1], [0.9, 0.9, 0.9]),
"inverse line should be inside");Sourcepub fn contains_capsule<V3: Into<Vec3>>(
&self,
line_pt1: V3,
line_pt2: V3,
radius: f32,
) -> bool
pub fn contains_capsule<V3: Into<Vec3>>( &self, line_pt1: V3, line_pt2: V3, radius: f32, ) -> bool
Does the bounds contain or intersect with the given capsule? https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/Contains.html
- pt1 - The first point of the capsule.
- pt2 - The second point of the capsule.
- radius - The radius of the capsule.
see also bounds_capsule_contains
§Examples
use stereokit_rust::maths::{Vec3, Bounds, Matrix};
// A cube of 1 meter per side at this position, aligned with x y and z axis.
let box_transform = Matrix::t([10.0, 1.0, 2.0]);
let box_bounds = Bounds::bounds_centered([1.0,1.0,1.0]);
let inv = box_transform.get_inverse();
let point1 = inv.transform_point([10.2, 1.3, 2.4]);
let point2 = inv.transform_point([10.9, 1.8, 2.1]);
let point3 = inv.transform_point([10.5, 2.01, 1.7]);
let point4 = inv.transform_point([9.5, 0.7, 1.5]);
assert!(box_bounds.contains_capsule(point1, point2, 0.1), "point1-point2 should be inside");
assert!(!box_bounds.contains_capsule(point2, point3, 0.1), "point2-point3 * 0.1 should be outside");
assert!(box_bounds.contains_capsule(point2, point3, 0.4), "point2-point3 * 0.4 should be inside");
assert!(box_bounds.contains_capsule(point3, point4, 0.1), "point3-point4 should be inside");
assert!(box_bounds.contains_capsule(point4, point1, 0.1), "point4-point1 should be inside");
assert!(box_bounds.contains_capsule([0.1, 0.1, 0.1], [0.9, 0.9, 0.9], 10.0),
"inverse line * 10 should be inside");Sourcepub fn intersect<R: Into<Ray>>(&self, ray: R) -> Option<Vec3>
pub fn intersect<R: Into<Ray>>(&self, ray: R) -> Option<Vec3>
Calculate the intersection between a Ray, and these bounds. Returns false if no intersection occurred, and ‘at’ will contain the nearest intersection point to the start of the ray if an intersection is found! https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/Intersect.html
- ray - Any Ray in the same coordinate space as the Bounds
Returns the closest intersection point to the origin of the ray or None if there isn’t an instersection
see also bounds_ray_intersect same as Ray::intersect_bounds
§Examples
use stereokit_rust::maths::{Vec3, Bounds, Matrix, Ray};
// A cube of 1 meter per side at this position, aligned with x y and z axis.
let box_transform = Matrix::t([10.0, 1.0, 2.0]);
let box_bounds = Bounds::bounds_centered([1.0,1.0,1.0]);
let inv = box_transform.get_inverse();
let ray1 = inv.transform_ray(Ray::new([10.2, 1.3, 2.4],[0.0, 1.0, 0.0]));
let ray2 = inv.transform_ray(Ray::new([10.9, 1.8, 2.6],[0.0, 0.0, 1.0]));
let ray3 = inv.transform_ray(Ray::new([10.5, 2.0, 2.7],[1.0, 0.0, 1.0]));
assert!(box_bounds.intersect(ray1).is_some(), "should be a point of contact");
assert_eq!(box_bounds.intersect(ray2), None);
assert_eq!(box_bounds.intersect(ray3), None);
assert_eq!(box_bounds.intersect(Ray::new([1.1, 1.1, 1.1], [-1.9, -1.9, -1.9])),
Some([0.5, 0.5, 0.5].into()));
// We want the contact point for ray1
let contact_point = box_bounds.intersect(ray1)
.expect ("There should be a point of contact");
let contact_point = box_transform.transform_point(contact_point);
assert_eq!(contact_point, [10.2, 1.3, 2.4 ].into());Sourcepub fn scaled(&self, scale: f32) -> Self
pub fn scaled(&self, scale: f32) -> Self
Scale the bounds. It will scale the center as well as the dimensions! Returns a new Bounds. equivalent to using multiply operator https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/Scaled.html
- scale - The scale to apply.
see also Bounds::scale Bounds::scaled_vec Bounds::scale_vec and ‘/’ ‘*’ operator
§Examples
use stereokit_rust::maths::{Vec3, Bounds};
let mut bounds = Bounds::from_corners( Vec3::ZERO, Vec3::ONE);
let bounds_scaled = bounds.scaled(2.0);
let bounds_plus = Bounds::from_corners( Vec3::ZERO, Vec3::ONE) * 2.0;
assert_eq!(*bounds.scale(2.0), bounds_scaled);
assert_eq!(bounds_scaled.center, bounds_plus.center);
assert_eq!(bounds_scaled.dimensions, bounds_plus.dimensions);Sourcepub fn scaled_vec(&self, scale: impl Into<Vec3>) -> Self
pub fn scaled_vec(&self, scale: impl Into<Vec3>) -> Self
Scale the bounds. It will scale the center as well as the dimensions! Returns a new Bounds. equivalent to using multiply operator https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/Scaled.html
- scale - The scale to apply.
see also Bounds::scale_vec Bounds::scale Bounds::scaled and ‘/’ ‘*’ operator
§Examples
use stereokit_rust::maths::{Vec3, Bounds};
let bounds = Bounds::from_corners( Vec3::ZERO, Vec3::ONE);
let bounds_scaled = bounds.scaled_vec([1.0, 2.0, 3.0]);
let bounds_plus = Bounds::from_corners( Vec3::ZERO, Vec3::ONE) * Vec3::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);
assert_eq!(bounds * Vec3::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0), bounds_scaled);
assert_eq!(bounds_scaled.center, bounds_plus.center);
assert_eq!(bounds_scaled.dimensions, bounds_plus.dimensions);Sourcepub fn transformed(&self, transform: impl Into<Matrix>) -> Self
pub fn transformed(&self, transform: impl Into<Matrix>) -> Self
This returns a Bounds that encapsulates the transformed points of the current Bounds’s corners. Note that this will likely introduce a lot of extra empty volume in many cases, as the result is still always axis aligned. https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/Transformed.html
- transform - A transform Matrix for the current Bounds’s corners.
see also `bounds_transform
§Examples
use stereokit_rust::maths::{Vec3, Bounds, Matrix};
let matrix = Matrix::r([90.0, 90.0, 90.0]);
let bounds = Bounds::bounds_centered([1.0, 1.0, 1.0]);
let bounds_transformed = bounds.transformed(matrix);
assert_eq!(bounds_transformed.dimensions, Vec3{x: 1.0000001, y: 0.99999994, z: 0.99999994});
assert_eq!(bounds_transformed.center, Vec3{x:0.0, y:0.0, z:0.0})Sourcepub fn tlc(&self) -> Vec3
pub fn tlc(&self) -> Vec3
From the front, this is the Top (Y+), Left (X+), Center (Z0) of the bounds. Useful when working with UI layout bounds. https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/TLC.html
see also Bounds::tlb
§Examples
use stereokit_rust::maths::{Vec3, Bounds};
let bounds = Bounds::bounds_centered([1.0, 1.0, 1.0]);
assert_eq!(bounds.tlc(), Vec3{x:0.5, y:0.5, z: 0.0});Sourcepub fn tlb(&self) -> Vec3
pub fn tlb(&self) -> Vec3
From the front, this is the Top (Y+), Left (X+), Back (Z+) of the bounds. Useful when working with UI layout bounds. https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/TLB.html
see also Bounds::tlb
§Examples
use stereokit_rust::maths::{Vec3, Bounds};
let bounds = Bounds::bounds_centered([1.0, 1.0, 1.0]);
assert_eq!(bounds.tlb(), Vec3{x:0.5, y:0.5, z: 0.5});Trait Implementations§
Source§impl Display for Bounds
impl Display for Bounds
Source§fn fmt(&self, f: &mut Formatter<'_>) -> Result
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut Formatter<'_>) -> Result
Creates a text description of the Bounds, in the format of “[center:X dimensions:X]” https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/ToString.html
§Examples
use stereokit_rust::maths::{Vec3, Bounds};
let bounds = Bounds::new([1.1, 2.0, 3.0], [4.0, 5.0, 6.0]);
assert_eq!(format!("{}", bounds),
"[center:[x:1.1, y:2, z:3] dimensions:[x:4, y:5, z:6]]");Source§impl Mul<Bounds> for f32
This operator will create a new Bounds that has been properly scaled up by the float. This does affect the center
position of the Bounds.
https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/op_Multiply.html
impl Mul<Bounds> for f32
This operator will create a new Bounds that has been properly scaled up by the float. This does affect the center position of the Bounds. https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/op_Multiply.html
Source§fn mul(self, rhs: Bounds) -> Self::Output
fn mul(self, rhs: Bounds) -> Self::Output
§Examples
use stereokit_rust::maths::{Vec3, Bounds};
let bounds = Bounds::from_corners( Vec3::ZERO, Vec3::ONE);
let bounds_scaled = 2.0 * bounds;
assert_eq!(bounds_scaled.center, Vec3::ONE);
assert_eq!(bounds_scaled.dimensions, Vec3::new(2.0, 2.0, 2.0));Source§impl Mul<Vec3> for Bounds
This operator will create a new Bounds that has been properly scaled up by the Vec3. This does affect the center
position of the Bounds.
https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/op_Multiply.html
impl Mul<Vec3> for Bounds
This operator will create a new Bounds that has been properly scaled up by the Vec3. This does affect the center position of the Bounds. https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/op_Multiply.html
Source§fn mul(self, rhs: Vec3) -> Self::Output
fn mul(self, rhs: Vec3) -> Self::Output
§Examples
use stereokit_rust::maths::{Vec3, Bounds};
let bounds = Bounds::from_corners( Vec3::ZERO, Vec3::ONE);
let bounds_scaled = bounds * Vec3::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);
assert_eq!(bounds_scaled.center, Vec3::new(0.5, 1.0, 1.5));
assert_eq!(bounds_scaled.dimensions, Vec3::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0));Source§impl Mul<f32> for Bounds
This operator will create a new Bounds that has been properly scaled up by the float. This does affect the center
position of the Bounds.
https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/op_Multiply.html
impl Mul<f32> for Bounds
This operator will create a new Bounds that has been properly scaled up by the float. This does affect the center position of the Bounds. https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/op_Multiply.html
Source§impl MulAssign<Vec3> for Bounds
This operator will create a new Bounds that has been properly scaled up by the Vec3. This does affect the center
position of the Bounds.
https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/op_Multiply.html
impl MulAssign<Vec3> for Bounds
This operator will create a new Bounds that has been properly scaled up by the Vec3. This does affect the center position of the Bounds. https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/op_Multiply.html
Source§fn mul_assign(&mut self, rhs: Vec3)
fn mul_assign(&mut self, rhs: Vec3)
§Examples
use stereokit_rust::maths::{Vec3, Bounds};
let mut bounds = Bounds::from_corners( Vec3::ZERO, Vec3::ONE);
bounds *= Vec3::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);
assert_eq!(bounds.center, Vec3::new(0.5, 1.0, 1.5));
assert_eq!(bounds.dimensions, Vec3::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0));Source§impl MulAssign<f32> for Bounds
This operator will create a new Bounds that has been properly scaled up by the float. This does affect the center
position of the Bounds.
https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/op_Multiply.html
impl MulAssign<f32> for Bounds
This operator will create a new Bounds that has been properly scaled up by the float. This does affect the center position of the Bounds. https://stereokit.net/Pages/StereoKit/Bounds/op_Multiply.html
Source§fn mul_assign(&mut self, rhs: f32)
fn mul_assign(&mut self, rhs: f32)
§Examples
use stereokit_rust::maths::{Vec3, Bounds};
let mut bounds = Bounds::from_corners( Vec3::ZERO, Vec3::ONE);
bounds *= 2.0;
assert_eq!(bounds.center, Vec3::ONE);
assert_eq!(bounds.dimensions, Vec3::new(2.0, 2.0, 2.0));impl Copy for Bounds
impl StructuralPartialEq for Bounds
Auto Trait Implementations§
impl Freeze for Bounds
impl RefUnwindSafe for Bounds
impl Send for Bounds
impl Sync for Bounds
impl Unpin for Bounds
impl UnwindSafe for Bounds
Blanket Implementations§
Source§impl<T> BorrowMut<T> for Twhere
T: ?Sized,
impl<T> BorrowMut<T> for Twhere
T: ?Sized,
Source§fn borrow_mut(&mut self) -> &mut T
fn borrow_mut(&mut self) -> &mut T
Source§impl<T> CloneToUninit for Twhere
T: Clone,
impl<T> CloneToUninit for Twhere
T: Clone,
Source§impl<T> Downcast for Twhere
T: Any,
impl<T> Downcast for Twhere
T: Any,
Source§fn into_any(self: Box<T>) -> Box<dyn Any>
fn into_any(self: Box<T>) -> Box<dyn Any>
Box<dyn Trait> (where Trait: Downcast) to Box<dyn Any>. Box<dyn Any> can
then be further downcast into Box<ConcreteType> where ConcreteType implements Trait.Source§fn into_any_rc(self: Rc<T>) -> Rc<dyn Any>
fn into_any_rc(self: Rc<T>) -> Rc<dyn Any>
Rc<Trait> (where Trait: Downcast) to Rc<Any>. Rc<Any> can then be
further downcast into Rc<ConcreteType> where ConcreteType implements Trait.Source§fn as_any(&self) -> &(dyn Any + 'static)
fn as_any(&self) -> &(dyn Any + 'static)
&Trait (where Trait: Downcast) to &Any. This is needed since Rust cannot
generate &Any’s vtable from &Trait’s.Source§fn as_any_mut(&mut self) -> &mut (dyn Any + 'static)
fn as_any_mut(&mut self) -> &mut (dyn Any + 'static)
&mut Trait (where Trait: Downcast) to &Any. This is needed since Rust cannot
generate &mut Any’s vtable from &mut Trait’s.