pub struct ExcelWriter<W>where
W: Write,{ /* private fields */ }Expand description
ExcelWriter implements the Polars SerWriter trait to serialize a
dataframe to an Excel Xlsx file.
ExcelWriter provides a simple interface for writing to an Excel file
similar to Polars CsvWriter. However, unless you specifically need to
use the SerWriter trait you should instead use the more configurable
PolarsXlsxWriter serializer interface, which is also part of this crate.
ExcelWriter uses PolarsXlsxWriter to do the Excel serialization which in
turn uses the rust_xlsxwriter crate.
§Examples
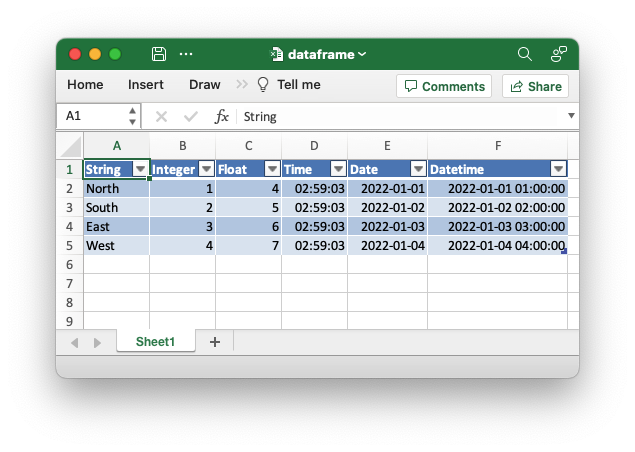
An example of writing a Polar Rust dataframe to an Excel file.
use chrono::prelude::*;
use polars::prelude::*;
use polars_excel_writer::ExcelWriter;
fn main() -> PolarsResult<()> {
// Create a sample dataframe for the example.
let mut df: DataFrame = df!(
"String" => &["North", "South", "East", "West"],
"Integer" => &[1, 2, 3, 4],
"Float" => &[4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 7.0],
"Time" => &[
NaiveTime::from_hms_milli_opt(2, 59, 3, 456).unwrap(),
NaiveTime::from_hms_milli_opt(2, 59, 3, 456).unwrap(),
NaiveTime::from_hms_milli_opt(2, 59, 3, 456).unwrap(),
NaiveTime::from_hms_milli_opt(2, 59, 3, 456).unwrap(),
],
"Date" => &[
NaiveDate::from_ymd_opt(2022, 1, 1).unwrap(),
NaiveDate::from_ymd_opt(2022, 1, 2).unwrap(),
NaiveDate::from_ymd_opt(2022, 1, 3).unwrap(),
NaiveDate::from_ymd_opt(2022, 1, 4).unwrap(),
],
"Datetime" => &[
NaiveDate::from_ymd_opt(2022, 1, 1).unwrap().and_hms_opt(1, 0, 0).unwrap(),
NaiveDate::from_ymd_opt(2022, 1, 2).unwrap().and_hms_opt(2, 0, 0).unwrap(),
NaiveDate::from_ymd_opt(2022, 1, 3).unwrap().and_hms_opt(3, 0, 0).unwrap(),
NaiveDate::from_ymd_opt(2022, 1, 4).unwrap().and_hms_opt(4, 0, 0).unwrap(),
],
)?;
// Create a new file object.
let mut file = std::fs::File::create("dataframe.xlsx").unwrap();
// Write the dataframe to an Excel file using the Polars SerWriter interface.
ExcelWriter::new(&mut file).finish(&mut df)?;
Ok(())
}Output file:
Implementations§
Source§impl<W> ExcelWriter<W>where
W: Write,
impl<W> ExcelWriter<W>where
W: Write,
Sourcepub fn has_header(self, has_header: bool) -> Self
pub fn has_header(self, has_header: bool) -> Self
Turn on/off the dataframe header in the exported Excel file.
Turn on/off the dataframe header row in the Excel table. It is on by default.
§Parameters
has_header- Export dataframe with/without header.
§Examples
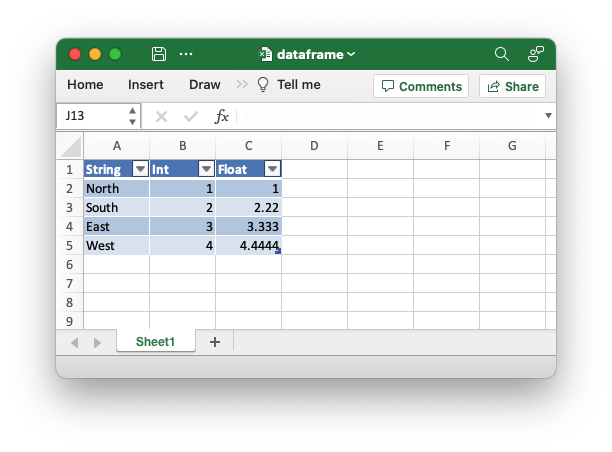
An example of writing a Polar Rust dataframe to an Excel file. This demonstrates saving the dataframe with a header (which is the default).
use polars::prelude::*;
use polars_excel_writer::ExcelWriter;
fn main() -> PolarsResult<()> {
// Create a sample dataframe for the example.
let mut df: DataFrame = df!(
"String" => &["North", "South", "East", "West"],
"Int" => &[1, 2, 3, 4],
"Float" => &[1.0, 2.22, 3.333, 4.4444],
)?;
// Create a new file object.
let mut file = std::fs::File::create("dataframe.xlsx").unwrap();
// Write the dataframe to an Excel file using the Polars SerWriter
// interface. This example also turns off the default header.
ExcelWriter::new(&mut file)
.has_header(false)
.finish(&mut df)?;
Ok(())
}Output file:
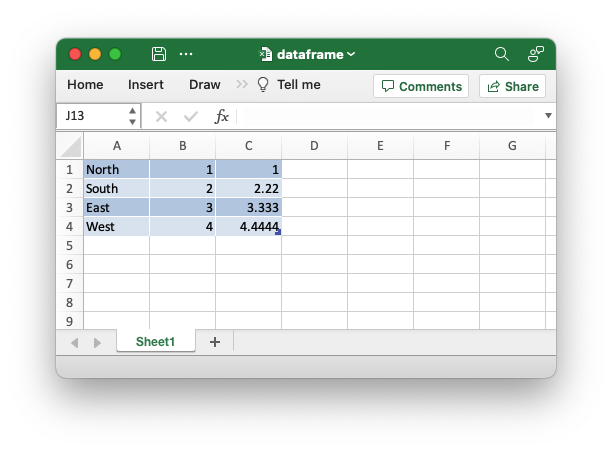
If we set has_header() to false we can output the dataframe from the
previous example without the header row:
use polars::prelude::*;
use polars_excel_writer::ExcelWriter;
fn main() -> PolarsResult<()> {
// Create a sample dataframe for the example.
let mut df: DataFrame = df!(
"String" => &["North", "South", "East", "West"],
"Int" => &[1, 2, 3, 4],
"Float" => &[1.0, 2.22, 3.333, 4.4444],
)?;
// Create a new file object.
let mut file = std::fs::File::create("dataframe.xlsx").unwrap();
// Write the dataframe to an Excel file using the Polars SerWriter
// interface. This example also turns on the header (this is the default).
ExcelWriter::new(&mut file)
.has_header(false)
.finish(&mut df)?;
Ok(())
}Output file:
Sourcepub fn with_time_format(self, format: impl Into<Format>) -> Self
pub fn with_time_format(self, format: impl Into<Format>) -> Self
Set the Excel number format for time values.
Datetimes in Excel are stored as f64 floats with a format used to
display them. The default time format used by this library is
hh:mm:ss;@. This method can be used to specify an alternative user
defined format.
§Parameters
format- Arust_xlsxwriterFormator an Excel number format string that can be converted to aFormat.
§Examples
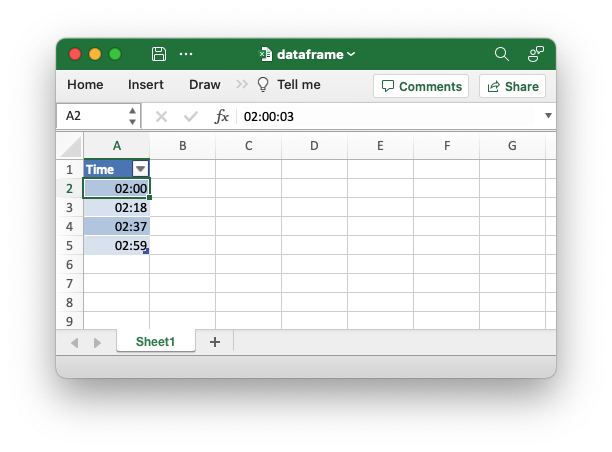
An example of writing a Polar Rust dataframe to an Excel file. This example demonstrates how to change the default format for Polars time types.
use chrono::prelude::*;
use polars::prelude::*;
use polars_excel_writer::ExcelWriter;
fn main() -> PolarsResult<()> {
// Create a sample dataframe for the example.
let mut df: DataFrame = df!(
"Time" => &[
NaiveTime::from_hms_milli_opt(2, 00, 3, 456).unwrap(),
NaiveTime::from_hms_milli_opt(2, 18, 3, 456).unwrap(),
NaiveTime::from_hms_milli_opt(2, 37, 3, 456).unwrap(),
NaiveTime::from_hms_milli_opt(2, 59, 3, 456).unwrap(),
],
)?;
// Create a new file object.
let mut file = std::fs::File::create("dataframe.xlsx").unwrap();
// Write the dataframe to an Excel file using the Polars SerWriter
// interface. This example also adds a time format.
ExcelWriter::new(&mut file)
.with_time_format("hh:mm")
.finish(&mut df)?;
Ok(())
}Output file:
Sourcepub fn with_date_format(self, format: impl Into<Format>) -> Self
pub fn with_date_format(self, format: impl Into<Format>) -> Self
Set the Excel number format for date values.
Datetimes in Excel are stored as f64 floats with a format used to
display them. The default date format used by this library is
yyyy-mm-dd;@. This method can be used to specify an alternative user
defined format.
§Parameters
format- Arust_xlsxwriterFormator an Excel number format string that can be converted to aFormat.
§Examples
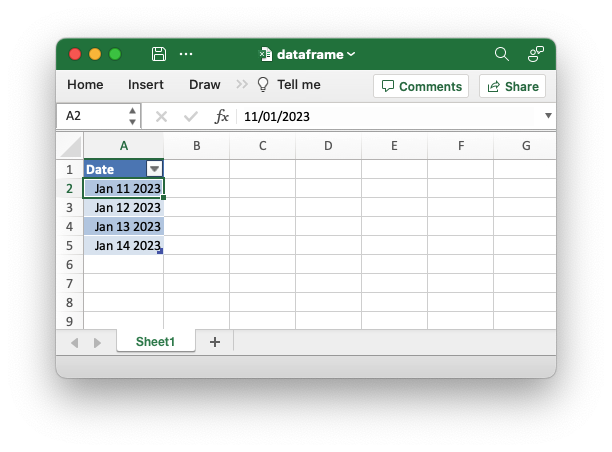
An example of writing a Polar Rust dataframe to an Excel file. This example demonstrates how to change the default format for Polars date types.
use chrono::prelude::*;
use polars::prelude::*;
use polars_excel_writer::ExcelWriter;
fn main() -> PolarsResult<()> {
// Create a sample dataframe for the example.
let mut df: DataFrame = df!(
"Date" => &[
NaiveDate::from_ymd_opt(2023, 1, 11),
NaiveDate::from_ymd_opt(2023, 1, 12),
NaiveDate::from_ymd_opt(2023, 1, 13),
NaiveDate::from_ymd_opt(2023, 1, 14),
],
)?;
// Create a new file object.
let mut file = std::fs::File::create("dataframe.xlsx").unwrap();
// Write the dataframe to an Excel file using the Polars SerWriter
// interface. This example also adds a date format.
ExcelWriter::new(&mut file)
.with_date_format("mmm d yyyy")
.finish(&mut df)?;
Ok(())
}Output file:
Sourcepub fn with_datetime_format(self, format: impl Into<Format>) -> Self
pub fn with_datetime_format(self, format: impl Into<Format>) -> Self
Set the Excel number format for datetime values.
Datetimes in Excel are stored as f64 floats with a format used to
display them. The default datetime format used by this library is
yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss. This method can be used to specify an alternative
user defined format.
§Parameters
format- Arust_xlsxwriterFormator an Excel number format string that can be converted to aFormat.
§Examples
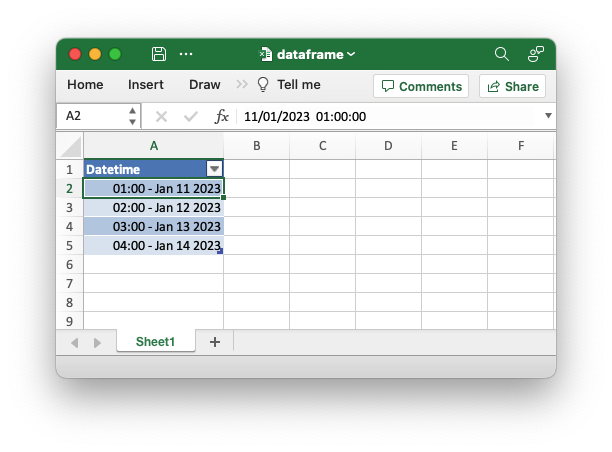
An example of writing a Polar Rust dataframe to an Excel file. This example demonstrates how to change the default format for Polars datetime types.
use chrono::prelude::*;
use polars::prelude::*;
use polars_excel_writer::ExcelWriter;
fn main() -> PolarsResult<()> {
// Create a sample dataframe for the example.
let mut df: DataFrame = df!(
"Datetime" => &[
NaiveDate::from_ymd_opt(2023, 1, 11).unwrap().and_hms_opt(1, 0, 0).unwrap(),
NaiveDate::from_ymd_opt(2023, 1, 12).unwrap().and_hms_opt(2, 0, 0).unwrap(),
NaiveDate::from_ymd_opt(2023, 1, 13).unwrap().and_hms_opt(3, 0, 0).unwrap(),
NaiveDate::from_ymd_opt(2023, 1, 14).unwrap().and_hms_opt(4, 0, 0).unwrap(),
],
)?;
// Create a new file object.
let mut file = std::fs::File::create("dataframe.xlsx").unwrap();
// Write the dataframe to an Excel file using the Polars SerWriter
// interface. This example also adds a datetime format.
ExcelWriter::new(&mut file)
.with_datetime_format("hh::mm - mmm d yyyy")
.finish(&mut df)?;
Ok(())
}Output file:
Sourcepub fn with_float_format(self, format: impl Into<Format>) -> Self
pub fn with_float_format(self, format: impl Into<Format>) -> Self
Set the Excel number format for floats.
Set the Excel number format for f32/f64 float types using an Excel
number format string. These format strings can be obtained from the
Format Cells -> Number dialog in Excel.
See the Number Format Categories section and subsequent Number Format
sections in the rust_xlsxwriter documentation.
Note, the numeric values aren’t truncated in Excel, this option just controls the display of the number.
§Parameters
format- Arust_xlsxwriterFormator an Excel number format string that can be converted to aFormat.
§Examples
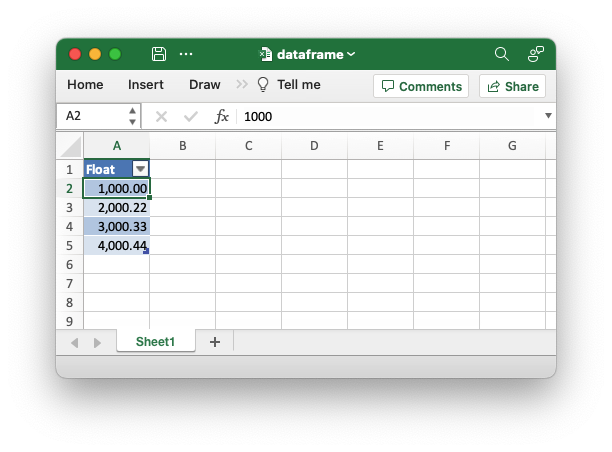
An example of writing a Polar Rust dataframe to an Excel file. This demonstrates setting an Excel number format for floats.
use polars::prelude::*;
use polars_excel_writer::ExcelWriter;
fn main() -> PolarsResult<()> {
// Create a sample dataframe for the example.
let mut df: DataFrame = df!(
"Float" => &[1000.0, 2000.22, 3000.333, 4000.4444],
)?;
// Create a new file object.
let mut file = std::fs::File::create("dataframe.xlsx").unwrap();
// Write the dataframe to an Excel file using the Polars SerWriter
// interface. This example also adds a float format.
ExcelWriter::new(&mut file)
.with_float_format("#,##0.00")
.finish(&mut df)?;
Ok(())
}Output file:
Sourcepub fn with_float_precision(self, precision: usize) -> Self
pub fn with_float_precision(self, precision: usize) -> Self
Set the Excel number precision for floats.
Set the number precision of all floats exported from the dataframe to
Excel. The precision is converted to an Excel number format (see
with_float_format() above), so for
example 3 is converted to the Excel format 0.000.
The precision should be in the Excel range 1-30.
Note, the numeric values aren’t truncated in Excel, this option just controls the display of the number.
§Parameters
precision- The floating point precision in the Excel range 1-30.
§Examples
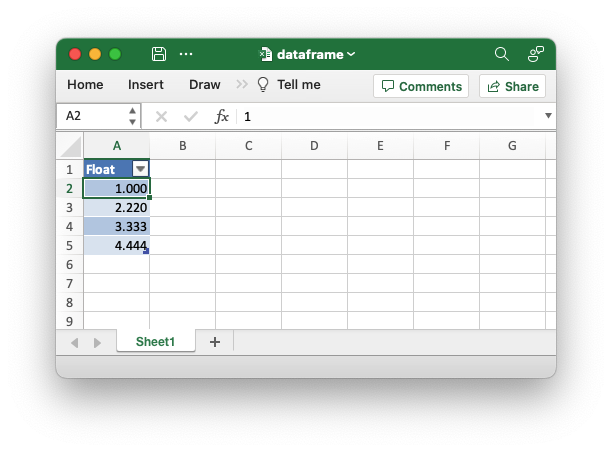
An example of writing a Polar Rust dataframe to an Excel file. This
example demonstrates how to set the precision of the float output.
Setting the precision to 3 is equivalent to an Excel number format of
0.000.
use polars::prelude::*;
use polars_excel_writer::ExcelWriter;
fn main() -> PolarsResult<()> {
// Create a sample dataframe for the example.
let mut df: DataFrame = df!(
"Float" => &[1.0, 2.22, 3.333, 4.4444],
)?;
// Create a new file object.
let mut file = std::fs::File::create("dataframe.xlsx").unwrap();
// Write the dataframe to an Excel file using the Polars SerWriter
// interface. This example also adds a float precision.
ExcelWriter::new(&mut file)
.with_float_precision(3)
.finish(&mut df)?;
Ok(())
}Output file:
Sourcepub fn with_null_value(self, null_value: impl Into<String>) -> Self
pub fn with_null_value(self, null_value: impl Into<String>) -> Self
Replace Null values in the exported dataframe with string values.
By default Null values in a dataframe aren’t exported to Excel and will appear as empty cells. If you wish you can specify a string such as “Null”, “NULL” or “N/A” as an alternative.
§Parameters
value- A replacement string for Null values.
§Examples
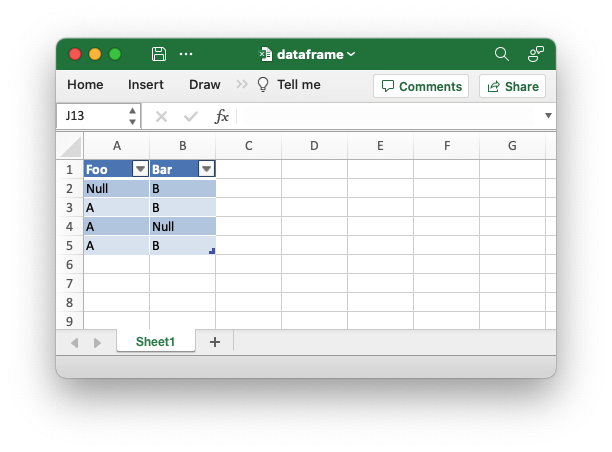
An example of writing a Polar Rust dataframe to an Excel file. This demonstrates setting a value for Null values in the dataframe. The default is to write them as blank cells.
// Create a new file object.
let mut file = std::fs::File::create("dataframe.xlsx").unwrap();
// Write the dataframe to an Excel file using the Polars SerWriter
// interface. This example also sets a string value for Null values.
ExcelWriter::new(&mut file)
.with_null_value("Null")
.finish(&mut df)?;Output file:
Sourcepub fn with_autofit(self) -> Self
pub fn with_autofit(self) -> Self
Simulate autofit for columns in the dataframe output.
Use a simulated autofit to adjust dataframe columns to the maximum string or number widths.
There are several limitations to this autofit method, see the
rust_xlsxwriter docs on worksheet.autofit() for details.
§Examples
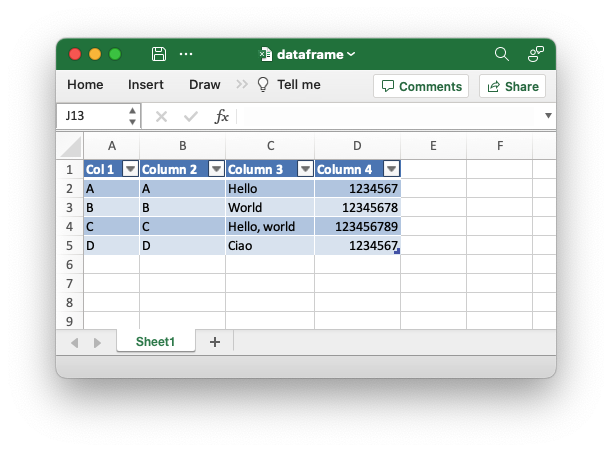
An example of writing a Polar Rust dataframe to an Excel file. This example demonstrates autofitting column widths in the output worksheet.
use polars::prelude::*;
use polars_excel_writer::ExcelWriter;
fn main() -> PolarsResult<()> {
// Create a sample dataframe for the example.
let mut df: DataFrame = df!(
"Col 1" => &["A", "B", "C", "D"],
"Column 2" => &["A", "B", "C", "D"],
"Column 3" => &["Hello", "World", "Hello, world", "Ciao"],
"Column 4" => &[1234567, 12345678, 123456789, 1234567],
)?;
// Create a new file object.
let mut file = std::fs::File::create("dataframe.xlsx").unwrap();
// Write the dataframe to an Excel file using the Polars SerWriter
// interface. This example also autofits the output.
ExcelWriter::new(&mut file).with_autofit().finish(&mut df)?;
Ok(())
}Output file:
Trait Implementations§
Auto Trait Implementations§
impl<W> Freeze for ExcelWriter<W>where
W: Freeze,
impl<W> !RefUnwindSafe for ExcelWriter<W>
impl<W> Send for ExcelWriter<W>where
W: Send,
impl<W> !Sync for ExcelWriter<W>
impl<W> Unpin for ExcelWriter<W>where
W: Unpin,
impl<W> !UnwindSafe for ExcelWriter<W>
Blanket Implementations§
Source§impl<T> BorrowMut<T> for Twhere
T: ?Sized,
impl<T> BorrowMut<T> for Twhere
T: ?Sized,
Source§fn borrow_mut(&mut self) -> &mut T
fn borrow_mut(&mut self) -> &mut T
Source§impl<T> IntoEither for T
impl<T> IntoEither for T
Source§fn into_either(self, into_left: bool) -> Either<Self, Self>
fn into_either(self, into_left: bool) -> Either<Self, Self>
self into a Left variant of Either<Self, Self>
if into_left is true.
Converts self into a Right variant of Either<Self, Self>
otherwise. Read moreSource§fn into_either_with<F>(self, into_left: F) -> Either<Self, Self>
fn into_either_with<F>(self, into_left: F) -> Either<Self, Self>
self into a Left variant of Either<Self, Self>
if into_left(&self) returns true.
Converts self into a Right variant of Either<Self, Self>
otherwise. Read more