pub mod ximgproc {
//! # Extended Image Processing
//! # Structured forests for fast edge detection
//!
//! This module contains implementations of modern structured edge detection algorithms,
//! i.e. algorithms which somehow takes into account pixel affinities in natural images.
//!
//! # EdgeBoxes
//!
//! # Filters
//!
//! # Superpixels
//!
//! # Image segmentation
//!
//! # Fast line detector
//!
//! # EdgeDrawing
//!
//! EDGE DRAWING LIBRARY FOR GEOMETRIC FEATURE EXTRACTION AND VALIDATION
//!
//! Edge Drawing (ED) algorithm is an proactive approach on edge detection problem. In contrast to many other existing edge detection algorithms which follow a subtractive
//! approach (i.e. after applying gradient filters onto an image eliminating pixels w.r.t. several rules, e.g. non-maximal suppression and hysteresis in Canny), ED algorithm
//! works via an additive strategy, i.e. it picks edge pixels one by one, hence the name Edge Drawing. Then we process those random shaped edge segments to extract higher level
//! edge features, i.e. lines, circles, ellipses, etc. The popular method of extraction edge pixels from the thresholded gradient magnitudes is non-maximal supression that tests
//! every pixel whether it has the maximum gradient response along its gradient direction and eliminates if it does not. However, this method does not check status of the
//! neighboring pixels, and therefore might result low quality (in terms of edge continuity, smoothness, thinness, localization) edge segments. Instead of non-maximal supression,
//! ED points a set of edge pixels and join them by maximizing the total gradient response of edge segments. Therefore it can extract high quality edge segments without need for
//! an additional hysteresis step.
//!
//! # Fourier descriptors
//!
//! # Binary morphology on run-length encoded image
//!
//! These functions support morphological operations on binary images. In order to be fast and space efficient binary images are encoded with a run-length representation.
//! This representation groups continuous horizontal sequences of "on" pixels together in a "run". A run is charactarized by the column position of the first pixel in the run, the column
//! position of the last pixel in the run and the row position. This representation is very compact for binary images which contain large continuous areas of "on" and "off" pixels. A checkerboard
//! pattern would be a good example. The representation is not so suitable for binary images created from random noise images or other images where little correlation between neighboring pixels
//! exists.
//!
//! The morphological operations supported here are very similar to the operations supported in the imgproc module. In general they are fast. However on several occasions they are slower than the functions
//! from imgproc. The structuring elements of cv::MORPH_RECT and cv::MORPH_CROSS have very good support from the imgproc module. Also small structuring elements are very fast in imgproc (presumably
//! due to opencl support). Therefore the functions from this module are recommended for larger structuring elements (cv::MORPH_ELLIPSE or self defined structuring elements). A sample application
//! (run_length_morphology_demo) is supplied which allows to compare the speed of some morphological operations for the functions using run-length encoding and the imgproc functions for a given image.
//!
//! Run length encoded images are stored in standard opencv images. Images have a single column of cv::Point3i elements. The number of rows is the number of run + 1. The first row contains
//! the size of the original (not encoded) image. For the runs the following mapping is used (x: column begin, y: column end (last column), z: row).
//!
//! The size of the original image is required for compatibility with the imgproc functions when the boundary handling requires that pixel outside the image boundary are
//! "on".
use crate::{mod_prelude::*, core, sys, types};
pub mod prelude {
pub use { super::DTFilterConst, super::DTFilter, super::GuidedFilterConst, super::GuidedFilter, super::AdaptiveManifoldFilterConst, super::AdaptiveManifoldFilter, super::FastBilateralSolverFilterConst, super::FastBilateralSolverFilter, super::FastGlobalSmootherFilterConst, super::FastGlobalSmootherFilter, super::DisparityFilterConst, super::DisparityFilter, super::DisparityWLSFilterConst, super::DisparityWLSFilter, super::SparseMatchInterpolatorConst, super::SparseMatchInterpolator, super::EdgeAwareInterpolatorConst, super::EdgeAwareInterpolator, super::RICInterpolatorConst, super::RICInterpolator, super::RFFeatureGetterConst, super::RFFeatureGetter, super::StructuredEdgeDetectionConst, super::StructuredEdgeDetection, super::EdgeBoxesConst, super::EdgeBoxes, super::EdgeDrawingConst, super::EdgeDrawing, super::ScanSegmentConst, super::ScanSegment, super::SuperpixelSEEDSConst, super::SuperpixelSEEDS, super::GraphSegmentationConst, super::GraphSegmentation, super::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyConst, super::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy, super::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyColorConst, super::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyColor, super::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategySizeConst, super::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategySize, super::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyTextureConst, super::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyTexture, super::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyFillConst, super::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyFill, super::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultipleConst, super::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultiple, super::SelectiveSearchSegmentationConst, super::SelectiveSearchSegmentation, super::SuperpixelSLICConst, super::SuperpixelSLIC, super::SuperpixelLSCConst, super::SuperpixelLSC, super::FastLineDetectorConst, super::FastLineDetector, super::ContourFittingTraitConst, super::ContourFittingTrait, super::RidgeDetectionFilterConst, super::RidgeDetectionFilter };
}
pub const AM_FILTER: i32 = 4;
pub const ARO_0_45: i32 = 0;
pub const ARO_315_0: i32 = 3;
pub const ARO_315_135: i32 = 6;
pub const ARO_315_45: i32 = 4;
pub const ARO_45_135: i32 = 5;
pub const ARO_45_90: i32 = 1;
pub const ARO_90_135: i32 = 2;
pub const ARO_CTR_HOR: i32 = 7;
pub const ARO_CTR_VER: i32 = 8;
/// Classic Niblack binarization. See [Niblack1985](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Niblack1985) .
pub const BINARIZATION_NIBLACK: i32 = 0;
/// NICK technique. See [Khurshid2009](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Khurshid2009) .
pub const BINARIZATION_NICK: i32 = 3;
/// Sauvola's technique. See [Sauvola1997](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Sauvola1997) .
pub const BINARIZATION_SAUVOLA: i32 = 1;
/// Wolf's technique. See [Wolf2004](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Wolf2004) .
pub const BINARIZATION_WOLF: i32 = 2;
pub const DTF_IC: i32 = 1;
pub const DTF_NC: i32 = 0;
pub const DTF_RF: i32 = 2;
pub const EdgeDrawing_LSD: i32 = 3;
pub const EdgeDrawing_PREWITT: i32 = 0;
pub const EdgeDrawing_SCHARR: i32 = 2;
pub const EdgeDrawing_SOBEL: i32 = 1;
pub const FHT_ADD: i32 = 2;
pub const FHT_AVE: i32 = 3;
pub const FHT_MAX: i32 = 1;
pub const FHT_MIN: i32 = 0;
pub const GUIDED_FILTER: i32 = 3;
pub const HDO_DESKEW: i32 = 1;
pub const HDO_RAW: i32 = 0;
pub const MSLIC: i32 = 102;
/// Skip validations of image borders.
pub const RO_IGNORE_BORDERS: i32 = 1;
/// Validate each rule in a proper way.
pub const RO_STRICT: i32 = 0;
pub const SLIC: i32 = 100;
pub const SLICO: i32 = 101;
pub const THINNING_GUOHALL: i32 = 1;
pub const THINNING_ZHANGSUEN: i32 = 0;
/// 
pub const WMF_COS: i32 = 8;
/// 
pub const WMF_EXP: i32 = 1;
/// 
pub const WMF_IV1: i32 = 2;
/// 
pub const WMF_IV2: i32 = 4;
/// 
pub const WMF_JAC: i32 = 16;
/// unweighted
pub const WMF_OFF: i32 = 32;
/// Specifies the part of Hough space to calculate
/// @details The enum specifies the part of Hough space to calculate. Each
/// member specifies primarily direction of lines (horizontal or vertical)
/// and the direction of angle changes.
/// Direction of angle changes is from multiples of 90 to odd multiples of 45.
/// The image considered to be written top-down and left-to-right.
/// Angles are started from vertical line and go clockwise.
/// Separate quarters and halves are written in orientation they should be in
/// full Hough space.
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum AngleRangeOption {
ARO_0_45 = 0,
ARO_45_90 = 1,
ARO_90_135 = 2,
ARO_315_0 = 3,
ARO_315_45 = 4,
ARO_45_135 = 5,
ARO_315_135 = 6,
ARO_CTR_HOR = 7,
ARO_CTR_VER = 8,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ximgproc::AngleRangeOption }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum EdgeAwareFiltersList {
DTF_NC = 0,
DTF_IC = 1,
DTF_RF = 2,
GUIDED_FILTER = 3,
AM_FILTER = 4,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ximgproc::EdgeAwareFiltersList }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum EdgeDrawing_GradientOperator {
PREWITT = 0,
SOBEL = 1,
SCHARR = 2,
LSD = 3,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ximgproc::EdgeDrawing_GradientOperator }
/// Specifies to do or not to do skewing of Hough transform image
/// @details The enum specifies to do or not to do skewing of Hough transform image
/// so it would be no cycling in Hough transform image through borders of image.
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum HoughDeskewOption {
HDO_RAW = 0,
HDO_DESKEW = 1,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ximgproc::HoughDeskewOption }
/// Specifies binary operations.
/// @details The enum specifies binary operations, that is such ones which involve
/// two operands. Formally, a binary operation @f$ f @f$ on a set @f$ S @f$
/// is a binary relation that maps elements of the Cartesian product
/// @f$ S \times S @f$ to @f$ S @f$:
/// @f[ f: S \times S \to S @f]
/// @ingroup MinUtils_MathOper
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum HoughOp {
FHT_MIN = 0,
FHT_MAX = 1,
FHT_ADD = 2,
FHT_AVE = 3,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ximgproc::HoughOp }
/// Specifies the binarization method to use in cv::ximgproc::niBlackThreshold
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum LocalBinarizationMethods {
/// Classic Niblack binarization. See [Niblack1985](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Niblack1985) .
BINARIZATION_NIBLACK = 0,
/// Sauvola's technique. See [Sauvola1997](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Sauvola1997) .
BINARIZATION_SAUVOLA = 1,
/// Wolf's technique. See [Wolf2004](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Wolf2004) .
BINARIZATION_WOLF = 2,
/// NICK technique. See [Khurshid2009](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Khurshid2009) .
BINARIZATION_NICK = 3,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ximgproc::LocalBinarizationMethods }
/// Specifies the degree of rules validation.
/// @details The enum specifies the degree of rules validation. This can be used,
/// for example, to choose a proper way of input arguments validation.
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum RulesOption {
/// Validate each rule in a proper way.
RO_STRICT = 0,
/// Skip validations of image borders.
RO_IGNORE_BORDERS = 1,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ximgproc::RulesOption }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum SLICType {
SLIC = 100,
SLICO = 101,
MSLIC = 102,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ximgproc::SLICType }
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum ThinningTypes {
THINNING_ZHANGSUEN = 0,
THINNING_GUOHALL = 1,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ximgproc::ThinningTypes }
/// Specifies weight types of weighted median filter.
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum WMFWeightType {
/// 
WMF_EXP = 1,
/// 
WMF_IV1 = 2,
/// 
WMF_IV2 = 4,
/// 
WMF_COS = 8,
/// 
WMF_JAC = 16,
/// unweighted
WMF_OFF = 32,
}
opencv_type_enum! { crate::ximgproc::WMFWeightType }
/// Specifies the degree of rules validation.
/// @details The enum specifies the degree of rules validation. This can be used,
/// for example, to choose a proper way of input arguments validation.
pub type rules_option = crate::ximgproc::RulesOption;
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * contrast: 1
/// * shortrange: 3
/// * longrange: 9
#[inline]
pub fn bright_edges(_original: &mut core::Mat, _edgeview: &mut core::Mat, contrast: i32, shortrange: i32, longrange: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_BrightEdges_MatR_MatR_int_int_int(_original.as_raw_mut_Mat(), _edgeview.as_raw_mut_Mat(), contrast, shortrange, longrange, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates 2D Fast Hough transform of an image.
/// ## Parameters
/// * dst: The destination image, result of transformation.
/// * src: The source (input) image.
/// * dstMatDepth: The depth of destination image
/// * op: The operation to be applied, see cv::HoughOp
/// * angleRange: The part of Hough space to calculate, see cv::AngleRangeOption
/// * makeSkew: Specifies to do or not to do image skewing, see cv::HoughDeskewOption
///
/// The function calculates the fast Hough transform for full, half or quarter
/// range of angles.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * angle_range: ARO_315_135
/// * op: FHT_ADD
/// * make_skew: HDO_DESKEW
#[inline]
pub fn fast_hough_transform(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, dst_mat_depth: i32, angle_range: i32, op: i32, make_skew: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_FastHoughTransform_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_int_int_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), dst_mat_depth, angle_range, op, make_skew, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Applies X Deriche filter to an image.
///
/// For more details about this implementation, please see <http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.476.5736&rep=rep1&type=pdf>
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * op: Source 8-bit or 16bit image, 1-channel or 3-channel image.
/// * dst: result CV_32FC image with same number of channel than _op.
/// * alpha: double see paper
/// * omega: double see paper
#[inline]
pub fn gradient_deriche_x(op: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, alpha: f64, omega: f64) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(op);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_GradientDericheX_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_double(op.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), alpha, omega, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Applies Y Deriche filter to an image.
///
/// For more details about this implementation, please see <http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.476.5736&rep=rep1&type=pdf>
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * op: Source 8-bit or 16bit image, 1-channel or 3-channel image.
/// * dst: result CV_32FC image with same number of channel than _op.
/// * alpha: double see paper
/// * omega: double see paper
#[inline]
pub fn gradient_deriche_y(op: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, alpha: f64, omega: f64) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(op);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_GradientDericheY_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_double(op.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), alpha, omega, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn gradient_paillou_x(op: &dyn core::ToInputArray, _dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, alpha: f64, omega: f64) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(op);
extern_container_arg!(_dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_GradientPaillouX_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_double(op.as_raw__InputArray(), _dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), alpha, omega, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Applies Paillou filter to an image.
///
/// For more details about this implementation, please see [paillou1997detecting](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_paillou1997detecting)
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * op: Source CV_8U(S) or CV_16U(S), 1-channel or 3-channels image.
/// * _dst: result CV_32F image with same number of channel than op.
/// * omega: double see paper
/// * alpha: double see paper
/// ## See also
/// GradientPaillouX, GradientPaillouY
#[inline]
pub fn gradient_paillou_y(op: &dyn core::ToInputArray, _dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, alpha: f64, omega: f64) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(op);
extern_container_arg!(_dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_GradientPaillouY_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_double(op.as_raw__InputArray(), _dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), alpha, omega, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates coordinates of line segment corresponded by point in Hough space.
/// ## Parameters
/// * houghPoint: Point in Hough space.
/// * srcImgInfo: The source (input) image of Hough transform.
/// * angleRange: The part of Hough space where point is situated, see cv::AngleRangeOption
/// * makeSkew: Specifies to do or not to do image skewing, see cv::HoughDeskewOption
/// * rules: Specifies strictness of line segment calculating, see cv::RulesOption
/// @retval [Vec4i] Coordinates of line segment corresponded by point in Hough space.
/// @remarks If rules parameter set to RO_STRICT
/// then returned line cut along the border of source image.
/// @remarks If rules parameter set to RO_WEAK then in case of point, which belongs
/// the incorrect part of Hough image, returned line will not intersect source image.
///
/// The function calculates coordinates of line segment corresponded by point in Hough space.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * angle_range: ARO_315_135
/// * make_skew: HDO_DESKEW
/// * rules: RO_IGNORE_BORDERS
#[inline]
pub fn hough_point2_line(hough_point: core::Point, src_img_info: &dyn core::ToInputArray, angle_range: i32, make_skew: i32, rules: i32) -> Result<core::Vec4i> {
extern_container_arg!(src_img_info);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_HoughPoint2Line_const_PointR_const__InputArrayR_int_int_int(&hough_point, src_img_info.as_raw__InputArray(), angle_range, make_skew, rules, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates an affine transformation that normalize given image using Pei&Lin Normalization.
///
/// Assume given image  where 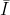 is a normalized image and 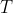 is an affine transformation distorting this image by translation, rotation, scaling and skew.
/// The function returns an affine transformation matrix corresponding to the transformation  described in [PeiLin95].
/// For more details about this implementation, please see
/// [PeiLin95] Soo-Chang Pei and Chao-Nan Lin. Image normalization for pattern recognition. Image and Vision Computing, Vol. 13, N.10, pp. 711-723, 1995.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * I: Given transformed image.
/// ## Returns
/// Transformation matrix corresponding to inversed image transformation
#[inline]
pub fn pei_lin_normalization(i: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<core::Matx23d> {
extern_container_arg!(i);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_PeiLinNormalization_const__InputArrayR(i.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates an affine transformation that normalize given image using Pei&Lin Normalization.
///
/// Assume given image  where 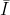 is a normalized image and 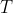 is an affine transformation distorting this image by translation, rotation, scaling and skew.
/// The function returns an affine transformation matrix corresponding to the transformation  described in [PeiLin95].
/// For more details about this implementation, please see
/// [PeiLin95] Soo-Chang Pei and Chao-Nan Lin. Image normalization for pattern recognition. Image and Vision Computing, Vol. 13, N.10, pp. 711-723, 1995.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * I: Given transformed image.
/// ## Returns
/// Transformation matrix corresponding to inversed image transformation
///
/// ## Overloaded parameters
#[inline]
pub fn pei_lin_normalization_1(i: &dyn core::ToInputArray, t: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(i);
extern_container_arg!(t);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_PeiLinNormalization_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(i.as_raw__InputArray(), t.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculate Radon Transform of an image.
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: The source (input) image.
/// * dst: The destination image, result of transformation.
/// * theta: Angle resolution of the transform in degrees.
/// * start_angle: Start angle of the transform in degrees.
/// * end_angle: End angle of the transform in degrees.
/// * crop: Crop the source image into a circle.
/// * norm: Normalize the output Mat to grayscale and convert type to CV_8U
///
/// This function calculates the Radon Transform of a given image in any range.
/// See <https://engineering.purdue.edu/~malcolm/pct/CTI_Ch03.pdf> for detail.
/// If the input type is CV_8U, the output will be CV_32S.
/// If the input type is CV_32F or CV_64F, the output will be CV_64F
/// The output size will be num_of_integral x src_diagonal_length.
/// If crop is selected, the input image will be crop into square then circle,
/// and output size will be num_of_integral x min_edge.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * theta: 1
/// * start_angle: 0
/// * end_angle: 180
/// * crop: false
/// * norm: false
#[inline]
pub fn radon_transform(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, theta: f64, start_angle: f64, end_angle: f64, crop: bool, norm: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RadonTransform_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_double_double_bool_bool(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), theta, start_angle, end_angle, crop, norm, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Simple one-line Adaptive Manifold Filter call.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * joint: joint (also called as guided) image or array of images with any numbers of channels.
///
/// * src: filtering image with any numbers of channels.
///
/// * dst: output image.
///
/// * sigma_s: spatial standard deviation.
///
/// * sigma_r: color space standard deviation, it is similar to the sigma in the color space into
/// bilateralFilter.
///
/// * adjust_outliers: optional, specify perform outliers adjust operation or not, (Eq. 9) in the
/// original paper.
///
///
/// Note: Joint images with CV_8U and CV_16U depth converted to images with CV_32F depth and [0; 1]
/// color range before processing. Hence color space sigma sigma_r must be in [0; 1] range, unlike same
/// sigmas in bilateralFilter and dtFilter functions. see also: bilateralFilter, dtFilter, guidedFilter
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * adjust_outliers: false
#[inline]
pub fn am_filter(joint: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, sigma_s: f64, sigma_r: f64, adjust_outliers: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(joint);
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_amFilter_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_double_bool(joint.as_raw__InputArray(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), sigma_s, sigma_r, adjust_outliers, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Performs anisotropic diffusion on an image.
///
/// The function applies Perona-Malik anisotropic diffusion to an image. This is the solution to the partial differential equation:
///
/// 
///
/// Suggested functions for c(x,y,t) are:
///
/// 
///
/// or
///
/// 
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Source image with 3 channels.
/// * dst: Destination image of the same size and the same number of channels as src .
/// * alpha: The amount of time to step forward by on each iteration (normally, it's between 0 and 1).
/// * K: sensitivity to the edges
/// * niters: The number of iterations
#[inline]
pub fn anisotropic_diffusion(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, alpha: f32, k: f32, niters: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_anisotropicDiffusion_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float_float_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), alpha, k, niters, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Applies the bilateral texture filter to an image. It performs structure-preserving texture filter.
/// For more details about this filter see [Cho2014](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Cho2014).
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Source image whose depth is 8-bit UINT or 32-bit FLOAT
///
/// * dst: Destination image of the same size and type as src.
///
/// * fr: Radius of kernel to be used for filtering. It should be positive integer
///
/// * numIter: Number of iterations of algorithm, It should be positive integer
///
/// * sigmaAlpha: Controls the sharpness of the weight transition from edges to smooth/texture regions, where
/// a bigger value means sharper transition. When the value is negative, it is automatically calculated.
///
/// * sigmaAvg: Range blur parameter for texture blurring. Larger value makes result to be more blurred. When the
/// value is negative, it is automatically calculated as described in the paper.
/// ## See also
/// rollingGuidanceFilter, bilateralFilter
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * fr: 3
/// * num_iter: 1
/// * sigma_alpha: -1.
/// * sigma_avg: -1.
#[inline]
pub fn bilateral_texture_filter(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, fr: i32, num_iter: i32, sigma_alpha: f64, sigma_avg: f64) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_bilateralTextureFilter_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_int_double_double(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), fr, num_iter, sigma_alpha, sigma_avg, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Compares a color template against overlapped color image regions.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * img: Image where the search is running. It must be 3 channels image
/// * templ: Searched template. It must be not greater than the source image and have 3 channels
/// * result: Map of comparison results. It must be single-channel 64-bit floating-point
#[inline]
pub fn color_match_template(img: &dyn core::ToInputArray, templ: &dyn core::ToInputArray, result: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(img);
extern_container_arg!(templ);
extern_container_arg!(result);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_colorMatchTemplate_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(img.as_raw__InputArray(), templ.as_raw__InputArray(), result.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Function for computing the percent of "bad" pixels in the disparity map
/// (pixels where error is higher than a specified threshold)
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * GT: ground truth disparity map
///
/// * src: disparity map to evaluate
///
/// * ROI: region of interest
///
/// * thresh: threshold used to determine "bad" pixels
///
/// @result returns mean square error between GT and src
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * thresh: 24
#[inline]
pub fn compute_bad_pixel_percent(gt: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, roi: core::Rect, thresh: i32) -> Result<f64> {
extern_container_arg!(gt);
extern_container_arg!(src);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_computeBadPixelPercent_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Rect_int(gt.as_raw__InputArray(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), roi.opencv_as_extern(), thresh, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Function for computing mean square error for disparity maps
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * GT: ground truth disparity map
///
/// * src: disparity map to evaluate
///
/// * ROI: region of interest
///
/// @result returns mean square error between GT and src
#[inline]
pub fn compute_mse(gt: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, roi: core::Rect) -> Result<f64> {
extern_container_arg!(gt);
extern_container_arg!(src);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_computeMSE_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Rect(gt.as_raw__InputArray(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), roi.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Contour sampling .
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: contour type vector<Point> , vector<Point2f> or vector<Point2d>
/// * out: Mat of type CV_64FC2 and nbElt rows
/// * nbElt: number of points in out contour
#[inline]
pub fn contour_sampling(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, out: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, nb_elt: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(out);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_contourSampling_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), out.as_raw__OutputArray(), nb_elt, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Computes the estimated covariance matrix of an image using the sliding
/// window forumlation.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: The source image. Input image must be of a complex type.
/// * dst: The destination estimated covariance matrix. Output matrix will be size (windowRows*windowCols, windowRows*windowCols).
/// * windowRows: The number of rows in the window.
/// * windowCols: The number of cols in the window.
/// The window size parameters control the accuracy of the estimation.
/// The sliding window moves over the entire image from the top-left corner
/// to the bottom right corner. Each location of the window represents a sample.
/// If the window is the size of the image, then this gives the exact covariance matrix.
/// For all other cases, the sizes of the window will impact the number of samples
/// and the number of elements in the estimated covariance matrix.
#[inline]
pub fn covariance_estimation(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, window_rows: i32, window_cols: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_covarianceEstimation_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), window_rows, window_cols, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Factory method, create instance of AdaptiveManifoldFilter and produce some initialization routines.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * sigma_s: spatial standard deviation.
///
/// * sigma_r: color space standard deviation, it is similar to the sigma in the color space into
/// bilateralFilter.
///
/// * adjust_outliers: optional, specify perform outliers adjust operation or not, (Eq. 9) in the
/// original paper.
///
/// For more details about Adaptive Manifold Filter parameters, see the original article [Gastal12](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Gastal12) .
///
///
/// Note: Joint images with CV_8U and CV_16U depth converted to images with CV_32F depth and [0; 1]
/// color range before processing. Hence color space sigma sigma_r must be in [0; 1] range, unlike same
/// sigmas in bilateralFilter and dtFilter functions.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * adjust_outliers: false
#[inline]
pub fn create_am_filter(sigma_s: f64, sigma_r: f64, adjust_outliers: bool) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::AdaptiveManifoldFilter>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_createAMFilter_double_double_bool(sigma_s, sigma_r, adjust_outliers, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::AdaptiveManifoldFilter>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// create ContourFitting algorithm object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * ctr: number of Fourier descriptors equal to number of contour points after resampling.
/// * fd: Contour defining second shape (Target).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * ctr: 1024
/// * fd: 16
#[inline]
pub fn create_contour_fitting(ctr: i32, fd: i32) -> Result<core::Ptr<crate::ximgproc::ContourFitting>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_createContourFitting_int_int(ctr, fd, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ximgproc::ContourFitting>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Factory method, create instance of DTFilter and produce initialization routines.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * guide: guided image (used to build transformed distance, which describes edge structure of
/// guided image).
///
/// * sigmaSpatial:  parameter in the original article, it's similar to the sigma in the
/// coordinate space into bilateralFilter.
///
/// * sigmaColor:  parameter in the original article, it's similar to the sigma in the
/// color space into bilateralFilter.
///
/// * mode: one form three modes DTF_NC, DTF_RF and DTF_IC which corresponds to three modes for
/// filtering 2D signals in the article.
///
/// * numIters: optional number of iterations used for filtering, 3 is quite enough.
///
/// For more details about Domain Transform filter parameters, see the original article [Gastal11](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Gastal11) and
/// [Domain Transform filter homepage](http://www.inf.ufrgs.br/~eslgastal/DomainTransform/).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * mode: DTF_NC
/// * num_iters: 3
#[inline]
pub fn create_dt_filter(guide: &dyn core::ToInputArray, sigma_spatial: f64, sigma_color: f64, mode: i32, num_iters: i32) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::DTFilter>> {
extern_container_arg!(guide);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_createDTFilter_const__InputArrayR_double_double_int_int(guide.as_raw__InputArray(), sigma_spatial, sigma_color, mode, num_iters, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::DTFilter>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// More generic factory method, create instance of DisparityWLSFilter and execute basic
/// initialization routines. When using this method you will need to set-up the ROI, matchers and
/// other parameters by yourself.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * use_confidence: filtering with confidence requires two disparity maps (for the left and right views) and is
/// approximately two times slower. However, quality is typically significantly better.
#[inline]
pub fn create_disparity_wls_filter_generic(use_confidence: bool) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::DisparityWLSFilter>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_createDisparityWLSFilterGeneric_bool(use_confidence, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::DisparityWLSFilter>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Convenience factory method that creates an instance of DisparityWLSFilter and sets up all the relevant
/// filter parameters automatically based on the matcher instance. Currently supports only StereoBM and StereoSGBM.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * matcher_left: stereo matcher instance that will be used with the filter
#[inline]
pub fn create_disparity_wls_filter(mut matcher_left: core::Ptr<dyn crate::calib3d::StereoMatcher>) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::DisparityWLSFilter>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_createDisparityWLSFilter_PtrLStereoMatcherG(matcher_left.as_raw_mut_PtrOfStereoMatcher(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::DisparityWLSFilter>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Factory method that creates an instance of the
/// EdgeAwareInterpolator.
#[inline]
pub fn create_edge_aware_interpolator() -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_createEdgeAwareInterpolator(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates a Edgeboxes
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * alpha: step size of sliding window search.
/// * beta: nms threshold for object proposals.
/// * eta: adaptation rate for nms threshold.
/// * minScore: min score of boxes to detect.
/// * maxBoxes: max number of boxes to detect.
/// * edgeMinMag: edge min magnitude. Increase to trade off accuracy for speed.
/// * edgeMergeThr: edge merge threshold. Increase to trade off accuracy for speed.
/// * clusterMinMag: cluster min magnitude. Increase to trade off accuracy for speed.
/// * maxAspectRatio: max aspect ratio of boxes.
/// * minBoxArea: minimum area of boxes.
/// * gamma: affinity sensitivity.
/// * kappa: scale sensitivity.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * alpha: 0.65f
/// * beta: 0.75f
/// * eta: 1
/// * min_score: 0.01f
/// * max_boxes: 10000
/// * edge_min_mag: 0.1f
/// * edge_merge_thr: 0.5f
/// * cluster_min_mag: 0.5f
/// * max_aspect_ratio: 3
/// * min_box_area: 1000
/// * gamma: 2
/// * kappa: 1.5f
#[inline]
pub fn create_edge_boxes(alpha: f32, beta: f32, eta: f32, min_score: f32, max_boxes: i32, edge_min_mag: f32, edge_merge_thr: f32, cluster_min_mag: f32, max_aspect_ratio: f32, min_box_area: f32, gamma: f32, kappa: f32) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::EdgeBoxes>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_createEdgeBoxes_float_float_float_float_int_float_float_float_float_float_float_float(alpha, beta, eta, min_score, max_boxes, edge_min_mag, edge_merge_thr, cluster_min_mag, max_aspect_ratio, min_box_area, gamma, kappa, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::EdgeBoxes>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates a smart pointer to a EdgeDrawing object and initializes it
#[inline]
pub fn create_edge_drawing() -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::EdgeDrawing>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_createEdgeDrawing(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::EdgeDrawing>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Factory method, create instance of FastBilateralSolverFilter and execute the initialization routines.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * guide: image serving as guide for filtering. It should have 8-bit depth and either 1 or 3 channels.
///
/// * sigma_spatial: parameter, that is similar to spatial space sigma (bandwidth) in bilateralFilter.
///
/// * sigma_luma: parameter, that is similar to luma space sigma (bandwidth) in bilateralFilter.
///
/// * sigma_chroma: parameter, that is similar to chroma space sigma (bandwidth) in bilateralFilter.
///
/// * lambda: smoothness strength parameter for solver.
///
/// * num_iter: number of iterations used for solver, 25 is usually enough.
///
/// * max_tol: convergence tolerance used for solver.
///
/// For more details about the Fast Bilateral Solver parameters, see the original paper [BarronPoole2016](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_BarronPoole2016).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * lambda: 128.0
/// * num_iter: 25
/// * max_tol: 1e-5
#[inline]
pub fn create_fast_bilateral_solver_filter(guide: &dyn core::ToInputArray, sigma_spatial: f64, sigma_luma: f64, sigma_chroma: f64, lambda: f64, num_iter: i32, max_tol: f64) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::FastBilateralSolverFilter>> {
extern_container_arg!(guide);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_createFastBilateralSolverFilter_const__InputArrayR_double_double_double_double_int_double(guide.as_raw__InputArray(), sigma_spatial, sigma_luma, sigma_chroma, lambda, num_iter, max_tol, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::FastBilateralSolverFilter>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Factory method, create instance of FastGlobalSmootherFilter and execute the initialization routines.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * guide: image serving as guide for filtering. It should have 8-bit depth and either 1 or 3 channels.
///
/// * lambda: parameter defining the amount of regularization
///
/// * sigma_color: parameter, that is similar to color space sigma in bilateralFilter.
///
/// * lambda_attenuation: internal parameter, defining how much lambda decreases after each iteration. Normally,
/// it should be 0.25. Setting it to 1.0 may lead to streaking artifacts.
///
/// * num_iter: number of iterations used for filtering, 3 is usually enough.
///
/// For more details about Fast Global Smoother parameters, see the original paper [Min2014](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Min2014). However, please note that
/// there are several differences. Lambda attenuation described in the paper is implemented a bit differently so do not
/// expect the results to be identical to those from the paper; sigma_color values from the paper should be multiplied by 255.0 to
/// achieve the same effect. Also, in case of image filtering where source and guide image are the same, authors
/// propose to dynamically update the guide image after each iteration. To maximize the performance this feature
/// was not implemented here.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * lambda_attenuation: 0.25
/// * num_iter: 3
#[inline]
pub fn create_fast_global_smoother_filter(guide: &dyn core::ToInputArray, lambda: f64, sigma_color: f64, lambda_attenuation: f64, num_iter: i32) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::FastGlobalSmootherFilter>> {
extern_container_arg!(guide);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_createFastGlobalSmootherFilter_const__InputArrayR_double_double_double_int(guide.as_raw__InputArray(), lambda, sigma_color, lambda_attenuation, num_iter, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::FastGlobalSmootherFilter>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates a smart pointer to a FastLineDetector object and initializes it
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * length_threshold: Segment shorter than this will be discarded
/// * distance_threshold: A point placed from a hypothesis line
/// segment farther than this will be regarded as an outlier
/// * canny_th1: First threshold for hysteresis procedure in Canny()
/// * canny_th2: Second threshold for hysteresis procedure in Canny()
/// * canny_aperture_size: Aperturesize for the sobel operator in Canny().
/// If zero, Canny() is not applied and the input image is taken as an edge image.
/// * do_merge: If true, incremental merging of segments will be performed
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * length_threshold: 10
/// * distance_threshold: 1.414213562f
/// * canny_th1: 50.0
/// * canny_th2: 50.0
/// * canny_aperture_size: 3
/// * do_merge: false
#[inline]
pub fn create_fast_line_detector(length_threshold: i32, distance_threshold: f32, canny_th1: f64, canny_th2: f64, canny_aperture_size: i32, do_merge: bool) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::FastLineDetector>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_createFastLineDetector_int_float_double_double_int_bool(length_threshold, distance_threshold, canny_th1, canny_th2, canny_aperture_size, do_merge, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::FastLineDetector>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Factory method, create instance of GuidedFilter and produce initialization routines.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * guide: guided image (or array of images) with up to 3 channels, if it have more then 3
/// channels then only first 3 channels will be used.
///
/// * radius: radius of Guided Filter.
///
/// * eps: regularization term of Guided Filter.  is similar to the sigma in the color
/// space into bilateralFilter.
///
/// For more details about Guided Filter parameters, see the original article [Kaiming10](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Kaiming10) .
#[inline]
pub fn create_guided_filter(guide: &dyn core::ToInputArray, radius: i32, eps: f64) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::GuidedFilter>> {
extern_container_arg!(guide);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_createGuidedFilter_const__InputArrayR_int_double(guide.as_raw__InputArray(), radius, eps, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::GuidedFilter>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// creates a quaternion image.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * img: Source 8-bit, 32-bit or 64-bit image, with 3-channel image.
/// * qimg: result CV_64FC4 a quaternion image( 4 chanels zero channel and B,G,R).
#[inline]
pub fn create_quaternion_image(img: &dyn core::ToInputArray, qimg: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(img);
extern_container_arg!(qimg);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_createQuaternionImage_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(img.as_raw__InputArray(), qimg.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn create_rf_feature_getter() -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::RFFeatureGetter>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_createRFFeatureGetter(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::RFFeatureGetter>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Factory method that creates an instance of the
/// RICInterpolator.
#[inline]
pub fn create_ric_interpolator() -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::RICInterpolator>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_createRICInterpolator(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::RICInterpolator>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Convenience method to set up the matcher for computing the right-view disparity map
/// that is required in case of filtering with confidence.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * matcher_left: main stereo matcher instance that will be used with the filter
#[inline]
pub fn create_right_matcher(mut matcher_left: core::Ptr<dyn crate::calib3d::StereoMatcher>) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::calib3d::StereoMatcher>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_createRightMatcher_PtrLStereoMatcherG(matcher_left.as_raw_mut_PtrOfStereoMatcher(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::calib3d::StereoMatcher>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Initializes a ScanSegment object.
///
/// The function initializes a ScanSegment object for the input image. It stores the parameters of
/// the image: image_width and image_height. It also sets the parameters of the F-DBSCAN superpixel
/// algorithm, which are: num_superpixels, threads, and merge_small.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * image_width: Image width.
/// * image_height: Image height.
/// * num_superpixels: Desired number of superpixels. Note that the actual number may be smaller
/// due to restrictions (depending on the image size). Use getNumberOfSuperpixels() to
/// get the actual number.
/// * slices: Number of processing threads for parallelisation. Setting -1 uses the maximum number
/// of threads. In practice, four threads is enough for smaller images and eight threads for larger ones.
/// * merge_small: merge small segments to give the desired number of superpixels. Processing is
/// much faster without merging, but many small segments will be left in the image.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * slices: 8
/// * merge_small: true
#[inline]
pub fn create_scan_segment(image_width: i32, image_height: i32, num_superpixels: i32, slices: i32, merge_small: bool) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::ScanSegment>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_createScanSegment_int_int_int_int_bool(image_width, image_height, num_superpixels, slices, merge_small, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::ScanSegment>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// !
/// * The only constructor
/// *
/// * \param model : name of the file where the model is stored
/// * \param howToGetFeatures : optional object inheriting from RFFeatureGetter.
/// * You need it only if you would like to train your
/// * own forest, pass NULL otherwise
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * how_to_get_features: Ptr<RFFeatureGetter>()
#[inline]
pub fn create_structured_edge_detection(model: &str, how_to_get_features: Option<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::RFFeatureGetter>>) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::StructuredEdgeDetection>> {
extern_container_arg!(model);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_createStructuredEdgeDetection_const_StringR_PtrLconst_RFFeatureGetterG(model.opencv_as_extern(), how_to_get_features.map_or(::core::ptr::null(), |how_to_get_features| how_to_get_features.as_raw_PtrOfRFFeatureGetter()), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::StructuredEdgeDetection>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Class implementing the LSC (Linear Spectral Clustering) superpixels
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: Image to segment
/// * region_size: Chooses an average superpixel size measured in pixels
/// * ratio: Chooses the enforcement of superpixel compactness factor of superpixel
///
/// The function initializes a SuperpixelLSC object for the input image. It sets the parameters of
/// superpixel algorithm, which are: region_size and ruler. It preallocate some buffers for future
/// computing iterations over the given image. An example of LSC is ilustrated in the following picture.
/// For enanched results it is recommended for color images to preprocess image with little gaussian blur
/// with a small 3 x 3 kernel and additional conversion into CieLAB color space.
///
/// 
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * region_size: 10
/// * ratio: 0.075f
#[inline]
pub fn create_superpixel_lsc(image: &dyn core::ToInputArray, region_size: i32, ratio: f32) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::SuperpixelLSC>> {
extern_container_arg!(image);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_createSuperpixelLSC_const__InputArrayR_int_float(image.as_raw__InputArray(), region_size, ratio, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::SuperpixelLSC>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Initializes a SuperpixelSEEDS object.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * image_width: Image width.
/// * image_height: Image height.
/// * image_channels: Number of channels of the image.
/// * num_superpixels: Desired number of superpixels. Note that the actual number may be smaller
/// due to restrictions (depending on the image size and num_levels). Use getNumberOfSuperpixels() to
/// get the actual number.
/// * num_levels: Number of block levels. The more levels, the more accurate is the segmentation,
/// but needs more memory and CPU time.
/// * prior: enable 3x3 shape smoothing term if \>0. A larger value leads to smoother shapes. prior
/// must be in the range [0, 5].
/// * histogram_bins: Number of histogram bins.
/// * double_step: If true, iterate each block level twice for higher accuracy.
///
/// The function initializes a SuperpixelSEEDS object for the input image. It stores the parameters of
/// the image: image_width, image_height and image_channels. It also sets the parameters of the SEEDS
/// superpixel algorithm, which are: num_superpixels, num_levels, use_prior, histogram_bins and
/// double_step.
///
/// The number of levels in num_levels defines the amount of block levels that the algorithm use in the
/// optimization. The initialization is a grid, in which the superpixels are equally distributed through
/// the width and the height of the image. The larger blocks correspond to the superpixel size, and the
/// levels with smaller blocks are formed by dividing the larger blocks into 2 x 2 blocks of pixels,
/// recursively until the smaller block level. An example of initialization of 4 block levels is
/// illustrated in the following figure.
///
/// 
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * prior: 2
/// * histogram_bins: 5
/// * double_step: false
#[inline]
pub fn create_superpixel_seeds(image_width: i32, image_height: i32, image_channels: i32, num_superpixels: i32, num_levels: i32, prior: i32, histogram_bins: i32, double_step: bool) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::SuperpixelSEEDS>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_createSuperpixelSEEDS_int_int_int_int_int_int_int_bool(image_width, image_height, image_channels, num_superpixels, num_levels, prior, histogram_bins, double_step, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::SuperpixelSEEDS>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Initialize a SuperpixelSLIC object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: Image to segment
/// * algorithm: Chooses the algorithm variant to use:
/// SLIC segments image using a desired region_size, and in addition SLICO will optimize using adaptive compactness factor,
/// while MSLIC will optimize using manifold methods resulting in more content-sensitive superpixels.
/// * region_size: Chooses an average superpixel size measured in pixels
/// * ruler: Chooses the enforcement of superpixel smoothness factor of superpixel
///
/// The function initializes a SuperpixelSLIC object for the input image. It sets the parameters of choosed
/// superpixel algorithm, which are: region_size and ruler. It preallocate some buffers for future
/// computing iterations over the given image. For enanched results it is recommended for color images to
/// preprocess image with little gaussian blur using a small 3 x 3 kernel and additional conversion into
/// CieLAB color space. An example of SLIC versus SLICO and MSLIC is ilustrated in the following picture.
///
/// 
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * algorithm: SLICO
/// * region_size: 10
/// * ruler: 10.0f
#[inline]
pub fn create_superpixel_slic(image: &dyn core::ToInputArray, algorithm: i32, region_size: i32, ruler: f32) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::SuperpixelSLIC>> {
extern_container_arg!(image);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_createSuperpixelSLIC_const__InputArrayR_int_int_float(image.as_raw__InputArray(), algorithm, region_size, ruler, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::SuperpixelSLIC>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Simple one-line Domain Transform filter call. If you have multiple images to filter with the same
/// guided image then use DTFilter interface to avoid extra computations on initialization stage.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * guide: guided image (also called as joint image) with unsigned 8-bit or floating-point 32-bit
/// depth and up to 4 channels.
/// * src: filtering image with unsigned 8-bit or floating-point 32-bit depth and up to 4 channels.
/// * dst: destination image
/// * sigmaSpatial:  parameter in the original article, it's similar to the sigma in the
/// coordinate space into bilateralFilter.
/// * sigmaColor:  parameter in the original article, it's similar to the sigma in the
/// color space into bilateralFilter.
/// * mode: one form three modes DTF_NC, DTF_RF and DTF_IC which corresponds to three modes for
/// filtering 2D signals in the article.
/// * numIters: optional number of iterations used for filtering, 3 is quite enough.
/// ## See also
/// bilateralFilter, guidedFilter, amFilter
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * mode: DTF_NC
/// * num_iters: 3
#[inline]
pub fn dt_filter(guide: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, sigma_spatial: f64, sigma_color: f64, mode: i32, num_iters: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(guide);
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_dtFilter_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_double_int_int(guide.as_raw__InputArray(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), sigma_spatial, sigma_color, mode, num_iters, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Smoothes an image using the Edge-Preserving filter.
///
/// The function smoothes Gaussian noise as well as salt & pepper noise.
/// For more details about this implementation, please see
/// [ReiWoe18] Reich, S. and Wörgötter, F. and Dellen, B. (2018). A Real-Time Edge-Preserving Denoising Filter. Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP): Visapp, 85-94, 4. DOI: 10.5220/0006509000850094.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Source 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Destination image of the same size and type as src.
/// * d: Diameter of each pixel neighborhood that is used during filtering. Must be greater or equal 3.
/// * threshold: Threshold, which distinguishes between noise, outliers, and data.
#[inline]
pub fn edge_preserving_filter(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, d: i32, threshold: f64) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_edgePreservingFilter_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_double(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), d, threshold, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Simple one-line Fast Bilateral Solver filter call. If you have multiple images to filter with the same
/// guide then use FastBilateralSolverFilter interface to avoid extra computations.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * guide: image serving as guide for filtering. It should have 8-bit depth and either 1 or 3 channels.
///
/// * src: source image for filtering with unsigned 8-bit or signed 16-bit or floating-point 32-bit depth and up to 4 channels.
///
/// * confidence: confidence image with unsigned 8-bit or floating-point 32-bit confidence and 1 channel.
///
/// * dst: destination image.
///
/// * sigma_spatial: parameter, that is similar to spatial space sigma (bandwidth) in bilateralFilter.
///
/// * sigma_luma: parameter, that is similar to luma space sigma (bandwidth) in bilateralFilter.
///
/// * sigma_chroma: parameter, that is similar to chroma space sigma (bandwidth) in bilateralFilter.
///
/// * lambda: smoothness strength parameter for solver.
///
/// * num_iter: number of iterations used for solver, 25 is usually enough.
///
/// * max_tol: convergence tolerance used for solver.
///
/// For more details about the Fast Bilateral Solver parameters, see the original paper [BarronPoole2016](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_BarronPoole2016).
///
///
/// Note: Confidence images with CV_8U depth are expected to in [0, 255] and CV_32F in [0, 1] range.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * sigma_spatial: 8
/// * sigma_luma: 8
/// * sigma_chroma: 8
/// * lambda: 128.0
/// * num_iter: 25
/// * max_tol: 1e-5
#[inline]
pub fn fast_bilateral_solver_filter(guide: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, confidence: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, sigma_spatial: f64, sigma_luma: f64, sigma_chroma: f64, lambda: f64, num_iter: i32, max_tol: f64) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(guide);
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(confidence);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_fastBilateralSolverFilter_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_double_double_double_int_double(guide.as_raw__InputArray(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), confidence.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), sigma_spatial, sigma_luma, sigma_chroma, lambda, num_iter, max_tol, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Simple one-line Fast Global Smoother filter call. If you have multiple images to filter with the same
/// guide then use FastGlobalSmootherFilter interface to avoid extra computations.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * guide: image serving as guide for filtering. It should have 8-bit depth and either 1 or 3 channels.
///
/// * src: source image for filtering with unsigned 8-bit or signed 16-bit or floating-point 32-bit depth and up to 4 channels.
///
/// * dst: destination image.
///
/// * lambda: parameter defining the amount of regularization
///
/// * sigma_color: parameter, that is similar to color space sigma in bilateralFilter.
///
/// * lambda_attenuation: internal parameter, defining how much lambda decreases after each iteration. Normally,
/// it should be 0.25. Setting it to 1.0 may lead to streaking artifacts.
///
/// * num_iter: number of iterations used for filtering, 3 is usually enough.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * lambda_attenuation: 0.25
/// * num_iter: 3
#[inline]
pub fn fast_global_smoother_filter(guide: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, lambda: f64, sigma_color: f64, lambda_attenuation: f64, num_iter: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(guide);
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_fastGlobalSmootherFilter_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_double_double_int(guide.as_raw__InputArray(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), lambda, sigma_color, lambda_attenuation, num_iter, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Finds ellipses fastly in an image using projective invariant pruning.
/// *
/// * The function detects ellipses in images using projective invariant pruning.
/// * For more details about this implementation, please see [jia2017fast](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_jia2017fast)
/// * Jia, Qi et al, (2017).
/// * A Fast Ellipse Detector using Projective Invariant Pruning. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing.
/// *
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: input image, could be gray or color.
/// * ellipses: output vector of found ellipses. each vector is encoded as five float $x, y, a, b, radius, score$.
/// * scoreThreshold: float, the threshold of ellipse score.
/// * reliabilityThreshold: float, the threshold of reliability.
/// * centerDistanceThreshold: float, the threshold of center distance.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * score_threshold: 0.7f
/// * reliability_threshold: 0.5f
/// * center_distance_threshold: 0.05f
#[inline]
pub fn find_ellipses(image: &dyn core::ToInputArray, ellipses: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, score_threshold: f32, reliability_threshold: f32, center_distance_threshold: f32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(image);
extern_container_arg!(ellipses);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_findEllipses_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float_float_float(image.as_raw__InputArray(), ellipses.as_raw__OutputArray(), score_threshold, reliability_threshold, center_distance_threshold, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Fourier descriptors for planed closed curves
///
/// For more details about this implementation, please see [PersoonFu1977](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_PersoonFu1977)
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: contour type vector<Point> , vector<Point2f> or vector<Point2d>
/// * dst: Mat of type CV_64FC2 and nbElt rows A VERIFIER
/// * nbElt: number of rows in dst or getOptimalDFTSize rows if nbElt=-1
/// * nbFD: number of FD return in dst dst = [FD(1...nbFD/2) FD(nbFD/2-nbElt+1...:nbElt)]
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * nb_elt: -1
/// * nb_fd: -1
#[inline]
pub fn fourier_descriptor(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, nb_elt: i32, nb_fd: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_fourierDescriptor_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), nb_elt, nb_fd, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Function for creating a disparity map visualization (clamped CV_8U image)
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input disparity map (CV_16S depth)
///
/// * dst: output visualization
///
/// * scale: disparity map will be multiplied by this value for visualization
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * scale: 1.0
#[inline]
pub fn get_disparity_vis(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, scale: f64) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_getDisparityVis_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), scale, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Simple one-line Guided Filter call.
///
/// If you have multiple images to filter with the same guided image then use GuidedFilter interface to
/// avoid extra computations on initialization stage.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * guide: guided image (or array of images) with up to 3 channels, if it have more then 3
/// channels then only first 3 channels will be used.
///
/// * src: filtering image with any numbers of channels.
///
/// * dst: output image.
///
/// * radius: radius of Guided Filter.
///
/// * eps: regularization term of Guided Filter.  is similar to the sigma in the color
/// space into bilateralFilter.
///
/// * dDepth: optional depth of the output image.
/// ## See also
/// bilateralFilter, dtFilter, amFilter
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * d_depth: -1
#[inline]
pub fn guided_filter(guide: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, radius: i32, eps: f64, d_depth: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(guide);
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_guidedFilter_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_double_int(guide.as_raw__InputArray(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), radius, eps, d_depth, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Applies the joint bilateral filter to an image.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * joint: Joint 8-bit or floating-point, 1-channel or 3-channel image.
///
/// * src: Source 8-bit or floating-point, 1-channel or 3-channel image with the same depth as joint
/// image.
///
/// * dst: Destination image of the same size and type as src .
///
/// * d: Diameter of each pixel neighborhood that is used during filtering. If it is non-positive,
/// it is computed from sigmaSpace .
///
/// * sigmaColor: Filter sigma in the color space. A larger value of the parameter means that
/// farther colors within the pixel neighborhood (see sigmaSpace ) will be mixed together, resulting in
/// larger areas of semi-equal color.
///
/// * sigmaSpace: Filter sigma in the coordinate space. A larger value of the parameter means that
/// farther pixels will influence each other as long as their colors are close enough (see sigmaColor ).
/// When d\>0 , it specifies the neighborhood size regardless of sigmaSpace . Otherwise, d is
/// proportional to sigmaSpace .
///
/// * borderType:
///
///
/// Note: bilateralFilter and jointBilateralFilter use L1 norm to compute difference between colors.
/// ## See also
/// bilateralFilter, amFilter
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * border_type: BORDER_DEFAULT
#[inline]
pub fn joint_bilateral_filter(joint: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, d: i32, sigma_color: f64, sigma_space: f64, border_type: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(joint);
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_jointBilateralFilter_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_double_double_int(joint.as_raw__InputArray(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), d, sigma_color, sigma_space, border_type, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Global image smoothing via L0 gradient minimization.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: source image for filtering with unsigned 8-bit or signed 16-bit or floating-point depth.
///
/// * dst: destination image.
///
/// * lambda: parameter defining the smooth term weight.
///
/// * kappa: parameter defining the increasing factor of the weight of the gradient data term.
///
/// For more details about L0 Smoother, see the original paper [xu2011image](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_xu2011image).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * lambda: 0.02
/// * kappa: 2.0
#[inline]
pub fn l0_smooth(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, lambda: f64, kappa: f64) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_l0Smooth_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_double(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), lambda, kappa, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Performs thresholding on input images using Niblack's technique or some of the
/// popular variations it inspired.
///
/// The function transforms a grayscale image to a binary image according to the formulae:
/// * **THRESH_BINARY**
/// 
/// * **THRESH_BINARY_INV**
/// 
/// where  is a threshold calculated individually for each pixel.
///
/// The threshold value  is determined based on the binarization method chosen. For
/// classic Niblack, it is the mean minus  times standard deviation of
///  neighborhood of 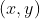.
///
/// The function can't process the image in-place.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * _src: Source 8-bit single-channel image.
/// * _dst: Destination image of the same size and the same type as src.
/// * maxValue: Non-zero value assigned to the pixels for which the condition is satisfied,
/// used with the THRESH_BINARY and THRESH_BINARY_INV thresholding types.
/// * type: Thresholding type, see cv::ThresholdTypes.
/// * blockSize: Size of a pixel neighborhood that is used to calculate a threshold value
/// for the pixel: 3, 5, 7, and so on.
/// * k: The user-adjustable parameter used by Niblack and inspired techniques. For Niblack, this is
/// normally a value between 0 and 1 that is multiplied with the standard deviation and subtracted from
/// the mean.
/// * binarizationMethod: Binarization method to use. By default, Niblack's technique is used.
/// Other techniques can be specified, see cv::ximgproc::LocalBinarizationMethods.
/// * r: The user-adjustable parameter used by Sauvola's technique. This is the dynamic range
/// of standard deviation.
/// ## See also
/// threshold, adaptiveThreshold
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * binarization_method: BINARIZATION_NIBLACK
/// * r: 128
#[inline]
pub fn ni_black_threshold(_src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, _dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, max_value: f64, typ: i32, block_size: i32, k: f64, binarization_method: i32, r: f64) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(_src);
extern_container_arg!(_dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_niBlackThreshold_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_int_int_double_int_double(_src.as_raw__InputArray(), _dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), max_value, typ, block_size, k, binarization_method, r, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// calculates conjugate of a quaternion image.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * qimg: quaternion image.
/// * qcimg: conjugate of qimg
#[inline]
pub fn qconj(qimg: &dyn core::ToInputArray, qcimg: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(qimg);
extern_container_arg!(qcimg);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_qconj_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(qimg.as_raw__InputArray(), qcimg.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Performs a forward or inverse Discrete quaternion Fourier transform of a 2D quaternion array.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * img: quaternion image.
/// * qimg: quaternion image in dual space.
/// * flags: quaternion image in dual space. only DFT_INVERSE flags is supported
/// * sideLeft: true the hypercomplex exponential is to be multiplied on the left (false on the right ).
#[inline]
pub fn qdft(img: &dyn core::ToInputArray, qimg: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32, side_left: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(img);
extern_container_arg!(qimg);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_qdft_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_bool(img.as_raw__InputArray(), qimg.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, side_left, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates the per-element quaternion product of two arrays
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src1: quaternion image.
/// * src2: quaternion image.
/// * dst: product dst(I)=src1(I) . src2(I)
#[inline]
pub fn qmultiply(src1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src1);
extern_container_arg!(src2);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_qmultiply_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src1.as_raw__InputArray(), src2.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// divides each element by its modulus.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * qimg: quaternion image.
/// * qnimg: conjugate of qimg
#[inline]
pub fn qunitary(qimg: &dyn core::ToInputArray, qnimg: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(qimg);
extern_container_arg!(qnimg);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_qunitary_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(qimg.as_raw__InputArray(), qnimg.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Function for reading ground truth disparity maps. Supports basic Middlebury
/// and MPI-Sintel formats. Note that the resulting disparity map is scaled by 16.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src_path: path to the image, containing ground-truth disparity map
///
/// * dst: output disparity map, CV_16S depth
///
/// @result returns zero if successfully read the ground truth
#[inline]
pub fn read_gt(src_path: &str, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<i32> {
extern_container_arg!(mut src_path);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_readGT_String_const__OutputArrayR(src_path.opencv_as_extern_mut(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates a run-length encoded image from a vector of runs (column begin, column end, row)
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * runs: vector of runs
/// * res: result
/// * size: image size (to be used if an "on" boundary should be used in erosion, using the default
/// means that the size is computed from the extension of the input)
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * size: Size(0,0)
#[inline]
pub fn create_rle_image(runs: &core::Vector<core::Point3i>, res: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, size: core::Size) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(res);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_rl_createRLEImage_const_vectorLPoint3iGR_const__OutputArrayR_Size(runs.as_raw_VectorOfPoint3i(), res.as_raw__OutputArray(), size.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Dilates an run-length encoded binary image by using a specific structuring element.
///
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * rlSrc: input image
/// * rlDest: result
/// * rlKernel: kernel
/// * anchor: position of the anchor within the element; default value (0, 0)
/// is usually the element center.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * anchor: Point(0,0)
#[inline]
pub fn dilate(rl_src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, rl_dest: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, rl_kernel: &dyn core::ToInputArray, anchor: core::Point) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(rl_src);
extern_container_arg!(rl_dest);
extern_container_arg!(rl_kernel);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_rl_dilate_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Point(rl_src.as_raw__InputArray(), rl_dest.as_raw__OutputArray(), rl_kernel.as_raw__InputArray(), anchor.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Erodes an run-length encoded binary image by using a specific structuring element.
///
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * rlSrc: input image
/// * rlDest: result
/// * rlKernel: kernel
/// * bBoundaryOn: indicates whether pixel outside the image boundary are assumed to be on
/// (True: works in the same way as the default of cv::erode, False: is a little faster)
/// * anchor: position of the anchor within the element; default value (0, 0)
/// is usually the element center.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * b_boundary_on: true
/// * anchor: Point(0,0)
#[inline]
pub fn erode(rl_src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, rl_dest: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, rl_kernel: &dyn core::ToInputArray, b_boundary_on: bool, anchor: core::Point) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(rl_src);
extern_container_arg!(rl_dest);
extern_container_arg!(rl_kernel);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_rl_erode_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_bool_Point(rl_src.as_raw__InputArray(), rl_dest.as_raw__OutputArray(), rl_kernel.as_raw__InputArray(), b_boundary_on, anchor.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns a run length encoded structuring element of the specified size and shape.
///
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * shape: Element shape that can be one of cv::MorphShapes
/// * ksize: Size of the structuring element.
#[inline]
pub fn get_structuring_element(shape: i32, ksize: core::Size) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_rl_getStructuringElement_int_Size(shape, ksize.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Check whether a custom made structuring element can be used with run length morphological operations.
/// (It must consist of a continuous array of single runs per row)
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * rlStructuringElement: mask to be tested
#[inline]
pub fn is_rl_morphology_possible(rl_structuring_element: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<bool> {
extern_container_arg!(rl_structuring_element);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_rl_isRLMorphologyPossible_const__InputArrayR(rl_structuring_element.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Applies a morphological operation to a run-length encoded binary image.
///
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * rlSrc: input image
/// * rlDest: result
/// * op: all operations supported by cv::morphologyEx (except cv::MORPH_HITMISS)
/// * rlKernel: kernel
/// * bBoundaryOnForErosion: indicates whether pixel outside the image boundary are assumed
/// to be on for erosion operations (True: works in the same way as the default of cv::erode,
/// False: is a little faster)
/// * anchor: position of the anchor within the element; default value (0, 0) is usually the element center.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * b_boundary_on_for_erosion: true
/// * anchor: Point(0,0)
#[inline]
pub fn morphology_ex(rl_src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, rl_dest: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, op: i32, rl_kernel: &dyn core::ToInputArray, b_boundary_on_for_erosion: bool, anchor: core::Point) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(rl_src);
extern_container_arg!(rl_dest);
extern_container_arg!(rl_kernel);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_rl_morphologyEx_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_const__InputArrayR_bool_Point(rl_src.as_raw__InputArray(), rl_dest.as_raw__OutputArray(), op, rl_kernel.as_raw__InputArray(), b_boundary_on_for_erosion, anchor.opencv_as_extern(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Paint run length encoded binary image into an image.
///
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: image to paint into (currently only single channel images).
/// * rlSrc: run length encoded image
/// * value: all foreground pixel of the binary image are set to this value
#[inline]
pub fn paint(image: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, rl_src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, value: core::Scalar) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(image);
extern_container_arg!(rl_src);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_rl_paint_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const_ScalarR(image.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), rl_src.as_raw__InputArray(), &value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Applies a fixed-level threshold to each array element.
///
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: input array (single-channel).
/// * rlDest: resulting run length encoded image.
/// * thresh: threshold value.
/// * type: thresholding type (only cv::THRESH_BINARY and cv::THRESH_BINARY_INV are supported)
#[inline]
pub fn threshold(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, rl_dest: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, thresh: f64, typ: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(rl_dest);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_rl_threshold_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), rl_dest.as_raw__OutputArray(), thresh, typ, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Applies the rolling guidance filter to an image.
///
/// For more details, please see [zhang2014rolling](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_zhang2014rolling)
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Source 8-bit or floating-point, 1-channel or 3-channel image.
///
/// * dst: Destination image of the same size and type as src.
///
/// * d: Diameter of each pixel neighborhood that is used during filtering. If it is non-positive,
/// it is computed from sigmaSpace .
///
/// * sigmaColor: Filter sigma in the color space. A larger value of the parameter means that
/// farther colors within the pixel neighborhood (see sigmaSpace ) will be mixed together, resulting in
/// larger areas of semi-equal color.
///
/// * sigmaSpace: Filter sigma in the coordinate space. A larger value of the parameter means that
/// farther pixels will influence each other as long as their colors are close enough (see sigmaColor ).
/// When d\>0 , it specifies the neighborhood size regardless of sigmaSpace . Otherwise, d is
/// proportional to sigmaSpace .
///
/// * numOfIter: Number of iterations of joint edge-preserving filtering applied on the source image.
///
/// * borderType:
///
///
/// Note: rollingGuidanceFilter uses jointBilateralFilter as the edge-preserving filter.
/// ## See also
/// jointBilateralFilter, bilateralFilter, amFilter
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * d: -1
/// * sigma_color: 25
/// * sigma_space: 3
/// * num_of_iter: 4
/// * border_type: BORDER_DEFAULT
#[inline]
pub fn rolling_guidance_filter(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, d: i32, sigma_color: f64, sigma_space: f64, num_of_iter: i32, border_type: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_rollingGuidanceFilter_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_double_double_int_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), d, sigma_color, sigma_space, num_of_iter, border_type, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates a graph based segmentor
/// ## Parameters
/// * sigma: The sigma parameter, used to smooth image
/// * k: The k parameter of the algorythm
/// * min_size: The minimum size of segments
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * sigma: 0.5
/// * k: 300
/// * min_size: 100
#[inline]
pub fn create_graph_segmentation(sigma: f64, k: f32, min_size: i32) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::GraphSegmentation>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_createGraphSegmentation_double_float_int(sigma, k, min_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::GraphSegmentation>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Create a new SelectiveSearchSegmentation class.
#[inline]
pub fn create_selective_search_segmentation() -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentation>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_createSelectiveSearchSegmentation(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentation>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Create a new color-based strategy
#[inline]
pub fn create_selective_search_segmentation_strategy_color() -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyColor>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_createSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyColor(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyColor>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Create a new fill-based strategy
#[inline]
pub fn create_selective_search_segmentation_strategy_fill() -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyFill>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_createSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyFill(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyFill>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Create a new multiple strategy
#[inline]
pub fn create_selective_search_segmentation_strategy_multiple() -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultiple>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_createSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultiple(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultiple>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Create a new multiple strategy and set one subtrategy
/// ## Parameters
/// * s1: The first strategy
#[inline]
pub fn create_selective_search_segmentation_strategy_multiple_1(mut s1: core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy>) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultiple>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_createSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultiple_PtrLSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyG(s1.as_raw_mut_PtrOfSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultiple>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Create a new multiple strategy and set two subtrategies, with equal weights
/// ## Parameters
/// * s1: The first strategy
/// * s2: The second strategy
#[inline]
pub fn create_selective_search_segmentation_strategy_multiple_2(mut s1: core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy>, mut s2: core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy>) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultiple>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_createSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultiple_PtrLSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyG_PtrLSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyG(s1.as_raw_mut_PtrOfSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy(), s2.as_raw_mut_PtrOfSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultiple>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Create a new multiple strategy and set three subtrategies, with equal weights
/// ## Parameters
/// * s1: The first strategy
/// * s2: The second strategy
/// * s3: The third strategy
#[inline]
pub fn create_selective_search_segmentation_strategy_multiple_3(mut s1: core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy>, mut s2: core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy>, mut s3: core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy>) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultiple>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_createSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultiple_PtrLSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyG_PtrLSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyG_PtrLSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyG(s1.as_raw_mut_PtrOfSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy(), s2.as_raw_mut_PtrOfSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy(), s3.as_raw_mut_PtrOfSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultiple>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Create a new multiple strategy and set four subtrategies, with equal weights
/// ## Parameters
/// * s1: The first strategy
/// * s2: The second strategy
/// * s3: The third strategy
/// * s4: The forth strategy
#[inline]
pub fn create_selective_search_segmentation_strategy_multiple_4(mut s1: core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy>, mut s2: core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy>, mut s3: core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy>, mut s4: core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy>) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultiple>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_createSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultiple_PtrLSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyG_PtrLSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyG_PtrLSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyG_PtrLSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyG(s1.as_raw_mut_PtrOfSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy(), s2.as_raw_mut_PtrOfSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy(), s3.as_raw_mut_PtrOfSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy(), s4.as_raw_mut_PtrOfSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultiple>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Create a new size-based strategy
#[inline]
pub fn create_selective_search_segmentation_strategy_size() -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategySize>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_createSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategySize(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategySize>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Create a new size-based strategy
#[inline]
pub fn create_selective_search_segmentation_strategy_texture() -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyTexture>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_createSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyTexture(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyTexture>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Applies a binary blob thinning operation, to achieve a skeletization of the input image.
///
/// The function transforms a binary blob image into a skeletized form using the technique of Zhang-Suen.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Source 8-bit single-channel image, containing binary blobs, with blobs having 255 pixel values.
/// * dst: Destination image of the same size and the same type as src. The function can work in-place.
/// * thinningType: Value that defines which thinning algorithm should be used. See cv::ximgproc::ThinningTypes
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * thinning_type: THINNING_ZHANGSUEN
#[inline]
pub fn thinning(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, thinning_type: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_thinning_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), thinning_type, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// transform a contour
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: contour or Fourier Descriptors if fd is true
/// * t: transform Mat given by estimateTransformation
/// * dst: Mat of type CV_64FC2 and nbElt rows
/// * fdContour: true src are Fourier Descriptors. fdContour false src is a contour
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * fd_contour: true
#[inline]
pub fn transform_fd(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, t: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, fd_contour: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(t);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_transformFD_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_bool(src.as_raw__InputArray(), t.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), fd_contour, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Applies weighted median filter to an image.
///
/// For more details about this implementation, please see [zhang2014100](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_zhang2014100)+
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * joint: Joint 8-bit, 1-channel or 3-channel image.
/// * src: Source 8-bit or floating-point, 1-channel or 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Destination image.
/// * r: Radius of filtering kernel, should be a positive integer.
/// * sigma: Filter range standard deviation for the joint image.
/// * weightType: weightType The type of weight definition, see WMFWeightType
/// * mask: A 0-1 mask that has the same size with I. This mask is used to ignore the effect of some pixels. If the pixel value on mask is 0,
/// the pixel will be ignored when maintaining the joint-histogram. This is useful for applications like optical flow occlusion handling.
/// ## See also
/// medianBlur, jointBilateralFilter
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * sigma: 25.5
/// * weight_type: WMF_EXP
/// * mask: noArray()
#[inline]
pub fn weighted_median_filter(joint: &dyn core::ToInputArray, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, r: i32, sigma: f64, weight_type: i32, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(joint);
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_weightedMedianFilter_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_double_int_const__InputArrayR(joint.as_raw__InputArray(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), r, sigma, weight_type, mask.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::AdaptiveManifoldFilter]
pub trait AdaptiveManifoldFilterConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_AdaptiveManifoldFilter(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// ## See also
/// setSigmaS
#[inline]
fn get_sigma_s(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_AdaptiveManifoldFilter_getSigmaS_const(self.as_raw_AdaptiveManifoldFilter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## See also
/// setSigmaR
#[inline]
fn get_sigma_r(&self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_AdaptiveManifoldFilter_getSigmaR_const(self.as_raw_AdaptiveManifoldFilter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## See also
/// setTreeHeight
#[inline]
fn get_tree_height(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_AdaptiveManifoldFilter_getTreeHeight_const(self.as_raw_AdaptiveManifoldFilter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## See also
/// setPCAIterations
#[inline]
fn get_pca_iterations(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_AdaptiveManifoldFilter_getPCAIterations_const(self.as_raw_AdaptiveManifoldFilter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## See also
/// setAdjustOutliers
#[inline]
fn get_adjust_outliers(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_AdaptiveManifoldFilter_getAdjustOutliers_const(self.as_raw_AdaptiveManifoldFilter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## See also
/// setUseRNG
#[inline]
fn get_use_rng(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_AdaptiveManifoldFilter_getUseRNG_const(self.as_raw_AdaptiveManifoldFilter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Interface for Adaptive Manifold Filter realizations.
///
/// For more details about this filter see [Gastal12](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Gastal12) and References_.
///
/// Below listed optional parameters which may be set up with Algorithm::set function.
/// * member double sigma_s = 16.0
/// Spatial standard deviation.
/// * member double sigma_r = 0.2
/// Color space standard deviation.
/// * member int tree_height = -1
/// Height of the manifold tree (default = -1 : automatically computed).
/// * member int num_pca_iterations = 1
/// Number of iterations to computed the eigenvector.
/// * member bool adjust_outliers = false
/// Specify adjust outliers using Eq. 9 or not.
/// * member bool use_RNG = true
/// Specify use random number generator to compute eigenvector or not.
pub trait AdaptiveManifoldFilter: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::ximgproc::AdaptiveManifoldFilterConst {
fn as_raw_mut_AdaptiveManifoldFilter(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Apply high-dimensional filtering using adaptive manifolds.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: filtering image with any numbers of channels.
///
/// * dst: output image.
///
/// * joint: optional joint (also called as guided) image with any numbers of channels.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * joint: noArray()
#[inline]
fn filter(&mut self, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, joint: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
extern_container_arg!(joint);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_AdaptiveManifoldFilter_filter_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_AdaptiveManifoldFilter(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), joint.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn collect_garbage(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_AdaptiveManifoldFilter_collectGarbage(self.as_raw_mut_AdaptiveManifoldFilter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## See also
/// setSigmaS getSigmaS
#[inline]
fn set_sigma_s(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_AdaptiveManifoldFilter_setSigmaS_double(self.as_raw_mut_AdaptiveManifoldFilter(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## See also
/// setSigmaR getSigmaR
#[inline]
fn set_sigma_r(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_AdaptiveManifoldFilter_setSigmaR_double(self.as_raw_mut_AdaptiveManifoldFilter(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## See also
/// setTreeHeight getTreeHeight
#[inline]
fn set_tree_height(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_AdaptiveManifoldFilter_setTreeHeight_int(self.as_raw_mut_AdaptiveManifoldFilter(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## See also
/// setPCAIterations getPCAIterations
#[inline]
fn set_pca_iterations(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_AdaptiveManifoldFilter_setPCAIterations_int(self.as_raw_mut_AdaptiveManifoldFilter(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## See also
/// setAdjustOutliers getAdjustOutliers
#[inline]
fn set_adjust_outliers(&mut self, val: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_AdaptiveManifoldFilter_setAdjustOutliers_bool(self.as_raw_mut_AdaptiveManifoldFilter(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## See also
/// setUseRNG getUseRNG
#[inline]
fn set_use_rng(&mut self, val: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_AdaptiveManifoldFilter_setUseRNG_bool(self.as_raw_mut_AdaptiveManifoldFilter(), val, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl dyn AdaptiveManifoldFilter + '_ {
#[inline]
pub fn create() -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::AdaptiveManifoldFilter>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_AdaptiveManifoldFilter_create(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::AdaptiveManifoldFilter>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::ContourFitting]
pub trait ContourFittingTraitConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_ContourFitting(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Mutable methods for [crate::ximgproc::ContourFitting]
pub trait ContourFittingTrait: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::ximgproc::ContourFittingTraitConst {
fn as_raw_mut_ContourFitting(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Fit two closed curves using fourier descriptors. More details in [PersoonFu1977](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_PersoonFu1977) and [BergerRaghunathan1998](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_BergerRaghunathan1998)
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Contour defining first shape.
/// * dst: Contour defining second shape (Target).
/// * alphaPhiST: : =alphaPhiST(0,0), =alphaPhiST(0,1) (in radian), s=alphaPhiST(0,2), Tx=alphaPhiST(0,3), Ty=alphaPhiST(0,4) rotation center
/// * dist: distance between src and dst after matching.
/// * fdContour: false then src and dst are contours and true src and dst are fourier descriptors.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * dist: 0
/// * fd_contour: false
#[inline]
fn estimate_transformation(&mut self, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &dyn core::ToInputArray, alpha_phi_st: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, dist: &mut f64, fd_contour: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
extern_container_arg!(alpha_phi_st);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_ContourFitting_estimateTransformation_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_doubleX_bool(self.as_raw_mut_ContourFitting(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__InputArray(), alpha_phi_st.as_raw__OutputArray(), dist, fd_contour, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Fit two closed curves using fourier descriptors. More details in [PersoonFu1977](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_PersoonFu1977) and [BergerRaghunathan1998](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_BergerRaghunathan1998)
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Contour defining first shape.
/// * dst: Contour defining second shape (Target).
/// * alphaPhiST: : =alphaPhiST(0,0), =alphaPhiST(0,1) (in radian), s=alphaPhiST(0,2), Tx=alphaPhiST(0,3), Ty=alphaPhiST(0,4) rotation center
/// * dist: distance between src and dst after matching.
/// * fdContour: false then src and dst are contours and true src and dst are fourier descriptors.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * fd_contour: false
#[inline]
fn estimate_transformation_1(&mut self, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &dyn core::ToInputArray, alpha_phi_st: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, dist: &mut f64, fd_contour: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
extern_container_arg!(alpha_phi_st);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_ContourFitting_estimateTransformation_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_doubleR_bool(self.as_raw_mut_ContourFitting(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__InputArray(), alpha_phi_st.as_raw__OutputArray(), dist, fd_contour, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// set number of Fourier descriptors used in estimateTransformation
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * n: number of Fourier descriptors equal to number of contour points after resampling.
#[inline]
fn set_ctr_size(&mut self, n: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_ContourFitting_setCtrSize_int(self.as_raw_mut_ContourFitting(), n, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// set number of Fourier descriptors when estimateTransformation used vector<Point>
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * n: number of fourier descriptors used for optimal curve matching.
#[inline]
fn set_fd_size(&mut self, n: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_ContourFitting_setFDSize_int(self.as_raw_mut_ContourFitting(), n, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## Returns
/// number of fourier descriptors
#[inline]
fn get_ctr_size(&mut self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_ContourFitting_getCtrSize(self.as_raw_mut_ContourFitting(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## Returns
/// number of fourier descriptors used for optimal curve matching
#[inline]
fn get_fd_size(&mut self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_ContourFitting_getFDSize(self.as_raw_mut_ContourFitting(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Class for ContourFitting algorithms.
/// ContourFitting match two contours  and  minimizing distance
///  where  and  are Fourier descriptors of  and  and s is a scaling factor and  is angle rotation and  is starting point factor adjustement
pub struct ContourFitting {
ptr: *mut c_void
}
opencv_type_boxed! { ContourFitting }
impl Drop for ContourFitting {
fn drop(&mut self) {
extern "C" { fn cv_ContourFitting_delete(instance: *mut c_void); }
unsafe { cv_ContourFitting_delete(self.as_raw_mut_ContourFitting()) };
}
}
unsafe impl Send for ContourFitting {}
impl core::AlgorithmTraitConst for ContourFitting {
#[inline] fn as_raw_Algorithm(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl core::AlgorithmTrait for ContourFitting {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_Algorithm(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl crate::ximgproc::ContourFittingTraitConst for ContourFitting {
#[inline] fn as_raw_ContourFitting(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() }
}
impl crate::ximgproc::ContourFittingTrait for ContourFitting {
#[inline] fn as_raw_mut_ContourFitting(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() }
}
impl ContourFitting {
/// Fit two closed curves using fourier descriptors. More details in [PersoonFu1977](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_PersoonFu1977) and [BergerRaghunathan1998](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_BergerRaghunathan1998)
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * ctr: number of Fourier descriptors equal to number of contour points after resampling.
/// * fd: Contour defining second shape (Target).
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * ctr: 1024
/// * fd: 16
#[inline]
pub fn new(ctr: i32, fd: i32) -> Result<crate::ximgproc::ContourFitting> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_ContourFitting_ContourFitting_int_int(ctr, fd, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { crate::ximgproc::ContourFitting::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
boxed_cast_base! { ContourFitting, core::Algorithm, cv_ContourFitting_to_Algorithm }
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::DTFilter]
pub trait DTFilterConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_DTFilter(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Interface for realizations of Domain Transform filter.
///
/// For more details about this filter see [Gastal11](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Gastal11) .
pub trait DTFilter: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::ximgproc::DTFilterConst {
fn as_raw_mut_DTFilter(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Produce domain transform filtering operation on source image.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: filtering image with unsigned 8-bit or floating-point 32-bit depth and up to 4 channels.
///
/// * dst: destination image.
///
/// * dDepth: optional depth of the output image. dDepth can be set to -1, which will be equivalent
/// to src.depth().
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * d_depth: -1
#[inline]
fn filter(&mut self, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, d_depth: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_DTFilter_filter_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTFilter(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), d_depth, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::DisparityFilter]
pub trait DisparityFilterConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_DisparityFilter(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Main interface for all disparity map filters.
pub trait DisparityFilter: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::ximgproc::DisparityFilterConst {
fn as_raw_mut_DisparityFilter(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Apply filtering to the disparity map.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * disparity_map_left: disparity map of the left view, 1 channel, CV_16S type. Implicitly assumes that disparity
/// values are scaled by 16 (one-pixel disparity corresponds to the value of 16 in the disparity map). Disparity map
/// can have any resolution, it will be automatically resized to fit left_view resolution.
///
/// * left_view: left view of the original stereo-pair to guide the filtering process, 8-bit single-channel
/// or three-channel image.
///
/// * filtered_disparity_map: output disparity map.
///
/// * disparity_map_right: optional argument, some implementations might also use the disparity map
/// of the right view to compute confidence maps, for instance.
///
/// * ROI: region of the disparity map to filter. Optional, usually it should be set automatically.
///
/// * right_view: optional argument, some implementations might also use the right view of the original
/// stereo-pair.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * disparity_map_right: Mat()
/// * roi: Rect()
/// * right_view: Mat()
#[inline]
fn filter(&mut self, disparity_map_left: &dyn core::ToInputArray, left_view: &dyn core::ToInputArray, filtered_disparity_map: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, disparity_map_right: &dyn core::ToInputArray, roi: core::Rect, right_view: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(disparity_map_left);
extern_container_arg!(left_view);
extern_container_arg!(filtered_disparity_map);
extern_container_arg!(disparity_map_right);
extern_container_arg!(right_view);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_DisparityFilter_filter_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Rect_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_DisparityFilter(), disparity_map_left.as_raw__InputArray(), left_view.as_raw__InputArray(), filtered_disparity_map.as_raw__OutputArray(), disparity_map_right.as_raw__InputArray(), roi.opencv_as_extern(), right_view.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::DisparityWLSFilter]
pub trait DisparityWLSFilterConst: crate::ximgproc::DisparityFilterConst {
fn as_raw_DisparityWLSFilter(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Disparity map filter based on Weighted Least Squares filter (in form of Fast Global Smoother that
/// is a lot faster than traditional Weighted Least Squares filter implementations) and optional use of
/// left-right-consistency-based confidence to refine the results in half-occlusions and uniform areas.
pub trait DisparityWLSFilter: crate::ximgproc::DisparityFilter + crate::ximgproc::DisparityWLSFilterConst {
fn as_raw_mut_DisparityWLSFilter(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Lambda is a parameter defining the amount of regularization during filtering. Larger values force
/// filtered disparity map edges to adhere more to source image edges. Typical value is 8000.
#[inline]
fn get_lambda(&mut self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_DisparityWLSFilter_getLambda(self.as_raw_mut_DisparityWLSFilter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## See also
/// getLambda
#[inline]
fn set_lambda(&mut self, _lambda: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_DisparityWLSFilter_setLambda_double(self.as_raw_mut_DisparityWLSFilter(), _lambda, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// SigmaColor is a parameter defining how sensitive the filtering process is to source image edges.
/// Large values can lead to disparity leakage through low-contrast edges. Small values can make the filter too
/// sensitive to noise and textures in the source image. Typical values range from 0.8 to 2.0.
#[inline]
fn get_sigma_color(&mut self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_DisparityWLSFilter_getSigmaColor(self.as_raw_mut_DisparityWLSFilter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## See also
/// getSigmaColor
#[inline]
fn set_sigma_color(&mut self, _sigma_color: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_DisparityWLSFilter_setSigmaColor_double(self.as_raw_mut_DisparityWLSFilter(), _sigma_color, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// LRCthresh is a threshold of disparity difference used in left-right-consistency check during
/// confidence map computation. The default value of 24 (1.5 pixels) is virtually always good enough.
#[inline]
fn get_lr_cthresh(&mut self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_DisparityWLSFilter_getLRCthresh(self.as_raw_mut_DisparityWLSFilter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## See also
/// getLRCthresh
#[inline]
fn set_lr_cthresh(&mut self, _lrc_thresh: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_DisparityWLSFilter_setLRCthresh_int(self.as_raw_mut_DisparityWLSFilter(), _lrc_thresh, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// DepthDiscontinuityRadius is a parameter used in confidence computation. It defines the size of
/// low-confidence regions around depth discontinuities.
#[inline]
fn get_depth_discontinuity_radius(&mut self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_DisparityWLSFilter_getDepthDiscontinuityRadius(self.as_raw_mut_DisparityWLSFilter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## See also
/// getDepthDiscontinuityRadius
#[inline]
fn set_depth_discontinuity_radius(&mut self, _disc_radius: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_DisparityWLSFilter_setDepthDiscontinuityRadius_int(self.as_raw_mut_DisparityWLSFilter(), _disc_radius, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Get the confidence map that was used in the last filter call. It is a CV_32F one-channel image
/// with values ranging from 0.0 (totally untrusted regions of the raw disparity map) to 255.0 (regions containing
/// correct disparity values with a high degree of confidence).
#[inline]
fn get_confidence_map(&mut self) -> Result<core::Mat> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_DisparityWLSFilter_getConfidenceMap(self.as_raw_mut_DisparityWLSFilter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Get the ROI used in the last filter call
#[inline]
fn get_roi(&mut self) -> Result<core::Rect> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_DisparityWLSFilter_getROI(self.as_raw_mut_DisparityWLSFilter(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolator]
pub trait EdgeAwareInterpolatorConst: crate::ximgproc::SparseMatchInterpolatorConst {
fn as_raw_EdgeAwareInterpolator(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Sparse match interpolation algorithm based on modified locally-weighted affine
/// estimator from [Revaud2015](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Revaud2015) and Fast Global Smoother as post-processing filter.
pub trait EdgeAwareInterpolator: crate::ximgproc::EdgeAwareInterpolatorConst + crate::ximgproc::SparseMatchInterpolator {
fn as_raw_mut_EdgeAwareInterpolator(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Interface to provide a more elaborated cost map, i.e. edge map, for the edge-aware term.
/// This implementation is based on a rather simple gradient-based edge map estimation.
/// To used more complex edge map estimator (e.g. StructuredEdgeDetection that has been
/// used in the original publication) that may lead to improved accuracies, the internal
/// edge map estimation can be bypassed here.
/// ## Parameters
/// * _costMap: a type CV_32FC1 Mat is required.
/// ## See also
/// cv::ximgproc::createSuperpixelSLIC
#[inline]
fn set_cost_map(&mut self, _cost_map: &core::Mat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeAwareInterpolator_setCostMap_const_MatR(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeAwareInterpolator(), _cost_map.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter to tune the approximate size of the superpixel used for oversegmentation.
/// ## See also
/// cv::ximgproc::createSuperpixelSLIC
/// /
/// K is a number of nearest-neighbor matches considered, when fitting a locally affine
/// model. Usually it should be around 128. However, lower values would make the interpolation
/// noticeably faster.
#[inline]
fn set_k(&mut self, _k: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeAwareInterpolator_setK_int(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeAwareInterpolator(), _k, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## See also
/// setK
#[inline]
fn get_k(&mut self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeAwareInterpolator_getK(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeAwareInterpolator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sigma is a parameter defining how fast the weights decrease in the locally-weighted affine
/// fitting. Higher values can help preserve fine details, lower values can help to get rid of noise in the
/// output flow.
#[inline]
fn set_sigma(&mut self, _sigma: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeAwareInterpolator_setSigma_float(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeAwareInterpolator(), _sigma, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## See also
/// setSigma
#[inline]
fn get_sigma(&mut self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeAwareInterpolator_getSigma(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeAwareInterpolator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Lambda is a parameter defining the weight of the edge-aware term in geodesic distance,
/// should be in the range of 0 to 1000.
#[inline]
fn set_lambda(&mut self, _lambda: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeAwareInterpolator_setLambda_float(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeAwareInterpolator(), _lambda, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## See also
/// setLambda
#[inline]
fn get_lambda(&mut self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeAwareInterpolator_getLambda(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeAwareInterpolator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets whether the fastGlobalSmootherFilter() post-processing is employed. It is turned on by
/// default.
#[inline]
fn set_use_post_processing(&mut self, _use_post_proc: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeAwareInterpolator_setUsePostProcessing_bool(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeAwareInterpolator(), _use_post_proc, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## See also
/// setUsePostProcessing
#[inline]
fn get_use_post_processing(&mut self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeAwareInterpolator_getUsePostProcessing(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeAwareInterpolator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the respective fastGlobalSmootherFilter() parameter.
#[inline]
fn set_fgs_lambda(&mut self, _lambda: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeAwareInterpolator_setFGSLambda_float(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeAwareInterpolator(), _lambda, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## See also
/// setFGSLambda
#[inline]
fn get_fgs_lambda(&mut self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeAwareInterpolator_getFGSLambda(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeAwareInterpolator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## See also
/// setFGSLambda
#[inline]
fn set_fgs_sigma(&mut self, _sigma: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeAwareInterpolator_setFGSSigma_float(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeAwareInterpolator(), _sigma, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## See also
/// setFGSLambda
#[inline]
fn get_fgs_sigma(&mut self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeAwareInterpolator_getFGSSigma(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeAwareInterpolator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::EdgeBoxes]
pub trait EdgeBoxesConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_EdgeBoxes(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Returns the step size of sliding window search.
#[inline]
fn get_alpha(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeBoxes_getAlpha_const(self.as_raw_EdgeBoxes(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the nms threshold for object proposals.
#[inline]
fn get_beta(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeBoxes_getBeta_const(self.as_raw_EdgeBoxes(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns adaptation rate for nms threshold.
#[inline]
fn get_eta(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeBoxes_getEta_const(self.as_raw_EdgeBoxes(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the min score of boxes to detect.
#[inline]
fn get_min_score(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeBoxes_getMinScore_const(self.as_raw_EdgeBoxes(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the max number of boxes to detect.
#[inline]
fn get_max_boxes(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeBoxes_getMaxBoxes_const(self.as_raw_EdgeBoxes(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the edge min magnitude.
#[inline]
fn get_edge_min_mag(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeBoxes_getEdgeMinMag_const(self.as_raw_EdgeBoxes(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the edge merge threshold.
#[inline]
fn get_edge_merge_thr(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeBoxes_getEdgeMergeThr_const(self.as_raw_EdgeBoxes(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the cluster min magnitude.
#[inline]
fn get_cluster_min_mag(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeBoxes_getClusterMinMag_const(self.as_raw_EdgeBoxes(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the max aspect ratio of boxes.
#[inline]
fn get_max_aspect_ratio(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeBoxes_getMaxAspectRatio_const(self.as_raw_EdgeBoxes(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the minimum area of boxes.
#[inline]
fn get_min_box_area(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeBoxes_getMinBoxArea_const(self.as_raw_EdgeBoxes(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the affinity sensitivity.
#[inline]
fn get_gamma(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeBoxes_getGamma_const(self.as_raw_EdgeBoxes(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the scale sensitivity.
#[inline]
fn get_kappa(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeBoxes_getKappa_const(self.as_raw_EdgeBoxes(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Class implementing EdgeBoxes algorithm from [ZitnickECCV14edgeBoxes](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_ZitnickECCV14edgeBoxes) :
pub trait EdgeBoxes: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::ximgproc::EdgeBoxesConst {
fn as_raw_mut_EdgeBoxes(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Returns array containing proposal boxes.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * edge_map: edge image.
/// * orientation_map: orientation map.
/// * boxes: proposal boxes.
/// * scores: of the proposal boxes, provided a vector of float types.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * scores: noArray()
#[inline]
fn get_bounding_boxes(&mut self, edge_map: &dyn core::ToInputArray, orientation_map: &dyn core::ToInputArray, boxes: &mut core::Vector<core::Rect>, scores: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(edge_map);
extern_container_arg!(orientation_map);
extern_container_arg!(scores);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeBoxes_getBoundingBoxes_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_vectorLRectGR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeBoxes(), edge_map.as_raw__InputArray(), orientation_map.as_raw__InputArray(), boxes.as_raw_mut_VectorOfRect(), scores.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the step size of sliding window search.
#[inline]
fn set_alpha(&mut self, value: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeBoxes_setAlpha_float(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeBoxes(), value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the nms threshold for object proposals.
#[inline]
fn set_beta(&mut self, value: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeBoxes_setBeta_float(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeBoxes(), value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the adaptation rate for nms threshold.
#[inline]
fn set_eta(&mut self, value: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeBoxes_setEta_float(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeBoxes(), value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the min score of boxes to detect.
#[inline]
fn set_min_score(&mut self, value: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeBoxes_setMinScore_float(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeBoxes(), value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets max number of boxes to detect.
#[inline]
fn set_max_boxes(&mut self, value: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeBoxes_setMaxBoxes_int(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeBoxes(), value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the edge min magnitude.
#[inline]
fn set_edge_min_mag(&mut self, value: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeBoxes_setEdgeMinMag_float(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeBoxes(), value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the edge merge threshold.
#[inline]
fn set_edge_merge_thr(&mut self, value: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeBoxes_setEdgeMergeThr_float(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeBoxes(), value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the cluster min magnitude.
#[inline]
fn set_cluster_min_mag(&mut self, value: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeBoxes_setClusterMinMag_float(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeBoxes(), value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the max aspect ratio of boxes.
#[inline]
fn set_max_aspect_ratio(&mut self, value: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeBoxes_setMaxAspectRatio_float(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeBoxes(), value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the minimum area of boxes.
#[inline]
fn set_min_box_area(&mut self, value: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeBoxes_setMinBoxArea_float(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeBoxes(), value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the affinity sensitivity
#[inline]
fn set_gamma(&mut self, value: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeBoxes_setGamma_float(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeBoxes(), value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the scale sensitivity.
#[inline]
fn set_kappa(&mut self, value: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeBoxes_setKappa_float(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeBoxes(), value, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::EdgeDrawing]
pub trait EdgeDrawingConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_EdgeDrawing(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn params(&self) -> crate::ximgproc::EdgeDrawing_Params {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeDrawing_getPropParams_const(self.as_raw_EdgeDrawing(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
ret
}
/// Returns for each line found in detectLines() its edge segment index in getSegments()
#[inline]
fn get_segment_indices_of_lines(&self) -> Result<core::Vector<i32>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeDrawing_getSegmentIndicesOfLines_const(self.as_raw_EdgeDrawing(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Vector::<i32>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Class implementing the ED (EdgeDrawing) [topal2012edge](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_topal2012edge), EDLines [akinlar2011edlines](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_akinlar2011edlines), EDPF [akinlar2012edpf](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_akinlar2012edpf) and EDCircles [akinlar2013edcircles](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_akinlar2013edcircles) algorithms
pub trait EdgeDrawing: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::ximgproc::EdgeDrawingConst {
fn as_raw_mut_EdgeDrawing(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
#[inline]
fn set_params(&mut self, val: crate::ximgproc::EdgeDrawing_Params) {
let ret = unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeDrawing_setPropParams_Params(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeDrawing(), val.opencv_as_extern()) };
ret
}
/// Detects edges in a grayscale image and prepares them to detect lines and ellipses.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: 8-bit, single-channel, grayscale input image.
#[inline]
fn detect_edges(&mut self, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeDrawing_detectEdges_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeDrawing(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns Edge Image prepared by detectEdges() function.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * dst: returns 8-bit, single-channel output image.
#[inline]
fn get_edge_image(&mut self, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeDrawing_getEdgeImage_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeDrawing(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// returns Gradient Image prepared by detectEdges() function.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * dst: returns 16-bit, single-channel output image.
#[inline]
fn get_gradient_image(&mut self, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeDrawing_getGradientImage_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeDrawing(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns std::vector<std::vector<Point>> of detected edge segments, see detectEdges()
#[inline]
fn get_segments(&mut self) -> Result<core::Vector<core::Vector<core::Point>>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeDrawing_getSegments(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeDrawing(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Vector::<core::Vector<core::Point>>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Detects lines.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * lines: output Vec<4f> contains the start point and the end point of detected lines.
///
/// Note: you should call detectEdges() before calling this function.
#[inline]
fn detect_lines(&mut self, lines: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(lines);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeDrawing_detectLines_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeDrawing(), lines.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Detects circles and ellipses.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * ellipses: output Vec<6d> contains center point and perimeter for circles, center point, axes and angle for ellipses.
///
/// Note: you should call detectEdges() before calling this function.
#[inline]
fn detect_ellipses(&mut self, ellipses: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(ellipses);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeDrawing_detectEllipses_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeDrawing(), ellipses.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// sets parameters.
///
/// this function is meant to be used for parameter setting in other languages than c++ like python.
/// ## Parameters
/// * parameters:
#[inline]
fn set_params_1(&mut self, parameters: crate::ximgproc::EdgeDrawing_Params) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeDrawing_setParams_const_ParamsR(self.as_raw_mut_EdgeDrawing(), ¶meters, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
#[repr(C)]
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)]
pub struct EdgeDrawing_Params {
/// Parameter Free mode will be activated when this value is set as true. Default value is false.
pub p_fmode: bool,
/// indicates the operator used for gradient calculation.
///
/// one of the flags cv::ximgproc::EdgeDrawing::GradientOperator. Default value is PREWITT
pub edge_detection_operator: i32,
/// threshold value of gradiential difference between pixels. Used to create gradient image. Default value is 20
pub gradient_threshold_value: i32,
/// threshold value used to select anchor points. Default value is 0
pub anchor_threshold_value: i32,
/// Default value is 1
pub scan_interval: i32,
/// minimun connected pixels length processed to create an edge segment.
///
/// in gradient image, minimum connected pixels length processed to create an edge segment. pixels having upper value than GradientThresholdValue
/// will be processed. Default value is 10
pub min_path_length: i32,
/// sigma value for internal GaussianBlur() function. Default value is 1.0
pub sigma: f32,
pub sum_flag: bool,
/// Default value is true. indicates if NFA (Number of False Alarms) algorithm will be used for line and ellipse validation.
pub nfa_validation: bool,
/// minimun line length to detect.
pub min_line_length: i32,
/// Default value is 6.0
pub max_distance_between_two_lines: f64,
/// Default value is 1.0
pub line_fit_error_threshold: f64,
/// Default value is 1.3
pub max_error_threshold: f64,
}
opencv_type_simple! { crate::ximgproc::EdgeDrawing_Params }
impl EdgeDrawing_Params {
#[inline]
pub fn write(self, fs: &mut core::FileStorage) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeDrawing_Params_write_const_FileStorageR(self.opencv_as_extern(), fs.as_raw_mut_FileStorage(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn default() -> Result<crate::ximgproc::EdgeDrawing_Params> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeDrawing_Params_Params(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
pub fn read(self, fn_: &core::FileNode) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_EdgeDrawing_Params_read_const_FileNodeR(self.opencv_as_extern(), fn_.as_raw_FileNode(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::FastBilateralSolverFilter]
pub trait FastBilateralSolverFilterConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_FastBilateralSolverFilter(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Interface for implementations of Fast Bilateral Solver.
///
/// For more details about this solver see [BarronPoole2016](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_BarronPoole2016) .
pub trait FastBilateralSolverFilter: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::ximgproc::FastBilateralSolverFilterConst {
fn as_raw_mut_FastBilateralSolverFilter(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Apply smoothing operation to the source image.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: source image for filtering with unsigned 8-bit or signed 16-bit or floating-point 32-bit depth and up to 3 channels.
///
/// * confidence: confidence image with unsigned 8-bit or floating-point 32-bit confidence and 1 channel.
///
/// * dst: destination image.
///
///
/// Note: Confidence images with CV_8U depth are expected to in [0, 255] and CV_32F in [0, 1] range.
#[inline]
fn filter(&mut self, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, confidence: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(confidence);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_FastBilateralSolverFilter_filter_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_FastBilateralSolverFilter(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), confidence.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::FastGlobalSmootherFilter]
pub trait FastGlobalSmootherFilterConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_FastGlobalSmootherFilter(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Interface for implementations of Fast Global Smoother filter.
///
/// For more details about this filter see [Min2014](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Min2014) and [Farbman2008](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Farbman2008) .
pub trait FastGlobalSmootherFilter: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::ximgproc::FastGlobalSmootherFilterConst {
fn as_raw_mut_FastGlobalSmootherFilter(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Apply smoothing operation to the source image.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: source image for filtering with unsigned 8-bit or signed 16-bit or floating-point 32-bit depth and up to 4 channels.
///
/// * dst: destination image.
#[inline]
fn filter(&mut self, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_FastGlobalSmootherFilter_filter_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_FastGlobalSmootherFilter(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::FastLineDetector]
pub trait FastLineDetectorConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_FastLineDetector(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// @include samples/fld_lines.cpp
pub trait FastLineDetector: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::ximgproc::FastLineDetectorConst {
fn as_raw_mut_FastLineDetector(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// @example fld_lines.cpp
/// An example using the FastLineDetector
///
/// Finds lines in the input image.
/// This is the output of the default parameters of the algorithm on the above
/// shown image.
///
/// 
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: A grayscale (CV_8UC1) input image. If only a roi needs to be
/// selected, use: `fld_ptr-\>detect(image(roi), lines, ...);
/// lines += Scalar(roi.x, roi.y, roi.x, roi.y);`
/// * lines: A vector of Vec4f elements specifying the beginning
/// and ending point of a line. Where Vec4f is (x1, y1, x2, y2), point
/// 1 is the start, point 2 - end. Returned lines are directed so that the
/// brighter side is on their left.
#[inline]
fn detect(&mut self, image: &dyn core::ToInputArray, lines: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(image);
extern_container_arg!(lines);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_FastLineDetector_detect_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_FastLineDetector(), image.as_raw__InputArray(), lines.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Draws the line segments on a given image.
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: The image, where the lines will be drawn. Should be bigger
/// or equal to the image, where the lines were found.
/// * lines: A vector of the lines that needed to be drawn.
/// * draw_arrow: If true, arrow heads will be drawn.
/// * linecolor: Line color.
/// * linethickness: Line thickness.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * draw_arrow: false
/// * linecolor: Scalar(0,0,255)
/// * linethickness: 1
#[inline]
fn draw_segments(&mut self, image: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, lines: &dyn core::ToInputArray, draw_arrow: bool, linecolor: core::Scalar, linethickness: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(image);
extern_container_arg!(lines);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_FastLineDetector_drawSegments_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_bool_Scalar_int(self.as_raw_mut_FastLineDetector(), image.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), lines.as_raw__InputArray(), draw_arrow, linecolor.opencv_as_extern(), linethickness, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::GuidedFilter]
pub trait GuidedFilterConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_GuidedFilter(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Interface for realizations of Guided Filter.
///
/// For more details about this filter see [Kaiming10](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Kaiming10) .
pub trait GuidedFilter: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::ximgproc::GuidedFilterConst {
fn as_raw_mut_GuidedFilter(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Apply Guided Filter to the filtering image.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: filtering image with any numbers of channels.
///
/// * dst: output image.
///
/// * dDepth: optional depth of the output image. dDepth can be set to -1, which will be equivalent
/// to src.depth().
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * d_depth: -1
#[inline]
fn filter(&mut self, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, d_depth: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_GuidedFilter_filter_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(self.as_raw_mut_GuidedFilter(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), d_depth, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::RFFeatureGetter]
pub trait RFFeatureGetterConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_RFFeatureGetter(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// !
/// * This functions extracts feature channels from src.
/// * Than StructureEdgeDetection uses this feature space
/// * to detect edges.
/// *
/// * \param src : source image to extract features
/// * \param features : output n-channel floating point feature matrix.
/// *
/// * \param gnrmRad : __rf.options.gradientNormalizationRadius
/// * \param gsmthRad : __rf.options.gradientSmoothingRadius
/// * \param shrink : __rf.options.shrinkNumber
/// * \param outNum : __rf.options.numberOfOutputChannels
/// * \param gradNum : __rf.options.numberOfGradientOrientations
#[inline]
fn get_features(&self, src: &core::Mat, features: &mut core::Mat, gnrm_rad: i32, gsmth_rad: i32, shrink: i32, out_num: i32, grad_num: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RFFeatureGetter_getFeatures_const_const_MatR_MatR_const_int_const_int_const_int_const_int_const_int(self.as_raw_RFFeatureGetter(), src.as_raw_Mat(), features.as_raw_mut_Mat(), gnrm_rad, gsmth_rad, shrink, out_num, grad_num, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// !
/// Helper class for training part of [P. Dollar and C. L. Zitnick. Structured Forests for Fast Edge Detection, 2013].
pub trait RFFeatureGetter: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::ximgproc::RFFeatureGetterConst {
fn as_raw_mut_RFFeatureGetter(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::RICInterpolator]
pub trait RICInterpolatorConst: crate::ximgproc::SparseMatchInterpolatorConst {
fn as_raw_RICInterpolator(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// K is a number of nearest-neighbor matches considered, when fitting a locally affine
/// model for a superpixel segment. However, lower values would make the interpolation
/// noticeably faster. The original implementation of [Hu2017](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Hu2017) uses 32.
/// * see also: setK
#[inline]
fn get_k(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_getK_const(self.as_raw_RICInterpolator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Get the internal cost, i.e. edge map, used for estimating the edge-aware term.
/// ## See also
/// setCostMap
/// * setSuperpixelSize
#[inline]
fn get_superpixel_size(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_getSuperpixelSize_const(self.as_raw_RICInterpolator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter defines the number of nearest-neighbor matches for each superpixel considered, when fitting a locally affine
/// model.
/// * see also: setSuperpixelNNCnt
#[inline]
fn get_superpixel_nn_cnt(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_getSuperpixelNNCnt_const(self.as_raw_RICInterpolator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter to tune enforcement of superpixel smoothness factor used for oversegmentation.
/// ## See also
/// cv::ximgproc::createSuperpixelSLIC
/// * setSuperpixelRuler
#[inline]
fn get_superpixel_ruler(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_getSuperpixelRuler_const(self.as_raw_RICInterpolator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter to choose superpixel algorithm variant to use:
/// - cv::ximgproc::SLICType SLIC segments image using a desired region_size (value: 100)
/// - cv::ximgproc::SLICType SLICO will optimize using adaptive compactness factor (value: 101)
/// - cv::ximgproc::SLICType MSLIC will optimize using manifold methods resulting in more content-sensitive superpixels (value: 102).
/// ## See also
/// cv::ximgproc::createSuperpixelSLIC
/// * setSuperpixelMode
#[inline]
fn get_superpixel_mode(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_getSuperpixelMode_const(self.as_raw_RICInterpolator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Alpha is a parameter defining a global weight for transforming geodesic distance into weight.
/// ## See also
/// setAlpha
#[inline]
fn get_alpha(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_getAlpha_const(self.as_raw_RICInterpolator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter defining the number of iterations for piece-wise affine model estimation.
/// ## See also
/// setModelIter
#[inline]
fn get_model_iter(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_getModelIter_const(self.as_raw_RICInterpolator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter to choose wether additional refinement of the piece-wise affine models is employed.
/// ## See also
/// setRefineModels
#[inline]
fn get_refine_models(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_getRefineModels_const(self.as_raw_RICInterpolator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// MaxFlow is a threshold to validate the predictions using a certain piece-wise affine model.
/// If the prediction exceeds the treshold the translational model will be applied instead.
/// * see also: setMaxFlow
#[inline]
fn get_max_flow(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_getMaxFlow_const(self.as_raw_RICInterpolator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter to choose wether the VariationalRefinement post-processing is employed.
/// ## See also
/// setUseVariationalRefinement
#[inline]
fn get_use_variational_refinement(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_getUseVariationalRefinement_const(self.as_raw_RICInterpolator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets whether the fastGlobalSmootherFilter() post-processing is employed.
/// ## See also
/// setUseGlobalSmootherFilter
#[inline]
fn get_use_global_smoother_filter(&self) -> Result<bool> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_getUseGlobalSmootherFilter_const(self.as_raw_RICInterpolator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the respective fastGlobalSmootherFilter() parameter.
/// ## See also
/// setFGSLambda
#[inline]
fn get_fgs_lambda(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_getFGSLambda_const(self.as_raw_RICInterpolator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the respective fastGlobalSmootherFilter() parameter.
/// ## See also
/// setFGSSigma
#[inline]
fn get_fgs_sigma(&self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_getFGSSigma_const(self.as_raw_RICInterpolator(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Sparse match interpolation algorithm based on modified piecewise locally-weighted affine
/// estimator called Robust Interpolation method of Correspondences or RIC from [Hu2017](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Hu2017) and Variational
/// and Fast Global Smoother as post-processing filter. The RICInterpolator is a extension of the EdgeAwareInterpolator.
/// Main concept of this extension is an piece-wise affine model based on over-segmentation via SLIC superpixel estimation.
/// The method contains an efficient propagation mechanism to estimate among the pieces-wise models.
pub trait RICInterpolator: crate::ximgproc::RICInterpolatorConst + crate::ximgproc::SparseMatchInterpolator {
fn as_raw_mut_RICInterpolator(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// K is a number of nearest-neighbor matches considered, when fitting a locally affine
/// model for a superpixel segment. However, lower values would make the interpolation
/// noticeably faster. The original implementation of [Hu2017](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Hu2017) uses 32.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * k: 32
#[inline]
fn set_k(&mut self, k: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_setK_int(self.as_raw_mut_RICInterpolator(), k, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Interface to provide a more elaborated cost map, i.e. edge map, for the edge-aware term.
/// This implementation is based on a rather simple gradient-based edge map estimation.
/// To used more complex edge map estimator (e.g. StructuredEdgeDetection that has been
/// used in the original publication) that may lead to improved accuracies, the internal
/// edge map estimation can be bypassed here.
/// ## Parameters
/// * costMap: a type CV_32FC1 Mat is required.
/// ## See also
/// cv::ximgproc::createSuperpixelSLIC
#[inline]
fn set_cost_map(&mut self, cost_map: &core::Mat) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_setCostMap_const_MatR(self.as_raw_mut_RICInterpolator(), cost_map.as_raw_Mat(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Get the internal cost, i.e. edge map, used for estimating the edge-aware term.
/// ## See also
/// setCostMap
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * sp_size: 15
#[inline]
fn set_superpixel_size(&mut self, sp_size: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_setSuperpixelSize_int(self.as_raw_mut_RICInterpolator(), sp_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter defines the number of nearest-neighbor matches for each superpixel considered, when fitting a locally affine
/// model.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * sp_nn: 150
#[inline]
fn set_superpixel_nn_cnt(&mut self, sp_nn: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_setSuperpixelNNCnt_int(self.as_raw_mut_RICInterpolator(), sp_nn, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter to tune enforcement of superpixel smoothness factor used for oversegmentation.
/// ## See also
/// cv::ximgproc::createSuperpixelSLIC
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * ruler: 15.f
#[inline]
fn set_superpixel_ruler(&mut self, ruler: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_setSuperpixelRuler_float(self.as_raw_mut_RICInterpolator(), ruler, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter to choose superpixel algorithm variant to use:
/// - cv::ximgproc::SLICType SLIC segments image using a desired region_size (value: 100)
/// - cv::ximgproc::SLICType SLICO will optimize using adaptive compactness factor (value: 101)
/// - cv::ximgproc::SLICType MSLIC will optimize using manifold methods resulting in more content-sensitive superpixels (value: 102).
/// ## See also
/// cv::ximgproc::createSuperpixelSLIC
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * mode: 100
#[inline]
fn set_superpixel_mode(&mut self, mode: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_setSuperpixelMode_int(self.as_raw_mut_RICInterpolator(), mode, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Alpha is a parameter defining a global weight for transforming geodesic distance into weight.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * alpha: 0.7f
#[inline]
fn set_alpha(&mut self, alpha: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_setAlpha_float(self.as_raw_mut_RICInterpolator(), alpha, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter defining the number of iterations for piece-wise affine model estimation.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * model_iter: 4
#[inline]
fn set_model_iter(&mut self, model_iter: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_setModelIter_int(self.as_raw_mut_RICInterpolator(), model_iter, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter to choose wether additional refinement of the piece-wise affine models is employed.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * refine_modles: true
#[inline]
fn set_refine_models(&mut self, refine_modles: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_setRefineModels_bool(self.as_raw_mut_RICInterpolator(), refine_modles, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// MaxFlow is a threshold to validate the predictions using a certain piece-wise affine model.
/// If the prediction exceeds the treshold the translational model will be applied instead.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * max_flow: 250.f
#[inline]
fn set_max_flow(&mut self, max_flow: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_setMaxFlow_float(self.as_raw_mut_RICInterpolator(), max_flow, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Parameter to choose wether the VariationalRefinement post-processing is employed.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * use_variational_refinement: false
#[inline]
fn set_use_variational_refinement(&mut self, use_variational_refinement: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_setUseVariationalRefinement_bool(self.as_raw_mut_RICInterpolator(), use_variational_refinement, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets whether the fastGlobalSmootherFilter() post-processing is employed.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * use_fgs: true
#[inline]
fn set_use_global_smoother_filter(&mut self, use_fgs: bool) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_setUseGlobalSmootherFilter_bool(self.as_raw_mut_RICInterpolator(), use_fgs, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the respective fastGlobalSmootherFilter() parameter.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * lambda: 500.f
#[inline]
fn set_fgs_lambda(&mut self, lambda: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_setFGSLambda_float(self.as_raw_mut_RICInterpolator(), lambda, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Sets the respective fastGlobalSmootherFilter() parameter.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * sigma: 1.5f
#[inline]
fn set_fgs_sigma(&mut self, sigma: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RICInterpolator_setFGSSigma_float(self.as_raw_mut_RICInterpolator(), sigma, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::RidgeDetectionFilter]
pub trait RidgeDetectionFilterConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_RidgeDetectionFilter(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Applies Ridge Detection Filter to an input image.
/// Implements Ridge detection similar to the one in [Mathematica](http://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/RidgeFilter.html)
/// using the eigen values from the Hessian Matrix of the input image using Sobel Derivatives.
/// Additional refinement can be done using Skeletonization and Binarization. Adapted from [segleafvein](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_segleafvein) and [M_RF](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_M_RF)
pub trait RidgeDetectionFilter: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::ximgproc::RidgeDetectionFilterConst {
fn as_raw_mut_RidgeDetectionFilter(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Apply Ridge detection filter on input image.
/// ## Parameters
/// * _img: InputArray as supported by Sobel. img can be 1-Channel or 3-Channels.
/// * out: OutputAray of structure as RidgeDetectionFilter::ddepth. Output image with ridges.
#[inline]
fn get_ridge_filtered_image(&mut self, _img: &dyn core::ToInputArray, out: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(_img);
extern_container_arg!(out);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RidgeDetectionFilter_getRidgeFilteredImage_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_RidgeDetectionFilter(), _img.as_raw__InputArray(), out.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
impl dyn RidgeDetectionFilter + '_ {
/// Create pointer to the Ridge detection filter.
/// ## Parameters
/// * ddepth: Specifies output image depth. Defualt is CV_32FC1
/// * dx: Order of derivative x, default is 1
/// * dy: Order of derivative y, default is 1
/// * ksize: Sobel kernel size , default is 3
/// * out_dtype: Converted format for output, default is CV_8UC1
/// * scale: Optional scale value for derivative values, default is 1
/// * delta: Optional bias added to output, default is 0
/// * borderType: Pixel extrapolation method, default is BORDER_DEFAULT
/// ## See also
/// Sobel, threshold, getStructuringElement, morphologyEx.( for additional refinement)
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * ddepth: CV_32FC1
/// * dx: 1
/// * dy: 1
/// * ksize: 3
/// * out_dtype: CV_8UC1
/// * scale: 1
/// * delta: 0
/// * border_type: BORDER_DEFAULT
#[inline]
pub fn create(ddepth: i32, dx: i32, dy: i32, ksize: i32, out_dtype: i32, scale: f64, delta: f64, border_type: i32) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::RidgeDetectionFilter>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_RidgeDetectionFilter_create_int_int_int_int_int_double_double_int(ddepth, dx, dy, ksize, out_dtype, scale, delta, border_type, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ximgproc::RidgeDetectionFilter>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::ScanSegment]
pub trait ScanSegmentConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_ScanSegment(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Class implementing the F-DBSCAN (Accelerated superpixel image segmentation with a parallelized DBSCAN algorithm) superpixels
/// algorithm by Loke SC, et al. [loke2021accelerated](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_loke2021accelerated) for original paper.
///
/// The algorithm uses a parallelised DBSCAN cluster search that is resistant to noise, competitive in segmentation quality, and faster than
/// existing superpixel segmentation methods. When tested on the Berkeley Segmentation Dataset, the average processing speed is 175 frames/s
/// with a Boundary Recall of 0.797 and an Achievable Segmentation Accuracy of 0.944. The computational complexity is quadratic O(n2) and
/// more suited to smaller images, but can still process a 2MP colour image faster than the SEEDS algorithm in OpenCV. The output is deterministic
/// when the number of processing threads is fixed, and requires the source image to be in Lab colour format.
pub trait ScanSegment: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::ximgproc::ScanSegmentConst {
fn as_raw_mut_ScanSegment(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Returns the actual superpixel segmentation from the last image processed using iterate.
///
/// Returns zero if no image has been processed.
#[inline]
fn get_number_of_superpixels(&mut self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_ScanSegment_getNumberOfSuperpixels(self.as_raw_mut_ScanSegment(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates the superpixel segmentation on a given image with the initialized
/// parameters in the ScanSegment object.
///
/// This function can be called again for other images without the need of initializing the algorithm with createScanSegment().
/// This save the computational cost of allocating memory for all the structures of the algorithm.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * img: Input image. Supported format: CV_8UC3. Image size must match with the initialized
/// image size with the function createScanSegment(). It MUST be in Lab color space.
#[inline]
fn iterate(&mut self, img: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(img);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_ScanSegment_iterate_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_ScanSegment(), img.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the segmentation labeling of the image.
///
/// Each label represents a superpixel, and each pixel is assigned to one superpixel label.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * labels_out: Return: A CV_32UC1 integer array containing the labels of the superpixel
/// segmentation. The labels are in the range [0, getNumberOfSuperpixels()].
#[inline]
fn get_labels(&mut self, labels_out: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(labels_out);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_ScanSegment_getLabels_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_ScanSegment(), labels_out.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the mask of the superpixel segmentation stored in the ScanSegment object.
///
/// The function return the boundaries of the superpixel segmentation.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: Return: CV_8UC1 image mask where -1 indicates that the pixel is a superpixel border, and 0 otherwise.
/// * thick_line: If false, the border is only one pixel wide, otherwise all pixels at the border are masked.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * thick_line: false
#[inline]
fn get_label_contour_mask(&mut self, image: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, thick_line: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(image);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_ScanSegment_getLabelContourMask_const__OutputArrayR_bool(self.as_raw_mut_ScanSegment(), image.as_raw__OutputArray(), thick_line, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::SparseMatchInterpolator]
pub trait SparseMatchInterpolatorConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_SparseMatchInterpolator(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Main interface for all filters, that take sparse matches as an
/// input and produce a dense per-pixel matching (optical flow) as an output.
pub trait SparseMatchInterpolator: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::ximgproc::SparseMatchInterpolatorConst {
fn as_raw_mut_SparseMatchInterpolator(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Interpolate input sparse matches.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * from_image: first of the two matched images, 8-bit single-channel or three-channel.
///
/// * from_points: points of the from_image for which there are correspondences in the
/// to_image (Point2f vector or Mat of depth CV_32F)
///
/// * to_image: second of the two matched images, 8-bit single-channel or three-channel.
///
/// * to_points: points in the to_image corresponding to from_points
/// (Point2f vector or Mat of depth CV_32F)
///
/// * dense_flow: output dense matching (two-channel CV_32F image)
#[inline]
fn interpolate(&mut self, from_image: &dyn core::ToInputArray, from_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, to_image: &dyn core::ToInputArray, to_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dense_flow: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(from_image);
extern_container_arg!(from_points);
extern_container_arg!(to_image);
extern_container_arg!(to_points);
extern_container_arg!(dense_flow);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_SparseMatchInterpolator_interpolate_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_SparseMatchInterpolator(), from_image.as_raw__InputArray(), from_points.as_raw__InputArray(), to_image.as_raw__InputArray(), to_points.as_raw__InputArray(), dense_flow.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::StructuredEdgeDetection]
pub trait StructuredEdgeDetectionConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_StructuredEdgeDetection(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// The function detects edges in src and draw them to dst.
///
/// The algorithm underlies this function is much more robust to texture presence, than common
/// approaches, e.g. Sobel
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: source image (RGB, float, in [0;1]) to detect edges
/// * dst: destination image (grayscale, float, in [0;1]) where edges are drawn
/// ## See also
/// Sobel, Canny
#[inline]
fn detect_edges(&self, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_StructuredEdgeDetection_detectEdges_const_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_StructuredEdgeDetection(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// The function computes orientation from edge image.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: edge image.
/// * dst: orientation image.
#[inline]
fn compute_orientation(&self, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_StructuredEdgeDetection_computeOrientation_const_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_StructuredEdgeDetection(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// The function edgenms in edge image and suppress edges where edge is stronger in orthogonal direction.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * edge_image: edge image from detectEdges function.
/// * orientation_image: orientation image from computeOrientation function.
/// * dst: suppressed image (grayscale, float, in [0;1])
/// * r: radius for NMS suppression.
/// * s: radius for boundary suppression.
/// * m: multiplier for conservative suppression.
/// * isParallel: enables/disables parallel computing.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * r: 2
/// * s: 0
/// * m: 1
/// * is_parallel: true
#[inline]
fn edges_nms(&self, edge_image: &dyn core::ToInputArray, orientation_image: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, r: i32, s: i32, m: f32, is_parallel: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(edge_image);
extern_container_arg!(orientation_image);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_StructuredEdgeDetection_edgesNms_const_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_int_float_bool(self.as_raw_StructuredEdgeDetection(), edge_image.as_raw__InputArray(), orientation_image.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), r, s, m, is_parallel, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Class implementing edge detection algorithm from [Dollar2013](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Dollar2013) :
pub trait StructuredEdgeDetection: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::ximgproc::StructuredEdgeDetectionConst {
fn as_raw_mut_StructuredEdgeDetection(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::SuperpixelLSC]
pub trait SuperpixelLSCConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_SuperpixelLSC(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Calculates the actual amount of superpixels on a given segmentation computed
/// and stored in SuperpixelLSC object.
#[inline]
fn get_number_of_superpixels(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_SuperpixelLSC_getNumberOfSuperpixels_const(self.as_raw_SuperpixelLSC(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the segmentation labeling of the image.
///
/// Each label represents a superpixel, and each pixel is assigned to one superpixel label.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * labels_out: Return: A CV_32SC1 integer array containing the labels of the superpixel
/// segmentation. The labels are in the range [0, getNumberOfSuperpixels()].
///
/// The function returns an image with the labels of the superpixel segmentation. The labels are in
/// the range [0, getNumberOfSuperpixels()].
#[inline]
fn get_labels(&self, labels_out: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(labels_out);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_SuperpixelLSC_getLabels_const_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_SuperpixelLSC(), labels_out.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the mask of the superpixel segmentation stored in SuperpixelLSC object.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: Return: CV_8U1 image mask where -1 indicates that the pixel is a superpixel border,
/// and 0 otherwise.
///
/// * thick_line: If false, the border is only one pixel wide, otherwise all pixels at the border
/// are masked.
///
/// The function return the boundaries of the superpixel segmentation.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * thick_line: true
#[inline]
fn get_label_contour_mask(&self, image: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, thick_line: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(image);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_SuperpixelLSC_getLabelContourMask_const_const__OutputArrayR_bool(self.as_raw_SuperpixelLSC(), image.as_raw__OutputArray(), thick_line, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Class implementing the LSC (Linear Spectral Clustering) superpixels
/// algorithm described in [LiCVPR2015LSC](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_LiCVPR2015LSC).
///
/// LSC (Linear Spectral Clustering) produces compact and uniform superpixels with low
/// computational costs. Basically, a normalized cuts formulation of the superpixel
/// segmentation is adopted based on a similarity metric that measures the color
/// similarity and space proximity between image pixels. LSC is of linear computational
/// complexity and high memory efficiency and is able to preserve global properties of images
pub trait SuperpixelLSC: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::ximgproc::SuperpixelLSCConst {
fn as_raw_mut_SuperpixelLSC(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Calculates the superpixel segmentation on a given image with the initialized
/// parameters in the SuperpixelLSC object.
///
/// This function can be called again without the need of initializing the algorithm with
/// createSuperpixelLSC(). This save the computational cost of allocating memory for all the
/// structures of the algorithm.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * num_iterations: Number of iterations. Higher number improves the result.
///
/// The function computes the superpixels segmentation of an image with the parameters initialized
/// with the function createSuperpixelLSC(). The algorithms starts from a grid of superpixels and
/// then refines the boundaries by proposing updates of edges boundaries.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * num_iterations: 10
#[inline]
fn iterate(&mut self, num_iterations: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_SuperpixelLSC_iterate_int(self.as_raw_mut_SuperpixelLSC(), num_iterations, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Enforce label connectivity.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * min_element_size: The minimum element size in percents that should be absorbed into a bigger
/// superpixel. Given resulted average superpixel size valid value should be in 0-100 range, 25 means
/// that less then a quarter sized superpixel should be absorbed, this is default.
///
/// The function merge component that is too small, assigning the previously found adjacent label
/// to this component. Calling this function may change the final number of superpixels.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * min_element_size: 25
#[inline]
fn enforce_label_connectivity(&mut self, min_element_size: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_SuperpixelLSC_enforceLabelConnectivity_int(self.as_raw_mut_SuperpixelLSC(), min_element_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::SuperpixelSEEDS]
pub trait SuperpixelSEEDSConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_SuperpixelSEEDS(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Class implementing the SEEDS (Superpixels Extracted via Energy-Driven Sampling) superpixels
/// algorithm described in [VBRV14](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_VBRV14) .
///
/// The algorithm uses an efficient hill-climbing algorithm to optimize the superpixels' energy
/// function that is based on color histograms and a boundary term, which is optional. The energy
/// function encourages superpixels to be of the same color, and if the boundary term is activated, the
/// superpixels have smooth boundaries and are of similar shape. In practice it starts from a regular
/// grid of superpixels and moves the pixels or blocks of pixels at the boundaries to refine the
/// solution. The algorithm runs in real-time using a single CPU.
pub trait SuperpixelSEEDS: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::ximgproc::SuperpixelSEEDSConst {
fn as_raw_mut_SuperpixelSEEDS(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Calculates the superpixel segmentation on a given image stored in SuperpixelSEEDS object.
///
/// The function computes the superpixels segmentation of an image with the parameters initialized
/// with the function createSuperpixelSEEDS().
#[inline]
fn get_number_of_superpixels(&mut self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_SuperpixelSEEDS_getNumberOfSuperpixels(self.as_raw_mut_SuperpixelSEEDS(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Calculates the superpixel segmentation on a given image with the initialized
/// parameters in the SuperpixelSEEDS object.
///
/// This function can be called again for other images without the need of initializing the
/// algorithm with createSuperpixelSEEDS(). This save the computational cost of allocating memory
/// for all the structures of the algorithm.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * img: Input image. Supported formats: CV_8U, CV_16U, CV_32F. Image size & number of
/// channels must match with the initialized image size & channels with the function
/// createSuperpixelSEEDS(). It should be in HSV or Lab color space. Lab is a bit better, but also
/// slower.
///
/// * num_iterations: Number of pixel level iterations. Higher number improves the result.
///
/// The function computes the superpixels segmentation of an image with the parameters initialized
/// with the function createSuperpixelSEEDS(). The algorithms starts from a grid of superpixels and
/// then refines the boundaries by proposing updates of blocks of pixels that lie at the boundaries
/// from large to smaller size, finalizing with proposing pixel updates. An illustrative example
/// can be seen below.
///
/// 
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * num_iterations: 4
#[inline]
fn iterate(&mut self, img: &dyn core::ToInputArray, num_iterations: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(img);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_SuperpixelSEEDS_iterate_const__InputArrayR_int(self.as_raw_mut_SuperpixelSEEDS(), img.as_raw__InputArray(), num_iterations, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the segmentation labeling of the image.
///
/// Each label represents a superpixel, and each pixel is assigned to one superpixel label.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * labels_out: Return: A CV_32UC1 integer array containing the labels of the superpixel
/// segmentation. The labels are in the range [0, getNumberOfSuperpixels()].
///
/// The function returns an image with ssthe labels of the superpixel segmentation. The labels are in
/// the range [0, getNumberOfSuperpixels()].
#[inline]
fn get_labels(&mut self, labels_out: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(labels_out);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_SuperpixelSEEDS_getLabels_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_SuperpixelSEEDS(), labels_out.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the mask of the superpixel segmentation stored in SuperpixelSEEDS object.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: Return: CV_8UC1 image mask where -1 indicates that the pixel is a superpixel border,
/// and 0 otherwise.
///
/// * thick_line: If false, the border is only one pixel wide, otherwise all pixels at the border
/// are masked.
///
/// The function return the boundaries of the superpixel segmentation.
///
///
/// Note:
/// * (Python) A demo on how to generate superpixels in images from the webcam can be found at
/// opencv_source_code/samples/python2/seeds.py
/// * (cpp) A demo on how to generate superpixels in images from the webcam can be found at
/// opencv_source_code/modules/ximgproc/samples/seeds.cpp. By adding a file image as a command
/// line argument, the static image will be used instead of the webcam.
/// * It will show a window with the video from the webcam with the superpixel boundaries marked
/// in red (see below). Use Space to switch between different output modes. At the top of the
/// window there are 4 sliders, from which the user can change on-the-fly the number of
/// superpixels, the number of block levels, the strength of the boundary prior term to modify
/// the shape, and the number of iterations at pixel level. This is useful to play with the
/// parameters and set them to the user convenience. In the console the frame-rate of the
/// algorithm is indicated.
///
/// 
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * thick_line: false
#[inline]
fn get_label_contour_mask(&mut self, image: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, thick_line: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(image);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_SuperpixelSEEDS_getLabelContourMask_const__OutputArrayR_bool(self.as_raw_mut_SuperpixelSEEDS(), image.as_raw__OutputArray(), thick_line, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::SuperpixelSLIC]
pub trait SuperpixelSLICConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_SuperpixelSLIC(&self) -> *const c_void;
/// Calculates the actual amount of superpixels on a given segmentation computed
/// and stored in SuperpixelSLIC object.
#[inline]
fn get_number_of_superpixels(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_SuperpixelSLIC_getNumberOfSuperpixels_const(self.as_raw_SuperpixelSLIC(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the segmentation labeling of the image.
///
/// Each label represents a superpixel, and each pixel is assigned to one superpixel label.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * labels_out: Return: A CV_32SC1 integer array containing the labels of the superpixel
/// segmentation. The labels are in the range [0, getNumberOfSuperpixels()].
///
/// The function returns an image with the labels of the superpixel segmentation. The labels are in
/// the range [0, getNumberOfSuperpixels()].
#[inline]
fn get_labels(&self, labels_out: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(labels_out);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_SuperpixelSLIC_getLabels_const_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_SuperpixelSLIC(), labels_out.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Returns the mask of the superpixel segmentation stored in SuperpixelSLIC object.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * image: Return: CV_8U1 image mask where -1 indicates that the pixel is a superpixel border,
/// and 0 otherwise.
///
/// * thick_line: If false, the border is only one pixel wide, otherwise all pixels at the border
/// are masked.
///
/// The function return the boundaries of the superpixel segmentation.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * thick_line: true
#[inline]
fn get_label_contour_mask(&self, image: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, thick_line: bool) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(image);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_SuperpixelSLIC_getLabelContourMask_const_const__OutputArrayR_bool(self.as_raw_SuperpixelSLIC(), image.as_raw__OutputArray(), thick_line, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Class implementing the SLIC (Simple Linear Iterative Clustering) superpixels
/// algorithm described in [Achanta2012](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Achanta2012).
///
/// SLIC (Simple Linear Iterative Clustering) clusters pixels using pixel channels and image plane space
/// to efficiently generate compact, nearly uniform superpixels. The simplicity of approach makes it
/// extremely easy to use a lone parameter specifies the number of superpixels and the efficiency of
/// the algorithm makes it very practical.
/// Several optimizations are available for SLIC class:
/// SLICO stands for "Zero parameter SLIC" and it is an optimization of baseline SLIC described in [Achanta2012](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Achanta2012).
/// MSLIC stands for "Manifold SLIC" and it is an optimization of baseline SLIC described in [Liu_2017_IEEE](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Liu_2017_IEEE).
pub trait SuperpixelSLIC: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::ximgproc::SuperpixelSLICConst {
fn as_raw_mut_SuperpixelSLIC(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Calculates the superpixel segmentation on a given image with the initialized
/// parameters in the SuperpixelSLIC object.
///
/// This function can be called again without the need of initializing the algorithm with
/// createSuperpixelSLIC(). This save the computational cost of allocating memory for all the
/// structures of the algorithm.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * num_iterations: Number of iterations. Higher number improves the result.
///
/// The function computes the superpixels segmentation of an image with the parameters initialized
/// with the function createSuperpixelSLIC(). The algorithms starts from a grid of superpixels and
/// then refines the boundaries by proposing updates of edges boundaries.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * num_iterations: 10
#[inline]
fn iterate(&mut self, num_iterations: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_SuperpixelSLIC_iterate_int(self.as_raw_mut_SuperpixelSLIC(), num_iterations, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Enforce label connectivity.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * min_element_size: The minimum element size in percents that should be absorbed into a bigger
/// superpixel. Given resulted average superpixel size valid value should be in 0-100 range, 25 means
/// that less then a quarter sized superpixel should be absorbed, this is default.
///
/// The function merge component that is too small, assigning the previously found adjacent label
/// to this component. Calling this function may change the final number of superpixels.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * min_element_size: 25
#[inline]
fn enforce_label_connectivity(&mut self, min_element_size: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_SuperpixelSLIC_enforceLabelConnectivity_int(self.as_raw_mut_SuperpixelSLIC(), min_element_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::GraphSegmentation]
pub trait GraphSegmentationConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_GraphSegmentation(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Graph Based Segmentation Algorithm.
/// The class implements the algorithm described in [PFF2004](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_PFF2004) .
pub trait GraphSegmentation: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::ximgproc::GraphSegmentationConst {
fn as_raw_mut_GraphSegmentation(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Segment an image and store output in dst
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: The input image. Any number of channel (1 (Eg: Gray), 3 (Eg: RGB), 4 (Eg: RGB-D)) can be provided
/// * dst: The output segmentation. It's a CV_32SC1 Mat with the same number of cols and rows as input image, with an unique, sequential, id for each pixel.
#[inline]
fn process_image(&mut self, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_GraphSegmentation_processImage_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_GraphSegmentation(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_sigma(&mut self, sigma: f64) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_GraphSegmentation_setSigma_double(self.as_raw_mut_GraphSegmentation(), sigma, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_sigma(&mut self) -> Result<f64> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_GraphSegmentation_getSigma(self.as_raw_mut_GraphSegmentation(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_k(&mut self, k: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_GraphSegmentation_setK_float(self.as_raw_mut_GraphSegmentation(), k, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_k(&mut self) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_GraphSegmentation_getK(self.as_raw_mut_GraphSegmentation(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn set_min_size(&mut self, min_size: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_GraphSegmentation_setMinSize_int(self.as_raw_mut_GraphSegmentation(), min_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_min_size(&mut self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_GraphSegmentation_getMinSize(self.as_raw_mut_GraphSegmentation(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentation]
pub trait SelectiveSearchSegmentationConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_SelectiveSearchSegmentation(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Selective search segmentation algorithm
/// The class implements the algorithm described in [uijlings2013selective](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_uijlings2013selective).
pub trait SelectiveSearchSegmentation: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationConst {
fn as_raw_mut_SelectiveSearchSegmentation(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Set a image used by switch* functions to initialize the class
/// ## Parameters
/// * img: The image
#[inline]
fn set_base_image(&mut self, img: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(img);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_SelectiveSearchSegmentation_setBaseImage_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_SelectiveSearchSegmentation(), img.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Initialize the class with the 'Single stragegy' parameters describled in [uijlings2013selective](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_uijlings2013selective).
/// ## Parameters
/// * k: The k parameter for the graph segmentation
/// * sigma: The sigma parameter for the graph segmentation
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * k: 200
/// * sigma: 0.8f
#[inline]
fn switch_to_single_strategy(&mut self, k: i32, sigma: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_SelectiveSearchSegmentation_switchToSingleStrategy_int_float(self.as_raw_mut_SelectiveSearchSegmentation(), k, sigma, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Initialize the class with the 'Selective search fast' parameters describled in [uijlings2013selective](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_uijlings2013selective).
/// ## Parameters
/// * base_k: The k parameter for the first graph segmentation
/// * inc_k: The increment of the k parameter for all graph segmentations
/// * sigma: The sigma parameter for the graph segmentation
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * base_k: 150
/// * inc_k: 150
/// * sigma: 0.8f
#[inline]
fn switch_to_selective_search_fast(&mut self, base_k: i32, inc_k: i32, sigma: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_SelectiveSearchSegmentation_switchToSelectiveSearchFast_int_int_float(self.as_raw_mut_SelectiveSearchSegmentation(), base_k, inc_k, sigma, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Initialize the class with the 'Selective search fast' parameters describled in [uijlings2013selective](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_uijlings2013selective).
/// ## Parameters
/// * base_k: The k parameter for the first graph segmentation
/// * inc_k: The increment of the k parameter for all graph segmentations
/// * sigma: The sigma parameter for the graph segmentation
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * base_k: 150
/// * inc_k: 150
/// * sigma: 0.8f
#[inline]
fn switch_to_selective_search_quality(&mut self, base_k: i32, inc_k: i32, sigma: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_SelectiveSearchSegmentation_switchToSelectiveSearchQuality_int_int_float(self.as_raw_mut_SelectiveSearchSegmentation(), base_k, inc_k, sigma, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Add a new image in the list of images to process.
/// ## Parameters
/// * img: The image
#[inline]
fn add_image(&mut self, img: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(img);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_SelectiveSearchSegmentation_addImage_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_SelectiveSearchSegmentation(), img.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Clear the list of images to process
#[inline]
fn clear_images(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_SelectiveSearchSegmentation_clearImages(self.as_raw_mut_SelectiveSearchSegmentation(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Add a new graph segmentation in the list of graph segementations to process.
/// ## Parameters
/// * g: The graph segmentation
#[inline]
fn add_graph_segmentation(&mut self, mut g: core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::GraphSegmentation>) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_SelectiveSearchSegmentation_addGraphSegmentation_PtrLGraphSegmentationG(self.as_raw_mut_SelectiveSearchSegmentation(), g.as_raw_mut_PtrOfGraphSegmentation(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Clear the list of graph segmentations to process;
#[inline]
fn clear_graph_segmentations(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_SelectiveSearchSegmentation_clearGraphSegmentations(self.as_raw_mut_SelectiveSearchSegmentation(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Add a new strategy in the list of strategy to process.
/// ## Parameters
/// * s: The strategy
#[inline]
fn add_strategy(&mut self, mut s: core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy>) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_SelectiveSearchSegmentation_addStrategy_PtrLSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyG(self.as_raw_mut_SelectiveSearchSegmentation(), s.as_raw_mut_PtrOfSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Clear the list of strategy to process;
#[inline]
fn clear_strategies(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_SelectiveSearchSegmentation_clearStrategies(self.as_raw_mut_SelectiveSearchSegmentation(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Based on all images, graph segmentations and stragies, computes all possible rects and return them
/// ## Parameters
/// * rects: The list of rects. The first ones are more relevents than the lasts ones.
#[inline]
fn process(&mut self, rects: &mut core::Vector<core::Rect>) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_SelectiveSearchSegmentation_process_vectorLRectGR(self.as_raw_mut_SelectiveSearchSegmentation(), rects.as_raw_mut_VectorOfRect(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy]
pub trait SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Strategie for the selective search segmentation algorithm
/// The class implements a generic stragery for the algorithm described in [uijlings2013selective](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_uijlings2013selective).
pub trait SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyConst {
fn as_raw_mut_SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Set a initial image, with a segmentation.
/// ## Parameters
/// * img: The input image. Any number of channel can be provided
/// * regions: A segmentation of the image. The parameter must be the same size of img.
/// * sizes: The sizes of different regions
/// * image_id: If not set to -1, try to cache pre-computations. If the same set og (img, regions, size) is used, the image_id need to be the same.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * image_id: -1
#[inline]
fn set_image(&mut self, img: &dyn core::ToInputArray, regions: &dyn core::ToInputArray, sizes: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_id: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(img);
extern_container_arg!(regions);
extern_container_arg!(sizes);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy_setImage_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int(self.as_raw_mut_SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy(), img.as_raw__InputArray(), regions.as_raw__InputArray(), sizes.as_raw__InputArray(), image_id, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Return the score between two regions (between 0 and 1)
/// ## Parameters
/// * r1: The first region
/// * r2: The second region
#[inline]
fn get(&mut self, r1: i32, r2: i32) -> Result<f32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy_get_int_int(self.as_raw_mut_SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy(), r1, r2, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Inform the strategy that two regions will be merged
/// ## Parameters
/// * r1: The first region
/// * r2: The second region
#[inline]
fn merge(&mut self, r1: i32, r2: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy_merge_int_int(self.as_raw_mut_SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy(), r1, r2, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyColor]
pub trait SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyColorConst: crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyConst {
fn as_raw_SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyColor(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Color-based strategy for the selective search segmentation algorithm
/// The class is implemented from the algorithm described in [uijlings2013selective](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_uijlings2013selective).
pub trait SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyColor: crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy + crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyColorConst {
fn as_raw_mut_SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyColor(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyFill]
pub trait SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyFillConst: crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyConst {
fn as_raw_SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyFill(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Fill-based strategy for the selective search segmentation algorithm
/// The class is implemented from the algorithm described in [uijlings2013selective](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_uijlings2013selective).
pub trait SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyFill: crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy + crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyFillConst {
fn as_raw_mut_SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyFill(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultiple]
pub trait SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultipleConst: crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyConst {
fn as_raw_SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultiple(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Regroup multiple strategies for the selective search segmentation algorithm
pub trait SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultiple: crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy + crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultipleConst {
fn as_raw_mut_SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultiple(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Add a new sub-strategy
/// ## Parameters
/// * g: The strategy
/// * weight: The weight of the strategy
#[inline]
fn add_strategy(&mut self, mut g: core::Ptr<dyn crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy>, weight: f32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultiple_addStrategy_PtrLSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyG_float(self.as_raw_mut_SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultiple(), g.as_raw_mut_PtrOfSelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy(), weight, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Remove all sub-strategies
#[inline]
fn clear_strategies(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_ximgproc_segmentation_SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultiple_clearStrategies(self.as_raw_mut_SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyMultiple(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategySize]
pub trait SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategySizeConst: crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyConst {
fn as_raw_SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategySize(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Size-based strategy for the selective search segmentation algorithm
/// The class is implemented from the algorithm described in [uijlings2013selective](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_uijlings2013selective).
pub trait SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategySize: crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy + crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategySizeConst {
fn as_raw_mut_SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategySize(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyTexture]
pub trait SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyTextureConst: crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyConst {
fn as_raw_SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyTexture(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// Texture-based strategy for the selective search segmentation algorithm
/// The class is implemented from the algorithm described in [uijlings2013selective](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_uijlings2013selective).
pub trait SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyTexture: crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategy + crate::ximgproc::SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyTextureConst {
fn as_raw_mut_SelectiveSearchSegmentationStrategyTexture(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
}
}