Meteostat for Rust
The Weather's Record Keeper - In Rust!
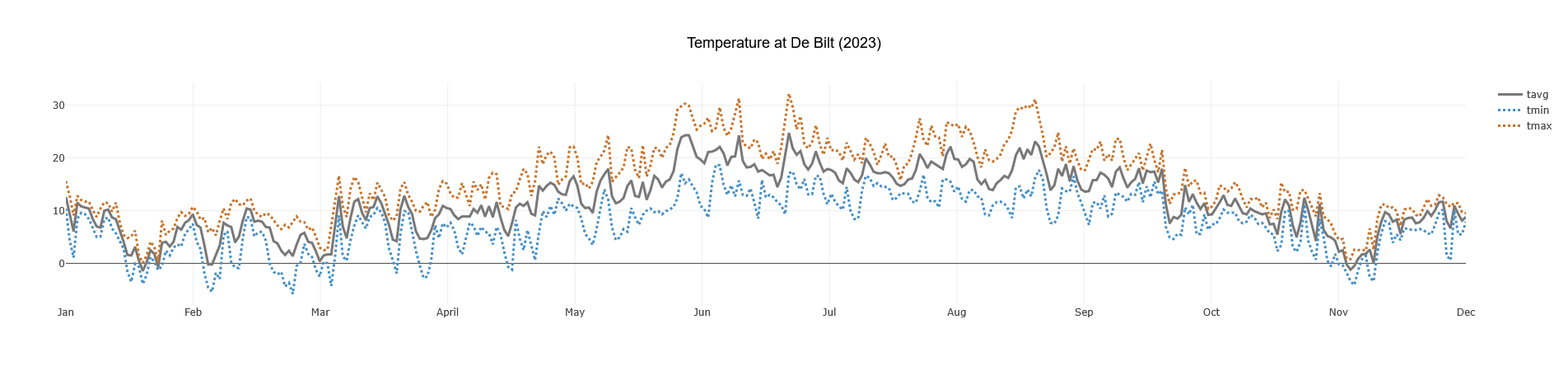
This crate provides a convenient asynchronous Rust interface for accessing historical weather and climate data from Meteostat, leveraging their publicly available bulk data interface. It allows fetching data for thousands of weather stations worldwide.
Meteostat is a free and open provider of weather & climate data. They do the hard work of collecting, processing, and providing the data. This crate is simply a Rust client for their bulk API. Please consider supporting Meteostat if you find their data useful: Donate to Meteostat.
Take a look at yesterday's temperatures or discover the weather hundreds of years ago, right from your Rust application.
Key Features
- Fetch by Station ID or Location: Initiate requests via frequency-specific clients (
client.hourly(),client.daily(), etc.) and then specify either.station("ID")or.location(LatLon). - Find Nearby Stations: Search for stations near coordinates using
client.find_stations(), optionally filtering by distance and required data availability (inventory). - Multiple Frequencies: Supports Hourly, Daily, Monthly, and Climate Normals data.
- Efficient Data Handling: Returns data as wrappers around Polars
LazyFrames (e.g.,HourlyLazyFrame), allowing for powerful, memory-efficient filtering and manipulation before collecting results. - Convenient Filtering: Frame wrappers provide methods for easy filtering by date, year, month, or datetime ranges (e.g.,
daily_lazy.get_for_period(Year(2023))). - Automatic Caching: Downloads and caches station metadata and weather data files locally to speed up subsequent requests and reduce load on Meteostat's servers.
- Asynchronous: Built with
tokiofor non-blocking I/O.
Installation
Add meteostat to your Cargo.toml dependencies:
Basic Usage
Here's a quick example demonstrating fetching data by location and station ID:
use ;
use *;
use ;
async
(See more examples in the examples directory)
Finding Stations
You can search for stations near a specific location using client.find_stations():
use ;
async
Data Handling
Polars LazyFrame Wrappers
All weather data fetching methods return a specific wrapper struct (e.g., HourlyLazyFrame, DailyLazyFrame) which contains a Polars LazyFrame. This allows you to:
- Use convenience filters: Apply common filters directly using methods on the wrapper (e.g.,
daily_lazy.get_for_period(Year(2023))). - Access the underlying frame: Get the
LazyFramevia the.framefield for advanced Polars operations (joins, aggregations, complex selections, etc.). - Optimize queries: Polars optimizes the execution plan built from chained operations.
- Collect when ready: Use
.frame.collect()?on the wrapper to execute the plan and get aDataFramein memory.
This is particularly beneficial when dealing with potentially large historical datasets.
Caching
The crate automatically caches downloaded data to avoid redundant downloads and respect Meteostat's resources:
- Station Metadata: The list of all stations (
stations/lite.json.gz) is downloaded once and cached. - Weather Data: Individual station data files (e.g.,
hourly/10637.csv.gz) are downloaded and cached per station and frequency.
By default, cache files are stored in your system's standard cache directory (e.g., ~/.cache/meteostat-rs on Linux, %LOCALAPPDATA%/meteostat_rs_cache on Windows).
You can specify a custom cache location using Meteostat::with_cache_folder(path).
Filtering Data Frames
Each data frequency (Hourly, Daily, Monthly, Climate) has its own LazyFrame wrapper struct (HourlyLazyFrame, DailyLazyFrame, etc.) that provides convenient methods for common filtering tasks.
Access these wrappers by first selecting the frequency client and then fetching the data:
use ;
use *;
use ;
async
See the documentation for the specific frame wrappers for all available filtering methods:
For more complex filtering or analysis, access the underlying Polars LazyFrame via the .frame field on the wrapper structs.
Data Source and Attribution
- All weather data is sourced from Meteostat.
- This crate uses Meteostat's free bulk data interface. No API key is required.
API Documentation
Full API documentation is available on docs.rs.
Example: Plotting Data
You can easily use the DataFrame output with plotting libraries like plotlars.
// Requires the 'examples' feature: cargo run --example graph_data --features examples
use Error;
use ; // Updated import
use ;
use *;
async
// Note: Added Result return type for potential polars errors in plot
To run this specific example, enable the examples feature:
cargo run --example graph_data --features examples
(This will generate a plot similar to the one shown at the top of this README)
Contributing
Contributions, bug reports, and feature requests are welcome! Please feel free to open an issue or submit a pull request on the GitHub repository.
License
This crate is licensed under the Apache License 2.0. See the LICENSE file for details.


