Struct requestty::question::MultiSelectBuilder [−][src]
pub struct MultiSelectBuilder<'a> { /* fields omitted */ }Expand description
The builder for a multi_select prompt.
Unlike the other list based prompts, this has a per choice boolean default.
The choices are represented with the Choice enum. Choice::Choice can be multi-line,
but Choice::Separators can only be single line.
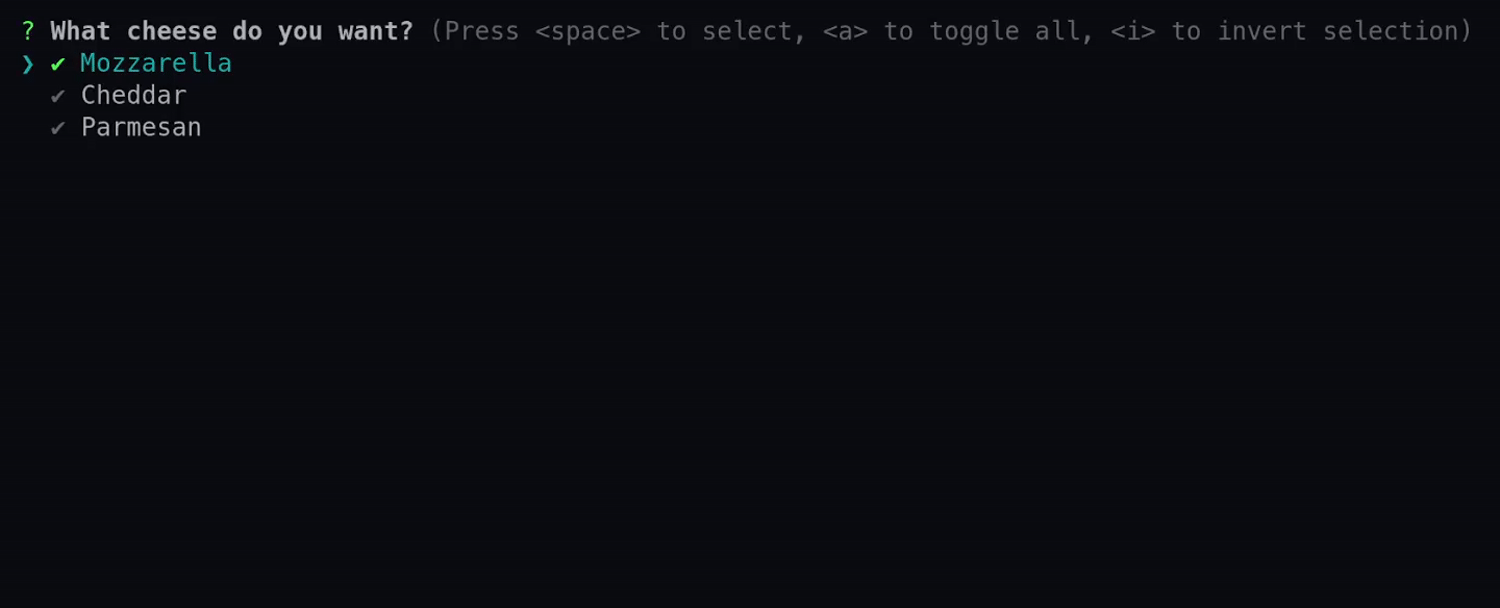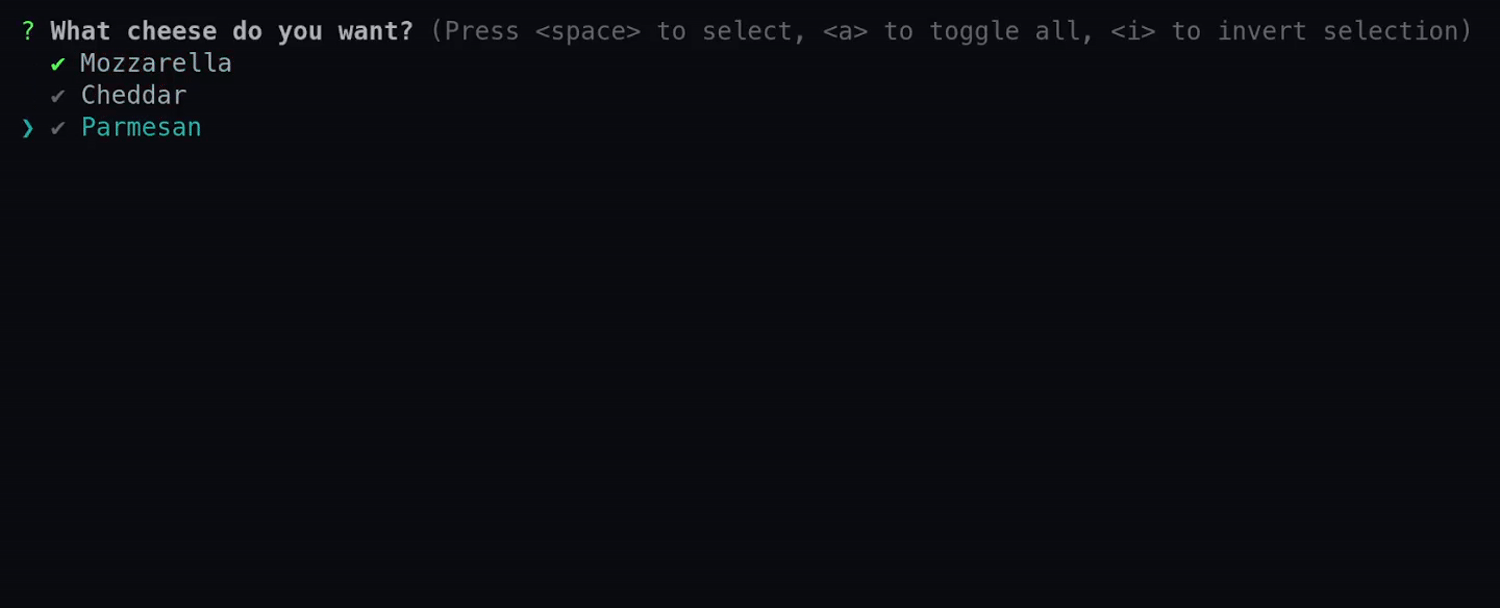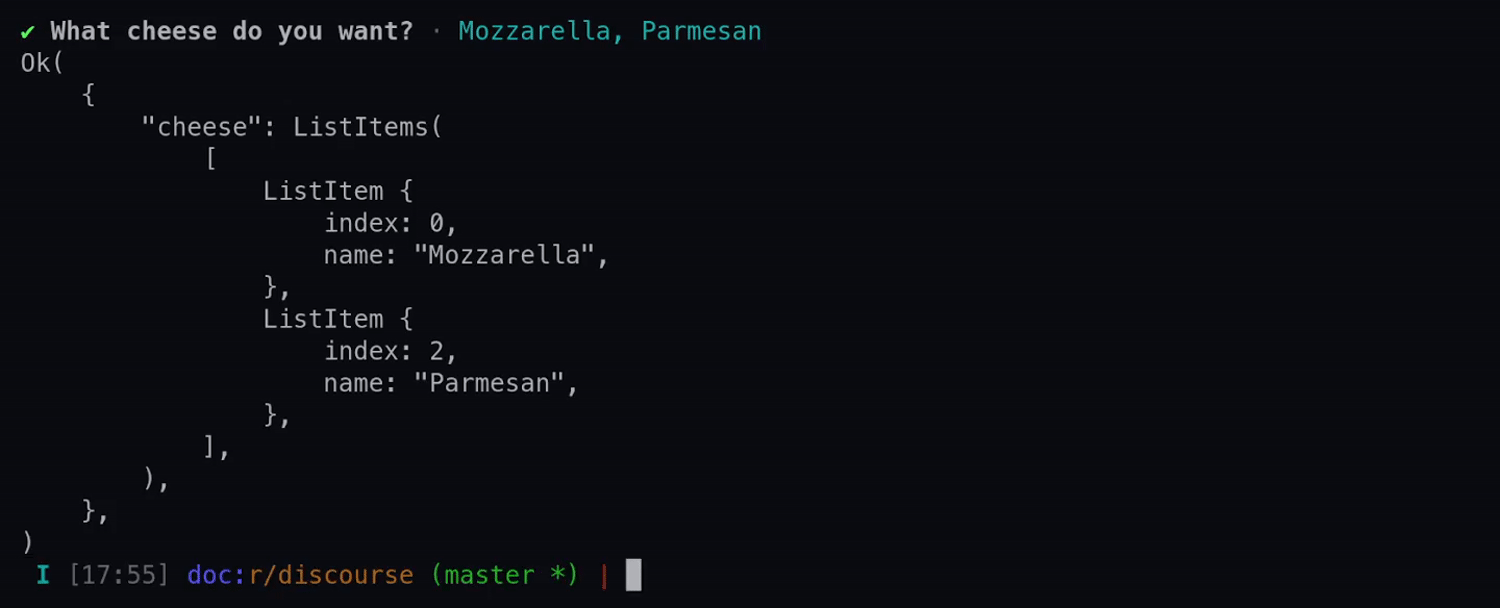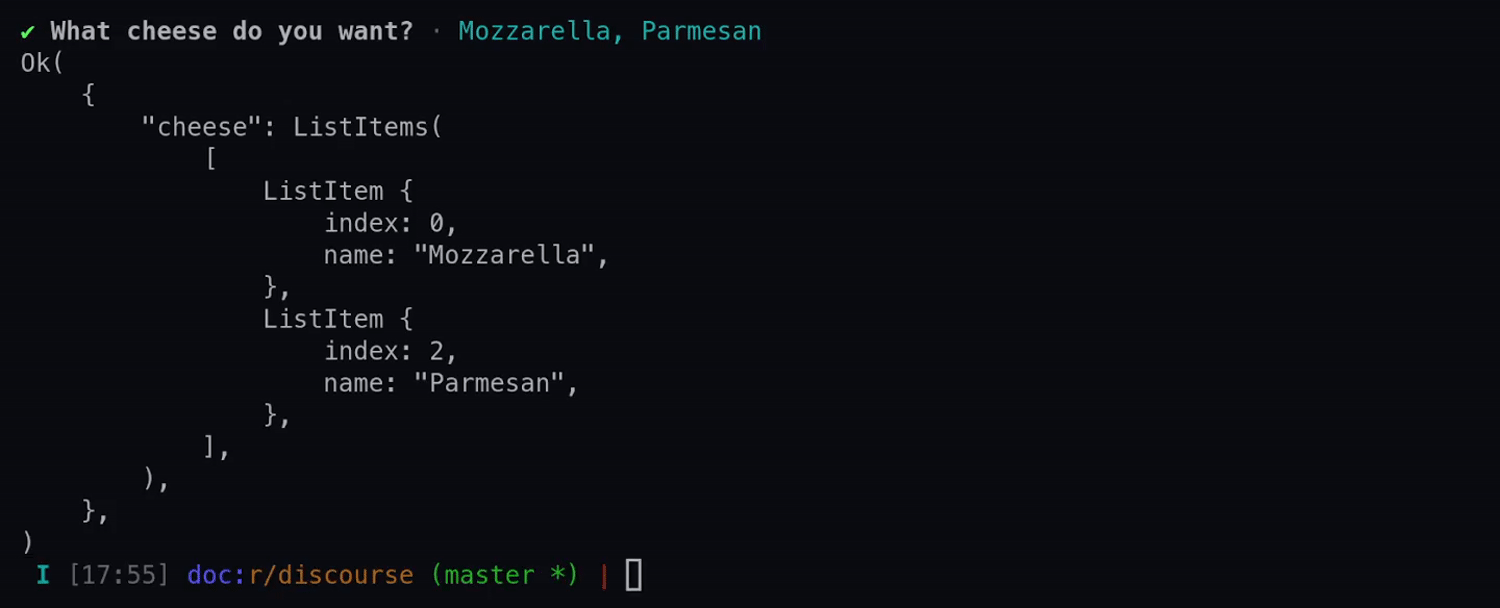
See the various methods for more details on each available option.
Examples
use requestty::{Question, DefaultSeparator}; let multi_select = Question::multi_select("cheese") .message("What cheese do you want?") .choice_with_default("Mozzarella", true) .choices(vec![ "Cheddar", "Parmesan", ]) .build();
Implementations
The message to display when the prompt is rendered in the terminal.
It can be either a String or a FnOnce that returns a String. If it is a
function, it is passed all the previous Answers, and will be called right before the
question is prompted to the user.
If it is not given, the message defaults to “<name>: “.
Examples
use requestty::Question; let multi_select = Question::multi_select("cheese") .message("What cheese do you want?") .build();
Whether to ask the question (true) or not (false).
It can be either a bool or a FnOnce that returns a bool. If it is a
function, it is passed all the previous Answers, and will be called right before the
question is prompted to the user.
If it is not given, it defaults to true.
Examples
use requestty::{Answers, Question}; let multi_select = Question::multi_select("cheese") .when(|previous_answers: &Answers| match previous_answers.get("vegan") { Some(ans) => ans.as_bool().unwrap(), None => true, }) .build();
Prompt the question even if it is answered.
By default if an answer with the given name already exists, the question will be
skipped. This can be overridden by setting ask_if_answered is set to true.
If this is not given, it defaults to false.
If you need to dynamically decide whether the question should be asked, use when.
Examples
use requestty::{Answers, Question}; let multi_select = Question::multi_select("cheese") .ask_if_answered(true) .build();
The maximum height that can be taken by the list
If the total height exceeds the page size, the list will be scrollable.
The page_size must be a minimum of 5. If page_size is not set, it will default to 15.
Panics
It will panic if the page_size is less than 5.
Examples
use requestty::Question; let multi_select = Question::multi_select("cheese") .page_size(10) .build();
Whether to wrap around when user gets to the last element.
If should_loop is not set, it will default to true.
Examples
use requestty::Question; let multi_select = Question::multi_select("cheese") .should_loop(false) .build();
Inserts a Choice with given text and its default checked state as false.
If you want to set the default checked state, use choice_with_default.
See multi_select for more information.
Examples
use requestty::Question; let multi_select = Question::multi_select("cheese") .choice("Cheddar") .build();
Inserts a Choice with a given text and default checked state.
See multi_select for more information.
Examples
use requestty::Question; let multi_select = Question::multi_select("cheese") .choice_with_default("Mozzarella", true) .build();
Inserts a Separator with the given text
See multi_select for more information.
Examples
use requestty::Question; let multi_select = Question::multi_select("cheese") .separator("-- custom separator text --") .build();
Inserts a DefaultSeparator
See multi_select for more information.
Examples
use requestty::Question; let multi_select = Question::multi_select("cheese") .default_separator() .build();
Extends the given iterator of Choices
Every Choice::Choice within will have a default checked value of false. If you want to
set the default checked value, use choices_with_default.
See multi_select for more information.
Examples
use requestty::Question; let multi_select = Question::multi_select("cheese") .choices(vec![ "Mozzarella", "Cheddar", "Parmesan", ]) .build();
pub fn choices_with_default<I, T>(self, choices: I) -> Self where
T: Into<Choice<(String, bool)>>,
I: IntoIterator<Item = T>,
pub fn choices_with_default<I, T>(self, choices: I) -> Self where
T: Into<Choice<(String, bool)>>,
I: IntoIterator<Item = T>, Extends the given iterator of Choices with the given default checked value.
See multi_select for more information.
Examples
use requestty::Question; let multi_select = Question::multi_select("cheese") .choices_with_default(vec![ ("Mozzarella", true), ("Cheddar", false), ("Parmesan", false), ]) .build();
Function to change the final submitted value before it is displayed to the user and
added to the Answers.
It is a FnOnce that is given the answer and the previous Answers, and should
return the new answer.
This will be called after the answer has been validated.
NOTE: The boolean Vec contains a boolean value for each index even if it is a separator.
However it is guaranteed that all the separator indices will be false.
Examples
use requestty::Question; let multi_select = Question::multi_select("evil-cheese") .filter(|mut cheeses, previous_answers| { cheeses.iter_mut().for_each(|checked| *checked = !*checked); cheeses }) .build();
Function to validate the submitted value before it’s returned.
It is a FnMut that is given the answer and the previous Answers, and should
return Ok(()) if the given answer is valid. If it is invalid, it should return an
Err with the error message to display to the user.
This will be called when the user presses the Enter key.
NOTE: The boolean slice contains a boolean value for each index even if it is a
separator. However it is guaranteed that all the separator indices will be false.
Examples
use requestty::Question; let multi_select = Question::multi_select("cheese") .validate(|cheeses, previous_answers| { if cheeses.iter().filter(|&&a| a).count() < 1 { Err("You must choose at least one cheese.".into()) } else { Ok(()) } }) .build();
Change the way the answer looks when displayed to the user.
It is a FnOnce that is given the answer, previous Answers and the Backend to
display the answer on. After the transform is called, a new line is also added.
It will only be called once the user finishes answering the question.
Examples
use requestty::Question; let multi_select = Question::multi_select("cheese") .transform(|cheeses, previous_answers, backend| { for cheese in cheeses { write!(backend, "({}) {}, ", cheese.index, cheese.text)?; } Ok(()) }) .build();
Trait Implementations
Consumes the builder returning a Question
Auto Trait Implementations
impl<'a> !RefUnwindSafe for MultiSelectBuilder<'a>impl<'a> !Send for MultiSelectBuilder<'a>impl<'a> !Sync for MultiSelectBuilder<'a>impl<'a> Unpin for MultiSelectBuilder<'a>impl<'a> !UnwindSafe for MultiSelectBuilder<'a>