[−][src]Struct qt_widgets::QBoxLayout
The QBoxLayout class lines up child widgets horizontally or vertically.
C++ class: QBoxLayout.
The QBoxLayout class lines up child widgets horizontally or vertically.
QBoxLayout takes the space it gets (from its parent layout or from the parentWidget()), divides it up into a row of boxes, and makes each managed widget fill one box.
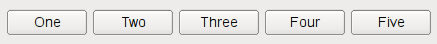
If the QBoxLayout's orientation is Qt::Horizontal the boxes are placed in a row, with suitable sizes. Each widget (or other box) will get at least its minimum size and at most its maximum size. Any excess space is shared according to the stretch factors (more about that below).
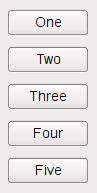
If the QBoxLayout's orientation is Qt::Vertical, the boxes are placed in a column, again with suitable sizes.
The easiest way to create a QBoxLayout is to use one of the convenience classes, e.g. QHBoxLayout (for Qt::Horizontal boxes) or QVBoxLayout (for Qt::Vertical boxes). You can also use the QBoxLayout constructor directly, specifying its direction as LeftToRight, RightToLeft, TopToBottom, or BottomToTop.
If the QBoxLayout is not the top-level layout (i.e. it is not managing all of the widget's area and children), you must add it to its parent layout before you can do anything with it. The normal way to add a layout is by calling parentLayout->addLayout().
Once you have done this, you can add boxes to the QBoxLayout using one of four functions:
- addWidget() to add a widget to the QBoxLayout and set the widget's stretch factor. (The stretch factor is along the row of boxes.)
- addSpacing() to create an empty box; this is one of the functions you use to create nice and spacious dialogs. See below for ways to set margins.
- addStretch() to create an empty, stretchable box.
- addLayout() to add a box containing another QLayout to the row and set that layout's stretch factor.
Use insertWidget(), insertSpacing(), insertStretch() or insertLayout() to insert a box at a specified position in the layout.
QBoxLayout also includes two margin widths:
- setContentsMargins() sets the width of the outer border on each side of the widget. This is the width of the reserved space along each of the QBoxLayout's four sides.
- setSpacing() sets the width between neighboring boxes. (You can use addSpacing() to get more space at a particular spot.)
The margin default is provided by the style. The default margin most Qt styles specify is 9 for child widgets and 11 for windows. The spacing defaults to the same as the margin width for a top-level layout, or to the same as the parent layout.
To remove a widget from a layout, call removeWidget(). Calling QWidget::hide() on a widget also effectively removes the widget from the layout until QWidget::show() is called.
You will almost always want to use QVBoxLayout and QHBoxLayout rather than QBoxLayout because of their convenient constructors.
Methods
impl QBoxLayout[src]
pub unsafe fn add_item(&mut self, arg1: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QLayoutItem>>)[src]
Reimplemented from QLayout::addItem().
Calls C++ function: virtual void QBoxLayout::addItem(QLayoutItem* arg1).
Reimplemented from QLayout::addItem().
pub unsafe fn add_layout_2a(
&mut self,
layout: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QLayout>>,
stretch: c_int
)[src]
&mut self,
layout: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QLayout>>,
stretch: c_int
)
Adds layout to the end of the box, with serial stretch factor stretch.
Calls C++ function: void QBoxLayout::addLayout(QLayout* layout, int stretch = …).
Adds layout to the end of the box, with serial stretch factor stretch.
See also insertLayout(), addItem(), and addWidget().
pub unsafe fn add_layout_1a(&mut self, layout: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QLayout>>)[src]
Adds layout to the end of the box, with serial stretch factor stretch.
Calls C++ function: void QBoxLayout::addLayout(QLayout* layout).
Adds layout to the end of the box, with serial stretch factor stretch.
See also insertLayout(), addItem(), and addWidget().
pub unsafe fn add_spacer_item(
&mut self,
spacer_item: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QSpacerItem>>
)[src]
&mut self,
spacer_item: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QSpacerItem>>
)
Adds spacerItem to the end of this box layout.
Calls C++ function: void QBoxLayout::addSpacerItem(QSpacerItem* spacerItem).
Adds spacerItem to the end of this box layout.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.4.
See also addSpacing() and addStretch().
pub unsafe fn add_spacing(&mut self, size: c_int)[src]
Adds a non-stretchable space (a QSpacerItem) with size size to the end of this box layout. QBoxLayout provides default margin and spacing. This function adds additional space.
Calls C++ function: void QBoxLayout::addSpacing(int size).
Adds a non-stretchable space (a QSpacerItem) with size size to the end of this box layout. QBoxLayout provides default margin and spacing. This function adds additional space.
See also insertSpacing(), addItem(), and QSpacerItem.
pub unsafe fn add_stretch_1a(&mut self, stretch: c_int)[src]
Adds a stretchable space (a QSpacerItem) with zero minimum size and stretch factor stretch to the end of this box layout.
Calls C++ function: void QBoxLayout::addStretch(int stretch = …).
Adds a stretchable space (a QSpacerItem) with zero minimum size and stretch factor stretch to the end of this box layout.
See also insertStretch(), addItem(), and QSpacerItem.
pub unsafe fn add_stretch_0a(&mut self)[src]
Adds a stretchable space (a QSpacerItem) with zero minimum size and stretch factor stretch to the end of this box layout.
Calls C++ function: void QBoxLayout::addStretch().
Adds a stretchable space (a QSpacerItem) with zero minimum size and stretch factor stretch to the end of this box layout.
See also insertStretch(), addItem(), and QSpacerItem.
pub unsafe fn add_strut(&mut self, arg1: c_int)[src]
Limits the perpendicular dimension of the box (e.g. height if the box is LeftToRight) to a minimum of size. Other constraints may increase the limit.
Calls C++ function: void QBoxLayout::addStrut(int arg1).
Limits the perpendicular dimension of the box (e.g. height if the box is LeftToRight) to a minimum of size. Other constraints may increase the limit.
See also addItem().
pub unsafe fn add_widget_3a(
&mut self,
arg1: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>,
stretch: c_int,
alignment: QFlags<AlignmentFlag>
)[src]
&mut self,
arg1: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>,
stretch: c_int,
alignment: QFlags<AlignmentFlag>
)
Adds widget to the end of this box layout, with a stretch factor of stretch and alignment alignment.
Calls C++ function: void QBoxLayout::addWidget(QWidget* arg1, int stretch = …, QFlags<Qt::AlignmentFlag> alignment = …).
Adds widget to the end of this box layout, with a stretch factor of stretch and alignment alignment.
The stretch factor applies only in the direction of the QBoxLayout, and is relative to the other boxes and widgets in this QBoxLayout. Widgets and boxes with higher stretch factors grow more.
If the stretch factor is 0 and nothing else in the QBoxLayout has a stretch factor greater than zero, the space is distributed according to the QWidget:sizePolicy() of each widget that's involved.
The alignment is specified by alignment. The default alignment is 0, which means that the widget fills the entire cell.
See also insertWidget(), addItem(), addLayout(), addStretch(), addSpacing(), and addStrut().
pub unsafe fn add_widget_2a(
&mut self,
arg1: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>,
stretch: c_int
)[src]
&mut self,
arg1: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>,
stretch: c_int
)
Adds widget to the end of this box layout, with a stretch factor of stretch and alignment alignment.
Calls C++ function: void QBoxLayout::addWidget(QWidget* arg1, int stretch = …).
Adds widget to the end of this box layout, with a stretch factor of stretch and alignment alignment.
The stretch factor applies only in the direction of the QBoxLayout, and is relative to the other boxes and widgets in this QBoxLayout. Widgets and boxes with higher stretch factors grow more.
If the stretch factor is 0 and nothing else in the QBoxLayout has a stretch factor greater than zero, the space is distributed according to the QWidget:sizePolicy() of each widget that's involved.
The alignment is specified by alignment. The default alignment is 0, which means that the widget fills the entire cell.
See also insertWidget(), addItem(), addLayout(), addStretch(), addSpacing(), and addStrut().
pub unsafe fn add_widget_1a(&mut self, arg1: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>)[src]
Adds widget to the end of this box layout, with a stretch factor of stretch and alignment alignment.
Calls C++ function: void QBoxLayout::addWidget(QWidget* arg1).
Adds widget to the end of this box layout, with a stretch factor of stretch and alignment alignment.
The stretch factor applies only in the direction of the QBoxLayout, and is relative to the other boxes and widgets in this QBoxLayout. Widgets and boxes with higher stretch factors grow more.
If the stretch factor is 0 and nothing else in the QBoxLayout has a stretch factor greater than zero, the space is distributed according to the QWidget:sizePolicy() of each widget that's involved.
The alignment is specified by alignment. The default alignment is 0, which means that the widget fills the entire cell.
See also insertWidget(), addItem(), addLayout(), addStretch(), addSpacing(), and addStrut().
pub unsafe fn count(&self) -> c_int[src]
Reimplemented from QLayout::count().
Calls C++ function: virtual int QBoxLayout::count() const.
Reimplemented from QLayout::count().
pub unsafe fn direction(&self) -> Direction[src]
Returns the direction of the box. addWidget() and addSpacing() work in this direction; the stretch stretches in this direction.
Calls C++ function: QBoxLayout::Direction QBoxLayout::direction() const.
Returns the direction of the box. addWidget() and addSpacing() work in this direction; the stretch stretches in this direction.
See also setDirection(), QBoxLayout::Direction, addWidget(), and addSpacing().
pub unsafe fn expanding_directions(&self) -> QFlags<Orientation>[src]
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::expandingDirections().
Calls C++ function: virtual QFlags<Qt::Orientation> QBoxLayout::expandingDirections() const.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::expandingDirections().
pub unsafe fn has_height_for_width(&self) -> bool[src]
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::hasHeightForWidth().
Calls C++ function: virtual bool QBoxLayout::hasHeightForWidth() const.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::hasHeightForWidth().
pub unsafe fn height_for_width(&self, arg1: c_int) -> c_int[src]
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::heightForWidth().
Calls C++ function: virtual int QBoxLayout::heightForWidth(int arg1) const.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::heightForWidth().
pub unsafe fn insert_item(
&mut self,
index: c_int,
arg2: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QLayoutItem>>
)[src]
&mut self,
index: c_int,
arg2: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QLayoutItem>>
)
Inserts item into this box layout at position index. If index is negative, the item is added at the end.
Calls C++ function: void QBoxLayout::insertItem(int index, QLayoutItem* arg2).
Inserts item into this box layout at position index. If index is negative, the item is added at the end.
See also addItem(), insertWidget(), insertLayout(), insertStretch(), and insertSpacing().
pub unsafe fn insert_layout_3a(
&mut self,
index: c_int,
layout: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QLayout>>,
stretch: c_int
)[src]
&mut self,
index: c_int,
layout: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QLayout>>,
stretch: c_int
)
Inserts layout at position index, with stretch factor stretch. If index is negative, the layout is added at the end.
Calls C++ function: void QBoxLayout::insertLayout(int index, QLayout* layout, int stretch = …).
Inserts layout at position index, with stretch factor stretch. If index is negative, the layout is added at the end.
layout becomes a child of the box layout.
See also addLayout() and insertItem().
pub unsafe fn insert_layout_2a(
&mut self,
index: c_int,
layout: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QLayout>>
)[src]
&mut self,
index: c_int,
layout: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QLayout>>
)
Inserts layout at position index, with stretch factor stretch. If index is negative, the layout is added at the end.
Calls C++ function: void QBoxLayout::insertLayout(int index, QLayout* layout).
Inserts layout at position index, with stretch factor stretch. If index is negative, the layout is added at the end.
layout becomes a child of the box layout.
See also addLayout() and insertItem().
pub unsafe fn insert_spacer_item(
&mut self,
index: c_int,
spacer_item: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QSpacerItem>>
)[src]
&mut self,
index: c_int,
spacer_item: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QSpacerItem>>
)
Inserts spacerItem at position index, with zero minimum size and stretch factor. If index is negative the space is added at the end.
Calls C++ function: void QBoxLayout::insertSpacerItem(int index, QSpacerItem* spacerItem).
Inserts spacerItem at position index, with zero minimum size and stretch factor. If index is negative the space is added at the end.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.4.
See also addSpacerItem(), insertStretch(), and insertSpacing().
pub unsafe fn insert_spacing(&mut self, index: c_int, size: c_int)[src]
Inserts a non-stretchable space (a QSpacerItem) at position index, with size size. If index is negative the space is added at the end.
Calls C++ function: void QBoxLayout::insertSpacing(int index, int size).
Inserts a non-stretchable space (a QSpacerItem) at position index, with size size. If index is negative the space is added at the end.
The box layout has default margin and spacing. This function adds additional space.
See also addSpacing(), insertItem(), and QSpacerItem.
pub unsafe fn insert_stretch_2a(&mut self, index: c_int, stretch: c_int)[src]
Inserts a stretchable space (a QSpacerItem) at position index, with zero minimum size and stretch factor stretch. If index is negative the space is added at the end.
Calls C++ function: void QBoxLayout::insertStretch(int index, int stretch = …).
Inserts a stretchable space (a QSpacerItem) at position index, with zero minimum size and stretch factor stretch. If index is negative the space is added at the end.
See also addStretch(), insertItem(), and QSpacerItem.
pub unsafe fn insert_stretch_1a(&mut self, index: c_int)[src]
Inserts a stretchable space (a QSpacerItem) at position index, with zero minimum size and stretch factor stretch. If index is negative the space is added at the end.
Calls C++ function: void QBoxLayout::insertStretch(int index).
Inserts a stretchable space (a QSpacerItem) at position index, with zero minimum size and stretch factor stretch. If index is negative the space is added at the end.
See also addStretch(), insertItem(), and QSpacerItem.
pub unsafe fn insert_widget_4a(
&mut self,
index: c_int,
widget: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>,
stretch: c_int,
alignment: QFlags<AlignmentFlag>
)[src]
&mut self,
index: c_int,
widget: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>,
stretch: c_int,
alignment: QFlags<AlignmentFlag>
)
Inserts widget at position index, with stretch factor stretch and alignment alignment. If index is negative, the widget is added at the end.
Calls C++ function: void QBoxLayout::insertWidget(int index, QWidget* widget, int stretch = …, QFlags<Qt::AlignmentFlag> alignment = …).
Inserts widget at position index, with stretch factor stretch and alignment alignment. If index is negative, the widget is added at the end.
The stretch factor applies only in the direction of the QBoxLayout, and is relative to the other boxes and widgets in this QBoxLayout. Widgets and boxes with higher stretch factors grow more.
If the stretch factor is 0 and nothing else in the QBoxLayout has a stretch factor greater than zero, the space is distributed according to the QWidget:sizePolicy() of each widget that's involved.
The alignment is specified by alignment. The default alignment is 0, which means that the widget fills the entire cell.
See also addWidget() and insertItem().
pub unsafe fn insert_widget_3a(
&mut self,
index: c_int,
widget: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>,
stretch: c_int
)[src]
&mut self,
index: c_int,
widget: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>,
stretch: c_int
)
Inserts widget at position index, with stretch factor stretch and alignment alignment. If index is negative, the widget is added at the end.
Calls C++ function: void QBoxLayout::insertWidget(int index, QWidget* widget, int stretch = …).
Inserts widget at position index, with stretch factor stretch and alignment alignment. If index is negative, the widget is added at the end.
The stretch factor applies only in the direction of the QBoxLayout, and is relative to the other boxes and widgets in this QBoxLayout. Widgets and boxes with higher stretch factors grow more.
If the stretch factor is 0 and nothing else in the QBoxLayout has a stretch factor greater than zero, the space is distributed according to the QWidget:sizePolicy() of each widget that's involved.
The alignment is specified by alignment. The default alignment is 0, which means that the widget fills the entire cell.
See also addWidget() and insertItem().
pub unsafe fn insert_widget_2a(
&mut self,
index: c_int,
widget: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>
)[src]
&mut self,
index: c_int,
widget: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>
)
Inserts widget at position index, with stretch factor stretch and alignment alignment. If index is negative, the widget is added at the end.
Calls C++ function: void QBoxLayout::insertWidget(int index, QWidget* widget).
Inserts widget at position index, with stretch factor stretch and alignment alignment. If index is negative, the widget is added at the end.
The stretch factor applies only in the direction of the QBoxLayout, and is relative to the other boxes and widgets in this QBoxLayout. Widgets and boxes with higher stretch factors grow more.
If the stretch factor is 0 and nothing else in the QBoxLayout has a stretch factor greater than zero, the space is distributed according to the QWidget:sizePolicy() of each widget that's involved.
The alignment is specified by alignment. The default alignment is 0, which means that the widget fills the entire cell.
See also addWidget() and insertItem().
pub unsafe fn invalidate(&mut self)[src]
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::invalidate().
Calls C++ function: virtual void QBoxLayout::invalidate().
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::invalidate().
Resets cached information.
pub unsafe fn item_at(&self, arg1: c_int) -> MutPtr<QLayoutItem>[src]
Reimplemented from QLayout::itemAt().
Calls C++ function: virtual QLayoutItem* QBoxLayout::itemAt(int arg1) const.
Reimplemented from QLayout::itemAt().
pub unsafe fn maximum_size(&self) -> CppBox<QSize>[src]
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::maximumSize().
Calls C++ function: virtual QSize QBoxLayout::maximumSize() const.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::maximumSize().
pub unsafe fn meta_object(&self) -> Ptr<QMetaObject>[src]
Calls C++ function: virtual const QMetaObject* QBoxLayout::metaObject() const.
pub unsafe fn minimum_height_for_width(&self, arg1: c_int) -> c_int[src]
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::minimumHeightForWidth().
Calls C++ function: virtual int QBoxLayout::minimumHeightForWidth(int arg1) const.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::minimumHeightForWidth().
pub unsafe fn minimum_size(&self) -> CppBox<QSize>[src]
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::minimumSize().
Calls C++ function: virtual QSize QBoxLayout::minimumSize() const.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::minimumSize().
pub unsafe fn new_2a(
arg1: Direction,
parent: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>
) -> CppBox<QBoxLayout>[src]
arg1: Direction,
parent: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>
) -> CppBox<QBoxLayout>
Constructs a new QBoxLayout with direction dir and parent widget parent.
Calls C++ function: [constructor] void QBoxLayout::QBoxLayout(QBoxLayout::Direction arg1, QWidget* parent = …).
Constructs a new QBoxLayout with direction dir and parent widget parent.
See also direction().
pub unsafe fn new_1a(arg1: Direction) -> CppBox<QBoxLayout>[src]
Constructs a new QBoxLayout with direction dir and parent widget parent.
Calls C++ function: [constructor] void QBoxLayout::QBoxLayout(QBoxLayout::Direction arg1).
Constructs a new QBoxLayout with direction dir and parent widget parent.
See also direction().
pub unsafe fn qt_metacall(
&mut self,
arg1: Call,
arg2: c_int,
arg3: impl CastInto<MutPtr<*mut c_void>>
) -> c_int[src]
&mut self,
arg1: Call,
arg2: c_int,
arg3: impl CastInto<MutPtr<*mut c_void>>
) -> c_int
Calls C++ function: virtual int QBoxLayout::qt_metacall(QMetaObject::Call arg1, int arg2, void** arg3).
pub unsafe fn qt_metacast(
&mut self,
arg1: impl CastInto<Ptr<c_char>>
) -> MutPtr<c_void>[src]
&mut self,
arg1: impl CastInto<Ptr<c_char>>
) -> MutPtr<c_void>
Calls C++ function: virtual void* QBoxLayout::qt_metacast(const char* arg1).
pub unsafe fn set_direction(&mut self, arg1: Direction)[src]
Sets the direction of this layout to direction.
Calls C++ function: void QBoxLayout::setDirection(QBoxLayout::Direction arg1).
Sets the direction of this layout to direction.
See also direction().
pub unsafe fn set_geometry(&mut self, arg1: impl CastInto<Ref<QRect>>)[src]
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::setGeometry().
Calls C++ function: virtual void QBoxLayout::setGeometry(const QRect& arg1).
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::setGeometry().
pub unsafe fn set_spacing(&mut self, spacing: c_int)[src]
Reimplements QLayout::setSpacing(). Sets the spacing property to spacing.
Calls C++ function: void QBoxLayout::setSpacing(int spacing).
Reimplements QLayout::setSpacing(). Sets the spacing property to spacing.
See also QLayout::setSpacing() and spacing().
pub unsafe fn set_stretch(&mut self, index: c_int, stretch: c_int)[src]
Sets the stretch factor at position index. to stretch.
Calls C++ function: void QBoxLayout::setStretch(int index, int stretch).
Sets the stretch factor at position index. to stretch.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.5.
See also stretch().
pub unsafe fn set_stretch_factor_q_widget_int(
&mut self,
w: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>,
stretch: c_int
) -> bool[src]
&mut self,
w: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>,
stretch: c_int
) -> bool
Sets the stretch factor for widget to stretch and returns true if widget is found in this layout (not including child layouts); otherwise returns false.
Calls C++ function: bool QBoxLayout::setStretchFactor(QWidget* w, int stretch).
Sets the stretch factor for widget to stretch and returns true if widget is found in this layout (not including child layouts); otherwise returns false.
See also setAlignment().
pub unsafe fn set_stretch_factor_q_layout_int(
&mut self,
l: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QLayout>>,
stretch: c_int
) -> bool[src]
&mut self,
l: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QLayout>>,
stretch: c_int
) -> bool
This is an overloaded function.
Calls C++ function: bool QBoxLayout::setStretchFactor(QLayout* l, int stretch).
This is an overloaded function.
Sets the stretch factor for the layout layout to stretch and returns true if layout is found in this layout (not including child layouts); otherwise returns false.
pub unsafe fn size_hint(&self) -> CppBox<QSize>[src]
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::sizeHint().
Calls C++ function: virtual QSize QBoxLayout::sizeHint() const.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::sizeHint().
pub unsafe fn spacing(&self) -> c_int[src]
Reimplements QLayout::spacing(). If the spacing property is valid, that value is returned. Otherwise, a value for the spacing property is computed and returned. Since layout spacing in a widget is style dependent, if the parent is a widget, it queries the style for the (horizontal or vertical) spacing of the layout. Otherwise, the parent is a layout, and it queries the parent layout for the spacing().
Calls C++ function: int QBoxLayout::spacing() const.
Reimplements QLayout::spacing(). If the spacing property is valid, that value is returned. Otherwise, a value for the spacing property is computed and returned. Since layout spacing in a widget is style dependent, if the parent is a widget, it queries the style for the (horizontal or vertical) spacing of the layout. Otherwise, the parent is a layout, and it queries the parent layout for the spacing().
See also QLayout::spacing() and setSpacing().
pub unsafe fn static_meta_object() -> Ref<QMetaObject>[src]
Returns a reference to the staticMetaObject field.
pub unsafe fn stretch(&self, index: c_int) -> c_int[src]
Returns the stretch factor at position index.
Calls C++ function: int QBoxLayout::stretch(int index) const.
Returns the stretch factor at position index.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.5.
See also setStretch().
pub unsafe fn take_at(&mut self, arg1: c_int) -> MutPtr<QLayoutItem>[src]
Reimplemented from QLayout::takeAt().
Calls C++ function: virtual QLayoutItem* QBoxLayout::takeAt(int arg1).
Reimplemented from QLayout::takeAt().
pub unsafe fn tr(
s: impl CastInto<Ptr<c_char>>,
c: impl CastInto<Ptr<c_char>>,
n: c_int
) -> CppBox<QString>[src]
s: impl CastInto<Ptr<c_char>>,
c: impl CastInto<Ptr<c_char>>,
n: c_int
) -> CppBox<QString>
Calls C++ function: static QString QBoxLayout::tr(const char* s, const char* c, int n).
pub unsafe fn tr_utf8(
s: impl CastInto<Ptr<c_char>>,
c: impl CastInto<Ptr<c_char>>,
n: c_int
) -> CppBox<QString>[src]
s: impl CastInto<Ptr<c_char>>,
c: impl CastInto<Ptr<c_char>>,
n: c_int
) -> CppBox<QString>
Calls C++ function: static QString QBoxLayout::trUtf8(const char* s, const char* c, int n).
Methods from Deref<Target = QLayout>
pub unsafe fn activate(&mut self) -> bool[src]
Redoes the layout for parentWidget() if necessary.
Calls C++ function: bool QLayout::activate().
Redoes the layout for parentWidget() if necessary.
You should generally not need to call this because it is automatically called at the most appropriate times. It returns true if the layout was redone.
See also update() and QWidget::updateGeometry().
pub unsafe fn add_item(&mut self, arg1: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QLayoutItem>>)[src]
Implemented in subclasses to add an item. How it is added is specific to each subclass.
Calls C++ function: pure virtual void QLayout::addItem(QLayoutItem* arg1).
Implemented in subclasses to add an item. How it is added is specific to each subclass.
This function is not usually called in application code. To add a widget to a layout, use the addWidget() function; to add a child layout, use the addLayout() function provided by the relevant QLayout subclass.
Note: The ownership of item is transferred to the layout, and it's the layout's responsibility to delete it.
See also addWidget(), QBoxLayout::addLayout(), and QGridLayout::addLayout().
pub unsafe fn add_widget(&mut self, w: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>)[src]
Adds widget w to this layout in a manner specific to the layout. This function uses addItem().
Calls C++ function: void QLayout::addWidget(QWidget* w).
Adds widget w to this layout in a manner specific to the layout. This function uses addItem().
pub unsafe fn contents_margins(&self) -> CppBox<QMargins>[src]
Returns the margins used around the layout.
Calls C++ function: QMargins QLayout::contentsMargins() const.
Returns the margins used around the layout.
By default, QLayout uses the values provided by the style. On most platforms, the margin is 11 pixels in all directions.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.6.
See also setContentsMargins().
pub unsafe fn contents_rect(&self) -> CppBox<QRect>[src]
Returns the layout's geometry() rectangle, but taking into account the contents margins.
Calls C++ function: QRect QLayout::contentsRect() const.
Returns the layout's geometry() rectangle, but taking into account the contents margins.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.3.
See also setContentsMargins() and getContentsMargins().
pub unsafe fn control_types(&self) -> QFlags<ControlType>[src]
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::controlTypes().
Calls C++ function: virtual QFlags<QSizePolicy::ControlType> QLayout::controlTypes() const.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::controlTypes().
pub unsafe fn count(&self) -> c_int[src]
Must be implemented in subclasses to return the number of items in the layout.
Calls C++ function: pure virtual int QLayout::count() const.
Must be implemented in subclasses to return the number of items in the layout.
See also itemAt().
pub unsafe fn expanding_directions(&self) -> QFlags<Orientation>[src]
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::expandingDirections().
Calls C++ function: virtual QFlags<Qt::Orientation> QLayout::expandingDirections() const.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::expandingDirections().
Returns whether this layout can make use of more space than sizeHint(). A value of Qt::Vertical or Qt::Horizontal means that it wants to grow in only one dimension, whereas Qt::Vertical | Qt::Horizontal means that it wants to grow in both dimensions.
The default implementation returns Qt::Horizontal | Qt::Vertical. Subclasses reimplement it to return a meaningful value based on their child widgets's size policies.
See also sizeHint().
pub unsafe fn geometry(&self) -> CppBox<QRect>[src]
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::geometry().
Calls C++ function: virtual QRect QLayout::geometry() const.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::geometry().
See also setGeometry().
pub unsafe fn get_contents_margins(
&self,
left: impl CastInto<MutPtr<c_int>>,
top: impl CastInto<MutPtr<c_int>>,
right: impl CastInto<MutPtr<c_int>>,
bottom: impl CastInto<MutPtr<c_int>>
)[src]
&self,
left: impl CastInto<MutPtr<c_int>>,
top: impl CastInto<MutPtr<c_int>>,
right: impl CastInto<MutPtr<c_int>>,
bottom: impl CastInto<MutPtr<c_int>>
)
Extracts the left, top, right, and bottom margins used around the layout, and assigns them to *left, *top, *right, and *bottom (unless they are null pointers).
Calls C++ function: void QLayout::getContentsMargins(int* left, int* top, int* right, int* bottom) const.
Extracts the left, top, right, and bottom margins used around the layout, and assigns them to *left, *top, *right, and *bottom (unless they are null pointers).
By default, QLayout uses the values provided by the style. On most platforms, the margin is 11 pixels in all directions.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.3.
See also setContentsMargins(), QStyle::pixelMetric(), PM_LayoutLeftMargin, PM_LayoutTopMargin, PM_LayoutRightMargin, and PM_LayoutBottomMargin.
pub unsafe fn index_of_q_widget(
&self,
arg1: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>
) -> c_int[src]
&self,
arg1: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>
) -> c_int
Searches for widget widget in this layout (not including child layouts).
Calls C++ function: virtual int QLayout::indexOf(QWidget* arg1) const.
Searches for widget widget in this layout (not including child layouts).
Returns the index of widget, or -1 if widget is not found.
The default implementation iterates over all items using itemAt()
pub unsafe fn invalidate(&mut self)[src]
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::invalidate().
Calls C++ function: virtual void QLayout::invalidate().
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::invalidate().
pub unsafe fn is_empty(&self) -> bool[src]
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::isEmpty().
Calls C++ function: virtual bool QLayout::isEmpty() const.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::isEmpty().
pub unsafe fn is_enabled(&self) -> bool[src]
Returns true if the layout is enabled; otherwise returns false.
Calls C++ function: bool QLayout::isEnabled() const.
Returns true if the layout is enabled; otherwise returns false.
See also setEnabled().
pub unsafe fn item_at(&self, index: c_int) -> MutPtr<QLayoutItem>[src]
Must be implemented in subclasses to return the layout item at index. If there is no such item, the function must return 0. Items are numbered consecutively from 0. If an item is deleted, other items will be renumbered.
Calls C++ function: pure virtual QLayoutItem* QLayout::itemAt(int index) const.
Must be implemented in subclasses to return the layout item at index. If there is no such item, the function must return 0. Items are numbered consecutively from 0. If an item is deleted, other items will be renumbered.
This function can be used to iterate over a layout. The following code will draw a rectangle for each layout item in the layout structure of the widget.
static void paintLayout(QPainter painter, QLayoutItem item) { QLayout *layout = item->layout(); if (layout) { for (int i = 0; i < layout->count(); ++i) paintLayout(painter, layout->itemAt(i)); } painter->drawRect(item->geometry()); }
void MyWidget::paintEvent(QPaintEvent *) { QPainter painter(this); if (layout()) paintLayout(&painter, layout()); }
pub unsafe fn layout(&mut self) -> MutPtr<QLayout>[src]
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::layout().
Calls C++ function: virtual QLayout* QLayout::layout().
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::layout().
pub unsafe fn margin(&self) -> c_int[src]
This property holds the width of the outside border of the layout
Calls C++ function: int QLayout::margin() const.
This property holds the width of the outside border of the layout
Use setContentsMargins() and getContentsMargins() instead.
Access functions:
See also contentsRect() and spacing.
Member Function Documentation
pub unsafe fn maximum_size(&self) -> CppBox<QSize>[src]
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::maximumSize().
Calls C++ function: virtual QSize QLayout::maximumSize() const.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::maximumSize().
Returns the maximum size of this layout. This is the largest size that the layout can have while still respecting the specifications.
The returned value doesn't include the space required by QWidget::setContentsMargins() or menuBar().
The default implementation allows unlimited resizing.
pub unsafe fn menu_bar(&self) -> MutPtr<QWidget>[src]
Returns the menu bar set for this layout, or 0 if no menu bar is set.
Calls C++ function: QWidget* QLayout::menuBar() const.
Returns the menu bar set for this layout, or 0 if no menu bar is set.
See also setMenuBar().
pub unsafe fn meta_object(&self) -> Ptr<QMetaObject>[src]
Calls C++ function: virtual const QMetaObject* QLayout::metaObject() const.
pub unsafe fn minimum_size(&self) -> CppBox<QSize>[src]
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::minimumSize().
Calls C++ function: virtual QSize QLayout::minimumSize() const.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::minimumSize().
Returns the minimum size of this layout. This is the smallest size that the layout can have while still respecting the specifications.
The returned value doesn't include the space required by QWidget::setContentsMargins() or menuBar().
The default implementation allows unlimited resizing.
pub unsafe fn parent_widget(&self) -> MutPtr<QWidget>[src]
Returns the parent widget of this layout, or 0 if this layout is not installed on any widget.
Calls C++ function: QWidget* QLayout::parentWidget() const.
Returns the parent widget of this layout, or 0 if this layout is not installed on any widget.
If the layout is a sub-layout, this function returns the parent widget of the parent layout.
See also parent().
pub unsafe fn qt_metacall(
&mut self,
arg1: Call,
arg2: c_int,
arg3: impl CastInto<MutPtr<*mut c_void>>
) -> c_int[src]
&mut self,
arg1: Call,
arg2: c_int,
arg3: impl CastInto<MutPtr<*mut c_void>>
) -> c_int
Calls C++ function: virtual int QLayout::qt_metacall(QMetaObject::Call arg1, int arg2, void** arg3).
pub unsafe fn qt_metacast(
&mut self,
arg1: impl CastInto<Ptr<c_char>>
) -> MutPtr<c_void>[src]
&mut self,
arg1: impl CastInto<Ptr<c_char>>
) -> MutPtr<c_void>
Calls C++ function: virtual void* QLayout::qt_metacast(const char* arg1).
pub unsafe fn remove_item(&mut self, arg1: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QLayoutItem>>)[src]
Removes the layout item item from the layout. It is the caller's responsibility to delete the item.
Calls C++ function: void QLayout::removeItem(QLayoutItem* arg1).
Removes the layout item item from the layout. It is the caller's responsibility to delete the item.
Notice that item can be a layout (since QLayout inherits QLayoutItem).
See also removeWidget() and addItem().
pub unsafe fn remove_widget(&mut self, w: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>)[src]
Removes the widget widget from the layout. After this call, it is the caller's responsibility to give the widget a reasonable geometry or to put the widget back into a layout or to explicitly hide it if necessary.
Calls C++ function: void QLayout::removeWidget(QWidget* w).
Removes the widget widget from the layout. After this call, it is the caller's responsibility to give the widget a reasonable geometry or to put the widget back into a layout or to explicitly hide it if necessary.
Note: The ownership of widget remains the same as when it was added.
See also removeItem(), QWidget::setGeometry(), and addWidget().
pub unsafe fn replace_widget_3a(
&mut self,
from: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>,
to: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>,
options: QFlags<FindChildOption>
) -> MutPtr<QLayoutItem>[src]
&mut self,
from: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>,
to: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>,
options: QFlags<FindChildOption>
) -> MutPtr<QLayoutItem>
Searches for widget from and replaces it with widget to if found. Returns the layout item that contains the widget from on success. Otherwise 0 is returned. If options contains Qt::FindChildrenRecursively (the default), sub-layouts are searched for doing the replacement. Any other flag in options is ignored.
Calls C++ function: QLayoutItem* QLayout::replaceWidget(QWidget* from, QWidget* to, QFlags<Qt::FindChildOption> options = …).
Searches for widget from and replaces it with widget to if found. Returns the layout item that contains the widget from on success. Otherwise 0 is returned. If options contains Qt::FindChildrenRecursively (the default), sub-layouts are searched for doing the replacement. Any other flag in options is ignored.
Notice that the returned item therefore might not belong to this layout, but to a sub-layout.
The returned layout item is no longer owned by the layout and should be either deleted or inserted to another layout. The widget from is no longer managed by the layout and may need to be deleted or hidden. The parent of widget from is left unchanged.
This function works for the built-in Qt layouts, but might not work for custom layouts.
This function was introduced in Qt 5.2.
See also indexOf().
pub unsafe fn replace_widget_2a(
&mut self,
from: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>,
to: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>
) -> MutPtr<QLayoutItem>[src]
&mut self,
from: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>,
to: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>
) -> MutPtr<QLayoutItem>
Searches for widget from and replaces it with widget to if found. Returns the layout item that contains the widget from on success. Otherwise 0 is returned. If options contains Qt::FindChildrenRecursively (the default), sub-layouts are searched for doing the replacement. Any other flag in options is ignored.
Calls C++ function: QLayoutItem* QLayout::replaceWidget(QWidget* from, QWidget* to).
Searches for widget from and replaces it with widget to if found. Returns the layout item that contains the widget from on success. Otherwise 0 is returned. If options contains Qt::FindChildrenRecursively (the default), sub-layouts are searched for doing the replacement. Any other flag in options is ignored.
Notice that the returned item therefore might not belong to this layout, but to a sub-layout.
The returned layout item is no longer owned by the layout and should be either deleted or inserted to another layout. The widget from is no longer managed by the layout and may need to be deleted or hidden. The parent of widget from is left unchanged.
This function works for the built-in Qt layouts, but might not work for custom layouts.
This function was introduced in Qt 5.2.
See also indexOf().
pub unsafe fn set_alignment_q_widget_q_flags_alignment_flag(
&mut self,
w: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>,
alignment: QFlags<AlignmentFlag>
) -> bool[src]
&mut self,
w: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>,
alignment: QFlags<AlignmentFlag>
) -> bool
Sets the alignment for widget w to alignment and returns true if w is found in this layout (not including child layouts); otherwise returns false.
Calls C++ function: bool QLayout::setAlignment(QWidget* w, QFlags<Qt::AlignmentFlag> alignment).
Sets the alignment for widget w to alignment and returns true if w is found in this layout (not including child layouts); otherwise returns false.
pub unsafe fn set_alignment_q_layout_q_flags_alignment_flag(
&mut self,
l: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QLayout>>,
alignment: QFlags<AlignmentFlag>
) -> bool[src]
&mut self,
l: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QLayout>>,
alignment: QFlags<AlignmentFlag>
) -> bool
This is an overloaded function.
Calls C++ function: bool QLayout::setAlignment(QLayout* l, QFlags<Qt::AlignmentFlag> alignment).
This is an overloaded function.
Sets the alignment for the layout l to alignment and returns true if l is found in this layout (not including child layouts); otherwise returns false.
pub unsafe fn set_contents_margins_4a(
&mut self,
left: c_int,
top: c_int,
right: c_int,
bottom: c_int
)[src]
&mut self,
left: c_int,
top: c_int,
right: c_int,
bottom: c_int
)
Sets the left, top, right, and bottom margins to use around the layout.
Calls C++ function: void QLayout::setContentsMargins(int left, int top, int right, int bottom).
Sets the left, top, right, and bottom margins to use around the layout.
By default, QLayout uses the values provided by the style. On most platforms, the margin is 11 pixels in all directions.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.3.
See also contentsMargins(), getContentsMargins(), QStyle::pixelMetric(), PM_LayoutLeftMargin, PM_LayoutTopMargin, PM_LayoutRightMargin, and PM_LayoutBottomMargin.
pub unsafe fn set_contents_margins_1a(
&mut self,
margins: impl CastInto<Ref<QMargins>>
)[src]
&mut self,
margins: impl CastInto<Ref<QMargins>>
)
Sets the margins to use around the layout.
Calls C++ function: void QLayout::setContentsMargins(const QMargins& margins).
Sets the margins to use around the layout.
By default, QLayout uses the values provided by the style. On most platforms, the margin is 11 pixels in all directions.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.6.
See also contentsMargins().
pub unsafe fn set_enabled(&mut self, arg1: bool)[src]
Enables this layout if enable is true, otherwise disables it.
Calls C++ function: void QLayout::setEnabled(bool arg1).
Enables this layout if enable is true, otherwise disables it.
An enabled layout adjusts dynamically to changes; a disabled layout acts as if it did not exist.
By default all layouts are enabled.
See also isEnabled().
pub unsafe fn set_geometry(&mut self, arg1: impl CastInto<Ref<QRect>>)[src]
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::setGeometry().
Calls C++ function: virtual void QLayout::setGeometry(const QRect& arg1).
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::setGeometry().
See also geometry().
pub unsafe fn set_margin(&mut self, arg1: c_int)[src]
Note: Setter function for property margin.
Calls C++ function: void QLayout::setMargin(int arg1).
pub unsafe fn set_menu_bar(&mut self, w: impl CastInto<MutPtr<QWidget>>)[src]
Tells the geometry manager to place the menu bar widget at the top of parentWidget(), outside QWidget::contentsMargins(). All child widgets are placed below the bottom edge of the menu bar.
Calls C++ function: void QLayout::setMenuBar(QWidget* w).
Tells the geometry manager to place the menu bar widget at the top of parentWidget(), outside QWidget::contentsMargins(). All child widgets are placed below the bottom edge of the menu bar.
See also menuBar().
pub unsafe fn set_size_constraint(&mut self, arg1: SizeConstraint)[src]
This property holds the resize mode of the layout
Calls C++ function: void QLayout::setSizeConstraint(QLayout::SizeConstraint arg1).
This property holds the resize mode of the layout
The default mode is SetDefaultConstraint.
Access functions:
| SizeConstraint | sizeConstraint() const |
| void | setSizeConstraint(SizeConstraint) |
pub unsafe fn set_spacing(&mut self, arg1: c_int)[src]
This property holds the spacing between widgets inside the layout
Calls C++ function: void QLayout::setSpacing(int arg1).
This property holds the spacing between widgets inside the layout
If no value is explicitly set, the layout's spacing is inherited from the parent layout, or from the style settings for the parent widget.
For QGridLayout and QFormLayout, it is possible to set different horizontal and vertical spacings using setHorizontalSpacing() and setVerticalSpacing(). In that case, spacing() returns -1.
Access functions:
| int | spacing() const |
| void | setSpacing(int) |
See also contentsRect(), getContentsMargins(), QStyle::layoutSpacing(), and QStyle::pixelMetric().
pub unsafe fn size_constraint(&self) -> SizeConstraint[src]
This property holds the resize mode of the layout
Calls C++ function: QLayout::SizeConstraint QLayout::sizeConstraint() const.
This property holds the resize mode of the layout
The default mode is SetDefaultConstraint.
Access functions:
| SizeConstraint | sizeConstraint() const |
| void | setSizeConstraint(SizeConstraint) |
pub unsafe fn spacing(&self) -> c_int[src]
This property holds the spacing between widgets inside the layout
Calls C++ function: int QLayout::spacing() const.
This property holds the spacing between widgets inside the layout
If no value is explicitly set, the layout's spacing is inherited from the parent layout, or from the style settings for the parent widget.
For QGridLayout and QFormLayout, it is possible to set different horizontal and vertical spacings using setHorizontalSpacing() and setVerticalSpacing(). In that case, spacing() returns -1.
Access functions:
| int | spacing() const |
| void | setSpacing(int) |
See also contentsRect(), getContentsMargins(), QStyle::layoutSpacing(), and QStyle::pixelMetric().
pub unsafe fn take_at(&mut self, index: c_int) -> MutPtr<QLayoutItem>[src]
Must be implemented in subclasses to remove the layout item at index from the layout, and return the item. If there is no such item, the function must do nothing and return 0. Items are numbered consecutively from 0. If an item is removed, other items will be renumbered.
Calls C++ function: pure virtual QLayoutItem* QLayout::takeAt(int index).
Must be implemented in subclasses to remove the layout item at index from the layout, and return the item. If there is no such item, the function must do nothing and return 0. Items are numbered consecutively from 0. If an item is removed, other items will be renumbered.
The following code fragment shows a safe way to remove all items from a layout:
QLayoutItem *child; while ((child = layout->takeAt(0)) != 0) { ... delete child; }
pub unsafe fn total_height_for_width(&self, w: c_int) -> c_int[src]
Calls C++ function: int QLayout::totalHeightForWidth(int w) const.
pub unsafe fn total_maximum_size(&self) -> CppBox<QSize>[src]
Calls C++ function: QSize QLayout::totalMaximumSize() const.
pub unsafe fn total_minimum_size(&self) -> CppBox<QSize>[src]
Calls C++ function: QSize QLayout::totalMinimumSize() const.
pub unsafe fn total_size_hint(&self) -> CppBox<QSize>[src]
Calls C++ function: QSize QLayout::totalSizeHint() const.
pub unsafe fn update(&mut self)[src]
Updates the layout for parentWidget().
Calls C++ function: void QLayout::update().
Updates the layout for parentWidget().
You should generally not need to call this because it is automatically called at the most appropriate times.
See also activate() and invalidate().
Trait Implementations
impl Deref for QBoxLayout[src]
type Target = QLayout
The resulting type after dereferencing.
fn deref(&self) -> &QLayout[src]
Calls C++ function: QLayout* static_cast<QLayout*>(QBoxLayout* ptr).
impl DerefMut for QBoxLayout[src]
fn deref_mut(&mut self) -> &mut QLayout[src]
Calls C++ function: QLayout* static_cast<QLayout*>(QBoxLayout* ptr).
impl StaticUpcast<QLayout> for QBoxLayout[src]
unsafe fn static_upcast(ptr: Ptr<QBoxLayout>) -> Ptr<QLayout>[src]
Calls C++ function: QLayout* static_cast<QLayout*>(QBoxLayout* ptr).
unsafe fn static_upcast_mut(ptr: MutPtr<QBoxLayout>) -> MutPtr<QLayout>[src]
Calls C++ function: QLayout* static_cast<QLayout*>(QBoxLayout* ptr).
impl StaticUpcast<QObject> for QBoxLayout[src]
unsafe fn static_upcast(ptr: Ptr<QBoxLayout>) -> Ptr<QObject>[src]
Calls C++ function: QObject* static_cast<QObject*>(QBoxLayout* ptr).
unsafe fn static_upcast_mut(ptr: MutPtr<QBoxLayout>) -> MutPtr<QObject>[src]
Calls C++ function: QObject* static_cast<QObject*>(QBoxLayout* ptr).
impl StaticUpcast<QLayoutItem> for QBoxLayout[src]
unsafe fn static_upcast(ptr: Ptr<QBoxLayout>) -> Ptr<QLayoutItem>[src]
Calls C++ function: QLayoutItem* static_cast<QLayoutItem*>(QBoxLayout* ptr).
unsafe fn static_upcast_mut(ptr: MutPtr<QBoxLayout>) -> MutPtr<QLayoutItem>[src]
Calls C++ function: QLayoutItem* static_cast<QLayoutItem*>(QBoxLayout* ptr).
impl StaticUpcast<QBoxLayout> for QHBoxLayout[src]
unsafe fn static_upcast(ptr: Ptr<QHBoxLayout>) -> Ptr<QBoxLayout>[src]
Calls C++ function: QBoxLayout* static_cast<QBoxLayout*>(QHBoxLayout* ptr).
unsafe fn static_upcast_mut(ptr: MutPtr<QHBoxLayout>) -> MutPtr<QBoxLayout>[src]
Calls C++ function: QBoxLayout* static_cast<QBoxLayout*>(QHBoxLayout* ptr).
impl StaticUpcast<QBoxLayout> for QVBoxLayout[src]
unsafe fn static_upcast(ptr: Ptr<QVBoxLayout>) -> Ptr<QBoxLayout>[src]
Calls C++ function: QBoxLayout* static_cast<QBoxLayout*>(QVBoxLayout* ptr).
unsafe fn static_upcast_mut(ptr: MutPtr<QVBoxLayout>) -> MutPtr<QBoxLayout>[src]
Calls C++ function: QBoxLayout* static_cast<QBoxLayout*>(QVBoxLayout* ptr).
impl StaticDowncast<QBoxLayout> for QLayout[src]
unsafe fn static_downcast(ptr: Ptr<QLayout>) -> Ptr<QBoxLayout>[src]
Calls C++ function: QBoxLayout* static_cast<QBoxLayout*>(QLayout* ptr).
unsafe fn static_downcast_mut(ptr: MutPtr<QLayout>) -> MutPtr<QBoxLayout>[src]
Calls C++ function: QBoxLayout* static_cast<QBoxLayout*>(QLayout* ptr).
impl StaticDowncast<QBoxLayout> for QObject[src]
unsafe fn static_downcast(ptr: Ptr<QObject>) -> Ptr<QBoxLayout>[src]
Calls C++ function: QBoxLayout* static_cast<QBoxLayout*>(QObject* ptr).
unsafe fn static_downcast_mut(ptr: MutPtr<QObject>) -> MutPtr<QBoxLayout>[src]
Calls C++ function: QBoxLayout* static_cast<QBoxLayout*>(QObject* ptr).
impl StaticDowncast<QBoxLayout> for QLayoutItem[src]
unsafe fn static_downcast(ptr: Ptr<QLayoutItem>) -> Ptr<QBoxLayout>[src]
Calls C++ function: QBoxLayout* static_cast<QBoxLayout*>(QLayoutItem* ptr).
unsafe fn static_downcast_mut(ptr: MutPtr<QLayoutItem>) -> MutPtr<QBoxLayout>[src]
Calls C++ function: QBoxLayout* static_cast<QBoxLayout*>(QLayoutItem* ptr).
impl StaticDowncast<QHBoxLayout> for QBoxLayout[src]
unsafe fn static_downcast(ptr: Ptr<QBoxLayout>) -> Ptr<QHBoxLayout>[src]
Calls C++ function: QHBoxLayout* static_cast<QHBoxLayout*>(QBoxLayout* ptr).
unsafe fn static_downcast_mut(ptr: MutPtr<QBoxLayout>) -> MutPtr<QHBoxLayout>[src]
Calls C++ function: QHBoxLayout* static_cast<QHBoxLayout*>(QBoxLayout* ptr).
impl StaticDowncast<QVBoxLayout> for QBoxLayout[src]
unsafe fn static_downcast(ptr: Ptr<QBoxLayout>) -> Ptr<QVBoxLayout>[src]
Calls C++ function: QVBoxLayout* static_cast<QVBoxLayout*>(QBoxLayout* ptr).
unsafe fn static_downcast_mut(ptr: MutPtr<QBoxLayout>) -> MutPtr<QVBoxLayout>[src]
Calls C++ function: QVBoxLayout* static_cast<QVBoxLayout*>(QBoxLayout* ptr).
impl DynamicCast<QBoxLayout> for QLayout[src]
unsafe fn dynamic_cast(ptr: Ptr<QLayout>) -> Ptr<QBoxLayout>[src]
Calls C++ function: QBoxLayout* dynamic_cast<QBoxLayout*>(QLayout* ptr).
unsafe fn dynamic_cast_mut(ptr: MutPtr<QLayout>) -> MutPtr<QBoxLayout>[src]
Calls C++ function: QBoxLayout* dynamic_cast<QBoxLayout*>(QLayout* ptr).
impl DynamicCast<QBoxLayout> for QObject[src]
unsafe fn dynamic_cast(ptr: Ptr<QObject>) -> Ptr<QBoxLayout>[src]
Calls C++ function: QBoxLayout* dynamic_cast<QBoxLayout*>(QObject* ptr).
unsafe fn dynamic_cast_mut(ptr: MutPtr<QObject>) -> MutPtr<QBoxLayout>[src]
Calls C++ function: QBoxLayout* dynamic_cast<QBoxLayout*>(QObject* ptr).
impl DynamicCast<QBoxLayout> for QLayoutItem[src]
unsafe fn dynamic_cast(ptr: Ptr<QLayoutItem>) -> Ptr<QBoxLayout>[src]
Calls C++ function: QBoxLayout* dynamic_cast<QBoxLayout*>(QLayoutItem* ptr).
unsafe fn dynamic_cast_mut(ptr: MutPtr<QLayoutItem>) -> MutPtr<QBoxLayout>[src]
Calls C++ function: QBoxLayout* dynamic_cast<QBoxLayout*>(QLayoutItem* ptr).
impl DynamicCast<QHBoxLayout> for QBoxLayout[src]
unsafe fn dynamic_cast(ptr: Ptr<QBoxLayout>) -> Ptr<QHBoxLayout>[src]
Calls C++ function: QHBoxLayout* dynamic_cast<QHBoxLayout*>(QBoxLayout* ptr).
unsafe fn dynamic_cast_mut(ptr: MutPtr<QBoxLayout>) -> MutPtr<QHBoxLayout>[src]
Calls C++ function: QHBoxLayout* dynamic_cast<QHBoxLayout*>(QBoxLayout* ptr).
impl DynamicCast<QVBoxLayout> for QBoxLayout[src]
unsafe fn dynamic_cast(ptr: Ptr<QBoxLayout>) -> Ptr<QVBoxLayout>[src]
Calls C++ function: QVBoxLayout* dynamic_cast<QVBoxLayout*>(QBoxLayout* ptr).
unsafe fn dynamic_cast_mut(ptr: MutPtr<QBoxLayout>) -> MutPtr<QVBoxLayout>[src]
Calls C++ function: QVBoxLayout* dynamic_cast<QVBoxLayout*>(QBoxLayout* ptr).
impl CppDeletable for QBoxLayout[src]
Auto Trait Implementations
impl Send for QBoxLayout
impl Sync for QBoxLayout
impl Unpin for QBoxLayout
impl RefUnwindSafe for QBoxLayout
impl UnwindSafe for QBoxLayout
Blanket Implementations
impl<T> From<T> for T[src]
impl<T, U> Into<U> for T where
U: From<T>, [src]
U: From<T>,
impl<T, U> TryFrom<U> for T where
U: Into<T>, [src]
U: Into<T>,
type Error = Infallible
The type returned in the event of a conversion error.
fn try_from(value: U) -> Result<T, <T as TryFrom<U>>::Error>[src]
impl<T, U> TryInto<U> for T where
U: TryFrom<T>, [src]
U: TryFrom<T>,
type Error = <U as TryFrom<T>>::Error
The type returned in the event of a conversion error.
fn try_into(self) -> Result<U, <U as TryFrom<T>>::Error>[src]
impl<T> BorrowMut<T> for T where
T: ?Sized, [src]
T: ?Sized,
fn borrow_mut(&mut self) -> &mut T[src]
impl<T> Borrow<T> for T where
T: ?Sized, [src]
T: ?Sized,
impl<T> Any for T where
T: 'static + ?Sized, [src]
T: 'static + ?Sized,
impl<T> StaticUpcast<T> for T[src]
unsafe fn static_upcast(ptr: Ptr<T>) -> Ptr<T>[src]
unsafe fn static_upcast_mut(ptr: MutPtr<T>) -> MutPtr<T>[src]
impl<T, U> CastInto<U> for T where
U: CastFrom<T>, [src]
U: CastFrom<T>,