pub struct Key<T = f64>where
T: Real,{Show 19 fields
pub legends: [Option<Legend>; 12],
pub color: Color,
pub x: T,
pub y: T,
pub width: T,
pub height: T,
pub x2: T,
pub y2: T,
pub width2: T,
pub height2: T,
pub rotation: T,
pub rx: T,
pub ry: T,
pub profile: String,
pub switch: Switch,
pub ghosted: bool,
pub stepped: bool,
pub homing: bool,
pub decal: bool,
}Expand description
A struct representing a single key.
Fields§
§legends: [Option<Legend>; 12]The key’s legends. This array is indexed in left to right, top to bottom order as shown in the image below.
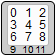
Legends that are empty in KLE will be deserialised as None.
color: ColorThe colour of the key
x: TThe X position of the key measured in keyboard units (typically 19.05 mm or 0.75 in).
KLE has some strange behaviour when it comes to positioning stepped and L-shaped keys.
The ‘true’ X position of the top left corner will be less if the key’s x2 field is
negative.
The actual position of the top left corner can be found using:
let x = key.x.min(key.x + key.x2);This behaviour can be observed by placing an ISO enter in the top left corner in KLE;
x is 0.25 and x2 is −0.25.
y: TThe Y position of the key measured in keyboard units (typically 19.05 mm or 0.75 in).
KLE has some strange behaviour when it comes to positioning stepped and L-shaped keys.
The ‘true’ Y position of the top left corner will be less if the key’s y2 field is
negative.
The actual position of the top left corner can be found using:
let y = key.y.min(key.y + key.y2);This behaviour can be observed by placing an ISO enter in the top left corner in KLE;
x is 0.25 and x2 is −0.25.
width: TThe width of the key measured in keyboard units (typically 19.05 mm or 0.75 in).
height: TThe height of the key measured in keyboard units (typically 19.05 mm or 0.75 in).
x2: TThe relative X position of a stepped or L-shaped part of the key. Measured in keyboard units (typically 19.05 mm or 0.75 in).
This is set to 0.0 for regular keys, but is used for stepped caps lock and ISO enter keys,
amongst others.
y2: TThe relative Y position of a stepped or L-shaped part of the key. Measured in keyboard units (typically 19.05 mm or 0.75 in).
This is set to 0.0 for regular keys, but is used for stepped caps lock and ISO enter keys,
amongst others.
width2: TThe width of a stepped or L-shaped part of the key. Measured in keyboard units (typically 19.05 mm or 0.75 in).
This is equal to width for regular keys, but is used for stepped caps lock and ISO
enter keys, amongst others.
height2: TThe height of a stepped or L-shaped part of the key. Measured in keyboard units (typically 19.05 mm or 0.75 in).
This is equal to height for regular keys, but is used for stepped caps lock and ISO
enter keys, amongst others.
rotation: TThe rotation of the key in degrees. Positive rotation values are clockwise.
rx: TThe X coordinate for the centre of rotation of the key. Measured in keyboard units (typically 19.05 mm or 0.75 in) from the top left corner of the layout.
ry: TThe Y coordinate for the centre of rotation of the key. Measured in keyboard units (typically 19.05 mm or 0.75 in) from the top left corner of the layout.
profile: StringThe keycap profile and row number of the key.
KLE uses special rendering for "SA", "DSA", "DCS", "OEM", "CHICKLET", and "FLAT"
profiles. It expects the row number to be one of "R1", "R2", "R3", "R4", "R5", or
"SPACE", although it only uses special rendering for "SPACE".
KLE suggests the format "<profile> [<row>]", but it will recognise any string containing
one of its supported profiles and/or rows. Any value is considered valid, but empty or
unrecognised values are rendered using the unnamed default profile.
switch: SwitchThe key switch.
ghosted: boolWhether the key is ghosted.
stepped: boolWhether the key is stepped.
homing: boolWhether this is a homing key.
decal: boolWhether this is a decal.