# ztensor
[](https://crates.io/crates/ztensor)
[](https://docs.rs/ztensor)
[](https://pypi.org/project/ztensor/)
[](https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
Simple tensor serialization format
## Key Features
- **Simple Spec** — Minimalist [spec](SPEC.md) for easy parsing.
- **Zero-Copy Access** — Instant memory-mapping (mmap) with no extra RAM copying overhead.
- **Efficient Writes** — Supports streaming and append-only operations without rewriting files.
- **Future-Proof** — Decouples physical storage from logical representation for long-term compatibility.
## Tools
- **Rust Core** — High-performance, SIMD-aligned implementation.
- **Python API** — First-class bindings for **NumPy** and **PyTorch**.
- **Universal Converters** — CLI tools to easily convert **Pickle**, **SafeTensors**, and **GGUF** files.
## Comparison
| **Zero-Copy Read** | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ⚠️ |
| **Safe (No Exec)** | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
| **Streaming / Append** | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| **Sparse Tensors** | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| **Compression** | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| **Quantization** | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| **Parser Complexity** | 🟢 Low | 🟢 Low | 🟡 Med | 🔴 High | 🔴 High |
## Benchmark
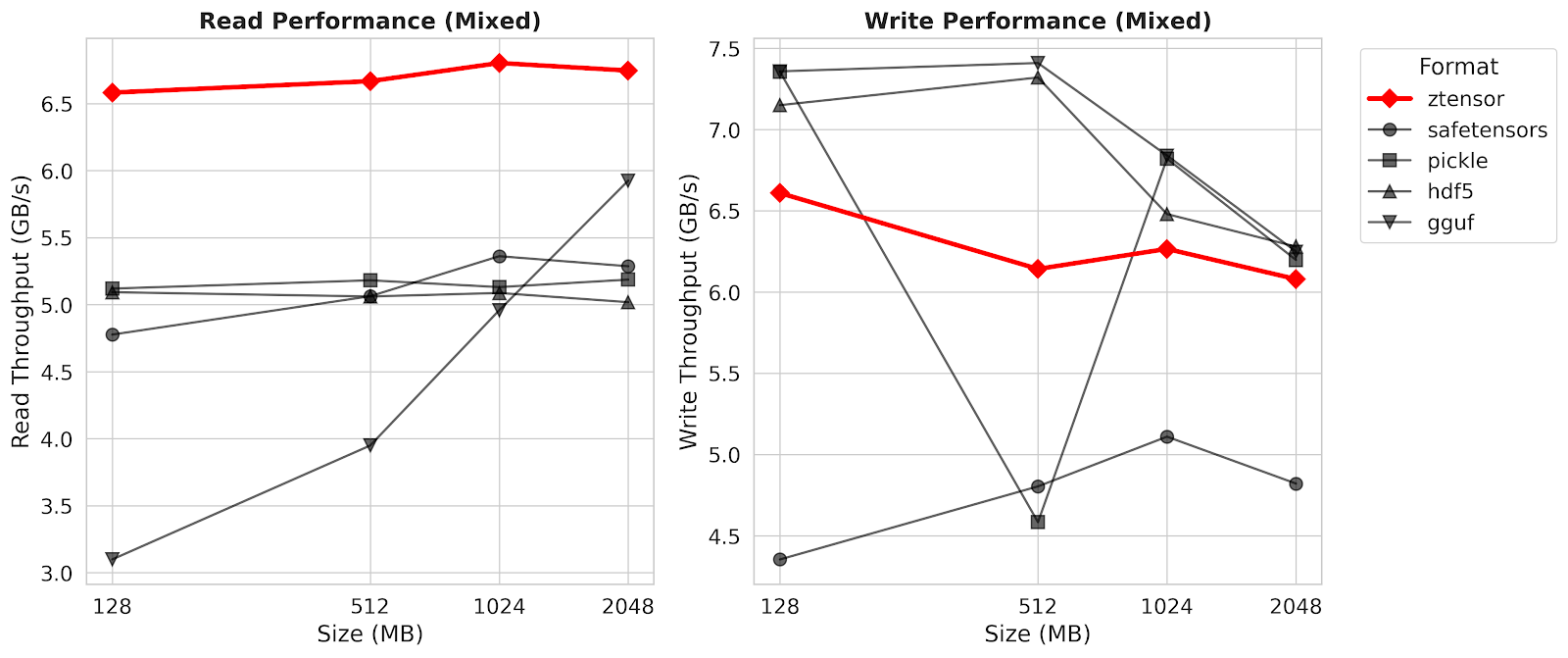
See [benchmark](benchmark/bench.py) for more details.
## Installation
### Python
```bash
pip install ztensor
```
### Rust
```toml
[dependencies]
ztensor = "0.1"
```
### CLI
```bash
cargo install ztensor-cli
```
## Quick Start: Python
### Basic Usage with NumPy
```python
import numpy as np
from ztensor import Writer, Reader
# Write tensors
with Writer("model.zt") as w:
w.add_tensor("weights", np.random.randn(1024, 768).astype(np.float32))
w.add_tensor("bias", np.zeros(768, dtype=np.float32))
# Read tensors (zero-copy where possible)
with Reader("model.zt") as r:
# Returns a numpy-like view
weights = r.read_tensor("weights")
print(f"Weights shape: {weights.shape}, dtype: {weights.dtype}")
```
### PyTorch Integration
```python
import torch
from ztensor import Writer, Reader
# Write PyTorch tensors directly
t = torch.randn(10, 10)
with Writer("torch_model.zt") as w:
w.add_tensor("embedding", t)
# Read back as PyTorch tensors
with Reader("torch_model.zt") as r:
# 'to="torch"' returns a torch.Tensor sharing memory with the file (if mmap)
embedding = r.read_tensor("embedding", to="torch")
print(embedding.size())
```
### Sparse Tensors
Supports **CSR** (Compressed Sparse Row) and **COO** (Coordinate) formats.
```python
import scipy.sparse
from ztensor import Writer, Reader
csr = scipy.sparse.csr_matrix([[1, 0], [0, 2]], dtype=np.float32)
with Writer("sparse.zt") as w:
# Add CSR tensor
w.add_sparse_csr("my_csr", csr.data, csr.indices, csr.indptr, csr.shape)
with Reader("sparse.zt") as r:
# Read back as scipy.sparse.csr_matrix
matrix = r.read_tensor("my_csr", to="numpy")
```
### Compression
Use Zstandard (zstd) compression to reduce file size.
```python
with Writer("compressed.zt") as w:
w.add_tensor("big_data", data, compress=True)
```
## Quick Start: Rust
### Basic Usage
```rust
use ztensor::{ZTensorWriter, ZTensorReader, DType, Compression, ChecksumAlgorithm};
// Write
let mut writer = ZTensorWriter::create("model.zt")?;
// Zero-copy generic write with generic Compression
writer.add_object("weights", vec![1024, 768], DType::F32,
Compression::Raw, &data_vec, ChecksumAlgorithm::None)?;
writer.finalize()?;
// Read
let mut reader = ZTensorReader::open("model.zt")?;
// Read as specific type (automatically handles endianness)
let weights: Vec<f32> = reader.read_object_as("weights")?;
```
### Sparse Tensors
```rust
// Write CSR (using generic method)
writer.add_csr_object(
"sparse_data",
vec![100, 100], // shape
DType::F32,
&values, // &[f32]
&indices, // &[u64]
&indptr, // &[u64]
Compression::Raw,
ChecksumAlgorithm::None
)?;
// Read CSR
let csr = reader.read_csr_object::<f32>("sparse_data")?;
println!("Values: {:?}", csr.values);
```
### Compression
```rust
// Write with compression (level 3)
writer.add_object(
"compressed_data",
vec![512, 512],
DType::F32,
Compression::Zstd(3), // Use zstd encoding with level 3
&data, // &[f32]
ChecksumAlgorithm::Crc32c // Optional checksum
)?;
// Read (auto-decompresses)
let data: Vec<f32> = reader.read_object_as("compressed_data")?;
```
## CLI
The `ztensor` CLI tool allows you to inspect and manipulate zTensor files.
### Inspect Metadata
Print tensor names, shapes, and properties.
```bash
ztensor info model.zt
```
### Convert Other Formats
Convert SafeTensors, GGUF, or Pickle files to zTensor.
```bash
# Auto-detect format from extension
ztensor convert model.safetensors -o model.zt
# Explicit format with compression (default level 3)
ztensor convert -f gguf -c llama.gguf -o llama.zt
# Specify compression level (1-22)
ztensor convert model.safetensors -o model.zt -l 10
# Delete originals after conversion
ztensor convert --delete-original *.safetensors -o model.zt
```
### Compression Tools
```bash
# Compress an existing raw file (default level 3)
ztensor compress raw.zt -o compressed.zt
# Compress with specific level (1-22)
ztensor compress raw.zt -o highly_compressed.zt -l 19
# Decompress a file
ztensor decompress compressed.zt -o raw.zt
```
### File Management
```bash
# Merge multiple files into one
ztensor merge part1.zt part2.zt -o merged.zt
# Migrate legacy v0.1.0 files to v1.1.0
ztensor migrate old_model.zt -o new_model.zt
```
### Download from HuggingFace
Download safetensors from HuggingFace and convert to zTensor:
```bash
ztensor download-hf microsoft/resnet-18 -o ./models
ztensor download-hf openai-community/gpt2 -o ./models --compress
```
## Supported Data Types
| `float32`, `float16`, `bfloat16`, `float64` | Floating point |
| `int8`, `int16`, `int32`, `int64` | Signed integers |
| `uint8`, `uint16`, `uint32`, `uint64` | Unsigned integers |
| `bool` | Boolean |
## File Format
See [SPEC.md](SPEC.md) for the complete specification.
## License
MIT