# vscli
[](https://choosealicense.com/licenses/mit/) [](https://github.com/michidk/vscli/actions/workflows/ci.yml)
A CLI/TUI which makes it easy to launch [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/) (vscode) [dev containers](https://containers.dev/). Also supports other editors like [Cursor](https://www.cursor.com/).
Read [here](https://blog.lohr.dev/launching-dev-containers) about the journey of reverse engineering Microsoft's dev container CLI in order to make this.
## Features
- A shorthand for launching vscode projects (to be used like the `code` command but with dev container support)
- Supports different editors like `vscode`, `vscode-insiders`, `cursor` and other vscode forks
- Detects whether a project is a [dev container](https://containers.dev/) project, and launches the dev container instead
- Supports [multiple dev containers](https://github.com/microsoft/vscode-docs/blob/main/remote-release-notes/v1_75.md#folders-with-multiple-devcontainerjson-files) in the same project
- Tracks your projects and allows you to open them using a CLI-based UI
## Installation
[](https://repology.org/project/vscli/versions)
[](https://github.com/michidk/homebrew-tools/blob/main/Formula/vscli.rb)
### [Cargo](https://doc.rust-lang.org/cargo/)
Install [vscli using cargo](https://crates.io/crates/vscli) on Windows or Linux:
```sh
cargo install vscli
```
### [Homebrew](https://brew.sh/)
Install [vscli using homebrew](https://github.com/michidk/homebrew-tools/blob/main/Formula/vscli.rb) on Linux or Mac:
```sh
brew install michidk/tools/vscli
```
### [Chocolatey](https://chocolatey.org/)
Install [vscli using Chocolatey](https://community.chocolatey.org/packages/vscli) on Windows:
```sh
choco install vscli
```
### [Winget](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/package-manager/winget/)
Install [vscli using winget](https://github.com/microsoft/winget-pkgs/tree/master/manifests/m/michidk/vscli) on Windows:
```sh
winget install vscli
```
### Additional steps
You can set a shorthand alias for `vscli` in your shell's configuration file:
```sh
alias vs="vscli open"
alias vsr="vscli recent"
```
## Usage
### Commands
After installation, the `vscli` command will be available:
```
Usage: vscli [OPTIONS] <COMMAND>
Commands:
open Opens a dev container
recent Opens an interactive list of recently used workspaces
help Print this message or the help of the given subcommand(s)
Options:
-s, --history-path <HISTORY_PATH> Overwrite the default path to the history file [env: HISTORY_PATH=]
-d, --dry-run Whether to launch in dry-run mode (not actually open vscode) [env: DRY_RUN=]
-v, --verbose... Increase logging verbosity
-q, --quiet... Decrease logging verbosity
-h, --help Print help
-V, --version Print version
```
#### Open Dev Containers
Opens a dev container.
```
Usage: vscli open [OPTIONS] [PATH] [ARGS]...
Arguments:
[PATH] The path of the vscode project to open [default: .]
[ARGS]... Additional arguments to pass to the editor [env: ARGS=]
Options:
-c, --command <COMMAND> The editor command to use (e.g. "code", "code-insiders", "cursor") [env: COMMAND=]
-s, --history-path <HISTORY_PATH> Overwrite the default path to the history file [env: HISTORY_PATH=]
-b, --behavior <BEHAVIOR> Launch behavior [possible values: detect, force-container, force-classic]
-d, --dry-run Whether to launch in dry-run mode (not actually open vscode) [env: DRY_RUN=]
--config <CONFIG> Overwrites the path to the dev container config file [env: CONFIG=]
-v, --verbose... Increase logging verbosity
-q, --quiet... Decrease logging verbosity
-h, --help Print help (see more with '--help')
```
#### Recent UI
Opens an interactive list of recently used workspaces.
```
Usage: vscli recent [OPTIONS] [ARGS]...
Arguments:
[ARGS]... Additional arguments to pass to the editor [env: ARGS=]
Options:
--hide-instructions Hide the instruction message in the UI
-s, --history-path <HISTORY_PATH> Overwrite the default path to the history file [env: HISTORY_PATH=]
-d, --dry-run Whether to launch in dry-run mode (not actually open vscode) [env: DRY_RUN=]
--hide-info Hide additional information like strategy, command, args and dev container path in the UI
-c, --command <COMMAND> The editor command to use (e.g. "code", "code-insiders", "cursor") [env: COMMAND=]
-v, --verbose... Increase logging verbosity
-b, --behavior <BEHAVIOR> Launch behavior [possible values: detect, force-container, force-classic]
-q, --quiet... Decrease logging verbosity
--config <CONFIG> Overwrites the path to the dev container config file [env: CONFIG=]
-h, --help Print help (see more with '--help')
```
Both the `open` and `recent` commands share the same set of launch arguments:
- `--command`: Specify which editor command to use (e.g., "code", "code-insiders", "cursor")
- `--behavior`: Set the launch behavior ("detect", "force-container", "force-classic")
- `--config`: Override the path to the dev container config file
- Additional arguments can be passed to the editor executable by specifying them after `--`
The `recent` command additionally supports:
- `--hide-instructions`: Hide the keybinding instructions from the UI
- `--hide-info`: Hide additional information like strategy, command, args and dev container path
##### Keybindings
| `Esc`, `Ctrl+Q` or `Ctrl+C` | Quit | Exits the application. |
| `Down` or `Ctrl+J` | Select Next | Moves to the next selectable item. |
| `Up` or `Ctrl+K` | Select Previous | Moves to the previous selectable item. |
| `KeypadBegin` or `Ctrl+1` | Select First | Selects the first item. |
| `End` or `Ctrl+0` | Select Last | Selects the last item. |
| `Enter` or `Ctrl+O` | Open Selected | Opens the currently selected item. |
| `Delete`, `Ctrl+R`, or `Ctrl+X` | Delete Selected Entry | Deletes the currently selected item. |
Note: If an input does not match any of the defined keybindings, it is treated as part of a search input.
##### Mouse Interactions
| Left Click | Selects an item. Clicking the same item again opens it. |
| Mouse Wheel | Scrolls through the list, moving selection up/down. |
##### Launch Behavior
There are three launch behaviors:
- `force-classic`: Launch vscode without a dev container
- `force-container`: Launch vscode with a dev container, error if no dev container is found
- `detect`: Detect whether the project is a dev container project, and launch the dev container if it is
##### Detection Algorithm
The detection algorithm determines which dev container config to launch.
- First, check whether a dev container config was specified via the `--config` flag -> launch it
- Then loads the first dev container it finds
- If more than one exists -> show a interactive list of dev containers and let the user select one
- If one exists -> launch it
- If none exists -> launch vscode normally without a dev container
### Examples
#### Launching a project
You can launch a project using the default behavior:
```sh
vscli open # open vscode in the current directory
vscli open . # open vscode in the current directory
vscli open /path/to/project # open vscode in the specified directory
```
The default behavior tries to detect whether the project is a [dev container](https://containers.dev/) project. If it is, it will launch the dev container instead - if not it will launch vscode normally.
You can change the launch behavior using the `--behavior` flag:
```sh
vscli open --behavior force-container . # force open vscode dev container (even if vscli did not detect a dev container)
vscli open --behavior force-classic . # force open vscode without a dev container (even if vscli did detect a dev container)
```
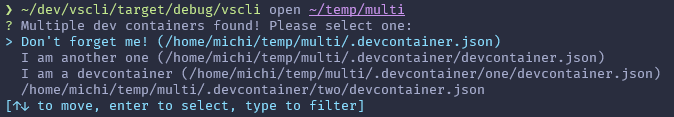
When you open a project containing more than one dev container config, you will be prompted to select one:
You can specify which editor command to use with the `--command` flag:
```sh
vscli open --command cursor . # open using cursor editor
vscli open --command code . # open using vscode (default)
vscli open --command code-insiders . # open using vscode insiders
```
Additional arguments can be passed to the editor executable, by specifying them after `--`:
```sh
vscli open . -- --disable-gpu # open the current directory without GPU hardware acceleration
```
Read more about the editor flags by executing `code --help` (or `cursor --help`, etc).
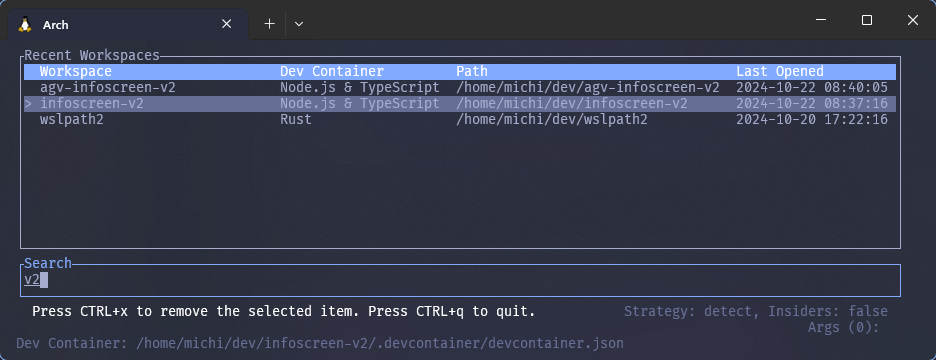
#### CLI UI
You can open a CLI-based user interface to display a list of recently opened projects using the `recent` command:
```sh
vscli recent # open the CLI-based UI to select a recently opened project to open
vscli recent --command cursor # open the selected project with cursor, ignoring the editor stored in history
vscli recent --behavior force-container # force open the selected project in a dev container
vscli recent --command cursor --behavior detect # open with cursor and detect if dev container should be used
vscli recent --config .devcontainer/custom.json # open with a specific dev container config
vscli recent -- --disable-gpu # pass additional arguments to the editor
vscli recent --hide-instructions # hide the keybinding instructions from the UI
vscli recent --hide-info # hide additional information like strategy, command, args and dev container path
```
The UI mode provides a convenient way to browse and manage your recent workspaces, with customizable display options and full support for all launch configurations.