Vomit - The Very Opinionated Mail Interaction Toolkit
NOTE: Vomit is still in a somewhat early stage. The functionality described here should work reasonably reliably, but the interfaces (subcommands, parameters) may change as new features get added.
Vomit currently provides only one tool: vmt. It is designed to let you do
anything with your email, except for reading and writing - there are plenty of
tools for that. Instead, it helps you locate emails (or attachments of emails)
you already know about and lets you efficiently work with those.
The central mechanism that vmt employs is providing an interactive search
mechanism based on Skim (the Rust equivalent to the somewhat more popular
fzf), which lets you pick one or more emails and will produce the
filenames of those. These filenames can then e.g. be passed to other tools. It
also provides a few built-in commands for common stuff you might want to use
other tools for.
The described base functionality is provided by the vmt pick command. It
captures your terminal, lets you interactively pick an email, and then writes
the email's filename to stdout. Here is an example:
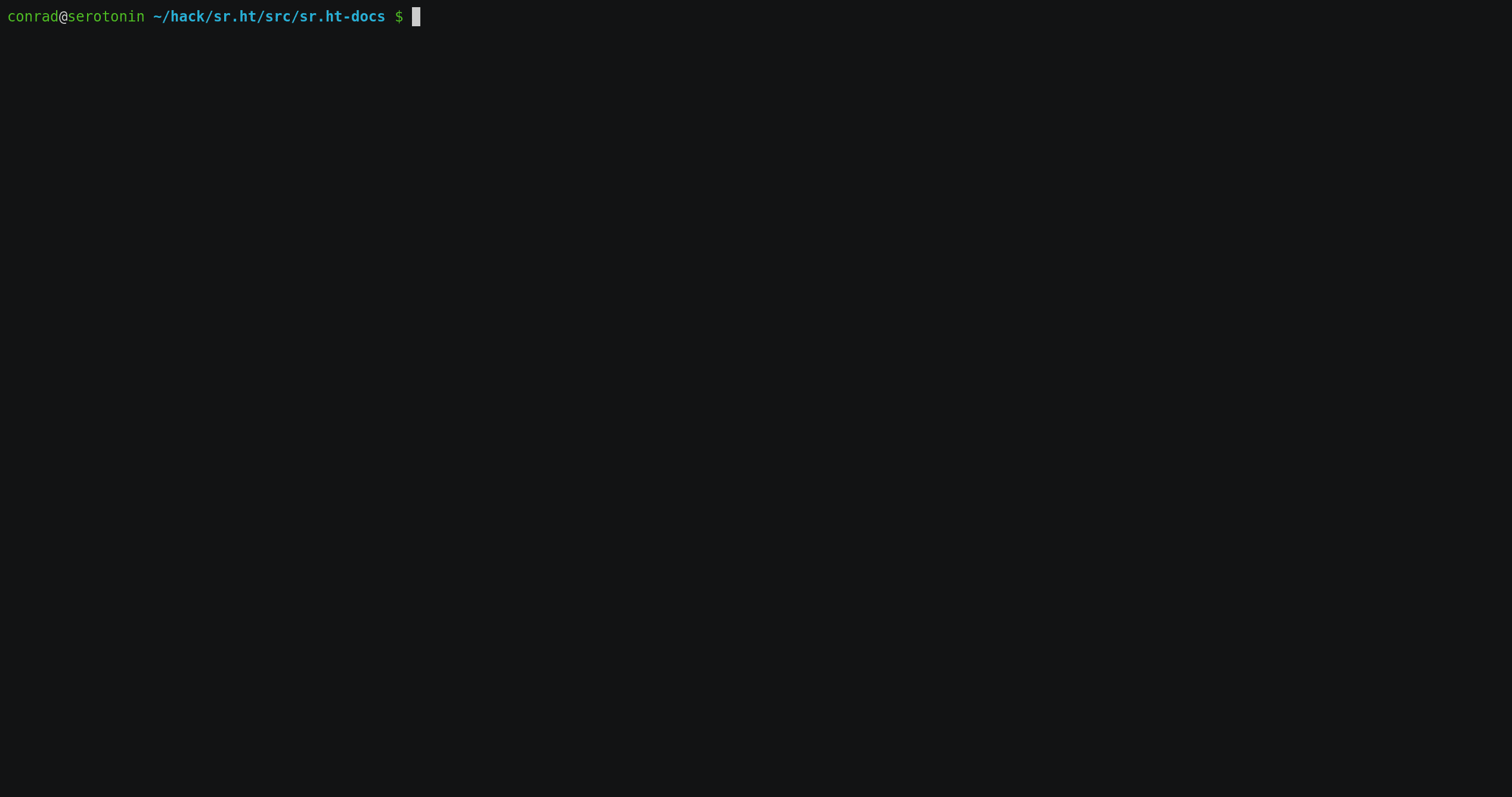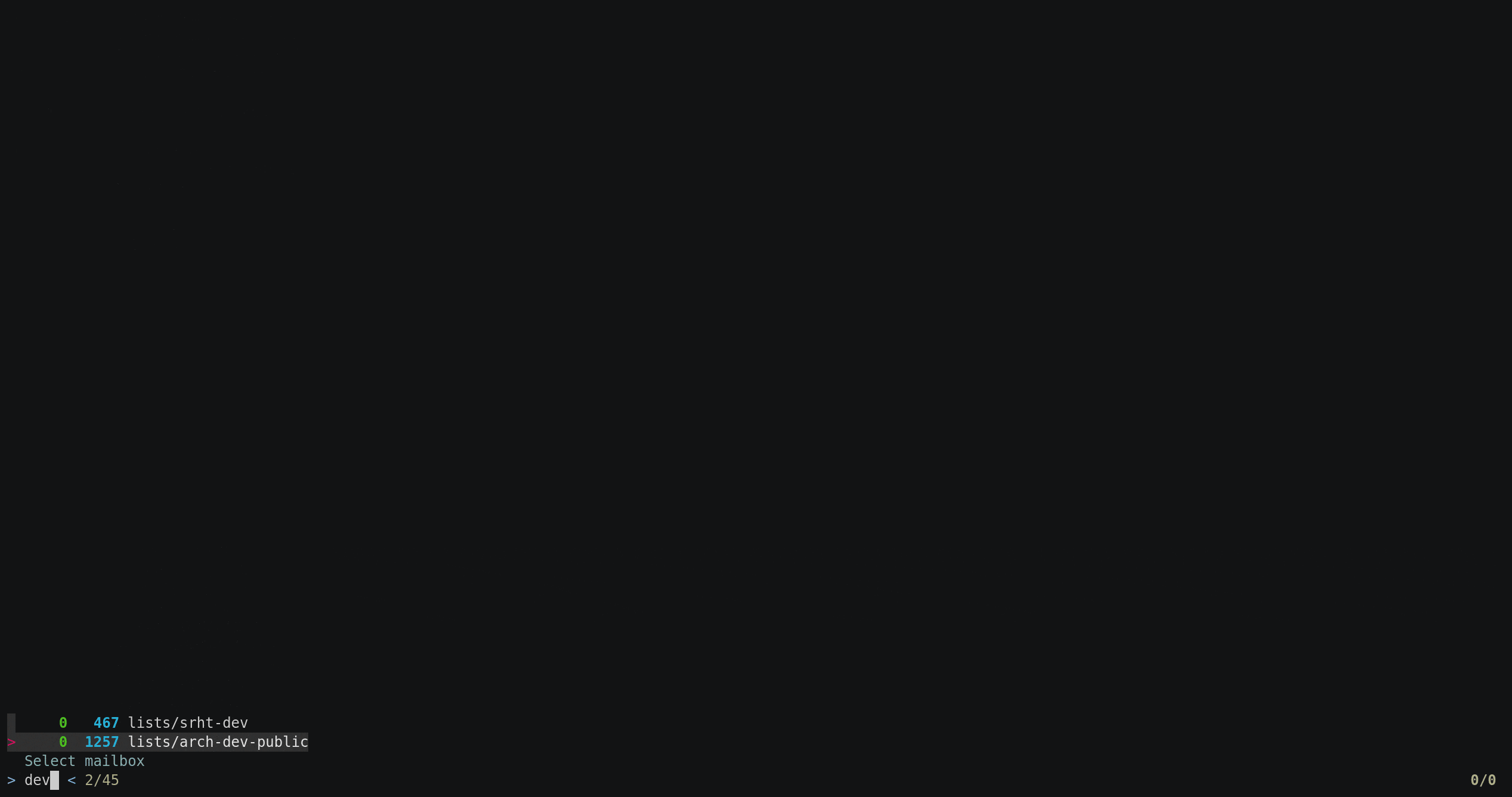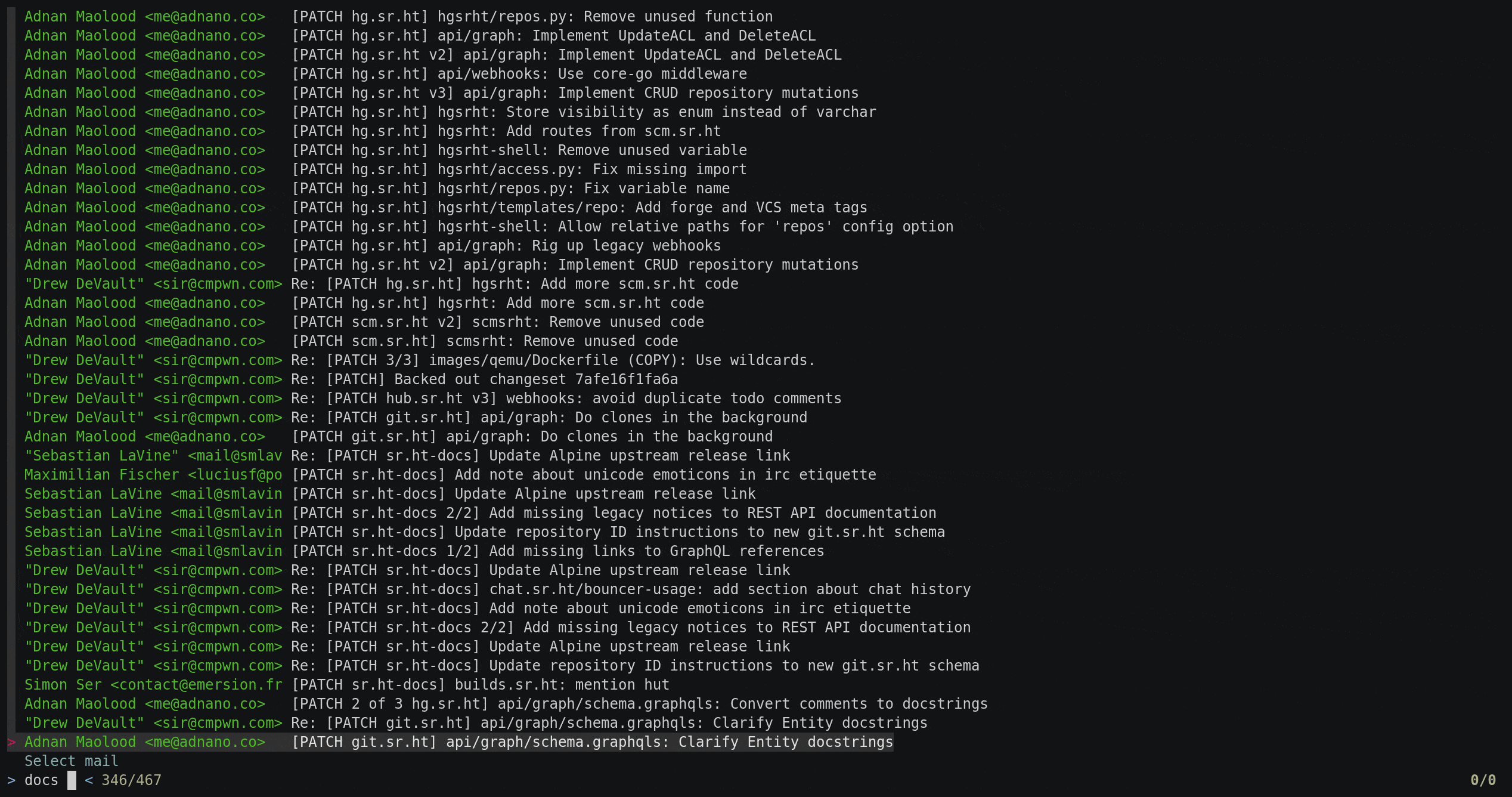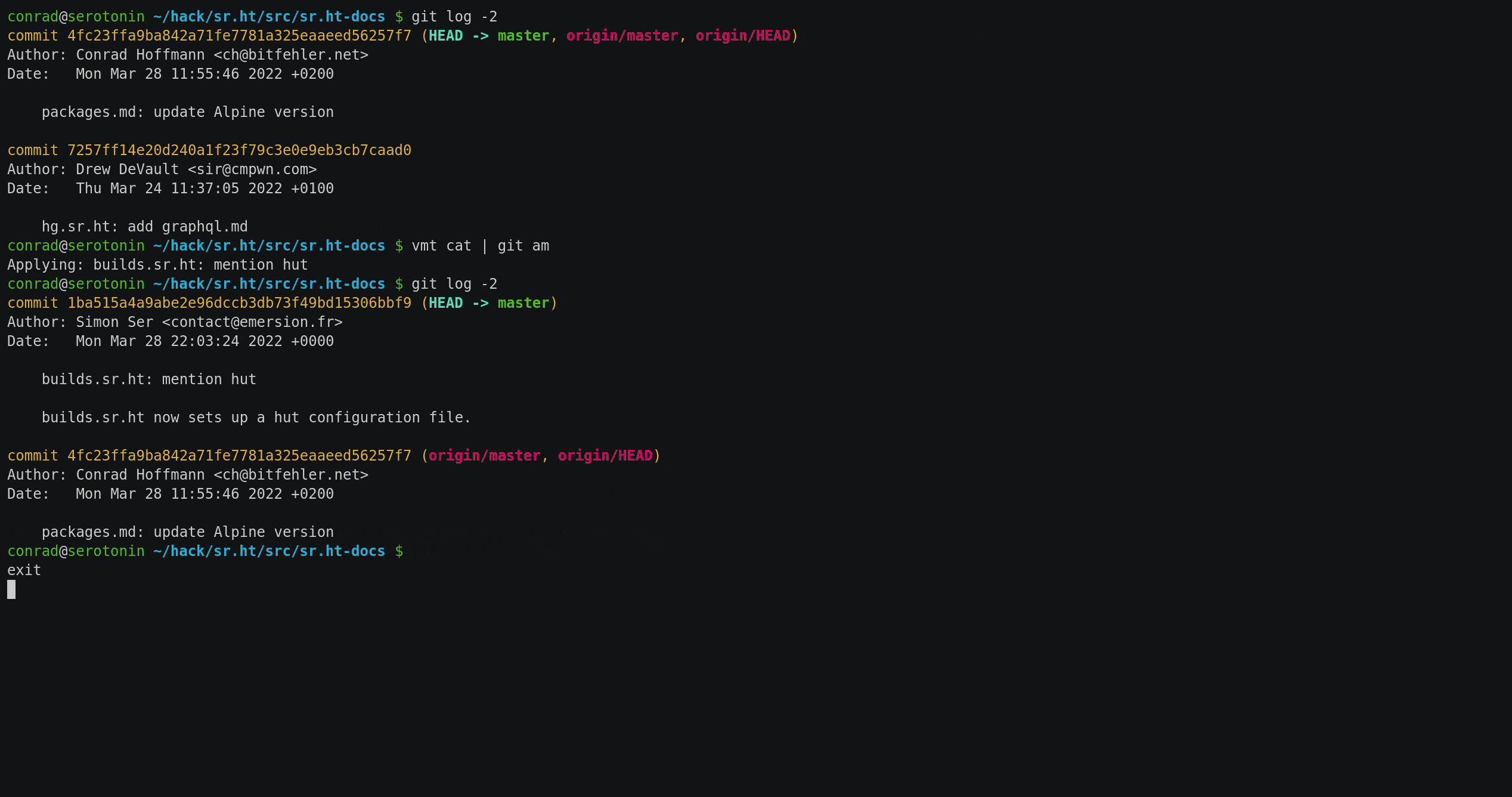
In the simplest case, this could be used to output the file and pipe the
contents to something that handles email as input, such as git am. Since this
is a common use case, vmt provides the cat subcommand. Here is an example
of applying a patch that was circulated on a mailing list:
Of course email is used for other stuff, like sending attachments. vmt has
you covered and offers the att subcommand (which itself has various
subcommands). Here is a little example listing and then saving attachments:
Opinions
- Vomit doesn't care how you read or write emails
- Vomit wants mail stored in Maildir++ format
- Vomit doesn't care how your mail gets there (see note below)
- Vomit does not alter your mail (i.e. mark as seen)
- Vomit wants to be used with tab completion (WIP)
Note about getting your mail into a maildir: if you need inspiration, Vomit
provides the vmt sync subcommand.
URIs
Most commands take an optional URI. In vomit, a URI can refer to either a mailbox, an email, or a MIME part (which can be an attachment). If a URI is omitted, the interactive picker will be executed. If a command expects e.g. an email, but only a mailbox is provided, the interactive picker will be executed to pick an email from the specified mailbox.
A URI consists of a path and, if it refers to a MIME part, a fragment. It can be absolute, in which case it is interpreted simply as an absolute path on the filesystem:
/home/conrad/.maildiris a mailbox (the "INBOX")/home/conrad/.maildir/.lists.knotis a mailbox ("lists/knot" in terms of IMAP folders)/home/conrad/.maildir/cur/1653391155.M355822260P144780V65024I15086234.serotonin,S=2685:2,Sis an email/home/conrad/.maildir/cur/1654768628.M769883767P813353V65024I15097034.serotonin,S=32881:2,S#0is the first MIME part of an email/home/conrad/.maildir/cur/1654768628.M769883767P813353V65024I15097034.serotonin,S=32881:2,S#1:0is the first MIME part inside the MIME container#1(e.g. in multipart/alternative).
Vomit supports two types of relative URLs - a relative path, using the configured maildir as base. The above examples could be written as:
..lists.knot./cur/1653391155.M355822260P144780V65024I15086234.serotonin,S=2685:2,S./cur/1654768628.M769883767P813353V65024I15097034.serotonin,S=32881:2,S#0./cur/1654768628.M769883767P813353V65024I15097034.serotonin,S=32881:2,S#1:0
Note that the leading ./ is only required for items in the INBOX,
.lists.knot/cur/... would also work.
In addition, a more folder-like representation can be used:
INBOXlists/knotINBOX/cur/1653391155.M355822260P144780V65024I15086234.serotonin,S=2685:2,S- ...
Commands
USAGE:
vmt [OPTIONS] <SUBCOMMAND>
OPTIONS:
-a, --account <ACCOUNT> The account to operate on (defaults to first account in config file)
-c, --config <CONFIG> Sets a custom config file location
-h, --help Print help information
-v, --verbose Increase output verbosity (can be used multiple times)
-V, --version Print version information
SUBCOMMANDS:
att Work with mail attachments
cat Output entire mail to stdout
help Print this message or the help of the given subcommand(s)
ls List mailboxes or emails
mime Work with MIME parts
pick Interactively pick mail(s) and print full path to stdout
show Show plain text mail body (if present)
sync Sync local maildir to remote IMAP account
pick
vmt-pick
Interactively pick mail(s) and print full path to stdout
USAGE:
vmt pick [OPTIONS] [URI]
ARGS:
<URI> URI of mailbox to pick mail in (omit to pick mailbox interactively)
OPTIONS:
-a, --attachments Show attachment marker (can be slow)
-A, --attachments-only Show only mails with attachment (can be slow)
-d, --date Show date
-e, --emtpy Show empty mailboxes (default: hide)
-h, --help Print help information
-m, --multiple Allow selection of multiple mails
ls
vmt-ls
List mailboxes or emails
USAGE:
vmt ls [OPTIONS] [URI]
ARGS:
<URI> The item to list (mailbox or mail, omit to list mailboxes)
OPTIONS:
-a, --all List all mailboxes (even if empty)
-h, --help Print help information
-l, --long Show more details
-r, --real-name Show real directory name
cat
vmt-cat
Output entire mail to stdout
USAGE:
vmt cat [URI]
ARGS:
<URI> URI of email to output, or mailbox hint for `pick`. If omitted, use `pick` to
select email
OPTIONS:
-h, --help Print help information
att
vmt-att
Work with mail attachments
USAGE:
vmt att <SUBCOMMAND>
OPTIONS:
-h, --help Print help information
SUBCOMMANDS:
cat Write attachment to stdout
help Print this message or the help of the given subcommand(s)
ls List attachments
save Save attachments in current directory
att ls
vmt-att-ls
List attachments
USAGE:
vmt att ls [OPTIONS] [URI]
ARGS:
<URI> URI of email or attachment to list, or mailbox as hint for `pick`. If omitted, uses
`pick` to select an email
OPTIONS:
-c, --color Use colored output
-h, --help Print help information
-l, --long Show more details
att cat
vmt-att-cat
Write attachment to stdout
USAGE:
vmt att cat [URI]
ARGS:
<URI> URI of attachment to output, or mailbox or email as hint for `pick`. If omitted,
uses `pick` to select an attachment
OPTIONS:
-h, --help Print help information
att save
vmt-att-save
Save attachments in current directory
USAGE:
vmt att save [OPTIONS] [URI]
ARGS:
<URI> URI of email or attachment to save, or mailbox as hint for `pick` . If omitted,
uses `pick` to select an attachment, or email if `--all` is used
OPTIONS:
-a, --all Save all attachments of an email
-h, --help Print help information
mime
vmt-mime
Work with MIME parts
USAGE:
vmt mime <SUBCOMMAND>
OPTIONS:
-h, --help Print help information
SUBCOMMANDS:
help Print this message or the help of the given subcommand(s)
ls List MIME parts
mime ls
vmt-mime-ls
List MIME parts
USAGE:
vmt mime ls [OPTIONS] [URI]
ARGS:
<URI> URI of email or part to list, or mailbox as hint for `pick`. If omitted, uses
`pick` to select an email
OPTIONS:
-c, --color Use colored output
-f, --full Display the full URI (default: only fragment)
-F, --only-full Display the full URI and nothing else
-h, --help Print help information
-l, --long Show more details
show
vmt-show
Show plain text mail body (if present)
USAGE:
vmt show [OPTIONS] [URI]
ARGS:
<URI> URI of email to process, or mailbox as hint for `pick`. If omitted, uses `pick` to
select an email
OPTIONS:
-h, --help Print help information
-l, --long Also show subject and sender
sync
vmt-sync
Sync local maildir to remote IMAP account
USAGE:
vmt sync [OPTIONS]
OPTIONS:
-h, --help Print help information
-r, --reconcile Force state cache reconciliation (can be slow, use only if prompted)
-t, --threads <THREADS> Number of threads (and IMAP sessions) to use [default: 3]
Config file
Per default located at ~/$XDG_CONFIG_HOME/vomit/config.toml, which usually
means ~/.config/vomit/config.toml. Fallback for platforms not supporting XDG
directories is ~/.vomitrc. A configuration file at an arbitrary
location can be used by using the global -c <path> flag.
A simple config example:
[<account>]
local = ~/.maildir
# Everything below is only needed if you intend to use `vmt sync`
remote = "imaps://imap.example.com:993"
user = "myusername"
pass-cmd = "pass show mail/myaccount"
# or use this:
#password = "s3cr34"
Multiple accounts can be specified, by default vmt will use the first one. To
use a different one, the global flag -a <account> can be used.
Installation
Sorry, nothing fancy yet. Build with cargo build --release and copy the
executable to your $PATH. If you have your $PATH set up to include your
cargo home dir, then cargo install should do.
You can also run cargo install vomit directly, but the version on crates.io
might be a few commits behind.