/// Angles are specified in one of two ways depending upon
/// whether they are used in CSS property syntax or SVG
/// presentation attribute syntax:
enum Angle { deg(float), grad(float), rad(float) }
/// A length is a distance Length, given as a number along with a unit which may be optional.
///
/// See [`length`](https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/types.html#DataTypeLength)
enum Length {
/// Represents the calculated font-size of the element. If used on the font-size property itself,
/// it represents the inherited font-size of the element.
em(float),
/// Represents the x-height of the element's font. In fonts with the x letter, this is generally
/// the height of lowercase letters in the font; 1ex ≈ 0.5em in many fonts.
ex(float),
/// Pixels
px(float),
/// Inches
inch(float),
/// Centimeters
cm(float),
/// Millimeters
mm(float),
/// Points, 1pt = 1/72nd of 1in
pt(float),
/// Picas, 1pc = 1/6th of 1in
pc(float),
/// A percentage value
percent(float),
}
/// Recognized color keyword names, compliant with svg 1.1.
enum ColorKeyWord {
aliceblue,
antiquewhite,
aqua,
aquamarine,
azure,
beige,
bisque,
black,
blanchedalmond,
blue,
blueviolet,
brown,
burlywood,
cadetblue,
chartreuse,
chocolate,
coral,
cornflowerblue,
cornsilk,
crimson,
cyan,
darkblue,
darkcyan,
darkgoldenrod,
darkgray,
darkgreen,
darkgrey,
darkkhaki,
darkmagenta,
darkolivegreen,
darkorange,
darkorchid,
darkred,
darksalmon,
darkseagreen,
darkslateblue,
darkslategray,
darkslategrey,
darkturquoise,
darkviolet,
deeppink,
deepskyblue,
dimgray,
dimgrey,
dodgerblue,
firebrick,
floralwhite,
forestgreen,
fuchsia,
gainsboro,
ghostwhite,
gold,
goldenrod,
gray,
grey,
green,
greenyellow,
honeydew,
hotpink,
indianred,
indigo,
ivory,
khaki,
lavender,
lavenderblush,
lawngreen,
lemonchiffon,
lightblue,
lightcoral,
lightcyan,
lightgoldenrodyellow,
lightgray,
lightgreen,
lightgrey,
lightpink,
lightsalmon,
lightseagreen,
lightskyblue,
lightslategray,
lightslategrey,
lightsteelblue,
lightyellow,
lime,
limegreen,
linen,
magenta,
maroon,
mediumaquamarine,
mediumblue,
mediumorchid,
mediumpurple,
mediumseagreen,
mediumslateblue,
mediumspringgreen,
mediumturquoise,
mediumvioletred,
midnightblue,
mintcream,
mistyrose,
moccasin,
navajowhite,
navy,
oldlace,
olive,
olivedrab,
orange,
orangered,
orchid,
palegoldenrod,
palegreen,
paleturquoise,
palevioletred,
papayawhip,
peachpuff,
peru,
pink,
plum,
powderblue,
purple,
red,
rosybrown,
royalblue,
saddlebrown,
salmon,
sandybrown,
seagreen,
seashell,
sienna,
silver,
skyblue,
slateblue,
slategray,
slategrey,
snow,
springgreen,
steelblue,
tan,
teal,
thistle,
tomato,
turquoise,
violet,
wheat,
white,
whitesmoke,
yellow,
yellowgreen,
}
/// Color variant.
enum Color {
/// A color represents with read,green and blue components.
Rgb(ubyte,ubyte,ubyte),
/// Represents as recognized color keywords.
Keyword(ColorKeyWord),
}
enum Iri {
Local(string),
Path(string),
}
/// Functional notation for a reference. The syntax for this reference is the same as the [`CSS URI`].
///
/// [`CSS URI`]: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/url_value
data FuncIri(string);
/// A 2d coordinate point.
data Point(float,float);
/// Percentages are specified as a number followed by a character:
data Percent(float);
/// ‘fill’ and ‘stroke’ take on a value of type [`Paint`], which is specified as follows:
enum Paint {
None,
/// the explicit color to be used to paint the current object
Color(Color),
/// A reference to a paint server.
Server(FuncIri),
}
/// A pair of `number`s, where the second `number` is optional.
data NumberOptNumber(float, #[option] float);
/// Defines the coordinate system for attributes ‘x1’, ‘y1’, ‘x2’ and ‘y2’.
///
/// If attribute ‘gradientUnits’ is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 'objectBoundingBox' were specified.
enum Coords {
/// If gradientUnits=, ‘x1’, ‘y1’, ‘x2’ and ‘y2’ represent values in the coordinate system
/// that results from taking the current user coordinate system in place at the time when the gradient element
/// is referenced (i.e., the user coordinate system for the element referencing the gradient element via a ‘fill’
/// or ‘stroke’ property) and then applying the transform specified by attribute ‘gradientTransform’.
UserSpaceOnUse,
/// If gradientUnits=, the user coordinate system for attributes ‘x1’, ‘y1’, ‘x2’ and ‘y2’ is
/// established using the bounding box of the element to which the gradient is applied (see Object bounding box units)
/// and then applying the transform specified by attribute ‘gradientTransform’.
///
/// When gradientUnits= and ‘gradientTransform’ is the identity matrix, the normal of the linear
/// gradient is perpendicular to the gradient vector in object bounding box space (i.e., the abstract coordinate
/// system where (0,0) is at the top/left of the object bounding box and (1,1) is at the bottom/right of the object bounding box).
/// When the object's bounding box is not square, the gradient normal which is initially perpendicular to the gradient vector
/// within object bounding box space may render non-perpendicular relative to the gradient vector in user space. If the gradient
/// vector is parallel to one of the axes of the bounding box, the gradient normal will remain perpendicular. This transformation
/// is due to application of the non-uniform scaling transformation from bounding box space to user space.
ObjectBoundingBox,
}
/// A `transform` matrix type.
enum Transform {
Translate(float,#[option] float),
Matrix([float;6]),
Scale(float,#[option] float),
Rotate { angle: float, #[option] center: Point },
SkewX(float),
SkewY(float),
}
/// Indicates which channel of rgba is selected.
enum Channel { R,G,B,A }
/// The property only applies to graphics elements that are contained within a [`ClipPath`](ClipPath) element.
enum ClipRule { Nonzero, EvenOdd }
/// Draws a cubic Bézier curve from the current point to `to` point,
/// using `ctrl1` as the control point at the beginning of the curve and `ctrl2` as the control point at the end of the curve.
data CubicBezier{ ctrl1: Point, ctrl2: Point, to: Point }
/// (smooth) Draws a cubic Bézier curve from the current point to `to` point,
/// using `ctrl1` as the control point at the beginning of the curve and `ctrl2` as the control point at the end of the curve.
data CubicBezierSmooth{ ctrl2: Point, to: Point }
/// Draws a quadratic Bézier curve from the current point to `to` point using `ctrl` as the control point.
data QuadraticBezier{ ctrl: Point, to: Point }
/// Draws an elliptical arc from the current point to `to` point.
///
/// The center (cx, cy) of the ellipse is calculated automatically to satisfy the constraints
/// imposed by the other parameters.
data Arc {
rx: float,
ry:float,
x_rotation: float,
large_arc: bool,
sweep: bool,
to: Point,
}
/// A direction that representation a path drawing commander.
enum PathEvent {
/// Close the current subpath by drawing a straight line from the current point to current subpath's initial point.
Close,
/// Start a new sub-path at the given (x,y) coordinate.
MoveTo {
points: vec[Point],
relative: bool,
},
/// Draw a line from the current point to the given (x,y) coordinate which becomes the new current point.
LineTo {
points: vec[Point],
relative: bool,
},
/// Draw a line from the current point to the given (x,y) coordinate which becomes the new current point.
Horizontal(float,bool),
/// Draw a line from the current point to the given (x,y) coordinate which becomes the new current point.
Vertical(float, bool),
/// Draws a cubic Bézier curve from the current point to `to` point,
/// using `ctrl1` as the control point at the beginning of the curve and `ctrl2` as the control point at the end of the curve.
CubicBezier(vec[CubicBezier],bool),
/// (smooth) Draws a cubic Bézier curve from the current point to `to` point,
/// using `ctrl1` as the control point at the beginning of the curve and `ctrl2` as the control point at the end of the curve.
CubicBezierSmooth(vec[CubicBezierSmooth],bool),
/// Draws a quadratic Bézier curve from the current point to `to` point using `ctrl` as the control point.
QuadraticBezier(vec[QuadraticBezier],bool),
/// (smooth) Draws a quadratic Bézier curve from the current point to `to` point using `ctrl` as the control point.
QuadraticBezierSmooth(vec[Point], bool),
/// Draws an elliptical arc from the current point to `to` point.
///
/// The center (cx, cy) of the ellipse is calculated automatically to satisfy the constraints
/// imposed by the other parameters.
Arc(vec[Arc],bool),
}
/// The ‘fill-rule’ property indicates the algorithm which is to be used to determine what parts of the canvas are
/// included inside the shape. For a simple, non-intersecting path, it is intuitively clear what region lies ;
/// however, for a more complex path, such as a path that intersects itself or where one subpath encloses another,
/// the interpretation of is not so obvious.
enum FillRule {
/// This rule determines the "insideness" of a point on the canvas by drawing a ray from that point to infinity in
/// any direction and then examining the places where a segment of the shape crosses the ray. Starting with a count of zero,
/// add one each time a path segment crosses the ray from left to right and subtract one each time a path segment crosses
/// the ray from right to left. After counting the crossings, if the result is zero then the point is outside the path.
/// Otherwise, it is inside.
Nonzero,
/// This rule determines the "insideness" of a point on the canvas by drawing a ray from that point to infinity in any direction
/// and counting the number of path segments from the given shape that the ray crosses. If this number is odd, the point is inside;
/// if even, the point is outside.
Evenodd,
}
/// Specifies the shape to be used at the end of open subpaths when they are stroked
#[rename()]
enum StrokeLineCap { Butt, Round, Square }
/// Specifies the shape to be used at the corners of paths or basic shapes when they are stroked.
#[rename()]
enum StrokeLineJoin { Miter(#[option] float), Round, Bevel }
/// Indicates what happens if the gradient starts or ends inside the bounds of the target rectangle.
/// Possible values are: 'pad', which says to use the terminal colors of the gradient to fill the remainder of the target region,
/// 'reflect', which says to reflect the gradient pattern start-to-end, end-to-start, start-to-end, etc. continuously until the
/// target rectangle is filled, and repeat, which says to repeat the gradient pattern start-to-end, start-to-end, start-to-end,
/// etc. continuously until the target region is filled.
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of 'pad' were specified.
enum SpreadMethod { Pad, Reflect, Repeat }
/// See [`css2`](https://www.w3.org/TR/2008/REC-CSS2-20080411/fonts.html#descdef-font-style)
enum FontStyle { Normal, Italic, Oblique }
/// Same syntax and semantics as the ‘font-variant’ descriptor within an @font-face rule.
/// Indication of whether this face is the small-caps variant of a font. Takes on the same values
/// as the ‘font-variant’ property, except that a comma-separated list is permitted.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of 'normal' were specified.
enum FontVariant { Normal, SmallCaps }
/// Same syntax and semantics as the ‘font-weight’ descriptor within an @font-face rule.
enum FontWeight { Normal,Bold,Bolder,Lighter,W100,W200,W300,W400,W500,W600,W700,W800,W900 }
/// This property specifies a prioritized font family names and/or generic family names.
enum FontFamily { Serif,SansSerif,Cursive,Fantasy,Monospace,Generic(string) }
/// Same syntax and semantics as the ‘font-stretch’ descriptor within an @font-face rule.
/// Indication of the condensed or expanded nature of the face relative to others in the same font family.
enum FontStretch {
Normal,
Wider,
Narrower,
UltraCondensed,
ExtraCondensed,
Condensed,
SemiCondensed,
SemiExpanded,
Expanded,
ExtraExpanded,
UltraExpanded,
}
/// Data value used by `enable-background` property.
enum Background {
/// A meaning of enable-background: accumulate (the initial/default value) depends on context:
///
/// * If an ancestor container element has a property value of enable-background: new, then all
/// graphics elements within the current container element are rendered both onto the parent container
/// element's background image canvas and onto the target device.
///
/// * Otherwise, there is no current background image canvas, so it is only necessary to render graphics
/// elements onto the target device. (No need to render to the background image canvas.)
Accumulate,
/// Indicate the subregion of the container element's user space where access to the background image is allowed to happen.
New(#[option] BackgroundNew)
}
data BackgroundNew {
x: float, y: float, width: float, height: float,
}
/// Identifies input for the given filter primitive. The value can be either one of six keywords or
/// can be a string which matches a previous ‘result’ attribute value within the same ‘filter’ element.
/// If no value is provided and this is the first filter primitive, then this filter primitive will use
/// SourceGraphic as its input. If no value is provided and this is a subsequent filter primitive, then
/// this filter primitive will use the result from the previous filter primitive as its input.
///
/// If the value for ‘result’ appears multiple times within a given ‘filter’ element, then a reference
/// to that result will use the closest preceding filter primitive with the given value for attribute
/// ‘result’. Forward references to results are an error.
enum FeIn {
/// This keyword represents the graphics elements that were the original input into the ‘filter’ element.
/// For raster effects filter primitives, the graphics elements will be rasterized into an initially clear
/// RGBA raster in image space. Pixels left untouched by the original graphic will be left clear. The image
/// is specified to be rendered in linear RGBA pixels. The alpha channel of this image captures any
/// anti-aliasing specified by SVG. (Since the raster is linear, the alpha channel of this image will
/// represent the exact percent coverage of each pixel.)
#[rename("SourceGraphic")]
SourceGraphic,
/// This keyword represents the graphics elements that were the original input into the ‘filter’ element.
/// SourceAlpha has all of the same rules as SourceGraphic except that only the alpha channel is used.
/// The input image is an RGBA image consisting of implicitly black color values for the RGB channels,
/// but whose alpha channel is the same as SourceGraphic. If this option is used, then some implementations
/// might need to rasterize the graphics elements in order to extract the alpha channel.
#[rename("SourceAlpha")]
SourceAlpha,
/// This keyword represents an image snapshot of the canvas under the filter region at the time that the
/// ‘filter’ element was invoked.
#[rename("BackgroundImage")]
BackgroundImage,
/// Same as BackgroundImage except only the alpha channel is used. See SourceAlpha and Accessing the background image.
#[rename("BackgroundAlpha")]
BackgroundAlpha,
/// This keyword represents the value of the ‘fill’ property on the target element for the filter effect.
/// The FillPaint image has conceptually infinite extent. Frequently this image is opaque everywhere,
/// but it might not be if the "paint" itself has alpha, as in the case of a gradient or pattern which
/// itself includes transparent or semi-transparent parts.
#[rename("FillPaint")]
FillPaint,
/// This keyword represents the value of the ‘stroke’ property on the target element for the filter effect.
/// The StrokePaint image has conceptually infinite extent. Frequently this image is opaque everywhere,
/// but it might not be if the "paint" itself has alpha, as in the case of a gradient or pattern which
/// itself includes transparent or semi-transparent parts.
#[rename("StrokePaint")]
StrokePaint,
/// Reference to another filter-primitive result .
Result(string),
}
/// Assign output to a named register. otherwise the filter output will only be referenced by next filter primitive.
enum FeOut { Position, Named(string) }
/// Image blending modes
/// For the compositing formulas below, the following definitions apply:
/// * cr = Result color (RGB) - premultiplied
/// * qa = Opacity value at a given pixel for image A
/// * qb = Opacity value at a given pixel for image B
/// * ca = Color (RGB) at a given pixel for image A - premultiplied
/// * cb = Color (RGB) at a given pixel for image B - premultiplied
enum FeBlendMode {
/// cr = (1 - qa) * cb + ca
Normal,
/// cr = (1-qa)*cb + (1-qb)*ca + ca*cb
Multiply,
/// cr = cb + ca - ca * cb
Screen,
/// cr = Min ((1 - qa) * cb + ca, (1 - qb) * ca + cb)
Darken,
/// cr = Max ((1 - qa) * cb + ca, (1 - qb) * ca + cb)
Lighten,
}
enum TextLengthAdjust {
/// 'spacing' indicates that only the advance values are adjusted. The glyphs themselves are not stretched or compressed.
Spacing,
/// 'spacingAndGlyphs' indicates that the advance values are adjusted and the glyphs themselves stretched or compressed
/// in one axis (i.e., a direction parallel to the inline-progression-direction).
SpacingAndGlyphs,
}
/// The ‘writing-mode’ property specifies whether the initial inline-progression-direction for a ‘text’ element shall be
/// left-to-right, right-to-left, or top-to-bottom. The ‘writing-mode’ property applies only to ‘text’ elements;
/// the property is ignored for ‘tspan’, ‘tref’, ‘altGlyph’ and ‘textPath’ sub-elements. (Note that the inline-progression-direction
/// can change within a ‘text’ element due to the Unicode bidirectional algorithm and properties ‘direction’ and ‘unicode-bidi’.
/// For more on bidirectional text, see Relationship with bidirectionality.)
enum WritingMode {
/// Sets the initial inline-progression-direction to left-to-right, as is common in most Latin-based documents.
/// For most characters, the current text position is advanced from left to right after each glyph is rendered.
/// (When the character data includes characters which are subject to the Unicode bidirectional algorithm, the text
/// advance rules are more complex. See Relationship with bidirectionality).
LrTb,
/// Sets the initial inline-progression-direction to right-to-left, as is common in Arabic or Hebrew scripts.
/// (See Relationship with bidirectionality.)
RlTb,
/// Sets the initial inline-progression-direction to top-to-bottom, as is common in some Asian scripts,
/// such as Chinese and Japanese. Though hardly as frequent as horizontal, this type of vertical layout also occurs
/// in Latin based documents, particularly in table column or row labels. In most cases, the vertical baselines
/// running through the middle of each glyph are aligned.
TbRl,
/// See [`LrTb`](WritingMode::LrTb)
Lr,
/// See [`RlTb`](WritingMode::RlTb)
Rl,
/// See [`TbRl`](WritingMode::TbRl)
Tb,
}
/// Within text content elements, the alignment of text with regards to the ‘text-anchor’ property is determined by
/// the value of the ‘direction’ property. For example, given a ‘text’ element with a ‘text-anchor’ value of ,
/// for a ‘direction’ value of , the text will extend to the left of the position of the ‘text’ element's ‘x’
/// attribute value, while for ‘direction’ value of , the text will extend to the right of the position of the
/// ‘text’ element's ‘x’ attribute value.
///
/// A more complete discussion of bidirectionality can be found in the Text direction section of
/// [`CSS 2`](https://www.w3.org/TR/CSS2/visuren.html#direction).
///
/// See [`direction`](https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/text.html#DirectionProperty)
enum TextDirection {
Ltr,
Rtl,
}
/// Except for any additional information provided in this specification, the normative definition of the
/// [`unicode-bidi`] property is in CSS2
///
/// [`unicode-bidi`]: https://www.w3.org/TR/2008/REC-CSS2-20080411/visuren.html#propdef-unicode-bidi
enum UnicodeBidi {
Normal,
Embed,
BidiOverride,
}
/// The ‘text-anchor’ property is used to align (start-, middle- or end-alignment) a string of text relative to a given point.
///
/// The ‘text-anchor’ property is applied to each individual text chunk within a given ‘text’ element. Each text chunk has an
/// initial current text position, which represents the point in the user coordinate system resulting from (depending on context)
/// application of the ‘x’ and ‘y’ attributes on the ‘text’ element, any ‘x’ or ‘y’ attribute values on a ‘tspan’, ‘tref’ or
/// ‘altGlyph’ element assigned explicitly to the first rendered character in a text chunk, or determination of the initial current
/// text position for a ‘textPath’ element.
enum TextAnchor {
/// The rendered characters are aligned such that the start of the resulting rendered text is at the initial current text position.
/// For an element with a ‘direction’ property value of "ltr" (typical for most European languages), the left side of the text is
/// rendered at the initial text position. For an element with a ‘direction’ property value of "rtl" (typical for Arabic and Hebrew),
/// the right side of the text is rendered at the initial text position. For an element with a vertical primary text direction
/// (often typical for Asian text), the top side of the text is rendered at the initial text position.
Start,
/// The rendered characters are aligned such that the geometric middle of the resulting rendered text is at the initial
/// current text position.
Middle,
/// The rendered characters are aligned such that the end of the resulting rendered text is at the initial current text position.
/// For an element with a ‘direction’ property value of "ltr" (typical for most European languages), the right side of the text is
/// rendered at the initial text position. For an element with a ‘direction’ property value of "rtl" (typical for Arabic and Hebrew),
/// the left side of the text is rendered at the initial text position. For an element with a vertical primary text direction (often
/// typical for Asian text), the bottom of the text is rendered at the initial text position.
End,
}
/// See [`baseline`](https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/text.html#BaselineAlignmentProperties)
enum DominantBaseline {
/// If this property occurs on a ‘text’ element, then the computed value depends on the value of the ‘writing-mode’ property.
/// If the 'writing-mode' is horizontal, then the value of the dominant-baseline component is 'alphabetic', else if the
/// 'writing-mode' is vertical, then the value of the dominant-baseline component is 'central'.
///
/// If this property occurs on a ‘tspan’, ‘tref’, ‘altGlyph’ or ‘textPath’ element, then the dominant-baseline and the
/// baseline-table components remain the same as those of the parent text content element. If the computed ‘baseline-shift’
/// value actually shifts the baseline, then the baseline-table font-size component is set to the value of the ‘font-size’
/// property on the element on which the ‘dominant-baseline’ property occurs, otherwise the baseline-table font-size remains
/// the same as that of the element. If there is no parent text content element, the scaled-baseline-table value is
/// constructed as above for ‘text’ elements.
Auto,
/// The dominant-baseline and the baseline-table components are set by determining the predominant script of the character
/// data content. The ‘writing-mode’, whether horizontal or vertical, is used to select the appropriate set of baseline-tables
/// and the dominant baseline is used to select the baseline-table that corresponds to that baseline. The baseline-table
/// font-size component is set to the value of the ‘font-size’ property on the element on which the ‘dominant-baseline’ property
/// occurs.
UseScript,
/// The dominant-baseline, the baseline-table, and the baseline-table font-size remain the same as that of the parent text
/// content element.
NoChange,
/// The dominant-baseline and the baseline-table remain the same, but the baseline-table font-size is changed to the value
/// of the ‘font-size’ property on this element. This re-scales the baseline-table for the current ‘font-size’.
ResetSize,
/// The baseline-identifier for the dominant-baseline is set to be 'ideographic', the derived baseline-table is constructed
/// using the 'ideographic' baseline-table in the nominal font, and the baseline-table font-size is changed to the value of
/// the ‘font-size’ property on this element.
Ideographic,
/// The baseline-identifier for the dominant-baseline is set to be 'alphabetic', the derived baseline-table is constructed
/// using the 'alphabetic' baseline-table in the nominal font, and the baseline-table font-size is changed to the value of
/// the ‘font-size’ property on this element.
Alphabetic,
/// The baseline-identifier for the dominant-baseline is set to be 'hanging', the derived baseline-table is constructed using
/// the 'hanging' baseline-table in the nominal font, and the baseline-table font-size is changed to the value of the
/// ‘font-size’ property on this element.
Hanging,
/// The baseline-identifier for the dominant-baseline is set to be 'mathematical', the derived baseline-table is constructed
/// using the 'mathematical' baseline-table in the nominal font, and the baseline-table font-size is changed to the value of
/// the ‘font-size’ property on this element.
Mathematical,
/// The baseline-identifier for the dominant-baseline is set to be 'central'. The derived baseline-table is constructed from
/// the defined baselines in a baseline-table in the nominal font. That font baseline-table is chosen using the following
/// priority order of baseline-table names: 'ideographic', 'alphabetic', 'hanging', 'mathematical'. The baseline-table font-size
/// is changed to the value of the ‘font-size’ property on this element.
Central,
/// The baseline-identifier for the dominant-baseline is set to be 'middle'. The derived baseline-table is constructed from
/// the defined baselines in a baseline-table in the nominal font. That font baseline -table is chosen using the following
/// priority order of baseline-table names: 'alphabetic', 'ideographic', 'hanging', 'mathematical'. The baseline-table
/// font-size is changed to the value of the ‘font-size’ property on this element.
Middle,
/// The baseline-identifier for the dominant-baseline is set to be 'text-after-edge'. The derived baseline-table is constructed
/// from the defined baselines in a baseline-table in the nominal font. The choice of which font baseline-table to use from the
/// baseline-tables in the nominal font is implementation defined. The baseline-table font-size is changed to the value of the
/// ‘font-size’ property on this element.
///
/// NOTE: using the following priority order of baseline-table names: 'alphabetic', 'ideographic', 'hanging', 'mathematical'
/// is probably a reasonable strategy for determining which font baseline-table to use.
TextAfterEdge,
/// The baseline-identifier for the dominant-baseline is set to be 'text-before-edge'. The derived baseline-table is constructed
/// from the defined baselines in a baseline-table in the nominal font. The choice of which baseline-table to use from the
/// baseline-tables in the nominal font is implementation defined. The baseline-table font-size is changed to the value of the
/// ‘font-size’ property on this element.
///
/// NOTE: Using the following priority order of baseline-table names: 'alphabetic', 'ideographic', 'hanging', 'mathematical'
/// is probably a reasonable strategy for determining which font baseline-table to use.
TextBeforeEdge,
}
enum AlignmentBaseline {
/// The value is the dominant-baseline of the script to which the character belongs - i.e.,
/// use the dominant-baseline of the parent.
Auto,
/// The alignment-point of the object being aligned is aligned with the dominant-baseline of
/// the parent text content element.
Baseline,
/// The alignment-point of the object being aligned is aligned with the "before-edge" baseline of
/// the parent text content element.
BeforeEdge,
/// The alignment-point of the object being aligned is aligned with the "text-before-edge" baseline of
/// the parent text content element.
TextBeforeEdge,
/// The alignment-point of the object being aligned is aligned with the "middle" baseline of the parent text content element.
Middle,
/// The alignment-point of the object being aligned is aligned with the "central" baseline of the parent text content element.
Central,
/// The alignment-point of the object being aligned is aligned with the "after-edge" baseline of the parent text content element.
AfterEdge,
/// The alignment-point of the object being aligned is aligned with the "text-after-edge" baseline of the parent text content element.
TextAfterEdge,
/// The alignment-point of the object being aligned is aligned with the "ideographic" baseline of the parent text content element.
Ideographic,
/// The alignment-point of the object being aligned is aligned with the "alphabetic" baseline of the parent text content element.
Alphabetic,
/// The alignment-point of the object being aligned is aligned with the "hanging" baseline of the parent text content element.
Hanging,
/// The alignment-point of the object being aligned is aligned with the "mathematical" baseline of the parent text content element.
Mathematical,
}
/// The ‘baseline-shift’ property allows repositioning of the dominant-baseline relative to the dominant-baseline of
/// the parent text content element. The shifted object might be a sub- or superscript. Within the shifted object,
/// the whole baseline-table is offset; not just a single baseline. The amount of the shift is determined from information
/// from the parent text content element, the sub- or superscript offset from the nominal font of the parent text content
/// element, percent of the of the parent text content element or an absolute value.
enum BaselineShift {
/// There is no baseline shift; the dominant-baseline remains in its original position.
Baseline,
/// The dominant-baseline is shifted to the default position for subscripts. The offset to this position
/// is determined using the font data for the nominal font. Because in most fonts the subscript position
/// is normally given relative to the "alphabetic" baseline, the user agent may compute the effective
/// position for subscripts for superscripts when some other baseline is dominant. The suggested computation
/// is to subtract the difference between the position of the dominant baseline and the position of the
/// "alphabetic" baseline from the position of the subscript. The resulting offset is determined by multiplying
/// the effective subscript position by the dominant baseline-table font-size. If there is no applicable font
/// data the user agent may use heuristics to determine the offset.
SubScripts,
/// The dominant-baseline is shifted to the default position for superscripts. The offset to this position is
/// determined using the font data for the nominal font. Because in most fonts the superscript position is normally
/// given relative to the "alphabetic" baseline, the user agent may compute the effective position for superscripts
/// when some other baseline is dominant. The suggested computation is to subtract the difference between the
/// position of the dominant baseline and the position of the "alphabetic" baseline from the position of the
/// superscript. The resulting offset is determined by multiplying the effective superscript position by the dominant
/// baseline-table font-size. If there is no applicable font data the user agent may use heuristics to determine the
/// offset.
SuperScripts,
/// The computed value of the property is this percentage multiplied by the computed "line-height" of the ‘text’ element.
/// The dominant-baseline is shifted in the shift direction (positive value) or opposite to the shift direction
/// (negative value) of the parent text content element by the computed value. A value of "0" is equivalent to "baseline".
Value(Length),
}
/// This property describes decorations that are added to the text of an element.
enum TextDecoration {
Underline,
Overline,
#[rename("line-through")]
LineThrough,
Blink,
}
/// Indicates the method by which text should be rendered along the path.
///
/// A value of align indicates that the glyphs should be rendered using simple 2x3 transformations such
/// that there is no stretching/warping of the glyphs. Typically, supplemental rotation, scaling and
/// translation transformations are done for each glyph to be rendered. As a result, with align, fonts
/// where the glyphs are designed to be connected (e.g., cursive fonts), the connections may not align
/// properly when text is rendered along a path.
///
/// A value of stretch indicates that the glyph outlines will be converted into paths, and then all end
/// points and control points will be adjusted to be along the perpendicular vectors from the path,
/// thereby stretching and possibly warping the glyphs. With this approach, connected glyphs, such as in
/// cursive scripts, will maintain their connections.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of align were specified.
enum TextPathMethod {
Align,
Stretch,
}
/// Indicates how the user agent should determine the spacing between glyphs that are to be rendered along a path.
///
/// A value of exact indicates that the glyphs should be rendered exactly according to the spacing rules as specified
/// in Text on a path layout rules.
///
///
/// A value of auto indicates that the user agent should use text-on-a-path layout algorithms to adjust the spacing
/// between glyphs in order to achieve visually appealing results.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of exact were specified.
enum TextPathSpacing {
Auto,
Exact,
}
/// The letter-spacing attribute controls spacing between text characters.
///
/// See [`letter-spacing`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/SVG/Attribute/letter-spacing)
enum LetterSpacing {
Normal,
Length(Length),
}
/// The word-spacing attribute specifies spacing behavior between words.
///
/// See [`word-spacing`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/SVG/Attribute/word-spacing)
enum WordSpacing {
Normal,
Length(Length),
}
/// see [`svg`] document for more information.
///
/// [`svg`]: https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/coords.html#PreserveAspectRatioAttribute
enum MeetOrSlice {
Meet,
Slice,
}
/// In some cases, typically when using the ‘viewBox’ attribute, i
/// t is desirable that the graphics stretch to fit non-uniformly
/// to take up the entire viewport. In other cases, it is desirable
/// that uniform scaling be used for the purposes of preserving
/// the aspect ratio of the graphics.
enum PreserveAspectRatio {
None,
/// Force uniform scaling
///
/// Align the `<min-x>` of the element's ‘viewBox’ with the smallest X value of the viewport.
/// Align the `<min-y>` of the element's ‘viewBox’ with the smallest Y value of the viewport.
xMinYMin(MeetOrSlice),
/// Force uniform scaling.
///
/// Align the midpoint X value of the element's ‘viewBox’ with the midpoint X value of the viewport.
/// Align the `<min-y>` of the element's ‘viewBox’ with the smallest Y value of the viewport.
xMidYMin(MeetOrSlice),
/// Force uniform scaling.
///
/// Align the `<min-x>`+`<width>` of the element's ‘viewBox’ with the maximum X value of the viewport.
/// Align the `<min-y>` of the element's ‘viewBox’ with the smallest Y value of the viewport.
xMaxYMin(MeetOrSlice),
/// Force uniform scaling.
///
/// Align the `<min-x>` of the element's ‘viewBox’ with the smallest X value of the viewport.
/// Align the midpoint Y value of the element's ‘viewBox’ with the midpoint Y value of the viewport.
xMinYMid(MeetOrSlice),
/// Force uniform scaling(the default).
///
/// Align the midpoint X value of the element's ‘viewBox’ with the midpoint X value of the viewport.
/// Align the midpoint Y value of the element's ‘viewBox’ with the midpoint Y value of the viewport.
xMidYMid(MeetOrSlice),
/// Force uniform scaling.
///
/// Align the `<min-x>`+`<width>` of the element's ‘viewBox’ with the maximum X value of the viewport.
/// Align the midpoint Y value of the element's ‘viewBox’ with the midpoint Y value of the viewport.
xMaxYMid(MeetOrSlice),
/// Force uniform scaling.
///
/// Align the `<min-x>` of the element's ‘viewBox’ with the smallest X value of the viewport.
/// Align the `<min-y>`+`<height>` of the element's ‘viewBox’ with the maximum Y value of the viewport.
xMinYMax(MeetOrSlice),
/// Force uniform scaling.
///
/// Align the midpoint X value of the element's ‘viewBox’ with the midpoint X value of the viewport.
/// Align the `<min-y>`+`<height>` of the element's ‘viewBox’ with the maximum Y value of the viewport.
xMidYMax(MeetOrSlice),
/// Force uniform scaling.
///
/// Align the `<min-x>`+`<width>` of the element's ‘viewBox’ with the maximum X value of the viewport.
/// Align the `<min-y>`+`<height>` of the element's ‘viewBox’ with the maximum Y value of the viewport.
xMaxYMax(MeetOrSlice),
}
/// support for various international writing directions, such as left-to-right (e.g., Latin scripts) and
/// bidirectional (e.g., Hebrew or Arabic) and vertical (e.g., Asian scripts).
attr TextLayout {
/// See [`WritingMode`]
#[option]
write_mode: WritingMode,
/// See [`TextDirection`]
#[option]
direction: TextDirection,
/// See [`UnicodeBidi`]
#[option]
unicode_bidi: UnicodeBidi,
/// See [`TextAnchor`]
#[option,variable,rename("text-anchor")]
anchor: TextAnchor,
/// See [`DominantBaseline`]
#[option,variable]
dominant_baseline: DominantBaseline,
/// See [`AlignmentBaseline`]
#[option,variable]
alignment_baseline: AlignmentBaseline,
/// See [`BaselineShift`]
#[option,variable]
baseline_shift: BaselineShift,
/// See [`TextDecoration`]
#[option,variable,rename("text-decoration")]
decoration: TextDecoration,
/// See [`LetterSpacing`]
#[option,variable]
letter_spacing: LetterSpacing,
/// See [`WordSpacing`]
#[option,variable]
word_spacing: WordSpacing,
}
/// support for various international writing directions, such as left-to-right (e.g., Latin scripts) and
/// bidirectional (e.g., Hebrew or Arabic) and vertical (e.g., Asian scripts).
attr WithTransform(
#[rename()]
vec[Transform]
);
/// Define a fragment with name.
attr Id(#[rename()] string);
/// The ‘fill’ instruction paints the interior of the given graphical element.
attr Fill {
/// paints color.
///
/// `Inherited: yes`
#[option, variable, init, rename("fill")]
paint: Paint,
/// fill painting rule, see [`FillRule`] for more information.
///
/// `Inherited: yes`
#[option, variable, rename("fill-rule")]
rule: FillRule,
/// defining the opacity of the paint server
#[option, variable, rename("fill-opacity")]
opacity: float,
}
/// This property affect how an element is stroked.
attr Stroke {
/// paints color paints along the outline of the given graphical element.
///
/// `Inherited: yes`
#[option, variable, init, rename("stroke")]
paint: Paint,
/// This property specifies the width of the stroke on the current object
///
/// `Inherited: yes`
#[option, variable, rename("stroke-width")]
width: Length,
/// specifies the shape to be used at the end of open subpaths when they are stroked.
///
/// `Inherited: yes`
#[option,variable,rename("stroke-linecap")]
linecap: StrokeLineCap,
/// specifies the shape to be used at the corners of paths or basic shapes when they are stroked.
///
/// `Inherited: yes`
#[option,variable,rename("stroke-linejoin")]
linejoin: StrokeLineJoin,
/// controls the pattern of dashes and gaps used to stroke paths. `<dasharray>` contains a list of comma and/or
/// white space separated `<length>s` and `<percentage>s` that specify the lengths of alternating dashes and gaps.
/// If an odd number of values is provided, then the list of values is repeated to yield an even number of values.
/// Thus, stroke-dasharray: 5,3,2 is equivalent to stroke-dasharray: 5,3,2,5,3,2.
///
/// `Inherited: yes`
#[option,variable,rename("stroke-dasharray")]
dasharray: vec[Length],
/// specifies the distance into the dash pattern to start the dash
///
/// `Inherited: yes`
#[option,variable,rename("stroke-dashoffset")]
dashoffset: Length,
/// specifies the opacity of the painting operation used to stroke the current object.
#[option,variable,rename("stroke-opacity")]
opacity: float,
}
/// Shorthand property for setting ‘font-style’, ‘font-variant’, ‘font-weight’, ‘font-size’, ‘line-height’ and ‘font-family’.
attr Font {
/// See [`FontFamily`]
#[option,variable,rename("font-family")]
family: vec[FontFamily],
/// See [`FontStyle`]
#[option,variable,rename("font-style")]
style: FontStyle,
/// See [`FontVariant`]
#[option,variable,rename("font-variant")]
variant: FontVariant,
/// See [`FontWeight`]
#[option,variable,rename("font-weight")]
weight: FontWeight,
/// This property refers to the size of the font from baseline to baseline when multiple lines of
/// text are set solid in a multiline layout environment.
#[option,variable,rename("font-size")]
size: Length,
/// See [`FontStretch`]
#[option,variable,rename("font-stretch")]
stretch: FontStretch,
}
/// enables access to the background image
attr EnableBackground(#[rename()]Background);
/// Define a fragment by name.
attr WithFilter(#[rename()]FuncIri);
/// Use mask to a element.
#[variable]
attr WithClipPath(#[rename()] FuncIri);
/// Use mask to a element.
#[variable]
attr WithMask(
#[rename()]
FuncIri
);
///Sspecifies object/group opacity
#[variable]
attr Opacity(
#[rename()]
float
);
/// It is often desirable to specify that a given set of graphics stretch to fit a particular container element.
/// The ‘viewBox’ attribute provides this capability.
attr ViewBox {
/// ViewBox left-top x coordinate,
#[variable]
minx: float,
/// ViewBox left-top y coordinate,
#[variable]
miny: float,
/// ViewBox width dimension.
#[variable]
width: float,
/// ViewBox height dimension.
#[variable]
height: float,
/// clip preserve aspect ratio.
#[option, variable]
aspect: PreserveAspectRatio,
}
/// All filter primitives have attributes ‘x’, ‘y’, ‘width’ and ‘height’ which identify a subregion which
/// restricts calculation and rendering of the given filter primitive. These attributes are defined according
/// to the same rules as other filter primitives' coordinate and length attributes and thus represent values
/// in the coordinate system established by attribute ‘primitiveUnits’ on the ‘filter’ element.
///
/// ‘x’, ‘y’, ‘width’ and ‘height’ default to the union (i.e., tightest fitting bounding box) of the subregions
/// defined for all referenced nodes. If there are no referenced nodes (e.g., for ‘feImage’ or ‘feTurbulence’),
/// or one or more of the referenced nodes is a standard input (one of SourceGraphic, SourceAlpha, BackgroundImage,
/// BackgroundAlpha, FillPaint or StrokePaint), or for ‘feTile’ (which is special because its principal function is
/// to replicate the referenced node in X and Y and thereby produce a usually larger result), the default subregion
/// is 0%,0%,100%,100%, where as a special-case the percentages are relative to the dimensions of the filter region,
/// thus making the the default filter primitive subregion equal to the filter region.
mixin FePrimitive {
/// The minimum x coordinate for the subregion which restricts calculation and rendering of the given filter primitive.
#[option, variable]
x: Length,
/// The minimum y coordinate for the subregion which restricts calculation and rendering of the given filter primitive
#[option, variable]
y: Length,
/// The width of the subregion which restricts calculation and rendering of the given filter primitive.
#[option, variable]
width: Length,
/// The height of the subregion which restricts calculation and rendering of the given filter primitive.
#[option, variable]
height: Length,
/// Assigned name for this filter primitive. If supplied, then graphics that result from processing this filter primitive can
/// be referenced by an ‘in’ attribute on a subsequent filter primitive within the same ‘filter’ element. If no value is provided,
/// the output will only be available for re-use as the implicit input into the next filter primitive if that filter primitive
/// provides no value for its ‘in’ attribute.
///
/// Note that a `filter-primitive-reference` is not an XML ID; instead, a `filter-primitive-reference` is only meaningful within a
/// given ‘filter’ element and thus have only local scope. It is legal for the same `filter-primitive-reference` to appear multiple
/// times within the same ‘filter’ element. When referenced, the `filter-primitive-reference` will use the closest preceding filter
/// primitive with the given result.
#[option, variable]
result: string,
}
/// Create a new layer into which the backend render child elements.
#[rename()]
el Canvas {
/// a number (usually an integer) that represents the width of the rendering layer.
#[variable]
width: Length,
/// a number (usually an integer) that represents the height of the rendering layer.
#[variable]
height: Length,
}
/// used as an alpha mask for compositing the current object into the background.
el Mask {
/// Defines the coordinate system for attributes ‘x’, ‘y’, ‘width’ and ‘height’.
///
/// If maskUnits=, ‘x’, ‘y’, ‘width’ and ‘height’ represent values in the current user coordinate system
/// in place at the time when the ‘mask’ element is referenced (i.e., the user coordinate system for the element
/// referencing the ‘mask’ element via the ‘mask’ property).
///
/// If maskUnits=, ‘x’, ‘y’, ‘width’ and ‘height’ represent fractions or percentages of the bounding box
/// of the element to which the mask is applied. (See Object bounding box units.)
///
/// If attribute ‘maskUnits’ is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 'objectBoundingBox' were specified.
#[option, variable,rename("maskUnits")]
units: Coords,
/// Defines the coordinate system for the contents of the ‘mask’.
///
/// If maskContentUnits=, the user coordinate system for the contents of the ‘mask’ element is the current user
/// coordinate system in place at the time when the ‘mask’ element is referenced (i.e., the user coordinate system for the element
/// referencing the ‘mask’ element via the ‘mask’ property).
///
/// If maskContentUnits=, the user coordinate system for the contents of the ‘mask’ is established using the
/// bounding box of the element to which the mask is applied. (See Object bounding box units.)
///
/// If attribute ‘maskContentUnits’ is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 'userSpaceOnUse' were specified.
#[option, variable]
content_units: Coords,
/// The x-axis coordinate of one corner of the rectangle for the largest possible offscreen buffer. Note that the clipping
/// path used to render any graphics within the mask will consist of the intersection of the current clipping path
/// associated with the given object and the rectangle defined by ‘x’, ‘y’, ‘width’ and ‘height’.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of '-10%' were specified.
#[option, variable, init]
x: Length,
/// The y-axis coordinate of one corner of the rectangle for the largest possible offscreen buffer.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of '-10%' were specified.
#[option, variable, init]
y: Length,
/// The width of the largest possible offscreen buffer. Note that the clipping path used to render any graphics within the
/// mask will consist of the intersection of the current clipping path associated with the given object and the rectangle
/// defined by ‘x’, ‘y’, ‘width’ and ‘height’.
///
/// A negative value is an error (see Error processing). A value of zero disables rendering of the element.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of '120%' were specified.
#[option, variable, init]
width: Length,
/// The height of the largest possible offscreen buffer.
///
/// A negative value is an error (see Error processing). A value of zero disables rendering of the element.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of '120%' were specified.
#[option, variable, init]
height: Length,
}
/// A clipping path is defined with a ‘clipPath’ element.
/// A clipping path is used/referenced using the ‘clip-path’ property.
el ClipPath(
/// Defines the coordinate system for the contents of the ‘clipPath’.
///
/// If clipPathUnits=, the contents of the ‘clipPath’ represent values in the current user coordinate
/// system in place at the time when the ‘clipPath’ element is referenced (i.e., the user coordinate system for the
/// element referencing the ‘clipPath’ element via the ‘clip-path’ property).
///
/// If clipPathUnits=, then the user coordinate system for the contents of the ‘clipPath’ element
/// is established using the bounding box of the element to which the clipping path is applied (see Object bounding
/// box units).
///
/// If attribute ‘clipPathUnits’ is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 'userSpaceOnUse' were specified.
#[option, variable]
Coords,
);
/// A filter effect consists of a series of graphics operations that are applied to a given source graphic to
/// produce a modified graphical result. The result of the filter effect is rendered to the target device
/// instead of the original source graphic. The following illustrates the process:
el Filter {
/// Defines the coordinate system for attributes ‘x’, ‘y’, ‘width’ and ‘height’.
///
/// If units=, ‘x’, ‘y’, ‘width’ and ‘height’ represent values in the current user
/// coordinate system in place at the time when the ‘filter’ is referenced (i.e., the user coordinate system
/// for the element referencing the ‘filter’ via a ‘filter’ property).
///
/// If units=, then ‘x’, ‘y’, ‘width’ and ‘height’ represent fractions or percentages
/// of the bounding box on the referencing element (see Object bounding box units).
///
/// If attribute units is not specified, then the effect is if a value of 'objectBoundingBox' were
/// specified.
#[option, variable,rename("filterUnits")]
units: Coords,
/// Specifies the coordinate system for the various length values within the filter primitives and for the
/// attributes that define the filter primitive subregion.
///
/// If primitive_units=, any length values within the filter definitions represent values in
/// the current user coordinate system in place at the time when the ‘filter’ element is referenced (i.e.,
/// the user coordinate system for the element referencing the ‘filter’ element via a ‘filter’ property).
///
/// If primitive_units=, then any length values within the filter definitions represent
/// fractions or percentages of the bounding box on the referencing element (see Object bounding box units).
/// Note that if only one number was specified in a `number-optional-number` value this number is expanded out
/// before the ‘primitiveUnits’ computation takes place.
///
/// If attribute primitive_units is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of userSpaceOnUse were specified.
#[option, variable]
primitive_units: Coords,
/// These attributes define a rectangular region on the canvas to which this filter applies.
///
/// The amount of memory and processing time required to apply the filter are related to the size of this rectangle
/// and the ‘filterRes’ attribute of the filter.
///
/// The coordinate system for these attributes depends on the value for attribute ‘filterUnits’.
///
/// Negative values for ‘width’ or ‘height’ are an error (see Error processing). Zero values disable rendering of the
/// element which referenced the filter.
///
/// The bounds of this rectangle act as a hard clipping region for each filter primitive included with a given ‘filter’
/// element; thus, if the effect of a given filter primitive would extend beyond the bounds of the rectangle (this
/// sometimes happens when using a ‘feGaussianBlur’ filter primitive with a very large ‘stdDeviation’), parts of the
/// effect will get clipped.
///
/// If ‘x’ or ‘y’ is not specified, the effect is as if a value of -10% were specified.
///
/// If ‘width’ or ‘height’ is not specified, the effect is as if a value of 120% were specified.
#[option, variable,init]
x: Length,
/// See [`x`](Self::x)
#[option, variable,init]
y: Length,
/// See [`x`](Self::x)
#[option, variable,init]
width: Length,
/// See [`x`](Self::x)
#[option, variable,init]
height: Length,
/// This attribute takes the form x-pixels [y-pixels], and indicates the width and height of the
/// intermediate images in pixels. If not provided, then the user agent will use reasonable values
/// to produce a high-quality result on the output device.
///
/// Care should be taken when assigning a non-default value to this attribute. Too small of a value
/// may result in unwanted pixelation in the result. Too large of a value may result in slow
/// processing and large memory usage.
///
/// Negative values are an error (see Error processing). Zero values disable rendering of the
/// element which referenced the filter.
///
/// Non-integer values are truncated, i.e rounded to the closest integer value towards zero.
#[option, variable]
res: NumberOptNumber,
}
/// Defines a distant light source that can be used within a lighting filter primitive:
/// [`FeDiffuseLighting`] or [`FeSpecularLighting`].
///
/// The following diagram illustrates the angles which ‘azimuth’ and ‘elevation’ represent in an XYZ coordinate system.
///
/// 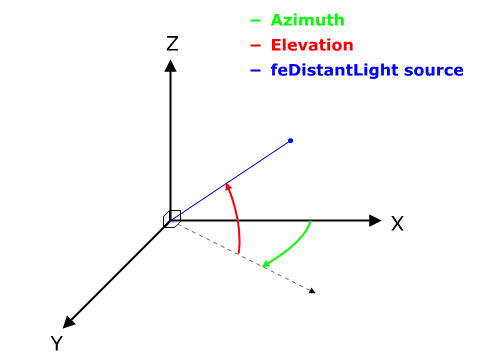
leaf FeDistantLight {
/// Direction angle for the light source on the XY plane (clockwise), in degrees from the x axis.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 0 were specified.
#[option, variable]
azimuth: float,
/// Direction angle for the light source from the XY plane towards the z axis, in degrees. Note the positive Z-axis points towards the viewer of the content.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 0 were specified.
#[option, variable]
elevation: float,
}
/// Defines a point light source that can be used within a lighting filter primitive:
/// [`FeDiffuseLighting`] or [`FeSpecularLighting`].
leaf FePointLight {
/// X location for the light source in the coordinate system established by attribute ‘primitiveUnits’ on the ‘filter’ element.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 0 were specified.
#[option, variable]
x: float,
/// Y location for the light source in the coordinate system established by attribute ‘primitiveUnits’ on the ‘filter’ element.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 0 were specified.
#[option, variable]
y: float,
/// Z location for the light source in the coordinate system established by attribute ‘primitiveUnits’ on the ‘filter’ element,
/// assuming that, in the initial coordinate system, the positive Z-axis comes out towards the person viewing the content and
/// assuming that one unit along the Z-axis equals one unit in X and Y.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 0 were specified.
#[option, variable]
z: float,
}
/// Defines a spot light source that can be used within a lighting filter primitive:
/// [`FeDiffuseLighting`] or [`FeSpecularLighting`].
leaf FeSpotLight {
/// X location for the light source in the coordinate system established by attribute ‘primitiveUnits’ on the ‘filter’ element.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 0 were specified.
#[option, variable]
x: float,
/// Y location for the light source in the coordinate system established by attribute ‘primitiveUnits’ on the ‘filter’ element.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 0 were specified.
#[option, variable]
y: float,
/// Z location for the light source in the coordinate system established by attribute ‘primitiveUnits’ on the ‘filter’ element,
/// assuming that, in the initial coordinate system, the positive Z-axis comes out towards the person viewing the content and
/// assuming that one unit along the Z-axis equals one unit in X and Y.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 0 were specified.
#[option, variable]
z: float,
/// X location in the coordinate system established by attribute ‘primitiveUnits’ on the ‘filter’ element of the point at which
/// the light source is pointing.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 0 were specified.
#[option, variable]
point_at_x: float,
/// Y location in the coordinate system established by attribute ‘primitiveUnits’ on the ‘filter’ element of the point at which
/// the light source is pointing.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 0 were specified.
#[option, variable]
point_at_y: float,
/// Z location in the coordinate system established by attribute ‘primitiveUnits’ on the ‘filter’ element of the point at which
/// the light source is pointing, assuming that, in the initial coordinate system, the positive Z-axis comes out towards the
/// person viewing the content and assuming that one unit along the Z-axis equals one unit in X and Y.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 0 were specified.
#[option, variable]
point_at_z: float,
/// Exponent value controlling the focus for the light source.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 1 were specified.
#[option, variable]
specular_exponent: float,
/// A limiting cone which restricts the region where the light is projected. No light is projected outside the cone.
/// ‘limitingConeAngle’ represents the angle in degrees between the spot light axis (i.e. the axis between the light
/// source and the point to which it is pointing at) and the spot light cone. User agents should apply a smoothing
/// technique such as anti-aliasing at the boundary of the cone.
///
/// If no value is specified, then no limiting cone will be applied.
#[option, variable]
limiting_cone_angle: float,
}
/// This filter composites two objects together using commonly used imaging software blending modes.
/// It performs a pixel-wise combination of two input images.
leaf FeBlend mixin FePrimitive {
/// Image blending mode
#[option, variable]
mode: FeBlendMode,
/// The first input image to the blending operation.
#[option, variable]
in: FeIn,
/// The second input image to the blending operation. This attribute can take on the same values as the ‘in’ attribute.
#[option, variable]
in2: FeIn,
}
/// Values of FeColorMatrix.
enum FeColorMatrixValues {
/// a list of 20 matrix values.
Matrix([float; 20]),
/// `Saturate` is a single real number value (0 to 1).
///
/// See [`feColorMatrixElement`](https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/filters.html#feColorMatrixElement)
Saturate(float),
/// `HueRotate` is a single one real number value (degrees)
///
/// See [`feColorMatrixElement`](https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/filters.html#feColorMatrixElement)
HueRotate(float),
/// `LuminanceToAlpha` is not applicable.
///
/// See [`feColorMatrixElement`](https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/filters.html#feColorMatrixElement)
LuminanceToAlpha,
}
/// This filter applies a matrix transformation.
///
/// on the RGBA color and alpha values of every pixel on the input graphics to produce a result with a new
/// set of RGBA color and alpha values.
///
/// The calculations are performed on non-premultiplied color values. If the input graphics consists of
/// premultiplied color values, those values are automatically converted into non-premultiplied color values
/// for this operation.
///
/// These matrices often perform an identity mapping in the alpha channel. If that is the case, an implementation
/// can avoid the costly undoing and redoing of the premultiplication for all pixels with A = 1.
///
/// See [`feColorMatrix`](https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/filters.html#feColorMatrixElement).
leaf FeColorMatrix mixin FePrimitive {
/// See [`FeIn`]
#[option, variable]
in: FeIn,
/// The contents of ‘values’ depends on the value of attribute ‘type’:
#[variable]
values: FeColorMatrixValues,
}
/// transfer functions for the rgba channels.
///
/// See [`FeComponentTransfer`](FeComponentTransfer)
enum FeFunc {
/// C' = C
Identity,
/// For table, the function is defined by linear interpolation between values given in the attribute ‘tableValues’.
/// The table has n+1 values (i.e., v0 to vn) specifying the start and end values for n evenly sized interpolation regions.
/// Interpolations use the following formula:
///
/// For a value C < 1 find k such that:
///
/// > k/n <= C < (k+1)/n
///
/// The result C' is given by:
///
/// > C' = vk + (C - k/n)*n * (vk+1 - vk)
///
/// If C = 1 then:
///
/// > C' = vn.
Table(vec[float]),
/// For discrete, the function is defined by the step function given in the attribute ‘tableValues’,
/// which provides a list of n values (i.e., v0 to vn-1) in order to identify a step function consisting of n steps.
/// The step function is defined by the following formula:
///
/// For a value C < 1 find k such that:
///
/// > k/n <= C < (k+1)/n
///
/// The result C' is given by:
///
/// > C' = vk
///
/// If C = 1 then:
///
/// > C' = vn-1.
Discrete(vec[float]),
/// For linear, the function is defined by the following linear equation:
///
/// > C' = slope * C + intercept
Linear {
/// the slope of the linear function.
slope: float,
/// the intercept of the linear function.
intercept: float,
},
/// For gamma, the function is defined by the following exponential function:
///
/// > C' = amplitude * pow(C, exponent) + offset
Gamma {
/// the amplitude of the gamma function.
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 1 were specified.
amplitude: float,
/// the exponent of the gamma function.
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 1 were specified.
exponent: float,
/// the offset of the gamma function.
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 0 were specified.
offset: float,
},
}
/// The compositing operation that is to be performed. All of the ‘operator’ types except arithmetic match the
/// corresponding operation as described in `PORTERDUFF`. The arithmetic operator is described above. If attribute
/// ‘operator’ is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of over were specified.
enum FeCompositeOperator {
Over,
In,
Out,
Atop,
Xor,
Arithmetic {
/// Only applicable if operator="arithmetic".
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of 0 were specified.
k1: float,
/// Only applicable if operator=.
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of 0 were specified.
k2: float,
/// Only applicable if operator=.
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of 0 were specified.
k3: float,
/// Only applicable if operator=.
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of 0 were specified.
k4: float,
},
}
/// Determines how to extend the input image as necessary with color values so that the matrix operations
/// can be applied when the kernel is positioned at or near the edge of the input image.
enum FeConvolveMatrixEdgeMode {
Duplicate,
Wrap,
None,
}
/// A keyword indicating whether to erode (i.e., thin) or dilate (fatten) the source graphic.
/// If attribute `mode` is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of erode were specified.
enum FeMorphologyOperator {
Erode,
Dilate,
}
/// See [`stitch_tiles`](FeTurbulence::stitch_tiles)
enum FeStitchTiles {
/// If stitchTiles="stitch", then the user agent will automatically adjust baseFrequency-x and baseFrequency-y values
/// such that the feTurbulence node's width and height (i.e., the width and height of the current subregion) contains
/// an integral number of the Perlin tile width and height for the first octave. The baseFrequency will be adjusted up /// or down depending on which way has the smallest relative (not absolute) change as follows: Given the frequency,
/// calculate lowFreq=floor(width*frequency)/width and hiFreq=ceil(width*frequency)/width. If frequency/lowFreq < hiFreq/frequency
/// then use lowFreq, else use hiFreq. While generating turbulence values, generate lattice vectors as normal for Perlin Noise,
/// except for those lattice points that lie on the right or bottom edges of the active area (the size of the resulting tile).
/// In those cases, copy the lattice vector from the opposite edge of the active area.
Stitch,
/// If stitchTiles="noStitch", no attempt it made to achieve smooth transitions at the border of tiles which contain a turbulence
/// function. Sometimes the result will show clear discontinuities at the tile borders.
NoStitch,
}
/// Indicates whether the filter primitive should perform a noise or turbulence function.
/// If attribute ‘type’ is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of turbulence were specified.
enum FeTurbulenceType {
FractalNoise,
Turbulence,
}
/// This filter primitive performs component-wise remapping of data as follows:
///
/// > R' = feFuncR( R )
///
/// > G' = feFuncG( G )
///
/// > B' = feFuncB( B )
///
/// > A' = feFuncA( A )
///
/// for every pixel. It allows operations like brightness adjustment, contrast adjustment, color balance or thresholding.
el FeComponentTransfer(#[option, variable, rename("in")] FeIn);
/// transfer function for the alpha component of the input graphic
///
/// See [`FeFunc`], [`FeComponentTransfer`]
leaf FeFuncA(FeFunc);
/// transfer function for the red component of the input graphic
///
/// See [`FeFunc`], [`FeComponentTransfer`]
leaf FeFuncR(FeFunc);
/// transfer function for the green component of the input graphic
///
/// See [`FeFunc`], [`FeComponentTransfer`]
leaf FeFuncG(FeFunc);
/// transfer function for the blue component of the input graphic
///
/// See [`FeFunc`], [`FeComponentTransfer`]
leaf FeFuncB(FeFunc);
/// This filter performs the combination of the two input images pixel-wise in image space using one of the Porter-Duff [`PORTERDUFF`]
/// compositing operations: over, in, atop, out, xor [`SVG-COMPOSITING`]. Additionally, a component-wise arithmetic operation (with
/// the result clamped between [0..1]) can be applied.
///
/// See [`feComposite`].
///
/// [`feComposite`]: https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/filters.html#feCompositeElement
/// [`PORTERDUFF`]: https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/refs.html#ref-PORTERDUFF
/// [`SVG-COMPOSITING`]: https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/refs.html#ref-SVG-COMPOSITING
leaf FeComposite mixin FePrimitive {
/// See [`FeIn`]
#[option,variable]
in: FeIn,
/// The second input image to the compositing operation. This attribute can take on the same values as the `r_in` attribute.
#[variable]
in2: FeIn,
/// See [`FeCompositeOperator`]
#[option,variable]
operator: FeCompositeOperator,
}
/// feConvolveMatrix applies a matrix convolution filter effect. A convolution combines pixels
/// in the input image with neighboring pixels to produce a resulting image. A wide variety
/// of imaging operations can be achieved through convolutions, including blurring, edge detection,
/// sharpening, embossing and beveling.
///
/// See [`feConvolveMatrix`](https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/filters.html#feConvolveMatrixElement)
leaf FeConvolveMatrix mixin FePrimitive {
/// See [`FeIn`]
#[option,variable]
in: FeIn,
/// Indicates the number of cells in each dimension for ‘kernelMatrix’. The values provided must be `integer`s greater than zero.
/// The first number, `orderX`, indicates the number of columns in the matrix. The second number, `orderY`, indicates the number
/// of rows in the matrix. If `orderY` is not provided, it defaults to `orderX`.
///
/// A typical value is order=. It is recommended that only small values (e.g., 3) be used; higher values may result in very
/// high CPU overhead and usually do not produce results that justify the impact on performance.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of 3 were specified.
#[option,variable]
order: NumberOptNumber,
/// The list of `number`s that make up the kernel matrix for the convolution. Values are separated by space
/// characters and/or a comma. The number of entries in the list must equal `orderX` times `orderY`.
#[variable]
kernel: vec[float],
/// After applying the ‘kernelMatrix’ to the input image to yield a number, that number is divided by ‘divisor’
/// to yield the final destination color value. A divisor that is the sum of all the matrix values tends to have
/// an evening effect on the overall color intensity of the result. It is an error to specify a divisor of zero.
/// The default value is the sum of all values in kernelMatrix, with the exception that if the sum is zero, then
/// the divisor is set to 1.
#[option,variable]
divisor: float,
/// After applying the ‘kernelMatrix’ to the input image to yield a number and applying the ‘divisor’, the ‘bias’
/// attribute is added to each component. One application of ‘bias’ is when it is desirable to have .5 gray value
/// be the zero response of the filter. The bias property shifts the range of the filter. This allows representation
/// of values that would otherwise be clamped to 0 or 1. If ‘bias’ is not specified, then the effect is as if a
/// value of 0 were specified.
#[option,variable]
bias: float,
/// After applying the ‘kernelMatrix’ to the input image to yield a number and applying the ‘divisor’, the ‘bias’
/// attribute is added to each component. One application of ‘bias’ is when it is desirable to have .5 gray value
/// be the zero response of the filter. The bias property shifts the range of the filter. This allows representation
/// of values that would otherwise be clamped to 0 or 1. If ‘bias’ is not specified, then the effect is as if a
/// value of 0 were specified.
#[option,variable]
target_x: int,
/// Determines the positioning in Y of the convolution matrix relative to a given target pixel in the input image.
/// The topmost row of the matrix is row number zero. The value must be such that: 0 <= targetY < orderY. By default,
/// the convolution matrix is centered in Y over each pixel of the input image (i.e., targetY = floor ( orderY / 2 )).
#[option,variable]
target_y: int,
/// Determines how to extend the input image as necessary with color values so that the matrix operations can be applied
/// when the kernel is positioned at or near the edge of the input image.
#[variable]
edge_mode: FeConvolveMatrixEdgeMode,
/// The first number is the `dx` value. The second number is the `dy` value. If the `dy` value is not specified,
/// it defaults to the same value as `dx`. Indicates the intended distance in current filter units (i.e., units
/// as determined by the value of attribute ‘primitiveUnits’) between successive columns and rows, respectively,
/// in the ‘kernelMatrix’. By specifying value(s) for ‘kernelUnitLength’, the kernel becomes defined in a
/// scalable, abstract coordinate system. If ‘kernelUnitLength’ is not specified, the default value is one pixel
/// in the offscreen bitmap, which is a pixel-based coordinate system, and thus potentially not scalable. For
/// some level of consistency across display media and user agents, it is necessary that a value be provided for
/// at least one of ‘filterRes’ and ‘kernelUnitLength’. In some implementations, the most consistent results and
/// the fastest performance will be achieved if the pixel grid of the temporary offscreen images aligns with the
/// pixel grid of the kernel.
///
/// A negative or zero value is an error (see Error processing).
#[option,variable]
kernel_unit_len: NumberOptNumber,
/// A value of false indicates that the convolution will apply to all channels, including the alpha channel.
///
/// See [`feConvolveMatrix`](https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/filters.html#feConvolveMatrixElement)
#[variable]
preserve_alpha: bool,
}
/// See [`feConvolveMatrix`](https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/filters.html#feDiffuseLightingElement)
el FeDiffuseLighting mixin FePrimitive {
/// See [`FeIn`]
#[variable]
in: FeIn,
/// height of surface when Ain = 1.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 1 were specified.
#[option,variable]
surface_scale: float,
/// kd in Phong lighting model. In SVG, this can be any non-negative number.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 1 were specified.
#[option,variable]
diffuse_constant: float,
/// The first number is the `dx` value. The second number is the `dy` value. If the `dy` value is not specified,
/// it defaults to the same value as `dx`. Indicates the intended distance in current filter units (i.e., units
/// as determined by the value of attribute ‘primitiveUnits’) for dx and dy, respectively, in the surface normal
/// calculation formulas. By specifying value(s) for ‘kernelUnitLength’, the kernel becomes defined in a scalable,
/// abstract coordinate system. If ‘kernelUnitLength’ is not specified, the dx and dy values should represent
/// very small deltas relative to a given (x,y) position, which might be implemented in some cases as one pixel
/// in the intermediate image offscreen bitmap, which is a pixel-based coordinate system, and thus potentially
/// not scalable. For some level of consistency across display media and user agents, it is necessary that a value
/// be provided for at least one of ‘filterRes’ and ‘kernelUnitLength’. Discussion of intermediate images are in the
/// Introduction and in the description of attribute ‘filterRes’.
///
/// A negative or zero value is an error (see Error processing).
#[option,variable]
kernel_unit_len: NumberOptNumber,
}
/// This filter primitive uses the pixels values from the image from ‘in2’ to spatially displace the image from ‘in’.
leaf FeDisplacementMap mixin FePrimitive {
/// See [`FeIn`]
#[option,variable]
in: FeIn,
/// See [`FeIn`]
#[variable]
in2: FeIn,
/// Displacement scale factor. The amount is expressed in the coordinate system established by attribute ‘primitiveUnits’
/// on the ‘filter’ element.
///
/// When the value of this attribute is 0, this operation has no effect on the source image.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 0 were specified.
#[option,variable]
scale: float,
/// Indicates which channel from ‘in2’ to use to displace the pixels in ‘in’ along the x-axis.
/// If attribute ‘xChannelSelector’ is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of A were
/// specified.
#[option,variable]
x_channel_selector: Channel,
/// Indicates which channel from ‘in2’ to use to displace the pixels in ‘in’ along the y-axis.
/// If attribute ‘yChannelSelector’ is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of A were
/// specified.
#[option,variable]
y_channel_selector: Channel,
}
/// This filter primitive creates a rectangle filled with the color and opacity values from properties ‘flood-color’ a ‘flood-opacity’.
/// The rectangle is as large as the filter primitive subregion established by the ‘x’, ‘y’, ‘width’ and ‘height’ attributes on the
/// ‘feFlood’ element.
leaf FeFlood mixin FePrimitive {
/// indicates what color to use to flood the current filter primitive subregion.
#[option,variable]
color: Color,
/// defines the opacity value to use across the entire filter primitive subregion.
#[option,variable]
opacity: float,
}
/// This filter primitive performs a Gaussian blur on the input image.
///
/// See [`feGaussianBlur`](https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/filters.html#feGaussianBlurElement)
leaf FeGaussianBlur mixin FePrimitive {
/// See [`FeIn`]
#[option,variable]
in: FeIn,
/// The standard deviation for the blur operation. If two `number`s are provided, the first number represents
/// a standard deviation value along the x-axis of the coordinate system established by attribute ‘primitiveUnits’
/// on the ‘filter’ element. The second value represents a standard deviation in Y. If one number is provided,
/// then that value is used for both X and Y.
///
/// A negative value is an error (see Error processing). A value of zero disables the effect of the given filter
/// primitive (i.e., the result is the filter input image). If ‘stdDeviation’ is 0 in only one of X or Y, then the
/// effect is that the blur is only applied in the direction that has a non-zero value.
#[option,variable,init]
std_deviation: NumberOptNumber,
}
/// This filter primitive composites input image layers on top of each other using the over operator with Input1
/// (corresponding to the first ‘feMergeNode’ child element) on the bottom and the last specified input, InputN
/// (corresponding to the last ‘feMergeNode’ child element), on top.
///
/// See [`feMerge`](https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/filters.html#feMergeElement)
el FeMerge mixin FePrimitive;
/// See [`FeMerge`]
leaf FeMergeNode(#[variable,rename()] FeIn);
/// This filter primitive refers to a graphic external to this filter element, which is loaded or rendered into an RGBA
/// raster and becomes the result of the filter primitive.
///
/// See [`feImage`](https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/filters.html#feImageElement)
leaf FeImage mixin FePrimitive {
/// An IRI reference to the image source.
#[variable]
href: FuncIri,
/// See [`PreserveAspectRatio`].
#[option, variable]
aspect: PreserveAspectRatio,
}
/// This filter primitive performs or of artwork.
/// It is particularly useful for fattening or thinning an alpha channel.
///
/// See [`feMorphology`](https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/filters.html#feMorphologyElement)
leaf FeMorphology mixin FePrimitive {
/// See [`FeIn`]
#[option, variable]
in: FeIn,
/// See [`FeMorphologyOperator`]
#[option, variable]
mode: FeMorphologyOperator,
/// The radius (or radii) for the operation. If two `number`s are provided, the first number represents
/// a x-radius and the second value represents a y-radius. If one number is provided, then that value
/// is used for both X and Y. The values are in the coordinate system established by attribute
/// ‘primitiveUnits’ on the ‘filter’ element.
///
/// A negative value is an error (see Error processing). A value of zero disables the effect of the given
/// filter primitive (i.e., the result is a transparent black image).
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 0 were specified.
#[option, variable]
radius: NumberOptNumber,
}
/// This filter primitive offsets the input image relative to its current position in the image space by the specified vector.
///
/// This is important for effects like drop shadows.
///
/// See [`feOffset`](https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/filters.html#feOffsetElement)
leaf FeOffset mixin FePrimitive {
/// See [`FeIn`]
#[option, variable]
in: FeIn,
/// The amount to offset the input graphic along the x-axis. The offset amount is expressed in the coordinate system established
/// by attribute ‘primitiveUnits’ on the ‘filter’ element.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 0 were specified.
#[option, variable,init]
dx: float,
/// The amount to offset the input graphic along the y-axis. The offset amount is expressed in the coordinate system established
/// by attribute ‘primitiveUnits’ on the ‘filter’ element.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 0 were specified.
#[option, variable,init]
dy: float,
}
/// This filter primitive lights a source graphic using the alpha channel as a bump map.
/// The resulting image is an RGBA image based on the light color. The lighting calculation follows the standard specular component of
/// the Phong lighting model. The resulting image depends on the light color, light position and surface geometry of the input bump map.
/// The result of the lighting calculation is added. The filter primitive assumes that the viewer is at infinity in the z direction (i.e.,
/// the unit vector in the eye direction is (0,0,1) everywhere).
///
/// See [`feSpecularLighting`](https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/filters.html#feSpecularLightingElement)
el FeSpecularLighting mixin FePrimitive {
/// See [`FeIn`]
#[option, variable,init]
in: FeIn,
/// height of surface when Ain = 1.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 1 were specified.
#[option, variable]
surface_scale: float,
/// height of surface when Ain = 1.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 1 were specified.
#[option, variable]
specular_constant: float,
/// Exponent for specular term, larger is more "shiny". Range 1.0 to 128.0.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 1 were specified.
#[option, variable]
specular_exponent: float,
/// The first number is the `dx` value. The second number is the `dy` value. If the `dy` value is not specified,
/// it defaults to the same value as `dx`. Indicates the intended distance in current filter units (i.e., units
/// as determined by the value of attribute ‘primitiveUnits’) for dx and dy, respectively, in the surface normal
/// calculation formulas. By specifying value(s) for ‘kernelUnitLength’, the kernel becomes defined in a scalable,
/// abstract coordinate system. If ‘kernelUnitLength’ is not specified, the dx and dy values should represent very
/// small deltas relative to a given (x,y) position, which might be implemented in some cases as one pixel in the
/// intermediate image offscreen bitmap, which is a pixel-based coordinate system, and thus potentially not scalable.
/// For some level of consistency across display media and user agents, it is necessary that a value be provided
/// for at least one of ‘filterRes’ and ‘kernelUnitLength’. Discussion of intermediate images are in the Introduction
/// and in the description of attribute ‘filterRes’.
///
/// A negative or zero value is an error (see Error processing).
#[option, variable]
kernel_unit_len: NumberOptNumber,
}
/// This filter primitive fills a target rectangle with a repeated, tiled pattern of an input image. The target rectangle is
/// as large as the filter primitive subregion established by the ‘x’, ‘y’, ‘width’ and ‘height’ attributes on the ‘feTile’
/// element.
///
/// See [`feTitle`](https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/filters.html#feTitleElement)
leaf FeTile mixin FePrimitive {
/// See [`FeIn`]
#[option, variable]
in: FeIn,
}
/// This filter primitive creates an image using the Perlin turbulence function.
/// It allows the synthesis of artificial textures like clouds or marble. For a detailed description the of the Perlin turbulence
/// function, see , Ebert et al, AP Professional, 1994. The resulting image will fill the entire filter
/// primitive subregion for this filter primitive.
///
/// See [`feTurbulence`](https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/filters.html#feTurbulenceElement)
leaf FeTurbulence mixin FePrimitive {
/// The base frequency (frequencies) parameter(s) for the noise function. If two `number`s are provided, the first number
/// represents a base frequency in the X direction and the second value represents a base frequency in the Y direction.
/// If one number is provided, then that value is used for both X and Y.
///
/// A negative value for base frequency is an error (see Error processing).
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 0 were specifie.
#[option, variable]
base_frequency: NumberOptNumber,
/// The numOctaves parameter for the noise function.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 1 were specified.
#[option, variable]
num_octaves: int,
/// The starting number for the pseudo random number generator.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 0 were specified.
/// When the seed number is handed over to the algorithm above it must first be truncated, i.e.
/// rounded to the closest integer value towards zero.
#[option, variable]
seed: float,
/// See [`FeStitchTiles`]
#[option, variable]
stitch_tiles: FeStitchTiles,
/// See [`FeStitchTiles`]
#[option, variable]
type: FeTurbulenceType,
}
/// Linear gradients are defined by a ‘linearGradient’ element.
el LinearGradient {
/// Defines the coordinate system for attributes ‘x1’, ‘y1’, ‘x2’ and ‘y2’.
#[option, variable,rename("gradientUnits")]
units: Coords,
/// Contains the definition of an optional additional transformation from the gradient coordinate system onto the
/// target coordinate system (i.e., userSpaceOnUse or objectBoundingBox). This allows for things such as skewing
/// the gradient. This additional transformation matrix is post-multiplied to (i.e., inserted to the right of)
/// any previously defined transformations, including the implicit transformation necessary to convert from object
/// bounding box units to user space.
///
/// If attribute ‘gradientTransform’ is not specified, then the effect is as if an identity transform were specified.
///
/// Variable: yes.
#[option, variable, rename("gradientTransform")]
transform: vec[Transform],
/// ‘x1’, ‘y1’, ‘x2’ and ‘y2’ define a gradient vector for the linear gradient.
/// This gradient vector provides starting and ending points onto which the gradient stops are mapped. The values
/// of ‘x1’, ‘y1’, ‘x2’ and ‘y2’ can be either numbers or percents.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of '0%' were specified.
///
/// Variable: yes.
#[option, variable, init]
x1: Length,
/// See [`x1`](LinearGradient::x1)
#[option, variable, init]
y1: Length,
/// See [`x1`](LinearGradient::x1)
#[option, variable, init]
x2: Length,
/// See [`x1`](LinearGradient::x1)
#[option, variable, init]
y2: Length,
/// Indicates what happens if the gradient starts or ends inside the bounds of the target rectangle.
#[option, variable]
spread: SpreadMethod,
#[option,variable, rename("xlink:href")]
href: Iri
}
/// Radial gradients are defined by a ‘radialGradient’ element.
el RadialGradient {
/// Defines the coordinate system for attributes ‘x1’, ‘y1’, ‘x2’ and ‘y2’.
#[option, variable, rename("gradientUnits")]
unit: Coords,
/// Contains the definition of an optional additional transformation from the gradient coordinate system onto the
/// target coordinate system (i.e., userSpaceOnUse or objectBoundingBox). This allows for things such as skewing
/// the gradient. This additional transformation matrix is post-multiplied to (i.e., inserted to the right of)
/// any previously defined transformations, including the implicit transformation necessary to convert from object
/// bounding box units to user space.
///
/// If attribute ‘gradientTransform’ is not specified, then the effect is as if an identity transform were specified.
///
/// Variable: yes.
#[option, variable, rename("gradientTransform")]
transform: vec[Transform],
/// ‘cx’, ‘cy’ and ‘r’ define the largest (i.e., outermost) circle for the radial gradient.
/// The gradient will be drawn such that the 100% gradient stop is mapped to the perimeter
/// of this largest (i.e., outermost) circle.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of '50%' were specified.
///
/// Variable: yes.
#[option, variable,init]
cx: Length,
/// See [`cx`](RadialGradient::cx)
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of '50%' were specified.
#[option, variable,init]
cy: Length,
/// See [`cx`](RadialGradient::cx)
///
/// A negative value is an error (see Error processing). A value of zero will cause the area to be painted as a single color
/// using the color and opacity of the last gradient stop.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of '50%' were specified.
///
/// Variable: yes.
#[option, variable,init]
r: Length,
/// ‘fx’ and ‘fy’ define the focal point for the radial gradient. The gradient will be drawn such that the
/// 0% gradient stop is mapped to (fx, fy).
///
/// If attribute ‘fx’ is not specified, ‘fx’ will coincide with the presentational value of ‘cx’ for the element whether the value
/// for 'cx' was inherited or not. If the element references an element that specifies a value for 'fx', then the value of 'fx'
/// is inherited from the referenced element.
///
/// Variable: yes.
#[option, variable,init]
fx: Length,
/// See [`fx`](RadialGradient::fx)
///
/// If attribute ‘fy’ is not specified, ‘fy’ will coincide with the presentational value of ‘cy’ for the element whether the value
/// for 'cy' was inherited or not. If the element references an element that specifies a value for 'fy', then the value of 'fy'
/// is inherited from the referenced element.
///
/// Variable: yes.
#[option, variable,init]
fy: Length,
/// Indicates what happens if the gradient starts or ends inside the bounds of the target rectangle.
#[option, variable]
spread: SpreadMethod,
#[option,variable, rename("xlink:href")]
href: Iri
}
/// The ramp of colors to use on a gradient is defined by the ‘stop’ elements that are child elements
/// to either the ‘linearGradient’ element or the ‘radialGradient’ element.
#[rename("stop")]
leaf GradientStop {
/// The ‘offset’ attribute is either a `<number>` (usually ranging from 0 to 1) or a `<percent>`
/// (usually ranging from 0% to 100%) which indicates where the gradient stop is placed.
/// For linear gradients, the ‘offset’ attribute represents a location along the gradient vector.
/// For radial gradients, it represents a percent distance from (fx,fy) to the edge of the
/// outermost/largest circle.
///
/// Variable: yes.
#[variable]
offset: float,
/// indicates what color to use at that gradient stop
#[option, variable,rename("stop-color")]
color: Color,
/// Defines the opacity of a given gradient stop.
#[option, variable,rename("stop-opacity")]
opacity: float,
}
/// A container element for grouping together related graphics elements.
#[rename("g")]
el Group;
/// Paths represent the outline of a shape which can be filled, stroked, used as a clipping path,
/// or any combination of the three.
leaf Path {
/// The definition of the outline of a shape.
#[variable,rename("d")]
events: vec[PathEvent],
/// The author's computation of the total length of the path, in user units.
/// This value is used to calibrate the user agent's own distance-along-a-path
/// calculations with that of the author. The user agent will scale all
/// distance-along-a-path computations by the ratio of ‘pathLength’ to the user
/// agent's own computed value for total path length. ‘pathLength’ potentially
/// affects calculations for text on a path, motion animation and various stroke
/// operations.
///
/// A negative value is an error (see Error processing).
#[option, variable]
length: Length,
}
/// A pattern is used to fill or stroke an object using a pre-defined graphic object which can be replicated ()
/// at fixed intervals in x and y to cover the areas to be painted. Patterns are defined using a ‘pattern’ element and
/// then referenced by properties ‘fill’ and ‘stroke’ on a given graphics element to indicate that the given element
/// shall be filled or stroked with the referenced pattern.
///
/// Attributes ‘x’, ‘y’, ‘width’, ‘height’ and ‘patternUnits’ define a reference rectangle somewhere on the infinite canvas.
/// The reference rectangle has its top/left at (x, y) and its bottom/right at (x + width, y + height). The tiling
/// theoretically extends a series of such rectangles to infinity in X and Y (positive and negative), with rectangles
/// starting at (x + m*width, y + n* height) for each possible integer value for m and n.
el Pattern {
/// Defines the coordinate system for attributes ‘x’, ‘y’, ‘width’ and ‘height’.
///
/// If patternUnits=, the user coordinate system for attributes ‘x’, ‘y’, ‘width’ and ‘height’
/// is established using the bounding box of the element to which the pattern is applied (see Object bounding box units)
/// and then applying the transform specified by attribute ‘patternTransform’.
///
/// If patternUnits=, ‘x’, ‘y’, ‘width’ and ‘height’ represent values in the coordinate system
/// that results from taking the current user coordinate system in place at the time when the ‘pattern’ element
/// is referenced (i.e., the user coordinate system for the element referencing the ‘pattern’ element via a ‘fill’
/// or ‘stroke’ property) and then applying the transform specified by attribute ‘patternTransform’.
///
/// If attribute `units` is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 'objectBoundingBox' were specified.
#[option, variable, rename("patternUnits")]
units: Coords,
/// Defines the coordinate system for the contents of the ‘pattern’. Note that this attribute has no effect
/// if attribute ‘viewBox’ is specified.
///
/// If patternContentUnits=, the user coordinate system for the contents of the ‘pattern’
/// element is the coordinate system that results from taking the current user coordinate system in place
/// at the time when the ‘pattern’ element is referenced (i.e., the user coordinate system for the element
/// referencing the ‘pattern’ element via a ‘fill’ or ‘stroke’ property) and then applying the transform
/// specified by attribute ‘patternTransform’.
///
/// If patternContentUnits=, the user coordinate system for the contents of the ‘pattern’
/// element is established using the bounding box of the element to which the pattern is applied (see Object
/// bounding box units) and then applying the transform specified by attribute ‘patternTransform’.
///
/// If attribute `content_units` is not specified, then the effect is as if a value of 'userSpaceOnUse'
/// were specified.
#[option, variable]
content_units: Coords,
/// Contains the definition of an optional additional transformation from the pattern coordinate system onto the
/// target coordinate system (i.e., 'userSpaceOnUse' or 'objectBoundingBox'). This allows for things such as
/// skewing the pattern tiles. This additional transformation matrix is post-multiplied to (i.e., inserted to
/// the right of) any previously defined transformations, including the implicit transformation necessary to convert
/// from object bounding box units to user space.
///
/// If attribute `transform` is not specified, then the effect is as if an identity transform were specified.
#[option, variable]
transform: Transform,
/// ‘x’, ‘y’, ‘width’ and ‘height’ indicate how the pattern tiles are placed and spaced. These attributes represent
/// coordinates and values in the coordinate space specified by the combination of attributes [`units`](Self::units) and
/// [`content_units`](Self::content_units).
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of zero were specified.
///
/// Animatable: yes.
#[option, variable, init]
x: Length,
/// See [`x`](Self::x).
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of zero were specified.
///
/// Animatable: yes.
#[option, variable, init]
y: Length,
/// See [`x`](Self::x).
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of zero were specified.
///
/// Animatable: yes.
#[option, variable, init]
width: Length,
/// See [`x`](Self::x).
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of zero were specified.
///
/// Animatable: yes.
#[option, variable, init]
height: Length,
#[option,variable, rename("xlink:href")]
href: Iri
}
/// Use a fragment by name.
leaf Use(#[variable,rename()] Iri);
/// The ‘rect’ element defines a rectangle which is axis-aligned with the current user coordinate system.
/// Rounded rectangles can be achieved by setting appropriate values for attributes ‘rx’ and ‘ry’.
///
///
/// The values used for the x- and y-axis rounded corner radii are determined implicitly if the ‘rx’ or ‘ry’ attributes (or both) are not specified, or are specified but with invalid values. The values are also subject to clamping so that the lengths of the straight segments of the rectangle are never negative. The effective values for ‘rx’ and ‘ry’ are determined by following these steps in order:
///
/// 1. Let rx and ry be length values.
/// 1. If neither ‘rx’ nor ‘ry’ are properly specified, then set both rx and ry to 0. (This will result in square corners.)
/// 1. Otherwise, if a properly specified value is provided for ‘rx’, but not for ‘ry’, then set both rx and ry to the value of ‘rx’.
/// 1. Otherwise, if a properly specified value is provided for ‘ry’, but not for ‘rx’, then set both rx and ry to the value of ‘ry’.
/// 1. Otherwise, both ‘rx’ and ‘ry’ were specified properly. Set rx to the value of ‘rx’ and ry to the value of ‘ry’.
/// 1. If rx is greater than half of ‘width’, then set rx to half of ‘width’.
/// 1. If ry is greater than half of ‘height’, then set ry to half of ‘height’.
/// 1. The effective values of ‘rx’ and ‘ry’ are rx and ry, respectively.
leaf Rect {
/// The x-axis coordinate of the side of the rectangle which has the smaller x-axis coordinate value in the current user coordinate system.
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of "0" were specified.
///
/// Animatable: yes.
#[variable]
x: Length,
/// The y-axis coordinate of the side of the rectangle which has the smaller y-axis coordinate value in the current user coordinate system.
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of "0" were specified.
///
/// Animatable: yes.
#[variable]
y: Length,
/// The width of the rectangle.
/// A negative value is an error (see Error processing). A value of zero disables rendering of the element.
///
/// Animatable: yes.
#[variable]
width: Length,
/// The height of the rectangle.
/// A negative value is an error (see Error processing). A value of zero disables rendering of the element.
///
/// Animatable: yes.
#[variable]
height: Length,
/// For rounded rectangles, the x-axis radius of the ellipse used to round off the corners of the rectangle.
/// A negative value is an error (see Error processing).
///
/// Animatable: yes.
#[option, variable]
rx: Length,
/// For rounded rectangles, the y-axis radius of the ellipse used to round off the corners of the rectangle.
/// A negative value is an error (see Error processing).
///
/// Animatable: yes.
#[option, variable]
ry: Length,
}
/// The ‘circle’ element defines a circle based on a center point and a radius.
leaf Circle {
/// The x-axis coordinate of the center of the circle.
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of "0" were specified.
///
/// Animatable: yes.
#[variable]
cx: Length,
/// The y-axis coordinate of the center of the circle.
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of "0" were specified.
///
/// Animatable: yes.
#[variable]
cy: Length,
/// The radius of the circle.
/// A negative value is an error (see Error processing). A value of zero disables rendering of the element.
///
/// Animatable: yes.
#[variable]
r: Length,
}
/// The ‘ellipse’ element defines an ellipse which is axis-aligned with the current user coordinate
/// system based on a center point and two radii.
leaf Ellipse {
/// The x-axis coordinate of the center of the ellipse.
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of "0" were specified.
///
/// Animatable: yes.
#[option, variable]
cx: Length,
/// The y-axis coordinate of the center of the ellipse.
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of "0" were specified.
///
/// Animatable: yes.
#[option, variable]
cy: Length,
/// The x-axis radius of the ellipse.
/// A negative value is an error (see Error processing). A value of zero disables rendering of the element.
///
/// Animatable: yes.
#[variable]
rx: Length,
/// The y-axis radius of the ellipse.
/// A negative value is an error (see Error processing). A value of zero disables rendering of the element.
///
/// Animatable: yes.
#[variable]
ry: Length,
}
/// The ‘line’ element defines a line segment that starts at one point and ends at another.
leaf Line {
/// The x-axis coordinate of the start of the line.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of "0" were specified.
///
/// Animatable: yes.
#[variable]
x1: Length,
/// The y-axis coordinate of the start of the line.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of "0" were specified.
///
/// Animatable: yes.
#[variable]
y1: Length,
/// The x-axis coordinate of the end of the line.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of "0" were specified.
///
/// Animatable: yes.
#[variable]
x2: Length,
/// The y-axis coordinate of the end of the line.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of "0" were specified.
///
/// Animatable: yes.
#[variable]
y2: Length,
}
/// The ‘polyline’ element defines a set of connected straight line segments. Typically, ‘polyline’ elements define open shapes.
leaf Polyline(
/// The points that make up the polygon. All coordinate values are in the user coordinate system.
///
/// Animatable: yes.
#[variable,rename()]
vec[Point],
);
/// The ‘polygon’ element defines a closed shape consisting of a set of connected straight line segments.
leaf Polygon(
/// The points that make up the polygon. All coordinate values are in the user coordinate system.
///
/// Animatable: yes.
#[variable,rename()]
vec[Point],
);
/// The ‘text’ element defines a graphics element consisting of text.
///
/// See [`text`](https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/text.html#TextElement)
mixin MixinText {
/// If a single `coordinate` is provided, then the value represents the new absolute X coordinate for
/// the current text position for rendering the glyphs that correspond to the first character within
/// this element or any of its descendants.
///
/// If a comma- or space-separated list of n `coordinate`s is provided, then the values represent new
/// absolute X coordinates for the current text position for rendering the glyphs corresponding to
/// each of the first n characters within this element or any of its descendants.
///
/// For additional processing rules, refer to the description of the ‘x’ attribute on the ‘tspan’ element.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of "0" were specified.
#[option, variable,init]
x: vec[Length],
/// The corresponding list of absolute Y coordinates for the glyphs corresponding to the characters within this element.
/// The processing rules for the ‘y’ attribute parallel the processing rules for the ‘x’ attribute.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of "0" were specified.
#[option, variable,init]
y: vec[Length],
/// Shifts in the current text position along the x-axis for the characters within this element or any of its descendants.
///
/// Refer to the description of the ‘dx’ attribute on the ‘tspan’ element.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified on this element or any of its descendants, no supplemental shifts along
/// the x-axis will occur.
#[option, variable]
dx: vec[Length],
/// Shifts in the current text position along the y-axis for the characters within this element or any of its descendants.
///
/// Refer to the description of the ‘dy’ attribute on the ‘tspan’ element.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified on this element or any of its descendants, no supplemental shifts along
/// the y-axis will occur.
#[option, variable]
dy: vec[Length],
/// The supplemental rotation about the current text position that will be applied to all of the glyphs corresponding
/// to each character within this element.
///
/// Refer to the description of the ‘rotate’ attribute on the ‘tspan’ element.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified on this element or any of its descendants, no supplemental rotations will occur.
#[option, variable]
rotate: vec[Angle],
/// The author's computation of the total sum of all of the advance values that correspond to character data within
/// this element, including the advance value on the glyph (horizontal or vertical), the effect of properties ‘kerning’,
/// ‘letter-spacing’ and ‘word-spacing’ and adjustments due to attributes ‘dx’ and ‘dy’ on ‘tspan’ elements. This value
/// is used to calibrate the user agent's own calculations with that of the author.
///
/// The purpose of this attribute is to allow the author to achieve exact alignment, in visual rendering order after any
/// bidirectional reordering, for the first and last rendered glyphs that correspond to this element; thus, for the last
/// rendered character (in visual rendering order after any bidirectional reordering), any supplemental inter-character
/// spacing beyond normal glyph advances are ignored (in most cases) when the user agent determines the appropriate amount
/// to expand/compress the text string to fit within a length of ‘textLength’.
///
/// A negative value is an error (see Error processing).
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if the author's computation exactly matched the value calculated
/// by the user agent; thus, no advance adjustments are made.
#[option, variable]
text_length: vec[Length],
/// Indicates the type of adjustments which the user agent shall make to make the rendered length of the text match the
/// value specified on the ‘textLength’ attribute.
///
/// The user agent is required to achieve correct start and end positions for the text strings, but the locations of
/// intermediate glyphs are not predictable because user agents might employ advanced algorithms to stretch or compress
/// text strings in order to balance correct start and end positioning with optimal typography.
///
/// Note that, for a text string that contains n characters, the adjustments to the advance values often occur only for n−1
/// characters (see description of attribute ‘textLength’), whereas stretching or compressing of the glyphs will be applied
/// to all n characters.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as a value of 'spacing' were specified.
#[option, variable]
length_adjust: TextLengthAdjust,
}
/// The ‘text’ element defines a graphics element consisting of text.
///
/// See [`text`](https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/text.html#TextElement)
el Text mixin MixinText;
/// The ‘text’ element defines a graphics element consisting of text.
///
/// See [`text`](https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/text.html#TextElement)
#[rename("tspan")]
el TextSpan mixin MixinText;
/// Text content chars.
leaf Characters(#[rename()] string);
/// In addition to text drawn in a straight line, SVG also includes the ability to place text along the
/// shape of a ‘path’ element. To specify that a block of text is to be rendered along the shape of a ‘path’,
/// include the given text within a ‘textPath’ element which includes an href’ attribute with an IRI
/// reference to a ‘path’ element.
el TextPath {
/// An offset from the start of the ‘path’ for the initial current text position,
/// calculated using the user agent's [`distance along the path`] algorithm.
///
/// If a `length` other than a percentage is given, then the ‘startOffset’ represents a
/// distance along the path measured in the current user coordinate system.
///
/// If a percentage is given, then the ‘startOffset’ represents a percentage distance along
/// the entire path. Thus, startOffset= indicates the start point of the ‘path’ and
/// startOffset= indicates the end point of the ‘path’.
///
/// If the attribute is not specified, the effect is as if a value of were specified.
///
/// [`distance along the path`]: https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/paths.html#DistanceAlongAPath
#[option, variable]
start_offset: Length,
/// See [`TextPathMethod`]
#[option, variable]
method: TextPathMethod,
/// See [`TextPathSpacing`]
#[option, variable]
spacing: TextPathSpacing,
/// An IRI reference to the ‘path’ element onto which the glyphs will be rendered.
/// If `iri` is an invalid reference (e.g., no such element exists, or the referenced element is not a ‘path’),
/// then the ‘textPath’ element is in error and its entire contents shall not be rendered by the user agent.
#[variable]
href: Iri,
}
group Shape := (Rect,Circle,Ellipse,Line,Polyline,Polygon);
group Gradient := (LinearGradient,RadialGradient);
children (Text,TextSpan,TextPath,Characters) of Text;
children (TextSpan,Characters) of TextSpan;
children (TextSpan,Characters) of TextPath;
children (
Text,
ClipPath,
Filter,
Mask,
Group,
Canvas,
Shape,
Gradient,
) of Group;
children (
Text,
ClipPath,
Filter,
Mask,
Group,
Canvas,
Shape,
Gradient,
) of Canvas;
children (
FeBlend,
FeColorMatrix,
FeComponentTransfer,
FeComposite,
FeConvolveMatrix,
FeDiffuseLighting,
FeDisplacementMap,
FeFlood,
FeGaussianBlur,
FeMerge,
FeImage,
FeMorphology,
FeOffset,
FeSpecularLighting,
FeTile,
FeTurbulence,
) of Filter;
children (
FeFuncR,
FeFuncG,
FeFuncB,
FeFuncA,
) of FeComponentTransfer;
children FeMergeNode of FeMerge;
children (
FeDistantLight,
FePointLight,
FeSpotLight,
) of FeDiffuseLighting;
children (
FeDistantLight,
FePointLight,
FeSpotLight,
) of FeSpecularLighting;
children GradientStop of Gradient;
children (
ClipPath,
Filter,
Mask,
Text,
) of Pattern;
children (Shape,Text,Use) of ClipPath;
children (
Text,
ClipPath,
Filter,
Group,
Canvas,
Use,
Shape,
Gradient,
) of Mask;
apply (
TextLayout,
Font,
WithFilter,
Fill,
Stroke,
) to (Text,TextSpan);
apply (
EnableBackground,
WithTransform,
Fill,
Stroke,
WithFilter,
WithClipPath,
WithMask,
Opacity,
Font,
) to (
Group,
Canvas,
Filter,
Mask,
Shape,
Use,
Path,
);
apply Id to (
RadialGradient,
LinearGradient,
Group,
Canvas,
Filter,
Mask,
Text,
TextSpan,
Pattern,
Path,
);
apply ViewBox to Canvas;
apply ViewBox to Pattern;