<p align="left">
<img src="./artefacts/simdna.svg" alt="SimDNA Logo" width="200">
</p>
*High-performance DNA/RNA sequence encoding and decoding using SIMD instructions with automatic fallback to scalar implementations.*
[](https://crates.io/crates/simdna)
[](https://docs.rs/simdna)
[](https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
## Table of Contents
- [Table of Contents](#table-of-contents)
- [Features](#features)
- [Installation](#installation)
- [IUPAC Nucleotide Codes](#iupac-nucleotide-codes)
- [Standard Nucleotides](#standard-nucleotides)
- [Two-Base Ambiguity Codes](#two-base-ambiguity-codes)
- [Three-Base Ambiguity Codes](#three-base-ambiguity-codes)
- [Wildcards and Gaps](#wildcards-and-gaps)
- [Bit Rotation Property](#bit-rotation-property)
- [Usage](#usage)
- [Reverse Complement](#reverse-complement)
- [IUPAC Ambiguity Code Complements](#iupac-ambiguity-code-complements)
- [Input Handling](#input-handling)
- [Integration](#integration)
- [Working with seq\_io](#working-with-seq_io)
- [Working with noodles](#working-with-noodles)
- [Working with rust-bio](#working-with-rust-bio)
- [Zero-Copy Integration](#zero-copy-integration)
- [Platform Support](#platform-support)
- [Performance](#performance)
- [Testing](#testing)
- [Unit Tests](#unit-tests)
- [Fuzz Testing](#fuzz-testing)
- [Contributing](#contributing)
- [Changelog](#changelog)
- [Citation](#citation)
- [License](#license)
## Features
- **4-bit encoding** supporting all IUPAC nucleotide codes (16 standard + U for RNA)
- **Bit-rotation-compatible encoding** enabling efficient complement calculation
- **SIMD-accelerated reverse complement** operations
- **SIMD acceleration** on x86_64 (SSSE3) and ARM64 (NEON)
- **Static lookup tables** for branch-free encoding/decoding
- **Prefetch hints** for improved cache utilization on large sequences
- **Automatic fallback** to optimized scalar implementation
- **Thread-safe** pure functions with no global state
- **2:1 compression** ratio compared to ASCII representation
- **RNA support** via U (Uracil) mapping to T
## Installation
Add simdna to your `Cargo.toml`:
```toml
[dependencies]
simdna = "1.0"
```
Or install via cargo:
```bash
cargo add simdna
```
## IUPAC Nucleotide Codes
simdna supports the complete IUPAC nucleotide alphabet with a bit-rotation-compatible encoding scheme. This encoding enables efficient complement calculation via a simple 2-bit rotation operation.
### Standard Nucleotides
| A | Adenine | 0x1 | T (0x4) |
| C | Cytosine | 0x2 | G (0x8) |
| G | Guanine | 0x8 | C (0x2) |
| T | Thymine | 0x4 | A (0x1) |
| U | Uracil (RNA → T) | 0x4 | A (0x1) |
### Two-Base Ambiguity Codes
| R | A or G (purine) | 0x9 | Y (0x6) |
| Y | C or T (pyrimidine) | 0x6 | R (0x9) |
| S | G or C (strong) | 0xA | S (0xA) |
| W | A or T (weak) | 0x5 | W (0x5) |
| K | G or T (keto) | 0xC | M (0x3) |
| M | A or C (amino) | 0x3 | K (0xC) |
### Three-Base Ambiguity Codes
| B | C, G, or T (not A) | 0xE | V (0xB) |
| D | A, G, or T (not C) | 0xD | H (0x7) |
| H | A, C, or T (not G) | 0x7 | D (0xD) |
| V | A, C, or G (not T) | 0xB | B (0xE) |
### Wildcards and Gaps
| N | Any base | 0xF | N (0xF) |
| - | Gap / deletion | 0x0 | - (0x0) |
| . | Gap (alternative) | 0x0 | - (0x0) |
### Bit Rotation Property
The encoding is designed so that the complement of any nucleotide can be computed via a 2-bit rotation:
```text
This enables SIMD-accelerated reverse complement operations that are ~2x faster than lookup table approaches.
## Usage
```rust
use simdna::dna_simd_encoder::{encode_dna_prefer_simd, decode_dna_prefer_simd};
// Encode a DNA sequence with IUPAC codes
let sequence = b"ACGTNRYSWKMBDHV-";
let encoded = encode_dna_prefer_simd(sequence);
// The encoded data is 2x smaller (2 nucleotides per byte)
assert_eq!(encoded.len(), sequence.len() / 2);
// Decode back to the original sequence
let decoded = decode_dna_prefer_simd(&encoded, sequence.len());
assert_eq!(decoded, sequence);
// RNA sequences work seamlessly (U maps to T)
let rna = b"ACGU";
let encoded_rna = encode_dna_prefer_simd(rna);
let decoded_rna = decode_dna_prefer_simd(&encoded_rna, rna.len());
assert_eq!(decoded_rna, b"ACGT"); // U decodes as T
```
## Reverse Complement
simdna provides efficient SIMD-accelerated reverse complement operations for DNA/RNA sequences:
```rust
use simdna::dna_simd_encoder::{reverse_complement, reverse_complement_encoded, encode_dna_prefer_simd};
// High-level API: ASCII in, ASCII out
let sequence = b"ACGT";
let rc = reverse_complement(sequence);
assert_eq!(rc, b"ACGT"); // ACGT is its own reverse complement
// Biological example
let forward = b"ATGCAACG";
let rc = reverse_complement(forward);
assert_eq!(rc, b"CGTTGCAT");
// Low-level API: operates directly on encoded data for maximum performance
let encoded = encode_dna_prefer_simd(b"ACGT");
let rc_encoded = reverse_complement_encoded(&encoded, 4);
// rc_encoded is the encoded form of "ACGT"
```
### IUPAC Ambiguity Code Complements
Reverse complement correctly handles all IUPAC ambiguity codes:
```rust
use simdna::dna_simd_encoder::reverse_complement;
```
## Input Handling
- **Case insensitive**: Both `"ACGT"` and `"acgt"` encode identically
- **Invalid characters**: Non-IUPAC characters (X, digits, etc.) encode as gap (0xF)
- **Decoding**: Always produces uppercase nucleotides
## Integration
**simdna** focuses exclusively on high-performance encoding/decoding, making it composable with any FASTA/FASTQ parser or custom format. This keeps the library lightweight and lets you choose the tools that fit your workflow.
### Working with seq_io
[seq_io](https://crates.io/crates/seq_io) is a fast FASTA/FASTQ parser. simdna works directly with its borrowed sequence data:
```rust
use seq_io::fasta::Reader;
use simdna::dna_simd_encoder::encode_dna_prefer_simd;
let mut reader = Reader::from_path("genome.fasta")?;
while let Some(record) = reader.next() {
let record = record?;
// seq_io provides &[u8] directly - no allocation needed
let encoded = encode_dna_prefer_simd(record.seq());
// ... use encoded data
}
```
### Working with noodles
[noodles](https://crates.io/crates/noodles) is a comprehensive bioinformatics I/O library:
```rust
use noodles::fasta;
use simdna::dna_simd_encoder::encode_dna_prefer_simd;
let mut reader = fasta::io::reader::Builder::default().build_from_path("genome.fasta")?;
for result in reader.records() {
let record = result?;
let encoded = encode_dna_prefer_simd(record.sequence().as_ref());
// ... use encoded data
}
```
### Working with rust-bio
[rust-bio](https://crates.io/crates/bio) provides algorithms and data structures for bioinformatics:
```rust
use bio::io::fasta;
use simdna::dna_simd_encoder::encode_dna_prefer_simd;
let reader = fasta::Reader::from_file("genome.fasta")?;
for result in reader.records() {
let record = result?;
let encoded = encode_dna_prefer_simd(record.seq());
// ... use encoded data
}
```
### Zero-Copy Integration
simdna accepts `&[u8]` slices, enabling zero-copy integration with parsers. Avoid unnecessary allocations:
```rust
// ✓ Good: Work directly with borrowed data
let encoded = encode_dna_prefer_simd(record.seq());
// ✗ Avoid: Unnecessary allocation
let owned: Vec<u8> = record.seq().to_vec();
let encoded = encode_dna_prefer_simd(&owned);
```
Most FASTA/FASTQ parsers provide sequence data as `&[u8]` or types that implement `AsRef<[u8]>`, which work directly with simdna's API.
## Platform Support
| x86_64 | SSSE3 | Scalar |
| ARM64 | NEON | Scalar |
| Other | - | Scalar |
## Performance
simdna employs multiple optimization strategies:
- **Static Lookup Tables**: Pre-computed encode/decode tables eliminate branch mispredictions
- **SIMD Processing**: Handles 32 nucleotides per iteration (two 16-byte chunks) with prefetching
- **Direct Case Handling**: LUT handles case-insensitivity without uppercase conversion overhead
- **Optimized Scalar Path**: Remainder processing uses 4-at-a-time scalar encoding
- **2:1 Compression**: 4 bits per nucleotide vs 8 bits ASCII
- **Expected speedup**: 4-8x over naive scalar code on modern CPUs
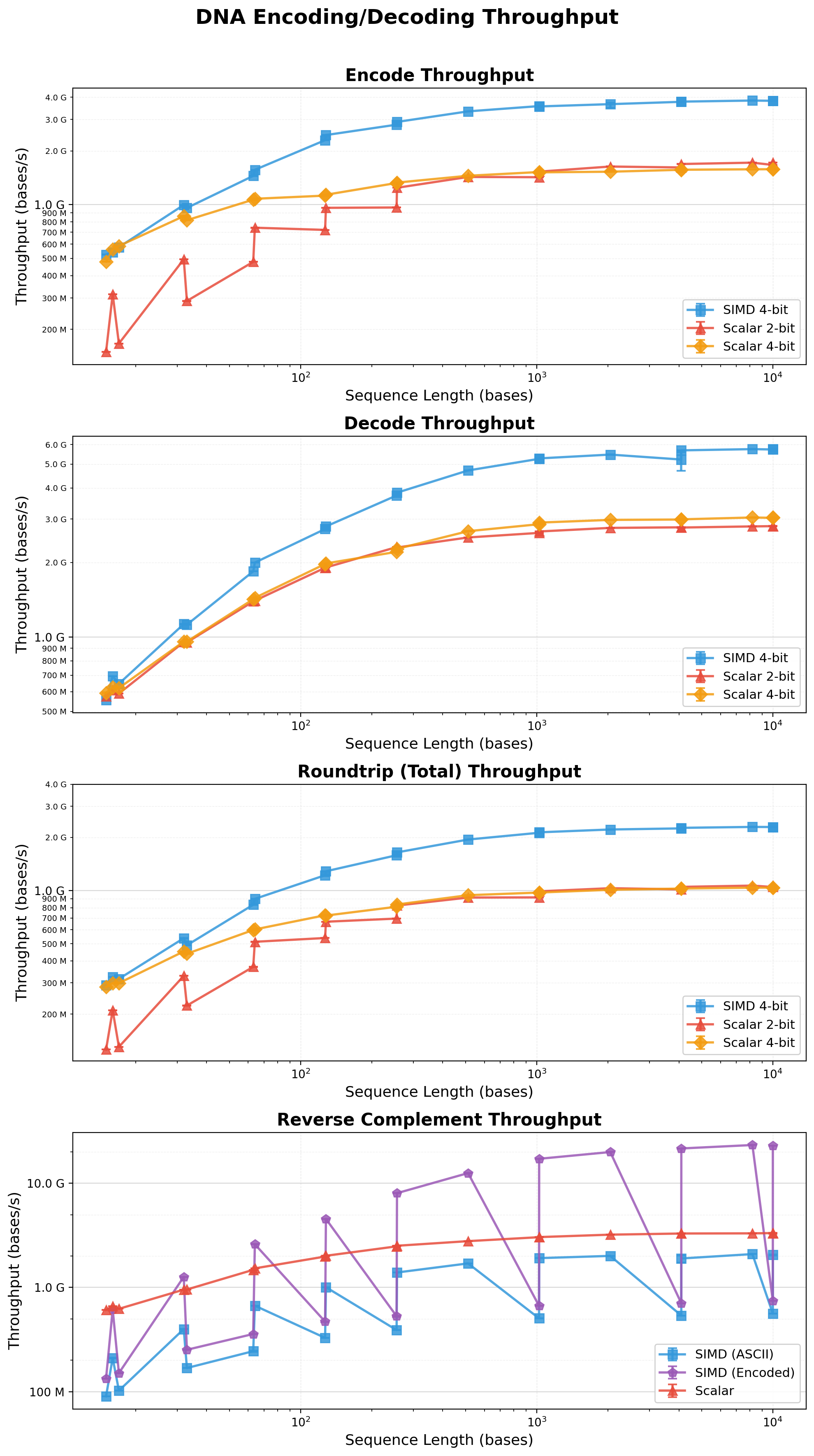
<sub>Benchmarks obtained on a Mac Studio with 32GB RAM and Apple M1 Max chip running macOS Tahoe 26.1 using the Criterion.rs statistics-driven micro-benchmarking library.</sub>
## Testing
simdna employs a comprehensive testing strategy to ensure correctness and robustness:
### Unit Tests
Run the standard test suite with:
```bash
cargo test
```
The unit tests cover:
- Encoding and decoding of all IUPAC nucleotide codes
- Case insensitivity handling
- Invalid character handling
- Odd and even length sequences
- Empty input edge cases
- SIMD and scalar implementation equivalence
### Fuzz Testing
simdna uses [`cargo-fuzz`](https://github.com/rust-fuzz/cargo-fuzz) for property-based fuzz testing to discover edge cases and potential bugs. The following fuzz targets are available:
| `roundtrip` | Verifies encode→decode produces consistent output |
| `valid_iupac` | Tests encoding of valid IUPAC sequences |
| `decode_robust` | Tests decoder resilience to arbitrary byte sequences |
| `boundaries` | Tests sequence length boundary conditions |
| `simd_scalar_equivalence` | Verifies SIMD and scalar implementations produce identical results |
| `bit_rotation` | Verifies bit rotation complement properties (involution, consistency) |
| `reverse_complement` | Tests reverse complement correctness (double-rc = original) |
Run fuzz tests with:
```bash
cargo +nightly fuzz run <target> -- -max_total_time=60
```
## Contributing
Contributions are welcome! Please see [CONTRIBUTING.md](CONTRIBUTING.md) for guidelines on bug reports and feature requests.
## Changelog
See [CHANGELOG.md](CHANGELOG.md) for a history of changes to this project.
## Citation
If you use simdna in your research, please cite it using the metadata in [CITATION.cff](CITATION.cff). GitHub can also generate citation information directly from the repository page.
## License
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see [LICENSE](LICENSE) for details.