#[repr(C)]pub struct QFormLayout { /* private fields */ }Expand description
The QFormLayout class manages forms of input widgets and their associated labels.
C++ class: QFormLayout.
The QFormLayout class manages forms of input widgets and their associated labels.
QFormLayout is a convenience layout class that lays out its children in a two-column form. The left column consists of labels and the right column consists of "field" widgets (line editors, spin boxes, etc.).
Traditionally, such two-column form layouts were achieved using QGridLayout. QFormLayout is a higher-level alternative that provides the following advantages:
- Adherence to the different platform's look and feel guidelines.
For example, the macOS Aqua and KDE guidelines specify that the labels should be right-aligned, whereas Windows and GNOME applications normally use left-alignment.
- Support for wrapping long rows.
For devices with small displays, QFormLayout can be set to wrap long rows, or even to wrap all rows.
- Convenient API for creating label--field pairs.
The addRow() overload that takes a QString and a QWidget * creates a QLabel behind the scenes and automatically set up its buddy. We can then write code like this:
QFormLayout *formLayout = new QFormLayout; formLayout->addRow(tr(“&Name:”), nameLineEdit); formLayout->addRow(tr(“&Email:”), emailLineEdit); formLayout->addRow(tr(“&Age:”), ageSpinBox); setLayout(formLayout);
Compare this with the following code, written using QGridLayout:
nameLabel = new QLabel(tr(“&Name:”)); nameLabel->setBuddy(nameLineEdit);
emailLabel = new QLabel(tr(“&Name:”)); emailLabel->setBuddy(emailLineEdit);
ageLabel = new QLabel(tr(“&Name:”)); ageLabel->setBuddy(ageSpinBox);
QGridLayout *gridLayout = new QGridLayout; gridLayout->addWidget(nameLabel, 0, 0); gridLayout->addWidget(nameLineEdit, 0, 1); gridLayout->addWidget(emailLabel, 1, 0); gridLayout->addWidget(emailLineEdit, 1, 1); gridLayout->addWidget(ageLabel, 2, 0); gridLayout->addWidget(ageSpinBox, 2, 1); setLayout(gridLayout);
The table below shows the default appearance in different styles.
| QCommonStyle derived styles (except QPlastiqueStyle) | QMacStyle | QPlastiqueStyle | Qt Extended styles |
|---|---|---|---|
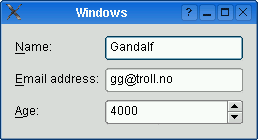 | 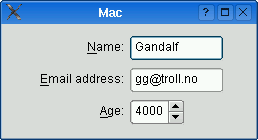 | 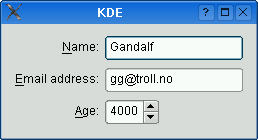 | 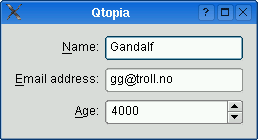 |
| Traditional style used for Windows, GNOME, and earlier versions of KDE. Labels are left aligned, and expanding fields grow to fill the available space. (This normally corresponds to what we would get using a two-column QGridLayout.) | Style based on the macOS Aqua guidelines. Labels are right-aligned, the fields don't grow beyond their size hint, and the form is horizontally centered. | Recommended style for KDE applications. Similar to MacStyle, except that the form is left-aligned and all fields grow to fill the available space. | Default style for Qt Extended styles. Labels are right-aligned, expanding fields grow to fill the available space, and row wrapping is enabled for long lines. |
The form styles can be also be overridden individually by calling setLabelAlignment(), setFormAlignment(), setFieldGrowthPolicy(), and setRowWrapPolicy(). For example, to simulate the form layout appearance of QMacStyle on all platforms, but with left-aligned labels, you could write:
formLayout->setRowWrapPolicy(QFormLayout::DontWrapRows); formLayout->setFieldGrowthPolicy(QFormLayout::FieldsStayAtSizeHint); formLayout->setFormAlignment(Qt::AlignHCenter | Qt::AlignTop); formLayout->setLabelAlignment(Qt::AlignLeft);
Implementations§
Source§impl QFormLayout
impl QFormLayout
Sourcepub unsafe fn add_item(&self, item: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayoutItem>>)
pub unsafe fn add_item(&self, item: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayoutItem>>)
Reimplemented from QLayout::addItem().
Calls C++ function: virtual void QFormLayout::addItem(QLayoutItem* item).
Reimplemented from QLayout::addItem().
Sourcepub unsafe fn add_row_2_q_widget(
&self,
label: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>,
field: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>,
)
pub unsafe fn add_row_2_q_widget( &self, label: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>, field: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>, )
Adds a new row to the bottom of this form layout, with the given label and field.
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::addRow(QWidget* label, QWidget* field).
Adds a new row to the bottom of this form layout, with the given label and field.
See also insertRow().
Sourcepub unsafe fn add_row_q_widget_q_layout(
&self,
label: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>,
field: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayout>>,
)
pub unsafe fn add_row_q_widget_q_layout( &self, label: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>, field: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayout>>, )
This is an overloaded function.
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::addRow(QWidget* label, QLayout* field).
This is an overloaded function.
Sourcepub unsafe fn add_row_q_string_q_widget(
&self,
label_text: impl CastInto<Ref<QString>>,
field: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>,
)
pub unsafe fn add_row_q_string_q_widget( &self, label_text: impl CastInto<Ref<QString>>, field: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>, )
This is an overloaded function.
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::addRow(const QString& labelText, QWidget* field).
Sourcepub unsafe fn add_row_q_string_q_layout(
&self,
label_text: impl CastInto<Ref<QString>>,
field: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayout>>,
)
pub unsafe fn add_row_q_string_q_layout( &self, label_text: impl CastInto<Ref<QString>>, field: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayout>>, )
This is an overloaded function.
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::addRow(const QString& labelText, QLayout* field).
This is an overloaded function.
This overload automatically creates a QLabel behind the scenes with labelText as its text.
Sourcepub unsafe fn add_row_q_widget(&self, widget: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>)
pub unsafe fn add_row_q_widget(&self, widget: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>)
This is an overloaded function.
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::addRow(QWidget* widget).
This is an overloaded function.
Adds the specified widget at the end of this form layout. The widget spans both columns.
Sourcepub unsafe fn add_row_q_layout(&self, layout: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayout>>)
pub unsafe fn add_row_q_layout(&self, layout: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayout>>)
This is an overloaded function.
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::addRow(QLayout* layout).
This is an overloaded function.
Adds the specified layout at the end of this form layout. The layout spans both columns.
Sourcepub unsafe fn count(&self) -> c_int
pub unsafe fn count(&self) -> c_int
Reimplemented from QLayout::count().
Calls C++ function: virtual int QFormLayout::count() const.
Reimplemented from QLayout::count().
Sourcepub unsafe fn expanding_directions(&self) -> QFlags<Orientation>
pub unsafe fn expanding_directions(&self) -> QFlags<Orientation>
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::expandingDirections().
Calls C++ function: virtual QFlags<Qt::Orientation> QFormLayout::expandingDirections() const.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::expandingDirections().
Sourcepub unsafe fn field_growth_policy(&self) -> FieldGrowthPolicy
pub unsafe fn field_growth_policy(&self) -> FieldGrowthPolicy
This property holds the way in which the form's fields grow
Calls C++ function: QFormLayout::FieldGrowthPolicy QFormLayout::fieldGrowthPolicy() const.
This property holds the way in which the form’s fields grow
The default value depends on the widget or application style. For QMacStyle, the default is FieldsStayAtSizeHint; for QCommonStyle derived styles (like Plastique and Windows), the default is ExpandingFieldsGrow; for Qt Extended styles, the default is AllNonFixedFieldsGrow.
If none of the fields can grow and the form is resized, extra space is distributed according to the current form alignment.
Access functions:
| FieldGrowthPolicy | fieldGrowthPolicy() const |
| void | setFieldGrowthPolicy(FieldGrowthPolicy policy) |
See also formAlignment and rowWrapPolicy.
Sourcepub unsafe fn form_alignment(&self) -> QFlags<AlignmentFlag>
pub unsafe fn form_alignment(&self) -> QFlags<AlignmentFlag>
This property holds the alignment of the form layout's contents within the layout's geometry
Calls C++ function: QFlags<Qt::AlignmentFlag> QFormLayout::formAlignment() const.
This property holds the alignment of the form layout’s contents within the layout’s geometry
The default value depends on the widget or application style. For QMacStyle, the default is Qt::AlignHCenter | Qt::AlignTop; for the other styles, the default is Qt::AlignLeft | Qt::AlignTop.
Access functions:
| Qt::Alignment | formAlignment() const |
| void | setFormAlignment(Qt::Alignment alignment) |
See also labelAlignment and rowWrapPolicy.
Sourcepub unsafe fn get_item_position(
&self,
index: c_int,
row_ptr: *mut c_int,
role_ptr: *mut ItemRole,
)
pub unsafe fn get_item_position( &self, index: c_int, row_ptr: *mut c_int, role_ptr: *mut ItemRole, )
Retrieves the row and role (column) of the item at the specified index. If index is out of bounds, *rowPtr is set to -1; otherwise the row is stored in *rowPtr and the role is stored in *rolePtr.
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::getItemPosition(int index, int* rowPtr, QFormLayout::ItemRole* rolePtr) const.
Retrieves the row and role (column) of the item at the specified index. If index is out of bounds, *rowPtr is set to -1; otherwise the row is stored in *rowPtr and the role is stored in *rolePtr.
See also itemAt(), count(), getLayoutPosition(), and getWidgetPosition().
Sourcepub unsafe fn get_layout_position(
&self,
layout: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayout>>,
row_ptr: *mut c_int,
role_ptr: *mut ItemRole,
)
pub unsafe fn get_layout_position( &self, layout: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayout>>, row_ptr: *mut c_int, role_ptr: *mut ItemRole, )
Retrieves the row and role (column) of the specified child layout. If layout is not in the form layout, *rowPtr is set to -1; otherwise the row is stored in *rowPtr and the role is stored in *rolePtr.
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::getLayoutPosition(QLayout* layout, int* rowPtr, QFormLayout::ItemRole* rolePtr) const.
Retrieves the row and role (column) of the specified child layout. If layout is not in the form layout, *rowPtr is set to -1; otherwise the row is stored in *rowPtr and the role is stored in *rolePtr.
Sourcepub unsafe fn get_widget_position(
&self,
widget: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>,
row_ptr: *mut c_int,
role_ptr: *mut ItemRole,
)
pub unsafe fn get_widget_position( &self, widget: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>, row_ptr: *mut c_int, role_ptr: *mut ItemRole, )
Retrieves the row and role (column) of the specified widget in the layout. If widget is not in the layout, *rowPtr is set to -1; otherwise the row is stored in *rowPtr and the role is stored in *rolePtr.
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::getWidgetPosition(QWidget* widget, int* rowPtr, QFormLayout::ItemRole* rolePtr) const.
Retrieves the row and role (column) of the specified widget in the layout. If widget is not in the layout, *rowPtr is set to -1; otherwise the row is stored in *rowPtr and the role is stored in *rolePtr.
See also getItemPosition() and itemAt().
Sourcepub unsafe fn has_height_for_width(&self) -> bool
pub unsafe fn has_height_for_width(&self) -> bool
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::hasHeightForWidth().
Calls C++ function: virtual bool QFormLayout::hasHeightForWidth() const.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::hasHeightForWidth().
Sourcepub unsafe fn height_for_width(&self, width: c_int) -> c_int
pub unsafe fn height_for_width(&self, width: c_int) -> c_int
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::heightForWidth().
Calls C++ function: virtual int QFormLayout::heightForWidth(int width) const.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::heightForWidth().
Sourcepub unsafe fn horizontal_spacing(&self) -> c_int
pub unsafe fn horizontal_spacing(&self) -> c_int
This property holds the spacing between widgets that are laid out side by side
Calls C++ function: int QFormLayout::horizontalSpacing() const.
This property holds the spacing between widgets that are laid out side by side
By default, if no value is explicitly set, the layout's horizontal spacing is inherited from the parent layout, or from the style settings for the parent widget.
Access functions:
| int | horizontalSpacing() const |
| void | setHorizontalSpacing(int spacing) |
See also verticalSpacing, QStyle::pixelMetric(), and PM_LayoutHorizontalSpacing.
Sourcepub unsafe fn insert_row_int2_q_widget(
&self,
row: c_int,
label: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>,
field: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>,
)
pub unsafe fn insert_row_int2_q_widget( &self, row: c_int, label: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>, field: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>, )
Inserts a new row at position row in this form layout, with the given label and field. If row is out of bounds, the new row is added at the end.
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::insertRow(int row, QWidget* label, QWidget* field).
Inserts a new row at position row in this form layout, with the given label and field. If row is out of bounds, the new row is added at the end.
See also addRow().
Sourcepub unsafe fn insert_row_int_q_widget_q_layout(
&self,
row: c_int,
label: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>,
field: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayout>>,
)
pub unsafe fn insert_row_int_q_widget_q_layout( &self, row: c_int, label: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>, field: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayout>>, )
This is an overloaded function.
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::insertRow(int row, QWidget* label, QLayout* field).
This is an overloaded function.
Sourcepub unsafe fn insert_row_int_q_string_q_widget(
&self,
row: c_int,
label_text: impl CastInto<Ref<QString>>,
field: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>,
)
pub unsafe fn insert_row_int_q_string_q_widget( &self, row: c_int, label_text: impl CastInto<Ref<QString>>, field: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>, )
This is an overloaded function.
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::insertRow(int row, const QString& labelText, QWidget* field).
Sourcepub unsafe fn insert_row_int_q_string_q_layout(
&self,
row: c_int,
label_text: impl CastInto<Ref<QString>>,
field: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayout>>,
)
pub unsafe fn insert_row_int_q_string_q_layout( &self, row: c_int, label_text: impl CastInto<Ref<QString>>, field: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayout>>, )
This is an overloaded function.
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::insertRow(int row, const QString& labelText, QLayout* field).
This is an overloaded function.
This overload automatically creates a QLabel behind the scenes with labelText as its text.
Sourcepub unsafe fn insert_row_int_q_widget(
&self,
row: c_int,
widget: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>,
)
pub unsafe fn insert_row_int_q_widget( &self, row: c_int, widget: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>, )
This is an overloaded function.
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::insertRow(int row, QWidget* widget).
This is an overloaded function.
Inserts the specified widget at position row in this form layout. The widget spans both columns. If row is out of bounds, the widget is added at the end.
Sourcepub unsafe fn insert_row_int_q_layout(
&self,
row: c_int,
layout: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayout>>,
)
pub unsafe fn insert_row_int_q_layout( &self, row: c_int, layout: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayout>>, )
This is an overloaded function.
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::insertRow(int row, QLayout* layout).
This is an overloaded function.
Inserts the specified layout at position row in this form layout. The layout spans both columns. If row is out of bounds, the widget is added at the end.
Sourcepub unsafe fn invalidate(&self)
pub unsafe fn invalidate(&self)
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::invalidate().
Calls C++ function: virtual void QFormLayout::invalidate().
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::invalidate().
Sourcepub unsafe fn item_at_2a(&self, row: c_int, role: ItemRole) -> Ptr<QLayoutItem>
pub unsafe fn item_at_2a(&self, row: c_int, role: ItemRole) -> Ptr<QLayoutItem>
Returns the layout item in the given row with the specified role (column). Returns 0 if there is no such item.
Calls C++ function: QLayoutItem* QFormLayout::itemAt(int row, QFormLayout::ItemRole role) const.
Returns the layout item in the given row with the specified role (column). Returns 0 if there is no such item.
See also QLayout::itemAt() and setItem().
Sourcepub unsafe fn item_at_1a(&self, index: c_int) -> Ptr<QLayoutItem>
pub unsafe fn item_at_1a(&self, index: c_int) -> Ptr<QLayoutItem>
Reimplemented from QLayout::itemAt().
Calls C++ function: virtual QLayoutItem* QFormLayout::itemAt(int index) const.
Reimplemented from QLayout::itemAt().
Sourcepub unsafe fn label_alignment(&self) -> QFlags<AlignmentFlag>
pub unsafe fn label_alignment(&self) -> QFlags<AlignmentFlag>
This property holds the horizontal alignment of the labels
Calls C++ function: QFlags<Qt::AlignmentFlag> QFormLayout::labelAlignment() const.
This property holds the horizontal alignment of the labels
The default value depends on the widget or application style. For QCommonStyle derived styles, except for QPlastiqueStyle, the default is Qt::AlignLeft; for the other styles, the default is Qt::AlignRight.
Access functions:
| Qt::Alignment | labelAlignment() const |
| void | setLabelAlignment(Qt::Alignment alignment) |
See also formAlignment.
Sourcepub unsafe fn label_for_field_q_widget(
&self,
field: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>,
) -> QPtr<QWidget>
pub unsafe fn label_for_field_q_widget( &self, field: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>, ) -> QPtr<QWidget>
Returns the label associated with the given field.
Calls C++ function: QWidget* QFormLayout::labelForField(QWidget* field) const.
Returns the label associated with the given field.
See also itemAt().
Sourcepub unsafe fn label_for_field_q_layout(
&self,
field: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayout>>,
) -> QPtr<QWidget>
pub unsafe fn label_for_field_q_layout( &self, field: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayout>>, ) -> QPtr<QWidget>
This is an overloaded function.
Calls C++ function: QWidget* QFormLayout::labelForField(QLayout* field) const.
This is an overloaded function.
Sourcepub unsafe fn meta_object(&self) -> Ptr<QMetaObject>
pub unsafe fn meta_object(&self) -> Ptr<QMetaObject>
Calls C++ function: virtual const QMetaObject* QFormLayout::metaObject() const.
Sourcepub unsafe fn minimum_size(&self) -> CppBox<QSize>
pub unsafe fn minimum_size(&self) -> CppBox<QSize>
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::minimumSize().
Calls C++ function: virtual QSize QFormLayout::minimumSize() const.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::minimumSize().
Sourcepub unsafe fn new_1a(parent: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>) -> QBox<QFormLayout>
pub unsafe fn new_1a(parent: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>) -> QBox<QFormLayout>
Constructs a new form layout with the given parent widget.
Calls C++ function: [constructor] void QFormLayout::QFormLayout(QWidget* parent = …).
Constructs a new form layout with the given parent widget.
See also QWidget::setLayout().
Sourcepub unsafe fn new_0a() -> QBox<QFormLayout>
pub unsafe fn new_0a() -> QBox<QFormLayout>
The QFormLayout class manages forms of input widgets and their associated labels.
Calls C++ function: [constructor] void QFormLayout::QFormLayout().
The QFormLayout class manages forms of input widgets and their associated labels.
QFormLayout is a convenience layout class that lays out its children in a two-column form. The left column consists of labels and the right column consists of "field" widgets (line editors, spin boxes, etc.).
Traditionally, such two-column form layouts were achieved using QGridLayout. QFormLayout is a higher-level alternative that provides the following advantages:
- Adherence to the different platform's look and feel guidelines.
For example, the macOS Aqua and KDE guidelines specify that the labels should be right-aligned, whereas Windows and GNOME applications normally use left-alignment.
- Support for wrapping long rows.
For devices with small displays, QFormLayout can be set to wrap long rows, or even to wrap all rows.
- Convenient API for creating label--field pairs.
The addRow() overload that takes a QString and a QWidget * creates a QLabel behind the scenes and automatically set up its buddy. We can then write code like this:
QFormLayout *formLayout = new QFormLayout; formLayout->addRow(tr(“&Name:”), nameLineEdit); formLayout->addRow(tr(“&Email:”), emailLineEdit); formLayout->addRow(tr(“&Age:”), ageSpinBox); setLayout(formLayout);
Compare this with the following code, written using QGridLayout:
nameLabel = new QLabel(tr(“&Name:”)); nameLabel->setBuddy(nameLineEdit);
emailLabel = new QLabel(tr(“&Name:”)); emailLabel->setBuddy(emailLineEdit);
ageLabel = new QLabel(tr(“&Name:”)); ageLabel->setBuddy(ageSpinBox);
QGridLayout *gridLayout = new QGridLayout; gridLayout->addWidget(nameLabel, 0, 0); gridLayout->addWidget(nameLineEdit, 0, 1); gridLayout->addWidget(emailLabel, 1, 0); gridLayout->addWidget(emailLineEdit, 1, 1); gridLayout->addWidget(ageLabel, 2, 0); gridLayout->addWidget(ageSpinBox, 2, 1); setLayout(gridLayout);
The table below shows the default appearance in different styles.
| QCommonStyle derived styles (except QPlastiqueStyle) | QMacStyle | QPlastiqueStyle | Qt Extended styles |
|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  |  |
| Traditional style used for Windows, GNOME, and earlier versions of KDE. Labels are left aligned, and expanding fields grow to fill the available space. (This normally corresponds to what we would get using a two-column QGridLayout.) | Style based on the macOS Aqua guidelines. Labels are right-aligned, the fields don't grow beyond their size hint, and the form is horizontally centered. | Recommended style for KDE applications. Similar to MacStyle, except that the form is left-aligned and all fields grow to fill the available space. | Default style for Qt Extended styles. Labels are right-aligned, expanding fields grow to fill the available space, and row wrapping is enabled for long lines. |
The form styles can be also be overridden individually by calling setLabelAlignment(), setFormAlignment(), setFieldGrowthPolicy(), and setRowWrapPolicy(). For example, to simulate the form layout appearance of QMacStyle on all platforms, but with left-aligned labels, you could write:
formLayout->setRowWrapPolicy(QFormLayout::DontWrapRows); formLayout->setFieldGrowthPolicy(QFormLayout::FieldsStayAtSizeHint); formLayout->setFormAlignment(Qt::AlignHCenter | Qt::AlignTop); formLayout->setLabelAlignment(Qt::AlignLeft);
Sourcepub unsafe fn qt_metacall(
&self,
arg1: Call,
arg2: c_int,
arg3: *mut *mut c_void,
) -> c_int
pub unsafe fn qt_metacall( &self, arg1: Call, arg2: c_int, arg3: *mut *mut c_void, ) -> c_int
Calls C++ function: virtual int QFormLayout::qt_metacall(QMetaObject::Call arg1, int arg2, void** arg3).
Sourcepub unsafe fn qt_metacast(&self, arg1: *const c_char) -> *mut c_void
pub unsafe fn qt_metacast(&self, arg1: *const c_char) -> *mut c_void
Calls C++ function: virtual void* QFormLayout::qt_metacast(const char* arg1).
Sourcepub unsafe fn remove_row_int(&self, row: c_int)
pub unsafe fn remove_row_int(&self, row: c_int)
Deletes row row from this form layout.
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::removeRow(int row).
Deletes row row from this form layout.
row must be non-negative and less than rowCount().
After this call, rowCount() is decremented by one. All widgets and nested layouts that occupied this row are deleted. That includes both the field widget(s) and the label, if any. All following rows are shifted up one row and the freed vertical space is redistributed amongst the remaining rows.
You can use this function to undo a previous addRow() or insertRow():
QFormLayout *flay = ...; QPointer<QLineEdit> le = new QLineEdit; flay->insertRow(2, “User:”, le); // later: flay->removeRow(2); // le == nullptr at this point
If you want to remove the row from the layout without deleting the widgets, use takeRow() instead.
This function was introduced in Qt 5.8.
See also takeRow().
Sourcepub unsafe fn remove_row_q_widget(&self, widget: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>)
pub unsafe fn remove_row_q_widget(&self, widget: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>)
This is an overloaded function.
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::removeRow(QWidget* widget).
This is an overloaded function.
Deletes the row corresponding to widget from this form layout.
After this call, rowCount() is decremented by one. All widgets and nested layouts that occupied this row are deleted. That includes both the field widget(s) and the label, if any. All following rows are shifted up one row and the freed vertical space is redistributed amongst the remaining rows.
You can use this function to undo a previous addRow() or insertRow():
QFormLayout *flay = ...; QPointer<QLineEdit> le = new QLineEdit; flay->insertRow(2, “User:”, le); // later: flay->removeRow(le); // le == nullptr at this point
If you want to remove the row from the layout without deleting the widgets, use takeRow() instead.
This function was introduced in Qt 5.8.
See also takeRow().
Sourcepub unsafe fn remove_row_q_layout(&self, layout: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayout>>)
pub unsafe fn remove_row_q_layout(&self, layout: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayout>>)
This is an overloaded function.
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::removeRow(QLayout* layout).
This is an overloaded function.
Deletes the row corresponding to layout from this form layout.
After this call, rowCount() is decremented by one. All widgets and nested layouts that occupied this row are deleted. That includes both the field widget(s) and the label, if any. All following rows are shifted up one row and the freed vertical space is redistributed amongst the remaining rows.
You can use this function to undo a previous addRow() or insertRow():
QFormLayout *flay = ...; QPointer<QVBoxLayout> vbl = new QVBoxLayout; flay->insertRow(2, “User:”, vbl); // later: flay->removeRow(layout); // vbl == nullptr at this point
If you want to remove the row from the form layout without deleting the inserted layout, use takeRow() instead.
This function was introduced in Qt 5.8.
See also takeRow().
Sourcepub unsafe fn row_count(&self) -> c_int
pub unsafe fn row_count(&self) -> c_int
Returns the number of rows in the form.
Calls C++ function: int QFormLayout::rowCount() const.
Returns the number of rows in the form.
See also QLayout::count().
Sourcepub unsafe fn row_wrap_policy(&self) -> RowWrapPolicy
pub unsafe fn row_wrap_policy(&self) -> RowWrapPolicy
This property holds the way in which the form's rows wrap
Calls C++ function: QFormLayout::RowWrapPolicy QFormLayout::rowWrapPolicy() const.
This property holds the way in which the form’s rows wrap
The default value depends on the widget or application style. For Qt Extended styles, the default is WrapLongRows; for the other styles, the default is DontWrapRows.
If you want to display each label above its associated field (instead of next to it), set this property to WrapAllRows.
Access functions:
| RowWrapPolicy | rowWrapPolicy() const |
| void | setRowWrapPolicy(RowWrapPolicy policy) |
See also fieldGrowthPolicy.
Sourcepub unsafe fn set_field_growth_policy(&self, policy: FieldGrowthPolicy)
pub unsafe fn set_field_growth_policy(&self, policy: FieldGrowthPolicy)
This property holds the way in which the form's fields grow
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::setFieldGrowthPolicy(QFormLayout::FieldGrowthPolicy policy).
This property holds the way in which the form’s fields grow
The default value depends on the widget or application style. For QMacStyle, the default is FieldsStayAtSizeHint; for QCommonStyle derived styles (like Plastique and Windows), the default is ExpandingFieldsGrow; for Qt Extended styles, the default is AllNonFixedFieldsGrow.
If none of the fields can grow and the form is resized, extra space is distributed according to the current form alignment.
Access functions:
| FieldGrowthPolicy | fieldGrowthPolicy() const |
| void | setFieldGrowthPolicy(FieldGrowthPolicy policy) |
See also formAlignment and rowWrapPolicy.
Sourcepub unsafe fn set_form_alignment(&self, alignment: QFlags<AlignmentFlag>)
pub unsafe fn set_form_alignment(&self, alignment: QFlags<AlignmentFlag>)
This property holds the alignment of the form layout's contents within the layout's geometry
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::setFormAlignment(QFlags<Qt::AlignmentFlag> alignment).
This property holds the alignment of the form layout’s contents within the layout’s geometry
The default value depends on the widget or application style. For QMacStyle, the default is Qt::AlignHCenter | Qt::AlignTop; for the other styles, the default is Qt::AlignLeft | Qt::AlignTop.
Access functions:
| Qt::Alignment | formAlignment() const |
| void | setFormAlignment(Qt::Alignment alignment) |
See also labelAlignment and rowWrapPolicy.
Sourcepub unsafe fn set_geometry(&self, rect: impl CastInto<Ref<QRect>>)
pub unsafe fn set_geometry(&self, rect: impl CastInto<Ref<QRect>>)
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::setGeometry().
Calls C++ function: virtual void QFormLayout::setGeometry(const QRect& rect).
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::setGeometry().
Sourcepub unsafe fn set_horizontal_spacing(&self, spacing: c_int)
pub unsafe fn set_horizontal_spacing(&self, spacing: c_int)
This property holds the spacing between widgets that are laid out side by side
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::setHorizontalSpacing(int spacing).
This property holds the spacing between widgets that are laid out side by side
By default, if no value is explicitly set, the layout's horizontal spacing is inherited from the parent layout, or from the style settings for the parent widget.
Access functions:
| int | horizontalSpacing() const |
| void | setHorizontalSpacing(int spacing) |
See also verticalSpacing, QStyle::pixelMetric(), and PM_LayoutHorizontalSpacing.
Sourcepub unsafe fn set_item(
&self,
row: c_int,
role: ItemRole,
item: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayoutItem>>,
)
pub unsafe fn set_item( &self, row: c_int, role: ItemRole, item: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayoutItem>>, )
Sets the item in the given row for the given role to item, extending the layout with empty rows if necessary.
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::setItem(int row, QFormLayout::ItemRole role, QLayoutItem* item).
Sets the item in the given row for the given role to item, extending the layout with empty rows if necessary.
If the cell is already occupied, the item is not inserted and an error message is sent to the console. The item spans both columns.
Warning: Do not use this function to add child layouts or child widget items. Use setLayout() or setWidget() instead.
See also setLayout().
Sourcepub unsafe fn set_label_alignment(&self, alignment: QFlags<AlignmentFlag>)
pub unsafe fn set_label_alignment(&self, alignment: QFlags<AlignmentFlag>)
This property holds the horizontal alignment of the labels
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::setLabelAlignment(QFlags<Qt::AlignmentFlag> alignment).
This property holds the horizontal alignment of the labels
The default value depends on the widget or application style. For QCommonStyle derived styles, except for QPlastiqueStyle, the default is Qt::AlignLeft; for the other styles, the default is Qt::AlignRight.
Access functions:
| Qt::Alignment | labelAlignment() const |
| void | setLabelAlignment(Qt::Alignment alignment) |
See also formAlignment.
Sourcepub unsafe fn set_layout(
&self,
row: c_int,
role: ItemRole,
layout: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayout>>,
)
pub unsafe fn set_layout( &self, row: c_int, role: ItemRole, layout: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayout>>, )
Sets the sub-layout in the given row for the given role to layout, extending the form layout with empty rows if necessary.
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::setLayout(int row, QFormLayout::ItemRole role, QLayout* layout).
Sets the sub-layout in the given row for the given role to layout, extending the form layout with empty rows if necessary.
If the cell is already occupied, the layout is not inserted and an error message is sent to the console.
Note: For most applications, addRow() or insertRow() should be used instead of setLayout().
See also setWidget().
Sourcepub unsafe fn set_row_wrap_policy(&self, policy: RowWrapPolicy)
pub unsafe fn set_row_wrap_policy(&self, policy: RowWrapPolicy)
This property holds the way in which the form's rows wrap
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::setRowWrapPolicy(QFormLayout::RowWrapPolicy policy).
This property holds the way in which the form’s rows wrap
The default value depends on the widget or application style. For Qt Extended styles, the default is WrapLongRows; for the other styles, the default is DontWrapRows.
If you want to display each label above its associated field (instead of next to it), set this property to WrapAllRows.
Access functions:
| RowWrapPolicy | rowWrapPolicy() const |
| void | setRowWrapPolicy(RowWrapPolicy policy) |
See also fieldGrowthPolicy.
Sourcepub unsafe fn set_spacing(&self, arg1: c_int)
pub unsafe fn set_spacing(&self, arg1: c_int)
This function sets both the vertical and horizontal spacing to spacing.
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::setSpacing(int arg1).
This function sets both the vertical and horizontal spacing to spacing.
See also spacing(), setVerticalSpacing(), and setHorizontalSpacing().
Sourcepub unsafe fn set_vertical_spacing(&self, spacing: c_int)
pub unsafe fn set_vertical_spacing(&self, spacing: c_int)
This property holds the spacing between widgets that are laid out vertically
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::setVerticalSpacing(int spacing).
This property holds the spacing between widgets that are laid out vertically
By default, if no value is explicitly set, the layout's vertical spacing is inherited from the parent layout, or from the style settings for the parent widget.
Access functions:
| int | verticalSpacing() const |
| void | setVerticalSpacing(int spacing) |
See also horizontalSpacing, QStyle::pixelMetric(), and PM_LayoutHorizontalSpacing.
Sourcepub unsafe fn set_widget(
&self,
row: c_int,
role: ItemRole,
widget: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>,
)
pub unsafe fn set_widget( &self, row: c_int, role: ItemRole, widget: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>, )
Sets the widget in the given row for the given role to widget, extending the layout with empty rows if necessary.
Calls C++ function: void QFormLayout::setWidget(int row, QFormLayout::ItemRole role, QWidget* widget).
Sets the widget in the given row for the given role to widget, extending the layout with empty rows if necessary.
If the cell is already occupied, the widget is not inserted and an error message is sent to the console.
Note: For most applications, addRow() or insertRow() should be used instead of setWidget().
See also setLayout().
Sourcepub unsafe fn size_hint(&self) -> CppBox<QSize>
pub unsafe fn size_hint(&self) -> CppBox<QSize>
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::sizeHint().
Calls C++ function: virtual QSize QFormLayout::sizeHint() const.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::sizeHint().
Sourcepub unsafe fn spacing(&self) -> c_int
pub unsafe fn spacing(&self) -> c_int
If the vertical spacing is equal to the horizontal spacing, this function returns that value; otherwise it returns -1.
Calls C++ function: int QFormLayout::spacing() const.
If the vertical spacing is equal to the horizontal spacing, this function returns that value; otherwise it returns -1.
See also setSpacing(), verticalSpacing(), and horizontalSpacing().
Sourcepub unsafe fn static_meta_object() -> Ref<QMetaObject>
pub unsafe fn static_meta_object() -> Ref<QMetaObject>
Returns a reference to the staticMetaObject field.
Sourcepub unsafe fn take_at(&self, index: c_int) -> Ptr<QLayoutItem>
pub unsafe fn take_at(&self, index: c_int) -> Ptr<QLayoutItem>
Reimplemented from QLayout::takeAt().
Calls C++ function: virtual QLayoutItem* QFormLayout::takeAt(int index).
Reimplemented from QLayout::takeAt().
Sourcepub unsafe fn take_row_int(&self, row: c_int) -> CppBox<TakeRowResult>
pub unsafe fn take_row_int(&self, row: c_int) -> CppBox<TakeRowResult>
Removes the specified row from this form layout.
Calls C++ function: QFormLayout::TakeRowResult QFormLayout::takeRow(int row).
Removes the specified row from this form layout.
row must be non-negative and less than rowCount().
Note: This function doesn't delete anything.
After this call, rowCount() is decremented by one. All following rows are shifted up one row and the freed vertical space is redistributed amongst the remaining rows.
You can use this function to undo a previous addRow() or insertRow():
QFormLayout *flay = ...; QPointer<QLineEdit> le = new QLineEdit; flay->insertRow(2, “User:”, le); // later: QFormLayout::TakeRowResult result = flay->takeRow(2);
If you want to remove the row from the layout and delete the widgets, use removeRow() instead.
Returns A structure containing both the widget and corresponding label layout items
This function was introduced in Qt 5.8.
See also removeRow().
Sourcepub unsafe fn take_row_q_widget(
&self,
widget: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>,
) -> CppBox<TakeRowResult>
pub unsafe fn take_row_q_widget( &self, widget: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>, ) -> CppBox<TakeRowResult>
This is an overloaded function.
Calls C++ function: QFormLayout::TakeRowResult QFormLayout::takeRow(QWidget* widget).
This is an overloaded function.
Removes the specified widget from this form layout.
Note: This function doesn't delete anything.
After this call, rowCount() is decremented by one. All following rows are shifted up one row and the freed vertical space is redistributed amongst the remaining rows.
QFormLayout *flay = ...; QPointer<QLineEdit> le = new QLineEdit; flay->insertRow(2, “User:”, le); // later: QFormLayout::TakeRowResult result = flay->takeRow(widget);
If you want to remove the row from the layout and delete the widgets, use removeRow() instead.
Returns A structure containing both the widget and corresponding label layout items
This function was introduced in Qt 5.8.
See also removeRow().
Sourcepub unsafe fn take_row_q_layout(
&self,
layout: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayout>>,
) -> CppBox<TakeRowResult>
pub unsafe fn take_row_q_layout( &self, layout: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayout>>, ) -> CppBox<TakeRowResult>
This is an overloaded function.
Calls C++ function: QFormLayout::TakeRowResult QFormLayout::takeRow(QLayout* layout).
This is an overloaded function.
Removes the specified layout from this form layout.
Note: This function doesn't delete anything.
After this call, rowCount() is decremented by one. All following rows are shifted up one row and the freed vertical space is redistributed amongst the remaining rows.
QFormLayout *flay = ...; QPointer<QVBoxLayout> vbl = new QVBoxLayout; flay->insertRow(2, “User:”, vbl); // later: QFormLayout::TakeRowResult result = flay->takeRow(widget);
If you want to remove the row from the form layout and delete the inserted layout, use removeRow() instead.
Returns A structure containing both the widget and corresponding label layout items
This function was introduced in Qt 5.8.
See also removeRow().
Sourcepub unsafe fn tr(
s: *const c_char,
c: *const c_char,
n: c_int,
) -> CppBox<QString>
pub unsafe fn tr( s: *const c_char, c: *const c_char, n: c_int, ) -> CppBox<QString>
Calls C++ function: static QString QFormLayout::tr(const char* s, const char* c, int n).
Sourcepub unsafe fn tr_utf8(
s: *const c_char,
c: *const c_char,
n: c_int,
) -> CppBox<QString>
pub unsafe fn tr_utf8( s: *const c_char, c: *const c_char, n: c_int, ) -> CppBox<QString>
Calls C++ function: static QString QFormLayout::trUtf8(const char* s, const char* c, int n).
Sourcepub unsafe fn vertical_spacing(&self) -> c_int
pub unsafe fn vertical_spacing(&self) -> c_int
This property holds the spacing between widgets that are laid out vertically
Calls C++ function: int QFormLayout::verticalSpacing() const.
This property holds the spacing between widgets that are laid out vertically
By default, if no value is explicitly set, the layout's vertical spacing is inherited from the parent layout, or from the style settings for the parent widget.
Access functions:
| int | verticalSpacing() const |
| void | setVerticalSpacing(int spacing) |
See also horizontalSpacing, QStyle::pixelMetric(), and PM_LayoutHorizontalSpacing.
Methods from Deref<Target = QLayout>§
Sourcepub unsafe fn activate(&self) -> bool
pub unsafe fn activate(&self) -> bool
Redoes the layout for parentWidget() if necessary.
Calls C++ function: bool QLayout::activate().
Redoes the layout for parentWidget() if necessary.
You should generally not need to call this because it is automatically called at the most appropriate times. It returns true if the layout was redone.
See also update() and QWidget::updateGeometry().
Sourcepub unsafe fn add_item(&self, arg1: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayoutItem>>)
pub unsafe fn add_item(&self, arg1: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayoutItem>>)
Implemented in subclasses to add an item. How it is added is specific to each subclass.
Calls C++ function: pure virtual void QLayout::addItem(QLayoutItem* arg1).
Implemented in subclasses to add an item. How it is added is specific to each subclass.
This function is not usually called in application code. To add a widget to a layout, use the addWidget() function; to add a child layout, use the addLayout() function provided by the relevant QLayout subclass.
Note: The ownership of item is transferred to the layout, and it's the layout's responsibility to delete it.
See also addWidget(), QBoxLayout::addLayout(), and QGridLayout::addLayout().
Sourcepub unsafe fn add_widget(&self, w: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>)
pub unsafe fn add_widget(&self, w: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>)
Sourcepub unsafe fn contents_margins(&self) -> CppBox<QMargins>
pub unsafe fn contents_margins(&self) -> CppBox<QMargins>
Returns the margins used around the layout.
Calls C++ function: QMargins QLayout::contentsMargins() const.
Returns the margins used around the layout.
By default, QLayout uses the values provided by the style. On most platforms, the margin is 11 pixels in all directions.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.6.
See also setContentsMargins().
Sourcepub unsafe fn contents_rect(&self) -> CppBox<QRect>
pub unsafe fn contents_rect(&self) -> CppBox<QRect>
Returns the layout's geometry() rectangle, but taking into account the contents margins.
Calls C++ function: QRect QLayout::contentsRect() const.
Returns the layout’s geometry() rectangle, but taking into account the contents margins.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.3.
See also setContentsMargins() and getContentsMargins().
Sourcepub unsafe fn control_types(&self) -> QFlags<ControlType>
pub unsafe fn control_types(&self) -> QFlags<ControlType>
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::controlTypes().
Calls C++ function: virtual QFlags<QSizePolicy::ControlType> QLayout::controlTypes() const.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::controlTypes().
Sourcepub unsafe fn count(&self) -> c_int
pub unsafe fn count(&self) -> c_int
Must be implemented in subclasses to return the number of items in the layout.
Calls C++ function: pure virtual int QLayout::count() const.
Must be implemented in subclasses to return the number of items in the layout.
See also itemAt().
Sourcepub unsafe fn expanding_directions(&self) -> QFlags<Orientation>
pub unsafe fn expanding_directions(&self) -> QFlags<Orientation>
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::expandingDirections().
Calls C++ function: virtual QFlags<Qt::Orientation> QLayout::expandingDirections() const.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::expandingDirections().
Returns whether this layout can make use of more space than sizeHint(). A value of Qt::Vertical or Qt::Horizontal means that it wants to grow in only one dimension, whereas Qt::Vertical | Qt::Horizontal means that it wants to grow in both dimensions.
The default implementation returns Qt::Horizontal | Qt::Vertical. Subclasses reimplement it to return a meaningful value based on their child widgets's size policies.
See also sizeHint().
Sourcepub unsafe fn geometry(&self) -> CppBox<QRect>
pub unsafe fn geometry(&self) -> CppBox<QRect>
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::geometry().
Calls C++ function: virtual QRect QLayout::geometry() const.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::geometry().
See also setGeometry().
Sourcepub unsafe fn get_contents_margins(
&self,
left: *mut c_int,
top: *mut c_int,
right: *mut c_int,
bottom: *mut c_int,
)
pub unsafe fn get_contents_margins( &self, left: *mut c_int, top: *mut c_int, right: *mut c_int, bottom: *mut c_int, )
Extracts the left, top, right, and bottom margins used around the layout, and assigns them to *left, *top, *right, and *bottom (unless they are null pointers).
Calls C++ function: void QLayout::getContentsMargins(int* left, int* top, int* right, int* bottom) const.
Extracts the left, top, right, and bottom margins used around the layout, and assigns them to *left, *top, *right, and *bottom (unless they are null pointers).
By default, QLayout uses the values provided by the style. On most platforms, the margin is 11 pixels in all directions.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.3.
See also setContentsMargins(), QStyle::pixelMetric(), PM_LayoutLeftMargin, PM_LayoutTopMargin, PM_LayoutRightMargin, and PM_LayoutBottomMargin.
Sourcepub unsafe fn index_of_q_widget(
&self,
arg1: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>,
) -> c_int
pub unsafe fn index_of_q_widget( &self, arg1: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>, ) -> c_int
Searches for widget widget in this layout (not including child layouts).
Calls C++ function: virtual int QLayout::indexOf(QWidget* arg1) const.
Searches for widget widget in this layout (not including child layouts).
Returns the index of widget, or -1 if widget is not found.
The default implementation iterates over all items using itemAt()
Sourcepub unsafe fn index_of_q_layout_item(
&self,
arg1: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayoutItem>>,
) -> c_int
Available on cpp_lib_version="5.12.2" or cpp_lib_version="5.13.0" or cpp_lib_version="5.14.0" only.
pub unsafe fn index_of_q_layout_item( &self, arg1: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayoutItem>>, ) -> c_int
cpp_lib_version="5.12.2" or cpp_lib_version="5.13.0" or cpp_lib_version="5.14.0" only.Searches for layout item layoutItem in this layout (not including child layouts).
Calls C++ function: int QLayout::indexOf(QLayoutItem* arg1) const.
Searches for layout item layoutItem in this layout (not including child layouts).
Returns the index of layoutItem, or -1 if layoutItem is not found.
This function was introduced in Qt 5.12.
Sourcepub unsafe fn invalidate(&self)
pub unsafe fn invalidate(&self)
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::invalidate().
Calls C++ function: virtual void QLayout::invalidate().
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::invalidate().
Sourcepub unsafe fn is_empty(&self) -> bool
pub unsafe fn is_empty(&self) -> bool
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::isEmpty().
Calls C++ function: virtual bool QLayout::isEmpty() const.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::isEmpty().
Sourcepub unsafe fn is_enabled(&self) -> bool
pub unsafe fn is_enabled(&self) -> bool
Returns true if the layout is enabled; otherwise returns false.
Calls C++ function: bool QLayout::isEnabled() const.
Returns true if the layout is enabled; otherwise returns false.
See also setEnabled().
Sourcepub unsafe fn item_at(&self, index: c_int) -> Ptr<QLayoutItem>
pub unsafe fn item_at(&self, index: c_int) -> Ptr<QLayoutItem>
Must be implemented in subclasses to return the layout item at index. If there is no such item, the function must return 0. Items are numbered consecutively from 0. If an item is deleted, other items will be renumbered.
Calls C++ function: pure virtual QLayoutItem* QLayout::itemAt(int index) const.
Must be implemented in subclasses to return the layout item at index. If there is no such item, the function must return 0. Items are numbered consecutively from 0. If an item is deleted, other items will be renumbered.
This function can be used to iterate over a layout. The following code will draw a rectangle for each layout item in the layout structure of the widget.
static void paintLayout(QPainter painter, QLayoutItem item) { QLayout *layout = item->layout(); if (layout) { for (int i = 0; i < layout->count(); ++i) paintLayout(painter, layout->itemAt(i)); } painter->drawRect(item->geometry()); }
void MyWidget::paintEvent(QPaintEvent *) { QPainter painter(this); if (layout()) paintLayout(&painter, layout()); }
Sourcepub unsafe fn layout(&self) -> QPtr<QLayout>
pub unsafe fn layout(&self) -> QPtr<QLayout>
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::layout().
Calls C++ function: virtual QLayout* QLayout::layout().
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::layout().
Sourcepub unsafe fn margin(&self) -> c_int
pub unsafe fn margin(&self) -> c_int
This property holds the width of the outside border of the layout
Calls C++ function: int QLayout::margin() const.
This property holds the width of the outside border of the layout
Use setContentsMargins() and getContentsMargins() instead.
Access functions:
See also contentsRect() and spacing.
Member Function Documentation
Sourcepub unsafe fn maximum_size(&self) -> CppBox<QSize>
pub unsafe fn maximum_size(&self) -> CppBox<QSize>
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::maximumSize().
Calls C++ function: virtual QSize QLayout::maximumSize() const.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::maximumSize().
Returns the maximum size of this layout. This is the largest size that the layout can have while still respecting the specifications.
The returned value doesn't include the space required by QWidget::setContentsMargins() or menuBar().
The default implementation allows unlimited resizing.
Returns the menu bar set for this layout, or 0 if no menu bar is set.
Calls C++ function: QWidget* QLayout::menuBar() const.
Returns the menu bar set for this layout, or 0 if no menu bar is set.
See also setMenuBar().
Sourcepub unsafe fn meta_object(&self) -> Ptr<QMetaObject>
pub unsafe fn meta_object(&self) -> Ptr<QMetaObject>
Calls C++ function: virtual const QMetaObject* QLayout::metaObject() const.
Sourcepub unsafe fn minimum_size(&self) -> CppBox<QSize>
pub unsafe fn minimum_size(&self) -> CppBox<QSize>
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::minimumSize().
Calls C++ function: virtual QSize QLayout::minimumSize() const.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::minimumSize().
Returns the minimum size of this layout. This is the smallest size that the layout can have while still respecting the specifications.
The returned value doesn't include the space required by QWidget::setContentsMargins() or menuBar().
The default implementation allows unlimited resizing.
Sourcepub unsafe fn parent_widget(&self) -> QPtr<QWidget>
pub unsafe fn parent_widget(&self) -> QPtr<QWidget>
Returns the parent widget of this layout, or 0 if this layout is not installed on any widget.
Calls C++ function: QWidget* QLayout::parentWidget() const.
Returns the parent widget of this layout, or 0 if this layout is not installed on any widget.
If the layout is a sub-layout, this function returns the parent widget of the parent layout.
See also parent().
Sourcepub unsafe fn qt_metacall(
&self,
arg1: Call,
arg2: c_int,
arg3: *mut *mut c_void,
) -> c_int
pub unsafe fn qt_metacall( &self, arg1: Call, arg2: c_int, arg3: *mut *mut c_void, ) -> c_int
Calls C++ function: virtual int QLayout::qt_metacall(QMetaObject::Call arg1, int arg2, void** arg3).
Sourcepub unsafe fn qt_metacast(&self, arg1: *const c_char) -> *mut c_void
pub unsafe fn qt_metacast(&self, arg1: *const c_char) -> *mut c_void
Calls C++ function: virtual void* QLayout::qt_metacast(const char* arg1).
Sourcepub unsafe fn remove_item(&self, arg1: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayoutItem>>)
pub unsafe fn remove_item(&self, arg1: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayoutItem>>)
Removes the layout item item from the layout. It is the caller's responsibility to delete the item.
Calls C++ function: void QLayout::removeItem(QLayoutItem* arg1).
Removes the layout item item from the layout. It is the caller’s responsibility to delete the item.
Notice that item can be a layout (since QLayout inherits QLayoutItem).
See also removeWidget() and addItem().
Sourcepub unsafe fn remove_widget(&self, w: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>)
pub unsafe fn remove_widget(&self, w: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>)
Removes the widget widget from the layout. After this call, it is the caller's responsibility to give the widget a reasonable geometry or to put the widget back into a layout or to explicitly hide it if necessary.
Calls C++ function: void QLayout::removeWidget(QWidget* w).
Removes the widget widget from the layout. After this call, it is the caller’s responsibility to give the widget a reasonable geometry or to put the widget back into a layout or to explicitly hide it if necessary.
Note: The ownership of widget remains the same as when it was added.
See also removeItem(), QWidget::setGeometry(), and addWidget().
Sourcepub unsafe fn replace_widget_3a(
&self,
from: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>,
to: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>,
options: QFlags<FindChildOption>,
) -> Ptr<QLayoutItem>
pub unsafe fn replace_widget_3a( &self, from: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>, to: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>, options: QFlags<FindChildOption>, ) -> Ptr<QLayoutItem>
Searches for widget from and replaces it with widget to if found. Returns the layout item that contains the widget from on success. Otherwise 0 is returned. If options contains Qt::FindChildrenRecursively (the default), sub-layouts are searched for doing the replacement. Any other flag in options is ignored.
Calls C++ function: QLayoutItem* QLayout::replaceWidget(QWidget* from, QWidget* to, QFlags<Qt::FindChildOption> options = …).
Searches for widget from and replaces it with widget to if found. Returns the layout item that contains the widget from on success. Otherwise 0 is returned. If options contains Qt::FindChildrenRecursively (the default), sub-layouts are searched for doing the replacement. Any other flag in options is ignored.
Notice that the returned item therefore might not belong to this layout, but to a sub-layout.
The returned layout item is no longer owned by the layout and should be either deleted or inserted to another layout. The widget from is no longer managed by the layout and may need to be deleted or hidden. The parent of widget from is left unchanged.
This function works for the built-in Qt layouts, but might not work for custom layouts.
This function was introduced in Qt 5.2.
See also indexOf().
Sourcepub unsafe fn replace_widget_2a(
&self,
from: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>,
to: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>,
) -> Ptr<QLayoutItem>
pub unsafe fn replace_widget_2a( &self, from: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>, to: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>, ) -> Ptr<QLayoutItem>
Searches for widget from and replaces it with widget to if found. Returns the layout item that contains the widget from on success. Otherwise 0 is returned. If options contains Qt::FindChildrenRecursively (the default), sub-layouts are searched for doing the replacement. Any other flag in options is ignored.
Calls C++ function: QLayoutItem* QLayout::replaceWidget(QWidget* from, QWidget* to).
Searches for widget from and replaces it with widget to if found. Returns the layout item that contains the widget from on success. Otherwise 0 is returned. If options contains Qt::FindChildrenRecursively (the default), sub-layouts are searched for doing the replacement. Any other flag in options is ignored.
Notice that the returned item therefore might not belong to this layout, but to a sub-layout.
The returned layout item is no longer owned by the layout and should be either deleted or inserted to another layout. The widget from is no longer managed by the layout and may need to be deleted or hidden. The parent of widget from is left unchanged.
This function works for the built-in Qt layouts, but might not work for custom layouts.
This function was introduced in Qt 5.2.
See also indexOf().
Sourcepub unsafe fn set_alignment_q_widget_q_flags_alignment_flag(
&self,
w: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>,
alignment: QFlags<AlignmentFlag>,
) -> bool
pub unsafe fn set_alignment_q_widget_q_flags_alignment_flag( &self, w: impl CastInto<Ptr<QWidget>>, alignment: QFlags<AlignmentFlag>, ) -> bool
Sets the alignment for widget w to alignment and returns true if w is found in this layout (not including child layouts); otherwise returns false.
Calls C++ function: bool QLayout::setAlignment(QWidget* w, QFlags<Qt::AlignmentFlag> alignment).
Sets the alignment for widget w to alignment and returns true if w is found in this layout (not including child layouts); otherwise returns false.
Sourcepub unsafe fn set_alignment_q_layout_q_flags_alignment_flag(
&self,
l: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayout>>,
alignment: QFlags<AlignmentFlag>,
) -> bool
pub unsafe fn set_alignment_q_layout_q_flags_alignment_flag( &self, l: impl CastInto<Ptr<QLayout>>, alignment: QFlags<AlignmentFlag>, ) -> bool
This is an overloaded function.
Calls C++ function: bool QLayout::setAlignment(QLayout* l, QFlags<Qt::AlignmentFlag> alignment).
This is an overloaded function.
Sets the alignment for the layout l to alignment and returns true if l is found in this layout (not including child layouts); otherwise returns false.
Sourcepub unsafe fn set_contents_margins_4a(
&self,
left: c_int,
top: c_int,
right: c_int,
bottom: c_int,
)
pub unsafe fn set_contents_margins_4a( &self, left: c_int, top: c_int, right: c_int, bottom: c_int, )
Sets the left, top, right, and bottom margins to use around the layout.
Calls C++ function: void QLayout::setContentsMargins(int left, int top, int right, int bottom).
Sets the left, top, right, and bottom margins to use around the layout.
By default, QLayout uses the values provided by the style. On most platforms, the margin is 11 pixels in all directions.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.3.
See also contentsMargins(), getContentsMargins(), QStyle::pixelMetric(), PM_LayoutLeftMargin, PM_LayoutTopMargin, PM_LayoutRightMargin, and PM_LayoutBottomMargin.
Sourcepub unsafe fn set_contents_margins_1a(
&self,
margins: impl CastInto<Ref<QMargins>>,
)
pub unsafe fn set_contents_margins_1a( &self, margins: impl CastInto<Ref<QMargins>>, )
Sets the margins to use around the layout.
Calls C++ function: void QLayout::setContentsMargins(const QMargins& margins).
Sets the margins to use around the layout.
By default, QLayout uses the values provided by the style. On most platforms, the margin is 11 pixels in all directions.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.6.
See also contentsMargins().
Sourcepub unsafe fn set_enabled(&self, arg1: bool)
pub unsafe fn set_enabled(&self, arg1: bool)
Enables this layout if enable is true, otherwise disables it.
Calls C++ function: void QLayout::setEnabled(bool arg1).
Enables this layout if enable is true, otherwise disables it.
An enabled layout adjusts dynamically to changes; a disabled layout acts as if it did not exist.
By default all layouts are enabled.
See also isEnabled().
Sourcepub unsafe fn set_geometry(&self, arg1: impl CastInto<Ref<QRect>>)
pub unsafe fn set_geometry(&self, arg1: impl CastInto<Ref<QRect>>)
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::setGeometry().
Calls C++ function: virtual void QLayout::setGeometry(const QRect& arg1).
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem::setGeometry().
See also geometry().
Sourcepub unsafe fn set_margin(&self, arg1: c_int)
pub unsafe fn set_margin(&self, arg1: c_int)
Note: Setter function for property margin.
Calls C++ function: void QLayout::setMargin(int arg1).
Tells the geometry manager to place the menu bar widget at the top of parentWidget(), outside QWidget::contentsMargins(). All child widgets are placed below the bottom edge of the menu bar.
Calls C++ function: void QLayout::setMenuBar(QWidget* w).
Tells the geometry manager to place the menu bar widget at the top of parentWidget(), outside QWidget::contentsMargins(). All child widgets are placed below the bottom edge of the menu bar.
See also menuBar().
Sourcepub unsafe fn set_size_constraint(&self, arg1: SizeConstraint)
pub unsafe fn set_size_constraint(&self, arg1: SizeConstraint)
This property holds the resize mode of the layout
Calls C++ function: void QLayout::setSizeConstraint(QLayout::SizeConstraint arg1).
This property holds the resize mode of the layout
The default mode is SetDefaultConstraint.
Access functions:
| SizeConstraint | sizeConstraint() const |
| void | setSizeConstraint(SizeConstraint) |
Sourcepub unsafe fn set_spacing(&self, arg1: c_int)
pub unsafe fn set_spacing(&self, arg1: c_int)
This property holds the spacing between widgets inside the layout
Calls C++ function: void QLayout::setSpacing(int arg1).
This property holds the spacing between widgets inside the layout
If no value is explicitly set, the layout's spacing is inherited from the parent layout, or from the style settings for the parent widget.
For QGridLayout and QFormLayout, it is possible to set different horizontal and vertical spacings using setHorizontalSpacing() and setVerticalSpacing(). In that case, spacing() returns -1.
Access functions:
| int | spacing() const |
| void | setSpacing(int) |
See also contentsRect(), getContentsMargins(), QStyle::layoutSpacing(), and QStyle::pixelMetric().
Sourcepub unsafe fn size_constraint(&self) -> SizeConstraint
pub unsafe fn size_constraint(&self) -> SizeConstraint
This property holds the resize mode of the layout
Calls C++ function: QLayout::SizeConstraint QLayout::sizeConstraint() const.
This property holds the resize mode of the layout
The default mode is SetDefaultConstraint.
Access functions:
| SizeConstraint | sizeConstraint() const |
| void | setSizeConstraint(SizeConstraint) |
Sourcepub unsafe fn spacing(&self) -> c_int
pub unsafe fn spacing(&self) -> c_int
This property holds the spacing between widgets inside the layout
Calls C++ function: int QLayout::spacing() const.
This property holds the spacing between widgets inside the layout
If no value is explicitly set, the layout's spacing is inherited from the parent layout, or from the style settings for the parent widget.
For QGridLayout and QFormLayout, it is possible to set different horizontal and vertical spacings using setHorizontalSpacing() and setVerticalSpacing(). In that case, spacing() returns -1.
Access functions:
| int | spacing() const |
| void | setSpacing(int) |
See also contentsRect(), getContentsMargins(), QStyle::layoutSpacing(), and QStyle::pixelMetric().
Sourcepub unsafe fn take_at(&self, index: c_int) -> Ptr<QLayoutItem>
pub unsafe fn take_at(&self, index: c_int) -> Ptr<QLayoutItem>
Must be implemented in subclasses to remove the layout item at index from the layout, and return the item. If there is no such item, the function must do nothing and return 0. Items are numbered consecutively from 0. If an item is removed, other items will be renumbered.
Calls C++ function: pure virtual QLayoutItem* QLayout::takeAt(int index).
Must be implemented in subclasses to remove the layout item at index from the layout, and return the item. If there is no such item, the function must do nothing and return 0. Items are numbered consecutively from 0. If an item is removed, other items will be renumbered.
The following code fragment shows a safe way to remove all items from a layout:
QLayoutItem *child; while ((child = layout->takeAt(0)) != 0) { ... delete child; }
Sourcepub unsafe fn total_height_for_width(&self, w: c_int) -> c_int
pub unsafe fn total_height_for_width(&self, w: c_int) -> c_int
Calls C++ function: int QLayout::totalHeightForWidth(int w) const.
Sourcepub unsafe fn total_maximum_size(&self) -> CppBox<QSize>
pub unsafe fn total_maximum_size(&self) -> CppBox<QSize>
Calls C++ function: QSize QLayout::totalMaximumSize() const.
Sourcepub unsafe fn total_minimum_size(&self) -> CppBox<QSize>
pub unsafe fn total_minimum_size(&self) -> CppBox<QSize>
Calls C++ function: QSize QLayout::totalMinimumSize() const.
Sourcepub unsafe fn total_size_hint(&self) -> CppBox<QSize>
pub unsafe fn total_size_hint(&self) -> CppBox<QSize>
Calls C++ function: QSize QLayout::totalSizeHint() const.
Sourcepub unsafe fn update(&self)
pub unsafe fn update(&self)
Updates the layout for parentWidget().
Calls C++ function: void QLayout::update().
Updates the layout for parentWidget().
You should generally not need to call this because it is automatically called at the most appropriate times.
See also activate() and invalidate().
Methods from Deref<Target = QObject>§
Sourcepub unsafe fn find_child<T>(
&self,
name: &str,
) -> Result<QPtr<T>, FindChildError>
pub unsafe fn find_child<T>( &self, name: &str, ) -> Result<QPtr<T>, FindChildError>
Finds a child of self with the specified object name
and casts it to type T.
The search is performed recursively. If there is more than one child matching the search, the most direct ancestor is returned. If there are several direct ancestors, it is undefined which one will be returned.
Returns an error if there is no child object with object name name or
the found object cannot be cast to T.
Sourcepub fn destroyed(&self) -> Signal<(*mut QObject,)>
pub fn destroyed(&self) -> Signal<(*mut QObject,)>
This signal is emitted immediately before the object obj is destroyed, and can not be blocked.
Returns a built-in Qt signal QObject::destroyed that can be passed to qt_core::Signal::connect.
This signal is emitted immediately before the object obj is destroyed, and can not be blocked.
All the objects's children are destroyed immediately after this signal is emitted.
See also deleteLater() and QPointer.
Sourcepub fn object_name_changed(&self) -> Signal<(*const QString,)>
pub fn object_name_changed(&self) -> Signal<(*const QString,)>
This signal is emitted after the object's name has been changed. The new object name is passed as objectName.
Returns a built-in Qt signal QObject::objectNameChanged that can be passed to qt_core::Signal::connect.
This signal is emitted after the object’s name has been changed. The new object name is passed as objectName.
Note: This is a private signal. It can be used in signal connections but cannot be emitted by the user.
Note: Notifier signal for property objectName.
See also QObject::objectName.
Sourcepub fn slot_delete_later(&self) -> Receiver<()>
pub fn slot_delete_later(&self) -> Receiver<()>
Schedules this object for deletion.
Returns a built-in Qt slot QObject::deleteLater that can be passed to qt_core::Signal::connect.
Schedules this object for deletion.
The object will be deleted when control returns to the event loop. If the event loop is not running when this function is called (e.g. deleteLater() is called on an object before QCoreApplication::exec()), the object will be deleted once the event loop is started. If deleteLater() is called after the main event loop has stopped, the object will not be deleted. Since Qt 4.8, if deleteLater() is called on an object that lives in a thread with no running event loop, the object will be destroyed when the thread finishes.
Note that entering and leaving a new event loop (e.g., by opening a modal dialog) will not perform the deferred deletion; for the object to be deleted, the control must return to the event loop from which deleteLater() was called.
Note: It is safe to call this function more than once; when the first deferred deletion event is delivered, any pending events for the object are removed from the event queue.
Sourcepub unsafe fn block_signals(&self, b: bool) -> bool
pub unsafe fn block_signals(&self, b: bool) -> bool
If block is true, signals emitted by this object are blocked (i.e., emitting a signal will not invoke anything connected to it). If block is false, no such blocking will occur.
Calls C++ function: bool QObject::blockSignals(bool b).
If block is true, signals emitted by this object are blocked (i.e., emitting a signal will not invoke anything connected to it). If block is false, no such blocking will occur.
The return value is the previous value of signalsBlocked().
Note that the destroyed() signal will be emitted even if the signals for this object have been blocked.
Signals emitted while being blocked are not buffered.
See also signalsBlocked() and QSignalBlocker.
Sourcepub unsafe fn children(&self) -> Ref<QListOfQObject>
pub unsafe fn children(&self) -> Ref<QListOfQObject>
Returns a list of child objects. The QObjectList class is defined in the <QObject> header file as the following:
Calls C++ function: const QList<QObject*>& QObject::children() const.
Returns a list of child objects. The QObjectList class is defined in the <QObject> header file as the following:
typedef QList<QObject*> QObjectList;
The first child added is the first object in the list and the last child added is the last object in the list, i.e. new children are appended at the end.
Note that the list order changes when QWidget children are raised or lowered. A widget that is raised becomes the last object in the list, and a widget that is lowered becomes the first object in the list.
See also findChild(), findChildren(), parent(), and setParent().
Sourcepub unsafe fn delete_later(&self)
pub unsafe fn delete_later(&self)
Schedules this object for deletion.
Calls C++ function: [slot] void QObject::deleteLater().
Schedules this object for deletion.
The object will be deleted when control returns to the event loop. If the event loop is not running when this function is called (e.g. deleteLater() is called on an object before QCoreApplication::exec()), the object will be deleted once the event loop is started. If deleteLater() is called after the main event loop has stopped, the object will not be deleted. Since Qt 4.8, if deleteLater() is called on an object that lives in a thread with no running event loop, the object will be destroyed when the thread finishes.
Note that entering and leaving a new event loop (e.g., by opening a modal dialog) will not perform the deferred deletion; for the object to be deleted, the control must return to the event loop from which deleteLater() was called.
Note: It is safe to call this function more than once; when the first deferred deletion event is delivered, any pending events for the object are removed from the event queue.
Sourcepub unsafe fn disconnect_char_q_object_char(
&self,
signal: *const i8,
receiver: impl CastInto<Ptr<QObject>>,
member: *const i8,
) -> bool
pub unsafe fn disconnect_char_q_object_char( &self, signal: *const i8, receiver: impl CastInto<Ptr<QObject>>, member: *const i8, ) -> bool
This function overloads disconnect().
Calls C++ function: bool QObject::disconnect(const char* signal = …, const QObject* receiver = …, const char* member = …) const.
This function overloads disconnect().
Disconnects signal from method of receiver.
A signal-slot connection is removed when either of the objects involved are destroyed.
Note: This function is thread-safe.
Sourcepub unsafe fn disconnect_q_object_char(
&self,
receiver: impl CastInto<Ptr<QObject>>,
member: *const i8,
) -> bool
pub unsafe fn disconnect_q_object_char( &self, receiver: impl CastInto<Ptr<QObject>>, member: *const i8, ) -> bool
This function overloads disconnect().
Calls C++ function: bool QObject::disconnect(const QObject* receiver, const char* member = …) const.
This function overloads disconnect().
Disconnects all signals in this object from receiver's method.
A signal-slot connection is removed when either of the objects involved are destroyed.
Sourcepub unsafe fn disconnect_char_q_object(
&self,
signal: *const i8,
receiver: impl CastInto<Ptr<QObject>>,
) -> bool
pub unsafe fn disconnect_char_q_object( &self, signal: *const i8, receiver: impl CastInto<Ptr<QObject>>, ) -> bool
This function overloads disconnect().
Calls C++ function: bool QObject::disconnect(const char* signal = …, const QObject* receiver = …) const.
This function overloads disconnect().
Disconnects signal from method of receiver.
A signal-slot connection is removed when either of the objects involved are destroyed.
Note: This function is thread-safe.
Sourcepub unsafe fn disconnect_char(&self, signal: *const i8) -> bool
pub unsafe fn disconnect_char(&self, signal: *const i8) -> bool
This function overloads disconnect().
Calls C++ function: bool QObject::disconnect(const char* signal = …) const.
This function overloads disconnect().
Disconnects signal from method of receiver.
A signal-slot connection is removed when either of the objects involved are destroyed.
Note: This function is thread-safe.
Sourcepub unsafe fn disconnect(&self) -> bool
pub unsafe fn disconnect(&self) -> bool
This function overloads disconnect().
Calls C++ function: bool QObject::disconnect() const.
This function overloads disconnect().
Disconnects signal from method of receiver.
A signal-slot connection is removed when either of the objects involved are destroyed.
Note: This function is thread-safe.
Sourcepub unsafe fn disconnect_q_object(
&self,
receiver: impl CastInto<Ptr<QObject>>,
) -> bool
pub unsafe fn disconnect_q_object( &self, receiver: impl CastInto<Ptr<QObject>>, ) -> bool
This function overloads disconnect().
Calls C++ function: bool QObject::disconnect(const QObject* receiver) const.
This function overloads disconnect().
Disconnects all signals in this object from receiver's method.
A signal-slot connection is removed when either of the objects involved are destroyed.
Sourcepub unsafe fn dump_object_info_mut(&self)
pub unsafe fn dump_object_info_mut(&self)
Dumps information about signal connections, etc. for this object to the debug output.
Calls C++ function: void QObject::dumpObjectInfo().
Dumps information about signal connections, etc. for this object to the debug output.
Note: before Qt 5.9, this function was not const.
See also dumpObjectTree().
Sourcepub unsafe fn dump_object_info(&self)
pub unsafe fn dump_object_info(&self)
Dumps information about signal connections, etc. for this object to the debug output.
Calls C++ function: void QObject::dumpObjectInfo() const.
Dumps information about signal connections, etc. for this object to the debug output.
Note: before Qt 5.9, this function was not const.
See also dumpObjectTree().
Sourcepub unsafe fn dump_object_tree_mut(&self)
pub unsafe fn dump_object_tree_mut(&self)
Dumps a tree of children to the debug output.
Calls C++ function: void QObject::dumpObjectTree().
Dumps a tree of children to the debug output.
Note: before Qt 5.9, this function was not const.
See also dumpObjectInfo().
Sourcepub unsafe fn dump_object_tree(&self)
pub unsafe fn dump_object_tree(&self)
Dumps a tree of children to the debug output.
Calls C++ function: void QObject::dumpObjectTree() const.
Dumps a tree of children to the debug output.
Note: before Qt 5.9, this function was not const.
See also dumpObjectInfo().
Sourcepub unsafe fn dynamic_property_names(&self) -> CppBox<QListOfQByteArray>
pub unsafe fn dynamic_property_names(&self) -> CppBox<QListOfQByteArray>
Returns the names of all properties that were dynamically added to the object using setProperty().
Calls C++ function: QList<QByteArray> QObject::dynamicPropertyNames() const.
Returns the names of all properties that were dynamically added to the object using setProperty().
This function was introduced in Qt 4.2.
Sourcepub unsafe fn eq(&self, p: impl CastInto<Ref<QPointerOfQObject>>) -> bool
pub unsafe fn eq(&self, p: impl CastInto<Ref<QPointerOfQObject>>) -> bool
Returns true if c1 and c2 are the same Unicode character; otherwise returns false.
Calls C++ function: bool operator==(QObject* o, const QPointer<QObject>& p).
Warning: no exact match found in C++ documentation. Below is the C++ documentation for bool operator==(QChar c1, QChar c2):
Returns true if c1 and c2 are the same Unicode character; otherwise returns false.
Sourcepub unsafe fn event(&self, event: impl CastInto<Ptr<QEvent>>) -> bool
pub unsafe fn event(&self, event: impl CastInto<Ptr<QEvent>>) -> bool
This virtual function receives events to an object and should return true if the event e was recognized and processed.
Calls C++ function: virtual bool QObject::event(QEvent* event).
This virtual function receives events to an object and should return true if the event e was recognized and processed.
The event() function can be reimplemented to customize the behavior of an object.
Make sure you call the parent event class implementation for all the events you did not handle.
Example:
class MyClass : public QWidget { Q_OBJECT
public: MyClass(QWidget *parent = 0); ~MyClass();
bool event(QEvent* ev) { if (ev->type() == QEvent::PolishRequest) { // overwrite handling of PolishRequest if any doThings(); return true; } else if (ev->type() == QEvent::Show) { // complement handling of Show if any doThings2(); QWidget::event(ev); return true; } // Make sure the rest of events are handled return QWidget::event(ev); } };
See also installEventFilter(), timerEvent(), QCoreApplication::sendEvent(), and QCoreApplication::postEvent().
Sourcepub unsafe fn event_filter(
&self,
watched: impl CastInto<Ptr<QObject>>,
event: impl CastInto<Ptr<QEvent>>,
) -> bool
pub unsafe fn event_filter( &self, watched: impl CastInto<Ptr<QObject>>, event: impl CastInto<Ptr<QEvent>>, ) -> bool
Filters events if this object has been installed as an event filter for the watched object.
Calls C++ function: virtual bool QObject::eventFilter(QObject* watched, QEvent* event).
Filters events if this object has been installed as an event filter for the watched object.
In your reimplementation of this function, if you want to filter the event out, i.e. stop it being handled further, return true; otherwise return false.
Example:
class MainWindow : public QMainWindow { public: MainWindow();
protected: bool eventFilter(QObject obj, QEvent ev);
private: QTextEdit *textEdit; };
MainWindow::MainWindow() { textEdit = new QTextEdit; setCentralWidget(textEdit);
textEdit->installEventFilter(this); }
bool MainWindow::eventFilter(QObject obj, QEvent event) { if (obj == textEdit) { if (event->type() == QEvent::KeyPress) { QKeyEvent keyEvent = static_cast<QKeyEvent>(event); qDebug() << “Ate key press” << keyEvent->key(); return true; } else { return false; } } else { // pass the event on to the parent class return QMainWindow::eventFilter(obj, event); } }
Notice in the example above that unhandled events are passed to the base class's eventFilter() function, since the base class might have reimplemented eventFilter() for its own internal purposes.
Warning: If you delete the receiver object in this function, be sure to return true. Otherwise, Qt will forward the event to the deleted object and the program might crash.
See also installEventFilter().
Sourcepub unsafe fn find_child_q_object_2a(
&self,
a_name: impl CastInto<Ref<QString>>,
options: QFlags<FindChildOption>,
) -> QPtr<QObject>
pub unsafe fn find_child_q_object_2a( &self, a_name: impl CastInto<Ref<QString>>, options: QFlags<FindChildOption>, ) -> QPtr<QObject>
Returns the child of this object that can be cast into type T and that is called name, or 0 if there is no such object. Omitting the name argument causes all object names to be matched. The search is performed recursively, unless options specifies the option FindDirectChildrenOnly.
Calls C++ function: QObject* QObject::findChild<QObject*>(const QString& aName = …, QFlags<Qt::FindChildOption> options = …) const.
Returns the child of this object that can be cast into type T and that is called name, or 0 if there is no such object. Omitting the name argument causes all object names to be matched. The search is performed recursively, unless options specifies the option FindDirectChildrenOnly.
If there is more than one child matching the search, the most direct ancestor is returned. If there are several direct ancestors, it is undefined which one will be returned. In that case, findChildren() should be used.
This example returns a child QPushButton of parentWidget named "button1", even if the button isn't a direct child of the parent:
QPushButton button = parentWidget->findChild<QPushButton >(“button1”);
This example returns a QListWidget child of parentWidget:
QListWidget list = parentWidget->findChild<QListWidget >();
This example returns a child QPushButton of parentWidget (its direct parent) named "button1":
QPushButton button = parentWidget->findChild<QPushButton >(“button1”, Qt::FindDirectChildrenOnly);
This example returns a QListWidget child of parentWidget, its direct parent:
QListWidget list = parentWidget->findChild<QListWidget >(QString(), Qt::FindDirectChildrenOnly);
See also findChildren().
Sourcepub unsafe fn find_child_q_object_1a(
&self,
a_name: impl CastInto<Ref<QString>>,
) -> QPtr<QObject>
pub unsafe fn find_child_q_object_1a( &self, a_name: impl CastInto<Ref<QString>>, ) -> QPtr<QObject>
Returns the child of this object that can be cast into type T and that is called name, or 0 if there is no such object. Omitting the name argument causes all object names to be matched. The search is performed recursively, unless options specifies the option FindDirectChildrenOnly.
Calls C++ function: QObject* QObject::findChild<QObject*>(const QString& aName = …) const.
Returns the child of this object that can be cast into type T and that is called name, or 0 if there is no such object. Omitting the name argument causes all object names to be matched. The search is performed recursively, unless options specifies the option FindDirectChildrenOnly.
If there is more than one child matching the search, the most direct ancestor is returned. If there are several direct ancestors, it is undefined which one will be returned. In that case, findChildren() should be used.
This example returns a child QPushButton of parentWidget named "button1", even if the button isn't a direct child of the parent:
QPushButton button = parentWidget->findChild<QPushButton >(“button1”);
This example returns a QListWidget child of parentWidget:
QListWidget list = parentWidget->findChild<QListWidget >();
This example returns a child QPushButton of parentWidget (its direct parent) named "button1":
QPushButton button = parentWidget->findChild<QPushButton >(“button1”, Qt::FindDirectChildrenOnly);
This example returns a QListWidget child of parentWidget, its direct parent:
QListWidget list = parentWidget->findChild<QListWidget >(QString(), Qt::FindDirectChildrenOnly);
See also findChildren().
Sourcepub unsafe fn find_child_q_object_0a(&self) -> QPtr<QObject>
pub unsafe fn find_child_q_object_0a(&self) -> QPtr<QObject>
Returns the child of this object that can be cast into type T and that is called name, or 0 if there is no such object. Omitting the name argument causes all object names to be matched. The search is performed recursively, unless options specifies the option FindDirectChildrenOnly.
Calls C++ function: QObject* QObject::findChild<QObject*>() const.
Returns the child of this object that can be cast into type T and that is called name, or 0 if there is no such object. Omitting the name argument causes all object names to be matched. The search is performed recursively, unless options specifies the option FindDirectChildrenOnly.
If there is more than one child matching the search, the most direct ancestor is returned. If there are several direct ancestors, it is undefined which one will be returned. In that case, findChildren() should be used.
This example returns a child QPushButton of parentWidget named "button1", even if the button isn't a direct child of the parent:
QPushButton button = parentWidget->findChild<QPushButton >(“button1”);
This example returns a QListWidget child of parentWidget:
QListWidget list = parentWidget->findChild<QListWidget >();
This example returns a child QPushButton of parentWidget (its direct parent) named "button1":
QPushButton button = parentWidget->findChild<QPushButton >(“button1”, Qt::FindDirectChildrenOnly);
This example returns a QListWidget child of parentWidget, its direct parent:
QListWidget list = parentWidget->findChild<QListWidget >(QString(), Qt::FindDirectChildrenOnly);
See also findChildren().
Sourcepub unsafe fn find_children_q_object_q_string_q_flags_find_child_option(
&self,
a_name: impl CastInto<Ref<QString>>,
options: QFlags<FindChildOption>,
) -> CppBox<QListOfQObject>
pub unsafe fn find_children_q_object_q_string_q_flags_find_child_option( &self, a_name: impl CastInto<Ref<QString>>, options: QFlags<FindChildOption>, ) -> CppBox<QListOfQObject>
Returns all children of this object with the given name that can be cast to type T, or an empty list if there are no such objects. Omitting the name argument causes all object names to be matched. The search is performed recursively, unless options specifies the option FindDirectChildrenOnly.
Calls C++ function: QList<QObject*> QObject::findChildren<QObject*>(const QString& aName = …, QFlags<Qt::FindChildOption> options = …) const.
Returns all children of this object with the given name that can be cast to type T, or an empty list if there are no such objects. Omitting the name argument causes all object names to be matched. The search is performed recursively, unless options specifies the option FindDirectChildrenOnly.
The following example shows how to find a list of child QWidgets of the specified parentWidget named widgetname:
QList<QWidget > widgets = parentWidget.findChildren<QWidget >(“widgetname”);
This example returns all QPushButtons that are children of parentWidget:
QList<QPushButton > allPButtons = parentWidget.findChildren<QPushButton >();
This example returns all QPushButtons that are immediate children of parentWidget:
QList<QPushButton > childButtons = parentWidget.findChildren<QPushButton >(QString(), Qt::FindDirectChildrenOnly);
See also findChild().
Sourcepub unsafe fn find_children_q_object_q_reg_exp_q_flags_find_child_option(
&self,
re: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegExp>>,
options: QFlags<FindChildOption>,
) -> CppBox<QListOfQObject>
pub unsafe fn find_children_q_object_q_reg_exp_q_flags_find_child_option( &self, re: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegExp>>, options: QFlags<FindChildOption>, ) -> CppBox<QListOfQObject>
This function overloads findChildren().
Calls C++ function: QList<QObject*> QObject::findChildren<QObject*>(const QRegExp& re, QFlags<Qt::FindChildOption> options = …) const.
This function overloads findChildren().
Returns the children of this object that can be cast to type T and that have names matching the regular expression regExp, or an empty list if there are no such objects. The search is performed recursively, unless options specifies the option FindDirectChildrenOnly.
Sourcepub unsafe fn find_children_q_object_q_regular_expression_q_flags_find_child_option(
&self,
re: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegularExpression>>,
options: QFlags<FindChildOption>,
) -> CppBox<QListOfQObject>
pub unsafe fn find_children_q_object_q_regular_expression_q_flags_find_child_option( &self, re: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegularExpression>>, options: QFlags<FindChildOption>, ) -> CppBox<QListOfQObject>
This function overloads findChildren().
Calls C++ function: QList<QObject*> QObject::findChildren<QObject*>(const QRegularExpression& re, QFlags<Qt::FindChildOption> options = …) const.
This function overloads findChildren().
Returns the children of this object that can be cast to type T and that have names matching the regular expression re, or an empty list if there are no such objects. The search is performed recursively, unless options specifies the option FindDirectChildrenOnly.
This function was introduced in Qt 5.0.
Sourcepub unsafe fn find_children_q_object_q_string(
&self,
a_name: impl CastInto<Ref<QString>>,
) -> CppBox<QListOfQObject>
pub unsafe fn find_children_q_object_q_string( &self, a_name: impl CastInto<Ref<QString>>, ) -> CppBox<QListOfQObject>
Returns all children of this object with the given name that can be cast to type T, or an empty list if there are no such objects. Omitting the name argument causes all object names to be matched. The search is performed recursively, unless options specifies the option FindDirectChildrenOnly.
Calls C++ function: QList<QObject*> QObject::findChildren<QObject*>(const QString& aName = …) const.
Returns all children of this object with the given name that can be cast to type T, or an empty list if there are no such objects. Omitting the name argument causes all object names to be matched. The search is performed recursively, unless options specifies the option FindDirectChildrenOnly.
The following example shows how to find a list of child QWidgets of the specified parentWidget named widgetname:
QList<QWidget > widgets = parentWidget.findChildren<QWidget >(“widgetname”);
This example returns all QPushButtons that are children of parentWidget:
QList<QPushButton > allPButtons = parentWidget.findChildren<QPushButton >();
This example returns all QPushButtons that are immediate children of parentWidget:
QList<QPushButton > childButtons = parentWidget.findChildren<QPushButton >(QString(), Qt::FindDirectChildrenOnly);
See also findChild().
Sourcepub unsafe fn find_children_q_object(&self) -> CppBox<QListOfQObject>
pub unsafe fn find_children_q_object(&self) -> CppBox<QListOfQObject>
Returns all children of this object with the given name that can be cast to type T, or an empty list if there are no such objects. Omitting the name argument causes all object names to be matched. The search is performed recursively, unless options specifies the option FindDirectChildrenOnly.
Calls C++ function: QList<QObject*> QObject::findChildren<QObject*>() const.
Returns all children of this object with the given name that can be cast to type T, or an empty list if there are no such objects. Omitting the name argument causes all object names to be matched. The search is performed recursively, unless options specifies the option FindDirectChildrenOnly.
The following example shows how to find a list of child QWidgets of the specified parentWidget named widgetname:
QList<QWidget > widgets = parentWidget.findChildren<QWidget >(“widgetname”);
This example returns all QPushButtons that are children of parentWidget:
QList<QPushButton > allPButtons = parentWidget.findChildren<QPushButton >();
This example returns all QPushButtons that are immediate children of parentWidget:
QList<QPushButton > childButtons = parentWidget.findChildren<QPushButton >(QString(), Qt::FindDirectChildrenOnly);
See also findChild().
Sourcepub unsafe fn find_children_q_object_q_reg_exp(
&self,
re: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegExp>>,
) -> CppBox<QListOfQObject>
pub unsafe fn find_children_q_object_q_reg_exp( &self, re: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegExp>>, ) -> CppBox<QListOfQObject>
This function overloads findChildren().
Calls C++ function: QList<QObject*> QObject::findChildren<QObject*>(const QRegExp& re) const.
This function overloads findChildren().
Returns the children of this object that can be cast to type T and that have names matching the regular expression regExp, or an empty list if there are no such objects. The search is performed recursively, unless options specifies the option FindDirectChildrenOnly.
Sourcepub unsafe fn find_children_q_object_q_regular_expression(
&self,
re: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegularExpression>>,
) -> CppBox<QListOfQObject>
pub unsafe fn find_children_q_object_q_regular_expression( &self, re: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegularExpression>>, ) -> CppBox<QListOfQObject>
This function overloads findChildren().
Calls C++ function: QList<QObject*> QObject::findChildren<QObject*>(const QRegularExpression& re) const.
This function overloads findChildren().
Returns the children of this object that can be cast to type T and that have names matching the regular expression re, or an empty list if there are no such objects. The search is performed recursively, unless options specifies the option FindDirectChildrenOnly.
This function was introduced in Qt 5.0.
Sourcepub unsafe fn inherits(&self, classname: *const i8) -> bool
pub unsafe fn inherits(&self, classname: *const i8) -> bool
Returns true if this object is an instance of a class that inherits className or a QObject subclass that inherits className; otherwise returns false.
Calls C++ function: bool QObject::inherits(const char* classname) const.
Returns true if this object is an instance of a class that inherits className or a QObject subclass that inherits className; otherwise returns false.
A class is considered to inherit itself.
Example:
QTimer *timer = new QTimer; // QTimer inherits QObject timer->inherits(“QTimer”); // returns true timer->inherits(“QObject”); // returns true timer->inherits(“QAbstractButton”); // returns false
// QVBoxLayout inherits QObject and QLayoutItem QVBoxLayout *layout = new QVBoxLayout; layout->inherits(“QObject”); // returns true layout->inherits(“QLayoutItem”); // returns true (even though QLayoutItem is not a QObject)
If you need to determine whether an object is an instance of a particular class for the purpose of casting it, consider using qobject_cast<Type *>(object) instead.
See also metaObject() and qobject_cast().
Sourcepub unsafe fn install_event_filter(
&self,
filter_obj: impl CastInto<Ptr<QObject>>,
)
pub unsafe fn install_event_filter( &self, filter_obj: impl CastInto<Ptr<QObject>>, )
Installs an event filter filterObj on this object. For example:
Calls C++ function: void QObject::installEventFilter(QObject* filterObj).
Installs an event filter filterObj on this object. For example:
monitoredObj->installEventFilter(filterObj);
An event filter is an object that receives all events that are sent to this object. The filter can either stop the event or forward it to this object. The event filter filterObj receives events via its eventFilter() function. The eventFilter() function must return true if the event should be filtered, (i.e. stopped); otherwise it must return false.
If multiple event filters are installed on a single object, the filter that was installed last is activated first.
Here's a KeyPressEater class that eats the key presses of its monitored objects:
class KeyPressEater : public QObject { Q_OBJECT ...
protected: bool eventFilter(QObject obj, QEvent event); };
bool KeyPressEater::eventFilter(QObject obj, QEvent event) { if (event->type() == QEvent::KeyPress) { QKeyEvent keyEvent = static_cast<QKeyEvent >(event); qDebug(“Ate key press %d”, keyEvent->key()); return true; } else { // standard event processing return QObject::eventFilter(obj, event); } }
And here's how to install it on two widgets:
KeyPressEater keyPressEater = new KeyPressEater(this); QPushButton pushButton = new QPushButton(this); QListView *listView = new QListView(this);
pushButton->installEventFilter(keyPressEater); listView->installEventFilter(keyPressEater);
The QShortcut class, for example, uses this technique to intercept shortcut key presses.
Warning: If you delete the receiver object in your eventFilter() function, be sure to return true. If you return false, Qt sends the event to the deleted object and the program will crash.
Note that the filtering object must be in the same thread as this object. If filterObj is in a different thread, this function does nothing. If either filterObj or this object are moved to a different thread after calling this function, the event filter will not be called until both objects have the same thread affinity again (it is not removed).
See also removeEventFilter(), eventFilter(), and event().
Sourcepub unsafe fn is_widget_type(&self) -> bool
pub unsafe fn is_widget_type(&self) -> bool
Returns true if the object is a widget; otherwise returns false.
Calls C++ function: bool QObject::isWidgetType() const.
Returns true if the object is a widget; otherwise returns false.
Calling this function is equivalent to calling inherits("QWidget"), except that it is much faster.
Sourcepub unsafe fn is_window_type(&self) -> bool
pub unsafe fn is_window_type(&self) -> bool
Returns true if the object is a window; otherwise returns false.
Calls C++ function: bool QObject::isWindowType() const.
Returns true if the object is a window; otherwise returns false.
Calling this function is equivalent to calling inherits("QWindow"), except that it is much faster.
Sourcepub unsafe fn kill_timer(&self, id: i32)
pub unsafe fn kill_timer(&self, id: i32)
Kills the timer with timer identifier, id.
Calls C++ function: void QObject::killTimer(int id).
Kills the timer with timer identifier, id.
The timer identifier is returned by startTimer() when a timer event is started.
See also timerEvent() and startTimer().
Sourcepub unsafe fn meta_object(&self) -> Ptr<QMetaObject>
pub unsafe fn meta_object(&self) -> Ptr<QMetaObject>
Returns a pointer to the meta-object of this object.
Calls C++ function: virtual const QMetaObject* QObject::metaObject() const.
Returns a pointer to the meta-object of this object.
A meta-object contains information about a class that inherits QObject, e.g. class name, superclass name, properties, signals and slots. Every QObject subclass that contains the Q_OBJECT macro will have a meta-object.
The meta-object information is required by the signal/slot connection mechanism and the property system. The inherits() function also makes use of the meta-object.
If you have no pointer to an actual object instance but still want to access the meta-object of a class, you can use staticMetaObject.
Example:
QObject *obj = new QPushButton; obj->metaObject()->className(); // returns “QPushButton”
QPushButton::staticMetaObject.className(); // returns “QPushButton”
See also staticMetaObject.
Sourcepub unsafe fn move_to_thread(&self, thread: impl CastInto<Ptr<QThread>>)
pub unsafe fn move_to_thread(&self, thread: impl CastInto<Ptr<QThread>>)
Changes the thread affinity for this object and its children. The object cannot be moved if it has a parent. Event processing will continue in the targetThread.
Calls C++ function: void QObject::moveToThread(QThread* thread).
Changes the thread affinity for this object and its children. The object cannot be moved if it has a parent. Event processing will continue in the targetThread.
To move an object to the main thread, use QApplication::instance() to retrieve a pointer to the current application, and then use QApplication::thread() to retrieve the thread in which the application lives. For example:
myObject->moveToThread(QApplication::instance()->thread());
If targetThread is zero, all event processing for this object and its children stops.
Note that all active timers for the object will be reset. The timers are first stopped in the current thread and restarted (with the same interval) in the targetThread. As a result, constantly moving an object between threads can postpone timer events indefinitely.
A QEvent::ThreadChange event is sent to this object just before the thread affinity is changed. You can handle this event to perform any special processing. Note that any new events that are posted to this object will be handled in the targetThread.
Warning: This function is not thread-safe; the current thread must be same as the current thread affinity. In other words, this function can only "push" an object from the current thread to another thread, it cannot "pull" an object from any arbitrary thread to the current thread.
See also thread().
Sourcepub unsafe fn object_name(&self) -> CppBox<QString>
pub unsafe fn object_name(&self) -> CppBox<QString>
This property holds the name of this object
Calls C++ function: QString QObject::objectName() const.
This property holds the name of this object
You can find an object by name (and type) using findChild(). You can find a set of objects with findChildren().
qDebug(“MyClass::setPrecision(): (%s) invalid precision %f”, qPrintable(objectName()), newPrecision);
By default, this property contains an empty string.
Access functions:
| QString | objectName() const |
| void | setObjectName(const QString &name) |
Notifier signal:
| void | objectNameChanged(const QString &objectName) | [see note below] |
Note: This is a private signal. It can be used in signal connections but cannot be emitted by the user.
See also metaObject() and QMetaObject::className().
Sourcepub unsafe fn parent(&self) -> QPtr<QObject>
pub unsafe fn parent(&self) -> QPtr<QObject>
Returns a pointer to the parent object.
Calls C++ function: QObject* QObject::parent() const.
Sourcepub unsafe fn property(&self, name: *const i8) -> CppBox<QVariant>
pub unsafe fn property(&self, name: *const i8) -> CppBox<QVariant>
Returns the value of the object's name property.
Calls C++ function: QVariant QObject::property(const char* name) const.
Returns the value of the object’s name property.
If no such property exists, the returned variant is invalid.
Information about all available properties is provided through the metaObject() and dynamicPropertyNames().
See also setProperty(), QVariant::isValid(), metaObject(), and dynamicPropertyNames().
Sourcepub unsafe fn qt_metacall(
&self,
arg1: Call,
arg2: i32,
arg3: *mut *mut c_void,
) -> i32
pub unsafe fn qt_metacall( &self, arg1: Call, arg2: i32, arg3: *mut *mut c_void, ) -> i32
Calls C++ function: virtual int QObject::qt_metacall(QMetaObject::Call arg1, int arg2, void** arg3).
Sourcepub unsafe fn qt_metacast(&self, arg1: *const i8) -> *mut c_void
pub unsafe fn qt_metacast(&self, arg1: *const i8) -> *mut c_void
Calls C++ function: virtual void* QObject::qt_metacast(const char* arg1).
Sourcepub unsafe fn remove_event_filter(&self, obj: impl CastInto<Ptr<QObject>>)
pub unsafe fn remove_event_filter(&self, obj: impl CastInto<Ptr<QObject>>)
Removes an event filter object obj from this object. The request is ignored if such an event filter has not been installed.
Calls C++ function: void QObject::removeEventFilter(QObject* obj).
Removes an event filter object obj from this object. The request is ignored if such an event filter has not been installed.
All event filters for this object are automatically removed when this object is destroyed.
It is always safe to remove an event filter, even during event filter activation (i.e. from the eventFilter() function).
See also installEventFilter(), eventFilter(), and event().
Sourcepub unsafe fn set_object_name(&self, name: impl CastInto<Ref<QString>>)
pub unsafe fn set_object_name(&self, name: impl CastInto<Ref<QString>>)
This property holds the name of this object
Calls C++ function: void QObject::setObjectName(const QString& name).
This property holds the name of this object
You can find an object by name (and type) using findChild(). You can find a set of objects with findChildren().
qDebug(“MyClass::setPrecision(): (%s) invalid precision %f”, qPrintable(objectName()), newPrecision);
By default, this property contains an empty string.
Access functions:
| QString | objectName() const |
| void | setObjectName(const QString &name) |
Notifier signal:
| void | objectNameChanged(const QString &objectName) | [see note below] |
Note: This is a private signal. It can be used in signal connections but cannot be emitted by the user.
See also metaObject() and QMetaObject::className().
Sourcepub unsafe fn set_parent(&self, parent: impl CastInto<Ptr<QObject>>)
pub unsafe fn set_parent(&self, parent: impl CastInto<Ptr<QObject>>)
Makes the object a child of parent.
Calls C++ function: void QObject::setParent(QObject* parent).
Sourcepub unsafe fn set_property(
&self,
name: *const i8,
value: impl CastInto<Ref<QVariant>>,
) -> bool
pub unsafe fn set_property( &self, name: *const i8, value: impl CastInto<Ref<QVariant>>, ) -> bool
Sets the value of the object's name property to value.
Calls C++ function: bool QObject::setProperty(const char* name, const QVariant& value).
Sets the value of the object’s name property to value.
If the property is defined in the class using Q_PROPERTY then true is returned on success and false otherwise. If the property is not defined using Q_PROPERTY, and therefore not listed in the meta-object, it is added as a dynamic property and false is returned.
Information about all available properties is provided through the metaObject() and dynamicPropertyNames().
Dynamic properties can be queried again using property() and can be removed by setting the property value to an invalid QVariant. Changing the value of a dynamic property causes a QDynamicPropertyChangeEvent to be sent to the object.
Note: Dynamic properties starting with "_q_" are reserved for internal purposes.
See also property(), metaObject(), dynamicPropertyNames(), and QMetaProperty::write().
Sourcepub unsafe fn signals_blocked(&self) -> bool
pub unsafe fn signals_blocked(&self) -> bool
Returns true if signals are blocked; otherwise returns false.
Calls C++ function: bool QObject::signalsBlocked() const.
Returns true if signals are blocked; otherwise returns false.
Signals are not blocked by default.
See also blockSignals() and QSignalBlocker.
Sourcepub unsafe fn start_timer_2a(&self, interval: i32, timer_type: TimerType) -> i32
pub unsafe fn start_timer_2a(&self, interval: i32, timer_type: TimerType) -> i32
Starts a timer and returns a timer identifier, or returns zero if it could not start a timer.
Calls C++ function: int QObject::startTimer(int interval, Qt::TimerType timerType = …).
Starts a timer and returns a timer identifier, or returns zero if it could not start a timer.
A timer event will occur every interval milliseconds until killTimer() is called. If interval is 0, then the timer event occurs once every time there are no more window system events to process.
The virtual timerEvent() function is called with the QTimerEvent event parameter class when a timer event occurs. Reimplement this function to get timer events.
If multiple timers are running, the QTimerEvent::timerId() can be used to find out which timer was activated.
Example:
class MyObject : public QObject { Q_OBJECT
public: MyObject(QObject *parent = 0);
protected: void timerEvent(QTimerEvent *event); };
MyObject::MyObject(QObject *parent) : QObject(parent) { startTimer(50); // 50-millisecond timer startTimer(1000); // 1-second timer startTimer(60000); // 1-minute timer
using namespace std::chrono; startTimer(milliseconds(50)); startTimer(seconds(1)); startTimer(minutes(1));
// since C++14 we can use std::chrono::duration literals, e.g.: startTimer(100ms); startTimer(5s); startTimer(2min); startTimer(1h); }
void MyObject::timerEvent(QTimerEvent *event) { qDebug() << “Timer ID:” << event->timerId(); }
Note that QTimer's accuracy depends on the underlying operating system and hardware. The timerType argument allows you to customize the accuracy of the timer. See Qt::TimerType for information on the different timer types. Most platforms support an accuracy of 20 milliseconds; some provide more. If Qt is unable to deliver the requested number of timer events, it will silently discard some.
The QTimer class provides a high-level programming interface with single-shot timers and timer signals instead of events. There is also a QBasicTimer class that is more lightweight than QTimer and less clumsy than using timer IDs directly.
See also timerEvent(), killTimer(), and QTimer::singleShot().
Sourcepub unsafe fn start_timer_1a(&self, interval: i32) -> i32
pub unsafe fn start_timer_1a(&self, interval: i32) -> i32
Starts a timer and returns a timer identifier, or returns zero if it could not start a timer.
Calls C++ function: int QObject::startTimer(int interval).
Starts a timer and returns a timer identifier, or returns zero if it could not start a timer.
A timer event will occur every interval milliseconds until killTimer() is called. If interval is 0, then the timer event occurs once every time there are no more window system events to process.
The virtual timerEvent() function is called with the QTimerEvent event parameter class when a timer event occurs. Reimplement this function to get timer events.
If multiple timers are running, the QTimerEvent::timerId() can be used to find out which timer was activated.
Example:
class MyObject : public QObject { Q_OBJECT
public: MyObject(QObject *parent = 0);
protected: void timerEvent(QTimerEvent *event); };
MyObject::MyObject(QObject *parent) : QObject(parent) { startTimer(50); // 50-millisecond timer startTimer(1000); // 1-second timer startTimer(60000); // 1-minute timer
using namespace std::chrono; startTimer(milliseconds(50)); startTimer(seconds(1)); startTimer(minutes(1));
// since C++14 we can use std::chrono::duration literals, e.g.: startTimer(100ms); startTimer(5s); startTimer(2min); startTimer(1h); }
void MyObject::timerEvent(QTimerEvent *event) { qDebug() << “Timer ID:” << event->timerId(); }
Note that QTimer's accuracy depends on the underlying operating system and hardware. The timerType argument allows you to customize the accuracy of the timer. See Qt::TimerType for information on the different timer types. Most platforms support an accuracy of 20 milliseconds; some provide more. If Qt is unable to deliver the requested number of timer events, it will silently discard some.
The QTimer class provides a high-level programming interface with single-shot timers and timer signals instead of events. There is also a QBasicTimer class that is more lightweight than QTimer and less clumsy than using timer IDs directly.
See also timerEvent(), killTimer(), and QTimer::singleShot().
Sourcepub unsafe fn thread(&self) -> QPtr<QThread>
pub unsafe fn thread(&self) -> QPtr<QThread>
Returns the thread in which the object lives.
Calls C++ function: QThread* QObject::thread() const.
Returns the thread in which the object lives.
See also moveToThread().
Trait Implementations§
Source§impl CppDeletable for QFormLayout
impl CppDeletable for QFormLayout
Source§impl Deref for QFormLayout
impl Deref for QFormLayout
Source§impl DynamicCast<QFormLayout> for QLayout
impl DynamicCast<QFormLayout> for QLayout
Source§unsafe fn dynamic_cast(ptr: Ptr<QLayout>) -> Ptr<QFormLayout>
unsafe fn dynamic_cast(ptr: Ptr<QLayout>) -> Ptr<QFormLayout>
Calls C++ function: QFormLayout* dynamic_cast<QFormLayout*>(QLayout* ptr).
Source§impl DynamicCast<QFormLayout> for QLayoutItem
impl DynamicCast<QFormLayout> for QLayoutItem
Source§unsafe fn dynamic_cast(ptr: Ptr<QLayoutItem>) -> Ptr<QFormLayout>
unsafe fn dynamic_cast(ptr: Ptr<QLayoutItem>) -> Ptr<QFormLayout>
Calls C++ function: QFormLayout* dynamic_cast<QFormLayout*>(QLayoutItem* ptr).
Source§impl DynamicCast<QFormLayout> for QObject
impl DynamicCast<QFormLayout> for QObject
Source§unsafe fn dynamic_cast(ptr: Ptr<QObject>) -> Ptr<QFormLayout>
unsafe fn dynamic_cast(ptr: Ptr<QObject>) -> Ptr<QFormLayout>
Calls C++ function: QFormLayout* dynamic_cast<QFormLayout*>(QObject* ptr).
Source§impl StaticDowncast<QFormLayout> for QLayout
impl StaticDowncast<QFormLayout> for QLayout
Source§unsafe fn static_downcast(ptr: Ptr<QLayout>) -> Ptr<QFormLayout>
unsafe fn static_downcast(ptr: Ptr<QLayout>) -> Ptr<QFormLayout>
Calls C++ function: QFormLayout* static_cast<QFormLayout*>(QLayout* ptr).
Source§impl StaticDowncast<QFormLayout> for QLayoutItem
impl StaticDowncast<QFormLayout> for QLayoutItem
Source§unsafe fn static_downcast(ptr: Ptr<QLayoutItem>) -> Ptr<QFormLayout>
unsafe fn static_downcast(ptr: Ptr<QLayoutItem>) -> Ptr<QFormLayout>
Calls C++ function: QFormLayout* static_cast<QFormLayout*>(QLayoutItem* ptr).
Source§impl StaticDowncast<QFormLayout> for QObject
impl StaticDowncast<QFormLayout> for QObject
Source§unsafe fn static_downcast(ptr: Ptr<QObject>) -> Ptr<QFormLayout>
unsafe fn static_downcast(ptr: Ptr<QObject>) -> Ptr<QFormLayout>
Calls C++ function: QFormLayout* static_cast<QFormLayout*>(QObject* ptr).
Source§impl StaticUpcast<QLayout> for QFormLayout
impl StaticUpcast<QLayout> for QFormLayout
Source§unsafe fn static_upcast(ptr: Ptr<QFormLayout>) -> Ptr<QLayout>
unsafe fn static_upcast(ptr: Ptr<QFormLayout>) -> Ptr<QLayout>
Calls C++ function: QLayout* static_cast<QLayout*>(QFormLayout* ptr).
Source§impl StaticUpcast<QLayoutItem> for QFormLayout
impl StaticUpcast<QLayoutItem> for QFormLayout
Source§unsafe fn static_upcast(ptr: Ptr<QFormLayout>) -> Ptr<QLayoutItem>
unsafe fn static_upcast(ptr: Ptr<QFormLayout>) -> Ptr<QLayoutItem>
Calls C++ function: QLayoutItem* static_cast<QLayoutItem*>(QFormLayout* ptr).
Source§impl StaticUpcast<QObject> for QFormLayout
impl StaticUpcast<QObject> for QFormLayout
Source§unsafe fn static_upcast(ptr: Ptr<QFormLayout>) -> Ptr<QObject>
unsafe fn static_upcast(ptr: Ptr<QFormLayout>) -> Ptr<QObject>
Calls C++ function: QObject* static_cast<QObject*>(QFormLayout* ptr).