kdam
kdam is a port of tqdm library which is written in python. kdam has almost same features as tqdm with extra features included. kdam is also 4 times faster than tqdm. kdam has only one external dependency which terminal-size.
Instantly make your loops show a smart progress meter. Just wrap any iterator with tqdm!(iterator) macro and you're done!
use tqdm;
100%|█████████████████████████████| 100/100 [00:00<00:00, 25854.49it/s]
kdam also supports different animation styles. All available animations styles are:
examples/showcase_animations.rs
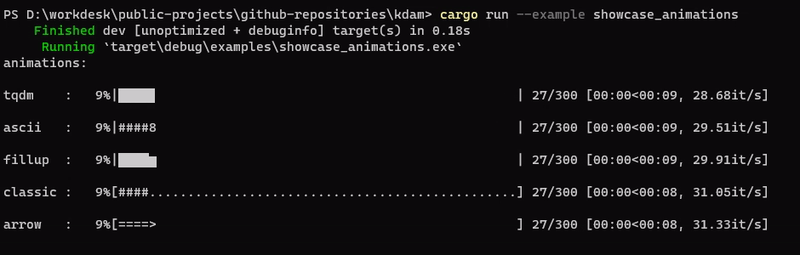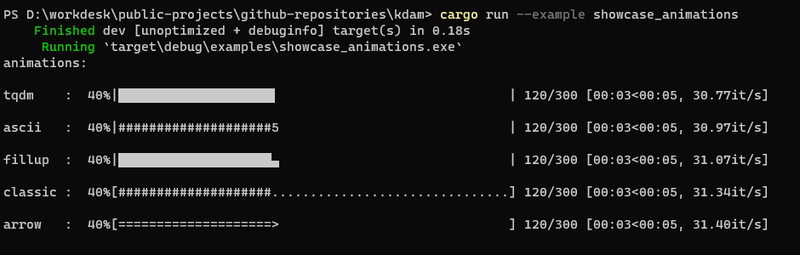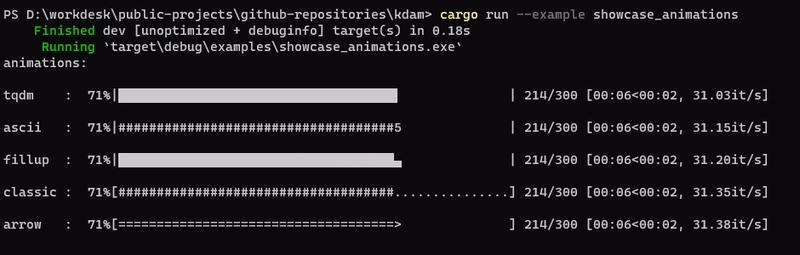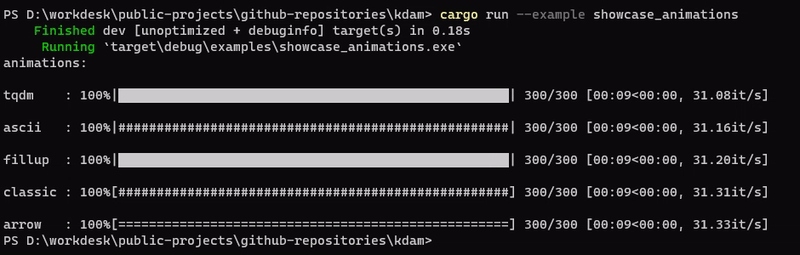
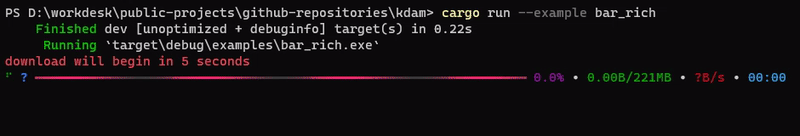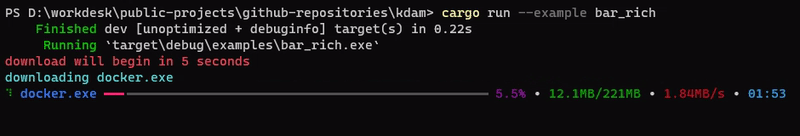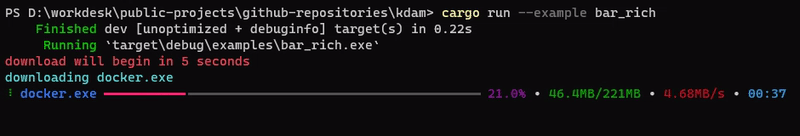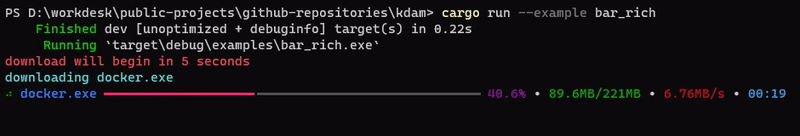
kdam also support rich.progress style bars with customizable columns.
Fira Code is the first programming font to offer dedicated glyphs to render progress bars. kdam has an animation style to support it.
Installations
Add this to your Cargo.toml file.
[]
= "0.1.2"
Or add from github main branch.
[]
= { = "https://github.com/clitic/kdam.git", = "main" }
Usage
Iterator Based
use tqdm;
Manual
use tqdm;
Another example without a total value. This only shows basic stats.
use tqdm;
10000000 [00:03, 2998660.35it/s]
Examples
Description And Additional Stats
Custom information can be displayed and updated dynamically on kdam bars with the desc and postfix.
use tqdm;
GEN 4: 50%|█████████▎ | 5/10 [00:02<00:02, 1.95it/s, str=h, lst=[1, 2]]
Nested Progress Bars
kdam supports nested progress bars. For manual control over positioning (e.g. for multi-processing use), you may specify position=n where n=0 for the outermost bar, n=1 for the next, and so on.
use tqdm;
1st loop: 50%|███████▎ | 2/4 [00:08<00:08, 0.25it/s]
2nd loop: 60%|████████▌ | 3/5 [00:02<00:01, 1.25it/s]
3rd loop: 0%|▎ | 0/50 [00:00<00:00, ?it/s]
Writing Messages And Inputs
Since kdam uses a simple printing mechanism to display progress bars, you should not write any message in the terminal using println!() while a progressbar is open.
To write messages in the terminal without any collision with kdam bar display, a .write() method is provided. This message will print at bar output location, which is stderr by default.
use tqdm;
Done task 0
Done task 1
Done task 2
Done task 3
Done task 4
Done task 5
Done task 6
Done task 7
Done task 8
Done task 9
100%|███████████████████████████| 10/10 [00:02<00:00, 4.31it/s]
Similarly .input() method can be called to store an user input.
use tqdm;
Break Loop [y/n]: y
50%|███████████████▎ | 5/10 [00:01<00:01, 3.83it/s]
License
© 2022 clitic
This repository is licensed under the MIT license. See LICENSE for details.