# Graph Solver
An undirected graph constraint solver for node and edge colors.
Brought to you by the [AdvancedResearch](https://github.com/advancedresearch) community!
- If you are looking for a generic solver that does not remove facts,
see [monotonic_solver](https://github.com/advancedresearch/monotonic_solver)
- If you are looking for a generic solver that can remove facts,
see [linear_solver](https://github.com/advancedresearch/linear_solver)
- If you are looking for a brute-force automated theorem prover for classical and path semantical logic,
see [pocket_prover](https://github.com/advancedresearch/pocket_prover)
### Motivation
Graph solving is used to find visual representations of various algebras,
such as [Adinkra diagrams](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adinkra_symbols_(physics)),
but where the rules for generating the graphs efficiently is unknown.
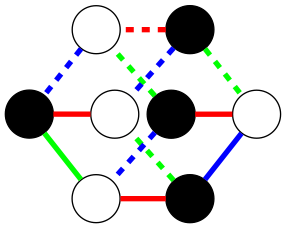
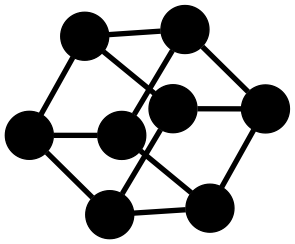
### Example: Cube
To construct a cube using a graph solver
requires specifying how nodes connect to other nodes.
The information you give the solver is which colors these connections have,
but without telling which nodes in the graph should be connected.
```rust̨
/*
=== CUBE EXAMPLE ===
Run with GraphViz (https://graphviz.org/):
cargo run --example cube | dot -Tpng > test.png
*/
use graph_solver::*;
// Notice that edges starts with `2`.
// This is because `0` is empty and `1` is no-edge.
const EDGE: Color = 2;
fn main() {
let mut g = Graph::new();
// Create a node pattern with 3 edges.
let a = Node {
color: 0,
self_connected: false,
edges: vec![Constraint {edge: EDGE, node: 0}; 3]
};
// Add 8 vertices.
for _ in 0..8 {g.push(a.clone())}
g.no_triangles = true;
let solve_settings = SolveSettings::new();
if let Some(solution) = g.solve(solve_settings) {
println!("{}", solution.puzzle.graphviz(
"sfdp",
&["black"],
&["black"]
));
} else {
eprintln!("<no solution>");
}
}
```
### Introduction to Graph Constraint Solving
Each node has a color and a list of edge constraints.
The edge constraint stores an edge color and a target color for the adjacent node.
This technique creates a powerful language to describe graphs compactly.
For example, all nodes that are locally similar,
can use a common description.
Any graphs can be determined using
sufficient local information about the nodes and edges.
To do this, one can assign each node and edge a unique number.
Therefore, to describe a graph in more detail,
one can simply add more colors!
### Design
Uses the [quickbacktrack](https://crates.io/crates/quickbacktrack) library
for constraint solving.
This allows starting with a partially solved graph,
override solving strategies, debug, or comparing the solution vs the original.
- Node and edge colors are represents as `u64`
- A node color can be any value
- Edge colors usually start with `2`
- An edge color `0` is means no choice (neither empty or colored).
- An edge color `1` is means empty