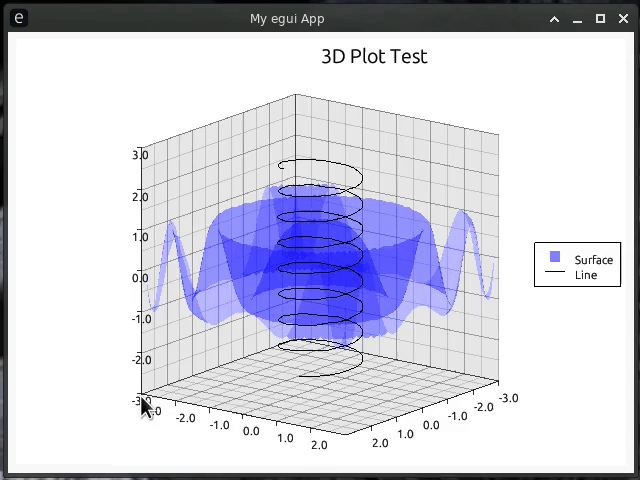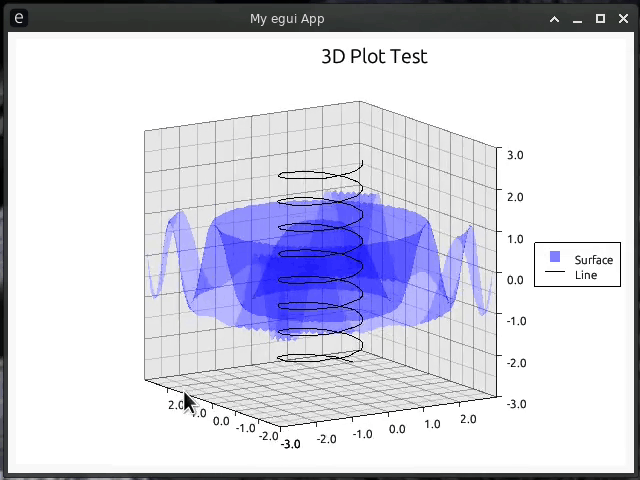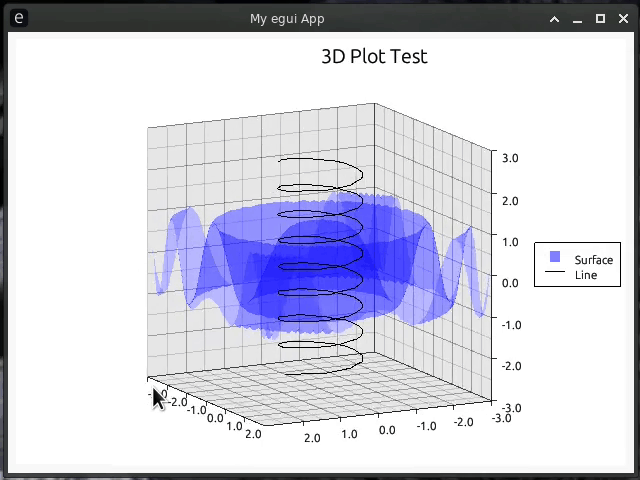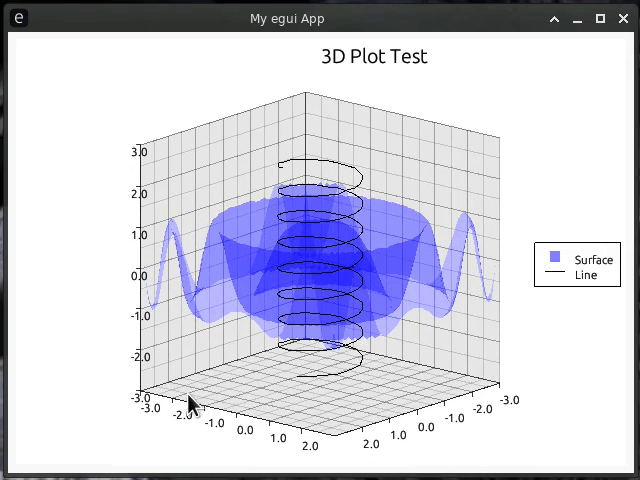
egui-plotter
simple to use utilties for integrating plotter into egui
Usage
This crate can be used by adding egui-plotter to the dependencies in your
project's Cargo.toml.
[dependencies]
egui-plotter = "0.6.0"
Features
timechart- Includes all the pre-made animatable charts like XyTimeData and TimeData.
Examples
Here's a simple plotter example being run on native eframe. Derived from eframe and plotters.
use eframe::egui::{self, CentralPanel, Visuals};
use egui_plotter::EguiBackend;
use plotters::prelude::*;
fn main() {
let native_options = eframe::NativeOptions::default();
eframe::run_native(
"Simple Example",
native_options,
Box::new(|cc| Ok(Box::new(Simple::new(cc)))),
)
.unwrap();
}
struct Simple;
impl Simple {
fn new(cc: &eframe::CreationContext<'_>) -> Self {
// Enable light mode
let context = &cc.egui_ctx;
context.set_visuals(Visuals::light());
Self
}
}
impl eframe::App for Simple {
fn update(&mut self, ctx: &egui::Context, _frame: &mut eframe::Frame) {
CentralPanel::default().show(ctx, |ui| {
let root = EguiBackend::new(ui).into_drawing_area();
root.fill(&WHITE).unwrap();
let mut chart = ChartBuilder::on(&root)
.caption("y=x^2", ("sans-serif", 50).into_font())
.margin(5)
.x_label_area_size(30)
.y_label_area_size(30)
.build_cartesian_2d(-1f32..1f32, -0.1f32..1f32)
.unwrap();
chart.configure_mesh().draw().unwrap();
chart
.draw_series(LineSeries::new(
(-50..=50).map(|x| x as f32 / 50.0).map(|x| (x, x * x)),
&RED,
))
.unwrap()
.label("y = x^2")
.legend(|(x, y)| PathElement::new(vec![(x, y), (x + 20, y)], &RED));
chart
.configure_series_labels()
.background_style(&WHITE.mix(0.8))
.border_style(&BLACK)
.draw()
.unwrap();
root.present().unwrap();
});
}
}
Charts
Alternatively, the above example can be made with a Chart type to allow easy
user interactivity with your plotter charts. You can either make your own chart or
use a prebuilt chart type included in the charts module.
use eframe::egui::{self, CentralPanel, Key, Visuals};
use egui_plotter::{Chart, MouseConfig};
use plotters::prelude::*;
use std::ops::Range;
fn main() {
let native_options = eframe::NativeOptions::default();
eframe::run_native(
"ParaChart Example",
native_options,
Box::new(|cc| Ok(Box::new(ParaChart::new(cc)))),
)
.unwrap();
}
struct ParaChart {
chart: Chart<(Range<f32>, Range<f32>)>,
}
impl ParaChart {
fn new(cc: &eframe::CreationContext<'_>) -> Self {
// Enable light mode
let context = &cc.egui_ctx;
context.set_visuals(Visuals::light());
// We use data to adjust the range of the chart. This can be useful for
// line plots where the X represents time and we want to play through
// the X, but that is not what we are using it for here
let chart = Chart::new((-3f32..3f32, -0.5f32..3f32))
.mouse(MouseConfig::enabled())
.builder_cb(Box::new(|area, _t, ranges| {
// Build a chart like you would in any other plotter chart.
// The drawing area and ranges are provided by the callback,
// but otherwise everything else is the same.
let (x_range, y_range) = ranges;
let mut chart = ChartBuilder::on(area)
.caption("y=x^2", ("sans-serif", 50).into_font())
.margin(5)
.x_label_area_size(30)
.y_label_area_size(30)
.build_cartesian_2d(x_range.to_owned(), y_range.to_owned())
.unwrap();
chart.configure_mesh().draw().unwrap();
chart
.draw_series(LineSeries::new(
(-50 * (x_range.end as i32)..=(50 * x_range.end as i32))
.map(|x| x as f32 / 50.0)
.map(|x| (x, x * x)),
&RED,
))
.unwrap()
.label("y = x^2")
.legend(|(x, y)| PathElement::new(vec![(x, y), (x + 20, y)], RED));
chart
.configure_series_labels()
.background_style(WHITE.mix(0.8))
.border_style(BLACK)
.draw()
.unwrap();
}));
Self { chart }
}
}
impl eframe::App for ParaChart {
fn update(&mut self, ctx: &egui::Context, _frame: &mut eframe::Frame) {
CentralPanel::default().show(ctx, |ui| {
// Press 1 for the range -1..1, 2 for -2..2, 3 for -3..3
ui.input(|input| {
if input.key_down(Key::Num1) {
*self.chart
.get_data_mut() = (-1f32..1f32, -0.5f32..1f32);
}
if input.key_down(Key::Num2) {
*self.chart
.get_data_mut() = (-2f32..2f32, -0.5f32..2f32);
}
if input.key_down(Key::Num3) {
*self.chart
.get_data_mut() = (-3f32..3f32, -0.5f32..3f32);
}
});
self.chart.draw(ui);
});
}
}