# b4s
Binary Search Single Sorted String: Perform binary search on a single, delimited string
slice of sorted but unevenly sized substrings.
The docs are best viewed via [docs.rs](https://docs.rs/b4s).
[](https://codecov.io/github/alexpovel/b4s)[](https://crates.io/crates/b4s)
## Usage
There are generally two ways to setup this crate: at compile-time, or at runtime. The
main (only...) method of interest is [`SortedString::binary_search()`]. View its
documentation for detailed context.
### Runtime
```rust
use b4s::{AsciiChar, SortedString};
fn main() {
match SortedString::new_checked("abc,def,ghi,jkl,mno,pqr,stu,vwx,yz", AsciiChar::Comma) {
Ok(ss) => {
match ss.binary_search("ghi") {
Ok(r) => println!("Found at range: {:?}", r),
Err(r) => println!("Not found, last looked at range: {:?}", r),
}
}
Err(e) => println!("Error: {:?}", e),
}
}
```
### Compile-time
For convenience, there's also a `const fn`, usable statically. As a tradeoff, instance
creation will not perform correctness checks. An unsorted string will result in binary
search misbehaving. Though no panics occur, you will be handed back an `Error`. See the
documentation of [`SortedString::new_unchecked()`] for details.
```rust
use b4s::{AsciiChar, SortedString};
static SS: SortedString =
SortedString::new_unchecked("abc,def,ghi,jkl,mno,pqr,stu,vwx,yz", AsciiChar::Comma);
fn main() {
match SS.binary_search("ghi") {
Ok(r) => println!("Found at range: {:?}", r),
Err(r) => println!("Not found, last looked at range: {:?}", r),
}
}
```
The source for the input string can be anything, for example a file prepared at compile
time:
```rust,ignore
static SS: SortedString =
SortedString::new_unchecked(include_str!("path/to/file"), AsciiChar::LineFeed);
```
This is convenient if a delimited (`\n`, ...) file is already at hand. It only needs to
be sorted once previously, and is then available for string containment checks at good,
albeit not perfect, runtime performance, at essentially no startup cost.
## Motivation
The itch to be scratched is the following:
- there's an array of strings to do lookup in, for example a word list
- the lookup is a simple containment check, with no modification
- the word list is available and prepared (sorted) at compile-time (e.g. in
[`build.rs`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/cargo/reference/build-scripts.html))
- the word list is large (potentially much larger than the code itself); think 5MB or
more
- the list is to be distributed as part of the binary
A couple possible approaches come to mind. The summary table, where `n` is the number of
words in the dictionary and `k` the number of characters in a word to look up, is (for
more context, see the individual sections below):
| `b4s` | [`O(n log n)`][slice-sort] | Single ref: `O(1)` | [`O(log n)`][b4s-lib] | `O(n)` |
| [`fst`][fst-repo] | [`O(n log n)`][fst-build] | Single ref: `O(1)` | [`O(k)`][fst-lookup] | [`< O(n)`][fst-size] |
| [slice][slice] | [`O(n log n)`][slice-sort] | Many refs: `O(n)` | [`O(log n)`][slice-binsearch] | `~ O(3n)` |
| [`phf`][phf-repo] | None | Many refs: `O(n)` | Hash: `O(1)` | `~ O(3n)` |
| [`HashSet`][hashset] | None | Many refs: `O(n)` | Hash: `O(1)` | `~ O(3n)` |
| padded `&str` | [`~ O(n log n)`][pad-file] | Single ref: `O(1)` | Bin. search: `O(log n)` | `~ O(n)` |
This crate is an attempt to provide a solution with:
1. **good, not perfect runtime performance**,
2. very little, [one-time](https://doc.rust-lang.org/cargo/reference/build-scripts.html#rerun-if-changed) compile-time preprocessing needed (just sorting),
3. **essentially no additional startup cost** (unlike, say, constructing a `HashSet` at
runtime),
4. **binary sizes as small as possible**,
5. **compile times as fast as possible**.
It was found that approaches using slices and hash sets (via `phf`) absolutely tanked
developer experience, with compile times north of 20 minutes (!) for 30 MB word lists
(even on [fast hardware](#note)), large binaries, and
[`clippy`](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-clippy) imploding, taking the IDE with it.
This crate was born as a solution. Its main downside is **suboptimal runtime
performance**. If that is your primary goal, opt for `phf` or similar crates. This crate
is not suitable for long-running applications, where initial e.g. `HashSet` creation is
a fraction of overall runtime costs.
## Alternative approaches
The following alternatives might be considered, but were found unsuitable for one reason
or another. See [this
thread](https://users.rust-lang.org/t/fast-string-lookup-in-a-single-str-containing-millions-of-unevenly-sized-substrings/98040)
for more discussion.
### Slices
A simple slice is an obvious choice, and can be generated in a build script.
```rust
static WORDS: &[&str] = &["abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl"];
assert_eq!(WORDS.binary_search(&"ghi").unwrap(), 2);
```
There are two large pains in this approach:
1. compile times become very slow (in the rough ballpark of 1 minute per 100.000 words,
YMMV considerably)
2. binary size becomes large.
The words are *much* shorter than the `&str` they are contained in. On 64-bit
hardware, [a `&str` is 16
bytes](https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/primitive.str.html#representation), with a
`usize` address pointer and [a `usize`
length](https://doc.rust-lang.org/book/ch15-00-smart-pointers.html). For large word
lists, this leads to incredible bloat for the resulting binary.
### Hash Set
Regular [`HashSet`s][hashset] are not available at compile time. Crates like
[`phf`][phf-repo] change that:
```rust
use phf::{phf_set, Set};
static WORDS: Set<&'static str> = phf_set! {
"abc",
"def",
"ghi",
"jkl"
};
assert!(WORDS.contains(&"ghi"))
```
Similar downsides as for the slices case apply: very long compile times, and
considerable binary bloat from smart pointers. A hash set ultimately is a slice with
computed indices, so this is expected.
### Finite State Transducer/Acceptor (Automaton)
The [`fst`][fst-repo] crate is a fantastic candidate, [brought
up](https://users.rust-lang.org/t/fast-string-lookup-in-a-single-str-containing-millions-of-unevenly-sized-substrings/98040/7?u=alexpovel)
by its author (same author as [`ripgrep`](https://github.com/BurntSushi/ripgrep) and
[`regex`](https://github.com/rust-lang/regex) fame):
```rust
use fst::Set; // Don't need FST, just FSA here
static WORDS: &[&str] = &["abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl"];
let set = Set::from_iter(WORDS.into_iter()).unwrap();
assert!(set.contains("ghi"));
```
It offers:
- [almost free (in time and space)
deserialization](https://users.rust-lang.org/t/fast-string-lookup-in-a-single-str-containing-millions-of-unevenly-sized-substrings/98040/9?u=alexpovel):
its serialization format is identical to its in-memory representation, unlike [other
solutions](#higher-order-data-structures), facilitating startup-up performance
- compression[^3] (important for
[publishing](https://github.com/rust-lang/crates.io/issues/195)), making it the only
candidate in this comparison natively leading to *smaller* size than the original word
list
- extension points (fuzzy and case-insensitive searching, bring-your-own-automaton etc.)
- [faster lookups than this crate](#benchmarks), by a factor of about 2
In some sense, for all intents and purposes, **`fst` is likely the best solution** for
the niche use case mentioned above.
For faster lookups than `fst` (closing the gap towards hash sets), [but giving up
compression](https://users.rust-lang.org/t/fast-string-lookup-in-a-single-str-containing-millions-of-unevenly-sized-substrings/98040/13?u=alexpovel)
([TANSTAAFL](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/No_such_thing_as_a_free_lunch)!), try an
automaton from
[`regex-automata`](https://docs.rs/regex-automata/latest/regex_automata/dfa/index.html#example-deserialize-a-dfa).
Note that should your use case involve an initial decompression step, the slower runtime
lookups but built-in compression of `fst` might still come out ahead in combination.
### Single, sorted and padded string
Another approach could be to use a single string (saving pointer bloat), but pad all
words to the longest occurring length, facilitating easy binary search (and increasing
bloat to some extent):
```rust
static WORDS: &str = "abc␣␣def␣␣ghi␣␣jklmn";
// Perform binary search...
```
The binary search implementation is then straightforward, as the elements are of known,
fixed lengths (in this case, 5). This approach was [found to not perform
well](#benchmarks). Find its (bare-bones) implementation in the
[benchmarks](./benches/main.rs).
### Higher-order data structures
In certain scenarios, one might reach for more sophisticated approaches, such as
[tries](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trie). This is not a case this crate is designed
for. Such a structure would have to be either:
- [built at runtime](https://docs.rs/trie-rs/0.1.1/trie_rs/index.html#usage-overview),
for example as
```rust
use trie_rs::TrieBuilder;
let mut builder = TrieBuilder::new();
builder.push("abc");
builder.push("def");
builder.push("ghi");
builder.push("jkl");
let trie = builder.build();
assert!(trie.exact_match("def"));
```
or alternatively
- [deserialized from a pre-built structure](https://serde.rs/).
While tools like [bincode](https://docs.rs/bincode/latest/bincode/) are fantastic, the
latter approach is still numbingly slow at application startup, compared to the (much
more ham-fisted) approach the crate at hand takes.
### Linear search
This is only included here and in the benchmarks as a sanity check and baseline. Linear
search like
```rust
static WORDS: &[&str] = &["abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl"];
assert!(WORDS.contains(&"ghi"));
```
is $O(n)$, and [slower by a couple orders of magnitude for large
lists](#linear-search-performance). If your current implementation relies on linear
search, this create might offer an almost drop-in replacement with a significant
performance improvement.
## Benchmarks
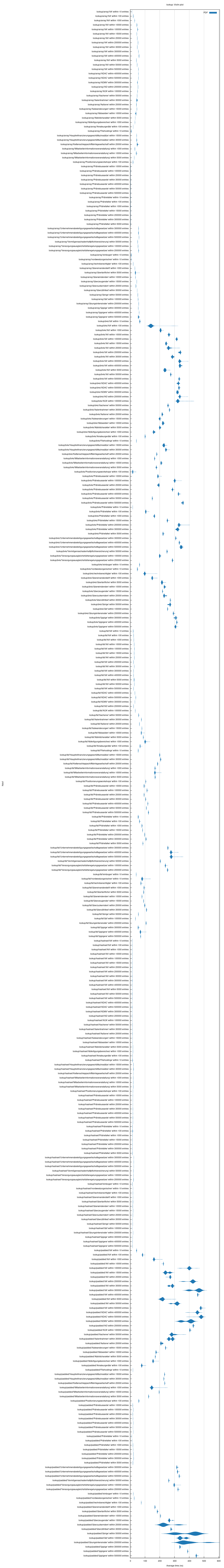
The below benchmarks show a performance comparison. The benchmarks run a search for
representative words (start, middle, end, shortest and longest words found in the
pre-sorted input list), on various different input word list lengths.
Sets are unsurprisingly fastest, but naive binary search (the built-in one) seems
incredibly optimized and just as fast. `b4s` is slower by a factor of 5 to 10. The
"padded string" variant is slowest. One can observe how, as the input lists get longer
("within *X* entries"), `b4s` becomes slower.
In the context of this crate's purpose, the slowness might not be an issue: if
application startup is measured in milliseconds, and lookups in nanoseconds (!), one can
perform in the rough ballpark of, say, 100,000 lookups before the tradeoff of this crate
(fast startup) becomes a problem (this crate would be terrible for a web server).
### Linear search performance
The [benchmark plot](./assets/benchmarks-with-linear-search.png) including [linear
search](#linear-search) is largely illegible, as the linear horizontal axis scaling
dwarfs all other search methods. It is therefore linked separately, but paints a clear
picture.
### Note
The benchmarks were run on a machine with the following specs:
- AMD Ryzen 7 5800X3D; DDR4 @ 3600MHz; NVMe SSD
- Debian 12 inside WSL 2 on Windows 10 21H2
- libraries with versions as of commit 9e2f11c39342f1ea3460dda810a92b225ee9d4b8 (refer
to its `Cargo.toml`)
The benchmarks are not terribly scientific (low sample sizes etc.), but serve as a rough
guideline and sanity check. Run them yourself from the repository root with `cargo
install just && just bench`.
## Note on name
The 3-letter name is neat. Should you have a more meaningful, larger project that could
make better use of it, let me know. I might move this crate to a different name.
[slice-sort]: https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/primitive.slice.html#method.sort
[fst-repo]: https://github.com/BurntSushi/fst
[fst-build]: https://docs.rs/fst/0.4.7/fst/struct.SetBuilder.html
[slice-binsearch]: https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/primitive.slice.html#method.binary_search
[phf-repo]: https://github.com/rust-phf/rust-phf
[hashset]: https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/collections/struct.HashSet.html
[pad-file]: ./benches/main.rs
[slice]: https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/primitive.slice.html
[b4s-lib]: ./src/lib.rs
[fst-lookup]: https://blog.burntsushi.net/transducers/#ordered-sets
[fst-size]: https://blog.burntsushi.net/transducers/#the-dictionary