pub struct HsvGradient { /* private fields */ }Expand description
A color interpolator that interpolates between colors in the HSV Color Space.
Implementations§
Source§impl HsvGradient
standard hsv color maps
impl HsvGradient
standard hsv color maps
Sourcepub fn standard(min: f32, max: f32) -> HsvGradient
pub fn standard(min: f32, max: f32) -> HsvGradient
Standard color map in HSV color space.
- step:

- linear:

Source§impl HsvGradient
matlab color maps
impl HsvGradient
matlab color maps
Sourcepub fn parula(min: f32, max: f32) -> HsvGradient
pub fn parula(min: f32, max: f32) -> HsvGradient
Parula color map in HSV color space.
- step:

- linear:

Sourcepub fn jet(min: f32, max: f32) -> HsvGradient
pub fn jet(min: f32, max: f32) -> HsvGradient
Jet color map in HSV color space.
- step:

- linear:

Sourcepub fn turbo(min: f32, max: f32) -> HsvGradient
pub fn turbo(min: f32, max: f32) -> HsvGradient
Turbo color map in HSV color space.
- step:

- linear:

Sourcepub fn hot(min: f32, max: f32) -> HsvGradient
pub fn hot(min: f32, max: f32) -> HsvGradient
Hot color map in HSV color space.
- step:
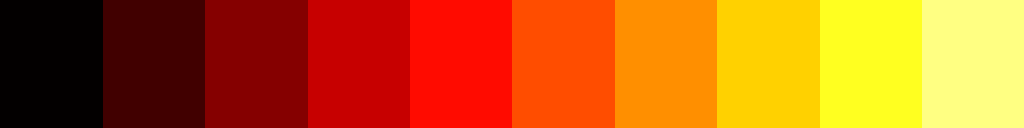
- linear:

Sourcepub fn cool(min: f32, max: f32) -> HsvGradient
pub fn cool(min: f32, max: f32) -> HsvGradient
Cool color map in HSV color space.
- step:

- linear:

Sourcepub fn spring(min: f32, max: f32) -> HsvGradient
pub fn spring(min: f32, max: f32) -> HsvGradient
Spring color map in HSV color space.
- step:

- linear:

Sourcepub fn summer(min: f32, max: f32) -> HsvGradient
pub fn summer(min: f32, max: f32) -> HsvGradient
Summer color map in HSV color space.
- step:

- linear:

Sourcepub fn autumn(min: f32, max: f32) -> HsvGradient
pub fn autumn(min: f32, max: f32) -> HsvGradient
Autumn color map in HSV color space.
- step:
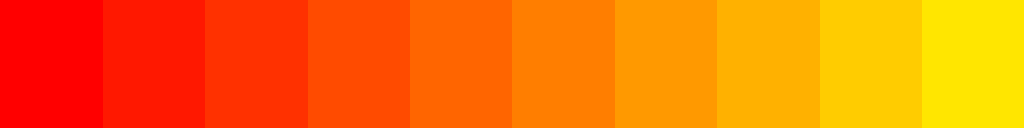
- linear:

Sourcepub fn winter(min: f32, max: f32) -> HsvGradient
pub fn winter(min: f32, max: f32) -> HsvGradient
Winter color map in HSV color space.
- step:

- linear:

Source§impl HsvGradient
impl HsvGradient
Sourcepub fn new(min: f32, max: f32) -> Self
pub fn new(min: f32, max: f32) -> Self
Creates a new gradient sampler with the given min and max values.
§Examples
let mut gradient = HsvGradient::default();
assert_eq!(gradient.get_linear(0.5), HSVA32::new(180.0, 100.0, 100.0, 100.0));Sourcepub fn rescale(&mut self, min: f32, max: f32)
pub fn rescale(&mut self, min: f32, max: f32)
Rescales the gradient to the given min and max values.
§Examples
let mut gradient = HsvGradient::default();
gradient.rescale(0.0, 360.0);
assert_eq!(gradient.get_linear(180.0), HSVA32::new(180.0, 100.0, 100.0, 100.0));Sourcepub fn insert_color<HSV>(&mut self, key: f32, color: HSV)
pub fn insert_color<HSV>(&mut self, key: f32, color: HSV)
Sourcepub fn remove_color(&mut self, key: f32)
pub fn remove_color(&mut self, key: f32)
Sourcepub fn insert_hue(&mut self, key: f32, value: f32)
pub fn insert_hue(&mut self, key: f32, value: f32)
Sourcepub fn remove_hue(&mut self, key: f32)
pub fn remove_hue(&mut self, key: f32)
Sourcepub fn insert_saturation(&mut self, key: f32, value: f32)
pub fn insert_saturation(&mut self, key: f32, value: f32)
Sourcepub fn remove_saturation(&mut self, key: f32)
pub fn remove_saturation(&mut self, key: f32)
Sourcepub fn insert_brightness(&mut self, key: f32, value: f32)
pub fn insert_brightness(&mut self, key: f32, value: f32)
Sourcepub fn remove_brightness(&mut self, key: f32)
pub fn remove_brightness(&mut self, key: f32)
Sourcepub fn insert_alpha(&mut self, key: f32, value: f32)
pub fn insert_alpha(&mut self, key: f32, value: f32)
Insert a new alpha control point at the given key.
§Examples
let mut gradient = HsvGradient::default();
assert_eq!(gradient.get_linear(0.5), HSVA32::new(180.0, 100.0, 100.0, 100.0));
gradient.insert_alpha(0.1, 50.0);
assert_eq!(gradient.get_linear(0.5), HSVA32::new(180.0, 100.0, 100.0, 72.22203));Sourcepub fn remove_alpha(&mut self, key: f32)
pub fn remove_alpha(&mut self, key: f32)
Remove the alpha control point at the given key.
§Examples
let mut gradient = HsvGradient::default();
gradient.insert_alpha(0.1, 50.0);
assert_eq!(gradient.get_linear(0.5), HSVA32::new(180.0, 100.0, 100.0, 72.22203));
gradient.remove_alpha(0.1);
assert_eq!(gradient.get_linear(0.5), HSVA32::new(180.0, 100.0, 100.0, 100.0));Sourcepub fn clear_alpha(&mut self)
pub fn clear_alpha(&mut self)
Clears all alpha control points from the gradient.
§Examples
let mut gradient = HsvGradient::default();
gradient.insert_alpha(0.0, 0.0);
gradient.insert_alpha(1.0, 1.0);
gradient.clear_alpha();Trait Implementations§
Source§impl Clone for HsvGradient
impl Clone for HsvGradient
Source§fn clone(&self) -> HsvGradient
fn clone(&self) -> HsvGradient
Returns a duplicate of the value. Read more
1.0.0 · Source§fn clone_from(&mut self, source: &Self)
fn clone_from(&mut self, source: &Self)
Performs copy-assignment from
source. Read moreSource§impl Debug for HsvGradient
impl Debug for HsvGradient
Source§impl Default for HsvGradient
impl Default for HsvGradient
Source§impl<'de> Deserialize<'de> for HsvGradient
impl<'de> Deserialize<'de> for HsvGradient
Source§fn deserialize<__D>(__deserializer: __D) -> Result<Self, __D::Error>where
__D: Deserializer<'de>,
fn deserialize<__D>(__deserializer: __D) -> Result<Self, __D::Error>where
__D: Deserializer<'de>,
Deserialize this value from the given Serde deserializer. Read more
Auto Trait Implementations§
impl Freeze for HsvGradient
impl RefUnwindSafe for HsvGradient
impl Send for HsvGradient
impl Sync for HsvGradient
impl Unpin for HsvGradient
impl UnwindSafe for HsvGradient
Blanket Implementations§
Source§impl<T> BorrowMut<T> for Twhere
T: ?Sized,
impl<T> BorrowMut<T> for Twhere
T: ?Sized,
Source§fn borrow_mut(&mut self) -> &mut T
fn borrow_mut(&mut self) -> &mut T
Mutably borrows from an owned value. Read more
Source§impl<T> CloneToUninit for Twhere
T: Clone,
impl<T> CloneToUninit for Twhere
T: Clone,
Source§impl<T> IntoEither for T
impl<T> IntoEither for T
Source§fn into_either(self, into_left: bool) -> Either<Self, Self>
fn into_either(self, into_left: bool) -> Either<Self, Self>
Converts
self into a Left variant of Either<Self, Self>
if into_left is true.
Converts self into a Right variant of Either<Self, Self>
otherwise. Read moreSource§fn into_either_with<F>(self, into_left: F) -> Either<Self, Self>
fn into_either_with<F>(self, into_left: F) -> Either<Self, Self>
Converts
self into a Left variant of Either<Self, Self>
if into_left(&self) returns true.
Converts self into a Right variant of Either<Self, Self>
otherwise. Read moreSource§impl<T> Pointable for T
impl<T> Pointable for T
Source§impl<R, P> ReadPrimitive<R> for P
impl<R, P> ReadPrimitive<R> for P
Source§fn read_from_little_endian(read: &mut R) -> Result<Self, Error>
fn read_from_little_endian(read: &mut R) -> Result<Self, Error>
Read this value from the supplied reader. Same as
ReadEndian::read_from_little_endian().