#[repr(u8)]pub enum Digit {
Neg = 0,
Zero = 1,
Pos = 2,
}Expand description
§Module: Balanced Ternary Digit
This module defines the Digit type for the balanced ternary numeral system,
along with its associated operations and functionality.
Represents a digit in the balanced ternary numeral system.
A digit can have one of three values:
Neg(-1): Represents the value -1 in the balanced ternary system.Zero(0): Represents the value 0 in the balanced ternary system.Pos(+1): Represents the value +1 in the balanced ternary system.
Provides utility functions for converting to/from characters, integers, and negation.
§Key Features
DigitType: Represents a digit in the balanced ternary numeral system.- Possible values:
Neg(-1),Zero(0),Pos(+1). - Provides utility functions for converting between characters, integers, and other formats.
- Possible values:
- Arithmetic Operators: Implements arithmetic operations for digits, including:
- Negation (
Neg) and Bitwise Not (Not). - Addition (
Add) and Subtraction (Sub). - Multiplication (
Mul) and Division (Div), with safe handling of divisors (division by zero panics).
- Negation (
- Logical Operators: Supports bitwise logical operations (AND, OR, XOR) based on ternary logic rules.
- Custom Methods: Additional utility methods implementing balanced ternary logic principles.
§Supported Use Cases
- Arithmetic in balanced ternary numeral systems.
- Logic operations in custom numeral systems.
- Conversion between balanced ternary representation and more common formats like integers and characters.
§Digit type arithmetical and logical operations
NegandNotforDigit: Negates the digit value, adhering to balanced ternary rules.Add<Digit>forDigit: Adds twoDigitvalues and returns aDigit.Sub<Digit>forDigit: Subtracts oneDigitfrom another and returns aDigit.Mul<Digit>forDigit: Multiplies twoDigitvalues and returns aDigit.Div<Digit>forDigit: Divides oneDigitby another and returns aDigit. Division by zero panics.
§Logical Operations for Digit
The Digit type supports bitwise logical operations, which are implemented according to logical rules applicable to balanced ternary digits.
§Digits operations
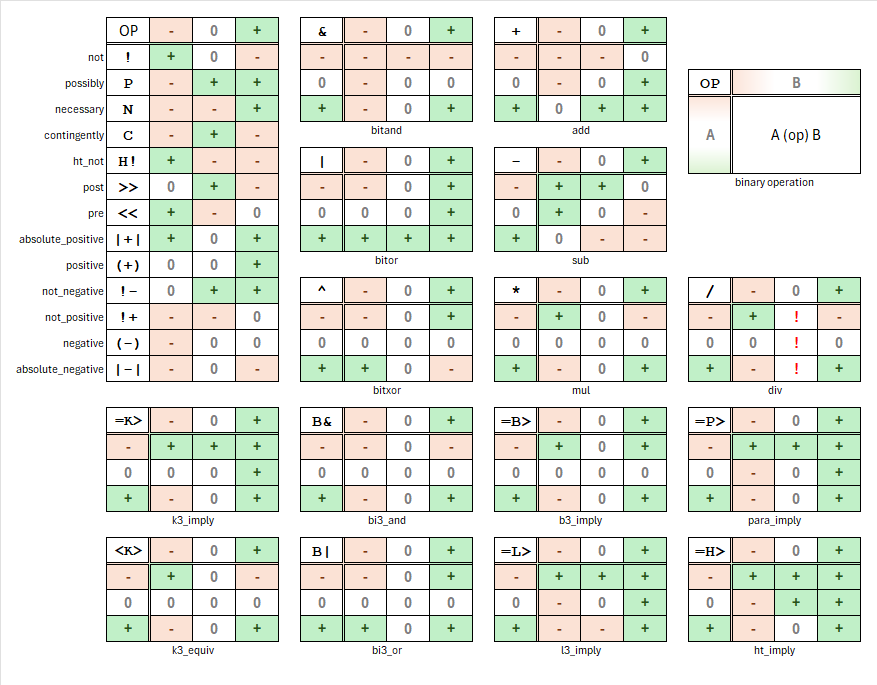
/, *, &, | and ^ should not be used with Ternary::each_{with,zip}().
Instead, use these operators from Ternary directly.
Do so to add and sub ternaries, too.
Variants§
Implementations§
Source§impl Digit
impl Digit
Sourcepub const fn to_char_theta(&self) -> char
pub const fn to_char_theta(&self) -> char
Converts the Digit into a character representation.
- Returns:
ΘforDigit::Neg0forDigit::Zero1forDigit::Pos
Sourcepub const fn to_char_z(&self) -> char
pub const fn to_char_z(&self) -> char
Converts the Digit into a character representation.
- Returns:
ZforDigit::Neg0forDigit::Zero1forDigit::Pos
Sourcepub const fn to_char_t(&self) -> char
pub const fn to_char_t(&self) -> char
Converts the Digit into a character representation.
- Returns:
TforDigit::Neg0forDigit::Zero1forDigit::Pos
Sourcepub const fn from_char_theta(c: char) -> Digit
pub const fn from_char_theta(c: char) -> Digit
Creates a Digit from a character representation.
- Accepts:
ΘforDigit::Neg0forDigit::Zero1forDigit::Pos
- Panics if the input character is invalid.
Sourcepub const fn from_char_z(c: char) -> Digit
pub const fn from_char_z(c: char) -> Digit
Creates a Digit from a character representation.
- Accepts:
ZforDigit::Neg0forDigit::Zero1forDigit::Pos
- Panics if the input character is invalid.
Sourcepub const fn from_char_t(c: char) -> Digit
pub const fn from_char_t(c: char) -> Digit
Creates a Digit from a character representation.
- Accepts:
TforDigit::Neg0forDigit::Zero1forDigit::Pos
- Panics if the input character is invalid.
Sourcepub const fn to_char(&self) -> char
pub const fn to_char(&self) -> char
Converts the Digit into its character representation.
- Returns:
-forDigit::Neg0forDigit::Zero+forDigit::Pos
Sourcepub const fn from_char(c: char) -> Digit
pub const fn from_char(c: char) -> Digit
Creates a Digit from its character representation.
- Accepts:
-forDigit::Neg0forDigit::Zero+forDigit::Pos
- Panics if the input character is invalid.
Sourcepub const fn to_i8(&self) -> i8
pub const fn to_i8(&self) -> i8
Converts the Digit into its integer representation.
- Returns:
- -1 for
Digit::Neg - 0 for
Digit::Zero - 1 for
Digit::Pos
- -1 for
Sourcepub const fn from_i8(i: i8) -> Digit
pub const fn from_i8(i: i8) -> Digit
Creates a Digit from its integer representation.
- Accepts:
- -1 for
Digit::Neg - 0 for
Digit::Zero - 1 for
Digit::Pos
- -1 for
- Panics if the input integer is invalid.
Sourcepub const fn possibly(self) -> Self
pub const fn possibly(self) -> Self
Returns the corresponding possible value of the current Digit.
- Returns:
Digit::NegforDigit::NegDigit::PosforDigit::ZeroDigit::PosforDigit::Pos
Sourcepub const fn necessary(self) -> Self
pub const fn necessary(self) -> Self
Determines the condition of necessity for the current Digit.
- Returns:
Digit::NegforDigit::NegDigit::NegforDigit::ZeroDigit::PosforDigit::Pos
This method is used to calculate necessity as part of balanced ternary logic systems.
Sourcepub const fn contingently(self) -> Self
pub const fn contingently(self) -> Self
Determines the condition of contingency for the current Digit.
- Returns:
Digit::NegforDigit::NegDigit::PosforDigit::ZeroDigit::NegforDigit::Pos
This method represents contingency in balanced ternary logic,
which defines the specific alternation of Digit values.
Sourcepub const fn absolute_positive(self) -> Self
pub const fn absolute_positive(self) -> Self
Returns the absolute positive value of the current Digit.
- Returns:
Digit::PosforDigit::NegDigit::ZeroforDigit::ZeroDigit::PosforDigit::Pos
Sourcepub const fn positive(self) -> Self
pub const fn positive(self) -> Self
Determines the strictly positive condition for the current Digit.
- Returns:
Digit::ZeroforDigit::NegDigit::ZeroforDigit::ZeroDigit::PosforDigit::Pos
This method is used to calculate strictly positive states in association with ternary logic.
Sourcepub const fn not_negative(self) -> Self
pub const fn not_negative(self) -> Self
Determines the condition of non-negativity for the current Digit.
- Returns:
Digit::ZeroforDigit::NegDigit::PosforDigit::ZeroDigit::PosforDigit::Pos
This method is used to filter out negative conditions in computations with balanced ternary representations.
Sourcepub const fn not_positive(self) -> Self
pub const fn not_positive(self) -> Self
Determines the condition of non-positivity for the current Digit.
- Returns:
Digit::NegforDigit::NegDigit::NegforDigit::ZeroDigit::ZeroforDigit::Pos
This method complements the positive condition and captures
states that are not strictly positive.
Sourcepub const fn negative(self) -> Self
pub const fn negative(self) -> Self
Determines the strictly negative condition for the current Digit.
- Returns:
Digit::NegforDigit::NegDigit::ZeroforDigit::ZeroDigit::ZeroforDigit::Pos
This method calculates strictly negative states in association with ternary logic.
Sourcepub const fn absolute_negative(self) -> Self
pub const fn absolute_negative(self) -> Self
Returns the absolute negative value of the current Digit.
- Returns:
Digit::NegforDigit::NegDigit::ZeroforDigit::ZeroDigit::NegforDigit::Pos
Sourcepub const fn k3_imply(self, other: Self) -> Self
pub const fn k3_imply(self, other: Self) -> Self
Performs Kleene implication with the current Digit as self and another Digit.
-
self: The antecedent of the implication. -
other: The consequent of the implication. -
Returns:
Digit::PoswhenselfisDigit::Neg.- The positive condition of
otherwhenselfisDigit::Zero. otherwhenselfisDigit::Pos.
Implements Kleene ternary implication logic, which includes determining the logical result based on antecedent and consequent.
Sourcepub const fn k3_equiv(self, other: Self) -> Self
pub const fn k3_equiv(self, other: Self) -> Self
Apply a ternary equivalence operation for the current Digit and another Digit.
-
self: The first operand of the equivalence operation. -
other: The second operand of the equivalence operation. -
Returns:
- The negation of
otherwhenselfisDigit::Neg. Digit::ZerowhenselfisDigit::Zero.otherwhenselfisDigit::Pos.
- The negation of
This method implements a ternary logic equivalence, which captures the relationship between
two balanced ternary Digits based on their logical equivalence.
Sourcepub const fn bi3_and(self, other: Self) -> Self
pub const fn bi3_and(self, other: Self) -> Self
Performs a ternary AND operation for the current Digit and another Digit.
-
self: The first operand of the AND operation. -
other: The second operand of the AND operation. -
Returns:
Digit::NegifselfisDigit::Negandotheris notDigit::Zero.Digit::Zeroif eitherselforotherisDigit::Zero.otherifselfisDigit::Pos.
This method implements Bochvar’s internal three-valued logic in balanced ternary AND operation,
which evaluates the logical conjunction of two Digits in the ternary logic system.
Sourcepub const fn bi3_or(self, other: Self) -> Self
pub const fn bi3_or(self, other: Self) -> Self
Performs a ternary OR operation for the current Digit and another Digit.
-
self: The first operand of the OR operation. -
other: The second operand of the OR operation. -
Returns:
otherifselfisDigit::Neg.Digit::ZeroifselfisDigit::Zero.Digit::PosifselfisDigit::Posandotheris notDigit::Zero.
This method implements Bochvar’s three-valued internal ternary logic for the OR operation,
determining the logical disjunction of two balanced ternary Digits.
Sourcepub const fn bi3_imply(self, other: Self) -> Self
pub const fn bi3_imply(self, other: Self) -> Self
Performs Bochvar’s internal three-valued implication with the current Digit as self
and another Digit as the consequent.
-
self: The antecedent of the implication. -
other: The consequent of the implication. -
Returns:
Digit::ZeroifselfisDigit::NegandotherisDigit::Zero.Digit::PosifselfisDigit::Negandotheris notDigit::Zero.Digit::ZeroifselfisDigit::Zero.otherifselfisDigit::Pos.
This method implements Bochvar’s internal implication logic, which evaluates
the logical consequence, between two balanced ternary Digits in a manner
consistent with three-valued logic principles.
Sourcepub const fn l3_imply(self, other: Self) -> Self
pub const fn l3_imply(self, other: Self) -> Self
Performs Łukasiewicz implication with the current Digit as self and another Digit.
-
self: The antecedent of the implication. -
other: The consequent of the implication. -
Returns:
Digit::PoswhenselfisDigit::Neg.- The non-negative condition of
otherwhenselfisDigit::Zero. otherwhenselfisDigit::Pos.
Implements Łukasiewicz ternary implication logic, which evaluates an alternative approach for implication compared to Kleene logic.
Sourcepub const fn rm3_imply(self, other: Self) -> Self
pub const fn rm3_imply(self, other: Self) -> Self
Performs RM3 implication with the current Digit as self and another Digit.
-
self: The antecedent of the implication. -
other: The consequent of the implication. -
Returns:
Digit::PoswhenselfisDigit::Neg.otherwhenselfisDigit::Zero.- The necessary condition of
otherwhenselfisDigit::Pos.
Implements RM3 ternary implication logic, which defines a unique perspective for implication operations in balanced ternary systems.
Sourcepub const fn para_imply(self, other: Self) -> Self
pub const fn para_imply(self, other: Self) -> Self
Performs the paraconsistent-logic implication with the current Digit as self and another Digit.
-
self: The antecedent of the implication. -
other: The consequent of the implication. -
Returns:
Digit::PoswhenselfisDigit::Neg.otherotherwise.
Sourcepub const fn ht_imply(self, other: Self) -> Self
pub const fn ht_imply(self, other: Self) -> Self
Performs HT implication with the current Digit as self and another Digit.
-
self: The antecedent of the implication. -
other: The consequent of the implication. -
Returns:
Digit::PoswhenselfisDigit::Neg.- The possibility condition of
otherwhenselfisDigit::Zero. otherwhenselfisDigit::Pos.
This method computes HT ternary implication based on heuristic logic.
Sourcepub const fn ht_not(self) -> Self
pub const fn ht_not(self) -> Self
Performs HT logical negation of the current Digit.
- Returns:
Digit::PoswhenselfisDigit::Neg.Digit::NegwhenselfisDigit::ZeroorDigit::Pos.
This method evaluates the HT negation result using heuristic ternary logic.
Sourcepub const fn ht_bool(self) -> bool
pub const fn ht_bool(self) -> bool
Converts the Digit to a bool in HT logic.
-
Returns:
truewhenselfisDigit::Pos.falsewhenselfisDigit::Neg.
-
Panics:
- Panics if
selfisDigit::Zero, asDigit::Zerocannot be directly converted to a boolean value.To ensure
PosorNegvalue, use one of :
- Panics if
Sourcepub const fn post(self) -> Self
pub const fn post(self) -> Self
Performs Post’s negation of the current Digit.
- Returns:
Digit::ZerowhenselfisDigit::Neg.Digit::PoswhenselfisDigit::Zero.Digit::NegwhenselfisDigit::Pos.
This method evaluates the negation based on Post’s logic in ternary systems, which differs from standard negation logic.
Sourcepub const fn pre(self) -> Self
pub const fn pre(self) -> Self
Performs the inverse operation from the Post’s negation of the current Digit.
- Returns:
Digit::PoswhenselfisDigit::Neg.Digit::NegwhenselfisDigit::Zero.Digit::ZerowhenselfisDigit::Pos.
Sourcepub const fn to_unbalanced(self) -> u8
pub const fn to_unbalanced(self) -> u8
This method maps this Digit value to its corresponding unbalanced ternary
integer representation.
- Returns:
0forDigit::Neg.1forDigit::Zero.2forDigit::Pos.
Sourcepub const fn from_unbalanced(u: u8) -> Digit
pub const fn from_unbalanced(u: u8) -> Digit
Creates a Digit from an unbalanced ternary integer representation.
§Arguments:
u: An unsigned 8-bit integer representing an unbalanced ternary value.
§Returns:
Digit::Negfor0.Digit::Zerofor1.Digit::Posfor2.
§Panics:
- Panics if the provided value is not
0,1, or2, as these are the only valid representations of unbalanced ternary values.
Sourcepub fn inc(self) -> Ternary
pub fn inc(self) -> Ternary
Increments the Digit value and returns a Ternary result.
-
The rules for incrementing are based on ternary arithmetic:
- For
Digit::Neg:- Incrementing results in
Digit::Zero(Ternary::parse("0")).
- Incrementing results in
- For
Digit::Zero:- Incrementing results in
Digit::Pos(Ternary::parse("+")).
- Incrementing results in
- For
Digit::Pos:- Incrementing results in “overflow” (
Ternary::parse("+-")).
- Incrementing results in “overflow” (
- For
-
Returns:
- A
Ternaryinstance representing the result of the increment operation.
- A
Sourcepub fn dec(self) -> Ternary
pub fn dec(self) -> Ternary
Decrements the Digit value and returns a Ternary result.
-
The rules for decrementing are based on ternary arithmetic:
- For
Digit::Neg:- Decrementing results in “underflow” (
Ternary::parse("-+")).
- Decrementing results in “underflow” (
- For
Digit::Zero:- Decrementing results in
Digit::Neg(Ternary::parse("-")).
- Decrementing results in
- For
Digit::Pos:- Decrementing results in
Digit::Zero(Ternary::parse("0")).
- Decrementing results in
- For
-
Returns:
- A
Ternaryinstance representing the result of the decrement operation.
- A
Trait Implementations§
Source§impl Add for Digit
impl Add for Digit
Source§impl BitAnd for Digit
impl BitAnd for Digit
Source§fn bitand(self, other: Self) -> Self::Output
fn bitand(self, other: Self) -> Self::Output
Performs a bitwise AND operation between two Digit values and returns the result.
- The rules for the bitwise AND (
&) operation are:- If
selfisDigit::Neg, the result is alwaysDigit::Neg. - If
selfisDigit::Zero, the result depends on the value ofother:Digit::Negresults inDigit::Neg.- Otherwise, the result is
Digit::Zero.
- If
selfisDigit::Pos, the result is simplyother.
- If
§Returns:
- A
Digitvalue that is the result of the bitwise AND operation.
§Examples:
use balanced_ternary::Digit;
use Digit::{Neg, Pos, Zero};
assert_eq!(Neg & Pos, Neg);
assert_eq!(Zero & Neg, Neg);
assert_eq!(Zero & Pos, Zero);
assert_eq!(Pos & Zero, Zero);Source§impl BitOr for Digit
impl BitOr for Digit
Source§fn bitor(self, other: Self) -> Self::Output
fn bitor(self, other: Self) -> Self::Output
Performs a bitwise OR operation between two Digit values and returns the result.
- The rules for the bitwise OR (
|) operation are as follows:- If
selfisDigit::Neg, the result is always the value ofother. - If
selfisDigit::Zero, the result depends on the value ofother:Digit::Posresults inDigit::Pos.- Otherwise, the result is
Digit::Zero.
- If
selfisDigit::Pos, the result is alwaysDigit::Pos.
- If
§Returns:
- A
Digitvalue that is the result of the bitwise OR operation.
§Examples:
use balanced_ternary::Digit;
use Digit::{Neg, Pos, Zero};
assert_eq!(Neg | Pos, Pos);
assert_eq!(Zero | Neg, Zero);
assert_eq!(Zero | Pos, Pos);
assert_eq!(Pos | Zero, Pos);Source§impl BitXor for Digit
impl BitXor for Digit
Source§fn bitxor(self, rhs: Self) -> Self::Output
fn bitxor(self, rhs: Self) -> Self::Output
Performs a bitwise XOR (exclusive OR) operation between two Digit values.
- The rules for the bitwise XOR (
^) operation are as follows:- If
selfisDigit::Neg, the result is always the value ofrhs. - If
selfisDigit::Zero, the result is alwaysDigit::Zero. - If
selfisDigit::Pos, the result is the negation ofrhs:Digit::NegbecomesDigit::Pos.Digit::ZerobecomesDigit::Zero.Digit::PosbecomesDigit::Neg.
- If
§Returns:
- A
Digitvalue that is the result of the bitwise XOR operation.
§Examples:
use balanced_ternary::Digit;
use Digit::{Neg, Pos, Zero};
assert_eq!(Neg ^ Pos, Pos);
assert_eq!(Zero ^ Neg, Zero);
assert_eq!(Pos ^ Pos, Neg);Source§impl Div for Digit
impl Div for Digit
Source§fn div(self, other: Digit) -> Self::Output
fn div(self, other: Digit) -> Self::Output
Divides one Digit value by another and returns the result as a Digit.
§Rules for division:
- For
Digit::Neg:- Dividing
Digit::NegbyDigit::Negresults inDigit::Pos. - Dividing
Digit::NegbyDigit::Zerowill panic with “Cannot divide by zero.” - Dividing
Digit::NegbyDigit::Posresults inDigit::Neg.
- Dividing
- For
Digit::Zero:- Dividing
Digit::ZerobyDigit::Negresults inDigit::Zero. - Dividing
Digit::ZerobyDigit::Zerowill panic with “Cannot divide by zero.” - Dividing
Digit::ZerobyDigit::Posresults inDigit::Zero.
- Dividing
- For
Digit::Pos:- Dividing
Digit::PosbyDigit::Negresults inDigit::Neg. - Dividing
Digit::PosbyDigit::Zerowill panic with “Cannot divide by zero.” - Dividing
Digit::PosbyDigit::Posresults inDigit::Pos.
- Dividing
§Returns:
- A
Digitvalue representing the result of the division.
§Panics:
- Panics with “Cannot divide by zero.” if the
otheroperand isDigit::Zero.
Source§impl Mul for Digit
impl Mul for Digit
Source§fn mul(self, other: Digit) -> Self::Output
fn mul(self, other: Digit) -> Self::Output
Multiplies two Digit values together and returns the product as a Digit.
-
The rules for multiplication in this implementation are straightforward:
Digit::Negmultiplied by:Digit::Negresults inDigit::Pos.Digit::Zeroresults inDigit::Zero.Digit::Posresults inDigit::Neg.
Digit::Zeromultiplied by anyDigitalways results inDigit::Zero.Digit::Posmultiplied by:Digit::Negresults inDigit::Neg.Digit::Zeroresults inDigit::Zero.Digit::Posresults inDigit::Pos.
-
Returns:
- A
Digitinstance representing the result of the multiplication.
- A