Struct qt_gui::QHoverEvent
source · #[repr(C)]pub struct QHoverEvent { /* private fields */ }Expand description
The QHoverEvent class contains parameters that describe a mouse event.
C++ class: QHoverEvent.
The QHoverEvent class contains parameters that describe a mouse event.
Mouse events occur when a mouse cursor is moved into, out of, or within a widget, and if the widget has the Qt::WA_Hover attribute.
The function pos() gives the current cursor position, while oldPos() gives the old mouse position.
There are a few similarities between the events QEvent::HoverEnter and QEvent::HoverLeave, and the events QEvent::Enter and QEvent::Leave. However, they are slightly different because we do an update() in the event handler of HoverEnter and HoverLeave.
QEvent::HoverMove is also slightly different from QEvent::MouseMove. Let us consider a top-level window A containing a child B which in turn contains a child C (all with mouse tracking enabled):
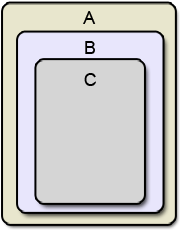
Now, if you move the cursor from the top to the bottom in the middle of A, you will get the following QEvent::MouseMove events:
- A::MouseMove
- B::MouseMove
- C::MouseMove
You will get the same events for QEvent::HoverMove, except that the event always propagates to the top-level regardless whether the event is accepted or not. It will only stop propagating with the Qt::WA_NoMousePropagation attribute.
In this case the events will occur in the following way:
- A::HoverMove
- A::HoverMove, B::HoverMove
- A::HoverMove, B::HoverMove, C::HoverMove
Implementations§
source§impl QHoverEvent
impl QHoverEvent
sourcepub unsafe fn copy_from(
&self,
other: impl CastInto<Ref<QHoverEvent>>
) -> Ref<QHoverEvent>
pub unsafe fn copy_from( &self, other: impl CastInto<Ref<QHoverEvent>> ) -> Ref<QHoverEvent>
The QHoverEvent class contains parameters that describe a mouse event.
Calls C++ function: QHoverEvent& QHoverEvent::operator=(const QHoverEvent& other).
The QHoverEvent class contains parameters that describe a mouse event.
Mouse events occur when a mouse cursor is moved into, out of, or within a widget, and if the widget has the Qt::WA_Hover attribute.
The function pos() gives the current cursor position, while oldPos() gives the old mouse position.
There are a few similarities between the events QEvent::HoverEnter and QEvent::HoverLeave, and the events QEvent::Enter and QEvent::Leave. However, they are slightly different because we do an update() in the event handler of HoverEnter and HoverLeave.
QEvent::HoverMove is also slightly different from QEvent::MouseMove. Let us consider a top-level window A containing a child B which in turn contains a child C (all with mouse tracking enabled):

Now, if you move the cursor from the top to the bottom in the middle of A, you will get the following QEvent::MouseMove events:
- A::MouseMove
- B::MouseMove
- C::MouseMove
You will get the same events for QEvent::HoverMove, except that the event always propagates to the top-level regardless whether the event is accepted or not. It will only stop propagating with the Qt::WA_NoMousePropagation attribute.
In this case the events will occur in the following way:
- A::HoverMove
- A::HoverMove, B::HoverMove
- A::HoverMove, B::HoverMove, C::HoverMove
sourcepub unsafe fn new_4a(
type_: Type,
pos: impl CastInto<Ref<QPointF>>,
old_pos: impl CastInto<Ref<QPointF>>,
modifiers: QFlags<KeyboardModifier>
) -> CppBox<QHoverEvent>
pub unsafe fn new_4a( type_: Type, pos: impl CastInto<Ref<QPointF>>, old_pos: impl CastInto<Ref<QPointF>>, modifiers: QFlags<KeyboardModifier> ) -> CppBox<QHoverEvent>
Constructs a hover event object.
Calls C++ function: [constructor] void QHoverEvent::QHoverEvent(QEvent::Type type, const QPointF& pos, const QPointF& oldPos, QFlags<Qt::KeyboardModifier> modifiers = …).
Constructs a hover event object.
The type parameter must be QEvent::HoverEnter, QEvent::HoverLeave, or QEvent::HoverMove.
The pos is the current mouse cursor's position relative to the receiving widget, while oldPos is its previous such position. modifiers hold the state of all keyboard modifiers at the time of the event.
sourcepub unsafe fn new_3a(
type_: Type,
pos: impl CastInto<Ref<QPointF>>,
old_pos: impl CastInto<Ref<QPointF>>
) -> CppBox<QHoverEvent>
pub unsafe fn new_3a( type_: Type, pos: impl CastInto<Ref<QPointF>>, old_pos: impl CastInto<Ref<QPointF>> ) -> CppBox<QHoverEvent>
Constructs a hover event object.
Calls C++ function: [constructor] void QHoverEvent::QHoverEvent(QEvent::Type type, const QPointF& pos, const QPointF& oldPos).
Constructs a hover event object.
The type parameter must be QEvent::HoverEnter, QEvent::HoverLeave, or QEvent::HoverMove.
The pos is the current mouse cursor's position relative to the receiving widget, while oldPos is its previous such position. modifiers hold the state of all keyboard modifiers at the time of the event.
sourcepub unsafe fn new_copy(
other: impl CastInto<Ref<QHoverEvent>>
) -> CppBox<QHoverEvent>
pub unsafe fn new_copy( other: impl CastInto<Ref<QHoverEvent>> ) -> CppBox<QHoverEvent>
The QHoverEvent class contains parameters that describe a mouse event.
Calls C++ function: [constructor] void QHoverEvent::QHoverEvent(const QHoverEvent& other).
The QHoverEvent class contains parameters that describe a mouse event.
Mouse events occur when a mouse cursor is moved into, out of, or within a widget, and if the widget has the Qt::WA_Hover attribute.
The function pos() gives the current cursor position, while oldPos() gives the old mouse position.
There are a few similarities between the events QEvent::HoverEnter and QEvent::HoverLeave, and the events QEvent::Enter and QEvent::Leave. However, they are slightly different because we do an update() in the event handler of HoverEnter and HoverLeave.
QEvent::HoverMove is also slightly different from QEvent::MouseMove. Let us consider a top-level window A containing a child B which in turn contains a child C (all with mouse tracking enabled):

Now, if you move the cursor from the top to the bottom in the middle of A, you will get the following QEvent::MouseMove events:
- A::MouseMove
- B::MouseMove
- C::MouseMove
You will get the same events for QEvent::HoverMove, except that the event always propagates to the top-level regardless whether the event is accepted or not. It will only stop propagating with the Qt::WA_NoMousePropagation attribute.
In this case the events will occur in the following way:
- A::HoverMove
- A::HoverMove, B::HoverMove
- A::HoverMove, B::HoverMove, C::HoverMove
sourcepub unsafe fn old_pos(&self) -> CppBox<QPoint>
pub unsafe fn old_pos(&self) -> CppBox<QPoint>
Returns the previous position of the mouse cursor, relative to the widget that received the event. If there is no previous position, oldPos() will return the same position as pos().
Calls C++ function: QPoint QHoverEvent::oldPos() const.
Returns the previous position of the mouse cursor, relative to the widget that received the event. If there is no previous position, oldPos() will return the same position as pos().
On QEvent::HoverEnter events, this position will always be QPoint(-1, -1).
See also pos().
sourcepub unsafe fn old_pos_f(&self) -> Ref<QPointF>
pub unsafe fn old_pos_f(&self) -> Ref<QPointF>
Returns the previous position of the mouse cursor, relative to the widget that received the event. If there is no previous position, oldPosF() will return the same position as posF().
Calls C++ function: const QPointF& QHoverEvent::oldPosF() const.
Returns the previous position of the mouse cursor, relative to the widget that received the event. If there is no previous position, oldPosF() will return the same position as posF().
On QEvent::HoverEnter events, this position will always be QPointF(-1, -1).
See also posF().
sourcepub unsafe fn pos(&self) -> CppBox<QPoint>
pub unsafe fn pos(&self) -> CppBox<QPoint>
Returns the position of the mouse cursor, relative to the widget that received the event.
Calls C++ function: QPoint QHoverEvent::pos() const.
Returns the position of the mouse cursor, relative to the widget that received the event.
On QEvent::HoverLeave events, this position will always be QPoint(-1, -1).
See also oldPos().
sourcepub unsafe fn pos_f(&self) -> Ref<QPointF>
pub unsafe fn pos_f(&self) -> Ref<QPointF>
Returns the position of the mouse cursor, relative to the widget that received the event.
Calls C++ function: const QPointF& QHoverEvent::posF() const.
Returns the position of the mouse cursor, relative to the widget that received the event.
On QEvent::HoverLeave events, this position will always be QPointF(-1, -1).
See also oldPosF().
Methods from Deref<Target = QInputEvent>§
sourcepub unsafe fn copy_from(
&self,
other: impl CastInto<Ref<QInputEvent>>
) -> Ref<QInputEvent>
pub unsafe fn copy_from( &self, other: impl CastInto<Ref<QInputEvent>> ) -> Ref<QInputEvent>
The QInputEvent class is the base class for events that describe user input.
Calls C++ function: QInputEvent& QInputEvent::operator=(const QInputEvent& other).
The QInputEvent class is the base class for events that describe user input.
sourcepub unsafe fn modifiers(&self) -> QFlags<KeyboardModifier>
pub unsafe fn modifiers(&self) -> QFlags<KeyboardModifier>
Returns the keyboard modifier flags that existed immediately before the event occurred.
Calls C++ function: QFlags<Qt::KeyboardModifier> QInputEvent::modifiers() const.
Returns the keyboard modifier flags that existed immediately before the event occurred.
See also QGuiApplication::keyboardModifiers().
sourcepub unsafe fn set_modifiers(&self, amodifiers: QFlags<KeyboardModifier>)
pub unsafe fn set_modifiers(&self, amodifiers: QFlags<KeyboardModifier>)
Calls C++ function: void QInputEvent::setModifiers(QFlags<Qt::KeyboardModifier> amodifiers).
sourcepub unsafe fn set_timestamp(&self, atimestamp: c_ulong)
pub unsafe fn set_timestamp(&self, atimestamp: c_ulong)
Calls C++ function: void QInputEvent::setTimestamp(unsigned long atimestamp).
sourcepub unsafe fn timestamp(&self) -> c_ulong
pub unsafe fn timestamp(&self) -> c_ulong
Returns the window system's timestamp for this event. It will normally be in milliseconds since some arbitrary point in time, such as the time when the system was started.
Calls C++ function: unsigned long QInputEvent::timestamp() const.
Returns the window system’s timestamp for this event. It will normally be in milliseconds since some arbitrary point in time, such as the time when the system was started.
Methods from Deref<Target = QEvent>§
sourcepub unsafe fn accept(&self)
pub unsafe fn accept(&self)
Sets the accept flag of the event object, the equivalent of calling setAccepted(true).
Calls C++ function: void QEvent::accept().
Sets the accept flag of the event object, the equivalent of calling setAccepted(true).
Setting the accept parameter indicates that the event receiver wants the event. Unwanted events might be propagated to the parent widget.
See also ignore().
sourcepub unsafe fn copy_from(&self, other: impl CastInto<Ref<QEvent>>) -> Ref<QEvent>
pub unsafe fn copy_from(&self, other: impl CastInto<Ref<QEvent>>) -> Ref<QEvent>
Calls C++ function: QEvent& QEvent::operator=(const QEvent& other).
sourcepub unsafe fn ignore(&self)
pub unsafe fn ignore(&self)
Clears the accept flag parameter of the event object, the equivalent of calling setAccepted(false).
Calls C++ function: void QEvent::ignore().
Clears the accept flag parameter of the event object, the equivalent of calling setAccepted(false).
Clearing the accept parameter indicates that the event receiver does not want the event. Unwanted events might be propagated to the parent widget.
See also accept().
sourcepub unsafe fn is_accepted(&self) -> bool
pub unsafe fn is_accepted(&self) -> bool
the accept flag of the event object
Calls C++ function: bool QEvent::isAccepted() const.
the accept flag of the event object
Setting the accept parameter indicates that the event receiver wants the event. Unwanted events might be propagated to the parent widget. By default, isAccepted() is set to true, but don't rely on this as subclasses may choose to clear it in their constructor.
For convenience, the accept flag can also be set with accept(), and cleared with ignore().
Access functions:
| bool | isAccepted() const |
| void | setAccepted(bool accepted) |
sourcepub unsafe fn set_accepted(&self, accepted: bool)
pub unsafe fn set_accepted(&self, accepted: bool)
the accept flag of the event object
Calls C++ function: void QEvent::setAccepted(bool accepted).
the accept flag of the event object
Setting the accept parameter indicates that the event receiver wants the event. Unwanted events might be propagated to the parent widget. By default, isAccepted() is set to true, but don't rely on this as subclasses may choose to clear it in their constructor.
For convenience, the accept flag can also be set with accept(), and cleared with ignore().
Access functions:
| bool | isAccepted() const |
| void | setAccepted(bool accepted) |
sourcepub unsafe fn spontaneous(&self) -> bool
pub unsafe fn spontaneous(&self) -> bool
Returns true if the event originated outside the application (a system event); otherwise returns false.
Calls C++ function: bool QEvent::spontaneous() const.
Returns true if the event originated outside the application (a system event); otherwise returns false.
The return value of this function is not defined for paint events.
Trait Implementations§
source§impl CppDeletable for QHoverEvent
impl CppDeletable for QHoverEvent
source§impl Deref for QHoverEvent
impl Deref for QHoverEvent
source§fn deref(&self) -> &QInputEvent
fn deref(&self) -> &QInputEvent
Calls C++ function: QInputEvent* static_cast<QInputEvent*>(QHoverEvent* ptr).
§type Target = QInputEvent
type Target = QInputEvent
source§impl DynamicCast<QHoverEvent> for QEvent
impl DynamicCast<QHoverEvent> for QEvent
source§unsafe fn dynamic_cast(ptr: Ptr<QEvent>) -> Ptr<QHoverEvent>
unsafe fn dynamic_cast(ptr: Ptr<QEvent>) -> Ptr<QHoverEvent>
Calls C++ function: QHoverEvent* dynamic_cast<QHoverEvent*>(QEvent* ptr).
source§impl DynamicCast<QHoverEvent> for QInputEvent
impl DynamicCast<QHoverEvent> for QInputEvent
source§unsafe fn dynamic_cast(ptr: Ptr<QInputEvent>) -> Ptr<QHoverEvent>
unsafe fn dynamic_cast(ptr: Ptr<QInputEvent>) -> Ptr<QHoverEvent>
Calls C++ function: QHoverEvent* dynamic_cast<QHoverEvent*>(QInputEvent* ptr).
source§impl StaticDowncast<QHoverEvent> for QEvent
impl StaticDowncast<QHoverEvent> for QEvent
source§unsafe fn static_downcast(ptr: Ptr<QEvent>) -> Ptr<QHoverEvent>
unsafe fn static_downcast(ptr: Ptr<QEvent>) -> Ptr<QHoverEvent>
Calls C++ function: QHoverEvent* static_cast<QHoverEvent*>(QEvent* ptr).
source§impl StaticDowncast<QHoverEvent> for QInputEvent
impl StaticDowncast<QHoverEvent> for QInputEvent
source§unsafe fn static_downcast(ptr: Ptr<QInputEvent>) -> Ptr<QHoverEvent>
unsafe fn static_downcast(ptr: Ptr<QInputEvent>) -> Ptr<QHoverEvent>
Calls C++ function: QHoverEvent* static_cast<QHoverEvent*>(QInputEvent* ptr).
source§impl StaticUpcast<QEvent> for QHoverEvent
impl StaticUpcast<QEvent> for QHoverEvent
source§unsafe fn static_upcast(ptr: Ptr<QHoverEvent>) -> Ptr<QEvent>
unsafe fn static_upcast(ptr: Ptr<QHoverEvent>) -> Ptr<QEvent>
Calls C++ function: QEvent* static_cast<QEvent*>(QHoverEvent* ptr).
source§impl StaticUpcast<QInputEvent> for QHoverEvent
impl StaticUpcast<QInputEvent> for QHoverEvent
source§unsafe fn static_upcast(ptr: Ptr<QHoverEvent>) -> Ptr<QInputEvent>
unsafe fn static_upcast(ptr: Ptr<QHoverEvent>) -> Ptr<QInputEvent>
Calls C++ function: QInputEvent* static_cast<QInputEvent*>(QHoverEvent* ptr).