[−][src]Struct qt_gui::QRegion
The QRegion class specifies a clip region for a painter.
C++ class: QRegion.
The QRegion class specifies a clip region for a painter.
QRegion is used with QPainter::setClipRegion() to limit the paint area to what needs to be painted. There is also a QWidget::repaint() function that takes a QRegion parameter. QRegion is the best tool for minimizing the amount of screen area to be updated by a repaint.
This class is not suitable for constructing shapes for rendering, especially as outlines. Use QPainterPath to create paths and shapes for use with QPainter.
QRegion is an implicitly shared class.
Methods
impl QRegion[src]
pub unsafe fn add_assign_q_region(
&self,
r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegion>>
) -> Ref<QRegion>[src]
&self,
r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegion>>
) -> Ref<QRegion>
Applies the united() function to this region and r and assigns the result to this region. r1+=r2 is equivalent to r1 = r1.united(r2).
Calls C++ function: QRegion& QRegion::operator+=(const QRegion& r).
Applies the united() function to this region and r and assigns the result to this region. r1+=r2 is equivalent to r1 = r1.united(r2).
See also intersected().
pub unsafe fn add_assign_q_rect(
&self,
r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRect>>
) -> Ref<QRegion>[src]
&self,
r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRect>>
) -> Ref<QRegion>
Returns a region that is the union of this region with the specified rect.
Calls C++ function: QRegion& QRegion::operator+=(const QRect& r).
Returns a region that is the union of this region with the specified rect.
See also united().
pub unsafe fn begin(&self) -> Ptr<QRect>[src]
Returns a const_iterator pointing to the beginning of the range of rectangles that make up this range, in the order in which rects() returns them.
Calls C++ function: const QRect* QRegion::begin() const.
Returns a const_iterator pointing to the beginning of the range of rectangles that make up this range, in the order in which rects() returns them.
This function was introduced in Qt 5.8.
pub unsafe fn bit_and_assign_q_region(
&self,
r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegion>>
) -> Ref<QRegion>[src]
&self,
r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegion>>
) -> Ref<QRegion>
Applies the intersected() function to this region and r and assigns the result to this region. r1&=r2 is equivalent to r1 = r1.intersected(r2).
Calls C++ function: QRegion& QRegion::operator&=(const QRegion& r).
Applies the intersected() function to this region and r and assigns the result to this region. r1&=r2 is equivalent to r1 = r1.intersected(r2).
See also intersected().
pub unsafe fn bit_and_assign_q_rect(
&self,
r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRect>>
) -> Ref<QRegion>[src]
&self,
r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRect>>
) -> Ref<QRegion>
This is an overloaded function.
Calls C++ function: QRegion& QRegion::operator&=(const QRect& r).
This is an overloaded function.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.4.
pub unsafe fn bit_or_assign(
&self,
r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegion>>
) -> Ref<QRegion>[src]
&self,
r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegion>>
) -> Ref<QRegion>
Applies the united() function to this region and r and assigns the result to this region. r1|=r2 is equivalent to r1 = r1.united(r2).
Calls C++ function: QRegion& QRegion::operator|=(const QRegion& r).
pub unsafe fn bit_xor_assign(
&self,
r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegion>>
) -> Ref<QRegion>[src]
&self,
r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegion>>
) -> Ref<QRegion>
Applies the xored() function to this region and r and assigns the result to this region. r1^=r2 is equivalent to r1 = r1.xored(r2).
Calls C++ function: QRegion& QRegion::operator^=(const QRegion& r).
pub unsafe fn bounding_rect(&self) -> CppBox<QRect>[src]
Returns the bounding rectangle of this region. An empty region gives a rectangle that is QRect::isNull().
Calls C++ function: QRect QRegion::boundingRect() const.
Returns the bounding rectangle of this region. An empty region gives a rectangle that is QRect::isNull().
pub unsafe fn cbegin(&self) -> Ptr<QRect>[src]
Same as begin().
Calls C++ function: const QRect* QRegion::cbegin() const.
Same as begin().
This function was introduced in Qt 5.8.
pub unsafe fn cend(&self) -> Ptr<QRect>[src]
Same as end().
Calls C++ function: const QRect* QRegion::cend() const.
Same as end().
This function was introduced in Qt 5.8.
pub unsafe fn contains_q_point(&self, p: impl CastInto<Ref<QPoint>>) -> bool[src]
Returns true if the region contains the point p; otherwise returns false.
Calls C++ function: bool QRegion::contains(const QPoint& p) const.
Returns true if the region contains the point p; otherwise returns false.
pub unsafe fn contains_q_rect(&self, r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRect>>) -> bool[src]
This is an overloaded function.
Calls C++ function: bool QRegion::contains(const QRect& r) const.
This is an overloaded function.
Returns true if the region overlaps the rectangle r; otherwise returns false.
pub unsafe fn copy_from(
&self,
arg1: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegion>>
) -> Ref<QRegion>[src]
&self,
arg1: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegion>>
) -> Ref<QRegion>
Assigns r to this region and returns a reference to the region.
Calls C++ function: QRegion& QRegion::operator=(const QRegion& arg1).
Assigns r to this region and returns a reference to the region.
pub unsafe fn end(&self) -> Ptr<QRect>[src]
Returns a const_iterator pointing to one past the end of the range of rectangles that make up this range, in the order in which rects() returns them.
Calls C++ function: const QRect* QRegion::end() const.
Returns a const_iterator pointing to one past the end of the range of rectangles that make up this range, in the order in which rects() returns them.
This function was introduced in Qt 5.8.
pub unsafe fn intersected_q_region(
&self,
r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegion>>
) -> CppBox<QRegion>[src]
&self,
r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegion>>
) -> CppBox<QRegion>
Returns a region which is the intersection of this region and r.
Calls C++ function: QRegion QRegion::intersected(const QRegion& r) const.
Returns a region which is the intersection of this region and r.
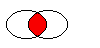
The figure shows the intersection of two elliptical regions.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.2.
See also subtracted(), united(), and xored().
pub unsafe fn intersected_q_rect(
&self,
r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRect>>
) -> CppBox<QRegion>[src]
&self,
r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRect>>
) -> CppBox<QRegion>
Returns a region which is the intersection of this region and the given rect.
Calls C++ function: QRegion QRegion::intersected(const QRect& r) const.
Returns a region which is the intersection of this region and the given rect.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.4.
See also subtracted(), united(), and xored().
pub unsafe fn intersects_q_region(&self, r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegion>>) -> bool[src]
Returns true if this region intersects with region, otherwise returns false.
Calls C++ function: bool QRegion::intersects(const QRegion& r) const.
Returns true if this region intersects with region, otherwise returns false.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.2.
pub unsafe fn intersects_q_rect(&self, r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRect>>) -> bool[src]
Returns true if this region intersects with rect, otherwise returns false.
Calls C++ function: bool QRegion::intersects(const QRect& r) const.
Returns true if this region intersects with rect, otherwise returns false.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.2.
pub unsafe fn is_empty(&self) -> bool[src]
Returns true if the region is empty; otherwise returns false. An empty region is a region that contains no points.
Calls C++ function: bool QRegion::isEmpty() const.
Returns true if the region is empty; otherwise returns false. An empty region is a region that contains no points.
Example:
QRegion r1(10, 10, 20, 20); r1.isEmpty(); // false
QRegion r3; r3.isEmpty(); // true
QRegion r2(40, 40, 20, 20); r3 = r1.intersected(r2); // r3: intersection of r1 and r2 r3.isEmpty(); // true
r3 = r1.united(r2); // r3: union of r1 and r2 r3.isEmpty(); // false
pub unsafe fn is_null(&self) -> bool[src]
Returns true if the region is empty; otherwise returns false. An empty region is a region that contains no points. This function is the same as isEmpty
Calls C++ function: bool QRegion::isNull() const.
pub unsafe fn new() -> CppBox<QRegion>[src]
Constructs an empty region.
Calls C++ function: [constructor] void QRegion::QRegion().
Constructs an empty region.
See also isEmpty().
pub unsafe fn from_4_int_region_type(
x: c_int,
y: c_int,
w: c_int,
h: c_int,
t: RegionType
) -> CppBox<QRegion>[src]
x: c_int,
y: c_int,
w: c_int,
h: c_int,
t: RegionType
) -> CppBox<QRegion>
Constructs a rectangular or elliptic region.
Calls C++ function: [constructor] void QRegion::QRegion(int x, int y, int w, int h, QRegion::RegionType t = …).
Constructs a rectangular or elliptic region.
If t is Rectangle, the region is the filled rectangle (x, y, w, h). If t is Ellipse, the region is the filled ellipse with center at (x + w / 2, y + h / 2) and size (w ,h).
pub unsafe fn from_q_rect_region_type(
r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRect>>,
t: RegionType
) -> CppBox<QRegion>[src]
r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRect>>,
t: RegionType
) -> CppBox<QRegion>
This is an overloaded function.
Calls C++ function: [constructor] void QRegion::QRegion(const QRect& r, QRegion::RegionType t = …).
This is an overloaded function.
Create a region based on the rectange r with region type t.
If the rectangle is invalid a null region will be created.
See also QRegion::RegionType.
pub unsafe fn from_q_polygon_fill_rule(
pa: impl CastInto<Ref<QPolygon>>,
fill_rule: FillRule
) -> CppBox<QRegion>[src]
pa: impl CastInto<Ref<QPolygon>>,
fill_rule: FillRule
) -> CppBox<QRegion>
Constructs a polygon region from the point array a with the fill rule specified by fillRule.
Calls C++ function: [constructor] void QRegion::QRegion(const QPolygon& pa, Qt::FillRule fillRule = …).
Constructs a polygon region from the point array a with the fill rule specified by fillRule.
If fillRule is Qt::WindingFill, the polygon region is defined using the winding algorithm; if it is Qt::OddEvenFill, the odd-even fill algorithm is used.
Warning: This constructor can be used to create complex regions that will slow down painting when used.
pub unsafe fn from_q_bitmap(
bitmap: impl CastInto<Ref<QBitmap>>
) -> CppBox<QRegion>[src]
bitmap: impl CastInto<Ref<QBitmap>>
) -> CppBox<QRegion>
Constructs a region from the bitmap bm.
Calls C++ function: [constructor] void QRegion::QRegion(const QBitmap& bitmap).
Constructs a region from the bitmap bm.
The resulting region consists of the pixels in bitmap bm that are Qt::color1, as if each pixel was a 1 by 1 rectangle.
This constructor may create complex regions that will slow down painting when used. Note that drawing masked pixmaps can be done much faster using QPixmap::setMask().
pub unsafe fn from_4_int(
x: c_int,
y: c_int,
w: c_int,
h: c_int
) -> CppBox<QRegion>[src]
x: c_int,
y: c_int,
w: c_int,
h: c_int
) -> CppBox<QRegion>
Constructs a rectangular or elliptic region.
Calls C++ function: [constructor] void QRegion::QRegion(int x, int y, int w, int h).
Constructs a rectangular or elliptic region.
If t is Rectangle, the region is the filled rectangle (x, y, w, h). If t is Ellipse, the region is the filled ellipse with center at (x + w / 2, y + h / 2) and size (w ,h).
pub unsafe fn from_q_rect(r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRect>>) -> CppBox<QRegion>[src]
This is an overloaded function.
Calls C++ function: [constructor] void QRegion::QRegion(const QRect& r).
This is an overloaded function.
Create a region based on the rectange r with region type t.
If the rectangle is invalid a null region will be created.
See also QRegion::RegionType.
pub unsafe fn from_q_polygon(
pa: impl CastInto<Ref<QPolygon>>
) -> CppBox<QRegion>[src]
pa: impl CastInto<Ref<QPolygon>>
) -> CppBox<QRegion>
Constructs a polygon region from the point array a with the fill rule specified by fillRule.
Calls C++ function: [constructor] void QRegion::QRegion(const QPolygon& pa).
Constructs a polygon region from the point array a with the fill rule specified by fillRule.
If fillRule is Qt::WindingFill, the polygon region is defined using the winding algorithm; if it is Qt::OddEvenFill, the odd-even fill algorithm is used.
Warning: This constructor can be used to create complex regions that will slow down painting when used.
pub unsafe fn new_copy(region: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegion>>) -> CppBox<QRegion>[src]
Constructs a new region which is equal to region r.
Calls C++ function: [constructor] void QRegion::QRegion(const QRegion& region).
Constructs a new region which is equal to region r.
pub unsafe fn rect_count(&self) -> c_int[src]
Returns the number of rectangles that will be returned in rects().
Calls C++ function: int QRegion::rectCount() const.
Returns the number of rectangles that will be returned in rects().
This function was introduced in Qt 4.6.
pub unsafe fn rects(&self) -> CppBox<QVectorOfQRect>[src]
Returns an array of non-overlapping rectangles that make up the region.
Calls C++ function: QVector<QRect> QRegion::rects() const.
Returns an array of non-overlapping rectangles that make up the region.
The union of all the rectangles is equal to the original region.
See also setRects().
pub unsafe fn set_rects(&self, rect: impl CastInto<Ptr<QRect>>, num: c_int)[src]
Sets the region using the array of rectangles specified by rects and number. The rectangles must be optimally Y-X sorted and follow these restrictions:
Calls C++ function: void QRegion::setRects(const QRect* rect, int num).
Sets the region using the array of rectangles specified by rects and number. The rectangles must be optimally Y-X sorted and follow these restrictions:
- The rectangles must not intersect.
- All rectangles with a given top coordinate must have the same height.
- No two rectangles may abut horizontally (they should be combined into a single wider rectangle in that case).
- The rectangles must be sorted in ascending order, with Y as the major sort key and X as the minor sort key.
See also rects().
pub unsafe fn sub_assign(&self, r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegion>>) -> Ref<QRegion>[src]
Applies the subtracted() function to this region and r and assigns the result to this region. r1-=r2 is equivalent to r1 = r1.subtracted(r2).
Calls C++ function: QRegion& QRegion::operator-=(const QRegion& r).
Applies the subtracted() function to this region and r and assigns the result to this region. r1-=r2 is equivalent to r1 = r1.subtracted(r2).
See also subtracted().
pub unsafe fn subtracted(
&self,
r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegion>>
) -> CppBox<QRegion>[src]
&self,
r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegion>>
) -> CppBox<QRegion>
Returns a region which is r subtracted from this region.
Calls C++ function: QRegion QRegion::subtracted(const QRegion& r) const.
Returns a region which is r subtracted from this region.
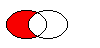
The figure shows the result when the ellipse on the right is subtracted from the ellipse on the left (left - right).
This function was introduced in Qt 4.2.
See also intersected(), united(), and xored().
pub unsafe fn swap(&self, other: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegion>>)[src]
Swaps region other with this region. This operation is very fast and never fails.
Calls C++ function: void QRegion::swap(QRegion& other).
Swaps region other with this region. This operation is very fast and never fails.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.8.
pub unsafe fn to_q_variant(&self) -> CppBox<QVariant>[src]
Returns the region as a QVariant
Calls C++ function: QVariant QRegion::operator QVariant() const.
Returns the region as a QVariant
pub unsafe fn translate_2a(&self, dx: c_int, dy: c_int)[src]
Translates (moves) the region dx along the X axis and dy along the Y axis.
Calls C++ function: void QRegion::translate(int dx, int dy).
Translates (moves) the region dx along the X axis and dy along the Y axis.
pub unsafe fn translate_1a(&self, p: impl CastInto<Ref<QPoint>>)[src]
This is an overloaded function.
Calls C++ function: void QRegion::translate(const QPoint& p).
This is an overloaded function.
Translates the region point.x() along the x axis and point.y() along the y axis, relative to the current position. Positive values move the region to the right and down.
Translates to the given point.
pub unsafe fn translated_2a(&self, dx: c_int, dy: c_int) -> CppBox<QRegion>[src]
Returns a copy of the region that is translated dx along the x axis and dy along the y axis, relative to the current position. Positive values move the region to the right and down.
Calls C++ function: QRegion QRegion::translated(int dx, int dy) const.
Returns a copy of the region that is translated dx along the x axis and dy along the y axis, relative to the current position. Positive values move the region to the right and down.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.1.
See also translate().
pub unsafe fn translated_1a(
&self,
p: impl CastInto<Ref<QPoint>>
) -> CppBox<QRegion>[src]
&self,
p: impl CastInto<Ref<QPoint>>
) -> CppBox<QRegion>
This is an overloaded function.
Calls C++ function: QRegion QRegion::translated(const QPoint& p) const.
This is an overloaded function.
Returns a copy of the regtion that is translated p.x() along the x axis and p.y() along the y axis, relative to the current position. Positive values move the rectangle to the right and down.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.1.
See also translate().
pub unsafe fn united_q_region(
&self,
r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegion>>
) -> CppBox<QRegion>[src]
&self,
r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegion>>
) -> CppBox<QRegion>
Returns a region which is the union of this region and r.
Calls C++ function: QRegion QRegion::united(const QRegion& r) const.
Returns a region which is the union of this region and r.
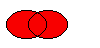
The figure shows the union of two elliptical regions.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.2.
See also intersected(), subtracted(), and xored().
pub unsafe fn united_q_rect(
&self,
r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRect>>
) -> CppBox<QRegion>[src]
&self,
r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRect>>
) -> CppBox<QRegion>
Returns a region which is the union of this region and the given rect.
Calls C++ function: QRegion QRegion::united(const QRect& r) const.
Returns a region which is the union of this region and the given rect.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.4.
See also intersected(), subtracted(), and xored().
pub unsafe fn xored(&self, r: impl CastInto<Ref<QRegion>>) -> CppBox<QRegion>[src]
Returns a region which is the exclusive or (XOR) of this region and r.
Calls C++ function: QRegion QRegion::xored(const QRegion& r) const.
Returns a region which is the exclusive or (XOR) of this region and r.
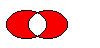
The figure shows the exclusive or of two elliptical regions.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.2.
See also intersected(), united(), and subtracted().
Trait Implementations
impl<'_> Add<Ref<QRect>> for &'_ QRegion[src]
type Output = CppBox<QRegion>
The resulting type after applying the + operator.
fn add(self, r: Ref<QRect>) -> CppBox<QRegion>[src]
This is an overloaded function.
Calls C++ function: QRegion QRegion::operator+(const QRect& r) const.
This is an overloaded function.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.4.
impl<'_> Add<Ref<QRegion>> for &'_ QRegion[src]
type Output = CppBox<QRegion>
The resulting type after applying the + operator.
fn add(self, r: Ref<QRegion>) -> CppBox<QRegion>[src]
Applies the united() function to this region and r. r1+r2 is equivalent to r1.united(r2).
Calls C++ function: QRegion QRegion::operator+(const QRegion& r) const.
impl Begin for QRegion[src]
type Output = Ptr<QRect>
Output type.
unsafe fn begin(&self) -> Ptr<QRect>[src]
Returns a const_iterator pointing to the beginning of the range of rectangles that make up this range, in the order in which rects() returns them.
Calls C++ function: const QRect* QRegion::begin() const.
Returns a const_iterator pointing to the beginning of the range of rectangles that make up this range, in the order in which rects() returns them.
This function was introduced in Qt 5.8.
impl<'_> BitAnd<Ref<QRect>> for &'_ QRegion[src]
type Output = CppBox<QRegion>
The resulting type after applying the & operator.
fn bitand(self, r: Ref<QRect>) -> CppBox<QRegion>[src]
This is an overloaded function.
Calls C++ function: QRegion QRegion::operator&(const QRect& r) const.
This is an overloaded function.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.4.
impl<'_> BitAnd<Ref<QRegion>> for &'_ QRegion[src]
type Output = CppBox<QRegion>
The resulting type after applying the & operator.
fn bitand(self, r: Ref<QRegion>) -> CppBox<QRegion>[src]
Applies the intersected() function to this region and r. r1&r2 is equivalent to r1.intersected(r2).
Calls C++ function: QRegion QRegion::operator&(const QRegion& r) const.
Applies the intersected() function to this region and r. r1&r2 is equivalent to r1.intersected(r2).
See also intersected().
impl<'_> BitOr<Ref<QRegion>> for &'_ QRegion[src]
type Output = CppBox<QRegion>
The resulting type after applying the | operator.
fn bitor(self, r: Ref<QRegion>) -> CppBox<QRegion>[src]
Applies the united() function to this region and r. r1|r2 is equivalent to r1.united(r2).
Calls C++ function: QRegion QRegion::operator|(const QRegion& r) const.
impl<'_> BitXor<Ref<QRegion>> for &'_ QRegion[src]
type Output = CppBox<QRegion>
The resulting type after applying the ^ operator.
fn bitxor(self, r: Ref<QRegion>) -> CppBox<QRegion>[src]
Applies the xored() function to this region and r. r1^r2 is equivalent to r1.xored(r2).
Calls C++ function: QRegion QRegion::operator^(const QRegion& r) const.
impl CppDeletable for QRegion[src]
impl End for QRegion[src]
type Output = Ptr<QRect>
Output type.
unsafe fn end(&self) -> Ptr<QRect>[src]
Returns a const_iterator pointing to one past the end of the range of rectangles that make up this range, in the order in which rects() returns them.
Calls C++ function: const QRect* QRegion::end() const.
Returns a const_iterator pointing to one past the end of the range of rectangles that make up this range, in the order in which rects() returns them.
This function was introduced in Qt 5.8.
impl<'_> Mul<Ref<QMatrix>> for &'_ QRegion[src]
type Output = CppBox<QRegion>
The resulting type after applying the * operator.
fn mul(self, m: Ref<QMatrix>) -> CppBox<QRegion>[src]
Calls C++ function: QRegion operator*(const QRegion& r, const QMatrix& m).
impl<'_> Mul<Ref<QTransform>> for &'_ QRegion[src]
type Output = CppBox<QRegion>
The resulting type after applying the * operator.
fn mul(self, m: Ref<QTransform>) -> CppBox<QRegion>[src]
Calls C++ function: QRegion operator*(const QRegion& r, const QTransform& m).
impl PartialEq<Ref<QRegion>> for QRegion[src]
fn eq(&self, r: &Ref<QRegion>) -> bool[src]
Returns true if the region is equal to r; otherwise returns false.
Calls C++ function: bool QRegion::operator==(const QRegion& r) const.
Returns true if the region is equal to r; otherwise returns false.
#[must_use]fn ne(&self, other: &Rhs) -> bool1.0.0[src]
impl<'_> Sub<Ref<QRegion>> for &'_ QRegion[src]
type Output = CppBox<QRegion>
The resulting type after applying the - operator.
fn sub(self, r: Ref<QRegion>) -> CppBox<QRegion>[src]
Applies the subtracted() function to this region and r. r1-r2 is equivalent to r1.subtracted(r2).
Calls C++ function: QRegion QRegion::operator-(const QRegion& r) const.
Applies the subtracted() function to this region and r. r1-r2 is equivalent to r1.subtracted(r2).
See also subtracted().
Auto Trait Implementations
impl RefUnwindSafe for QRegion
impl Send for QRegion
impl Sync for QRegion
impl Unpin for QRegion
impl UnwindSafe for QRegion
Blanket Implementations
impl<T> Any for T where
T: 'static + ?Sized, [src]
T: 'static + ?Sized,
impl<T> Borrow<T> for T where
T: ?Sized, [src]
T: ?Sized,
impl<T> BorrowMut<T> for T where
T: ?Sized, [src]
T: ?Sized,
fn borrow_mut(&mut self) -> &mut T[src]
impl<T, U> CastInto<U> for T where
U: CastFrom<T>, [src]
U: CastFrom<T>,
impl<T> From<T> for T[src]
impl<T, U> Into<U> for T where
U: From<T>, [src]
U: From<T>,
impl<T> StaticUpcast<T> for T[src]
unsafe fn static_upcast(ptr: Ptr<T>) -> Ptr<T>[src]
impl<T, U> TryFrom<U> for T where
U: Into<T>, [src]
U: Into<T>,
type Error = Infallible
The type returned in the event of a conversion error.
fn try_from(value: U) -> Result<T, <T as TryFrom<U>>::Error>[src]
impl<T, U> TryInto<U> for T where
U: TryFrom<T>, [src]
U: TryFrom<T>,