Expand description
§What is an Entity Component System?
An Entity Component System or ECS is very similar to a relational database like SQL. The
World is the data store where game objects (also known as Entity) live. An Entity
contains data or Components.
The ECS can efficiently query those components.
Give me all entities that have a position and velocity component, and then update the position based on the velocity.
type PosVelQuery = (Write<Pos>, Read<Vel>);
// ^^^^^ ^^^^
// Mutable Immutable
world.matcher::<All<PosVelQuery>>().for_each(|(pos, vel)|{
pos += vel;
})§Internals
§Overview
- Iteration is always linear.
- Different component combinations live in a separate storage
- Removing entities does not create holes.
- All operations are designed to be used in bulk.
- Borrow rules are enforced at runtime. See
RuntimeBorrow Entityis using a wrapping generational index. SeeEntity::version
// A Storage that contains `Pos`, `Vel`, `Health`.
(
[Pos1, Pos2, Pos3, .., PosN],
[Vel1, Vel2, Vel3, .., VelN],
[Health1, Health2, Health3, .., HealthN],
)
// A Storage that contains `Pos`, `Vel`.
(
[Pos1, Pos2, Pos3, .., PosM]
[Vel1, Vel2, Vel3, .., VelM]
)
Iteration is fully linear with the exception of jumping to different storages.
The iteration pattern from the query above would be
positions: [Pos1, Pos2, Pos3, .., PosN], [Pos1, Pos2, Pos3, .., PosM]
velocities: [Vel1, Vel2, Vel3, .., VelN], [Vel1, Vel2, Vel3, .., VelM]
^
Jump occurs hereThe jump is something like a chain of two iterators. We look at all the storages
that match specific query. If the query would be Write<Position>, then we would
look for all the storages that contain a position array, extract the iterators and chain them
Every combination of components will be in a separate storage. This guarantees that iteration will always be linear.
§Benchmarks
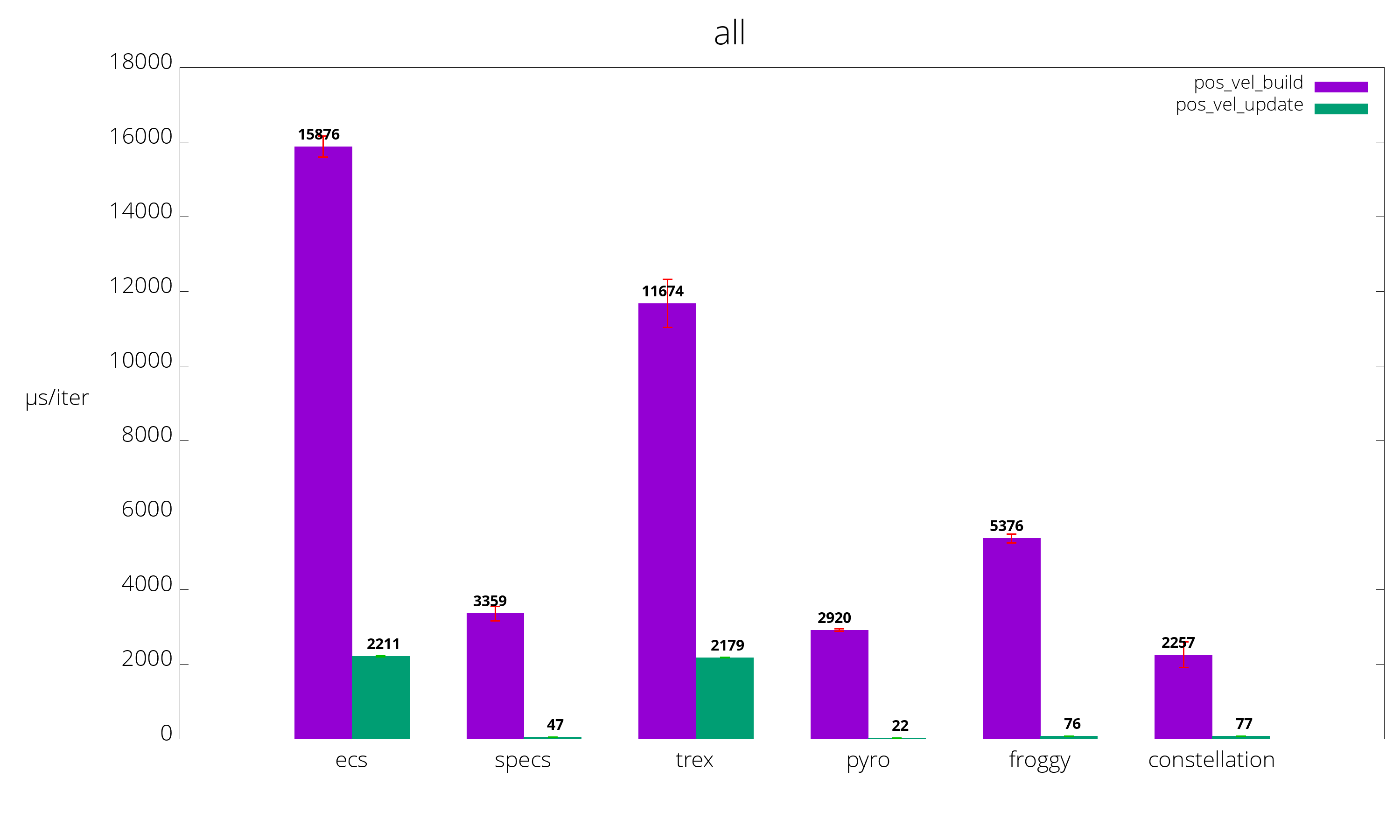
§Getting started
extern crate pyro;
use pyro::{ World, Entity, Read, Write, All, SoaStorage };
struct Position;
struct Velocity;
// By default creates a world backed by a [`SoaStorage`]
let mut world: World<SoaStorage> = World::new();
let add_pos_vel = (0..99).map(|_| (Position{}, Velocity{}));
// ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
// A tuple of (Position, Velocity),
// Note: Order does *not* matter
// Appends 99 entities with a Position and Velocity component.
world.append_components(add_pos_vel);
// Appends a single entity
world.append_components(Some((Position{}, Velocity{})));
// Requests a mutable borrow to Position, and an immutable borrow to Velocity.
// Common queries can be reused with a typedef like this but it is not necessary.
type PosVelQuery = (Write<Position>, Read<Velocity>);
// Retrieves all entities that have a Position and Velocity component as an iterator.
world.matcher::<All<PosVelQuery>>().for_each(|(pos, vel)|{
// ...
});
// The same query as above but also retrieves the entities and collects the entities into a
// `Vec<Entity>`.
let entities: Vec<Entity> =
world.matcher_with_entities::<All<PosVelQuery>>()
.filter_map(|(entity, (pos, vel))|{
Some(entity)
}).collect();
// Removes all the entities
world.remove_entities(entities);
let count = world.matcher::<All<PosVelQuery>>().count();
assert_eq!(count, 0);Structs§
- All
- Is satisfied when a storages contains all of the specified components.
- Borrow
- Borrow
Iter - The
Iteratoris used to end a borrow from a query likeWorld::matcher. - Empty
Storage - Entity
- Serves as an ID to lookup components for entities which can be in different storages.
- Read
- Implements
Fetchand allows components to be borrowed immutable. - Runtime
Borrow - Rust’s borrowing rules are not flexible enough for an ECS. Often it would preferred to nest multiple
queries like
World::matcher, but this is not possible if both borrows would be mutable. Instead we track active borrows at runtime. Multiple reads are allowed butread/writeandwrite/writeare not. - SoaStorage
- A runtime SoA storage. It stands for Structure of Arrays.
- Unsafe
Storage - World
Worldis the heart of this library. It owns all theComponents andStorages. It also manages entities and allowsComponents to be safely queried.- Write
- Implements
Fetchand allows components to be borrowed mutable.
Traits§
- Append
Components - Build
Storage BuildStorageis used to create differentStorages at runtime. See alsoAppendComponentsandWorld::append_components- Component
- Fetch
- A helper trait that works in lockstep with
ReadandWriteto borrow components either mutable or immutable. - Iterator
Soa - Matcher
- Allows to match over different
Storages. See alsoAll. - Push
Borrow - Is implemented for
ReadandWriteand is used to insert reads and writes into the correctHashSet. - Query
- Allows to query multiple components from a
Storage. See alsoAll. - Register
Borrow - Register
Component - A
Storagewon’t have any arrays or vectors when it is created.RegisterComponentcan register or add those component arrays. See alsoEmptyStorage::register_component - Runtime
Storage - Storage
Storageallows to abstract over different types of storages. The most common storage that implements this trait isSoaStorage.