pub fn solve_pnp_generic(
object_points: &impl ToInputArray,
image_points: &impl ToInputArray,
camera_matrix: &impl ToInputArray,
dist_coeffs: &impl ToInputArray,
rvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray,
tvecs: &mut impl ToOutputArray,
use_extrinsic_guess: bool,
flags: SolvePnPMethod,
rvec: &impl ToInputArray,
tvec: &impl ToInputArray,
reprojection_error: &mut impl ToOutputArray,
) -> Result<i32>Expand description
Finds an object pose from 3D-2D point correspondences.
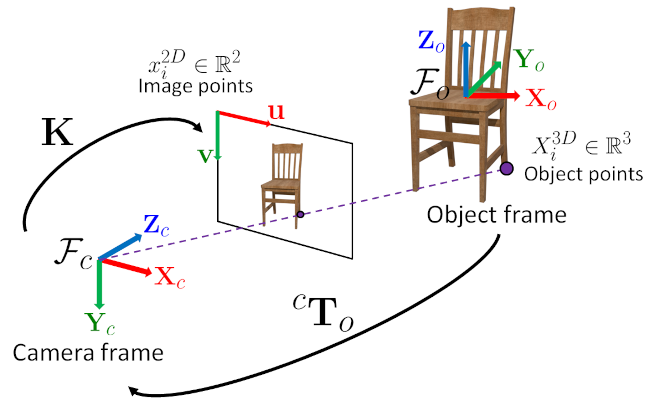 { width=50% }
{ width=50% }
§See also
[calib3d_solvePnP]
This function returns a list of all the possible solutions (a solution is a <rotation vector, translation vector> couple), depending on the number of input points and the chosen method:
- P3P methods (SOLVEPNP_P3P, SOLVEPNP_AP3P): 3 or 4 input points. Number of returned solutions can be between 0 and 4 with 3 input points.
- SOLVEPNP_IPPE Input points must be >= 4 and object points must be coplanar. Returns 2 solutions.
- SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE Special case suitable for marker pose estimation.
Number of input points must be 4 and 2 solutions are returned. Object points must be defined in the following order:
- point 0: [-squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
- point 1: [ squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
- point 2: [ squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
- point 3: [-squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
- for all the other flags, number of input points must be >= 4 and object points can be in any configuration. Only 1 solution is returned.
§Parameters
- objectPoints: Array of object points in the object coordinate space, Nx3 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 3-channel, where N is the number of points. vector<Point3d> can be also passed here.
- imagePoints: Array of corresponding image points, Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel, where N is the number of points. vector<Point2d> can be also passed here.
- cameraMatrix: Input camera intrinsic matrix
.
- distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients
. If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed.
- rvecs: Vector of output rotation vectors (see [Rodrigues] ) that, together with tvecs, brings points from the model coordinate system to the camera coordinate system.
- tvecs: Vector of output translation vectors.
- useExtrinsicGuess: Parameter used for #SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE. If true (1), the function uses the provided rvec and tvec values as initial approximations of the rotation and translation vectors, respectively, and further optimizes them.
- flags: Method for solving a PnP problem: see [calib3d_solvePnP_flags]
- rvec: Rotation vector used to initialize an iterative PnP refinement algorithm, when flag is SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE and useExtrinsicGuess is set to true.
- tvec: Translation vector used to initialize an iterative PnP refinement algorithm, when flag is SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE and useExtrinsicGuess is set to true.
- reprojectionError: Optional vector of reprojection error, that is the RMS error
(
) between the input image points and the 3D object points projected with the estimated pose.
More information is described in [calib3d_solvePnP]
Note:
- An example of how to use solvePnP for planar augmented reality can be found at opencv_source_code/samples/python/plane_ar.py
- If you are using Python:
- Numpy array slices won’t work as input because solvePnP requires contiguous arrays (enforced by the assertion using cv::Mat::checkVector() around line 55 of modules/calib3d/src/solvepnp.cpp version 2.4.9)
- The P3P algorithm requires image points to be in an array of shape (N,1,2) due to its calling of undistort_points (around line 75 of modules/calib3d/src/solvepnp.cpp version 2.4.9) which requires 2-channel information.
- Thus, given some data D = np.array(…) where D.shape = (N,M), in order to use a subset of it as, e.g., imagePoints, one must effectively copy it into a new array: imagePoints = np.ascontiguousarray(D[:,:2]).reshape((N,1,2))
- The methods SOLVEPNP_DLS and SOLVEPNP_UPNP cannot be used as the current implementations are unstable and sometimes give completely wrong results. If you pass one of these two flags, SOLVEPNP_EPNP method will be used instead.
- The minimum number of points is 4 in the general case. In the case of SOLVEPNP_P3P and SOLVEPNP_AP3P methods, it is required to use exactly 4 points (the first 3 points are used to estimate all the solutions of the P3P problem, the last one is used to retain the best solution that minimizes the reprojection error).
- With SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE method and
useExtrinsicGuess=true, the minimum number of points is 3 (3 points are sufficient to compute a pose but there are up to 4 solutions). The initial solution should be close to the global solution to converge. - With SOLVEPNP_IPPE input points must be >= 4 and object points must be coplanar.
- With SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE this is a special case suitable for marker pose estimation.
Number of input points must be 4. Object points must be defined in the following order:
- point 0: [-squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
- point 1: [ squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0]
- point 2: [ squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
- point 3: [-squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0]
- With SOLVEPNP_SQPNP input points must be >= 3
§C++ default parameters
- use_extrinsic_guess: false
- flags: SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE
- rvec: noArray()
- tvec: noArray()
- reprojection_error: noArray()