1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 451 452 453 454 455 456 457 458 459 460 461 462 463 464 465 466 467 468 469 470 471 472 473 474 475 476 477 478 479 480 481 482 483 484 485 486 487 488 489 490 491 492 493 494 495 496 497 498 499 500 501 502 503 504 505 506 507 508 509 510 511 512 513 514 515 516 517 518 519 520 521 522 523 524 525 526 527 528 529 530 531 532 533 534 535 536 537 538 539 540 541 542 543 544 545 546 547 548 549 550 551 552 553 554 555 556 557 558 559 560 561 562 563 564 565 566 567 568 569 570 571 572 573 574 575 576 577 578 579 580 581 582 583 584 585 586 587 588 589 590 591 592 593 594 595 596 597 598 599 600 601 602 603 604 605 606 607 608 609 610 611 612 613 614 615 616 617 618 619 620 621 622 623 624 625 626 627 628 629 630 631 632 633 634 635 636 637 638 639 640 641 642 643 644 645 646 647 648 649 650 651 652 653 654 655 656 657 658 659 660 661 662 663 664 665 666 667 668 669 670 671 672 673 674 675 676 677 678 679 680 681 682 683 684 685 686 687 688 689 690 691 692 693 694 695 696 697 698 699 700 701 702 703 704 705 706 707 708 709 710 711 712 713 714 715 716 717 718 719 720 721 722 723 724 725 726 727 728 729 730 731 732 733 734 735 736 737 738 739 740 741 742 743 744 745 746 747 748 749 750 751 752 753 754 755 756 757 758 759 760 761 762 763 764 765 766 767 768 769 770 771 772 773 774 775 776 777 778 779 780 781 782 783 784 785 786 787 788 789 790 791 792 793 794 795 796 797 798 799 800 801 802 803 804 805 806 807 808 809 810 811 812 813 814 815 816 817 818 819 820 821 822 823 824 825 826 827 828 829 830 831 832 833 834 835 836 837 838 839 840 841 842 843 844 845 846 847 848 849 850 851 852 853 854 855 856 857 858 859 860 861 862 863 864 865 866 867 868 869 870 871 872 873 874 875 876 877 878 879 880 881 882 883 884 885 886 887 888 889 890 891 892 893 894 895 896 897 898 899 900 901 902 903 904 905 906 907 908 909 910 911 912 913 914 915 916 917 918 919 920 921 922 923 924 925 926 927 928 929 930 931 932 933 934 935 936 937 938 939 940 941 942 943 944 945 946 947 948 949 950 951 952 953 954 955 956 957 958 959 960 961 962 963 964 965 966 967 968 969 970 971 972 973 974 975 976 977 978 979 980 981 982 983 984 985 986 987 988 989 990 991 992 993 994 995 996 997 998 999 1000 1001 1002 1003 1004 1005 1006 1007 1008 1009 1010 1011 1012 1013 1014 1015 1016 1017 1018 1019 1020 1021 1022 1023 1024 1025 1026 1027 1028 1029 1030 1031 1032 1033 1034 1035 1036 1037 1038 1039 1040 1041 1042 1043 1044 1045 1046 1047 1048 1049 1050 1051 1052 1053 1054 1055 1056 1057 1058 1059 1060 1061 1062 1063 1064 1065 1066 1067 1068 1069 1070 1071 1072 1073 1074 1075 1076 1077 1078 1079 1080 1081 1082 1083 1084 1085 1086 1087 1088 1089 1090 1091 1092 1093 1094 1095 1096 1097 1098 1099 1100 1101 1102 1103 1104 1105 1106 1107 1108 1109 1110 1111 1112 1113 1114 1115 1116 1117 1118 1119 1120 1121 1122 1123 1124 1125 1126 1127 1128 1129 1130 1131 1132 1133 1134 1135 1136 1137 1138 1139 1140 1141 1142 1143 1144 1145 1146 1147 1148 1149 1150 1151 1152 1153 1154 1155 1156 1157 1158 1159 1160 1161 1162 1163 1164 1165 1166 1167 1168 1169 1170 1171 1172 1173 1174 1175 1176 1177 1178 1179 1180 1181 1182 1183 1184 1185 1186 1187 1188 1189 1190 1191 1192 1193 1194 1195 1196 1197 1198 1199 1200 1201 1202 1203 1204 1205 1206 1207 1208 1209 1210 1211 1212 1213 1214 1215 1216 1217 1218 1219 1220 1221 1222 1223 1224 1225 1226 1227 1228 1229 1230 1231 1232 1233 1234 1235 1236 1237 1238 1239 1240 1241 1242 1243 1244 1245 1246 1247 1248 1249 1250 1251 1252 1253 1254 1255 1256 1257 1258 1259 1260 1261 1262 1263 1264 1265 1266 1267 1268 1269 1270 1271 1272 1273 1274 1275 1276 1277 1278 1279 1280 1281 1282 1283 1284 1285 1286 1287 1288 1289 1290 1291 1292 1293 1294 1295 1296 1297 1298 1299 1300 1301 1302 1303 1304 1305 1306 1307 1308 1309 1310 1311 1312 1313 1314 1315 1316 1317 1318 1319 1320 1321 1322 1323 1324 1325 1326 1327 1328 1329 1330 1331 1332 1333 1334 1335 1336 1337 1338 1339 1340 1341 1342 1343 1344 1345 1346 1347 1348 1349 1350 1351 1352 1353 1354 1355 1356 1357 1358 1359 1360 1361 1362 1363 1364 1365 1366 1367 1368 1369 1370 1371 1372 1373 1374 1375 1376 1377 1378 1379 1380 1381 1382 1383 1384 1385 1386 1387 1388 1389 1390 1391 1392 1393 1394 1395 1396 1397 1398 1399 1400 1401 1402 1403 1404 1405 1406 1407 1408 1409 1410 1411 1412 1413 1414 1415 1416 1417 1418 1419 1420 1421 1422 1423 1424 1425 1426 1427 1428 1429 1430 1431 1432 1433 1434 1435 1436 1437 1438 1439 1440 1441 1442 1443 1444 1445 1446 1447 1448 1449 1450 1451 1452 1453 1454 1455 1456 1457 1458 1459 1460 1461 1462 1463 1464 1465 1466 1467 1468 1469 1470 1471 1472 1473 1474 1475 1476 1477 1478 1479 1480 1481 1482 1483 1484 1485 1486 1487 1488 1489 1490 1491 1492 1493 1494 1495 1496 1497 1498 1499 1500 1501 1502 1503 1504 1505 1506 1507 1508 1509 1510 1511 1512 1513 1514 1515 1516 1517 1518 1519 1520 1521 1522 1523 1524 1525 1526 1527 1528 1529 1530 1531 1532 1533 1534 1535 1536 1537 1538 1539 1540 1541 1542 1543 1544 1545 1546 1547 1548 1549 1550 1551 1552 1553 1554 1555 1556 1557 1558 1559 1560 1561 1562 1563 1564 1565 1566 1567 1568 1569 1570 1571 1572 1573 1574 1575 1576 1577 1578 1579 1580 1581 1582 1583 1584 1585 1586 1587 1588 1589 1590 1591 1592 1593 1594 1595 1596 1597 1598 1599 1600 1601 1602 1603 1604 1605 1606 1607 1608 1609 1610 1611 1612 1613 1614 1615 1616 1617 1618 1619 1620 1621 1622 1623 1624 1625 1626 1627 1628 1629 1630 1631 1632 1633 1634 1635 1636 1637 1638 1639 1640 1641 1642 1643 1644 1645 1646 1647 1648 1649 1650 1651 1652 1653 1654 1655 1656 1657 1658 1659 1660 1661 1662 1663 1664 1665 1666 1667 1668 1669 1670 1671 1672 1673 1674 1675 1676 1677 1678 1679 1680 1681 1682 1683 1684 1685 1686 1687 1688 1689 1690 1691 1692 1693 1694 1695 1696 1697 1698 1699 1700 1701 1702 1703 1704 1705 1706 1707 1708 1709 1710 1711 1712 1713 1714 1715 1716 1717 1718 1719 1720 1721 1722 1723 1724 1725 1726 1727 1728 1729 1730 1731 1732 1733 1734 1735 1736 1737 1738 1739 1740 1741 1742 1743 1744 1745 1746 1747 1748 1749 1750 1751 1752 1753 1754 1755 1756 1757 1758 1759 1760 1761 1762 1763 1764 1765 1766 1767 1768 1769 1770 1771 1772 1773 1774 1775 1776 1777 1778 1779 1780 1781 1782 1783 1784 1785 1786 1787 1788 1789 1790 1791 1792 1793 1794 1795 1796 1797 1798 1799 1800 1801 1802 1803 1804 1805 1806 1807 1808 1809 1810 1811 1812 1813 1814 1815 1816 1817 1818 1819 1820 1821 1822 1823 1824 1825 1826 1827 1828 1829 1830 1831 1832 1833 1834 1835 1836 1837 1838 1839 1840 1841 1842 1843 1844 1845 1846 1847 1848 1849 1850 1851 1852 1853 1854 1855 1856 1857 1858 1859 1860 1861 1862 1863 1864 1865 1866 1867 1868 1869 1870 1871 1872 1873 1874 1875 1876 1877 1878 1879 1880 1881 1882 1883 1884 1885 1886 1887 1888 1889 1890 1891 1892 1893 1894 1895 1896 1897 1898 1899 1900 1901 1902 1903 1904 1905 1906 1907 1908 1909 1910 1911 1912 1913 1914 1915 1916 1917 1918 1919 1920 1921 1922 1923 1924 1925 1926 1927 1928 1929 1930 1931 1932 1933 1934 1935 1936 1937 1938 1939 1940 1941 1942 1943 1944 1945 1946 1947 1948 1949 1950 1951 1952 1953 1954 1955 1956 1957 1958 1959 1960 1961 1962 1963 1964 1965 1966 1967 1968 1969 1970 1971 1972 1973 1974 1975 1976 1977 1978 1979 1980 1981 1982 1983 1984 1985 1986 1987 1988 1989 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 2026 2027 2028 2029 2030 2031 2032 2033 2034 2035 2036 2037 2038 2039 2040 2041 2042 2043 2044 2045 2046 2047 2048 2049 2050 2051 2052 2053 2054 2055 2056 2057 2058 2059 2060 2061 2062 2063 2064 2065 2066 2067 2068 2069 2070 2071 2072 2073 2074 2075 2076 2077 2078 2079 2080 2081 2082 2083 2084 2085 2086 2087 2088 2089 2090 2091 2092 2093 2094 2095 2096 2097 2098 2099 2100 2101 2102 2103 2104 2105 2106 2107 2108 2109 2110 2111 2112 2113 2114 2115 2116 2117 2118 2119 2120 2121 2122 2123 2124 2125 2126 2127 2128 2129 2130 2131 2132 2133 2134 2135 2136 2137 2138 2139 2140 2141 2142 2143 2144 2145 2146 2147 2148 2149 2150 2151 2152 2153 2154 2155 2156 2157 2158 2159 2160 2161 2162 2163 2164 2165 2166 2167 2168 2169 2170 2171 2172 2173 2174 2175 2176 2177 2178 2179 2180 2181 2182 2183 2184 2185 2186 2187 2188 2189 2190 2191 2192 2193 2194 2195 2196 2197 2198 2199 2200 2201 2202 2203 2204 2205 2206 2207 2208 2209 2210 2211 2212 2213 2214 2215 2216 2217 2218 2219 2220 2221 2222 2223 2224 2225 2226 2227 2228 2229 2230 2231 2232 2233 2234 2235 2236 2237 2238 2239 2240 2241 2242 2243 2244 2245 2246 2247 2248 2249 2250 2251 2252 2253 2254 2255 2256 2257 2258 2259 2260 2261 2262 2263 2264 2265 2266 2267 2268 2269 2270 2271 2272 2273 2274 2275 2276 2277 2278 2279 2280 2281 2282 2283 2284 2285 2286 2287 2288 2289 2290 2291 2292 2293 2294 2295 2296 2297 2298 2299 2300 2301 2302 2303 2304 2305 2306 2307 2308 2309 2310 2311 2312 2313 2314 2315 2316 2317 2318 2319 2320 2321 2322 2323 2324 2325 2326 2327 2328 2329 2330 2331 2332 2333 2334 2335 2336 2337 2338 2339 2340 2341 2342 2343 2344 2345 2346 2347 2348 2349 2350 2351 2352 2353 2354 2355 2356 2357 2358 2359 2360 2361 2362 2363 2364 2365 2366 2367 2368 2369 2370 2371 2372 2373 2374 2375 2376 2377 2378 2379 2380 2381 2382 2383 2384 2385 2386 2387 2388 2389 2390 2391 2392 2393 2394 2395 2396 2397 2398 2399 2400 2401 2402 2403 2404 2405 2406 2407 2408 2409 2410 2411 2412 2413 2414 2415 2416 2417 2418 2419 2420 2421 2422 2423 2424 2425 2426 2427 2428 2429 2430 2431 2432 2433 2434 2435 2436 2437 2438 2439 2440 2441 2442 2443 2444 2445 2446 2447 2448 2449 2450 2451 2452 2453 2454 2455 2456 2457 2458 2459 2460 2461 2462 2463 2464 2465 2466 2467 2468 2469 2470 2471 2472 2473 2474 2475 2476 2477 2478 2479 2480 2481 2482 2483 2484 2485 2486 2487 2488 2489 2490 2491 2492 2493 2494 2495 2496 2497 2498 2499 2500 2501 2502 2503 2504 2505 2506 2507 2508 2509 2510 2511 2512 2513 2514 2515 2516 2517 2518 2519 2520 2521 2522 2523 2524 2525 2526 2527 2528 2529 2530 2531 2532 2533 2534 2535 2536 2537 2538 2539 2540 2541 2542 2543 2544 2545 2546 2547 2548 2549 2550 2551 2552 2553 2554 2555 2556 2557 2558 2559 2560 2561 2562 2563 2564 2565 2566 2567 2568 2569 2570 2571 2572 2573 2574 2575 2576 2577 2578 2579 2580 2581 2582 2583 2584 2585 2586 2587 2588 2589 2590 2591 2592 2593 2594 2595 2596 2597 2598 2599 2600 2601 2602 2603 2604 2605 2606 2607 2608 2609 2610 2611 2612 2613 2614 2615 2616 2617 2618 2619 2620 2621 2622 2623 2624 2625 2626 2627 2628 2629 2630 2631 2632 2633 2634 2635 2636 2637 2638 2639 2640 2641 2642 2643 2644 2645 2646 2647 2648 2649 2650 2651 2652 2653 2654 2655 2656 2657 2658 2659 2660 2661 2662 2663 2664 2665 2666 2667 2668 2669 2670 2671 2672 2673 2674 2675 2676 2677 2678 2679 2680 2681 2682 2683 2684 2685 2686 2687 2688 2689 2690 2691 2692 2693 2694 2695 2696 2697 2698 2699 2700 2701 2702 2703 2704 2705 2706 2707 2708 2709 2710 2711 2712 2713 2714 2715 2716 2717 2718 2719 2720 2721 2722 2723 2724 2725 2726 2727 2728 2729 2730 2731 2732 2733 2734 2735 2736 2737 2738 2739 2740 2741 2742 2743 2744 2745 2746 2747 2748 2749 2750 2751 2752 2753 2754 2755 2756 2757 2758 2759 2760 2761 2762 2763 2764 2765 2766 2767 2768 2769 2770 2771 2772 2773 2774 2775 2776 2777 2778 2779 2780 2781 2782 2783 2784 2785 2786 2787 2788 2789 2790 2791 2792 2793 2794 2795 2796 2797 2798 2799 2800 2801 2802 2803 2804 2805 2806 2807 2808 2809 2810 2811 2812 2813 2814 2815 2816 2817 2818 2819 2820 2821 2822 2823 2824 2825 2826 2827 2828 2829 2830 2831 2832 2833 2834 2835 2836 2837 2838 2839 2840 2841 2842 2843 2844 2845 2846 2847 2848 2849 2850 2851 2852 2853 2854 2855 2856 2857 2858 2859 2860 2861 2862 2863 2864 2865 2866 2867 2868 2869 2870 2871 2872 2873 2874 2875 2876 2877 2878 2879 2880 2881 2882 2883 2884 2885 2886 2887 2888 2889 2890 2891 2892 2893 2894 2895 2896 2897 2898 2899 2900 2901 2902 2903 2904 2905 2906 2907 2908 2909 2910 2911 2912 2913 2914 2915 2916 2917 2918 2919 2920 2921 2922 2923 2924 2925 2926 2927 2928 2929 2930 2931 2932 2933 2934 2935 2936 2937 2938 2939 2940 2941 2942 2943 2944 2945 2946 2947 2948 2949 2950 2951 2952 2953 2954 2955 2956 2957 2958 2959 2960 2961 2962 2963 2964 2965 2966 2967 2968 2969 2970 2971 2972 2973 2974 2975 2976 2977 2978 2979 2980 2981 2982 2983 2984 2985 2986 2987 2988 2989 2990 2991 2992 2993 2994 2995 2996 2997 2998 2999 3000 3001 3002 3003 3004 3005 3006 3007 3008 3009 3010 3011 3012 3013 3014 3015 3016 3017 3018 3019 3020 3021 3022 3023 3024 3025 3026 3027 3028 3029 3030 3031 3032 3033 3034 3035 3036 3037 3038 3039 3040 3041 3042 3043 3044 3045 3046 3047 3048 3049 3050 3051 3052 3053 3054 3055 3056 3057 3058 3059 3060 3061 3062 3063 3064 3065 3066 3067 3068 3069 3070 3071 3072 3073 3074 3075 3076 3077 3078 3079 3080 3081 3082 3083 3084 3085 3086 3087
#![allow( unused_parens, clippy::excessive_precision, clippy::missing_safety_doc, clippy::not_unsafe_ptr_arg_deref, clippy::should_implement_trait, clippy::too_many_arguments, clippy::unused_unit, )] //! # Machine Learning //! //! The Machine Learning Library (MLL) is a set of classes and functions for statistical //! classification, regression, and clustering of data. //! //! Most of the classification and regression algorithms are implemented as C++ classes. As the //! algorithms have different sets of features (like an ability to handle missing measurements or //! categorical input variables), there is a little common ground between the classes. This common //! ground is defined by the class cv::ml::StatModel that all the other ML classes are derived from. //! //! See detailed overview here: @ref ml_intro. use crate::{mod_prelude::*, core, sys, types}; pub mod prelude { pub use { super::ParamGridTrait, super::TrainData, super::StatModel, super::NormalBayesClassifier, super::KNearest, super::SVM_Kernel, super::SVM, super::EM, super::DTrees_NodeTrait, super::DTrees_SplitTrait, super::DTrees, super::RTrees, super::Boost, super::ANN_MLP, super::LogisticRegression, super::SVMSGD }; } /// each training sample occupies a column of samples pub const COL_SAMPLE: i32 = 1; pub const EM_DEFAULT_MAX_ITERS: i32 = 100; pub const EM_DEFAULT_NCLUSTERS: i32 = 5; pub const EM_START_AUTO_STEP: i32 = 0; pub const EM_START_E_STEP: i32 = 1; pub const EM_START_M_STEP: i32 = 2; /// each training sample is a row of samples pub const ROW_SAMPLE: i32 = 0; pub const TEST_ERROR: i32 = 0; pub const TRAIN_ERROR: i32 = 1; /// categorical variables pub const VAR_CATEGORICAL: i32 = 1; /// same as VAR_ORDERED pub const VAR_NUMERICAL: i32 = 0; /// ordered variables pub const VAR_ORDERED: i32 = 0; /// possible activation functions #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum ANN_MLP_ActivationFunctions { /// Identity function: 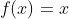 IDENTITY = 0, /// Symmetrical sigmoid: 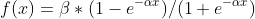 /// /// Note: /// If you are using the default sigmoid activation function with the default parameter values /// fparam1=0 and fparam2=0 then the function used is y = 1.7159\*tanh(2/3 \* x), so the output /// will range from [-1.7159, 1.7159], instead of [0,1]. SIGMOID_SYM = 1, /// Gaussian function: 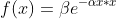 GAUSSIAN = 2, /// ReLU function: 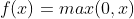 RELU = 3, /// Leaky ReLU function: for x>0 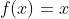 and x<=0 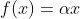 LEAKYRELU = 4, } opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::ANN_MLP_ActivationFunctions } /// Train options #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum ANN_MLP_TrainFlags { /// Update the network weights, rather than compute them from scratch. In the latter case /// the weights are initialized using the Nguyen-Widrow algorithm. UPDATE_WEIGHTS = 1, /// Do not normalize the input vectors. If this flag is not set, the training algorithm /// normalizes each input feature independently, shifting its mean value to 0 and making the /// standard deviation equal to 1. If the network is assumed to be updated frequently, the new /// training data could be much different from original one. In this case, you should take care /// of proper normalization. NO_INPUT_SCALE = 2, /// Do not normalize the output vectors. If the flag is not set, the training algorithm /// normalizes each output feature independently, by transforming it to the certain range /// depending on the used activation function. NO_OUTPUT_SCALE = 4, } opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::ANN_MLP_TrainFlags } /// Available training methods #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum ANN_MLP_TrainingMethods { /// The back-propagation algorithm. BACKPROP = 0, /// The RPROP algorithm. See [RPROP93](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_RPROP93) for details. RPROP = 1, /// The simulated annealing algorithm. See [Kirkpatrick83](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Kirkpatrick83) for details. ANNEAL = 2, } opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::ANN_MLP_TrainingMethods } /// Boosting type. /// Gentle AdaBoost and Real AdaBoost are often the preferable choices. #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum Boost_Types { /// Discrete AdaBoost. DISCRETE = 0, /// Real AdaBoost. It is a technique that utilizes confidence-rated predictions /// and works well with categorical data. REAL = 1, /// LogitBoost. It can produce good regression fits. LOGIT = 2, /// Gentle AdaBoost. It puts less weight on outlier data points and for that /// reason is often good with regression data. GENTLE = 3, } opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::Boost_Types } /// Predict options #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum DTrees_Flags { PREDICT_AUTO = 0, PREDICT_SUM = 256, PREDICT_MAX_VOTE = 512, PREDICT_MASK = 768, } opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::DTrees_Flags } /// Type of covariation matrices #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum EM_Types { /// A scaled identity matrix 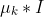. There is the only /// parameter 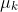 to be estimated for each matrix. The option may be used in special cases, /// when the constraint is relevant, or as a first step in the optimization (for example in case /// when the data is preprocessed with PCA). The results of such preliminary estimation may be /// passed again to the optimization procedure, this time with /// covMatType=EM::COV_MAT_DIAGONAL. COV_MAT_SPHERICAL = 0, /// A diagonal matrix with positive diagonal elements. The number of /// free parameters is d for each matrix. This is most commonly used option yielding good /// estimation results. COV_MAT_DIAGONAL = 1, /// A symmetric positively defined matrix. The number of free /// parameters in each matrix is about 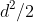. It is not recommended to use this option, unless /// there is pretty accurate initial estimation of the parameters and/or a huge number of /// training samples. COV_MAT_GENERIC = 2, // A symmetric positively defined matrix. The number of free // parameters in each matrix is about 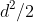. It is not recommended to use this option, unless // there is pretty accurate initial estimation of the parameters and/or a huge number of // training samples. // COV_MAT_DEFAULT = 1 as isize, // duplicate discriminant } opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::EM_Types } /// %Error types #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum ErrorTypes { TEST_ERROR = 0, TRAIN_ERROR = 1, } opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::ErrorTypes } /// Implementations of KNearest algorithm #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum KNearest_Types { BRUTE_FORCE = 1, KDTREE = 2, } opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::KNearest_Types } /// Training methods #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum LogisticRegression_Methods { BATCH = 0, /// Set MiniBatchSize to a positive integer when using this method. MINI_BATCH = 1, } opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::LogisticRegression_Methods } /// Regularization kinds #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum LogisticRegression_RegKinds { /// Regularization disabled REG_DISABLE = -1, /// %L1 norm REG_L1 = 0, /// %L2 norm REG_L2 = 1, } opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::LogisticRegression_RegKinds } /// Margin type. #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum SVMSGD_MarginType { /// General case, suits to the case of non-linearly separable sets, allows outliers. SOFT_MARGIN = 0, /// More accurate for the case of linearly separable sets. HARD_MARGIN = 1, } opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::SVMSGD_MarginType } /// SVMSGD type. /// ASGD is often the preferable choice. #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum SVMSGD_SvmsgdType { /// Stochastic Gradient Descent SGD = 0, /// Average Stochastic Gradient Descent ASGD = 1, } opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::SVMSGD_SvmsgdType } /// %SVM kernel type /// /// A comparison of different kernels on the following 2D test case with four classes. Four /// SVM::C_SVC SVMs have been trained (one against rest) with auto_train. Evaluation on three /// different kernels (SVM::CHI2, SVM::INTER, SVM::RBF). The color depicts the class with max score. /// Bright means max-score \> 0, dark means max-score \< 0. ///  #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum SVM_KernelTypes { /// Returned by SVM::getKernelType in case when custom kernel has been set CUSTOM = -1, /// Linear kernel. No mapping is done, linear discrimination (or regression) is /// done in the original feature space. It is the fastest option. 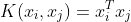. LINEAR = 0, /// Polynomial kernel: /// 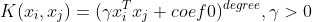. POLY = 1, /// Radial basis function (RBF), a good choice in most cases. /// 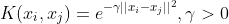. RBF = 2, /// Sigmoid kernel: 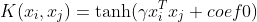. SIGMOID = 3, /// Exponential Chi2 kernel, similar to the RBF kernel: /// 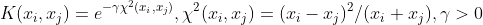. CHI2 = 4, /// Histogram intersection kernel. A fast kernel. 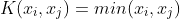. INTER = 5, } opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::SVM_KernelTypes } /// %SVM params type #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum SVM_ParamTypes { C = 0, GAMMA = 1, P = 2, NU = 3, COEF = 4, DEGREE = 5, } opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::SVM_ParamTypes } /// %SVM type #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum SVM_Types { /// C-Support Vector Classification. n-class classification (n 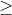 2), allows /// imperfect separation of classes with penalty multiplier C for outliers. C_SVC = 100, /// -Support Vector Classification. n-class classification with possible /// imperfect separation. Parameter  (in the range 0..1, the larger the value, the smoother /// the decision boundary) is used instead of C. NU_SVC = 101, /// Distribution Estimation (One-class %SVM). All the training data are from /// the same class, %SVM builds a boundary that separates the class from the rest of the feature /// space. ONE_CLASS = 102, /// -Support Vector Regression. The distance between feature vectors /// from the training set and the fitting hyper-plane must be less than p. For outliers the /// penalty multiplier C is used. EPS_SVR = 103, /// -Support Vector Regression. 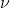 is used instead of p. /// See [LibSVM](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_LibSVM) for details. NU_SVR = 104, } opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::SVM_Types } /// Sample types #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum SampleTypes { /// each training sample is a row of samples ROW_SAMPLE = 0, /// each training sample occupies a column of samples COL_SAMPLE = 1, } opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::SampleTypes } /// Predict options #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum StatModel_Flags { UPDATE_MODEL = 1, // makes the method return the raw results (the sum), not the class label // RAW_OUTPUT = 1 as isize, // duplicate discriminant COMPRESSED_INPUT = 2, PREPROCESSED_INPUT = 4, } opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::StatModel_Flags } /// Variable types #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum VariableTypes { /// same as VAR_ORDERED VAR_NUMERICAL = 0, // ordered variables // VAR_ORDERED = 0 as isize, // duplicate discriminant /// categorical variables VAR_CATEGORICAL = 1, } opencv_type_enum! { crate::ml::VariableTypes } pub type ANN_MLP_ANNEAL = dyn crate::ml::ANN_MLP; /// Creates test set pub fn create_concentric_spheres_test_set(nsamples: i32, nfeatures: i32, nclasses: i32, samples: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, responses: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> { output_array_arg!(samples); output_array_arg!(responses); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_createConcentricSpheresTestSet_int_int_int_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(nsamples, nfeatures, nclasses, samples.as_raw__OutputArray(), responses.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Generates _sample_ from multivariate normal distribution /// /// ## Parameters /// * mean: an average row vector /// * cov: symmetric covariation matrix /// * nsamples: returned samples count /// * samples: returned samples array pub fn rand_mv_normal(mean: &dyn core::ToInputArray, cov: &dyn core::ToInputArray, nsamples: i32, samples: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(mean); input_array_arg!(cov); output_array_arg!(samples); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_randMVNormal_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int_const__OutputArrayR(mean.as_raw__InputArray(), cov.as_raw__InputArray(), nsamples, samples.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Artificial Neural Networks - Multi-Layer Perceptrons. /// /// Unlike many other models in ML that are constructed and trained at once, in the MLP model these /// steps are separated. First, a network with the specified topology is created using the non-default /// constructor or the method ANN_MLP::create. All the weights are set to zeros. Then, the network is /// trained using a set of input and output vectors. The training procedure can be repeated more than /// once, that is, the weights can be adjusted based on the new training data. /// /// Additional flags for StatModel::train are available: ANN_MLP::TrainFlags. /// ## See also /// @ref ml_intro_ann pub trait ANN_MLP: crate::ml::StatModel { fn as_raw_ANN_MLP(&self) -> *const c_void; fn as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(&mut self) -> *mut c_void; /// Sets training method and common parameters. /// ## Parameters /// * method: Default value is ANN_MLP::RPROP. See ANN_MLP::TrainingMethods. /// * param1: passed to setRpropDW0 for ANN_MLP::RPROP and to setBackpropWeightScale for ANN_MLP::BACKPROP and to initialT for ANN_MLP::ANNEAL. /// * param2: passed to setRpropDWMin for ANN_MLP::RPROP and to setBackpropMomentumScale for ANN_MLP::BACKPROP and to finalT for ANN_MLP::ANNEAL. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * param1: 0 /// * param2: 0 fn set_train_method(&mut self, method: i32, param1: f64, param2: f64) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setTrainMethod_int_double_double(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), method, param1, param2) }.into_result() } /// Returns current training method fn get_train_method(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getTrainMethod_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP()) }.into_result() } /// Initialize the activation function for each neuron. /// Currently the default and the only fully supported activation function is ANN_MLP::SIGMOID_SYM. /// ## Parameters /// * type: The type of activation function. See ANN_MLP::ActivationFunctions. /// * param1: The first parameter of the activation function, 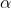. Default value is 0. /// * param2: The second parameter of the activation function, 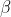. Default value is 0. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * param1: 0 /// * param2: 0 fn set_activation_function(&mut self, typ: i32, param1: f64, param2: f64) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setActivationFunction_int_double_double(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), typ, param1, param2) }.into_result() } /// Integer vector specifying the number of neurons in each layer including the input and output layers. /// The very first element specifies the number of elements in the input layer. /// The last element - number of elements in the output layer. Default value is empty Mat. /// ## See also /// getLayerSizes fn set_layer_sizes(&mut self, _layer_sizes: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(_layer_sizes); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setLayerSizes_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), _layer_sizes.as_raw__InputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Integer vector specifying the number of neurons in each layer including the input and output layers. /// The very first element specifies the number of elements in the input layer. /// The last element - number of elements in the output layer. /// ## See also /// setLayerSizes fn get_layer_sizes(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getLayerSizes_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Termination criteria of the training algorithm. /// You can specify the maximum number of iterations (maxCount) and/or how much the error could /// change between the iterations to make the algorithm continue (epsilon). Default value is /// TermCriteria(TermCriteria::MAX_ITER + TermCriteria::EPS, 1000, 0.01). /// ## See also /// setTermCriteria fn get_term_criteria(&self) -> Result<core::TermCriteria> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getTermCriteria_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP()) }.into_result() } /// Termination criteria of the training algorithm. /// You can specify the maximum number of iterations (maxCount) and/or how much the error could /// change between the iterations to make the algorithm continue (epsilon). Default value is /// TermCriteria(TermCriteria::MAX_ITER + TermCriteria::EPS, 1000, 0.01). /// ## See also /// setTermCriteria getTermCriteria fn set_term_criteria(&mut self, val: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setTermCriteria_TermCriteria(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), val.opencv_as_extern()) }.into_result() } /// BPROP: Strength of the weight gradient term. /// The recommended value is about 0.1. Default value is 0.1. /// ## See also /// setBackpropWeightScale fn get_backprop_weight_scale(&self) -> Result<f64> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getBackpropWeightScale_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP()) }.into_result() } /// BPROP: Strength of the weight gradient term. /// The recommended value is about 0.1. Default value is 0.1. /// ## See also /// setBackpropWeightScale getBackpropWeightScale fn set_backprop_weight_scale(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setBackpropWeightScale_double(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), val) }.into_result() } /// BPROP: Strength of the momentum term (the difference between weights on the 2 previous iterations). /// This parameter provides some inertia to smooth the random fluctuations of the weights. It can /// vary from 0 (the feature is disabled) to 1 and beyond. The value 0.1 or so is good enough. /// Default value is 0.1. /// ## See also /// setBackpropMomentumScale fn get_backprop_momentum_scale(&self) -> Result<f64> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getBackpropMomentumScale_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP()) }.into_result() } /// BPROP: Strength of the momentum term (the difference between weights on the 2 previous iterations). /// This parameter provides some inertia to smooth the random fluctuations of the weights. It can /// vary from 0 (the feature is disabled) to 1 and beyond. The value 0.1 or so is good enough. /// Default value is 0.1. /// ## See also /// setBackpropMomentumScale getBackpropMomentumScale fn set_backprop_momentum_scale(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setBackpropMomentumScale_double(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), val) }.into_result() } /// RPROP: Initial value 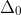 of update-values 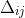. /// Default value is 0.1. /// ## See also /// setRpropDW0 fn get_rprop_dw0(&self) -> Result<f64> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getRpropDW0_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP()) }.into_result() } /// RPROP: Initial value 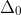 of update-values 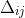. /// Default value is 0.1. /// ## See also /// setRpropDW0 getRpropDW0 fn set_rprop_dw0(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setRpropDW0_double(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), val) }.into_result() } /// RPROP: Increase factor 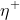. /// It must be \>1. Default value is 1.2. /// ## See also /// setRpropDWPlus fn get_rprop_dw_plus(&self) -> Result<f64> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getRpropDWPlus_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP()) }.into_result() } /// RPROP: Increase factor 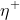. /// It must be \>1. Default value is 1.2. /// ## See also /// setRpropDWPlus getRpropDWPlus fn set_rprop_dw_plus(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setRpropDWPlus_double(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), val) }.into_result() } /// RPROP: Decrease factor 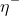. /// It must be \<1. Default value is 0.5. /// ## See also /// setRpropDWMinus fn get_rprop_dw_minus(&self) -> Result<f64> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getRpropDWMinus_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP()) }.into_result() } /// RPROP: Decrease factor 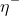. /// It must be \<1. Default value is 0.5. /// ## See also /// setRpropDWMinus getRpropDWMinus fn set_rprop_dw_minus(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setRpropDWMinus_double(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), val) }.into_result() } /// RPROP: Update-values lower limit 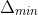. /// It must be positive. Default value is FLT_EPSILON. /// ## See also /// setRpropDWMin fn get_rprop_dw_min(&self) -> Result<f64> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getRpropDWMin_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP()) }.into_result() } /// RPROP: Update-values lower limit 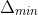. /// It must be positive. Default value is FLT_EPSILON. /// ## See also /// setRpropDWMin getRpropDWMin fn set_rprop_dw_min(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setRpropDWMin_double(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), val) }.into_result() } /// RPROP: Update-values upper limit 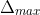. /// It must be \>1. Default value is 50. /// ## See also /// setRpropDWMax fn get_rprop_dw_max(&self) -> Result<f64> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getRpropDWMax_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP()) }.into_result() } /// RPROP: Update-values upper limit 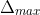. /// It must be \>1. Default value is 50. /// ## See also /// setRpropDWMax getRpropDWMax fn set_rprop_dw_max(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setRpropDWMax_double(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), val) }.into_result() } /// ANNEAL: Update initial temperature. /// It must be \>=0. Default value is 10. /// ## See also /// setAnnealInitialT fn get_anneal_initial_t(&self) -> Result<f64> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getAnnealInitialT_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP()) }.into_result() } /// ANNEAL: Update initial temperature. /// It must be \>=0. Default value is 10. /// ## See also /// setAnnealInitialT getAnnealInitialT fn set_anneal_initial_t(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setAnnealInitialT_double(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), val) }.into_result() } /// ANNEAL: Update final temperature. /// It must be \>=0 and less than initialT. Default value is 0.1. /// ## See also /// setAnnealFinalT fn get_anneal_final_t(&self) -> Result<f64> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getAnnealFinalT_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP()) }.into_result() } /// ANNEAL: Update final temperature. /// It must be \>=0 and less than initialT. Default value is 0.1. /// ## See also /// setAnnealFinalT getAnnealFinalT fn set_anneal_final_t(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setAnnealFinalT_double(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), val) }.into_result() } /// ANNEAL: Update cooling ratio. /// It must be \>0 and less than 1. Default value is 0.95. /// ## See also /// setAnnealCoolingRatio fn get_anneal_cooling_ratio(&self) -> Result<f64> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getAnnealCoolingRatio_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP()) }.into_result() } /// ANNEAL: Update cooling ratio. /// It must be \>0 and less than 1. Default value is 0.95. /// ## See also /// setAnnealCoolingRatio getAnnealCoolingRatio fn set_anneal_cooling_ratio(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setAnnealCoolingRatio_double(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), val) }.into_result() } /// ANNEAL: Update iteration per step. /// It must be \>0 . Default value is 10. /// ## See also /// setAnnealItePerStep fn get_anneal_ite_per_step(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getAnnealItePerStep_const(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP()) }.into_result() } /// ANNEAL: Update iteration per step. /// It must be \>0 . Default value is 10. /// ## See also /// setAnnealItePerStep getAnnealItePerStep fn set_anneal_ite_per_step(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setAnnealItePerStep_int(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), val) }.into_result() } /// Set/initialize anneal RNG fn set_anneal_energy_rng(&mut self, rng: &core::RNG) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_setAnnealEnergyRNG_const_RNGR(self.as_raw_mut_ANN_MLP(), rng.as_raw_RNG()) }.into_result() } fn get_weights(&self, layer_idx: i32) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_getWeights_const_int(self.as_raw_ANN_MLP(), layer_idx) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } } impl dyn ANN_MLP + '_ { /// Creates empty model /// /// Use StatModel::train to train the model, Algorithm::load\<ANN_MLP\>(filename) to load the pre-trained model. /// Note that the train method has optional flags: ANN_MLP::TrainFlags. pub fn create() -> Result<core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::ANN_MLP>> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_create() }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::ANN_MLP>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Loads and creates a serialized ANN from a file /// /// Use ANN::save to serialize and store an ANN to disk. /// Load the ANN from this file again, by calling this function with the path to the file. /// /// ## Parameters /// * filepath: path to serialized ANN pub fn load(filepath: &str) -> Result<core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::ANN_MLP>> { extern_container_arg!(filepath); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ANN_MLP_load_const_StringR(filepath.opencv_as_extern()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::ANN_MLP>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } } /// Boosted tree classifier derived from DTrees /// ## See also /// @ref ml_intro_boost pub trait Boost: crate::ml::DTrees { fn as_raw_Boost(&self) -> *const c_void; fn as_raw_mut_Boost(&mut self) -> *mut c_void; /// Type of the boosting algorithm. /// See Boost::Types. Default value is Boost::REAL. /// ## See also /// setBoostType fn get_boost_type(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_Boost_getBoostType_const(self.as_raw_Boost()) }.into_result() } /// Type of the boosting algorithm. /// See Boost::Types. Default value is Boost::REAL. /// ## See also /// setBoostType getBoostType fn set_boost_type(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_Boost_setBoostType_int(self.as_raw_mut_Boost(), val) }.into_result() } /// The number of weak classifiers. /// Default value is 100. /// ## See also /// setWeakCount fn get_weak_count(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_Boost_getWeakCount_const(self.as_raw_Boost()) }.into_result() } /// The number of weak classifiers. /// Default value is 100. /// ## See also /// setWeakCount getWeakCount fn set_weak_count(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_Boost_setWeakCount_int(self.as_raw_mut_Boost(), val) }.into_result() } /// A threshold between 0 and 1 used to save computational time. /// Samples with summary weight 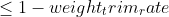 do not participate in the *next* /// iteration of training. Set this parameter to 0 to turn off this functionality. Default value is 0.95. /// ## See also /// setWeightTrimRate fn get_weight_trim_rate(&self) -> Result<f64> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_Boost_getWeightTrimRate_const(self.as_raw_Boost()) }.into_result() } /// A threshold between 0 and 1 used to save computational time. /// Samples with summary weight 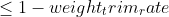 do not participate in the *next* /// iteration of training. Set this parameter to 0 to turn off this functionality. Default value is 0.95. /// ## See also /// setWeightTrimRate getWeightTrimRate fn set_weight_trim_rate(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_Boost_setWeightTrimRate_double(self.as_raw_mut_Boost(), val) }.into_result() } } impl dyn Boost + '_ { /// Creates the empty model. /// Use StatModel::train to train the model, Algorithm::load\<Boost\>(filename) to load the pre-trained model. pub fn create() -> Result<core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::Boost>> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_Boost_create() }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::Boost>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Loads and creates a serialized Boost from a file /// /// Use Boost::save to serialize and store an RTree to disk. /// Load the Boost from this file again, by calling this function with the path to the file. /// Optionally specify the node for the file containing the classifier /// /// ## Parameters /// * filepath: path to serialized Boost /// * nodeName: name of node containing the classifier /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * node_name: String() pub fn load(filepath: &str, node_name: &str) -> Result<core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::Boost>> { extern_container_arg!(filepath); extern_container_arg!(node_name); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_Boost_load_const_StringR_const_StringR(filepath.opencv_as_extern(), node_name.opencv_as_extern()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::Boost>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } } /// The class represents a single decision tree or a collection of decision trees. /// /// The current public interface of the class allows user to train only a single decision tree, however /// the class is capable of storing multiple decision trees and using them for prediction (by summing /// responses or using a voting schemes), and the derived from DTrees classes (such as RTrees and Boost) /// use this capability to implement decision tree ensembles. /// ## See also /// @ref ml_intro_trees pub trait DTrees: crate::ml::StatModel { fn as_raw_DTrees(&self) -> *const c_void; fn as_raw_mut_DTrees(&mut self) -> *mut c_void; /// Cluster possible values of a categorical variable into K\<=maxCategories clusters to /// find a suboptimal split. /// If a discrete variable, on which the training procedure tries to make a split, takes more than /// maxCategories values, the precise best subset estimation may take a very long time because the /// algorithm is exponential. Instead, many decision trees engines (including our implementation) /// try to find sub-optimal split in this case by clustering all the samples into maxCategories /// clusters that is some categories are merged together. The clustering is applied only in n \> /// 2-class classification problems for categorical variables with N \> max_categories possible /// values. In case of regression and 2-class classification the optimal split can be found /// efficiently without employing clustering, thus the parameter is not used in these cases. /// Default value is 10. /// ## See also /// setMaxCategories fn get_max_categories(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_getMaxCategories_const(self.as_raw_DTrees()) }.into_result() } /// Cluster possible values of a categorical variable into K\<=maxCategories clusters to /// find a suboptimal split. /// If a discrete variable, on which the training procedure tries to make a split, takes more than /// maxCategories values, the precise best subset estimation may take a very long time because the /// algorithm is exponential. Instead, many decision trees engines (including our implementation) /// try to find sub-optimal split in this case by clustering all the samples into maxCategories /// clusters that is some categories are merged together. The clustering is applied only in n \> /// 2-class classification problems for categorical variables with N \> max_categories possible /// values. In case of regression and 2-class classification the optimal split can be found /// efficiently without employing clustering, thus the parameter is not used in these cases. /// Default value is 10. /// ## See also /// setMaxCategories getMaxCategories fn set_max_categories(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_setMaxCategories_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees(), val) }.into_result() } /// The maximum possible depth of the tree. /// That is the training algorithms attempts to split a node while its depth is less than maxDepth. /// The root node has zero depth. The actual depth may be smaller if the other termination criteria /// are met (see the outline of the training procedure @ref ml_intro_trees "here"), and/or if the /// tree is pruned. Default value is INT_MAX. /// ## See also /// setMaxDepth fn get_max_depth(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_getMaxDepth_const(self.as_raw_DTrees()) }.into_result() } /// The maximum possible depth of the tree. /// That is the training algorithms attempts to split a node while its depth is less than maxDepth. /// The root node has zero depth. The actual depth may be smaller if the other termination criteria /// are met (see the outline of the training procedure @ref ml_intro_trees "here"), and/or if the /// tree is pruned. Default value is INT_MAX. /// ## See also /// setMaxDepth getMaxDepth fn set_max_depth(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_setMaxDepth_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees(), val) }.into_result() } /// If the number of samples in a node is less than this parameter then the node will not be split. /// /// Default value is 10. /// ## See also /// setMinSampleCount fn get_min_sample_count(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_getMinSampleCount_const(self.as_raw_DTrees()) }.into_result() } /// If the number of samples in a node is less than this parameter then the node will not be split. /// /// Default value is 10. /// ## See also /// setMinSampleCount getMinSampleCount fn set_min_sample_count(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_setMinSampleCount_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees(), val) }.into_result() } /// If CVFolds \> 1 then algorithms prunes the built decision tree using K-fold /// cross-validation procedure where K is equal to CVFolds. /// Default value is 10. /// ## See also /// setCVFolds fn get_cv_folds(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_getCVFolds_const(self.as_raw_DTrees()) }.into_result() } /// If CVFolds \> 1 then algorithms prunes the built decision tree using K-fold /// cross-validation procedure where K is equal to CVFolds. /// Default value is 10. /// ## See also /// setCVFolds getCVFolds fn set_cv_folds(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_setCVFolds_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees(), val) }.into_result() } /// If true then surrogate splits will be built. /// These splits allow to work with missing data and compute variable importance correctly. /// Default value is false. /// /// Note: currently it's not implemented. /// ## See also /// setUseSurrogates fn get_use_surrogates(&self) -> Result<bool> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_getUseSurrogates_const(self.as_raw_DTrees()) }.into_result() } /// If true then surrogate splits will be built. /// These splits allow to work with missing data and compute variable importance correctly. /// Default value is false. /// /// Note: currently it's not implemented. /// ## See also /// setUseSurrogates getUseSurrogates fn set_use_surrogates(&mut self, val: bool) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_setUseSurrogates_bool(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees(), val) }.into_result() } /// If true then a pruning will be harsher. /// This will make a tree more compact and more resistant to the training data noise but a bit less /// accurate. Default value is true. /// ## See also /// setUse1SERule fn get_use1_se_rule(&self) -> Result<bool> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_getUse1SERule_const(self.as_raw_DTrees()) }.into_result() } /// If true then a pruning will be harsher. /// This will make a tree more compact and more resistant to the training data noise but a bit less /// accurate. Default value is true. /// ## See also /// setUse1SERule getUse1SERule fn set_use1_se_rule(&mut self, val: bool) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_setUse1SERule_bool(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees(), val) }.into_result() } /// If true then pruned branches are physically removed from the tree. /// Otherwise they are retained and it is possible to get results from the original unpruned (or /// pruned less aggressively) tree. Default value is true. /// ## See also /// setTruncatePrunedTree fn get_truncate_pruned_tree(&self) -> Result<bool> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_getTruncatePrunedTree_const(self.as_raw_DTrees()) }.into_result() } /// If true then pruned branches are physically removed from the tree. /// Otherwise they are retained and it is possible to get results from the original unpruned (or /// pruned less aggressively) tree. Default value is true. /// ## See also /// setTruncatePrunedTree getTruncatePrunedTree fn set_truncate_pruned_tree(&mut self, val: bool) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_setTruncatePrunedTree_bool(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees(), val) }.into_result() } /// Termination criteria for regression trees. /// If all absolute differences between an estimated value in a node and values of train samples /// in this node are less than this parameter then the node will not be split further. Default /// value is 0.01f /// ## See also /// setRegressionAccuracy fn get_regression_accuracy(&self) -> Result<f32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_getRegressionAccuracy_const(self.as_raw_DTrees()) }.into_result() } /// Termination criteria for regression trees. /// If all absolute differences between an estimated value in a node and values of train samples /// in this node are less than this parameter then the node will not be split further. Default /// value is 0.01f /// ## See also /// setRegressionAccuracy getRegressionAccuracy fn set_regression_accuracy(&mut self, val: f32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_setRegressionAccuracy_float(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees(), val) }.into_result() } /// The array of a priori class probabilities, sorted by the class label value. /// /// The parameter can be used to tune the decision tree preferences toward a certain class. For /// example, if you want to detect some rare anomaly occurrence, the training base will likely /// contain much more normal cases than anomalies, so a very good classification performance /// will be achieved just by considering every case as normal. To avoid this, the priors can be /// specified, where the anomaly probability is artificially increased (up to 0.5 or even /// greater), so the weight of the misclassified anomalies becomes much bigger, and the tree is /// adjusted properly. /// /// You can also think about this parameter as weights of prediction categories which determine /// relative weights that you give to misclassification. That is, if the weight of the first /// category is 1 and the weight of the second category is 10, then each mistake in predicting /// the second category is equivalent to making 10 mistakes in predicting the first category. /// Default value is empty Mat. /// ## See also /// setPriors fn get_priors(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_getPriors_const(self.as_raw_DTrees()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// The array of a priori class probabilities, sorted by the class label value. /// /// The parameter can be used to tune the decision tree preferences toward a certain class. For /// example, if you want to detect some rare anomaly occurrence, the training base will likely /// contain much more normal cases than anomalies, so a very good classification performance /// will be achieved just by considering every case as normal. To avoid this, the priors can be /// specified, where the anomaly probability is artificially increased (up to 0.5 or even /// greater), so the weight of the misclassified anomalies becomes much bigger, and the tree is /// adjusted properly. /// /// You can also think about this parameter as weights of prediction categories which determine /// relative weights that you give to misclassification. That is, if the weight of the first /// category is 1 and the weight of the second category is 10, then each mistake in predicting /// the second category is equivalent to making 10 mistakes in predicting the first category. /// Default value is empty Mat. /// ## See also /// setPriors getPriors fn set_priors(&mut self, val: &core::Mat) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_setPriors_const_MatR(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees(), val.as_raw_Mat()) }.into_result() } /// Returns indices of root nodes fn get_roots(&self) -> Result<core::Vector::<i32>> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_getRoots_const(self.as_raw_DTrees()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Vector::<i32>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Returns all the nodes /// /// all the node indices are indices in the returned vector fn get_nodes(&self) -> Result<core::Vector::<crate::ml::DTrees_Node>> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_getNodes_const(self.as_raw_DTrees()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Vector::<crate::ml::DTrees_Node>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Returns all the splits /// /// all the split indices are indices in the returned vector fn get_splits(&self) -> Result<core::Vector::<crate::ml::DTrees_Split>> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_getSplits_const(self.as_raw_DTrees()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Vector::<crate::ml::DTrees_Split>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Returns all the bitsets for categorical splits /// /// Split::subsetOfs is an offset in the returned vector fn get_subsets(&self) -> Result<core::Vector::<i32>> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_getSubsets_const(self.as_raw_DTrees()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Vector::<i32>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } } impl dyn DTrees + '_ { /// Creates the empty model /// /// The static method creates empty decision tree with the specified parameters. It should be then /// trained using train method (see StatModel::train). Alternatively, you can load the model from /// file using Algorithm::load\<DTrees\>(filename). pub fn create() -> Result<core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::DTrees>> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_create() }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::DTrees>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Loads and creates a serialized DTrees from a file /// /// Use DTree::save to serialize and store an DTree to disk. /// Load the DTree from this file again, by calling this function with the path to the file. /// Optionally specify the node for the file containing the classifier /// /// ## Parameters /// * filepath: path to serialized DTree /// * nodeName: name of node containing the classifier /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * node_name: String() pub fn load(filepath: &str, node_name: &str) -> Result<core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::DTrees>> { extern_container_arg!(filepath); extern_container_arg!(node_name); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_load_const_StringR_const_StringR(filepath.opencv_as_extern(), node_name.opencv_as_extern()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::DTrees>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } } /// The class represents a decision tree node. pub trait DTrees_NodeTrait { fn as_raw_DTrees_Node(&self) -> *const c_void; fn as_raw_mut_DTrees_Node(&mut self) -> *mut c_void; /// Value at the node: a class label in case of classification or estimated /// function value in case of regression. fn value(&self) -> f64 { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_getPropValue_const(self.as_raw_DTrees_Node()) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: value") } /// Value at the node: a class label in case of classification or estimated /// function value in case of regression. fn set_value(&mut self, val: f64) -> () { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_setPropValue_double(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Node(), val) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: set_value") } /// Class index normalized to 0..class_count-1 range and assigned to the /// node. It is used internally in classification trees and tree ensembles. fn class_idx(&self) -> i32 { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_getPropClassIdx_const(self.as_raw_DTrees_Node()) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: class_idx") } /// Class index normalized to 0..class_count-1 range and assigned to the /// node. It is used internally in classification trees and tree ensembles. fn set_class_idx(&mut self, val: i32) -> () { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_setPropClassIdx_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Node(), val) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: set_class_idx") } /// Index of the parent node fn parent(&self) -> i32 { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_getPropParent_const(self.as_raw_DTrees_Node()) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: parent") } /// Index of the parent node fn set_parent(&mut self, val: i32) -> () { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_setPropParent_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Node(), val) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: set_parent") } /// Index of the left child node fn left(&self) -> i32 { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_getPropLeft_const(self.as_raw_DTrees_Node()) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: left") } /// Index of the left child node fn set_left(&mut self, val: i32) -> () { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_setPropLeft_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Node(), val) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: set_left") } /// Index of right child node fn right(&self) -> i32 { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_getPropRight_const(self.as_raw_DTrees_Node()) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: right") } /// Index of right child node fn set_right(&mut self, val: i32) -> () { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_setPropRight_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Node(), val) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: set_right") } /// Default direction where to go (-1: left or +1: right). It helps in the /// case of missing values. fn default_dir(&self) -> i32 { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_getPropDefaultDir_const(self.as_raw_DTrees_Node()) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: default_dir") } /// Default direction where to go (-1: left or +1: right). It helps in the /// case of missing values. fn set_default_dir(&mut self, val: i32) -> () { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_setPropDefaultDir_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Node(), val) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: set_default_dir") } /// Index of the first split fn split(&self) -> i32 { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_getPropSplit_const(self.as_raw_DTrees_Node()) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: split") } /// Index of the first split fn set_split(&mut self, val: i32) -> () { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_setPropSplit_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Node(), val) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: set_split") } } /// The class represents a decision tree node. pub struct DTrees_Node { ptr: *mut c_void } opencv_type_boxed! { DTrees_Node } impl Drop for DTrees_Node { fn drop(&mut self) { extern "C" { fn cv_DTrees_Node_delete(instance: *mut c_void); } unsafe { cv_DTrees_Node_delete(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Node()) }; } } impl DTrees_Node { #[inline] pub fn as_raw_DTrees_Node(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() } #[inline] pub fn as_raw_mut_DTrees_Node(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() } } unsafe impl Send for DTrees_Node {} impl crate::ml::DTrees_NodeTrait for DTrees_Node { #[inline] fn as_raw_DTrees_Node(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() } #[inline] fn as_raw_mut_DTrees_Node(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() } } impl DTrees_Node { pub fn default() -> Result<crate::ml::DTrees_Node> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Node_Node() }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { crate::ml::DTrees_Node::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } } /// The class represents split in a decision tree. pub trait DTrees_SplitTrait { fn as_raw_DTrees_Split(&self) -> *const c_void; fn as_raw_mut_DTrees_Split(&mut self) -> *mut c_void; /// Index of variable on which the split is created. fn var_idx(&self) -> i32 { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Split_getPropVarIdx_const(self.as_raw_DTrees_Split()) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: var_idx") } /// Index of variable on which the split is created. fn set_var_idx(&mut self, val: i32) -> () { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Split_setPropVarIdx_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Split(), val) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: set_var_idx") } /// If true, then the inverse split rule is used (i.e. left and right /// branches are exchanged in the rule expressions below). fn inversed(&self) -> bool { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Split_getPropInversed_const(self.as_raw_DTrees_Split()) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: inversed") } /// If true, then the inverse split rule is used (i.e. left and right /// branches are exchanged in the rule expressions below). fn set_inversed(&mut self, val: bool) -> () { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Split_setPropInversed_bool(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Split(), val) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: set_inversed") } /// The split quality, a positive number. It is used to choose the best split. fn quality(&self) -> f32 { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Split_getPropQuality_const(self.as_raw_DTrees_Split()) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: quality") } /// The split quality, a positive number. It is used to choose the best split. fn set_quality(&mut self, val: f32) -> () { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Split_setPropQuality_float(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Split(), val) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: set_quality") } /// Index of the next split in the list of splits for the node fn next(&self) -> i32 { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Split_getPropNext_const(self.as_raw_DTrees_Split()) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: next") } /// Index of the next split in the list of splits for the node fn set_next(&mut self, val: i32) -> () { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Split_setPropNext_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Split(), val) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: set_next") } /// < The threshold value in case of split on an ordered variable. /// The rule is: /// ```ignore /// if var_value < c /// then next_node <- left /// else next_node <- right /// ``` /// fn c(&self) -> f32 { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Split_getPropC_const(self.as_raw_DTrees_Split()) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: c") } /// < The threshold value in case of split on an ordered variable. /// The rule is: /// ```ignore /// if var_value < c /// then next_node <- left /// else next_node <- right /// ``` /// fn set_c(&mut self, val: f32) -> () { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Split_setPropC_float(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Split(), val) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: set_c") } /// < Offset of the bitset used by the split on a categorical variable. /// The rule is: /// ```ignore /// if bitset[var_value] == 1 /// then next_node <- left /// else next_node <- right /// ``` /// fn subset_ofs(&self) -> i32 { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Split_getPropSubsetOfs_const(self.as_raw_DTrees_Split()) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: subset_ofs") } /// < Offset of the bitset used by the split on a categorical variable. /// The rule is: /// ```ignore /// if bitset[var_value] == 1 /// then next_node <- left /// else next_node <- right /// ``` /// fn set_subset_ofs(&mut self, val: i32) -> () { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Split_setPropSubsetOfs_int(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Split(), val) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: set_subset_ofs") } } /// The class represents split in a decision tree. pub struct DTrees_Split { ptr: *mut c_void } opencv_type_boxed! { DTrees_Split } impl Drop for DTrees_Split { fn drop(&mut self) { extern "C" { fn cv_DTrees_Split_delete(instance: *mut c_void); } unsafe { cv_DTrees_Split_delete(self.as_raw_mut_DTrees_Split()) }; } } impl DTrees_Split { #[inline] pub fn as_raw_DTrees_Split(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() } #[inline] pub fn as_raw_mut_DTrees_Split(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() } } unsafe impl Send for DTrees_Split {} impl crate::ml::DTrees_SplitTrait for DTrees_Split { #[inline] fn as_raw_DTrees_Split(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() } #[inline] fn as_raw_mut_DTrees_Split(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() } } impl DTrees_Split { pub fn default() -> Result<crate::ml::DTrees_Split> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_DTrees_Split_Split() }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { crate::ml::DTrees_Split::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } } /// The class implements the Expectation Maximization algorithm. /// ## See also /// @ref ml_intro_em pub trait EM: crate::ml::StatModel { fn as_raw_EM(&self) -> *const c_void; fn as_raw_mut_EM(&mut self) -> *mut c_void; /// The number of mixture components in the Gaussian mixture model. /// Default value of the parameter is EM::DEFAULT_NCLUSTERS=5. Some of %EM implementation could /// determine the optimal number of mixtures within a specified value range, but that is not the /// case in ML yet. /// ## See also /// setClustersNumber fn get_clusters_number(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_getClustersNumber_const(self.as_raw_EM()) }.into_result() } /// The number of mixture components in the Gaussian mixture model. /// Default value of the parameter is EM::DEFAULT_NCLUSTERS=5. Some of %EM implementation could /// determine the optimal number of mixtures within a specified value range, but that is not the /// case in ML yet. /// ## See also /// setClustersNumber getClustersNumber fn set_clusters_number(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_setClustersNumber_int(self.as_raw_mut_EM(), val) }.into_result() } /// Constraint on covariance matrices which defines type of matrices. /// See EM::Types. /// ## See also /// setCovarianceMatrixType fn get_covariance_matrix_type(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_getCovarianceMatrixType_const(self.as_raw_EM()) }.into_result() } /// Constraint on covariance matrices which defines type of matrices. /// See EM::Types. /// ## See also /// setCovarianceMatrixType getCovarianceMatrixType fn set_covariance_matrix_type(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_setCovarianceMatrixType_int(self.as_raw_mut_EM(), val) }.into_result() } /// The termination criteria of the %EM algorithm. /// The %EM algorithm can be terminated by the number of iterations termCrit.maxCount (number of /// M-steps) or when relative change of likelihood logarithm is less than termCrit.epsilon. Default /// maximum number of iterations is EM::DEFAULT_MAX_ITERS=100. /// ## See also /// setTermCriteria fn get_term_criteria(&self) -> Result<core::TermCriteria> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_getTermCriteria_const(self.as_raw_EM()) }.into_result() } /// The termination criteria of the %EM algorithm. /// The %EM algorithm can be terminated by the number of iterations termCrit.maxCount (number of /// M-steps) or when relative change of likelihood logarithm is less than termCrit.epsilon. Default /// maximum number of iterations is EM::DEFAULT_MAX_ITERS=100. /// ## See also /// setTermCriteria getTermCriteria fn set_term_criteria(&mut self, val: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_setTermCriteria_const_TermCriteriaR(self.as_raw_mut_EM(), &val) }.into_result() } /// Returns weights of the mixtures /// /// Returns vector with the number of elements equal to the number of mixtures. fn get_weights(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_getWeights_const(self.as_raw_EM()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Returns the cluster centers (means of the Gaussian mixture) /// /// Returns matrix with the number of rows equal to the number of mixtures and number of columns /// equal to the space dimensionality. fn get_means(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_getMeans_const(self.as_raw_EM()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Returns covariation matrices /// /// Returns vector of covariation matrices. Number of matrices is the number of gaussian mixtures, /// each matrix is a square floating-point matrix NxN, where N is the space dimensionality. fn get_covs(&self, covs: &mut core::Vector::<core::Mat>) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_getCovs_const_vector_Mat_R(self.as_raw_EM(), covs.as_raw_mut_VectorOfMat()) }.into_result() } /// Returns posterior probabilities for the provided samples /// /// ## Parameters /// * samples: The input samples, floating-point matrix /// * results: The optional output 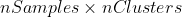 matrix of results. It contains /// posterior probabilities for each sample from the input /// * flags: This parameter will be ignored /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * results: noArray() /// * flags: 0 fn predict(&self, samples: &dyn core::ToInputArray, results: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<f32> { input_array_arg!(samples); output_array_arg!(results); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_predict_const_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(self.as_raw_EM(), samples.as_raw__InputArray(), results.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags) }.into_result() } /// Returns a likelihood logarithm value and an index of the most probable mixture component /// for the given sample. /// /// ## Parameters /// * sample: A sample for classification. It should be a one-channel matrix of /// 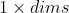 or 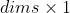 size. /// * probs: Optional output matrix that contains posterior probabilities of each component /// given the sample. It has 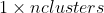 size and CV_64FC1 type. /// /// The method returns a two-element double vector. Zero element is a likelihood logarithm value for /// the sample. First element is an index of the most probable mixture component for the given /// sample. fn predict2(&self, sample: &dyn core::ToInputArray, probs: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<core::Vec2d> { input_array_arg!(sample); output_array_arg!(probs); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_predict2_const_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_EM(), sample.as_raw__InputArray(), probs.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Estimate the Gaussian mixture parameters from a samples set. /// /// This variation starts with Expectation step. Initial values of the model parameters will be /// estimated by the k-means algorithm. /// /// Unlike many of the ML models, %EM is an unsupervised learning algorithm and it does not take /// responses (class labels or function values) as input. Instead, it computes the *Maximum /// Likelihood Estimate* of the Gaussian mixture parameters from an input sample set, stores all the /// parameters inside the structure: 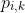 in probs, 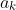 in means , 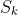 in /// covs[k], 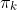 in weights , and optionally computes the output "class label" for each /// sample:  (indices of the most /// probable mixture component for each sample). /// /// The trained model can be used further for prediction, just like any other classifier. The /// trained model is similar to the NormalBayesClassifier. /// /// ## Parameters /// * samples: Samples from which the Gaussian mixture model will be estimated. It should be a /// one-channel matrix, each row of which is a sample. If the matrix does not have CV_64F type /// it will be converted to the inner matrix of such type for the further computing. /// * logLikelihoods: The optional output matrix that contains a likelihood logarithm value for /// each sample. It has 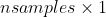 size and CV_64FC1 type. /// * labels: The optional output "class label" for each sample: ///  (indices of the most probable /// mixture component for each sample). It has 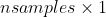 size and CV_32SC1 type. /// * probs: The optional output matrix that contains posterior probabilities of each Gaussian /// mixture component given the each sample. It has 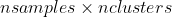 size and /// CV_64FC1 type. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * log_likelihoods: noArray() /// * labels: noArray() /// * probs: noArray() fn train_em(&mut self, samples: &dyn core::ToInputArray, log_likelihoods: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, labels: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, probs: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<bool> { input_array_arg!(samples); output_array_arg!(log_likelihoods); output_array_arg!(labels); output_array_arg!(probs); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_trainEM_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_EM(), samples.as_raw__InputArray(), log_likelihoods.as_raw__OutputArray(), labels.as_raw__OutputArray(), probs.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Estimate the Gaussian mixture parameters from a samples set. /// /// This variation starts with Expectation step. You need to provide initial means 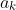 of /// mixture components. Optionally you can pass initial weights 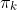 and covariance matrices /// 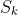 of mixture components. /// /// ## Parameters /// * samples: Samples from which the Gaussian mixture model will be estimated. It should be a /// one-channel matrix, each row of which is a sample. If the matrix does not have CV_64F type /// it will be converted to the inner matrix of such type for the further computing. /// * means0: Initial means 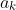 of mixture components. It is a one-channel matrix of /// 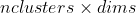 size. If the matrix does not have CV_64F type it will be /// converted to the inner matrix of such type for the further computing. /// * covs0: The vector of initial covariance matrices 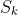 of mixture components. Each of /// covariance matrices is a one-channel matrix of 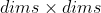 size. If the matrices /// do not have CV_64F type they will be converted to the inner matrices of such type for the /// further computing. /// * weights0: Initial weights 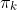 of mixture components. It should be a one-channel /// floating-point matrix with 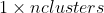 or 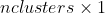 size. /// * logLikelihoods: The optional output matrix that contains a likelihood logarithm value for /// each sample. It has 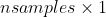 size and CV_64FC1 type. /// * labels: The optional output "class label" for each sample: ///  (indices of the most probable /// mixture component for each sample). It has 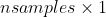 size and CV_32SC1 type. /// * probs: The optional output matrix that contains posterior probabilities of each Gaussian /// mixture component given the each sample. It has 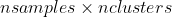 size and /// CV_64FC1 type. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * covs0: noArray() /// * weights0: noArray() /// * log_likelihoods: noArray() /// * labels: noArray() /// * probs: noArray() fn train_e(&mut self, samples: &dyn core::ToInputArray, means0: &dyn core::ToInputArray, covs0: &dyn core::ToInputArray, weights0: &dyn core::ToInputArray, log_likelihoods: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, labels: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, probs: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<bool> { input_array_arg!(samples); input_array_arg!(means0); input_array_arg!(covs0); input_array_arg!(weights0); output_array_arg!(log_likelihoods); output_array_arg!(labels); output_array_arg!(probs); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_trainE_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_EM(), samples.as_raw__InputArray(), means0.as_raw__InputArray(), covs0.as_raw__InputArray(), weights0.as_raw__InputArray(), log_likelihoods.as_raw__OutputArray(), labels.as_raw__OutputArray(), probs.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Estimate the Gaussian mixture parameters from a samples set. /// /// This variation starts with Maximization step. You need to provide initial probabilities /// 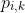 to use this option. /// /// ## Parameters /// * samples: Samples from which the Gaussian mixture model will be estimated. It should be a /// one-channel matrix, each row of which is a sample. If the matrix does not have CV_64F type /// it will be converted to the inner matrix of such type for the further computing. /// * probs0: the probabilities /// * logLikelihoods: The optional output matrix that contains a likelihood logarithm value for /// each sample. It has 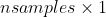 size and CV_64FC1 type. /// * labels: The optional output "class label" for each sample: ///  (indices of the most probable /// mixture component for each sample). It has 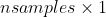 size and CV_32SC1 type. /// * probs: The optional output matrix that contains posterior probabilities of each Gaussian /// mixture component given the each sample. It has 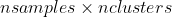 size and /// CV_64FC1 type. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * log_likelihoods: noArray() /// * labels: noArray() /// * probs: noArray() fn train_m(&mut self, samples: &dyn core::ToInputArray, probs0: &dyn core::ToInputArray, log_likelihoods: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, labels: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, probs: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<bool> { input_array_arg!(samples); input_array_arg!(probs0); output_array_arg!(log_likelihoods); output_array_arg!(labels); output_array_arg!(probs); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_trainM_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_EM(), samples.as_raw__InputArray(), probs0.as_raw__InputArray(), log_likelihoods.as_raw__OutputArray(), labels.as_raw__OutputArray(), probs.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } } impl dyn EM + '_ { /// Creates empty %EM model. /// The model should be trained then using StatModel::train(traindata, flags) method. Alternatively, you /// can use one of the EM::train\* methods or load it from file using Algorithm::load\<EM\>(filename). pub fn create() -> Result<core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::EM>> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_create() }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::EM>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Loads and creates a serialized EM from a file /// /// Use EM::save to serialize and store an EM to disk. /// Load the EM from this file again, by calling this function with the path to the file. /// Optionally specify the node for the file containing the classifier /// /// ## Parameters /// * filepath: path to serialized EM /// * nodeName: name of node containing the classifier /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * node_name: String() pub fn load(filepath: &str, node_name: &str) -> Result<core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::EM>> { extern_container_arg!(filepath); extern_container_arg!(node_name); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_EM_load_const_StringR_const_StringR(filepath.opencv_as_extern(), node_name.opencv_as_extern()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::EM>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } } /// The class implements K-Nearest Neighbors model /// ## See also /// @ref ml_intro_knn pub trait KNearest: crate::ml::StatModel { fn as_raw_KNearest(&self) -> *const c_void; fn as_raw_mut_KNearest(&mut self) -> *mut c_void; /// Default number of neighbors to use in predict method. /// ## See also /// setDefaultK fn get_default_k(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_KNearest_getDefaultK_const(self.as_raw_KNearest()) }.into_result() } /// Default number of neighbors to use in predict method. /// ## See also /// setDefaultK getDefaultK fn set_default_k(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_KNearest_setDefaultK_int(self.as_raw_mut_KNearest(), val) }.into_result() } /// Whether classification or regression model should be trained. /// ## See also /// setIsClassifier fn get_is_classifier(&self) -> Result<bool> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_KNearest_getIsClassifier_const(self.as_raw_KNearest()) }.into_result() } /// Whether classification or regression model should be trained. /// ## See also /// setIsClassifier getIsClassifier fn set_is_classifier(&mut self, val: bool) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_KNearest_setIsClassifier_bool(self.as_raw_mut_KNearest(), val) }.into_result() } /// Parameter for KDTree implementation. /// ## See also /// setEmax fn get_emax(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_KNearest_getEmax_const(self.as_raw_KNearest()) }.into_result() } /// Parameter for KDTree implementation. /// ## See also /// setEmax getEmax fn set_emax(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_KNearest_setEmax_int(self.as_raw_mut_KNearest(), val) }.into_result() } /// %Algorithm type, one of KNearest::Types. /// ## See also /// setAlgorithmType fn get_algorithm_type(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_KNearest_getAlgorithmType_const(self.as_raw_KNearest()) }.into_result() } /// %Algorithm type, one of KNearest::Types. /// ## See also /// setAlgorithmType getAlgorithmType fn set_algorithm_type(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_KNearest_setAlgorithmType_int(self.as_raw_mut_KNearest(), val) }.into_result() } /// Finds the neighbors and predicts responses for input vectors. /// /// ## Parameters /// * samples: Input samples stored by rows. It is a single-precision floating-point matrix of /// `<number_of_samples> * k` size. /// * k: Number of used nearest neighbors. Should be greater than 1. /// * results: Vector with results of prediction (regression or classification) for each input /// sample. It is a single-precision floating-point vector with `<number_of_samples>` elements. /// * neighborResponses: Optional output values for corresponding neighbors. It is a single- /// precision floating-point matrix of `<number_of_samples> * k` size. /// * dist: Optional output distances from the input vectors to the corresponding neighbors. It /// is a single-precision floating-point matrix of `<number_of_samples> * k` size. /// /// For each input vector (a row of the matrix samples), the method finds the k nearest neighbors. /// In case of regression, the predicted result is a mean value of the particular vector's neighbor /// responses. In case of classification, the class is determined by voting. /// /// For each input vector, the neighbors are sorted by their distances to the vector. /// /// In case of C++ interface you can use output pointers to empty matrices and the function will /// allocate memory itself. /// /// If only a single input vector is passed, all output matrices are optional and the predicted /// value is returned by the method. /// /// The function is parallelized with the TBB library. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * neighbor_responses: noArray() /// * dist: noArray() fn find_nearest(&self, samples: &dyn core::ToInputArray, k: i32, results: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, neighbor_responses: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, dist: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<f32> { input_array_arg!(samples); output_array_arg!(results); output_array_arg!(neighbor_responses); output_array_arg!(dist); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_KNearest_findNearest_const_const__InputArrayR_int_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_KNearest(), samples.as_raw__InputArray(), k, results.as_raw__OutputArray(), neighbor_responses.as_raw__OutputArray(), dist.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } } impl dyn KNearest + '_ { /// Creates the empty model /// /// The static method creates empty %KNearest classifier. It should be then trained using StatModel::train method. pub fn create() -> Result<core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::KNearest>> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_KNearest_create() }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::KNearest>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Loads and creates a serialized knearest from a file /// /// Use KNearest::save to serialize and store an KNearest to disk. /// Load the KNearest from this file again, by calling this function with the path to the file. /// /// ## Parameters /// * filepath: path to serialized KNearest pub fn load(filepath: &str) -> Result<core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::KNearest>> { extern_container_arg!(filepath); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_KNearest_load_const_StringR(filepath.opencv_as_extern()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::KNearest>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } } /// Implements Logistic Regression classifier. /// ## See also /// @ref ml_intro_lr pub trait LogisticRegression: crate::ml::StatModel { fn as_raw_LogisticRegression(&self) -> *const c_void; fn as_raw_mut_LogisticRegression(&mut self) -> *mut c_void; /// Learning rate. /// ## See also /// setLearningRate fn get_learning_rate(&self) -> Result<f64> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_getLearningRate_const(self.as_raw_LogisticRegression()) }.into_result() } /// Learning rate. /// ## See also /// setLearningRate getLearningRate fn set_learning_rate(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_setLearningRate_double(self.as_raw_mut_LogisticRegression(), val) }.into_result() } /// Number of iterations. /// ## See also /// setIterations fn get_iterations(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_getIterations_const(self.as_raw_LogisticRegression()) }.into_result() } /// Number of iterations. /// ## See also /// setIterations getIterations fn set_iterations(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_setIterations_int(self.as_raw_mut_LogisticRegression(), val) }.into_result() } /// Kind of regularization to be applied. See LogisticRegression::RegKinds. /// ## See also /// setRegularization fn get_regularization(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_getRegularization_const(self.as_raw_LogisticRegression()) }.into_result() } /// Kind of regularization to be applied. See LogisticRegression::RegKinds. /// ## See also /// setRegularization getRegularization fn set_regularization(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_setRegularization_int(self.as_raw_mut_LogisticRegression(), val) }.into_result() } /// Kind of training method used. See LogisticRegression::Methods. /// ## See also /// setTrainMethod fn get_train_method(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_getTrainMethod_const(self.as_raw_LogisticRegression()) }.into_result() } /// Kind of training method used. See LogisticRegression::Methods. /// ## See also /// setTrainMethod getTrainMethod fn set_train_method(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_setTrainMethod_int(self.as_raw_mut_LogisticRegression(), val) }.into_result() } /// Specifies the number of training samples taken in each step of Mini-Batch Gradient /// Descent. Will only be used if using LogisticRegression::MINI_BATCH training algorithm. It /// has to take values less than the total number of training samples. /// ## See also /// setMiniBatchSize fn get_mini_batch_size(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_getMiniBatchSize_const(self.as_raw_LogisticRegression()) }.into_result() } /// Specifies the number of training samples taken in each step of Mini-Batch Gradient /// Descent. Will only be used if using LogisticRegression::MINI_BATCH training algorithm. It /// has to take values less than the total number of training samples. /// ## See also /// setMiniBatchSize getMiniBatchSize fn set_mini_batch_size(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_setMiniBatchSize_int(self.as_raw_mut_LogisticRegression(), val) }.into_result() } /// Termination criteria of the algorithm. /// ## See also /// setTermCriteria fn get_term_criteria(&self) -> Result<core::TermCriteria> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_getTermCriteria_const(self.as_raw_LogisticRegression()) }.into_result() } /// Termination criteria of the algorithm. /// ## See also /// setTermCriteria getTermCriteria fn set_term_criteria(&mut self, val: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_setTermCriteria_TermCriteria(self.as_raw_mut_LogisticRegression(), val.opencv_as_extern()) }.into_result() } /// Predicts responses for input samples and returns a float type. /// /// ## Parameters /// * samples: The input data for the prediction algorithm. Matrix [m x n], where each row /// contains variables (features) of one object being classified. Should have data type CV_32F. /// * results: Predicted labels as a column matrix of type CV_32S. /// * flags: Not used. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * results: noArray() /// * flags: 0 fn predict(&self, samples: &dyn core::ToInputArray, results: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<f32> { input_array_arg!(samples); output_array_arg!(results); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_predict_const_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(self.as_raw_LogisticRegression(), samples.as_raw__InputArray(), results.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags) }.into_result() } /// This function returns the trained parameters arranged across rows. /// /// For a two class classification problem, it returns a row matrix. It returns learnt parameters of /// the Logistic Regression as a matrix of type CV_32F. fn get_learnt_thetas(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_get_learnt_thetas_const(self.as_raw_LogisticRegression()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } } impl dyn LogisticRegression + '_ { /// Creates empty model. /// /// Creates Logistic Regression model with parameters given. pub fn create() -> Result<core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::LogisticRegression>> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_create() }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::LogisticRegression>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Loads and creates a serialized LogisticRegression from a file /// /// Use LogisticRegression::save to serialize and store an LogisticRegression to disk. /// Load the LogisticRegression from this file again, by calling this function with the path to the file. /// Optionally specify the node for the file containing the classifier /// /// ## Parameters /// * filepath: path to serialized LogisticRegression /// * nodeName: name of node containing the classifier /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * node_name: String() pub fn load(filepath: &str, node_name: &str) -> Result<core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::LogisticRegression>> { extern_container_arg!(filepath); extern_container_arg!(node_name); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_LogisticRegression_load_const_StringR_const_StringR(filepath.opencv_as_extern(), node_name.opencv_as_extern()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::LogisticRegression>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } } /// Bayes classifier for normally distributed data. /// ## See also /// @ref ml_intro_bayes pub trait NormalBayesClassifier: crate::ml::StatModel { fn as_raw_NormalBayesClassifier(&self) -> *const c_void; fn as_raw_mut_NormalBayesClassifier(&mut self) -> *mut c_void; /// Predicts the response for sample(s). /// /// The method estimates the most probable classes for input vectors. Input vectors (one or more) /// are stored as rows of the matrix inputs. In case of multiple input vectors, there should be one /// output vector outputs. The predicted class for a single input vector is returned by the method. /// The vector outputProbs contains the output probabilities corresponding to each element of /// result. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * flags: 0 fn predict_prob(&self, inputs: &dyn core::ToInputArray, outputs: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, output_probs: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<f32> { input_array_arg!(inputs); output_array_arg!(outputs); output_array_arg!(output_probs); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_NormalBayesClassifier_predictProb_const_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(self.as_raw_NormalBayesClassifier(), inputs.as_raw__InputArray(), outputs.as_raw__OutputArray(), output_probs.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags) }.into_result() } } impl dyn NormalBayesClassifier + '_ { /// Creates empty model /// Use StatModel::train to train the model after creation. pub fn create() -> Result<core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::NormalBayesClassifier>> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_NormalBayesClassifier_create() }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::NormalBayesClassifier>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Loads and creates a serialized NormalBayesClassifier from a file /// /// Use NormalBayesClassifier::save to serialize and store an NormalBayesClassifier to disk. /// Load the NormalBayesClassifier from this file again, by calling this function with the path to the file. /// Optionally specify the node for the file containing the classifier /// /// ## Parameters /// * filepath: path to serialized NormalBayesClassifier /// * nodeName: name of node containing the classifier /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * node_name: String() pub fn load(filepath: &str, node_name: &str) -> Result<core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::NormalBayesClassifier>> { extern_container_arg!(filepath); extern_container_arg!(node_name); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_NormalBayesClassifier_load_const_StringR_const_StringR(filepath.opencv_as_extern(), node_name.opencv_as_extern()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::NormalBayesClassifier>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } } /// The structure represents the logarithmic grid range of statmodel parameters. /// /// It is used for optimizing statmodel accuracy by varying model parameters, the accuracy estimate /// being computed by cross-validation. pub trait ParamGridTrait { fn as_raw_ParamGrid(&self) -> *const c_void; fn as_raw_mut_ParamGrid(&mut self) -> *mut c_void; /// Minimum value of the statmodel parameter. Default value is 0. fn min_val(&self) -> f64 { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ParamGrid_getPropMinVal_const(self.as_raw_ParamGrid()) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: min_val") } /// Minimum value of the statmodel parameter. Default value is 0. fn set_min_val(&mut self, val: f64) -> () { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ParamGrid_setPropMinVal_double(self.as_raw_mut_ParamGrid(), val) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: set_min_val") } /// Maximum value of the statmodel parameter. Default value is 0. fn max_val(&self) -> f64 { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ParamGrid_getPropMaxVal_const(self.as_raw_ParamGrid()) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: max_val") } /// Maximum value of the statmodel parameter. Default value is 0. fn set_max_val(&mut self, val: f64) -> () { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ParamGrid_setPropMaxVal_double(self.as_raw_mut_ParamGrid(), val) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: set_max_val") } /// Logarithmic step for iterating the statmodel parameter. /// /// The grid determines the following iteration sequence of the statmodel parameter values: /// 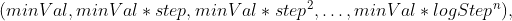 /// where 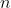 is the maximal index satisfying /// 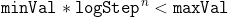 /// The grid is logarithmic, so logStep must always be greater than 1. Default value is 1. fn log_step(&self) -> f64 { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ParamGrid_getPropLogStep_const(self.as_raw_ParamGrid()) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: log_step") } /// Logarithmic step for iterating the statmodel parameter. /// /// The grid determines the following iteration sequence of the statmodel parameter values: /// 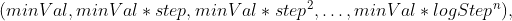 /// where  is the maximal index satisfying /// 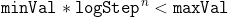 /// The grid is logarithmic, so logStep must always be greater than 1. Default value is 1. fn set_log_step(&mut self, val: f64) -> () { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ParamGrid_setPropLogStep_double(self.as_raw_mut_ParamGrid(), val) }.into_result().expect("Infallible function failed: set_log_step") } } /// The structure represents the logarithmic grid range of statmodel parameters. /// /// It is used for optimizing statmodel accuracy by varying model parameters, the accuracy estimate /// being computed by cross-validation. pub struct ParamGrid { ptr: *mut c_void } opencv_type_boxed! { ParamGrid } impl Drop for ParamGrid { fn drop(&mut self) { extern "C" { fn cv_ParamGrid_delete(instance: *mut c_void); } unsafe { cv_ParamGrid_delete(self.as_raw_mut_ParamGrid()) }; } } impl ParamGrid { #[inline] pub fn as_raw_ParamGrid(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() } #[inline] pub fn as_raw_mut_ParamGrid(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() } } unsafe impl Send for ParamGrid {} impl crate::ml::ParamGridTrait for ParamGrid { #[inline] fn as_raw_ParamGrid(&self) -> *const c_void { self.as_raw() } #[inline] fn as_raw_mut_ParamGrid(&mut self) -> *mut c_void { self.as_raw_mut() } } impl ParamGrid { /// Default constructor pub fn default() -> Result<crate::ml::ParamGrid> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ParamGrid_ParamGrid() }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { crate::ml::ParamGrid::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Constructor with parameters pub fn for_range(_min_val: f64, _max_val: f64, _log_step: f64) -> Result<crate::ml::ParamGrid> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ParamGrid_ParamGrid_double_double_double(_min_val, _max_val, _log_step) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { crate::ml::ParamGrid::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Creates a ParamGrid Ptr that can be given to the %SVM::trainAuto method /// /// ## Parameters /// * minVal: minimum value of the parameter grid /// * maxVal: maximum value of the parameter grid /// * logstep: Logarithmic step for iterating the statmodel parameter /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * min_val: 0. /// * max_val: 0. /// * logstep: 1. pub fn create(min_val: f64, max_val: f64, logstep: f64) -> Result<core::Ptr::<crate::ml::ParamGrid>> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_ParamGrid_create_double_double_double(min_val, max_val, logstep) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ml::ParamGrid>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } } /// The class implements the random forest predictor. /// ## See also /// @ref ml_intro_rtrees pub trait RTrees: crate::ml::DTrees { fn as_raw_RTrees(&self) -> *const c_void; fn as_raw_mut_RTrees(&mut self) -> *mut c_void; /// If true then variable importance will be calculated and then it can be retrieved by RTrees::getVarImportance. /// Default value is false. /// ## See also /// setCalculateVarImportance fn get_calculate_var_importance(&self) -> Result<bool> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_RTrees_getCalculateVarImportance_const(self.as_raw_RTrees()) }.into_result() } /// If true then variable importance will be calculated and then it can be retrieved by RTrees::getVarImportance. /// Default value is false. /// ## See also /// setCalculateVarImportance getCalculateVarImportance fn set_calculate_var_importance(&mut self, val: bool) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_RTrees_setCalculateVarImportance_bool(self.as_raw_mut_RTrees(), val) }.into_result() } /// The size of the randomly selected subset of features at each tree node and that are used /// to find the best split(s). /// If you set it to 0 then the size will be set to the square root of the total number of /// features. Default value is 0. /// ## See also /// setActiveVarCount fn get_active_var_count(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_RTrees_getActiveVarCount_const(self.as_raw_RTrees()) }.into_result() } /// The size of the randomly selected subset of features at each tree node and that are used /// to find the best split(s). /// If you set it to 0 then the size will be set to the square root of the total number of /// features. Default value is 0. /// ## See also /// setActiveVarCount getActiveVarCount fn set_active_var_count(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_RTrees_setActiveVarCount_int(self.as_raw_mut_RTrees(), val) }.into_result() } /// The termination criteria that specifies when the training algorithm stops. /// Either when the specified number of trees is trained and added to the ensemble or when /// sufficient accuracy (measured as OOB error) is achieved. Typically the more trees you have the /// better the accuracy. However, the improvement in accuracy generally diminishes and asymptotes /// pass a certain number of trees. Also to keep in mind, the number of tree increases the /// prediction time linearly. Default value is TermCriteria(TermCriteria::MAX_ITERS + /// TermCriteria::EPS, 50, 0.1) /// ## See also /// setTermCriteria fn get_term_criteria(&self) -> Result<core::TermCriteria> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_RTrees_getTermCriteria_const(self.as_raw_RTrees()) }.into_result() } /// The termination criteria that specifies when the training algorithm stops. /// Either when the specified number of trees is trained and added to the ensemble or when /// sufficient accuracy (measured as OOB error) is achieved. Typically the more trees you have the /// better the accuracy. However, the improvement in accuracy generally diminishes and asymptotes /// pass a certain number of trees. Also to keep in mind, the number of tree increases the /// prediction time linearly. Default value is TermCriteria(TermCriteria::MAX_ITERS + /// TermCriteria::EPS, 50, 0.1) /// ## See also /// setTermCriteria getTermCriteria fn set_term_criteria(&mut self, val: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_RTrees_setTermCriteria_const_TermCriteriaR(self.as_raw_mut_RTrees(), &val) }.into_result() } /// Returns the variable importance array. /// The method returns the variable importance vector, computed at the training stage when /// CalculateVarImportance is set to true. If this flag was set to false, the empty matrix is /// returned. fn get_var_importance(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_RTrees_getVarImportance_const(self.as_raw_RTrees()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Returns the result of each individual tree in the forest. /// In case the model is a regression problem, the method will return each of the trees' /// results for each of the sample cases. If the model is a classifier, it will return /// a Mat with samples + 1 rows, where the first row gives the class number and the /// following rows return the votes each class had for each sample. /// ## Parameters /// * samples: Array containing the samples for which votes will be calculated. /// * results: Array where the result of the calculation will be written. /// * flags: Flags for defining the type of RTrees. fn get_votes(&self, samples: &dyn core::ToInputArray, results: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(samples); output_array_arg!(results); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_RTrees_getVotes_const_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(self.as_raw_RTrees(), samples.as_raw__InputArray(), results.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags) }.into_result() } fn get_oob_error(&self) -> Result<f64> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_RTrees_getOOBError_const(self.as_raw_RTrees()) }.into_result() } } impl dyn RTrees + '_ { /// Creates the empty model. /// Use StatModel::train to train the model, StatModel::train to create and train the model, /// Algorithm::load to load the pre-trained model. pub fn create() -> Result<core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::RTrees>> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_RTrees_create() }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::RTrees>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Loads and creates a serialized RTree from a file /// /// Use RTree::save to serialize and store an RTree to disk. /// Load the RTree from this file again, by calling this function with the path to the file. /// Optionally specify the node for the file containing the classifier /// /// ## Parameters /// * filepath: path to serialized RTree /// * nodeName: name of node containing the classifier /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * node_name: String() pub fn load(filepath: &str, node_name: &str) -> Result<core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::RTrees>> { extern_container_arg!(filepath); extern_container_arg!(node_name); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_RTrees_load_const_StringR_const_StringR(filepath.opencv_as_extern(), node_name.opencv_as_extern()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::RTrees>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } } /// Support Vector Machines. /// ## See also /// @ref ml_intro_svm pub trait SVM: crate::ml::StatModel { fn as_raw_SVM(&self) -> *const c_void; fn as_raw_mut_SVM(&mut self) -> *mut c_void; /// Type of a %SVM formulation. /// See SVM::Types. Default value is SVM::C_SVC. /// ## See also /// setType fn get_type(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getType_const(self.as_raw_SVM()) }.into_result() } /// Type of a %SVM formulation. /// See SVM::Types. Default value is SVM::C_SVC. /// ## See also /// setType getType fn set_type(&mut self, val: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_setType_int(self.as_raw_mut_SVM(), val) }.into_result() } /// Parameter  of a kernel function. /// For SVM::POLY, SVM::RBF, SVM::SIGMOID or SVM::CHI2. Default value is 1. /// ## See also /// setGamma fn get_gamma(&self) -> Result<f64> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getGamma_const(self.as_raw_SVM()) }.into_result() } /// Parameter 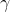 of a kernel function. /// For SVM::POLY, SVM::RBF, SVM::SIGMOID or SVM::CHI2. Default value is 1. /// ## See also /// setGamma getGamma fn set_gamma(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_setGamma_double(self.as_raw_mut_SVM(), val) }.into_result() } /// Parameter _coef0_ of a kernel function. /// For SVM::POLY or SVM::SIGMOID. Default value is 0. /// ## See also /// setCoef0 fn get_coef0(&self) -> Result<f64> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getCoef0_const(self.as_raw_SVM()) }.into_result() } /// Parameter _coef0_ of a kernel function. /// For SVM::POLY or SVM::SIGMOID. Default value is 0. /// ## See also /// setCoef0 getCoef0 fn set_coef0(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_setCoef0_double(self.as_raw_mut_SVM(), val) }.into_result() } /// Parameter _degree_ of a kernel function. /// For SVM::POLY. Default value is 0. /// ## See also /// setDegree fn get_degree(&self) -> Result<f64> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getDegree_const(self.as_raw_SVM()) }.into_result() } /// Parameter _degree_ of a kernel function. /// For SVM::POLY. Default value is 0. /// ## See also /// setDegree getDegree fn set_degree(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_setDegree_double(self.as_raw_mut_SVM(), val) }.into_result() } /// Parameter _C_ of a %SVM optimization problem. /// For SVM::C_SVC, SVM::EPS_SVR or SVM::NU_SVR. Default value is 0. /// ## See also /// setC fn get_c(&self) -> Result<f64> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getC_const(self.as_raw_SVM()) }.into_result() } /// Parameter _C_ of a %SVM optimization problem. /// For SVM::C_SVC, SVM::EPS_SVR or SVM::NU_SVR. Default value is 0. /// ## See also /// setC getC fn set_c(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_setC_double(self.as_raw_mut_SVM(), val) }.into_result() } /// Parameter 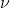 of a %SVM optimization problem. /// For SVM::NU_SVC, SVM::ONE_CLASS or SVM::NU_SVR. Default value is 0. /// ## See also /// setNu fn get_nu(&self) -> Result<f64> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getNu_const(self.as_raw_SVM()) }.into_result() } /// Parameter 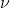 of a %SVM optimization problem. /// For SVM::NU_SVC, SVM::ONE_CLASS or SVM::NU_SVR. Default value is 0. /// ## See also /// setNu getNu fn set_nu(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_setNu_double(self.as_raw_mut_SVM(), val) }.into_result() } /// Parameter  of a %SVM optimization problem. /// For SVM::EPS_SVR. Default value is 0. /// ## See also /// setP fn get_p(&self) -> Result<f64> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getP_const(self.as_raw_SVM()) }.into_result() } /// Parameter  of a %SVM optimization problem. /// For SVM::EPS_SVR. Default value is 0. /// ## See also /// setP getP fn set_p(&mut self, val: f64) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_setP_double(self.as_raw_mut_SVM(), val) }.into_result() } /// Optional weights in the SVM::C_SVC problem, assigned to particular classes. /// They are multiplied by _C_ so the parameter _C_ of class _i_ becomes `classWeights(i) * C`. Thus /// these weights affect the misclassification penalty for different classes. The larger weight, /// the larger penalty on misclassification of data from the corresponding class. Default value is /// empty Mat. /// ## See also /// setClassWeights fn get_class_weights(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getClassWeights_const(self.as_raw_SVM()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Optional weights in the SVM::C_SVC problem, assigned to particular classes. /// They are multiplied by _C_ so the parameter _C_ of class _i_ becomes `classWeights(i) * C`. Thus /// these weights affect the misclassification penalty for different classes. The larger weight, /// the larger penalty on misclassification of data from the corresponding class. Default value is /// empty Mat. /// ## See also /// setClassWeights getClassWeights fn set_class_weights(&mut self, val: &core::Mat) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_setClassWeights_const_MatR(self.as_raw_mut_SVM(), val.as_raw_Mat()) }.into_result() } /// Termination criteria of the iterative %SVM training procedure which solves a partial /// case of constrained quadratic optimization problem. /// You can specify tolerance and/or the maximum number of iterations. Default value is /// `TermCriteria( TermCriteria::MAX_ITER + TermCriteria::EPS, 1000, FLT_EPSILON )`; /// ## See also /// setTermCriteria fn get_term_criteria(&self) -> Result<core::TermCriteria> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getTermCriteria_const(self.as_raw_SVM()) }.into_result() } /// Termination criteria of the iterative %SVM training procedure which solves a partial /// case of constrained quadratic optimization problem. /// You can specify tolerance and/or the maximum number of iterations. Default value is /// `TermCriteria( TermCriteria::MAX_ITER + TermCriteria::EPS, 1000, FLT_EPSILON )`; /// ## See also /// setTermCriteria getTermCriteria fn set_term_criteria(&mut self, val: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_setTermCriteria_const_TermCriteriaR(self.as_raw_mut_SVM(), &val) }.into_result() } /// Type of a %SVM kernel. /// See SVM::KernelTypes. Default value is SVM::RBF. fn get_kernel_type(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getKernelType_const(self.as_raw_SVM()) }.into_result() } /// Initialize with one of predefined kernels. /// See SVM::KernelTypes. fn set_kernel(&mut self, kernel_type: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_setKernel_int(self.as_raw_mut_SVM(), kernel_type) }.into_result() } /// Initialize with custom kernel. /// See SVM::Kernel class for implementation details fn set_custom_kernel(&mut self, _kernel: &core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::SVM_Kernel>) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_setCustomKernel_const_Ptr_Kernel_R(self.as_raw_mut_SVM(), _kernel.as_raw_PtrOfSVM_Kernel()) }.into_result() } /// Trains an %SVM with optimal parameters. /// /// ## Parameters /// * data: the training data that can be constructed using TrainData::create or /// TrainData::loadFromCSV. /// * kFold: Cross-validation parameter. The training set is divided into kFold subsets. One /// subset is used to test the model, the others form the train set. So, the %SVM algorithm is /// executed kFold times. /// * Cgrid: grid for C /// * gammaGrid: grid for gamma /// * pGrid: grid for p /// * nuGrid: grid for nu /// * coeffGrid: grid for coeff /// * degreeGrid: grid for degree /// * balanced: If true and the problem is 2-class classification then the method creates more /// balanced cross-validation subsets that is proportions between classes in subsets are close /// to such proportion in the whole train dataset. /// /// The method trains the %SVM model automatically by choosing the optimal parameters C, gamma, p, /// nu, coef0, degree. Parameters are considered optimal when the cross-validation /// estimate of the test set error is minimal. /// /// If there is no need to optimize a parameter, the corresponding grid step should be set to any /// value less than or equal to 1. For example, to avoid optimization in gamma, set `gammaGrid.step /// = 0`, `gammaGrid.minVal`, `gamma_grid.maxVal` as arbitrary numbers. In this case, the value /// `Gamma` is taken for gamma. /// /// And, finally, if the optimization in a parameter is required but the corresponding grid is /// unknown, you may call the function SVM::getDefaultGrid. To generate a grid, for example, for /// gamma, call `SVM::getDefaultGrid(SVM::GAMMA)`. /// /// This function works for the classification (SVM::C_SVC or SVM::NU_SVC) as well as for the /// regression (SVM::EPS_SVR or SVM::NU_SVR). If it is SVM::ONE_CLASS, no optimization is made and /// the usual %SVM with parameters specified in params is executed. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * k_fold: 10 /// * cgrid: getDefaultGrid(C) /// * gamma_grid: getDefaultGrid(GAMMA) /// * p_grid: getDefaultGrid(P) /// * nu_grid: getDefaultGrid(NU) /// * coeff_grid: getDefaultGrid(COEF) /// * degree_grid: getDefaultGrid(DEGREE) /// * balanced: false fn train_auto(&mut self, data: &core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::TrainData>, k_fold: i32, mut cgrid: crate::ml::ParamGrid, mut gamma_grid: crate::ml::ParamGrid, mut p_grid: crate::ml::ParamGrid, mut nu_grid: crate::ml::ParamGrid, mut coeff_grid: crate::ml::ParamGrid, mut degree_grid: crate::ml::ParamGrid, balanced: bool) -> Result<bool> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_trainAuto_const_Ptr_TrainData_R_int_ParamGrid_ParamGrid_ParamGrid_ParamGrid_ParamGrid_ParamGrid_bool(self.as_raw_mut_SVM(), data.as_raw_PtrOfTrainData(), k_fold, cgrid.as_raw_mut_ParamGrid(), gamma_grid.as_raw_mut_ParamGrid(), p_grid.as_raw_mut_ParamGrid(), nu_grid.as_raw_mut_ParamGrid(), coeff_grid.as_raw_mut_ParamGrid(), degree_grid.as_raw_mut_ParamGrid(), balanced) }.into_result() } /// Trains an %SVM with optimal parameters /// /// ## Parameters /// * samples: training samples /// * layout: See ml::SampleTypes. /// * responses: vector of responses associated with the training samples. /// * kFold: Cross-validation parameter. The training set is divided into kFold subsets. One /// subset is used to test the model, the others form the train set. So, the %SVM algorithm is /// * Cgrid: grid for C /// * gammaGrid: grid for gamma /// * pGrid: grid for p /// * nuGrid: grid for nu /// * coeffGrid: grid for coeff /// * degreeGrid: grid for degree /// * balanced: If true and the problem is 2-class classification then the method creates more /// balanced cross-validation subsets that is proportions between classes in subsets are close /// to such proportion in the whole train dataset. /// /// The method trains the %SVM model automatically by choosing the optimal parameters C, gamma, p, /// nu, coef0, degree. Parameters are considered optimal when the cross-validation /// estimate of the test set error is minimal. /// /// This function only makes use of SVM::getDefaultGrid for parameter optimization and thus only /// offers rudimentary parameter options. /// /// This function works for the classification (SVM::C_SVC or SVM::NU_SVC) as well as for the /// regression (SVM::EPS_SVR or SVM::NU_SVR). If it is SVM::ONE_CLASS, no optimization is made and /// the usual %SVM with parameters specified in params is executed. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * k_fold: 10 /// * cgrid: SVM::getDefaultGridPtr(SVM::C) /// * gamma_grid: SVM::getDefaultGridPtr(SVM::GAMMA) /// * p_grid: SVM::getDefaultGridPtr(SVM::P) /// * nu_grid: SVM::getDefaultGridPtr(SVM::NU) /// * coeff_grid: SVM::getDefaultGridPtr(SVM::COEF) /// * degree_grid: SVM::getDefaultGridPtr(SVM::DEGREE) /// * balanced: false fn train_auto_with_data(&mut self, samples: &dyn core::ToInputArray, layout: i32, responses: &dyn core::ToInputArray, k_fold: i32, mut cgrid: core::Ptr::<crate::ml::ParamGrid>, mut gamma_grid: core::Ptr::<crate::ml::ParamGrid>, mut p_grid: core::Ptr::<crate::ml::ParamGrid>, mut nu_grid: core::Ptr::<crate::ml::ParamGrid>, mut coeff_grid: core::Ptr::<crate::ml::ParamGrid>, mut degree_grid: core::Ptr::<crate::ml::ParamGrid>, balanced: bool) -> Result<bool> { input_array_arg!(samples); input_array_arg!(responses); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_trainAuto_const__InputArrayR_int_const__InputArrayR_int_Ptr_ParamGrid__Ptr_ParamGrid__Ptr_ParamGrid__Ptr_ParamGrid__Ptr_ParamGrid__Ptr_ParamGrid__bool(self.as_raw_mut_SVM(), samples.as_raw__InputArray(), layout, responses.as_raw__InputArray(), k_fold, cgrid.as_raw_mut_PtrOfParamGrid(), gamma_grid.as_raw_mut_PtrOfParamGrid(), p_grid.as_raw_mut_PtrOfParamGrid(), nu_grid.as_raw_mut_PtrOfParamGrid(), coeff_grid.as_raw_mut_PtrOfParamGrid(), degree_grid.as_raw_mut_PtrOfParamGrid(), balanced) }.into_result() } /// Retrieves all the support vectors /// /// The method returns all the support vectors as a floating-point matrix, where support vectors are /// stored as matrix rows. fn get_support_vectors(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getSupportVectors_const(self.as_raw_SVM()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Retrieves all the uncompressed support vectors of a linear %SVM /// /// The method returns all the uncompressed support vectors of a linear %SVM that the compressed /// support vector, used for prediction, was derived from. They are returned in a floating-point /// matrix, where the support vectors are stored as matrix rows. fn get_uncompressed_support_vectors(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getUncompressedSupportVectors_const(self.as_raw_SVM()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Retrieves the decision function /// /// ## Parameters /// * i: the index of the decision function. If the problem solved is regression, 1-class or /// 2-class classification, then there will be just one decision function and the index should /// always be 0. Otherwise, in the case of N-class classification, there will be 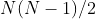 /// decision functions. /// * alpha: the optional output vector for weights, corresponding to different support vectors. /// In the case of linear %SVM all the alpha's will be 1's. /// * svidx: the optional output vector of indices of support vectors within the matrix of /// support vectors (which can be retrieved by SVM::getSupportVectors). In the case of linear /// %SVM each decision function consists of a single "compressed" support vector. /// /// The method returns rho parameter of the decision function, a scalar subtracted from the weighted /// sum of kernel responses. fn get_decision_function(&self, i: i32, alpha: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, svidx: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<f64> { output_array_arg!(alpha); output_array_arg!(svidx); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getDecisionFunction_const_int_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_SVM(), i, alpha.as_raw__OutputArray(), svidx.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } } impl dyn SVM + '_ { /// Generates a grid for %SVM parameters. /// /// ## Parameters /// * param_id: %SVM parameters IDs that must be one of the SVM::ParamTypes. The grid is /// generated for the parameter with this ID. /// /// The function generates a grid for the specified parameter of the %SVM algorithm. The grid may be /// passed to the function SVM::trainAuto. pub fn get_default_grid(param_id: i32) -> Result<crate::ml::ParamGrid> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getDefaultGrid_int(param_id) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { crate::ml::ParamGrid::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Generates a grid for %SVM parameters. /// /// ## Parameters /// * param_id: %SVM parameters IDs that must be one of the SVM::ParamTypes. The grid is /// generated for the parameter with this ID. /// /// The function generates a grid pointer for the specified parameter of the %SVM algorithm. /// The grid may be passed to the function SVM::trainAuto. pub fn get_default_grid_ptr(param_id: i32) -> Result<core::Ptr::<crate::ml::ParamGrid>> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_getDefaultGridPtr_int(param_id) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<crate::ml::ParamGrid>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Creates empty model. /// Use StatModel::train to train the model. Since %SVM has several parameters, you may want to /// find the best parameters for your problem, it can be done with SVM::trainAuto. pub fn create() -> Result<core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::SVM>> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_create() }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::SVM>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Loads and creates a serialized svm from a file /// /// Use SVM::save to serialize and store an SVM to disk. /// Load the SVM from this file again, by calling this function with the path to the file. /// /// ## Parameters /// * filepath: path to serialized svm pub fn load(filepath: &str) -> Result<core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::SVM>> { extern_container_arg!(filepath); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_load_const_StringR(filepath.opencv_as_extern()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::SVM>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } } pub trait SVM_Kernel: core::AlgorithmTrait { fn as_raw_SVM_Kernel(&self) -> *const c_void; fn as_raw_mut_SVM_Kernel(&mut self) -> *mut c_void; fn get_type(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_Kernel_getType_const(self.as_raw_SVM_Kernel()) }.into_result() } fn calc(&mut self, vcount: i32, n: i32, vecs: &f32, another: &f32, results: &mut f32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVM_Kernel_calc_int_int_const_floatX_const_floatX_floatX(self.as_raw_mut_SVM_Kernel(), vcount, n, vecs, another, results) }.into_result() } } /// ! /// Stochastic Gradient Descent SVM classifier /// /// SVMSGD provides a fast and easy-to-use implementation of the SVM classifier using the Stochastic Gradient Descent approach, /// as presented in [bottou2010large](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_bottou2010large). /// /// The classifier has following parameters: /// - model type, /// - margin type, /// - margin regularization (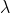), /// - initial step size (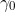), /// - step decreasing power (), /// - and termination criteria. /// /// The model type may have one of the following values: \ref SGD and \ref ASGD. /// /// - \ref SGD is the classic version of SVMSGD classifier: every next step is calculated by the formula /// 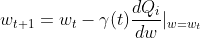 /// where /// -  is the weights vector for decision function at step 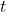, /// - 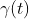 is the step size of model parameters at the iteration 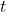, it is decreased on each step by the formula /// 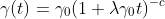 /// - 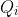 is the target functional from SVM task for sample with number , this sample is chosen stochastically on each step of the algorithm. /// /// - \ref ASGD is Average Stochastic Gradient Descent SVM Classifier. ASGD classifier averages weights vector on each step of algorithm by the formula /// 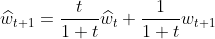 /// /// The recommended model type is ASGD (following [bottou2010large](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_bottou2010large)). /// /// The margin type may have one of the following values: \ref SOFT_MARGIN or \ref HARD_MARGIN. /// /// - You should use \ref HARD_MARGIN type, if you have linearly separable sets. /// - You should use \ref SOFT_MARGIN type, if you have non-linearly separable sets or sets with outliers. /// - In the general case (if you know nothing about linear separability of your sets), use SOFT_MARGIN. /// /// The other parameters may be described as follows: /// - Margin regularization parameter is responsible for weights decreasing at each step and for the strength of restrictions on outliers /// (the less the parameter, the less probability that an outlier will be ignored). /// Recommended value for SGD model is 0.0001, for ASGD model is 0.00001. /// /// - Initial step size parameter is the initial value for the step size . /// You will have to find the best initial step for your problem. /// /// - Step decreasing power is the power parameter for 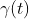 decreasing by the formula, mentioned above. /// Recommended value for SGD model is 1, for ASGD model is 0.75. /// /// - Termination criteria can be TermCriteria::COUNT, TermCriteria::EPS or TermCriteria::COUNT + TermCriteria::EPS. /// You will have to find the best termination criteria for your problem. /// /// Note that the parameters margin regularization, initial step size, and step decreasing power should be positive. /// /// To use SVMSGD algorithm do as follows: /// /// - first, create the SVMSGD object. The algorithm will set optimal parameters by default, but you can set your own parameters via functions setSvmsgdType(), /// setMarginType(), setMarginRegularization(), setInitialStepSize(), and setStepDecreasingPower(). /// /// - then the SVM model can be trained using the train features and the correspondent labels by the method train(). /// /// - after that, the label of a new feature vector can be predicted using the method predict(). /// /// ```ignore /// // Create empty object /// cv::Ptr<SVMSGD> svmsgd = SVMSGD::create(); /// /// // Train the Stochastic Gradient Descent SVM /// svmsgd->train(trainData); /// /// // Predict labels for the new samples /// svmsgd->predict(samples, responses); /// ``` /// pub trait SVMSGD: crate::ml::StatModel { fn as_raw_SVMSGD(&self) -> *const c_void; fn as_raw_mut_SVMSGD(&mut self) -> *mut c_void; /// ## Returns /// the weights of the trained model (decision function f(x) = weights * x + shift). fn get_weights(&mut self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_getWeights(self.as_raw_mut_SVMSGD()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// ## Returns /// the shift of the trained model (decision function f(x) = weights * x + shift). fn get_shift(&mut self) -> Result<f32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_getShift(self.as_raw_mut_SVMSGD()) }.into_result() } /// Function sets optimal parameters values for chosen SVM SGD model. /// ## Parameters /// * svmsgdType: is the type of SVMSGD classifier. /// * marginType: is the type of margin constraint. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * svmsgd_type: SVMSGD::ASGD /// * margin_type: SVMSGD::SOFT_MARGIN fn set_optimal_parameters(&mut self, svmsgd_type: i32, margin_type: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_setOptimalParameters_int_int(self.as_raw_mut_SVMSGD(), svmsgd_type, margin_type) }.into_result() } /// %Algorithm type, one of SVMSGD::SvmsgdType. /// ## See also /// setSvmsgdType fn get_svmsgd_type(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_getSvmsgdType_const(self.as_raw_SVMSGD()) }.into_result() } /// %Algorithm type, one of SVMSGD::SvmsgdType. /// ## See also /// setSvmsgdType getSvmsgdType fn set_svmsgd_type(&mut self, svmsgd_type: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_setSvmsgdType_int(self.as_raw_mut_SVMSGD(), svmsgd_type) }.into_result() } /// %Margin type, one of SVMSGD::MarginType. /// ## See also /// setMarginType fn get_margin_type(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_getMarginType_const(self.as_raw_SVMSGD()) }.into_result() } /// %Margin type, one of SVMSGD::MarginType. /// ## See also /// setMarginType getMarginType fn set_margin_type(&mut self, margin_type: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_setMarginType_int(self.as_raw_mut_SVMSGD(), margin_type) }.into_result() } /// Parameter marginRegularization of a %SVMSGD optimization problem. /// ## See also /// setMarginRegularization fn get_margin_regularization(&self) -> Result<f32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_getMarginRegularization_const(self.as_raw_SVMSGD()) }.into_result() } /// Parameter marginRegularization of a %SVMSGD optimization problem. /// ## See also /// setMarginRegularization getMarginRegularization fn set_margin_regularization(&mut self, margin_regularization: f32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_setMarginRegularization_float(self.as_raw_mut_SVMSGD(), margin_regularization) }.into_result() } /// Parameter initialStepSize of a %SVMSGD optimization problem. /// ## See also /// setInitialStepSize fn get_initial_step_size(&self) -> Result<f32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_getInitialStepSize_const(self.as_raw_SVMSGD()) }.into_result() } /// Parameter initialStepSize of a %SVMSGD optimization problem. /// ## See also /// setInitialStepSize getInitialStepSize fn set_initial_step_size(&mut self, initial_step_size: f32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_setInitialStepSize_float(self.as_raw_mut_SVMSGD(), initial_step_size) }.into_result() } /// Parameter stepDecreasingPower of a %SVMSGD optimization problem. /// ## See also /// setStepDecreasingPower fn get_step_decreasing_power(&self) -> Result<f32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_getStepDecreasingPower_const(self.as_raw_SVMSGD()) }.into_result() } /// Parameter stepDecreasingPower of a %SVMSGD optimization problem. /// ## See also /// setStepDecreasingPower getStepDecreasingPower fn set_step_decreasing_power(&mut self, step_decreasing_power: f32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_setStepDecreasingPower_float(self.as_raw_mut_SVMSGD(), step_decreasing_power) }.into_result() } /// Termination criteria of the training algorithm. /// You can specify the maximum number of iterations (maxCount) and/or how much the error could /// change between the iterations to make the algorithm continue (epsilon). /// ## See also /// setTermCriteria fn get_term_criteria(&self) -> Result<core::TermCriteria> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_getTermCriteria_const(self.as_raw_SVMSGD()) }.into_result() } /// Termination criteria of the training algorithm. /// You can specify the maximum number of iterations (maxCount) and/or how much the error could /// change between the iterations to make the algorithm continue (epsilon). /// ## See also /// setTermCriteria getTermCriteria fn set_term_criteria(&mut self, val: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_setTermCriteria_const_TermCriteriaR(self.as_raw_mut_SVMSGD(), &val) }.into_result() } } impl dyn SVMSGD + '_ { /// Creates empty model. /// Use StatModel::train to train the model. Since %SVMSGD has several parameters, you may want to /// find the best parameters for your problem or use setOptimalParameters() to set some default parameters. pub fn create() -> Result<core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::SVMSGD>> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_create() }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::SVMSGD>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Loads and creates a serialized SVMSGD from a file /// /// Use SVMSGD::save to serialize and store an SVMSGD to disk. /// Load the SVMSGD from this file again, by calling this function with the path to the file. /// Optionally specify the node for the file containing the classifier /// /// ## Parameters /// * filepath: path to serialized SVMSGD /// * nodeName: name of node containing the classifier /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * node_name: String() pub fn load(filepath: &str, node_name: &str) -> Result<core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::SVMSGD>> { extern_container_arg!(filepath); extern_container_arg!(node_name); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_SVMSGD_load_const_StringR_const_StringR(filepath.opencv_as_extern(), node_name.opencv_as_extern()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::SVMSGD>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } } /// Base class for statistical models in OpenCV ML. pub trait StatModel: core::AlgorithmTrait { fn as_raw_StatModel(&self) -> *const c_void; fn as_raw_mut_StatModel(&mut self) -> *mut c_void; /// Returns the number of variables in training samples fn get_var_count(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_StatModel_getVarCount_const(self.as_raw_StatModel()) }.into_result() } fn empty(&self) -> Result<bool> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_StatModel_empty_const(self.as_raw_StatModel()) }.into_result() } /// Returns true if the model is trained fn is_trained(&self) -> Result<bool> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_StatModel_isTrained_const(self.as_raw_StatModel()) }.into_result() } /// Returns true if the model is classifier fn is_classifier(&self) -> Result<bool> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_StatModel_isClassifier_const(self.as_raw_StatModel()) }.into_result() } /// Trains the statistical model /// /// ## Parameters /// * trainData: training data that can be loaded from file using TrainData::loadFromCSV or /// created with TrainData::create. /// * flags: optional flags, depending on the model. Some of the models can be updated with the /// new training samples, not completely overwritten (such as NormalBayesClassifier or ANN_MLP). /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * flags: 0 fn train_with_data(&mut self, train_data: &core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::TrainData>, flags: i32) -> Result<bool> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_StatModel_train_const_Ptr_TrainData_R_int(self.as_raw_mut_StatModel(), train_data.as_raw_PtrOfTrainData(), flags) }.into_result() } /// Trains the statistical model /// /// ## Parameters /// * samples: training samples /// * layout: See ml::SampleTypes. /// * responses: vector of responses associated with the training samples. fn train(&mut self, samples: &dyn core::ToInputArray, layout: i32, responses: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<bool> { input_array_arg!(samples); input_array_arg!(responses); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_StatModel_train_const__InputArrayR_int_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_StatModel(), samples.as_raw__InputArray(), layout, responses.as_raw__InputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Computes error on the training or test dataset /// /// ## Parameters /// * data: the training data /// * test: if true, the error is computed over the test subset of the data, otherwise it's /// computed over the training subset of the data. Please note that if you loaded a completely /// different dataset to evaluate already trained classifier, you will probably want not to set /// the test subset at all with TrainData::setTrainTestSplitRatio and specify test=false, so /// that the error is computed for the whole new set. Yes, this sounds a bit confusing. /// * resp: the optional output responses. /// /// The method uses StatModel::predict to compute the error. For regression models the error is /// computed as RMS, for classifiers - as a percent of missclassified samples (0%-100%). fn calc_error(&self, data: &core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::TrainData>, test: bool, resp: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<f32> { output_array_arg!(resp); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_StatModel_calcError_const_const_Ptr_TrainData_R_bool_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_StatModel(), data.as_raw_PtrOfTrainData(), test, resp.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Predicts response(s) for the provided sample(s) /// /// ## Parameters /// * samples: The input samples, floating-point matrix /// * results: The optional output matrix of results. /// * flags: The optional flags, model-dependent. See cv::ml::StatModel::Flags. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * results: noArray() /// * flags: 0 fn predict(&self, samples: &dyn core::ToInputArray, results: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<f32> { input_array_arg!(samples); output_array_arg!(results); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_StatModel_predict_const_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(self.as_raw_StatModel(), samples.as_raw__InputArray(), results.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags) }.into_result() } } /// Class encapsulating training data. /// /// Please note that the class only specifies the interface of training data, but not implementation. /// All the statistical model classes in _ml_ module accepts Ptr\<TrainData\> as parameter. In other /// words, you can create your own class derived from TrainData and pass smart pointer to the instance /// of this class into StatModel::train. /// ## See also /// @ref ml_intro_data pub trait TrainData { fn as_raw_TrainData(&self) -> *const c_void; fn as_raw_mut_TrainData(&mut self) -> *mut c_void; fn get_layout(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getLayout_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result() } fn get_n_train_samples(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getNTrainSamples_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result() } fn get_n_test_samples(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getNTestSamples_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result() } fn get_n_samples(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getNSamples_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result() } fn get_n_vars(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getNVars_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result() } fn get_n_all_vars(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getNAllVars_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result() } fn get_sample(&self, var_idx: &dyn core::ToInputArray, sidx: i32, buf: &mut f32) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(var_idx); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getSample_const_const__InputArrayR_int_floatX(self.as_raw_TrainData(), var_idx.as_raw__InputArray(), sidx, buf) }.into_result() } fn get_samples(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getSamples_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } fn get_missing(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getMissing_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Returns matrix of train samples /// /// ## Parameters /// * layout: The requested layout. If it's different from the initial one, the matrix is /// transposed. See ml::SampleTypes. /// * compressSamples: if true, the function returns only the training samples (specified by /// sampleIdx) /// * compressVars: if true, the function returns the shorter training samples, containing only /// the active variables. /// /// In current implementation the function tries to avoid physical data copying and returns the /// matrix stored inside TrainData (unless the transposition or compression is needed). /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * layout: ROW_SAMPLE /// * compress_samples: true /// * compress_vars: true fn get_train_samples(&self, layout: i32, compress_samples: bool, compress_vars: bool) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getTrainSamples_const_int_bool_bool(self.as_raw_TrainData(), layout, compress_samples, compress_vars) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Returns the vector of responses /// /// The function returns ordered or the original categorical responses. Usually it's used in /// regression algorithms. fn get_train_responses(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getTrainResponses_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Returns the vector of normalized categorical responses /// /// The function returns vector of responses. Each response is integer from `0` to `<number of /// classes>-1`. The actual label value can be retrieved then from the class label vector, see /// TrainData::getClassLabels. fn get_train_norm_cat_responses(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getTrainNormCatResponses_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } fn get_test_responses(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getTestResponses_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } fn get_test_norm_cat_responses(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getTestNormCatResponses_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } fn get_responses(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getResponses_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } fn get_norm_cat_responses(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getNormCatResponses_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } fn get_sample_weights(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getSampleWeights_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } fn get_train_sample_weights(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getTrainSampleWeights_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } fn get_test_sample_weights(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getTestSampleWeights_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } fn get_var_idx(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getVarIdx_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } fn get_var_type(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getVarType_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } fn get_var_symbol_flags(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getVarSymbolFlags_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } fn get_response_type(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getResponseType_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result() } fn get_train_sample_idx(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getTrainSampleIdx_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } fn get_test_sample_idx(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getTestSampleIdx_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } fn get_values(&self, vi: i32, sidx: &dyn core::ToInputArray, values: &mut f32) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(sidx); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getValues_const_int_const__InputArrayR_floatX(self.as_raw_TrainData(), vi, sidx.as_raw__InputArray(), values) }.into_result() } fn get_norm_cat_values(&self, vi: i32, sidx: &dyn core::ToInputArray, values: &mut i32) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(sidx); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getNormCatValues_const_int_const__InputArrayR_intX(self.as_raw_TrainData(), vi, sidx.as_raw__InputArray(), values) }.into_result() } fn get_default_subst_values(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getDefaultSubstValues_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } fn get_cat_count(&self, vi: i32) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getCatCount_const_int(self.as_raw_TrainData(), vi) }.into_result() } /// Returns the vector of class labels /// /// The function returns vector of unique labels occurred in the responses. fn get_class_labels(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getClassLabels_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } fn get_cat_ofs(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getCatOfs_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } fn get_cat_map(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getCatMap_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Splits the training data into the training and test parts /// ## See also /// TrainData::setTrainTestSplitRatio /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * shuffle: true fn set_train_test_split(&mut self, count: i32, shuffle: bool) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_setTrainTestSplit_int_bool(self.as_raw_mut_TrainData(), count, shuffle) }.into_result() } /// Splits the training data into the training and test parts /// /// The function selects a subset of specified relative size and then returns it as the training /// set. If the function is not called, all the data is used for training. Please, note that for /// each of TrainData::getTrain\* there is corresponding TrainData::getTest\*, so that the test /// subset can be retrieved and processed as well. /// ## See also /// TrainData::setTrainTestSplit /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * shuffle: true fn set_train_test_split_ratio(&mut self, ratio: f64, shuffle: bool) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_setTrainTestSplitRatio_double_bool(self.as_raw_mut_TrainData(), ratio, shuffle) }.into_result() } fn shuffle_train_test(&mut self) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_shuffleTrainTest(self.as_raw_mut_TrainData()) }.into_result() } /// Returns matrix of test samples fn get_test_samples(&self) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getTestSamples_const(self.as_raw_TrainData()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Returns vector of symbolic names captured in loadFromCSV() fn get_names(&self, names: &mut core::Vector::<String>) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getNames_const_vector_String_R(self.as_raw_TrainData(), names.as_raw_mut_VectorOfString()) }.into_result() } } impl dyn TrainData + '_ { pub fn missing_value() -> Result<f32> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_missingValue() }.into_result() } /// Extract from 1D vector elements specified by passed indexes. /// ## Parameters /// * vec: input vector (supported types: CV_32S, CV_32F, CV_64F) /// * idx: 1D index vector pub fn get_sub_vector(vec: &core::Mat, idx: &core::Mat) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getSubVector_const_MatR_const_MatR(vec.as_raw_Mat(), idx.as_raw_Mat()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Extract from matrix rows/cols specified by passed indexes. /// ## Parameters /// * matrix: input matrix (supported types: CV_32S, CV_32F, CV_64F) /// * idx: 1D index vector /// * layout: specifies to extract rows (cv::ml::ROW_SAMPLES) or to extract columns (cv::ml::COL_SAMPLES) pub fn get_sub_matrix(matrix: &core::Mat, idx: &core::Mat, layout: i32) -> Result<core::Mat> { unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_getSubMatrix_const_MatR_const_MatR_int(matrix.as_raw_Mat(), idx.as_raw_Mat(), layout) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Reads the dataset from a .csv file and returns the ready-to-use training data. /// /// ## Parameters /// * filename: The input file name /// * headerLineCount: The number of lines in the beginning to skip; besides the header, the /// function also skips empty lines and lines staring with `#` /// * responseStartIdx: Index of the first output variable. If -1, the function considers the /// last variable as the response /// * responseEndIdx: Index of the last output variable + 1. If -1, then there is single /// response variable at responseStartIdx. /// * varTypeSpec: The optional text string that specifies the variables' types. It has the /// format `ord[n1-n2,n3,n4-n5,...]cat[n6,n7-n8,...]`. That is, variables from `n1 to n2` /// (inclusive range), `n3`, `n4 to n5` ... are considered ordered and `n6`, `n7 to n8` ... are /// considered as categorical. The range `[n1..n2] + [n3] + [n4..n5] + ... + [n6] + [n7..n8]` /// should cover all the variables. If varTypeSpec is not specified, then algorithm uses the /// following rules: /// - all input variables are considered ordered by default. If some column contains has non- /// numerical values, e.g. 'apple', 'pear', 'apple', 'apple', 'mango', the corresponding /// variable is considered categorical. /// - if there are several output variables, they are all considered as ordered. Error is /// reported when non-numerical values are used. /// - if there is a single output variable, then if its values are non-numerical or are all /// integers, then it's considered categorical. Otherwise, it's considered ordered. /// * delimiter: The character used to separate values in each line. /// * missch: The character used to specify missing measurements. It should not be a digit. /// Although it's a non-numerical value, it surely does not affect the decision of whether the /// variable ordered or categorical. /// /// Note: If the dataset only contains input variables and no responses, use responseStartIdx = -2 /// and responseEndIdx = 0. The output variables vector will just contain zeros. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * response_start_idx: -1 /// * response_end_idx: -1 /// * var_type_spec: String() /// * delimiter: ',' /// * missch: '?' pub fn load_from_csv(filename: &str, header_line_count: i32, response_start_idx: i32, response_end_idx: i32, var_type_spec: &str, delimiter: i8, missch: i8) -> Result<core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::TrainData>> { extern_container_arg!(filename); extern_container_arg!(var_type_spec); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_loadFromCSV_const_StringR_int_int_int_const_StringR_char_char(filename.opencv_as_extern(), header_line_count, response_start_idx, response_end_idx, var_type_spec.opencv_as_extern(), delimiter, missch) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::TrainData>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Creates training data from in-memory arrays. /// /// ## Parameters /// * samples: matrix of samples. It should have CV_32F type. /// * layout: see ml::SampleTypes. /// * responses: matrix of responses. If the responses are scalar, they should be stored as a /// single row or as a single column. The matrix should have type CV_32F or CV_32S (in the /// former case the responses are considered as ordered by default; in the latter case - as /// categorical) /// * varIdx: vector specifying which variables to use for training. It can be an integer vector /// (CV_32S) containing 0-based variable indices or byte vector (CV_8U) containing a mask of /// active variables. /// * sampleIdx: vector specifying which samples to use for training. It can be an integer /// vector (CV_32S) containing 0-based sample indices or byte vector (CV_8U) containing a mask /// of training samples. /// * sampleWeights: optional vector with weights for each sample. It should have CV_32F type. /// * varType: optional vector of type CV_8U and size `<number_of_variables_in_samples> + /// <number_of_variables_in_responses>`, containing types of each input and output variable. See /// ml::VariableTypes. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * var_idx: noArray() /// * sample_idx: noArray() /// * sample_weights: noArray() /// * var_type: noArray() pub fn create(samples: &dyn core::ToInputArray, layout: i32, responses: &dyn core::ToInputArray, var_idx: &dyn core::ToInputArray, sample_idx: &dyn core::ToInputArray, sample_weights: &dyn core::ToInputArray, var_type: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::TrainData>> { input_array_arg!(samples); input_array_arg!(responses); input_array_arg!(var_idx); input_array_arg!(sample_idx); input_array_arg!(sample_weights); input_array_arg!(var_type); unsafe { sys::cv_ml_TrainData_create_const__InputArrayR_int_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(samples.as_raw__InputArray(), layout, responses.as_raw__InputArray(), var_idx.as_raw__InputArray(), sample_idx.as_raw__InputArray(), sample_weights.as_raw__InputArray(), var_type.as_raw__InputArray()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::ml::TrainData>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } }