1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 451 452 453 454 455 456 457 458 459 460 461 462 463 464 465 466 467 468 469 470 471 472 473 474 475 476 477 478 479 480 481 482 483 484 485 486 487 488 489 490 491 492 493 494 495 496 497 498 499 500 501 502 503 504 505 506 507 508 509 510 511 512 513 514 515 516 517 518 519 520 521 522 523 524 525 526 527 528 529 530 531 532 533 534 535 536 537 538 539 540 541 542 543 544 545 546 547 548 549 550 551 552 553 554 555 556 557 558 559 560 561 562 563 564 565 566 567 568 569 570 571 572 573 574 575 576 577 578 579 580 581 582 583 584 585 586 587 588 589 590 591 592 593 594 595 596 597 598 599 600 601 602 603 604 605 606 607 608 609 610 611 612 613 614 615 616 617 618 619 620 621 622 623 624 625 626 627 628 629 630 631 632 633 634 635 636 637 638 639 640 641 642 643 644 645 646 647 648 649 650 651 652 653 654 655 656 657 658 659 660 661 662 663 664 665 666 667 668 669 670 671 672 673 674 675 676 677 678 679 680 681 682 683 684 685 686 687 688 689 690 691 692 693 694 695 696 697 698 699 700 701 702 703 704 705 706 707 708 709 710 711 712 713 714 715 716
//! bindings to Nvidia Labs's [ꟻLIP] image comparison and error visualization library.
//!
//! This library allows you to visualize and reason about the human-noticable differences
//! between rendered images. Especially when comparing images that are noisy or other small
//! differences, FLIP's comparison can be more meaningful than a simple pixel-wise comparison.
//!
//! 
//!
//! In order to keep a small dependency closure, this crate does not depend on `image`,
//! but interop is simple.
//!
//! # Example
//!
//! ```rust
//! // First we load the "reference image". This is the image we want to compare against.
//! //
//! // We make sure to turn the image into RGB8 as FLIP doesn't deal with alpha.
//! let ref_image_data = image::open("../etc/tree-ref.png").unwrap().into_rgb8();
//! let ref_image = nv_flip::FlipImageRgb8::with_data(
//! ref_image_data.width(),
//! ref_image_data.height(),
//! &ref_image_data
//! );
//!
//! // We then load the "test image". This is the image we want to compare to the reference.
//! let test_image_data = image::open("../etc/tree-test.png").unwrap().into_rgb8();
//! let test_image = nv_flip::FlipImageRgb8::with_data(
//! test_image_data.width(),
//! test_image_data.height(),
//! &test_image_data
//! );
//!
//! // We now run the comparison. This will produce a "error map" that that is the per-pixel
//! // visual difference between the two images between 0 and 1.
//! //
//! // The last parameter is the number of pixels per degree of visual angle. This is used
//! // to determine the size of imperfections that can be seen. See the `pixels_per_degree`
//! // for more information. By default this value is 67.0.
//! let error_map = nv_flip::flip(ref_image, test_image, nv_flip::DEFAULT_PIXELS_PER_DEGREE);
//!
//! // We can now visualize the error map using a LUT that maps the error value to a color.
//! let visualized = error_map.apply_color_lut(&nv_flip::magma_lut());
//!
//! // Finally we can the final image into an `image` crate image and save it.
//! let image = image::RgbImage::from_raw(
//! visualized.width(),
//! visualized.height(),
//! visualized.to_vec()
//! ).unwrap();
//! # let _ = image;
//!
//! // We can get statistics about the error map by using their "Pool" type,
//! // which is essentially a weighted histogram.
//! let mut pool = nv_flip::FlipPool::from_image(&error_map);
//!
//! // These are the same statistics shown by the command line.
//! //
//! // The paper's writers recommend that, if you are to use a single number to
//! // represent the error, they recommend the mean.
//! println!("Mean: {}", pool.mean());
//! println!("Weighted median: {}", pool.get_percentile(0.5, true));
//! println!("1st weighted quartile: {}", pool.get_percentile(0.25, true));
//! println!("3rd weighted quartile: {}", pool.get_percentile(0.75, true));
//! println!("Min: {}", pool.min_value());
//! println!("Max: {}", pool.max_value());
//! ```
//! The result of this example looks like this:
//!
//! <!-- This table uses U+2800 BRAILLE PATTERN BLANK in the header make the images vaguely the same size. -->
//!
//! | Reference | ⠀⠀Test⠀⠀ | ⠀Result⠀ |
//! |:---------:|:---------:|:---------:|
//! |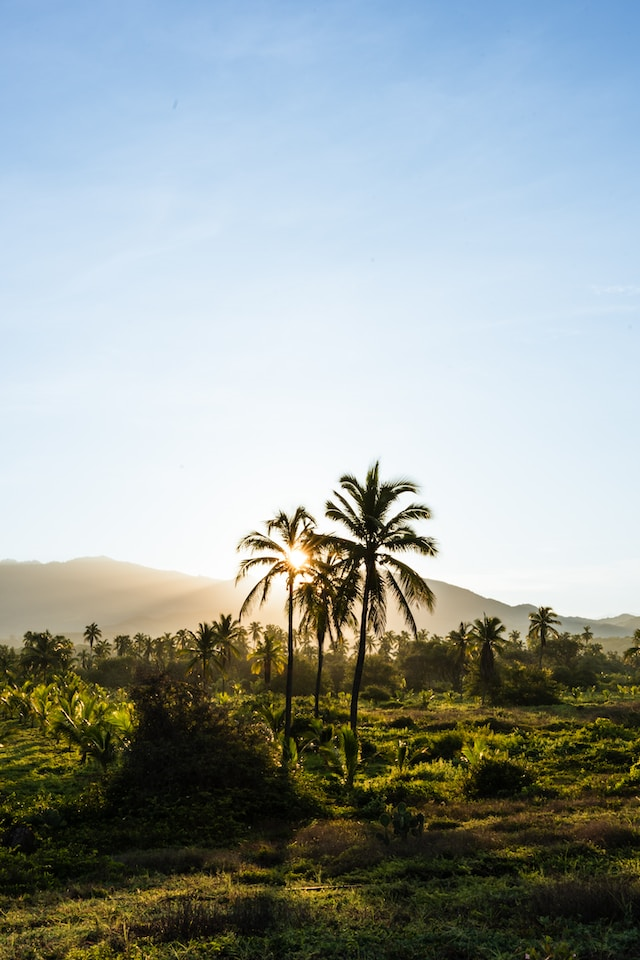  |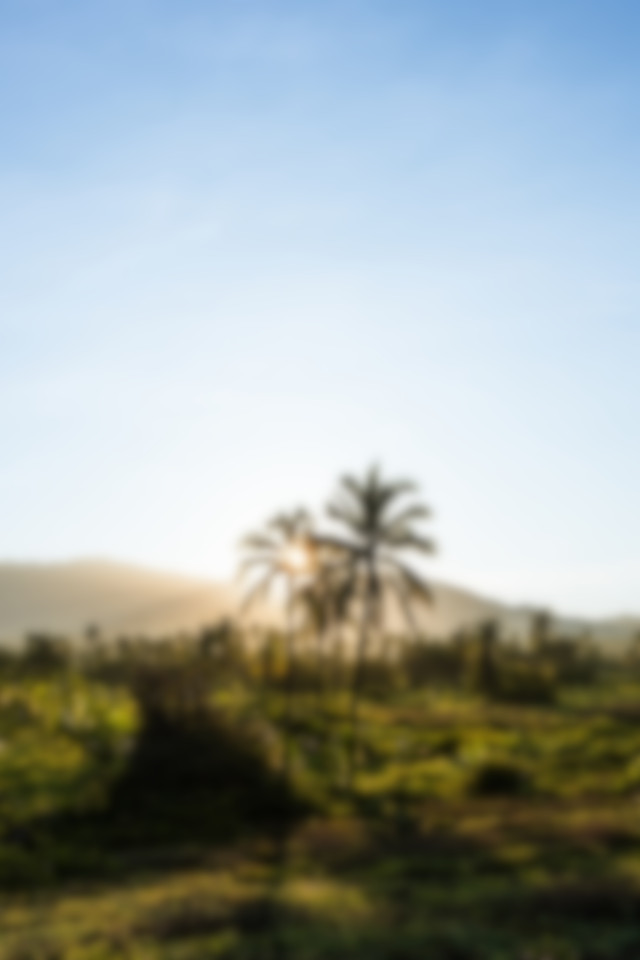  | 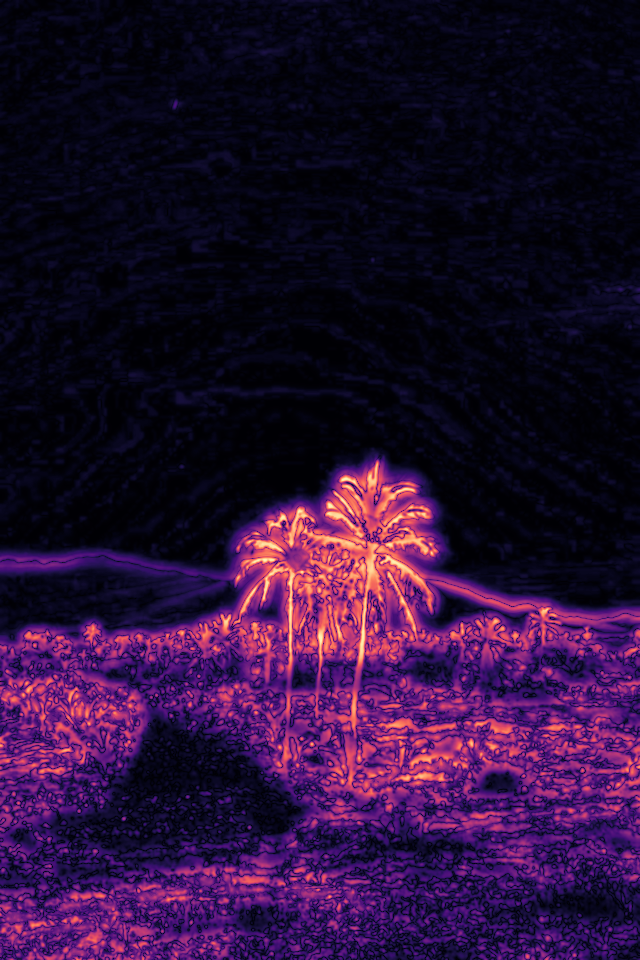 |
//!
//! # License
//!
//! The binding and rust interop code is tri-licensed under MIT, Apache-2.0, and ZLib.
//!
//! The ꟻLIP library itself is licensed under the BSD-3-Clause license.
//!
//! The example images used are licensed under the [Unsplash License].
//!
//! [ꟻLIP]: https://github.com/NVlabs/flip
//! [Unsplash License]: https://unsplash.com/license
use std::marker::PhantomData;
pub use nv_flip_sys::{pixels_per_degree, DEFAULT_PIXELS_PER_DEGREE};
/// 2D FLIP image that is accessed as Rgb8.
///
/// Internally this is Rgb32f, but the values are converted when read.
pub struct FlipImageRgb8 {
inner: *mut nv_flip_sys::FlipImageColor3,
width: u32,
height: u32,
}
unsafe impl Send for FlipImageRgb8 {}
unsafe impl Sync for FlipImageRgb8 {}
impl Clone for FlipImageRgb8 {
fn clone(&self) -> Self {
let inner = unsafe { nv_flip_sys::flip_image_color3_clone(self.inner) };
assert!(!inner.is_null());
Self {
inner,
width: self.width,
height: self.height,
}
}
}
impl FlipImageRgb8 {
/// Create a new image with the given dimensions and zeroed contents.
pub fn new(width: u32, height: u32) -> Self {
let inner = unsafe { nv_flip_sys::flip_image_color3_new(width, height, std::ptr::null()) };
assert!(!inner.is_null());
Self {
inner,
width,
height,
}
}
/// Creates a new image with the given dimensions and copies the data into it.
///
/// The data must be in Rgb8 format. Do not include alpha.
///
/// Data is expected in row-major orderm from the top left, tightly packed.
///
/// # Panics
///
/// - If the data is not large enough to fill the image.
pub fn with_data(width: u32, height: u32, data: &[u8]) -> Self {
assert!(data.len() >= (width * height * 3) as usize);
let inner = unsafe { nv_flip_sys::flip_image_color3_new(width, height, data.as_ptr()) };
assert!(!inner.is_null());
Self {
inner,
width,
height,
}
}
/// Extracts the data from the image and returns it as a vector.
///
/// Data is returned in row-major order, from the top left, tightly packed.
pub fn to_vec(&self) -> Vec<u8> {
let mut data = vec![0u8; (self.width * self.height * 3) as usize];
unsafe {
nv_flip_sys::flip_image_color3_get_data(self.inner, data.as_mut_ptr());
}
data
}
/// Returns the width of the image.
pub fn width(&self) -> u32 {
self.width
}
/// Returns the height of the image.
pub fn height(&self) -> u32 {
self.height
}
}
impl Drop for FlipImageRgb8 {
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe {
nv_flip_sys::flip_image_color3_free(self.inner);
}
}
}
/// 2D FLIP image that stores a single float per pixel.
pub struct FlipImageFloat {
inner: *mut nv_flip_sys::FlipImageFloat,
width: u32,
height: u32,
}
unsafe impl Send for FlipImageFloat {}
unsafe impl Sync for FlipImageFloat {}
impl Clone for FlipImageFloat {
fn clone(&self) -> Self {
// SAFETY: The clone function does not mutate the image, despite taking a mutable pointer.
let inner = unsafe { nv_flip_sys::flip_image_float_clone(self.inner) };
assert!(!inner.is_null());
Self {
inner,
width: self.width,
height: self.height,
}
}
}
impl FlipImageFloat {
/// Create a new image with the given dimensions and zeroed contents.
pub fn new(width: u32, height: u32) -> Self {
let inner = unsafe { nv_flip_sys::flip_image_float_new(width, height, std::ptr::null()) };
assert!(!inner.is_null());
Self {
inner,
width,
height,
}
}
/// Creates a new image with the given dimensions and copies the data into it.
///
/// Data is expected in row-major order, from the top left, tightly packed.
///
/// # Panics
///
/// - If the data is not large enough to fill the image.
pub fn with_data(width: u32, height: u32, data: &[f32]) -> Self {
assert!(data.len() >= (width * height) as usize);
let inner = unsafe { nv_flip_sys::flip_image_float_new(width, height, data.as_ptr()) };
assert!(!inner.is_null());
Self {
inner,
width,
height,
}
}
/// Applies the given 1D color lut to turn this single channel values into 3 channel values.
///
/// Applies the following algorithm to each pixel:
///
/// ```text
/// value_mapping[(pixel_value * 255).round() % value_mapping.width()]
/// ```
pub fn apply_color_lut(&self, value_mapping: &FlipImageRgb8) -> FlipImageRgb8 {
let output = FlipImageRgb8::new(self.width, self.height);
unsafe {
nv_flip_sys::flip_image_color3_color_map(output.inner, self.inner, value_mapping.inner);
}
output
}
/// Converts the image to a color image by copying the single channel value to all 3 channels.
pub fn to_color3(&self) -> FlipImageRgb8 {
let color3 = FlipImageRgb8::new(self.width, self.height);
unsafe {
nv_flip_sys::flip_image_float_copy_float_to_color3(self.inner, color3.inner);
}
color3
}
/// Extracts the data from the image and returns it as a vector.
///
/// Data is returned in row-major order, from the top left, tightly packed.
pub fn to_vec(&self) -> Vec<f32> {
let mut data = vec![0f32; (self.width * self.height) as usize];
unsafe {
nv_flip_sys::flip_image_float_get_data(self.inner, data.as_mut_ptr());
}
data
}
/// Returns the width of the image.
pub fn width(&self) -> u32 {
self.width
}
/// Returns the height of the image.
pub fn height(&self) -> u32 {
self.height
}
}
impl Drop for FlipImageFloat {
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe {
nv_flip_sys::flip_image_float_free(self.inner);
}
}
}
/// Generates a 1D lut using the builtin magma colormap for mapping error values to colors.
pub fn magma_lut() -> FlipImageRgb8 {
let inner = unsafe { nv_flip_sys::flip_image_color3_magma_map() };
assert!(!inner.is_null());
FlipImageRgb8 {
inner,
width: 256,
height: 1,
}
}
/// Performs a FLIP comparison between the two images.
///
/// The images must be the same size.
///
/// Returns an error map image, where each pixel represents the error between the two images
/// at that location between 0 and 1.
///
/// The pixels_per_degree parameter is used to determine the sensitivity to differences. See the
/// documentation for [`DEFAULT_PIXELS_PER_DEGREE`] and [`pixels_per_degree`] for more information.
///
/// Consumes both images as the algorithm uses them for scratch space. If you want to re-use
/// the images, clone them while passing them in.
///
/// # Panics
///
/// - If the images are not the same size.
pub fn flip(
reference_image: FlipImageRgb8,
test_image: FlipImageRgb8,
pixels_per_degree: f32,
) -> FlipImageFloat {
assert_eq!(
reference_image.width(),
test_image.width(),
"Width mismatch between reference and test image"
);
assert_eq!(
reference_image.height(),
test_image.height(),
"Height mismatch between reference and test image"
);
let error_map = FlipImageFloat::new(reference_image.width(), reference_image.height());
unsafe {
nv_flip_sys::flip_image_float_flip(
error_map.inner,
reference_image.inner,
test_image.inner,
pixels_per_degree,
);
}
error_map
}
/// Bucket based histogram used internally by [`FlipPool`].
///
/// Generally you should not need to use this directly and any mutating
/// operations are unsafe to prevent violating FlipPool invariants.
pub struct FlipHistogram<'a> {
inner: *mut nv_flip_sys::FlipImageHistogramRef,
_phantom: PhantomData<&'a ()>,
}
impl<'a> FlipHistogram<'a> {
/// Returns the difference between the maximum and minimum bucket values.
pub fn bucket_size(&self) -> usize {
unsafe { nv_flip_sys::flip_image_histogram_ref_get_bucket_size(self.inner) }
}
/// Returns the index of the lowest bucket currently in use.
///
/// If no buckets are in use, returns None.
pub fn bucket_id_min(&self) -> Option<usize> {
let value = unsafe { nv_flip_sys::flip_image_histogram_ref_get_bucket_id_min(self.inner) };
if value == usize::MAX {
None
} else {
Some(value)
}
}
/// Returns the index of the highest bucket currently in use.
///
/// If no buckets are in use, returns 0.
pub fn bucket_id_max(&self) -> usize {
unsafe { nv_flip_sys::flip_image_histogram_ref_get_bucket_id_max(self.inner) }
}
/// Returns the amount of values contained within a given bucket.
///
/// # Panics
///
/// - If the bucket_id is out of bounds.
pub fn bucket_value_count(&self, bucket_id: usize) -> usize {
assert!(bucket_id < self.bucket_count());
unsafe { nv_flip_sys::flip_image_histogram_ref_get_bucket_value(self.inner, bucket_id) }
}
/// Returns the amount of buckets in the histogram.
pub fn bucket_count(&self) -> usize {
unsafe { nv_flip_sys::flip_image_histogram_ref_size(self.inner) }
}
/// Returns the smallest value the histogram can handle.
pub fn minimum_allowed_value(&self) -> f32 {
unsafe { nv_flip_sys::flip_image_histogram_ref_get_min_value(self.inner) }
}
/// Returns the largest value the histogram can handle.
pub fn maximum_allowed_value(&self) -> f32 {
unsafe { nv_flip_sys::flip_image_histogram_ref_get_max_value(self.inner) }
}
/// Clears the histogram of all values
///
/// # Safety
///
/// Due to the many invariants between the histogram and the pool,
/// we do not provide any safty guarentees when mutating the histogram.
pub unsafe fn clear(&mut self) {
unsafe {
nv_flip_sys::flip_image_histogram_ref_clear(self.inner);
}
}
/// Resizes the histogram to have `bucket_size` buckets.
///
/// # Safety
///
/// Due to the many invariants between the histogram and the pool,
/// we do not provide any safty guarentees when mutating the histogram.
pub unsafe fn resize(&mut self, bucket_size: usize) {
unsafe {
nv_flip_sys::flip_image_histogram_ref_resize(self.inner, bucket_size);
}
}
/// Returns which bucket a given value would fall into.
pub fn bucket_id(&self, value: f32) -> usize {
unsafe { nv_flip_sys::flip_image_histogram_ref_value_bucket_id(self.inner, value) }
}
/// Includes `count` instances of the following `value` in the histogram.
///
/// # Safety
///
/// Due to the many invariants between the histogram and the pool,
/// we do not provide any safty guarentees when mutating the histogram.
pub unsafe fn include_value(&mut self, value: f32, count: usize) {
unsafe {
nv_flip_sys::flip_image_histogram_ref_inc_value(self.inner, value, count);
}
}
/// Includes one instance of each value in the given image in the histogram.
///
/// # Safety
///
/// Due to the many invariants between the histogram and the pool,
/// we do not provide any safty guarentees when mutating the histogram.
pub unsafe fn include_image(&mut self, image: &FlipImageFloat) {
unsafe {
nv_flip_sys::flip_image_histogram_ref_inc_image(self.inner, image.inner);
}
}
}
impl Drop for FlipHistogram<'_> {
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe {
nv_flip_sys::flip_image_histogram_ref_free(self.inner);
}
}
}
/// Histogram-like value pool for determining if error map has significant differences.
///
/// This is how you can programmatically determine if images count as different.
pub struct FlipPool {
inner: *mut nv_flip_sys::FlipImagePool,
values_added: usize,
}
impl FlipPool {
/// Creates a new pool with 100 buckets.
pub fn new() -> Self {
Self::with_buckets(100)
}
/// Creates a new pool with the given amount of buckets.
pub fn with_buckets(bucket_count: usize) -> Self {
let inner = unsafe { nv_flip_sys::flip_image_pool_new(bucket_count) };
assert!(!inner.is_null());
Self {
inner,
values_added: 0,
}
}
/// Creates a new pool and initializes the buckets with the values given image.
pub fn from_image(image: &FlipImageFloat) -> Self {
let mut pool = Self::new();
pool.update_with_image(image);
pool
}
/// Accesses the internal histogram of the pool.
pub fn histogram(&mut self) -> FlipHistogram<'_> {
let inner = unsafe { nv_flip_sys::flip_image_pool_get_histogram(self.inner) };
assert!(!inner.is_null());
FlipHistogram {
inner,
_phantom: PhantomData,
}
}
/// Gets the minimum value stored in the pool.
///
/// Returns 0.0 if no values have been added to the pool.
pub fn min_value(&self) -> f32 {
if self.values_added == 0 {
return 0.0;
}
unsafe { nv_flip_sys::flip_image_pool_get_min_value(self.inner) }
}
/// Gets the maximum value stored in the pool.
///
/// Returns 0.0 if no values have been added to the pool.
pub fn max_value(&self) -> f32 {
if self.values_added == 0 {
return 0.0;
}
unsafe { nv_flip_sys::flip_image_pool_get_max_value(self.inner) }
}
/// Gets the mean value stored in the pool.
///
/// Returns 0.0 if no values have been added to the pool.
pub fn mean(&self) -> f32 {
// Avoid div by zero in body.
if self.values_added == 0 {
return 0.0;
}
unsafe { nv_flip_sys::flip_image_pool_get_mean(self.inner) }
}
/// Gets the given weighted percentile [0.0, 1.0] from the pool.
///
/// I currently do not understand the difference between this and [`Self::get_percentile`] with weighted = true,
/// except that this function uses doubles and doesn't require mutation of internal state.
///
/// Returns 0.0 if no values have been added to the pool.
pub fn get_weighted_percentile(&self, percentile: f64) -> f64 {
if self.values_added == 0 {
return 0.0;
}
let bounds_percentile = f64::clamp(percentile, 0.0, next_f64_down(1.0));
unsafe {
nv_flip_sys::flip_image_pool_get_weighted_percentile(self.inner, bounds_percentile)
}
}
/// Get the value of the given percentile [0.0, 1.0] from the pool.
///
/// If `weighted` is true, is almost equivalent to [`Self::get_weighted_percentile`].
///
/// Returns 0.0 if no values have been added to the pool.
pub fn get_percentile(&mut self, percentile: f32, weighted: bool) -> f32 {
// Avoids a division by zero when bounds checking.
if self.values_added == 0 {
return 0.0;
}
// The implementaion doesn't actually do any bounds checking on the percentile,
// so we need to do it here, including tracking count of values added.
let bounds_percentile =
f32::clamp(percentile, 0.0, 1.0 - (self.values_added as f32).recip());
// Replicates the indexing behavior of the C++ implementation.
debug_assert!(
(f32::ceil(bounds_percentile * self.values_added as f32) as usize) < self.values_added
);
unsafe {
nv_flip_sys::flip_image_pool_get_percentile(self.inner, bounds_percentile, weighted)
}
}
/// Updates the given pool with the contents of the given image.
pub fn update_with_image(&mut self, image: &FlipImageFloat) {
unsafe {
nv_flip_sys::flip_image_pool_update_image(self.inner, image.inner);
}
self.values_added += image.width() as usize * image.height() as usize;
}
/// Clears the pool.
pub fn clear(&mut self) {
unsafe {
nv_flip_sys::flip_image_pool_clear(self.inner);
}
self.values_added = 0;
}
}
impl Default for FlipPool {
fn default() -> Self {
Self::new()
}
}
impl Drop for FlipPool {
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe {
nv_flip_sys::flip_image_pool_free(self.inner);
}
}
}
// This next_f64_down impl only works for positive, normal values that are
// more than one ulp away from f64::MIN_POSITIVE.
fn next_f64_down(value: f64) -> f64 {
f64::from_bits(value.to_bits() - 1)
}
#[cfg(test)]
mod tests {
pub use super::*;
use float_eq::assert_float_eq;
#[test]
fn zeroed_init() {
assert_eq!(FlipImageRgb8::new(10, 10).to_vec(), vec![0u8; 10 * 10 * 3]);
assert_eq!(FlipImageFloat::new(10, 10).to_vec(), vec![0.0f32; 10 * 10]);
}
#[test]
fn zero_size_pool_ops() {
let mut pool = FlipPool::new();
assert_eq!(pool.min_value(), 0.0);
assert_eq!(pool.max_value(), 0.0);
assert_eq!(pool.mean(), 0.0);
assert_eq!(pool.get_percentile(0.0, false), 0.0);
assert_eq!(pool.get_percentile(0.0, true), 0.0);
assert_eq!(pool.get_weighted_percentile(0.0), 0.0);
}
#[test]
fn end_to_end() {
let reference_image = image::open("../etc/tree-ref.png").unwrap().into_rgb8();
let reference_image = FlipImageRgb8::with_data(
reference_image.width(),
reference_image.height(),
&reference_image,
);
let test_image = image::open("../etc/tree-test.png").unwrap().into_rgb8();
let test_image =
FlipImageRgb8::with_data(test_image.width(), test_image.height(), &test_image);
let error_map = flip(reference_image, test_image, DEFAULT_PIXELS_PER_DEGREE);
let mut pool = FlipPool::from_image(&error_map);
let magma_lut = magma_lut();
let color = error_map.apply_color_lut(&magma_lut);
let image =
image::RgbImage::from_raw(color.width(), color.height(), color.to_vec()).unwrap();
let reference = image::open("../etc/tree-comparison-cli.png")
.unwrap()
.into_rgb8();
for (a, b) in image.pixels().zip(reference.pixels()) {
assert!(a.0[0].abs_diff(b.0[0]) <= 3);
assert!(a.0[1].abs_diff(b.0[1]) <= 3);
assert!(a.0[2].abs_diff(b.0[2]) <= 3);
}
// These numbers pulled directly from the command line tool
const TOLERENCE: f32 = 0.000_1;
assert_float_eq!(pool.mean(), 0.133285, abs <= TOLERENCE);
assert_float_eq!(pool.get_percentile(0.25, true), 0.184924, abs <= TOLERENCE);
assert_float_eq!(pool.get_percentile(0.50, true), 0.333241, abs <= TOLERENCE);
assert_float_eq!(pool.get_percentile(0.75, true), 0.503441, abs <= TOLERENCE);
assert_float_eq!(pool.min_value(), 0.000000, abs <= TOLERENCE);
assert_float_eq!(pool.get_percentile(0.0, true), 0.000000, abs <= 0.001);
assert_float_eq!(pool.max_value(), 0.983044, abs <= TOLERENCE);
assert_float_eq!(pool.get_percentile(1.0, true), 0.983044, abs <= 0.001);
assert_float_eq!(
pool.get_weighted_percentile(0.25),
0.184586,
abs <= TOLERENCE as f64
);
assert_float_eq!(
pool.get_weighted_percentile(0.50),
0.333096,
abs <= TOLERENCE as f64
);
assert_float_eq!(
pool.get_weighted_percentile(0.75),
0.503230,
abs <= TOLERENCE as f64
);
let histogram = pool.histogram();
assert_float_eq!(histogram.minimum_allowed_value(), 0.0, abs <= TOLERENCE);
assert_float_eq!(histogram.maximum_allowed_value(), 1.0, abs <= TOLERENCE);
drop(histogram);
// Absurd values, trying to edge case the histogram
assert_float_eq!(pool.get_percentile(-10000.0, false), 0.0, abs <= TOLERENCE);
assert_float_eq!(pool.get_percentile(-10000.0, true), 0.0, abs <= TOLERENCE);
assert_float_eq!(
pool.get_percentile(10000.0, false),
0.983044,
abs <= TOLERENCE
);
assert_float_eq!(
pool.get_percentile(10000.0, true),
0.983044,
abs <= TOLERENCE
);
assert_float_eq!(
pool.get_weighted_percentile(-10000.0),
0.0,
abs <= TOLERENCE as _
);
assert_float_eq!(
pool.get_weighted_percentile(10000.0),
0.989999,
abs <= TOLERENCE as _
);
}
}