Expand description
Lotus is a game engine with the main focus of being easy-to-use and straight forward on developing 2D games.
It’s based on the Entity-Component-System paradigm, providing windowing, rendering, physics, input handling, and more.
Heavily inspired by awesome open-source projects like Bevy, Comfy and LÖVE.
§How it works?
With the power of macros, the engine basic template could be very abstracted and easy to look up to.
The your_game! macro only needs three parameters to make a game real.
-> The window configuration
- This parameter will be used to personalize and create the game window.
-> The setup function
- This parameter is a real function that will be ran once at the start of the application.
- The function should contain a mutable reference to the context as the parameter.
- Should contain all the initial entity spawning code for the game.
-> The update function
- This parameter is a real function as well, that will be ran at each frame of the application.
- The function should contain a mutable reference to the context as the parameter.
- Should contain all the logic functions behind the game.
§About assets
Make sure your textures, fonts, sounds and all that nice stuff are inside of the assets folder located in the root of your project!
The engine will use the CARGO_MANIFEST_DIR to search for your assets and make sure that all is loaded correctly.
Your folder tree should look similar to this:
my_awesome_2d_application/
├── assets/
│ ├── textures/
│ ├── fonts/
│ ├── sounds/
│ └── ...
├── src/
│ ├── main.rs
└── Cargo.tomlYou should use your relative paths like this:
use lotus_engine::*;
your_game!(
WindowConfiguration::default(),
setup,
update
);
fn setup(_context: &mut Context) {
// As you can see, you DON'T need to use 'assets/' in your relative path.
let sprite: Sprite = Sprite::new("textures/lotus_pink_256x256.png".to_string());
}
fn update(_context: &mut Context) {}§The Entity-Component-System paradigm
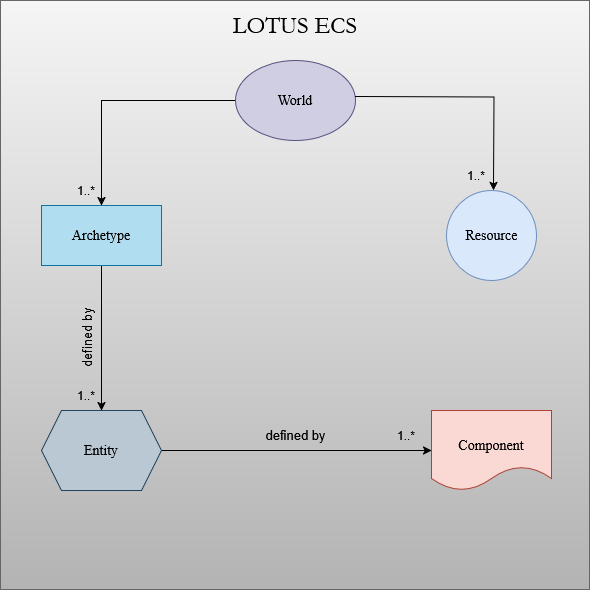
Lotus uses a custom Entity-Component-System (ECS) archictecture.
You can see the documentation about it here.
As a brief overview:
- Structs defined with the derive macro Component are Components that can be spawned in our World within an Entity.
- Structs defined with the derive macro Resource are Resources that can be added to in our World.
- Entities are defined by it’s components and every entity has a unique ID.
- Entities are stored in what is called as Archetypes in our World.
- Archetypes are defined by the Components that our Entities have, so a Archetype will only have Entities with the same Components.
- The World can store multiple Archetypes, Entities, Components and Resources!
- And all of them can be queried using the Query struct.
§Examples
The classic hello world:
use lotus_engine::*;
your_game!(
WindowConfiguration::default(),
setup,
update
);
fn setup(_context: &mut Context) {}
fn update(_context: &mut Context) {
eprintln!("Hello World!");
}Refer to the tutorial.
And here are some more complex initial examples to demonstrate the engine’s potential:
- Pong:
examples/pong.rs - Breakout:
examples/breakout.rs - Rendering geometric forms:
examples/simple_shapes.rs - Rendering sprites:
examples/simple_sprite.rs - Physics simulation:
examples/physics_simulation.rs - Gravity simulation:
examples/gravity_simulation.rs
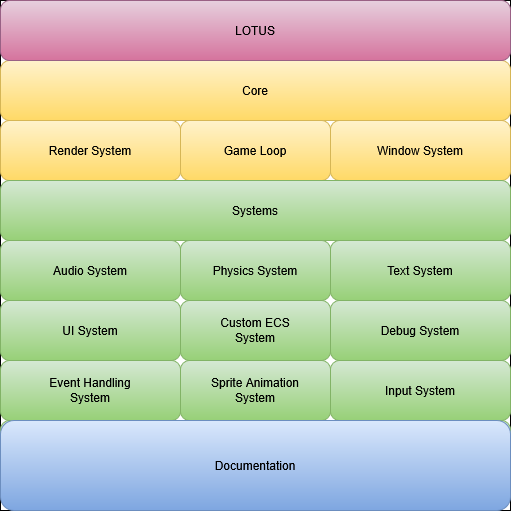
§Engine Architecture Overview
Re-exports§
pub use core::asset_loader::AssetLoader;pub use core::physics::transform::Transform;pub use core::managers::rendering::manager::*;pub use core::managers::windowing::manager::*;pub use core::game_loop::*;pub use core::context::*;pub use core::color::*;pub use core::visibility::*;pub use core::shape::*;pub use core::texture::sprite::*;pub use core::texture::sprite_sheet::*;pub use core::input::*;pub use core::text::*;pub use core::text::text::*;pub use core::text::font::*;pub use core::animation::*;pub use core::camera::camera2d::*;pub use core::physics::transform::*;pub use core::physics::acceleration::*;pub use core::physics::collision::*;pub use core::physics::velocity::*;pub use core::physics::gravity::*;pub use core::physics::rigid_body::*;pub use core::time::timer::*;pub use core::draw_order::*;pub use core::audio::audio_source::*;pub use core::audio::audio_error::*;pub use core::ecs::world::*;pub use core::ecs::entity::*;pub use core::ecs::component::*;pub use core::ecs::resource::*;pub use core::ecs::query::*;
Modules§
- backend
- Communication between Kira and a low-level audio API.
- clock
- Precise timing for audio events.
- command
- Helpers for sending commands from the gameplay thread to the audio thread.
You’ll only need to use this if you’re making your own implementation of
Sound,Effect, orModulator. - conv
- Constrained conversion functions for assisting in situations where type inference is difficult.
- core
- Module with the main features of the engine.
- effect
- Modifies audio signals.
- info
- Types for providing info about resources to trait implementors.
- listener
- Types related to spatial listeners.
- modulator
- Global values that parameters (like volume and playback rate) can be linked to.
- num_
traits - Numeric traits for generic mathematics
- prelude
- This module contains the most common traits used in
cgmath. By glob-importing this module, you can avoid the need to import each trait individually, while still being selective about what types you import. - sound
- Sources of audio.
- track
- Organizes and applies effects to audio.
- utils
- Module with utilities of the engine.
Macros§
- abs_
diff_ eq - Approximate equality of using the absolute difference.
- abs_
diff_ ne - Approximate inequality of using the absolute difference.
- assert_
abs_ diff_ eq - An assertion that delegates to
abs_diff_eq!, and panics with a helpful error on failure. - assert_
abs_ diff_ ne - An assertion that delegates to
abs_diff_ne!, and panics with a helpful error on failure. - assert_
relative_ eq - An assertion that delegates to
relative_eq!, and panics with a helpful error on failure. - assert_
relative_ ne - An assertion that delegates to
relative_ne!, and panics with a helpful error on failure. - assert_
ulps_ eq - An assertion that delegates to
ulps_eq!, and panics with a helpful error on failure. - assert_
ulps_ ne - An assertion that delegates to
ulps_ne!, and panics with a helpful error on failure. - command_
writers_ and_ readers - Creates a set of command writers and readers and a constructor for them.
You’ll only need to use this if you’re making your own implementation of
Sound,Effect, orModulator. - relative_
eq - Approximate equality using both the absolute difference and relative based comparisons.
- relative_
ne - Approximate inequality using both the absolute difference and relative based comparisons.
- ulps_eq
- Approximate equality using both the absolute difference and ULPs (Units in Last Place).
- ulps_ne
- Approximate inequality using both the absolute difference and ULPs (Units in Last Place).
- your_
game - The your_game! macro.
Structs§
- AbsDiff
- The requisite parameters for testing for approximate equality using a absolute difference based comparison.
- Audio
Manager - Controls audio from gameplay code.
- Audio
Manager Settings - Settings for an
AudioManager. - Basis2
- A two-dimensional rotation matrix.
- Basis3
- A three-dimensional rotation matrix.
- Capacities
- Specifies how many of each resource type an audio context can have.
- Decibels
- Represents a change in volume.
- Decomposed
- A generic transformation consisting of a rotation, displacement vector and scale amount.
- Deg
- An angle, in degrees.
- Euler
- A set of Euler angles representing a rotation in three-dimensional space.
- Frame
- A stereo audio sample.
- Mapping
- A transformation from a modulator’s value to a parameter value.
- Matrix2
- A 2 x 2, column major matrix
- Matrix3
- A 3 x 3, column major matrix
- Matrix4
- A 4 x 4, column major matrix
- Mix
- An amount to blend the “dry” and “wet” outputs from an effect.
- Ortho
- An orthographic projection with arbitrary left/right/bottom/top distances
- Panning
- The stereo positioning of a sound.
- Parameter
- Manages and updates a value that can be smoothly transitioned and linked to modulators.
- Perspective
- A perspective projection with arbitrary left/right/bottom/top distances
- Perspective
Fov - A perspective projection based on a vertical field-of-view angle.
- Playback
Rate - How quickly a sound should be played, where
1.0is the default playback rate. - Point1
- A point in 1-dimensional space.
- Point2
- A point in 2-dimensional space.
- Point3
- A point in 3-dimensional space.
- Quaternion
- A quaternion in scalar/vector form.
- Rad
- An angle, in radians.
- Relative
- The requisite parameters for testing for approximate equality using a relative based comparison.
- Resource
Limit Reached - An error that is returned when a resource cannot be added because the maximum capacity for that resource has been reached.
- Semitones
- A change in pitch in semitones.
- Tween
- Describes a smooth transition between values.
- Ulps
- The requisite parameters for testing for approximate equality using an ULPs based comparison.
- Vector1
- A 1-dimensional vector.
- Vector2
- A 2-dimensional vector.
- Vector3
- A 3-dimensional vector.
- Vector4
- A 4-dimensional vector.
- Window
Buttons
Enums§
- Easing
- Curves the motion of a
Tween. - KeyCode
- Code representing the location of a physical key
- Mouse
Button - Describes a button of a mouse controller.
- Physical
Key - Represents the location of a physical key.
- Play
Sound Error - Errors that can occur when playing a sound.
- Present
Mode - Timing and queueing with which frames are actually displayed to the user.
- Start
Time - Describes when an action should occur.
- Value
- A value that a parameter can be linked to.
Traits§
- AbsDiff
Eq - Equality that is defined using the absolute difference of two numbers.
- Angle
- Angles and their associated trigonometric functions.
- Array
- An array containing elements of type
Element - Base
Float - Base floating point types
- BaseNum
- Base numeric types with partial ordering
- Bounded
- Numbers which have upper and lower bounds
- Element
Wise - Element-wise arithmetic operations. These are supplied for pragmatic reasons, but will usually fall outside of traditional algebraic properties.
- Euclidean
Space - Points in a Euclidean space with an associated space of displacement vectors.
- Inner
Space - Vectors that also have a dot (or inner) product.
- Matrix
- A column-major matrix of arbitrary dimensions.
- Metric
Space - A type with a distance function between values.
- One
- Defines a multiplicative identity element for
Self. - Relative
Eq - Equality comparisons between two numbers using both the absolute difference and relative based comparisons.
- Rotation
- A trait for a generic rotation. A rotation is a transformation that creates a circular motion, and preserves at least one point in the space.
- Rotation2
- A two-dimensional rotation.
- Rotation3
- A three-dimensional rotation.
- Square
Matrix - A column-major major matrix where the rows and column vectors are of the same dimensions.
- Transform2
- Transform3
- Tweenable
- A trait for types that can be smoothly interpolated.
- UlpsEq
- Equality comparisons between two numbers using both the absolute difference and ULPs (Units in Last Place) based comparisons.
- Vector
Space - Vectors that can be added together and multiplied by scalars.
- Zero
- Defines an additive identity element for
Self.
Functions§
- block_
on - Block the thread until the future is ready.
- dot
- Dot product of two vectors.
- frustum
- Create a perspective matrix from a view frustum.
- interpolate_
frame - Given a previous frame, a current frame, the two next frames,
and a position
xfrom 0.0 to 1.0 between the current frame and next frame, get an approximated frame. - ortho
- Create an orthographic projection matrix.
- perspective
- Create a perspective projection matrix.
- point1
- The short constructor.
- point2
- The short constructor.
- point3
- The short constructor.
- vec1
- The short constructor.
- vec2
- The short constructor.
- vec3
- The short constructor.
- vec4
- The short constructor.
Type Aliases§
- Default
Backend - The default backend used by
AudioManagers.