1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 451 452 453 454 455 456 457 458 459 460 461 462 463 464 465 466 467 468 469 470 471 472 473 474 475 476 477 478 479 480 481 482 483 484 485 486 487 488 489 490 491 492 493 494 495 496 497 498 499 500 501 502 503 504 505 506 507 508 509 510 511 512 513 514 515 516 517 518 519 520 521 522 523 524 525 526 527 528 529 530 531 532 533 534 535 536 537 538 539 540 541 542 543 544 545 546 547 548 549 550 551 552 553 554 555 556 557 558 559 560 561 562 563 564 565 566 567 568 569 570 571 572 573 574 575 576 577 578 579 580 581 582 583 584 585 586 587 588 589 590 591 592 593 594 595 596 597 598 599 600 601 602 603 604 605 606 607 608 609 610 611 612 613 614 615 616 617 618 619 620 621 622 623 624 625 626 627 628 629 630 631 632 633 634 635 636 637 638 639 640 641 642 643 644 645 646 647 648 649 650 651 652 653 654 655 656 657 658 659 660 661 662 663 664 665 666 667 668 669 670 671 672 673 674 675 676 677 678 679 680 681 682 683 684 685 686 687 688 689 690 691 692 693 694 695 696 697 698 699 700 701 702 703 704 705 706 707 708 709 710 711 712 713 714 715 716 717 718 719 720 721 722 723 724 725 726 727 728 729 730 731 732 733 734 735 736 737 738 739 740 741 742 743 744 745 746 747 748 749 750 751 752 753 754 755 756 757 758 759 760 761 762 763 764 765 766 767 768 769 770 771 772 773 774 775 776 777 778 779 780 781 782 783 784 785 786 787 788 789 790 791 792 793 794 795 796 797 798 799 800 801 802 803 804 805 806 807 808 809 810 811 812 813 814 815 816 817 818 819 820 821 822 823 824 825 826 827 828 829 830 831 832 833 834 835 836 837 838 839 840 841 842 843 844 845 846 847 848 849 850 851 852 853 854 855 856 857 858 859 860 861 862 863 864 865 866 867 868 869 870 871 872 873 874 875 876 877 878 879 880 881 882 883 884 885 886 887 888 889 890 891 892 893 894 895 896 897 898 899 900 901 902 903 904 905 906 907 908 909 910 911 912 913 914 915 916 917 918 919 920 921 922 923 924 925 926 927 928 929 930 931 932 933 934 935 936 937 938 939 940 941 942 943 944 945 946 947 948 949 950 951 952 953 954 955 956 957 958 959 960 961 962 963 964 965 966 967 968 969 970 971 972 973 974 975 976 977 978 979 980 981 982 983 984 985 986 987 988 989 990 991 992 993 994 995 996 997 998 999 1000 1001 1002 1003 1004 1005 1006 1007 1008 1009 1010 1011 1012 1013 1014 1015 1016 1017 1018 1019 1020 1021 1022 1023 1024 1025 1026 1027 1028 1029 1030 1031 1032 1033 1034 1035 1036 1037 1038 1039 1040 1041 1042 1043 1044 1045 1046 1047 1048 1049 1050 1051 1052 1053 1054 1055 1056 1057 1058 1059 1060 1061 1062 1063 1064 1065 1066 1067 1068 1069 1070 1071 1072 1073 1074 1075 1076 1077 1078 1079 1080 1081 1082 1083 1084 1085 1086 1087 1088 1089 1090 1091 1092 1093 1094 1095 1096 1097 1098 1099 1100 1101 1102 1103 1104 1105 1106 1107 1108 1109 1110 1111 1112 1113 1114 1115 1116 1117 1118 1119 1120 1121 1122 1123 1124 1125 1126 1127 1128 1129 1130 1131 1132 1133 1134 1135 1136 1137 1138 1139 1140 1141 1142 1143 1144 1145 1146 1147 1148 1149 1150 1151 1152 1153 1154 1155 1156 1157 1158 1159 1160 1161 1162 1163 1164 1165 1166 1167 1168 1169 1170 1171 1172 1173 1174 1175 1176 1177 1178 1179 1180 1181 1182 1183 1184 1185 1186 1187 1188 1189 1190 1191 1192 1193 1194 1195 1196 1197 1198 1199 1200 1201 1202 1203 1204 1205 1206 1207 1208 1209 1210 1211 1212 1213 1214 1215 1216 1217 1218 1219 1220 1221 1222 1223 1224 1225 1226 1227 1228 1229 1230 1231 1232 1233 1234 1235 1236 1237 1238 1239 1240 1241 1242 1243 1244 1245 1246 1247 1248 1249 1250 1251 1252 1253 1254 1255 1256 1257 1258 1259 1260 1261 1262 1263 1264 1265 1266 1267 1268 1269 1270 1271 1272 1273 1274 1275 1276 1277 1278 1279 1280 1281 1282 1283 1284 1285 1286 1287 1288 1289 1290 1291 1292 1293 1294 1295 1296 1297 1298 1299 1300 1301 1302 1303 1304 1305 1306 1307 1308 1309 1310 1311 1312 1313 1314 1315 1316 1317 1318 1319 1320 1321 1322 1323 1324 1325 1326 1327 1328 1329 1330 1331 1332 1333 1334 1335 1336 1337 1338 1339 1340 1341 1342 1343 1344 1345 1346 1347 1348 1349 1350 1351 1352 1353 1354 1355 1356 1357 1358 1359 1360 1361 1362 1363 1364 1365 1366 1367 1368 1369 1370 1371 1372 1373 1374 1375 1376 1377 1378 1379 1380 1381 1382 1383 1384 1385 1386 1387 1388 1389 1390 1391 1392 1393 1394 1395 1396 1397 1398 1399 1400 1401 1402 1403 1404 1405 1406 1407 1408 1409 1410 1411 1412 1413 1414 1415 1416 1417 1418 1419 1420 1421 1422 1423 1424 1425 1426 1427 1428 1429 1430 1431 1432 1433 1434 1435 1436 1437 1438 1439 1440 1441 1442 1443 1444 1445 1446 1447 1448 1449 1450 1451 1452 1453 1454 1455 1456 1457 1458 1459 1460 1461 1462 1463 1464 1465 1466 1467 1468 1469 1470 1471 1472 1473 1474 1475 1476 1477 1478 1479 1480 1481 1482 1483 1484 1485 1486 1487 1488 1489 1490 1491 1492 1493 1494 1495 1496 1497 1498 1499 1500 1501 1502 1503 1504 1505 1506 1507 1508 1509 1510 1511 1512 1513 1514 1515 1516 1517 1518 1519 1520 1521 1522 1523 1524 1525 1526 1527 1528 1529 1530 1531 1532 1533 1534 1535 1536 1537 1538 1539 1540 1541 1542 1543 1544 1545 1546 1547 1548 1549 1550 1551 1552 1553 1554 1555 1556 1557 1558 1559 1560 1561 1562 1563 1564 1565 1566 1567 1568 1569 1570 1571 1572 1573 1574 1575 1576 1577 1578 1579 1580 1581 1582 1583 1584 1585 1586 1587 1588 1589 1590 1591 1592 1593 1594 1595 1596 1597 1598 1599 1600 1601 1602 1603 1604 1605 1606 1607 1608 1609 1610 1611 1612 1613 1614 1615 1616 1617 1618 1619 1620 1621 1622 1623 1624 1625 1626 1627 1628 1629 1630 1631 1632 1633 1634 1635 1636 1637 1638 1639 1640 1641 1642 1643 1644 1645 1646 1647 1648 1649 1650 1651 1652 1653 1654 1655 1656 1657 1658 1659 1660 1661 1662 1663 1664 1665 1666 1667 1668 1669 1670 1671 1672 1673 1674 1675 1676 1677 1678 1679 1680 1681 1682 1683 1684 1685 1686 1687 1688 1689 1690 1691 1692 1693 1694 1695 1696 1697 1698 1699 1700 1701 1702 1703 1704 1705 1706 1707 1708 1709 1710 1711 1712 1713 1714 1715 1716 1717 1718 1719 1720 1721 1722 1723 1724 1725 1726 1727 1728 1729 1730 1731 1732 1733 1734 1735 1736 1737 1738 1739 1740 1741 1742 1743 1744 1745 1746 1747 1748 1749 1750 1751 1752 1753 1754 1755 1756 1757 1758 1759 1760 1761 1762 1763 1764 1765 1766 1767 1768 1769 1770 1771 1772 1773 1774 1775 1776 1777 1778 1779 1780 1781 1782 1783 1784 1785 1786 1787 1788 1789 1790 1791 1792 1793 1794 1795 1796 1797 1798 1799 1800 1801 1802 1803 1804 1805 1806 1807 1808 1809 1810 1811 1812 1813 1814 1815 1816 1817 1818 1819 1820 1821 1822 1823 1824 1825 1826 1827 1828 1829 1830 1831 1832 1833 1834 1835 1836 1837 1838 1839 1840 1841 1842 1843 1844 1845 1846 1847 1848 1849 1850 1851 1852 1853 1854 1855 1856 1857 1858 1859 1860 1861 1862 1863 1864 1865 1866 1867 1868 1869 1870 1871 1872 1873 1874 1875 1876 1877 1878 1879 1880 1881 1882 1883 1884 1885 1886 1887 1888 1889 1890 1891 1892 1893 1894 1895 1896 1897 1898 1899 1900 1901 1902 1903 1904 1905 1906 1907 1908 1909 1910 1911 1912 1913 1914 1915 1916 1917 1918 1919 1920 1921 1922 1923 1924 1925 1926 1927 1928 1929 1930 1931 1932 1933 1934 1935 1936 1937 1938 1939 1940 1941 1942 1943 1944 1945 1946 1947 1948 1949 1950 1951 1952 1953 1954 1955 1956 1957 1958 1959 1960 1961 1962 1963 1964 1965 1966 1967 1968 1969 1970 1971 1972 1973 1974 1975 1976 1977 1978 1979 1980 1981 1982 1983 1984 1985 1986 1987 1988 1989 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 2026 2027 2028 2029 2030 2031 2032 2033 2034 2035 2036 2037 2038 2039 2040 2041 2042 2043 2044 2045 2046 2047 2048 2049 2050 2051 2052 2053 2054 2055 2056 2057 2058 2059 2060 2061 2062 2063 2064 2065 2066 2067 2068 2069 2070 2071 2072 2073 2074 2075 2076 2077 2078 2079 2080 2081 2082 2083 2084 2085 2086 2087 2088 2089 2090 2091 2092 2093 2094 2095 2096 2097 2098 2099 2100 2101 2102 2103 2104 2105 2106 2107 2108 2109 2110 2111 2112 2113 2114 2115 2116 2117 2118 2119 2120 2121 2122 2123 2124 2125 2126 2127 2128 2129 2130 2131 2132 2133 2134 2135 2136 2137 2138 2139 2140 2141 2142 2143 2144 2145 2146 2147 2148 2149 2150 2151 2152 2153 2154 2155 2156 2157 2158 2159 2160 2161 2162 2163 2164 2165 2166 2167 2168 2169 2170 2171 2172 2173 2174 2175 2176 2177 2178 2179 2180 2181 2182 2183 2184 2185 2186 2187 2188 2189 2190 2191 2192 2193 2194 2195 2196 2197 2198 2199 2200 2201 2202 2203 2204 2205 2206 2207 2208 2209 2210 2211 2212 2213 2214 2215 2216 2217 2218 2219 2220 2221 2222 2223 2224 2225 2226 2227 2228 2229 2230 2231 2232 2233 2234 2235 2236 2237 2238 2239 2240 2241 2242 2243 2244 2245 2246 2247 2248 2249 2250 2251 2252 2253 2254 2255 2256 2257 2258 2259 2260 2261 2262 2263 2264 2265 2266 2267 2268 2269 2270 2271 2272 2273 2274 2275 2276 2277 2278 2279 2280 2281 2282 2283 2284 2285 2286 2287 2288 2289 2290 2291 2292 2293 2294 2295 2296 2297 2298 2299 2300 2301 2302 2303 2304 2305 2306 2307 2308 2309 2310 2311 2312 2313 2314 2315 2316 2317 2318 2319 2320 2321 2322 2323 2324 2325 2326 2327 2328 2329 2330 2331 2332 2333 2334 2335 2336 2337 2338 2339 2340 2341 2342 2343 2344 2345 2346 2347 2348 2349 2350 2351 2352 2353 2354 2355 2356 2357 2358 2359 2360 2361 2362 2363 2364 2365 2366 2367 2368 2369 2370 2371 2372 2373 2374 2375 2376 2377 2378 2379 2380 2381 2382 2383 2384 2385 2386 2387 2388 2389 2390 2391 2392 2393 2394 2395 2396 2397 2398 2399 2400 2401 2402 2403 2404 2405 2406 2407 2408 2409 2410 2411 2412 2413 2414 2415 2416 2417 2418 2419 2420 2421 2422 2423 2424 2425 2426 2427 2428 2429 2430 2431 2432 2433 2434 2435 2436 2437 2438 2439 2440 2441 2442 2443 2444 2445 2446 2447 2448 2449 2450 2451 2452 2453 2454 2455 2456 2457 2458 2459 2460 2461 2462 2463 2464 2465 2466 2467 2468 2469 2470 2471 2472 2473 2474 2475 2476 2477 2478 2479 2480 2481 2482 2483 2484 2485 2486 2487 2488 2489 2490 2491 2492 2493 2494 2495 2496 2497 2498 2499 2500 2501 2502 2503 2504 2505 2506 2507 2508 2509 2510 2511 2512 2513 2514 2515 2516 2517 2518 2519 2520 2521 2522 2523 2524 2525 2526 2527 2528 2529 2530 2531 2532 2533 2534 2535 2536 2537 2538 2539 2540 2541 2542 2543 2544 2545 2546 2547 2548 2549 2550 2551 2552 2553 2554 2555 2556 2557 2558 2559 2560 2561 2562 2563 2564 2565 2566 2567 2568 2569 2570 2571 2572 2573 2574 2575 2576 2577 2578 2579 2580 2581 2582 2583 2584 2585 2586 2587 2588 2589 2590 2591 2592 2593 2594 2595 2596 2597 2598 2599 2600 2601 2602 2603 2604 2605 2606 2607 2608 2609 2610 2611 2612 2613 2614 2615 2616 2617 2618 2619 2620 2621 2622 2623 2624 2625 2626 2627 2628 2629 2630 2631 2632 2633 2634 2635 2636 2637 2638 2639 2640 2641 2642 2643 2644 2645 2646 2647 2648 2649 2650 2651 2652 2653 2654 2655 2656 2657 2658 2659 2660 2661 2662 2663 2664 2665 2666 2667 2668 2669 2670 2671 2672 2673 2674 2675 2676 2677 2678 2679 2680 2681 2682 2683 2684 2685 2686 2687 2688 2689 2690 2691 2692 2693 2694 2695 2696 2697 2698 2699 2700 2701 2702 2703 2704 2705 2706 2707 2708 2709 2710 2711 2712 2713 2714 2715 2716 2717 2718 2719 2720 2721 2722 2723 2724 2725 2726 2727 2728 2729 2730 2731 2732 2733 2734 2735 2736 2737 2738 2739 2740 2741 2742 2743 2744 2745 2746 2747 2748 2749 2750 2751 2752 2753 2754 2755 2756 2757 2758 2759 2760 2761 2762 2763 2764 2765 2766 2767 2768 2769 2770 2771 2772 2773 2774 2775 2776 2777 2778 2779 2780 2781 2782 2783 2784 2785 2786 2787 2788 2789 2790 2791 2792 2793 2794 2795 2796 2797 2798 2799 2800 2801 2802 2803 2804 2805 2806 2807 2808 2809 2810 2811 2812 2813 2814 2815 2816 2817 2818 2819 2820 2821 2822 2823 2824 2825 2826 2827 2828 2829 2830 2831 2832 2833 2834 2835 2836 2837 2838 2839 2840 2841 2842 2843 2844 2845 2846 2847 2848 2849 2850 2851 2852 2853 2854 2855 2856 2857 2858 2859 2860 2861 2862 2863 2864 2865 2866 2867 2868 2869 2870 2871 2872 2873 2874 2875 2876 2877 2878 2879 2880 2881 2882 2883 2884 2885 2886 2887 2888 2889 2890 2891 2892 2893 2894 2895 2896 2897 2898 2899 2900 2901 2902 2903 2904 2905 2906 2907 2908 2909 2910 2911 2912 2913 2914 2915 2916 2917 2918 2919 2920 2921 2922 2923 2924 2925 2926 2927 2928 2929 2930 2931 2932 2933 2934 2935 2936 2937 2938 2939 2940 2941 2942 2943 2944 2945 2946 2947 2948 2949 2950 2951 2952 2953 2954 2955 2956 2957 2958 2959 2960 2961 2962 2963 2964 2965 2966 2967 2968 2969 2970 2971 2972 2973 2974 2975 2976 2977 2978 2979 2980 2981 2982 2983 2984 2985 2986 2987 2988 2989 2990 2991 2992 2993 2994 2995 2996 2997 2998 2999 3000 3001 3002 3003 3004 3005 3006 3007 3008 3009 3010 3011 3012 3013 3014 3015 3016 3017 3018 3019 3020 3021 3022 3023 3024 3025 3026 3027 3028 3029 3030 3031 3032 3033 3034 3035 3036 3037 3038 3039 3040 3041 3042 3043 3044 3045 3046 3047 3048 3049 3050 3051 3052 3053 3054 3055 3056 3057 3058 3059 3060 3061 3062 3063 3064 3065 3066 3067 3068 3069 3070 3071 3072 3073 3074 3075 3076 3077 3078 3079 3080 3081 3082 3083 3084 3085 3086 3087 3088 3089 3090 3091 3092 3093 3094 3095 3096 3097 3098 3099 3100 3101 3102 3103 3104 3105 3106 3107 3108 3109 3110 3111 3112 3113 3114 3115 3116 3117 3118 3119 3120 3121 3122 3123 3124 3125 3126 3127 3128 3129 3130 3131 3132 3133 3134 3135 3136 3137 3138 3139 3140 3141 3142 3143 3144 3145 3146 3147 3148 3149 3150 3151 3152 3153 3154 3155 3156 3157 3158 3159 3160 3161 3162 3163 3164 3165 3166 3167 3168 3169 3170 3171 3172 3173 3174 3175 3176 3177 3178 3179 3180 3181 3182 3183 3184 3185 3186 3187 3188 3189 3190 3191 3192 3193 3194 3195 3196 3197 3198 3199 3200 3201 3202 3203 3204 3205 3206 3207 3208 3209 3210 3211 3212 3213 3214 3215 3216 3217 3218 3219 3220 3221 3222 3223 3224 3225 3226 3227 3228 3229 3230 3231 3232 3233 3234 3235 3236 3237 3238 3239 3240 3241 3242 3243 3244 3245 3246 3247 3248 3249 3250 3251 3252 3253 3254 3255 3256 3257 3258 3259 3260 3261 3262 3263 3264 3265 3266 3267 3268 3269 3270 3271 3272 3273 3274 3275 3276 3277 3278 3279 3280 3281 3282 3283 3284 3285 3286 3287 3288 3289 3290 3291 3292 3293 3294 3295 3296 3297 3298 3299 3300 3301 3302 3303 3304 3305 3306 3307 3308 3309 3310 3311 3312 3313 3314 3315 3316 3317 3318 3319 3320 3321 3322 3323 3324 3325 3326 3327 3328 3329 3330 3331 3332 3333 3334 3335 3336 3337 3338 3339 3340 3341 3342 3343 3344 3345 3346 3347 3348 3349 3350 3351 3352 3353 3354 3355 3356 3357 3358 3359 3360 3361 3362 3363 3364 3365 3366 3367 3368 3369 3370 3371 3372 3373 3374 3375 3376 3377 3378 3379 3380 3381 3382 3383 3384 3385 3386 3387 3388 3389 3390 3391 3392 3393 3394 3395 3396 3397 3398 3399 3400 3401 3402 3403 3404 3405 3406 3407 3408 3409 3410 3411 3412 3413 3414 3415 3416 3417 3418 3419 3420 3421 3422 3423 3424 3425 3426 3427 3428 3429 3430 3431 3432 3433 3434 3435 3436 3437 3438 3439 3440 3441 3442 3443 3444 3445 3446 3447 3448 3449 3450 3451 3452 3453 3454 3455 3456 3457 3458 3459 3460 3461 3462 3463 3464 3465 3466 3467 3468 3469 3470 3471 3472 3473 3474 3475 3476 3477 3478 3479 3480 3481 3482 3483 3484 3485 3486 3487 3488 3489 3490 3491 3492 3493 3494 3495 3496 3497 3498 3499 3500 3501 3502 3503 3504 3505 3506 3507 3508 3509 3510 3511 3512 3513 3514 3515 3516 3517 3518 3519 3520 3521 3522 3523 3524 3525 3526 3527 3528 3529 3530 3531 3532 3533 3534 3535 3536 3537 3538 3539 3540 3541 3542 3543 3544 3545 3546 3547 3548 3549 3550 3551 3552 3553 3554 3555 3556 3557 3558 3559 3560 3561 3562 3563 3564 3565 3566 3567 3568 3569 3570 3571 3572 3573 3574 3575 3576 3577 3578 3579 3580 3581 3582 3583 3584 3585 3586 3587 3588 3589 3590 3591 3592 3593 3594 3595 3596 3597 3598 3599 3600 3601 3602 3603 3604 3605 3606 3607 3608 3609 3610 3611 3612 3613 3614 3615 3616 3617 3618 3619 3620 3621 3622 3623 3624 3625 3626 3627 3628 3629 3630 3631 3632 3633 3634 3635 3636 3637 3638 3639 3640 3641 3642 3643 3644 3645 3646 3647 3648 3649 3650 3651 3652 3653 3654 3655 3656 3657 3658 3659 3660 3661 3662 3663 3664 3665 3666 3667 3668 3669 3670 3671 3672 3673 3674 3675 3676 3677 3678 3679 3680 3681 3682 3683 3684 3685 3686 3687 3688 3689 3690 3691 3692 3693 3694 3695 3696 3697 3698 3699 3700 3701 3702 3703 3704 3705 3706 3707 3708 3709 3710 3711 3712 3713 3714 3715 3716 3717 3718 3719 3720 3721 3722 3723 3724 3725 3726 3727 3728 3729 3730 3731 3732 3733 3734 3735 3736 3737 3738 3739 3740 3741 3742 3743 3744 3745 3746 3747 3748 3749 3750 3751 3752 3753 3754 3755 3756 3757 3758 3759 3760 3761 3762 3763 3764 3765 3766 3767 3768 3769 3770 3771 3772 3773 3774 3775 3776 3777 3778 3779 3780 3781 3782 3783 3784 3785 3786 3787 3788 3789 3790 3791 3792 3793 3794 3795 3796 3797 3798 3799 3800 3801 3802 3803 3804 3805 3806 3807 3808 3809 3810 3811 3812 3813 3814 3815 3816 3817 3818 3819 3820 3821 3822 3823 3824 3825 3826 3827 3828 3829 3830 3831 3832 3833 3834 3835 3836 3837 3838 3839 3840 3841 3842 3843 3844 3845 3846 3847 3848 3849 3850 3851 3852 3853 3854 3855 3856 3857 3858 3859 3860 3861 3862 3863 3864 3865 3866 3867 3868 3869 3870 3871 3872 3873 3874 3875 3876 3877 3878 3879 3880 3881 3882 3883 3884 3885 3886 3887 3888 3889 3890 3891 3892 3893 3894 3895 3896 3897 3898 3899 3900 3901 3902 3903 3904 3905 3906 3907 3908 3909 3910 3911 3912 3913 3914 3915 3916 3917 3918 3919 3920 3921 3922 3923 3924 3925 3926 3927 3928 3929 3930 3931 3932 3933 3934 3935 3936 3937 3938 3939 3940 3941 3942 3943 3944 3945 3946 3947 3948 3949 3950 3951 3952 3953 3954 3955 3956 3957 3958 3959 3960 3961 3962 3963 3964 3965 3966 3967 3968 3969 3970 3971 3972 3973 3974 3975 3976 3977 3978 3979 3980 3981 3982 3983 3984 3985 3986 3987 3988 3989 3990 3991 3992 3993 3994 3995 3996 3997 3998 3999 4000 4001 4002 4003 4004 4005 4006 4007 4008 4009 4010 4011 4012 4013 4014 4015 4016 4017 4018 4019 4020 4021 4022 4023 4024 4025 4026 4027 4028 4029 4030 4031 4032 4033 4034 4035 4036 4037 4038 4039 4040 4041 4042 4043 4044 4045 4046 4047 4048 4049 4050 4051 4052 4053 4054 4055 4056 4057 4058 4059 4060 4061 4062 4063 4064 4065 4066 4067 4068 4069 4070 4071 4072 4073 4074 4075 4076 4077 4078 4079 4080 4081 4082 4083 4084 4085 4086 4087 4088 4089 4090 4091 4092 4093 4094 4095 4096 4097 4098 4099 4100 4101 4102 4103 4104 4105 4106 4107 4108 4109 4110 4111 4112 4113 4114 4115 4116 4117 4118 4119 4120 4121 4122 4123 4124 4125 4126 4127 4128 4129 4130 4131 4132 4133 4134 4135 4136 4137 4138 4139 4140 4141 4142 4143 4144 4145 4146 4147 4148 4149 4150 4151 4152 4153 4154 4155 4156 4157 4158 4159 4160 4161 4162 4163 4164 4165 4166 4167 4168 4169 4170 4171 4172 4173 4174 4175 4176 4177 4178 4179 4180 4181 4182 4183 4184 4185 4186 4187 4188 4189 4190 4191 4192 4193 4194 4195 4196 4197 4198 4199 4200 4201 4202 4203 4204 4205 4206 4207 4208 4209 4210 4211 4212 4213 4214 4215 4216 4217 4218 4219 4220 4221 4222 4223 4224 4225 4226 4227 4228 4229 4230 4231 4232 4233 4234 4235 4236 4237 4238 4239 4240 4241 4242 4243 4244 4245 4246 4247 4248 4249 4250 4251 4252 4253 4254 4255 4256 4257 4258 4259 4260 4261 4262 4263 4264 4265 4266 4267 4268 4269 4270 4271 4272 4273 4274 4275 4276 4277 4278 4279 4280 4281 4282 4283 4284 4285 4286 4287 4288 4289 4290 4291 4292 4293 4294 4295 4296 4297 4298 4299 4300 4301 4302 4303 4304 4305 4306 4307 4308 4309 4310 4311 4312 4313 4314 4315 4316 4317 4318 4319 4320 4321 4322 4323 4324 4325 4326 4327 4328 4329 4330 4331 4332 4333 4334 4335 4336 4337 4338 4339 4340 4341 4342 4343 4344 4345 4346 4347 4348 4349 4350 4351 4352 4353 4354 4355 4356 4357 4358 4359 4360 4361 4362 4363 4364 4365 4366 4367 4368 4369 4370 4371 4372 4373 4374 4375 4376 4377 4378 4379 4380 4381 4382 4383 4384 4385 4386 4387 4388 4389 4390 4391 4392 4393 4394 4395 4396 4397 4398 4399 4400 4401 4402 4403 4404 4405 4406 4407 4408 4409 4410 4411 4412 4413 4414 4415 4416 4417 4418 4419 4420 4421 4422 4423 4424 4425 4426 4427 4428 4429 4430 4431 4432 4433 4434 4435 4436 4437 4438 4439 4440 4441 4442 4443 4444 4445 4446 4447 4448 4449 4450 4451 4452 4453 4454 4455 4456 4457 4458 4459 4460 4461 4462 4463 4464 4465 4466 4467 4468 4469 4470 4471 4472 4473 4474 4475 4476 4477 4478 4479 4480 4481 4482 4483 4484 4485 4486 4487 4488 4489 4490 4491 4492 4493 4494 4495 4496 4497 4498 4499 4500 4501 4502 4503 4504 4505 4506 4507 4508 4509 4510 4511 4512 4513 4514 4515 4516 4517 4518 4519 4520 4521 4522 4523 4524 4525 4526 4527 4528 4529 4530 4531 4532 4533 4534 4535 4536 4537 4538 4539 4540 4541 4542 4543 4544 4545 4546 4547 4548 4549 4550 4551 4552 4553 4554 4555 4556 4557 4558 4559 4560 4561 4562 4563 4564 4565 4566 4567 4568 4569 4570 4571 4572 4573 4574 4575 4576 4577 4578 4579 4580 4581 4582 4583 4584 4585 4586 4587 4588 4589 4590 4591 4592 4593 4594 4595 4596 4597 4598 4599 4600 4601 4602 4603 4604 4605 4606 4607 4608 4609 4610 4611 4612 4613 4614 4615 4616 4617 4618 4619 4620 4621 4622 4623 4624 4625 4626 4627 4628 4629 4630 4631 4632 4633 4634 4635 4636 4637 4638 4639 4640 4641 4642 4643 4644 4645 4646 4647 4648 4649 4650 4651 4652 4653 4654 4655 4656 4657 4658 4659 4660 4661 4662 4663 4664 4665 4666 4667 4668 4669 4670 4671 4672 4673 4674 4675 4676 4677 4678 4679 4680 4681 4682 4683 4684 4685 4686 4687 4688 4689 4690 4691 4692 4693 4694 4695 4696 4697 4698 4699 4700 4701 4702 4703 4704 4705 4706 4707 4708 4709 4710 4711 4712 4713 4714 4715 4716 4717 4718 4719 4720 4721 4722 4723 4724 4725 4726 4727 4728 4729 4730 4731 4732 4733 4734 4735 4736 4737 4738 4739 4740 4741 4742 4743 4744 4745 4746 4747 4748 4749 4750 4751 4752 4753 4754 4755 4756 4757 4758 4759 4760 4761 4762 4763 4764 4765 4766 4767 4768 4769 4770 4771 4772 4773 4774 4775 4776 4777 4778 4779 4780 4781 4782 4783 4784 4785 4786 4787 4788 4789 4790 4791 4792 4793 4794 4795 4796 4797 4798 4799 4800 4801 4802 4803 4804 4805 4806 4807 4808 4809 4810 4811 4812 4813 4814 4815 4816 4817 4818 4819 4820 4821 4822 4823 4824 4825 4826 4827 4828 4829 4830 4831 4832 4833 4834 4835 4836 4837 4838 4839 4840 4841 4842 4843 4844 4845 4846 4847 4848 4849 4850 4851 4852 4853 4854 4855 4856 4857 4858 4859 4860 4861 4862 4863 4864 4865 4866 4867 4868 4869 4870 4871 4872 4873 4874 4875 4876 4877 4878 4879 4880 4881 4882 4883 4884 4885 4886 4887 4888 4889 4890 4891 4892 4893 4894 4895 4896 4897 4898 4899 4900 4901 4902 4903 4904 4905 4906 4907 4908 4909 4910 4911 4912 4913 4914 4915 4916 4917 4918 4919 4920 4921 4922 4923 4924 4925 4926 4927 4928 4929 4930 4931 4932 4933 4934 4935 4936 4937 4938 4939 4940 4941 4942 4943 4944 4945 4946 4947 4948 4949 4950 4951 4952 4953 4954 4955 4956 4957 4958 4959 4960 4961 4962 4963 4964 4965 4966 4967 4968 4969 4970 4971 4972 4973 4974 4975 4976 4977 4978 4979 4980 4981 4982 4983 4984 4985 4986 4987 4988 4989
#![allow( unused_parens, clippy::excessive_precision, clippy::missing_safety_doc, clippy::not_unsafe_ptr_arg_deref, clippy::should_implement_trait, clippy::too_many_arguments, clippy::unused_unit, )] //! # Camera Calibration and 3D Reconstruction //! //! The functions in this section use a so-called pinhole camera model. The view of a scene //! is obtained by projecting a scene's 3D point  into the image plane using a perspective //! transformation which forms the corresponding pixel 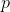. Both  and 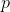 are //! represented in homogeneous coordinates, i.e. as 3D and 2D homogeneous vector respectively. You will //! find a brief introduction to projective geometry, homogeneous vectors and homogeneous //! transformations at the end of this section's introduction. For more succinct notation, we often drop //! the 'homogeneous' and say vector instead of homogeneous vector. //! //! The distortion-free projective transformation given by a pinhole camera model is shown below. //! //!  //! //! where  is a 3D point expressed with respect to the world coordinate system, //! 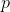 is a 2D pixel in the image plane, 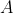 is the camera intrinsic matrix, //!  and 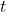 are the rotation and translation that describe the change of coordinates from //! world to camera coordinate systems (or camera frame) and  is the projective transformation's //! arbitrary scaling and not part of the camera model. //! //! The camera intrinsic matrix 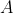 (notation used as in [Zhang2000](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Zhang2000) and also generally notated //! as 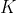) projects 3D points given in the camera coordinate system to 2D pixel coordinates, i.e. //! //!  //! //! The camera intrinsic matrix 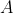 is composed of the focal lengths  and , which are //! expressed in pixel units, and the principal point , that is usually close to the //! image center: //! //!  //! //! and thus //! //!  //! //! The matrix of intrinsic parameters does not depend on the scene viewed. So, once estimated, it can //! be re-used as long as the focal length is fixed (in case of a zoom lens). Thus, if an image from the //! camera is scaled by a factor, all of these parameters need to be scaled (multiplied/divided, //! respectively) by the same factor. //! //! The joint rotation-translation matrix 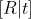 is the matrix product of a projective //! transformation and a homogeneous transformation. The 3-by-4 projective transformation maps 3D points //! represented in camera coordinates to 2D points in the image plane and represented in normalized //! camera coordinates  and : //! //!  //! //! The homogeneous transformation is encoded by the extrinsic parameters  and 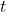 and //! represents the change of basis from world coordinate system 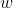 to the camera coordinate sytem //! . Thus, given the representation of the point 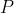 in world coordinates, , we //! obtain 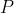's representation in the camera coordinate system, , by //! //!  //! //! This homogeneous transformation is composed out of , a 3-by-3 rotation matrix, and 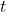, a //! 3-by-1 translation vector: //! //!  //! //! and therefore //! //!  //! //! Combining the projective transformation and the homogeneous transformation, we obtain the projective //! transformation that maps 3D points in world coordinates into 2D points in the image plane and in //! normalized camera coordinates: //! //!  //! //! with  and . Putting the equations for instrincs and extrinsics together, we can write out //!  as //! //!  //! //! If , the transformation above is equivalent to the following, //! //!  //! //! with //! //!  //! //! The following figure illustrates the pinhole camera model. //! //!  //! //! Real lenses usually have some distortion, mostly radial distortion, and slight tangential distortion. //! So, the above model is extended as: //! //!  //! //! where //! //!  //! //! with //! //!  //! //! and //! //!  //! //! if . //! //! The distortion parameters are the radial coefficients , , , , , and  //! , and  are the tangential distortion coefficients, and , , , and , //! are the thin prism distortion coefficients. Higher-order coefficients are not considered in OpenCV. //! //! The next figures show two common types of radial distortion: barrel distortion //! ( monotonically decreasing) //! and pincushion distortion ( monotonically increasing). //! Radial distortion is always monotonic for real lenses, //! and if the estimator produces a non-monotonic result, //! this should be considered a calibration failure. //! More generally, radial distortion must be monotonic and the distortion function must be bijective. //! A failed estimation result may look deceptively good near the image center //! but will work poorly in e.g. AR/SFM applications. //! The optimization method used in OpenCV camera calibration does not include these constraints as //! the framework does not support the required integer programming and polynomial inequalities. //! See [issue #15992](https://github.com/opencv/opencv/issues/15992) for additional information. //! //!  //!  //! //! In some cases, the image sensor may be tilted in order to focus an oblique plane in front of the //! camera (Scheimpflug principle). This can be useful for particle image velocimetry (PIV) or //! triangulation with a laser fan. The tilt causes a perspective distortion of 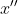 and //! 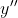. This distortion can be modeled in the following way, see e.g. [Louhichi07](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Louhichi07). //! //!  //! //! where //! //!  //! //! and the matrix  is defined by two rotations with angular parameter //!  and , respectively, //! //!  //! //! In the functions below the coefficients are passed or returned as //! //!  //! //! vector. That is, if the vector contains four elements, it means that  . The distortion //! coefficients do not depend on the scene viewed. Thus, they also belong to the intrinsic camera //! parameters. And they remain the same regardless of the captured image resolution. If, for example, a //! camera has been calibrated on images of 320 x 240 resolution, absolutely the same distortion //! coefficients can be used for 640 x 480 images from the same camera while , , //! , and  need to be scaled appropriately. //! //! The functions below use the above model to do the following: //! //! * Project 3D points to the image plane given intrinsic and extrinsic parameters. //! * Compute extrinsic parameters given intrinsic parameters, a few 3D points, and their //! projections. //! * Estimate intrinsic and extrinsic camera parameters from several views of a known calibration //! pattern (every view is described by several 3D-2D point correspondences). //! * Estimate the relative position and orientation of the stereo camera "heads" and compute the //! *rectification* transformation that makes the camera optical axes parallel. //! //! <B> Homogeneous Coordinates </B><br> //! Homogeneous Coordinates are a system of coordinates that are used in projective geometry. Their use //! allows to represent points at infinity by finite coordinates and simplifies formulas when compared //! to the cartesian counterparts, e.g. they have the advantage that affine transformations can be //! expressed as linear homogeneous transformation. //! //! One obtains the homogeneous vector  by appending a 1 along an n-dimensional cartesian //! vector 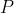 e.g. for a 3D cartesian vector the mapping  is: //! //!  //! //! For the inverse mapping , one divides all elements of the homogeneous vector //! by its last element, e.g. for a 3D homogeneous vector one gets its 2D cartesian counterpart by: //! //!  //! //! if . //! //! Due to this mapping, all multiples , for , of a homogeneous point represent //! the same point . An intuitive understanding of this property is that under a projective //! transformation, all multiples of  are mapped to the same point. This is the physical //! observation one does for pinhole cameras, as all points along a ray through the camera's pinhole are //! projected to the same image point, e.g. all points along the red ray in the image of the pinhole //! camera model above would be mapped to the same image coordinate. This property is also the source //! for the scale ambiguity s in the equation of the pinhole camera model. //! //! As mentioned, by using homogeneous coordinates we can express any change of basis parameterized by //!  and 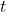 as a linear transformation, e.g. for the change of basis from coordinate system //! 0 to coordinate system 1 becomes: //! //!  //! //! //! Note: //! * Many functions in this module take a camera intrinsic matrix as an input parameter. Although all //! functions assume the same structure of this parameter, they may name it differently. The //! parameter's description, however, will be clear in that a camera intrinsic matrix with the structure //! shown above is required. //! * A calibration sample for 3 cameras in a horizontal position can be found at //! opencv_source_code/samples/cpp/3calibration.cpp //! * A calibration sample based on a sequence of images can be found at //! opencv_source_code/samples/cpp/calibration.cpp //! * A calibration sample in order to do 3D reconstruction can be found at //! opencv_source_code/samples/cpp/build3dmodel.cpp //! * A calibration example on stereo calibration can be found at //! opencv_source_code/samples/cpp/stereo_calib.cpp //! * A calibration example on stereo matching can be found at //! opencv_source_code/samples/cpp/stereo_match.cpp //! * (Python) A camera calibration sample can be found at //! opencv_source_code/samples/python/calibrate.py //! # Fisheye camera model //! //! Definitions: Let P be a point in 3D of coordinates X in the world reference frame (stored in the //! matrix X) The coordinate vector of P in the camera reference frame is: //! //! 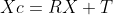 //! //! where R is the rotation matrix corresponding to the rotation vector om: R = rodrigues(om); call x, y //! and z the 3 coordinates of Xc: //! //!  //! //! The pinhole projection coordinates of P is [a; b] where //! //! 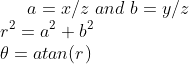 //! //! Fisheye distortion: //! //!  //! //! The distorted point coordinates are [x'; y'] where //! //!  //! //! Finally, conversion into pixel coordinates: The final pixel coordinates vector [u; v] where: //! //!  //! //! # C API use crate::{mod_prelude::*, core, sys, types}; pub mod prelude { pub use { super::LMSolver_Callback, super::LMSolver, super::StereoMatcher, super::StereoBM, super::StereoSGBM }; } pub const CALIB_CB_ACCURACY: i32 = 32; pub const CALIB_CB_ADAPTIVE_THRESH: i32 = 1; pub const CALIB_CB_ASYMMETRIC_GRID: i32 = 2; pub const CALIB_CB_CLUSTERING: i32 = 4; pub const CALIB_CB_EXHAUSTIVE: i32 = 16; pub const CALIB_CB_FAST_CHECK: i32 = 8; pub const CALIB_CB_FILTER_QUADS: i32 = 4; pub const CALIB_CB_LARGER: i32 = 64; pub const CALIB_CB_MARKER: i32 = 128; pub const CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE: i32 = 2; pub const CALIB_CB_SYMMETRIC_GRID: i32 = 1; pub const CALIB_FIX_ASPECT_RATIO: i32 = 2; pub const CALIB_FIX_FOCAL_LENGTH: i32 = 16; pub const CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC: i32 = 256; pub const CALIB_FIX_K1: i32 = 32; pub const CALIB_FIX_K2: i32 = 64; pub const CALIB_FIX_K3: i32 = 128; pub const CALIB_FIX_K4: i32 = 2048; pub const CALIB_FIX_K5: i32 = 4096; pub const CALIB_FIX_K6: i32 = 8192; pub const CALIB_FIX_PRINCIPAL_POINT: i32 = 4; pub const CALIB_FIX_S1_S2_S3_S4: i32 = 65536; pub const CALIB_FIX_TANGENT_DIST: i32 = 2097152; pub const CALIB_FIX_TAUX_TAUY: i32 = 524288; /// On-line Hand-Eye Calibration [Andreff99](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Andreff99) pub const CALIB_HAND_EYE_ANDREFF: i32 = 3; /// Hand-Eye Calibration Using Dual Quaternions [Daniilidis98](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Daniilidis98) pub const CALIB_HAND_EYE_DANIILIDIS: i32 = 4; /// Hand-eye Calibration [Horaud95](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Horaud95) pub const CALIB_HAND_EYE_HORAUD: i32 = 2; /// Robot Sensor Calibration: Solving AX = XB on the Euclidean Group [Park94](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Park94) pub const CALIB_HAND_EYE_PARK: i32 = 1; /// A New Technique for Fully Autonomous and Efficient 3D Robotics Hand/Eye Calibration [Tsai89](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Tsai89) pub const CALIB_HAND_EYE_TSAI: i32 = 0; pub const CALIB_NINTRINSIC: i32 = 18; pub const CALIB_RATIONAL_MODEL: i32 = 16384; /// Simultaneous robot-world and hand-eye calibration using dual-quaternions and kronecker product [Li2010SimultaneousRA](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Li2010SimultaneousRA) pub const CALIB_ROBOT_WORLD_HAND_EYE_LI: i32 = 1; /// Solving the robot-world/hand-eye calibration problem using the kronecker product [Shah2013SolvingTR](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Shah2013SolvingTR) pub const CALIB_ROBOT_WORLD_HAND_EYE_SHAH: i32 = 0; pub const CALIB_SAME_FOCAL_LENGTH: i32 = 512; pub const CALIB_THIN_PRISM_MODEL: i32 = 32768; pub const CALIB_TILTED_MODEL: i32 = 262144; /// for stereoCalibrate pub const CALIB_USE_EXTRINSIC_GUESS: i32 = 4194304; pub const CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS: i32 = 1; /// use LU instead of SVD decomposition for solving. much faster but potentially less precise pub const CALIB_USE_LU: i32 = 131072; /// use QR instead of SVD decomposition for solving. Faster but potentially less precise pub const CALIB_USE_QR: i32 = 1048576; pub const CALIB_ZERO_DISPARITY: i32 = 1024; pub const CALIB_ZERO_TANGENT_DIST: i32 = 8; /// 7-point algorithm pub const FM_7POINT: i32 = 1; /// 8-point algorithm pub const FM_8POINT: i32 = 2; /// least-median algorithm. 7-point algorithm is used. pub const FM_LMEDS: i32 = 4; /// RANSAC algorithm. It needs at least 15 points. 7-point algorithm is used. pub const FM_RANSAC: i32 = 8; pub const Fisheye_CALIB_CHECK_COND: i32 = 4; pub const Fisheye_CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC: i32 = 256; pub const Fisheye_CALIB_FIX_K1: i32 = 16; pub const Fisheye_CALIB_FIX_K2: i32 = 32; pub const Fisheye_CALIB_FIX_K3: i32 = 64; pub const Fisheye_CALIB_FIX_K4: i32 = 128; pub const Fisheye_CALIB_FIX_PRINCIPAL_POINT: i32 = 512; pub const Fisheye_CALIB_FIX_SKEW: i32 = 8; pub const Fisheye_CALIB_RECOMPUTE_EXTRINSIC: i32 = 2; pub const Fisheye_CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS: i32 = 1; pub const Fisheye_CALIB_ZERO_DISPARITY: i32 = 1024; /// least-median of squares algorithm pub const LMEDS: i32 = 4; pub const LOCAL_OPTIM_GC: i32 = 3; pub const LOCAL_OPTIM_INNER_AND_ITER_LO: i32 = 2; pub const LOCAL_OPTIM_INNER_LO: i32 = 1; pub const LOCAL_OPTIM_NULL: i32 = 0; pub const LOCAL_OPTIM_SIGMA: i32 = 4; pub const NEIGH_FLANN_KNN: i32 = 0; pub const NEIGH_FLANN_RADIUS: i32 = 2; pub const NEIGH_GRID: i32 = 1; pub const PROJ_SPHERICAL_EQRECT: i32 = 1; pub const PROJ_SPHERICAL_ORTHO: i32 = 0; /// RANSAC algorithm pub const RANSAC: i32 = 8; /// RHO algorithm pub const RHO: i32 = 16; pub const SAMPLING_NAPSAC: i32 = 2; pub const SAMPLING_PROGRESSIVE_NAPSAC: i32 = 1; pub const SAMPLING_PROSAC: i32 = 3; pub const SAMPLING_UNIFORM: i32 = 0; pub const SCORE_METHOD_LMEDS: i32 = 3; pub const SCORE_METHOD_MAGSAC: i32 = 2; pub const SCORE_METHOD_MSAC: i32 = 1; pub const SCORE_METHOD_RANSAC: i32 = 0; /// An Efficient Algebraic Solution to the Perspective-Three-Point Problem [Ke17](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Ke17) pub const SOLVEPNP_AP3P: i32 = 5; /// **Broken implementation. Using this flag will fallback to EPnP.** /// /// A Direct Least-Squares (DLS) Method for PnP [hesch2011direct](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_hesch2011direct) pub const SOLVEPNP_DLS: i32 = 3; /// EPnP: Efficient Perspective-n-Point Camera Pose Estimation [lepetit2009epnp](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_lepetit2009epnp) pub const SOLVEPNP_EPNP: i32 = 1; /// Infinitesimal Plane-Based Pose Estimation [Collins14](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Collins14) /// /// Object points must be coplanar. pub const SOLVEPNP_IPPE: i32 = 6; /// Infinitesimal Plane-Based Pose Estimation [Collins14](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Collins14) /// /// This is a special case suitable for marker pose estimation. /// /// 4 coplanar object points must be defined in the following order: /// - point 0: [-squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0] /// - point 1: [ squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0] /// - point 2: [ squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0] /// - point 3: [-squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0] pub const SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE: i32 = 7; pub const SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE: i32 = 0; /// Used for count pub const SOLVEPNP_MAX_COUNT: i32 = 9; /// Complete Solution Classification for the Perspective-Three-Point Problem [gao2003complete](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_gao2003complete) pub const SOLVEPNP_P3P: i32 = 2; /// SQPnP: A Consistently Fast and Globally OptimalSolution to the Perspective-n-Point Problem [Terzakis20](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Terzakis20) pub const SOLVEPNP_SQPNP: i32 = 8; /// **Broken implementation. Using this flag will fallback to EPnP.** /// /// Exhaustive Linearization for Robust Camera Pose and Focal Length Estimation [penate2013exhaustive](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_penate2013exhaustive) pub const SOLVEPNP_UPNP: i32 = 4; pub const StereoBM_PREFILTER_NORMALIZED_RESPONSE: i32 = 0; pub const StereoBM_PREFILTER_XSOBEL: i32 = 1; pub const StereoMatcher_DISP_SCALE: i32 = 16; pub const StereoMatcher_DISP_SHIFT: i32 = 4; pub const StereoSGBM_MODE_HH: i32 = 1; pub const StereoSGBM_MODE_HH4: i32 = 3; pub const StereoSGBM_MODE_SGBM: i32 = 0; pub const StereoSGBM_MODE_SGBM_3WAY: i32 = 2; /// USAC, accurate settings pub const USAC_ACCURATE: i32 = 36; /// USAC algorithm, default settings pub const USAC_DEFAULT: i32 = 32; /// USAC, fast settings pub const USAC_FAST: i32 = 35; /// USAC, fundamental matrix 8 points pub const USAC_FM_8PTS: i32 = 34; /// USAC, runs MAGSAC++ pub const USAC_MAGSAC: i32 = 38; /// USAC, parallel version pub const USAC_PARALLEL: i32 = 33; /// USAC, sorted points, runs PROSAC pub const USAC_PROSAC: i32 = 37; #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum CirclesGridFinderParameters_GridType { SYMMETRIC_GRID = 0, ASYMMETRIC_GRID = 1, } opencv_type_enum! { crate::calib3d::CirclesGridFinderParameters_GridType } #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum HandEyeCalibrationMethod { /// A New Technique for Fully Autonomous and Efficient 3D Robotics Hand/Eye Calibration [Tsai89](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Tsai89) CALIB_HAND_EYE_TSAI = 0, /// Robot Sensor Calibration: Solving AX = XB on the Euclidean Group [Park94](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Park94) CALIB_HAND_EYE_PARK = 1, /// Hand-eye Calibration [Horaud95](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Horaud95) CALIB_HAND_EYE_HORAUD = 2, /// On-line Hand-Eye Calibration [Andreff99](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Andreff99) CALIB_HAND_EYE_ANDREFF = 3, /// Hand-Eye Calibration Using Dual Quaternions [Daniilidis98](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Daniilidis98) CALIB_HAND_EYE_DANIILIDIS = 4, } opencv_type_enum! { crate::calib3d::HandEyeCalibrationMethod } #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum LocalOptimMethod { LOCAL_OPTIM_NULL = 0, LOCAL_OPTIM_INNER_LO = 1, LOCAL_OPTIM_INNER_AND_ITER_LO = 2, LOCAL_OPTIM_GC = 3, LOCAL_OPTIM_SIGMA = 4, } opencv_type_enum! { crate::calib3d::LocalOptimMethod } #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum NeighborSearchMethod { NEIGH_FLANN_KNN = 0, NEIGH_GRID = 1, NEIGH_FLANN_RADIUS = 2, } opencv_type_enum! { crate::calib3d::NeighborSearchMethod } #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum RobotWorldHandEyeCalibrationMethod { /// Solving the robot-world/hand-eye calibration problem using the kronecker product [Shah2013SolvingTR](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Shah2013SolvingTR) CALIB_ROBOT_WORLD_HAND_EYE_SHAH = 0, /// Simultaneous robot-world and hand-eye calibration using dual-quaternions and kronecker product [Li2010SimultaneousRA](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Li2010SimultaneousRA) CALIB_ROBOT_WORLD_HAND_EYE_LI = 1, } opencv_type_enum! { crate::calib3d::RobotWorldHandEyeCalibrationMethod } #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum SamplingMethod { SAMPLING_UNIFORM = 0, SAMPLING_PROGRESSIVE_NAPSAC = 1, SAMPLING_NAPSAC = 2, SAMPLING_PROSAC = 3, } opencv_type_enum! { crate::calib3d::SamplingMethod } #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum ScoreMethod { SCORE_METHOD_RANSAC = 0, SCORE_METHOD_MSAC = 1, SCORE_METHOD_MAGSAC = 2, SCORE_METHOD_LMEDS = 3, } opencv_type_enum! { crate::calib3d::ScoreMethod } #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum SolvePnPMethod { SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE = 0, /// EPnP: Efficient Perspective-n-Point Camera Pose Estimation [lepetit2009epnp](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_lepetit2009epnp) SOLVEPNP_EPNP = 1, /// Complete Solution Classification for the Perspective-Three-Point Problem [gao2003complete](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_gao2003complete) SOLVEPNP_P3P = 2, /// **Broken implementation. Using this flag will fallback to EPnP.** /// /// A Direct Least-Squares (DLS) Method for PnP [hesch2011direct](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_hesch2011direct) SOLVEPNP_DLS = 3, /// **Broken implementation. Using this flag will fallback to EPnP.** /// /// Exhaustive Linearization for Robust Camera Pose and Focal Length Estimation [penate2013exhaustive](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_penate2013exhaustive) SOLVEPNP_UPNP = 4, /// An Efficient Algebraic Solution to the Perspective-Three-Point Problem [Ke17](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Ke17) SOLVEPNP_AP3P = 5, /// Infinitesimal Plane-Based Pose Estimation [Collins14](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Collins14) /// /// Object points must be coplanar. SOLVEPNP_IPPE = 6, /// Infinitesimal Plane-Based Pose Estimation [Collins14](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Collins14) /// /// This is a special case suitable for marker pose estimation. /// /// 4 coplanar object points must be defined in the following order: /// - point 0: [-squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0] /// - point 1: [ squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0] /// - point 2: [ squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0] /// - point 3: [-squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0] SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE = 7, /// SQPnP: A Consistently Fast and Globally OptimalSolution to the Perspective-n-Point Problem [Terzakis20](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Terzakis20) SOLVEPNP_SQPNP = 8, /// Used for count SOLVEPNP_MAX_COUNT = 9, } opencv_type_enum! { crate::calib3d::SolvePnPMethod } /// cv::undistort mode #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub enum UndistortTypes { PROJ_SPHERICAL_ORTHO = 0, PROJ_SPHERICAL_EQRECT = 1, } opencv_type_enum! { crate::calib3d::UndistortTypes } pub type CirclesGridFinderParameters2 = crate::calib3d::CirclesGridFinderParameters; /// Computes an RQ decomposition of 3x3 matrices. /// /// ## Parameters /// * src: 3x3 input matrix. /// * mtxR: Output 3x3 upper-triangular matrix. /// * mtxQ: Output 3x3 orthogonal matrix. /// * Qx: Optional output 3x3 rotation matrix around x-axis. /// * Qy: Optional output 3x3 rotation matrix around y-axis. /// * Qz: Optional output 3x3 rotation matrix around z-axis. /// /// The function computes a RQ decomposition using the given rotations. This function is used in /// decomposeProjectionMatrix to decompose the left 3x3 submatrix of a projection matrix into a camera /// and a rotation matrix. /// /// It optionally returns three rotation matrices, one for each axis, and the three Euler angles in /// degrees (as the return value) that could be used in OpenGL. Note, there is always more than one /// sequence of rotations about the three principal axes that results in the same orientation of an /// object, e.g. see [Slabaugh](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Slabaugh) . Returned tree rotation matrices and corresponding three Euler angles /// are only one of the possible solutions. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * qx: noArray() /// * qy: noArray() /// * qz: noArray() pub fn rq_decomp3x3(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mtx_r: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, mtx_q: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, qx: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, qy: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, qz: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<core::Vec3d> { input_array_arg!(src); output_array_arg!(mtx_r); output_array_arg!(mtx_q); output_array_arg!(qx); output_array_arg!(qy); output_array_arg!(qz); unsafe { sys::cv_RQDecomp3x3_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), mtx_r.as_raw__OutputArray(), mtx_q.as_raw__OutputArray(), qx.as_raw__OutputArray(), qy.as_raw__OutputArray(), qz.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Converts a rotation matrix to a rotation vector or vice versa. /// /// ## Parameters /// * src: Input rotation vector (3x1 or 1x3) or rotation matrix (3x3). /// * dst: Output rotation matrix (3x3) or rotation vector (3x1 or 1x3), respectively. /// * jacobian: Optional output Jacobian matrix, 3x9 or 9x3, which is a matrix of partial /// derivatives of the output array components with respect to the input array components. /// ///  /// /// Inverse transformation can be also done easily, since /// ///  /// /// A rotation vector is a convenient and most compact representation of a rotation matrix (since any /// rotation matrix has just 3 degrees of freedom). The representation is used in the global 3D geometry /// optimization procedures like @ref calibrateCamera, @ref stereoCalibrate, or @ref solvePnP . /// /// /// Note: More information about the computation of the derivative of a 3D rotation matrix with respect to its exponential coordinate /// can be found in: /// - A Compact Formula for the Derivative of a 3-D Rotation in Exponential Coordinates, Guillermo Gallego, Anthony J. Yezzi [Gallego2014ACF](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Gallego2014ACF) /// /// /// Note: Useful information on SE(3) and Lie Groups can be found in: /// - A tutorial on SE(3) transformation parameterizations and on-manifold optimization, Jose-Luis Blanco [blanco2010tutorial](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_blanco2010tutorial) /// - Lie Groups for 2D and 3D Transformation, Ethan Eade [Eade17](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Eade17) /// - A micro Lie theory for state estimation in robotics, Joan Solà, Jérémie Deray, Dinesh Atchuthan [Sol2018AML](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Sol2018AML) /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * jacobian: noArray() pub fn rodrigues(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, jacobian: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(src); output_array_arg!(dst); output_array_arg!(jacobian); unsafe { sys::cv_Rodrigues_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), jacobian.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Finds the camera intrinsic and extrinsic parameters from several views of a calibration pattern. /// /// This function is an extension of calibrateCamera() with the method of releasing object which was /// proposed in [strobl2011iccv](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_strobl2011iccv). In many common cases with inaccurate, unmeasured, roughly planar /// targets (calibration plates), this method can dramatically improve the precision of the estimated /// camera parameters. Both the object-releasing method and standard method are supported by this /// function. Use the parameter **iFixedPoint** for method selection. In the internal implementation, /// calibrateCamera() is a wrapper for this function. /// /// ## Parameters /// * objectPoints: Vector of vectors of calibration pattern points in the calibration pattern /// coordinate space. See calibrateCamera() for details. If the method of releasing object to be used, /// the identical calibration board must be used in each view and it must be fully visible, and all /// objectPoints[i] must be the same and all points should be roughly close to a plane. **The calibration /// target has to be rigid, or at least static if the camera (rather than the calibration target) is /// shifted for grabbing images.** /// * imagePoints: Vector of vectors of the projections of calibration pattern points. See /// calibrateCamera() for details. /// * imageSize: Size of the image used only to initialize the intrinsic camera matrix. /// * iFixedPoint: The index of the 3D object point in objectPoints[0] to be fixed. It also acts as /// a switch for calibration method selection. If object-releasing method to be used, pass in the /// parameter in the range of [1, objectPoints[0].size()-2], otherwise a value out of this range will /// make standard calibration method selected. Usually the top-right corner point of the calibration /// board grid is recommended to be fixed when object-releasing method being utilized. According to /// \cite strobl2011iccv, two other points are also fixed. In this implementation, objectPoints[0].front /// and objectPoints[0].back.z are used. With object-releasing method, accurate rvecs, tvecs and /// newObjPoints are only possible if coordinates of these three fixed points are accurate enough. /// * cameraMatrix: Output 3x3 floating-point camera matrix. See calibrateCamera() for details. /// * distCoeffs: Output vector of distortion coefficients. See calibrateCamera() for details. /// * rvecs: Output vector of rotation vectors estimated for each pattern view. See calibrateCamera() /// for details. /// * tvecs: Output vector of translation vectors estimated for each pattern view. /// * newObjPoints: The updated output vector of calibration pattern points. The coordinates might /// be scaled based on three fixed points. The returned coordinates are accurate only if the above /// mentioned three fixed points are accurate. If not needed, noArray() can be passed in. This parameter /// is ignored with standard calibration method. /// * stdDeviationsIntrinsics: Output vector of standard deviations estimated for intrinsic parameters. /// See calibrateCamera() for details. /// * stdDeviationsExtrinsics: Output vector of standard deviations estimated for extrinsic parameters. /// See calibrateCamera() for details. /// * stdDeviationsObjPoints: Output vector of standard deviations estimated for refined coordinates /// of calibration pattern points. It has the same size and order as objectPoints[0] vector. This /// parameter is ignored with standard calibration method. /// * perViewErrors: Output vector of the RMS re-projection error estimated for each pattern view. /// * flags: Different flags that may be zero or a combination of some predefined values. See /// calibrateCamera() for details. If the method of releasing object is used, the calibration time may /// be much longer. CALIB_USE_QR or CALIB_USE_LU could be used for faster calibration with potentially /// less precise and less stable in some rare cases. /// * criteria: Termination criteria for the iterative optimization algorithm. /// /// ## Returns /// the overall RMS re-projection error. /// /// The function estimates the intrinsic camera parameters and extrinsic parameters for each of the /// views. The algorithm is based on [Zhang2000](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Zhang2000), [BouguetMCT](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_BouguetMCT) and [strobl2011iccv](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_strobl2011iccv). See /// calibrateCamera() for other detailed explanations. /// ## See also /// calibrateCamera, findChessboardCorners, solvePnP, initCameraMatrix2D, stereoCalibrate, undistort /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * flags: 0 /// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,30,DBL_EPSILON) pub fn calibrate_camera_ro_extended(object_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, i_fixed_point: i32, camera_matrix: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, rvecs: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, tvecs: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, new_obj_points: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, std_deviations_intrinsics: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, std_deviations_extrinsics: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, std_deviations_obj_points: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, per_view_errors: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32, criteria: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<f64> { input_array_arg!(object_points); input_array_arg!(image_points); input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix); input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs); output_array_arg!(rvecs); output_array_arg!(tvecs); output_array_arg!(new_obj_points); output_array_arg!(std_deviations_intrinsics); output_array_arg!(std_deviations_extrinsics); output_array_arg!(std_deviations_obj_points); output_array_arg!(per_view_errors); unsafe { sys::cv_calibrateCameraRO_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_int_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_TermCriteria(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_size.opencv_as_extern(), i_fixed_point, camera_matrix.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), rvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), new_obj_points.as_raw__OutputArray(), std_deviations_intrinsics.as_raw__OutputArray(), std_deviations_extrinsics.as_raw__OutputArray(), std_deviations_obj_points.as_raw__OutputArray(), per_view_errors.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, criteria.opencv_as_extern()) }.into_result() } /// Finds the camera intrinsic and extrinsic parameters from several views of a calibration pattern. /// /// This function is an extension of calibrateCamera() with the method of releasing object which was /// proposed in [strobl2011iccv](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_strobl2011iccv). In many common cases with inaccurate, unmeasured, roughly planar /// targets (calibration plates), this method can dramatically improve the precision of the estimated /// camera parameters. Both the object-releasing method and standard method are supported by this /// function. Use the parameter **iFixedPoint** for method selection. In the internal implementation, /// calibrateCamera() is a wrapper for this function. /// /// ## Parameters /// * objectPoints: Vector of vectors of calibration pattern points in the calibration pattern /// coordinate space. See calibrateCamera() for details. If the method of releasing object to be used, /// the identical calibration board must be used in each view and it must be fully visible, and all /// objectPoints[i] must be the same and all points should be roughly close to a plane. **The calibration /// target has to be rigid, or at least static if the camera (rather than the calibration target) is /// shifted for grabbing images.** /// * imagePoints: Vector of vectors of the projections of calibration pattern points. See /// calibrateCamera() for details. /// * imageSize: Size of the image used only to initialize the intrinsic camera matrix. /// * iFixedPoint: The index of the 3D object point in objectPoints[0] to be fixed. It also acts as /// a switch for calibration method selection. If object-releasing method to be used, pass in the /// parameter in the range of [1, objectPoints[0].size()-2], otherwise a value out of this range will /// make standard calibration method selected. Usually the top-right corner point of the calibration /// board grid is recommended to be fixed when object-releasing method being utilized. According to /// \cite strobl2011iccv, two other points are also fixed. In this implementation, objectPoints[0].front /// and objectPoints[0].back.z are used. With object-releasing method, accurate rvecs, tvecs and /// newObjPoints are only possible if coordinates of these three fixed points are accurate enough. /// * cameraMatrix: Output 3x3 floating-point camera matrix. See calibrateCamera() for details. /// * distCoeffs: Output vector of distortion coefficients. See calibrateCamera() for details. /// * rvecs: Output vector of rotation vectors estimated for each pattern view. See calibrateCamera() /// for details. /// * tvecs: Output vector of translation vectors estimated for each pattern view. /// * newObjPoints: The updated output vector of calibration pattern points. The coordinates might /// be scaled based on three fixed points. The returned coordinates are accurate only if the above /// mentioned three fixed points are accurate. If not needed, noArray() can be passed in. This parameter /// is ignored with standard calibration method. /// * stdDeviationsIntrinsics: Output vector of standard deviations estimated for intrinsic parameters. /// See calibrateCamera() for details. /// * stdDeviationsExtrinsics: Output vector of standard deviations estimated for extrinsic parameters. /// See calibrateCamera() for details. /// * stdDeviationsObjPoints: Output vector of standard deviations estimated for refined coordinates /// of calibration pattern points. It has the same size and order as objectPoints[0] vector. This /// parameter is ignored with standard calibration method. /// * perViewErrors: Output vector of the RMS re-projection error estimated for each pattern view. /// * flags: Different flags that may be zero or a combination of some predefined values. See /// calibrateCamera() for details. If the method of releasing object is used, the calibration time may /// be much longer. CALIB_USE_QR or CALIB_USE_LU could be used for faster calibration with potentially /// less precise and less stable in some rare cases. /// * criteria: Termination criteria for the iterative optimization algorithm. /// /// ## Returns /// the overall RMS re-projection error. /// /// The function estimates the intrinsic camera parameters and extrinsic parameters for each of the /// views. The algorithm is based on [Zhang2000](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Zhang2000), [BouguetMCT](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_BouguetMCT) and [strobl2011iccv](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_strobl2011iccv). See /// calibrateCamera() for other detailed explanations. /// ## See also /// calibrateCamera, findChessboardCorners, solvePnP, initCameraMatrix2D, stereoCalibrate, undistort /// /// ## Overloaded parameters /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * flags: 0 /// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,30,DBL_EPSILON) pub fn calibrate_camera_ro(object_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, i_fixed_point: i32, camera_matrix: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, rvecs: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, tvecs: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, new_obj_points: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32, criteria: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<f64> { input_array_arg!(object_points); input_array_arg!(image_points); input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix); input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs); output_array_arg!(rvecs); output_array_arg!(tvecs); output_array_arg!(new_obj_points); unsafe { sys::cv_calibrateCameraRO_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_int_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_TermCriteria(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_size.opencv_as_extern(), i_fixed_point, camera_matrix.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), rvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), new_obj_points.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, criteria.opencv_as_extern()) }.into_result() } /// Finds the camera intrinsic and extrinsic parameters from several views of a calibration /// pattern. /// /// ## Parameters /// * objectPoints: In the new interface it is a vector of vectors of calibration pattern points in /// the calibration pattern coordinate space (e.g. std::vector<std::vector<cv::Vec3f>>). The outer /// vector contains as many elements as the number of pattern views. If the same calibration pattern /// is shown in each view and it is fully visible, all the vectors will be the same. Although, it is /// possible to use partially occluded patterns or even different patterns in different views. Then, /// the vectors will be different. Although the points are 3D, they all lie in the calibration pattern's /// XY coordinate plane (thus 0 in the Z-coordinate), if the used calibration pattern is a planar rig. /// In the old interface all the vectors of object points from different views are concatenated /// together. /// * imagePoints: In the new interface it is a vector of vectors of the projections of calibration /// pattern points (e.g. std::vector<std::vector<cv::Vec2f>>). imagePoints.size() and /// objectPoints.size(), and imagePoints[i].size() and objectPoints[i].size() for each i, must be equal, /// respectively. In the old interface all the vectors of object points from different views are /// concatenated together. /// * imageSize: Size of the image used only to initialize the camera intrinsic matrix. /// * cameraMatrix: Input/output 3x3 floating-point camera intrinsic matrix ///  . If @ref CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS /// and/or @ref CALIB_FIX_ASPECT_RATIO are specified, some or all of fx, fy, cx, cy must be /// initialized before calling the function. /// * distCoeffs: Input/output vector of distortion coefficients /// . /// * rvecs: Output vector of rotation vectors (@ref Rodrigues ) estimated for each pattern view /// (e.g. std::vector<cv::Mat>>). That is, each i-th rotation vector together with the corresponding /// i-th translation vector (see the next output parameter description) brings the calibration pattern /// from the object coordinate space (in which object points are specified) to the camera coordinate /// space. In more technical terms, the tuple of the i-th rotation and translation vector performs /// a change of basis from object coordinate space to camera coordinate space. Due to its duality, this /// tuple is equivalent to the position of the calibration pattern with respect to the camera coordinate /// space. /// * tvecs: Output vector of translation vectors estimated for each pattern view, see parameter /// describtion above. /// * stdDeviationsIntrinsics: Output vector of standard deviations estimated for intrinsic /// parameters. Order of deviations values: ///  If one of parameters is not estimated, it's deviation is equals to zero. /// * stdDeviationsExtrinsics: Output vector of standard deviations estimated for extrinsic /// parameters. Order of deviations values:  where M is /// the number of pattern views. 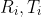 are concatenated 1x3 vectors. /// * perViewErrors: Output vector of the RMS re-projection error estimated for each pattern view. /// * flags: Different flags that may be zero or a combination of the following values: /// * @ref CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS cameraMatrix contains valid initial values of /// fx, fy, cx, cy that are optimized further. Otherwise, (cx, cy) is initially set to the image /// center ( imageSize is used), and focal distances are computed in a least-squares fashion. /// Note, that if intrinsic parameters are known, there is no need to use this function just to /// estimate extrinsic parameters. Use solvePnP instead. /// * @ref CALIB_FIX_PRINCIPAL_POINT The principal point is not changed during the global /// optimization. It stays at the center or at a different location specified when /// @ref CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS is set too. /// * @ref CALIB_FIX_ASPECT_RATIO The functions consider only fy as a free parameter. The /// ratio fx/fy stays the same as in the input cameraMatrix . When /// @ref CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS is not set, the actual input values of fx and fy are /// ignored, only their ratio is computed and used further. /// * @ref CALIB_ZERO_TANGENT_DIST Tangential distortion coefficients  are set /// to zeros and stay zero. /// * @ref CALIB_FIX_K1,..., @ref CALIB_FIX_K6 The corresponding radial distortion /// coefficient is not changed during the optimization. If @ref CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS is /// set, the coefficient from the supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0. /// * @ref CALIB_RATIONAL_MODEL Coefficients k4, k5, and k6 are enabled. To provide the /// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the /// calibration function use the rational model and return 8 coefficients. If the flag is not /// set, the function computes and returns only 5 distortion coefficients. /// * @ref CALIB_THIN_PRISM_MODEL Coefficients s1, s2, s3 and s4 are enabled. To provide the /// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the /// calibration function use the thin prism model and return 12 coefficients. If the flag is not /// set, the function computes and returns only 5 distortion coefficients. /// * @ref CALIB_FIX_S1_S2_S3_S4 The thin prism distortion coefficients are not changed during /// the optimization. If @ref CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS is set, the coefficient from the /// supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0. /// * @ref CALIB_TILTED_MODEL Coefficients tauX and tauY are enabled. To provide the /// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the /// calibration function use the tilted sensor model and return 14 coefficients. If the flag is not /// set, the function computes and returns only 5 distortion coefficients. /// * @ref CALIB_FIX_TAUX_TAUY The coefficients of the tilted sensor model are not changed during /// the optimization. If @ref CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS is set, the coefficient from the /// supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0. /// * criteria: Termination criteria for the iterative optimization algorithm. /// /// ## Returns /// the overall RMS re-projection error. /// /// The function estimates the intrinsic camera parameters and extrinsic parameters for each of the /// views. The algorithm is based on [Zhang2000](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Zhang2000) and [BouguetMCT](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_BouguetMCT) . The coordinates of 3D object /// points and their corresponding 2D projections in each view must be specified. That may be achieved /// by using an object with known geometry and easily detectable feature points. Such an object is /// called a calibration rig or calibration pattern, and OpenCV has built-in support for a chessboard as /// a calibration rig (see @ref findChessboardCorners). Currently, initialization of intrinsic /// parameters (when @ref CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS is not set) is only implemented for planar calibration /// patterns (where Z-coordinates of the object points must be all zeros). 3D calibration rigs can also /// be used as long as initial cameraMatrix is provided. /// /// The algorithm performs the following steps: /// /// * Compute the initial intrinsic parameters (the option only available for planar calibration /// patterns) or read them from the input parameters. The distortion coefficients are all set to /// zeros initially unless some of CALIB_FIX_K? are specified. /// /// * Estimate the initial camera pose as if the intrinsic parameters have been already known. This is /// done using solvePnP . /// /// * Run the global Levenberg-Marquardt optimization algorithm to minimize the reprojection error, /// that is, the total sum of squared distances between the observed feature points imagePoints and /// the projected (using the current estimates for camera parameters and the poses) object points /// objectPoints. See projectPoints for details. /// /// /// Note: /// If you use a non-square (i.e. non-N-by-N) grid and @ref findChessboardCorners for calibration, /// and @ref calibrateCamera returns bad values (zero distortion coefficients,  and ///  very far from the image center, and/or large differences between  and ///  (ratios of 10:1 or more)), then you are probably using patternSize=cvSize(rows,cols) /// instead of using patternSize=cvSize(cols,rows) in @ref findChessboardCorners. /// ## See also /// calibrateCameraRO, findChessboardCorners, solvePnP, initCameraMatrix2D, stereoCalibrate, /// undistort /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * flags: 0 /// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,30,DBL_EPSILON) pub fn calibrate_camera_extended(object_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, camera_matrix: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, rvecs: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, tvecs: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, std_deviations_intrinsics: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, std_deviations_extrinsics: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, per_view_errors: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32, criteria: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<f64> { input_array_arg!(object_points); input_array_arg!(image_points); input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix); input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs); output_array_arg!(rvecs); output_array_arg!(tvecs); output_array_arg!(std_deviations_intrinsics); output_array_arg!(std_deviations_extrinsics); output_array_arg!(per_view_errors); unsafe { sys::cv_calibrateCamera_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_TermCriteria(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_size.opencv_as_extern(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), rvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), std_deviations_intrinsics.as_raw__OutputArray(), std_deviations_extrinsics.as_raw__OutputArray(), per_view_errors.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, criteria.opencv_as_extern()) }.into_result() } /// Finds the camera intrinsic and extrinsic parameters from several views of a calibration /// pattern. /// /// ## Parameters /// * objectPoints: In the new interface it is a vector of vectors of calibration pattern points in /// the calibration pattern coordinate space (e.g. std::vector<std::vector<cv::Vec3f>>). The outer /// vector contains as many elements as the number of pattern views. If the same calibration pattern /// is shown in each view and it is fully visible, all the vectors will be the same. Although, it is /// possible to use partially occluded patterns or even different patterns in different views. Then, /// the vectors will be different. Although the points are 3D, they all lie in the calibration pattern's /// XY coordinate plane (thus 0 in the Z-coordinate), if the used calibration pattern is a planar rig. /// In the old interface all the vectors of object points from different views are concatenated /// together. /// * imagePoints: In the new interface it is a vector of vectors of the projections of calibration /// pattern points (e.g. std::vector<std::vector<cv::Vec2f>>). imagePoints.size() and /// objectPoints.size(), and imagePoints[i].size() and objectPoints[i].size() for each i, must be equal, /// respectively. In the old interface all the vectors of object points from different views are /// concatenated together. /// * imageSize: Size of the image used only to initialize the camera intrinsic matrix. /// * cameraMatrix: Input/output 3x3 floating-point camera intrinsic matrix ///  . If @ref CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS /// and/or @ref CALIB_FIX_ASPECT_RATIO are specified, some or all of fx, fy, cx, cy must be /// initialized before calling the function. /// * distCoeffs: Input/output vector of distortion coefficients /// . /// * rvecs: Output vector of rotation vectors (@ref Rodrigues ) estimated for each pattern view /// (e.g. std::vector<cv::Mat>>). That is, each i-th rotation vector together with the corresponding /// i-th translation vector (see the next output parameter description) brings the calibration pattern /// from the object coordinate space (in which object points are specified) to the camera coordinate /// space. In more technical terms, the tuple of the i-th rotation and translation vector performs /// a change of basis from object coordinate space to camera coordinate space. Due to its duality, this /// tuple is equivalent to the position of the calibration pattern with respect to the camera coordinate /// space. /// * tvecs: Output vector of translation vectors estimated for each pattern view, see parameter /// describtion above. /// * stdDeviationsIntrinsics: Output vector of standard deviations estimated for intrinsic /// parameters. Order of deviations values: ///  If one of parameters is not estimated, it's deviation is equals to zero. /// * stdDeviationsExtrinsics: Output vector of standard deviations estimated for extrinsic /// parameters. Order of deviations values:  where M is /// the number of pattern views. 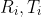 are concatenated 1x3 vectors. /// * perViewErrors: Output vector of the RMS re-projection error estimated for each pattern view. /// * flags: Different flags that may be zero or a combination of the following values: /// * @ref CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS cameraMatrix contains valid initial values of /// fx, fy, cx, cy that are optimized further. Otherwise, (cx, cy) is initially set to the image /// center ( imageSize is used), and focal distances are computed in a least-squares fashion. /// Note, that if intrinsic parameters are known, there is no need to use this function just to /// estimate extrinsic parameters. Use solvePnP instead. /// * @ref CALIB_FIX_PRINCIPAL_POINT The principal point is not changed during the global /// optimization. It stays at the center or at a different location specified when /// @ref CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS is set too. /// * @ref CALIB_FIX_ASPECT_RATIO The functions consider only fy as a free parameter. The /// ratio fx/fy stays the same as in the input cameraMatrix . When /// @ref CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS is not set, the actual input values of fx and fy are /// ignored, only their ratio is computed and used further. /// * @ref CALIB_ZERO_TANGENT_DIST Tangential distortion coefficients  are set /// to zeros and stay zero. /// * @ref CALIB_FIX_K1,..., @ref CALIB_FIX_K6 The corresponding radial distortion /// coefficient is not changed during the optimization. If @ref CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS is /// set, the coefficient from the supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0. /// * @ref CALIB_RATIONAL_MODEL Coefficients k4, k5, and k6 are enabled. To provide the /// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the /// calibration function use the rational model and return 8 coefficients. If the flag is not /// set, the function computes and returns only 5 distortion coefficients. /// * @ref CALIB_THIN_PRISM_MODEL Coefficients s1, s2, s3 and s4 are enabled. To provide the /// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the /// calibration function use the thin prism model and return 12 coefficients. If the flag is not /// set, the function computes and returns only 5 distortion coefficients. /// * @ref CALIB_FIX_S1_S2_S3_S4 The thin prism distortion coefficients are not changed during /// the optimization. If @ref CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS is set, the coefficient from the /// supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0. /// * @ref CALIB_TILTED_MODEL Coefficients tauX and tauY are enabled. To provide the /// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the /// calibration function use the tilted sensor model and return 14 coefficients. If the flag is not /// set, the function computes and returns only 5 distortion coefficients. /// * @ref CALIB_FIX_TAUX_TAUY The coefficients of the tilted sensor model are not changed during /// the optimization. If @ref CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS is set, the coefficient from the /// supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0. /// * criteria: Termination criteria for the iterative optimization algorithm. /// /// ## Returns /// the overall RMS re-projection error. /// /// The function estimates the intrinsic camera parameters and extrinsic parameters for each of the /// views. The algorithm is based on [Zhang2000](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Zhang2000) and [BouguetMCT](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_BouguetMCT) . The coordinates of 3D object /// points and their corresponding 2D projections in each view must be specified. That may be achieved /// by using an object with known geometry and easily detectable feature points. Such an object is /// called a calibration rig or calibration pattern, and OpenCV has built-in support for a chessboard as /// a calibration rig (see @ref findChessboardCorners). Currently, initialization of intrinsic /// parameters (when @ref CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS is not set) is only implemented for planar calibration /// patterns (where Z-coordinates of the object points must be all zeros). 3D calibration rigs can also /// be used as long as initial cameraMatrix is provided. /// /// The algorithm performs the following steps: /// /// * Compute the initial intrinsic parameters (the option only available for planar calibration /// patterns) or read them from the input parameters. The distortion coefficients are all set to /// zeros initially unless some of CALIB_FIX_K? are specified. /// /// * Estimate the initial camera pose as if the intrinsic parameters have been already known. This is /// done using solvePnP . /// /// * Run the global Levenberg-Marquardt optimization algorithm to minimize the reprojection error, /// that is, the total sum of squared distances between the observed feature points imagePoints and /// the projected (using the current estimates for camera parameters and the poses) object points /// objectPoints. See projectPoints for details. /// /// /// Note: /// If you use a non-square (i.e. non-N-by-N) grid and @ref findChessboardCorners for calibration, /// and @ref calibrateCamera returns bad values (zero distortion coefficients,  and ///  very far from the image center, and/or large differences between  and ///  (ratios of 10:1 or more)), then you are probably using patternSize=cvSize(rows,cols) /// instead of using patternSize=cvSize(cols,rows) in @ref findChessboardCorners. /// ## See also /// calibrateCameraRO, findChessboardCorners, solvePnP, initCameraMatrix2D, stereoCalibrate, /// undistort /// /// ## Overloaded parameters /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * flags: 0 /// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,30,DBL_EPSILON) pub fn calibrate_camera(object_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, camera_matrix: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, rvecs: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, tvecs: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32, criteria: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<f64> { input_array_arg!(object_points); input_array_arg!(image_points); input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix); input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs); output_array_arg!(rvecs); output_array_arg!(tvecs); unsafe { sys::cv_calibrateCamera_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_TermCriteria(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_size.opencv_as_extern(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), rvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, criteria.opencv_as_extern()) }.into_result() } /// Computes Hand-Eye calibration:  /// /// ## Parameters /// * R_gripper2base: Rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point /// expressed in the gripper frame to the robot base frame (). /// This is a vector (`vector<Mat>`) that contains the rotation, `(3x3)` rotation matrices or `(3x1)` rotation vectors, /// for all the transformations from gripper frame to robot base frame. /// * t_gripper2base: Translation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point /// expressed in the gripper frame to the robot base frame (). /// This is a vector (`vector<Mat>`) that contains the `(3x1)` translation vectors for all the transformations /// from gripper frame to robot base frame. /// * R_target2cam: Rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point /// expressed in the target frame to the camera frame (). /// This is a vector (`vector<Mat>`) that contains the rotation, `(3x3)` rotation matrices or `(3x1)` rotation vectors, /// for all the transformations from calibration target frame to camera frame. /// * t_target2cam: Rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point /// expressed in the target frame to the camera frame (). /// This is a vector (`vector<Mat>`) that contains the `(3x1)` translation vectors for all the transformations /// from calibration target frame to camera frame. /// * R_cam2gripper:[out] Estimated `(3x3)` rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point /// expressed in the camera frame to the gripper frame (). /// * t_cam2gripper:[out] Estimated `(3x1)` translation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point /// expressed in the camera frame to the gripper frame (). /// * method: One of the implemented Hand-Eye calibration method, see cv::HandEyeCalibrationMethod /// /// The function performs the Hand-Eye calibration using various methods. One approach consists in estimating the /// rotation then the translation (separable solutions) and the following methods are implemented: /// - R. Tsai, R. Lenz A New Technique for Fully Autonomous and Efficient 3D Robotics Hand/EyeCalibration \cite Tsai89 /// - F. Park, B. Martin Robot Sensor Calibration: Solving AX = XB on the Euclidean Group \cite Park94 /// - R. Horaud, F. Dornaika Hand-Eye Calibration \cite Horaud95 /// /// Another approach consists in estimating simultaneously the rotation and the translation (simultaneous solutions), /// with the following implemented methods: /// - N. Andreff, R. Horaud, B. Espiau On-line Hand-Eye Calibration \cite Andreff99 /// - K. Daniilidis Hand-Eye Calibration Using Dual Quaternions \cite Daniilidis98 /// /// The following picture describes the Hand-Eye calibration problem where the transformation between a camera ("eye") /// mounted on a robot gripper ("hand") has to be estimated. This configuration is called eye-in-hand. /// /// The eye-to-hand configuration consists in a static camera observing a calibration pattern mounted on the robot /// end-effector. The transformation from the camera to the robot base frame can then be estimated by inputting /// the suitable transformations to the function, see below. /// ///  /// /// The calibration procedure is the following: /// - a static calibration pattern is used to estimate the transformation between the target frame /// and the camera frame /// - the robot gripper is moved in order to acquire several poses /// - for each pose, the homogeneous transformation between the gripper frame and the robot base frame is recorded using for /// instance the robot kinematics ///  /// - for each pose, the homogeneous transformation between the calibration target frame and the camera frame is recorded using /// for instance a pose estimation method (PnP) from 2D-3D point correspondences ///  /// /// The Hand-Eye calibration procedure returns the following homogeneous transformation ///  /// /// This problem is also known as solving the 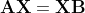 equation: /// - for an eye-in-hand configuration ///  /// /// - for an eye-to-hand configuration ///  /// /// \note /// Additional information can be found on this [website](http://campar.in.tum.de/Chair/HandEyeCalibration). /// \note /// A minimum of 2 motions with non parallel rotation axes are necessary to determine the hand-eye transformation. /// So at least 3 different poses are required, but it is strongly recommended to use many more poses. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * method: CALIB_HAND_EYE_TSAI pub fn calibrate_hand_eye(r_gripper2base: &dyn core::ToInputArray, t_gripper2base: &dyn core::ToInputArray, r_target2cam: &dyn core::ToInputArray, t_target2cam: &dyn core::ToInputArray, r_cam2gripper: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, t_cam2gripper: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, method: crate::calib3d::HandEyeCalibrationMethod) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(r_gripper2base); input_array_arg!(t_gripper2base); input_array_arg!(r_target2cam); input_array_arg!(t_target2cam); output_array_arg!(r_cam2gripper); output_array_arg!(t_cam2gripper); unsafe { sys::cv_calibrateHandEye_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_HandEyeCalibrationMethod(r_gripper2base.as_raw__InputArray(), t_gripper2base.as_raw__InputArray(), r_target2cam.as_raw__InputArray(), t_target2cam.as_raw__InputArray(), r_cam2gripper.as_raw__OutputArray(), t_cam2gripper.as_raw__OutputArray(), method) }.into_result() } /// Computes Robot-World/Hand-Eye calibration:  and  /// /// ## Parameters /// * R_world2cam: Rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point /// expressed in the world frame to the camera frame (). /// This is a vector (`vector<Mat>`) that contains the rotation, `(3x3)` rotation matrices or `(3x1)` rotation vectors, /// for all the transformations from world frame to the camera frame. /// * t_world2cam: Translation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point /// expressed in the world frame to the camera frame (). /// This is a vector (`vector<Mat>`) that contains the `(3x1)` translation vectors for all the transformations /// from world frame to the camera frame. /// * R_base2gripper: Rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point /// expressed in the robot base frame to the gripper frame (). /// This is a vector (`vector<Mat>`) that contains the rotation, `(3x3)` rotation matrices or `(3x1)` rotation vectors, /// for all the transformations from robot base frame to the gripper frame. /// * t_base2gripper: Rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point /// expressed in the robot base frame to the gripper frame (). /// This is a vector (`vector<Mat>`) that contains the `(3x1)` translation vectors for all the transformations /// from robot base frame to the gripper frame. /// * R_base2world:[out] Estimated `(3x3)` rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point /// expressed in the robot base frame to the world frame (). /// * t_base2world:[out] Estimated `(3x1)` translation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point /// expressed in the robot base frame to the world frame (). /// * R_gripper2cam:[out] Estimated `(3x3)` rotation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point /// expressed in the gripper frame to the camera frame (). /// * t_gripper2cam:[out] Estimated `(3x1)` translation part extracted from the homogeneous matrix that transforms a point /// expressed in the gripper frame to the camera frame (). /// * method: One of the implemented Robot-World/Hand-Eye calibration method, see cv::RobotWorldHandEyeCalibrationMethod /// /// The function performs the Robot-World/Hand-Eye calibration using various methods. One approach consists in estimating the /// rotation then the translation (separable solutions): /// - M. Shah, Solving the robot-world/hand-eye calibration problem using the kronecker product \cite Shah2013SolvingTR /// /// Another approach consists in estimating simultaneously the rotation and the translation (simultaneous solutions), /// with the following implemented method: /// - A. Li, L. Wang, and D. Wu, Simultaneous robot-world and hand-eye calibration using dual-quaternions and kronecker product \cite Li2010SimultaneousRA /// /// The following picture describes the Robot-World/Hand-Eye calibration problem where the transformations between a robot and a world frame /// and between a robot gripper ("hand") and a camera ("eye") mounted at the robot end-effector have to be estimated. /// ///  /// /// The calibration procedure is the following: /// - a static calibration pattern is used to estimate the transformation between the target frame /// and the camera frame /// - the robot gripper is moved in order to acquire several poses /// - for each pose, the homogeneous transformation between the gripper frame and the robot base frame is recorded using for /// instance the robot kinematics ///  /// - for each pose, the homogeneous transformation between the calibration target frame (the world frame) and the camera frame is recorded using /// for instance a pose estimation method (PnP) from 2D-3D point correspondences ///  /// /// The Robot-World/Hand-Eye calibration procedure returns the following homogeneous transformations ///  ///  /// /// This problem is also known as solving the  equation, with: /// -  /// -  /// -  /// -  /// /// \note /// At least 3 measurements are required (input vectors size must be greater or equal to 3). /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * method: CALIB_ROBOT_WORLD_HAND_EYE_SHAH pub fn calibrate_robot_world_hand_eye(r_world2cam: &dyn core::ToInputArray, t_world2cam: &dyn core::ToInputArray, r_base2gripper: &dyn core::ToInputArray, t_base2gripper: &dyn core::ToInputArray, r_base2world: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, t_base2world: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, r_gripper2cam: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, t_gripper2cam: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, method: crate::calib3d::RobotWorldHandEyeCalibrationMethod) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(r_world2cam); input_array_arg!(t_world2cam); input_array_arg!(r_base2gripper); input_array_arg!(t_base2gripper); output_array_arg!(r_base2world); output_array_arg!(t_base2world); output_array_arg!(r_gripper2cam); output_array_arg!(t_gripper2cam); unsafe { sys::cv_calibrateRobotWorldHandEye_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_RobotWorldHandEyeCalibrationMethod(r_world2cam.as_raw__InputArray(), t_world2cam.as_raw__InputArray(), r_base2gripper.as_raw__InputArray(), t_base2gripper.as_raw__InputArray(), r_base2world.as_raw__OutputArray(), t_base2world.as_raw__OutputArray(), r_gripper2cam.as_raw__OutputArray(), t_gripper2cam.as_raw__OutputArray(), method) }.into_result() } /// Computes useful camera characteristics from the camera intrinsic matrix. /// /// ## Parameters /// * cameraMatrix: Input camera intrinsic matrix that can be estimated by calibrateCamera or /// stereoCalibrate . /// * imageSize: Input image size in pixels. /// * apertureWidth: Physical width in mm of the sensor. /// * apertureHeight: Physical height in mm of the sensor. /// * fovx: Output field of view in degrees along the horizontal sensor axis. /// * fovy: Output field of view in degrees along the vertical sensor axis. /// * focalLength: Focal length of the lens in mm. /// * principalPoint: Principal point in mm. /// * aspectRatio:  /// /// The function computes various useful camera characteristics from the previously estimated camera /// matrix. /// /// /// Note: /// Do keep in mind that the unity measure 'mm' stands for whatever unit of measure one chooses for /// the chessboard pitch (it can thus be any value). pub fn calibration_matrix_values(camera_matrix: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, aperture_width: f64, aperture_height: f64, fovx: &mut f64, fovy: &mut f64, focal_length: &mut f64, principal_point: &mut core::Point2d, aspect_ratio: &mut f64) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(camera_matrix); unsafe { sys::cv_calibrationMatrixValues_const__InputArrayR_Size_double_double_doubleR_doubleR_doubleR_Point2dR_doubleR(camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), image_size.opencv_as_extern(), aperture_width, aperture_height, fovx, fovy, focal_length, principal_point, aspect_ratio) }.into_result() } pub fn check_chessboard(img: &dyn core::ToInputArray, size: core::Size) -> Result<bool> { input_array_arg!(img); unsafe { sys::cv_checkChessboard_const__InputArrayR_Size(img.as_raw__InputArray(), size.opencv_as_extern()) }.into_result() } /// Combines two rotation-and-shift transformations. /// /// ## Parameters /// * rvec1: First rotation vector. /// * tvec1: First translation vector. /// * rvec2: Second rotation vector. /// * tvec2: Second translation vector. /// * rvec3: Output rotation vector of the superposition. /// * tvec3: Output translation vector of the superposition. /// * dr3dr1: Optional output derivative of rvec3 with regard to rvec1 /// * dr3dt1: Optional output derivative of rvec3 with regard to tvec1 /// * dr3dr2: Optional output derivative of rvec3 with regard to rvec2 /// * dr3dt2: Optional output derivative of rvec3 with regard to tvec2 /// * dt3dr1: Optional output derivative of tvec3 with regard to rvec1 /// * dt3dt1: Optional output derivative of tvec3 with regard to tvec1 /// * dt3dr2: Optional output derivative of tvec3 with regard to rvec2 /// * dt3dt2: Optional output derivative of tvec3 with regard to tvec2 /// /// The functions compute: /// ///  /// /// where  denotes a rotation vector to a rotation matrix transformation, and ///  denotes the inverse transformation. See Rodrigues for details. /// /// Also, the functions can compute the derivatives of the output vectors with regards to the input /// vectors (see matMulDeriv ). The functions are used inside stereoCalibrate but can also be used in /// your own code where Levenberg-Marquardt or another gradient-based solver is used to optimize a /// function that contains a matrix multiplication. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * dr3dr1: noArray() /// * dr3dt1: noArray() /// * dr3dr2: noArray() /// * dr3dt2: noArray() /// * dt3dr1: noArray() /// * dt3dt1: noArray() /// * dt3dr2: noArray() /// * dt3dt2: noArray() pub fn compose_rt(rvec1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, tvec1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, rvec2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, tvec2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, rvec3: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, tvec3: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, dr3dr1: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, dr3dt1: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, dr3dr2: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, dr3dt2: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, dt3dr1: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, dt3dt1: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, dt3dr2: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, dt3dt2: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(rvec1); input_array_arg!(tvec1); input_array_arg!(rvec2); input_array_arg!(tvec2); output_array_arg!(rvec3); output_array_arg!(tvec3); output_array_arg!(dr3dr1); output_array_arg!(dr3dt1); output_array_arg!(dr3dr2); output_array_arg!(dr3dt2); output_array_arg!(dt3dr1); output_array_arg!(dt3dt1); output_array_arg!(dt3dr2); output_array_arg!(dt3dt2); unsafe { sys::cv_composeRT_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(rvec1.as_raw__InputArray(), tvec1.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec2.as_raw__InputArray(), tvec2.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec3.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvec3.as_raw__OutputArray(), dr3dr1.as_raw__OutputArray(), dr3dt1.as_raw__OutputArray(), dr3dr2.as_raw__OutputArray(), dr3dt2.as_raw__OutputArray(), dt3dr1.as_raw__OutputArray(), dt3dt1.as_raw__OutputArray(), dt3dr2.as_raw__OutputArray(), dt3dt2.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// For points in an image of a stereo pair, computes the corresponding epilines in the other image. /// /// ## Parameters /// * points: Input points. 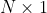 or 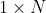 matrix of type CV_32FC2 or /// vector\<Point2f\> . /// * whichImage: Index of the image (1 or 2) that contains the points . /// * F: Fundamental matrix that can be estimated using findFundamentalMat or stereoRectify . /// * lines: Output vector of the epipolar lines corresponding to the points in the other image. /// Each line 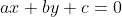 is encoded by 3 numbers 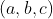 . /// /// For every point in one of the two images of a stereo pair, the function finds the equation of the /// corresponding epipolar line in the other image. /// /// From the fundamental matrix definition (see findFundamentalMat ), line  in the second /// image for the point  in the first image (when whichImage=1 ) is computed as: /// ///  /// /// And vice versa, when whichImage=2,  is computed from  as: /// ///  /// /// Line coefficients are defined up to a scale. They are normalized so that  . pub fn compute_correspond_epilines(points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, which_image: i32, f: &dyn core::ToInputArray, lines: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(points); input_array_arg!(f); output_array_arg!(lines); unsafe { sys::cv_computeCorrespondEpilines_const__InputArrayR_int_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(points.as_raw__InputArray(), which_image, f.as_raw__InputArray(), lines.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Converts points from homogeneous to Euclidean space. /// /// ## Parameters /// * src: Input vector of N-dimensional points. /// * dst: Output vector of N-1-dimensional points. /// /// The function converts points homogeneous to Euclidean space using perspective projection. That is, /// each point (x1, x2, ... x(n-1), xn) is converted to (x1/xn, x2/xn, ..., x(n-1)/xn). When xn=0, the /// output point coordinates will be (0,0,0,...). pub fn convert_points_from_homogeneous(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(src); output_array_arg!(dst); unsafe { sys::cv_convertPointsFromHomogeneous_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Converts points to/from homogeneous coordinates. /// /// ## Parameters /// * src: Input array or vector of 2D, 3D, or 4D points. /// * dst: Output vector of 2D, 3D, or 4D points. /// /// The function converts 2D or 3D points from/to homogeneous coordinates by calling either /// convertPointsToHomogeneous or convertPointsFromHomogeneous. /// /// /// Note: The function is obsolete. Use one of the previous two functions instead. pub fn convert_points_homogeneous(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(src); output_array_arg!(dst); unsafe { sys::cv_convertPointsHomogeneous_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Converts points from Euclidean to homogeneous space. /// /// ## Parameters /// * src: Input vector of N-dimensional points. /// * dst: Output vector of N+1-dimensional points. /// /// The function converts points from Euclidean to homogeneous space by appending 1's to the tuple of /// point coordinates. That is, each point (x1, x2, ..., xn) is converted to (x1, x2, ..., xn, 1). pub fn convert_points_to_homogeneous(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(src); output_array_arg!(dst); unsafe { sys::cv_convertPointsToHomogeneous_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Refines coordinates of corresponding points. /// /// ## Parameters /// * F: 3x3 fundamental matrix. /// * points1: 1xN array containing the first set of points. /// * points2: 1xN array containing the second set of points. /// * newPoints1: The optimized points1. /// * newPoints2: The optimized points2. /// /// The function implements the Optimal Triangulation Method (see Multiple View Geometry for details). /// For each given point correspondence points1[i] \<-\> points2[i], and a fundamental matrix F, it /// computes the corrected correspondences newPoints1[i] \<-\> newPoints2[i] that minimize the geometric /// error  (where  is the /// geometric distance between points  and 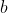 ) subject to the epipolar constraint ///  . pub fn correct_matches(f: &dyn core::ToInputArray, points1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, points2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, new_points1: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, new_points2: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(f); input_array_arg!(points1); input_array_arg!(points2); output_array_arg!(new_points1); output_array_arg!(new_points2); unsafe { sys::cv_correctMatches_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(f.as_raw__InputArray(), points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), new_points1.as_raw__OutputArray(), new_points2.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Decompose an essential matrix to possible rotations and translation. /// /// ## Parameters /// * E: The input essential matrix. /// * R1: One possible rotation matrix. /// * R2: Another possible rotation matrix. /// * t: One possible translation. /// /// This function decomposes the essential matrix E using svd decomposition [HartleyZ00](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_HartleyZ00). In /// general, four possible poses exist for the decomposition of E. They are , /// , , . /// /// If E gives the epipolar constraint  between the image /// points  in the first image and  in second image, then any of the tuples /// , , ,  is a change of basis from the first /// camera's coordinate system to the second camera's coordinate system. However, by decomposing E, one /// can only get the direction of the translation. For this reason, the translation t is returned with /// unit length. pub fn decompose_essential_mat(e: &dyn core::ToInputArray, r1: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, r2: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, t: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(e); output_array_arg!(r1); output_array_arg!(r2); output_array_arg!(t); unsafe { sys::cv_decomposeEssentialMat_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(e.as_raw__InputArray(), r1.as_raw__OutputArray(), r2.as_raw__OutputArray(), t.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Decompose a homography matrix to rotation(s), translation(s) and plane normal(s). /// /// ## Parameters /// * H: The input homography matrix between two images. /// * K: The input camera intrinsic matrix. /// * rotations: Array of rotation matrices. /// * translations: Array of translation matrices. /// * normals: Array of plane normal matrices. /// /// This function extracts relative camera motion between two views of a planar object and returns up to /// four mathematical solution tuples of rotation, translation, and plane normal. The decomposition of /// the homography matrix H is described in detail in [Malis](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Malis). /// /// If the homography H, induced by the plane, gives the constraint ///  on the source image points /// 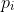 and the destination image points , then the tuple of rotations[k] and /// translations[k] is a change of basis from the source camera's coordinate system to the destination /// camera's coordinate system. However, by decomposing H, one can only get the translation normalized /// by the (typically unknown) depth of the scene, i.e. its direction but with normalized length. /// /// If point correspondences are available, at least two solutions may further be invalidated, by /// applying positive depth constraint, i.e. all points must be in front of the camera. pub fn decompose_homography_mat(h: &dyn core::ToInputArray, k: &dyn core::ToInputArray, rotations: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, translations: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, normals: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<i32> { input_array_arg!(h); input_array_arg!(k); output_array_arg!(rotations); output_array_arg!(translations); output_array_arg!(normals); unsafe { sys::cv_decomposeHomographyMat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(h.as_raw__InputArray(), k.as_raw__InputArray(), rotations.as_raw__OutputArray(), translations.as_raw__OutputArray(), normals.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Decomposes a projection matrix into a rotation matrix and a camera intrinsic matrix. /// /// ## Parameters /// * projMatrix: 3x4 input projection matrix P. /// * cameraMatrix: Output 3x3 camera intrinsic matrix . /// * rotMatrix: Output 3x3 external rotation matrix R. /// * transVect: Output 4x1 translation vector T. /// * rotMatrixX: Optional 3x3 rotation matrix around x-axis. /// * rotMatrixY: Optional 3x3 rotation matrix around y-axis. /// * rotMatrixZ: Optional 3x3 rotation matrix around z-axis. /// * eulerAngles: Optional three-element vector containing three Euler angles of rotation in /// degrees. /// /// The function computes a decomposition of a projection matrix into a calibration and a rotation /// matrix and the position of a camera. /// /// It optionally returns three rotation matrices, one for each axis, and three Euler angles that could /// be used in OpenGL. Note, there is always more than one sequence of rotations about the three /// principal axes that results in the same orientation of an object, e.g. see [Slabaugh](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Slabaugh) . Returned /// tree rotation matrices and corresponding three Euler angles are only one of the possible solutions. /// /// The function is based on RQDecomp3x3 . /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * rot_matrix_x: noArray() /// * rot_matrix_y: noArray() /// * rot_matrix_z: noArray() /// * euler_angles: noArray() pub fn decompose_projection_matrix(proj_matrix: &dyn core::ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, rot_matrix: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, trans_vect: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, rot_matrix_x: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, rot_matrix_y: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, rot_matrix_z: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, euler_angles: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(proj_matrix); output_array_arg!(camera_matrix); output_array_arg!(rot_matrix); output_array_arg!(trans_vect); output_array_arg!(rot_matrix_x); output_array_arg!(rot_matrix_y); output_array_arg!(rot_matrix_z); output_array_arg!(euler_angles); unsafe { sys::cv_decomposeProjectionMatrix_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(proj_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__OutputArray(), rot_matrix.as_raw__OutputArray(), trans_vect.as_raw__OutputArray(), rot_matrix_x.as_raw__OutputArray(), rot_matrix_y.as_raw__OutputArray(), rot_matrix_z.as_raw__OutputArray(), euler_angles.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Renders the detected chessboard corners. /// /// ## Parameters /// * image: Destination image. It must be an 8-bit color image. /// * patternSize: Number of inner corners per a chessboard row and column /// (patternSize = cv::Size(points_per_row,points_per_column)). /// * corners: Array of detected corners, the output of findChessboardCorners. /// * patternWasFound: Parameter indicating whether the complete board was found or not. The /// return value of findChessboardCorners should be passed here. /// /// The function draws individual chessboard corners detected either as red circles if the board was not /// found, or as colored corners connected with lines if the board was found. pub fn draw_chessboard_corners(image: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, pattern_size: core::Size, corners: &dyn core::ToInputArray, pattern_was_found: bool) -> Result<()> { input_output_array_arg!(image); input_array_arg!(corners); unsafe { sys::cv_drawChessboardCorners_const__InputOutputArrayR_Size_const__InputArrayR_bool(image.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), pattern_size.opencv_as_extern(), corners.as_raw__InputArray(), pattern_was_found) }.into_result() } /// Draw axes of the world/object coordinate system from pose estimation. see also: solvePnP /// /// ## Parameters /// * image: Input/output image. It must have 1 or 3 channels. The number of channels is not altered. /// * cameraMatrix: Input 3x3 floating-point matrix of camera intrinsic parameters. ///  /// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients /// . If the vector is empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed. /// * rvec: Rotation vector (see @ref Rodrigues ) that, together with tvec, brings points from /// the model coordinate system to the camera coordinate system. /// * tvec: Translation vector. /// * length: Length of the painted axes in the same unit than tvec (usually in meters). /// * thickness: Line thickness of the painted axes. /// /// This function draws the axes of the world/object coordinate system w.r.t. to the camera frame. /// OX is drawn in red, OY in green and OZ in blue. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * thickness: 3 pub fn draw_frame_axes(image: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, camera_matrix: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &dyn core::ToInputArray, rvec: &dyn core::ToInputArray, tvec: &dyn core::ToInputArray, length: f32, thickness: i32) -> Result<()> { input_output_array_arg!(image); input_array_arg!(camera_matrix); input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs); input_array_arg!(rvec); input_array_arg!(tvec); unsafe { sys::cv_drawFrameAxes_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_float_int(image.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec.as_raw__InputArray(), tvec.as_raw__InputArray(), length, thickness) }.into_result() } pub fn estimate_affine_2d_1(pts1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, pts2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, inliers: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, params: crate::calib3d::UsacParams) -> Result<core::Mat> { input_array_arg!(pts1); input_array_arg!(pts2); output_array_arg!(inliers); unsafe { sys::cv_estimateAffine2D_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const_UsacParamsR(pts1.as_raw__InputArray(), pts2.as_raw__InputArray(), inliers.as_raw__OutputArray(), ¶ms) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Computes an optimal affine transformation between two 2D point sets. /// /// It computes ///  /// /// ## Parameters /// * from: First input 2D point set containing 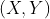. /// * to: Second input 2D point set containing 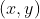. /// * inliers: Output vector indicating which points are inliers (1-inlier, 0-outlier). /// * method: Robust method used to compute transformation. The following methods are possible: /// * @ref RANSAC - RANSAC-based robust method /// * @ref LMEDS - Least-Median robust method /// RANSAC is the default method. /// * ransacReprojThreshold: Maximum reprojection error in the RANSAC algorithm to consider /// a point as an inlier. Applies only to RANSAC. /// * maxIters: The maximum number of robust method iterations. /// * confidence: Confidence level, between 0 and 1, for the estimated transformation. Anything /// between 0.95 and 0.99 is usually good enough. Values too close to 1 can slow down the estimation /// significantly. Values lower than 0.8-0.9 can result in an incorrectly estimated transformation. /// * refineIters: Maximum number of iterations of refining algorithm (Levenberg-Marquardt). /// Passing 0 will disable refining, so the output matrix will be output of robust method. /// /// ## Returns /// Output 2D affine transformation matrix 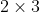 or empty matrix if transformation /// could not be estimated. The returned matrix has the following form: ///  /// /// The function estimates an optimal 2D affine transformation between two 2D point sets using the /// selected robust algorithm. /// /// The computed transformation is then refined further (using only inliers) with the /// Levenberg-Marquardt method to reduce the re-projection error even more. /// /// /// Note: /// The RANSAC method can handle practically any ratio of outliers but needs a threshold to /// distinguish inliers from outliers. The method LMeDS does not need any threshold but it works /// correctly only when there are more than 50% of inliers. /// ## See also /// estimateAffinePartial2D, getAffineTransform /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * inliers: noArray() /// * method: RANSAC /// * ransac_reproj_threshold: 3 /// * max_iters: 2000 /// * confidence: 0.99 /// * refine_iters: 10 pub fn estimate_affine_2d(from: &dyn core::ToInputArray, to: &dyn core::ToInputArray, inliers: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, method: i32, ransac_reproj_threshold: f64, max_iters: size_t, confidence: f64, refine_iters: size_t) -> Result<core::Mat> { input_array_arg!(from); input_array_arg!(to); output_array_arg!(inliers); unsafe { sys::cv_estimateAffine2D_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_double_size_t_double_size_t(from.as_raw__InputArray(), to.as_raw__InputArray(), inliers.as_raw__OutputArray(), method, ransac_reproj_threshold, max_iters, confidence, refine_iters) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Computes an optimal affine transformation between two 3D point sets. /// /// It computes ///  /// /// ## Parameters /// * src: First input 3D point set containing 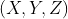. /// * dst: Second input 3D point set containing 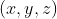. /// * out: Output 3D affine transformation matrix 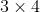 of the form ///  /// * inliers: Output vector indicating which points are inliers (1-inlier, 0-outlier). /// * ransacThreshold: Maximum reprojection error in the RANSAC algorithm to consider a point as /// an inlier. /// * confidence: Confidence level, between 0 and 1, for the estimated transformation. Anything /// between 0.95 and 0.99 is usually good enough. Values too close to 1 can slow down the estimation /// significantly. Values lower than 0.8-0.9 can result in an incorrectly estimated transformation. /// /// The function estimates an optimal 3D affine transformation between two 3D point sets using the /// RANSAC algorithm. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * ransac_threshold: 3 /// * confidence: 0.99 pub fn estimate_affine_3d(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &dyn core::ToInputArray, out: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, inliers: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, ransac_threshold: f64, confidence: f64) -> Result<i32> { input_array_arg!(src); input_array_arg!(dst); output_array_arg!(out); output_array_arg!(inliers); unsafe { sys::cv_estimateAffine3D_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_double(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__InputArray(), out.as_raw__OutputArray(), inliers.as_raw__OutputArray(), ransac_threshold, confidence) }.into_result() } /// Computes an optimal limited affine transformation with 4 degrees of freedom between /// two 2D point sets. /// /// ## Parameters /// * from: First input 2D point set. /// * to: Second input 2D point set. /// * inliers: Output vector indicating which points are inliers. /// * method: Robust method used to compute transformation. The following methods are possible: /// * @ref RANSAC - RANSAC-based robust method /// * @ref LMEDS - Least-Median robust method /// RANSAC is the default method. /// * ransacReprojThreshold: Maximum reprojection error in the RANSAC algorithm to consider /// a point as an inlier. Applies only to RANSAC. /// * maxIters: The maximum number of robust method iterations. /// * confidence: Confidence level, between 0 and 1, for the estimated transformation. Anything /// between 0.95 and 0.99 is usually good enough. Values too close to 1 can slow down the estimation /// significantly. Values lower than 0.8-0.9 can result in an incorrectly estimated transformation. /// * refineIters: Maximum number of iterations of refining algorithm (Levenberg-Marquardt). /// Passing 0 will disable refining, so the output matrix will be output of robust method. /// /// ## Returns /// Output 2D affine transformation (4 degrees of freedom) matrix 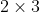 or /// empty matrix if transformation could not be estimated. /// /// The function estimates an optimal 2D affine transformation with 4 degrees of freedom limited to /// combinations of translation, rotation, and uniform scaling. Uses the selected algorithm for robust /// estimation. /// /// The computed transformation is then refined further (using only inliers) with the /// Levenberg-Marquardt method to reduce the re-projection error even more. /// /// Estimated transformation matrix is: ///  /// Where 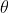 is the rotation angle,  the scaling factor and  are /// translations in  axes respectively. /// /// /// Note: /// The RANSAC method can handle practically any ratio of outliers but need a threshold to /// distinguish inliers from outliers. The method LMeDS does not need any threshold but it works /// correctly only when there are more than 50% of inliers. /// ## See also /// estimateAffine2D, getAffineTransform /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * inliers: noArray() /// * method: RANSAC /// * ransac_reproj_threshold: 3 /// * max_iters: 2000 /// * confidence: 0.99 /// * refine_iters: 10 pub fn estimate_affine_partial_2d(from: &dyn core::ToInputArray, to: &dyn core::ToInputArray, inliers: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, method: i32, ransac_reproj_threshold: f64, max_iters: size_t, confidence: f64, refine_iters: size_t) -> Result<core::Mat> { input_array_arg!(from); input_array_arg!(to); output_array_arg!(inliers); unsafe { sys::cv_estimateAffinePartial2D_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_double_size_t_double_size_t(from.as_raw__InputArray(), to.as_raw__InputArray(), inliers.as_raw__OutputArray(), method, ransac_reproj_threshold, max_iters, confidence, refine_iters) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Estimates the sharpness of a detected chessboard. /// /// Image sharpness, as well as brightness, are a critical parameter for accuracte /// camera calibration. For accessing these parameters for filtering out /// problematic calibraiton images, this method calculates edge profiles by traveling from /// black to white chessboard cell centers. Based on this, the number of pixels is /// calculated required to transit from black to white. This width of the /// transition area is a good indication of how sharp the chessboard is imaged /// and should be below ~3.0 pixels. /// /// ## Parameters /// * image: Gray image used to find chessboard corners /// * patternSize: Size of a found chessboard pattern /// * corners: Corners found by findChessboardCorners(SB) /// * rise_distance: Rise distance 0.8 means 10% ... 90% of the final signal strength /// * vertical: By default edge responses for horizontal lines are calculated /// * sharpness: Optional output array with a sharpness value for calculated edge responses (see description) /// /// The optional sharpness array is of type CV_32FC1 and has for each calculated /// profile one row with the following five entries: /// * 0 = x coordinate of the underlying edge in the image /// * 1 = y coordinate of the underlying edge in the image /// * 2 = width of the transition area (sharpness) /// * 3 = signal strength in the black cell (min brightness) /// * 4 = signal strength in the white cell (max brightness) /// /// ## Returns /// Scalar(average sharpness, average min brightness, average max brightness,0) /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * rise_distance: 0.8F /// * vertical: false /// * sharpness: noArray() pub fn estimate_chessboard_sharpness(image: &dyn core::ToInputArray, pattern_size: core::Size, corners: &dyn core::ToInputArray, rise_distance: f32, vertical: bool, sharpness: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<core::Scalar> { input_array_arg!(image); input_array_arg!(corners); output_array_arg!(sharpness); unsafe { sys::cv_estimateChessboardSharpness_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__InputArrayR_float_bool_const__OutputArrayR(image.as_raw__InputArray(), pattern_size.opencv_as_extern(), corners.as_raw__InputArray(), rise_distance, vertical, sharpness.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Computes an optimal translation between two 3D point sets. /// /// It computes ///  /// /// ## Parameters /// * src: First input 3D point set containing 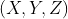. /// * dst: Second input 3D point set containing 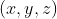. /// * out: Output 3D translation vector 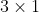 of the form ///  /// * inliers: Output vector indicating which points are inliers (1-inlier, 0-outlier). /// * ransacThreshold: Maximum reprojection error in the RANSAC algorithm to consider a point as /// an inlier. /// * confidence: Confidence level, between 0 and 1, for the estimated transformation. Anything /// between 0.95 and 0.99 is usually good enough. Values too close to 1 can slow down the estimation /// significantly. Values lower than 0.8-0.9 can result in an incorrectly estimated transformation. /// /// The function estimates an optimal 3D translation between two 3D point sets using the /// RANSAC algorithm. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * ransac_threshold: 3 /// * confidence: 0.99 pub fn estimate_translation_3d(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &dyn core::ToInputArray, out: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, inliers: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, ransac_threshold: f64, confidence: f64) -> Result<i32> { input_array_arg!(src); input_array_arg!(dst); output_array_arg!(out); output_array_arg!(inliers); unsafe { sys::cv_estimateTranslation3D_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_double(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__InputArray(), out.as_raw__OutputArray(), inliers.as_raw__OutputArray(), ransac_threshold, confidence) }.into_result() } /// Filters homography decompositions based on additional information. /// /// ## Parameters /// * rotations: Vector of rotation matrices. /// * normals: Vector of plane normal matrices. /// * beforePoints: Vector of (rectified) visible reference points before the homography is applied /// * afterPoints: Vector of (rectified) visible reference points after the homography is applied /// * possibleSolutions: Vector of int indices representing the viable solution set after filtering /// * pointsMask: optional Mat/Vector of 8u type representing the mask for the inliers as given by the findHomography function /// /// This function is intended to filter the output of the decomposeHomographyMat based on additional /// information as described in [Malis](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Malis) . The summary of the method: the decomposeHomographyMat function /// returns 2 unique solutions and their "opposites" for a total of 4 solutions. If we have access to the /// sets of points visible in the camera frame before and after the homography transformation is applied, /// we can determine which are the true potential solutions and which are the opposites by verifying which /// homographies are consistent with all visible reference points being in front of the camera. The inputs /// are left unchanged; the filtered solution set is returned as indices into the existing one. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * points_mask: noArray() pub fn filter_homography_decomp_by_visible_refpoints(rotations: &dyn core::ToInputArray, normals: &dyn core::ToInputArray, before_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, after_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, possible_solutions: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, points_mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(rotations); input_array_arg!(normals); input_array_arg!(before_points); input_array_arg!(after_points); output_array_arg!(possible_solutions); input_array_arg!(points_mask); unsafe { sys::cv_filterHomographyDecompByVisibleRefpoints_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(rotations.as_raw__InputArray(), normals.as_raw__InputArray(), before_points.as_raw__InputArray(), after_points.as_raw__InputArray(), possible_solutions.as_raw__OutputArray(), points_mask.as_raw__InputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Filters off small noise blobs (speckles) in the disparity map /// /// ## Parameters /// * img: The input 16-bit signed disparity image /// * newVal: The disparity value used to paint-off the speckles /// * maxSpeckleSize: The maximum speckle size to consider it a speckle. Larger blobs are not /// affected by the algorithm /// * maxDiff: Maximum difference between neighbor disparity pixels to put them into the same /// blob. Note that since StereoBM, StereoSGBM and may be other algorithms return a fixed-point /// disparity map, where disparity values are multiplied by 16, this scale factor should be taken into /// account when specifying this parameter value. /// * buf: The optional temporary buffer to avoid memory allocation within the function. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * buf: noArray() pub fn filter_speckles(img: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, new_val: f64, max_speckle_size: i32, max_diff: f64, buf: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray) -> Result<()> { input_output_array_arg!(img); input_output_array_arg!(buf); unsafe { sys::cv_filterSpeckles_const__InputOutputArrayR_double_int_double_const__InputOutputArrayR(img.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), new_val, max_speckle_size, max_diff, buf.as_raw__InputOutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// finds subpixel-accurate positions of the chessboard corners pub fn find4_quad_corner_subpix(img: &dyn core::ToInputArray, corners: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, region_size: core::Size) -> Result<bool> { input_array_arg!(img); input_output_array_arg!(corners); unsafe { sys::cv_find4QuadCornerSubpix_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_Size(img.as_raw__InputArray(), corners.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), region_size.opencv_as_extern()) }.into_result() } /// Finds the positions of internal corners of the chessboard using a sector based approach. /// /// ## Parameters /// * image: Source chessboard view. It must be an 8-bit grayscale or color image. /// * patternSize: Number of inner corners per a chessboard row and column /// ( patternSize = cv::Size(points_per_row,points_per_colum) = cv::Size(columns,rows) ). /// * corners: Output array of detected corners. /// * flags: Various operation flags that can be zero or a combination of the following values: /// * **CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE** Normalize the image gamma with equalizeHist before detection. /// * **CALIB_CB_EXHAUSTIVE** Run an exhaustive search to improve detection rate. /// * **CALIB_CB_ACCURACY** Up sample input image to improve sub-pixel accuracy due to aliasing effects. /// * **CALIB_CB_LARGER** The detected pattern is allowed to be larger than patternSize (see description). /// * **CALIB_CB_MARKER** The detected pattern must have a marker (see description). /// This should be used if an accurate camera calibration is required. /// * meta: Optional output arrray of detected corners (CV_8UC1 and size = cv::Size(columns,rows)). /// Each entry stands for one corner of the pattern and can have one of the following values: /// * 0 = no meta data attached /// * 1 = left-top corner of a black cell /// * 2 = left-top corner of a white cell /// * 3 = left-top corner of a black cell with a white marker dot /// * 4 = left-top corner of a white cell with a black marker dot (pattern origin in case of markers otherwise first corner) /// /// The function is analog to findchessboardCorners but uses a localized radon /// transformation approximated by box filters being more robust to all sort of /// noise, faster on larger images and is able to directly return the sub-pixel /// position of the internal chessboard corners. The Method is based on the paper /// [duda2018](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_duda2018) "Accurate Detection and Localization of Checkerboard Corners for /// Calibration" demonstrating that the returned sub-pixel positions are more /// accurate than the one returned by cornerSubPix allowing a precise camera /// calibration for demanding applications. /// /// In the case, the flags **CALIB_CB_LARGER** or **CALIB_CB_MARKER** are given, /// the result can be recovered from the optional meta array. Both flags are /// helpful to use calibration patterns exceeding the field of view of the camera. /// These oversized patterns allow more accurate calibrations as corners can be /// utilized, which are as close as possible to the image borders. For a /// consistent coordinate system across all images, the optional marker (see image /// below) can be used to move the origin of the board to the location where the /// black circle is located. /// /// /// Note: The function requires a white boarder with roughly the same width as one /// of the checkerboard fields around the whole board to improve the detection in /// various environments. In addition, because of the localized radon /// transformation it is beneficial to use round corners for the field corners /// which are located on the outside of the board. The following figure illustrates /// a sample checkerboard optimized for the detection. However, any other checkerboard /// can be used as well. ///  /// /// ## Overloaded parameters /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * flags: 0 pub fn find_chessboard_corners_sb(image: &dyn core::ToInputArray, pattern_size: core::Size, corners: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<bool> { input_array_arg!(image); output_array_arg!(corners); unsafe { sys::cv_findChessboardCornersSB_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__OutputArrayR_int(image.as_raw__InputArray(), pattern_size.opencv_as_extern(), corners.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags) }.into_result() } /// Finds the positions of internal corners of the chessboard using a sector based approach. /// /// ## Parameters /// * image: Source chessboard view. It must be an 8-bit grayscale or color image. /// * patternSize: Number of inner corners per a chessboard row and column /// ( patternSize = cv::Size(points_per_row,points_per_colum) = cv::Size(columns,rows) ). /// * corners: Output array of detected corners. /// * flags: Various operation flags that can be zero or a combination of the following values: /// * **CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE** Normalize the image gamma with equalizeHist before detection. /// * **CALIB_CB_EXHAUSTIVE** Run an exhaustive search to improve detection rate. /// * **CALIB_CB_ACCURACY** Up sample input image to improve sub-pixel accuracy due to aliasing effects. /// * **CALIB_CB_LARGER** The detected pattern is allowed to be larger than patternSize (see description). /// * **CALIB_CB_MARKER** The detected pattern must have a marker (see description). /// This should be used if an accurate camera calibration is required. /// * meta: Optional output arrray of detected corners (CV_8UC1 and size = cv::Size(columns,rows)). /// Each entry stands for one corner of the pattern and can have one of the following values: /// * 0 = no meta data attached /// * 1 = left-top corner of a black cell /// * 2 = left-top corner of a white cell /// * 3 = left-top corner of a black cell with a white marker dot /// * 4 = left-top corner of a white cell with a black marker dot (pattern origin in case of markers otherwise first corner) /// /// The function is analog to findchessboardCorners but uses a localized radon /// transformation approximated by box filters being more robust to all sort of /// noise, faster on larger images and is able to directly return the sub-pixel /// position of the internal chessboard corners. The Method is based on the paper /// [duda2018](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_duda2018) "Accurate Detection and Localization of Checkerboard Corners for /// Calibration" demonstrating that the returned sub-pixel positions are more /// accurate than the one returned by cornerSubPix allowing a precise camera /// calibration for demanding applications. /// /// In the case, the flags **CALIB_CB_LARGER** or **CALIB_CB_MARKER** are given, /// the result can be recovered from the optional meta array. Both flags are /// helpful to use calibration patterns exceeding the field of view of the camera. /// These oversized patterns allow more accurate calibrations as corners can be /// utilized, which are as close as possible to the image borders. For a /// consistent coordinate system across all images, the optional marker (see image /// below) can be used to move the origin of the board to the location where the /// black circle is located. /// /// /// Note: The function requires a white boarder with roughly the same width as one /// of the checkerboard fields around the whole board to improve the detection in /// various environments. In addition, because of the localized radon /// transformation it is beneficial to use round corners for the field corners /// which are located on the outside of the board. The following figure illustrates /// a sample checkerboard optimized for the detection. However, any other checkerboard /// can be used as well. ///  pub fn find_chessboard_corners_sb_with_meta(image: &dyn core::ToInputArray, pattern_size: core::Size, corners: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32, meta: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<bool> { input_array_arg!(image); output_array_arg!(corners); output_array_arg!(meta); unsafe { sys::cv_findChessboardCornersSB_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__OutputArrayR_int_const__OutputArrayR(image.as_raw__InputArray(), pattern_size.opencv_as_extern(), corners.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, meta.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Finds the positions of internal corners of the chessboard. /// /// ## Parameters /// * image: Source chessboard view. It must be an 8-bit grayscale or color image. /// * patternSize: Number of inner corners per a chessboard row and column /// ( patternSize = cv::Size(points_per_row,points_per_colum) = cv::Size(columns,rows) ). /// * corners: Output array of detected corners. /// * flags: Various operation flags that can be zero or a combination of the following values: /// * @ref CALIB_CB_ADAPTIVE_THRESH Use adaptive thresholding to convert the image to black /// and white, rather than a fixed threshold level (computed from the average image brightness). /// * @ref CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE Normalize the image gamma with equalizeHist before /// applying fixed or adaptive thresholding. /// * @ref CALIB_CB_FILTER_QUADS Use additional criteria (like contour area, perimeter, /// square-like shape) to filter out false quads extracted at the contour retrieval stage. /// * @ref CALIB_CB_FAST_CHECK Run a fast check on the image that looks for chessboard corners, /// and shortcut the call if none is found. This can drastically speed up the call in the /// degenerate condition when no chessboard is observed. /// /// The function attempts to determine whether the input image is a view of the chessboard pattern and /// locate the internal chessboard corners. The function returns a non-zero value if all of the corners /// are found and they are placed in a certain order (row by row, left to right in every row). /// Otherwise, if the function fails to find all the corners or reorder them, it returns 0. For example, /// a regular chessboard has 8 x 8 squares and 7 x 7 internal corners, that is, points where the black /// squares touch each other. The detected coordinates are approximate, and to determine their positions /// more accurately, the function calls cornerSubPix. You also may use the function cornerSubPix with /// different parameters if returned coordinates are not accurate enough. /// /// Sample usage of detecting and drawing chessboard corners: : /// ```ignore /// Size patternsize(8,6); //interior number of corners /// Mat gray = ....; //source image /// vector<Point2f> corners; //this will be filled by the detected corners /// /// //CALIB_CB_FAST_CHECK saves a lot of time on images /// //that do not contain any chessboard corners /// bool patternfound = findChessboardCorners(gray, patternsize, corners, /// CALIB_CB_ADAPTIVE_THRESH + CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE /// + CALIB_CB_FAST_CHECK); /// /// if(patternfound) /// cornerSubPix(gray, corners, Size(11, 11), Size(-1, -1), /// TermCriteria(CV_TERMCRIT_EPS + CV_TERMCRIT_ITER, 30, 0.1)); /// /// drawChessboardCorners(img, patternsize, Mat(corners), patternfound); /// ``` /// /// /// Note: The function requires white space (like a square-thick border, the wider the better) around /// the board to make the detection more robust in various environments. Otherwise, if there is no /// border and the background is dark, the outer black squares cannot be segmented properly and so the /// square grouping and ordering algorithm fails. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * flags: CALIB_CB_ADAPTIVE_THRESH+CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE pub fn find_chessboard_corners(image: &dyn core::ToInputArray, pattern_size: core::Size, corners: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<bool> { input_array_arg!(image); output_array_arg!(corners); unsafe { sys::cv_findChessboardCorners_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__OutputArrayR_int(image.as_raw__InputArray(), pattern_size.opencv_as_extern(), corners.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags) }.into_result() } /// Finds centers in the grid of circles. /// /// ## Parameters /// * image: grid view of input circles; it must be an 8-bit grayscale or color image. /// * patternSize: number of circles per row and column /// ( patternSize = Size(points_per_row, points_per_colum) ). /// * centers: output array of detected centers. /// * flags: various operation flags that can be one of the following values: /// * @ref CALIB_CB_SYMMETRIC_GRID uses symmetric pattern of circles. /// * @ref CALIB_CB_ASYMMETRIC_GRID uses asymmetric pattern of circles. /// * @ref CALIB_CB_CLUSTERING uses a special algorithm for grid detection. It is more robust to /// perspective distortions but much more sensitive to background clutter. /// * blobDetector: feature detector that finds blobs like dark circles on light background. /// If `blobDetector` is NULL then `image` represents Point2f array of candidates. /// * parameters: struct for finding circles in a grid pattern. /// /// The function attempts to determine whether the input image contains a grid of circles. If it is, the /// function locates centers of the circles. The function returns a non-zero value if all of the centers /// have been found and they have been placed in a certain order (row by row, left to right in every /// row). Otherwise, if the function fails to find all the corners or reorder them, it returns 0. /// /// Sample usage of detecting and drawing the centers of circles: : /// ```ignore /// Size patternsize(7,7); //number of centers /// Mat gray = ...; //source image /// vector<Point2f> centers; //this will be filled by the detected centers /// /// bool patternfound = findCirclesGrid(gray, patternsize, centers); /// /// drawChessboardCorners(img, patternsize, Mat(centers), patternfound); /// ``` /// /// /// Note: The function requires white space (like a square-thick border, the wider the better) around /// the board to make the detection more robust in various environments. /// /// ## Overloaded parameters /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * flags: CALIB_CB_SYMMETRIC_GRID /// * blob_detector: SimpleBlobDetector::create() pub fn find_circles_grid_1(image: &dyn core::ToInputArray, pattern_size: core::Size, centers: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32, blob_detector: &core::Ptr::<crate::features2d::Feature2D>) -> Result<bool> { input_array_arg!(image); output_array_arg!(centers); unsafe { sys::cv_findCirclesGrid_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__OutputArrayR_int_const_Ptr_Feature2D_R(image.as_raw__InputArray(), pattern_size.opencv_as_extern(), centers.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, blob_detector.as_raw_PtrOfFeature2D()) }.into_result() } /// Finds centers in the grid of circles. /// /// ## Parameters /// * image: grid view of input circles; it must be an 8-bit grayscale or color image. /// * patternSize: number of circles per row and column /// ( patternSize = Size(points_per_row, points_per_colum) ). /// * centers: output array of detected centers. /// * flags: various operation flags that can be one of the following values: /// * @ref CALIB_CB_SYMMETRIC_GRID uses symmetric pattern of circles. /// * @ref CALIB_CB_ASYMMETRIC_GRID uses asymmetric pattern of circles. /// * @ref CALIB_CB_CLUSTERING uses a special algorithm for grid detection. It is more robust to /// perspective distortions but much more sensitive to background clutter. /// * blobDetector: feature detector that finds blobs like dark circles on light background. /// If `blobDetector` is NULL then `image` represents Point2f array of candidates. /// * parameters: struct for finding circles in a grid pattern. /// /// The function attempts to determine whether the input image contains a grid of circles. If it is, the /// function locates centers of the circles. The function returns a non-zero value if all of the centers /// have been found and they have been placed in a certain order (row by row, left to right in every /// row). Otherwise, if the function fails to find all the corners or reorder them, it returns 0. /// /// Sample usage of detecting and drawing the centers of circles: : /// ```ignore /// Size patternsize(7,7); //number of centers /// Mat gray = ...; //source image /// vector<Point2f> centers; //this will be filled by the detected centers /// /// bool patternfound = findCirclesGrid(gray, patternsize, centers); /// /// drawChessboardCorners(img, patternsize, Mat(centers), patternfound); /// ``` /// /// /// Note: The function requires white space (like a square-thick border, the wider the better) around /// the board to make the detection more robust in various environments. pub fn find_circles_grid(image: &dyn core::ToInputArray, pattern_size: core::Size, centers: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32, blob_detector: &core::Ptr::<crate::features2d::Feature2D>, parameters: crate::calib3d::CirclesGridFinderParameters) -> Result<bool> { input_array_arg!(image); output_array_arg!(centers); unsafe { sys::cv_findCirclesGrid_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__OutputArrayR_int_const_Ptr_Feature2D_R_const_CirclesGridFinderParametersR(image.as_raw__InputArray(), pattern_size.opencv_as_extern(), centers.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, blob_detector.as_raw_PtrOfFeature2D(), ¶meters) }.into_result() } pub fn find_essential_mat_2(points1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, points2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, camera_matrix1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, camera_matrix2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dist_coeff1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dist_coeff2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mask: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, params: crate::calib3d::UsacParams) -> Result<core::Mat> { input_array_arg!(points1); input_array_arg!(points2); input_array_arg!(camera_matrix1); input_array_arg!(camera_matrix2); input_array_arg!(dist_coeff1); input_array_arg!(dist_coeff2); output_array_arg!(mask); unsafe { sys::cv_findEssentialMat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const_UsacParamsR(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix1.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix2.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeff1.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeff2.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__OutputArray(), ¶ms) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Calculates an essential matrix from the corresponding points in two images from potentially two different cameras. /// /// ## Parameters /// * points1: Array of N (N \>= 5) 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should /// be floating-point (single or double precision). /// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1 . /// * cameraMatrix1: Camera matrix 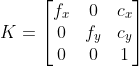 . /// Note that this function assumes that points1 and points2 are feature points from cameras with the /// same camera matrix. If this assumption does not hold for your use case, use /// `undistortPoints()` with `P = cv::NoArray()` for both cameras to transform image points /// to normalized image coordinates, which are valid for the identity camera matrix. When /// passing these coordinates, pass the identity matrix for this parameter. /// * cameraMatrix2: Camera matrix 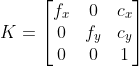 . /// Note that this function assumes that points1 and points2 are feature points from cameras with the /// same camera matrix. If this assumption does not hold for your use case, use /// `undistortPoints()` with `P = cv::NoArray()` for both cameras to transform image points /// to normalized image coordinates, which are valid for the identity camera matrix. When /// passing these coordinates, pass the identity matrix for this parameter. /// * distCoeffs1: Input vector of distortion coefficients ///  /// of 4, 5, 8, 12 or 14 elements. If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed. /// * distCoeffs2: Input vector of distortion coefficients ///  /// of 4, 5, 8, 12 or 14 elements. If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed. /// * method: Method for computing an essential matrix. /// * **RANSAC** for the RANSAC algorithm. /// * **LMEDS** for the LMedS algorithm. /// * prob: Parameter used for the RANSAC or LMedS methods only. It specifies a desirable level of /// confidence (probability) that the estimated matrix is correct. /// * threshold: Parameter used for RANSAC. It is the maximum distance from a point to an epipolar /// line in pixels, beyond which the point is considered an outlier and is not used for computing the /// final fundamental matrix. It can be set to something like 1-3, depending on the accuracy of the /// point localization, image resolution, and the image noise. /// * mask: Output array of N elements, every element of which is set to 0 for outliers and to 1 /// for the other points. The array is computed only in the RANSAC and LMedS methods. /// /// This function estimates essential matrix based on the five-point algorithm solver in [Nister03](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Nister03) . /// [SteweniusCFS](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_SteweniusCFS) is also a related. The epipolar geometry is described by the following equation: /// ///  /// /// where  is an essential matrix,  and  are corresponding points in the first and the /// second images, respectively. The result of this function may be passed further to /// decomposeEssentialMat or recoverPose to recover the relative pose between cameras. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * method: RANSAC /// * prob: 0.999 /// * threshold: 1.0 /// * mask: noArray() pub fn find_essential_mat_1(points1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, points2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, camera_matrix1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dist_coeffs1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, camera_matrix2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dist_coeffs2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, method: i32, prob: f64, threshold: f64, mask: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> { input_array_arg!(points1); input_array_arg!(points2); input_array_arg!(camera_matrix1); input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs1); input_array_arg!(camera_matrix2); input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs2); output_array_arg!(mask); unsafe { sys::cv_findEssentialMat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int_double_double_const__OutputArrayR(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix1.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs1.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix2.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs2.as_raw__InputArray(), method, prob, threshold, mask.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Calculates an essential matrix from the corresponding points in two images. /// /// ## Parameters /// * points1: Array of N (N \>= 5) 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should /// be floating-point (single or double precision). /// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1 . /// * cameraMatrix: Camera intrinsic matrix  . /// Note that this function assumes that points1 and points2 are feature points from cameras with the /// same camera intrinsic matrix. If this assumption does not hold for your use case, use /// `undistortPoints()` with `P = cv::NoArray()` for both cameras to transform image points /// to normalized image coordinates, which are valid for the identity camera intrinsic matrix. When /// passing these coordinates, pass the identity matrix for this parameter. /// * method: Method for computing an essential matrix. /// * @ref RANSAC for the RANSAC algorithm. /// * @ref LMEDS for the LMedS algorithm. /// * prob: Parameter used for the RANSAC or LMedS methods only. It specifies a desirable level of /// confidence (probability) that the estimated matrix is correct. /// * threshold: Parameter used for RANSAC. It is the maximum distance from a point to an epipolar /// line in pixels, beyond which the point is considered an outlier and is not used for computing the /// final fundamental matrix. It can be set to something like 1-3, depending on the accuracy of the /// point localization, image resolution, and the image noise. /// * mask: Output array of N elements, every element of which is set to 0 for outliers and to 1 /// for the other points. The array is computed only in the RANSAC and LMedS methods. /// /// This function estimates essential matrix based on the five-point algorithm solver in [Nister03](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Nister03) . /// [SteweniusCFS](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_SteweniusCFS) is also a related. The epipolar geometry is described by the following equation: /// ///  /// /// where  is an essential matrix,  and  are corresponding points in the first and the /// second images, respectively. The result of this function may be passed further to /// decomposeEssentialMat or recoverPose to recover the relative pose between cameras. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * method: RANSAC /// * prob: 0.999 /// * threshold: 1.0 /// * mask: noArray() pub fn find_essential_mat_matrix(points1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, points2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &dyn core::ToInputArray, method: i32, prob: f64, threshold: f64, mask: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> { input_array_arg!(points1); input_array_arg!(points2); input_array_arg!(camera_matrix); output_array_arg!(mask); unsafe { sys::cv_findEssentialMat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int_double_double_const__OutputArrayR(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), method, prob, threshold, mask.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Calculates an essential matrix from the corresponding points in two images from potentially two different cameras. /// /// ## Parameters /// * points1: Array of N (N \>= 5) 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should /// be floating-point (single or double precision). /// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1 . /// * cameraMatrix1: Camera matrix 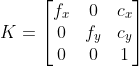 . /// Note that this function assumes that points1 and points2 are feature points from cameras with the /// same camera matrix. If this assumption does not hold for your use case, use /// `undistortPoints()` with `P = cv::NoArray()` for both cameras to transform image points /// to normalized image coordinates, which are valid for the identity camera matrix. When /// passing these coordinates, pass the identity matrix for this parameter. /// * cameraMatrix2: Camera matrix 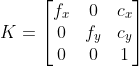 . /// Note that this function assumes that points1 and points2 are feature points from cameras with the /// same camera matrix. If this assumption does not hold for your use case, use /// `undistortPoints()` with `P = cv::NoArray()` for both cameras to transform image points /// to normalized image coordinates, which are valid for the identity camera matrix. When /// passing these coordinates, pass the identity matrix for this parameter. /// * distCoeffs1: Input vector of distortion coefficients ///  /// of 4, 5, 8, 12 or 14 elements. If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed. /// * distCoeffs2: Input vector of distortion coefficients ///  /// of 4, 5, 8, 12 or 14 elements. If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed. /// * method: Method for computing an essential matrix. /// * **RANSAC** for the RANSAC algorithm. /// * **LMEDS** for the LMedS algorithm. /// * prob: Parameter used for the RANSAC or LMedS methods only. It specifies a desirable level of /// confidence (probability) that the estimated matrix is correct. /// * threshold: Parameter used for RANSAC. It is the maximum distance from a point to an epipolar /// line in pixels, beyond which the point is considered an outlier and is not used for computing the /// final fundamental matrix. It can be set to something like 1-3, depending on the accuracy of the /// point localization, image resolution, and the image noise. /// * mask: Output array of N elements, every element of which is set to 0 for outliers and to 1 /// for the other points. The array is computed only in the RANSAC and LMedS methods. /// /// This function estimates essential matrix based on the five-point algorithm solver in [Nister03](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Nister03) . /// [SteweniusCFS](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_SteweniusCFS) is also a related. The epipolar geometry is described by the following equation: /// ///  /// /// where  is an essential matrix,  and  are corresponding points in the first and the /// second images, respectively. The result of this function may be passed further to /// decomposeEssentialMat or recoverPose to recover the relative pose between cameras. /// /// ## Overloaded parameters /// /// * points1: Array of N (N \>= 5) 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should /// be floating-point (single or double precision). /// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1 . /// * focal: focal length of the camera. Note that this function assumes that points1 and points2 /// are feature points from cameras with same focal length and principal point. /// * pp: principal point of the camera. /// * method: Method for computing a fundamental matrix. /// * @ref RANSAC for the RANSAC algorithm. /// * @ref LMEDS for the LMedS algorithm. /// * threshold: Parameter used for RANSAC. It is the maximum distance from a point to an epipolar /// line in pixels, beyond which the point is considered an outlier and is not used for computing the /// final fundamental matrix. It can be set to something like 1-3, depending on the accuracy of the /// point localization, image resolution, and the image noise. /// * prob: Parameter used for the RANSAC or LMedS methods only. It specifies a desirable level of /// confidence (probability) that the estimated matrix is correct. /// * mask: Output array of N elements, every element of which is set to 0 for outliers and to 1 /// for the other points. The array is computed only in the RANSAC and LMedS methods. /// /// This function differs from the one above that it computes camera intrinsic matrix from focal length and /// principal point: /// ///  /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * focal: 1.0 /// * pp: Point2d(0,0) /// * method: RANSAC /// * prob: 0.999 /// * threshold: 1.0 /// * mask: noArray() pub fn find_essential_mat(points1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, points2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, focal: f64, pp: core::Point2d, method: i32, prob: f64, threshold: f64, mask: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> { input_array_arg!(points1); input_array_arg!(points2); output_array_arg!(mask); unsafe { sys::cv_findEssentialMat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_double_Point2d_int_double_double_const__OutputArrayR(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), focal, pp.opencv_as_extern(), method, prob, threshold, mask.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } pub fn find_fundamental_mat_2(points1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, points2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mask: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, params: crate::calib3d::UsacParams) -> Result<core::Mat> { input_array_arg!(points1); input_array_arg!(points2); output_array_arg!(mask); unsafe { sys::cv_findFundamentalMat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const_UsacParamsR(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__OutputArray(), ¶ms) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Calculates a fundamental matrix from the corresponding points in two images. /// /// ## Parameters /// * points1: Array of N points from the first image. The point coordinates should be /// floating-point (single or double precision). /// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1 . /// * method: Method for computing a fundamental matrix. /// * @ref FM_7POINT for a 7-point algorithm.  /// * @ref FM_8POINT for an 8-point algorithm.  /// * @ref FM_RANSAC for the RANSAC algorithm.  /// * @ref FM_LMEDS for the LMedS algorithm.  /// * ransacReprojThreshold: Parameter used only for RANSAC. It is the maximum distance from a point to an epipolar /// line in pixels, beyond which the point is considered an outlier and is not used for computing the /// final fundamental matrix. It can be set to something like 1-3, depending on the accuracy of the /// point localization, image resolution, and the image noise. /// * confidence: Parameter used for the RANSAC and LMedS methods only. It specifies a desirable level /// of confidence (probability) that the estimated matrix is correct. /// * mask:[out] optional output mask /// * maxIters: The maximum number of robust method iterations. /// /// The epipolar geometry is described by the following equation: /// ///  /// /// where  is a fundamental matrix,  and  are corresponding points in the first and the /// second images, respectively. /// /// The function calculates the fundamental matrix using one of four methods listed above and returns /// the found fundamental matrix. Normally just one matrix is found. But in case of the 7-point /// algorithm, the function may return up to 3 solutions (  matrix that stores all 3 /// matrices sequentially). /// /// The calculated fundamental matrix may be passed further to computeCorrespondEpilines that finds the /// epipolar lines corresponding to the specified points. It can also be passed to /// stereoRectifyUncalibrated to compute the rectification transformation. : /// ```ignore /// // Example. Estimation of fundamental matrix using the RANSAC algorithm /// int point_count = 100; /// vector<Point2f> points1(point_count); /// vector<Point2f> points2(point_count); /// /// // initialize the points here ... /// for( int i = 0; i < point_count; i++ ) /// { /// points1[i] = ...; /// points2[i] = ...; /// } /// /// Mat fundamental_matrix = /// findFundamentalMat(points1, points2, FM_RANSAC, 3, 0.99); /// ``` /// /// /// ## Overloaded parameters /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * method: FM_RANSAC /// * ransac_reproj_threshold: 3. /// * confidence: 0.99 pub fn find_fundamental_mat_mask(points1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, points2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mask: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, method: i32, ransac_reproj_threshold: f64, confidence: f64) -> Result<core::Mat> { input_array_arg!(points1); input_array_arg!(points2); output_array_arg!(mask); unsafe { sys::cv_findFundamentalMat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_double_double(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__OutputArray(), method, ransac_reproj_threshold, confidence) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Calculates a fundamental matrix from the corresponding points in two images. /// /// ## Parameters /// * points1: Array of N points from the first image. The point coordinates should be /// floating-point (single or double precision). /// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1 . /// * method: Method for computing a fundamental matrix. /// * @ref FM_7POINT for a 7-point algorithm.  /// * @ref FM_8POINT for an 8-point algorithm.  /// * @ref FM_RANSAC for the RANSAC algorithm.  /// * @ref FM_LMEDS for the LMedS algorithm.  /// * ransacReprojThreshold: Parameter used only for RANSAC. It is the maximum distance from a point to an epipolar /// line in pixels, beyond which the point is considered an outlier and is not used for computing the /// final fundamental matrix. It can be set to something like 1-3, depending on the accuracy of the /// point localization, image resolution, and the image noise. /// * confidence: Parameter used for the RANSAC and LMedS methods only. It specifies a desirable level /// of confidence (probability) that the estimated matrix is correct. /// * mask:[out] optional output mask /// * maxIters: The maximum number of robust method iterations. /// /// The epipolar geometry is described by the following equation: /// ///  /// /// where  is a fundamental matrix,  and  are corresponding points in the first and the /// second images, respectively. /// /// The function calculates the fundamental matrix using one of four methods listed above and returns /// the found fundamental matrix. Normally just one matrix is found. But in case of the 7-point /// algorithm, the function may return up to 3 solutions (  matrix that stores all 3 /// matrices sequentially). /// /// The calculated fundamental matrix may be passed further to computeCorrespondEpilines that finds the /// epipolar lines corresponding to the specified points. It can also be passed to /// stereoRectifyUncalibrated to compute the rectification transformation. : /// ```ignore /// // Example. Estimation of fundamental matrix using the RANSAC algorithm /// int point_count = 100; /// vector<Point2f> points1(point_count); /// vector<Point2f> points2(point_count); /// /// // initialize the points here ... /// for( int i = 0; i < point_count; i++ ) /// { /// points1[i] = ...; /// points2[i] = ...; /// } /// /// Mat fundamental_matrix = /// findFundamentalMat(points1, points2, FM_RANSAC, 3, 0.99); /// ``` /// /// /// ## Overloaded parameters /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * method: FM_RANSAC /// * ransac_reproj_threshold: 3. /// * confidence: 0.99 /// * mask: noArray() pub fn find_fundamental_mat_1(points1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, points2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, method: i32, ransac_reproj_threshold: f64, confidence: f64, mask: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> { input_array_arg!(points1); input_array_arg!(points2); output_array_arg!(mask); unsafe { sys::cv_findFundamentalMat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int_double_double_const__OutputArrayR(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), method, ransac_reproj_threshold, confidence, mask.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Calculates a fundamental matrix from the corresponding points in two images. /// /// ## Parameters /// * points1: Array of N points from the first image. The point coordinates should be /// floating-point (single or double precision). /// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1 . /// * method: Method for computing a fundamental matrix. /// * @ref FM_7POINT for a 7-point algorithm.  /// * @ref FM_8POINT for an 8-point algorithm.  /// * @ref FM_RANSAC for the RANSAC algorithm.  /// * @ref FM_LMEDS for the LMedS algorithm.  /// * ransacReprojThreshold: Parameter used only for RANSAC. It is the maximum distance from a point to an epipolar /// line in pixels, beyond which the point is considered an outlier and is not used for computing the /// final fundamental matrix. It can be set to something like 1-3, depending on the accuracy of the /// point localization, image resolution, and the image noise. /// * confidence: Parameter used for the RANSAC and LMedS methods only. It specifies a desirable level /// of confidence (probability) that the estimated matrix is correct. /// * mask:[out] optional output mask /// * maxIters: The maximum number of robust method iterations. /// /// The epipolar geometry is described by the following equation: /// ///  /// /// where  is a fundamental matrix,  and  are corresponding points in the first and the /// second images, respectively. /// /// The function calculates the fundamental matrix using one of four methods listed above and returns /// the found fundamental matrix. Normally just one matrix is found. But in case of the 7-point /// algorithm, the function may return up to 3 solutions (  matrix that stores all 3 /// matrices sequentially). /// /// The calculated fundamental matrix may be passed further to computeCorrespondEpilines that finds the /// epipolar lines corresponding to the specified points. It can also be passed to /// stereoRectifyUncalibrated to compute the rectification transformation. : /// ```ignore /// // Example. Estimation of fundamental matrix using the RANSAC algorithm /// int point_count = 100; /// vector<Point2f> points1(point_count); /// vector<Point2f> points2(point_count); /// /// // initialize the points here ... /// for( int i = 0; i < point_count; i++ ) /// { /// points1[i] = ...; /// points2[i] = ...; /// } /// /// Mat fundamental_matrix = /// findFundamentalMat(points1, points2, FM_RANSAC, 3, 0.99); /// ``` /// /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * mask: noArray() pub fn find_fundamental_mat(points1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, points2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, method: i32, ransac_reproj_threshold: f64, confidence: f64, max_iters: i32, mask: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<core::Mat> { input_array_arg!(points1); input_array_arg!(points2); output_array_arg!(mask); unsafe { sys::cv_findFundamentalMat_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int_double_double_int_const__OutputArrayR(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), method, ransac_reproj_threshold, confidence, max_iters, mask.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } pub fn find_homography_1(src_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mask: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, params: crate::calib3d::UsacParams) -> Result<core::Mat> { input_array_arg!(src_points); input_array_arg!(dst_points); output_array_arg!(mask); unsafe { sys::cv_findHomography_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const_UsacParamsR(src_points.as_raw__InputArray(), dst_points.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__OutputArray(), ¶ms) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Finds a perspective transformation between two planes. /// /// ## Parameters /// * srcPoints: Coordinates of the points in the original plane, a matrix of the type CV_32FC2 /// or vector\<Point2f\> . /// * dstPoints: Coordinates of the points in the target plane, a matrix of the type CV_32FC2 or /// a vector\<Point2f\> . /// * method: Method used to compute a homography matrix. The following methods are possible: /// * **0** - a regular method using all the points, i.e., the least squares method /// * @ref RANSAC - RANSAC-based robust method /// * @ref LMEDS - Least-Median robust method /// * @ref RHO - PROSAC-based robust method /// * ransacReprojThreshold: Maximum allowed reprojection error to treat a point pair as an inlier /// (used in the RANSAC and RHO methods only). That is, if ///  /// then the point  is considered as an outlier. If srcPoints and dstPoints are measured in pixels, /// it usually makes sense to set this parameter somewhere in the range of 1 to 10. /// * mask: Optional output mask set by a robust method ( RANSAC or LMeDS ). Note that the input /// mask values are ignored. /// * maxIters: The maximum number of RANSAC iterations. /// * confidence: Confidence level, between 0 and 1. /// /// The function finds and returns the perspective transformation  between the source and the /// destination planes: /// ///  /// /// so that the back-projection error /// ///  /// /// is minimized. If the parameter method is set to the default value 0, the function uses all the point /// pairs to compute an initial homography estimate with a simple least-squares scheme. /// /// However, if not all of the point pairs ( ,  ) fit the rigid perspective /// transformation (that is, there are some outliers), this initial estimate will be poor. In this case, /// you can use one of the three robust methods. The methods RANSAC, LMeDS and RHO try many different /// random subsets of the corresponding point pairs (of four pairs each, collinear pairs are discarded), estimate the homography matrix /// using this subset and a simple least-squares algorithm, and then compute the quality/goodness of the /// computed homography (which is the number of inliers for RANSAC or the least median re-projection error for /// LMeDS). The best subset is then used to produce the initial estimate of the homography matrix and /// the mask of inliers/outliers. /// /// Regardless of the method, robust or not, the computed homography matrix is refined further (using /// inliers only in case of a robust method) with the Levenberg-Marquardt method to reduce the /// re-projection error even more. /// /// The methods RANSAC and RHO can handle practically any ratio of outliers but need a threshold to /// distinguish inliers from outliers. The method LMeDS does not need any threshold but it works /// correctly only when there are more than 50% of inliers. Finally, if there are no outliers and the /// noise is rather small, use the default method (method=0). /// /// The function is used to find initial intrinsic and extrinsic matrices. Homography matrix is /// determined up to a scale. Thus, it is normalized so that . Note that whenever an 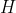 matrix /// cannot be estimated, an empty one will be returned. /// ## See also /// getAffineTransform, estimateAffine2D, estimateAffinePartial2D, getPerspectiveTransform, warpPerspective, /// perspectiveTransform /// /// ## Overloaded parameters /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * method: 0 /// * ransac_reproj_threshold: 3 pub fn find_homography(src_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mask: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, method: i32, ransac_reproj_threshold: f64) -> Result<core::Mat> { input_array_arg!(src_points); input_array_arg!(dst_points); output_array_arg!(mask); unsafe { sys::cv_findHomography_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_double(src_points.as_raw__InputArray(), dst_points.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__OutputArray(), method, ransac_reproj_threshold) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Finds a perspective transformation between two planes. /// /// ## Parameters /// * srcPoints: Coordinates of the points in the original plane, a matrix of the type CV_32FC2 /// or vector\<Point2f\> . /// * dstPoints: Coordinates of the points in the target plane, a matrix of the type CV_32FC2 or /// a vector\<Point2f\> . /// * method: Method used to compute a homography matrix. The following methods are possible: /// * **0** - a regular method using all the points, i.e., the least squares method /// * @ref RANSAC - RANSAC-based robust method /// * @ref LMEDS - Least-Median robust method /// * @ref RHO - PROSAC-based robust method /// * ransacReprojThreshold: Maximum allowed reprojection error to treat a point pair as an inlier /// (used in the RANSAC and RHO methods only). That is, if ///  /// then the point 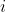 is considered as an outlier. If srcPoints and dstPoints are measured in pixels, /// it usually makes sense to set this parameter somewhere in the range of 1 to 10. /// * mask: Optional output mask set by a robust method ( RANSAC or LMeDS ). Note that the input /// mask values are ignored. /// * maxIters: The maximum number of RANSAC iterations. /// * confidence: Confidence level, between 0 and 1. /// /// The function finds and returns the perspective transformation 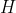 between the source and the /// destination planes: /// ///  /// /// so that the back-projection error /// ///  /// /// is minimized. If the parameter method is set to the default value 0, the function uses all the point /// pairs to compute an initial homography estimate with a simple least-squares scheme. /// /// However, if not all of the point pairs ( ,  ) fit the rigid perspective /// transformation (that is, there are some outliers), this initial estimate will be poor. In this case, /// you can use one of the three robust methods. The methods RANSAC, LMeDS and RHO try many different /// random subsets of the corresponding point pairs (of four pairs each, collinear pairs are discarded), estimate the homography matrix /// using this subset and a simple least-squares algorithm, and then compute the quality/goodness of the /// computed homography (which is the number of inliers for RANSAC or the least median re-projection error for /// LMeDS). The best subset is then used to produce the initial estimate of the homography matrix and /// the mask of inliers/outliers. /// /// Regardless of the method, robust or not, the computed homography matrix is refined further (using /// inliers only in case of a robust method) with the Levenberg-Marquardt method to reduce the /// re-projection error even more. /// /// The methods RANSAC and RHO can handle practically any ratio of outliers but need a threshold to /// distinguish inliers from outliers. The method LMeDS does not need any threshold but it works /// correctly only when there are more than 50% of inliers. Finally, if there are no outliers and the /// noise is rather small, use the default method (method=0). /// /// The function is used to find initial intrinsic and extrinsic matrices. Homography matrix is /// determined up to a scale. Thus, it is normalized so that . Note that whenever an 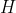 matrix /// cannot be estimated, an empty one will be returned. /// ## See also /// getAffineTransform, estimateAffine2D, estimateAffinePartial2D, getPerspectiveTransform, warpPerspective, /// perspectiveTransform /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * method: 0 /// * ransac_reproj_threshold: 3 /// * mask: noArray() /// * max_iters: 2000 /// * confidence: 0.995 pub fn find_homography_ext(src_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, method: i32, ransac_reproj_threshold: f64, mask: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, max_iters: i32, confidence: f64) -> Result<core::Mat> { input_array_arg!(src_points); input_array_arg!(dst_points); output_array_arg!(mask); unsafe { sys::cv_findHomography_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int_double_const__OutputArrayR_const_int_const_double(src_points.as_raw__InputArray(), dst_points.as_raw__InputArray(), method, ransac_reproj_threshold, mask.as_raw__OutputArray(), max_iters, confidence) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Performs camera calibaration /// /// ## Parameters /// * objectPoints: vector of vectors of calibration pattern points in the calibration pattern /// coordinate space. /// * imagePoints: vector of vectors of the projections of calibration pattern points. /// imagePoints.size() and objectPoints.size() and imagePoints[i].size() must be equal to /// objectPoints[i].size() for each i. /// * image_size: Size of the image used only to initialize the camera intrinsic matrix. /// * K: Output 3x3 floating-point camera intrinsic matrix ///  . If /// @ref fisheye::CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS is specified, some or all of fx, fy, cx, cy must be /// initialized before calling the function. /// * D: Output vector of distortion coefficients . /// * rvecs: Output vector of rotation vectors (see Rodrigues ) estimated for each pattern view. /// That is, each k-th rotation vector together with the corresponding k-th translation vector (see /// the next output parameter description) brings the calibration pattern from the model coordinate /// space (in which object points are specified) to the world coordinate space, that is, a real /// position of the calibration pattern in the k-th pattern view (k=0.. *M* -1). /// * tvecs: Output vector of translation vectors estimated for each pattern view. /// * flags: Different flags that may be zero or a combination of the following values: /// * @ref fisheye::CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS cameraMatrix contains valid initial values of /// fx, fy, cx, cy that are optimized further. Otherwise, (cx, cy) is initially set to the image /// center ( imageSize is used), and focal distances are computed in a least-squares fashion. /// * @ref fisheye::CALIB_RECOMPUTE_EXTRINSIC Extrinsic will be recomputed after each iteration /// of intrinsic optimization. /// * @ref fisheye::CALIB_CHECK_COND The functions will check validity of condition number. /// * @ref fisheye::CALIB_FIX_SKEW Skew coefficient (alpha) is set to zero and stay zero. /// * @ref fisheye::CALIB_FIX_K1,..., @ref fisheye::CALIB_FIX_K4 Selected distortion coefficients /// are set to zeros and stay zero. /// * @ref fisheye::CALIB_FIX_PRINCIPAL_POINT The principal point is not changed during the global /// optimization. It stays at the center or at a different location specified when @ref fisheye::CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS is set too. /// * criteria: Termination criteria for the iterative optimization algorithm. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * flags: 0 /// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,100,DBL_EPSILON) pub fn calibrate(object_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, k: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, d: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, rvecs: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, tvecs: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32, criteria: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<f64> { input_array_arg!(object_points); input_array_arg!(image_points); input_output_array_arg!(k); input_output_array_arg!(d); output_array_arg!(rvecs); output_array_arg!(tvecs); unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_calibrate_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const_SizeR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_TermCriteria(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, k.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), d.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), rvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, criteria.opencv_as_extern()) }.into_result() } /// Distorts 2D points using fisheye model. /// /// ## Parameters /// * undistorted: Array of object points, 1xN/Nx1 2-channel (or vector\<Point2f\> ), where N is /// the number of points in the view. /// * K: Camera intrinsic matrix . /// * D: Input vector of distortion coefficients . /// * alpha: The skew coefficient. /// * distorted: Output array of image points, 1xN/Nx1 2-channel, or vector\<Point2f\> . /// /// Note that the function assumes the camera intrinsic matrix of the undistorted points to be identity. /// This means if you want to transform back points undistorted with undistortPoints() you have to /// multiply them with . /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * alpha: 0 pub fn distort_points(undistorted: &dyn core::ToInputArray, distorted: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, k: &dyn core::ToInputArray, d: &dyn core::ToInputArray, alpha: f64) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(undistorted); output_array_arg!(distorted); input_array_arg!(k); input_array_arg!(d); unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_distortPoints_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_double(undistorted.as_raw__InputArray(), distorted.as_raw__OutputArray(), k.as_raw__InputArray(), d.as_raw__InputArray(), alpha) }.into_result() } /// Estimates new camera intrinsic matrix for undistortion or rectification. /// /// ## Parameters /// * K: Camera intrinsic matrix . /// * image_size: Size of the image /// * D: Input vector of distortion coefficients . /// * R: Rectification transformation in the object space: 3x3 1-channel, or vector: 3x1/1x3 /// 1-channel or 1x1 3-channel /// * P: New camera intrinsic matrix (3x3) or new projection matrix (3x4) /// * balance: Sets the new focal length in range between the min focal length and the max focal /// length. Balance is in range of [0, 1]. /// * new_size: the new size /// * fov_scale: Divisor for new focal length. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * balance: 0.0 /// * new_size: Size() /// * fov_scale: 1.0 pub fn estimate_new_camera_matrix_for_undistort_rectify(k: &dyn core::ToInputArray, d: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, r: &dyn core::ToInputArray, p: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, balance: f64, new_size: core::Size, fov_scale: f64) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(k); input_array_arg!(d); input_array_arg!(r); output_array_arg!(p); unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_estimateNewCameraMatrixForUndistortRectify_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const_SizeR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_const_SizeR_double(k.as_raw__InputArray(), d.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, r.as_raw__InputArray(), p.as_raw__OutputArray(), balance, &new_size, fov_scale) }.into_result() } /// Computes undistortion and rectification maps for image transform by cv::remap(). If D is empty zero /// distortion is used, if R or P is empty identity matrixes are used. /// /// ## Parameters /// * K: Camera intrinsic matrix . /// * D: Input vector of distortion coefficients . /// * R: Rectification transformation in the object space: 3x3 1-channel, or vector: 3x1/1x3 /// 1-channel or 1x1 3-channel /// * P: New camera intrinsic matrix (3x3) or new projection matrix (3x4) /// * size: Undistorted image size. /// * m1type: Type of the first output map that can be CV_32FC1 or CV_16SC2 . See convertMaps() /// for details. /// * map1: The first output map. /// * map2: The second output map. pub fn fisheye_init_undistort_rectify_map(k: &dyn core::ToInputArray, d: &dyn core::ToInputArray, r: &dyn core::ToInputArray, p: &dyn core::ToInputArray, size: core::Size, m1type: i32, map1: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, map2: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(k); input_array_arg!(d); input_array_arg!(r); input_array_arg!(p); output_array_arg!(map1); output_array_arg!(map2); unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_initUndistortRectifyMap_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const_SizeR_int_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(k.as_raw__InputArray(), d.as_raw__InputArray(), r.as_raw__InputArray(), p.as_raw__InputArray(), &size, m1type, map1.as_raw__OutputArray(), map2.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Projects points using fisheye model /// /// ## Parameters /// * objectPoints: Array of object points, 1xN/Nx1 3-channel (or vector\<Point3f\> ), where N is /// the number of points in the view. /// * imagePoints: Output array of image points, 2xN/Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel, or /// vector\<Point2f\>. /// * affine: /// * K: Camera intrinsic matrix . /// * D: Input vector of distortion coefficients . /// * alpha: The skew coefficient. /// * jacobian: Optional output 2Nx15 jacobian matrix of derivatives of image points with respect /// to components of the focal lengths, coordinates of the principal point, distortion coefficients, /// rotation vector, translation vector, and the skew. In the old interface different components of /// the jacobian are returned via different output parameters. /// /// The function computes projections of 3D points to the image plane given intrinsic and extrinsic /// camera parameters. Optionally, the function computes Jacobians - matrices of partial derivatives of /// image points coordinates (as functions of all the input parameters) with respect to the particular /// parameters, intrinsic and/or extrinsic. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * alpha: 0 /// * jacobian: noArray() pub fn fisheye_project_points(object_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_points: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, affine: core::Affine3d, k: &dyn core::ToInputArray, d: &dyn core::ToInputArray, alpha: f64, jacobian: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(object_points); output_array_arg!(image_points); input_array_arg!(k); input_array_arg!(d); output_array_arg!(jacobian); unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_projectPoints_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const_Affine3dR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_double_const__OutputArrayR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__OutputArray(), &affine, k.as_raw__InputArray(), d.as_raw__InputArray(), alpha, jacobian.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Projects points using fisheye model /// /// ## Parameters /// * objectPoints: Array of object points, 1xN/Nx1 3-channel (or vector\<Point3f\> ), where N is /// the number of points in the view. /// * imagePoints: Output array of image points, 2xN/Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel, or /// vector\<Point2f\>. /// * affine: /// * K: Camera intrinsic matrix . /// * D: Input vector of distortion coefficients . /// * alpha: The skew coefficient. /// * jacobian: Optional output 2Nx15 jacobian matrix of derivatives of image points with respect /// to components of the focal lengths, coordinates of the principal point, distortion coefficients, /// rotation vector, translation vector, and the skew. In the old interface different components of /// the jacobian are returned via different output parameters. /// /// The function computes projections of 3D points to the image plane given intrinsic and extrinsic /// camera parameters. Optionally, the function computes Jacobians - matrices of partial derivatives of /// image points coordinates (as functions of all the input parameters) with respect to the particular /// parameters, intrinsic and/or extrinsic. /// /// ## Overloaded parameters /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * alpha: 0 /// * jacobian: noArray() pub fn fisheye_project_points_vec(object_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_points: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, rvec: &dyn core::ToInputArray, tvec: &dyn core::ToInputArray, k: &dyn core::ToInputArray, d: &dyn core::ToInputArray, alpha: f64, jacobian: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(object_points); output_array_arg!(image_points); input_array_arg!(rvec); input_array_arg!(tvec); input_array_arg!(k); input_array_arg!(d); output_array_arg!(jacobian); unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_projectPoints_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_double_const__OutputArrayR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__OutputArray(), rvec.as_raw__InputArray(), tvec.as_raw__InputArray(), k.as_raw__InputArray(), d.as_raw__InputArray(), alpha, jacobian.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Performs stereo calibration /// /// ## Parameters /// * objectPoints: Vector of vectors of the calibration pattern points. /// * imagePoints1: Vector of vectors of the projections of the calibration pattern points, /// observed by the first camera. /// * imagePoints2: Vector of vectors of the projections of the calibration pattern points, /// observed by the second camera. /// * K1: Input/output first camera intrinsic matrix: ///  , 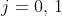 . If /// any of @ref fisheye::CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS , @ref fisheye::CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC are specified, /// some or all of the matrix components must be initialized. /// * D1: Input/output vector of distortion coefficients  of 4 elements. /// * K2: Input/output second camera intrinsic matrix. The parameter is similar to K1 . /// * D2: Input/output lens distortion coefficients for the second camera. The parameter is /// similar to D1 . /// * imageSize: Size of the image used only to initialize camera intrinsic matrix. /// * R: Output rotation matrix between the 1st and the 2nd camera coordinate systems. /// * T: Output translation vector between the coordinate systems of the cameras. /// * flags: Different flags that may be zero or a combination of the following values: /// * @ref fisheye::CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC Fix K1, K2? and D1, D2? so that only R, T matrices /// are estimated. /// * @ref fisheye::CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS K1, K2 contains valid initial values of /// fx, fy, cx, cy that are optimized further. Otherwise, (cx, cy) is initially set to the image /// center (imageSize is used), and focal distances are computed in a least-squares fashion. /// * @ref fisheye::CALIB_RECOMPUTE_EXTRINSIC Extrinsic will be recomputed after each iteration /// of intrinsic optimization. /// * @ref fisheye::CALIB_CHECK_COND The functions will check validity of condition number. /// * @ref fisheye::CALIB_FIX_SKEW Skew coefficient (alpha) is set to zero and stay zero. /// * @ref fisheye::CALIB_FIX_K1,..., @ref fisheye::CALIB_FIX_K4 Selected distortion coefficients are set to zeros and stay /// zero. /// * criteria: Termination criteria for the iterative optimization algorithm. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * flags: fisheye::CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC /// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,100,DBL_EPSILON) pub fn fisheye_stereo_calibrate(object_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_points1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_points2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, k1: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, d1: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, k2: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, d2: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, image_size: core::Size, r: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, t: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32, criteria: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<f64> { input_array_arg!(object_points); input_array_arg!(image_points1); input_array_arg!(image_points2); input_output_array_arg!(k1); input_output_array_arg!(d1); input_output_array_arg!(k2); input_output_array_arg!(d2); output_array_arg!(r); output_array_arg!(t); unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_stereoCalibrate_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_Size_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_TermCriteria(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points1.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points2.as_raw__InputArray(), k1.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), d1.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), k2.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), d2.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), image_size.opencv_as_extern(), r.as_raw__OutputArray(), t.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, criteria.opencv_as_extern()) }.into_result() } /// Stereo rectification for fisheye camera model /// /// ## Parameters /// * K1: First camera intrinsic matrix. /// * D1: First camera distortion parameters. /// * K2: Second camera intrinsic matrix. /// * D2: Second camera distortion parameters. /// * imageSize: Size of the image used for stereo calibration. /// * R: Rotation matrix between the coordinate systems of the first and the second /// cameras. /// * tvec: Translation vector between coordinate systems of the cameras. /// * R1: Output 3x3 rectification transform (rotation matrix) for the first camera. /// * R2: Output 3x3 rectification transform (rotation matrix) for the second camera. /// * P1: Output 3x4 projection matrix in the new (rectified) coordinate systems for the first /// camera. /// * P2: Output 3x4 projection matrix in the new (rectified) coordinate systems for the second /// camera. /// * Q: Output 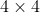 disparity-to-depth mapping matrix (see reprojectImageTo3D ). /// * flags: Operation flags that may be zero or @ref fisheye::CALIB_ZERO_DISPARITY . If the flag is set, /// the function makes the principal points of each camera have the same pixel coordinates in the /// rectified views. And if the flag is not set, the function may still shift the images in the /// horizontal or vertical direction (depending on the orientation of epipolar lines) to maximize the /// useful image area. /// * newImageSize: New image resolution after rectification. The same size should be passed to /// initUndistortRectifyMap (see the stereo_calib.cpp sample in OpenCV samples directory). When (0,0) /// is passed (default), it is set to the original imageSize . Setting it to larger value can help you /// preserve details in the original image, especially when there is a big radial distortion. /// * balance: Sets the new focal length in range between the min focal length and the max focal /// length. Balance is in range of [0, 1]. /// * fov_scale: Divisor for new focal length. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * new_image_size: Size() /// * balance: 0.0 /// * fov_scale: 1.0 pub fn fisheye_stereo_rectify(k1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, d1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, k2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, d2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, r: &dyn core::ToInputArray, tvec: &dyn core::ToInputArray, r1: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, r2: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, p1: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, p2: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, q: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32, new_image_size: core::Size, balance: f64, fov_scale: f64) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(k1); input_array_arg!(d1); input_array_arg!(k2); input_array_arg!(d2); input_array_arg!(r); input_array_arg!(tvec); output_array_arg!(r1); output_array_arg!(r2); output_array_arg!(p1); output_array_arg!(p2); output_array_arg!(q); unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_stereoRectify_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const_SizeR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_const_SizeR_double_double(k1.as_raw__InputArray(), d1.as_raw__InputArray(), k2.as_raw__InputArray(), d2.as_raw__InputArray(), &image_size, r.as_raw__InputArray(), tvec.as_raw__InputArray(), r1.as_raw__OutputArray(), r2.as_raw__OutputArray(), p1.as_raw__OutputArray(), p2.as_raw__OutputArray(), q.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, &new_image_size, balance, fov_scale) }.into_result() } /// Transforms an image to compensate for fisheye lens distortion. /// /// ## Parameters /// * distorted: image with fisheye lens distortion. /// * undistorted: Output image with compensated fisheye lens distortion. /// * K: Camera intrinsic matrix . /// * D: Input vector of distortion coefficients . /// * Knew: Camera intrinsic matrix of the distorted image. By default, it is the identity matrix but you /// may additionally scale and shift the result by using a different matrix. /// * new_size: the new size /// /// The function transforms an image to compensate radial and tangential lens distortion. /// /// The function is simply a combination of fisheye::initUndistortRectifyMap (with unity R ) and remap /// (with bilinear interpolation). See the former function for details of the transformation being /// performed. /// /// See below the results of undistortImage. /// * a\) result of undistort of perspective camera model (all possible coefficients (k_1, k_2, k_3, /// k_4, k_5, k_6) of distortion were optimized under calibration) /// * b\) result of fisheye::undistortImage of fisheye camera model (all possible coefficients (k_1, k_2, /// k_3, k_4) of fisheye distortion were optimized under calibration) /// * c\) original image was captured with fisheye lens /// /// Pictures a) and b) almost the same. But if we consider points of image located far from the center /// of image, we can notice that on image a) these points are distorted. /// ///  /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * knew: cv::noArray() /// * new_size: Size() pub fn fisheye_undistort_image(distorted: &dyn core::ToInputArray, undistorted: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, k: &dyn core::ToInputArray, d: &dyn core::ToInputArray, knew: &dyn core::ToInputArray, new_size: core::Size) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(distorted); output_array_arg!(undistorted); input_array_arg!(k); input_array_arg!(d); input_array_arg!(knew); unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_undistortImage_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const_SizeR(distorted.as_raw__InputArray(), undistorted.as_raw__OutputArray(), k.as_raw__InputArray(), d.as_raw__InputArray(), knew.as_raw__InputArray(), &new_size) }.into_result() } /// Undistorts 2D points using fisheye model /// /// ## Parameters /// * distorted: Array of object points, 1xN/Nx1 2-channel (or vector\<Point2f\> ), where N is the /// number of points in the view. /// * K: Camera intrinsic matrix . /// * D: Input vector of distortion coefficients . /// * R: Rectification transformation in the object space: 3x3 1-channel, or vector: 3x1/1x3 /// 1-channel or 1x1 3-channel /// * P: New camera intrinsic matrix (3x3) or new projection matrix (3x4) /// * undistorted: Output array of image points, 1xN/Nx1 2-channel, or vector\<Point2f\> . /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * r: noArray() /// * p: noArray() pub fn fisheye_undistort_points(distorted: &dyn core::ToInputArray, undistorted: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, k: &dyn core::ToInputArray, d: &dyn core::ToInputArray, r: &dyn core::ToInputArray, p: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(distorted); output_array_arg!(undistorted); input_array_arg!(k); input_array_arg!(d); input_array_arg!(r); input_array_arg!(p); unsafe { sys::cv_fisheye_undistortPoints_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(distorted.as_raw__InputArray(), undistorted.as_raw__OutputArray(), k.as_raw__InputArray(), d.as_raw__InputArray(), r.as_raw__InputArray(), p.as_raw__InputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Returns the default new camera matrix. /// /// The function returns the camera matrix that is either an exact copy of the input cameraMatrix (when /// centerPrinicipalPoint=false ), or the modified one (when centerPrincipalPoint=true). /// /// In the latter case, the new camera matrix will be: /// ///  /// /// where  and  are 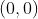 and 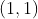 elements of cameraMatrix, respectively. /// /// By default, the undistortion functions in OpenCV (see #initUndistortRectifyMap, #undistort) do not /// move the principal point. However, when you work with stereo, it is important to move the principal /// points in both views to the same y-coordinate (which is required by most of stereo correspondence /// algorithms), and may be to the same x-coordinate too. So, you can form the new camera matrix for /// each view where the principal points are located at the center. /// /// ## Parameters /// * cameraMatrix: Input camera matrix. /// * imgsize: Camera view image size in pixels. /// * centerPrincipalPoint: Location of the principal point in the new camera matrix. The /// parameter indicates whether this location should be at the image center or not. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * imgsize: Size() /// * center_principal_point: false pub fn get_default_new_camera_matrix(camera_matrix: &dyn core::ToInputArray, imgsize: core::Size, center_principal_point: bool) -> Result<core::Mat> { input_array_arg!(camera_matrix); unsafe { sys::cv_getDefaultNewCameraMatrix_const__InputArrayR_Size_bool(camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), imgsize.opencv_as_extern(), center_principal_point) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Returns the new camera intrinsic matrix based on the free scaling parameter. /// /// ## Parameters /// * cameraMatrix: Input camera intrinsic matrix. /// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients /// . If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are /// assumed. /// * imageSize: Original image size. /// * alpha: Free scaling parameter between 0 (when all the pixels in the undistorted image are /// valid) and 1 (when all the source image pixels are retained in the undistorted image). See /// stereoRectify for details. /// * newImgSize: Image size after rectification. By default, it is set to imageSize . /// * validPixROI: Optional output rectangle that outlines all-good-pixels region in the /// undistorted image. See roi1, roi2 description in stereoRectify . /// * centerPrincipalPoint: Optional flag that indicates whether in the new camera intrinsic matrix the /// principal point should be at the image center or not. By default, the principal point is chosen to /// best fit a subset of the source image (determined by alpha) to the corrected image. /// ## Returns /// new_camera_matrix Output new camera intrinsic matrix. /// /// The function computes and returns the optimal new camera intrinsic matrix based on the free scaling parameter. /// By varying this parameter, you may retrieve only sensible pixels alpha=0 , keep all the original /// image pixels if there is valuable information in the corners alpha=1 , or get something in between. /// When alpha\>0 , the undistorted result is likely to have some black pixels corresponding to /// "virtual" pixels outside of the captured distorted image. The original camera intrinsic matrix, distortion /// coefficients, the computed new camera intrinsic matrix, and newImageSize should be passed to /// initUndistortRectifyMap to produce the maps for remap . /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * new_img_size: Size() /// * valid_pix_roi: 0 /// * center_principal_point: false pub fn get_optimal_new_camera_matrix(camera_matrix: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, alpha: f64, new_img_size: core::Size, valid_pix_roi: &mut core::Rect, center_principal_point: bool) -> Result<core::Mat> { input_array_arg!(camera_matrix); input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs); unsafe { sys::cv_getOptimalNewCameraMatrix_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_double_Size_RectX_bool(camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), image_size.opencv_as_extern(), alpha, new_img_size.opencv_as_extern(), valid_pix_roi, center_principal_point) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// computes valid disparity ROI from the valid ROIs of the rectified images (that are returned by cv::stereoRectify()) pub fn get_valid_disparity_roi(roi1: core::Rect, roi2: core::Rect, min_disparity: i32, number_of_disparities: i32, block_size: i32) -> Result<core::Rect> { unsafe { sys::cv_getValidDisparityROI_Rect_Rect_int_int_int(roi1.opencv_as_extern(), roi2.opencv_as_extern(), min_disparity, number_of_disparities, block_size) }.into_result() } /// Finds an initial camera intrinsic matrix from 3D-2D point correspondences. /// /// ## Parameters /// * objectPoints: Vector of vectors of the calibration pattern points in the calibration pattern /// coordinate space. In the old interface all the per-view vectors are concatenated. See /// calibrateCamera for details. /// * imagePoints: Vector of vectors of the projections of the calibration pattern points. In the /// old interface all the per-view vectors are concatenated. /// * imageSize: Image size in pixels used to initialize the principal point. /// * aspectRatio: If it is zero or negative, both  and  are estimated independently. /// Otherwise,  . /// /// The function estimates and returns an initial camera intrinsic matrix for the camera calibration process. /// Currently, the function only supports planar calibration patterns, which are patterns where each /// object point has z-coordinate =0. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * aspect_ratio: 1.0 pub fn init_camera_matrix_2d(object_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, aspect_ratio: f64) -> Result<core::Mat> { input_array_arg!(object_points); input_array_arg!(image_points); unsafe { sys::cv_initCameraMatrix2D_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_double(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_size.opencv_as_extern(), aspect_ratio) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Mat::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } /// Computes the undistortion and rectification transformation map. /// /// The function computes the joint undistortion and rectification transformation and represents the /// result in the form of maps for remap. The undistorted image looks like original, as if it is /// captured with a camera using the camera matrix =newCameraMatrix and zero distortion. In case of a /// monocular camera, newCameraMatrix is usually equal to cameraMatrix, or it can be computed by /// #getOptimalNewCameraMatrix for a better control over scaling. In case of a stereo camera, /// newCameraMatrix is normally set to P1 or P2 computed by #stereoRectify . /// /// Also, this new camera is oriented differently in the coordinate space, according to R. That, for /// example, helps to align two heads of a stereo camera so that the epipolar lines on both images /// become horizontal and have the same y- coordinate (in case of a horizontally aligned stereo camera). /// /// The function actually builds the maps for the inverse mapping algorithm that is used by remap. That /// is, for each pixel 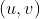 in the destination (corrected and rectified) image, the function /// computes the corresponding coordinates in the source image (that is, in the original image from /// camera). The following process is applied: ///  /// where  /// are the distortion coefficients. /// /// In case of a stereo camera, this function is called twice: once for each camera head, after /// stereoRectify, which in its turn is called after #stereoCalibrate. But if the stereo camera /// was not calibrated, it is still possible to compute the rectification transformations directly from /// the fundamental matrix using #stereoRectifyUncalibrated. For each camera, the function computes /// homography H as the rectification transformation in a pixel domain, not a rotation matrix R in 3D /// space. R can be computed from H as ///  /// where cameraMatrix can be chosen arbitrarily. /// /// ## Parameters /// * cameraMatrix: Input camera matrix  . /// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients ///  /// of 4, 5, 8, 12 or 14 elements. If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed. /// * R: Optional rectification transformation in the object space (3x3 matrix). R1 or R2 , /// computed by #stereoRectify can be passed here. If the matrix is empty, the identity transformation /// is assumed. In cvInitUndistortMap R assumed to be an identity matrix. /// * newCameraMatrix: New camera matrix . /// * size: Undistorted image size. /// * m1type: Type of the first output map that can be CV_32FC1, CV_32FC2 or CV_16SC2, see #convertMaps /// * map1: The first output map. /// * map2: The second output map. pub fn init_undistort_rectify_map(camera_matrix: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &dyn core::ToInputArray, r: &dyn core::ToInputArray, new_camera_matrix: &dyn core::ToInputArray, size: core::Size, m1type: i32, map1: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, map2: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(camera_matrix); input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs); input_array_arg!(r); input_array_arg!(new_camera_matrix); output_array_arg!(map1); output_array_arg!(map2); unsafe { sys::cv_initUndistortRectifyMap_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_int_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), r.as_raw__InputArray(), new_camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), size.opencv_as_extern(), m1type, map1.as_raw__OutputArray(), map2.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// initializes maps for #remap for wide-angle /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * proj_type: PROJ_SPHERICAL_EQRECT /// * alpha: 0 pub fn init_wide_angle_proj_map(camera_matrix: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, dest_image_width: i32, m1type: i32, map1: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, map2: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, proj_type: crate::calib3d::UndistortTypes, alpha: f64) -> Result<f32> { input_array_arg!(camera_matrix); input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs); output_array_arg!(map1); output_array_arg!(map2); unsafe { sys::cv_initWideAngleProjMap_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_int_int_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_UndistortTypes_double(camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), image_size.opencv_as_extern(), dest_image_width, m1type, map1.as_raw__OutputArray(), map2.as_raw__OutputArray(), proj_type, alpha) }.into_result() } /// Computes partial derivatives of the matrix product for each multiplied matrix. /// /// ## Parameters /// * A: First multiplied matrix. /// * B: Second multiplied matrix. /// * dABdA: First output derivative matrix d(A\*B)/dA of size ///  . /// * dABdB: Second output derivative matrix d(A\*B)/dB of size ///  . /// /// The function computes partial derivatives of the elements of the matrix product  with regard to /// the elements of each of the two input matrices. The function is used to compute the Jacobian /// matrices in stereoCalibrate but can also be used in any other similar optimization function. pub fn mat_mul_deriv(a: &dyn core::ToInputArray, b: &dyn core::ToInputArray, d_a_bd_a: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, d_a_bd_b: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(a); input_array_arg!(b); output_array_arg!(d_a_bd_a); output_array_arg!(d_a_bd_b); unsafe { sys::cv_matMulDeriv_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(a.as_raw__InputArray(), b.as_raw__InputArray(), d_a_bd_a.as_raw__OutputArray(), d_a_bd_b.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Projects 3D points to an image plane. /// /// ## Parameters /// * objectPoints: Array of object points expressed wrt. the world coordinate frame. A 3xN/Nx3 /// 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 3-channel (or vector\<Point3f\> ), where N is the number of points in the view. /// * rvec: The rotation vector (@ref Rodrigues) that, together with tvec, performs a change of /// basis from world to camera coordinate system, see @ref calibrateCamera for details. /// * tvec: The translation vector, see parameter description above. /// * cameraMatrix: Camera intrinsic matrix  . /// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients ///  . If the vector is empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed. /// * imagePoints: Output array of image points, 1xN/Nx1 2-channel, or /// vector\<Point2f\> . /// * jacobian: Optional output 2Nx(10+\<numDistCoeffs\>) jacobian matrix of derivatives of image /// points with respect to components of the rotation vector, translation vector, focal lengths, /// coordinates of the principal point and the distortion coefficients. In the old interface different /// components of the jacobian are returned via different output parameters. /// * aspectRatio: Optional "fixed aspect ratio" parameter. If the parameter is not 0, the /// function assumes that the aspect ratio () is fixed and correspondingly adjusts the /// jacobian matrix. /// /// The function computes the 2D projections of 3D points to the image plane, given intrinsic and /// extrinsic camera parameters. Optionally, the function computes Jacobians -matrices of partial /// derivatives of image points coordinates (as functions of all the input parameters) with respect to /// the particular parameters, intrinsic and/or extrinsic. The Jacobians are used during the global /// optimization in @ref calibrateCamera, @ref solvePnP, and @ref stereoCalibrate. The function itself /// can also be used to compute a re-projection error, given the current intrinsic and extrinsic /// parameters. /// /// /// Note: By setting rvec = tvec = , or by setting cameraMatrix to a 3x3 identity matrix, /// or by passing zero distortion coefficients, one can get various useful partial cases of the /// function. This means, one can compute the distorted coordinates for a sparse set of points or apply /// a perspective transformation (and also compute the derivatives) in the ideal zero-distortion setup. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * jacobian: noArray() /// * aspect_ratio: 0 pub fn project_points(object_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, rvec: &dyn core::ToInputArray, tvec: &dyn core::ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_points: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, jacobian: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, aspect_ratio: f64) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(object_points); input_array_arg!(rvec); input_array_arg!(tvec); input_array_arg!(camera_matrix); input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs); output_array_arg!(image_points); output_array_arg!(jacobian); unsafe { sys::cv_projectPoints_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec.as_raw__InputArray(), tvec.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__OutputArray(), jacobian.as_raw__OutputArray(), aspect_ratio) }.into_result() } /// Recovers the relative camera rotation and the translation from an estimated essential /// matrix and the corresponding points in two images, using cheirality check. Returns the number of /// inliers that pass the check. /// /// ## Parameters /// * E: The input essential matrix. /// * points1: Array of N 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should be /// floating-point (single or double precision). /// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1 . /// * cameraMatrix: Camera intrinsic matrix  . /// Note that this function assumes that points1 and points2 are feature points from cameras with the /// same camera intrinsic matrix. /// * R: Output rotation matrix. Together with the translation vector, this matrix makes up a tuple /// that performs a change of basis from the first camera's coordinate system to the second camera's /// coordinate system. Note that, in general, t can not be used for this tuple, see the parameter /// described below. /// * t: Output translation vector. This vector is obtained by @ref decomposeEssentialMat and /// therefore is only known up to scale, i.e. t is the direction of the translation vector and has unit /// length. /// * mask: Input/output mask for inliers in points1 and points2. If it is not empty, then it marks /// inliers in points1 and points2 for then given essential matrix E. Only these inliers will be used to /// recover pose. In the output mask only inliers which pass the cheirality check. /// /// This function decomposes an essential matrix using @ref decomposeEssentialMat and then verifies /// possible pose hypotheses by doing cheirality check. The cheirality check means that the /// triangulated 3D points should have positive depth. Some details can be found in [Nister03](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Nister03). /// /// This function can be used to process the output E and mask from @ref findEssentialMat. In this /// scenario, points1 and points2 are the same input for findEssentialMat.: /// ```ignore /// // Example. Estimation of fundamental matrix using the RANSAC algorithm /// int point_count = 100; /// vector<Point2f> points1(point_count); /// vector<Point2f> points2(point_count); /// /// // initialize the points here ... /// for( int i = 0; i < point_count; i++ ) /// { /// points1[i] = ...; /// points2[i] = ...; /// } /// /// // cametra matrix with both focal lengths = 1, and principal point = (0, 0) /// Mat cameraMatrix = Mat::eye(3, 3, CV_64F); /// /// Mat E, R, t, mask; /// /// E = findEssentialMat(points1, points2, cameraMatrix, RANSAC, 0.999, 1.0, mask); /// recoverPose(E, points1, points2, cameraMatrix, R, t, mask); /// ``` /// /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * mask: noArray() pub fn recover_pose_camera(e: &dyn core::ToInputArray, points1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, points2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &dyn core::ToInputArray, r: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, t: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, mask: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray) -> Result<i32> { input_array_arg!(e); input_array_arg!(points1); input_array_arg!(points2); input_array_arg!(camera_matrix); output_array_arg!(r); output_array_arg!(t); input_output_array_arg!(mask); unsafe { sys::cv_recoverPose_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR(e.as_raw__InputArray(), points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), r.as_raw__OutputArray(), t.as_raw__OutputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputOutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Recovers the relative camera rotation and the translation from an estimated essential /// matrix and the corresponding points in two images, using cheirality check. Returns the number of /// inliers that pass the check. /// /// ## Parameters /// * E: The input essential matrix. /// * points1: Array of N 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should be /// floating-point (single or double precision). /// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1 . /// * cameraMatrix: Camera intrinsic matrix  . /// Note that this function assumes that points1 and points2 are feature points from cameras with the /// same camera intrinsic matrix. /// * R: Output rotation matrix. Together with the translation vector, this matrix makes up a tuple /// that performs a change of basis from the first camera's coordinate system to the second camera's /// coordinate system. Note that, in general, t can not be used for this tuple, see the parameter /// described below. /// * t: Output translation vector. This vector is obtained by @ref decomposeEssentialMat and /// therefore is only known up to scale, i.e. t is the direction of the translation vector and has unit /// length. /// * mask: Input/output mask for inliers in points1 and points2. If it is not empty, then it marks /// inliers in points1 and points2 for then given essential matrix E. Only these inliers will be used to /// recover pose. In the output mask only inliers which pass the cheirality check. /// /// This function decomposes an essential matrix using @ref decomposeEssentialMat and then verifies /// possible pose hypotheses by doing cheirality check. The cheirality check means that the /// triangulated 3D points should have positive depth. Some details can be found in [Nister03](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Nister03). /// /// This function can be used to process the output E and mask from @ref findEssentialMat. In this /// scenario, points1 and points2 are the same input for findEssentialMat.: /// ```ignore /// // Example. Estimation of fundamental matrix using the RANSAC algorithm /// int point_count = 100; /// vector<Point2f> points1(point_count); /// vector<Point2f> points2(point_count); /// /// // initialize the points here ... /// for( int i = 0; i < point_count; i++ ) /// { /// points1[i] = ...; /// points2[i] = ...; /// } /// /// // cametra matrix with both focal lengths = 1, and principal point = (0, 0) /// Mat cameraMatrix = Mat::eye(3, 3, CV_64F); /// /// Mat E, R, t, mask; /// /// E = findEssentialMat(points1, points2, cameraMatrix, RANSAC, 0.999, 1.0, mask); /// recoverPose(E, points1, points2, cameraMatrix, R, t, mask); /// ``` /// /// /// ## Overloaded parameters /// /// * E: The input essential matrix. /// * points1: Array of N 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should be /// floating-point (single or double precision). /// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1. /// * cameraMatrix: Camera intrinsic matrix  . /// Note that this function assumes that points1 and points2 are feature points from cameras with the /// same camera intrinsic matrix. /// * R: Output rotation matrix. Together with the translation vector, this matrix makes up a tuple /// that performs a change of basis from the first camera's coordinate system to the second camera's /// coordinate system. Note that, in general, t can not be used for this tuple, see the parameter /// description below. /// * t: Output translation vector. This vector is obtained by @ref decomposeEssentialMat and /// therefore is only known up to scale, i.e. t is the direction of the translation vector and has unit /// length. /// * distanceThresh: threshold distance which is used to filter out far away points (i.e. infinite /// points). /// * mask: Input/output mask for inliers in points1 and points2. If it is not empty, then it marks /// inliers in points1 and points2 for then given essential matrix E. Only these inliers will be used to /// recover pose. In the output mask only inliers which pass the cheirality check. /// * triangulatedPoints: 3D points which were reconstructed by triangulation. /// /// This function differs from the one above that it outputs the triangulated 3D point that are used for /// the cheirality check. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * mask: noArray() /// * triangulated_points: noArray() pub fn recover_pose_camera_with_points(e: &dyn core::ToInputArray, points1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, points2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &dyn core::ToInputArray, r: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, t: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, distance_thresh: f64, mask: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, triangulated_points: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<i32> { input_array_arg!(e); input_array_arg!(points1); input_array_arg!(points2); input_array_arg!(camera_matrix); output_array_arg!(r); output_array_arg!(t); input_output_array_arg!(mask); output_array_arg!(triangulated_points); unsafe { sys::cv_recoverPose_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(e.as_raw__InputArray(), points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), r.as_raw__OutputArray(), t.as_raw__OutputArray(), distance_thresh, mask.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), triangulated_points.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Recovers the relative camera rotation and the translation from an estimated essential /// matrix and the corresponding points in two images, using cheirality check. Returns the number of /// inliers that pass the check. /// /// ## Parameters /// * E: The input essential matrix. /// * points1: Array of N 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should be /// floating-point (single or double precision). /// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1 . /// * cameraMatrix: Camera intrinsic matrix  . /// Note that this function assumes that points1 and points2 are feature points from cameras with the /// same camera intrinsic matrix. /// * R: Output rotation matrix. Together with the translation vector, this matrix makes up a tuple /// that performs a change of basis from the first camera's coordinate system to the second camera's /// coordinate system. Note that, in general, t can not be used for this tuple, see the parameter /// described below. /// * t: Output translation vector. This vector is obtained by @ref decomposeEssentialMat and /// therefore is only known up to scale, i.e. t is the direction of the translation vector and has unit /// length. /// * mask: Input/output mask for inliers in points1 and points2. If it is not empty, then it marks /// inliers in points1 and points2 for then given essential matrix E. Only these inliers will be used to /// recover pose. In the output mask only inliers which pass the cheirality check. /// /// This function decomposes an essential matrix using @ref decomposeEssentialMat and then verifies /// possible pose hypotheses by doing cheirality check. The cheirality check means that the /// triangulated 3D points should have positive depth. Some details can be found in [Nister03](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Nister03). /// /// This function can be used to process the output E and mask from @ref findEssentialMat. In this /// scenario, points1 and points2 are the same input for findEssentialMat.: /// ```ignore /// // Example. Estimation of fundamental matrix using the RANSAC algorithm /// int point_count = 100; /// vector<Point2f> points1(point_count); /// vector<Point2f> points2(point_count); /// /// // initialize the points here ... /// for( int i = 0; i < point_count; i++ ) /// { /// points1[i] = ...; /// points2[i] = ...; /// } /// /// // cametra matrix with both focal lengths = 1, and principal point = (0, 0) /// Mat cameraMatrix = Mat::eye(3, 3, CV_64F); /// /// Mat E, R, t, mask; /// /// E = findEssentialMat(points1, points2, cameraMatrix, RANSAC, 0.999, 1.0, mask); /// recoverPose(E, points1, points2, cameraMatrix, R, t, mask); /// ``` /// /// /// ## Overloaded parameters /// /// * E: The input essential matrix. /// * points1: Array of N 2D points from the first image. The point coordinates should be /// floating-point (single or double precision). /// * points2: Array of the second image points of the same size and format as points1 . /// * R: Output rotation matrix. Together with the translation vector, this matrix makes up a tuple /// that performs a change of basis from the first camera's coordinate system to the second camera's /// coordinate system. Note that, in general, t can not be used for this tuple, see the parameter /// description below. /// * t: Output translation vector. This vector is obtained by @ref decomposeEssentialMat and /// therefore is only known up to scale, i.e. t is the direction of the translation vector and has unit /// length. /// * focal: Focal length of the camera. Note that this function assumes that points1 and points2 /// are feature points from cameras with same focal length and principal point. /// * pp: principal point of the camera. /// * mask: Input/output mask for inliers in points1 and points2. If it is not empty, then it marks /// inliers in points1 and points2 for then given essential matrix E. Only these inliers will be used to /// recover pose. In the output mask only inliers which pass the cheirality check. /// /// This function differs from the one above that it computes camera intrinsic matrix from focal length and /// principal point: /// ///  /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * focal: 1.0 /// * pp: Point2d(0,0) /// * mask: noArray() pub fn recover_pose(e: &dyn core::ToInputArray, points1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, points2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, r: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, t: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, focal: f64, pp: core::Point2d, mask: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray) -> Result<i32> { input_array_arg!(e); input_array_arg!(points1); input_array_arg!(points2); output_array_arg!(r); output_array_arg!(t); input_output_array_arg!(mask); unsafe { sys::cv_recoverPose_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_Point2d_const__InputOutputArrayR(e.as_raw__InputArray(), points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), r.as_raw__OutputArray(), t.as_raw__OutputArray(), focal, pp.opencv_as_extern(), mask.as_raw__InputOutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// computes the rectification transformations for 3-head camera, where all the heads are on the same line. pub fn rectify3_collinear(camera_matrix1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dist_coeffs1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, camera_matrix2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dist_coeffs2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, camera_matrix3: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dist_coeffs3: &dyn core::ToInputArray, imgpt1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, imgpt3: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, r12: &dyn core::ToInputArray, t12: &dyn core::ToInputArray, r13: &dyn core::ToInputArray, t13: &dyn core::ToInputArray, r1: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, r2: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, r3: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, p1: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, p2: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, p3: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, q: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, alpha: f64, new_img_size: core::Size, roi1: &mut core::Rect, roi2: &mut core::Rect, flags: i32) -> Result<f32> { input_array_arg!(camera_matrix1); input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs1); input_array_arg!(camera_matrix2); input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs2); input_array_arg!(camera_matrix3); input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs3); input_array_arg!(imgpt1); input_array_arg!(imgpt3); input_array_arg!(r12); input_array_arg!(t12); input_array_arg!(r13); input_array_arg!(t13); output_array_arg!(r1); output_array_arg!(r2); output_array_arg!(r3); output_array_arg!(p1); output_array_arg!(p2); output_array_arg!(p3); output_array_arg!(q); unsafe { sys::cv_rectify3Collinear_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_Size_RectX_RectX_int(camera_matrix1.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs1.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix2.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix3.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs3.as_raw__InputArray(), imgpt1.as_raw__InputArray(), imgpt3.as_raw__InputArray(), image_size.opencv_as_extern(), r12.as_raw__InputArray(), t12.as_raw__InputArray(), r13.as_raw__InputArray(), t13.as_raw__InputArray(), r1.as_raw__OutputArray(), r2.as_raw__OutputArray(), r3.as_raw__OutputArray(), p1.as_raw__OutputArray(), p2.as_raw__OutputArray(), p3.as_raw__OutputArray(), q.as_raw__OutputArray(), alpha, new_img_size.opencv_as_extern(), roi1, roi2, flags) }.into_result() } /// Reprojects a disparity image to 3D space. /// /// ## Parameters /// * disparity: Input single-channel 8-bit unsigned, 16-bit signed, 32-bit signed or 32-bit /// floating-point disparity image. The values of 8-bit / 16-bit signed formats are assumed to have no /// fractional bits. If the disparity is 16-bit signed format, as computed by @ref StereoBM or /// @ref StereoSGBM and maybe other algorithms, it should be divided by 16 (and scaled to float) before /// being used here. /// * _3dImage: Output 3-channel floating-point image of the same size as disparity. Each element of /// _3dImage(x,y) contains 3D coordinates of the point (x,y) computed from the disparity map. If one /// uses Q obtained by @ref stereoRectify, then the returned points are represented in the first /// camera's rectified coordinate system. /// * Q:  perspective transformation matrix that can be obtained with /// @ref stereoRectify. /// * handleMissingValues: Indicates, whether the function should handle missing values (i.e. /// points where the disparity was not computed). If handleMissingValues=true, then pixels with the /// minimal disparity that corresponds to the outliers (see StereoMatcher::compute ) are transformed /// to 3D points with a very large Z value (currently set to 10000). /// * ddepth: The optional output array depth. If it is -1, the output image will have CV_32F /// depth. ddepth can also be set to CV_16S, CV_32S or CV_32F. /// /// The function transforms a single-channel disparity map to a 3-channel image representing a 3D /// surface. That is, for each pixel (x,y) and the corresponding disparity d=disparity(x,y) , it /// computes: /// ///  /// ## See also /// To reproject a sparse set of points {(x,y,d),...} to 3D space, use perspectiveTransform. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * handle_missing_values: false /// * ddepth: -1 pub fn reproject_image_to_3d(disparity: &dyn core::ToInputArray, _3d_image: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, q: &dyn core::ToInputArray, handle_missing_values: bool, ddepth: i32) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(disparity); output_array_arg!(_3d_image); input_array_arg!(q); unsafe { sys::cv_reprojectImageTo3D_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_bool_int(disparity.as_raw__InputArray(), _3d_image.as_raw__OutputArray(), q.as_raw__InputArray(), handle_missing_values, ddepth) }.into_result() } /// Calculates the Sampson Distance between two points. /// /// The function cv::sampsonDistance calculates and returns the first order approximation of the geometric error as: ///  /// The fundamental matrix may be calculated using the cv::findFundamentalMat function. See [HartleyZ00](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_HartleyZ00) 11.4.3 for details. /// ## Parameters /// * pt1: first homogeneous 2d point /// * pt2: second homogeneous 2d point /// * F: fundamental matrix /// ## Returns /// The computed Sampson distance. pub fn sampson_distance(pt1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, pt2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, f: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<f64> { input_array_arg!(pt1); input_array_arg!(pt2); input_array_arg!(f); unsafe { sys::cv_sampsonDistance_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(pt1.as_raw__InputArray(), pt2.as_raw__InputArray(), f.as_raw__InputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Finds an object pose from 3 3D-2D point correspondences. /// /// ## Parameters /// * objectPoints: Array of object points in the object coordinate space, 3x3 1-channel or /// 1x3/3x1 3-channel. vector\<Point3f\> can be also passed here. /// * imagePoints: Array of corresponding image points, 3x2 1-channel or 1x3/3x1 2-channel. /// vector\<Point2f\> can be also passed here. /// * cameraMatrix: Input camera intrinsic matrix  . /// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients /// . If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are /// assumed. /// * rvecs: Output rotation vectors (see @ref Rodrigues ) that, together with tvecs, brings points from /// the model coordinate system to the camera coordinate system. A P3P problem has up to 4 solutions. /// * tvecs: Output translation vectors. /// * flags: Method for solving a P3P problem: /// * @ref SOLVEPNP_P3P Method is based on the paper of X.S. Gao, X.-R. Hou, J. Tang, H.-F. Chang /// "Complete Solution Classification for the Perspective-Three-Point Problem" ([gao2003complete](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_gao2003complete)). /// * @ref SOLVEPNP_AP3P Method is based on the paper of T. Ke and S. Roumeliotis. /// "An Efficient Algebraic Solution to the Perspective-Three-Point Problem" ([Ke17](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Ke17)). /// /// The function estimates the object pose given 3 object points, their corresponding image /// projections, as well as the camera intrinsic matrix and the distortion coefficients. /// /// /// Note: /// The solutions are sorted by reprojection errors (lowest to highest). pub fn solve_p3p(object_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &dyn core::ToInputArray, rvecs: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, tvecs: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<i32> { input_array_arg!(object_points); input_array_arg!(image_points); input_array_arg!(camera_matrix); input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs); output_array_arg!(rvecs); output_array_arg!(tvecs); unsafe { sys::cv_solveP3P_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), rvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags) }.into_result() } /// Finds an object pose from 3D-2D point correspondences. /// This function returns a list of all the possible solutions (a solution is a <rotation vector, translation vector> /// couple), depending on the number of input points and the chosen method: /// - P3P methods (@ref SOLVEPNP_P3P, @ref SOLVEPNP_AP3P): 3 or 4 input points. Number of returned solutions can be between 0 and 4 with 3 input points. /// - @ref SOLVEPNP_IPPE Input points must be >= 4 and object points must be coplanar. Returns 2 solutions. /// - @ref SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE Special case suitable for marker pose estimation. /// Number of input points must be 4 and 2 solutions are returned. Object points must be defined in the following order: /// - point 0: [-squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0] /// - point 1: [ squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0] /// - point 2: [ squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0] /// - point 3: [-squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0] /// - for all the other flags, number of input points must be >= 4 and object points can be in any configuration. /// Only 1 solution is returned. /// /// ## Parameters /// * objectPoints: Array of object points in the object coordinate space, Nx3 1-channel or /// 1xN/Nx1 3-channel, where N is the number of points. vector\<Point3d\> can be also passed here. /// * imagePoints: Array of corresponding image points, Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel, /// where N is the number of points. vector\<Point2d\> can be also passed here. /// * cameraMatrix: Input camera intrinsic matrix  . /// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients /// . If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are /// assumed. /// * rvecs: Vector of output rotation vectors (see @ref Rodrigues ) that, together with tvecs, brings points from /// the model coordinate system to the camera coordinate system. /// * tvecs: Vector of output translation vectors. /// * useExtrinsicGuess: Parameter used for #SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE. If true (1), the function uses /// the provided rvec and tvec values as initial approximations of the rotation and translation /// vectors, respectively, and further optimizes them. /// * flags: Method for solving a PnP problem: /// * @ref SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE Iterative method is based on a Levenberg-Marquardt optimization. In /// this case the function finds such a pose that minimizes reprojection error, that is the sum /// of squared distances between the observed projections imagePoints and the projected (using /// projectPoints ) objectPoints . /// * @ref SOLVEPNP_P3P Method is based on the paper of X.S. Gao, X.-R. Hou, J. Tang, H.-F. Chang /// "Complete Solution Classification for the Perspective-Three-Point Problem" ([gao2003complete](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_gao2003complete)). /// In this case the function requires exactly four object and image points. /// * @ref SOLVEPNP_AP3P Method is based on the paper of T. Ke, S. Roumeliotis /// "An Efficient Algebraic Solution to the Perspective-Three-Point Problem" ([Ke17](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Ke17)). /// In this case the function requires exactly four object and image points. /// * @ref SOLVEPNP_EPNP Method has been introduced by F.Moreno-Noguer, V.Lepetit and P.Fua in the /// paper "EPnP: Efficient Perspective-n-Point Camera Pose Estimation" ([lepetit2009epnp](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_lepetit2009epnp)). /// * @ref SOLVEPNP_DLS **Broken implementation. Using this flag will fallback to EPnP.** /// /// Method is based on the paper of Joel A. Hesch and Stergios I. Roumeliotis. /// "A Direct Least-Squares (DLS) Method for PnP" ([hesch2011direct](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_hesch2011direct)). /// * @ref SOLVEPNP_UPNP **Broken implementation. Using this flag will fallback to EPnP.** /// /// Method is based on the paper of A.Penate-Sanchez, J.Andrade-Cetto, /// F.Moreno-Noguer. "Exhaustive Linearization for Robust Camera Pose and Focal Length /// Estimation" ([penate2013exhaustive](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_penate2013exhaustive)). In this case the function also estimates the parameters  and  /// assuming that both have the same value. Then the cameraMatrix is updated with the estimated /// focal length. /// * @ref SOLVEPNP_IPPE Method is based on the paper of T. Collins and A. Bartoli. /// "Infinitesimal Plane-Based Pose Estimation" ([Collins14](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Collins14)). This method requires coplanar object points. /// * @ref SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE Method is based on the paper of Toby Collins and Adrien Bartoli. /// "Infinitesimal Plane-Based Pose Estimation" ([Collins14](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Collins14)). This method is suitable for marker pose estimation. /// It requires 4 coplanar object points defined in the following order: /// - point 0: [-squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0] /// - point 1: [ squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0] /// - point 2: [ squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0] /// - point 3: [-squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0] /// * rvec: Rotation vector used to initialize an iterative PnP refinement algorithm, when flag is @ref SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE /// and useExtrinsicGuess is set to true. /// * tvec: Translation vector used to initialize an iterative PnP refinement algorithm, when flag is @ref SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE /// and useExtrinsicGuess is set to true. /// * reprojectionError: Optional vector of reprojection error, that is the RMS error /// () between the input image points /// and the 3D object points projected with the estimated pose. /// /// The function estimates the object pose given a set of object points, their corresponding image /// projections, as well as the camera intrinsic matrix and the distortion coefficients, see the figure below /// (more precisely, the X-axis of the camera frame is pointing to the right, the Y-axis downward /// and the Z-axis forward). /// ///  /// /// Points expressed in the world frame  are projected into the image plane 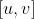 /// using the perspective projection model  and the camera intrinsic parameters matrix : /// ///  /// /// The estimated pose is thus the rotation (`rvec`) and the translation (`tvec`) vectors that allow transforming /// a 3D point expressed in the world frame into the camera frame: /// ///  /// /// /// Note: /// * An example of how to use solvePnP for planar augmented reality can be found at /// opencv_source_code/samples/python/plane_ar.py /// * If you are using Python: /// - Numpy array slices won't work as input because solvePnP requires contiguous /// arrays (enforced by the assertion using cv::Mat::checkVector() around line 55 of /// modules/calib3d/src/solvepnp.cpp version 2.4.9) /// - The P3P algorithm requires image points to be in an array of shape (N,1,2) due /// to its calling of cv::undistortPoints (around line 75 of modules/calib3d/src/solvepnp.cpp version 2.4.9) /// which requires 2-channel information. /// - Thus, given some data D = np.array(...) where D.shape = (N,M), in order to use a subset of /// it as, e.g., imagePoints, one must effectively copy it into a new array: imagePoints = /// np.ascontiguousarray(D[:,:2]).reshape((N,1,2)) /// * The methods @ref SOLVEPNP_DLS and @ref SOLVEPNP_UPNP cannot be used as the current implementations are /// unstable and sometimes give completely wrong results. If you pass one of these two /// flags, @ref SOLVEPNP_EPNP method will be used instead. /// * The minimum number of points is 4 in the general case. In the case of @ref SOLVEPNP_P3P and @ref SOLVEPNP_AP3P /// methods, it is required to use exactly 4 points (the first 3 points are used to estimate all the solutions /// of the P3P problem, the last one is used to retain the best solution that minimizes the reprojection error). /// * With @ref SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE method and `useExtrinsicGuess=true`, the minimum number of points is 3 (3 points /// are sufficient to compute a pose but there are up to 4 solutions). The initial solution should be close to the /// global solution to converge. /// * With @ref SOLVEPNP_IPPE input points must be >= 4 and object points must be coplanar. /// * With @ref SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE this is a special case suitable for marker pose estimation. /// Number of input points must be 4. Object points must be defined in the following order: /// - point 0: [-squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0] /// - point 1: [ squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0] /// - point 2: [ squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0] /// - point 3: [-squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0] /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * use_extrinsic_guess: false /// * flags: SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE /// * rvec: noArray() /// * tvec: noArray() /// * reprojection_error: noArray() pub fn solve_pnp_generic(object_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &dyn core::ToInputArray, rvecs: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, tvecs: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, use_extrinsic_guess: bool, flags: crate::calib3d::SolvePnPMethod, rvec: &dyn core::ToInputArray, tvec: &dyn core::ToInputArray, reprojection_error: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<i32> { input_array_arg!(object_points); input_array_arg!(image_points); input_array_arg!(camera_matrix); input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs); output_array_arg!(rvecs); output_array_arg!(tvecs); input_array_arg!(rvec); input_array_arg!(tvec); output_array_arg!(reprojection_error); unsafe { sys::cv_solvePnPGeneric_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_bool_SolvePnPMethod_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), rvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvecs.as_raw__OutputArray(), use_extrinsic_guess, flags, rvec.as_raw__InputArray(), tvec.as_raw__InputArray(), reprojection_error.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Finds an object pose from 3D-2D point correspondences using the RANSAC scheme. /// /// ## Parameters /// * objectPoints: Array of object points in the object coordinate space, Nx3 1-channel or /// 1xN/Nx1 3-channel, where N is the number of points. vector\<Point3d\> can be also passed here. /// * imagePoints: Array of corresponding image points, Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel, /// where N is the number of points. vector\<Point2d\> can be also passed here. /// * cameraMatrix: Input camera intrinsic matrix  . /// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients /// . If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are /// assumed. /// * rvec: Output rotation vector (see @ref Rodrigues ) that, together with tvec, brings points from /// the model coordinate system to the camera coordinate system. /// * tvec: Output translation vector. /// * useExtrinsicGuess: Parameter used for @ref SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE. If true (1), the function uses /// the provided rvec and tvec values as initial approximations of the rotation and translation /// vectors, respectively, and further optimizes them. /// * iterationsCount: Number of iterations. /// * reprojectionError: Inlier threshold value used by the RANSAC procedure. The parameter value /// is the maximum allowed distance between the observed and computed point projections to consider it /// an inlier. /// * confidence: The probability that the algorithm produces a useful result. /// * inliers: Output vector that contains indices of inliers in objectPoints and imagePoints . /// * flags: Method for solving a PnP problem (see @ref solvePnP ). /// /// The function estimates an object pose given a set of object points, their corresponding image /// projections, as well as the camera intrinsic matrix and the distortion coefficients. This function finds such /// a pose that minimizes reprojection error, that is, the sum of squared distances between the observed /// projections imagePoints and the projected (using @ref projectPoints ) objectPoints. The use of RANSAC /// makes the function resistant to outliers. /// /// /// Note: /// * An example of how to use solvePNPRansac for object detection can be found at /// opencv_source_code/samples/cpp/tutorial_code/calib3d/real_time_pose_estimation/ /// * The default method used to estimate the camera pose for the Minimal Sample Sets step /// is #SOLVEPNP_EPNP. Exceptions are: /// - if you choose #SOLVEPNP_P3P or #SOLVEPNP_AP3P, these methods will be used. /// - if the number of input points is equal to 4, #SOLVEPNP_P3P is used. /// * The method used to estimate the camera pose using all the inliers is defined by the /// flags parameters unless it is equal to #SOLVEPNP_P3P or #SOLVEPNP_AP3P. In this case, /// the method #SOLVEPNP_EPNP will be used instead. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * use_extrinsic_guess: false /// * iterations_count: 100 /// * reprojection_error: 8.0 /// * confidence: 0.99 /// * inliers: noArray() /// * flags: SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE pub fn solve_pnp_ransac(object_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &dyn core::ToInputArray, rvec: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, tvec: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, use_extrinsic_guess: bool, iterations_count: i32, reprojection_error: f32, confidence: f64, inliers: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<bool> { input_array_arg!(object_points); input_array_arg!(image_points); input_array_arg!(camera_matrix); input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs); output_array_arg!(rvec); output_array_arg!(tvec); output_array_arg!(inliers); unsafe { sys::cv_solvePnPRansac_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_bool_int_float_double_const__OutputArrayR_int(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvec.as_raw__OutputArray(), use_extrinsic_guess, iterations_count, reprojection_error, confidence, inliers.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags) }.into_result() } /// ## C++ default parameters /// * params: UsacParams() pub fn solve_pnp_ransac_1(object_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs: &dyn core::ToInputArray, rvec: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, tvec: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, inliers: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, params: crate::calib3d::UsacParams) -> Result<bool> { input_array_arg!(object_points); input_array_arg!(image_points); input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix); input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs); output_array_arg!(rvec); output_array_arg!(tvec); output_array_arg!(inliers); unsafe { sys::cv_solvePnPRansac_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const_UsacParamsR(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvec.as_raw__OutputArray(), inliers.as_raw__OutputArray(), ¶ms) }.into_result() } /// Refine a pose (the translation and the rotation that transform a 3D point expressed in the object coordinate frame /// to the camera coordinate frame) from a 3D-2D point correspondences and starting from an initial solution. /// /// ## Parameters /// * objectPoints: Array of object points in the object coordinate space, Nx3 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 3-channel, /// where N is the number of points. vector\<Point3d\> can also be passed here. /// * imagePoints: Array of corresponding image points, Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel, /// where N is the number of points. vector\<Point2d\> can also be passed here. /// * cameraMatrix: Input camera intrinsic matrix  . /// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients /// . If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are /// assumed. /// * rvec: Input/Output rotation vector (see @ref Rodrigues ) that, together with tvec, brings points from /// the model coordinate system to the camera coordinate system. Input values are used as an initial solution. /// * tvec: Input/Output translation vector. Input values are used as an initial solution. /// * criteria: Criteria when to stop the Levenberg-Marquard iterative algorithm. /// /// The function refines the object pose given at least 3 object points, their corresponding image /// projections, an initial solution for the rotation and translation vector, /// as well as the camera intrinsic matrix and the distortion coefficients. /// The function minimizes the projection error with respect to the rotation and the translation vectors, according /// to a Levenberg-Marquardt iterative minimization [Madsen04](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Madsen04) [Eade13](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Eade13) process. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::EPS+TermCriteria::COUNT,20,FLT_EPSILON) pub fn solve_pnp_refine_lm(object_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &dyn core::ToInputArray, rvec: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, tvec: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, criteria: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(object_points); input_array_arg!(image_points); input_array_arg!(camera_matrix); input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs); input_output_array_arg!(rvec); input_output_array_arg!(tvec); unsafe { sys::cv_solvePnPRefineLM_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_TermCriteria(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), tvec.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), criteria.opencv_as_extern()) }.into_result() } /// Refine a pose (the translation and the rotation that transform a 3D point expressed in the object coordinate frame /// to the camera coordinate frame) from a 3D-2D point correspondences and starting from an initial solution. /// /// ## Parameters /// * objectPoints: Array of object points in the object coordinate space, Nx3 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 3-channel, /// where N is the number of points. vector\<Point3d\> can also be passed here. /// * imagePoints: Array of corresponding image points, Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel, /// where N is the number of points. vector\<Point2d\> can also be passed here. /// * cameraMatrix: Input camera intrinsic matrix  . /// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients /// . If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are /// assumed. /// * rvec: Input/Output rotation vector (see @ref Rodrigues ) that, together with tvec, brings points from /// the model coordinate system to the camera coordinate system. Input values are used as an initial solution. /// * tvec: Input/Output translation vector. Input values are used as an initial solution. /// * criteria: Criteria when to stop the Levenberg-Marquard iterative algorithm. /// * VVSlambda: Gain for the virtual visual servoing control law, equivalent to the  /// gain in the Damped Gauss-Newton formulation. /// /// The function refines the object pose given at least 3 object points, their corresponding image /// projections, an initial solution for the rotation and translation vector, /// as well as the camera intrinsic matrix and the distortion coefficients. /// The function minimizes the projection error with respect to the rotation and the translation vectors, using a /// virtual visual servoing (VVS) [Chaumette06](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Chaumette06) [Marchand16](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Marchand16) scheme. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::EPS+TermCriteria::COUNT,20,FLT_EPSILON) /// * vv_slambda: 1 pub fn solve_pnp_refine_vvs(object_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &dyn core::ToInputArray, rvec: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, tvec: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, criteria: core::TermCriteria, vv_slambda: f64) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(object_points); input_array_arg!(image_points); input_array_arg!(camera_matrix); input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs); input_output_array_arg!(rvec); input_output_array_arg!(tvec); unsafe { sys::cv_solvePnPRefineVVS_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_TermCriteria_double(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), tvec.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), criteria.opencv_as_extern(), vv_slambda) }.into_result() } /// Finds an object pose from 3D-2D point correspondences. /// This function returns the rotation and the translation vectors that transform a 3D point expressed in the object /// coordinate frame to the camera coordinate frame, using different methods: /// - P3P methods (@ref SOLVEPNP_P3P, @ref SOLVEPNP_AP3P): need 4 input points to return a unique solution. /// - @ref SOLVEPNP_IPPE Input points must be >= 4 and object points must be coplanar. /// - @ref SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE Special case suitable for marker pose estimation. /// Number of input points must be 4. Object points must be defined in the following order: /// - point 0: [-squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0] /// - point 1: [ squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0] /// - point 2: [ squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0] /// - point 3: [-squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0] /// - for all the other flags, number of input points must be >= 4 and object points can be in any configuration. /// /// ## Parameters /// * objectPoints: Array of object points in the object coordinate space, Nx3 1-channel or /// 1xN/Nx1 3-channel, where N is the number of points. vector\<Point3d\> can be also passed here. /// * imagePoints: Array of corresponding image points, Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel, /// where N is the number of points. vector\<Point2d\> can be also passed here. /// * cameraMatrix: Input camera intrinsic matrix  . /// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients /// . If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are /// assumed. /// * rvec: Output rotation vector (see @ref Rodrigues ) that, together with tvec, brings points from /// the model coordinate system to the camera coordinate system. /// * tvec: Output translation vector. /// * useExtrinsicGuess: Parameter used for #SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE. If true (1), the function uses /// the provided rvec and tvec values as initial approximations of the rotation and translation /// vectors, respectively, and further optimizes them. /// * flags: Method for solving a PnP problem: /// * @ref SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE Iterative method is based on a Levenberg-Marquardt optimization. In /// this case the function finds such a pose that minimizes reprojection error, that is the sum /// of squared distances between the observed projections imagePoints and the projected (using /// @ref projectPoints ) objectPoints . /// * @ref SOLVEPNP_P3P Method is based on the paper of X.S. Gao, X.-R. Hou, J. Tang, H.-F. Chang /// "Complete Solution Classification for the Perspective-Three-Point Problem" ([gao2003complete](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_gao2003complete)). /// In this case the function requires exactly four object and image points. /// * @ref SOLVEPNP_AP3P Method is based on the paper of T. Ke, S. Roumeliotis /// "An Efficient Algebraic Solution to the Perspective-Three-Point Problem" ([Ke17](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Ke17)). /// In this case the function requires exactly four object and image points. /// * @ref SOLVEPNP_EPNP Method has been introduced by F. Moreno-Noguer, V. Lepetit and P. Fua in the /// paper "EPnP: Efficient Perspective-n-Point Camera Pose Estimation" ([lepetit2009epnp](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_lepetit2009epnp)). /// * @ref SOLVEPNP_DLS **Broken implementation. Using this flag will fallback to EPnP.** /// /// Method is based on the paper of J. Hesch and S. Roumeliotis. /// "A Direct Least-Squares (DLS) Method for PnP" ([hesch2011direct](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_hesch2011direct)). /// * @ref SOLVEPNP_UPNP **Broken implementation. Using this flag will fallback to EPnP.** /// /// Method is based on the paper of A. Penate-Sanchez, J. Andrade-Cetto, /// F. Moreno-Noguer. "Exhaustive Linearization for Robust Camera Pose and Focal Length /// Estimation" ([penate2013exhaustive](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_penate2013exhaustive)). In this case the function also estimates the parameters  and  /// assuming that both have the same value. Then the cameraMatrix is updated with the estimated /// focal length. /// * @ref SOLVEPNP_IPPE Method is based on the paper of T. Collins and A. Bartoli. /// "Infinitesimal Plane-Based Pose Estimation" ([Collins14](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Collins14)). This method requires coplanar object points. /// * @ref SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE Method is based on the paper of Toby Collins and Adrien Bartoli. /// "Infinitesimal Plane-Based Pose Estimation" ([Collins14](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Collins14)). This method is suitable for marker pose estimation. /// It requires 4 coplanar object points defined in the following order: /// - point 0: [-squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0] /// - point 1: [ squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0] /// - point 2: [ squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0] /// - point 3: [-squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0] /// * @ref SOLVEPNP_SQPNP Method is based on the paper "A Consistently Fast and Globally Optimal Solution to the /// Perspective-n-Point Problem" by G. Terzakis and M.Lourakis ([Terzakis20](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Terzakis20)). It requires 3 or more points. /// /// /// The function estimates the object pose given a set of object points, their corresponding image /// projections, as well as the camera intrinsic matrix and the distortion coefficients, see the figure below /// (more precisely, the X-axis of the camera frame is pointing to the right, the Y-axis downward /// and the Z-axis forward). /// ///  /// /// Points expressed in the world frame  are projected into the image plane  /// using the perspective projection model  and the camera intrinsic parameters matrix : /// ///  /// /// The estimated pose is thus the rotation (`rvec`) and the translation (`tvec`) vectors that allow transforming /// a 3D point expressed in the world frame into the camera frame: /// ///  /// /// /// Note: /// * An example of how to use solvePnP for planar augmented reality can be found at /// opencv_source_code/samples/python/plane_ar.py /// * If you are using Python: /// - Numpy array slices won't work as input because solvePnP requires contiguous /// arrays (enforced by the assertion using cv::Mat::checkVector() around line 55 of /// modules/calib3d/src/solvepnp.cpp version 2.4.9) /// - The P3P algorithm requires image points to be in an array of shape (N,1,2) due /// to its calling of cv::undistortPoints (around line 75 of modules/calib3d/src/solvepnp.cpp version 2.4.9) /// which requires 2-channel information. /// - Thus, given some data D = np.array(...) where D.shape = (N,M), in order to use a subset of /// it as, e.g., imagePoints, one must effectively copy it into a new array: imagePoints = /// np.ascontiguousarray(D[:,:2]).reshape((N,1,2)) /// * The methods @ref SOLVEPNP_DLS and @ref SOLVEPNP_UPNP cannot be used as the current implementations are /// unstable and sometimes give completely wrong results. If you pass one of these two /// flags, @ref SOLVEPNP_EPNP method will be used instead. /// * The minimum number of points is 4 in the general case. In the case of @ref SOLVEPNP_P3P and @ref SOLVEPNP_AP3P /// methods, it is required to use exactly 4 points (the first 3 points are used to estimate all the solutions /// of the P3P problem, the last one is used to retain the best solution that minimizes the reprojection error). /// * With @ref SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE method and `useExtrinsicGuess=true`, the minimum number of points is 3 (3 points /// are sufficient to compute a pose but there are up to 4 solutions). The initial solution should be close to the /// global solution to converge. /// * With @ref SOLVEPNP_IPPE input points must be >= 4 and object points must be coplanar. /// * With @ref SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE this is a special case suitable for marker pose estimation. /// Number of input points must be 4. Object points must be defined in the following order: /// - point 0: [-squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0] /// - point 1: [ squareLength / 2, squareLength / 2, 0] /// - point 2: [ squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0] /// - point 3: [-squareLength / 2, -squareLength / 2, 0] /// * With @ref SOLVEPNP_SQPNP input points must be >= 3 /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * use_extrinsic_guess: false /// * flags: SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE pub fn solve_pnp(object_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, camera_matrix: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &dyn core::ToInputArray, rvec: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, tvec: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, use_extrinsic_guess: bool, flags: i32) -> Result<bool> { input_array_arg!(object_points); input_array_arg!(image_points); input_array_arg!(camera_matrix); input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs); output_array_arg!(rvec); output_array_arg!(tvec); unsafe { sys::cv_solvePnP_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_bool_int(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), rvec.as_raw__OutputArray(), tvec.as_raw__OutputArray(), use_extrinsic_guess, flags) }.into_result() } /// Calibrates a stereo camera set up. This function finds the intrinsic parameters /// for each of the two cameras and the extrinsic parameters between the two cameras. /// /// ## Parameters /// * objectPoints: Vector of vectors of the calibration pattern points. The same structure as /// in @ref calibrateCamera. For each pattern view, both cameras need to see the same object /// points. Therefore, objectPoints.size(), imagePoints1.size(), and imagePoints2.size() need to be /// equal as well as objectPoints[i].size(), imagePoints1[i].size(), and imagePoints2[i].size() need to /// be equal for each i. /// * imagePoints1: Vector of vectors of the projections of the calibration pattern points, /// observed by the first camera. The same structure as in @ref calibrateCamera. /// * imagePoints2: Vector of vectors of the projections of the calibration pattern points, /// observed by the second camera. The same structure as in @ref calibrateCamera. /// * cameraMatrix1: Input/output camera intrinsic matrix for the first camera, the same as in /// @ref calibrateCamera. Furthermore, for the stereo case, additional flags may be used, see below. /// * distCoeffs1: Input/output vector of distortion coefficients, the same as in /// @ref calibrateCamera. /// * cameraMatrix2: Input/output second camera intrinsic matrix for the second camera. See description for /// cameraMatrix1. /// * distCoeffs2: Input/output lens distortion coefficients for the second camera. See /// description for distCoeffs1. /// * imageSize: Size of the image used only to initialize the camera intrinsic matrices. /// * R: Output rotation matrix. Together with the translation vector T, this matrix brings /// points given in the first camera's coordinate system to points in the second camera's /// coordinate system. In more technical terms, the tuple of R and T performs a change of basis /// from the first camera's coordinate system to the second camera's coordinate system. Due to its /// duality, this tuple is equivalent to the position of the first camera with respect to the /// second camera coordinate system. /// * T: Output translation vector, see description above. /// * E: Output essential matrix. /// * F: Output fundamental matrix. /// * perViewErrors: Output vector of the RMS re-projection error estimated for each pattern view. /// * flags: Different flags that may be zero or a combination of the following values: /// * @ref CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC Fix cameraMatrix? and distCoeffs? so that only R, T, E, and F /// matrices are estimated. /// * @ref CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS Optimize some or all of the intrinsic parameters /// according to the specified flags. Initial values are provided by the user. /// * @ref CALIB_USE_EXTRINSIC_GUESS R and T contain valid initial values that are optimized further. /// Otherwise R and T are initialized to the median value of the pattern views (each dimension separately). /// * @ref CALIB_FIX_PRINCIPAL_POINT Fix the principal points during the optimization. /// * @ref CALIB_FIX_FOCAL_LENGTH Fix  and  . /// * @ref CALIB_FIX_ASPECT_RATIO Optimize  . Fix the ratio  /// . /// * @ref CALIB_SAME_FOCAL_LENGTH Enforce  and  . /// * @ref CALIB_ZERO_TANGENT_DIST Set tangential distortion coefficients for each camera to /// zeros and fix there. /// * @ref CALIB_FIX_K1,..., @ref CALIB_FIX_K6 Do not change the corresponding radial /// distortion coefficient during the optimization. If @ref CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS is set, /// the coefficient from the supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0. /// * @ref CALIB_RATIONAL_MODEL Enable coefficients k4, k5, and k6. To provide the backward /// compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the calibration /// function use the rational model and return 8 coefficients. If the flag is not set, the /// function computes and returns only 5 distortion coefficients. /// * @ref CALIB_THIN_PRISM_MODEL Coefficients s1, s2, s3 and s4 are enabled. To provide the /// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the /// calibration function use the thin prism model and return 12 coefficients. If the flag is not /// set, the function computes and returns only 5 distortion coefficients. /// * @ref CALIB_FIX_S1_S2_S3_S4 The thin prism distortion coefficients are not changed during /// the optimization. If @ref CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS is set, the coefficient from the /// supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0. /// * @ref CALIB_TILTED_MODEL Coefficients tauX and tauY are enabled. To provide the /// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the /// calibration function use the tilted sensor model and return 14 coefficients. If the flag is not /// set, the function computes and returns only 5 distortion coefficients. /// * @ref CALIB_FIX_TAUX_TAUY The coefficients of the tilted sensor model are not changed during /// the optimization. If @ref CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS is set, the coefficient from the /// supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0. /// * criteria: Termination criteria for the iterative optimization algorithm. /// /// The function estimates the transformation between two cameras making a stereo pair. If one computes /// the poses of an object relative to the first camera and to the second camera, /// ( , ) and (,), respectively, for a stereo camera where the /// relative position and orientation between the two cameras are fixed, then those poses definitely /// relate to each other. This means, if the relative position and orientation (,) of the /// two cameras is known, it is possible to compute (,) when (,) is /// given. This is what the described function does. It computes (,) such that: /// ///  ///  /// /// Therefore, one can compute the coordinate representation of a 3D point for the second camera's /// coordinate system when given the point's coordinate representation in the first camera's coordinate /// system: /// ///  /// /// /// Optionally, it computes the essential matrix E: /// ///  /// /// where  are components of the translation vector  :  . /// And the function can also compute the fundamental matrix F: /// ///  /// /// Besides the stereo-related information, the function can also perform a full calibration of each of /// the two cameras. However, due to the high dimensionality of the parameter space and noise in the /// input data, the function can diverge from the correct solution. If the intrinsic parameters can be /// estimated with high accuracy for each of the cameras individually (for example, using /// calibrateCamera ), you are recommended to do so and then pass @ref CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC flag to the /// function along with the computed intrinsic parameters. Otherwise, if all the parameters are /// estimated at once, it makes sense to restrict some parameters, for example, pass /// @ref CALIB_SAME_FOCAL_LENGTH and @ref CALIB_ZERO_TANGENT_DIST flags, which is usually a /// reasonable assumption. /// /// Similarly to calibrateCamera, the function minimizes the total re-projection error for all the /// points in all the available views from both cameras. The function returns the final value of the /// re-projection error. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * flags: CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC /// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,30,1e-6) pub fn stereo_calibrate_extended(object_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_points1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_points2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, camera_matrix1: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs1: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, camera_matrix2: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs2: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, image_size: core::Size, r: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, t: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, e: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, f: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, per_view_errors: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32, criteria: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<f64> { input_array_arg!(object_points); input_array_arg!(image_points1); input_array_arg!(image_points2); input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix1); input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs1); input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix2); input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs2); input_output_array_arg!(r); input_output_array_arg!(t); output_array_arg!(e); output_array_arg!(f); output_array_arg!(per_view_errors); unsafe { sys::cv_stereoCalibrate_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_Size_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_TermCriteria(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points1.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix1.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs1.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), camera_matrix2.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs2.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), image_size.opencv_as_extern(), r.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), t.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), e.as_raw__OutputArray(), f.as_raw__OutputArray(), per_view_errors.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, criteria.opencv_as_extern()) }.into_result() } /// Calibrates a stereo camera set up. This function finds the intrinsic parameters /// for each of the two cameras and the extrinsic parameters between the two cameras. /// /// ## Parameters /// * objectPoints: Vector of vectors of the calibration pattern points. The same structure as /// in @ref calibrateCamera. For each pattern view, both cameras need to see the same object /// points. Therefore, objectPoints.size(), imagePoints1.size(), and imagePoints2.size() need to be /// equal as well as objectPoints[i].size(), imagePoints1[i].size(), and imagePoints2[i].size() need to /// be equal for each i. /// * imagePoints1: Vector of vectors of the projections of the calibration pattern points, /// observed by the first camera. The same structure as in @ref calibrateCamera. /// * imagePoints2: Vector of vectors of the projections of the calibration pattern points, /// observed by the second camera. The same structure as in @ref calibrateCamera. /// * cameraMatrix1: Input/output camera intrinsic matrix for the first camera, the same as in /// @ref calibrateCamera. Furthermore, for the stereo case, additional flags may be used, see below. /// * distCoeffs1: Input/output vector of distortion coefficients, the same as in /// @ref calibrateCamera. /// * cameraMatrix2: Input/output second camera intrinsic matrix for the second camera. See description for /// cameraMatrix1. /// * distCoeffs2: Input/output lens distortion coefficients for the second camera. See /// description for distCoeffs1. /// * imageSize: Size of the image used only to initialize the camera intrinsic matrices. /// * R: Output rotation matrix. Together with the translation vector T, this matrix brings /// points given in the first camera's coordinate system to points in the second camera's /// coordinate system. In more technical terms, the tuple of R and T performs a change of basis /// from the first camera's coordinate system to the second camera's coordinate system. Due to its /// duality, this tuple is equivalent to the position of the first camera with respect to the /// second camera coordinate system. /// * T: Output translation vector, see description above. /// * E: Output essential matrix. /// * F: Output fundamental matrix. /// * perViewErrors: Output vector of the RMS re-projection error estimated for each pattern view. /// * flags: Different flags that may be zero or a combination of the following values: /// * @ref CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC Fix cameraMatrix? and distCoeffs? so that only R, T, E, and F /// matrices are estimated. /// * @ref CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS Optimize some or all of the intrinsic parameters /// according to the specified flags. Initial values are provided by the user. /// * @ref CALIB_USE_EXTRINSIC_GUESS R and T contain valid initial values that are optimized further. /// Otherwise R and T are initialized to the median value of the pattern views (each dimension separately). /// * @ref CALIB_FIX_PRINCIPAL_POINT Fix the principal points during the optimization. /// * @ref CALIB_FIX_FOCAL_LENGTH Fix  and  . /// * @ref CALIB_FIX_ASPECT_RATIO Optimize  . Fix the ratio  /// . /// * @ref CALIB_SAME_FOCAL_LENGTH Enforce  and  . /// * @ref CALIB_ZERO_TANGENT_DIST Set tangential distortion coefficients for each camera to /// zeros and fix there. /// * @ref CALIB_FIX_K1,..., @ref CALIB_FIX_K6 Do not change the corresponding radial /// distortion coefficient during the optimization. If @ref CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS is set, /// the coefficient from the supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0. /// * @ref CALIB_RATIONAL_MODEL Enable coefficients k4, k5, and k6. To provide the backward /// compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the calibration /// function use the rational model and return 8 coefficients. If the flag is not set, the /// function computes and returns only 5 distortion coefficients. /// * @ref CALIB_THIN_PRISM_MODEL Coefficients s1, s2, s3 and s4 are enabled. To provide the /// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the /// calibration function use the thin prism model and return 12 coefficients. If the flag is not /// set, the function computes and returns only 5 distortion coefficients. /// * @ref CALIB_FIX_S1_S2_S3_S4 The thin prism distortion coefficients are not changed during /// the optimization. If @ref CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS is set, the coefficient from the /// supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0. /// * @ref CALIB_TILTED_MODEL Coefficients tauX and tauY are enabled. To provide the /// backward compatibility, this extra flag should be explicitly specified to make the /// calibration function use the tilted sensor model and return 14 coefficients. If the flag is not /// set, the function computes and returns only 5 distortion coefficients. /// * @ref CALIB_FIX_TAUX_TAUY The coefficients of the tilted sensor model are not changed during /// the optimization. If @ref CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS is set, the coefficient from the /// supplied distCoeffs matrix is used. Otherwise, it is set to 0. /// * criteria: Termination criteria for the iterative optimization algorithm. /// /// The function estimates the transformation between two cameras making a stereo pair. If one computes /// the poses of an object relative to the first camera and to the second camera, /// ( , ) and (,), respectively, for a stereo camera where the /// relative position and orientation between the two cameras are fixed, then those poses definitely /// relate to each other. This means, if the relative position and orientation (,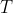) of the /// two cameras is known, it is possible to compute (,) when (,) is /// given. This is what the described function does. It computes (,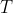) such that: /// ///  ///  /// /// Therefore, one can compute the coordinate representation of a 3D point for the second camera's /// coordinate system when given the point's coordinate representation in the first camera's coordinate /// system: /// ///  /// /// /// Optionally, it computes the essential matrix E: /// ///  /// /// where  are components of the translation vector 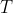 :  . /// And the function can also compute the fundamental matrix F: /// ///  /// /// Besides the stereo-related information, the function can also perform a full calibration of each of /// the two cameras. However, due to the high dimensionality of the parameter space and noise in the /// input data, the function can diverge from the correct solution. If the intrinsic parameters can be /// estimated with high accuracy for each of the cameras individually (for example, using /// calibrateCamera ), you are recommended to do so and then pass @ref CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC flag to the /// function along with the computed intrinsic parameters. Otherwise, if all the parameters are /// estimated at once, it makes sense to restrict some parameters, for example, pass /// @ref CALIB_SAME_FOCAL_LENGTH and @ref CALIB_ZERO_TANGENT_DIST flags, which is usually a /// reasonable assumption. /// /// Similarly to calibrateCamera, the function minimizes the total re-projection error for all the /// points in all the available views from both cameras. The function returns the final value of the /// re-projection error. /// /// ## Overloaded parameters /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * flags: CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC /// * criteria: TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS,30,1e-6) pub fn stereo_calibrate(object_points: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_points1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_points2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, camera_matrix1: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs1: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, camera_matrix2: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, dist_coeffs2: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, image_size: core::Size, r: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, t: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, e: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, f: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32, criteria: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<f64> { input_array_arg!(object_points); input_array_arg!(image_points1); input_array_arg!(image_points2); input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix1); input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs1); input_output_array_arg!(camera_matrix2); input_output_array_arg!(dist_coeffs2); output_array_arg!(r); output_array_arg!(t); output_array_arg!(e); output_array_arg!(f); unsafe { sys::cv_stereoCalibrate_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputOutputArrayR_Size_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_TermCriteria(object_points.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points1.as_raw__InputArray(), image_points2.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix1.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs1.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), camera_matrix2.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), dist_coeffs2.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), image_size.opencv_as_extern(), r.as_raw__OutputArray(), t.as_raw__OutputArray(), e.as_raw__OutputArray(), f.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, criteria.opencv_as_extern()) }.into_result() } /// Computes a rectification transform for an uncalibrated stereo camera. /// /// ## Parameters /// * points1: Array of feature points in the first image. /// * points2: The corresponding points in the second image. The same formats as in /// findFundamentalMat are supported. /// * F: Input fundamental matrix. It can be computed from the same set of point pairs using /// findFundamentalMat . /// * imgSize: Size of the image. /// * H1: Output rectification homography matrix for the first image. /// * H2: Output rectification homography matrix for the second image. /// * threshold: Optional threshold used to filter out the outliers. If the parameter is greater /// than zero, all the point pairs that do not comply with the epipolar geometry (that is, the points /// for which 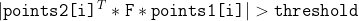 ) are /// rejected prior to computing the homographies. Otherwise, all the points are considered inliers. /// /// The function computes the rectification transformations without knowing intrinsic parameters of the /// cameras and their relative position in the space, which explains the suffix "uncalibrated". Another /// related difference from stereoRectify is that the function outputs not the rectification /// transformations in the object (3D) space, but the planar perspective transformations encoded by the /// homography matrices H1 and H2 . The function implements the algorithm [Hartley99](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Hartley99) . /// /// /// Note: /// While the algorithm does not need to know the intrinsic parameters of the cameras, it heavily /// depends on the epipolar geometry. Therefore, if the camera lenses have a significant distortion, /// it would be better to correct it before computing the fundamental matrix and calling this /// function. For example, distortion coefficients can be estimated for each head of stereo camera /// separately by using calibrateCamera . Then, the images can be corrected using undistort , or /// just the point coordinates can be corrected with undistortPoints . /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * threshold: 5 pub fn stereo_rectify_uncalibrated(points1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, points2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, f: &dyn core::ToInputArray, img_size: core::Size, h1: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, h2: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, threshold: f64) -> Result<bool> { input_array_arg!(points1); input_array_arg!(points2); input_array_arg!(f); output_array_arg!(h1); output_array_arg!(h2); unsafe { sys::cv_stereoRectifyUncalibrated_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double(points1.as_raw__InputArray(), points2.as_raw__InputArray(), f.as_raw__InputArray(), img_size.opencv_as_extern(), h1.as_raw__OutputArray(), h2.as_raw__OutputArray(), threshold) }.into_result() } /// Computes rectification transforms for each head of a calibrated stereo camera. /// /// ## Parameters /// * cameraMatrix1: First camera intrinsic matrix. /// * distCoeffs1: First camera distortion parameters. /// * cameraMatrix2: Second camera intrinsic matrix. /// * distCoeffs2: Second camera distortion parameters. /// * imageSize: Size of the image used for stereo calibration. /// * R: Rotation matrix from the coordinate system of the first camera to the second camera, /// see @ref stereoCalibrate. /// * T: Translation vector from the coordinate system of the first camera to the second camera, /// see @ref stereoCalibrate. /// * R1: Output 3x3 rectification transform (rotation matrix) for the first camera. This matrix /// brings points given in the unrectified first camera's coordinate system to points in the rectified /// first camera's coordinate system. In more technical terms, it performs a change of basis from the /// unrectified first camera's coordinate system to the rectified first camera's coordinate system. /// * R2: Output 3x3 rectification transform (rotation matrix) for the second camera. This matrix /// brings points given in the unrectified second camera's coordinate system to points in the rectified /// second camera's coordinate system. In more technical terms, it performs a change of basis from the /// unrectified second camera's coordinate system to the rectified second camera's coordinate system. /// * P1: Output 3x4 projection matrix in the new (rectified) coordinate systems for the first /// camera, i.e. it projects points given in the rectified first camera coordinate system into the /// rectified first camera's image. /// * P2: Output 3x4 projection matrix in the new (rectified) coordinate systems for the second /// camera, i.e. it projects points given in the rectified first camera coordinate system into the /// rectified second camera's image. /// * Q: Output 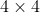 disparity-to-depth mapping matrix (see @ref reprojectImageTo3D). /// * flags: Operation flags that may be zero or @ref CALIB_ZERO_DISPARITY . If the flag is set, /// the function makes the principal points of each camera have the same pixel coordinates in the /// rectified views. And if the flag is not set, the function may still shift the images in the /// horizontal or vertical direction (depending on the orientation of epipolar lines) to maximize the /// useful image area. /// * alpha: Free scaling parameter. If it is -1 or absent, the function performs the default /// scaling. Otherwise, the parameter should be between 0 and 1. alpha=0 means that the rectified /// images are zoomed and shifted so that only valid pixels are visible (no black areas after /// rectification). alpha=1 means that the rectified image is decimated and shifted so that all the /// pixels from the original images from the cameras are retained in the rectified images (no source /// image pixels are lost). Any intermediate value yields an intermediate result between /// those two extreme cases. /// * newImageSize: New image resolution after rectification. The same size should be passed to /// initUndistortRectifyMap (see the stereo_calib.cpp sample in OpenCV samples directory). When (0,0) /// is passed (default), it is set to the original imageSize . Setting it to a larger value can help you /// preserve details in the original image, especially when there is a big radial distortion. /// * validPixROI1: Optional output rectangles inside the rectified images where all the pixels /// are valid. If alpha=0 , the ROIs cover the whole images. Otherwise, they are likely to be smaller /// (see the picture below). /// * validPixROI2: Optional output rectangles inside the rectified images where all the pixels /// are valid. If alpha=0 , the ROIs cover the whole images. Otherwise, they are likely to be smaller /// (see the picture below). /// /// The function computes the rotation matrices for each camera that (virtually) make both camera image /// planes the same plane. Consequently, this makes all the epipolar lines parallel and thus simplifies /// the dense stereo correspondence problem. The function takes the matrices computed by stereoCalibrate /// as input. As output, it provides two rotation matrices and also two projection matrices in the new /// coordinates. The function distinguishes the following two cases: /// /// * **Horizontal stereo**: the first and the second camera views are shifted relative to each other /// mainly along the x-axis (with possible small vertical shift). In the rectified images, the /// corresponding epipolar lines in the left and right cameras are horizontal and have the same /// y-coordinate. P1 and P2 look like: /// ///  /// ///  /// /// where  is a horizontal shift between the cameras and  if /// @ref CALIB_ZERO_DISPARITY is set. /// /// * **Vertical stereo**: the first and the second camera views are shifted relative to each other /// mainly in the vertical direction (and probably a bit in the horizontal direction too). The epipolar /// lines in the rectified images are vertical and have the same x-coordinate. P1 and P2 look like: /// ///  /// ///  /// /// where  is a vertical shift between the cameras and  if /// @ref CALIB_ZERO_DISPARITY is set. /// /// As you can see, the first three columns of P1 and P2 will effectively be the new "rectified" camera /// matrices. The matrices, together with R1 and R2 , can then be passed to initUndistortRectifyMap to /// initialize the rectification map for each camera. /// /// See below the screenshot from the stereo_calib.cpp sample. Some red horizontal lines pass through /// the corresponding image regions. This means that the images are well rectified, which is what most /// stereo correspondence algorithms rely on. The green rectangles are roi1 and roi2 . You see that /// their interiors are all valid pixels. /// ///  /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * flags: CALIB_ZERO_DISPARITY /// * alpha: -1 /// * new_image_size: Size() /// * valid_pix_roi1: 0 /// * valid_pix_roi2: 0 pub fn stereo_rectify(camera_matrix1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dist_coeffs1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, camera_matrix2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dist_coeffs2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, image_size: core::Size, r: &dyn core::ToInputArray, t: &dyn core::ToInputArray, r1: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, r2: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, p1: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, p2: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, q: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32, alpha: f64, new_image_size: core::Size, valid_pix_roi1: &mut core::Rect, valid_pix_roi2: &mut core::Rect) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(camera_matrix1); input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs1); input_array_arg!(camera_matrix2); input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs2); input_array_arg!(r); input_array_arg!(t); output_array_arg!(r1); output_array_arg!(r2); output_array_arg!(p1); output_array_arg!(p2); output_array_arg!(q); unsafe { sys::cv_stereoRectify_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Size_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_double_Size_RectX_RectX(camera_matrix1.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs1.as_raw__InputArray(), camera_matrix2.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs2.as_raw__InputArray(), image_size.opencv_as_extern(), r.as_raw__InputArray(), t.as_raw__InputArray(), r1.as_raw__OutputArray(), r2.as_raw__OutputArray(), p1.as_raw__OutputArray(), p2.as_raw__OutputArray(), q.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, alpha, new_image_size.opencv_as_extern(), valid_pix_roi1, valid_pix_roi2) }.into_result() } /// This function reconstructs 3-dimensional points (in homogeneous coordinates) by using /// their observations with a stereo camera. /// /// ## Parameters /// * projMatr1: 3x4 projection matrix of the first camera, i.e. this matrix projects 3D points /// given in the world's coordinate system into the first image. /// * projMatr2: 3x4 projection matrix of the second camera, i.e. this matrix projects 3D points /// given in the world's coordinate system into the second image. /// * projPoints1: 2xN array of feature points in the first image. In the case of the c++ version, /// it can be also a vector of feature points or two-channel matrix of size 1xN or Nx1. /// * projPoints2: 2xN array of corresponding points in the second image. In the case of the c++ /// version, it can be also a vector of feature points or two-channel matrix of size 1xN or Nx1. /// * points4D: 4xN array of reconstructed points in homogeneous coordinates. These points are /// returned in the world's coordinate system. /// /// /// Note: /// Keep in mind that all input data should be of float type in order for this function to work. /// /// /// Note: /// If the projection matrices from @ref stereoRectify are used, then the returned points are /// represented in the first camera's rectified coordinate system. /// ## See also /// reprojectImageTo3D pub fn triangulate_points(proj_matr1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, proj_matr2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, proj_points1: &dyn core::ToInputArray, proj_points2: &dyn core::ToInputArray, points4_d: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(proj_matr1); input_array_arg!(proj_matr2); input_array_arg!(proj_points1); input_array_arg!(proj_points2); output_array_arg!(points4_d); unsafe { sys::cv_triangulatePoints_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(proj_matr1.as_raw__InputArray(), proj_matr2.as_raw__InputArray(), proj_points1.as_raw__InputArray(), proj_points2.as_raw__InputArray(), points4_d.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Computes the ideal point coordinates from the observed point coordinates. /// /// The function is similar to #undistort and #initUndistortRectifyMap but it operates on a /// sparse set of points instead of a raster image. Also the function performs a reverse transformation /// to projectPoints. In case of a 3D object, it does not reconstruct its 3D coordinates, but for a /// planar object, it does, up to a translation vector, if the proper R is specified. /// /// For each observed point coordinate 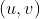 the function computes: ///  /// /// where *undistort* is an approximate iterative algorithm that estimates the normalized original /// point coordinates out of the normalized distorted point coordinates ("normalized" means that the /// coordinates do not depend on the camera matrix). /// /// The function can be used for both a stereo camera head or a monocular camera (when R is empty). /// ## Parameters /// * src: Observed point coordinates, 2xN/Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel (CV_32FC2 or CV_64FC2) (or /// vector\<Point2f\> ). /// * dst: Output ideal point coordinates (1xN/Nx1 2-channel or vector\<Point2f\> ) after undistortion and reverse perspective /// transformation. If matrix P is identity or omitted, dst will contain normalized point coordinates. /// * cameraMatrix: Camera matrix  . /// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients ///  /// of 4, 5, 8, 12 or 14 elements. If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed. /// * R: Rectification transformation in the object space (3x3 matrix). R1 or R2 computed by /// #stereoRectify can be passed here. If the matrix is empty, the identity transformation is used. /// * P: New camera matrix (3x3) or new projection matrix (3x4) . P1 or P2 computed by /// #stereoRectify can be passed here. If the matrix is empty, the identity new camera matrix is used. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * r: noArray() /// * p: noArray() pub fn undistort_points(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, camera_matrix: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &dyn core::ToInputArray, r: &dyn core::ToInputArray, p: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(src); output_array_arg!(dst); input_array_arg!(camera_matrix); input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs); input_array_arg!(r); input_array_arg!(p); unsafe { sys::cv_undistortPoints_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), r.as_raw__InputArray(), p.as_raw__InputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Computes the ideal point coordinates from the observed point coordinates. /// /// The function is similar to #undistort and #initUndistortRectifyMap but it operates on a /// sparse set of points instead of a raster image. Also the function performs a reverse transformation /// to projectPoints. In case of a 3D object, it does not reconstruct its 3D coordinates, but for a /// planar object, it does, up to a translation vector, if the proper R is specified. /// /// For each observed point coordinate 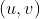 the function computes: ///  /// /// where *undistort* is an approximate iterative algorithm that estimates the normalized original /// point coordinates out of the normalized distorted point coordinates ("normalized" means that the /// coordinates do not depend on the camera matrix). /// /// The function can be used for both a stereo camera head or a monocular camera (when R is empty). /// ## Parameters /// * src: Observed point coordinates, 2xN/Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel (CV_32FC2 or CV_64FC2) (or /// vector\<Point2f\> ). /// * dst: Output ideal point coordinates (1xN/Nx1 2-channel or vector\<Point2f\> ) after undistortion and reverse perspective /// transformation. If matrix P is identity or omitted, dst will contain normalized point coordinates. /// * cameraMatrix: Camera matrix  . /// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients ///  /// of 4, 5, 8, 12 or 14 elements. If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed. /// * R: Rectification transformation in the object space (3x3 matrix). R1 or R2 computed by /// #stereoRectify can be passed here. If the matrix is empty, the identity transformation is used. /// * P: New camera matrix (3x3) or new projection matrix (3x4) . P1 or P2 computed by /// #stereoRectify can be passed here. If the matrix is empty, the identity new camera matrix is used. /// /// ## Overloaded parameters /// /// /// Note: Default version of #undistortPoints does 5 iterations to compute undistorted points. pub fn undistort_points_iter(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, camera_matrix: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &dyn core::ToInputArray, r: &dyn core::ToInputArray, p: &dyn core::ToInputArray, criteria: core::TermCriteria) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(src); output_array_arg!(dst); input_array_arg!(camera_matrix); input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs); input_array_arg!(r); input_array_arg!(p); unsafe { sys::cv_undistortPoints_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_TermCriteria(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), r.as_raw__InputArray(), p.as_raw__InputArray(), criteria.opencv_as_extern()) }.into_result() } /// Transforms an image to compensate for lens distortion. /// /// The function transforms an image to compensate radial and tangential lens distortion. /// /// The function is simply a combination of #initUndistortRectifyMap (with unity R ) and #remap /// (with bilinear interpolation). See the former function for details of the transformation being /// performed. /// /// Those pixels in the destination image, for which there is no correspondent pixels in the source /// image, are filled with zeros (black color). /// /// A particular subset of the source image that will be visible in the corrected image can be regulated /// by newCameraMatrix. You can use #getOptimalNewCameraMatrix to compute the appropriate /// newCameraMatrix depending on your requirements. /// /// The camera matrix and the distortion parameters can be determined using #calibrateCamera. If /// the resolution of images is different from the resolution used at the calibration stage,  and  need to be scaled accordingly, while the distortion coefficients remain /// the same. /// /// ## Parameters /// * src: Input (distorted) image. /// * dst: Output (corrected) image that has the same size and type as src . /// * cameraMatrix: Input camera matrix 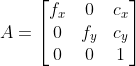 . /// * distCoeffs: Input vector of distortion coefficients ///  /// of 4, 5, 8, 12 or 14 elements. If the vector is NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed. /// * newCameraMatrix: Camera matrix of the distorted image. By default, it is the same as /// cameraMatrix but you may additionally scale and shift the result by using a different matrix. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * new_camera_matrix: noArray() pub fn undistort(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, camera_matrix: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dist_coeffs: &dyn core::ToInputArray, new_camera_matrix: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(src); output_array_arg!(dst); input_array_arg!(camera_matrix); input_array_arg!(dist_coeffs); input_array_arg!(new_camera_matrix); unsafe { sys::cv_undistort_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray(), dist_coeffs.as_raw__InputArray(), new_camera_matrix.as_raw__InputArray()) }.into_result() } /// validates disparity using the left-right check. The matrix "cost" should be computed by the stereo correspondence algorithm /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * disp12_max_disp: 1 pub fn validate_disparity(disparity: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray, cost: &dyn core::ToInputArray, min_disparity: i32, number_of_disparities: i32, disp12_max_disp: i32) -> Result<()> { input_output_array_arg!(disparity); input_array_arg!(cost); unsafe { sys::cv_validateDisparity_const__InputOutputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_int_int_int(disparity.as_raw__InputOutputArray(), cost.as_raw__InputArray(), min_disparity, number_of_disparities, disp12_max_disp) }.into_result() } #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub struct CirclesGridFinderParameters { pub density_neighborhood_size: core::Size2f, pub min_density: f32, pub kmeans_attempts: i32, pub min_distance_to_add_keypoint: i32, pub keypoint_scale: i32, pub min_graph_confidence: f32, pub vertex_gain: f32, pub vertex_penalty: f32, pub existing_vertex_gain: f32, pub edge_gain: f32, pub edge_penalty: f32, pub convex_hull_factor: f32, pub min_rng_edge_switch_dist: f32, pub grid_type: crate::calib3d::CirclesGridFinderParameters_GridType, /// Distance between two adjacent points. Used by CALIB_CB_CLUSTERING. pub square_size: f32, /// Max deviation from prediction. Used by CALIB_CB_CLUSTERING. pub max_rectified_distance: f32, } opencv_type_simple! { crate::calib3d::CirclesGridFinderParameters } impl CirclesGridFinderParameters { pub fn default() -> Result<crate::calib3d::CirclesGridFinderParameters> { unsafe { sys::cv_CirclesGridFinderParameters_CirclesGridFinderParameters() }.into_result() } } /// Levenberg-Marquardt solver. Starting with the specified vector of parameters it /// optimizes the target vector criteria "err" /// (finds local minima of each target vector component absolute value). /// /// When needed, it calls user-provided callback. pub trait LMSolver: core::AlgorithmTrait { fn as_raw_LMSolver(&self) -> *const c_void; fn as_raw_mut_LMSolver(&mut self) -> *mut c_void; /// Runs Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm using the passed vector of parameters as the start point. /// The final vector of parameters (whether the algorithm converged or not) is stored at the same /// vector. The method returns the number of iterations used. If it's equal to the previously specified /// maxIters, there is a big chance the algorithm did not converge. /// /// ## Parameters /// * param: initial/final vector of parameters. /// /// Note that the dimensionality of parameter space is defined by the size of param vector, /// and the dimensionality of optimized criteria is defined by the size of err vector /// computed by the callback. fn run(&self, param: &mut dyn core::ToInputOutputArray) -> Result<i32> { input_output_array_arg!(param); unsafe { sys::cv_LMSolver_run_const_const__InputOutputArrayR(self.as_raw_LMSolver(), param.as_raw__InputOutputArray()) }.into_result() } /// Sets the maximum number of iterations /// ## Parameters /// * maxIters: the number of iterations fn set_max_iters(&mut self, max_iters: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_LMSolver_setMaxIters_int(self.as_raw_mut_LMSolver(), max_iters) }.into_result() } /// Retrieves the current maximum number of iterations fn get_max_iters(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_LMSolver_getMaxIters_const(self.as_raw_LMSolver()) }.into_result() } } impl dyn LMSolver + '_ { /// Creates Levenberg-Marquard solver /// /// ## Parameters /// * cb: callback /// * maxIters: maximum number of iterations that can be further /// modified using setMaxIters() method. pub fn create(cb: &core::Ptr::<dyn crate::calib3d::LMSolver_Callback>, max_iters: i32) -> Result<core::Ptr::<dyn crate::calib3d::LMSolver>> { unsafe { sys::cv_LMSolver_create_const_Ptr_Callback_R_int(cb.as_raw_PtrOfLMSolver_Callback(), max_iters) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::calib3d::LMSolver>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } pub fn create_ext(cb: &core::Ptr::<dyn crate::calib3d::LMSolver_Callback>, max_iters: i32, eps: f64) -> Result<core::Ptr::<dyn crate::calib3d::LMSolver>> { unsafe { sys::cv_LMSolver_create_const_Ptr_Callback_R_int_double(cb.as_raw_PtrOfLMSolver_Callback(), max_iters, eps) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::calib3d::LMSolver>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } } pub trait LMSolver_Callback { fn as_raw_LMSolver_Callback(&self) -> *const c_void; fn as_raw_mut_LMSolver_Callback(&mut self) -> *mut c_void; /// computes error and Jacobian for the specified vector of parameters /// /// ## Parameters /// * param: the current vector of parameters /// * err: output vector of errors: err_i = actual_f_i - ideal_f_i /// * J: output Jacobian: J_ij = d(err_i)/d(param_j) /// /// when J=noArray(), it means that it does not need to be computed. /// Dimensionality of error vector and param vector can be different. /// The callback should explicitly allocate (with "create" method) each output array /// (unless it's noArray()). fn compute(&self, param: &dyn core::ToInputArray, err: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, j: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<bool> { input_array_arg!(param); output_array_arg!(err); output_array_arg!(j); unsafe { sys::cv_LMSolver_Callback_compute_const_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_LMSolver_Callback(), param.as_raw__InputArray(), err.as_raw__OutputArray(), j.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } } /// Class for computing stereo correspondence using the block matching algorithm, introduced and /// contributed to OpenCV by K. Konolige. pub trait StereoBM: crate::calib3d::StereoMatcher { fn as_raw_StereoBM(&self) -> *const c_void; fn as_raw_mut_StereoBM(&mut self) -> *mut c_void; fn get_pre_filter_type(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_getPreFilterType_const(self.as_raw_StereoBM()) }.into_result() } fn set_pre_filter_type(&mut self, pre_filter_type: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_setPreFilterType_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoBM(), pre_filter_type) }.into_result() } fn get_pre_filter_size(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_getPreFilterSize_const(self.as_raw_StereoBM()) }.into_result() } fn set_pre_filter_size(&mut self, pre_filter_size: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_setPreFilterSize_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoBM(), pre_filter_size) }.into_result() } fn get_pre_filter_cap(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_getPreFilterCap_const(self.as_raw_StereoBM()) }.into_result() } fn set_pre_filter_cap(&mut self, pre_filter_cap: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_setPreFilterCap_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoBM(), pre_filter_cap) }.into_result() } fn get_texture_threshold(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_getTextureThreshold_const(self.as_raw_StereoBM()) }.into_result() } fn set_texture_threshold(&mut self, texture_threshold: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_setTextureThreshold_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoBM(), texture_threshold) }.into_result() } fn get_uniqueness_ratio(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_getUniquenessRatio_const(self.as_raw_StereoBM()) }.into_result() } fn set_uniqueness_ratio(&mut self, uniqueness_ratio: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_setUniquenessRatio_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoBM(), uniqueness_ratio) }.into_result() } fn get_smaller_block_size(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_getSmallerBlockSize_const(self.as_raw_StereoBM()) }.into_result() } fn set_smaller_block_size(&mut self, block_size: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_setSmallerBlockSize_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoBM(), block_size) }.into_result() } fn get_roi1(&self) -> Result<core::Rect> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_getROI1_const(self.as_raw_StereoBM()) }.into_result() } fn set_roi1(&mut self, roi1: core::Rect) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_setROI1_Rect(self.as_raw_mut_StereoBM(), roi1.opencv_as_extern()) }.into_result() } fn get_roi2(&self) -> Result<core::Rect> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_getROI2_const(self.as_raw_StereoBM()) }.into_result() } fn set_roi2(&mut self, roi2: core::Rect) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_setROI2_Rect(self.as_raw_mut_StereoBM(), roi2.opencv_as_extern()) }.into_result() } } impl dyn StereoBM + '_ { /// Creates StereoBM object /// /// ## Parameters /// * numDisparities: the disparity search range. For each pixel algorithm will find the best /// disparity from 0 (default minimum disparity) to numDisparities. The search range can then be /// shifted by changing the minimum disparity. /// * blockSize: the linear size of the blocks compared by the algorithm. The size should be odd /// (as the block is centered at the current pixel). Larger block size implies smoother, though less /// accurate disparity map. Smaller block size gives more detailed disparity map, but there is higher /// chance for algorithm to find a wrong correspondence. /// /// The function create StereoBM object. You can then call StereoBM::compute() to compute disparity for /// a specific stereo pair. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * num_disparities: 0 /// * block_size: 21 pub fn create(num_disparities: i32, block_size: i32) -> Result<core::Ptr::<dyn crate::calib3d::StereoBM>> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoBM_create_int_int(num_disparities, block_size) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::calib3d::StereoBM>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } } /// The base class for stereo correspondence algorithms. pub trait StereoMatcher: core::AlgorithmTrait { fn as_raw_StereoMatcher(&self) -> *const c_void; fn as_raw_mut_StereoMatcher(&mut self) -> *mut c_void; /// Computes disparity map for the specified stereo pair /// /// ## Parameters /// * left: Left 8-bit single-channel image. /// * right: Right image of the same size and the same type as the left one. /// * disparity: Output disparity map. It has the same size as the input images. Some algorithms, /// like StereoBM or StereoSGBM compute 16-bit fixed-point disparity map (where each disparity value /// has 4 fractional bits), whereas other algorithms output 32-bit floating-point disparity map. fn compute(&mut self, left: &dyn core::ToInputArray, right: &dyn core::ToInputArray, disparity: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> { input_array_arg!(left); input_array_arg!(right); output_array_arg!(disparity); unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_compute_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_StereoMatcher(), left.as_raw__InputArray(), right.as_raw__InputArray(), disparity.as_raw__OutputArray()) }.into_result() } fn get_min_disparity(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_getMinDisparity_const(self.as_raw_StereoMatcher()) }.into_result() } fn set_min_disparity(&mut self, min_disparity: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_setMinDisparity_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoMatcher(), min_disparity) }.into_result() } fn get_num_disparities(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_getNumDisparities_const(self.as_raw_StereoMatcher()) }.into_result() } fn set_num_disparities(&mut self, num_disparities: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_setNumDisparities_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoMatcher(), num_disparities) }.into_result() } fn get_block_size(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_getBlockSize_const(self.as_raw_StereoMatcher()) }.into_result() } fn set_block_size(&mut self, block_size: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_setBlockSize_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoMatcher(), block_size) }.into_result() } fn get_speckle_window_size(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_getSpeckleWindowSize_const(self.as_raw_StereoMatcher()) }.into_result() } fn set_speckle_window_size(&mut self, speckle_window_size: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_setSpeckleWindowSize_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoMatcher(), speckle_window_size) }.into_result() } fn get_speckle_range(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_getSpeckleRange_const(self.as_raw_StereoMatcher()) }.into_result() } fn set_speckle_range(&mut self, speckle_range: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_setSpeckleRange_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoMatcher(), speckle_range) }.into_result() } fn get_disp12_max_diff(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_getDisp12MaxDiff_const(self.as_raw_StereoMatcher()) }.into_result() } fn set_disp12_max_diff(&mut self, disp12_max_diff: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoMatcher_setDisp12MaxDiff_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoMatcher(), disp12_max_diff) }.into_result() } } /// The class implements the modified H. Hirschmuller algorithm [HH08](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_HH08) that differs from the original /// one as follows: /// /// * By default, the algorithm is single-pass, which means that you consider only 5 directions /// instead of 8. Set mode=StereoSGBM::MODE_HH in createStereoSGBM to run the full variant of the /// algorithm but beware that it may consume a lot of memory. /// * The algorithm matches blocks, not individual pixels. Though, setting blockSize=1 reduces the /// blocks to single pixels. /// * Mutual information cost function is not implemented. Instead, a simpler Birchfield-Tomasi /// sub-pixel metric from [BT98](https://docs.opencv.org/4.3.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_BT98) is used. Though, the color images are supported as well. /// * Some pre- and post- processing steps from K. Konolige algorithm StereoBM are included, for /// example: pre-filtering (StereoBM::PREFILTER_XSOBEL type) and post-filtering (uniqueness /// check, quadratic interpolation and speckle filtering). /// /// /// Note: /// * (Python) An example illustrating the use of the StereoSGBM matching algorithm can be found /// at opencv_source_code/samples/python/stereo_match.py pub trait StereoSGBM: crate::calib3d::StereoMatcher { fn as_raw_StereoSGBM(&self) -> *const c_void; fn as_raw_mut_StereoSGBM(&mut self) -> *mut c_void; fn get_pre_filter_cap(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoSGBM_getPreFilterCap_const(self.as_raw_StereoSGBM()) }.into_result() } fn set_pre_filter_cap(&mut self, pre_filter_cap: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoSGBM_setPreFilterCap_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoSGBM(), pre_filter_cap) }.into_result() } fn get_uniqueness_ratio(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoSGBM_getUniquenessRatio_const(self.as_raw_StereoSGBM()) }.into_result() } fn set_uniqueness_ratio(&mut self, uniqueness_ratio: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoSGBM_setUniquenessRatio_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoSGBM(), uniqueness_ratio) }.into_result() } fn get_p1(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoSGBM_getP1_const(self.as_raw_StereoSGBM()) }.into_result() } fn set_p1(&mut self, p1: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoSGBM_setP1_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoSGBM(), p1) }.into_result() } fn get_p2(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoSGBM_getP2_const(self.as_raw_StereoSGBM()) }.into_result() } fn set_p2(&mut self, p2: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoSGBM_setP2_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoSGBM(), p2) }.into_result() } fn get_mode(&self) -> Result<i32> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoSGBM_getMode_const(self.as_raw_StereoSGBM()) }.into_result() } fn set_mode(&mut self, mode: i32) -> Result<()> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoSGBM_setMode_int(self.as_raw_mut_StereoSGBM(), mode) }.into_result() } } impl dyn StereoSGBM + '_ { /// Creates StereoSGBM object /// /// ## Parameters /// * minDisparity: Minimum possible disparity value. Normally, it is zero but sometimes /// rectification algorithms can shift images, so this parameter needs to be adjusted accordingly. /// * numDisparities: Maximum disparity minus minimum disparity. The value is always greater than /// zero. In the current implementation, this parameter must be divisible by 16. /// * blockSize: Matched block size. It must be an odd number \>=1 . Normally, it should be /// somewhere in the 3..11 range. /// * P1: The first parameter controlling the disparity smoothness. See below. /// * P2: The second parameter controlling the disparity smoothness. The larger the values are, /// the smoother the disparity is. P1 is the penalty on the disparity change by plus or minus 1 /// between neighbor pixels. P2 is the penalty on the disparity change by more than 1 between neighbor /// pixels. The algorithm requires P2 \> P1 . See stereo_match.cpp sample where some reasonably good /// P1 and P2 values are shown (like 8\*number_of_image_channels\*blockSize\*blockSize and /// 32\*number_of_image_channels\*blockSize\*blockSize , respectively). /// * disp12MaxDiff: Maximum allowed difference (in integer pixel units) in the left-right /// disparity check. Set it to a non-positive value to disable the check. /// * preFilterCap: Truncation value for the prefiltered image pixels. The algorithm first /// computes x-derivative at each pixel and clips its value by [-preFilterCap, preFilterCap] interval. /// The result values are passed to the Birchfield-Tomasi pixel cost function. /// * uniquenessRatio: Margin in percentage by which the best (minimum) computed cost function /// value should "win" the second best value to consider the found match correct. Normally, a value /// within the 5-15 range is good enough. /// * speckleWindowSize: Maximum size of smooth disparity regions to consider their noise speckles /// and invalidate. Set it to 0 to disable speckle filtering. Otherwise, set it somewhere in the /// 50-200 range. /// * speckleRange: Maximum disparity variation within each connected component. If you do speckle /// filtering, set the parameter to a positive value, it will be implicitly multiplied by 16. /// Normally, 1 or 2 is good enough. /// * mode: Set it to StereoSGBM::MODE_HH to run the full-scale two-pass dynamic programming /// algorithm. It will consume O(W\*H\*numDisparities) bytes, which is large for 640x480 stereo and /// huge for HD-size pictures. By default, it is set to false . /// /// The first constructor initializes StereoSGBM with all the default parameters. So, you only have to /// set StereoSGBM::numDisparities at minimum. The second constructor enables you to set each parameter /// to a custom value. /// /// ## C++ default parameters /// * min_disparity: 0 /// * num_disparities: 16 /// * block_size: 3 /// * p1: 0 /// * p2: 0 /// * disp12_max_diff: 0 /// * pre_filter_cap: 0 /// * uniqueness_ratio: 0 /// * speckle_window_size: 0 /// * speckle_range: 0 /// * mode: StereoSGBM::MODE_SGBM pub fn create(min_disparity: i32, num_disparities: i32, block_size: i32, p1: i32, p2: i32, disp12_max_diff: i32, pre_filter_cap: i32, uniqueness_ratio: i32, speckle_window_size: i32, speckle_range: i32, mode: i32) -> Result<core::Ptr::<dyn crate::calib3d::StereoSGBM>> { unsafe { sys::cv_StereoSGBM_create_int_int_int_int_int_int_int_int_int_int_int(min_disparity, num_disparities, block_size, p1, p2, disp12_max_diff, pre_filter_cap, uniqueness_ratio, speckle_window_size, speckle_range, mode) }.into_result().map(|r| unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::calib3d::StereoSGBM>::opencv_from_extern(r) } ) } } #[repr(C)] #[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq)] pub struct UsacParams { pub confidence: f64, pub is_parallel: bool, pub lo_iterations: i32, pub lo_method: crate::calib3d::LocalOptimMethod, pub lo_sample_size: i32, pub max_iterations: i32, pub neighbors_search: crate::calib3d::NeighborSearchMethod, pub random_generator_state: i32, pub sampler: crate::calib3d::SamplingMethod, pub score: crate::calib3d::ScoreMethod, pub threshold: f64, } opencv_type_simple! { crate::calib3d::UsacParams } impl UsacParams { pub fn default() -> Result<crate::calib3d::UsacParams> { unsafe { sys::cv_UsacParams_UsacParams() }.into_result() } }