#[repr(u8)]pub enum Mix {
Show 17 variants
Normal = 0,
Multiply = 1,
Screen = 2,
Overlay = 3,
Darken = 4,
Lighten = 5,
ColorDodge = 6,
ColorBurn = 7,
HardLight = 8,
SoftLight = 9,
Difference = 10,
Exclusion = 11,
Hue = 12,
Saturation = 13,
Color = 14,
Luminosity = 15,
Clip = 128,
}Expand description
Defines the color mixing function for a blend operation.
See W3C’s Compositing and Blending Level 1 draft for more details. Illustrations fall under the W3C open license.
Variants§
Normal = 0
Default attribute which specifies no blending. The blending formula simply selects the source color.

Multiply = 1
Source color is multiplied by the destination color and replaces the destination.
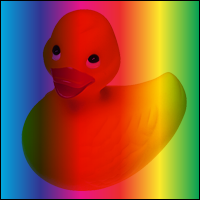
Screen = 2
Multiplies the complements of the backdrop and source color values, then complements the result.

Overlay = 3
Multiplies or screens the colors, depending on the backdrop color value.
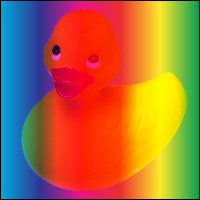
Darken = 4
Selects the darker of the backdrop and source colors.
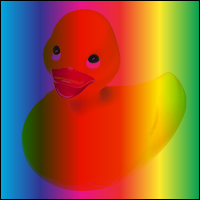
Lighten = 5
Selects the lighter of the backdrop and source colors.

ColorDodge = 6
Brightens the backdrop color to reflect the source color. Painting with black produces no change.

ColorBurn = 7
Darkens the backdrop color to reflect the source color. Painting with white produces no change.
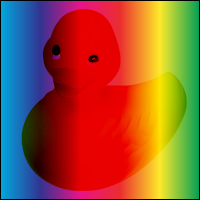
HardLight = 8
Multiplies or screens the colors, depending on the source color value. The effect is similar to shining a harsh spotlight on the backdrop.

SoftLight = 9
Darkens or lightens the colors, depending on the source color value. The effect is similar to shining a diffused spotlight on the backdrop.
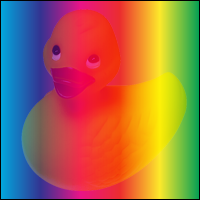
Difference = 10
Subtracts the darker of the two constituent colors from the lighter color.

Exclusion = 11
Produces an effect similar to that of the Difference mode but lower in contrast. Painting
with white inverts the backdrop color; painting with black produces no change.

Hue = 12
Creates a color with the hue of the source color and the saturation and luminosity of the backdrop color.

Saturation = 13
Creates a color with the saturation of the source color and the hue and luminosity of the backdrop color. Painting with this mode in an area of the backdrop that is a pure gray (no saturation) produces no change.
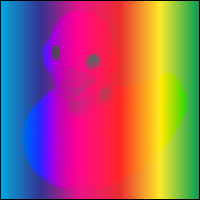
Color = 14
Creates a color with the hue and saturation of the source color and the luminosity of the backdrop color. This preserves the gray levels of the backdrop and is useful for coloring monochrome images or tinting color images.
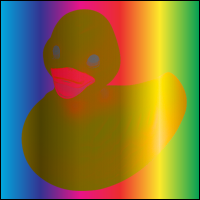
Luminosity = 15
Creates a color with the luminosity of the source color and the hue and saturation of the
backdrop color. This produces an inverse effect to that of the Color mode.

Clip = 128
push_clip_layer instead.Clip was similar to Normal, but was optimised for clipping (by avoiding
blending in areas where there was no clip path).
This optimisation is however unrelated to mixing, and so will no longer be indicated with this enum.
If you were using this with Vello, you should use the (new) push_clip_layer function instead.
Trait Implementations§
impl Copy for Mix
impl Eq for Mix
impl StructuralPartialEq for Mix
Auto Trait Implementations§
impl Freeze for Mix
impl RefUnwindSafe for Mix
impl Send for Mix
impl Sync for Mix
impl Unpin for Mix
impl UnwindSafe for Mix
Blanket Implementations§
Source§impl<T> BorrowMut<T> for Twhere
T: ?Sized,
impl<T> BorrowMut<T> for Twhere
T: ?Sized,
Source§fn borrow_mut(&mut self) -> &mut T
fn borrow_mut(&mut self) -> &mut T
Source§impl<T> CloneToUninit for Twhere
T: Clone,
impl<T> CloneToUninit for Twhere
T: Clone,
Source§impl<T> Downcast for Twhere
T: Any,
impl<T> Downcast for Twhere
T: Any,
Source§fn into_any(self: Box<T>) -> Box<dyn Any>
fn into_any(self: Box<T>) -> Box<dyn Any>
Box<dyn Trait> (where Trait: Downcast) to Box<dyn Any>. Box<dyn Any> can
then be further downcast into Box<ConcreteType> where ConcreteType implements Trait.Source§fn into_any_rc(self: Rc<T>) -> Rc<dyn Any>
fn into_any_rc(self: Rc<T>) -> Rc<dyn Any>
Rc<Trait> (where Trait: Downcast) to Rc<Any>. Rc<Any> can then be
further downcast into Rc<ConcreteType> where ConcreteType implements Trait.Source§fn as_any(&self) -> &(dyn Any + 'static)
fn as_any(&self) -> &(dyn Any + 'static)
&Trait (where Trait: Downcast) to &Any. This is needed since Rust cannot
generate &Any’s vtable from &Trait’s.Source§fn as_any_mut(&mut self) -> &mut (dyn Any + 'static)
fn as_any_mut(&mut self) -> &mut (dyn Any + 'static)
&mut Trait (where Trait: Downcast) to &Any. This is needed since Rust cannot
generate &mut Any’s vtable from &mut Trait’s.Source§impl<T> DowncastSync for T
impl<T> DowncastSync for T
Source§impl<T> Instrument for T
impl<T> Instrument for T
Source§fn instrument(self, span: Span) -> Instrumented<Self>
fn instrument(self, span: Span) -> Instrumented<Self>
Source§fn in_current_span(self) -> Instrumented<Self>
fn in_current_span(self) -> Instrumented<Self>
Source§impl<SS, SP> SupersetOf<SS> for SPwhere
SS: SubsetOf<SP>,
impl<SS, SP> SupersetOf<SS> for SPwhere
SS: SubsetOf<SP>,
Source§fn to_subset(&self) -> Option<SS>
fn to_subset(&self) -> Option<SS>
self from the equivalent element of its
superset. Read moreSource§fn is_in_subset(&self) -> bool
fn is_in_subset(&self) -> bool
self is actually part of its subset T (and can be converted to it).Source§fn to_subset_unchecked(&self) -> SS
fn to_subset_unchecked(&self) -> SS
self.to_subset but without any property checks. Always succeeds.Source§fn from_subset(element: &SS) -> SP
fn from_subset(element: &SS) -> SP
self to the equivalent element of its superset.