1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388
//! This crate provides a mechanism for "jumbling" byte slices in a reversible way.
//!
//! Many byte encodings such as [Base64] and [Bech32] do not have "cascading" behaviour:
//! changing an input byte at one position has no effect on the encoding of bytes at
//! distant positions. This can be a problem if users generally check the correctness of
//! encoded strings by eye, as they will tend to only check the first and/or last few
//! characters of the encoded string. In some situations (for example, a hardware device
//! displaying on its screen an encoded string provided by an untrusted computer), it is
//! potentially feasible for an adversary to change some internal portion of the encoded
//! string in a way that is beneficial to them, without the user noticing.
//!
//! [Base64]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Base64
//! [Bech32]: https://github.com/bitcoin/bips/blob/master/bip-0173.mediawiki#Bech32
//!
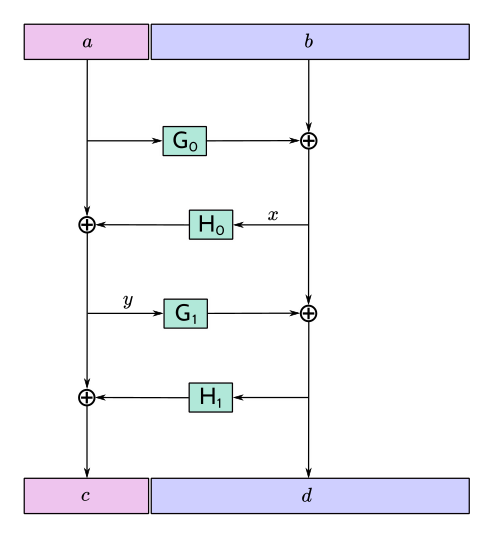
//! The function F4Jumble (and its inverse function, F4Jumble⁻¹) are length-preserving
//! transformations can be used to trivially introduce cascading behaviour to existing
//! encodings:
//! - Prepare the raw `message` bytes as usual.
//! - Pass `message` through [`f4jumble`] or [`f4jumble_mut`] to obtain the jumbled bytes.
//! - Encode the jumbled bytes with the encoding scheme.
//!
//! Changing any byte of `message` will result in a completely different sequence of
//! jumbled bytes. Specifically, F4Jumble uses an unkeyed 4-round Feistel construction to
//! approximate a random permutation.
//!
//! 
//!
//! ## Efficiency
//!
//! The cost is dominated by 4 BLAKE2b compressions for message lengths up to 128 bytes.
//! For longer messages, the cost increases to 6 BLAKE2b compressions for 128 < lₘ ≤ 192,
//! and 10 BLAKE2b compressions for 192 < lₘ ≤ 256, for example. The maximum cost for
//! which the algorithm is defined would be 196608 BLAKE2b compressions at lₘ = 4194368.
//!
//! The implementations in this crate require memory of roughly lₘ bytes plus the size of
//! a BLAKE2b hash state. It is possible to reduce this by (for example, with F4Jumble⁻¹)
//! streaming the `d` part of the jumbled encoding three times from a less
//! memory-constrained device. It is essential that the streamed value of `d` is the same
//! on each pass, which can be verified using a Message Authentication Code (with key held
//! only by the Consumer) or collision-resistant hash function. After the first pass of
//! `d`, the implementation is able to compute `y`; after the second pass it is able to
//! compute `a`; and the third allows it to compute and incrementally parse `b`. The
//! maximum memory usage during this process would be 128 bytes plus two BLAKE2b hash
//! states.
#![no_std]
#![cfg_attr(docsrs, feature(doc_cfg))]
use blake2b_simd::{Params as Blake2bParams, OUTBYTES};
use core::cmp::min;
use core::fmt;
use core::ops::RangeInclusive;
use core::result::Result;
#[cfg(feature = "std")]
#[macro_use]
extern crate std;
#[cfg(feature = "std")]
use std::vec::Vec;
#[cfg(test)]
mod test_vectors;
#[cfg(all(test, feature = "std"))]
mod test_vectors_long;
/// Length of F4Jumbled message must lie in the range VALID_LENGTH.
///
/// VALID_LENGTH = 48..=4194368
pub const VALID_LENGTH: RangeInclusive<usize> = 48..=4194368;
/// Errors produced by F4Jumble.
#[derive(Debug)]
pub enum Error {
/// Value error indicating that length of F4Jumbled message does not
/// lie in the range [`VALID_LENGTH`].
InvalidLength,
}
impl fmt::Display for Error {
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut fmt::Formatter<'_>) -> fmt::Result {
match self {
Self::InvalidLength => write!(
f,
"Message length must be in interval ({}..={})",
*VALID_LENGTH.start(),
*VALID_LENGTH.end()
),
}
}
}
#[cfg(feature = "std")]
impl std::error::Error for Error {}
macro_rules! H_PERS {
( $i:expr ) => {
[
85, 65, 95, 70, 52, 74, 117, 109, 98, 108, 101, 95, 72, $i, 0, 0,
]
};
}
macro_rules! G_PERS {
( $i:expr, $j:expr ) => {
[
85,
65,
95,
70,
52,
74,
117,
109,
98,
108,
101,
95,
71,
$i,
($j & 0xFF) as u8,
($j >> 8) as u8,
]
};
}
struct State<'a> {
left: &'a mut [u8],
right: &'a mut [u8],
}
impl<'a> State<'a> {
fn new(message: &'a mut [u8]) -> Self {
let left_length = min(OUTBYTES, message.len() / 2);
let (left, right) = message.split_at_mut(left_length);
State { left, right }
}
fn h_round(&mut self, i: u8) {
let hash = Blake2bParams::new()
.hash_length(self.left.len())
.personal(&H_PERS!(i))
.hash(self.right);
xor(self.left, hash.as_bytes())
}
fn g_round(&mut self, i: u8) {
for j in 0..ceildiv(self.right.len(), OUTBYTES) {
let hash = Blake2bParams::new()
.hash_length(OUTBYTES)
.personal(&G_PERS!(i, j as u16))
.hash(self.left);
xor(&mut self.right[j * OUTBYTES..], hash.as_bytes());
}
}
fn apply_f4jumble(&mut self) {
self.g_round(0);
self.h_round(0);
self.g_round(1);
self.h_round(1);
}
fn apply_f4jumble_inv(&mut self) {
self.h_round(1);
self.g_round(1);
self.h_round(0);
self.g_round(0);
}
}
/// XORs bytes of the `source` to bytes of the `target`.
///
/// This method operates over the first `min(source.len(), target.len())` bytes.
fn xor(target: &mut [u8], source: &[u8]) {
for (source, target) in source.iter().zip(target.iter_mut()) {
*target ^= source;
}
}
fn ceildiv(num: usize, den: usize) -> usize {
(num + den - 1) / den
}
/// Encodes the given message in-place using F4Jumble.
///
/// Returns an error if the message is an invalid length. `message` will be unmodified in
/// this case.
///
/// # Examples
///
/// ```
/// let mut message_a = *b"The package from Alice arrives tomorrow morning.";
/// f4jumble::f4jumble_mut(&mut message_a[..]).unwrap();
/// assert_eq!(
/// hex::encode(message_a),
/// "861c51ee746b0313476967a3483e7e1ff77a2952a17d3ed9e0ab0f502e1179430322da9967b613545b1c36353046ca27",
/// );
///
/// let mut message_b = *b"The package from Sarah arrives tomorrow morning.";
/// f4jumble::f4jumble_mut(&mut message_b[..]).unwrap();
/// assert_eq!(
/// hex::encode(message_b),
/// "af1d55f2695aea02440867bbbfae3b08e8da55b625de3fa91432ab7b2c0a7dff9033ee666db1513ba5761ef482919fb8",
/// );
/// ```
pub fn f4jumble_mut(message: &mut [u8]) -> Result<(), Error> {
if VALID_LENGTH.contains(&message.len()) {
State::new(message).apply_f4jumble();
Ok(())
} else {
Err(Error::InvalidLength)
}
}
/// Decodes the given message in-place using F4Jumble⁻¹.
///
/// Returns an error if the message is an invalid length. `message` will be unmodified in
/// this case.
///
/// # Examples
///
/// ```
/// let mut message_a = hex::decode(
/// "861c51ee746b0313476967a3483e7e1ff77a2952a17d3ed9e0ab0f502e1179430322da9967b613545b1c36353046ca27")
/// .unwrap();
/// f4jumble::f4jumble_inv_mut(&mut message_a).unwrap();
/// assert_eq!(message_a, b"The package from Alice arrives tomorrow morning.");
///
/// let mut message_b = hex::decode(
/// "af1d55f2695aea02440867bbbfae3b08e8da55b625de3fa91432ab7b2c0a7dff9033ee666db1513ba5761ef482919fb8")
/// .unwrap();
/// f4jumble::f4jumble_inv_mut(&mut message_b).unwrap();
/// assert_eq!(message_b, b"The package from Sarah arrives tomorrow morning.");
/// ```
pub fn f4jumble_inv_mut(message: &mut [u8]) -> Result<(), Error> {
if VALID_LENGTH.contains(&message.len()) {
State::new(message).apply_f4jumble_inv();
Ok(())
} else {
Err(Error::InvalidLength)
}
}
/// Encodes the given message using F4Jumble, and returns the encoded message as a vector
/// of bytes.
///
/// Returns an error if the message is an invalid length.
///
/// # Examples
///
/// ```
/// let message_a = b"The package from Alice arrives tomorrow morning.";
/// let encoded_a = f4jumble::f4jumble(message_a).unwrap();
/// assert_eq!(
/// hex::encode(encoded_a),
/// "861c51ee746b0313476967a3483e7e1ff77a2952a17d3ed9e0ab0f502e1179430322da9967b613545b1c36353046ca27",
/// );
///
/// let message_b = b"The package from Sarah arrives tomorrow morning.";
/// let encoded_b = f4jumble::f4jumble(message_b).unwrap();
/// assert_eq!(
/// hex::encode(encoded_b),
/// "af1d55f2695aea02440867bbbfae3b08e8da55b625de3fa91432ab7b2c0a7dff9033ee666db1513ba5761ef482919fb8",
/// );
/// ```
#[cfg(feature = "std")]
#[cfg_attr(docsrs, doc(cfg(feature = "std")))]
pub fn f4jumble(message: &[u8]) -> Result<Vec<u8>, Error> {
let mut result = message.to_vec();
f4jumble_mut(&mut result).map(|()| result)
}
/// Decodes the given message using F4Jumble⁻¹, and returns the decoded message as a
/// vector of bytes.
///
/// Returns an error if the message is an invalid length.
///
/// # Examples
///
/// ```
/// let encoded_a = hex::decode(
/// "861c51ee746b0313476967a3483e7e1ff77a2952a17d3ed9e0ab0f502e1179430322da9967b613545b1c36353046ca27")
/// .unwrap();
/// let message_a = f4jumble::f4jumble_inv(&encoded_a).unwrap();
/// assert_eq!(message_a, b"The package from Alice arrives tomorrow morning.");
///
/// let encoded_b = hex::decode(
/// "af1d55f2695aea02440867bbbfae3b08e8da55b625de3fa91432ab7b2c0a7dff9033ee666db1513ba5761ef482919fb8")
/// .unwrap();
/// let message_b = f4jumble::f4jumble_inv(&encoded_b).unwrap();
/// assert_eq!(message_b, b"The package from Sarah arrives tomorrow morning.");
/// ```
#[cfg(feature = "std")]
#[cfg_attr(docsrs, doc(cfg(feature = "std")))]
pub fn f4jumble_inv(message: &[u8]) -> Result<Vec<u8>, Error> {
let mut result = message.to_vec();
f4jumble_inv_mut(&mut result).map(|()| result)
}
#[cfg(test)]
mod common_tests {
use super::{f4jumble_inv_mut, f4jumble_mut, test_vectors};
#[test]
fn h_pers() {
assert_eq!(&H_PERS!(7), b"UA_F4Jumble_H\x07\x00\x00");
}
#[test]
fn g_pers() {
assert_eq!(&G_PERS!(7, 13), b"UA_F4Jumble_G\x07\x0d\x00");
assert_eq!(&G_PERS!(7, 65535), b"UA_F4Jumble_G\x07\xff\xff");
}
#[test]
fn f4jumble_check_vectors_mut() {
#[cfg(not(feature = "std"))]
let mut cache = [0u8; test_vectors::MAX_VECTOR_LENGTH];
#[cfg(feature = "std")]
let mut cache = vec![0u8; test_vectors::MAX_VECTOR_LENGTH];
for v in test_vectors::TEST_VECTORS {
let data = &mut cache[..v.normal.len()];
data.clone_from_slice(v.normal);
f4jumble_mut(data).unwrap();
assert_eq!(data, v.jumbled);
f4jumble_inv_mut(data).unwrap();
assert_eq!(data, v.normal);
}
}
}
#[cfg(feature = "std")]
#[cfg(test)]
mod std_tests {
use blake2b_simd::blake2b;
use proptest::collection::vec;
use proptest::prelude::*;
use std::format;
use std::vec::Vec;
use super::{f4jumble, f4jumble_inv, test_vectors, test_vectors_long, VALID_LENGTH};
proptest! {
#![proptest_config(ProptestConfig::with_cases(5))]
#[test]
fn f4jumble_roundtrip(msg in vec(any::<u8>(), VALID_LENGTH)) {
let jumbled = f4jumble(&msg).unwrap();
let jumbled_len = jumbled.len();
prop_assert_eq!(
msg.len(), jumbled_len,
"Jumbled length {} was not equal to message length {}",
jumbled_len, msg.len()
);
let unjumbled = f4jumble_inv(&jumbled).unwrap();
prop_assert_eq!(
jumbled_len, unjumbled.len(),
"Unjumbled length {} was not equal to jumbled length {}",
unjumbled.len(), jumbled_len
);
prop_assert_eq!(msg, unjumbled, "Unjumbled message did not match original message.");
}
}
#[test]
fn f4jumble_check_vectors() {
for v in test_vectors::TEST_VECTORS {
let jumbled = f4jumble(v.normal).unwrap();
assert_eq!(jumbled, v.jumbled);
let unjumbled = f4jumble_inv(v.jumbled).unwrap();
assert_eq!(unjumbled, v.normal);
}
}
#[test]
fn f4jumble_check_vectors_long() {
for v in test_vectors_long::TEST_VECTORS {
let normal: Vec<u8> = (0..v.length).map(|i| i as u8).collect();
let jumbled = f4jumble(&normal).unwrap();
assert_eq!(blake2b(&jumbled).as_bytes(), v.jumbled_hash);
let unjumbled = f4jumble_inv(&jumbled).unwrap();
assert_eq!(unjumbled, normal);
}
}
}