[−][src]Function cdshealpix::proj
pub fn proj(lon: f64, lat: f64) -> (f64, f64)
Performs the HEALPix projection: (x, y) = proj(lon, lat).
The chosen scale is such that: base cell vertices and center coordinates are integers;
the distance from a cell center to its vertices equals one.
This projection is multi-purpose in the sense that if lon is in [-pi, pi], then
x is in [-4, 4] and if lon is in [0, 2pi], then x is in [0, 8].
It means that a same position on the sphere can lead to different positions in the projected
Euclidean plane.
Simplified projection formulae are:
- Equatorial region
\boxed{
\left\{
\begin{array}{lcl}
X & = & \alpha \times \frac{4}{\pi} \\
Y & = & \sin(\delta) \times \frac{3}{2}
\end{array}
\right.
}
\Rightarrow
\left\{
\begin{array}{lcl}
\alpha \in [0, 2\pi] & \leadsto & X \in [0, 8] \\
\sin\delta \in [-\frac{2}{3}, \frac{2}{3}] & \leadsto & Y \in [-1, 1]
\end{array}
\right.
- Polar caps:
\boxed{
\left\{
\begin{array}{lcl}
t & = & \sqrt{3(1-\sin\delta)} \\
X & = & (\alpha\frac{4}{\pi} - 1)t+1 \\
Y & = & 2 - t
\end{array}
\right.
}
\Rightarrow
\left\{
\begin{array}{l}
\alpha \in [0, \frac{\pi}{2}] \\
\sin\delta \in ]\frac{2}{3}, 1]
\end{array}
\right.
\leadsto
\begin{array}{l}
t \in [0, 1[ \\
X \in ]0, 2[ \\
Y \in ]1, 2]
\end{array}
It is the responsibility of the caller to homogenize the result according to its needs.
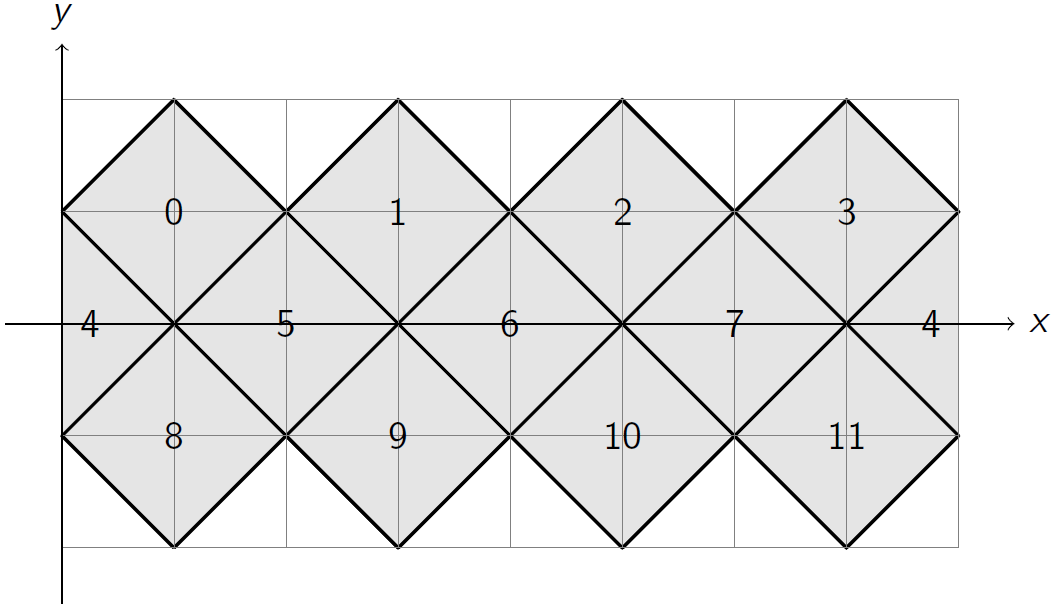
Inputs
lonlongitude in radians, support positive and negative reasonably large values (naive approach, no Cody-Waite nor Payne Hanek range reduction).latlatitude in radians, must be in[-pi/2, pi/2]
Output
(x, y)the projected planar Euclidean coordinates of the point of given coordinates(lon, lat)on the unit spherelon≤0=>x in [-8, 0]lon≥0=>x in [0, 8]y in [-2, 2]
Panics
If lat not in [-pi/2, pi/2], this method panics.
Examples
To obtain the WCS projection (see Calabretta2007), you can write:
use cdshealpix::{HALF_PI, PI_OVER_FOUR, proj}; use std::f64::consts::{PI}; let lon = 25.1f64; let lat = 46.7f64; let (mut x, mut y) = proj(lon.to_radians(), lat.to_radians()); if x > 4f64 { x -= 8f64; } x *= PI_OVER_FOUR; y *= PI_OVER_FOUR; assert!(-PI <= x && x <= PI); assert!(-HALF_PI <= y && y <= HALF_PI);
Other test example:
use cdshealpix::{TRANSITION_LATITUDE, HALF_PI, PI_OVER_FOUR, proj}; let (x, y) = proj(0.0, 0.0); assert_eq!(0f64, x); assert_eq!(0f64, y); assert_eq!((0.0, 1.0), proj(0.0 * HALF_PI, TRANSITION_LATITUDE)); fn dist(p1: (f64, f64), p2: (f64, f64)) -> f64 { f64::sqrt((p2.0 - p1.0) * (p2.0 - p1.0) + (p2.1 - p1.1) * (p2.1 - p1.1)) } assert!(dist((0.0, 0.0), proj(0.0 * HALF_PI, 0.0)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((0.0, 1.0), proj(0.0 * HALF_PI, TRANSITION_LATITUDE)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((1.0, 2.0), proj(0.0 * HALF_PI + PI_OVER_FOUR, HALF_PI)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((2.0, 1.0), proj(1.0 * HALF_PI, TRANSITION_LATITUDE)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((3.0, 2.0), proj(1.0 * HALF_PI + PI_OVER_FOUR, HALF_PI)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((4.0, 1.0), proj(2.0 * HALF_PI , TRANSITION_LATITUDE)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((5.0, 2.0), proj(2.0 * HALF_PI + PI_OVER_FOUR, HALF_PI)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((6.0, 1.0), proj(3.0 * HALF_PI, TRANSITION_LATITUDE)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((7.0, 2.0), proj(3.0 * HALF_PI + PI_OVER_FOUR, HALF_PI)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((0.0, 1.0), proj(4.0 * HALF_PI, TRANSITION_LATITUDE)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((0.0, 0.0), proj(4.0 * HALF_PI, 0.0)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((0.0, -1.0), proj(0.0 * HALF_PI, -TRANSITION_LATITUDE)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((1.0, -2.0), proj(0.0 * HALF_PI + PI_OVER_FOUR, -HALF_PI)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((2.0, -1.0), proj(1.0 * HALF_PI, -TRANSITION_LATITUDE)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((3.0, -2.0), proj(1.0 * HALF_PI + PI_OVER_FOUR, -HALF_PI)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((4.0, -1.0), proj(2.0 * HALF_PI, -TRANSITION_LATITUDE)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((5.0, -2.0), proj(2.0 * HALF_PI + PI_OVER_FOUR, -HALF_PI)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((6.0, -1.0), proj(3.0 * HALF_PI, -TRANSITION_LATITUDE)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((7.0, -2.0), proj(3.0 * HALF_PI + PI_OVER_FOUR, -HALF_PI)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((0.0, -1.0), proj(4.0 * HALF_PI, -TRANSITION_LATITUDE)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((-0.0, 0.0), proj(-0.0 * HALF_PI, 0.0)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((-0.0, 1.0), proj(-0.0 * HALF_PI, TRANSITION_LATITUDE)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((-1.0, 2.0), proj(-0.0 * HALF_PI - PI_OVER_FOUR, HALF_PI)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((-2.0, 1.0), proj(-1.0 * HALF_PI, TRANSITION_LATITUDE)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((-3.0, 2.0), proj(-1.0 * HALF_PI - PI_OVER_FOUR, HALF_PI)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((-4.0, 1.0), proj(-2.0 * HALF_PI , TRANSITION_LATITUDE)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((-5.0, 2.0), proj(-2.0 * HALF_PI - PI_OVER_FOUR, HALF_PI)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((-6.0, 1.0), proj(-3.0 * HALF_PI, TRANSITION_LATITUDE)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((-7.0, 2.0), proj(-3.0 * HALF_PI - PI_OVER_FOUR, HALF_PI)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((-0.0, 1.0), proj(-4.0 * HALF_PI, TRANSITION_LATITUDE)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((-0.0, 0.0), proj(-4.0 * HALF_PI, 0.0)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((-0.0, -1.0), proj(-0.0 * HALF_PI, -TRANSITION_LATITUDE)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((-1.0, -2.0), proj(-0.0 * HALF_PI - PI_OVER_FOUR, -HALF_PI)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((-2.0, -1.0), proj(-1.0 * HALF_PI, -TRANSITION_LATITUDE)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((-3.0, -2.0), proj(-1.0 * HALF_PI - PI_OVER_FOUR, -HALF_PI)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((-4.0, -1.0), proj(-2.0 * HALF_PI, -TRANSITION_LATITUDE)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((-5.0, -2.0), proj(-2.0 * HALF_PI - PI_OVER_FOUR, -HALF_PI)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((-6.0, -1.0), proj(-3.0 * HALF_PI, -TRANSITION_LATITUDE)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((-7.0, -2.0), proj(-3.0 * HALF_PI - PI_OVER_FOUR, -HALF_PI)) < 1e-15); assert!(dist((-0.0, -1.0), proj(-4.0 * HALF_PI, -TRANSITION_LATITUDE)) < 1e-15);